Page 1

WATA-Standard
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Page 2

-2-
INDEX
1. Presentation .......................................................................................................3
2. Necessary materials ..........................................................................................4
3. Recommendations for the production of sodium hypochlorite ........................ 4
4. Water quality ....................................................................................................... 6
5. Sources of electricity/energy .............................................................................8
6. Procedure for producing sodium hypochlorite solution .................................10
7. Storage ..............................................................................................................11
8. Measuring active chlorine concentration (WataTest) ...................................... 12
9. Using sodium hypochlorite solution to chlorinate drinking water ................. 13
10. Testing drinking water with WataBlue
(determination of residual chlorine) .................................................................... 15
11. Using the sodium hypochlorite solution for disinfection/cleaning ............... 16
12. Stabilising the chlorine solution ....................................................................18
Page 3
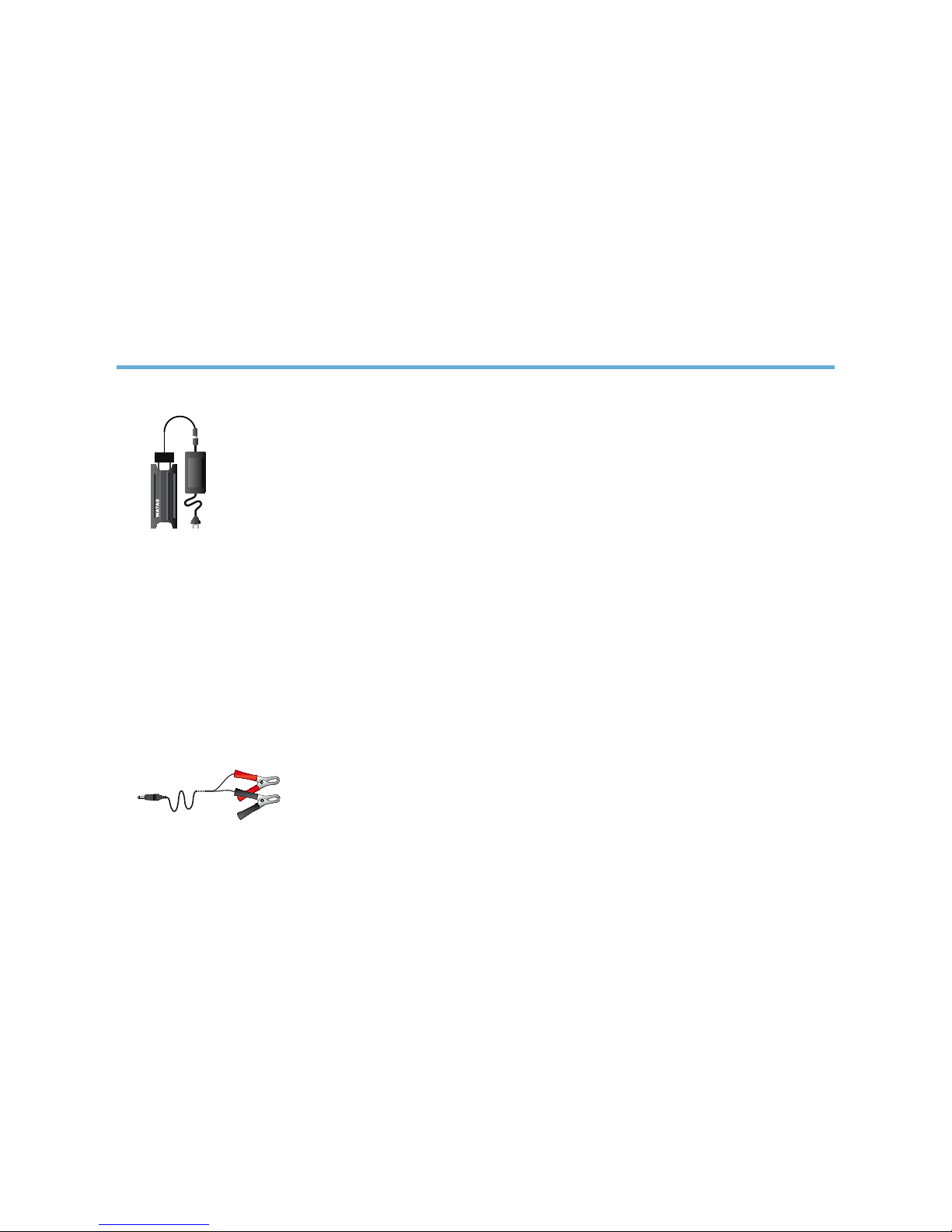
This guide explains how to use the WATA-Standard electrolyser to produce
a sodium hypochlorite solution with a 0.6% concentration of active chlorine
(6 g/L) that can be used for water treatment or disinfection purposes.
