Page 1

Winona, Minnesota USA
ISO 9001
N
EZ-ZONE® RMC (Control) Module
User’s Guide
Control Module
TOTAL
CUSTOMER
SATISFACTIO
3 Year Warranty
Registered Company
1241 Bundy Boulevard., Winona, Minnesota USA 55987
Phone: +1 (507) 454-5300, Fax: +1 (507) 452-4507 http://www.watlow.com
0600-0070-0000 Rev. E Made in the U.S.A.
March 2016
Page 2
Safety Information
• We use note, caution and warning symbols throughout this book to draw your attention to
important operational and safety information.
• A “NOTE” marks a short message to alert you to an important detail.
• A “CAUTION” safety alert appears with information that is important for protecting your
equipment and performance. Be especially careful to read and follow all cautions that
apply to your application.
• A “WARNING” safety alert appears with information that is important for protecting you,
others and equipment from damage. Pay very close attention to all warnings that apply to
your application.
• The safety alert symbol, (an exclamation point in a triangle) precedes a general
CAUTION or WARNING statement.
• The electrical hazard symbol, (a lightning bolt in a triangle) precedes an electric shock
hazard CAUTION or WARNING safety statement. Further explanations follow:
Symbol Explanation
CAUTION – Warning or Hazard that needs further explanation than label on
unit can provide. Consult User's Guide for further information.
ESD Sensitive product, use proper grounding and handling techniques when
installing or servicing product.
Unit protected by double/reinforced insulation for shock hazard prevention.
Do not throw in trash, use proper recycling techniques or consult manufacturer for proper disposal.
Enclosure made of Polycarbonate material. Use proper recycling techniques
or consult manufacturer for proper disposal.
Unit can be powered with either alternating current (ac) voltage or direct
current (dc) voltage.
Unit is a Listed device per Underwriters Laboratories®. It has been evaluated
to United States and Canadian requirements for Process Control Equipment.
UL 61010 and CSA C22.2 No. 61010. File E185611 QUYX, QUYX7. See: www.
ul.com
Unit is a Listed device per Underwriters Laboratories®. It has been evaluated
to United States and Canadian requirements for Hazardous Locations Class
1 Division II Groups A, B, C and D. ANSI/ISA 12.12.01-2007. File E184390
QUZW, QUZW7. See: www.ul.com
Page 3

Unit is compliant with European Union directives. See Declaration of Conformity for further details on Directives and Standards used for Compliance.
Unit has been reviewed and approved by Factory Mutual as a Temperature
Limit Device per FM Class 3545 standard. See: www.fmglobal.com
Unit has been reviewed and approved by CSA International for use as Temperature Indicating-Regulating Equipment per CSA C22.2 No. 24. See: www.
csa-international.org
Warranty
The EZ-ZONE® RMC (Control) module is manufactured by ISO 9001-registered processes and is
backed by a three-year warranty to the first purchaser for use, providing that the units have
not been misapplied. Since Watlow has no control over their use, and sometimes misuse, we
cannot guarantee against failure. Watlows’ obligations hereunder, at Watlows’ option, are
limited to replacement, repair or refund of purchase price, and parts which upon examination prove to be defective within the warranty period specified. This warranty does not apply
to damage resulting from transportation, alteration, misuse or abuse. The purchaser must use
Watlow parts to maintain all listed ratings.
Technical Assistance
If you encounter a problem with your Watlow controller, review your configuration information to verify that your selections are consistent with your application: inputs, outputs,
alarms, limits, etc. If the problem persists, you can get technical assistance from your local
Watlow representative (see back cover), by e-mailing your questions to wintechsupport@watlow.com or by dialing +1 (507) 494-5656 between 7 a.m. and 5 p.m., Central Standard Time
(CST). Ask for for an Applications Engineer. Please have the following information available
when calling:
• Complete model number
• All configuration information
• User’s Guide
• Factory Page
Return Material Authorization (RMA)
1. Call Watlow Customer Service, (507) 454-5300, for a Return Material Authorization (RMA)
number before returning any item for repair. If you do not know why the product failed, contact an Application Engineer or Product Manager. All RMA’s require:
• Ship-to address
• Bill-to address
• Contact name
• Phone number
• Method of return shipment
• Your P.O. number
• Detailed description of the problem
Page 4

• Any special instructions
• Name and phone number of person returning the product.
2. Prior approval and an RMA number from the Customer Service Department is required when
returning any product for credit, repair or evaluation. Make sure the RMA number is on the
outside of the carton and on all paperwork returned. Ship on a Freight Prepaid basis.
3. After we receive your return, we will examine it and try to verify the reason for returning
it.
4. In cases of manufacturing defect, we will enter a repair order, replacement order or issue
credit for material returned. In cases of customer misuse, we will provide repair costs and
request a purchase order to proceed with the repair work.
5. To return products that are not defective, goods must be in new condition, in the original boxes and they must be returned within 120 days of receipt. A 20 percent restocking
charge is applied for all returned stock controls and accessories.
6. If the unit cannot be repaired, you will receive a letter of explanation. and be given the
option to have the unit returned to you at your expense or to have us scrap the unit.
7. Watlow reserves the right to charge for no trouble found (NTF) returns.
This EZ-ZONE RMC User’s Guide is copyrighted by Watlow Electric, Inc., © March 2016 with all
rights reserved.
EZ-ZONE RM is covered by U.S. Patent No. 6,005,577 and Patents Pending
Page 5

TC
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ..................................1
Chapter 1: Overview ................................5
Available EZ-ZONE RM System Literature and Resources ...........5
Introduction ..............................................6
A Conceptual View of the RMC Module .........................8
Functions .............................................10
Inputs ................................................10
Outputs ...............................................11
What is a Profile ........................................11
Input Events and Output Events ............................12
Actions ...............................................12
Chapter 2: Install and Wire ...........................17
Dimensions .............................................17
RMC Installation and Removal on a DIN Rail ...................21
Wiring .................................................24
Conventions Used in the Menu Pages .........................50
Chapter 3: Operations Pages .........................53
Analog Input Menu .......................................56
Process Value Menu ......................................57
Digital Input/Output Menu ..................................59
Action Menu .............................................60
Limit Menu ..............................................60
Monitor Menu ...........................................61
Control Loop Menu .......................................63
Alarm Menu .............................................67
Current Menu ............................................69
Linearization Menu ........................................71
Compare Menu ..........................................72
Timer Menu .............................................73
Counter Menu ...........................................74
Logic Menu .............................................75
Math Menu ..............................................77
Special Output Function Menu ...............................78
Profile Status Menu .......................................81
Chapter 4: Setup Pages .............................87
Analog Input Menu .......................................91
Process Value Menu ......................................97
Digital Input/Output Menu .................................102
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 1 • Table of Contents
Page 6

TC
Table of Contents (cont.)
Action Menu ............................................106
Limit Menu .............................................108
Control Loop Menu ......................................110
Output Menu ...........................................121
Alarm Menu ............................................127
Current Menu ...........................................132
Linearization Menu .......................................134
Compare Menu .........................................139
Timer Menu ............................................141
Counter Menu ..........................................145
Logic Menu ............................................149
Math Menu .............................................162
Special Output Function Menu ..............................168
Variable Menu ..........................................174
Global Menu ............................................175
Profile Menu ...........................................177
Communications Menu ...................................186
Chapter 5: Profiling Page ...........................189
How to Setup and Start a Profile ............................189
Chapter 6: Factory Pages ...........................216
Custom Setup Menu .....................................217
Security Setting Menu ....................................218
Diagnostics Menu .......................................222
Calibration Menu ........................................223
Chapter 7: Features ...............................225
Saving and Restoring Settings Using an RUI ..................228
Tuning the PID Parameters ................................228
Autotune .............................................228
Manual Tuning ........................................229
Autotuning with TRU-TUNE+
Inputs .................................................231
Calibration Offset ......................................231
Calibration ............................................231
Filter Time Constant ....................................233
Sensor Selection .......................................233
Sensor Backup ........................................233
Set Point Low Limit and High Limit ........................234
Scale High and Scale Low ...............................234
® ..................................230
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 2 • Table of Contents
Page 7

TC
Table of Contents (cont.)
Range High and Range Low ..............................234
Receiving a Remote Set Point ............................234
Ten Point Linearization ..................................235
Outputs ...............................................235
NO-ARC Relay .........................................235
Duplex ...............................................236
Retransmitting a Process Value or Set Point .................236
Cool Output Curve .....................................237
Control Methods ........................................237
Output Configuration ...................................237
Auto (closed loop) and Manual (open loop) Control. . . . . . . . . . . . 237
On-Off Control ........................................239
Proportional (P) Control .................................239
Proportional plus Integral (PI) Control ......................240
Proportional, Integral and Derivative (PID) Control ............240
Variable Time Base .....................................241
Single Set Point Ramping ................................242
Cascade Control .......................................243
Compressor Control ....................................244
Differential Control .....................................244
Ratio Control ..........................................245
Motorized Valve Control .................................245
Alarms ................................................246
Process and Deviation Alarms ............................246
Alarm Set Points .......................................246
Hysteresis ............................................246
Latching .............................................246
Silencing .............................................247
Blocking .............................................248
Resetting a Tripped Limit ..................................248
Current Sensing .........................................249
Open Heater Circuit Detection .............................249
Shorted Heater Circuit Detection ...........................249
Open Loop Detection ...................................249
Using Password Security .................................250
Modbus - Using Programmable Memory Blocks ................251
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 3 • Table of Contents
Page 8

TC
Table of Contents (cont.)
Software Configuration ...................................252
EZ-ZONE Configurator Software ...........................252
Using EZ-ZONE Configurator Software .....................255
Function Block Descriptions ...............................257
Action Function ........................................257
Alarm Function ........................................258
Analog Input Function ...................................260
Compare Function ......................................262
Control Loop Function ..................................264
Counter Function ......................................266
Custom Function .......................................267
Diagnostic Function ....................................267
Digital Input/Output Function .............................268
Global Function ........................................269
Limit Function .........................................270
Linearization Function ...................................271
Logic Function ........................................273
Math Function .........................................277
Modbus® Function .....................................282
Output Function .......................................283
Profile Function ........................................284
Process Value Function. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
Security Function ......................................296
Special Output Function .................................297
Timer Function ........................................300
Variable Function ......................................306
Chapter 9: Appendix ..............................307
Troubleshooting Alarms, Errors and Control Issues .............307
Modbus - Programmable Memory Blocks .....................314
Control Module Specifications ..............................317
RM Ordering Information ..................................324
How to Reach Us ........................................326
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 4 • Table of Contents
Page 9
1
Chapter 1: Overview
Available EZ-ZONE RM System Literature and Resources
Document Title and Part Number Description
EZ-ZONE Rail Mount Access (RMA)
User's Guide, part number: 06000072-0000
EZ-ZONE Rail Mount Expansion (RME)
User's Guide, part number: 06000073-0000
EZ-ZONE Rail Mount High Density
(RMH) User's Guide, part number:
0600-0074-0000
EZ-ZONE Rail Mount Scanner (RMS)
User's Guide, part number: 06000071-0000
EZ-ZONE Rail Mount Limit (RML) User's Guide, part number: 0600-00750000
EZ-ZONE Remote User Interface (RUI)
User's Guide, part number: 06000060-0000
Describes how to connect the RM system into an
industrial network, how to use data logging, module backup and the real-time clock.
When additional I/O is needed the Expansion module fills the gap. This document describes common
usage and the various types of I/O available.
This module extends the density of the standard
RM modules (number of control loops and I/O
points). The User Guide describes common usage,
communications and the number I/O points available.
This module adds monitoring points to the RM system. This document describes common usage and
the various types of I/O available.
This module will protect against unwanted thermal runaway and over temperature conditions.
The User Guide describes configuration, programming and communications capabilities.
The RUI provides a visual LED display to the RM
configuration and setup menus. This document
illustrates and describes connections and also
describes the Home Page for each RM module as
viewed from the RUI.
EZ-ZONE RM Specification Sheet, part
number: WIN-EZRM-0414
Watlow Support Tools DVD, part
number: 0601-0001-0000
The DVD described above ships with the product and as stated contains all of the literature
above as well as much more. If the DVD is not available one can be acquired by contacting
Watlow Customer Service at 1-507-454-5300.
As an alternative to the DVD, all of the user documentation described above can also be
found on the Watlow website. Click on the following link to find your document of choice:
http://www.watlow.com/literature/index.cfm. Once there, simply type in the desired part
number (or name) into the search box and download free copies.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 5 • Chapter 1 Overview
Describes RM hardware options, features, benefits
and technical specifications.
Contains all related user documents, tutorial videos, application notes, utility tools, etc...
Page 10
Your Comments are Appreciated
In an effort to continually improve our technical literature and ensure that we are providing
information that is useful to you, we would very much appreciate your comments and suggestions. Please send any comments you may have to the following e-mail address: TechlitComments@watlow.com
Introduction
The EZ-ZONE® Rail Mount Control module (RMC) takes the pain out of solving your thermal
loop requirements whether it be for a single loop, multi-loop, stand-alone or distributed control applications.
It just got a whole lot easier to solve the thermal requirements of your system. The RMC
module is provided in a space-saving, rail-mount package and is highly scalable where you only
pay for what you need. For those applications that require the ability to configure/monitor
the control over a network, Modbus RTU communications is an option. Other communications
protocols are also available (e.g., EtherNet/IP, DeviceNet, Modbus TCP and Profibus DP) when
used in conjunction with an RM Access (RMA) module or when using a Remote User Interface/
Gateway (RUI/GTW).
Standard Features and Benefits
Integrated PID and over/under safety limit controller in one package
• Provides two mounting options (DIN rail, chassis mount)
• Reduces wiring time and termination complexity compared to connecting discrete products
• Reduces panel space and installation cost
• Increases user and equipment safety for over/under temperature conditions
Integrated power controller output
• Includes the patented NO-ARC, which drives up to 15 amp resistive loads directly
• Reduces component count and cost of ownership
• Saves panel space and simplifies wiring
Current monitoring (traditional or algorithm)
• Detects heater current flow and provides alarm indication of a failed output device or
heater load
• For use in single phase loads
Communication Capabilities
• Supports network connectivity to a PC or PLC
• Watlow Standard Bus or Modbus® RTU
• Provides plug and play capabilities with Remote User Interface (RUI’s) and RMA module
• Free standard bus communications port and free PC software EZ-ZONE Configurator and
Composer
Additional Control Integration Options
• Provides a sequencer function
• Includes programmable timer functions
• Includes programmable counter functions
• Allows for simple math and logic programming options
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 6 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 11

Advanced PID Control Algorithm
• Offers TRU-TUNE®+ adaptive control to provide tighter control for demanding applications
• Provides auto-tune for fast, efficient startup
Integrated Thermal Loop Diagnostics
• Users can easily tell that the entire thermal system is functioning properly
• Provides complete system diagnostics that are far superior to simple discrete level diagnostics
• Allows for flexible synergistic use of hardware, such as using one loop's sensor as a backup
to another loop in the event of sensor failure.
• Helps prevent load loss or allow for maintenance to be scheduled when more convenient.
• Provides notification of system problems to help reduce maintenance and service costs
Off-the-Shelf Designed System Solution
• Improves system reliability with a factory integrated solution that minimizes inter-module
connections and potential problems at screw termination points.
• Reduces installation cost
• Eliminates compatibility headaches often encountered with using many different components and brands
Controller Handles High Ambient Temperatures
• Operates in an unprecedented temperature range of -18 to 65°C (0 to 149°F) for cabinets
and panel enclosures with elevated temperature levels
Memory for Saving and Restoring User-Defined Parameter Default Settings
• Allows customers to save and restore their own defined defaults for machine parameter
settings
• Reduces service calls and downtime due to inadvertent end user parameter adjustments
RMC Modules Allow for Greater Design Flexibility
• Allows PID loops to be added in increments of one.
• Saves money because you do not pay for any more than you need and don’t settle for any
less functionality than you need
Synergistic Module Control (SMC)
• Allows outputs selected for control (heat/cool), alarms or events to be located in any physical module, regardless of which module is connected to the input sensor
Split-Rail Control (SRC)
• Allows modules to be mounted together or mounted remotely from one another (maximum
distance 200 feet or 61 meters)
• Shares control operation via Synergistic Module Control (SMC) capability
• Allows individual modules to be mounted closer to the physical input and output devices
to which they are wired
• Improves system reliability and lowers wiring costs
Factory Mutual (FM) Approved Safety Limit
• Increases user and equipment safety for over/under temperature conditions
• Supports SEMI S2 specification
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 7 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 12

Agency Approvals: UL® listed, CE, RoHS, W.E.E.E. FM, SEMI F47-0200, Class 1 Div. 2 Rating
on Selected Models
• Assures prompt product acceptance
• Reduces panel builder's documentation and agency costs
Removable Connectors
• Assures reliable wiring and reduces service calls
• Simplifies installation
Prole Capability
• Allows ramp/soak programming
• Provides 25 profiles and 400 total steps
Remote Set Point Operation
• Supports efficient set point manipulation from a remote device such as a master control or
PLC
• Allows one or more loops to be programmed to control based on another loop's set point
eliminating the cost of purchasing additional retransmit and remote set point hardware
Retransmit
• Supports industry needs for process recording
Three-Year Warranty
• Demonstrates Watlow’s reliability and product support
A Conceptual View of the RMC Module
The flexibility of the RMC software and hardware allows a large range of configurations. Acquiring a better understanding of the controller’s overall functionality and capabilities while at
the same time planning out how the controller can be used will deliver maximum effectiveness in your application.
The RMC can be connected at the system level to as many as 17 modules, one of which can
be an Access module and the others (16 maximum) can be any combination of available modules. The user will define each address via the button on the face of each module. Each installed RMC module must have a unique Standard Bus address ranging from 1-9, A-F, where the
factory defaults for each is Standard Bus address 1.
Getting Started Quickly
The RMC (Controller) can be ordered with up to four PID loops with default loop configurations (all loops) out of the box as follows:
• Analog Input functions set to thermocouple, type J
• Control loops 1-4 use Analog Inputs 1-4
• Heat algorithm set for PID, Cool algorithm set to off
• Outputs set to off
• Control mode set to Auto
• Set point set to 75 °F
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 8 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 13
To enable a loop for heat simply follow the steps below:
1. Navigate to the Setup Page
2. Once on the Setup Page navigate to the Output Menu and then the output of choice
3. Change the default setting of Off to Heat Power
4. Select the desired loop instance
EZ-ZONE RMC Default Configuration
Input
Function
Input Sensor
Analog Input 1
Thermocouple Type J
PID
Controller
Heat
Slot A
Loop 1
Output 1
Off
Output
Function
Heat
Note:
Zones can communicate with one another over the backplane (local and split rail). Once
the system is configured and running, changing zone addresses without careful deliberation may cause disruption in operation.
Some of the user selectable ordering options are listed below:
1. Class 2 or SELV (Safety Extra Low Voltage) equivalent Power Supplies:
• 90-264 Vac to 24Vdc @ 31 watts
• 90-264 Vac to 24Vdc @ 60 watts
• 90-264 Vac to 24Vdc @ 91 watts
2. RMC Module can provide:
• 1 to 4 control loops, limits or CT inputs
• 1 to 9 inputs (various types)
• 1 to 12 outputs (various types)
• Modbus RTU communications
As can be seen above the RMC module is fully scalable with regards to power requirements,
number of loops, inputs, and outputs.
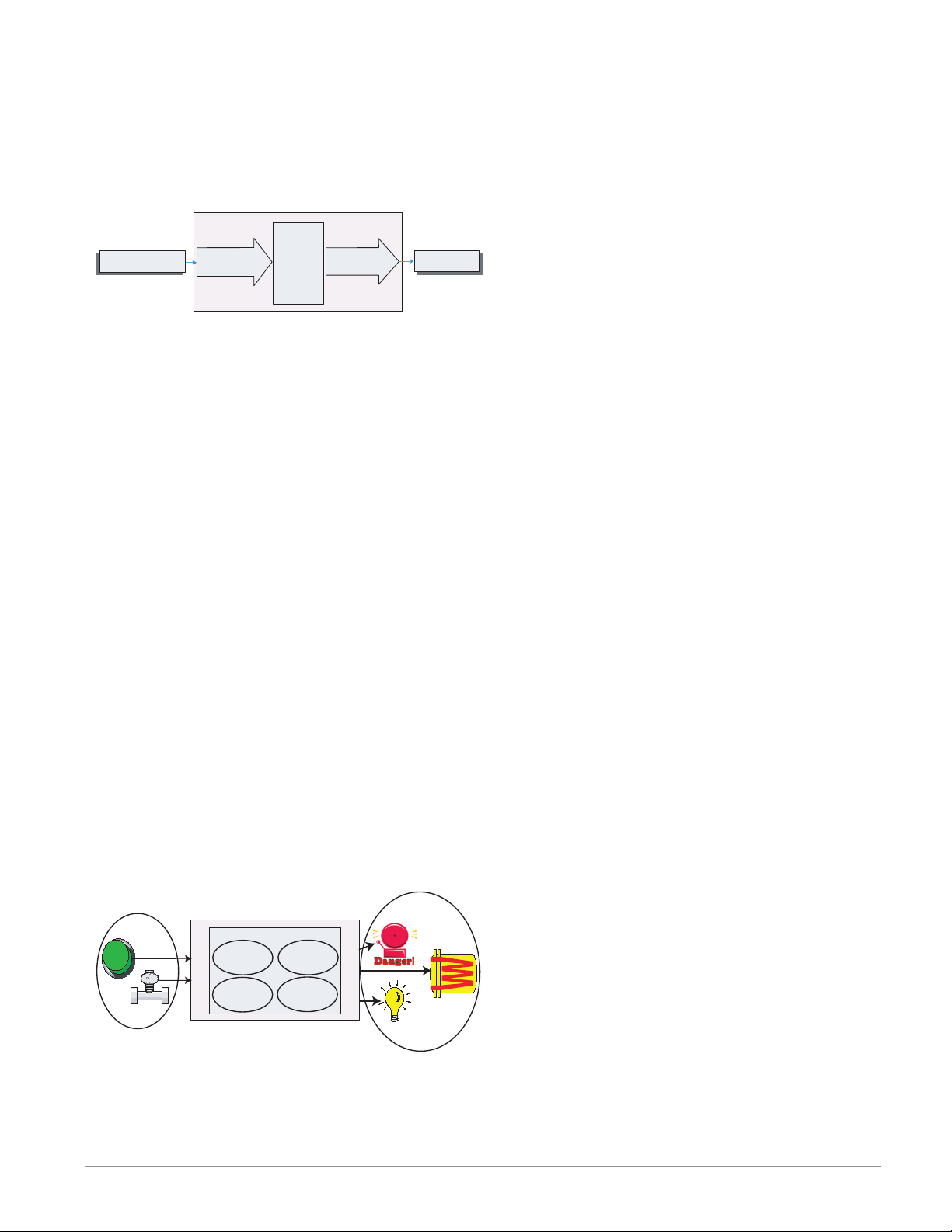
It is useful to think of the controller in three parts: inputs, functions and outputs. Information
flows from an input to a function to an output when the controller is properly configured. An
RMC module can carry out several functions at the same time, e.g., PID control, monitoring
for several different alarm situations, monitoring and acting upon Digital Inputs and driving
output devices such as heaters, audible alarms, lights. Each process needs to be thought out
carefully and the controller’s inputs, functions and outputs set up properly.
Outputs
Inputs
Functions
PID
Heat
Power
Silence
Alarms
Process
Alarm
High
Sequencing
Outputs
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 9 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 14

