Page 1

WLR 8900/8905
Programming Guide
Please Read
Note:
The Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanner is ready to scan the
most popular bar codes out of the box.
should only be used to make changes in the
configuration of the scanner for specific applications.
This scanner does not require software or drivers to
operate. The scanner enters data as keyboard data. Please
review this manual before scanning any of the programming
bar codes in this manual.
This manual
Tech Tip
If you are unsure of the scanner configuration or have
scanned the incorrect codes, please scan the default
bar code on page 6. This will reset the scanner to its
factory settings.
ersion
V
k
Chec
Page 2

© Copyright Wasp Technologies 2006
All rights reserved. Ver AMC-a-1.01
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form
or by any means without the written permission of Wasp Technologies.The
information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
Wasp is a trademark of Wasp Technologies. All other trademarks or registered trademarks are the
property of their respective owners.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction ..............................................................................1
Chapter 2. Bar Code Symbologies............................................................2
Chapter 3. Installation................................................................................3
Chapter 4. Quick Start ..............................................................................4
Chapter 5. WLR 8900/8905 Setup & Configuration ............................5-28
1. Factory Default & Keyboard Connection ....................6
2. Autosense Stand Mode ..............................................6
3. Beep and Delay ......................................................7-8
4. Upper/Lower Case......................................................9
5. Keyboard Language ................................................10
6. Preamble/Postamble Configuration ..........................11
7. Terminator/Code ID ..................................................12
8. Enable/Disable Bar Code Symbologies ..............13-14
9. Bar Code Symbology Settings ............................15-27
Code 39 ..........................................................15
Interleaved 2 of 5 and Code 93 ......................16
Code 128 and UCC/EAN 128..........................17
MSI/Plessey ....................................................18
Codabar ..........................................................19
UPC-A..............................................................20
UPC-A Supplemental / UPC-A to EAN-13 ......21
UPC-E..............................................................22
UPC-E Supplemental ......................................23
EAN-8 ..............................................................24
EAN-8 Supplemental ......................................25
EAN-13 ............................................................26
EAN-13 Supplemental ....................................27
Appendix A Bar Code Test Symbols ....................................................28-30
Appendix B ASCII Table ......................................................................31-34
Appendix C Codes for PC ........................................................................35
Appendix D Technical Specifications ........................................................36
....................................................................37
Product Suppor
Warranty ................................................................................37
Frequently Asked Questions..................................................38
t
Page 4
Chapter 1
Introduction
Bar coding is the most common Automated Data Collection (ADC) technology
providing timely, error-free information that can be used to increase productivity,
accuracy, and efficiency in the workplace. Virtually every type of industry is
using bar codes to replace keyboard data entry. Studies have shown that a
proficient data entry operator will make one error for every 300 characters that
are manually entered. The error rate using bar codes is almost negligible and
can be error-free using bar code symbologies with the check digit enabled.
The Wasp Charged Coupled Device (CCD) technology is a technique whereby a
bar code is photographed, digitized, and electronically sampled by built-in
photodetectors. The detectors process the measurement of every bar and
space using the number of adjacent photodetectors which contrast a black mark
and a white space. Wasp WLR 8900 series scanners extremely rugged since
they have no moving parts. Wasp WLR 8900 series scanners are support PS/2
or USB keyboard interfaces and easily wedges between the computer and
keyboard. Bar code data is passed directly into the keyboard buffer as if it had
been typed in by hand by a data entry operator.
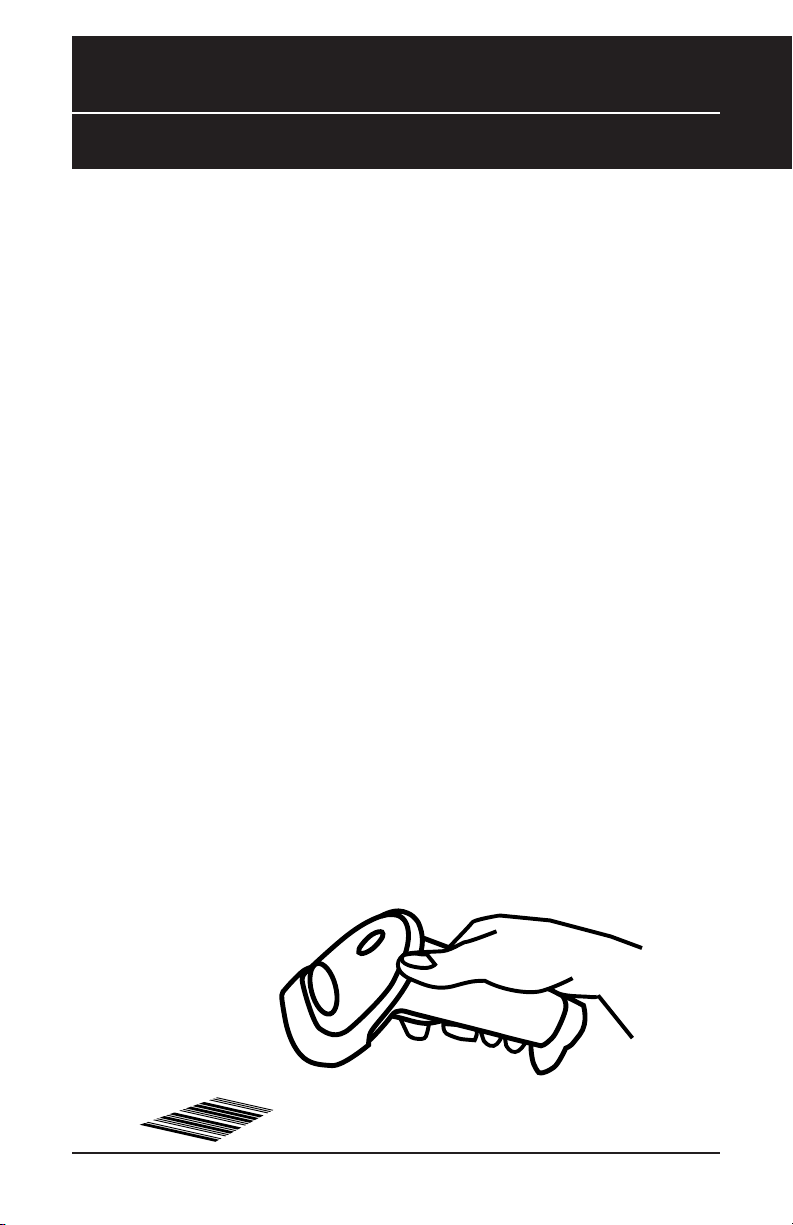
Of all the hand held bar code scanning devices on the market, the CCD reader
is the easiest to use and most cost effective for the typical business user. The
Wasp WLR 8900 series scanners are extended distance scanners with a depth
of reading of up to one foot depending on the mil size of the bar code. To
activate the scanner, the user simply points the scanning aperture towards the
bar code, pulls the trigger, and aims the red LED beam across the bar code.
1
Page 5

