Watchguard Firebox X5, Firebox X50, Firebox X10E-W, Firebox X15-W, Firebox X20E-W User Manual
...
®
WatchGuard
®
Firebox
X Edge
User Guide
Firebox X Edge - Firmware Version 7.5
All Firebox X Edge Standard and Wireless Models

Notice to Users
Information in this guide is subject to change without notice. Companies, names, and data used in
examples herein are fictitious unless otherwise noted. No part of this guide may be reproduced or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the express
written permission of WatchGuard Technologies, Inc.
Copyright, Trademark, and Patent Information
Copyright© 1998 - 2005 WatchGuard Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Complete copyright, trademark, patent, and licensing
information can be found in an appendix at the end of this
book. You can also find it online at:
http://www.watchguard.com/help/documentation/
All trademarks or trade names mentioned herein, if any, are the property of their respective
owners.
This product is for indoor use only.
WatchGuard Firebox Software
End-User License Agreement
IMPORTANT - READ CAREFULLY BEFORE ACCESSING WATCHGUARD SOFTWARE:
This Firebox Software End-User License Agreement (“AGREEMENT”) is a legal agreement between you
(either an individual or a single entity) and WatchGuard Technologies, Inc. (“WATCHGUARD”) for the
WATCHGUARD Firebox software product, which includes computer software components (whether
installed separately on a computer workstation or on the WATCHGUARD hardware product or included on
the WATCHGUARD hardware product) and may include associated media, printed materials, and on-line or
electronic documentation, and any updates or modifications thereto, including those received through the
WatchGuard LiveSecurity Service (or its equivalent), (the “SOFTWARE PRODUCT”). WATCHGUARD is willing
to license the SOFTWARE PRODUCT to you only on the condition that you accept all of the terms contained
in this Agreement. Please read this Agreement carefully. By installing or using the SOFTWARE PRODUCT you
agree to be bound by the terms of this Agreement. If you do not agree to the terms of this AGREEMENT,
WATCHGUARD will not license the SOFTWARE PRODUCT to you, and you will not have any rights in the
SOFTWARE PRODUCT. In that case, promptly return the SOFTWARE PRODUCT, along with proof of payment,
to the authorized dealer from whom you obtained the SOFTWARE PRODUCT for a full refund of the price
you paid. The WATCHGUARD hardware product is subject to a separate agreement and limited hardware
warranty included with the WATCHGUARD hardware product packaging and/or in the associated user
documentation.
1. Ownership and License. The SOFTWARE PRODUCT is protected by copyright laws and international
copyright treaties, as well as other intellectual property laws and treaties. This is a license agreement and
NOT an agreement for sale. All title and copyrights in and to the SOFTWARE PRODUCT (including but not
limited to any images, photographs, animations, video, audio, music, text, and applets incorporated into
the SOFTWARE PRODUCT), the accompanying printed materials, and any copies of the SOFTWARE
PRODUCT are owned by WATCHGUARD or its licensors. Your rights to use the SOFTWARE PRODUCT are as
specified in this AGREEMENT, and WATCHGUARD retains all rights not expressly granted to you in this
ii WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

End-User License Agreement
AGREEMENT. Nothing in this AGREEMENT constitutes a waiver of our rights under U.S. copyright law or
any other law or treaty.
2. Permitted Uses. You are granted the following rights to the SOFTWARE PRODUCT:
(A) You may install and use the SOFTWARE PRODUCT on any single WATCHGUARD hardware product at
any single location and may install and use the SOFTWARE PRODUCT on multiple workstation computers.
(B) To use the SOFTWARE PRODUCT on more than one WATCHGUARD hardware product at once, you
must purchase an additional copy of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT for each additional WATCHGUARD hardware
product which you want to use it. To the extent that you install copies of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT on
additional WATCHGUARD hardware products in accordance with the prior sentence without installing the
additional copies of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT included with such WATCHGUARD hardware products, you
agree that use of any software provided with or included on the additional WATCHGUARD hardware
products that does not require installation will be subject to the terms and conditions of this AGREEMENT.
You must also maintain a current subscription to the WatchGuard LiveSecurity Service (or its equivalent)
for each additional WATCHGUARD hardware product on which you will use a copy of an updated or
modified version of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT received through the WatchGuard LiveSecurity Service (or its
equivalent).
(C) In addition to the copies described in Section 2(A), you may make a single copy of the SOFTWARE
PRODUCT for backup or archival purposes only.
3. Prohibited Uses. You may not, without express written permission from WATCHGUARD:
(A) Use, copy, modify, merge or transfer copies of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT or printed materials except
as provided in this AGREEMENT;
(B) Use any backup or archival copy of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT (or allow someone else to use such a
copy) for any purpose other than to replace the original copy in the event it is destroyed or becomes
defective;
(C) Sublicense, lend, lease or rent the SOFTWARE PRODUCT;
(D) Transfer this license to another party unless
(i) the transfer is permanent,
(ii) the third party recipient agrees to the terms of this AGREEMENT, and
(iii) you do not retain any copies of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT; or
(E) Reverse engineer, disassemble or decompile the SOFTWARE PRODUCT.
4. Limited Warranty. WATCHGUARD makes the following limited warranties for a period of ninety (90) days
from the date you obtained the SOFTWARE PRODUCT from WATCHGUARD or an authorized dealer:
(A) Media. The disks and documentation will be free from defects in materials and workmanship under
normal use. If the disks or documentation fail to conform to this warranty, you may, as your sole and
exclusive remedy, obtain a replacement free of charge if you return the defective disk or documentation to
WATCHGUARD with a dated proof of purchase.
(B) SOFTWARE PRODUCT. The SOFTWARE PRODUCT will materially conform to the documentation that
accompanies it. If the SOFTWARE PRODUCT fails to operate in accordance with this warranty, you may, as
your sole and exclusive remedy, return all of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT and the documentation to the
authorized dealer from whom you obtained it, along with a dated proof of purchase, specifying the
problems, and they will provide you with a new version of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT or a full refund, at their
election.
Disclaimer and Release. THE WARRANTIES, OBLIGATIONS AND LIABILITIES OF WATCHGUARD, AND YOUR
REMEDIES, SET FORTH IN PARAGRAPHS 4, 4(A) AND 4(B) ABOVE ARE EXCLUSIVE AND IN SUBSTITUTION
FOR, AND YOU HEREBY WAIVE, DISCLAIM AND RELEASE ANY AND ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, OBLIGATIONS
AND LIABILITIES OF WATCHGUARD AND ITS LICENSORS AND ALL OTHER RIGHTS, CLAIMS AND REMEDIES
YOU MAY HAVE AGAINST WATCHGUARD AND ITS LICENSORS, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, ARISING BY LAW OR
User Guide iii