Functions
Functions use input signals to calculate a value. A function may be as simple as reading a digital input to set a state to true or false, or reading a temperature to set an alarm state to on
or off. Alternatively, if a failure with the primary sensing device should occur, sensor backup
could be utilized to avoid an unwanted shutdown.
To set up a function, one of the first things that must be considered is the function source
and instance. For example, if the control is equipped with Digital Inputs (source) and it was
decided to use DI 9 (instance) it can then be associated with an Action to reset an individual
alarm or all alarms.
To configure a Digital Input as described above:
1. Navigate to the Setup Page and then to the Digital I/O menu.
2. Select the desired instance and set the direction to input voltage or input dry contact.
3. Navigate to the Setup Page and then the Action menu.
4. Set the Action Function to Alarm
5. Select which alarm instance will be reset (0 equals all)
6. Select the Source Function to Digital I/O
7. Select the Source Instance (step 2 above)
8. Select the Source Zone (0 equals the module being configured).
9. Select the Transmitter Active Level to execute the desired function.
This configuration is now complete. When the selected digital input is active, the alarm or all
alarms that are latched without a currently existing alarm condition will be reset. If a specific
alarm instance (1 - 8) is selected (step 5) it will be that instance alone that will be reset.
Note:
Alarms will reset automatically when the condition that caused the alarm goes back to a
non-alarm state if the Latching prompt is set to non-latching (Setup Page, Alarm Menu).
Keep in mind that a function is a user-programmed internal process that does not execute any
action outside of the controller. To have any effect outside of the controller, an output must
be configured to respond to a function.
Inputs
The inputs provide the information that any given programmed function can act upon. In a
simple form, this information may come from an operator pushing a button, or as part of a
more complex function it may represent a remote set point being received from another zone.
Each analog input can be configured for thermistors, thermocouples, or RTDs to read the process variable. It can also read mV/volts, current or resistance, enabling usage of various devices to read humidity, air pressure, operator inputs and other values. The settings in the Analog
Input Menu (Setup Page) for each analog input must be configured to match the device connected to that input.
Each digital input reads whether a device is active or inactive. A RM system can be equipped
with multiple digital I/O. Each I/O point must be configured to function as either an input or
output with the direction parameter in the digital I/O Menu (Setup Page).
Another concept that needs to be understood is the difference between an input tied to a real-world device such as a thermocouple and one that is tied to an internal function.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 10 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 15
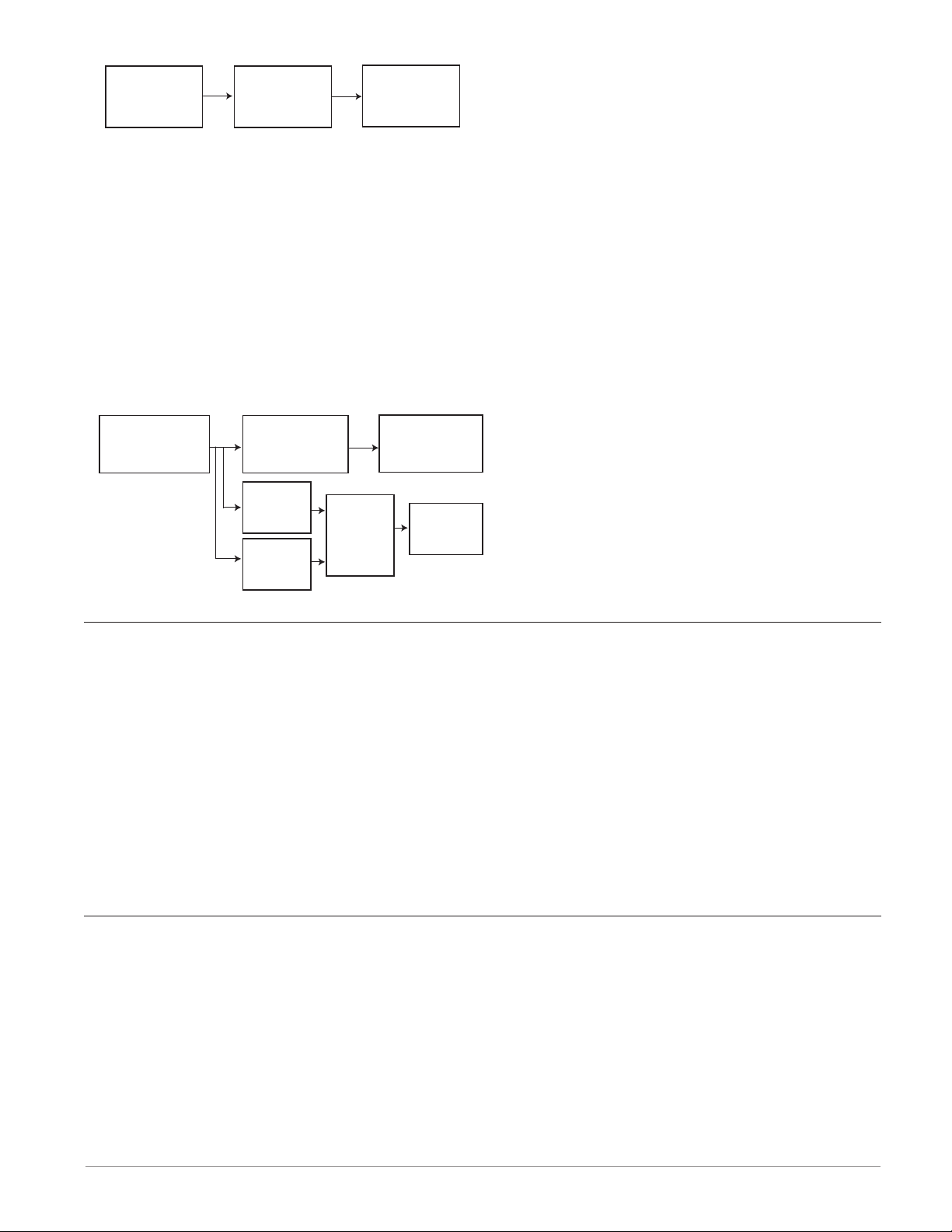
Analog
Input
Function
Control
Function
Output
Function
In the example above the analog input function on the left is tied directly to the control function where its internal output is routed to a real-world output.
With a slight modification of the graphic above the example below now ties the real-world inputs directly to the control and alarm functions. For the sake of this example the following is
true:
- Two unique high process alarms are congured for analog inputs 1 and 2
- The logic block is congured as an OR function
- The output function is tied to the internal output of the logical OR function
When either process alarm is true (analog input value is greater than the alarm high set point,
the real-world output will be driven on.
Analog
Input
Function
1
2
Control
Function
Alarm
Function
Alarm
Function
Logic
Function
Output
Function
Output
Function
Outputs
Outputs can perform various functions or actions in response to information provided by a
function such as: heat power from the output of the control, using a digital output to serve as
a profile event, drive a light on or off, unlocking a door or turning on a buzzer.
Assign an output to a function in the Output Menu or Digital I/O Menu. Then select which instance of that function will drive the selected output. For example, you might assign an output to respond to an internal output of a compare function or to retransmit the value of analog input 2 (instance 2).
You can assign more than one output to respond to a single instance of a function. For example, alarm 2 could be used to trigger a light connected to output 1 and a siren connected to
digital output 5.
What is a Profile
A profile is a set of instructions consisting of a sequence of steps. When a profile runs, the
controller automatically executes its steps in sequence. The step type determines what action the controller performs. Steps can change temperatures and other process values gradually over time, maintain the temperatures and process values for specific periods, or repeat a
sequence of steps numerous times. At each step the profile can activate or deactivate outputs
that control other equipment. Also a step can have the controller wait for specific conditions
before proceeding such as, waiting for a switch closure and/or a specific process value to be
detected by a sensor.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 11 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 16
Input Events and Output Events
Input and output events are internal states that are used exclusively by profiles. The source of
an event input can come from a real-world digital input or an output from another function.
Likewise, event outputs may control a physical output such as an output function block or be
used as an input to another function.
Actions
Based on a given input (Digital I/O, Event output, Logic function, etc..) the Action function
can cause other functions to occur. To name a few, starting and stopping a profile, silencing
alarms, turn control loops off and placing alarms in non-alarm state.
A Conceptual View of RM Hardware Configurations
Due to the scalability and flexibility in the RM system a user has several options available in
the way that the hardware can be connected. Listed below are a few examples.
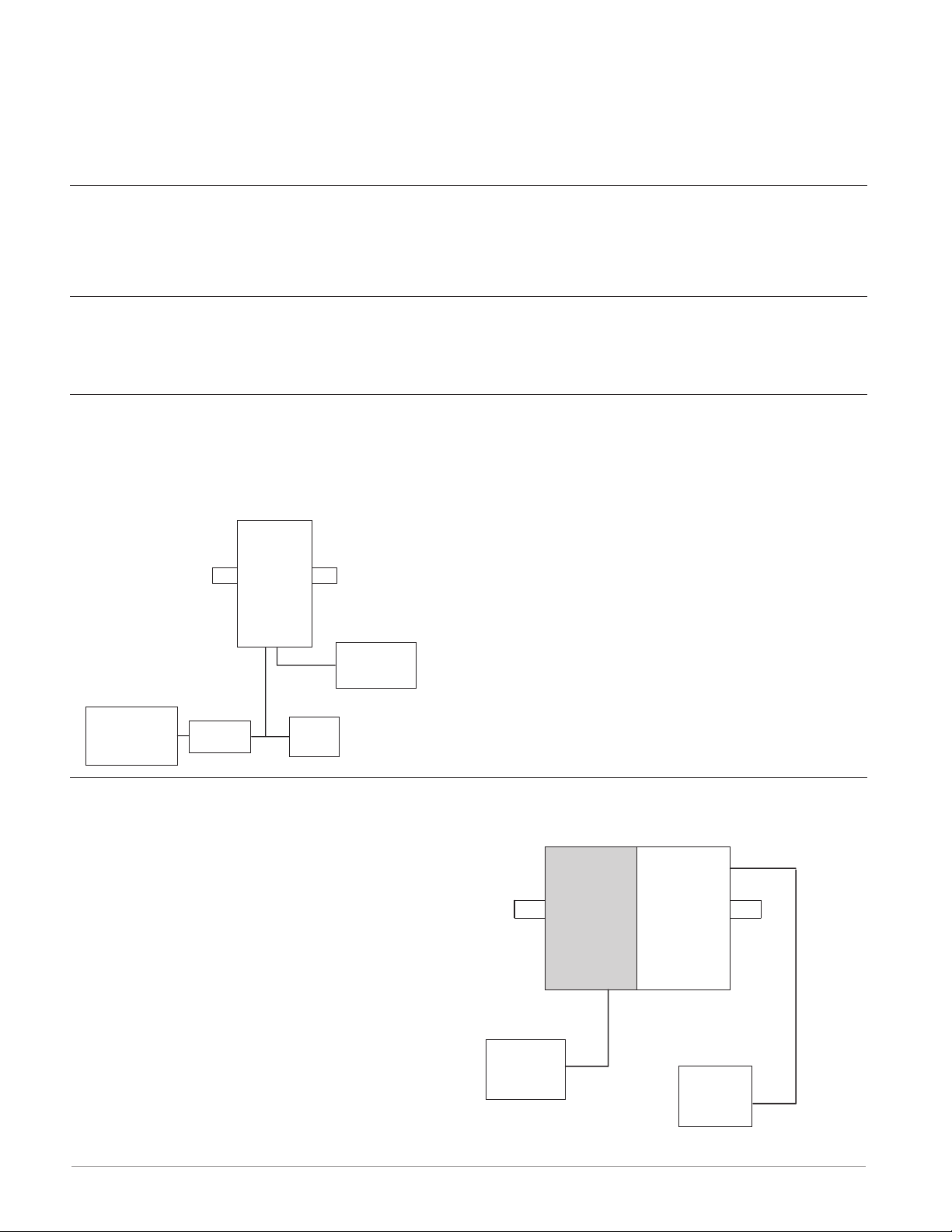
RMC Module Connected to a Remote User Interface (RUI) and a PC
In this configuration the RUI and PC are connected to the RMC module via Watlow's Standard
Bus where both will be able to talk directly to the RMC module. The PC running EZ-ZONE
Configurator software and the RUI can be used to configure and then monitor the RMC module.
RM
Control
Slot C
Powe r
Supply
PC
EZ-ZONE
Configurator
485 to USB
Converter
RUI
RMC Module Connected to a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) on a DIN Rail
In this configuration the PLC can be connected to the RMC module via the Access module using one or more available protocols:
1. EtherNet/IP and or Modbus TCP
2. DeviceNet
3. Modbus RTU
RM
Control
RM
Access
Slot CSlot C
Slot E
Power
Supply
PLC
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 12 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 17
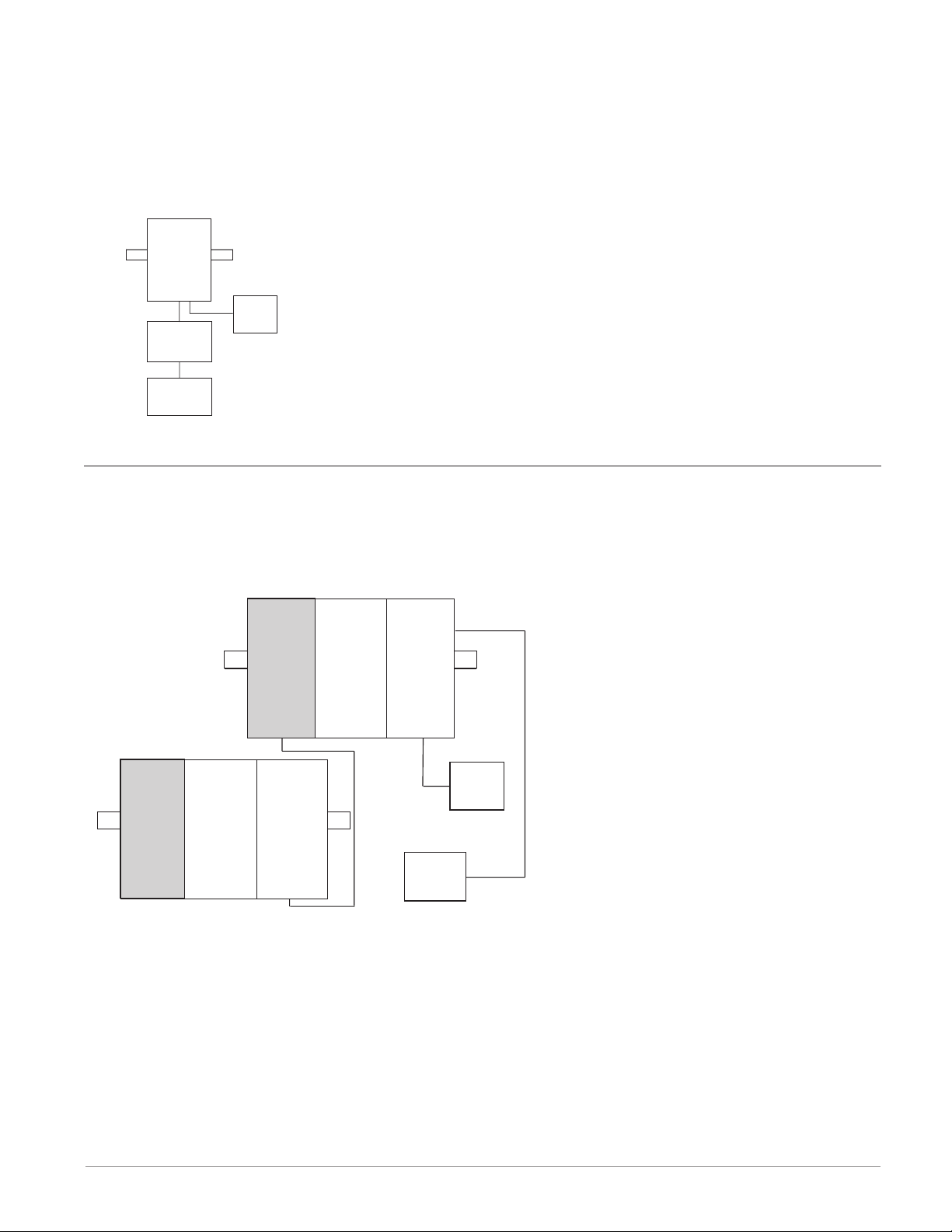
RMC Module Connected to an Operator Interface Terminal (OIT) through an RUI/Gateway
In this configuration the OIT can be running any of a number of protocols communicating to
the RM system through Watlow's RUI/Gateway. Available protocols for the RUI/Gateway follow:
1. EtherNet/IP and or Modbus TCP
2. DeviceNet
3. Modbus RTU
RM
Control
Slot C
RUI
Gateway
OIT
Powe r
Supply
RM System Connected to a Split Rail with OIT
In this configuration both the Inter-module Bus (backplane communications) and Standard Bus
are connected between rails to allow for remote capabilities. It is recommended that the split
rail connection not exceed 200 feet. In this configuration the OIT can communicate with all
modules (maximum 16 modules any combination with one Access module).
Slot E
RM
Control
Slot C
RM
Expansion
Slot C
RM
Access
Slot C
Power
Supply
RM
Control
Slot C
RM
Expansion
Slot C
RM
Expansion
Slot C
OIT
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 13 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 18
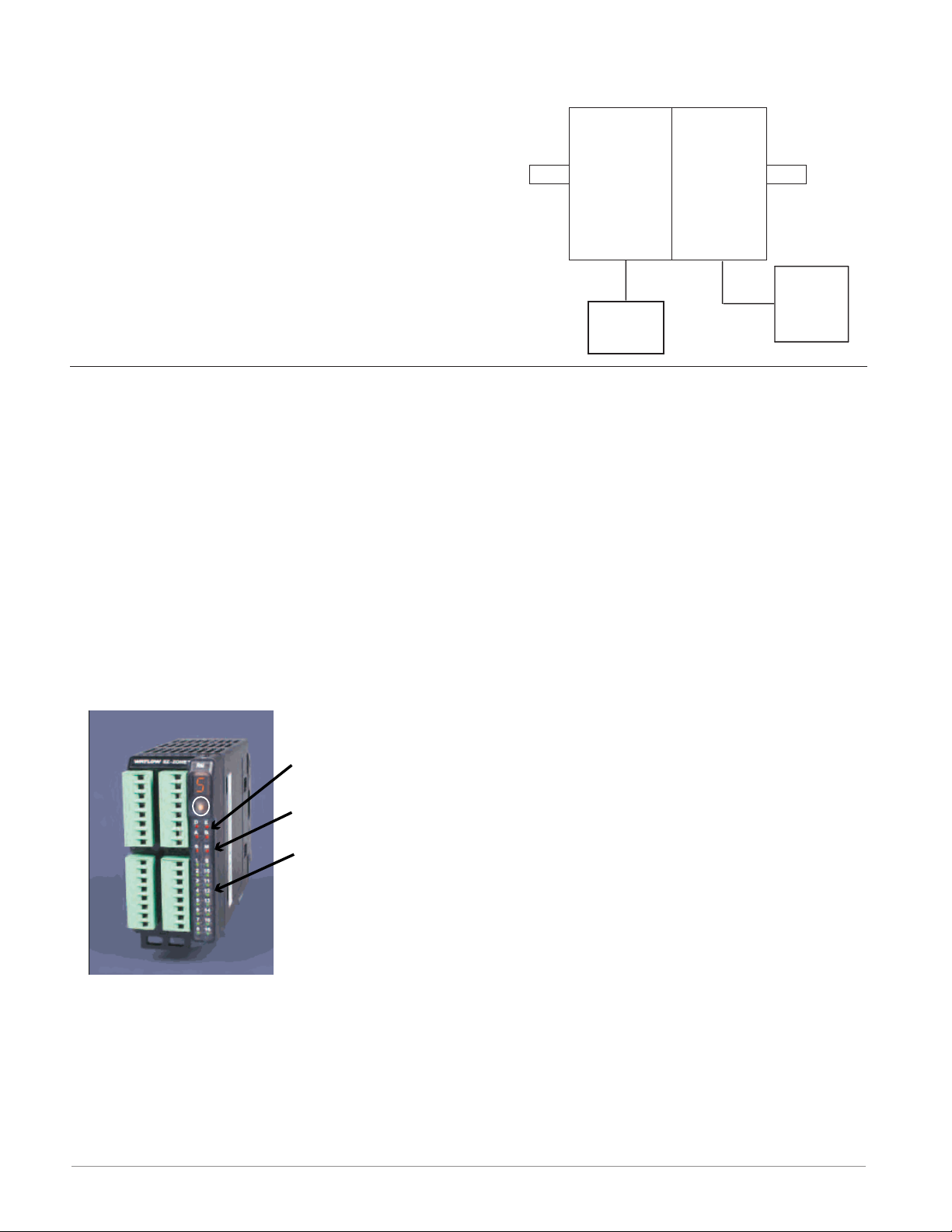
RM Control Module Connected to an OIT Running Modbus RTU
In this configuration the control module connected to the OIT is equipped with the Modbus
RTU protocol (RMCxxxxxxxxx1xx). It is important to
note that Modbus communications takes place between the OIT and the control it is connected to. All
modules must be set for the same protocol with the
Modbus wiring connected to one module.
RM
Control
RM
Control
Slot C
Slot C
Power
Supply
OIT
Module Orientation
The picture below represents one of six possible RM modules. All six will have four slots on
the face (slot A, B, D, and E) and one on the bottom (slot C) not shown. All of these slots are
not always used on all modules. On the face of the module there is a button (white circle) under the Zone address (5) that when pushed and held has the following functions:
1. For any module, push and hold for approximately 2 seconds. The address will intensify indi-
cating that it can now be changed. Release and repeatedly press to change to the desired
unique address.
2. For the control module, if equipped with the Modbus protocol (RMCxxxxxxxxx1xx) pushing
and holding this button for approximately 6 seconds will cause the display to reflect P for
protocol. Releasing the button and then pushing it again (within 6 seconds), the display will
toggle between N (Modbus) and S (Standard Bus). Valid addresses for Modbus and Standard
bus range from 1 -16 (1-q, a is 10, b is 11, C is 12, d is 13, E is 14, f is 15, and h is 16).
The Access module is shipped at address J or 17.
Module Status
(Slot A, B, D, or E)
E
D
B
A
Protocol
Standard Bus - red
Modbus - green
Module Outputs
1 through 16, all may or
may not be used depending
on module type
Note:
For correct operation and accuracy, the
module must be mounted in a vertical
orientation as shown.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 14 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 19
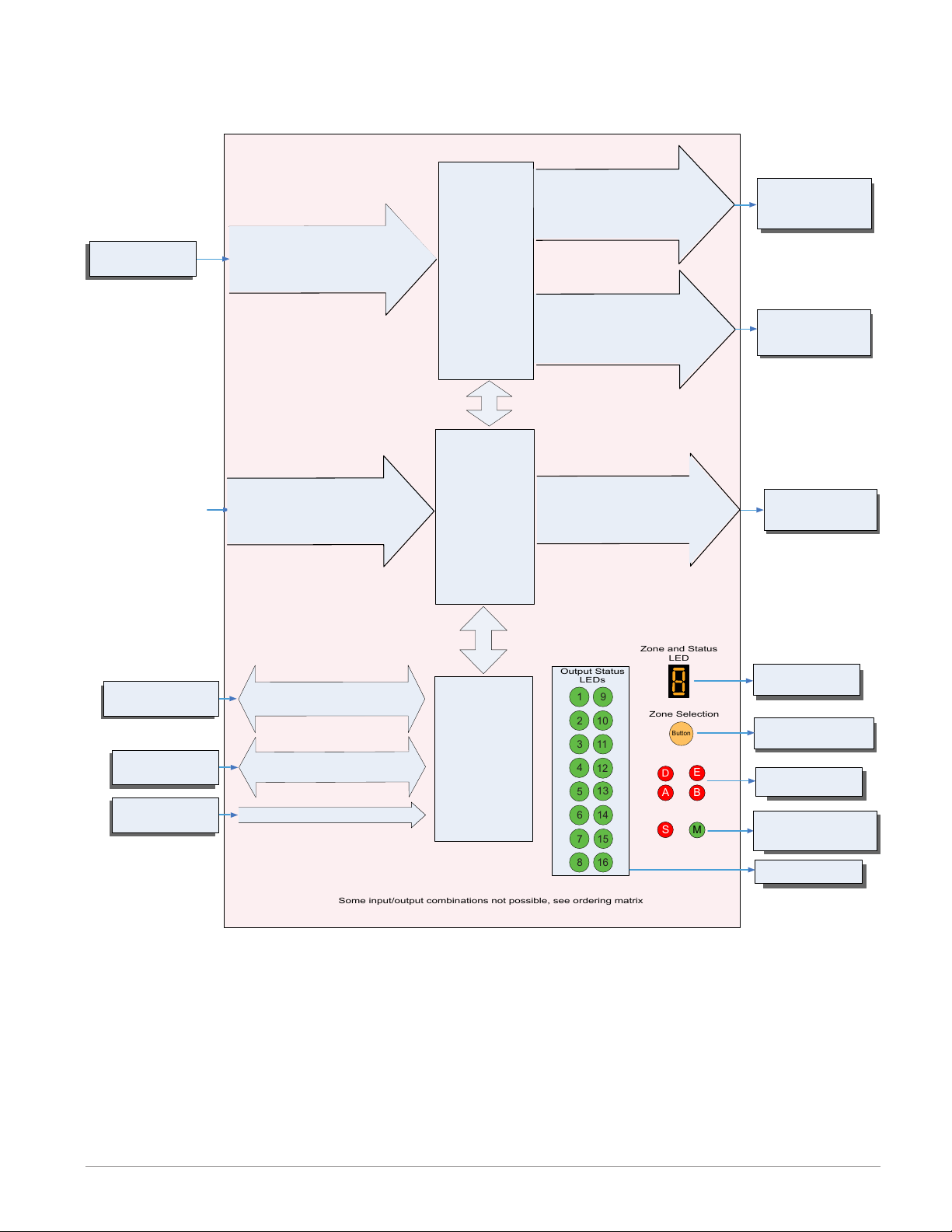
Input
Some input/output combinations not possible, see ordering matrix
Zone and Status
LED
Zone Selection
Output Status
LEDs
2
3
4
5
6
1
10
11
12
13
14
9
7
81516
Button
D
E
B
A
S
M
Function
Input Sensor
EZ-ZONE RM-Control Module - System Diagram
with 6-Digital Input/Output card in slot E
Analog Input 1, 2, 3, 4
None, CT, Thermocouple, RTD (100, 1k),
Thermistor (5k, 10K, 20k, 40k), Process
(mV, V, mA) or 1k Potentionmeter
Current
Transformer
Sense (CT),
Limit or
PID Controller
(When ordered, all
loops have Ramp/
Soak, max 25 files
& 400 steps.)
Slot A, B, or D
(optional)
Output 1, 3, 5
None, Switched dc/Open Collector,
5A Mechanical Relay Form C, Process,
or 0.5A Solid-State Relay Form A
Class 1 Div II not available
with mechanical relay
outputs.
Output 2, 4, 6
None, 15A NO-ARC Form A,
Switched dc, 5A Mechanical Relay
Form A, or 0.5A Solid-State Relay
Form A
Output
Function
Options
See:
Setup Page,
Output Menu
See:
Setup Page,
Output Menu
If Limit, this output
must be Limit.
RUI,
PC, PLC or HMI
Other RM Modules
Power Supply
Digital Input (or output) 7 - 12
Switch contact or volts dc
EIA - 485 Communications
Standard Bus
(optional Modbus RTU)
Inter-module Bus
20.4 to 30.8 Vac or Vdc
6 - Digital
Inputs or Outputs
Slot E
Modbus RTU
Address 1 - 16
Standard Bus
Zone 1 - 16
Supervisory &
Power Board
Slot C
Digital Output (or input) 7 - 12
Switch contact or volts dc
See:
Setup Page,
Output Menu
Indicates Zone
Address
Push to select Zone
Address and Protocol
Card Status
Slots A, B, D, E
Indicates communications activity (Modbus
or Standard Bus)
Indicates I/O
Status
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 15 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 20
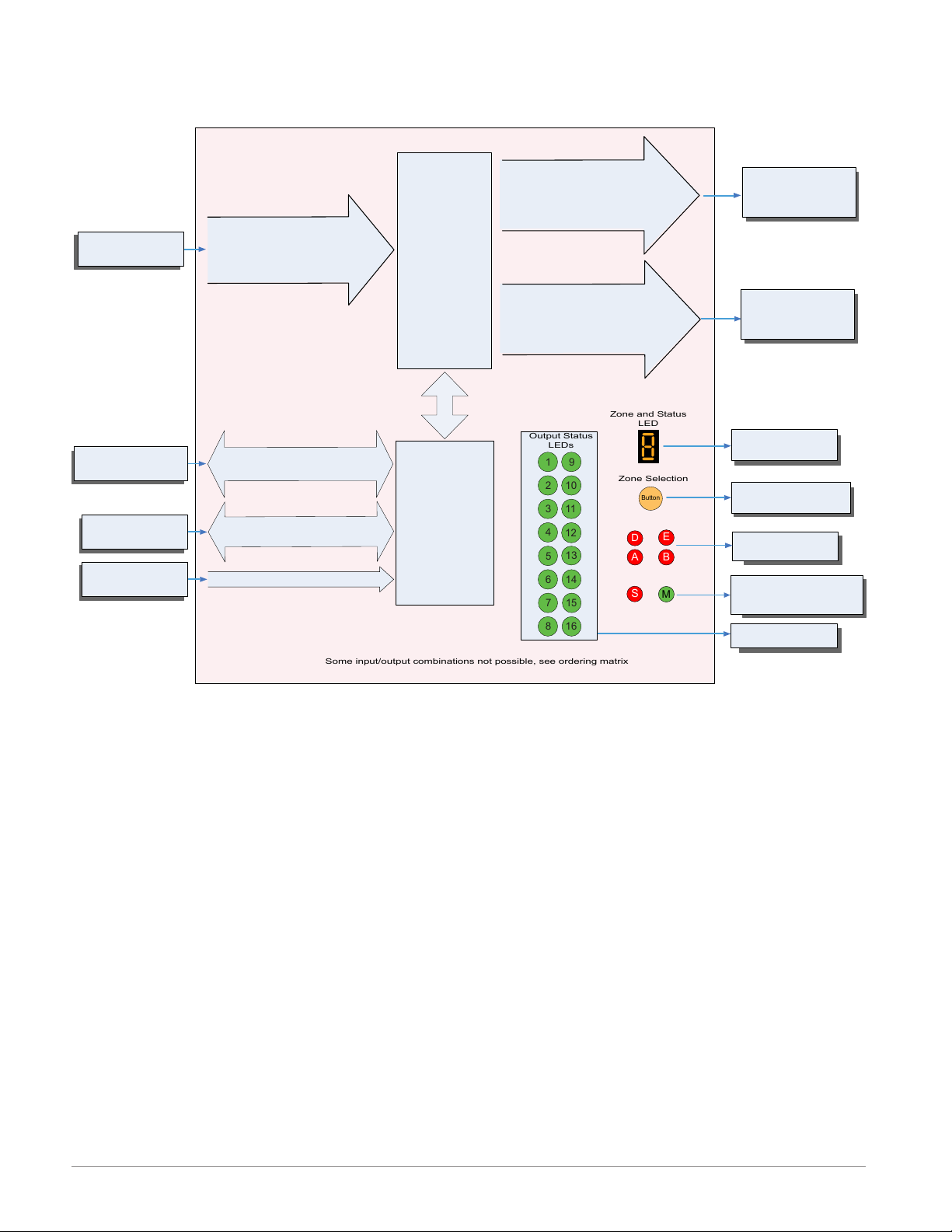
Some input/output combinations not possible, see ordering matrix
Zone and Status
LED
Zone Selection
Output Status
LEDs
2
3
4
5
6
1
10
11
12
13
14
9
7
81516
Button
D
E
B
A
S
M
Input
Function
Input Sensor
RUI,
PC, PLC or HMI
Other RM Modules
Power Supply
EZ-ZONE RM-Control Module - System Diagram
without 6-Digital Input/Output card in slot E
Analog Input 1, 2, 3, 4
None, CT, Thermocouple, RTD (100, 1k),
Thermistor (5k, 10K, 20k, 40k), Process
(mV, V, mA) or 1k Potentionmeter
EIA - 485 Communications
Standard Bus
(optional Modbus RTU)
Inter-module Bus
20.4 to 30.8 Vac or Vdc
Current
Transformer
Sense (CT),
Limit or
PID Controller
(When ordered, all
loops have Ramp/
Soak, max 25 files
& 400 steps.)
Slot A, B, D or E
(optional)
Modbus RTU
Address 1 - 16
Standard Bus
Zone 1 - 16
Supervisory &
Power Board
Slot C
Output 1, 3, 5, 7
None, Switched dc/Open Collector,
5A Mechanical Relay Form C, Process,
or 0.5A Solid-State Relay Form A
Class 1 Div II not available
with mechanical relay
outputs.
Output 2, 4, 6, 8
None, 15A NO-ARC Form A,
Switched dc, 5A Mechanical Relay
Form A, or 0.5A Solid-State Relay
Form A
Output
Function
Options
See:
Setup Page,
Output Menu
See:
Setup Page,
Output Menu
If Limit, this output
must be Limit.
Indicates Zone
Address
Push to select Zone
Address and Protocol
Card Status
Slots A, B, D, E
Indicates communications
activity (Modbus or Standard Bus)
Indicates I/O
Status
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 16 • Chapter 1 Overview
Page 21
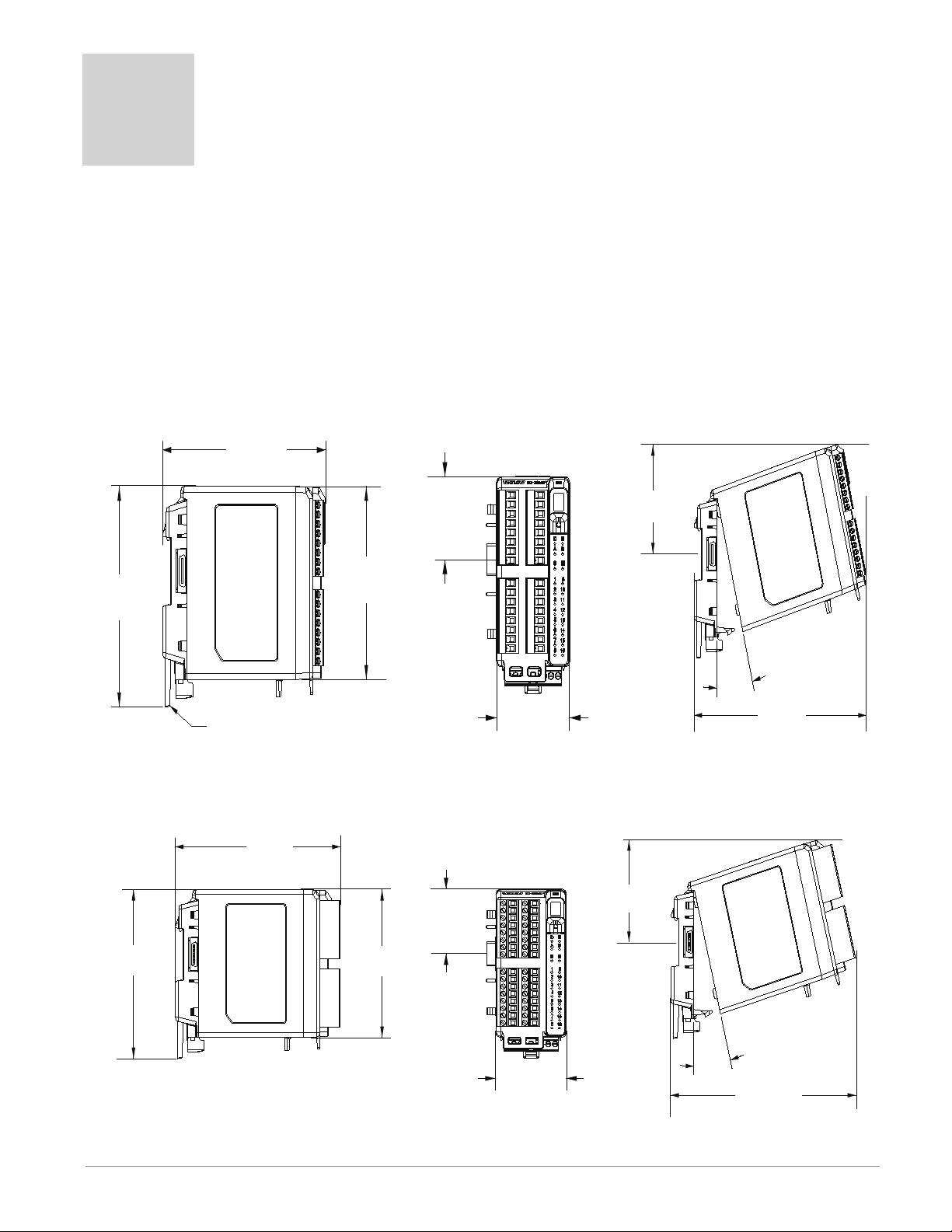
2
Chapter 2: Install and Wire
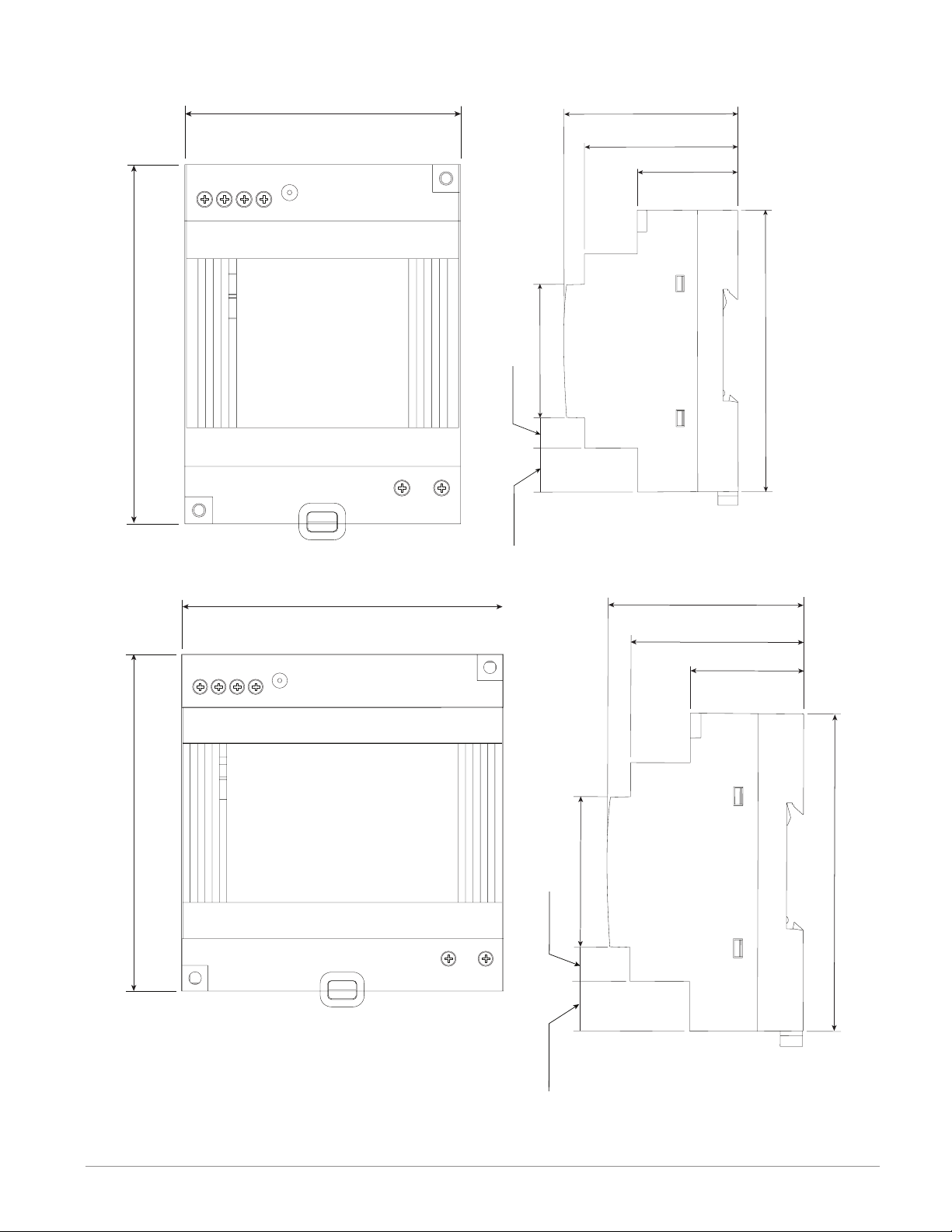
Dimensions
As can be seen below the dimensions of the RMC module will change slightly based on the
type of connector used.
Note:
Modules should always be mounted vertically. For easy removal and placement of modules
it is recommended that there be a 76.2 mm (3.00 in) clearance on the top and bottom of
each module.
Module Removal Clearance Standard Connectors
147.07 mm
( 5.8 in )
75.08 mm
116.08 mm
( 4.57 in )
44.45 mm
( 1.75 in )
101.60 mm
( 4.00 in )
( 3.0 in )
51.56 mm
Latch in open position
( 2.03 in )
Module Removal Clearance Straight Connectors
155 mm
( 6.10 )
44.45 mm
( 1.75 in )
116.08 mm
( 4.57 in )
101.60 mm
( 4.00 in )
51.56 mm
( 2.03 in )
75.08 mm
( 3.0 in )
0
15
165 mm
( 6.50 in )
Module Removal Displacement
15
°
173.90 mm
( 6.85 in )
Module Removal Displacement
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 17 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 22
Dimensions (cont.)
53.00 mm
91.00 mm
14.20 mm
9.75 mm
55.6 mm
0.559 in
Chassis Mount Front View (Module Removed) - Screw Connection Pattern
58.67 mm
17.53 mm
( 0.69 in )
60.45 mm
( 2.38 in )
35.81 mm
( 1.41 in )
( 2.31 in )
32.77 mm
( 1.29 in )
35.05 mm
( 1.38 in )
51.56 mm
( 2.03 in )
16.76 mm
( 0.67 in )
The view above is representative of the modular backplane without the module.
Recommended chassis mount hardware:
1. #8 screw, 3/4" long
2. Torque to 10 -15 in-lb
3. No washers of any kind
Power Supplies
DSP 30
2.189 in
32.10 mm
1.264 in
3.583 in
91.00 mm
1234
++
3.583 in
-
DC LO
DC OK
2.087 in
-
DSP30
1.697 in
43.1 mm
49.00 mm
1.929 in
0.384 in
LN
56
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 18 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 23
DSP 60
56
71.00 mm
91.00 mm
14.20 mm
9.75 mm
55.6 mm
0.559 in
LN
56
89.9 mm
91.00 mm
14.20 mm
9.75 mm
56.8 mm
0.559 in
1234
++
3.583 in
-
-
DC LO
DC OK
2.795 in
vout ADJ.
DSP60
LN
DSP 100
1.697 in
43.1 mm
0.384 in
49.00 mm
1.929 in
2.189 in
32.10 mm
1.264 in
3.583 in
91.00 mm
1234
++
3.583 in
-
-
DC LO
DC OK
3.539 in
vout ADJ.
DSP100
1.697 in
43.1 mm
0.384 in
49.00 mm
1.929 in
2.236 in
32.10 mm
1.264 in
3.583 in
91.00 mm
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 19 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 24
Power Supply Specifications
DSP 30 DSP60 DSP100
AC Input Voltage Range VAC
Input Frequency Hz 47 - 63Hz
DC Input Voltage range VDC 120 - 370VDC
Inrush Current (115 / 230VAC) A 25 / 50A 30 / 60A 30 / 60A
Output Voltage Accuracy % ±1% of Nominal
Over voltage Protection V 120 - 145%
LED Indicators - - - - Green LED = On, Red LED = DC Output Low
Operating Temperature - - - -
Storage Temperature - - - - -25 to +85°C
Operating Humidity - - - - 20 - 95% RH (non condensing)
Vibration (Operating) - - - -
Safety Agency Approvals
90 - 264VAC, Class II double insulated (No ground
connection required)
-25 to +71°C (Derate linearly 2.5%/°C from 55 to
71°C)
IEC 60068-2-6 (Mounting by rail: Random wave,
10-500 Hz, 2G, ea. along X, Y, Z axes 10 min/
cycle, 60 min)
UL1310 Class 2(1), UL508 Listed, UL60950-1,
EN60950-1, CE
For a comprehensive listing of these specifications point your browser to : http://us.tdk-lamb-
da.com/lp/products/dsp-series.htm
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 20 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 25
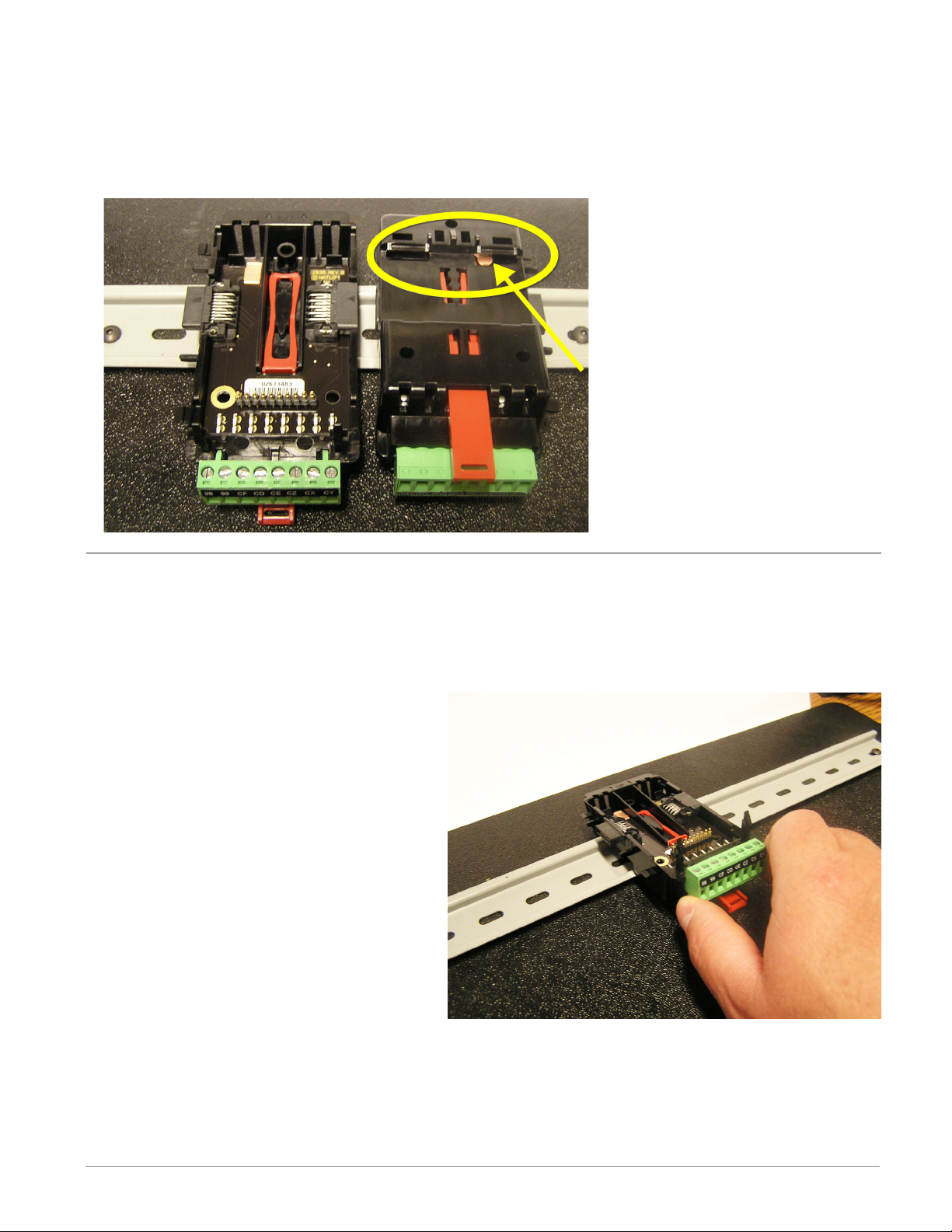
RMC Installation and Removal on a DIN Rail
Modular Backplane Connector
The picture on the right shows the Modular Backplane Connector, both front and rear view.
The rear view is bringing in to focus a metal clip. If the DIN rail is grounded the Modular
Backplane Connector and the module connected to it will be also (recommended).
Installing the Modular Backplane Connector
To install the backplane follow the steps below:
1. Hook backplane assembly to upper edge of DIN rail, (see rear view above, backplane hook
detail that mates with upper rail edge is circled)
2. Next, rotate back plane assembly downward to engage the lower edge of the rail. (Note:
Din Rail clipping distance ranges from
1.366 -1.389 inches. The back plane
assembly will not latch onto the rail
successfully if the rail is out of dimension).
3. For final positioning and locking, the
red tab is to be pushed upward to further engage the bottom edge of the
rail with an over center snap action
latch. (The red locking tab protrudes
from the bottom side of the back
plane assembly).
Note:
For easy removal and placement of
modules it is recommended that there
be a 76.2 mm (3.00 in) clearance on the top, bottom and front of each module.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 21 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 26