Chapter 2
Bar Code Symbologies
Bar codes are symbols consisting of a series of bars and spaces which can be
applied to packages, cartons, bottles, and other commercial products. The bars
and spaces in each symbol are grouped in such a way to represent a specific
ASCII character or function. The interpretation of these groups is based on a
particular set of rules called symbologies. Various symbologies have been
developed for particular applications. Some examples are shipping and
receiving, manufacturing, retail, healthcare, transportation, document processing
and tracking, and libraries.
The resolution of a bar code is dependent on the narrowest element of a bar
code (X dimension), and can vary from high density (nominally less than 0.009
in./0.23 mm), medium density (between 0.009 in./0.23 mm and 0.020 in./0.50
mm), and low density (greater than 0.020 in./0.50 mm). Medium and low
densities are the most common since these are the easiest to read (scan) with
nearly all scanning devices. Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanners can read bar
codes with X-dimensions as low as 5 mils (0.005 in/0.13mm).
Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanners can read the most popular bar code
symbologies including Code 39, Code 93, Code 128, Interleaved 2 of 5, UPC-A,
UPC-E, EAN/JAN-8, EAN/JAN-13, Codabar, and MSI/Plessey.
Please see test chart on pages 28-30.
2
Page 6
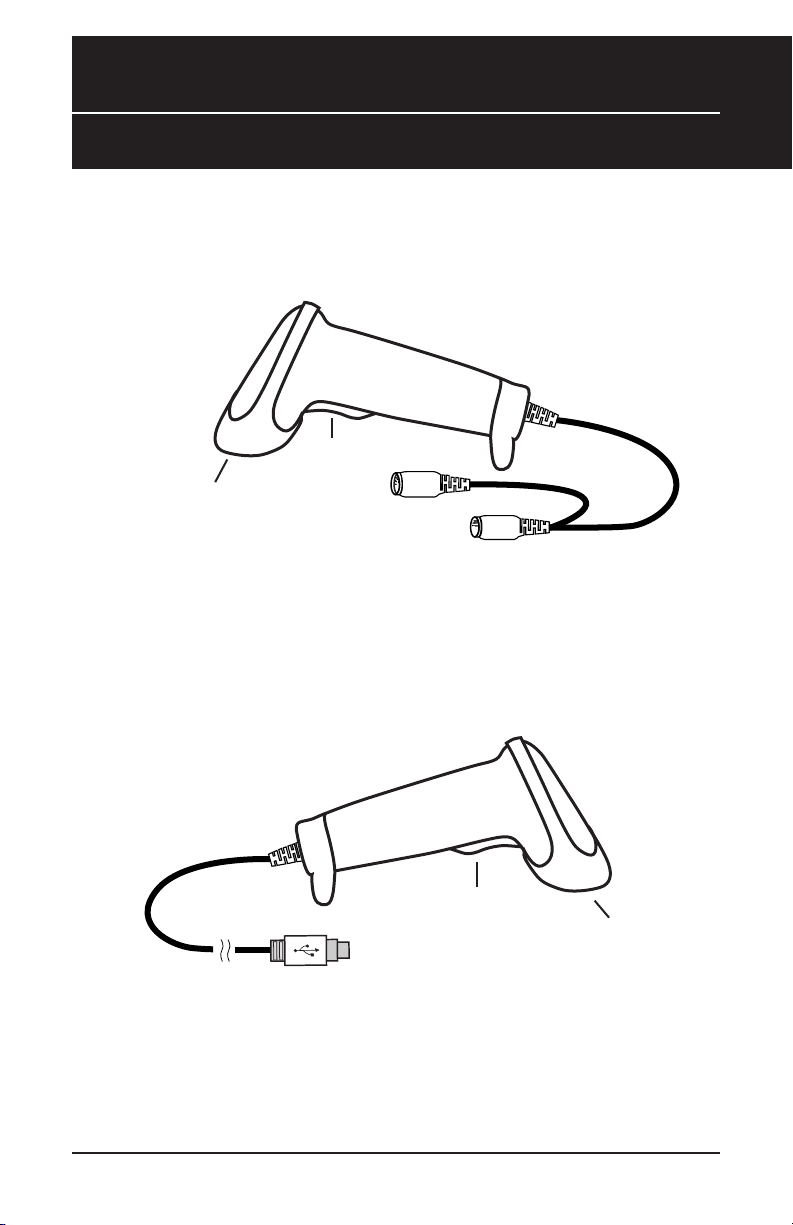
Installation
WLR 8900 PS2
Scanner
Trigger
Chapter 3
Scanning Aperture
1. Turn off your computer.
2. Unplug your PC keyboard cable and plug the male end (Din 6) of the WLR
8900 Scanner directly into your PC keyboard port. Plug your keyboard
cable into the other end (female Din 6) of the the scanner.
3. Turn your computer on.
Din-6M
Din-6F
WLR 8905 USB
Scanner
Trigger
USB Por t
1. Plug the USB of the WLR 8905 Scanner directly into your PC’s USB port.
Scanning Aperture
3
Page 7
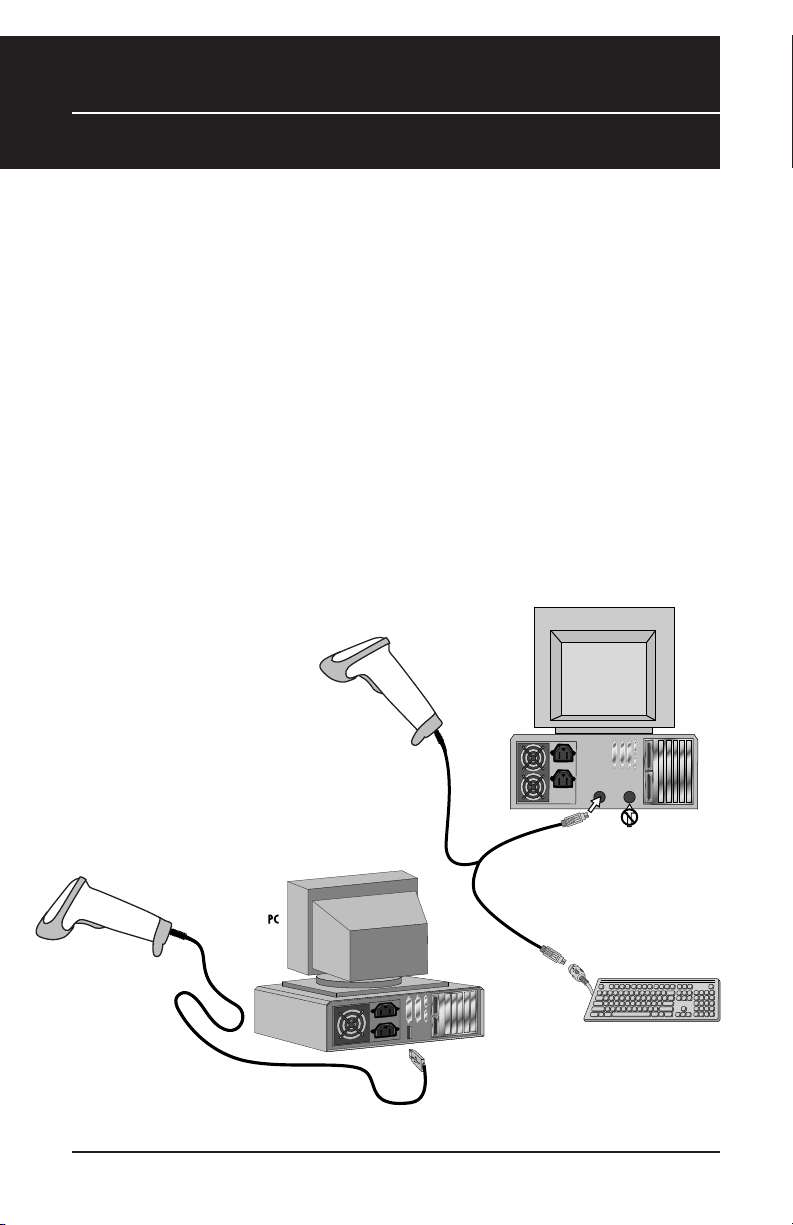
Chapter 4
KEYBOARD
Y-CABLE
BACK OF PC
KEYBOARD MOUSE
DO NOT PLUG
IN MOUSE PORT!
KEYBOARD
WLR 8900
PS2 Scanner
KEYBOARD
Y-CABLE
BACK OF PC
K
EYBOARD MOUSE
DO NOT PLUG
IN MOUSE PORT!
KEYBOARD
W
LR 8900
P
S2 Scanner
WLR 8905
USB Scanner
USB Connector
Quick Start
Your Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanners are ready for use. The default settings of
the scanners have been pre-programmed for the most common bar code
configurations. Use the “WLR 8900/8905 Setup & Configuration” sections only to
customize the scanners settings. Please review the “Enable Bar Code
Symbologies” configuration beginning on page 14 to see the list of bar codes
symbologies which are enabled by default.
Tip:
• Use the pre-printed “Bar Code Test Symbols” in Appendix A on pages
28-30 as a test chart to practice scanning.
USB Connection
PS2 Connection
4
Page 8

