Page 1

Using This Retrofit Guide
This document is best viewed with Adobe Reader 6.0. To obtain the latest version of Adobe Reader, visit
http://www.adobe.com
Specification sheets on Watlow product may be obtained at http://www.watlow.com/literature/specsheets/
User Manuals on Watlow product may be obtained at http://www.watlow.com/literature/prodtechinfo/
Additional information on other Watlow products may be obtained by visiting http://www.watlow.com/
To locate a controller, search on the part number such as 965A-1CD0-00RG. Use the Help feature in Adobe Reader on
how to search documents.
If there are multiple listings, then the retrofit is conditional upon field use. Select the appropriate selection. The User’s
Manual is included at the bottom of this document when availab le.
Before selecting a replacement controller:
1. Know the application.
• Temperature range
• Sensor type
• Is the sensor upgradable if required?
• Additional input requirements – remote set points, secondary sensor or events
• Output required – control, alarm, event
• Is the power-switching device upgradable?
• Operating voltage of controller
• Mounting requirements – panel space
• Is a safety limit device required?
2. Know the product.
• Inputs – type and number of
• Control function – direct (cool) or reverse (heat )
• Outputs – switched DC, SSR, or mechanical relay
• Communication requirements
• Which control features are required? (cascade, slidewire, differential, remote control, other)
3. Use your best judgment for selecting a replacement controller. All applications require close examination of input,
output and the control mode needs to have the controller function properly.
4. Safety: Remember to make sure all redundant safety equipment is in place and working when retrofitting equipment.
If a system has been retrofitted without the proper safety equipment, you could be liable if an accident occurs.
This is only a guide to replacement controllers. If you have doubts, please call (507) 454-5300
and ask for technical support or email wintechsupport@watlow.com. We’re here to help. The
suggested replacement will differ in fit and form. Please review the replacement controller
specifications for suitability. Carefully check the notes for additional information that may
apply.
Your comments or suggestions on the Retrofit Guide are welcome. Please send comments or corrections to: Technical
Writer, Watlow Controls, 1241 Bundy Boulevard, P.O. Box 5580, Winona, MN 55987-5580; phone (507) 454-5300; fax
(507) 452-4507.
This Retrofit Guide is copyrighted by Watlow Winona, Inc., © February 2004 with all rights reserved. (1455)
Page 2

Abbreviation & Terminology
(as used in this document)
0.5 – 0.5 amperes of current switching capability
2A – 2 amperes of current switching capability
5A - 5 amperes of current switching capability
10A – 10 amperes of current switching capability
15A – 15 amperes of current switching capability
12-24 – Supply voltage can be between 12 to 24 Volts
100-240 – Supply voltage can be between 100 to 240 Volts
100 ohm DIN – refers to 100-ohm platinum RTD that has a DIN curve.
100 ohm JIS – refers to 100-ohm platinum RTD that has a JIS curve.
1/32 DIN – Deutsche Industrial Norm standard for panel mounted controller, hole size is cut to 1.78”w x 0.88”h.
1/16 DIN – Deutsche Industrial Norm standard for panel mounted controller, hole size is cut to 1.78”w x 1.77”h.
1/8V DIN – Deutsche Industrial Norm standard for panel mounted controller, hole size is cut to 1.78”w x 3.63”h.
1/8H DIN – Deutsche Industrial Norm standard for panel mounted controller, hole size is cut to 3.63”w x 1.77”h”
1/8S DIN – Deutsche Industrial Norm standard for panel mounted controller, hole size is cut to 2.68”w x 2.68”h.
¼ DIN – Deutsche Industrial Norm standard for panel mounted controller, hole size is cut to 3.63”w x 3.63”h.
Action – determines the direction of control. Heat (reverse acting) or Cool (direct acting).
Auto Reset – the limit will automatically reset on a power cycle but requires manual reset on limit trip.
Cascade – a control algorithm in which the output of one control loop provides a set point for another loop. The second
loop, in turn, determines the control action.
Ch – Channel refers to an analog input. There are single and dual channel controllers.
Control Mode – the method that a controller uses to switch the outputs such as PID, ON/OFF, and Manual.
Differential - control algorithm in which the output is based on the difference of the inputs plus set point.
DIN – Deutsche Industrial Norm, a set of technical, scientific and dimensional standards developed in Germany. RTD
sensors with the DIN curve change resistance at a rate of 0.00385 ohms/ohms/C.
DIN Rail – standard DIN EN50022 mounting method for attaching devices onto a metal rail.
Fixed – refers to a set point that is fixed at one value.
High Limit - device will deactivate output on a temperature rise above set point.
Inductive Load – any device that has a wire winding such as solenoids, electromechanical relays or transformers.
Input – refers to the sensor types that may be connected.
Page 3

Integral – the set point in integral (on board) to the controller.
JIS – Joint Industrial Standards, a set of technical, scientific and dimensional standards developed in Japan. RTD sensors
with the JIS curve change resistance at a rate of 0.00396 ohms/ohms/C.
Line Voltage – the voltage required powering the electronics of the controller.
Low Limit - device will deactivate output on a temperature drop below set point.
On/Off – a method of control that turns the output full on until set point is reached and then off until the process error
exceeds the hysteresis.