OTHERWISE, WITH RESPECT TO ANY NONCONFORMANCE OR DEFECT IN THE SOFTWARE PRODUCT
(INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY ARISING FROM COURSE OF PERFORMANCE, COURSE OF
DEALING, OR USAGE OF TRADE, ANY WARRANTY OF NONINFRINGEMENT, ANY WARRANTY THAT THE
SOFTWARE PRODUCT WILL MEET YOUR REQUIREMENTS, ANY WARRANTY OF UNINTERRUPTED OR ERRORFREE OPERATION, ANY OBLIGATION, LIABILITY, RIGHT, CLAIM OR REMEDY IN TORT, WHETHER OR NOT
ARISING FROM THE NEGLIGENCE (WHETHER ACTIVE, PASSIVE OR IMPUTED) OR FAULT OF WATCHGUARD
AND ITS LICENSORS AND ANY OBLIGATION, LIABILITY, RIGHT, CLAIM OR REMEDY FOR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO,
OR CAUSED BY OR CONTRIBUTED TO BY, THE SOFTWARE PRODUCT).
Limitation of Liability. WATCHGUARD'S LIABILITY (WHETHER IN CONTRACT, TORT, OR OTHERWISE; AND
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY FAULT, NEGLIGENCE, STRICT LIABILITY OR PRODUCT LIABILITY) WITH REGARD TO
THE SOFTWARE PRODUCT WILL IN NO EVENT EXCEED THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID BY YOU FOR SUCH
PRODUCT. THIS SHALL BE TRUE EVEN IN THE EVENT OF THE FAILURE OF AN AGREED REMEDY. IN NO EVENT
WILL WATCHGUARD BE LIABLE TO YOU OR ANY THIRD PARTY, WHETHER ARISING IN CONTRACT
(INCLUDING WARRANTY), TORT (INCLUDING ACTIVE, PASSIVE OR IMPUTED NEGLIGENCE AND STRICT
LIABILITY AND FAULT), FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
(INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION LOSS OF BUSINESS PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, OR LOSS OF
BUSINESS INFORMATION) ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THIS WARRANTY OR THE USE OF OR
INABILITY TO USE THE SOFTWARE PRODUCT, EVEN IF WATCHGUARD HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. THIS SHALL BE TRUE EVEN IN THE EVENT OF THE FAILURE OF AN AGREED
REMEDY.
5. United States Government Restricted Rights. The SOFTWARE PRODUCT is provided with Restricted
Rights. Use, duplication or disclosure by the U.S. Government or any agency or instrumentality thereof is
subject to restrictions as set forth in subdivision (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer
Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013, or in subdivision (c)(1) and (2) of the Commercial Computer
Software -- Restricted Rights Clause at 48 C.F.R. 52.227-19, as applicable. Manufacturer is WatchGuard
Technologies, Inc., 505 5th Ave. South, Suite 500, Seattle, WA 98104.
6. Export Controls. You agree not to directly or indirectly transfer the SOFTWARE PRODUCT or
documentation to any country to which such transfer would be prohibited by the U.S. Export
Administration Act and the regulations issued thereunder.
7. Termination. This license and your right to use the SOFTWARE PRODUCT will automatically terminate if
you fail to comply with any provisions of this AGREEMENT, destroy all copies of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT in
your possession, or voluntarily return the SOFTWARE PRODUCT to WATCHGUARD. Upon termination you
will destroy all copies of the SOFTWARE PRODUCT and documentation remaining in your control or
possession.
8. Miscellaneous Provisions. This AGREEMENT will be governed by and construed in accordance with the
substantive laws of Washington excluding the 1980 United National Convention on Contracts for the
International Sale of Goods, as amended. This is the entire AGREEMENT between us relating to the
SOFTWARE PRODUCT, and supersedes any prior purchase order, communications, advertising or
representations concerning the SOFTWARE PRODUCT AND BY USING THE SOFTWARE PRODUCT YOU AGREE
TO THESE TERMS. IF THE SOFTWARE PRODUCT IS BEING USED BY AN ENTITY, THE INDIVIDUAL INDICATING
AGREEMENT TO THESE TERMS REPRESENTS AND WARRANTS THAT (A) SUCH INDIVIDUAL IS DULY
AUTHORIZED TO ACCEPT THIS AGREEMENT ON BEHALF OF THE ENTITY AND TO BIND THE ENTITY TO THE
TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT; (B) THE ENTITY HAS THE FULL POWER, CORPORATE OR OTHERWISE, TO ENTER
INTO THIS AGREEMENT AND PERFORM ITS OBLIGATIONS UNDER THIS AGREEMENT AD// (C) THIS
AGREEMENT AND THE PERFORMANCE OF THE ENTITY’S OBLIGATIONS UNDER THIS AGREEMENT DO NOT
VIOLATE ANY THIRD-PARTY AGREEMENT TO WHICH THE ENTITY IS A PARTY. No change or modification of
this AGREEMENT will be valid unless it is in writing and is signed by WATCHGUARD.
Version: 040226
iv WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

Firmware Version: 7.5
Part Number: 1776-0000
Guide Version: 7.5
Abbreviations Used in this Guide
3DES Triple Data Encryption Standard
BOVPN Branch Office Virtual Private Network
DES Data Encryption Standard
DNS Domain Name Service
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DSL Digital Subscriber Line
IP Internet Protocol
Abbreviations Used in this Guide
IPSec Internet Protocol Security
ISDN Integrated Services Digital Network
ISP Internet Service Provider
MAC Media Access Control
MUVPN Mobile User Virtual Private Network
NAT Network Address Translation
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol
PPPoE Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
TCP Transfer Control Protocol
UDP User Datagram Protocol
URL Universal Resource Locator
VPN Virtual Private Network
WAN Wide Area Network
WSEP WatchGuard Security Event Processor
User Guide v