Chapter 5
Setup & Configuration
In order to configure Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanners, you must familiarize
yourself with the setup procedures on the following pages. The default settings
of the Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanners are identified on each page and clearly
marked using an asterisk (*). The default settings have been preprogrammed
for the most common bar code configurations. Use the Setup &
Configuration only to customize the Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanners
settings.
overwritten. All the programmed settings are stored permanently in non-volatile
memory; therefore, your configuration will be maintained even if the keyboard
power to Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanners is removed by turning off your PC.
In order to configure Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanners, two basic steps need
to be followed:
(1) Locate the group that contains the options to be changed.
(2) Scan the bar code representing the option to be changed. The scanner will
If you need to configure the scanner, the default settings will be
sound two beeps.
To change Minimum/Maximum Length:
(1) Scan the Minimum or Maximum Length bar code.
(2) Scan a 2 digit value from the ASCII table on pages 31-34
(3) Scan the Minimum or Maximum Length bar code again.
Example: To have a minimum length bar code of 1, you must scan a 0 then 1, then scan
the minimum bar code again. To have a maximum length bar code of 10, you must scan
a 1 then 0, then scan the maximum bar code again.
5
Page 9
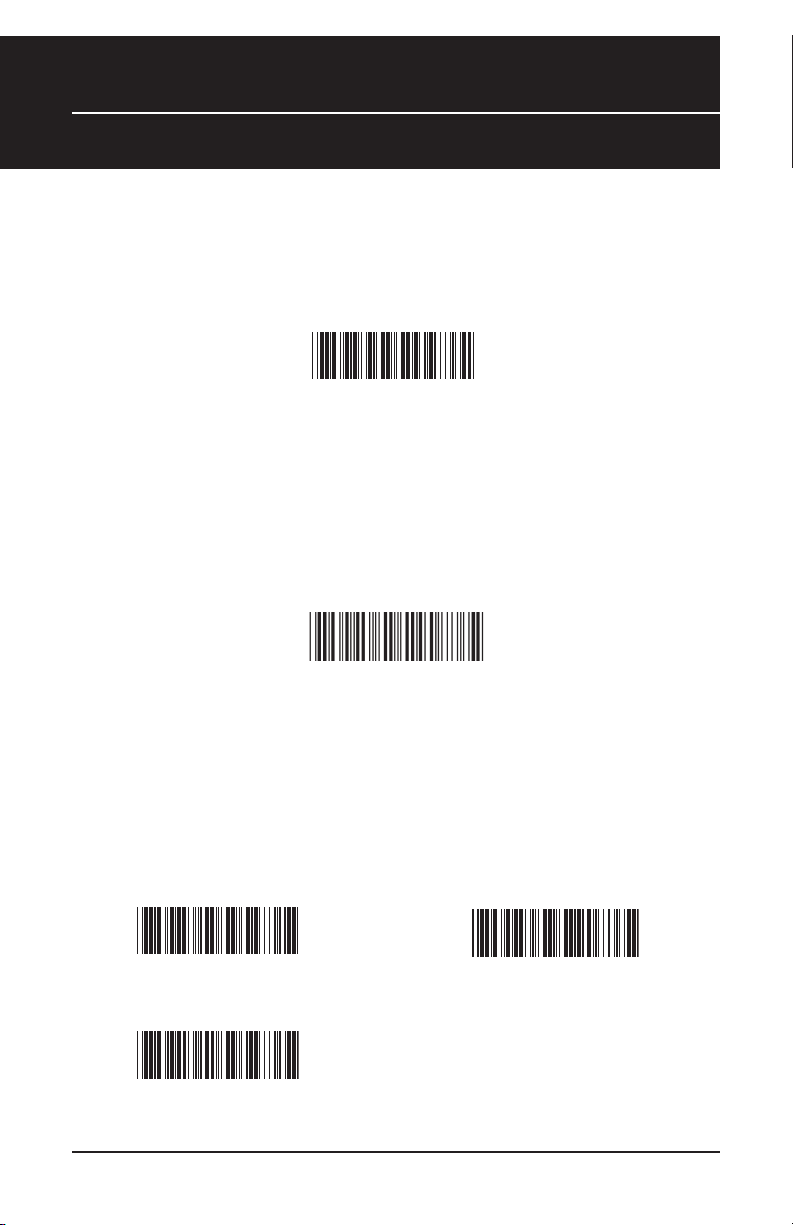
Chapter 5
Factory Default & Keyboard Connection
Factory Default
Use the Factory Default bar code to reset the scanner to the Default settings.
Factory Default
Autosense Stand Mode
Scan this Autosense Stand Mode bar code to enable the hands-free autosense
feature of the WLR 8900/8905 Scanners. If you desire to turn this mode “off,”
please scan the default bar code above.
Autosense Flash Mode
Enable
Keyboard Connection
The Keyboard Connection is used to program the Wasp WLR 8900/8905
Scanners for the type of computer it is attached.
PC - AT (PS/2) *
Notebook
6
PC - XT
*Default
Page 10