Open Brd – the form factor of this controller is an open circuit board mounted on four standoffs.
Manual Reset – the limit must be reset on a power cycle and requires manual reset on limit trip.
Multi RSP – multiple remote set potentiometers were supported. Each allowed the set point to be selected and adjusted.
Relay – refers to an electromechanical relay.
Remote – set point is adjusted using a remote potentiometer.
Panel – the form factor of this controller is mounted through a hole cut in the panel.
PI – Proportional and Integral, a control mode with two functions: proportional action dampens the systems response,
and integral corrects for droop.
PID – Proportional, Integral, and Derivative, a control mode with three functions: proportional action dampens the
systems response, integral corrects for droop, and derivative prevents overshoot and undershoot.
Potted – the circuit board and electronics are encased in epoxy.
Proc – Process input may accept 0-5, 1-5, 0-10 volts or 0-20 and 4-20 mA.
Profiling – Controller will perform a sequence of programmed steps.
Programmable – The feature is changeable in the field through jumpers and/or parameter selection.
RTD – Resistance Temperature Detector, a sensor that is 100 ohms at 0 degrees C and made of platinum material.
SSR – Solid State Relay, these devices will switch AC voltage only and require a load to latch on.
Sw DC – Switched DC, a time proportioning DC output used to drive DC input solid state relays.
t/c – Thermocouple sensor device made by joining two dissimilar metals whose standards is identified by a letter.
Temp Range – the range over which the controller could have the set point adjustment.
Thermistor – a sensor that changes resistance as the temperature changes. Similar but not the same as an RTD.
Universal – Input can be a thermocouple, 100 ohm DIN RTD or process (volts or milliamperes)
VAC – Volts Alternating Current
VAC/DC- Volts Alternating Current or Direct Current
VDC – Volts Direct Current
Page 4

VTB Sw DC – Variable Time Base Switched Direct Current, a time proportioning DC output where the cycle time is
variable.
Page 5

These notes are used to signify areas of concern in changing to a retrofit choice. These notes are also printed at the end
of the retrofit listing.
Note 1: Retrofit controller requires a substitution of a 100 Ohm RTD sensor for the thermistor.
Note 2: Mounting and dimensions of retrofit controller are different. Verify that sufficient panel space and depth is
available.
Note 3: Retrofit controller outputs are different. Add external interposing mechanical or solid state relay if applicable.
Note 4: Retrofit controller has a programmable, not fixed set point. Lock set point using controller's lockout parameter.
Note 5: For DIN rail mounting or sub-panel mounting, purchase DIN rail adapter p/n 0822-0586-P001 for 1/32 DIN or
p/n 0822-0586-P002 for 1/16 DIN.
Note 6: Add a suppressor, Watlow p/n 0804-0147-0000, for inductive loads.
Note 7: Retrofit does not have equivalent action (as example, no manual reset)
Note 8: Retrofit controller does not have dual dial scale.
Note 9: Hardware lockout is not available on retrofit.
Note 10:Retrofit controller does not have user selectable line voltage.
Note 11:Retrofit does not support remote set point or retransmit. Check if pins 13, 14, 15 or 16 have termination. If
wires are on these pins, select a different retrofit.
Note 12:Retrofit co ntroller does not have user selectable control action.
Note 13:Solid state sensor required for humidity. See http://www.vaisala.com
Note 14:Retrofit co ntroller does not have user selectable control mode.
Note 15:Use auxiliary event board A007-1732-F4B8
Note 16:Retrofit communications are different, consult specifications.
Note 17:Verify retrofit input range matches application.
Page 6

HG Series Watlow Part
2
1
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
2
1
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
2
1
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
0
)
0
)
)
)
0
)
)
Number
HG30-1KD1-0000 LF-701120AC
HG30-4KD1-0000 LF-70124AC
HG30-6KD1-0000 LF-70124DC
HG30-9KD1-0000 LF-701208ACDV
HG30-1KD2-0000 LF2-701120AC
HG30-4KD2-0000 LF2-70124AC
HG30-6KD2-0000 LF2-70124DC
HG30-9KD2-0000 LF2-701208ACDV
HG30-1KD3-0000 LF3-701120AC
HG30-4KD3-0000 LF3-70124AC
HG30-6KD3-0000 LF3-70124DC
HG30-9KD3-0000 LF3-701208ACDV
HG35-1LD1-0000 1035A120AC
HG35-4LD1-0000 1035A24AC
HG35-6LD1-0000 1035A24DC
HG35-9LD1-0000 1035A208ACDV
HG35-1LD2-0000 2035A120AC
HG35-4LD2-0000 2035A24AC
HG35-6LD2-0000 2035A24DC
HG35-9LD2-0000 2035A208ACDV
HG35-1LD3-0000 3035A120AC
HG35-4LD3-0000 3035A24AC
HG35-6LD3-0000 3035A24DC
HG35-9LD3-0000 3035A208ACDV
HG50-1MD1-0000 1050A120AC
HG50-4MD1-0000 1050A24AC
HG50-6MD1-0000 1050A24DC
HG50-9MD1-0000 1050A208ACDV
HG50-1MD2-0000 2050A120AC
HG50-4MD2-0000 2050A24AC
HG50-6MD2-0000 2050A24DC
HG50-9MD2-0000 2050A208ACDV
HG50-1MD3-0000 3050A120AC
HG50-4MD3-0000 3050A24AC
HG50-6MD3-0000 3050A24DC
HG50-9MD3-0000 3050A208ACDV
HG60-1PD1-0000 1060APS120AC
HG60-4PD1-0000 1060APS24AC
HG60-6PD1-0000 1060APS24DC
HG60-9PD1-0000 1060APS208ACDV
HG60-1PD2-0000 2060APS120AC
HG60-4PD2-0000 2060APS24AC
HG60-6PD2-0000 2060APS24DC