The WATA-Standard produces a sodium hypochlorite solution by electrolyzing
salt water. All that is needed are clear water, salt and electricity to use the
WATA-Standard. Water is chlorinated by adding a dose of sodium hypochlorite to
potentially contaminated water, thereby destroying at least 99%* of pathogenic
microorganisms in approximately 30 minutes.
1. PRESENTATION
The WATA-Standard produces 1 litre of sodium hypochlorite
solution per hour. Therefore, in 10 hours, it produces 10 litres
of solution, which can disinfect approximately 40,000 litres of
water per day, meeting the drinking water needs of 10,000 people
(4 L/pers/day). The WATA-Standard works with direct current and
consumes a nominal power of 48 W.
AC/DC power supply provided to hook up to the grid:
` Input voltage: 100 – 240 V AC
` Input frequency: 47 – 63 Hz
` Input current: 0.4 A / 230 VA C
` Output voltage: 12 V DC
` Nominal output current: 5 A
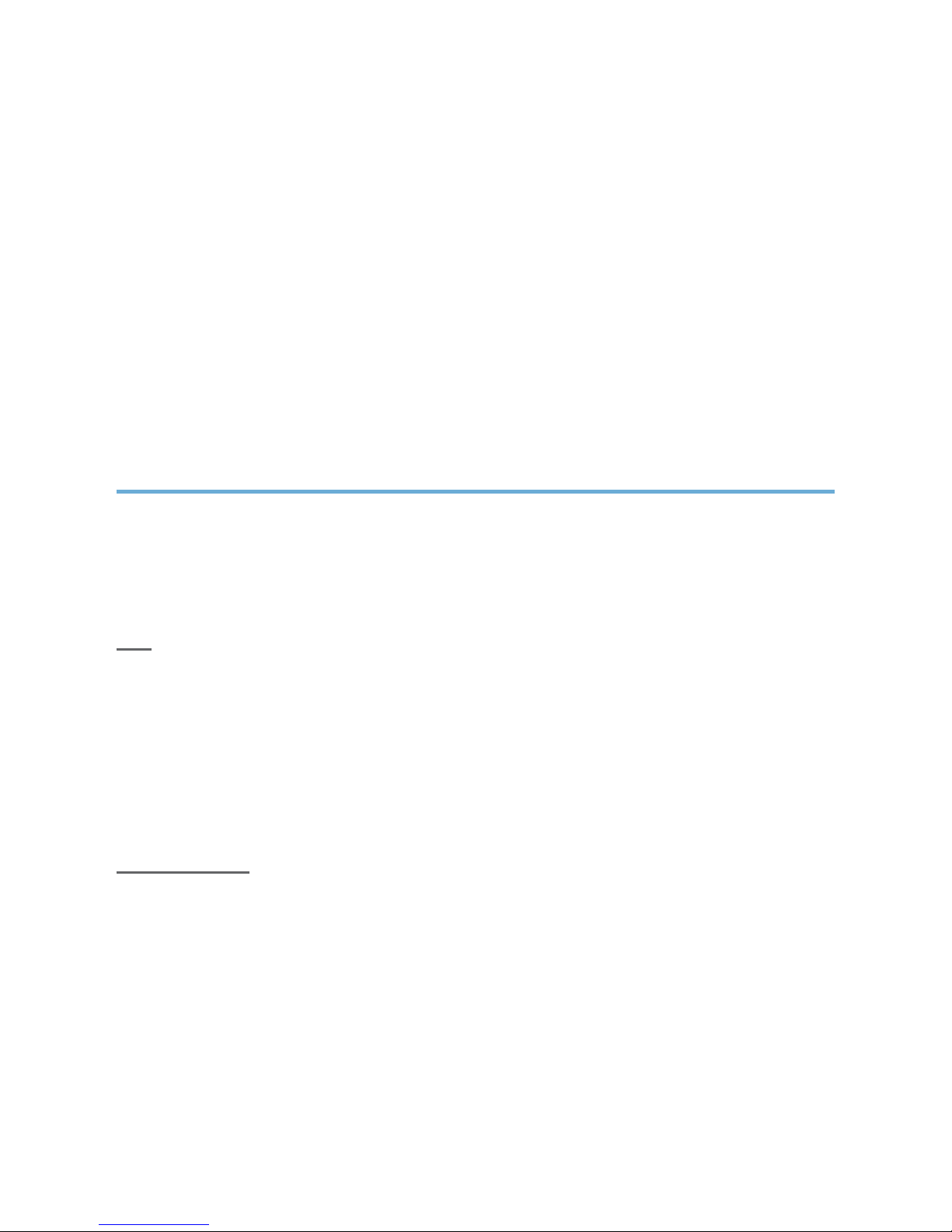
For use with solar power or a battery, a pair of crocodile
clips is provided, allowing for direct connection to a solar
electric panel or a battery. These should deliver a voltage
of 12 V DC.
W The device should only be used by a responsible person familiar with this
user guide.
W The sodium hypochlorite solution is harmless. In case of accidental
contact, rinse with clear water. Do not inhale or ingest.
W Store the sodium hypochlorite solution in an opaque, clean, labelled and
well-sealed flask, out of the reach of children.
W Never use metal containers for the procedure or for storage.
W Do not use or store near fire, flame or sparks.
*WHO, 2004, Water treatment and pathogen control, IWA publishing, p44-50
Page 4