Chapter 5
Beep and Delay
The 'Beep and Delay' configuration supports the general control options for the
Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanners. These options include the volume,
intercharacter delay, and interblock delay.
Interblock delay is the minimum time interval between two adjacent scans. If the
processing speed of your host device is slower than your scanning speed, a
longer interblock delay may ensure the data integrity.
Intercharacter delay is the time period that the scanner will wait before
transmitting the next character. If data sent by the scanner has incorrect or
missing characters, a longer intercharacter delay may solve the problem. The
intercharacter delay should be changed only if the transfer rate cannot be
maintained between the scanner and the keyboard buffer of the computer.
Note: The default for the intercharacter delay is set to '140us' and is the most
common configuration; however, your PC may be different. When you scan a bar
code, if some stray or scrambled characters appear, increase the intercharacter
delay to slow down the transfer rate.
Beep Settings
Beep Off
Beep Medium *
Beep High to Low
Beep Hi
Beep Low to High
Beep Low
*Default
7
Page 11

Chapter 5
Beep and Delay
Interblock Delay Intercharacter Delay
0ms *
10ms
50ms
100ms
200ms
140µs *
500µs
1ms
4ms
16ms
500ms
*Default
8
Page 12
Chapter 5
Upper/Lower Case
• Caps Lock Auto (For PC XT/AT only):
In Auto Trace mode, the scanner will keep track of the Caps Lock status
automatically. For some PCs, the scanning performance may be
compromised because of the auto tracing. If the scanning performance
is poor (or cannot scan) or the scanner cannot output the upper/lower
case characters correctly, try to select one of the next two choices
instead of auto tracing.
• Caps Lock Off:
When the keyboard is in the unshifted state (Caps Lock is not pressed),
select “Lower Case.”
• Caps Lock On:
When the keyboard is in the shifted state (Caps Lock is on), select
“Upper Case.”
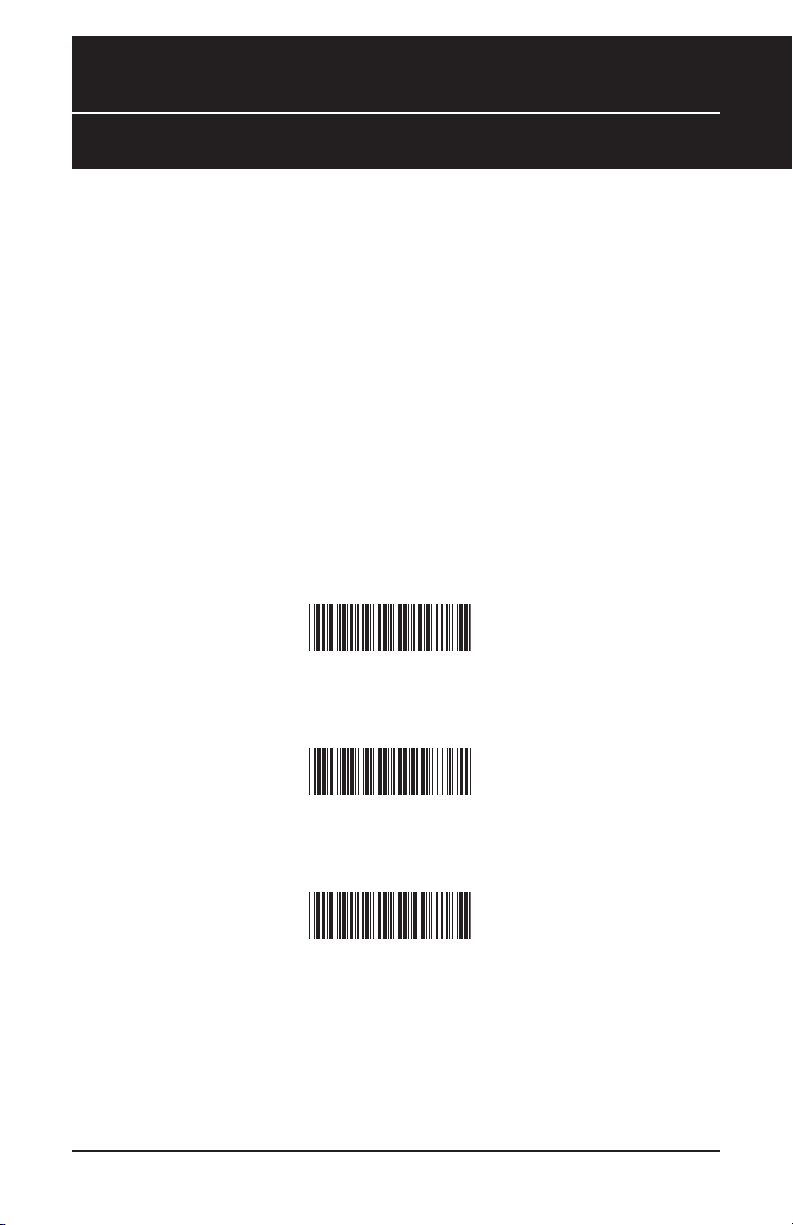
Caps Lock On
Caps Lock Off *
Caps Lock Auto
9
*Default
Page 13
Chapter 5
Keyboard Language
The ‘Keyboard Language’ setting controls the key codes for your keyboard’s language.
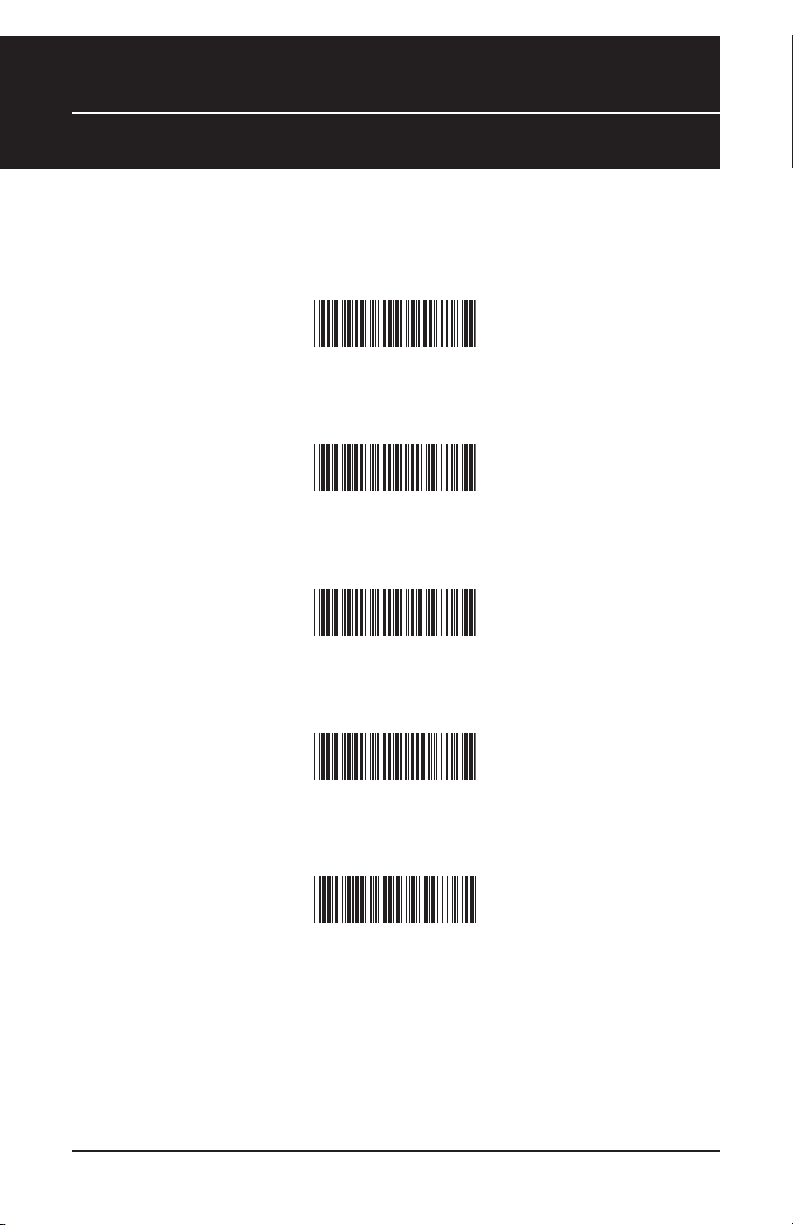
U.S. *
German
French
Spanish
Italian
10
*Default
Page 14