HG60-9PD2-0000 2060APS208ACDV
HG60-1PD3-0000 3060APS120AC
HG60-4PD3-0000 3060APS24AC
HG60-6PD3-0000 3060APS24DC
HG60-9PD3-0000 3060APS208ACDV
Durakool Equivalent Product Description Potential Solid State Alternatives
MDR to Solid State Alternatives Cross Reference
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 1 POLE, 120VAC COIL DB10-60K2-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC1, SSR-480-50A-AC1
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 1 POLE, 24VAC COIL DB10-60K1-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 1 POLE, 24VDC COIL DB10-60C0-0000, CZ34-A48V-DC1, SSR-480-50A-DC
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 1 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DB10-60K3-0000, SSR-480-50A-AC1
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 2 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC20-60K2-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC1 (2PCS.), SSR-480-50A-AC1 (2 PCS.
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 2 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC20-60K1-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC2 (2 PCS.
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 2 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC20-60C0-0000, CZ34-A48V-DC1 (2PCS.), SSR-480-50A-DC1 (2 PCS
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 2 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC20-60K3-0000, SSR-480-50A-AC1 (2pcs.
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 3 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC30-60K2-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC1 (3PCS.), SSR-480-50A-AC1 (3 PCS.
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 3 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC30-60K1-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC2 (3 PCS.
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 3 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC20-60C0-0000, CZ34-A48V-DC1 (3 PCS.), SSR-480-50A-DC1 (3 PCS
(30A NEW)(25A OLD), 3 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC30-60K3-0000, SSR-480-50A-AC1 (3 pcs.
35A, 1 POLE, 120VAC COIL DB10-60K2-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC1, SSR-480-50A-AC1
35A, 1 POLE, 24VAC COIL DB10-60K1-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC
35A, 1 POLE, 24VDC COIL DB10-60C0-0000, CZ34-A48V-DC1, SSR-480-50A-DC
35A, 1 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DB10-60K3-0000, SSR-480-50A-AC1
35A, 2 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC20-60K2-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC1 (2PCS.), SSR-480-50A-AC1 (2 PCS.
35A, 2 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC20-60K1-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC2 (2 PCS.
35A, 2 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC20-60C0-0000, CZ34-A48V-DC1 (2PCS.), SSR-480-50A-DC1 (2 PCS
35A, 2 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC20-60K3-0000, SSR-480-50A-AC1 (2pcs.
35A, 3 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC30-60K2-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC1 (3PCS.), SSR-480-50A-AC1 (3 PCS.
35A, 3 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC30-60K1-0000, CZ34-A60V-AC2 (3 PCS.
35A, 3 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC20-60C0-0000, CZ34-A48V-DC1 (3 PCS.), SSR-480-50A-DC1 (3 PCS
35A, 3 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC30-60K3-0000, SSR-480-50A-AC1 (3 pcs.
50A, 1 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC10-60K2-0000, CZ50-A48V-AC1, SSR-480-50A-AC1
50A, 1 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC10-60K1-0000, CZ50-A48V-AC
50A, 1 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC10-60C0-0000, CZ50-A48V-DC1, SSR-480-50A-DC
50A, 1 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC10-60K3-0000, SSR-480-50A-AC1
50A, 2 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC21-60K2-0000, CZ50-A48V-AC1 (2 PCS.),SSR-480-75A-AC1 (2 PCS.
50A, 2 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC21-60K1-0000, CZ50-A48V-AC2 (2 PCS.
50A, 2 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC21-60C0-0000, CZ50-A48V-DC1 (2 PCS.), SSR-480-75A-DC1 (2 PCS.
50A, 2 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC21-60K3-0000, SSR-480-75A-AC1 (2 PCS.
50A, 3 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC31-60K2-0000, CZ50-A48V-AC1 (3 PCS.),SSR-480-75A-AC1 (3 PCS.
50A, 3 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC31-60K1-0000, CZ50-A48V-AC2 (3 PCS.
50A, 3 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC31-60C0-0000, CZ50-A48V-DC1 (3 PCS.), SSR-480-75A-DC1 (3 PCS.
50A, 3 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC31-60K3-0000, SSR-480-75A-AC1 (3 PCS.
60A, 1 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC11-60K2-0000, SSR-480-75A-AC1
60A, 1 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC11-60K1-000
60A, 1 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC11-60C0-0000, SSR-480-75A-DC1
60A, 1 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC11-60K3-0000, SSR-480-75A-AC1
60A, 2 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC21-60K2-0000, SSR-480-75A-AC1 (2 PCS.
