Page 1

WatchGuard
®
Firebox™ System
Reference Guide
Firebox System 4.6
Page 2

Disclaimer
Information in this guide is subject to change without notice. Companies, names, and data used in
examples herein are fictitious unless otherwise noted. No part of this guide may be reproduced or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the
express written permission of WatchGuard Technologies, Inc.
Copyright and Patent Information
Copyright© 1998 - 2001 WatchGuard Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved.
WatchGuard, Firebox, LiveSecurity, and SpamScreen are either registered trademarks or
trademarks of WatchGuard Technologies, Inc. in the United States and other countries. This product
is covered by one or more pending patent applications.
All other trademarks and tradenames are the property of their respective owners.
Printed in the United States of America.
DocVer:WatchGuard Firebox System 4.6 Reference Guide - 4.6.1
ii
Page 3

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 Internet Protocol Reference ............................................. 1
Internet Protocol header ................................................................1
Internet Protocol options ............................................................... 5
Transfer protocols ...........................................................................5
Standard ports and random ports .................................................. 7
CHAPTER 2 Content Types ...................................................................9
Mime content types list .................................................................. 9
CHAPTER 3 Services and Ports ........................................................... 19
Ports used by WatchGuard products ............................................ 19
Ports used by Microsoft products ................................................. 20
Well-known services list ................................................................ 21
CHAPTER 4 WebBlocker Content ...................................................... 29
WebBlocker categories ................................................................ 29
Searching for Blocked Sites .......................................................... 31
CHAPTER 5 Resources .........................................................................33
Publishers .....................................................................................33
Books ............................................................................................34
White papers & requests for comments .......................................35
Mailing Lists .................................................................................. 35
Web Sites .....................................................................................35
Newsgroups .................................................................................37
User Guide iii
Page 4

CHAPTER 6 Firebox Read-Only System Area ....................................39
Initializing a Firebox using Hands-Free Installation ......................40
Initializing a Firebox using a serial cable ......................................40
Initializing a Firebox using a modem ............................................43
Initializing using remote provisioning ...........................................43
Managing flash disk memory ........................................................44
CHAPTER 7 Out-of-Band Initialization Strings ..................................47
PPP initialization strings ................................................................47
Modem initialization strings ..........................................................51
CHAPTER 8 Glossary ............................................................................55
Index ............................................................................................... 73
iv
Page 5

CHAPTER 1 Internet Protocol Reference
Internet Protocol (IP) specifies the format of packets and the addressing scheme for
sending data over the Internet. By itself, it functions like a postal system allowing you
to address a package and drop it into the system. There is, however, no direct link
between you and the recipient. In other words, there is no package.
Most networks combine IP with higher-level protocols like Transmission Control
Protocol (TCP). Unlike simple IP, TCP/IP establishes a connection between two host
servers so that they can send messages back and forth. TCP/IP provides the
“packaging.”
Internet Protocol header
Internet Protocol (IP) is an Internet standard and enables the shipment of datagrams
– self-contained packets of information that include their own address and delivery
instructions. IP prepends a header to each datagram. The IP header contains a
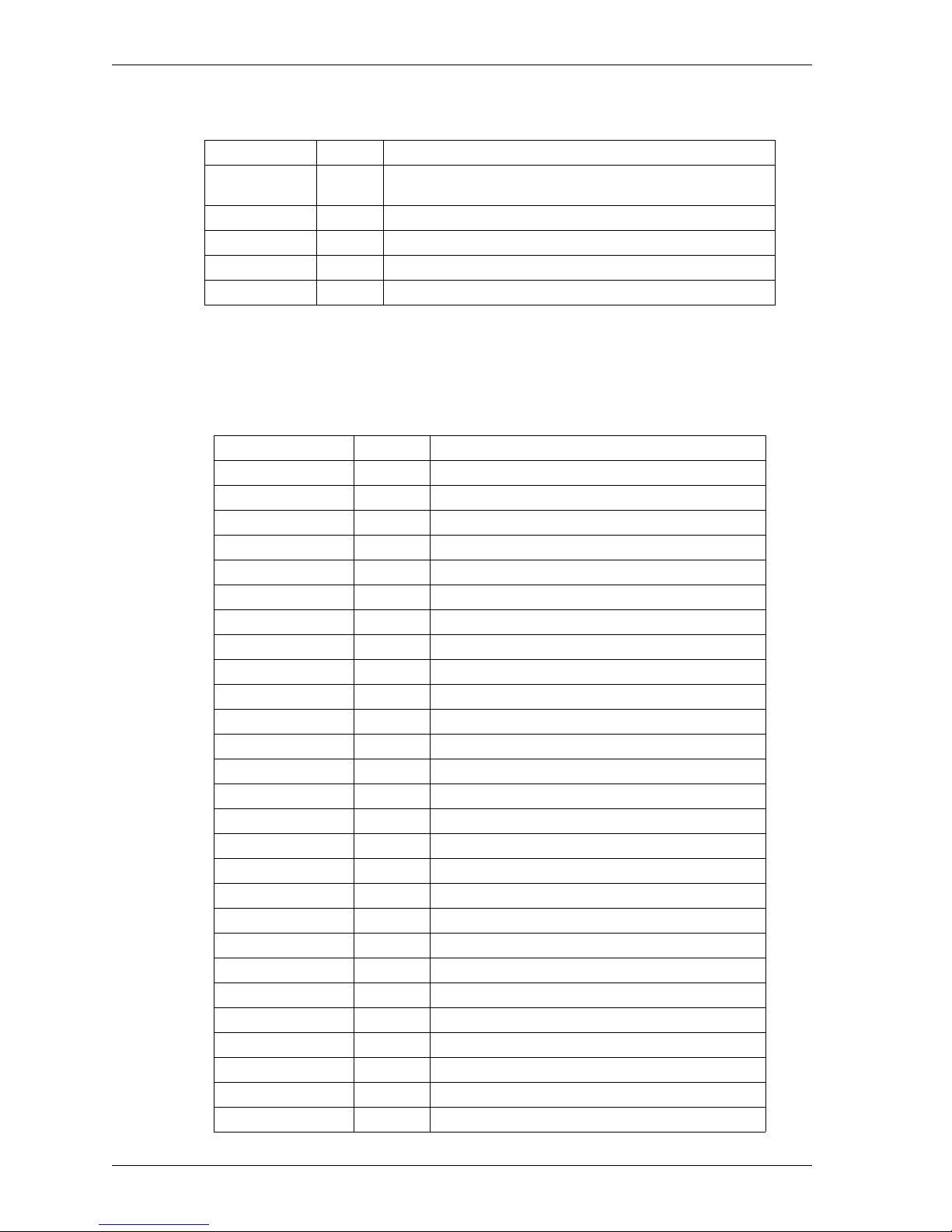
minimum of twelve attributes as well as additional optional attributes.
Attribute Size Description
Version 4 bits IP format number (Current version = 4)
IHL 4 bits Header length in 32-bit words (Minimum = 5)
TOS 8 bits Type of service sets routing priorities. It is generally
Tot _L en 16 bits Total length of packet measured in octets. It is used in
ID 16 bits Packet ID, used for reassembling fragments.
Flags 3 bits Miscellaneous flags
Frag_Off 13 bits Identifies fragment part for this packet.
TTL 8 bits Time to live. It sets the maximum time the datagram
under-utilized because few application layers can set it.
reassembling fragments.
remains alive in the system.
Reference Guide 1
Page 6
Internet Protocol header
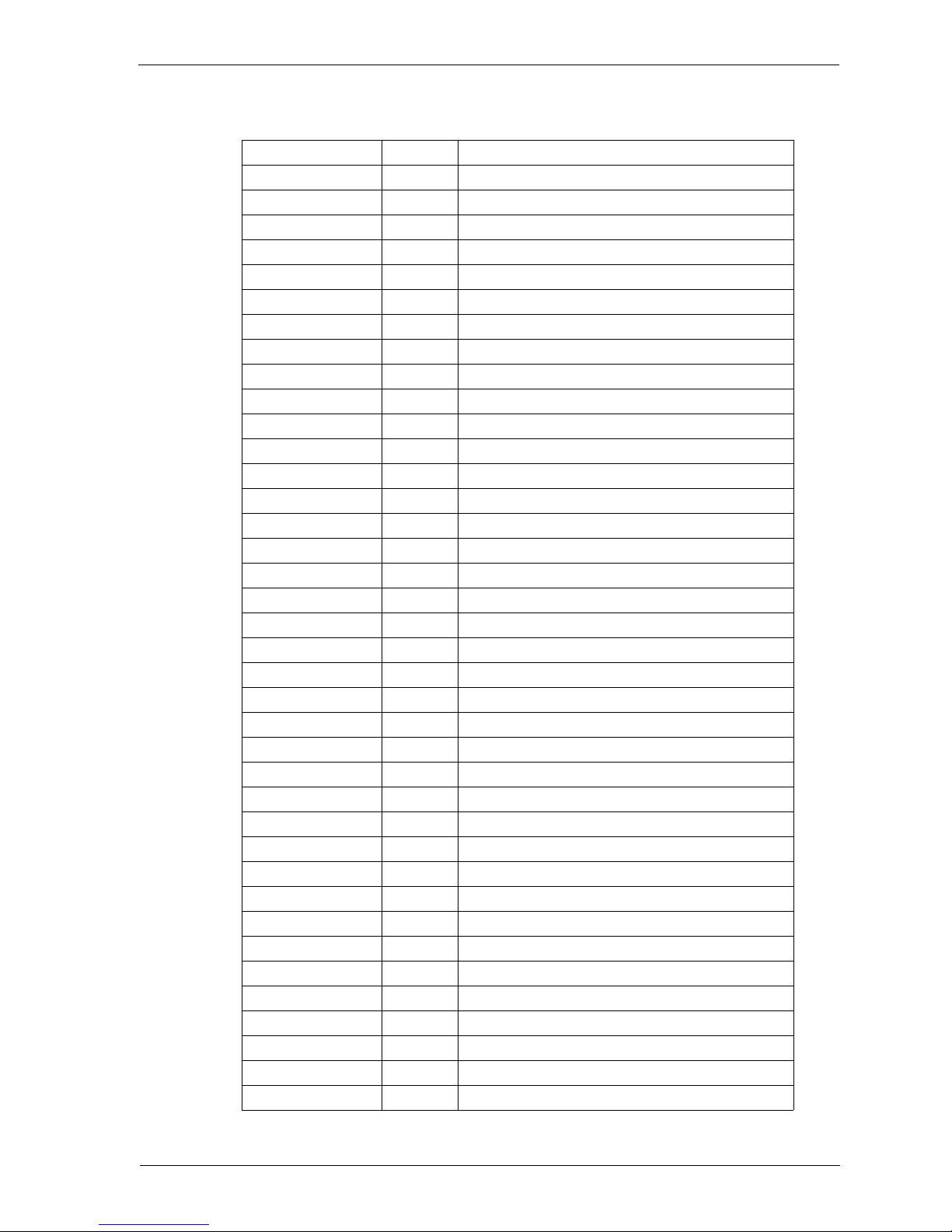
Attribute Size Description
Protocol 8 bits IP protocol number. Indicates which of TCP, UDP, ICMP,
Check 16 bits Checksum for the IP header
Sour_Addr 32 bits Source IP address
Dest_Addr 32 bits Destination IP address
Options 24 bits IP Options (Present if IHL is 6)
IP header number list
The IP Protocol header contains an 8-bit field that identifies the protocol for the
Transport layer for the datagram.
Keyword Number Protocol
ICMP 1 Internet Control Message
IGMP 2 Internet Group Management
GGP 3 Gateway-to-Gateway
IP 4 IP-within-IP (encapsulation)
ST 5 Stream
TCP 6 Transmission Control Protocol
UCL 7 UCL
EGP 8 Exterior Gateway Protocol
IGP 9 Any private interior gateway
BBN-RCC-MON 10 BBN RCC Monitoring
NVP-II 11 Network Voice Protocol
PUP 12 PUP
ARGUS 13 ARGUS
EMCON 14 EMCON
XNET 15 Cross Net Debugger
CHAOS 16 Chaos
UDP 17 User Datagram Protocol
MUX 18 Multiplexing
DCN-MEAS 19 DCN Measurement Subsystems
HMP 20 Host Monitoring
PRM 21 Packet Radio Measurement
XNS-IDP 22 XEROX NS IDP
TRUNK-1 23 Trunk-1
TRUNK-2 24 Trunk-2
LEAF-1 25 Leaf-1
LEAF-2 26 Leaf-2
IGMP, or other Transport protocol is inside.
0 Reserved
2
Page 7
Internet Protocol header
Keyword Number Protocol
RDP 27 Reliable Data Protocol
IRTP 28 Internet Reliable Transaction
ISO-TP4 29 ISO Transport Protocol Class 4
NETBLT 30 Bulk Data Transfer Protocol
MFE-NSP 31 MFE Network Services Protocol
MERIT-INP 32 MERIT Internodal Protocol
SEP 33 Sequential Exchange Protocol
3PC 34 Third Party Connect Protocol
IDPR 35 Inter-Domain Policy Routing Protocol
XTP 36 XTP
DDP 37 Datagram Delivery Protocol
IDPR-CMTP 38 IDPR Control Message Transport Protocol
TP++ 39 TP++ Transport Protocol
IL 40 IL Transport Protocol
SIP 41 Simple Internet Protocol
SDRP 42 Source Demand Routing Protocol
SIP-SR 43 SIP Source Route
SIP-FRAG 44 SIP Fragment
IDRP 45 Inter-Domain Routing Protocol
RSVP 46 Reservation Protocol
GRE 47 General Routing Encapsulation
MHRP 48 Mobile Host Routing Protocol
BNA 49 BNA
ESP 50 Encapsulated Security Payload
AH 51 Authentication Header
I-NLSP 52 Integrated Net Layer Security TUBA
SWIPE 53 IP with Encryption
NHRP 54 NBMA Next Hop Resolution Protocol
55-60 Unassigned
61 Any host internal protocol
CFTP 62 CFTP
63 Any local network
SAT-EXPAK 64 SATNET and Backroom EXPAK
KRYPTOLAN 65 Kryptolan
RVD 66 MIT Remote Virtual Disk Protocol
IPPC 67 Internet Pluribus Packet Core
68 Any distributed file system
SAT-MON 69 SATNET Monitoring
Reference Guide 3
Page 8

Internet Protocol header
Keyword Number Protocol
VISA 70 VISA Protocol
IPCV 71 Internet Packet Core Utility
CPNX 72 Computer Protocol Network Executive
CPHB 73 Computer Protocol Heart Beat
WSN 74 Wang Span Network
PVP 75 Packet Video Protocol
BR-SAT-MON 76 Backroom SATNET Monitoring
SUN-ND 77 SUN NDPROTOCOL-Temporary
WB-MON 78 WIDEBAND Monitoring
WB-EXPAK 79 WIDEBAND EXPAK
ISO-IP 80 ISO Internet Protocol
VMTP 81 VMTP
SECURE-VMTP 82 SECURE-VMTP
VINES 83 VINES
TTP 84 TTP
NSFNET-IGP 85 NSFNET-IGP
DGP 86 Dissimilar Gateway Protocol
TCF 87 TCF
IGRP 88 IGRP
OSPFIGP 89 OSPFIGP
SPRITE-RPC 90 Sprite RPC Protocol
LARP 91 Locus Address Resolution Protocol
MTP 92 Multicast Transport Protocol
AX.25 93 AX.25 Frames
IPIP 94 IP-within-IP Encapsulation Protocol
MICP 95 Mobile Internetworking Control Protocol
SCC-SP 96 Semaphore Communications Security Protocol
ETHERIP 97 Ethernet-within-IP Encapsulation
ENCAP 98 Encapsulation Header
GMTP 100 GMTP
99 Any private encryption scheme
101-254 Unassigned
255 Reserved
4
Page 9