ADDRESS:
505 Fifth Avenue South
Suite 500
Seattle, WA 98104
ABOUT WATCHGUARD
WatchGuard network security solutions provide small- to
mid-sized enterprises worldwide with effective, affordable security. Our Firebox line of extendable, integrated
security appliances is designed to be fully upgradeable
as an organization grows, and to deliver the industry's
SUPPORT:
www.watchguard.com/support
support@watchguard.com
U.S. and Canada +877.232.3531
All Other Countries +1.206.613.0456
best combination of security, performance, intuitive
interface, and value. WatchGuard Intelligent Layered
Security architecture protects against emerging threats
effectively and efficiently, and provides the flexibility to
integrate additional security functionality and services
offered through WatchGuard. Every WatchGuard product
comes with an initial LiveSecurity Service subscription
SALES:
U.S. and Canada +1.800.734.9905
All Other Countries +1.206.521.8340
to help customers stay on top of security with vulnerability alerts, software updates, expert security instruction,
and superior customer care.
FOR MORE INFORMATION: Please visit us at
www.watchguard.com or contact your reseller for more
information.
vi WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

Contents
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Network Security ........................1
Network Security .....................................................................1
About Networks .......................................................................2
Clients and servers ...............................................................2
Connecting to the Internet .......................................................2
Protocols .................................................................................3
How Information Travels on the Internet ...................................4
IP Addresses ...........................................................................5
Network addressing ..............................................................5
About DHCP .........................................................................5
About PPPoE ........................................................................5
Domain Name Service (DNS) ...................................................6
Services ..................................................................................6
Ports .......................................................................................6
Firewalls ..................................................................................8
Firebox® X Edge and Your Network ..........................................9
CHAPTER 2
Package Contents .................................................................11
Installation Requirements ......................................................12
Identifying Your Network Settings ...........................................13
User Guide vii
Installing the Firebox X Edge ...........................11
About network addressing ...................................................13
Static addresses, DHCP, and PPPoE ......................................13

Finding your TCP/IP properties ............................................14
Finding PPPoE settings .......................................................17
Disabling the HTTP Proxy Setting ...........................................17
Connecting the Firebox X Edge ...............................................19
Connecting the Edge to more than seven devices ...................20
Setting Your Computer to Connect to the Edge .......................22
If your computer gets its address from DHCP .........................22
If your computer has a static IP address ...............................23
Using the Quick Setup Wizard ................................................24
Registering and Activating LiveSecurity Service ......................26
CHAPTER 3
Navigating the Firebox X Edge Configuration Pages
...................................................................29
Navigating the Configuration Pages ........................................30
Using the navigation bar ......................................................31
Configuration Overview ..........................................................32
Firebox System Status Page .................................................32
Network Page .....................................................................33
Administration Page ............................................................34
Firewall Page .....................................................................35
Logging Page .....................................................................37
WebBlocker Page ................................................................38
VPN Page ..........................................................................38
Wizards Page .....................................................................39
CHAPTER 4
Factory Default Settings ........................................................41
Restarting the Firebox ...........................................................43
Selecting HTTP or HTTPS for Management .............................44
Changing the HTTP Server Port ..............................................45
Setting up WatchGuard System Manager Access ...................46
Updating the Firebox X Edge Software ....................................52
Activating Upgrade Options ....................................................54
Configuration and Management Basics ............41
Resetting the Firebox to the factory-default settings ...............42
Local restart ......................................................................43
Remote reboot ...................................................................44
Enable remote management with WSM v8.2 or higher ............46
Enable remote management with WSM v8.0 or v8.1 ..............48
Enable remote management with WSM v7.3 or earlier ...........50
Method 1 - Installing software automatically ..........................52
Method 2 - Installing software manually ................................53
viii WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

Enabling the Model Upgrade Option .......................................56
Viewing the Configuration File ................................................57
CHAPTER 5
Changing Your Network Settings ......................59
Using the Network Setup Wizard ............................................59
Configuring the External Network ...........................................60
If your ISP uses DHCP .........................................................61
If your ISP uses static IP addresses ......................................62
If your ISP uses PPPoE ........................................................63
Configuring the Trusted Network ............................................66
Changing the IP address of the trusted network .....................67
Using DHCP on the trusted network ......................................68
Setting trusted network DHCP address reservations ...............69
Configuring the trusted network for DHCP relay .....................70
Using static IP addresses for trusted computers ....................71
Adding computers to the trusted network ..............................71
Configuring the Optional Network ...........................................72
Enabling the optional network ..............................................73
Changing the IP address of the optional network ...................73
Using DHCP on the optional network ....................................74
Setting optional network DHCP address reservations ..............75
Configuring the optional network for DHCP relay ....................76
Using static IP addresses for optional computers ...................77
Adding computers to the optional network ............................77
Making Static Routes ............................................................78
Viewing Network Statistics ....................................................80
Registering with the Dynamic DNS Service ............................81
Enabling the WAN Failover Option ..........................................83
Using the WAN Failover Setup Wizard ...................................84
Using the Network page ......................................................85
If you are using a broadband connection for failover ..............85
If you are using an external modem for failover .....................87
Dial-up DNS settings ...........................................................88
Dial-up settings ..................................................................88
CHAPTER 6
Firebox X Edge Wireless Setup .......................89
Connecting to the Firebox X Edge Wireless ............................90
Using the Wireless Network Wizard ........................................90
Configuring Basic Wireless Settings .......................................91
Selecting the wireless network assignment ...........................91
Setting the SSID .................................................................92
User Guide ix