60A, 2 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC21-60K1-000
60A, 2 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC21-60C0-0000, SSR-480-75A-DC1 (2 PCS.
60A, 2 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC21-60K3-0000, SSR-480-75A-AC1 (2 PCS.
60A, 3 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC31-60K2-0000, SSR-480-75A-AC1 (3 PCS.
60A, 3 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC31-60K1-000
60A, 3 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC31-60C0-0000, SSR-480-75A-DC1 (3 PCS.
60A, 3 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC31-60K3-0000, SSR-480-75A-AC1 (3 PCS.
Watlow Controls 5/6/2004 Page 1
Page 7

HG Series Watlow Part
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
0
0
0
0
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
Number
HG30-1AA2-0000 2030APS120AC
HG30-4AA2-0000 2030APS24AC
HG30-6AA2-0000 2030APS24DC
HG30-9AA2-0000 2030APS208ACDV
HG30-1AA3-0000 3030APS120AC
HG30-4AA3-0000 3030APS24AC
HG30-6AA3-0000 3030APS24DC
HG30-9AA3-0000 3030APS208ACDV
HG80-1AB1-0000 CF-702
HG80-4AB1-0000 CF-701
HG80-6AB1-0000 CF-707
HG80-9AB1-0000 CF-713
HG80-1AB2-0000 CF2-702
HG80-4AB2-0000 CF2-701
HG80-6AB2-0000 CF2-708
HG80-9AB2-0000 CF2-713
HG80-1AB3-0000 CF3-702
HG80-4AB3-0000 CF3-701
HG80-6AB3-0000 CF3-708
HG80-9AB3-0000 CF3-713
HG1M-1AC1-0000 CFC-718
HG1M-4AC1-0000 CFC-717
HG1M-6AC1-0000 CFC-723
HG1M-9AC1-0000 CFC-734
HG1M-1AC2-0000 CFC2-727
HG1M-4AC2-0000 CFC2-726
HG1M-6AC2-0000 CFC2-733
HG1M-9AC2-0000 CFC2-734
HG1M-1AC3-0000 CFC3-708
HG1M-4AC3-0000 CFC3-707
HG1M-6AC3-0000 CFC3-721
HG1M-9AC3-0000 CFC3-734
HG2M-1AD1-0000 DFC-301
HG2M-4AD1-0000 DFC-307
HG2M-6AD1-0000 DFC-310
HG2M-9AD1-0000 DFC-311
HG2M-1AD2-0000 DFC2-301
HG2M-4AD2-0000 DFC2-307
HG2M-6AD2-0000 DFC2-310
HG2M-9AD2-0000 DFC2-311
HG2M-1AD3-0000 DFC3-301
HG2M-4AD3-0000 DFC3-307
HG2M-6AD3-0000 DFC3-310
HG2M-9AD3-0000 DFC3-311
Durakool Equivalent Product Description Potential Solid State Alternatives
MDR to Solid State Alternatives Cross Reference
30A, 2 POLE, 120VAC COIL DC20-60K2-0000, ES40-3120-AC00, SSR-480-50A-AC1 (2PCS.
30A, 2 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC20-60K1-0000, ES40-3024-AC00, CZ34-A48V-AC2 (2 PCS.
30A, 2 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC20-60C0-0000, CZ34-A60V-DC1 (2PCS.), SSR-480-50A-DC1 (2 PCS.
30A, 2 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC20-60K3-0000, ES40-3220-AC00, SSR-480-50A-AC1 (2 PCS.
30A, 3 POLE, 120VAC COIL
30A, 3 POLE, 24VAC COIL DC30-60K1-0000, ES40-3024-AC00, CZ34-A48V-AC2 (3 PCS.
30A, 3 POLE, 24VDC COIL DC30-60C0-0000, CZ34-A60V-DC1 (3 PCS.), SSR-480-50A-DC1 (3 PCS.
30A, 3 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DC20-60K3-0000, ES40-3220-AC00, SSR-480-50A-AC1 (3 PCS.
80A, 1 POLE, 120VAC COIL DD10-60K2-000
80A, 1 POLE, 24VAC COIL DD10-60K1-000
80A, 1 POLE, 24VDC COIL DD10-60C0-000
80A, 1 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DD10-60K3-000
80A, 2 POLE, 120VAC COIL DD10-60K2-0000 (2 PCS.
80A, 2 POLE, 24VAC COIL DD10-60K1-0000 (2 PCS.
80A, 2 POLE, 24VDC COIL DD10-60C0-0000 (2 PCS.
80A, 2 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DD10-60K3-0000 (2 PCS.
80A, 3 POLE, 120VAC COIL DD10-60K2-0000 (3PCS.
80A, 3 POLE, 24VAC COIL DD10-60K1-0000 (3 PCS.
80A, 3 POLE, 24VDC COIL DD10-60C0-0000 (3 PCS.
80A, 3 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL DD10-60K3-0000 (3 PCS.