-4-
2. NECESSARY MATERIALS
` WATA-Standard kit
` Ordinary salt
` Clear water
` Funnel
3. RECOMMENDATIONS
FOR THE PRODUCTION OF
SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE
W Choose one or several persons to be responsible for production
These persons should be trained and possess a general knowledge of
chemistry. Production with the WATA-Standard involves more than adding
salt to water. Failure to follow indicated procedures will lead to excessive
energy consumption that will adversely affect the proper functioning and life
span of the power supply.
W Choose an appropriate area and time for production
Production should be carried out in a ventilated area protected from dust
and the Sun’s rays, which has a temperature ideally between 25 and 30°C.
In countries with a hot climate, it is best to work early in the morning or in
the evening.
W Target output and concentration
The WATA-Standard works by electrolyzing salt water at 25 g/L to produce a
sodium hypochlorite solution with 6 g/L active chlorine. These parameters
should be followed in order to protect the life span of the device.
W In cases of unstable current, use a voltage regulator
If the power grid is subject to intermittent outages or sudden voltage
dips and surges (fluctuations in the intensity of light emitted by the bulbs
provides sufficient evidence that this is occurring), the power supply could
be destroyed. If this is the case, use a voltage regulator.
W Use with a generator
The generator should not run out of fuel while the WATA-Standard is in use.
Wait until the generator is stable before plugging in the WATA-Standard.
Page 5