Internet Protocol options
Internet Protocol options are variable-length additions to the standard IP header. IP
options can either be of limited usefulness or very dangerous. There are several kinds
of IP options:
Security
Control routing of IP packets that carry sensitive data. Security options are
rarely supported.
Stream ID (SID)
The stream ID option is rarely supported.
Source Routing
Both the loose source route option and the strict source route option enable
the source of an Internet packet to provide routing information. Source
routing options can be very dangerous, because a clever attacker might use
them to masquerade as another site. However, loose source routing and the
traceroute facility can also help debug some obscure routing problems.
Record Route
The record route option was originally intended for use in testing the Internet.
Unfortunately, record route can record only ten IP addresses. On the present
Internet, typical long-haul transmissions can involve twenty or thirty hops,
rendering the record route option obsolete.
Internet Protocol options
Time Stamp
The time stamp option helps measure network propagation delays. This task
is done more effectively, however, with higher-level time protocols or timestamp messages.
Because most applications make it very obscure or difficult to use IP options, they are
rarely used.
Transfer protocols
The IP protocol encapsulates information contained in the transport layer. The
transport layer has several protocols that specify how to transmit data between
applications: for example, UDP, TCP, ICMP, and others.
UDP
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a connectionless, potentially unreliable datagram
protocol. It trades reliability for speed and low overhead. To ensure accurate
transmission, it requires that the application layer verify that packets arrive at their
destination.
Characteristics of UDP include:
Reference Guide 5
Page 10

Transfer protocols
• Often used for services involving the transfer of small amounts of data where
retransmitting a request is not a problem.
• Used for services such as time synchronization in which an occasionally lost
packet will not affect continued operation. Many systems using UDP resend
packets at a constant rate to inform their peers about interesting events.
• Primarily used on LANs, in particular for NFS services where its low overhead
gives it a substantial performance advantage. A lack of congestion control
means that using UDP for bulk data transfer over long-haul connections is not
recommended.
• Supports broadcasts.
• Provides abstraction of ports.
• A connection is described by its source and destination ports and its source and
destination IP addresses. In typical usage, port numbers below 1024 are
reserved for well-known services (destinations), and the client side is supposed
to use ports above 1023 for the source of the connection. However, this rule has
many notable exceptions. In particular, NFS (port 2049) and Archie (port 1525)
use server ports at numbers above 1024. Some services use the same source and
destination port for server-to-server connections. Common examples are DNS
(53), NTP (123), syslog (514), and RIP (520).
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) provides reliable stream-oriented services. It
trades speed and overhead for increased reliability. Like UDP, TCP provides source
and destination ports that are used in a similar fashion.
TCP uses a rather complicated state machine to manage connections. There are
several attribute bits that control the state of a connection. Three very important
attribute bits of TCP packets are the SYN, ACK, and FIN bits. The SYN bit is set only
on the first packet sent in each direction for a given connection. The ACK bit is set
when the other side is acknowledging the receipt of data to the peer. The FIN bit is set
when either side chooses to close the connection.
ICMP
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is used primarily to deliver error
information about other services. It is otherwise quite similar in practical operation to
UDP. That is, it is connectionless and does not guarantee that packets are delivered to
their destination. One dangerous ICMP packet is the ICMP redirect packet, which can
change routing information on the machines that receive it.
Other protocols
The vast majority of the traffic on the Internet uses one of the three protocols
mentioned above. There are some others that are of interest:
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol)
A protocol supporting multicasts used by SGI’s Dogfight game.
6
Page 11

IPIP (IP-within-IP)
An encapsulation protocol used to build virtual networks over the Internet.
GGP (Gateway-Gateway Protocol)
A routing protocol used between autonomous systems.
GRE
A protocol used for PPTP.
ESP
An encryption protocol used for IPSec.
Standard ports and random ports
UDP and TCP encapsulate information contained within the application layer. The
appropriate application processes are designated by source and destination port
numbers. These port numbers, along with the source and destination IP addresses,
specify a unique connection on the Internet.
Standard ports and random ports
For example, it is reasonable to have two telnet sessions from one host to another.
However, since telnet uses a well-known service number of 23, something must
distinguish these two connections. The other port in these cases will be a port that is
typically greater than 1023. This alternative port designation is dynamically allocated
by the operating system on the client side.
Random ports can cause a great amount of trouble if they happen to match a wellknown service on a port above 1023. If some client machine assigns a random port of
2049, the connection may mysteriously fail. Similar problems can occur with the X
Window and Archie services.
In practice, most operating systems cycle port numbers between 1024 and a number
somewhere in the range of 2100, depending on how many TCP connections are
currently open and whether a recently closed connection used a similar port number.
This makes the above problem rare.
Reference Guide 7
Page 12

Standard ports and random ports
8
Page 13

CHAPTER 2 Content Types
A content-type header is used by applications to determine what kind of data they
are receiving, thus allowing them to make decisions about how it should be handled.
It allows clients to correctly identify and display video clips, images, sound, or nonHTML data. People are probably most familiar with the MIME content-types sent in
e-mail.
The WatchGuard Proxied HTTP service uses content-type headers to determine
whether to allow or deny an HTTP transaction. Use the Policy Manager to configure
the Proxied HTTP service to allow or deny content-types. Content types are also used
in SMTP and are configurable in the SMTP proxy. This chapter contains a list of the
more commonly used MIME content-types. The MIME content-types are written as
follows:
type/sub-type
Wildcards may be used to select all sub-types within a type, thereby denying all or
allowing all of that MIME type. For example, to allow all content-types that are text
(including text/enriched, text/plain, and others), use the content-type
New, registered MIME content-types appear regularly. WatchGuard
recommends frequent checking of an online reference for the most current list.
One source of current MIME types is
ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/iana/assignments/mediatypes
In addition, WatchGuard encourages you to e-mail requests for inclusion of new
content types in our master list to manual@watchguard.com
Mime content types list
application/*
application/activemessage Active message
application/andrew-inset AFS EZ inset
text/*.
Reference Guide 9
Page 14
Mime content types list
application/applefile Generic Macintosh files
application/astound Astound Web Player
application/atomicmail Atomic Mail
application/cals-1840 CALS (RFC 1895)
application/commonground
application/cybercash
application/dca-rft
application/dec-dx
application/eshop
application/hyperstudio
application/iges
application/mac-binhex40
application/macwriteii
application/marc
application/mathematica
application/ms-excel Excel spreadsheet
application/msword Word document
application/news-message-id
application/news-transmission
application/octet-stream
application/oda
application/pdf
application/pgp-encrypted PGP encrypted (RFC 2015)
application/pgp-keys PGP keys (RFC 2015)
application/pgp-signature PGP signature (RFC 2015)
application/pkcs10
application/pkcs7-mime
application/pkcs7-signature
application/postscript PostScript
application/prs.alvestrand.titrax+
application/prs.cww
application/prs.nprend
application/remote-printing
application/riscos
application/rtf Microsoft Rich Text Format
application/set-payment SET payment
application/set-payment-initiation
application/set-registration
application/set-registration-initiation
10
Page 15
Mime content types list
application/sgml SGML application (RFC 1874)
application/sgml-open-catalog
application/slate
application/vis5d Vis5D 5-dimensional data
application/vnd.3M.Post-it-Notes
application/vnd.FloGraphIt
application/vnd.acucobol
application/vnd.acucobol~
application/vnd.anser-web-certificate-issueinitiation
application/vnd.anser-web-funds-transferinitiation
application/vnd.audiograph
application/vnd.businessobjects
application/vnd.claymore
application/vnd.commerce-battelle
application/vnd.commonspace
application/vnd.cosmocaller
application/vnd.cybank
application/vnd.dna
application/vnd.dxr
application/vnd.ecdis-update
application/vnd.ecowin.chart
application/vnd.ecowin.filerequest
application/vnd.ecowin.fileupdate
application/vnd.ecowin.series
application/vnd.ecowin.seriesrequest
application/vnd.ecowin.seriesupdate
application/vnd.ecowin.seriesupdate
application/vnd.enliven
application/vnd.epson.quickanime
application/vnd.epson.salt
application/vnd.fdf
application/vnd.ffsns
application/vnd.framemaker
application/vnd.fujitsu.oasys
application/vnd.fujitsu.oasys2
application/vnd.fujitsu.oasys3
application/vnd.fujitsu.oasysgp
application/vnd.fujitsu.oasysprs
Reference Guide 11
Page 16