100A, 1 POLE, 120VAC COIL N
100A, 1 POLE, 24VAC COIL N
100A, 1 POLE, 24VDC COIL N
100A, 1 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL N
100A, 2 POLE, 120VAC COIL N
100A, 2 POLE, 24VAC COIL N
100A, 2 POLE, 24VDC COIL N
100A, 2 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL N
100A, 3 POLE, 120VAC COIL N
100A, 3 POLE, 24VAC COIL N
100A, 3 POLE, 24VDC COIL N
100A, 3 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL N
150A, 1 POLE, 120VAC COIL N
150A, 1 POLE, 24VAC COIL N
150A, 1 POLE, 24VDC COIL N
150A, 1 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL N
150A, 2 POLE, 120VAC COIL N
150A, 2 POLE, 24VAC COIL N
150A, 2 POLE, 24VDC COIL N
150A, 2 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL N
150A, 3 POLE, 120VAC COIL N
150A, 3 POLE, 24VAC COIL N
150A, 3 POLE, 24VDC COIL N
150A, 3 POLE, 208/240VAC COIL N
DC30-60K2-0000, ES40-3120-AC00, SSR-480-50A-AC1 (3 PCS.), CZ34-A48V-AC1
(3 PCS.)
Watlow Controls 5/6/2004 Page 2
Page 8

HG Series
Mercury Displacement Relay
WMDR-XUMN-1097
June 1997
Supersedes: WMDR-XUMN Rev A00
Made in the U.S.A.
Printed on Recycled Paper 10% Postconsumer Waste
Power Controls
Watlow Controls, 1241 Bundy Blvd., P.O. Box 5580, Winona, MN, USA 55987-5580, Phone: (507) 454-5300, Fax: (507) 452-4507
Registered Company
Winona, Minnesota USA
ISO 9001
User’s Manual
Page 9

3.25
(83)
2.16
(55)
.25
Typ.
(6)
Up
3.14
(80)
Mounting
Slot
For #8 To
#10 Screw
3.75
(95)
#10-32
Binding
Head
Screw
Up To #10
A.W.G.
3.43
(87)
Dimensions
1.19
(30)
"A"
1.63
(41)
.20 (5)
Dia. Mtg.
Hole
2.25
(57)
1.94
(49)
Pressure
Connector
2.00
(51)
1 Pole
.21 (5)
Dia. Mtg.
Hole For
#10 Screw
.21 (5)
Wide Slot
For #10
Screw
Hole
3.13
(79)
2.65
(67)
1.94
(49)
40°
Typ.
4.00
(102)
2.62
(67)
"A"
Pressure
Connector
2 Pole
3.13
(79)
4.00
(102)
2.65
(67)
.21
(5)
Dia. Mtg.
Hole For
#10
Screw
.21 (5)
Wide Slot
For #10
Screw
Hole
40°
TYP.
3.75
(95)
"A"
Pressure
Connector
1.94
(49)
3 Pole
ÓÓ
WARNING: Mercury displacement relay must be
mounted vertically. Failure to do this will prevent the
contacts from turning off, which will supply full
voltage to the load. Failure to follow this guideline
could result in damage to equipment, and personal
injury or death.
ÓÓ
WARNING: Mercury displacement relay contacts
will switch ac current only. Not for use with dc
current. Failure to follow this guideline could result
in damage to equipment, and personal injury or
death.
2 Watlow Series HG Mercury Displacement Relay User’s Manual
.21 (5)
Dia.
Mounting
Hole
1.19
(30)
2.25
(57)
#8-32
Binding
Head
Screw
#10-#14
A.W.G.
1.63
(41)
3.58
(91)
2.00
(51)
Dia.
1.94
(49)
.21 (5)
Dia.
Mounting
Hole
3.13
(79)
4.00
(102)
#8-32 Binding
Head Screw
#10-#14 A.W.G.
2.62
(67)
2.65
(67)
1.94
(49)
.21 (5)
Wide Slot
For #10
Screw
Hole
40°
Typ.
4.00
(102)
2 Pole
.21 (5)
Dia.
Mounting
Hole
3.13
(79)
3.75
(95)
4.00
(102)
#8-32
Binding
Head Screw
#10-#14
A.W.G
4.00
(102)
1.94
(49)
.21 (5)
Wide
Slot
For#10
Screw
Hole
40°
Typ.
2.65
(67)
3 Pole
30 Amp Models
HG30-XKDX-0000
Definite Purpose Relay Foot Print
HG30-XAAX-0000
1 Pole
NOTE:
Watlow recommends that ring terminal lugs be used
with stranded wire
on all binding head
screw terminals.
All 35, 50, and 60 Amp Models
“A” Pressure
Dimensions Connectors
HG35-XLDX-0000 4.62 (117) #4-14 A.W.G.
HG50-XMDX-0000 4.62 (117) #4-14 A.W.G.
HG60-XPDX-0000 5.12 (130) #1 - 8 A.W.G.
Page 10

2.62
(67)
Pressure
Connector
"A"
2.18
(55)
1.88
(48)
(5)
.20 Dia.
Mtg Hole
2.13
(54)
2.50
(64)
1 Pole
(7)
.27 Dia.
Mtg. Hole
5.70
(145)
4.70
(119)
2.79
(71)
.27
(7)
Wide Mtg.
Slot
40°
Typ.