Installing Multiple Modular Backplane Connectors
Multiple modules are easily aligned and latched together. Each module includes matched mating geometry that facilitates accurate and consistent interconnections.
To install backplane connectors follow the steps below:
1. Attach individual modules to the rail separately.
2. Laterally slide the modules together until they
touch.
3. When the multi-module system is attached
and laterally positioned to the desired placement the locking tab should be engaged to
secure the control system to the rail.
Module Installation
In the picture to the right notice that the arrow is pointing at the top lip of the module (on
side).
To install modules on the backplane follow the steps below:
1. Slide the lip of the module over the top of the Modular Backplane Connector and then
push down on the rear of the module. The module will then slide over the two posts just
above the green connector (see pictures below).
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 22 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 27
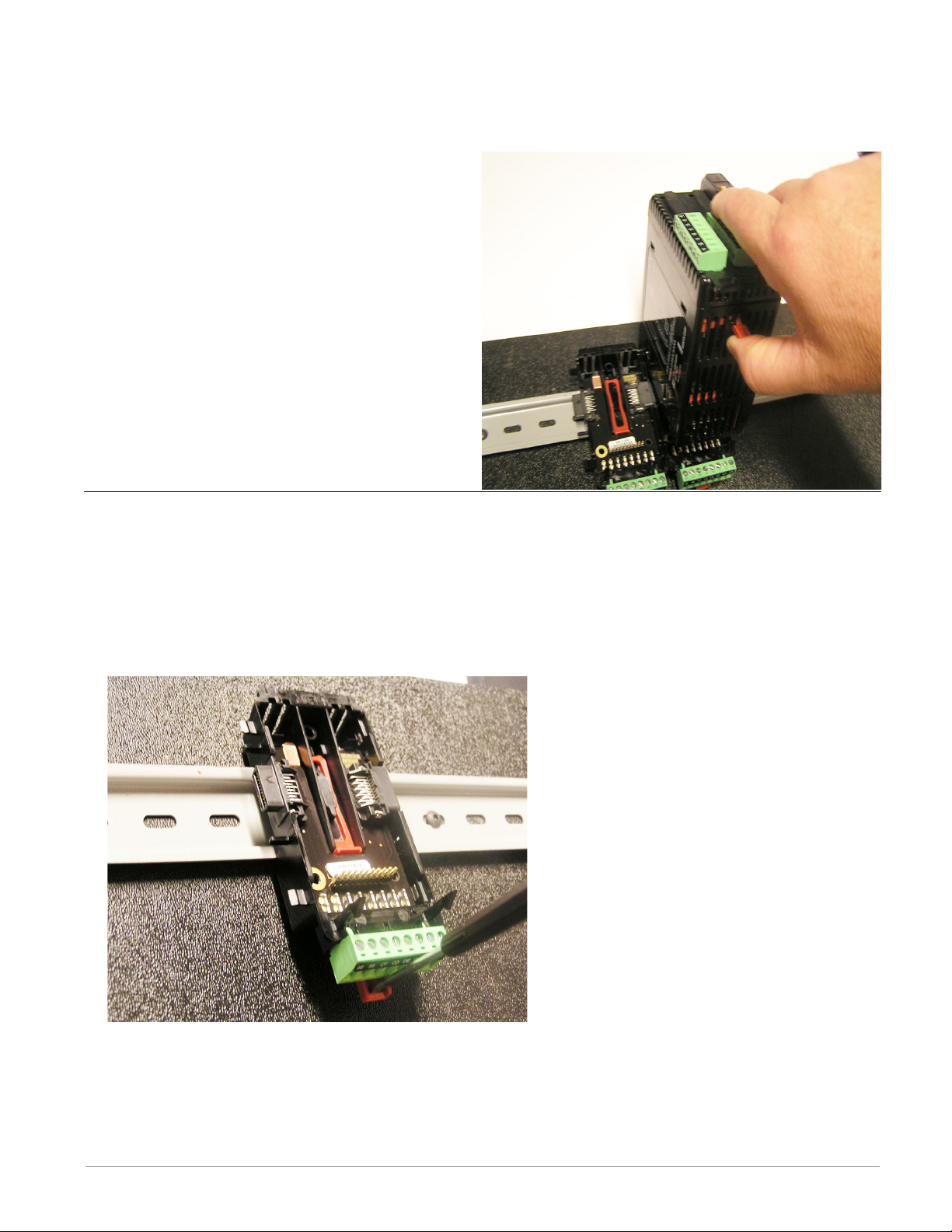
Module Removal
To remove a module from the backplane follow the steps below:
1. Find the red tab protruding from the bottom of the module and pull back on it as shown to
the right.
2. Pull back on the red tab, the two mounting posts will then release the module.
3. Lift the module up and slide it up; this will
release the module lip from the backplane.
Backplane Removal from DIN Rail
To remove a modular backplane connector from the DIN rail follow the steps below:
1. Insert a screw driver into the red locking tab just behind the green connector.
2. Apply downward pressure on the tab by lifting the screwdriver upwards.
3. When released, the tab will move downward and the connector can then be lifted up off
of the DIN rail.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 23 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 28
Wiring
Controller Module (RMCxxxxxxxxxxxx)
Slot A Slot B Slot D Slot E Terminal Function Configuration
Inputs Universal, RTD, Potentiometer and Thermistor Inputs 1 - 4
1 2 3 4
T1
S1
R1
T1
S1
T2
S2
R2
T2
S2
T3
S3
R3
T3
S3
T4
S4
R4
T4
S4
B7
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
Z7
T_ (RTD) or current
+S_ (RTD), thermocouple -,
current -, potentiometer,
thermistor or volts -
R_ (RTD), thermocouple
+, volts +, potentiometer
wiper or thermistor
Current Transformer Inputs 1 - 4
mA ac
mA ac
Digital Inputs 7 - 12
Common
dc +input
dc +input
dc +input
dc +input
dc +input
dc +input
Internal Supply
Universal/Thermistor Input
Part # Digits 4, 6, 8, 10
Input 1: RMC[1,2,3,4,5,6]
xxxxxxxxxxx
Input 2: RMCxx[1,2,5,6]xxxxxxxxx
Input 3: RMCxxxx[1,2,5,6]xxxxxxx
Input 4: RMCxxxxxx[1,2,5,6]xxxxx
Current Transformer
Part # Digits 4, 6, 8, 10
Input 1: RMC[7]xxxxxxxxxxx
Input 2: RMCxx[7]xxxxxxxxx
Input 3: RMCxxxx[7]xxxxxxx
Input 4: RMCxxxxxx[7]xxxxx
Digital Inputs/Outputs
Part # Digit 11
Slot A: Option not valid
Slot B: Option not valid
Slot D: Option not valid
Slot E: RMCxxxxxxx[C]xxxx
Outputs Switched dc / Open Collector Outputs 1, 3, 5 and 7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
X1
W1
Y1
X3
W3
Y3
X5
W5
Y5
X7
W7
Y7
common
dc- (open collector)
dc+
Switched DC/Open Collector
Part # Digits 5, 7, 9, 11
Output 1: RMCx[U,D,E,F,G]
xxxxxxxxxx
Output 3: RMCxxx[U,D,E,F,G]
xxxxxxxx
Output 5: RMCxxxxx[U,D,E,F,G]
xxxxxx
Output 7: RMCxxxxxxx[U,D,E,F,G]
xxxx
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 24 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 29
Controller Module (RMCxxxxxxxxxxxx)
Slot A Slot B Slot D Slot E Terminal Function Configuration
Outputs (cont.) Switched dc Outputs 2, 4, 6 and 8
W2
Y2
F1
G1
H1
L1
K1
J1
L2
K2
L2
K2
F3
G3
H3
L3
K3
J3
W4
Y4
L4
K4
L4
K4
F5
G5
H5
L5
K5
J5
W6
Y6
L6
K6
L6
K6
W8Y8dc-
dc+
F7
G7
H7
L7
K7
J7
voltage or current -
voltage +
current +
normally open
common
normally closed
L8K8normally open
common
L8K8normally open
common
Switched DC
Part # Digits 5, 7, 9, 11
Output 2: RMCx[E,K,P]xxxxxxxxxx
Output 4: RMCxxx[E,K,P]xxxxxxxx
Output 6: RMCxxxxx[E,K,P]xxxxxx
Output 8: RMCxxxxxxx(E,K,P]xxxx
Universal Process Outputs 1, 3, 5 and 7
Universal Process
Part # Digits 5, 7, 9, 11
Output 1: RMCx[N,P,R,S]xxxxxxxxxx
Output 3: RMCxxx[N,P,R,S]xxxxxxxx
Output 5: RMCxxxxx[N,P,R,S]xxxxxx
Output 7: RMCxxxxxxx[N,P,R,S]xxxx
Form C - Mechanical Relay Outputs 1, 3, 5 and 7
Mechanical Relay 5 A, Form C
Part # Digits 5, 7, 9, 11
Output 1: RMCx[H,J,K,L,M]
xxxxxxxxxx
Output 3: RMCxxx[H,J,K,L,M]
xxxxxxxx
Output 5: RMCxxxxx[H,J,K,L,M]
xxxxxx
Output 7: RMCxxxxxxx[H,J,K,L,M]
xxxx
NO-ARC Form A - Mechanical Relay Outputs 2, 4, 6 and 8
NO-ARC 15 A, Form A
Part # Digits 5, 7, 9, 11
Output 2: RMCx[D,J,Y]xxxxxxxxxx
Output 4: RMCxxx[D,J,Y]xxxxxxxx
Output 6: RMCxxxxx[D,J,Y]xxxxxx
Output 8: RMCxxxxxxx[D,J,Y]xxxx
Form A - Mechanical Relay Outputs 2, 4, 6 and 8
Mechanical Relay 5 A, Form A
Part # Digits 5, 7, 9, 11
Output 2: RMCx[B,F,L,R]xxxxxxxxxx
Output 4: RMCxxx[B,F,L,R]xxxxxxxx
Output 6: RMCxxxxx[B,F,L,R]xxxxxx
Output 8: RMCxxxxxxx[B,F,L,R]xxxx
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 25 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 30
Controller Module (RMCxxxxxxxxxxxx)
Slot A Slot B Slot D Slot E Terminal Function Configuration
Outputs (cont.) Solid State Relay Outputs 1 - 8
L1K1L2K2L3K3L4K4L5K5L6K6L7K7L8K8normally open
common
B7
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
Z7
Common
open collector/ switched dc
open collector/ switched dc
open collector/ switched dc
open collector/ switched dc
open collector/ switched dc
open collector/ switched dc
Internal Supply
Digital Outputs 7 - 12
Solid-State Relay 0.5 A, Form A
Part # Digits 5, 7, 9, 11
Output 1: RMCx[G,M,S,T,Y,Z]
xxxxxxxxxx
Output 2: RMCx[G,M,S,T,Y,Z]
xxxxxxxxxx
Output 3: RMCxxx[G,M,S,T,Y,Z]
xxxxxxxx
Output 4: RMCxxx[G,M,S,T,Y,Z]
xxxxxxxx
Output 5: RMCxxxxx[G,M,S,T,Y,Z]
xxxxxx
Output 6: RMCxxxxx[G,M,S,T,Y,Z]
xxxxxx
Output 7: RMCxxxxxxx[G,M,S,T,Y,Z]
xxxx
Output 8: RMCxxxxxxx[G,M,S,T,Y,Z]
xxxx
Digital Inputs/Outputs
Part # Digit 11
Slot A: Option not valid
Slot B: Option not valid
Slot D: Option not valid
Slot E: RMCxxxxxxx[C]xxxx
Power and Communications
Slot C Terminal Function Configuration
98
99
CF
CD
CE
CC
CA
CB
CZ
CX
CY
Power input: ac or dc+
Power input: ac or dc-
Standard Bus EIA-485 common
Standard Bus EIA-485 T-/RStandard Bus EIA-485 T+/R+
Standard Bus or Modbus RTU EIA-485 common
Standard Bus or Modbus RTU EIA-485 T-/RStandard Bus or Modbus RTU EIA-485 T+/R+
Inter-module Bus
Inter-module Bus
Inter-module Bus
All
Standard Bus
Part # Digit 13
RMCxxxxxxxxxAxx
Standard Bus or Modbus
Part # Digit 13
RMCxxxxxxxxx1xx
Inter-module Bus
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 26 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 31