Chapter 5
Preamble/Postamble Configuration
The ‘Preamble/Postamble’ configuration is used to add a prefix or suffix set of
characters to the bar code value. Up to 8 characters may be added for each
option separately. Preamble and postamble characters can function
concurrently, but need to be configured separately.
To add preamble or postamble characters, follow the steps below:
1) Scan the ‘Clear Pre/Postamble’ bar code on this page.
2) Scan the ‘Preamble’ or ‘Postamble’ bar code.
3) Use Appendix B on pages 31-34 to locate the characters you want to
add as preamble or postamble characters. Make sure that you scan the
bar code associated with each letter before preceding to the next
character. For example, to add the letter “A,” scan the bar code
corresponding to the letter “A” on page 33. The letter “A” will always
appear in your data as prefix or suffix to the bar code value.
4) Scan the corresponding 'Pre/Postamble' bar code on this page to exit
this setting.
Clear Pre/Postamble
Preamble
ostamble
P
11
Page 15

Chapter 5
Terminator/Code ID
Terminator
The ‘Terminator’ option is used to specify the end-of-text message and is primarily used to
denote the end of the bar code value.
CR *
None
LF
CR + LF
Ta b
Space
ESC
Code ID
The ‘Code ID’ option sends a specific value when a particular bar code symbology is
scanned. For example, if ‘Code ID’ is enabled and Code 39 is scanned, an “M” will appear
in the data stream in front of the bar code value.
O - MSI/Plessey T - EAN 128
S - EAN 8 K - Code 128
Code ID On
Code ID
Off *
E - UPC E N - Codabar
A - UPC A
F - EAN 13
L - Code 93 I - Interleaved 2 of 5
D - Full ASCII Code 39
M - Std. Code 39
*Default
12
Page 16

Chapter 5
Enable/Disable Bar Code Symbologies
Enable Disable
Enable All
MSI Plessey
Interleaved 2 of 5 *
Code 128 *
Codabar *
Disable All
MSI Plessey *
Interleaved 2 of 5
Code 128
Codabar
Code 39 *
Code 39
*Default
13
Page 17

Chapter 5
Enable/Disable Bar Code Symbologies
Enable Disable
UPC A *
UPC E *
EAN 8 *
EAN 13 *
Code 93
UPC A
UPC E
EAN 8
EAN 13
Code 93 *
14
*Default
Page 18

Chapter 5
Code 39 Settings
Code 39 is variable length and is the most frequently used symbology in industrial bar code
systems today. It is extensively used within the Department of Defense (DOD). The principal
feature is to encode messages using the full alphanumeric character set. Standard Code 39
contains only 43 characters (0-9, A-Z, $, /, %, +, -, ., SPACE) and can be extended to a 128
character symbology (full ASCII) by combining one of the special characters (S, /, %, +) with a
letter (A-Z) to form the characters that are not present in the standard Code 39 symbology.
See page 5 for information on setting the minimum and maximum lengths.
Enable Code 39 *
Enable Code 39
Full ASCII *
Check Digit Do
Not Calculate *
Check Digit Calculate
But Do Not Send *
Disable Code 39
Disable Code 39
Full ASCII
Check Digit Calculate
And Send
Minimum Length (1 *)
Maximum Length (48 *)
*Default
15
Page 19

Chapter 5
Interleaved 2 of 5 and Code 93 Settings
Interleaved 2 of 5 is a variable length, even numbered, numeric bar code. It is typically used in
industrial and master carton labeling and also in the automobile industry. The symbology uses
bars to represent the first digit of a pair and the interleaved (white) spaces to represent the
second digit of a character pair. See page 5 for information on setting the minimum and
maximum lengths.
Enable Interleaved
2 of 5 *
Check Digit Do
Not Calculate *
Check Digit Calculate
But Do Not Send
Minimum Length (6 *) Maximum Length (48 *)
Code 93 encodes the full 128 ASCII character set using 9 modules arranged into 3 bars with
adjacent spaces. Two of the characters are check characters. Code 93 is similar to Code 39
but encodes more characters per inch.
Disable Interleaved
2 of 5
Check Digit Calculate
And Send
Enable Code 93 Disable Code 93 *
Minimum Length (6 *)
Maximum Length (48 *)
16
*Default
Page 20

Chapter 5
Code 128 and UCC/EAN 128 Settings
Code 128 is the most flexible of all the common linear symbologies. It supports alpha and
numeric characters easily, has the highest number of characters per inch, and is variable length.
See page 5 for information on setting the minimum and maximum lengths.
Enable Code 128 *
Disable Code 128
UCC/EAN 128
Enable *
UCC/EAN 128
Code ID Enable
Function 1
Character Send
Minimum Length (5 *)
Maximum Length (48 *)
UCC/EAN 128
Disable
UCC/EAN 128
Code ID Disable *
Function 1
Character Do Not Send *
Define UCC/EAN 128
Group Separ
ator
To Define UCC/EAN 128 Group Separator:
Scan Define UCC/EAN 128 Group Separ
1.
2. Scan ASCII code from pages 31-34
3. Scan Define UCC/EAN 128 Group Separator
Note: Default Group Separator is GS
ator
*Default
17
Page 21