3.25
(83)
3.78
(96)
"A"
Pressure
Connector
2 Pole
(7)
.27 Dia.
Mtg. Hole
(7)
.27 Dia.
Mtg. Slot
40°
Typ.
5.70
(145)
2.79
(71)
4.70
(119)
5.00
(127)
Pressure
Connector
"A"
3.78
(96)
3 Pole
All 80, 100, and 150 Amp Models
Dimensions
Watlow Series HG Mercury Displacement Relay User’s Manual 3
1 Pole Wiring Example
2 Pole Wiring Example
3 Pole Wiring Example
Wiring
120V~(ac)
Fuse
Fuse
1 Pole
120V~(ac)
Coil
Control
Heater
L2
Neutral
L1
Control
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
Heater
2 Pole
240V~(ac)
Single
Phase
L1
L2
240V~(ac)
Single
Phase
}
Fuse
Fuses
Fuse
3 Pole
120V~(ac)
Coil
Control
N
3-Phase
Wye Heater
208V~ (ac)
3 Phase
Wye
L1
L2
L3
{
“A” Pressure
Dimensions Connectors:
HG80-XABX-0000 5.77 (147) #1-8 A.W.G.
HG1M-XACX-0000 5.77 (147) #1-8 A.W.G.
HG2M-XADX-0000 6.40 (163) #1/0 - #2 A.W.G.
∑∑
WARNING: Wiring must conform to
National Electric Code (NEC) safety
standards, as well as locally applicable
codes. Failure to do so could result in
personal injury or death. See page 6 for
fusing recommendations.
çç
Use copper conductors only.
Page 11
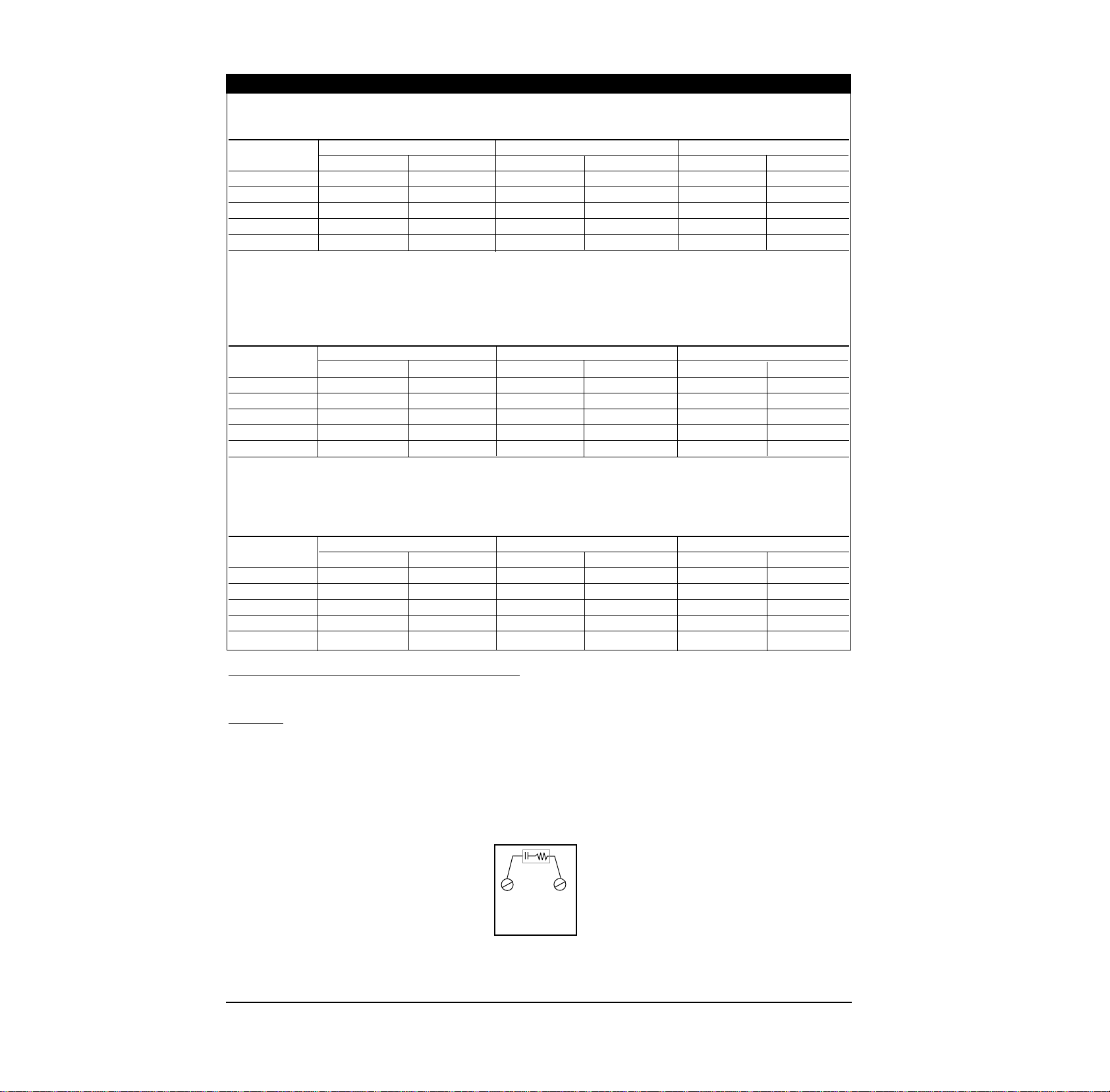
Temperature Control Output to MDR Coil Input
Please refer to the Field Coil Power Requirements when selecting the correct temperature control output.