Setting the operating region and channel ..............................93
Controlling SSID broadcasts ................................................93
Logging authentication events .............................................93
Setting the wireless mode ...................................................93
Setting the fragmentation threshold .....................................94
Configuring Wireless Security Settings ...................................94
Setting the wireless authentication method ...........................96
Configuring encryption ........................................................96
Configuring wireless clients to use MUVPN ............................97
Restricting Wireless Access by MAC Address .........................97
Configuring Wireless Guest Services .....................................99
Enabling guest services ......................................................99
Setting password protection ..............................................100
Setting network access rules for guests ..............................100
Connecting to the Firebox as a wireless guest .....................101
Configuring the Wireless Card on Your Computer .................101
CHAPTER 7
Configuring Firewall Settings .........................103
About Services ....................................................................103
Incoming and outgoing traffic ............................................104
Traffic through VPN tunnels ...............................................104
About This Chapter ..............................................................104
Configuring Incoming Services .............................................105
Configuring common services for incoming traffic ................106
About custom services for incoming traffic ..........................107
Adding a custom service using the wizard ...........................107
Adding a custom incoming service manually ........................108
Filtering incoming traffic for ser vices ..................................110
Filtering outgoing traffic for services ...................................110
Configuring Outgoing Services .............................................111
Configuring common services for outgoing traffic .................112
About custom services for outgoing traffic ...........................113
Adding a custom service using the wizard ...........................113
Adding a custom outgoing service manually ........................114
Filtering incoming traffic for ser vices ..................................116
Filtering outgoing traffic for services ...................................116
Services for the Optional Network ........................................116
Controlling traffic from the trusted to optional network .........117
Disabling traffic filters .......................................................118
Blocking External Sites ........................................................119
x WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

Configuring Firewall Options .................................................120
Responding to ping requests .............................................120
Denying FTP access to the Firebox X Edge ...........................121
SOCKS implementation for the Firebox X Edge .....................121
Logging all allowed outgoing traffic .....................................123
Changing the MAC address of the external interface ............123
CHAPTER 8
Configuring Logging and System Time ............125
Viewing Log Messages ........................................................125
Log to a WatchGuard Log Server ..........................................126
Logging to a Syslog Host .....................................................128
Setting the System Time .....................................................129
CHAPTER 9
Managing Users and Groups .........................133
Seeing Current Sessions and Users ....................................133
Firebox Users Settings ......................................................134
Active Sessions ................................................................134
Stopping a session ...........................................................135
Local User Accounts .........................................................136
About User Licenses ...........................................................137
About User Authentication ...................................................137
Setting authentication options for all users .........................138
Configuring MUVPN client settings ......................................140
Authenticating to the Edge ................................................141
Using Local Firebox Authentication ......................................142
Creating a read-only administrative account ........................144
Setting a WebBlocker profile for a user ...............................145
Enabling MUVPN for a user ...............................................145
The Administrator account .................................................145
Changing a user account name or password .......................146
Using LDAP/Active Directory Authentication .........................146
Configuring the LDAP/Active Directory authentication service 147
Using the LDAP authentication test feature .........................149
Configuring groups for LDAP authentication ........................150
Adding a group .................................................................150
Setting a WebBlocker profile for a user ...............................152
LDAP Authentication and MUVPN .......................................152
Allowing Internal Hosts to Bypass User Authentication .........152
CHAPTER 10
Configuring WebBlocker ................................155
How WebBlocker Works .......................................................155
Configuring Global WebBlocker Settings ...............................155
User Guide xi

Creating WebBlocker Profiles ...............................................159
WebBlocker Categories ........................................................161
Allowing Certain Sites to Bypass WebBlocker .......................171
Blocking Additional Web Sites ..............................................172
Bypassing WebBlocker .........................................................173
CHAPTER 11
Configuring Virtual Private Networks ..............175
About This Chapter ..............................................................175
What You Need to Create a VPN ..........................................176
Managed VPN ......................................................................177
Manual VPN: Setting Up Manual VPN Tunnels ......................178
What you need for Manual VPN ..........................................178
Phase 1 settings ..............................................................181
Phase 2 settings ..............................................................184
VPN Keep Alive ....................................................................186
Viewing VPN Statistics .........................................................187
Frequently Asked Questions .................................................187
CHAPTER 12
Configuring the MUVPN Client .......................191
About This Chapter ..............................................................192
Enabling MUVPN for Edge Users ..........................................193
Configuring MUVPN client settings ......................................193
Enabling MUVPN access for a Firebox user account .............194
Configuring the Firebox for MUVPN clients using a Pocket PC 196
Distributing the Software and the .wgx File ..........................196
Preparing Remote Computers for MUVPN ............................197
WINS and DNS servers .....................................................198
Windows NT setup ............................................................198
Windows 2000 setup ........................................................200
Windows XP setup ............................................................202
Installing and Configuring the MUVPN Client ........................204
Installing the MUVPN client ................................................204
Uninstalling the MUVPN client ............................................206
Connecting and Disconnecting the MUVPN Client .................207
Connecting the MUVPN client ............................................207
The MUVPN client icon ......................................................207
Allowing the MUVPN client through a personal firewall ..........208
Disconnecting the MUVPN client ........................................209
Monitoring the MUVPN Client Connection ............................209
Using Log Viewer ..............................................................210
xii WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

Using Connection Monitor .................................................210
The ZoneAlarm Personal Firewall .........................................211
Allowing traffic through ZoneAlarm .....................................211
Shutting down ZoneAlarm .................................................212
Uninstalling ZoneAlarm .....................................................212
Using MUVPN on the Edge Wireless Network .......................213
Tips for Configuring the Pocket PC .......................................214
Troubleshooting Tips ............................................................216
APPENDIX A
Firebox X Edge Hardware ..............................219
Package Contents and Specifications ..................................219
Hardware Description ..........................................................221
Front panel ......................................................................221
Rear view ........................................................................223
Side panels .....................................................................223
About IEEE 802.11g/b Wireless ..........................................224
Noise level .......................................................................224
Signal strength (Watts) ......................................................225
Channel bandwidth ...........................................................226
APPENDIX B
Legal Notifications .......................................229
Copyright, Trademark, and Patent Information ......................229
Certifications and Notices ...................................................233
Declaration of Conformity ....................................................236
Limited Hardware Warranty ..................................................237
User Guide xiii

xiv WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

CHAPTER 1 Introduction to
Network Security
Thank you for your purchase of the WatchGuard® Firebox® X Edge.
This security device helps protect your computer network from threat
and attack.
This chapter gives you basic information about networks and network
security. This information can help you when you configure the Edge.
If you are experienced with computer networks, we recommend that
you go to the subsequent chapter.
Network Security
While the Internet gives you access to a large quantity of information
and business opportunity, it also opens your network to attackers. A
good network security policy helps you find and prevent attacks to
your computer or network.
Many people think that their computer holds no important information. They do not think that their computer is a target for a hacker.
This is not correct. A hacker can use your computer as a platform to
attack other computers or networks or use your account information
to send e-mail spam or attacks. Your account information is also vulnerable and valuable to hackers.
User Guide 1