Slot D
Slot A
RMC Front View
Standard Connector
Slot E
Slot B
98
99
power
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 27 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 32

RMC Module Isolation Diagram
Controller Power Supply
20.4 to 30.8VÎ (dc)
20.4 to 30.8VÅ (ac)
Safety Isolation
Mechanical Relay,
Solid-State Relay,
NO-ARC Relay
Outputs
Safety Isolation
Safety Isolation
Controller
Low Voltage Power Bus
Low-voltage Isolation: 42V peak
Safety Isolation: 1,528VÅ (ac)
No Isolation
No Isolation
Low-voltage
Isolation
Low-voltage
Isolation
Digital Inputs & Outputs
Switched DC, Open Collector,
Process outputs
Analog Input 1 - 4
Communications Ports
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 28 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 33

Warning:
ç
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
• 0.56 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
.
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs
to
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Controller Module Wiring (RMCxxxxxxxxxxxx)
Low Power RMC - All Model Numbers
• 20.4 to 30.8 V Å (ac) / Î (dc) 14VA
• 47 to 63 Hz
98
99
power
Communications RMC Part # Digit 13 is A
Slot C
CF CD
Standard Bus
Common
T- / R-
CE
T+ / R+
CZ
CX
Inter-module Bus
Common
Communications RMC Part # Digit 13 is 1
Slot C
CC CA
CB
CZ CX
Common
T- / R-
T+ / R+
Common
Modbus
• Controller module power consumption, 7
Watts maximum
• 31 Watts maximum power available for
P/S part #:0847-0299-0000
• 60 Watts maximum power available for
P/S part #:0847-0300-0000
• 91 Watts maximum power available for
P/S part #:0847-0301-0000
• Class 2 or Safety Extra Low Voltage
(SELV) power source required to meet UL
compliance standards
• CF, CD, CE - Standard Bus EIA485 Communications
• CZ, CX, CY - Inter-module Bus EIA485
CY
Communications
• Do not route network wires with power
-
+
wires. Connect network wires in daisychain fashion when connecting multiple
devices in a network
• CC, CA, CB - Modbus and Standard Bus
EIA485 Communications (selectable via
push button under zone address)
• CZ, CX, CY - Inter-module Bus EIA485
CY
Communications
• Do not route network wires with power
Inter-module Bus
-
+
wires. Connect network wires in daisychain fashion when connecting multiple
devices in a network
ModbusIDA Ter-
minal
EIA/TIA-
485 Name
DO A CA or CD T-/R-
D1 B CB or CE T+/R+
common common CC or CF common
Watlow
Terminal
Label
Function
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 29 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 34

Warning:
Slot A, B, D, E
Slot A, B, D, E
Slot A, B, D, E
Slot A, B, D, E
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
• 0.56 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs to
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Warning:
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
Warning:
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
ç
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
ç
ç
2
(16 AWG)
.
Input 1, 2, 3, 4 Thermocouple RMC Part # Digits 4, 6, 8, 10
• >20 MΩ input impedance
• 3 microampere open-sensor detection
• Thermocouples are polarity sensitive. The
negative lead (usually red) must be connected to S terminal
-
S_
+
R_
• To reduce errors, the extension wire for
thermocouples must be of the same alloy
as the thermocouple.
Input 1: RMC(1,3,5)xxxxxxxxxxx
Input 2: RMCxx(1,5)xxxxxxxxx
Input 3: RMCxxxx(1,5)xxxxxxx
Input 4: RMCxxxxxx(1,5)xxxxx
Input 1, 2, 3, 4 Thermistor RMC Part # Digits 4, 6, 8, 10
• >20 MΩ input impedance
Input 1: RMC(2,4,6)xxxxxxxxxxx
Input 2: RMCxx(2,6)xxxxxxxxx
Input 3: RMCxxxx(2,6)xxxxxxx
Input 4: RMCxxxxxx(2,6)xxxxx
S_
R_
Input 1, 2, 3, 4 Process RMC Part # Digits 4, 6, 8, 10
• 0 to 20 mA @ 100 Ω input impedance
• 0 to 10VÎ (dc) @ 20 kΩ input im-
pedance
• 0 to 50 mVÎ (dc) @ 20 MΩ input
impedance
+
-
S_
+
R_
volts
T_
-
S_
amperes
• Scalable
Input 1: RMC(1,3,5)xxxxxxxxxxx
(S1-/R1+),( T1+/S1-)
Input 2: RMCxx(1,5)xxxxxxxxx
(S2-/R 2+),(T 2+/S2-)
Input 3: RMCxxxx(1,5)xxxxxxx
(S3-/R3+),(T3-S3-R3)
Input 4: RMCxxxxxx(1,5)xxxxx
(S4-/R4+),(T4+/S4-)
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 30 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 35

Warning:
Slot A, B, D, E
Slot A, B, D, E
Slot A, B, D, E
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
• 0.56 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Warning:
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
ç
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
.
to
ç
Input 1, 2, 3, 4 RTD RMC Part # Digits 4, 6, 8, 10
• Platinum, 100 and 1,000 Ω @ 0°C
• Calibration to DIN curve (0.00385
Ω/Ω/°C)
• 20 Ω total lead resistance
S2
S3
S_
R_
S1
2-wire
RTD
T_
S3
S_
R_
S1
3-wire
RTD
• RTD excitation current of 0.09 mA
typical. Each ohm of lead resistance
may affect the reading by 0.03°C for
100 Ω.
• For 3-wire RTDs, the S1 lead (usually
white) must be connected to R terminal
• For best accuracy use a 3-wire RTD
to compensate for lead-length resistance. All three lead wires must have
the same resistance.
Input 1: RMC(1,3,5)xxxxxxxxxxx
(S1,R1),( T1-S1-R1)
Input 2: RMCxx(1,5)xxxxxxxxx
(S2,R 2),(T2-S2-R 2)
Input 3: RMCxxxx(1,5)xxxxxxx
(S3,R3),(T3-S3-R3)
Input 4: RMCxxxxxx(1,5)xxxxx
(S4,R4),(T4-S4-R4)
Input 1, 2, 3, 4 Potentiometer RMC Part # Digits 4, 6, 8, 10
• Use a 1 kΩ potentiometer.
Input 1: RMC(1,3,5)xxxxxxxxxxx (S1/R1)
Input 2: RMCxx(1,5)xxxxxxxxx (S2/R2)
Input 3: RMCxxxx(1,5)xxxxxxx (S3/R3)
Input 4: RMCxxxxxx(1,5)xxxxx (S4/R4)
CW
S_
Warning:
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 31 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
ç
CCW
R_
Page 36

Warning:
Slot A, B, D, E
Is = IpT/R = 50mA
ç
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
• 0.56 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
.
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs to
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
Input 1, 2, 3, 4 Current Transformer RMC Part # Digits 4, 6, 8, 10
• Input range is 0 to 50 mA (ac).
• Current transformer part number: 16-0246
• 100 Ω input impedance
• Response time: 1 second maximum
• Accuracy +/-1 mA typical
Input 1: RMC(7)xxxxxxxxxxx (T1/S1)
T_
S_
Input 2: RMCxx(7)xxxxxxxxx (T2/S2)
Input 3: RMCxxxx(7)xxxxxxx (T3/S3)
Input 4: RMCxxxxxx(7)xxxxx (T4/S4)
Example: Using a Current Transformer
CSC = Ip(full scale) = 50mA(R)/T
CSI = Output N
s = Current in secondary of current transformer
I
Ip = Current in primary of current transformer
T = Number of turns through the primary of the transformer
R = Number of turns in the secondary of the current
transformer (Turns ratio, assuming one primary turn)
CSC = Current Scaling (parameter found in Current Menu
of Setup Page)
CSI = Current Source Instance (parameter found in Current
Menu of Setup Page)
Output N
CT Input
3A x 4
12A
12A x 4 = 48A
L2 L1
Fuse
Turns around CT
CT Ratio R = 1000:1
:
48mA
CT Secondary Current
CT Primary Current
Turns around CT
Total current
48mA
SSR
Controller
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Suppressor Note:
Switching pilot duty inductive
loads (relay coils, solenoids,
etc.) with the mechanical relay,
solid state relay or open collector output options requires use
of an R.C. suppressor.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 32 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 37