-5-
When the procedure is complete, first unplug the WATA-Standard’s power
supply and then turn off the generator.
W Respect the 10-hour maximum period of use
To avoid the risk of overheating the power supply, do not use the
WATA-Standard for more than 10 consecutive hours. Successive productions
of 2 L are recommended.
W Overheating of the power supply
If overheating occurs, power will automatically shut off and then restart when
its internal temperature falls below 70°C. However, it is advisable to stop the
procedure and allow the power supply to cool down for 15 minutes.
W Respect the 6 g/L concentration
The WATA-Standard is designed to produce a sodium hypochlorite solution
with a 0.1 to 0.6% concentration of active chlorine. The concentration must
not exceed 0.7%. Prolonged use or excessive salt will result in raising the
temperature of the bath, not in increasing the concentration. If this occurs,
there is a risk of damaging the power supply and/or not achieving the 0.6%
concentration. Use WataTest to measure concentration once the procedure
is complete.
W Water temperature should be less than 42°C
In order to avoid the formation of undesirable by-products, the temperature
of the water should be checked regularly during production, using a clean
thermometer. The temperature should be less than 42°C. To begin the
procedure, use water with a temperature between 20 and 27°C.
W Use a log book
To facilitate the monitoring of chlorine production and to trace the origin
of problems that might arise, use a log book to record, each time the
WATA-Standard is used, the name of the person responsible for production,
the starting and finishing times of production and a short description of the
procedure. You’ll find examples in the “tool kit” on our website, www.antenna.ch.
W Regularly check production
Production should be checked at least every two hours or more frequently.
Watch for bubbles in the solution; this is proof that electrolysis is working
properly. Make sure that the power supply does not overheat. If there is a
possibility that dust or elements could fall into the solution, cover it with a
mosquito net type lid. This will allow the gas to escape and, if the area is well
ventilated, to dissipate.
Page 6
-6-
W Always clean the WATA-Standard after use
After each use, rinse the WATA-Standard with clean water. If after several
uses you notice white marks on the WATA-Standard, prepare a solution of 50%
vinegar (or lemon juice) and 50% clean water. Leave the device to soak for
several hours and then rinse it with clear water. Never scrub the titanium plates.
W Precautions
Do not bend the rods of the WATA-Standard or the electrical cables.
W Maintenance and repairs
Do not attempt to make electrical repairs if you are not competent in this
area. Contact Antenna or a specialist who will assist you or refer you to
appropriate services.
4. WATER QUALITY
The initial quality of the water used affects the efficiency of the sodium hypochlorite
production and efficacy of the water disinfection. The main parameters
characterizing the initial quality required for the water are pH and turbidity.
PH
PH is a measure of a solution’s acidity or alkalinity on a scale from 0 to 14, with a
pH of 7 indicating a neutral solution (such as pure water), <7 indicating an acid
solution (such as lemon juice) and >7 indicating an alkaline solution (such as
soap). PH affects chlorine’s ability to destroy microbes and viruses. Based on
World Health Organization recommendations, to effectively disinfect water with
sodium hypochlorite, the water used should have a pH between 6.5 and 8.5. It is
therefore recommended to measure pH.
TURBIDITY
Turbidity measures the opacity of a liquid. Water’s turbidity is caused by the
presence of solid particles in suspension (clay, sand, bacteria, chemical or metallic
residues, etc.) that make the water cloudy. Water with an elevated turbidity could
lead to the formation of undesirable products during the production of sodium
hypochlorite. During the chlorination process, elevated turbidity could diminish
the treatment’s efficacy. Following recommendations in the Sphere Handbook, to
guarantee optimal efficiency in producing sodium hypochlorite and chlorinating
drinking water, the water used should measure less than 5 units of turbidity.
For more than 5 units of turbidity, when the water is mildly turbid (<30 units of
turbidity), a double dose of sodium hypochlorite can be used, and when the water
Page 7

-7-
is more turbid (>30 units of turbidity), it can be filtered and/or decanted and then
disinfected with a double dose of sodium hypochlorite. However, it is absolutely
necessary to verify that residual chlorine remains in the water 30 minutes after
disinfection (see chapter 10).
If it is not possible to use a turbidity meter, we suggest an alternate, though
imprecise, method to measure turbidity.
To determine whether the water can be
used to produce sodium hypochlorite or
to chlorinate drinking water, fill a water
bottle to the height of this manual when
it is open and in a vertical position. 1.
Then place the bottle over the WATA logo
and look at it from above through the
bottle. 2. If you can read the WATA logo
through the water, this means the water
measures less than 5 units of turbidity.
W There should be ample illumination but the light should not be blinding.
The bottle should be transparent, colourless, clear and without
scratches or dirt. A flat-bottomed bottle is preferable. Since it is not
always possible to meet all of these conditions, catching a slight glimpse
of the WATA logo is acceptable.
1 2
Page 8