Chapter 5
MSI Plessey Settings
MSI Plessey is a variable length numeric symbology and is primarily used in marking retail
shelves. Each character consists of four bars with intervening spaces for each encoded digit,
one or two symbol check digits, and a reverse start code.
See page 5 for information on setting the minimum and maximum lengths.
Enable
Check Digit Verify
And Send *
Check Digit Double
MOD 10
Check Digit Single
MOD 10
Disable *
Check Digit Verify
And Do Not Send
Check Digit Double
11 Plus MOD 10
Minimum Length (6 *)
um Length (48 *)
Maxim
18
*Default
Page 22

Chapter 5
Codabar Settings
Codabar is a variable length symbology capable of encoding six special alphanumeric
characters, capital letters A through D, T, N, *, E, and all numeric digits. Codabar is one of
the oldest bar code symbologies and is still used in some library applications. It should not
be considered for new applications except under unusual circumstances.
See page 5 for information on setting the minimum and maximum lengths.
Codabar Enable *
Send Start/Stop *
Check Digit
Do Not Verify *
Check Digit Verify
And Do Not Send
Codabar Disable
Do Not Send
Start/Stop
Check Digit
Verify And Send
Minimum Length (6 *)
Maxim
um Length (48 *)
19
*Default
Page 23

Chapter 5
UPC-A Settings
UPC-A (Universal Product Code-A) is fixed length and is the most common UPC bar code
for retail product labeling. It is seen in most grocery stores across the United States. The
symbology encodes a 12-digit number. The first six digits are assigned from the Uniform
Code Council (UCC). The next five digits are assigned by the manufacturer, and the final
digit is a modulo 10 check digit. The nominal height for the UPC-A bar code is one inch. The
reduced size is 80% of the nominal size.
UPC-A Enable *
Send Leading Digit *
Send Check Digit *
UPC-A Disable
Do Not Send
Leading Digit
Do Not Send
Check Digit
20
*Default
Page 24

Chapter 5
UPC-A Supplement Settings / UPC-A to EAN-13
This option enables the two and five digit supplements for the UPC and EAN/JAN bar code
symbologies.
5 Digit Supplement
Enable
2 Digit Supplement
Enable
Transmit if Present
This option expands the UPC-A bar code to EAN-13.
UPC-A to EAN-13
Enable
5 Digit Supplement
2 Digit Supplement
Must Be Present *
UPC-A to EAN-13
Disable *
Disable *
Disable *
21
*Default
Page 25

Chapter 5
UPC-E Settings
UPC-E (Universal Product Code-E) is fixed length and is a compressed six digit code used
for marking small packages, including magazines and paperback books. UPC-E symbols
are UPC-A symbols that have been zero suppressed (i.e. consecutive zeros are not included
in the symbol). The printed value of the UPC-E code is a twelve digit code. The nominal
height for the UPC-E bar code is one inch. The reduced size is 80% of the nominal size.
UPC-E Enable *
Send Leading Digit *
Send Check Digit *
Zero Digit Expansion
On
UPC-E Disable
Do Not Send
Leading Digit
Do Not Send
Check Digit
Zero Digit Expansion
Off *
22
*Default
Page 26

Chapter 5
UPC-E Supplement Settings
This option enables the two and five digit supplements for the UPC and EAN/JAN bar code
symbologies.
5 Digit Supplement
Enable
2 Digit Supplement
Enable
Transmit if Present
5 Digit Supplement
Disable *
2 Digit Supplement
Disable *
Must Be Present *
23
*Default
Page 27

Chapter 5
EAN-8 Settings
The EAN/JAN-8 is fixed length and is similar to the UPC-E code, but includes two more
digits for the country code. The nominal height for the EAN/JAN-8 bar code is one inch. The
reduced size is 80% of the nominal size.
EAN-8 Enable *
Send Leading Digit *
Send Check Digit *
EAN-8 Disable
Do Not Send
Leading Digit
Do Not Send
Check Digit
24
*Default
Page 28

Chapter 5
EAN-8 Supplement Settings
This option enables the two and five digit supplements for the UPC and EAN/JAN bar code
symbologies.
5 Digit Supplement
Enable
2 Digit Supplement
Enable
Transmit if Present
5 Digit Supplement
Disable *
2 Digit Supplement
Disable *
Must Be Present *
25
*Default
Page 29

Chapter 5
EAN-13 Settings
The EAN/JAN-13 (European Article Number/Japanese Article Number) is fixed length and
is similar to the UPC-A symbology, but encodes a 13th digit. The nominal height for the
EAN/JAN-8 bar code is one inch. The reduced size is 80% of the nominal size.
EAN-13 Enable *
Send Leading Digit *
Send Check Digit *
ISBN Enable
EAN-13 Disable
Do Not Send
Leading Digit
Do Not Send
Check Digit
ISBN Disable *
ISSN Enable
ISSN Disable *
*Default
26
Page 30

Chapter 5
EAN-13 Supplement Settings
This option enables the two and five digit supplements for the UPC and EAN/JAN
bar code symbologies.
5 Digit Supplement
Enable
2 Digit Supplement
Enable
Transmit if Present
5 Digit Supplement
Disable *
2 Digit Supplement
Disable *
Must Be Present *
27
*Default
Page 31

Appendix A
Bar Code Test Symbols
Note: Make sure that the appropriate bar code symbology is configured
properly and enabled before trying to scan. Use the 'Bar Code Symbologies'
configuration beginning on page 18 to enable specific symbologies.
Code 39*
Code 93
Interleaved 2 of 5 *
Codabar *
Code 128*
MSI/Plessey
*Default
28
Page 32