Introduction to Network Security
About Networks
A network is a group of computers and other devices that are connected to each other. It can be two computers that you connect
with a serial cable, or many computers around the world connected
through the Internet. Computers on the same network can do work
together and share data.
A LAN (Local Area Network) is a connected group of computers that
use the same method of communication to share data.
A WAN (Wide Area Network) is a connected group of computers that
can be far apart in different locations.
Clients and servers
Clients and servers are components of a network. A server is a computer that makes its resources available to the network. Some of
these resources are documents, printers, and programs. A client is a
computer that uses the resources made available by the server.
Connecting to the Internet
ISPs (Internet service providers) are companies that give access to
the Internet through network connections. Bandwidth is the rate at
which a network connection can send data: for example, 3 megabits
per second (Mbps).
A high-speed Internet connection, such as a cable modem or a DSL
(Digital Subscriber Line), is known as a broadband connection.
Broadband connections are much faster than dial-up connections:
the bandwidth of a dial-up connection is less than .1 Mbps, while a
cable modem can be 5 Mbps or more.
Typical speeds for cable modems are usually lower than the maximum speeds, because each person in a neighborhood is a member of
a LAN. Each computer in that LAN uses some of the bandwidth.
Because of this “shared-medium” system, cable modem connections
can become slow when more users are on the network.
DSL connections supply constant bandwidth, but they are usually
slower than cable modem connections. Also, the bandwidth is only
constant between your home or office and the DSL central office.
The DSL central office cannot supply a constant connection to a
Web site or network.
2 WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

Protocols
A protocol is a group of rules that allow computers to connect
across a network. Protocols are the “grammar” that computers use
to speak to each other.
The standard protocol when you connect to the Internet is the IP
(Internet Protocol). This protocol is the usual language of computers
on the Internet.
A protocol also tells how data is sent through a network. The most
frequently used protocols are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). Other protocols are less frequently used.
TCP/IP is the basic protocol used by computers that connect to the
Internet. You must know some settings of TCP/IP when you set up
your Firebox® X Edge. For more information on TCP/IP, see “Finding
your TCP/IP properties” on page 15.
Protocols
User Guide 3
Introduction to Network Security
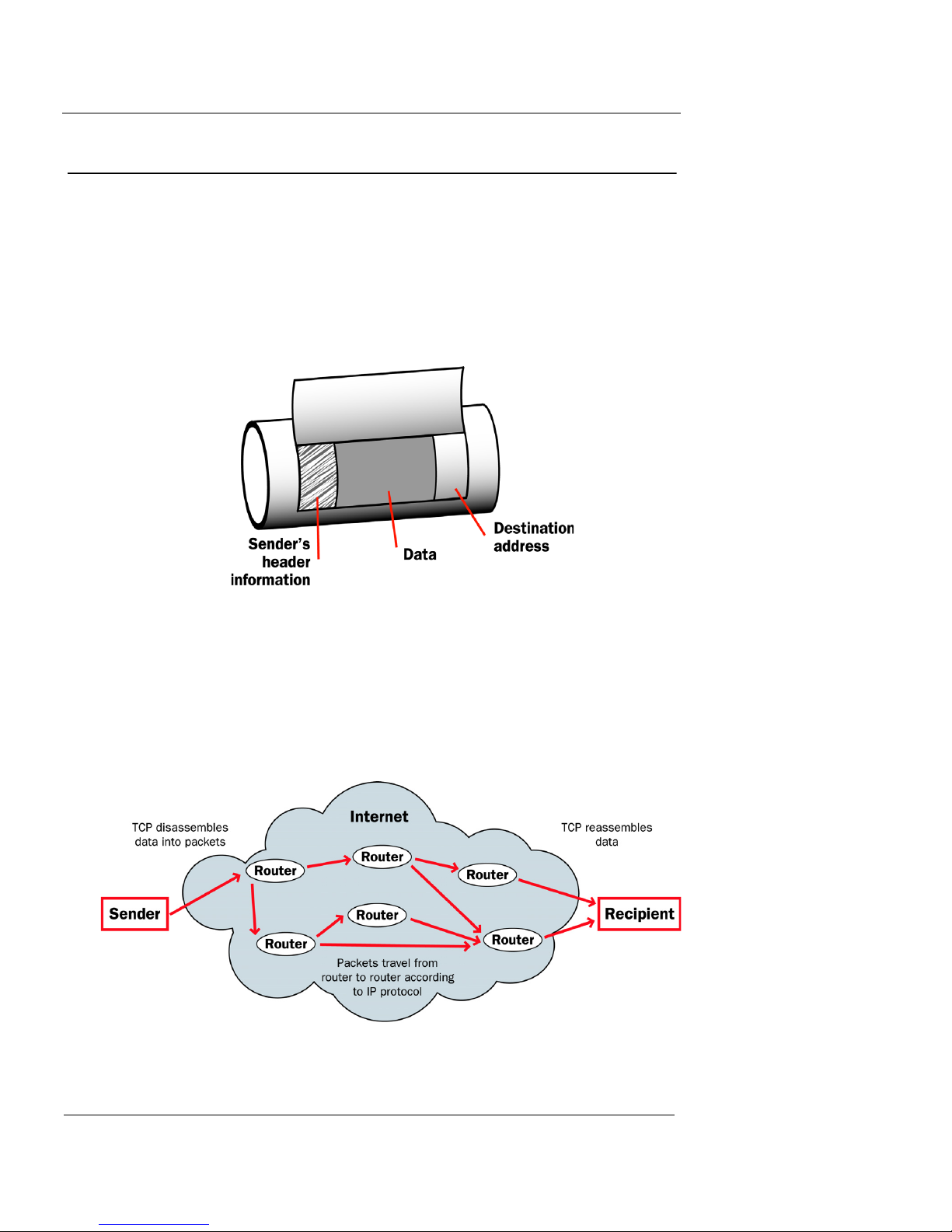
How Information Travels on the Internet
The data that you send through the Internet is cut into units, or
packets. Each packet includes the Internet address of the destination. The packets that make up a connection can use different
routes through the Internet. When they all get to their destination,
they are assembled back into a file. To make sure that the packets
get to the destination, address information is added to the packets.
Data packet
The TCP and IP protocols are used to send and receive these packets.
TCP disassembles the data and assembles it again. IP adds information to the packets, such as the sender, the recipient, and any special
instructions.
Packets traveling on the Internet
4 WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