5. SOURCES OF ELECTRICITY/ENERGY
The WATA-Standard can function with a variety of power options.
USING THE POWER GRID
To use the device with a power grid or an alternate current generator, simply plug
in the power supply provided.
USING DIRECT SOLAR POWER
For use with direct solar power, plug the WATA-Standard device directly to a solar
electric panel using the crocodile clips provided. The solar panel should deliver
12 V DC, its size depending on the amount of solar radiation at the point of use.
Example: With 1.2 kWh/m2/h hourly radiation (Ouagadougou region (12.4°N,
-1.5°E) at midday in May), a solar electric panel with a peak capacity of at least
70 Wp is needed for production with the WATA-Standard.
USING A SOLAR MODULE
For use with a solar module: Since the energy generated by a solar electric panel
varies depending on the amount of sunshine, it is strongly recommended to use
a solar module (see diagram) whose regulator will supply constant energy to the
WATA-Standard and protect your battery, ensuring that the sodium hypochlorite
solution is produced in the necessary conditions. The size of the solar panel
always depends on the amount of solar radiation at the point of use. The battery
should function with 12 V DC.
Solar module
Regulator
(STECA solsum 6,6F)
WATA
Battery
-8-
Page 9

-9-
To determine the size of your solar module (solar electric panel, battery and
regulator), we recommend that you consult a specialist. To give an idea of what
is required, the tables below show approximately the capacity of the battery and
peak power of the solar panel that are necessary depending on your needs and
on the amount of solar radiation.
SOLAR MODULE: USING THE BATTERY, NECESSARY CAPACITY [AH]
Minimum capacity required for a lead-acid battery (12 V)
with a depth of discharge of 50%
1 production of 2 L per day 16 Ah
2 productions of 2 L per day 32 Ah
3 productions of 2 L per day 48 Ah
4 productions of 2 L per day 64 Ah
5 productions of 2 L per day 80 Ah
SOLAR MODULE: USING THE SOLAR ELECTRIC
PANEL, NECESSARY PEAK POWER [WP]
Daily sunshine
at site of use
*
7 kWh/m2/d 5 kWh/m2/d 3 kWh/m2/d 1 kWh/m2/d
1 production of 2 L per day 23 Wp 23 Wp 55 Wp 160 Wp
2 productions of 2 L per day 46 Wp 64 Wp 107 Wp 320 Wp
3 productions of 2L per day 70 Wp 96 Wp 160 Wp 480 Wp
4 productions of 2 L per day 92 Wp 128 Wp 215 Wp 640 Wp
5 productions of 2 L per day 115 Wp 160 Wp 270 Wp 800 Wp
*
For an example, refer to our website: https://eosweb.larc.nasa.gov/
USING A BATTERY
For use with a battery, plug the WATA-Standard device directly to a pre-charged
battery using the crocodile clips provided. The battery should deliver 12 V DC.
A 2 L production with the WATA-Standard consumes 8 Ah of the battery’s capacity.
For an idea of the capacity possible when using a battery with the WATA-Standard,
the table below shows maximum time of use for several batteries if only the
WATA-Standard is plugged in and the batteries are lead-acid with a 50% depth of
discharge.
MAXIMUM TIME OF USE BEFORE RECHARCHING BATTERY (12 V BATTERY)
Battery capacity [Amp-hours] 40 Ah 60 Ah 75 Ah 100 Ah
Maximum time of use 5 hours 7 hours 9 hours 12 hours
Page 10

-10-
6. PROCEDURE FOR
PRODUCING SODIUM
HYPOCHLORITE SOLUTION
6.1 PREPARING THE SATURATED BRINE
1
Take a container of any size (but it must not be of metal) and fill it with water.
2
Add large quantities of salt (approximately 400 g of salt per litre of water).
Preferably use refined salt.
3
Shake/mix steadily for 15 minutes to dissolve a maximum of salt.
4
Ensure that salt remains in the bottom of the container. Close and label it.
If no salt remains at the bottom of the container, add more salt and resume
from step number 3.
The brine so prepared will keep for 5 to 6 months. Do not forget to check whether
salt remains undissolved at the bottom of the container after each use.
6.2 PREPARING THE SOLUTION FOR ELECTROLYSIS
Using the large syringe (50 mL, supplied in the kit), inject 160 mL of saturated
brine for 2 L of water to be electrolysed, then top up your container using clean
water (total volume 2 L).
1 2 3 4
160 mL
160 mL
Saturated
brine
2L
160 mL
Page 11