Mime content types list
application/vnd.fujixerox.docuworks
application/vnd.fut-misnet
application/vnd.hp-HPGL
application/vnd.hp-PCL
application/vnd.hp-PCLXL
application/vnd.hp-hps
application/vnd.ibm.MiniPay
application/vnd.ibm.modcap
application/vnd.intercon.formnet
application/vnd.intertrust.digibo+
application/vnd.intertrust.nncp
application/vnd.intu.qbo
application/vnd.is-xpr
application/vnd.japannet-directory-service
application/vnd.japannet-jpnstore-wakeup
application/vnd.japannet-payment-wakeup
application/vnd.japannet-registration
application/vnd.japannet-registration-wakeup
application/vnd.japannet-setstore-wakeup
application/vnd.japannet-verification
application/vnd.japannet-verification-wakeup
application/vnd.koan
application/vnd.lotus-1-2-3
application/vnd.lotus-approach
application/vnd.lotus-freelance
application/vnd.lotus-organizer
application/vnd.lotus-screencam
application/vnd.lotus-wordpro
application/vnd.meridian-slingshot
application/vnd.mif
application/vnd.minisoft-hp3000-save
application/vnd.mitsubishi.misty-guard.trustweb
application/vnd.ms-artgalry
application/vnd.ms-asf
application/vnd.ms-powerpoint
application/vnd.ms-project
application/vnd.ms-tnef
application/vnd.ms-works
application/vnd.music-niff
12
Page 17
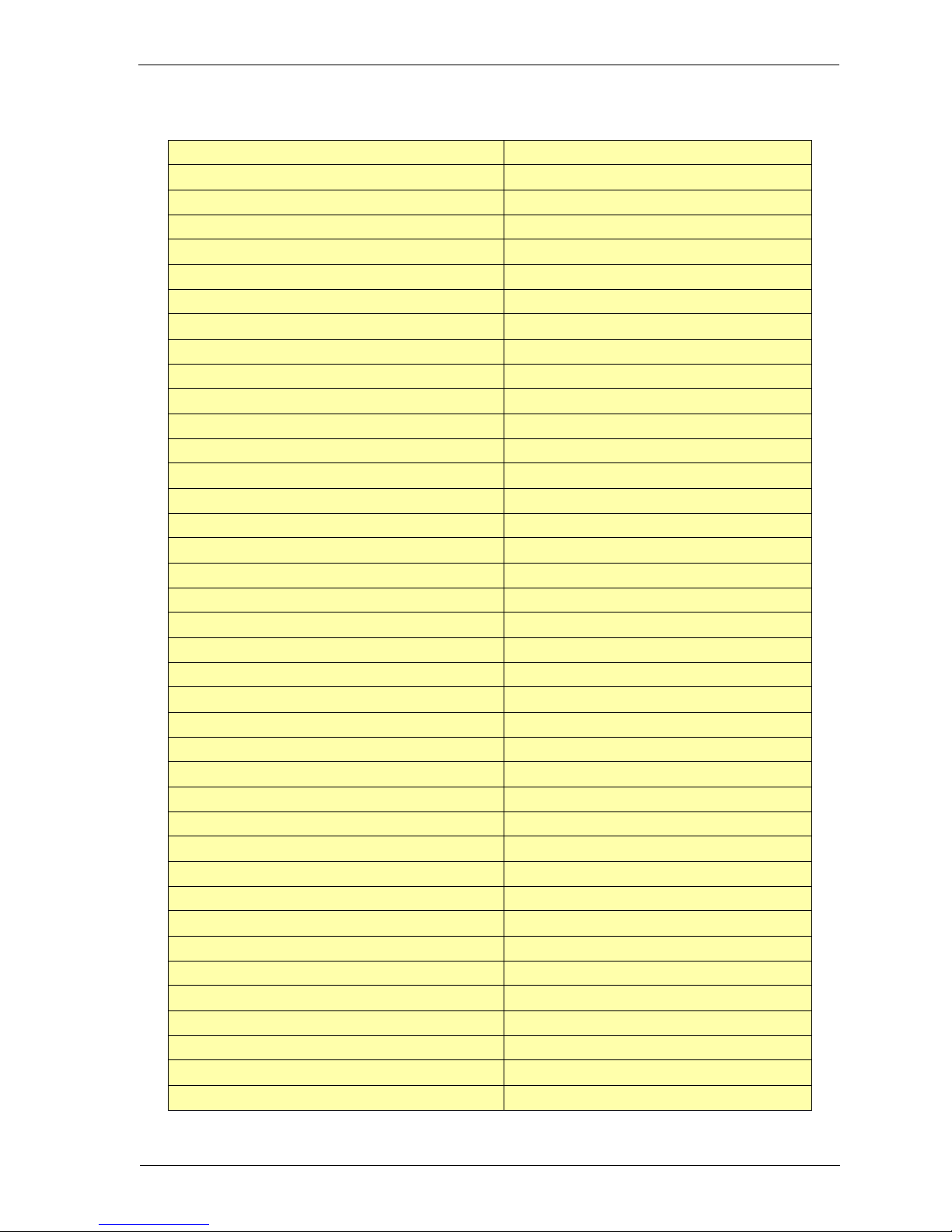
application/vnd.musician
application/vnd.netfpx
application/vnd.noblenet-directory
application/vnd.noblenet-sealer
application/vnd.noblenet-web
application/vnd.novadigm.EDM
application/vnd.novadigm.EDX
application/vnd.novadigm.EXT
application/vnd.osa.netdeploy
application/vnd.powerbuilder6
application/vnd.powerbuilder6-s
application/vnd.powerbuilder6~
application/vnd.publishare-delta-tree
application/vnd.rapid
application/vnd.seemail
application/vnd.shana.informed.formdata
application/vnd.shana.informed.formtemp
application/vnd.shana.informed.interchange
application/vnd.shana.informed.package
application/vnd.street-stream
application/vnd.svd
application/vnd.swiftview-ics
application/vnd.truedoc
application/vnd.uplanet.alert
application/vnd.uplanet.alert-wbxml
application/vnd.uplanet.bearer-choi-wbxml
application/vnd.uplanet.bearer-choice
application/vnd.uplanet.cacheop
application/vnd.uplanet.cacheop-wbxml
application/vnd.uplanet.channel
application/vnd.uplanet.channel-wbxml
application/vnd.uplanet.list
application/vnd.uplanet.list-wbxml
application/vnd.uplanet.listcmd
application/vnd.uplanet.listcmd-wbxml
application/vnd.uplanet.signal
application/vnd.visio
application/vnd.webturbo
application/vnd.wrq-hp3000-labelled
Mime content types list
Reference Guide 13
Page 18
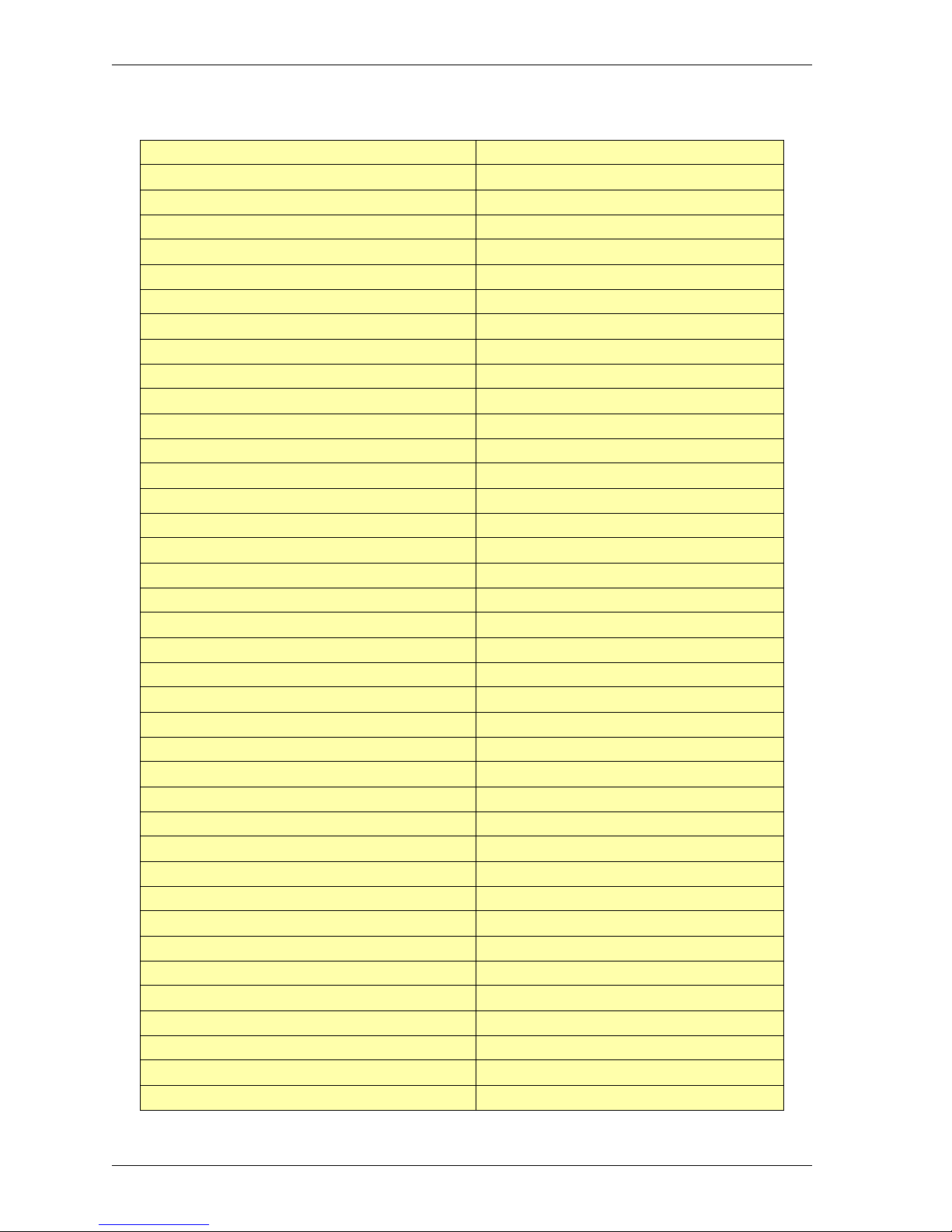
Mime content types list
application/vnd.wt.stf
application/vnd.xara
application/vnd.yellowriver-custom-menu
application/wita Wang Info. Transfer Format (Wang)
application/wordperfect5.1 WordPerfect 5.1 document
application/x-alpha-form Specialized data entry forms
application/x-asap ASAP WordPower
application/x-bcpio Old CPIO format
application/x-chat Interactive chat (Ichat)
application/x-cpio POSIX CPIO format
application/x-csh UNIX c-shell program
application/x-director Macromedia Shockwave
application/x-dvi TeX dvi format
application/x-framemaker FrameMaker Documents (Frame)
application/x-gtar Gnu tar format
application/x-koan Koan music data (SSeyo)
application/x-latex LaTeX document
application/x-mif Maker Interchange Format (FrameMaker)
application/x-net-install Net Install (20/20 Software)
application/x-ns-proxy-autoconfig Autoconfiguration (Netscape)
application/x-oleobject OLE Object
application/x-olescript OLE script e.g., Visual Basic
application/x-p3d Play3D 3-D scene data (Play3D)
application/x-pcn Pointcast news data
application/x-pdf Adobe Acrobat PDF
application/x-perl Perl program
application/x-pn-realaudio Realaudio (Progressive Networks)
application/x-pointplus PointPlus presentation data
application/x-rad-powermedia PowerMedia multimedia
application/x-sh UNIX bourne shell program
application/x-shar UNIX sh shell archive
application/x-sprite Sizzler real-time video/animation
application/x-stuffit Macintosh Stuffit Archive
application/x-tar 4.3BSD TAR format
application/x-tcl Tcl (Tool Control Language) program
application/x-tex Te X /L a TeX d oc u me nt
application/x-texinfo GNU TexInfo document
application/x-troff Tro f f d ocume n t
application/x-troff-man Troff document with MAN macros
14
Page 19
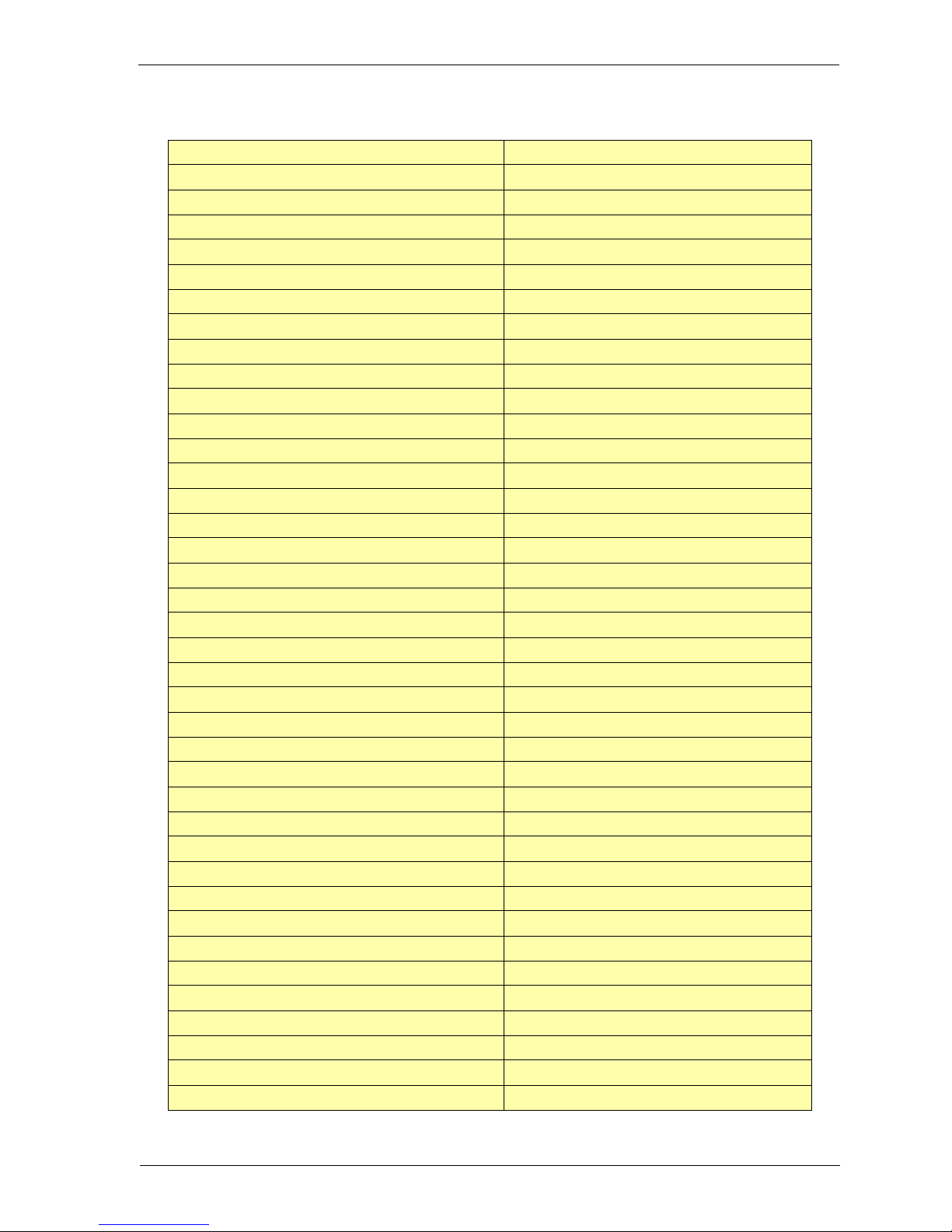
Mime content types list
application/x-troff-me Troff document with ME macros
application/x-troff-ms Troff document with MS macros
application/x-ustar POSIX tar format
application/x-wais-source WAIS sources
application/x-webbasic Visual Basic objects
application/x400-bp X.400 mail message body part (RFC 1494)
application/xml
application/zip DOS/PC - Pkzipped archive
audio/*
audio/32kadpcm
audio/basic
audio/basic Basic audio
audio/echospeech Compressed speech (Echo Speech Corp.)
audio/vnd.qcelp
audio/voxware Toolvox speech audio (Voxware)
audio/x-aiff Macintosh audio format (Apple)
audio/x-mpeg MPEG audio
audio/x-mpeg-2 MPEG-2 audio
audio/x-wav Microsoft audio
chemical/* (several types)
drawing/*
drawing/x-dwf Autocad WHIP vector drawings
graphics/*
graphics/x-inventor Open Inventor 3-D scenes
image/*
image/cgm Computer Graphics Metafile
image/fif Fractal Image Format
image/g3fax Group III Fax (RFC 1494)
image/gif Graphic Interchange Format (Compuserve)
image/ief Image Exchange Format (RFC 1314)
image/jpeg JPEG image file
image/naplps North Am. Presentation Layer Protocol
image/png Portable Network Graphics format
image/prs.btif
image/tiff TIFF image file
image/vnd.dwg
image/vnd.dxf
image/vnd.fastbidsheet
image/vnd.fpx
Reference Guide 15
Page 20
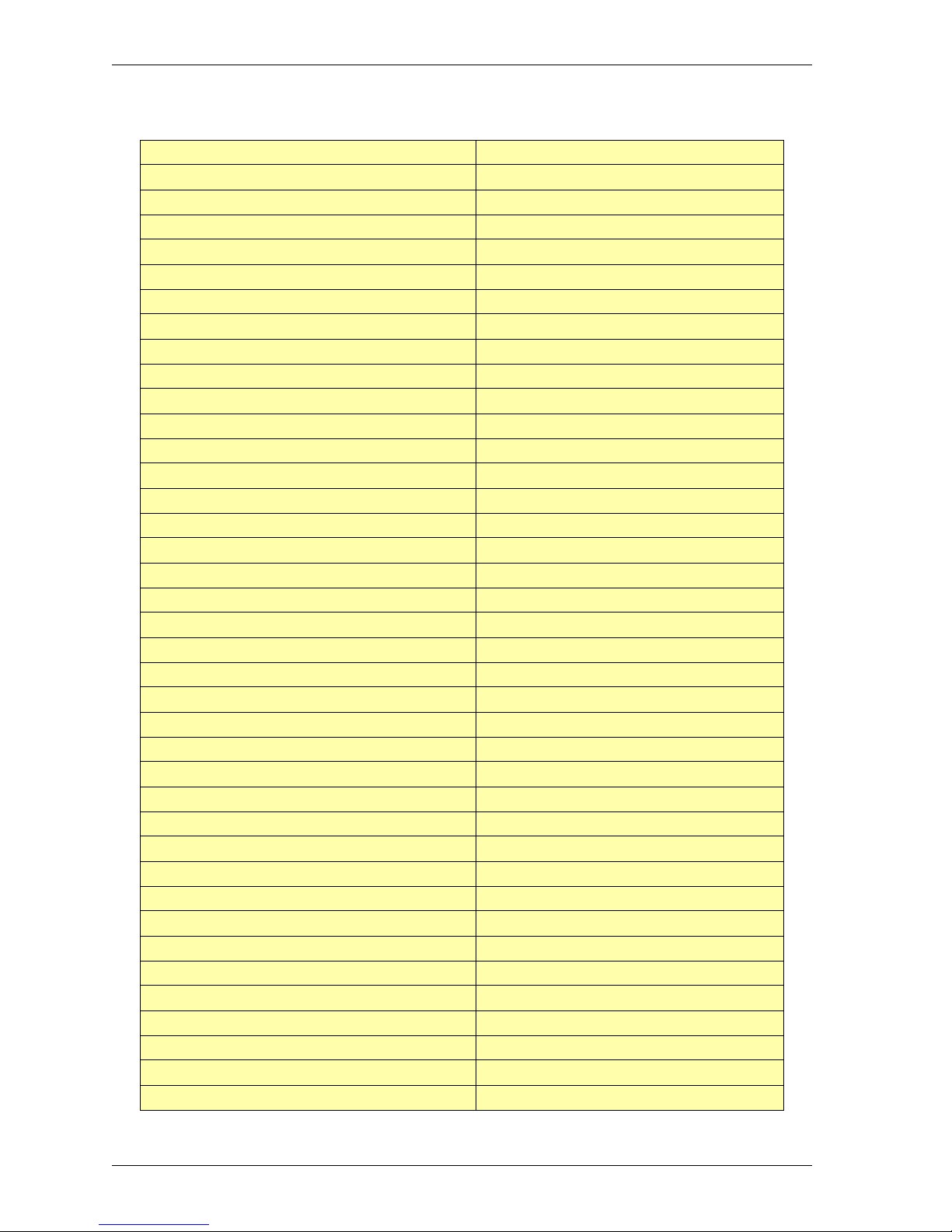
Mime content types list
image/vnd.net-fpx
image/vnd.svf
image/vnd.xiff
image/wavelet Wavelet-compressed
image/x-cals CALS Type 1 or 2
image/x-cmu-raster CMU raster
image/x-cmx CMX vector image
image/x-dwg AutoCad Drawing
image/x-dxf AutoCad DXF file
image/x-mgx-dsf QuickSilver active image
image/x-ms-bmp Microsoft Windows bitmap
image/x-photo-cd Kodak Photo-CD
image/x-pict Macintosh PICT format
image/x-png Portable Network Graphics format
image/x-portable-anymap PNM (UNIX PPM package)
image/x-portable-bitmap PBM (UNIX PPM package)
image/x-portable-graymap PGM (UNIX PPM package)
image/x-portable-pixmap PPM (UNIX PPM package)
image/x-rgb RGB
image/x-svf Simple Vector Format
image/x-xbitmap X-Windows bitmap (b/w)
image/x-xwindowdump X Windowdump format
image/xpm X-Windows pixelmap (8-bit color)
message/*
message/delivery-status
message/disposition-notification
message/external-body
message/http
message/news
message/partial
message/rfc822
model/*
model/iges cad files
model/mesh see RFC 2077
model/vnd.dwf cad files
model/vrml VRML models
multipart/*
multipart/alternative
multipart/appledouble
16
Page 21
Mime content types list
multipart/byteranges
multipart/digest
multipart/encrypted
multipart/form-data
multipart/header-set
multipart/mixed
multipart/parallel
multipart/related
multipart/report
multipart/signed
multipart/voice-message
qfn/updatedir Quicken Financial News
qfn/stockqt Quicken Financial News
qfn/datadld Quicken Finanical News
text/*
text/css Cascading Stylesheets
text/enriched Enriched text markup (RFC 1896)
text/html HTML text data (RFC 1866)
text/javascript Javascript program
text/plain Plain text: documents; program listings
text/richtext richtext (RFC 1521)
text/sgml SGML documents (RFC 1874)
text/tab-separated-values Tab-separated values (tabular)
text/uri-list lists of URLs
text/vbscript VBScript program
text/vnd.abc
text/vnd.fmi.flexstor
text/vnd.in3d.3dml
text/vnd.in3d.spot
text/vnd.latex-z
text/x-setext Structure enhanced text
text/x-speech Speech synthesis data
text/x-speech Speech synthesis data (MVP Solutions)
text/xml
video/*
video/mpeg MPEG video
video/mpeg-2 MPEG-2 video
video/quicktime Macintosh Quicktime
video/vdo VDOlive streaming video (VDOnet)
Reference Guide 17
Page 22

Mime content types list
video/vivo Vivo streaming video (Vivo software)
video/vnd.motorola.video
video/vnd.motorola.videop
video/vnd.vivo
video/x-ms-asf Microsoft NetShow (streaming audio and
video)
video/x-msvideo Microsoft video
video/x-sgi-movie SGI Movie format
workbook/*
workbook/formulaone Spreadsheets (Visual Components)
x-conference/x-cooltalk Netscape Cooltalk chat data (Netscape)
x-form/x-openscape OpenScape OLE/OCX object
x-model/x-mesh Computational meshes for numerical
simulations
x-music/x-midi MIDI music data
x-script/x-wfxclient Client-server objects (Wayfarer)
x-world/*
x-world/x-3dmf QuickDraw3-D scene data
x-world/x-svr Viscape Interactive 3-D world data
x-world/x-vream WIRL - VRML data (VREAM)
x-world/x-vrml VRML data file
x-world/x-wvr WebActive 3d data
18
Page 23