IP Addresses
To send mail to a person, you must first know their physical address.
For a computer to send data to a different computer, it must first
know the address of that computer. A computer address is known as
an IP address. Only one device can use an IP address at a time.
An IP address is a group of four numbers divided by decimal points.
Some examples of IP addresses are:
• 192.168.0.11
• 10.1.20.18
• 208.15.15.15
Network addressing
ISPs (Internet service providers) assign an IP address to each device
on their network. The IP address can be static or dynamic. Each ISP
has a small number of IP addresses.
IP Addresses
Static IP addresses are permanently assigned to a device. These
addresses do not change automatically, and are frequently used for
servers.
Dynamic IP addresses change with time. If a dynamic address is not
in use, it can be automatically assigned to a different device.
Your ISP can tell you how their system assigns IP addresses.
About DHCP
Many ISPs assign dynamic IP addresses through DHCP (Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol). When a computer connects to the
network, a DHCP server at the ISP assigns that computer an IP
address. It is not necessary to assign IP addresses manually when
you use DHCP.
About PPPoE
Some ISPs assign their IP addresses through Point-to-Point Protocol
over Ethernet (PPPoE). PPPoE expands a standard dial-up connection to add some of the features of Ethernet and PPP. This system
allows the ISP to use the billing, authentication, and security systems of their dial-up infrastructure with DSL modem and cable
modem products.
User Guide 5

Introduction to Network Security
Domain Name Service (DNS)
If you do not know the address of a person, you can frequently find
it in the telephone directory. On the Internet, the equivalent to a
telephone directory is the DNS (Domain Name Service). Each Web
site has a domain name (such as “mysite.com”) that is equal to an IP
address. When you type a domain name to show a Web site, your
computer gets the IP address from a DNS server.
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) includes a domain name and a
protocol. An example of a URL is:
http://www.watchguard.com/
Services
A service opens access from your network to a computer that is
external to your network. You use services to send e-mail or move
files from one computer to a different computer through the network. These services use protocols. Frequently used Internet services
are:
Ports
• World Wide Web access uses Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
• E-mail uses Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
• File transfer uses File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
• Changing a domain name to an Internet address uses Domain
Name Service (DNS)
• Remote terminal access uses Telnet or SSH (Secure Shell)
Some services are necessary, but each service you add to your security policy can also add a security risk. To send and receive data, you
must “open a door” in your computer, which puts your network at
risk. Attackers can use open access of a service to try to get into a
network. We recommend that you only add services that are necessary for your business.
Usually, a port is a connection point where you use a socket and a
plug to connect two devices. Computers also have ports that are not
physical locations. These ports are where programs transmit data.
6 WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