-11-
6.3 INSTALLING AND CONNECTING
THE WATA-STANDARD DEVICE
1
Once the brine solution is ready, totally immerse the WATA-Standard device
in the solution.
2
Connect the WATA-Standard device to the electrical mains (110 or 220 V).
When using solar energy, connect the WATA-Standard device’s connector
clips to the rechargeable battery or the solar panel taking care to connect
them to the right terminals. Bubbles are immediately seen to be given off
in the bottle
3
Wait 2 hours to obtain 2 litres of sodium hypochlorite solution (6 g/L).
4
At the end of the process, disconnect the WATA-Standard device, remove it
from the sodium hypochlorite solution, rinse it with clean water and store it.
7. STORAGE
Store the sodium hypochlorite solution in a clean,
tightly-closed, opaque, non-metallic container, and
label it with the production date. Place the container in
a cool place, out of the reach of children. Do not expose
to sunlight.
W Sodium hypochlorite can keep for 24 hours
without needing testing. After that time has
elapsed, measure the concentration with the
WataTest and adapt the dilutions accordingly.
For use of sodium hypochlorite after 24 hours, particularly when distributing it in
jars or bottles, it is advisable to stabilise it by adding caustic soda (see section 12).
WATA
110 or 220 V
110 or 220 V
2L=2h
1
2
3 4
Page 12

-12-
8. MEASURING ACTIVE CHLORINE
CONCENTRATION (WATATEST)
It is essential to test the quality of the sodium hypochlorite solution
produced in order to determine the dosage to apply depending on
its use.
Materials: WataTest reagent, 1 mL syringe (supplied), graduated
pipette (supplied), small container with a white base.
This reagent measures the concentration of active chlorine in
grams per liter (Cl2, HOCl, OCl-) ranging between 1 to 7 g/L.
Measurement accuracy is ± 0.5 g/L.
W The ideal result should be 6 g/L. If you obtain a different concentration,
make sure you adjust the dilution of the sodium hypochlorite solution in
the water to treat, or begin the procedure again with fresh brine solution.
W Always use a clean, dry syringe to collect the WataTest reagent.
2 mL
QUALITY CONT
ROL CHECK FOR CONCENTR
A
TED
CH
LORINE SOLUTION PRODUCED BY WAT
A
Contrôle de qualité d'une
solution concentrée de
chlore produite par leWATA
WataTest
QU
ALITY CONTROL CHECK FOR CONCENTRA
TED
CHLORINE SOLUTION PRODUCED BY WATA
Contrôle de qualité d'une
solution concentrée
de
chlore produite par leWATA
WataTest
1 2 3 4 5
1
Thoroughly mix the concentrated sodium hypochlorite solution you wish to
test.
2
Using the plastic pipette, collect exactly 2 mL of the concentrated solution,
and place that amount in a cup, or the small container with a white base.
3
Shake the bottle of WataTest reagent.
4
Fill the syringe with the WataTest reagent and be ready to count the number
of drops that will be used.
5
Holding the syringe vertically, let the WataTest reagent fall one drop at a time
into the cup or the small container with a white base and count the number
of drops added until the solution changes color. Divide the number of drops
by 2 to obtain the concentration in grams per liter (e.g. : 12 drops = 6 g/L).
W Shake gently after adding each drop. If the solution in the cup or small
container turns light-colored again, add one more drop, repeating until
the color change no longer reverses.
W Store the WataTest reagent away from light and at room temperature
(25°C).
ALITY CONTROL CHECK FOR CONCENTRA
TED
CHLORINE SOLUTION PRODUCED BY WATA
solution concentrée
de
chlore produite par leWATA
WataTest
Page 13