Example: An HG35-1LD3-X000 requires 224mA to energize the coil and could be used with Watlow
temperature control output options ‘B’ or ‘K’ (i.e. 988A-XXBB-XXXX or 988A-XXKK-XXXX) models. The
best selection is the ‘B’ output option because it includes an RC snubber across the output. If you select
the ‘K’ option, it is recommended that you also purchase a Quencharc® snubber separately (Watlow part
number 0804-0147-0000). Place the snubber across the MDR coil terminals to protect the temperature
control solid state output. When placing the snubber across the coil of a 2 and 3 pole relay, you may have
to add some lead wire to the snubber. The MDR coil is an inductive load and the snubber will reduce the
flyback voltage produced by the MDR coil when it de-energizes. See below.
Note: Watlow temperature control solid state outputs will not drive VDC coils directly. Refer to the coil
current specifications above and any temperature control output specifications as required by the
application.
Quencharc
Snubber
(Purchase
Separately)
HG30-XAAX-0000
1 Pole 2 Pole 3 Pole
Voltage Current Power Current Power Current Power
24V~ (ac) NA NA 0.456A 10.9VA 0.510A 12.2VA
120V~ (ac) NA NA 0.121A 14.5VA 0.106A 12.7VA
208V~ (ac) NA NA 0.055A 11.4VA 0.055A 11.4VA
240V~ (ac) NA NA 0.063A 15.1VA 0.062A 14.9VA
24VÎ (dc) NA NA 0.240A 5.8W 0.250A 6.0W
HG30-XKDX-0000
HG35-XLDX-0000
HG50-XMDX-0000
HG60-XPDX-0000
1 Pole 2 Pole 3 Pole
Voltage Current Power Current Power Current Power
24V~ (ac) 0.235A 5.6VA 0.529A 12.7VA 1.270A 30.5VA
120V~ (ac) 0.057A 6.8VA 0.133A 16.0VA 0.224A 26.9VA
208V~ (ac) 0.030A 6.2VA 0.075A 15.6VA 0.111A 23.1VA
240V~ (ac) 0.035A 8.4VA 0.087A 20.9VA 0.128A 30.7VA
24VÎ (dc) 0.146A 3.5W 0.266A 6.4W 0.470A 11.3W
HG80-XABX-0000
HG1M-XACX-0000
HG2M-XADX-0000
1 Pole 2 Pole 3 Pole
Voltage Current Power Current Power Current Power
24V~ (ac) 0.930A 22.3VA 2.310A 55.4VA 5.060A 121.4VA
120V~ (ac) 0.195A 23.4VA 0.448A 53.8VA 0.968A 116.2VA
208V~ (ac) 0.097A 20.2VA 0.280A 58.2VA 0.482A 100.3VA
240V~ (ac) 0.112A 26.9VA 0.323A 77.5VA 0.563A 135.1VA
24VÎ (dc) 0.219A 5.2W 0.572A 13.7W 0.555A 13.3W
Field Coil Power Requirements
Watlow Series HG Mercury Displacement Relay User’s Manual 4
Page 12

HG _ _ - _ _ _ _ - 0 0 _ _
Amperage
30 = 30 Amp
35 = 35 Amp
50 = 50 Amp
60 = 60 Amp
80 = 80 Amp
1M = 100 Amp
2M = 150 Amp
Coil Voltage
1 = 120V~ (ac)
4 = 24V~ (ac)
6 = 24VÎ (dc)
9 = 208/240V~ (ac)
Option
KD = 30 Amp (Standard)
LD = 35 Amp
MD = 50 Amp
PD = 60 Amp
AA = 30 Amp (Definite Purpose
Relay Footprint)
AB = 80 Amp
AC = 100 Amp
AD = 150 Amp
Poles
1 = 1 Pole (Not For Option “AA”)
2 = 2 Pole
3 = 3 Pole
Type
00 = Standard
(Includes Definite Purpose Relay Footprint)
XX = Custom
Ordering Information WMDR-XMNN-1099
1. Call Customer Service: 507-454-5300, or
fax: 507-452-4507, for a Return Material
Authorization (RMA) number before returning any
item for repair.
2. Make sure the RMA number is on the outside of the
carton, and on all paperwork returned. Ship on a
freight prepaid basis.
3. A restocking charge of 20% of the net price applies
for all returned stock controls and accessories in like
new condition and within 120 days after shipment.
Non-stock and modified stock items are not
returnable.
4. If the unit is unrepairable, it will be returned to you
with a letter of explanation. Repair costs will not
exceed 50% of the original cost.
Recycle
To provide proper disposal, Watlow accepts used MDRs.
Phone (507) 454-5300 for an Return Materials
Authorization (RMA) number. Contact your Watlow
representative for details.