Warning:
Common
Collector out
Collector out
B7
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
Z7
Slot E
Collector out
Collector out
Collector out
Collector out
Internal Supply
Common
Internal
Supply
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
B7
D7
Z7
ç
Digital Inputs 7 through 12 RMC Part # Digit 11 is C
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
• 0.57 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
.
Note:
Common
DC Input
DC Input
DC Input
DC Input
DC Input
DC Input
Internal Supply
Slot E
B7
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
Z7
Digital Input Event
Conditions
• Dry Contact
- Input inactive
when > 100KΩ
- Input active
when < 50Ω
• Voltage
- Input inactive
when < 2V
- Input active
when > 3V
• Six user configurable Digital Inputs/outputs per
slot
- Slot E DIO 7-12
Voltage Input
_
B
Vdc
_
D
Dry Contact
_
D
common
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
_
Z
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
Digital Inputs/Outputs 7 through 12 RMC Part # Digit 11 is C
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for
CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
to
• Maximum
switched voltage is 32VÎ (dc)
• Internal supply
provides a constant power output of 750mW
• Maximum output sink current
per output is
1.5A (external
class 2 or *SELV
Warning:
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Warning:
Explosion Hazard - Dry contact
closure Digital Inputs shall not
be used in Class I Division 2
Hazardous Locations unless
switch used is approved for this
application.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 33 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
ç
ç
supply required)
• Total sink current for all outputs not to exceed 8A
• Do not connect
outputs in parallel
*Safety Extra Low
Voltage
24 Vdc
Page 38

Warning:
ç
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
• 0.56 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
.
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs to
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Connecting a Digital Output from One Zone to a Digital Input of
Another Zone (Zone 1 to Zone 2 in this example)
In the example above, digital output D8 from Zone 1 is connected
to digital input D8 of Zone 2.
Note:
As shown in the graphic above, for this configuration, a pull-up
resistor is required.
Switched DC Wiring Example Using DO 7-12
Collector Outputs
Vdc
Internal Circuitry
Common
B_
D_
D_
D_
D_
D_
D_
Z_
Internal Supply
Htr 1
Htr 2
Htr 3
+
+
+
-
DC90-60C0-0000
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 34 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 39

Warning:
ç
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
• 0.56 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
.
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs
to
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Note:
As a switched DC output; this output is a constant current output delivering 750 mW, current limited to 400 mA. The internal supply does
have a maximum open circuit voltage of 22 VDC and minimum open
circuit voltage of 19 VDC. Pin Z7 is shared to all digital outputs. This
type of output is meant to drive solid state relays, not mechanical relays.
As an open collector output, use an external power supply with the
negative wired to B7, the positive to the coil of a pilot mechanical
relay and the other side of the coil wired to D_. Each open collector
output can sink 1.5 A with the total for all open collector outputs not
exceeding 8 amperes. Ensure that a kickback diode is reversed wired
across the relay coil to prevent damage to the internal transistor.
Open Collector Wiring Example Using DO 7-12
Power Supply
5 to 32 Vdc
Vdc
Collector Outputs
Internal Circuitry
Common
B_
D_
D_
D_
D_
D_
D_
Z_
Internal Supply
-
Fuse
Diode
+
An example fuse is
Bussmann AGC-1 1/2
Relay
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for
Warning:
CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
ç
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Quencharc Note:
Switching pilot duty inductive
loads (relay coils, solenoids,
etc.) with the mechanical relay,
solid state relay or open collector
output options requires use of an
R.C. suppressor.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 35 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 40

Warning:
or)
Slot A, B, D, E
ç
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
• 0.57 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
.
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs
to
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Output 1, 3, 5, 7 Switched DC/Open Collector
RMC Part # Digit 5, 7, 9, 11 is U, D, E, F or G
common
X_
dc - (open collect
W_
dc +
Y_
Switched DC
• 30 mA dc maximum
supply current
• short circuit limited
to <50 mA
• 22 to 32VÎ (dc)
open circuit voltage
• Use dc- and dc+ to
drive external solidstate relay.
• DIN-A-MITE compatible
Open Collector
• 100 mA maximum
output current sink
• 30VÎ (dc) maximum
supply voltage
• Any switched dc
output can use the
common terminal.
• Use an external
class 2 or *SELV
power supply to
control a dc load,
with the load positive to the positive
of the power supply, the load negative to the open
collector and common to the power
supply negative.
Switched DC
X_
common
dc -
W_
24V
dc +
Y_
Open Collector
common
X1
dc -
24V
W1
_
Y1
Power Supply
Load
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
*Safety Extra Low
Voltage
of component may impair suitability for
Warning:
CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
ç
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Quencharc Note:
Switching pilot duty inductive
loads (relay coils, solenoids,
etc.) with the mechanical relay,
solid state relay or open collector
output options requires use of an
R.C. suppressor.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 36 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 41

Warning:
Slot A, B, D, E
Slot A, B, D, E
ç
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
• 0.57 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
.
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs
to
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for
CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
Output 2, 4, 6, 8 Switched DC
RMC Part # Digit 5, 7, 9, 11 is U, D, E, F or G
Switched DC
common
_
W
_
Y
W_
Y_
dc -
dc +
• 30 mA dc maximum
supply current
• short circuit limited
to <50 mA
24V
• 22 to 32VÎ (dc) open
circuit voltage
• Use dc- and dc+ to
drive external solidstate relay.
• DIN-A-MITE compatible
Output 1, 3, 5, 7 Mechanical Relay, Form C
RMC Part # Digit 5, 7, 9, 11 is H, J, K, L or M
normally open
L_
common
K_
normally closed
J_
• 5 A at 240VÅ
(ac) or 30VÎ (dc)
maximum resistive
load
• 20 mA at 24V minimum load
• 125 VA pilot duty
at 120/240VÅ (ac),
25 VA at 24VÅ (ac)
• 100,000 cycles at
rated load
• Output does not
supply power.
• For use with ac or
dc
See Quencharc note.
_
L
K
_
J
dc -
dc +
normally open
_
common
normally closed
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Quencharc Note:
Switching pilot duty inductive
loads (relay coils, solenoids,
etc.) with the mechanical relay,
solid state relay or open collector
output options requires use of an
R.C. suppressor.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 37 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 42

Slot A, B, D, E
Warning:
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
• 0.57 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Warning:
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for
Warning:
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
ç
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
.
to
ç
CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
ç
Output 2, 4, 6, 8 Mechanical Relay, Form A
RMC Part # Digit 5, 7, 9, 11 is B, F, L or R
• 5 A at 240VÅ (ac)
_
or 30VÎ (dc) maxi-
L
mum resistive load
normally open
L_
common
K_
• 20 mA at 24V minimum inductive load
• 125 VA pilot duty at
K
_
120/240V Å(ac), 25
VA at 24V Å(ac)
• 100,000 cycles at
rated load
• Output does not
supply power.
• for use with ac or
dc
• See Quencharc
note.
Output 1, 3, 5, 7 Universal Process
RMC Part # Digit 5, 7, 9, 11 is N, P, R, or S
Slot A, B, D, E
F_
G_
H_
volts or current -
volts +
current +
• 0 to 20 mA into
800 Ω maximum
load
• 0 to 10VÎ (dc) in-
to 1 kΩ minimum
load
• scalable
• output supplies
power
• cannot use voltage
and current outputs at same time
• Output may be
used as retransmit
or control.
4 to 20 mA
0 to 10 V
_
F
negative
_
G
volts +
_
H
current +
Quencharc Note:
Switching pilot duty inductive
loads (relay coils, solenoids,
etc.) with the mechanical relay,
solid state relay or open collector
output options requires use of an
R.C. suppressor.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 38 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 43

Warning:
Slot A, B, D, E
ç
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
• 0.57 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
.
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs
to
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Output 2, 4, 6, 8 NO-ARC Relay, Form A
RMC Part # Digit 5, 7, 9, 11 is D, J or Y
• 15 A at 85 to 264VÅ
L
K
normally open
L_
common
K_
(ac) resistive load only
• 2,000,000 cycle rating for NO-ARC circuit (preliminary)
• 100 mA minimum
load
• 2 mA maximum off
state leakage
• Do not use on dc
loads.
• Output does not supply power.
• Do not drive another
relay or solenoid with
this output type.
15
10
Output Amps
5
0
20
25
403530
45
Ambient Temperature (oC)
50
60 65
55
_
_
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for
Warning:
CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
ç
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Quencharc Note:
Switching pilot duty inductive
loads (relay coils, solenoids,
etc.) with the mechanical relay,
solid state relay or open collector
output options requires use of an
R.C. suppressor.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 39 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 44

Warning:
Safe Operating Area
ç
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
• 0.56 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
.
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs to
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Output 1, 3, 5, 7 Universal Process
RMC Part # Digit 5, 7, 9, 11 is N, P, R, or S
Slot A, B, D, E
F_
G_
H_
volts or current -
volts +
current +
• 0 to 20 mA into
800 Ω maximum
load
F
0 to 10 V
• 0 to 10VÎ (dc) in-
to 1 kΩ minimum
4 to 20 mA
G
load
• Scalable
• Output supplies
H
power
• Cannot use voltage and current
outputs at same
time
• Output may be
used as retransmit
or control.
Outputs 1, 3, 5, 7 Solid-State Relay, Form A
RMC Part # Digit 5, 7, 9, 11 is G, M, S, T, Y or Z
Slot A, B, D, E
L_
K_
normally open
common
• 1 A at 20 to 264VÅ
(ac) maximum resistive load
• 20 VA 120/240VÅ (ac)
pilot duty
• Optical isolation,
without contact suppression
• Maximum off state
leakage of 105 microamperes
• Output does not
supply power.
• Do not use on dc
loads.
• Minimum holding
current of 10 mA.
• See Quencharc note.
1.1
1
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
Amps RMS
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
-20
1 Amp SSR Derating Curve
-10
Ambient Temperature (oC)
40
20100
30
_
negative
_
volts +
_
current +
60 70
50
_
L
_
K
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 40 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 45

Warning:
ç
Use National Electric (NEC) or
other country-specific standard
wiring and safety practices when
wiring and connecting this controller to a power source and to
electrical sensors or peripheral
devices. Failure to do so may
result in damage to equipment
and property, and/or injury or
loss of life.
Note:
Maximum wire size termination
and torque rating:
• 0.0507 to 3.30 mm2 (30 to 12
AWG) single-wire termination
or two 1.31 mm
2
(16 AWG)
• 0.56 Nm (5.0 in-lb.) torque
Note:
Adjacent terminals may be labeled differently, depending on
the model number
.
Note:
To prevent damage to the controller, do not connect wires to
unused terminals.
Note:
Maintain electrical isolation
between digital input-outputs,
switched dc/open collector
outputs and process outputs
to
prevent ground loops.
Note:
If the last two digits of the part
number are "12", this equipment
is suitable for use in CLASS I,
DIVISION 2, Groups A, B, C and
D or Non-Hazardous locations
only. Temperature Code T4
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard – Substitution
of component may impair suitability for CLASS I, DIVISION 2.
Outputs 2, 4, 6, 8 Solid-State Relay, Form A
RMC Part # Digit 5, 7, 9, 11 is G, M, S, T, Y or Z
Slot A, B, D, E
L_
K_
normally open
common
Amps RMS
• 1 A at 20 to
264VÅ (ac) maxi-
mum resistive load
• 20 VA 120/240VÅ
(ac) pilot duty
• Optical isolation,
without contact
suppression
• maximum off
state leakage of
105 microamperes
• Output does not
supply power.
• Do not use on dc
loads.
• Minimum holding
current of 10 mA.
• See Quencharc
note.
1.1
1
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
-20
1 Amp SSR Derating Curve
-10
Ambient Temperature (oC)
20100
_
L
_
K
Safe Operating Area
40
30
60 70
50
Warning:
ç
Explosion Hazard - Do not disconnect while the circuit is live
or unless the area is known to be
free of ignitable concentrations
of flammable substances.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 41 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 46

Quencharc Wiring Example
http://www.bb-elec.com/
In this example the Quencharc circuit (Watlow part# 0804-0147-0000) is used to protect the
RMC internal circuitry from the counter electromagnetic force from the inductive user load when
_
L
User Load
N
de-engergized. It is recommended that this or an
equivalent Quencharc be used when connecting inductive loads to RMC outputs.
K
Quencharc
_
Standard Bus EIA-485 Communications
Slot C
98 99 CF CD CE CZ CX CY
common
T-/R-
T+/R+
• Wire T-/R- to the A terminal of
the EIA-485 port.
• Wire T+/R+ to the B terminal of
the EIA-485 port.
• Wire common to the common
terminal of the EIA-485 port.
• Do not route network wires
with power wires. Connect network wires in daisy-chain fashion when connecting multiple
devices in a network.
• A 120 Ω termination resistor may
be required across T+/R+ and T/R-, placed on the last controller
on the network.
• Do not connect more than 16
EZ-ZONE RM controllers on a network.
• Maximum network length: 1,200
meters (4,000 feet)
• 1/8th unit load on EIA-485 bus
RMCxxxxxxxx(A)xx
* All models include Standard Bus
communications
Note:
Do not leave a USB to EIA-485 converter connected to Standard Bus without power
(i.e., disconnecting the USB end from the computer while leaving the converter connected on Standard Bus). Disturbance on the Standard Bus may occur.
R
USB
Port
PC Software Protocol
Standard Bus
EZ-Configurator
EZ-ZONE® RM
to B&B Converter
Model ULINXTM 485USBTB-2W
USB to RS-485 Adapter
using Standard Bus
98 99
CF CD CE CZ CW CY
Data format
38,400 baud
8 data bits
no parity
1 start bit
1 stop bit
EZ ZONE
DE
AB
RM
1
D E
A
B
SM
9
1
10
2
3
11
4
12
5
13
6
14
7 15
16
8
TM
USB
LINX
USB Serial Conversion
U
Model 485TB-2W
B&B electronics
0847-0326-0000
Use twisted pair wires such as Cat 5 cabling.
Do not route with power carrying conductors.
A(-)
B(+)
A(-)
B(+)
GND
98 99
CF CD CE CZ CW CY
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 42 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 47

EZ-ZONE RM
Scr
1 is
2 is
6 is GND
DB9 connect
1 is
2 is
5 is GND
DB9 connect
1 is DC
2 is RX
3 is
4 is DT
5 is Gn
6 is DS
http://serialgear.com/1-Port-Serial-USB-USB-COMi-M.html
®
to Serial Gear Converter
Model USB-COMi-M
EZ ZONE
R
RM
1
ew terminal connector pin-out:
Data –(A), connects to pin CD or CA
Data +(B), connects to pin CE or CB
, connects to pin CF or CC
or, EIA485 half duplex pin-out:
Data –(A), connects to pin CD or CA
Data +(B), connects to pin CE or CB
, connects to pin CF or CC
or, EIA232 pin-out:
D
D
TXD
R
d
R
If first device on 485 network, set
jumpers as shown
1 - 2
Tx termination 120 ohm
3 - 4
Tx pull-up 750 ohm
Tx pull-down 750 ohm
5 - 6
7 - 8
Rx termination 120 (422)
Rx pull-up 750 ohm
9 - 10
Rx pull-down 750 ohm
11 - 12
13 - 14
CTS termination 120 (422)
Use twisted pair wires such as Cat 5 cabling.
Do not route with power carrying conductors.
Daisy chain wire up to 247 EZ-ZONE
98 99
USB
Internal
Jumpers
JP1
1
2
USB-COMi-M
SerialGear
SW
ON
1234
Mode
13
14
485
232
Modbus RTU or Standard Bus EIA-485 Communcations
Slot C
98 99 CC CA CB CZ CX CY
common
T-/R-
T+/R+
Modbus-IDA
Terminal
• Wire T-/R- to the A terminal of
the EIA-485 port.
• Wire T+/R+ to the B terminal of
the EIA-485 port.
• Wire common to the common
terminal of the EIA-485 port.
• Do not route network wires
with power wires. Connect network wires in daisy-chain fashion
when connecting multiple devices in a network.
• A termination resistor may be
required. Place a 120 Ω resistor
across T+/R+ and T-/R- of last
controller on network.
EIA/TIA-
485 Name
Watlow Terminal
Label
DO A CA or CD T-/R-
D1 B CB or CE T+/R+
common common CC or CF common
®
devices.
CF CD CE CZ CW CY
6
5
1
234
PWR
RxD
TxD
Serial
DB9
3
2
OFF
OFF OFF
ON ON ON
4
1
ON
OFF
• Only one protocol per port
• Do not connect more than 16
• Maximum number of EZ-ZONE
• Maximum network length:
• 1/8th unit load on EIA-485 bus
RMCxxxxxxxx(1)xx
D
E
A
B
DE
AB
98 99
CF CD CE CZ CW CY
SM
9
1
10
2
3
11
4
12
5
13
6
14
7 15
16
8
C
t
o
l
S
is available at a time: either
Modbus RTU or Standard Bus.
EZ-ZONE controllers on a Standard Bus network.
controllers on a Modbus network is 247.
1,200 meters (4,000 feet)
Function
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 43 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 48

USB
Port
PC Software Protocol
Modbus RTU Third Party
EZ-ZONE® RM
to B&B Converter
Model ULINXTM 485USBTB-2W
USB to RS-485 Adapter
using Modbus RTU
98 99
Data format
9,600, 19,200, 38,400 baud
8 data bits
even, odd, no parity
1 start bit
1 stop bit
CF CD CE CZ CW CY
R
EZ ZONE
RM
1
D E
A
B
DE
AB
SM
9
1
10
2
3
11
4
12
5
13
6
14
7 15
16
8
USB
Use twisted pair wires such as Cat 5 cabling.
Do not route with power carrying conductors.
TM
LINX
USB Serial Conversion
U
Model 485TB-2W
B&B electronics
0847-0326-0000
http://www.bb-elec.com/
A(-)
B(+)
A(-)
B(+)
GND
98 99
CF CD CE CZ CW CY
Note:
Do not leave a USB to EIA-485 converter connected to Standard Bus without power (i.e.,
disconnecting the USB end from the computer while leaving the converter connected on
Standard Bus). Disturbance on the Standard Bus may occur.
Note:
When connecting the USB converter to the PC it is suggested that the Latency Timer be
changed from the default of 16 msec to 1 msec. Failure to make this change may cause
communication loss between the PC running EZ-ZONE Configurator software and the control.
To modify Latency Timer settings follow the steps below:
1. Navigate to Device Manager on the PC.
2. Double click on Ports.
3. Right click on the USB serial port in use and select Properties.
4. Click the tab labeled Port settings and then click the Advance button.
Graphic below shows the advanced settings dialog box for the com port in use.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 44 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 49

Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 45 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 50

Wiring a Serial EIA-485 Network
Do not route network wires with power wires. Connect network wires in daisy-chain fashion
when connecting multiple devices in a network. A termination resistor may be required. Place
a 120 Ω resistor across T+/R+ and T-/R- of the last controller on a network. Only one protocol
per port is available at a time: either Modbus RTU or Standard Bus.
Note:
Termination resistors when used, require a termination resistor at both ends of the network.
A Network Using Watlow's Standard Bus and an RUI/Gateway
EZ-ZONE ST
ST_ _ - (B or F) _ M _ -_ _ _ _
CD
CE
+ B
CF
- A
98
99
power
common
power
D5
D6
B5
EZ-ZONE PM
RUI/Gateway
EZKB-_ A _ _- _ _ _ _
98
99
CF
CD
CE
B5
D6
D5
power
com
- A
+ B
Power
Supply
fuse
EZ-ZONE RM
t
C
l
o
S
98
99
power
CZ
CX
CD
CE
CF
CY
98
power
99
CF
CD
CE
common
- A
+ B
common
- A
+ B
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 46 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 51

A Network Using Modbus RTU
EZ-ZONE ST
ST_ _ - (B or F) _ M _ -_ _ _ _
CC
CB
D5
D6
CA
B5
+ B
- A
98
99
power
power
common
EZ-ZONE PM
98
99
CC
CA
CB
B5
D6
D5
power
power
com
- A
+ B
Power
Supply
fuse
EZ-ZONE RM
t
C
l
o
S
98
99
power
CZ
CX
CA
CB
CC
CY
PLC
power
power
common
- A
+ B
common
- A
+ B
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 47 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 52

Connecting the Modules
RM System Connections
The RMC module can be installed as a stand-alone module or it can be interconnected on the
DIN rail as shown below. When modules are connected together as shown, power and communications are shared between modules over the modular backplane
interconnection (red circle). Therefore, bringing the necessary
power and communications wiring to any one module (connector
in slot C) is sufficient. The modular backplane interconnect comes
standard with every module ordered and is generic in nature,
meaning any of the RM modules can use it.
Notice in the split rail system diagram that a single power supply
is being used across both DIN rails. One notable consideration
when designing the hardware layout would be the available power supplied and the loading
affect of all of the modules used. Watlow provides three options for power supplies listed below:
1. 90-264 Vac to 24Vdc @ 31 watts (Part
#: 0847-0299-0000)
2. 90-264 Vac to 24Vdc @ 60 watts (Part
#: 0847-0300-0000)
3. 90-264 Vac to 24Vdc @ 91 watts (Part
#: 0847-0301-0000)
With regards to the modular loading affect, maximum power for each is listed
below:
1. RMCxxxxxxxxxxxx @ 7 watts / 14VA
2. RMEx-xxxx-xxxx @ 7 watts / 14VA
3. RMAx-xxxx-xxxx @ 4 watts / 9VA
4. RMLx-xxxx-xxxx @ 7 watts / 14VA
Low Voltage
Class 2
Power Supply
RM Controller
Module
RMCxxxxxxxxxAxx
Slot D
Slot A
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
99
98
Standard Bus
Address 1
Slot C
CD
CE
CF
Slot E
Slot B
CX
CZ
Split Rail Configuration
RM Scanner
Module
RMSx-xxxx-Axxx
Slot D
_
_
Standard Bus
_
_
Address 4
_
_
_
_
Slot A
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
CF
99
98
5. RMHx-xxxx-xxxx @ 7 watts / 14VA
Modular Backplane Interconnect
Slot E
Slot B
CZ
Module
_
_
_
Standard Bus
_
Address 5
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
99
98
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
CX
CF
CY
Slot C
CD
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
RM Access
Module
Slot D
Standard Bus
Address 3
Slot A
99
98
Slot E
Slot B
CX
CE
CZ
Slot E
_
_
_
_
_
Slot B
_
_
_
Slot C
CD
CE
CZ
CF
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
CY
RM Expansion
Module
RMEx-xxxx-xxx RMAx-xxxx-xxx
Slot D
_
_
_
_
_
Standard Bus
_
_
Address 2
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
Slot A
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
Slot C
_
_
CD
CE
CF
CY
99
98
_
Standard Bus
RM High Density
RMHx-xxxx-Axxx
Slot E
Slot D
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
Slot A
Slot B
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
Slot C
CD
CX
CE
CY
CZ
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
CX
CY
_
Inter-module
Bus
It is recommended
that twisted pair
shielded wire be
used for each bus.
6. RMSx-xxxx-xxxx @ 7 watts / 14VA
So, in the split rail system diagram, the
maximum current draw on the supply
would be 38 Watts.
RUI
EZKB-xA xx - xxxx
CD
CE
CF
98
99
Standard Bus
- 1 RMC modules consumes 7W
- 1 RME modules consumes 7W
- 1 RMA module consumes 4W
- 1 RMS modules consumes 7W
- 1 RMH modules consumes 7W
- 1 Remote User Interface consumes 6W
With this power requirement the second or third power supply could be used.
Another hardware configuration scenario that could present itself (graphic not shown) would
be a configuration that requires more than one supply. Lets make some assumptions pertaining to the split rail system diagram shown above. The power supply used is the 91W supply.
The top DIN rail now has the following modules:
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 48 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 53