Ports
Some protocols, such as HTTP, have ports with assigned numbers.
For example, most computers transmit e-mail on port 25 because
the SMTP protocol is assigned to port 25. Other programs are
assigned port numbers dynamically for each connection. The IANA
(Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) keeps a list of well known
ports. You can see this list at www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers.
Most services are given a port number in the range from 0 to 1024,
but possible port numbers range from 0 to 65535.
User Guide 7
Introduction to Network Security
Firewalls
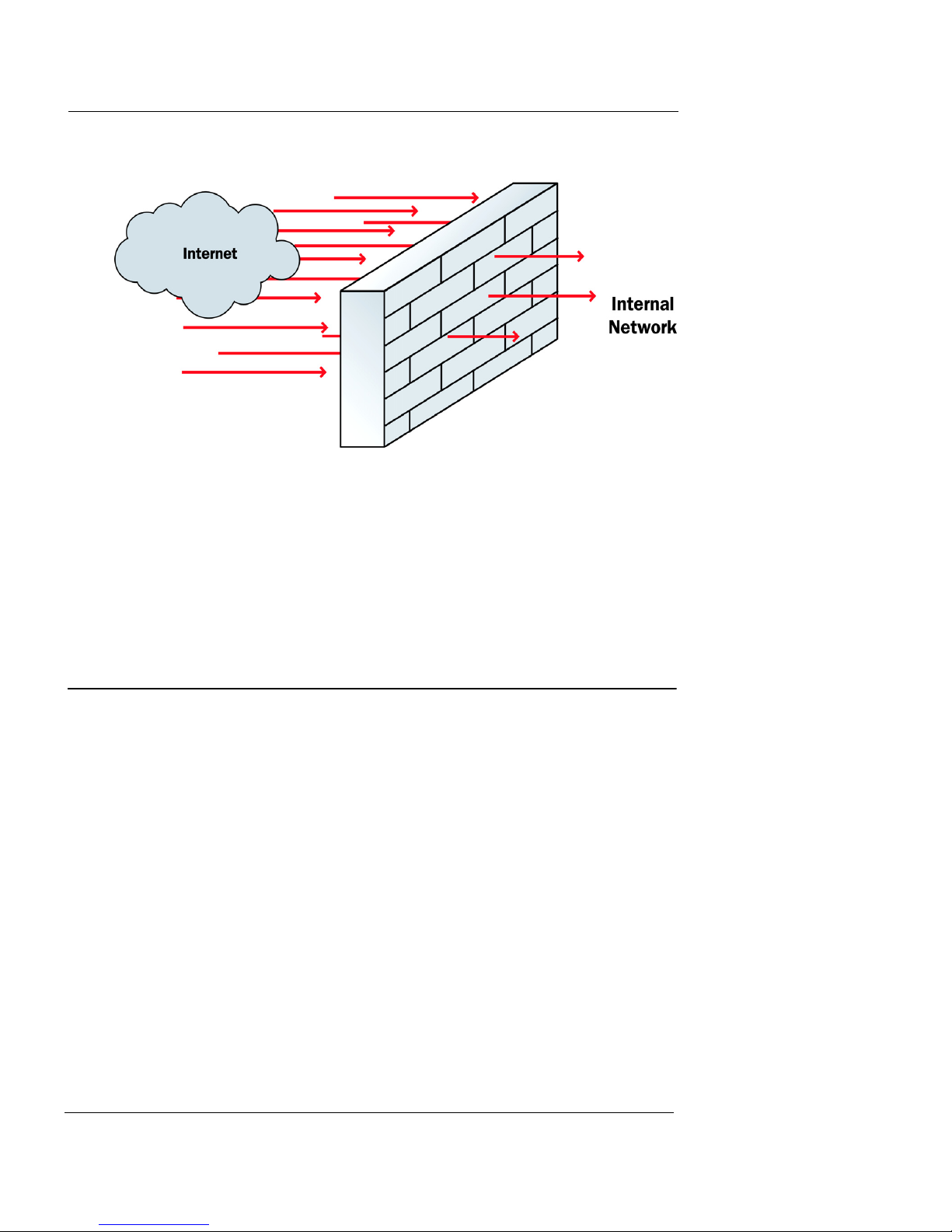
A firewall divides your internal network from the Internet to
decrease risk from an external attack. We refer to the computers and
networks on the Internet as the external network. The computers on
the internal side of the firewall are protected. We refer to these as
trusted computers. The figure below shows how a firewall divides
the trusted computers from the Internet.
Firewalls use access policies to identify different types of information. They can also control which services or ports the protected
computers can use on the Internet (outbound access). Many firewalls have sample security policies and users can select the policy
that is best for them. With others—such as the Firebox® X Edge—the
user can customize these policies.
8 WatchGuard Firebox X Edge
Firebox® X Edge and Your Network
Firewalls can be in the form of hardware or software. They can
prevent unauthorized Internet users from accessing private
networks connected to the Internet. All messages that enter or
go out of the trusted or protected networks go through the
firewall, which examines each message and denies those that do
not match the security criteria.
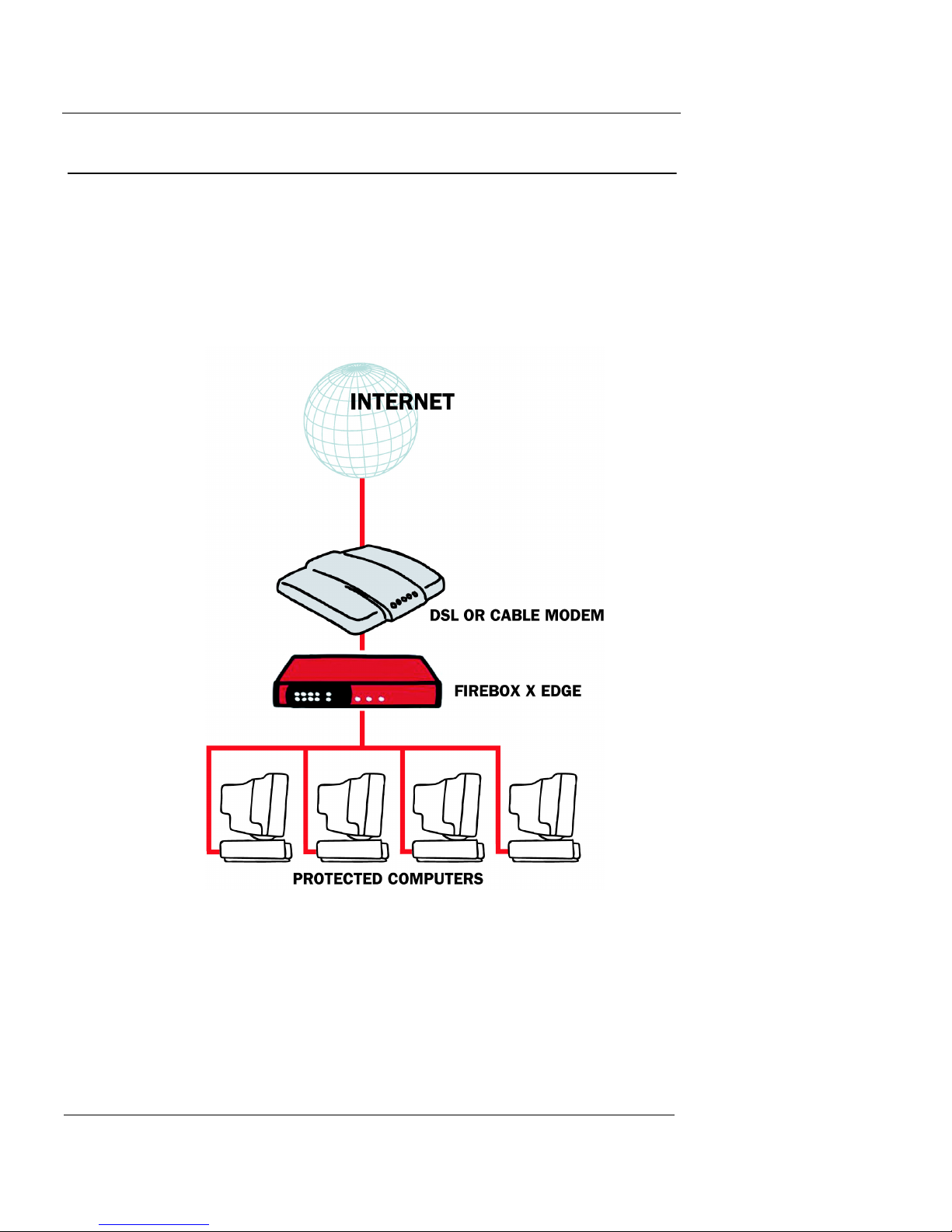
Firebox® X Edge and Your Network
The Firebox® X Edge controls all traffic between the external network and the trusted network. The Edge also includes an optional
network. Use the optional network for computers with “mixed
trust.” For example, customers frequently use the optional network
for their remote users or for public servers such as a Web server or email server. Your firewall can stop all suspicious traffic from the
external network to your trusted and optional networks. The rules
and policies that identify the suspicious traffic appear in Chapter 7,
“Configuring Firewall Settings.”
The Firebox X Edge is a firewall for small and remote offices. Customers who purchase an Edge frequently do not know much about
computer networks or network security. There are wizards and many
self-help tools for these customers. Advanced customers can use
integration features to connect an Edge to a larger wide area net-
User Guide 9

Introduction to Network Security
work. The Edge connects to a cable modem, DSL modem, or ISDN
router.
The Web-based user interface of the Firebox X Edge lets you manage your network safely. You can manage your Edge from different
locations and at different times. It gives you more time and
resources to use on other components of your business.
10 WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