CHAPTER 3 Services and Ports
Well-known services are a combination of port number and transport protocol for
specific, standard applications. This chapter contains several tables that list service
names, port number, protocol and description.
Ports used by WatchGuard products
The WatchGuard Firebox, Management Station, and LiveSecurity Event Processor
(LSEP) use several ports during normal functioning.
Port # Protocol Purpose
4100 TCP Authentication applet
4101 TCP LSEP and Management Station
4107 TCP LSEP and Firebox
Port #Protocol Used
By
4103 TCP dbfetch Connect to webblocker.sealabs.com to retrieve
4102 TCP Firebox Used only in LSS 3.0x or earlier for logs
Purpose
WebBlocker database
Reference Guide 19
Page 24

Ports used by Microsoft products
Ports used by Microsoft products
Port # Protocol Purpose
137, 138 UDP Browsing
67, 68 UDP DHCP Lease
135 TCP DHCP Manager
138
139
135 TCP DNS Administration
53 UDP DNS Resolution
139 TCP Event Viewer
139 TCP File Sharing
137, 138
139
138 UDP NetLogon
137, 138
139
139 TCP Performance Monitor
1723
47
137, 138
139
139 TCP Registry Editor
139 TCP Server Manager
137, 138
139
139 TCP User Manager
139 TCP WinNT Diagnostics
137, 138
139
42 TCP WINS Replication
135 TCP WINS Manager
137 TCP WINS Registration
UDP
TCP
UDP
TCP
UDP
TCP
TCP
IP
UDP
TCP
UDP
TCP
UDP
TCP
Directory Replication
Logon Sequence
Pass Through Validation
PPTP
Printing
Trust s
WinNT Secure Channel
Port # Protocol Purpose
135 TCP Client/Server
135 TCP Exchange Administrator
143 TCP IMAP
993 TCP IMAP (SSL)
389 TCP LDAP
636 TCP LDAP (SSL)
20
Communications
Page 25

Port # Protocol Purpose
102 TCP MTA - X.400 over TCP/IP
110 TCP POP3
995 TCP POP3 (SSL)
135 TCP RCP
25 TCP SMTP
119 TCP NNTP
563 TCP NNTP (SSL)
Well-known services list
In addition to the ports used by services described above, WatchGuard maintains a
list of well-known services. Because software developers regularly add new services,
this does not represent a comprehensive list of all possible services. For more
information, see J. Reynolds and J. Postel, Assigned Numbers, RFC1700, available at
these Web sites:
Well-known services list
http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/htbin/rfc/rfc1700.html
ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/iana/assignments/port-numbers
If you would like to send us additions to this list, please send them to
manual@watchguard.com.
Service Name Port # Protocol Description
tcpmux 1 TCP/UDP TCP Port Service Multiplexer
compressnet 2,3 TCP/UDP Management Utility
rje 5 TCP/UDP Remote Job Entry
echo 7 TCP/UDP Echo
discard 9 TCP/UDP Discard
systat 11 TCP/UDP Active Users
daytime 13 TCP/UDP Daytime
qotd 17 TCP/UDP Quote of the Day
msp 18 TCP/UDP Message Send Protocol
chargen 19 TCP/UDP Character Generator
ftp-data 20 TCP/UDP File Transfer [Default Data]
ftp 21 TCP/UDP File Transfer [Control]
ssh 22 TCP/UDP SSH Remote Login Protocol
telnet 23 TCP/UDP Te ln e t
smtp 25 TCP/UDP Simple Mail Transfer
nsw-fe 27 TCP/UDP NSW User system FE
msg-icp 29 TCP/UDP MSG ICP
Reference Guide 21
Page 26

Well-known services list
Service Name Port # Protocol Description
msg-auth 31 TCP/UDP MSG Authentication
dsp 33 TCP/UDP Display Support Protocol
time 37 TCP/UDP Time
rap 38 TCP/UDP Route Access Protocol
rlp 39 TCP/UDP Resource Location Protocol
graphics 41 TCP/UDP Graphics
nameserver 42 TCP/UDP Host Name Server
nicname 43 TCP/UDP whois
mpm-flags 44 TCP/UDP MPM Flags
mpm 45 TCP/UDP MPM
mpm-snd 46 MPM Send
ni-ftp 47 TCP/UDP NI FTP
auditd 48 TCP/UDP Digital Audit Daemon
tacacs 49 TCP/UDP Login Host Protocol (TACACS)
re-mail-ck 50 TCP/UDP Remote Mail Checking Protocol
la-maint 51 TCP/UDP IMP Logical Address Maintenance
xns-time 52 TCP/UDP XNS Time Protocol
domain 53 TCP/UDP Domain Name Server
xns-ch 54 TCP/UDP XNS Clearinghouse
isi-gl 55 TCP/UDP ISI Graphics Language
xns-auth 56 TCP/UDP XNS Authentication
xns-mail 58 TCP/UDP XNS Mail
ni-mail 61 TCP/UDP NI MAIL
acas 62 TCP/UDP ACA Services
whois++ 63 TCP/UDP whois++
covia 64 TCP/UDP Communications Integrator (CI)
tacacs-ds 65 TCP/UDP TACACS-Database Service
sql*net 66 TCP/UDP Oracle SQL*NET
bootps 67 TCP/UDP Bootstrap Protocol Server
bootpc 68 TCP/UDP Bootstrap Protocol Client
tftp 69 TCP/UDP Trivial File Transfer
gopher 70 TCP/UDP Gopher
netrjs-1 71 TCP/UDP Remote Job Service
netrjs-2 72 TCP/UDP Remote Job Service
netrjs-3 73 TCP/UDP Remote Job Service
netrjs-4 74 TCP/UDP Remote Job Service
deos 76 TCP/UDP Distributed External Object Store
vettcp 78 TCP/UDP vettcp
22
Page 27

Well-known services list
Service Name Port # Protocol Description
finger 79 TCP/UDP Finger
www-http 80 TCP/UDP World Wide Web HTTP
hosts2-ns 81 TCP/UDP HOSTS2 Name Server
xfer 82 TCP/UDP XFER utility
mit-ml-dev 83 TCP/UDP MIT ML device
ctf 84 TCP/UDP Common Trace Facility
mit-ml-dev 85 TCP/UDP MIT ML device
mfcobol 86 TCP/UDP Micro Focus Cobol
kerberos 88 TCP/UDP Kerberos
sug-mit-tug 89 TCP/UDP SU/MIT Telnet gateway
dnsix 90 TCP/UDP DNSIX Secure Application Token Map
mit-dov 91 TCP/UDP MIT Dover Spooler
npp 92 TCP/UDP Network Printing Protocol
dcp 93 TCP/UDP Device Control Protocol
objcall 94 TCP/UDP Tivoli Object Dispatcher
supdup 95 TCP/UDP SUPDUP
dixie 96 TCP/UDP DIXIE Protocol Specification
swift-rvf 97 TCP/UDP Swift Remote Virtual File Protocol
tacnews 98 TCP/UDP TAC News
metagram 99 TCP/UDP Metagram Relay
newacct 100 TCP [unauthorized use]
hostname 101 TCP/UDP NIC Host Name Server
iso-tsap 102 TCP/UDP ISO-TSAP
gppitnp 103 TCP/UDP Genesis Point-to-Point Trans Net
acr-nema 104 TCP/UDP ACR-NEMA Digital Imag. Comm. 300
cso 105 TCP/UDP CCSO name server protocol
csnet-ns 105 TCP/UDP Mailbox Name Nameserver
3com-tsmux 106 TCP/UDP 3COM-TSMUX
rtelnet 107 TCP/UDP Remote Telnet Service
snagas 108 TCP/UDP SNA Gateway Access Server
pop2 109 TCP/UDP Post Office Protocol - Version 2
pop3 110 TCP/UDP Post Office Protocol - Version 3
sunrpc 111 TCP/UDP SUN Remote Procedure Call
mcidas 112 TCP/UDP McIDAS Data Transmission Protocol
auth(ident) 113 TCP/UDP Authentication Service
audionews 114 TCP/UDP Audio News Multicast
sftp 115 TCP/UDP Simple File Transfer Protocol
ansanotify 116 TCP/UDP ANSA REX Notify
Reference Guide 23
Page 28

Well-known services list
Service Name Port # Protocol Description
uucp-path 117 TCP/UDP UUCP Path Service
sqlserv 118 TCP/UDP SQL Services
nntp 119 TCP/UDP Network News Transfer Protocol
cfdptkt 120 TCP/UDP CFDPTKT
erpc 121 TCP/UDP Encore Expedited RPC
smakynet 122 TCP/UDP SMAKYNET
ntp 123 TCP/UDP Network Time Protocol
ansatrader 124 TCP/UDP ANSA REX Trader
locus-map 125 TCP/UDP Locus PC-Interface Net Map
unitary 126 TCP/UDP Unisys Unitary Login
locus-con 127 TCP/UDP Locus PC-Interface Conn Server
gss-xlicen 128 TCP/UDP GSS X License Verification
pwdgen 129 TCP/UDP Password Generator Protocol
cisco-fna 130 TCP/UDP cisco FNATIVE
cisco-tna 131 TCP/UDP cisco TNATIVE
cisco-sys 132 TCP/UDP cisco SYSMAINT
statsrv 133 TCP/UDP Statistics Service
ingres-net 134 TCP/UDP INGRES-NET Service
epmap 135 TCP/UDP DCE-RPC Endpoint resolution
profile 136 TCP/UDP PROFILE naming system
netbios-ns 137 TCP/UDP NETBIOS Name Service
netbios-dgm 138 TCP/UDP NETBIOS Datagram Service
netbios-ssn 139 TCP/UDP NETBIOS Session Service
imap 143 TCP/UDP Internet Message Access Protocol
news 144 TCP/UDP NewS
jargon 148 TCP/UDP Jargon
sql-net 150 TCP/UDP SQL-NET
bftp 152 TCP/UDP Background File Transfer
sgmp 153 TCP/UDP SGMP
sqlsrv 156 TCP/UDP SQL Service
pcmail-srv 158 TCP/UDP PCMail Server
sgmp-traps 160 TCP/UDP SGMP-TRAPS
snmp 161 TCP/UDP SNMP
snmptrap 162 TCP/UDP SNMPTRAP
cmip-man 163 TCP/UDP CMIP/TCP Manager
cmip-agent 164 TCP CMIP/TCP Agent
smip-agent 164 UDP CMIP/TCP Agent
namp 167 TCP/UDP NAMP
24
Page 29

Well-known services list
Service Name Port # Protocol Description
rsvd 168 TCP/UDP RSVD
send 169 TCP/UDP SEND
xyplex-mux 173 TCP/UDP Xyplex MUX
xdmcp 177 TCP/UDP X Display Manager Control Protocol
NextStep 178 TCP/UDP NextStep Window Server
bgp 179 TCP/UDP Border Gateway Protocol
unify 181 TCP/UDP Unify
irc 194 TCP/UDP Internet Relay Chat Protocol
at-rtmp 201 TCP/UDP AppleTalk Routing Maintenance
at-nbp 202 TCP/UDP AppleTalk Name Binding
at-3 203 TCP/UDP AppleTalk Unused
at-echo 204 TCP/UDP AppleTalk Echo
at-5 205 TCP/UDP AppleTalk Unused
at-zis 206 TCP/UDP AppleTalk Zone Information
at-7 207 TCP/UDP AppleTalk Unused
at-8 208 TCP/UDP AppleTalk Unused
qmtp 209 TCP/UDP Quick Mail Transfer Protocol
z39.50 210 TCP/UDP ANSI Z39.50 (WAIS)
ipx 213 TCP/UDP IPX
imap3 220 TCP/UDP Interactive Mail Access Protocol v3
fln-spx 221 TCP/UDP Berkeley rlogind with SPX auth
rsh-spx 222 TCP/UDP Berkeley rshd with SPX auth
backweb 371 UDP BackWeb
ulistserv 372 TCP/UDP Unix Listserv
netware-ip 396 TCP/UDP Novell Netware over IP
biff 512 UDP Used by mail system to notify users
exec 512 TCP Remote process execution
login 513 TCP/UDP Login Host Protocol
who 513 UDP Maintains databases showing who’s who
cmd 514 TCP Like exec, but automatic
syslog 514 UDP logging facilities
printer 515 TCP/UDP Spooler
talk 517 TCP/UDP Talk protocol
ntalk 518 TCP/UDP another Talk
utime 519 TCP/UDP Unixtime
router 520 UDP RIP local routing process (on site)
timed 525 TCP/UDP Timeserver
tempo 526 TCP/UDP Newdate
Reference Guide 25
Page 30

Well-known services list
Service Name Port # Protocol Description
courier 530 TCP/UDP Rpc
conference 531 TCP/UDP Chat
netnews 532 TCP/UDP Readnews
netwall 533 TCP/UDP For emergency broadcasts
uucp 540 TCP/UDP Uucpd
uucp-rlogin 541 TCP/UDP Uucp-rlogin Stuart Lynne
klogin 543 TCP/UDP
kshell 544 TCP/UDP Krcmd
dhcpv6-client 546 TCP/UDP DHCPv6 Client
dhcpv6-server 547 TCP/UDP DHCPv6 Server
cybercash 551 TCP/UDP Cybercash
remotefs 556 TCP/UDP Rfs server
9pfs 564 TCP/UDP Plan 9 file service
whoami 565 TCP/UDP Whoami
msn 569 TCP Microsoft Network
doom 666 TCP/UDP Doom Id Software
kerberos-adm 749 TCP/UDP Kerberos administration
webster 765 TCP/UDP
phonebook 767 TCP/UDP Phone
socks 1080 TCP/UDP Socks
hermes 1248 TCP/UDP
lotusnote 1352 TCP/UDP Lotus Notes
netware-csp 1366 TCP/UDP Novell NetWare Comm Service Platform
novell-lu6.2 1416 TCP/UDP Novell LU6.2
netopia 1419
ms-sql-s 1433 TCP/UDP Microsoft-SQL-Server
ms-sql-m 1434 TCP/UDP Microsoft-SQL-Monitor
winframe 1494 TCP WinFrame
watcom-sql 1498 TCP/UDP Watcom-SQL
ingreslock 1524 TCP/UDP Ingres
groupwise 1677 TCP GroupWise
nfs 2049 TCP/UDP
www-dev 2784 TCP/UDP World Wide Web - development
ccmail 3264 TCP/UDP Cc:mail/lotus
ICQ 2109
Firstclass 3000
compuserve 4144 TCP CompuServe Online
8000
4000
30004
UDP
Netopia Virtual Office
TCP
TCP
ICQ used for chat
UDP
TCP FirstClass (ftp channel on 510 TCP)
26
Page 31

Well-known services list
Service Name Port # Protocol Description
rfe 5002 TCP/UDP Radio free ethernet
aol 5190 TCP America OnLine
x11 6000 TCP/UDP X Window System (through 6063)
font-service 7100 TCP/UDP X Font Service
nas 8000 TCP/UDP NCD Network Audio Server
iphone 6670 TCP for connecting to the phone server
iphone 22555 UDP for audio
iphone 25793 TCP for the address server, in 4.x and 5.0
iphone 1490 TCP for the conference engine in 4.x and 5.0
Source: J. Reynolds and J. Postel, Assigned Numbers, RFC1700, available at these Web
sites:
• http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/htbin/rfc/rfc1700.html
• ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/iana/assignments/port-numbers
Reference Guide 27
Page 32