- 2 RMC modules consumes 14W
- 1 RMA consumes 4W
- 11 RME modules consumes 77W
As it can now be understood, the total power requirement exceeds 91W. In this case, another
power supply would be required. To incorporate another supply in this system simply disconnect pins 99 and 98 on the remote DIN rail and connect another appropriately sized power
supply to those same pins.
When using a split rail configuration ensure that the interconnections for the Inter-module Bus
and Standard Bus do not exceed 200 feet. Standard Bus and the Inter-module Buses are different protocols and both are required for split rail configurations. Without having both connected, communications between modules would not be possible.
Note:
Unit is not provided with a disconnect, use of an external disconnect is required. It should
be located in close proximity to the unit and be labeled as the disconnect for the unit.
Note:
Connecting power supplies in parallel is not allowed. When power consumption is greater
than 91 watts use a split rail configuration.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 49 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 54

Conventions Used in the Menu Pages
To better understand the menu pages that follow review the naming conventions used. When
encountered throughout this document, the word "default" implies as shipped from the factory. Each page (Operations, Setup, Profile and Factory) and their associated menus have identical headers defined below:
Header Name Definition
Display Visually displayed information from the control.
Parameter Name Describes the function of the given parameter.
Range
Default Values as delivered from the factory.
Modbus Relative
Address
CIP (Common Industrial Protocol)
Profibus Index
Parameter ID
Data Type and Access (R/W)
Defines options available for this prompt, i.e., min/max values (numerical), yes/no, etc... (further explanation below).
Identifies unique parameters using either the Modbus RTU or Modbus
TCP protocols (further explanation below).
If used in conjunction with an RMA module identifies unique parameters using either the DeviceNet or EtherNet/IP protocol (further explanation below).
If used in conjunction with an RMA module identifies unique parameters using Profibus DP protocol (further explanation below).
Identifies unique parameters used with other software such as, LabVIEW.
uint = Unsigned 16 bit integer
dint = Signed 32-bit, long
string = ASCII (8 bits per character)
float = IEEE 754 32-bit
RWES = Readable
Writable
EEPROM (saved)
User Set (saved)
Display
When the RMC module is used in conjunction with the RUI (optional equipment) visual information from the control is displayed to the observer using a fairly standard 7 segment display.
Due to the use of this technology, several characters displayed need some interpretation, see
the list below:
1 = 1 ϯ = 7
, {= c i= i o= o u= u
щ
2 = 2 8 = 8 ц= d J= J P= P v= v
3 = 3 q = 9 E= E H= K q= q ФІ= W
4 = 4 0 = 0 F= F L= L r= r y= y
5 = 5 џ = g= g ЛЏ= M S= S Z= Z
6 = 6 Ѥ= b h= h n= n t= t
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 50 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 55

Range
Within this column notice that on occasion there will be numbers found within parenthesis.
This number represents the enumerated value for that particular selection. Range selections
can be made simply by writing the enumerated value of choice using any of the available
communications protocols. As an example, turn to the Control Module Setup Page and look at
the Analog Input menu and then the Sensor Type. To turn the sensor off using Modbus, simply
write the value of 62 (off) to register 368 and send that value to the control.
Note:
With firmware release 9.0 and above, two new parameters (Minimum and Maximum) were
added to allow ranges to be opened up to display full values. Unsigned integer may take
on a range of 0 to 65,535 and floating point may take on a range of -3.4E+38 to 3.4E+38.
Prior to revision 9.0, ranges were clamped to accommodate the seven segment LED display of the RUI. Both of these new parameters can be found in the Setup Page under the
Global Menu.
Communication Protocols
All modules come with the standard offering of Watlow's Standard Bus protocol used primarily for inter-module communications as well as for configuration using EZ-ZONE Configurator or
Composer software (free download from Watlow's web site (http://w ww.watlow.com). Along
with Standard Bus, the RMC module can also be ordered with Modbus RTU (only one protocol
can be active at any given time). The RMA module has options for several different protocols
listed below:
- Modbus RTU 232/485
- EtherNet/IP, Modbus TCP
- DeviceNet
- Probus DP
To learn more about the RM Access module click on the link below. Once there simply type in
RM in the Keyword field. http://w ww.watlow.com/literature/manuals.c fm
Modbus RTU Protocol
All Modbus registers are 16-bits and as displayed in this manual are relative addresses (actual).
Some legacy software packages limit available Modbus registers to 40000 to 49999 (5 digits).
Many applications today require access to all available Modbus registers which range from
400001 to 465535 (6 digits). Watlow controls support 6 digit Modbus registers.
Note:
In this User's Guide all values shown representing Modbus addresses are added to 400,001
or 40,001 to acquire the absolute address.
For parameters listed as float, notice that only one (low order) of the two registers is listed,
this is true throughout this document. By default, the low order word contains the two low
bytes of the 32-bit parameter. As an example, look in the Controller Operations Page for the
Analog Input Value. Find the column identified in the header as Modbus and notice that it
lists register 360 under Map 1. Because this parameter is a float it is actually represented by
registers 360 (low order bytes) and 361 (high order bytes). The Modbus specification does not
dictate which register should be high or low order so Watlow provides the user the ability to
swap this order (Setup Page, Communications Menu) from the default low/high to high/low.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 51 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 56

Note:
With the release of firmware revision 9.00 and above, new functions where introduced
into this product line. With the introduction of these new functions there was a reorganization of Modbus registers. Notice the reference to Map 1 and Map 2 registers in the column identified as Modbus Relative Address in each of the tables that follow. Select Map 1
or Map 2 in the Setup Page under the Communications Menu. This setting, Map 1 or Map 2,
will apply across the controller.
It should also be noted that most of the cells in the Modbus column contain wording pertaining to an offset for Map 1 and Map 2. Several parameters in the controller contain more than
one instance; such as, Profiles (25), Alarms (8), Analog inputs (4), etc... The Modbus register shown always represents instance one. Take for an example the Silence Alarm parameter
found in the Setup Page under the Alarm Menu. Instance one of Map 1 is shown as address
1766 and +60 is identified as the offset to the next instance for Map 1 and Map 2. If there was
a desire to silence the alarm for instance 3, simply add 120 to 1766 to find its address, in this
case, the instance 3 address for Alarm Silence is 1886 and write the value of 0 to it.
RMC _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ [1] _ _
or
RMA _ - A [2, 3] _ _ - A A _
or
EZKB - x [2,3] _ _ - _ _ _ _
To learn more about the Modbus protocol point your browser to http://www.modbus.org.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 52 • Chapter 2 Install and Wire
Page 57

3
Chapter 3: Operations Pages
Control Module Operation Page Parameters
To navigate to the Operations Page using the RUI, follow the steps below:
1. From the Home Page, press both the Up ¿ and Down ¯ keys for three seconds. Ai will ap-
pear in the upper display and oPEr will appear in the lower display.
2. Press the Up ¿ or Down ¯ key to view available menus.
3. Press the Advance Key ‰ to enter the menu of choice.
4. If a submenu exists (more than one instance), press the Up ¿ or Down ¯ key to select and
then press the Advance Key ‰ to enter.
5. Press the Up ¿ or Down ¯ key to move through available menu prompts.
6. Press the Infinity Key ˆ to move backwards through the levels: parameter to submenu, sub-
menu to menu, menu to Home Page.
7. Press and hold the Infinity Key ˆ for two seconds to return to the Home Page.
On the following pages, top level menus are identified with a yellow background color.
Note:
Some of these menus and parameters may not appear, depending on the controller's options. See model number information in the Appendix for more information. If there is
only one instance of a menu, no submenus will appear.
Note:
Some of the listed parameters may not be visible. Parameter visibility is dependent upon
controller part number.
Ai
opEr Analog Input Menu
1
Ai Analog Input (1 to 4)
Ain Analog Input Value
i.Er Input Error
i.CA Calibration Offset
Pu
opEr Process Value Menu
1
Pu Process Value (1 to 4)
Su.A Source Value A
Su.b Source Value B
Su.C Source Value C
Su.d Source Value D
Su.E Source Value E
oFSt Offset
o.u Output Value
dio
opEr Digital Input/Output
Menu
1
dio Digital Input/Output (7
to 12)
do.S Output State
di.S Input State
ACt
opEr Action Menu
1
ACt Action (1 to 8)
Ei.S Event Status
LiЛЏ
opEr Limit Menu
1
LiЛЏ Limit (1 to 4)
LL.S Low Limit Set Point
Lh.S High Limit Set Point
LCr Clear Limit *
L.St Limit Status *
ЛЏon
opEr Monitor Menu
1
ЛЏon Monitor (1 to 4)
C.ЛЏA Control Mode Ac-
tive
h.pr Heat Power
C.pr Cool Power
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 53 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 58

C.sp Closed-Loop Set
Point
pu.a Process Value Ac-
tive
Loop
opEr Control Loop Menu
1
Loop Control Loop (1 to 4)
r.En Remote Set Point
C.ЛЏ Control Mode
A.tsp Autotune Set Point
aUt Autotune
C.sp Set Point
id.S Idle Set Point
h.pb Heat Proportional
Band
h.hy On / Off Heat Hys-
teresis
C.pb Cool Proportional
Band
C.hy On / Off Cool Hys-
teresis
ti Time Integral
td Time Derivative
db Dead Band
o.sp Manual Power
aLЛЏ
opEr Alarm Menu
1
aLЛЏ Alarm (1 to 8)
A.Lo Low Set Point
a.hi High Set Point
a.CLr Clear Alarm *
a.Sir Silence Alarm *
a.st Alarm State *
CUrr
opEr Current Menu
1
CUrr Current (1 to 4)
C.hi High Set Point
C.Lo Low Set Point
Ld.Cu Load Current RMS
C.Er Current Error
h.Er Heater Error
Lnr
opEr Linearization Menu
1
Lnr Linearization (1 to 4)
Su.a Source Value A
ofst Offset
o.u Output Value
CpE
opEr Compare Menu
1
CpE Compare (1 to 4)
Su.a Source Value A
Su.b Source Value B
o.u Output Value
tЛЏr
opEr Timer Menu
1
tЛЏr Timer (1 to 4)
Su.a Source Value A
Su.b Source Value B
E.t Elapsed Time
o.u Output Value
Ctr
opEr Counter Menu
1
Ctr Counter (1 to 4)
Cnt Count
Su.a Source Value A
Su.b Source Value B
o.u Output Value
LgC
opEr Logic Menu
1
LgC Logic (1 to 16)
Su.a Source Value A
Su.b Source Value B
Su.C Source Value C
Su.d Source Value D
Su.E Source Value E
Su.F Source Value F
Su.g Source Value G
Su.h Source Value H
o.u Output Value
ЛЏat
opEr Math Menu
1
ЛЏat Math (1 to 8)
Su.a Source Value A
Su.b Source Value B
Su.C Source Value C
Su.d Source Value D
Su.E Source Value E
ofst Offset
o.u Output Value
sof
opEr Special Output Func-
tion Menu
1
sof Special Output Func-
tion (1 to 4)
Su.a Source Value A
Su.b Source Value B
ou.1 Output Value 1
ou.2 Output Value 2
ou.3 Output Value 3
ou.4 Output Value 4
P.sta
opEr Profile Status Menu
1
P.sta Profile Status 1
P.str Profile Start
pasr Profile Action Re-
quest
stp Current Step
sub.s Current Sub Step
s.typ Step Type
t.Sp1 Target Set Point
Loop 1
t.Sp2 Target Set Point
Loop 2
t.Sp3 Target Set Point
Loop 3
t.Sp4 Target Set Point
Loop 4
p.sp1 Produced Set
Point 1
p.sp2 Produced Set Point
2
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and
above.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 54 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 59

p.sp3 Produced Set Point
3
p.sp4 Produced Set Point
4
hour Hours
ЛЏin Minutes
sEC Seconds
Ent1 Event 1
Ent2 Event 2
Ent3 Event 3
Ent4 Event 4
Ent5 Event 5
Ent6 Event 6
Ent7 Event 7
Ent8 Event 8
JC Jump Count Re-
maining
Note:
Some values will be rounded off to fit in the four-character RUI display. Full values can be
read with other interfaces. In firmware 9.0 and above, a user may specify ranges greater
than may displayed by an RUI. If greater or less than an RUI can display, the display will
show Value High uAL.H or Value Low uAL.L.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 55 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 60

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
Ai
opEr
Analog Input Menu
Ain
Ain
i.Er
i.Er
Analog Input (1 to 4)
Analog Input Value
View the process
value.
Note:
Ensure that the Error Status (below)
indicates no error
(61) when reading
this value using a
field bus protocol.
If an error exists,
the last known
value prior to the
error occurring will
be returned.
Analog Input (1 to 4)
Input Error
View the cause of
the most recent error. If the attn
message is Er.i1,
Er.i2, Er.i3 or
Er.i4, this param-
eter will display the
cause of the input
error.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
nonE None (61)
OpEn Open (65)
shrt Shorted
(127)
E.ЛЏ Measurement
Error (140)
E.CaL Bad Cali-
bration Data (139)
Er.ab Ambient
Error (9)
- - - -
- - - -
E.rtd RTD Error
(141)
faiL Fail (32)
i.Ca
i.CA
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Analog Input (1 to 4)
Calibration Offset
Offset the input
reading to compensate for lead wire
resistance or other
factors that cause
the input reading to
vary from the actual
process value.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,110.555 to
5,555.000°C
0.0
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
360 420
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
362 422
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
382 442
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
0x68
(104)
1 to 4
1
0x68
(104)
1 to 4
2
0x68
(104)
1 to 4
0xC (12)
0 4001 float
1 4002 uint
2 4012 float
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
RWES
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 56 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 61

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
No Dis-
play
Parameter Name
Description
Analog Input (1 to 4)
Clear Error
Clear latched input
when input error
condition no longer
exists.
Range Default
Clear Error (1221) - - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
416 476
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x68
(104)
1 to 4
0x1D (29)
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 4029 uint
Pu
opEr
Process Value Menu
Su.a
Su.A
Su.b
Su.b
Su.C
Su.C
Su.d
Su.d
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Process Value (1 to
4)
Source Value A
View the value of
Source A.
Process Value (1 to
4)
Source Value B
View the value of
Source B.
Process Value (1 to
4)
Source Value C
View the value of
Source C.
Process Value (1 to
4)
Source Value D
View the value of
Source D.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3430 4270
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3432 4272
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3434 4274
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3436 4276
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
0x7E
(126)
1 to 4
0x10 (16)
0x7E
(126)
1 to 4
0x11 (17)
0x7E
(126)
1 to 4
0x12 (18)
0x7E
(126)
1 to 4
0x13 (19)
- - - - 26016 float
- - - - 26017 float
- - - - 26018 float
- - - - 26019 float
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RW
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 57 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 62

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Su.E
Su.E
ofst
oFSt
o.u
o.u
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Parameter Name
Description
Process Value (1 to
4)
Source Value E
View the value of
Source E.
Process Value (1 to
4)
Offset
Set an offset to be
applied to this function's output.
Process Value (1 to
4)
Output Value
View the value of
this function block's
output.
Process Value (1
to 4)
Error
View reported cause
for Process output
malfunction.
Range Default
off Off (62)
on On (63)
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement error (140)
Bad calibration
data (139)
Ambient error (9)
RTD error (14)
Fail (32)
Math error (1423)
Not sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
- - - -
0
- - - -
- - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3438 4278
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3444 4284
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3442 4282
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3452 4292
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x7E
(126)
1 to 4
0x14 (20)
0x7E
(126)
1 to 4
0x17 (23)
0x7E
(126)
1 to 4
0x16 (22)
0x7E
(126)
1 to 4
0x1B
(27)
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 26020 float
- - - - 26023 float
- - - - 26022 float
- - - - 26027 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
RWES
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 58 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 63

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
dio
opEr
Digital Input/Output Menu
do.s
do.S
di.s
di.S
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Digital Output (7 to
12)
Output State
View the state of
this output.
Digital Input (7 to
12)
Input State
View this event input
state.
Digital Input (7 to
12)
Error
View reported cause
for input malfunction.
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement error (140)
Bad calibration
data (139)
Ambient error (9)
RTD error (14)
Fail (32)
Math error (1423)
Not sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1212 1792
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+30
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1220 1800
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+30
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1228 1808
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+30
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
0x6A
(106)
7 to C
(12)
7
0x6A
(106)
7 to C
(12)
0xB (11)
0x6A
(106)
7 to C
(12)
0x0F
(15)
90 6007 uint
- - - - 6011 uint
- - - - 6015 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 59 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 64

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
aCt
opEr
Action Menu
Ei.s
Ei.S
Action (1 to 8)
Event Status
View this input
state.
off Off (62)
on On (63)
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1588 2428
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+20
0x6E
(110)
1 to 8
5
140 10005 uint
LiЛЏ
opEr
Limit Menu
LL.s
LL.S
Lh.s
Lh.S
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Limit (1 to 4)
Low Limit Set Point
Set the low process
value that will trigger the limit.
Limit (1 to 4)
High Limit Set
Point
Set the high process
value that will trigger the limit.
Limit (1 - 4)
Limit State
Clear limit once
limit condition is
cleared.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
Off (62)
None (61)
Limit High (51)
Limit Low (52)
Error (28)
0.0°F or
units
-18.0°C
0.0°F or
units
-18.0°C
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
724 824
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+30
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
726 826
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+30
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
730 830
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+30
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
0x70
(112)
1 to 4
3
0x70
(112)
1 to 4
4
0x70
(112)
1
6
38 12003 float
39 12004 float
- - - - 12006 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
RWES
RWES
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 60 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 65

Display
LCr
LCr
L.st
L.St
Parameter Name
Description
Limit (1-4)
Clear Limit *
Clear limit once
limit condition is
cleared.
Limit (1 to 4)
Limit Status *
Reflects whether or
not the limit is in a
safe or failed mode.
RMC Module • Operations Page
Range Default
Clear (0)
No Change (255)
faiL Fail (32)
- - - -
- - - -
safE Safe
(1667)
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
720 820
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+30
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
744 844
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+30
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
CIP
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x70
(112)
1
1
0x70
(112)
1 to 4
0x0D (13)
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 12001 uint
- - - - 12013 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Type
Access
W
R
Data
and
**
ЛЏon
opEr
Monitor Menu
C.ЛЏA
C.MA
h.pr
h.Pr
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Monitor (1 to 4)
Control Mode Active
View the current
control mode.
Monitor (1 to 4)
Heat Power
View the current
heat output level.
off Off (62)
aUto Auto (10)
ЛЏan Manual
(54)
0.0 to 100.0% - - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2222 3062
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2244 3084
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
2
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
0xD (13)
- - - - 8002 uint
- - - - 8011 float
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 61 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 66

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
C.pr
C.Pr
C.sp
C.SP
pu.a
Pv.A
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Parameter Name
Description
Monitor (1 to 4)
Cool Power
View the current
cool output level.
Monitor (1 to 4)
Closed-Loop Set
Point
View the set point
currently in effect.
Monitor (1 to 4)
Filtered Process
Value
View the current filtered process value
using the control
input.
Monitor (1 to 4)
Autotune Status
Read the present
status of Autotune.
Range Default
-100.0 to 0.0% - - - -
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
Off (62)
Waiting for cross 1
positive (119)
Waiting for cross 1
negative (120)
Waiting for cross 2
positive (121)
Waiting for cross 2
negative (122)
Waiting for cross 3
positive (123)
Waiting for cross 3
negative (150)
Measuring maximum peak (151)
Measuring minimum peak (152)
Calculating (153)
Complete (18)
Timeout (118)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2246 3086
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2272 3112
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
0xE (14)
- - - - - - - - 8029 float
- - - - - - - - 8031 float
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
27
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 8014 float
- - - - 8027 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 62 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 67

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
Loop
opEr
Control Loop Menu
r.En
r.En
C.ЛЏ
C.M
a.tsp
A.tSP
aUt
AUt
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Remote Set Point
Enable this loop
to switch control
to the remote set
point.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Control Mode
Select the method
that this loop will
use to control.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Autotune Set Point
Set the set point
that the autotune
will use, as a percentage of the current set point.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Autotune
Start an autotune.
While the autotune
is active, the Home
Page will display
no No (59)
yEs Yes (106)
off Off (62)
aUto Auto (10)
ЛЏan Manual
(54)
50.0 to 200.0% 90.0
no No (59)
yEs Yes (106)
No
Auto
No
attn tUn1,
tUn2, tUn3, or
tUn4. When the
autotune is complete, the message
will clear automatically.
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2540 3380
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2220 3060
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2258 3098
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2260 3100
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
0x6B
(107)
1 to 4
0x15
(21)
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
1
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
0x14
(20)
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
0x15
(21)
48 7021 uint
63 8001 uint
- - - - 8025 float
64 8026 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
RWES
RWES
RW
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 63 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 68

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2500 3340
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2516 3356
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2230 3070
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2240 3080
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Display
C.sp
C.SP
id.s
id.S
h.pb
h.Pb
h.hy
h.hy
Parameter Name
Description
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Set Point
Set the closed loop
set point that the
controller will automatically control
to.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Idle Set Point
Define a set point
that can be triggered by an event
state.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Heat Proportional
Band
Set the PID proportional band for the
heat outputs.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
On / Off Heat Hysteresis
Set the control
switching hysteresis
for on-off control.
This determines
Range Default
Low Set Point
to Maximum Set
Point (Setup
Page)
Low Set Point to
High Set Point
(Setup Page)
0.001 to
9,999.000°F or
units
0.001 to
5,555.000°C
0.001 to
9,999.000°F or
units
0.001 to
5,555.000°C
75.0°F
or units
24.0°C
75.0°F
or units
24.0°C
25.0°F
or units
14.0°C
3.0°F or
units
2.0°C
how far into the
“on” region the
process value needs
to move before the
output turns on.
C.pb
C.Pb
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Cool Proportional
Band
Set the PID proportional band for the
cool outputs.
0.001 to
9,999.000°F or
units
0.001 to
5,555.000°C
25.0°F
or units
14.0°C
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2232 3072
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x6B
(107)
1 to 4
1
0x6B
(107)
1 to 4
9
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
6
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
0xB (11)
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
7
Pro-
fibus
Index
49 7001 float
50 7009 float
65 8009 float
66 8010 float
67 8012 float
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
RWES
RWES
RWES
RWES
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 64 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 69