The Mercury Relay is warranted to be free of defects in
material and workmanship for 18 months after delivery to
the first purchaser for use, providing that the units have
not been misapplied. Since Watlow has no control over
their use, and sometimes misuse, we cannot guarantee
against failure. Watlow’s obligations hereunder, at
Watlow’s option, are limited to replacement, repair or
refund of purchase price, and parts which upon
examination prove to be defective within the warranty
period specified. This warranty does not apply to
damage resulting from transportation, alteration, misuse,
abuse or improper fusing.
Returns
Warranty
5
Watlow Series HG Mercury Displacement Relay User’s Manual
Page 13

Model Number HG30-XKDX HG30-XAAX HG35-XLDX HG50-XMDX HG60-XPDX HG80-XABX HG1M-XACX HG2M-XADX
Contact Type N.O. N.O. N.O. N.O. N.O. N.O. N.O. N.O.
Maximum Load See Table
Current ac 30A 30A 35A 50A 60A 80A 100A Below
(typ) Contact
Resistance 4mΩ 4mΩ 4mΩ 4mΩ 4mΩ 4mΩ 4mΩ 4mΩ
Load Wire 10-14AWG 10-14AWG 4-14AWG 4-14AWG 1-8AWG 1-8AWG 1-8AWG 1/0-2AWG
Terminations bhs bhs pc pc pc pc pc pc
Coil Wire #6-32bhs #6-32bhs #6-32bhs #6-32bhs #6-32bhs #6-32bhs #6-32bhs #6-32bhs
Terminations up to up to up to up to up to up to up to up to
#12AWG #16AWG #12AWG #12AWG #12AWG #12AWG #12AWG #12AWG
Load Type Resistive Resistive Resistive Resistive Resistive Resistive Resistive Resistive
Maximum Load
Voltage ac 480/600** 480/600** 600**** 600**** 480/600**** 480*** 480*** 480/600
Load Frequency 50/60 Hz. 50/60 Hz. 50/60 Hz. 50/60 Hz. 50/60 Hz. 50/60 Hz. 50/60 Hz. 50/60 Hz.
Pull-in Time 70 mS 50 mS 70 mS 70 mS 70 mS 90 mS 90 mS 90 mS
Drop-out Time 90 mS 70 mS 90 mS 90 mS 90 mS 140 mS 140 mS 140 mS
Operating
Ambient -35 to 55°C -35 to 55°C -35 to 55°C -35 to 55°C -35 to 55°C -35 to 55°C -35 to 55°C -35 to 55°C
Storage
Temperature -40 to 100°C -40 to 100°C -40 to 100°C -40 to 100°C -40 to 100°C -40 to 100°C -40 to 100°C -40 to 100°C
Hg - Mass/Contact 1.82 oz. 0.84 oz. 1.75 oz. 1.75 oz. 1.75 oz. 8.93 oz 8.93 oz. 9.46 oz.
Weight : 1 Pole 1.0 lbs. 1.0 lbs. 1.0 lbs. 1.0 lbs. 1.0 lbs. 2.0 lbs. 2.0 lbs. 2.5 lbs.
2 Pole 2.0 lbs. 2.0 lbs. 2.0 lbs. 2.0 lbs. 2.0 lbs. 3.5 lbs. 4.0 lbs. 4.5 lbs.
3 Pole 2.5 lbs. 2.0 lbs. 3.0 lbs. 3.0 lbs. 3.0 lbs. 4.5 lbs. 7.0 lbs. 7.0 lbs.
Note: pc = pressure connector
bhs = binding head screw
Note: Watlow recommends that you do not exceed 30
cycles per minute.
Note: Watlow recommends that ring terminal lugs be
used on all binding head screw terminals.
Note: When replacing Watlow MD style relays,
consider the HG60 model if larger gauge or
multiple wires are required. See the load
termination specification above.
Specifications WMDR-XSPN-1098
Note: The 150 Amp relay (HG2M-XADX) is not UL or
CSA approved.
** UL listed to 480V
ÅÅ
(ac); CSA certified to 600VÅÅ(ac)
*** UL listed to 480V
ÅÅ
(ac)
**** UL listed and CSA certified to 600V
ÅÅ
(ac)
Watlow Series HG Mercury Displacement Relay User’s Manual 6
Volts 120 208 240 277 480 600
Amps 150 140 135 130 120 120
HG2M-XADX Load Current Table
Fusing
To prevent the MDR from rupture in the event of a heater
short circuit, you should always fuse the MDR load circuit.
Watlow recommends a Bussmann type JJN or JJS (Class
T) fuse or equivalent. Select a fuse size 1.25 times the
connected load or the next size above, but do not exceed
1.6 times the MDR rating. To fuse the MDR field coil, you
can use Bussmann fuse number MDL-2 for coils up to
240V~ (ac). For coils up to 480V~ (ac), use Bussmann fuse
number JJS-1.
∑∑
WARNING: Install high or low temperature control
protection in systems where an overtemperature or
undertemperature fault condition could present a
fire hazard or other hazard. Failure to install
temperature control protection where a potential
hazard exists could result in damage to equipment
and property, and personal injury or death.
Agency Approvals
• UL, File #ULE177629
• CSA File #LR22416
 Loading...
Loading...