UPC-A*
UPC-A
w/5 digit supplement
UPC-A
w/2 digit supplement
Appendix A
Bar Code Test Symbols
UPC-E*
UPC-E
w/5 digit supplement
UPC-E
w/2 digit supplement
*Default
29
Page 33

Appendix A
Bar Code Test Symbols
EAN/JAN-13*
EAN/JAN-13
w/5 digit supplement
EAN/JAN-13
w/2 digit supplement
EAN/JAN-8*
EAN/JAN-8
w/5 digit supplement
EAN/JAN-8
w/2 digit supplement
*Default
30
Page 34

Appendix B
ASCII Table
Use this ASCII Table to add preamble and postamble characters to your bar
code value. Please refer to the appropriate configuration section for the number
of characters that can be configured.
ASCII Character
NUL
SOH
STX
ETX
EO
ENQ
ACK
LF
VT
FF
CR
T
SO
SI
DLE
DC4
NAK
SYN
ETB
CAN
EM
SUB
BEL
BS
HT
DC1
DC2
DC3
31
ESC
FS
GS
Page 35

Appendix B
ASCII Table
ASCII Character
RS
US
SP
!
"
#
$
)
*
+
,
-
.
/
4
5
6
7
8
9
:
%
&
0
1
'
(
2
3
;
<
=
>
32
Page 36

ASCII Character
Appendix B
ASCii Table
?
@
A
B
C
D
E
M
J
K
L
N
O
P
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
[
F
G
H
I
Q
R
S
T
\
]
^
_
33
Page 37

Appendix B
ASCII Table
ASCII Character
`
a
b
c
d
e
f
k
l
m
n
o
p
q
v
w
x
y
z
{
|
g
h
i
j
r
s
t
u
}
~
DEL
34
Page 38

Appendix C
Function Code for PC
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
F7
F10
F11
F12
Ta b
Back Tab
Esc
End
Cursor Right
Cursor Up
Cursor Left
Cursor Down
Page Up
Page Down
Ins
F8
F9
Home
Bac
k Space
35
Enter
Del
Page 39

2.0"
1.2"
1.6"
40
16
13
10
6
5
2.2"
2.6"
3.3"
3.5"
3.9"
5.9"
7.9"
7.9"
7.1"
6.7"
5.7"
5.5"
9.8"
11.8"
13.8"
13.8"
mil
1"
6.2"
4.2"
2.4"
Appendix D
Technical Specifications
MODEL WLR890X
PERFORMANCE
Sensor 2660 pixels CCD linear imager sensor
Depth of Field 30mm to 330mm (40 mil) ± 20mm
Best Resolution 0.127mm ( 5mil ).
Scan Rate 45 scan / sec
Decoding Rate 100 scan / sec ( 10m / sec )
Scanning Width 120mm (1 mm barcode )
Sunlight 5000 Lux / Max ( Flourescent Light )
MECHANICAL
Dimensions 106 (L) x 62 (W) x 160 (H) mm
Weight Approximately 160g ( without cable )
Cable 210 cm in length ( Interchangeable cable )
ELECTRICAL
Operating Voltage + 5 VDC ± 10%
POWER STANDBY WORKING SURGE
CONSUMPTION <100mA <220mA <1000mA
ENVIRONMENTAL
Operating Temperature 0˚C to 50˚C
Storage Temperature -20˚C to 60˚C
Relative Humidity 0% to 95% non-condensing
Mechancial Shock 1.5m drop onto concrete
Conformance FCC class A and CE approval in progress
SYMBOLOGIES UPC-E, UPC-A, EAN-8, EAN13, UCC/EAN128
JAN, ISBN, ISSN, Code 39, Code 93, Code 128
Interleave 2 of 5, Industrial 2 of 5, Matrix 2 of 5
IATA 2 of 5, China Post Code (Toshiba Code),
MSI, Codabar, ABC Codabar, CX Codabar,
Code 11, UK
y, Telepen, Code 128,
Plesse
RSS
SCANNING RANGE
36
OUTER
DIMENSIONS
Page 40

Product Support
If you experience any problems with Wasp WLR 8900/8905 Scanners that you
are unable to resolve, call for technical assistance at (214) 547-4100, Monday
through Friday, 8:00 AM - 5:00 PM Central Standard Time. Our web site is
www.waspbarcode.com
You may also contact us in writing at:
Wasp Technologies
1400 10th Street
Plano, TX 75074
(214) 547-4100
(214) 547-4101 Fax
Warranty Information
Wasp Technologies products are warranted against defects in workmanship and
materials for a period of one year from the date of shipment, provided that the
product remains unmodified and is operated under normal and proper conditions.
This warranty is limited to repair or replacement at Wasp Technologies option,
with reasonable promptness after being notified. These provisions do not
prolong the original warranty term for any product which has been repaired or
replaced by Wasp Technologies.
This warranty applies to the original owner and does not extend to any
product which has been subject to
unauthorized repair, or tampering.
No other express warranty is given. The replacement or repair of a product is
your exclusive remedy. Any other implied warranty of merchantability or fitness
is limited to the duration of this written warranty. Some states, provinces, and
countries do not allow limits on how long an implied warranty lasts, so the above
limitation may not apply to you.
In no event shall Wasp Technologies be liable for consequential damages. Some
states, provinces, and countries do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental
or consequential damages, so the above limitations may not apply to you.
misuse, neglect, accidental damage,
37
Page 41

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do I configure the scanner for a notebook (or laptop) computer?
A: Scan the “Notebook” bar code on page 6.
Q: How do I change the terminator to a Tab?
A: Scan the “Tab” bar code on page 12.
Q: How do I remove the terminator?
A: Scan the “None” bar code on page 12.
Q: How do I enable the Full ASCII character set for the Code 39
bar code symbology?
A: Scan the following “Enable Code 39 Full ASCII” bar code on page 15.
38
 Loading...
Loading...