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2242 3082
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Display
C.hy
C.hy
Parameter Name
Description
Control Loop (1 to
4)
On / Off Cool Hysteresis
Set the control
switching hysteresis
for on-off control.
This determines
Range Default
0.001 to
9,999.000°F or
units
0.001 to
5,555.000°C
3.0°F or
units
2.0°C
how far into the
“on” region the
process value needs
to move before the
output turns on.
ti
ti
td
td
db
db
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Time Integral
Set the PID integral
for the outputs.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Time Derivative
Set the PID derivative time for the
outputs.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Dead Band
Set the offset to
the proportional
band. With a negative value, both
heating and cooling
0 to 9,999 seconds per repeat
0 to 9,999 seconds
-1,000.0 to
1,000.0°F or units
-556 to 556°C
180 seconds per
repeat
0
seconds
0.0
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2234 3074
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2236 3076
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2238 3078
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
outputs are active
when the process
value is near the
set point. A positive
value keeps heating
and cooling outputs
from fighting each
other.
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
0xC (12)
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
8
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
9
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
0xA (10)
Pro-
fibus
Index
68 8013 float
69 8006 float
70 8007 float
71 8008 float
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
RWES
RWES
RWES
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 65 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 70

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2502 3342
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2268 3108
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2270 3110
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2248 3088
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Display
o.sp
o.SP
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
Parameter Name
Description
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Manual Power
Set a fixed level of
output power when
in manual (openloop) mode.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Error State
Read to see if loop
is in an error state.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Clear Error
Write to this register to clear loop
error.
Control Loop (1 to
4)
Loop Output Power
View the loop output power.
Range Default
-100 to 100%
0.0
(heat and cool)
0 to 100% (heat
only)
-100 to 0% (cool
only)
None (61)
- - - Open Loop (1274)
Reversed Loop
(1275)
Clear (129)
Ignore
Ignore (204)
-100.0 to 100.0 - - - -
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x6B
(107)
1 to 4
2
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
0x19(25)
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
0x1A(26)
0x97
(151)
1 to 4
0x0F (15)
Pro-
fibus
Index
51 7002 float
- - - - 8048 uint
- - - - 8049 uint
- - - - 8033
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
R
W
float
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 66 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 71

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
aLЛЏ
opEr
Alarm Menu
a.Lo
A.Lo
a.hi
A.hi
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Alarm (1 to 8)
Low Set Point
If Type (Setup Page,
Alarm Menu) is set
to:
process - set the
process value that
will trigger a low
alarm.
deviation - set the
span of units from
the set point that
will trigger a low
alarm. A negative
set point represents a value below
closed loop set
point. A positive set
point represents a
value above closed
loop set point.
Alarm (1 to 8)
High Set Point
If Type (Setup Page,
Alarm Menu) is set
to:
process - set the
process value that
will trigger a high
alarm.
deviation - set the
span of units from
the set point that
will trigger a low
alarm. A negative
set point represents a value below
closed loop set
point. A positive set
point represents a
value above closed
loop set point.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
32.0°F
or units
0.0°C
300.0°F
or units
150.0°C
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1742 2582
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1740 2580
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
0x6D
(109)
1 to 8
2
0x6D
(109)
1 to 8
1
18 9002 float
19 9001 float
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
RWES
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 67 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 72

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
Pro-
fibus
Index
hex (dec)
A.CLr
A.CLr
A.sir
A.Sir
A.st
A.St
Alarm (1 to 8)
Clear Alarm
Write to this register to clear an
alarm
Alarm (1 to 8)
Silence Alarm
Write to this register to silence an
alarm
Alarm (1 to 8)
Alarm State
Current state of
alarm
0 - - - -
0 - - - -
str Startup (88)
- - - -
nonE None (61)
bLo Blocked (12)
aL.L Alarm low
(8)
aL.h Alarm high
(7)
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1764 2604
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1766 2606
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1756 2596
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
0x6D
(109)
1 to 8
0xD (13)
0x6D
(109)
1 to 8
0xE (14)
0x6D
(109)
1 to 8
9
32 9013
33 9014
- - - - 9009 uint
aL.E Error (28)
No Dis-
play
Alarm (1 to 8)
Alarm Clearable
No (59)
Yes (106)
- - - -
Read to see if alarm
can be cleared.
No Dis-
play
Alarm (1 to 8)
Silenced
Yes (106)
No (59)
- - - -
Read to see if alarm
is active but has
been silenced by
Silence Alarm.
No Dis-
play
Alarm (1 to 8)
Latched
Yes (106)
No (59)
- - - -
Read to see if alarm
is currently latched.
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1762 2602
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1760 2600
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1758 2598
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+60
0x6D
(109)
1 to 8
0xC (12)
0x6D
(109)
1 to 4
0x0B
(11)
0x6D
(109)
1 to 4
0x0A
(10)
- - - - 9012 uint
- - - - 9011 uint
- - - - 9010 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
uint
W
uint
W
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 68 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 73

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
CUrr
opEr
Current Menu
C.hi
C.hi
C.Lo
C.Lo
Ld.Cu
Ld.Cu
No Dis-
play
Current (1 to 4)
High Set Point
Set the current value that will trigger
a high heater error
state.
Current (1 to 4)
Low Set Point
Set the current value that will trigger
a low heater error
state.
Current (1 to 4)
Current
The measured current value with
scaling and offset
applied when associated output is on.
Current (1 to 4)
Sample and Hold
Current
Samples and holds
the last valid current reading, this
transmitter will reset on a controller
power cycle.
Description
Range Default
-1,999.000 to
50.0
9,999.000
-1,999.000 to
0.0
9,999.000
0 to 9,999.000 - - - -
0 to 9,999.000 - - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Note:
To use the current sensing feature, Time Base
(Setup Page, Output Menu) must be set to 0.7
seconds or more.
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1394 2034
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1396 2036
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1392 2032
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1380 2020
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x73
(115)
1 to 4
8
0x73
(115)
1 to 4
9
0x73
(115)
1 to 4
7
0x73
(115)
1 to 4
1
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 15008 float
- - - - 15009 float
- - - - 15007 float
- - - - 15001 float
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
RWES
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 69 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 74

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1382 2022
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1384 2024
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1418 2058
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
1420 2060
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Display
C.Er
C.Er
h.Er
h.Er
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
Parameter Name
Description
Current (1 to 4)
Current Error
View the cause of
the most recent
load fault.
Current (1 to 4)
Heater Error
View the cause of
the most recent
load fault monitored by the current
transformer.
Current (1 to 4)
Actual Power
Power delivered to
output monitored
by CT.
Current (1 to 4)
Error Status
View the cause of
the most recent
load fault
Range Default
nonE None (61)
- - - -
Shrt Shorted
(127)
opEn Open (65)
nonE None (61)
- - - -
high High (37)
LoФІ Low (53)
0.0 to 100.0% - - - -
None (61)
Fail (32)
- - - -
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x73
(115)
1 to 4
2
0x73
(115)
1 to 4
3
0x73
(115)
1 to 4
0x14
(20)
0x73
(115)
1 to 4
21
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 15002 uint
- - - - 15003 uint
- - - - 15020 float
- - - - 15021 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 70 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 75

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
Lnr
opEr
Linearization Menu
Su.a
Su.A
ofst
oFSt
o.u
o.v
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Linearization (1 to
4)
Source Value A
View the value of
Source A.
Linearization (1 to
4)
Offset
Set an offset to be
applied to this function's output.
Linearization (1 to
4)
Output Value
View the value of
this function's output.
Linearization (1 to
4)
Error
View reported cause
for Linearization
output malfunction.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement error (140)
Bad calibration
data (139)
Ambient error (9)
RTD error (14)
Fail (32)
Math error (1423)
Not sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
Can't process
(1659)
- - - -
0
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4526 6326
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4530 6330
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4532 6332
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4574 6374
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
0x86
(134)
1 to 4
4
0x86
(134)
1 to 4
6
0x86
(134)
1 to 4
7
0x86
(134)
1 to 4
0x1C
(28)
- - - - 34004 float
- - - - 34006 float
- - - - 34007 float
- - - - 34028 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
RWES
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 71 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 76

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
CpE
opEr
Compare Menu
Su.a
Su.A
Su.b
Su.b
o.u
o.v
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Compare (1 to 4)
Source Value A
View the value of
Source A.
Compare (1 to 4)
Source Value B
View the value of
Source B.
Compare (1 to 4)
Output Value
View the value of
this function's output.
Compare (1 to 4)
Error
Read reported
cause for compare
error
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
off Off (62)
on On (63)
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement Error (140)
Bad Cal Data
(139)
Ambient Error (9)
RTD Error (141)
Fail (32)
Math Error (1423)
Not Sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4012 5812
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4014 5814
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4018 5818
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4024 5824
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
0x80
(128)
1 to 4
7
0x80
(128)
1 to 4
8
0x80
(128)
1 to 4
0xA (10)
0x80
(128)
1 to 4
0x0D
(13)
- - - - 28007 float
- - - - 28008 float
- - - - 28010 uint
- - - - 28013 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 72 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 77

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
tЛЏr
opEr
Timer Menu
Su.a
Su.A
Su.b
Su.b
E.t
E.t
o.u
o.v
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Timer (1 to 4)
Source Value A
View the value of
Source A.
Timer (1 to 4)
Source Value B
View the value of
Source B.
Timer (1 to 4)
Elapsed Time
View the value
of this function's
elapsed time.
Timer (1 to 4)
Output Value
View the value of
this function's output.
Timer (1 to 4)
Error
Read reported cause
for timer error
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
0 to 9,999.000
seconds
off Off (62)
on On (63)
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement Error (140)
Bad Cal Data
(139)
Ambient Error (9)
RTD Error (141)
Fail (32)
Math Error (1423)
Not Sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4322 6132
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4334 6134
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4350 6150
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4338 6138
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4354 6154
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+50
0x83
(131)
1 to 4
7
0x83
(131)
1 to 4
8
0x83
(131)
1 to 4
0x10
(16)
0x83
(131)
1 to 4
0xA (10)
0x83
(131)
1 to 4
0x12
(18)
- - - - 31007 uint
- - - - 31008 uint
- - - - 31016 float
- - - - 31010 uint
- - - - 31018 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 73 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 78

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
Ctr
opEr
Counter Menu
Cnt
Cnt
Su.a
Su.A
Su.b
Su.b
o.u
o.v
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Counter (1 to 4)
Count
View the function's
total count.
Counter (1 to 4)
Source Value A
View the value of
Source A.
Counter (1 to 4)
Source Value B
View the value of
Source B.
Counter (1 to 4)
Output Value
View the value of
this function's output.
Counter (1 to 4)
Error
Read reported
cause for counter
error
0 to 9,999 - - - -
off Off (62)
- - - -
on On (63)
off Off (62)
- - - -
on On (63)
off Off (62)
- - - -
on On (63)
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement Error (140)
Bad Cal Data
(139)
Ambient Error (9)
RTD Error (141)
Fail (32)
Math Error (1423)
Not Sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4188 5988
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4172 5972
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4174 5974
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4178 5978
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4190 5990
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+40
0x82
(130)
1 to 4
0xF (15)
0x82
(130)
1 to 4
7
0x82
(130)
1 to 4
8
0x82
(130)
1 to 4
0xA (10)
0x82
(130)
1 to 4
0x10
(16)
217 30015 uint
- - - - 30007 uint
- - - - 30008 uint
- - - - 30010 uint
- - - - 30016 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 74 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 79

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
LgC
opEr
Logic Menu
Su.a
Su.A
Su.b
Su.b
Su.C
Su.C
Su.d
Su.d
Su.E
Su.E
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Logic (1 to 16)
Source Value A
View the value of
Source A.
Logic (1 to 16)
Source Value B
View the value of
Source B.
Logic (1 to 16)
Source Value C
View the value of
Source C.
Logic (1 to 16)
Source Value D
View the value of
Source D.
Logic (1 to 16)
Source Value E
View the value of
Source E.
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3728 4568
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3730 4570
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3732 4572
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3734 4574
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3736 4576
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
0x7F
(127)
1 to 16
0x19
(25)
0x7F
(127)
1 to 16
0x1A
(26)
0x7F
(127)
1 to 16
0x1B
(27)
0x7F
(127)
1 to 16
0x1C
(28)
0x7F
(127)
1 to 16
0x1D
(29)
- - - - 27025 uint
- - - - 27026 uint
- - - - 27027 uint
- - - - 27028 uint
- - - - 27029 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 75 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 80

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Su.f
Su.F
Su.g
Su.g
Su.h
Su.h
o.u
o.v
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Parameter Name
Description
Logic (1 to 16)
Source Value F
View the value of
Source F.
Logic (1 to 16)
Value Source G
View the value of
Source G.
Logic (1 to 16)
Source Value H
View the value of
Source H.
Logic (1 to 16)
Output Value
View the value of
this function's output.
Logic (1 to 16)
Error
Read reported
cause for logic error
Range Default
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement Error (140)
Bad Cal Data
(139)
Ambient Error (9)
RTD Error (141)
Fail (32)
Math Error (1423)
Not Sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3738 4578
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3740 4580
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3742 4582
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3746 4586
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
3750 4590
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x7F
(127)
1 to 16
0x1E
(30)
0x7F
(127)
1 to 16
0x1F
(31)
0x7F
(127)
1 to 16
0x20
(32)
7F (127)
1 to 16
0x22
(34)
0x7F
(127)
1 to 16
0x24
(36)
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 27030 uint
- - - - 27031 uint
- - - - 27032 uint
- - - - 27034 uint
- - - - 27036 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 76 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 81

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Pro-
fibus
Index
ЛЏat
opEr
Math Menu
Su.a
Su.A
Su.b
Su.b
Su.C
Su.C
Su.d
Su.d
Su.E
Su.E
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Math (1 to 8)
Source Value A
View the value of
Source A.
Math (1 to 8)
Source Value B
View the value of
Source B.
Math (1 to 8)
Source Value C
View the value of
Source C.
Math (1 to 8)
Source Value D
View the value of
Source D.
Math (1 to 8)
Source Value E
View the value of
Source E.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
off Off (62)
on On (63)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2870 3710
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2872 3712
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2874 3714
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2876 3716
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2878 3718
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
0x7D
(125)
1 to 8
0x10
(16)
0x7D
(125)
1 to 8
0x11
(17)
0x7D
(125)
1 to 8
0x12
(18)
0x7D
(125)
1 to 8
0x13
(19)
0x7D
(125)
1 to 8
0x14
(20)
- - - - 25016 float
- - - - 25017 float
- - - - 25018 float
- - - - 25019 float
- - - - 25020 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 77 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 82

Display
ofst
oFSt
o.u
o.v
No Dis-
play
Parameter Name
Description
Math (1 to 8)
Offset
Set an offset to be
applied to this function's output.
Math (1 to 8)
Output Value
View the value of
this function's output.
Math (1 to 8)
Error
Read reported
cause for logic error
RMC Module • Operations Page
Range Default
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement Error (140)
Bad Cal Data
(139)
Ambient Error (9)
RTD Error (141)
Fail (32)
Math Error (1423)
Not Sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
0
- - - -
- - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2884 3724
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2882 3722
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
2896 3736
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+70
CIP
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x7D
(125)
1 to 8
0x17
(23)
0x7D
(125)
1 to 8
0x16
(22)
0x7D
(125)
1 to 8
0x1D
(29)
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 25023 float
- - - - 25022 float
- - - - 25029 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
RWES
R
R
**
Sof
opEr
Special Output Function Menu
Su.a
Su.A
Su.b
Su.b
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Special Output
Function (1 to 4)
Source Value A
View the value of
Source A.
Special Output
Function (1 to 4)
Source Value B
View the value of
Source B.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
- - - -
- - - -
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 78 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4972 6932
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4974 6934
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
0x87
(135)
1 to 4
7
0x87
(135)
1 to 4
8
- - - - 35007 float
R
- - - - 35008 float
R
Page 83

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4978 6938
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4980 6940
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Display
o.u1
o.v1
No Dis-
play
Parameter Name
Description
Special Output
Function (1 to 4)
Output Value 1
View the value of
this function's Output 1.
Special Output
Function (1 to 4)
Error 1
View reported cause
for output malfunction.
Range Default
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement error (140)
Bad calibration
data (139)
Ambient error (9)
- - - -
- - - -
RTD error (14)
Fail (32)
Math error (1423)
Not sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
Can't process
(1659)
o.u2
o.v2
No Dis-
play
Special Output
Function (1 to 4)
Output Value 2
View the value of
this function's Output 2.
Special Output
Function (1 to 4)
Error 2
View reported cause
for output malfunction.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement error (140)
Bad calibration
data (139)
Ambient error (9)
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4982 6942
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4984 6944
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
RTD error (14)
Fail (32)
Math error (1423)
Not sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
Can't process
(1659)
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x87
(135)
1 to 4
0xA (10)
0x87
(135)
1 to 4
0x0B
(11)
0x87
(135)
1 to 4
0xC (12)
0x87
(135)
1 to 4
0x0D
(13)
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 35010 float
- - - - 35011 uint
- - - - 35012 float
- - - - 35013 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 79 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 84

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4986 6946
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4988 6948
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Display
o.u3
o.v3
No Dis-
play
Parameter Name
Description
Special Output
Function (1 to 4)
Output Value 3
View the value of
this function's Output 3.
Special Output
Function (1 to 4)
Error 3
View reported cause
for output malfunction.
Range Default
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement error (140)
Bad calibration
data (139)
Ambient error (9)
- - - -
- - - -
RTD error (14)
Fail (32)
Math error (1423)
Not sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
Can't process
(1659)
o.u4
o.v4
No Dis-
play
Special Output
Function (1 to 4)
Output Value 4
View the value of
this function's Output 4.
Special Output
Function (1 to 4)
Error 4
View reported cause
for output malfunction.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
None (61)
Open (65)
Shorted (127)
Measurement error (140)
Bad calibration
data (139)
Ambient error (9)
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4990 6950
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
4992 6952
Map 1 and
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+80
RTD error (14)
Fail (32)
Math error (1423)
Not sourced (246)
Stale (1617)
Can't process
(1659)
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x87
(135)
1 to 4
0xE (14)
0x87
(135)
1 to 4
0x0F
(15)
0x87
(135)
1 to 4
0x10
(16)
0x87
(135)
1 to 4
0x11
(17)
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 35014 float
- - - - 35015 uint
- - - - 35016 float
- - - - 35017 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 80 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 85

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Parameter Name
Description
P.sta
opEr
Profile Status Menu
p.str
P.Str
p.ACr
PACr
Profile Status
Profile Start
Profile Status
Profile Action Request
Modbus
Range Default
* Some parameters in the Profile Status Menu can be changed for the currently
running profile, but should only be changed by knowledgeable personnel and
with caution. Changing parameters via the Profile Status Menu will not change
the stored profile but will have an immediate impact on the profile that is
running.
Changes made to profile parameters in the Profiling Pages will be saved and
will also have an immediate impact on the running profile.
1 to 250 1
nonE None (61)
None
stEp Step (89)
End Terminate
(148)
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5280 7240
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5300 7260
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x7A
(122)
1
1
0x7A
(122)
1
0xB (11)
Pro-
fibus
Index
204 22001 uint
205 22011 uint
rEsU Resume
(147)
paUs Pause
(146)
prof Profile
(77)
stp
StP
sub.s
SUb.S
s.typ
S.typ
Profile Status
Current Step
View the currently
running step.
Profile Status
Current Sub Step
View the current ly
running subroutine.
Profile Status
Step Type
View the currently
running step type.
0 to 250
0 (none)
0 to 150
0 (none)
Ustp Unused
Step (50)
ti Time (143)
ratE Ramp Rate
(81)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5286 7246
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5388 7348
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5304 7264
0x7A
(122)
1
4
0x7A
(122)
1
0x37
(55)
0x7A
(122)
1
0xD (13)
- - - - 22004 uint
- - - - 22055 uint
- - - - 22013 uint
SoaH Soak (87)
CLoC Wait For
Time (1543)
ФІpE Wait For
Process or Event
(1542)
stat Instant
Change (1515)
subr Subroutine
Step (1516)
JL Jump (116)
End End (27)
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
W
W
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 81 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 86

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
t.sp1
[t.SP1
t.sp2
t.SP2
t.sp3
t.SP3
t.sp4
t.SP4
p.sp1
P.SP1
p.sp2
P.SP2
p.sp3
P.SP3
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Parameter Name
Description
Profile Status
*Target Set Point
Loop 1
View or change the
target set point of
the current step.
Profile Status
*Target Set Point
Loop 2
View or change the
target set point of
the current step.
Profile Status
*Target Set Point
Loop 3
View or change the
target set point of
the current step.
Profile Status
*Target Set Point
Loop 4
View or change the
target set point of
the current step.
Profile Status
Produced Set Point
1
Display the current
set point, even if
the profile is ramping.
Profile Status
Produced Set Point
2
Display the current
set point, even if
the profile is ramping.
Profile Status
Produced Set Point
3
Display the current
set point, even if
the profile is ramping.
Range Default
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
0.0°F
or units
-18.0°C
0.0°F
or units
-18.0°C
0.0°F
or units
-18.0°C
0.0°F
or units
-18.0°C
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5302 7262
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5374 7334
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5376 7336
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5378 7338
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5288 7248
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5380 7340
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5382 7342
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x7A
(122)
1
0xC (12)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x30
(48)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x31
(49)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x32
(50)
- - - - - - - - 22005 float
- - - - - - - - 22051 float
- - - - - - - - 22052 float
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 22012 float
- - - - 22048 float
- - - - 22049 float
- - - - 22050 float
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RW
RW
RW
RW
R
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 82 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 87

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
p.sp4
P.SP4
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
hoUr
hoUr
ЛЏin
Min
SEC
SEC
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Parameter Name
Description
Profile Status
Produced Set Point
4
Display the current
set point, even if
the profile is ramping.
Profile Status
Produced Control
Mode 1
Display the current
control mode.
Profile Status
Produced Control
Mode 2
Display the current
control mode.
Profile Status
Produced Control
Mode 3
Display the current
control mode.
Profile Status
Produced Control
Mode 4
Display the current
control mode.
Profile Status
Hours
Step time remaining
in hours.
Profile Status
Minutes
Step time remaining
in minutes.
Profile Status
Seconds
Step time remaining
in seconds.
Profile Status
Wait for Event
Source Value 1
Read the present
state of event input
1.
Range Default
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or
units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
Off (62)
Auto (10)
Manual (54)
Off (62)
Auto (10)
Manual (54)
Off (62)
Auto (10)
Manual (54)
Off (62)
Auto (10)
Manual (54)
0 to 99 0
0 to 59 0
0 to 59 0
off Off (62)
on On (63)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5384 7344
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5366 7326
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5368 7328
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5370 7330
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5372 7332
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5434 7394
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5432 7392
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5430 7390
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5346 7306
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
- - - - - - - - 22053 float
0x7A
(122)
1
0x2C
(44)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x2D
(45)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x2E
(46)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x2F
(47)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x4E
(78)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x4D
(77)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x4C
(76)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x22
(34)
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 22044 uint
- - - - 22045 uint
- - - - 22046 uint
- - - - 22047 uint
- - - - 22078 uint
- - - - 22077 uint
- - - - 22076 uint
- - - - 22034 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
R
RW
RW
RW
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 83 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 88