CHAPTER 2 Installing the
Firebox X Edge
To install the WatchGuard® Firebox® X Edge in your network, you must
complete these steps:
• Identify and record the TCP/IP properties for your Internet
connection.
• Disable the HTTP proxy properties of your Web browser.
• Connect the Firebox X Edge to your network.
• Connect your computer to the Edge.
• Use the Quick Setup Wizard to configure the Edge.
• Activate the LiveSecurity® Service.
Package Contents
Make sure that the package for your Firebox® X Edge includes these
items:
• The Firebox X Edge QuickStart Guide
• A LiveSecurity® Service activation card
• A Hardware Warranty Card
• An AC power adapter (12 V)
User Guide 11

Installing the Firebox X Edge
• A power cable clip
Use this clip to attach the cable to the side of the Edge. It decreases the
tension on the power cable.
• One straight-through Ethernet cable
• A wall mount plate (Wireless models only)
• Two antennae (Wireless models only)
Installation Requirements
The Firebox® X Edge installation requirements are:
• A computer with a 10/100BaseT Ethernet network interface
card to configure the Firebox.
• A Web browser. You can use Netscape 7.0 (or later), Internet
Explorer 6.0 (or later), or an equivalent browser.
• The serial number of the Firebox X Edge.
You can find the serial number on the bottom of the Firebox. You use
the serial number to register the Edge.
12 WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

Identifying Your Network Settings
• An Internet connection.
The external network connection can be a cable or DSL modem with a
10/100BaseT port, an ISDN router, or a direct LAN connection. If you
have problems with your Internet connection, call your ISP (Internet
Service Provider) to correct the problem before you install the Firebox X
Edge.
Identifying Your Network Settings
You use an ISP (Internet Service Provider) to connect to the Internet.
An ISP assigns your computer or firewall an IP (Internet Protocol)
address. The IP address can be static or dynamic, and this address
lets you connect to Web sites on the Internet.
About network addressing
You must ask your ISP or corporate network administrator how your
computer gets its external IP address. Use the same method to connect to the Internet with the Edge that you use with your computer.
If you connect your computer directly to the Internet with a broadband connection, you can put the Firebox® X Edge between your
computer and the Internet and use the network configuration from
your computer to configure the Edge external interface. You can use
a static IP address, DHCP, or PPPoE to configure the Edge external
interface.
You must also configure your computer to connect with a Web
browser to configure and manage the Edge. Your computer must
have an IP address in a range that is the same as the Edge. In the
factory default configuration, the Edge assigns your computer an IP
address with DHCP. You can set your computer to use DHCP and
you can then connect to the Edge to manage it. You can also give
your computer a static IP address that is in the range of the trusted
network on the Edge. For information on setting your computer to
connect to the Edge, see “Setting Your Computer to Connect to the
Edge” on page 22.
Static addresses, DHCP, and PPPoE
Your ISP gives you an IP address using one of these methods:
• Static: A static IP address is an IP address that always stays the
same. If you have a Web server, FTP server, or other Internet
resource that must have an address that cannot change, you can
User Guide 13

Installing the Firebox X Edge
get a static IP address from your ISP. A static IP address can cost
more money than a dynamic IP address.
•DHCP: A dynamic IP address is an IP address that an ISP lets
you use temporarily. ISPs use DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol) to assign you a dynamic IP address.
With DHCP, your computer does not always use the same IP
address. Each time you connect to the ISP, a DHCP server
assigns you an IP address. It could be the same IP address you
had before, or it could be a new IP address. When you close an
Internet connection that uses a dynamic IP address, the ISP can
assign that IP address to a different customer.
• PPPoE: An ISP can also use PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over
Ethernet) to assign you an IP address. Usually, a PPPoE address
is dynamic. You must have a user name and a password to use
PPPoE.
The ISP also assigns a subnet mask (also known as the netmask) to a
computer. A subnet mask divides a larger network into smaller net-
works. A subnet mask is a string of bits that “mask” one section of
an IP address to show how many IP addresses can be on the smaller
network.
Read your DSL or cable modem instructions or speak to your ISP to
learn if you have a dynamic IP address or a static IP address.
Finding your TCP/IP properties
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is the primary protocol computers use to connect to the Internet. To use
TCP/IP, your computer must have an IP address and information
about the computer network of your ISP. You must have this information to install your Firebox X Edge.
N
OTE
N
OTE
If your ISP assigns your computer an IP address that starts with
10, 192.168, or 172.16 to 172.31, then your ISP uses NAT (Network
Address Translation) and your IP address is private. We recommend
that you get a public IP address for your Edge external IP address.
If you use a private IP address, you can have problems with some
features, including VPN.
14 WatchGuard Firebox X Edge

Identifying Your Network Settings
Your TCP/IP Properties Table
TCP/IP Property Value
IP Address
. . .
Subnet Mask
. . .
Default Gateway
. . .
DHCP Enabled Yes No
DNS Server(s) Primary
. . .
Secondary
. . .
User Guide 15

Installing the Firebox X Edge
To find your TCP/IP properties, use the instructions for your computer operating system.
Microsoft Windows 2000, Windows 2003 and
Windows XP
1 Click Start > Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
The Command Prompt window appears.
2 At the command prompt, type ipconfig /all and then press
Enter.
3 Record the values in Your TCP/IP Properties Table on page 15.
4 Close the window.
Microsoft Windows NT
1 Click Start > Programs > Command Prompt.
The Command Prompt window appears.
2 At the command prompt, type ipconfig /all and then press
Enter.
3 Record the values in Your TCP/IP Properties Table on page 15.
4 Close the window.
Microsoft Windows 98 or ME
1 Click Start > Run.
The Run window appears.
2 Type winipcfg and then press Enter.
The IP Configuration window appears.
3 Select the Ethernet Adapter from the drop-down list.
4 Click More Info for additional settings.
5 Record the values in Your TCP/IP Properties Table on page 15.
6 Close the window.
Macintosh OS 9
1 Click the Apple menu > Control Panels > TCP/IP.
2 Record the values in Your TCP/IP Properties Table on page 15.
3 Close the window.
16 WatchGuard Firebox X Edge
 Loading...
Loading...