Well-known services list
28
Page 33

CHAPTER 4 WebBlocker Content
WebBlocker works in conjunction with the HTTP proxy to provide content-based
URL-filtering capabilities.
WebBlocker categories
WebBlocker relies on a URL database built and maintained by SurfControl. The
Firebox automatically and regularly downloads a current version of the WebBlocker
database from the WatchGuard Web site to your log host. The Firebox then copies the
new version into memory. This process ensures the most up-to-date Web filtering
and blocking capabilities.
SurfControl constantly searches the Internet to update the list of blocked sites. The
WebBlocker database contains the following 14 categories.
In all of the categories sites to be blocked are selected by advocacy
rather than opinion or educational material. For example, the Drugs/
Drug Culture category blocks sites describing how to grow and use
marijuana but does not block sites discussing the historical use of
marijuana.
Alcohol/Tobacco
Pictures or text advocating the sale, consumption, or production of alcoholic
beverages and tobacco products.
Illegal Gambling
Pictures or text advocating materials or activities of a dubious nature that may
be illegal in any or all jurisdictions, such as illegal business schemes, chain
letters, copyright infringement, computer hacking, phreaking (using
someone’s phone lines without permission), and software piracy. Also
includes text advocating gambling relating to lotteries, casinos, betting,
numbers games, online sports, or financial betting, including non-monetary
dares.
Reference Guide 29
Page 34

WebBlocker categories
Militant/Extremist
Pictures or text advocating extremely aggressive or combative behavior or
advocacy of unlawful political measures. Topic includes groups that advocate
violence as a means to achieve their goals. It also includes pages devoted to
“how to” information on the making of weapons (for both lawful and
unlawful reasons), ammunition, and pyrotechnics.
Drug Culture
Pictures or text advocating the illegal use of drugs for entertainment. Includes
substances used for other than their primary purpose to alter the individual’s
state of mind, such as glue sniffing. This does not include (that is, if selected
these sites would not be WebBlocked under this category) currently illegal
drugs legally prescribed for medicinal purposes (such as, drugs used to treat
glaucoma or cancer).
Satanic/Cult
Pictures or text advocating devil worship, an affinity for evil, wickedness, or
the advocacy to join a cult. A cult is defined as: A closed society that is headed
by a single individual where loyalty is demanded and leaving is punishable.
Intolerance
Pictures or text advocating prejudice or discrimination against any race, color,
national origin, religion, disability or handicap, gender, or sexual orientation.
Any picture or text that elevates one group over another. Also includes
intolerant jokes or slurs.
Gross Depictions
Pictures or text describing anyone or anything that is either crudely vulgar,
grossly deficient in civility or behavior, or shows scatological impropriety.
Topic includes depictions of maiming, bloody figures, and indecent depiction
of bodily functions.
Violence/Profanity
Pictures or text exposing extreme cruelty or profanity. Cruelty is defined as:
Physical or emotional acts against any animal or person that are primarily
intended to hurt or inflict pain. Topic includes obscene words, phrases, and
profanity in either audio, text, or pictures.
Search Engines
Search engine sites such as AltaVista, InfoSeek, Yahoo!, and WebCrawler.
Sports and Leisure
Pictures or text describing sporting events, sports figures, or other
entertainment activities.
Sex Education
Pictures or text advocating the proper use of contraceptives. Topic includes
sites devoted to the explanation and description of condoms, oral
contraceptives, intrauterine devices, and other types of contraceptives. It also
includes discussion sites devoted to conversations with partners about
sexually transmitted diseases, pregnancy, and sexual boundaries. Not
30
Page 35

Searching for Blocked Sites
included in this category are commercial sites selling sexual paraphernalia
(topics included under Sexual Acts).
Sexual Acts
Pictures or text exposing anyone or anything involved in explicit sexual acts
and/or lewd and lascivious behavior. Topic includes masturbation,
copulation, pedophilia, as well as intimacy involving nude or partially nude
people in heterosexual, bisexual, lesbian, or homosexual encounters. It also
includes phone sex advertisements, dating services, adult personals, and sites
devoted to selling pornographic CD-ROMs and videos.
Full Nudity
Pictures exposing any or all portions of human genitalia. Topic does not
include sites categorized as Partial/Artistic Nudity containing partial nudity
of a wholesome nature. For example, it does not include Web sites for
publications such as National Geographic or Smithsonian magazine nor sites
hosted by museums such as the Guggenheim, the Louvre, or the Museum of
Modern Art.
Partial/Artistic Nudity
Pictures exposing the female breast or full exposure of either male or female
buttocks except when exposing genitalia which is handled under the Full
Nudity category. Topic does not include swimsuits, including thongs.
Searching for Blocked Sites
To verify whether WebBlocker is blocking a site as part of a category block, visit the
Search/Submit form on the Cyber Patrol Web site.
1 Open a Web browser and enter:
http://www.cyberpatrol.com/cyberNOT/default.htm
2 Scroll down to display the Cyber Patrol CyberNOT
3 Type the URL of the site to check.
4Click Check if the URL is on the CyberNOT List.
The search engine results notify you whether or not the site is on the CyberNOT list. Use this site
also to suggest a new site for both the CyberNOT and CyberYES list, as well as to request a site
review.
®
Search Engine.
Reference Guide 31
Page 36

Searching for Blocked Sites
32
Page 37

CHAPTER 5 Resources
There are many resources you can draw upon to support your efforts to improve
network security. This chapter lists several sources of information commonly used by
WatchGuard engineers, developers, and Technical Support teams to learn more
about network security in general and the WatchGuard product line in particular.
These include:
•Publishers
• Books
• White Papers and Requests for Comments
•Mailing Lists
•Web Sites
•Newsgroups
Publishers
Several publishers emphasize network security in their offerings.
Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.
O'Reilly & Associates, Inc. (ORA)
Publishes a Professional Computing Series that includes several titles about
networking and network security.
http://www.awl.com/
Publishes many books on network security.
http://www.ora.com/
Reference Guide 33
Page 38

Books
Books
Non-Fiction
Amoroso, Edward and Bellovin, Steven. Intranet and Internet Firewall Strategies.
Indianapolis: Que Corporation, 1996. ISBN 1562764225
Chapman, Brent, and Zwicky, Elizabeth D. Building Internet Firewalls. Sebastopol:
O'Reilly & Associates, 1994. ISBN 1-56592-124-0.
Cheswick and Bellovin. Firewalls and Internet Security: Repelling the Wily Hacker.
Reading, MA: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc., 1994. ISBN 0-201-63357-4.
Curry, David A. UNIX System Security: A Guide for Users and System Administrators.
Reading, MA: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc., 1992.
Denning, Dorothy E. Information Warfare and Security. Addison-Wesley, 1999. ISBN
0201433036.
Farley, Stearns, and Mark Farley Hsu, Tom Stearns, and Jeffrey Hsu, LAN Times Guide
to Security and Data Integrity. Berkeley: Osborne McGraw-Hill, 1996. ISBN 0-07882166-5.
Garfinkel and Spafford, Simson Garfinkel and Gene Spafford. Practical Unix and
Internet Security. Sebastopol: O'Reilly & Associates, 1994. ISBN 1565921488.
Goncalves, Marcus, Firewalls Complete. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1998. ISBN 0-07-
024645-9.
McClure, Stewart; Scambray, Joel; and Kurtz, George. Hacking Exposed. Second
Edition. McGraw-Hill Publishing, January 2000. ISBN 0072127481.
Power, Richard. Tangled Web: Tales of Digital Crime from the Shadows of Cyberspace. Que;
September 2000. ISBN 078973443x.
Schneier, Bruce. Applied Cryptography. Second Edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons,
Inc., 1996. ISBN 0-471-11709-9.
Schwartau, Winn. Cybershock: Surviving Hacker, Phreakers, Identity Theives, Internet
Terrorists and Weapons of Mass Disruption. New York: Thunder’s Mouth Press, 2000.
ISBN 1-56025-246-4.
Sheldon, Tom (Editor); Cox, Phil. Windows 2000 Security Handbook. McGraw-Hill
Publishing, November 2000. ISBN 0072124334.
Stevens, W. Richard. TCP/IP Illustrated. Reading MA: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.,
1994. ISBN 0201633469. (Note: This is a 3-volume set.)
Vacca, John, Intranet Security. Rockland, MA: Charles River Media, Inc., 1997. ISBN 1886801-56-8.
34
Page 39

Fiction
Stoll, Cliff. Cuckoo’s Egg. Pocket Books, 1995. ISBN 0671726889.
White papers & requests for comments
Reynolds, J. and J. Postel, Assigned Numbers, RFC1700. Available at these Web sites:
http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/htbin/rfc/rfc1700.html
ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/iana/assignments/port-numbers
Request for Comments Editor
http://www.rfc-editor.org
Internet Request for Comments (RFC)
http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/hypertext/information/rfc.html
White papers & requests for comments
Mailing Lists
wg-users@watchguard.com
WatchGuard sponsors a listserv for our customers. For more information, see
the Technical Support chapter in the User Guide.
firewall-wizards@nfr.net
firewalls@list.gnac.net
Web Sites
WatchGuard Frequently Asked Questions
http://support.watchguard.com/FAQS.asp
Complete Intranet Resource Page
http://www.intrack.com/intranet/firewall.shtml
Computer Communications Laboratory: Intro to Firewalls
http://www.cs.technion.ac.il/~cs236340/projects/winter2000/dist_app/
index.html
CSI Firewall Product Search Center
http://www.gocsi.com/firewall.htm
Dave Central Linux Software Archive
http://linux.davecentral.com/4218_tutadmin.html
Explanation of Firewall Logs
http://www.robertgraham.com/pubs/firewall-seen.html
Reference Guide 35
Page 40

Web Sites
Firewall.com
http://www.firewall.com
Firewall and Proxy Server How To
http://metalab.unc.edu/mdw/HOWTO/Firewall-HOWTO.html
FishNet Security Information
http://www.kcfishnet.com/secinfo/types.html
Information Security Magazine
http://www.truesecure.com/html/tspub/index.shtml
Internet Firewalls - Frequently Asked Questions
http://www.interhack.net/pubs/fwfaq/
Internet Firewalls — Resources
http://www.cerias.purdue.edu/coast/firewalls/
Introduction to Firewalls
http://www.soscorp.com/products/BS_FireIntro.html
The Java Security Web Site
http://www.rstcorp.com/javasecurity/
Archive of Vandalized Web Pages
http://www.attrition.org/
Gene Spafford’s Homepage
http://www.cerias.purdue.edu/homes/spaf/
Firewall Components
http://www-08.nist.gov/nistpubs/800-10/node44.html
Note: Yes, the dash after “www” is correct.
Firewall Wizards List Archives
http://www.nfr.net/firewall-wizards/
Microsoft Security Advisor
http://www.microsoft.com/security/
Model Security Policies
http://www.sans.org/newlook/resources/policies/policies.htm
Intrusion Detection Frequently Asked Questions
http://www.sans.org/newlook/resources/IDFAQ/ID_FAQ.htm
Bugtraq
http://www.securityfocus.com
National Institute of Standards and Technology, Computer Security Division
http://csrc.nist.gov/
Network Computing: Technology Solution Center
http://www.networkcomputing.com/1106/1106fl.html
36
Page 41

Newsgroups
Center for Education and Research in Information Assurance and Security
http://www.cerias.purdue.edu/
Reality Check
http://www.dilbert.com/
The RealPlayer Website
http://service.real.com/firewall
Vicomsoft Network Definitions Webpage
http://www.vicomsoft.com/knowledge/reference
UNIX Insider Guide to Firewall Design
http://www.sun.com/sunworldonline/swol-01-1996/swol-01-firewall.html
Zeuros Firewall Resource Page
http://www.zeuros.co.uk/firewall
Dictionaries of Computer Terminology
http://www.webopedia.com/
http://www.whatis.com/
http://info.astrian.net/jargon/
http://www.zdwebopedia.com
Newsgroups
comp.security.firewalls
Use your newsreader or electronic messaging application to subscribe to the
comp.security.firewalls Usenet newsgroup.
Deja.com
Deja.com provides a Web-based alternative to news reader services. In
addition to comp.security.firewalls, it includes several discussion groups and
the occasional room discussing network security issues. It can be found at:
http://www.deja.com/
Reference Guide 37
Page 42

Newsgroups
38
Page 43

CHAPTER 6 Firebox Read-Only System Area
WatchGuard ships all Fireboxes with a fixed, baseline set of functionality stored on
the read-only system area of the Firebox flash disk memory. It is possible to start the
Firebox using this read-only system area when the primary user area is
misconfigured or corrupted. This functionality allows you to:
• Troubleshoot problems where all access to the Firebox is lost
• Reset Firebox passphrases when you do not know or have forgotten them
Fireboxes shipped before LiveSecurity System 4.1 shipped with the original, standard
functionality called the read-only system area. Fireboxes shipped with LiveSecurity
System 4.1 or later contain both the older functions and a new set of features designed
to enhance usability, called the enhanced system area.
Read-only system area
All Fireboxes, both new and old, have a read-only system area which the unit can be
booted into utilizing the serial cable shipped with the Firebox. When a Firebox is
running from the read-only system area, the SysB light on the front panel is yellow
and the Armed light is green.
With the Firebox running the read-only system area, use one of two methods to
initialize the Firebox and prepare it for configuration:
• Out-of-band via a modem
• Direct via a serial cable
Enhanced System Mode
By default, all new Fireboxes (shipped with LiveSecurity System 4.1 or later) boot into
an Enhanced System Mode. When a Firebox is running from the Enhanced System
Mode, the SysA light on the front panel flickers yellow in a repeating pattern.
In a Firebox installed with Enhanced System Mode, the following methods are
available to initialize the Firebox and prepare it for configuration:
Reference Guide 39
Page 44

Initializing a Firebox using Hands-Free Installation
• Out-of-band via a modem
• Direct via a serial cable
• Hands-Free Installation via a local area network
• IP connection using Remote Provisioning
Initializing an older Firebox with the LiveSecurity System 4.1 or later automatically
upgrades the Firebox and enables the Firebox to run in the Enhanced System Mode
from that point forward. Until a Firebox is initialized with LiveSecurity System 4.1 or
later, it can not run in Enhanced System Mode.
Initializing a Firebox using Hands-Free Installation
Hands-Free Installation is the recommended method for installing a new Firebox. It
requires that a Firebox is capable of running in Enhanced System Mode. All Fireboxes
shipped with LiveSecurity System (Firebox System) 4.1 or later can run in Enhanced
System Mode; any older box already initialized using System 4.1 or later is
automatically upgraded to run in Enhanced System Mode.
To confirm that your Firebox is upgraded to run in Enhanced System
Mode, use a cross-over cable to connect any two Firebox Ethernet
interfaces. Turn on the Firebox. A flickering SysA light indicates that
the Firebox is running System 4.1 or later.
• A newly shipped Firebox or any model of Firebox already
initialized with System 4.1 or later
• Management Station running LSS/WFS that can attach via local
LAN connection to the Trusted interface of the Firebox
1 Use a cross-over cable to connect the Firebox External and Optional ethernet
interfaces.
A red, cross-over cable is included with the Firebox for this purpose.
2 Connect the Management Station to the same LAN as the Firebox Trusted
interface.
3 Turn the Firebox off and then on. Allow time for the Firebox to boot, then confirm
that the SysA light is flickering.
If the Firebox SysA light is not flickering, the Firebox is running release prior to System 4.1 and
you must use either the serial or modem initialization methods.
4 Use the QuickSetup Wizard to configure and initialize the Firebox. When
prompted to upload the security policy, select Use TCP/IP to Configure.
For more information, see the
Install Guide
.
Initializing a Firebox using a serial cable
For Fireboxes that shipped prior to LiveSecurity System 4.1, the read-only system
area is accessible using the Flash Disk Management Tool. It is necessary to restart the
Firebox from the read-only system area to
• Initialize a Firebox version 4.0 or prior for the first time
40
Page 45