-13-
W Carefully close the reagent bottle after each use in order to prevent the
liquid from oxidising.
W Do not exceed the expiration date shown on the WataTest bottle label.
W The WataTest reagent can also measure concentration of other chlorine
solutions (NaDCC, HTH, Bleaching powder, bleach), following procedures
at: www.antenna.ch
9. USING A SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE
SOLUTION TO CHLORINATE
DRINKING WATER
W It is important to chlorinate only water of sufficient quality, i.e. with a
turbidity of less than 5 units, and a pH between 6.5 and 8.5 (see section
4). If the water is muddy, cloudy or colored, it is crucial to filter or clarify
it beforehand.
The dose of active chlorine to add to the water so as to make it drinkable depends
on how contaminated the water is initially. To ensure that 99% of pathogenic
organisms are destroyed 30 minutes after chlorination, it is sufficient to check
whether any residual chlorine remains in the water. For this purpose, we propose
a pragmatic method that is ideal for visual checking using the WataBlue reagent
to determine whether a sufficient quantity of residual chlorine remains in the
water.
To guide you for the first dosage, we recommend a dose of 1.5 mg/L of sodium
hypochlorite. At this dose, 1 litre of sodium hypochlorite at a 6 g/L concentration
produced by the WATA device can be used to treat approximately 4,000 litres of
water, if the initial water quality is compliant with the above-mentioned turbidity
and pH criteria.
W Drinking water must contain between 0.5 et 1 mg/L of free residual
chlorine.
W The treated water must be stored in a clean, opaque, closed tank.
W Chlorination must be performed under the supervision of a qualified
person.
Page 14

-14-
INDICATIVE DOSAGES FOR CHLORINATING DRINKING WATER
DEPENDING ON THE CONCENTRATION PRODUCED BY WATA:
Volume of water to be disinfected
10 L 20 L 100 L
Active chlorine
concentration
per the WataTest
3 g/L 5.0 mL 10.0 mL 50.0 mL
4 g/L 3.8 mL 7.5 mL 37.5 mL
5 g/L 3.0 mL 6.0 mL 30.0 mL
6 g/L 2.5 mL 5.0 mL 25.0 mL
7 g/L 2.1 mL 4.3 mL 21.4 mL
W It is absolutely necessary to test for residual chlorine using the WataBlue
test 30 minutes after chlorinating your drinking water.
Only this test result will guarantee protection against waterborne
diseases.
EXAMPLE OF CHLORINATION FOR 20L OF DRINKING WATER
5 ML
30 min.
1
2 3 4
1
Using a small syringe collect 5 mL of your sodium hypochlorite solution.
2
Add 5 mL of sodium hypochlorite per 20L of plain water.
3
Shake vigorously (for chlorinating a water tank, add the sodium hypochlorite
to the half-full tank, then add the rest of the water).
4
Wait 30 minutes for the sodium hypochlorite to act and to inactivate the
microbes.
5
Test for the presence of residual chlorine using the WataBlue reagent.
Page 15

-15-
10. TESTING DRINKING WATER
WITH WATABLUE (DETERMINATION
OF RESIDUAL CHLORINE)
The WataBlue reagent test determines the concentration of
residual chlorine in the treated water.
Materials : WataBlue reagent, graduated pipette, test tube
(all supplied).
W Always carefully rinse the test tube between tests.
W When checking the result, place the test tube on a
white surface and look at it from above.
1
For the first use, cut the tip off the reagent-bottle spout.
2
30 minutes after chlorination, collect 5 mL of treated water and transfer it
to the test tube.
3
Add one drop of WataBlue then shake the test tube.
4
The blue color produced by the reaction indicates the residual chlorine concentration in the drinking water..
`
If the sample remains colorless, there is insufficient
residual chlorine in the water (0-0.5 ppm). Increase the
chlorine dose, wait 30 minutes and perform the test again.
`
If the sample is light blue, the dosage is correct
and the water can be consumed without any
worry (0.5-1 ppm).
`
If the sample is too dark blue, there is too much
chlorine in the water (>1ppm). Dilute the treated
water by half, wait 30 minutes and perform the test
again.
RESIDUAL CHLORINE
MEASUREMENT CHECK
1 DROP / 5mL WATER
Test de dosage du chlore
1 goutte / 5 mL eau
WataBlue
OK
www.antenna.ch
5 mL
20L
CLEAR
WATER
5 mL
RESIDUAL CHLORINE
MEASUREMENT CHECK
1 DROP / 5mL WATER
Test de dosage du chlore
1 goutte / 5 mL eau
WataBlue
06.09.2008
www.antenna.ch
1
2 3
4
Page 16