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
Ent1
Ent1
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Parameter Name
Description
Profile Status
Wait for Event
Source Value 2
Read the present
state of event input
1.
Profile Status
Wait for Event
Source Value 3
Read the present
state of event input
1.
Profile Status
Wait for Event
Source Value 4
Read the present
state of event input
1.
Profile Status
Wait for Analog
Source Value 1
Read the present
value of analog
source 1.
Profile Status
Wait for Analog
Source Value 2
Read the present
value of analog
source 2.
Profile Status
Wait for Analog
Source Value 3
Read the present
value of analog
source 3.
Profile Status
Wait for Analog
Source Value 4
Read the present
value of analog
source 4.
Profile Status
*Event 1
View or change the
event output states.
Range Default
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
off Off (62)
on On (63)
-1999.000 to
9999.000
-1999.000 to
9999.000
-1999.000 to
9999.000
-1999.000 to
9999.000
off Off (62)
on On (63)
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Off
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5348 7308
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5350 7310
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5352 7312
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5414 7374
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5416 7376
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5418 7378
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5420 7380
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5306 7266
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x23
(35)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x24
(36)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x25
(37)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x44
(68)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x45
(69)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x46
(70)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x47
(71)
0x7A
(122)
1
0xE (14)
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 22035 uint
- - - - 22036 uint
- - - - 22037 uint
- - - - 22068 float
- - - - 22069 float
- - - - 22070 float
- - - - 22071 float
- - - - 22014 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
RW
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 84 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 89

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
Ent2
Ent2
Ent3
Ent3
Ent4
Ent4
Ent5
Ent5
Ent6
Ent6
Ent7
Ent7
Ent8
Ent8
JC
JC
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Parameter Name
Description
Profile Status
*Event 2
View or change the
event output states.
Profile Status
*Event 3
View or change the
event output states.
Profile Status
*Event 4
View or change the
event output states.
Profile Status
*Event 5
View or change the
event output states.
Profile Status
*Event 6
View or change the
event output states.
Profile Status
*Event 7
View or change the
event output states.
Profile Status
*Event 8
View or change the
event output states.
Profile Status
Jump Count Remaining
View the jump
counts remaining for the current
loop. In a profile
with nested loops,
this may not indicate the actual
jump counts remaining.
Range Default
off Off (62)
Off
on On (63)
off Off (62)
Off
on On (63)
off Off (62)
Off
on On (63)
off Off (62)
Off
on On (63)
off Off (62)
Off
on On (63)
off Off (62)
Off
on On (63)
off Off (62)
Off
on On (63)
0 to 9,999 - - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5308 7268
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5310 7270
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5312 7272
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5314 7274
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5316 7276
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5318 7278
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5320 7280
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5298 7258
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x7A
(122)
1
0xF (15)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x10
(16)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x11
(17)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x12
(18)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x13
(19)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x14
(20)
0x7A
(122)
1
0x15
(21)
0x7A
(122)
1
0xA (10)
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 22015 uint
- - - - 22016 uint
- - - - 22017 uint
- - - - 22018 uint
- - - - 22019 uint
- - - - 22020 uint
- - - - 22021 uint
- - - - 22010 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 85 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 90

RMC Module • Operations Page
CIP
Display
No Dis-
play
No Dis-
play
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Parameter Name
Description
Profile Status
Current File
Indicates current
file being executed.
Profile Status
Profile State
Read current Profile
state.
Range Default
1 to 25
0 (none)
Off (62)
Running (149)
Pause (146)
- - - -
- - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5284 7244
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
5282 7242
Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x7A
(122)
1
3
0x7A
(122)
1
2
Pro-
fibus
Index
- - - - 22003 uint
- - - - 22002 uint
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
R
R
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 86 • Chapter 3 Operations Page
Page 91

4
Chapter 4: Setup Pages
Control Module Setup Page Parameters
To navigate to the Setup Page using the RUI, follow the steps below:
1. From the Home Page, press and hold both the Up ¿ and Down ¯ keys for six seconds. Ai
will appear in the upper display and SEt will appear in the lower display.
Note:
If keys are released when opEr is displayed, press the Infinity Key ˆ or reset key to exit
and repeat until SEt is displayed.
2. Press the Up ¿ or Down ¯ key to view available menus.
3. Press the Advance Key ‰ to enter the menu of choice.
4. If a submenu exists (more than one instance), press the Up ¿ or Down ¯ key to select and
then press the Advance Key ‰ to enter.
5. Press the Up ¿ or Down ¯ key to move through available menu prompts.
6. Press the Infinity Key ˆ to move backwards through the levels: parameter to submenu, sub-
menu to menu, menu to Home Page.
7. Press and hold the Infinity Key ˆ for two seconds to return to the Home Page.
On the following pages, top level menus are identified with a yellow background color.
Note:
Some of these menus and parameters may not appear, depending on the controller's options. See model number information in the Appendix for more information. If there is
only one instance of a menu, no submenus will appear.
Note:
Some of the listed parameters may not be visible. Parameter visibility is dependent upon
controller part number.
Ai
sEt Analog Input Menu
1
Ai Analog Input 1 to 4
sEn Sensor Type
Lin TC Linearization
rtL RTD Leads
Unit Units
s.Lo Scale Low
s.hi Scale High
r.Lo Range Low
r.hi Range High
P.EE Process Error En-
able
P.EL Process Error Low
Value
t.C Thermistor Curve
r.r Resistance Range
Co.a Custom Coefficient
A
Co.b Custom Coefficient
B
Co.C Custom Coefficient
C
fiL Filter
i.Er Input Error Latching
dEC Display Precision
i.Ca Calibration Offset *
ain Analog Input Value *
i.Er Input Error *
Pu
sEt Process Value
1
Pu Process Value 1 to 4
fn Function
Sfn.a Source Function A
Si.a Source Instance A
Sfn.b Source Function B
Si.b Source Instance B
sz.b Source Zone B
Sfn.C Source Function C
Si.C Source Instance C
sz.C Source Zone C
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 87 • Chapter 4 Setup Page
Page 92

Sfn.d Source Function D
Si.d Source Instance D
sz.d Source Zone D
Sfn.E Source Function E
Si.E Source Instance E
sz.E Source Zone E
C.p Cross Over Point
C.b Cross Over Band
p.unt Pressure Units
a.unt Altitude Units
b.pr Barometric Pres-
sure
fil Filter
dio
sEt Digital Input/Output
Menu
1
dio Digital Input/Output 7
to 12
dir Direction
fn Function
fi Output Function In-
stance
sz.a Output Source Zone
o.Ct Time Base Type
o.tb Fixed Time Base
o.Lo Low Power Scale
o.hi High Power Scale
aCt
sEt Action Menu
1
aCt Action 1 to 8
fn Action Function
fi Function Instance
sfn.a Source Function A
si.a Source Instance A
sz.a Source Zone A
LEv Active Level
LiЛЏ
sEt Limit Menu
1
LiЛЏ Limit 1 to 4
L.sd Sides
L.hy Hysteresis
sp.Lh Maximum Set
Point
sp.LL Minimum Set
Point
Lh.s High Limit Set Point
*
LL.s Low Limit Set Point
*
sfn.a Source Function
A*
si.a Source Instance
A*
sz.a Source Zone A *
L.Cr Clear Limit *
L.st Limit Status *
Loop
sEt Control Loop Menu
1
Loop Control Loop 1 to 4
Sfn.a Source Function A
is.a Source Instance A
h.ag Heat Algorithm
C.ag Cool Algorithm
C.Cr Cool Output Curve
h.pb Heat Proportional
Band *
h.hy On / Off Heat Hys-
teresis *
C.pb Cool Proportional
Band *
C.hy On / Off Cool Hys-
teresis *
ti Time Integral *
td Time Derivative *
db Dead Band *
t.tun TRU-TUNE+
able
t.bnd TRU-TUNE+ Band
t.gn TRU-TUNE+ Gain
a.tsp Autotune Set
Point *
t.agr Autotune Aggres-
siveness
p.dL Peltier Delay
r.En Remote Set Point
Sfn.b Source Function B
Si.b Source Instance B
Sz.b Source Zone B
®
En-
r.ty Remote Set Point
Type
Ufa Auto-to-Manual
Power
faiL Input Error Power
ЛЏan Fixed Power
L.dE Open Loop Detect
Enable
L.dt Open Loop Detect
Time
L.dd Open Loop Detect
Deviation
rp Ramp Action
r.sC Ramp Scale
r.rt Ramp Rate
pro.E Profiling Enable
L.sp Minimum Set Point
h.sp Maximum Set Point
C.sp Set Point*
id.sp Idle Set Point *
sp.Lo Minimum Manual
Power
SP.hi Maximum Manual
Power
o.sp Manual Power *
C.ЛЏ Control Mode *
otpt
sEt Output Menu
1
otpt Output 1 to 8
fn Function
fi Output Function In-
stance
sz.a Source Zone A
o.Ct Time Base Type
o.tp Fixed Time Base
o.Lo Low Power Scale
o.hi High Power Scale
otpt Output 1, 3, 5 or 7
process
o.ty Output Type
fn Function
fi Output Function In-
stance
sz.a Source Zone A
s.Lo Scale Low
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 88 • Chapter 4 Setup Page
Page 93

s.hi Scale High
r.Lo Range Low
r.hi Range High
o.Ca Calibration Offset
aLЛЏ
sEt Alarm Menu
1
aLЛЏ Alarm 1 to 8
a.ty Type
sr.a Alarm Source
is.a Alarm Source In-
stance
sz.a Alarm Source Zone
Loop Control Loop
a.hy Hysteresis
a.Lg Logic
a.sd Sides
a.Lo Low Set Point *
a.hi High Set Point *
a.La Latching
a.bL Blocking
a.si Silencing
a.dsp Display
a.dL Delay Time
a.CLr Clear Alarm *
a.sir Silence Alarm *
a.st Alarm State *
CUrr
sEt Current Menu
1
CUrr Current 1 to 4
C.sd Sides
CU.r Indicate Reading
C.dt Detection Thresh-
old
C.sC Input Scaling
C.ofs Heater Offset
C.si Monitored Output
Erяя Monitored Zone
Lnr
sEt Linearization Menu
1
Lnr Linearization 1 to 4
fn Function
sfn.a Source Function A
Si.a Source Instance A
sz.a Source Zone A
Unit Units
ip.1 Input Point 1
op.1 Output Point 1
ip.2 Input Point 2
op.2 Output Point 2
ip.3 Input Point 3
op.3 Output Point 3
ip.4 Input Point 4
op.4 Output Point 4
ip.5 Input Point 5
op.5 Output Point 5
ip.6 Input Point 6
op.6 Output Point 6
ip.7 Input Point 7
op.7 Output Point 7
ip.8 Input Point 8
op.8 Output Point 8
ip.q Input Point 9
op.q Output Point 9
ip.10 Input Point 10
op.10 Output Point 10
CpE
sEt Compare Menu
1
CpE Compare 1 to 4
fn Function
toL Tolerance
Sfn.a Source Function A
Si.a Source Instance A
Sz.a Source Zone A
Sfn.b Source Function B
Si.b Source Instance B
Sz.b Source Zone B
Er.h Error Handling
tЛЏr
sEt Timer Menu
1
tЛЏr Timer 1 to 4
fn Function
Sfn.a Source Function A
Si.a Source Instance A
Sz.a Source Zone A
sas.a Run Active Level
Sfn.b Source Function B
Si.b Source Instance B
Sz.b Source Zone B
sas.b Reset Active Level
State B
ti Time
LEv Transmitter Active
Level
Ctr
sEt Counter Menu
1
Ctr Counter 1 to 4
fn Function
Sfn.a Source Function A
Si.a Source Instance A
Sz.a Source Zone A
sas.a Count Active Level
Sfn.b Source Function B
Si.b Source Instance B
Sz.b Source Zone B
sas.b Reset Active Level
Load Load Value
trgt Target Value
Lat Latching
LgC
sEt Logic Menu
1
LgC Logic 1 to 4
fn Function
Sfn.a Source Function A
Si.a Source Instance A
Sz.a Source Zone A
Sfn.b Source Function B
Si.b Source Instance B
Sz.b Source Zone B
Sfn.C Source Function C
Si.C Source Instance C
Sz.C Source Zone C
Sfn.d Source Function D
Si.d Source Instance D
Sz.d Source Zone D
Sfn.E Source Function E
Si.E Source Instance E
Sz.E Source Zone E
Sfn.f Source Function F
Si.f Source Instance F
Sz.f Source Zone F
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 89 • Chapter 4 Setup Page
Page 94

Sfn.g Source Function G
Si.g Source Instance G
Sz.g Source Zone G
Sfn.h Source Function H
Si.h Source Instance H
Sz.H Source Zone H
Er.h Error Handling
ЛЏat
sEt Math Menu
1
ЛЏat Math 1 to 8
fn Function
Sfn.a Source Function A
Si.a Source Instance A
Sz.a Source Zone A
Sfn.b Source Function B
Si.b Source Instance B
Sz.b Source Zone B
Sfn.C Source Function C
Si.C Source Instance C
Sz.C Source Zone C
Sfn.d Source Function D
Si.d Source Instance D
Sz.d Source Zone D
Sfn.E Source Function E
Si.E Source Instance E
Sz.E Source Zone E
s.Lo Scale Low
S.hi Scale High
Unit Units
r.Lo Range Low
r.hi Range High
p.unt Pressure Units
a.unt Altitude Units
fiL Filter
sof
sEt Special Output Function
Menu
1
sof Special Output Function 1
to 4
fn Function
Sfn.a Source Function A
Si.a Source Instance A
Sz.a Source Zone A
Sfn.b Source Function B
Si.b Source Instance B
Sz.b Source Zone B
pon.a Input A Turn On
pof.a Input A Turn Off
pon.b Input B Turn On
pof.b Input B Turn Off
on.t On Time
of.t Off Time
t.t Valve Travel Time
db Dead Band
os.1 Output 1 Size
os.2 Output 2 Size
os.3 Output 3 Size
os.4 Output 4 Size
t.dL Time Delay
ot.L Output Order
var
sEt Variable Menu
1
var Variable 1 to 16
typE Data Type
Unit Units
dig Digital
anLg Analog
gLbL
.sEt Global Menu
gLbL Global
C_f Display Units
aC.Lf AC Line Frequency
ЛЏaK Maximum
ЛЏin Minimum
sutb Synchronized Vari-
able Time Base
d.prs Display Pairs
Usr.s Save Settings As
Usr.r Restore Settings
From
pro
sEt Profile Menu
pro Profile
r.typ Ramping Type
p.typ Profile Type
gsE Guaranteed Soak
Enable
gsd1 Guaranteed Soak De-
viation 1
gsd2 Guaranteed Soak De-
viation 2
gsd3 Guaranteed Soak De-
viation 3
gsd4 Guaranteed Soak De-
viation 4
CЛЏ.E Control Mode En-
able
ФІ.ЛЏ Wait for Mode
Sfn.a Source Function A
Si.a Source Instance A
Sz.a Source Zone A
Sfn.b Source Function B
Si.b Source Instance B
Sz.b Source Zone B
Sfn.C Source Function C
Si.C Source Instance C
Sz.C Source Zone C
Sfn.d Source Function D
Si.d Source Instance D
Sz.d Source Zone D
Sfn.E Source Function E
Si.E Source Instance E
Sz.E Source Zone E
Sfn.f Source Function F
Si.f Source Instance F
Sz.f Source Zone F
Sfn.g Source Function G
Si.g Source Instance G
Sz.g Source Zone G
Sfn.H Source Function H
Si.H Source Instance H
Sz.H Source Zone H
COЛЏ
sEt Communications Menu
COЛЏ Communications
baUd Baud Rate
par Parity
ЛЏ.hL Modbus Word Order
C_f Display Units
ЛЏap Data Map
nu.s Non-volatile Save
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 90 • Chapter 4 Setup Page
Page 95

Note:
Some values will be rounded off to fit in the four-character RUI display. Full values can be
read with other interfaces. In firmware 9.0 and above, a user may specify ranges greater
than may displayed by an RUI. If greater or less than an RUI can display, the display will
show Value High uAL.H or Value Low uAL.L.
RMC Module • Setup Page
Display
Parameter Name
Description
Range Default
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
CIP - Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
Profibus
Index
Parameter
ID
Ai
sEt
Analog Input Menu
sEn
SEn
Lin
Lin
rt.L
rt.L
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Sensor Type
Set the analog
sensor type to
match the device wired to
this input.
Note:
There is no
open sensor
protection for
process inputs.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
TC Linearization
Set the linearization to match
the thermocouple wired to this
input.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
RTD Leads
Set to match
the number of
leads on the RTD
wired to this
input.
off Off (62)
tC Thermocouple (95)
ЛЏu Millivolts (56)
voLt Volts dc (104)
ЛЏa
Milliamps dc (112)
r0.1H RTD 100 Ω (113)
r1.0H RTD 1,000 Ω
(114)
pot Potentiometer 1
kΩ (155)
thEr Thermistor (229)
b B (11) H K (48)
C C (15) n N (58)
d D (23) r R (80)
E E (26) s S (84)
f F (30) t T (93)
J J (46)
2 2 (1)
3 3 (2)
Thermocouple or
Thermistor
J
2
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
368 428
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
370 430
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
372 432
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
5
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
6
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
7
3 4005 uint
4 4006 uint
- - - - 4007 uint
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
RWES
RWES
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 91 • Chapter 4 Setup Page
Page 96

RMC Module • Setup Page
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
442 502
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
388 448
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Display
Unit
Unit
s.Lo
S.Lo
Parameter Name
Description
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Units
Set the type of
units the sensor
will measure.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Scale Low
Set the low
scale for process inputs. This
value, in millivolts, volts or
milliamps, will
correspond to
the Range Low
Range Default
a.tp Absolute Tempera-
Process
ture (1540)
rh Relative Humidity
(1538)
pro Process (75)
PФІr Power (73)
-100.0 to 1,000.0 0.0
output of this
function block.
s.hi
S.hi
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Scale High
Set the high
scale for process
inputs. This value, in millivolts,
volts or milliamperes, will
correspond to
the Range High
-100.0 to 1,000.0 20.0
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
390 450
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
output of this
function block.
r.Lo
r.Lo
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Range Low
Set the low
range for this
function block's
output.
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000
0.0
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
392 452
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
CIP - Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0x2A (42)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0xF (15)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0x10 (16)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0x11 (17)
Profibus
Index
5 4042 uint
6 4015 float
7 4016 float
8 4017 float
Pa-
ram-
eter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
RWES
RWES
RWES
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 92 • Chapter 4 Setup Page
Page 97

RMC Module • Setup Page
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
394 454
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
418 478
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
420 480
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
434 494
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Display
r.hi
r.hi
p.EE
P.EE
p.EL
P.EL
t.C
t.C
Parameter Name
Description
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Range High
Set the high
range for this
function block's
output.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Process Error
Enable
Turn the Process
Error Low feature on or off.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Process Error
Low Value
If the process
value drops below this value,
it will trigger an
input error.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Thermistor
Curve
Select a curve
to apply to the
thermistor input.
Range Default
-1,999.000 to 9,999.000 9,999
off Off (62)
Off
LoФІ Low (53)
-100.0 to 1,000.0 0.0
a Curve A (1451)
Curve A
b Curve B (1452)
C Curve C (1453)
CUst Custom (180)
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
CIP - Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0x12 (18)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0x1E (30)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0x1F (31)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0x26 (38)
Profibus
Index
9 4018 float
10 4030 uint
11 4031 float
- - - - 4038 uint
Parameter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
RWES
RWES
RWES
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 93 • Chapter 4 Setup Page
Page 98

Display
r.r
r.r
Co.a
Co.A
Co.b
Co.b
Co.C
Co.C
Parameter Name
Description
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Resistance
Range
Set the maximum resistance
of the thermistor
input.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Custom Coefficient A
Enter custom
Thermistor coefficients.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Custom Coefficient B
Enter custom
Thermistor coefficients.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Custom Coefficient C
Enter custom
Thermistor coefficients.
RMC Module • Setup Page
Range Default
5 5K (1448)
10 10K (1360)
20 20K (1361)
40 40K (1449)
-3.4e38 to 3.4e38 0
-3.4e38 to 3.4e38 0
-3.4e38 to 3.4e38 0
40K
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
432 492
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
CIP - Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0x25 (37)
- - - - - - - - 4039 float
- - - - - - - - 4040 float
- - - - - - - - 4041 float
Profibus
Index
- - - - 4037 uint
ram-
eter
Pa-
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
RWES
RWES
RWES
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 94 • Chapter 4 Setup Page
Page 99

RMC Module • Setup Page
Display
fiL
FiL
i.Er
i.Er
dEC
dEC
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Parameter Name
Description
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Filter
Filtering smooths
out the process
signal to both
the display and
the input. Increase the time
to increase filtering.
Note:
Filter does not
apply to the
Limit sensor but
does apply to
all other functions.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Input Error
Latching
Turn input error
latching on or
off. If latching is
on, errors must
be manually
cleared.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Display Precision
Set the precision
of the displayed
value.
Range Default
0.0 to 60.0 seconds 0.5
off Off (62)
Off
on On (63)
0 Whole (105)
Whole
0.0 Tenths (94)
0.00 Hundredths (40)
0.000 Thousandths (96)
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
386 446
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
414 474
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
398 458
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
CIP - Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0xE (14)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0x1C (28)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0x14 (20)
Profibus
Index
12 4014 float
- - - - 4028 uint
- - - - 4020 uint
Parameter
ID
Data
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
RWES
RWES
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 95 • Chapter 4 Setup Page
Page 100

Display
i.Ca
i.CA
ain
Ain
i.Er
i.Er
Parameter Name
Description
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Calibration Offset *
Offset the input
reading to compensate for lead
wire resistance
or other factors
that cause the
input reading to
vary from the
actual process
value.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Value *
View the process
value.
Note:
Ensure that the
Error Status (below) indicates no
error (61) when
reading this value using a field
bus protocol. If
an error exists,
the last known
value prior to
the error occurring will be
returned.
Analog Input (1
to 4)
Input Error *
View the cause
of the most recent error.
RMC Module • Setup Page
Range Default
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or units
-1,110.555 to
5,555.000°C
-1,999.000 to
9,999.000°F or units
-1,128.000 to
5,537.000°C
nonE None (61)
OpEn Open (65)
shrt Shorted (127)
E.ЛЏ Measurement Error
(140)
E.CaL Bad Calibration
Data (139)
Er.ab Ambient Error (9)
E.rtd RTD Error (141)
faiL Fail (32)
0.0
- - - -
- - - -
Modbus
Relative Ad-
dress
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
382 442
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
360 420
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
Instance 1
Map 1 Map 2
362 422
Map 1 Offset
to next instance equals
+90
Map 2 Offset
to next instance equals
+100
CIP - Class
Instance
Attribute
hex (dec)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
0xC (12)
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
1
0x68 (104)
1 to 4
2
Data
Pa-
eter
ID
Type
and
Access
**
RWES
R
R
Profibus
Index
2 4012 float
0 4001 float
1 4002 uint
ram-
* These parameters/prompts are available in these menus with firmware revisions 6.0 and above.
** R: Read, W: Write, E: EEPROM, S: User Set
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RMC Module • 96 • Chapter 4 Setup Page
 Loading...
Loading...