Initializing a Firebox using a serial cable
• Troubleshoot problems where all access to the Firebox is lost
Before starting this procedure, establish a connection between the
Firebox console port and an available serial port on the
Management Station. Use a null modem cable (not a standard
serial cable). A null modem cable is shipped with the Firebox.
Also, make sure the Ethernet cables are plugged into the Trusted
interface.
• Any model Firebox
• Management Station running System 4.1 or later
Booting from the system area
From the Control Center:
1 Select LiveSecurity Control Center => Tools => Advanced => Flash Disk
Management.
The Flash Disk Management Tool dialog box appears.
2 Select Serial Line Creation.
3 Select Boot From the System Area. Click Continue.
A verification prompt appears. Verify that the Management Station connects to the Firebox
Trusted interface or through a direct connection (null modem cable).
4Click Yes.
The read-only system area Setup dialog box appears.
5 Enter the IP address you want to temporarily assign to the Firebox Trusted
interface. Click OK.
The Firebox uses this address for only a brief period of time until the Firebox reboots. However,
the address
Setup dialog box appears.
6 Turn the Firebox off and then on.
Check the Firebox front panel indicator lights. The SysB light should be illuminated indicating
that the Firebox is running from its read-only system area configuration. An Operation Complete
dialog box appears.
7Click OK.
must
be available on the same IP subnet as the Management Station. The COM Port
Working with a Firebox booted from the read-only system area
After you successfully boot the Firebox from the read-only system area, you can copy
a new configuration file to the primary area of the Firebox flash disk and reset Firebox
passphrases. The read-only system area configuration file enables you to
Reference Guide 41
Page 46

Initializing a Firebox using a serial cable
communicate only with the Firebox Trusted interface; while booted from the readonly system area, the Firebox will not pass traffic or perform other normal operations.
Do not attempt to use the read-only system area configuration file as a
base or template for your working configuration. It will not work. You
must create a new configuration file using the QuickSetup Wizard or
open an existing configuration file.
1 Verify that you can communicate with the Firebox.
The Firebox read-only system area configuration image allows the Firebox to respond to
network pings. Ping the temporary address assigned to the Trusted interface. If the Firebox does
not respond to the ping command, you may have a connectivity problem.
2 Start the Policy Manager. Use it to copy a valid configuration file to the primary
area of the Firebox flash disk.
- Initializing an older Firebox for the first time– Create a valid
configuration file using the Policy Manager.
- Recovering a previously configured Firebox– Use the configuration file on
the Management Station hard drive.
- Attempting to solve some other problem– Create a valid configuration file
using the Policy Manager.
3 Save the configuration file to the primary area of the Firebox flash disk.
For instructions, see the
Firebox.”
User Guide
4 To test whether the configuration file saved successfully to the Firebox, use the
Policy Manager to open it.
For instructions, see the
from the Firebox.”
User Guide
chapter on Firebox Basics, “Saving a Configuration to the
chapter on Firebox Basics, “Opening a Configuration File
Troubleshooting
The COM was successful, but I didn’t get the “Operation Complete” dialog box
when I rebooted the Firebox.
Check the cables. The null modem cable must be connected from the Console
port of the Firebox to the COM port on the Management Station.
Confirm that the COM port is enabled.
Try a different cable or another device (like a modem) to test that the COM
port is responding.
If these solutions do not work, contact WatchGuard Technical Support.
Why is the Flash Disk Management Tool unable to open the COM port on my
computer?
Enable the serial port (COM). The COM port must be enabled for the Flash
Disk Management Tool to recognize it.
Verify that you do not have two sessions of the Flash Disk Management Tool
open.
42
Page 47

Initializing a Firebox using a modem
The WatchGuard Firebox can accept both external and PCMCIA modems. Use a
modem for out-of-band initialization and configuration in cases where the Firebox is
located remotely from the Management Station
• Management Station running System 4.1 or later and
equipped with a modem, Dial-Up Networking software, and
a working telephone line
• Any Firebox model, equipped with an external modem and
modem cable or PCMCIA modem and a working telephone
line
To initialize a Firebox via out-of-band over a modem, the Firebox must first be
prepared:
• Use the blue null serial cable and adaptors included with the Firebox to connect
the Firebox CONSOLE port and external serial port in a loopback
configuration. Connect the Firebox CONSOLE port and external serial.
• Turn the power on the Firebox off then on. Confirm that the SysB light is lit.
• The Firebox is now ready to accept the out-of-band connection.
Initializing a Firebox using a modem
Initializing using remote provisioning
Use remote provisioning to initialize a Firebox in the case where a router sits between
the Management Station and the Firebox network connection. Because of the
flexibility of being able to initialize a Firebox from virtually any location on a
network, it is a very versatile option. However, remote provisioning has the
following restrictions:
• During provisioning, the Firebox and the router should be the only devices on
the network
• You must be able to flush the local router’s ARP tables, preferably by rebooting
• The Firebox must be running System 4.1 or later
• Firebox model initialized with System 4.1 or later
• Firebox attached as the only device behind a working router
• Management Station running System 4.1 or later that has
IP connectivity to the network on which the Firebox is
connected
• The network address and the netmask of the net behind the
router must be known
• One or more unused IP connections behind the router.
In order to provision a Firebox remotely via an IP connection, the Firebox must
belong to one of the following categories:
• New Firebox– By default, newly shipped Fireboxes boot into Enhanced
System Mode which supports remote provisioning.
Reference Guide 43
Page 48

Managing flash disk memory
• Older Firebox– For Fireboxes shipped before LiveSecurity System 4.1,
initialize the Firebox with LiveSecurity System 4.1 software. Then use the red
cross-over cable supplied with the Firebox to connect the Trusted and Optional
Ethernet interfaces in a loopback configuration.
During remote provisioning, one light appears on the front panel Traffic Volume
Indicator for each successful IP address the Firebox claims. The Firebox can claim up
to eight addresses.
The Processor Load Indicator marks the total number of different MAC addresses the
Firebox sees on the cable. If the number exceeds eight, the Firebox stops claiming
addresses; the SysA light remains lit. This feature is designed to prevent an
uninitialized Firebox from claiming addresses on a busy LAN. (If this happens,
reboot into Enhanced System Mode and try again.)
The Firebox and the router should be the only two devices on the LAN. Complete the
following:
1 Attach both the Firebox External interface and the router’s interface to a common
local area network, or use the red cross-over cable to connect them directly.
2 Turn the Firebox off and then on. Allow time for the Firebox to boot. Confirm that
there is a flashing pattern with a red, blinking, Trusted deny light on the lower
edge of the Security Triangle Display.
3 Flush the router ARP cache.
Rebooting the router will usually accomplish this.
4 From the Policy Manager on the Management Station, select File => Open
Firebox.
5 Select an unused IP address behind the router on the same network to which the
Firebox is attached. Set the Firebox’s read-write passphrase to wg. Set the timeout
to 90 seconds. Click OK.
6 If the procedure is successful, the open operation on the Management Station
completes. You can then follow regular procedures described in the User Guide to
configure and download a new flash image to the Firebox.
Managing flash disk memory
The Flash Disk Management Tool performs specific tasks involving the Firebox flash
memory. The flash disk is divided into three areas:
• System (SysB)– Contains a permanently stored, basic Firebox software image
with the passphrase wg.
• Primary (SysA)– Contains the Firebox software image used in normal
operation and the enhanced read-only system area.
• Backup– Contains a copy of the user-defined configuration file.
The Flash Disk Management Tool performs three different tasks for manipulating the
Firebox boot configuration file.
44
Page 49

Managing flash disk memory
Making a backup of the current configuration file
To ensure that you always have a backup version of a current, working configuration
file, copy the configuration file stored in the primary area to the Firebox flash disk
backup area. From the Control Center:
1 Select LiveSecurity Desktop => Tools => Advanced => Flash Disk Management.
2 Select Make Backup of Current Image. Click Continue.
A verification prompt appears. Verify that the Management Station connects to the Firebox
Trusted interface either over the network (TCP/IP) or via a modem using out-of-band
management.
3Click Yes.
The Connect To Firebox dialog box appears.
4Use the Firebox drop list to select a Firebox or type the IP address used by the
Management Station to communicate with the Firebox. Enter the configuration
(read/write) passphrase. Click OK.
When the backup is successful, an Operation Complete alert appears.
5Click OK.
You do not need to reboot the Firebox.
Restoring a backup configuration file
Backing up and restoring a configuration file acts not only on the configuration file
but on the enture flash image. This is important to note if you are loading a new
version, patch, or component onto the Firebox.
Restore the backup configuration file to the primary area of the Firebox flash disk
when:
• You incorrectly overwrite the primary configuration file.
• The primary configuration file is incorrectly configured or is otherwise
unusable.
This procedure is only possible when a backup configuration
file is on the backup area of the Firebox's flash disk. See
“Making a backup of the current configuration file” on
page 45. There is no backup file on the Firebox until you copy
one there.
1 Select LiveSecurity Desktop => Tools => Advanced => Flash Disk Management.
The Flash Disk Management Tool dialog box appears.
2 Select Restore Backup Image. Click Continue.
A verification prompt appears. Verify that the Management Station connects to the Firebox
Trusted interface either over the network (TCP/IP) or via a modem using out-of-band
management.
3Click Yes.
The Connect To Firebox dialog box appears.
4Use the Firebox drop list to select a Firebox or type the IP address used by the
Management Station to communicate with the Firebox. Enter the configuration
(read/write) passphrase. Click OK.
The Firebox copies the configuration file from the backup area to the primary area of its flash
disk and reboots from the backup configuration file.
Reference Guide 45
Page 50

Managing flash disk memory
46
Page 51

CHAPTER 7 Out-of-Band Initialization Strings
This chapter provides a reference list of PPP and modem initialization strings used to
configure out-of-band (OOB) management.
PPP initialization strings
These are the strings and syntaxes available for use when configuring a Firebox for
out-of-band management in Policy Manager:
asyncmap <map>
Set the async character map to <map>. This map describes which control
characters cannot be successfully received over the serial line. Pppd will ask
the peer to send these characters as a 2-byte escape sequence. The argument is
a 32-bit hex number with each bit representing a character to escape. Bit 0
(00000001) represents the character 0x00; bit 31 (80000000) represents the
character 0x1f or ^_. If multiple asyncmap options are given, the values are
ORed together. If no asyncmap option is given, no async character map will
be negotiated for the receive direction; the peer should then escape all control
characters. To escape transmitted characters, use the escape option.
escape xx,yy,..
Specifies that certain characters should be escaped on transmission
(regardless of whether the peer requests them to be escaped with its async
control character map). The characters to be escaped are specified as a list of
hex numbers separated by commas. Note: Almost any character can be
specified for the escape option, unlike the asyncmap option which only allows
control characters to be specified. The characters which may not be escaped
are those with hex values 0x20 — 0x3f or 0x5e.
Reference Guide 47
Page 52

PPP initialization strings
mpfto <period>
Specifies how long the PPP session should wait for a valid management
session to begin. If no valid session starts, then PPP will disconnect after this
time-out period. The default is 90 seconds.
mru n
Set the MRU (Maximum Receive Unit) value to n. Pppd will ask the peer to
send packets of no more than n bytes. The minimum MRU value is 128. The
default MRU value is 1,500. A value of 296 is recommended for slow links (40
bytes for TCP/IP header + 256 bytes of data).
mtu n
Set the MTU (Maximum Transmit Unit) value to n. Unless the peer requests a
smaller value via MRU negotiation, pppd will request that the kernel
networking code send data packets of no more than n bytes through the PPP
network interface.
passive
Enables the “passive” option in the LCP. With this option, pppd will attempt
to initiate a connection; if no reply is received from the peer, pppd will then
just wait passively for a valid LCP packet from the peer, instead of exiting, as
it would without this option.
bsdcomp nr,nt
Request that the peer compress packets that it sends, using the BSD-Compress
scheme, with a maximum code size of nr bits, and agree to compress packets
sent to the peer with a maximum code size of nt bits. If nt is not specified, it
defaults to the value given for nr. Values in the range 9 to 15 can be used for nr
and nt; larger values give better compression but consume more kernel
memory for compression dictionaries. Alternatively, a value of 0 for nr or nt
disables compression in the corresponding direction. Use nobsdcomp or
bsdcomp 0 to disable BSD-Compress compression entirely.
debug
Enables connection debugging facilities. If this option is given, pppd will log
the contents of all control packets sent or received in a readable form.
default-asyncmap
Disable asyncmap negotiation, forcing all control.
default-mru
Disable MRU (Maximum Receive Unit) negotiation. With this option, pppd
will use the default MRU value of 1,500 bytes for both the transmit and
receive direction.
deflate nr,nt
Request that the peer compress packets that it sends, using the Deflate
scheme, with a maximum window size of 2**nr bytes, and agree to compress
packets sent to the peer with a maximum window size of 2**nt bytes. If nt is
not specified, it defaults to the value given for nr. Values in the range 8 to 15
can be used for nr and nt; larger values give better compression but consume
more kernel memory for compression dictionaries. Alternatively, a value of 0
48
Page 53

PPP initialization strings
for nr or nt disables compression in the corresponding direction. Use
nodeflate or deflate 0 to disable Deflate compression entirely.
Pppd requests Deflate compression in preference to BSDCompress if the peer can do either.
idle n
Specifies that pppd should disconnect if the link is idle for n seconds. The link
is idle when no data packets (that is, IP packets) are being sent or received.
Note: It is not advisable to use this option with the persist option without the
demand option. If the active-filter option is given, data packets that are
rejected by the specified activity filter also count as the link being idle.
ipcp-accept-local
With this option, pppd will accept the peer’s idea of our local IP address, even
if the local IP address was specified in an option.
ipcp-accept-remote
With this option, pppd will accept the peer’s idea of its (remote) IP address,
even if the remote IP address was specified in an option.
ipcp-max-configure n
Set the maximum number of IPCP configure-request transmissions to n
(default 10).
ipcp-max-failure n
Set the maximum number of IPCP configure-NAKs returned before starting to
send configure-rejects instead to n (default 10).
ipcp-max-terminate n
Set the maximum number of IPCP terminate-request transmissions to n
(default 3).
ipcp-restart n
Set the IPCP restart interval (retransmission time-out) to n seconds (default 3).
lcp-echo-failure n
If this option is given, pppd will presume the peer to be dead if n LCP echorequests are sent without receiving a valid LCP echo-reply. If this happens,
pppd will terminate the connection. Use of this option requires a non-zero
value for the lcp-echo interval parameter. This option can be used to enable
pppd to terminate after the physical connection has been broken (for example,
the modem has hung up) in situations where no hardware modem control
lines are available.
lcp-echo-interval n
If this option is given, pppd will send an LCP echo-request frame to the peer
every n seconds. Normally the peer should respond to the echo-request by
sending an echo-reply. This option can be used with the lcp-echo-failure
option to detect that the peer is no longer connected.
Reference Guide 49
Page 54

PPP initialization strings
lcp-max-configure n
Set the maximum number of LCP configure-request transmissions to n
(default 10).
lcp-max-failure n
Set the maximum number of LCP configure-NAKs.
lcp-max-terminate n
Set the maximum number of LCP terminate-request transmissions to n
(default 3).
lcp-restart n
Set the LCP restart interval (retransmission time-out) to n seconds (default 3).
local
Don't use the modem control lines. With this option, pppd will ignore the
state of the CD (Carrier Detect) signal from the modem and will not change
the state of the DTR (Data Terminal Ready) signal.
maxconnect n
Terminate the connection when it has been available for network traffic for n
seconds (that is, n seconds after the first network control protocol comes up).
modem
Use the modem control lines. This option is the default. With this option,
pppd will wait for the CD (Carrier Detect) signal from the modem to be
asserted when opening the serial device (unless a connect script is specified),
and it will drop the DTR (Data Terminal Ready) signal briefly when the
connection is terminated and before executing the connect script.
netmask n
Set the interface netmask to n, a 32-bit netmask in decimal dot notation (for
example, 255.255.255.0). If this option is given, the value specified is ORed
with the default netmask. The default netmask is chosen based on the
negotiated remote IP address; it is the appropriate network mask for the class
of the remote IP address, ORed with the netmasks for any non-point-to-point
network interfaces in the system that are on the same network.
noauth
Do not require the peer to authenticate itself.
nobsdcomp
Disables BSD-Compress compression; pppd will not request or agree to
compress packets using the BSD-Compress scheme.
noccp
Disable CCP (Compression Control Protocol) negotiation. This option should
only be required if the peer is buggy and gets confused by requests from pppd
for CCP negotiation.
50
Page 55