-16-
W If you needed to add 4 times the initial amount of chlorine, i.e. 20 mL (as
opposed to 5 mL) for 20 litres, that means that the water is too cloudy
for the sodium hypochlorite to act and your water must be filtered once
again (see section 4) and the chlorination process must be repeated.
W Store the WataBlue reagent away from light and at room temperature
(25°C). Carefully close the reagent bottle after each use in order to
prevent the liquid from oxidising. Do not exceed the expiration date.
Over time, its color may change to red/brown, without impairing the test
quality.
W We recommend conducting this test regularly, since water quality
can vary at different water sources. Similarly, the quantity of sodium
hypochlorite to add may vary according to season, by as much as twice
the quantity in the wet season as in the dry.
11. USING THE SODIUM
HYPOCHLORITE SOLUTION FOR
DISINFECTION/CLEANING
Disinfection is a process eliminating pathogenic organisms, designed to halt or
prevent infection by microorganisms.
PREPARING DISINFECTANT SOLUTIONS AT HOME
Use
Advised
concentration
of chlorinated
solution
Vol. of
water
Vol. of sodium
hypochlorite
equivalent to a
concentration
of 6 g/L
Procedure
Washing hands 0.5 g/L 10 1
Rub hands with the chlorinated
solution for 30 seconds; allow
to dry.
Floors (including
floors and walls
of latrines)
0.8 g/L 6 1
Wash with chlorinated solution;
leave in contact for 5 min., then
rinse
Washing food and
fresh vegetables
0.05 g/L 100 1
Soak food items in the chlorinated
solution for 5 min., rub, and then
rinse.
Dishwashing 0.5 g/L 10 1
Rinse the dishes in the
chlorinated solution and then
wash as usual.
Page 17

-17-
Use
Advised
concentration
of chlorinated
solution
Vol. of
water
Vol. of sodium
hypochlorite
equivalent to a
concentration
of 6 g/L
Procedure
Clothing / laundry 0.2 g/L 30 1
Soak garments in the chlorinated
solution for 5 min, then rinse
carefully. Do not use chlorine to
disinfect wool, silk or nylon.
PREPARING DISINFECTANT SOLUTIONS AT HEALTH CENTRES
W Surgery and sterilisation : disinfection by sodium hypochlorite is not
sterilisation. Surgical instruments must be sterilised in an autoclave or a
Poupinel sterilising oven.
Use
Advised
concentration
of chlorinated
solution
Vol. of
water
Vol. of sodium
hypochlorite
equivalent to a
concentration
of 6 g/L
Procedure
Washing hands 0.5 g/L 10 1
Clean and dry the hands, then
rub with the chlorinated solution
for 30 seconds; allow to dry.
Disinfecting
wounds (Dakin's
solution) only
with chlorine at
6 g/L
6 g/L - 1
Use the solution pure, on a clean
compress applied directly to the
wound.
Floors (including
floors and walls
of latrines)
2 g/L 2 1
First sweep the floors and wash
them with soap and water. Next
apply the chlorinated solution for
10 min., then rinse and allow to
dry.
Clothes, gowns
and bed linen
2 g/L 2 1
Soak the clothes in the
chlorinated solution for 10 min.,
rinse then wash as usual. Hang
out to dry.
Containers and
objects
2 g/L 2 1
Soak in the chlorinated solution
for 10 min., then rinse and dry.
W The sodium hypochlorite must be diluted in cold water.
W Never mix the sodium hypochlorite solutions with soap, detergents
or other household cleaning products, since mixing with strong acids
generates chlorine gas fumes.
Page 18

-18-
12. STABILISING THE
CHLORINE SOLUTION
To use a sodium hypochlorite solution produced by the Midi-WATA electrical
chlorinator device after more than 24 hours, we propose a stabilisation method
using caustic soda (NaOH).
This new process requires the use of a pH meter or pH testing strips. Laboratory
skills and equipment are also required, but the process ensures a six-month
minimum storage life. you must comply with legislation effective in the country
where you operate. A quality control procedure validated by the local authorities
must be implemented.
If you would like to produce sodium hypochlorite for the purposes of distributing
it in vials, stabilisation will be required. Information about this procedure is
available at http://www.antenna.ch/recherche/eau-potable/stabilisation
All the scientific references used in compiling this manual are available on
request. Kindly translated by Translators Without Borders.
Page 19

Page 20

FONDATION ANTENNA TECHNOLOGIES
Av. de la Grenade 24
1207 Genève
Suisse
T : 0041 22 737 12 40
Email : wata@antenna.ch
WWW.ANTENNA.CH
 Loading...
Loading...