Modem initialization strings
nocrtscts
Disable hardware flow control (that is, RTS/CTS) on the serial port. If neither
the crtscts nor the nocrtscts option is given, the hardware flow control setting
for the serial port is left unchanged.
noipdefault
Disables the default behavior when no local IP address is specified, which is to
determine (if possible) the local IP address from the hostname. With this
option, the peer will have to supply the local IP address during IPCP
negotiation (unless it was specified explicitly on the command line or in an
options file).
nomagic
Disable magic number negotiation. With this option, pppd cannot detect a
looped-back line. This option should only be needed if the peer is buggy.
nopersist
Exit once a connection has been made and terminated. This is the default
unless the persist or demand option has been specified.
novjccomp
Disable the connection-ID compression option in Van Jacobson-style TCP/IP
header compression. With this option, pppd will not omit the connection-ID
byte from Van Jacobson compressed TCP/IP headers, nor ask the peer to do
so.
silent
Pppd will not transmit LCP packets to initiate a connection until a valid LCP
packet is received from the peer (as for the “passive” option with older
versions of pppd).
xonxoff
Use software flow control (that is, XON/XOFF) to control the flow of data on
the serial port.
Modem initialization strings
These parameters specify a chat session that occurs between the Firebox and the
modem to properly initialize the modem. In most cases the default initializations
work with a wide variety of modems. The default initializations are known to work
with the list of approved modems.
In the default initializations below, the parameters marked with ^ specify what the
Firebox should expect back from the modem, and the portions marked with '_____'
specify what is to be sent to the modem:
Reference Guide 51
Page 56

Modem initialization strings
"" +\p+\p+\d\r\pATH "" \dAT&F OK ATE0 OK ATS0=1 OK
^^ ________________ ^^ ______ ^^ ____ ^^ ______ ^^
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Explanation of fields
1 Specifies that the Firebox should expect nothing back from the modem at this
point in the chat.
2 Specifies that three plus characters (+) should be sent with short pauses in
between, then a 1-second delay, then a return character, a short pause, then the
characters “ATH” are sent, finally followed by a carriage return (which is not
shown, but implied). This sequence commands most modems to hang up.
3 Specifies that the Firebox should expect nothing back from the modem at this
point in the chat.
4 Send a 1-second delay followed by the characters “AT&F” to command the
modem to recall its factory-default configuration.
5 Expect “OK” back from the modem.
6 Send “ATE0” to modem, which directs it not to echo back commands characters
sent.
7Expect “OK” back.
8 Send “ATS0=1” to direct the modem to answer incoming calls after one ring.
9 Expect back a final “OK” from the modem.
For an out-of-band management connection, the modem needs to be set up to answer the phone
when it rings, and to use hardware flow control on the serial line. The Flow Control and Modem
Initialization fields on the OOB tab enable you to make these settings.
Common initialization string values
Auto-answer
Send the string
pickup after one ring, enter
ATS0=
x, where x = the number of rings before answering. For a
ATS0=1
.
Special sequences
TIMEOUT value
The initial time-out value is 45 seconds. Once changed, the time-out setting
remains in effect until it is changed again.
EOT
The special reply string of EOT indicates that the chat program should send
an EOT character to the remote. This is normally the end-of-file character
sequence. A return character is not sent following the EOT. The EOT sequence
can be embedded into the send string using the sequence Ctrl+D.
52
Page 57

BREAK
The special reply string of BREAK will cause a break condition to be sent. The
break is a special signal on the transmitter. The break sequence can be
embedded into the send string using the \K sequence.
Escape sequences
The expect and reply strings may contain escape sequences. All of the sequences are
legal in the reply string. Many are legal in the expect sequence. Those that are not
valid in the expect sequence are so indicated.
"" or ‘ ‘
Expect or send a null string. If you send a null string, it will still send the
return character. This sequence can either be a pair of apostrophes or quotes.
\b
Backspace.
\c
Suppress the new line at the end of the reply string. This is the only method to
send a string without a trailing return character. It must be at the end of the
send string. For example, the sequence hello\c will simply send the characters
h, e, l, l, o (not valid in expect).
Modem initialization strings
\d
Delay for 1 second (not valid in expect).
\K
Insert a BREAK (not valid in expect).
\n
Send a newline or linefeed character.
\N
Send a null character. The same sequence can be represented by \0 (not valid
in expect).
\p
Pause for a fraction of a second. The delay is 1/10th of a second (not valid in
expect).
\q
Suppress writing the string to the logging system. The string ?????? is written
to the log in its place (not valid in expect).
\r
Send or expect a carriage return.
\s
A space character in the string. This can be used when it is not desirable to
quote the strings that contains spaces. For example, the sequence 'HI TIM' and
HI\sTIM are the same.
Reference Guide 53
Page 58

Modem initialization strings
\t
Send or expect a tab character
\\
Send or expect a backslash character
\ddd
Collapse the octal digits (ddd) into a single ASCII character and send that
character. Some characters are not valid in Ctrl+C; for these characters,
substitute the sequence with the control character represented by C. For
example, the character DC1 (17) is shown as Ctrl+Q. Some characters are not
valid in expect.
54
Page 59

CHAPTER 8 Glossary
This glossary contains a list of terms, abbreviations, and acronyms frequently used
when discussing networks, firewalls, and WatchGuard products.
active mode FTP
One of two ways an FTP data connection is made. In active mode, the FTP
server establishes the data connection. In passive mode, the client establishes
the connection. In general, FTP user agents use active mode and Web user
agents use passive mode.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
A TCP/IP protocol used to convert an IP address into a physical address such
as an Ethernet address.
address space probe
An intrusion measure in which a hacker sequentially attacks IP addresses.
These probes are usually attempts to map IP address space to look for security
holes that a sender might exploit to compromise system security.
AH (authentication header)
A protocol used in IPSec available for use with IPSec Branch Office VPN. AH
provides authentication for as much of the IP header as possible (except for
mutable fields that are nondeterministic, such as TTL fields) and all upper
protocols and payload. It offers the functionality of ESP except for
confidentiality, which ESP’s encryption provides.
Alias
Aliases are shortcuts that enable you to identify groups of hosts, networks, or
users with one identifying name. They are used to speed user authentication
and service configuration.
armed
When a Firebox is armed, it is actively guarding against intrusion and attack.
ARP
See Address Resolution Protocol.
Reference Guide 55
Page 60

ARP tables
A table of active ARP addresses on a computer.
ascending
A method of ordering a group of items from lowest to highest, such as from A
to Z.
authentication
Authentication is a method of mapping a username to a workstation IP
address, allowing the tracking of connections based on name rather than IP
address. With authentication, it doesn’t matter what IP address is used or
from which machine a person chooses to work.
backbone
A term often used to describe the main network connections composing the
Internet.
Bandwidth Meter
A monitoring tool that provides a real-time graphical display of network
activities across a Firebox. Formerly known as the Mazameter.
bastion host
A computer placed outside a firewall to provide public services (such as
WWW and FTP) to other Internet sites. The term is sometimes generalized to
refer to any host critical to the defense of a local network. In WatchGuard
documentation, also called the Optional network.
bitmask
A pattern of bits for an IP address that determines how much of the IP address
identifies the host and how much identifies the network.
blocked port
A security measure in which a specific port associated with a network service
is explicitly disabled, blocking users outside the firewall from gaining access
to that service port. A blocked port takes precedence over any service settings
that are generally enabled.
blocked site
An IP address outside the Firebox explicitly blocked so it cannot connect with
hosts behind the Firebox. Blocked sites can be manual and permanent, or
automatic and temporary.
boot up
To star t a compu ter.
Branch Office Virtual Private Networking (BOVPN)
BOVPN creates a secure tunnel over an unsecure network, between two
networks that are protected by the WatchGuard LiveSecurity System, or
between a WatchGuard Firebox and an IPSec-compliant device. It allows you
to connect two or more locations over the Internet while protecting the
resources on the Trusted and Optional networks.
56
Page 61

broadcast address
An address used to broadcast a request to a network, usually to discover the
presence of a machine.
browser
See Web browser.
cascade
A command that arranges windows so that they are overlapped, with the
active window in front.
CD-ROM (Compact Disc Read-Only Memory)
A disk on which data is stored.
checkbox
A dialog box option that is not mutually exclusive with other options.
Clicking a checkbox inserts or removes an X or a checkmark.
CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)
A routing mechanism designed to deal with the exhaustion of Class B
network addresses, and the subsequent allocation of multiple Class C
addresses to sites. CIDR is described in RFC 1519.
cipher block chaining
A form of DES encryption that requires the entire message to decrypt rather
than a portion of the message.
Class A, Class B, Class C
See Internet address class.
click
To press the primary mouse button once.
client
Software installed on a hard disk used to access resources on the Internet.
cold boot
The process of starting a computer by turning on the power to the system
unit.
compress
To compact a file or group of files so that they occupy less disk space. See also
decompress.
connected enterprise
A company or organization with a computer network exchanging data with
the Internet or some other public network.
Control Center
The WatchGuard Control Center is a toolkit of applications run from a single
location, enabling configuration, management, and monitoring of a network
security policy.
Reference Guide 57
Page 62

Control Panel
The set of Windows 95/98 or Windows NT programs used to change system
hardware, software, and Windows settings.
coprocessor
A separate processor designed to assist in specific functions, such as handling
complex mathematics or graphics, and to temporarily reduce the workload of
the microprocessor.
CPU (central processing unit)
The microprocessor chip that interprets and carries out instructions.
CRYPTOCard
An authentication system that uses an offline card to hash encryption keys,
which increases their safety against unauthorized decryption.
CSLIP (Compressed Serial Line Internet Protocol)
A protocol for exchanging IP packets over a serial line, which compresses the
headers of many TCP/IP packets.
custom filter rules
Filter rules created in WatchGuard Policy Manager to allow specific content
types through the Firebox.
data
Distinct pieces of information, usually formatted in a special way.
datagram
A packet of data that stands alone. Generally used in reference to UDP and
ICMP packets when talking about IP protocols.
DCERPC (Distributed Computing Environment Remote Procedure Call)
Allows connections bound for port 135 on a machine. These initial calls
typically result in a response from the trusted machine that redirects the client
to a new port for the actual service the client wants.
descending
A method of ordering a group of items from highest to lowest, such as from Z
to A.
decompress
To expand a compressed file or group of files so that the file or files can be
opened. See also compress.
decrypt
The process of decoding data that has been encrypted and requires a key or
password.
default
A predefined setting that is built into a program and is used when an
alternative setting is not specified.
58
Page 63

default packet handling
Default packet handling automatically and temporarily blocks hosts that
originate probes and attacks against a network.
denial of service (DoS)
A way of monopolizing system resources so that other users are ignored. For
example, someone could Finger an unsecured host continuously so that the
system is incapable of running or executing other services.
DES (Data Encryption Standard)
A block-oriented cipher that encrypts blocks of 64 bits. The encryption is
controlled by a key of 56 bits. See also Triple-DES.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
A means of dynamically allocating IP addresses to devices on a network.
dialog box
A box that displays additional options when a command is chosen from a
menu.
dial-up connection
A connection between your remote computer and a server using software, a
modem, and a telephone.
dimmed
The grayed appearance of a command or option that is unavailable.
disarmed
The state of a Firebox when it is not actively protecting a network.
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
Another name for the optional bastion network. One common use for this
network is as a public Web server.
DNS (Domain Name System)
A network system of servers that converts numeric IP addresses into readable,
hierarchical Internet addresses.
Domain Name System (DNS)
A network system of servers that converts numeric IP addresses into readable,
hierarchical Internet addresses.
dotted notation
The notation used to write IP addresses as four decimal numbers separated by
dots (periods), sometimes called dotted quad – 123.212.12.4 is an example.
double-click
To press the primary mouse button twice rapidly.
download
To transfer a file from a remote computer to your local computer.
Reference Guide 59
Page 64

drop-in configuration
A configuration in which the Firebox is physically located between the router
and the LAN without any of the computers on the Trusted interface being
reconfigured. This protects a single network that is not subdivided into
smaller networks.
drop-in network
This configuration allows for distribution of logical address space across the
Firebox interface.
DVCP (Dynamic VPN Configuration Protocol)
A WatchGuard proprietary protocol that simplifies configuration of VPNs.
dynamic NAT
Dynamic NAT is also known as IP masquerading or port address translation.
It hides network addresses from hosts on the external network. Hosts
elsewhere on the Internet see only outgoing packets from the Firebox itself.
dynamic packet filtering
Filtering based not only on service types, but also on conditions surrounding
the initiation of a connection.
encryption
The translation of data into a secret code. To read an encrypted file, you must
use a key or password that enables decryption.
ESP (Encapsulation Security Payload)
A protocol used in IPSec available for use with IPSec Branch Office VPN. ESP
encapsulates and authenticates IP packets to be passed over the tunnel,
providing confidentiality, data integrity, and origin authentication. ESP is
similar to AH, except that it provides encryption.
Event Processor
See LiveSecurity Event Processor.
expand
To display all subordinate entries in an outline or in a folder.
extension
See file extension.
External interface
An interface connected to the external network that presents the security
challenge, typically the Internet.
failover
Configuration that allows a secondary machine to take over in the event of a
failure in the first machine, thus allowing normal use to return or continue.
fail-shut mode
A condition in which a firewall blocks all incoming and outgoing traffic in the
event of a firewall failure. This is the opposite of fail-open mode, in which a
60
Page 65

firewall crash opens all traffic in both directions. Fail-shut is the default failure
mode of the WatchGuard LiveSecurity System.
field
An area in a form or Web page in which to enter or view specific information
about an individual task or resource.
file extension
A period and up to three characters at the end of a file name. The extension
can help identify the kind of information a file contains.
filters
Small, fast programs in a firewall that examine the header files of incoming
packets and route or reject the packets based on the rules for the filter.
Firebox
The WatchGuard firewall appliance, consisting of a red box with a purposebuilt computer and input/output architecture optimized as the resident
computer for network firewall software.
firewall
Any technological measures taken to secure a computer network against
unwanted use and abuse via net connections.
firewalling
The creation or running of a firewall.
flash disk
An 8-megabyte, on-board flash ROM disk that acts like a hard disk in a
Firebox.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
The most common protocol for copying files over the Internet. See also active
mode FTP.
gateway
The IP address through which messages pass.
graphical user interface (GUI)
The visual representation on a computer screen that allows users to view,
enter, or change information.
header
A series of bytes at the beginning of a communication packet that provide
identification information about the packet such as its computer of origin, the
intended recipient, packet size, and destination port number.
Help system
A form of online information about a software or hardware system.
High Availability
High Availability enables the installation of two Fireboxes on one network in
a failover configuration. At any given moment, one Firebox is in active mode
while the other is in standby mode, ready to take over if the first box fails.
Reference Guide 61
Page 66

home page
The first page of a Web site used as an entrance into the site.
host route
A setup in which an additional router is behind the Firebox and one host is
behind that router. You configure a host route to inform the Firebox of this
additional host behind the additional router.
HostWatch
A graphical monitor providing a real-time display of which hosts are
connected from behind the Firebox to hosts on the Internet.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
A set of rules used to format Web pages, including methods to specify text
characteristics, graphic placement, and links. HTML files are read and
interpreted by a Web browser.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol)
A communications standard designed and used to transfer information and
documents created using languages such as HTML.
HTTPS (Secure HTTP)
A variation of HTTP enabling the secure transmission of data and HTML files.
Generally used in conjunction with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
hyperlink
An object on a Web page such as a graphic or underlined text that represents a
link to another location in the same file or a different file. When clicked, the
page or graphic appears.
IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority)
The central authority charged with assigning parameter values to Internet
protocols. For example, IANA controls the assignment of well-known TCP/IP
port numbers. Currently IANA manages port numbers 1 through 1023.
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
A protocol used to pass control and error messages back and forth between
nodes on the Internet.
IKE (Internet Key Exchange)
Used with IPSec virtual private networks. Automates the process of
negotiating keys, changing keys and determining when to change keys.
initialize
To prepare a disk for information storage.
installation wizard
A wizard specifically designed to guide a user through the process of
installing software. See wizard.
62
Page 67

Internet address class
To efficiently administer the 32-bit IP address class space, IP addresses are
separated into three classes that describe networks of varying sizes:
Class AIIf the first octet of an IP address is less than 128, it is a Class A
address. A network with a Class A address can have up to about 16 million
hosts.
Class B If the first octet of an IP address is from 128 to 191, it is a Class B
address. A network with a Class B address can have up to 64,000 hosts.
Class C If the first octet of an IP address is from 192 to 223, it is a Class C
address. A network with a Class C address can have up to 254 hosts.
intranet
A self-contained network that uses the same communications protocols and
file formats as the Internet.
IP (Internet Protocol)
A protocol used by the Internet that enables computers to communicate over
various physical media.
IP address host
The 32-bit address that identifies a host. Technically, a host is a network
device connected to the Internet. In common usage, a host is a computer or
some other device that has a unique IP address. Computers with more than
one IP address are known as multihomed hosts.
IP fragment
An IP datagram that is actually part of a larger IP packet. IP fragments are
typically used when an IP packet is too large for the physical media that the
data must cross. For example, the IP standard for Ethernet limits IP packets to
about 1,500 bytes, but the maximum IP packet size is 65,536 bytes. To send
packets larger than 1,500 bytes over an Ethernet, IP fragments must be used.
IP masquerading
See dynamic NAT.
IP options
Extensions to the Internet Protocol used mainly for debugging and special
applications on local networks. In general, there are no legitimate uses of IP
options over an Internet connection.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security)
An open-standard methodology of creating a secure tunnel through the
Internet, connecting two remote hosts or networks. IPSec provides several
encryption and authentication options to maximize the security of the
transmission over a public medium such as the Internet.
ISP (Internet service provider)
Typically, a business that sells access to the Internet. A government
organization or an educational institution may be the ISP for some
organizations.
Reference Guide 63
Page 68

Java applet
A Java applet is a program written in the Java programming language that can
be included on an HTML page, much in the same way an image is included.
When you use a Java technology—enabled browser to view a page that
contains an applet, the applet’s code is transferred to your system and carried
out by the browser's Java virtual machine (JVM).
LAN (local area network)
A computer network that spans a relatively small area generally confined to a
single building or group of buildings.
link
See hyperlink.
LiveSecurity Event Processor (LSEP)
A program that controls notification and logging on the log hosts. It provides
critical timing services for the Firebox and includes its own GUI.
LiveSecurity Inbox
The client software for the WatchGuard LiveSecurity Service.
LogViewer
As a part of the Control Center, the LogViewer displays a static view of the
Logdb file.
loopback interface
A pseudo interface that allows a host to use IP to talk to its own services. A
host is generally configured to trust packets coming from addresses assigned
to this interface. The Class A address group 127.0.0.0 has been reserved for
these interfaces.
LSEP
See LiveSecurity Event Processor.
mail server
Refers to both the application and the physical machine tasked with routing
incoming and outgoing electronic mail.
Management Station
The computer on which you run the WatchGuard LiveSecurity System
Control Center and Policy Manager; sometimes referred to as the
administration host.
network address translation (NAT)
Network address translation hides internal network addresses from hosts on
an external network.
MAC address
Media Access Control address that is unique to your computer, and is used to
identify its hardware.
64
Page 69

masquerading
In the LiveSecurity System, masquerading sets up addressing so that a
Firebox presents its IP address to the outside world in lieu of the IP addresses
of the hosts protected by the Firebox.
Mazameter
See Bandwidth Meter.
MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)
Extensions to the SMTP format that allow binary data, such as that found in
graphic files or documents, to be published and read on the Internet.
MSDUN
Microsoft Dial-Up Networking is an executable program required for remote
user VPN.
multiple network configuration
A configuration used in situations in which a Firebox is placed with separate
logical networks on its interface.
MUVPN
Multi-user VPN.
network address translation (NAT)
Network address translation hides or masquerades network addresses from
hosts on another network, protecting the confidentiality and architecture of
the network.
netmask
An inverse mask of the significant bits of a network address. On a local net,
the range of addresses one can expect to be found directly connected to the
network. Netmasks generally occur with a Class C license address space of 8
bits, so the netmask is 255.255.255.0. It can be a smaller number of bits if
subnetting is in effect. Some systems require the netmask to be an even
number of bits.
Network Configuration wizard
Creates a basic Firebox configuration. It consists of a series of windows that
prompt for essential configuration information for drop-in or advanced
network installations.
NFS (Network File System)
A popular TCP/IP service for providing shared file systems over a network.
NTP (Network Time Protocol)
An Internet service used to synchronize clocks between Internet hosts.
Properly configured, NTP can usually keep the clocks of participating hosts
within a few milliseconds of each other.
octet
A byte. Used instead of “byte” in most IP documents because historically
many hosts did not use 8-bit bytes.
Reference Guide 65
Page 70

Optional interface
An interface that connects to a second secured network, typically any network
of servers provided for public access.
out-of-band (OOB)
A management feature that enables the Management Station to communicate
with the Firebox via a telephone line and a modem. OOB is very useful for
remotely configuring a Firebox when Ethernet access is unavailable.
packet filtering
Controlling access to a network by analyzing the incoming and outgoing
packets and letting them pass or halting them based on the IP addresses of the
source and destination. Packet filtering is one technique, among many, for
implementing security firewalls.
passive mode FTP
See active mode FTP.
PCMCIA (Personal Computer Memory Code International Association) card
A standard compact physical interface used in personal computers. The most
common application of PCMCIA cards is for modems and storage.
permission
Authorization to perform an action.
PLIP (Parallel Line Internet Protocol)
A protocol for exchanging IP packets over a parallel cable.
Policy Manager
One component in the WatchGuard LiveSecurity System, consisting of the
user interface used to modify and upload a Firebox configuration file.
pop-up window
A window that suddenly appears (pops up) when an option is selected with a
mouse or a function key is pressed.
port
A channel for transferring electronic information between a computer and a
network, peripherals, or another computer.
port address translation
See dynamic NAT.
port forwarding
In the LiveSecurity System, an option in which the Firebox redirects IP
packets to a specific masqueraded host behind the firewall based on the
original destination port number.
port space probe
An intrusion measure whereby a hacker sequentially attacks port numbers.
These probes are usually attempts to map port space to look for security holes
which the sender might exploit.
66
Page 71

port, TCP or UDP
A TCP or UDP service endpoint. Together with the hosts’ IP addresses, ports
uniquely identify the two peers of a TCP connection.
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol)
A link-layer protocol used to exchange IP packets across a point-to-point
connection, usually a serial line.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
One of the two standards for dial-up connection of computers to the Internet,
with stable data negotiation, compression, and error correction.
principle of precedence
Rules that determine which permissions and prohibitions override which
others when creating a combination of security policies.
probe
A type of hacking attempt characterized by repetitious, sequential access
attempts. For example, one might try to probe a series of ports for one that is
more open and less secure.
provisioning
The process of setting the parameters of the Firebox or SOHO before it is sent
to a customer. With respect to the Firebox, the minimum Policy Manager
configuration is set with the most basic services on the box, Ping and
WatchGuard. It also sets the IP addresses on the Firebox.
proxy server
A server that stands in place of another server. In firewalling, a proxy server
poses as a specific service but has more rigid access and routing rules.
protocol
An agreed-upon format for transmitting data between two devices. The
protocol determines the following: the type of error checking to be used, data
compression method, if any; how the sending device will indicate that it has
finished sending a message, and how the receiving device will indicate that it
has received a message.
RADIUS server
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is an open, crossplatform system for authenticating network users.
related hosts
A method to place hosts on the Optional or External interface when using a
simple or drop-in network configuration. Examples include placing a router
on the External interface or an HTTP server on the Optional interface.
related networks
Networks on the same physical wire as the Firebox interfaces but with
network addresses that belong to an entirely different network.
Reference Guide 67
Page 72

report
A formatted collection of information that is organized to provide project data
on a specific subject.
RFC (Request for Comments)
RFC documents describe standards used or proposed for the Internet. Each
RFC is identified by a number, such as RFC 1700. RFCs can be retrieved either
by e-mail or FTP.
route
The sequence of hosts through which information travels to reach its
destination host.
routed configuration or network
A configuration with separate network addresses assigned to at least two of
the three Firebox interfaces. This type of configuration is intended for
situations in which the Firebox is put in place with separate logical networks
on its interfaces.
router
A device, connected to at least two networks, that receives and sends packets
between those networks. Routers use headers and a forwarding table to
forward packets to their destination. Most rely on ICMP to communicate with
one another and configure the best route between any two hosts.
RUVPN (Remote User VPN)
Remote User Virtual Private Networking establishes a secure connection
between an unsecured remote host and a protected network over an
unsecured network.
scalable architecture
Software and/or hardware constructed so that, after configuring a single
machine, the same configuration can be propagated to a group of connected
machines.
screening router
A machine that performs packet filtering.
secondary network
A network on the same physical wire as a Firebox interface that has an
address belonging to an entirely different network.
SecurID server
Each time an end user connects to the specialized-HTTP server running on the
Firebox on port 4100, a Java-enabled applet opens prompting for the
username, password, and whether or not to use SecurID (PAP)
Authentication. The username and password are DES-encrypted using a
secret key shared between the Java client and the Firebox. The Firebox then
decrypts the name and password to create a RADIUS PAP Access-Request
packet, and then sends it to the configured RADIUS server.
68
Page 73

Security Triangle Display
An LED indicator on the front of a Firebox that indicates the directions of
traffic between the three Firebox interfaces.
self-extracting file
A compressed file that automatically decompresses when double-clicked.
Server Message Block (SMB)
A message format used by DOS and Windows to share files, directories and
devices. NetBIOS is based on the SMB format, and many network products
use SMB. These SMB-based networks include LAN Manager, Windows for
Workgroups, Windows NT, and LAN Server.
Services Arena
An area in Policy Manager that displays the icons that represent the services
(proxies and packet filters) configured for a Firebox.
ServiceWatch
A graphical monitor that provides a real-time display graphing how many
connections exist, by service.
session stealing
An intrusion maneuver whereby a hacker sends a command to an already
existing connection in order to have that command provide the information
needed to stage a separate attack.
shared secret
A passphrase or password that is the same on the host and the client
computer. It is used for authentication.
SHTTP
See HTTPS.
slash notation
A format for writing IP addresses in which the number of bits in the IP
number is specified at the end of the IP address. For example: 192.168.44.0/24.
SLIP (Serial Line Internet Protocol)
A protocol for exchanging IP packets over a serial line.
SMS (Security Management System)
The former name of the GUI used to configure a Firebox. Now known as the
WatchGuard Policy Manager.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
A protocol for sending electronic messages between servers.
social engineering attack
An attack in which an individual is persuaded or tricked into divulging
privileged information to an attacker.
SOHO
Small Office—Home Office. Also the name of the WatchGuard firewall devices
designed for this segment of the market.
Reference Guide 69
Page 74

spam
The practice of sending unsolicited e-mail to many recipients, much like an
electronic version of junk mail.
spoofing
Altering packets to falsely identify the originating computer to confuse or
attack another computer. The originating computer is usually misidentified as
a trusted computer within an organization.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)
A protocol for transmitting private documents over the Internet. SSL works
by using a private key to encrypt data transferred over an SSL connection.
stance
The policy of a firewall regarding the default handling of IP packets. Stance
dictates what the firewall will do with any given packet in the absence of
explicit instructions. WatchGuard’s default stance is to discard all packets that
are not explicitly allowed, often stated as “That which is not explicitly allowed
is denied.”
static NAT
Static network address translation works on a host-to-host basis. Incoming
packets destined for a public address on an external network are remapped to
an address behind the firewall.
subnet
To split a network into multiple smaller networks. For example, one could
take a class C network with 256 available addresses and create two additional
netmasks under it that separate the first 128 and last 128 addresses into
separate identifiable networks. Subnetting enables a client with a single
network to create multiple networks; the advanced or multiple network
configurations can then be used when setting up the Firebox.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
A reliable byte-streaming protocol that implements a virtual connection. Most
long-haul traffic on the Internet uses TCP.
Tel ne t
A terminal emulation program for TCP/IP networks. It runs on a computer
and connects a workstation to a server on a network.
tooltip
A name or phrase that appears when you pause the mouse pointer over a
button or icon.
triple-DES
An advanced form of encryption using three keys rather than one or two. It is
roughly as secure as single DES would be if it had a 112-bit key.
Trusted interface
The interface on the Firebox that connects to the internal network, which
should be protected to the maximum practical amount.
70
Page 75

tunnel
A technology that enables one network to send its data via another network’s
connections. Tunneling works by encapsulating a network protocol within
packets carried by the second network. For example, Microsoft’s PPTP
technology enables organizations to use the Internet to transmit data across a
virtual private network (VPN). It does this by embedding its own network
protocol within the TCP/IP packets carried by the Internet.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
A connectionless protocol. Used less frequently for long-distance connections,
largely because it lacks TCP’s congestion control features. Used quite heavily
in local area networks for NFS.
URL (Universal Resource Locator)
The user-friendly address that identifies the location of a Web site such as
http:// www.watchguard.com.
VPN (virtual private network)
A virtual, secured network over a public or unsecure network (such as the
Internet) where the alternative – a dedicated physical network – is either
prohibitively expensive or impossible to create. Companies with branch
offices commonly use VPNs to connect multiple locations.
WAN (wide area network)
A computer network that spans a relatively large geographical area.
Typically, a WAN consists of two or more local area networks (LANs).
WatchGuard LiveSecurity Service
Part of the WatchGuard Firebox System offering, separate from the software
and the Firebox, which keeps your defenses current. It includes the broadcast
network that transmits alerts, editorials, threat responses, and software
updates directly to your desktop; your technical support contract; and a Web
site containing information, archives, and the latest software.
Web browser
Software that interprets and displays documents formatted for the Internet or
an intranet.
Web page
A single HTML-formatted file.
Web site
A collection of Web pages located in the directory tree under a single home
page.
WebBlocker
An optional WatchGuard software module that blocks users behind the
Firebox from accessing undesirable Web sites based content type, on time of
day, and/or specific URL.
Reference Guide 71
Page 76

WINS (Windows Internet Name Service)
WINS provides name resolution for clients running Windows NT and earlier
versions of Microsoft operating systems. With name resolution, users access
servers by name rather than needing to use an IP address.
wizard
A tool that guides you through a complex task by asking questions and then
performing the task based on responses.
World Wide Web (WWW)
The collection of available information on the Internet viewable using a Web
browser.
72
Page 77

Index
B
backup
making
restoring 45
backup area 44
Blocked sites
searching for
Booting from the system area 41
45
31
C
Categories, WebBlocker 29
configuration file
making backup
restoring backup 45
Content Types 9
HTML 9
45
F
Firebox
booting from the system area
flash memory 44
Flash Disk Management Tool 44
flash memory 44
41
Internet Protocol Options 5
IP
Header Number List
protocol reference 1
2
M
Modem
initialization strings
setting NVRAM defaults 51
51
O
Out-of-Band
initialization strings
47
P
primary area 44
Procedure
searching for blocked sites
system area
booting from the system area
R
31
41
H
Headers
content type
9
I
Initialization Strings
modem
PPP 47
Internet Protocol Header 1
Reference Guide 73
51
Random Ports 7
Reference
IP protocol
1
S
Setting Modem Defaults for OOB Management 51
Standard Ports 7
System area
booting from
troubleshooting 42
41
Page 78

working with Firebox from 41
system area 44
T
TCP 1
TCP/IP 1
Transfer Protocols
ESP
6
general 5
GGP 6
GRE 6
ICMP 6
IGMP 6
IPIP 6
TCP 6
UDP 5
Troubleshooting 42
W
WebBlocker
categories
searching for blocked sites 31
The Learning Company 29
29
74
 Loading...
Loading...