Page 1

IN ARC-I / IN TIG-I Series
Inverter Ar c W elding Machines
Operating Manual
WARPP ENGINEERS PVT. LTD.
B-1005, Western Edge II, Western Express Highway,
Near Metro Mall, Borivali (E), Mumbai-400 066.
Tel: 91-22-28542272/ 73/74. Fax: 91-22-28542275.
E-mail:sales@warpp.co.in
Web Site: www.warpp.co.in
1
Page 2

Thank you for selecting WARPP brand inverter welding machine. In order to keep you safe away from
unexpected accidents, and enjoy full benefits offered by our qua lity products during welding, please read the
instruction in details prior to operation. Complying with procedures defined in this manual is always
appreciated.
INDEX
1. Usage& Features……………………………………...…………………..(3)
2. Safety Precautions………………………………………………………...(3)
3. Installation…………….……………………………….………………….(5)
4. Definition of Product Model Number………………….…………………(6)
5. Principle in Brief…………….……………………………………………(6)
6. Operating Instruction………………………………….…………………..(7)
7. Repair and Maintenance.………………………….………….………….(12)
8. Main technical parameters……………………………………………….(15)
9. Appendix A: Common failures, probable cause & countermeasures…... (19)
10. Spare Part List…………………………………………………………(20)
2
Page 3
Usage & Features
This Series Inverter Arc welding machines include 2 welding combinations: IN ARC
(SMAW) & IN TIG (SMAW/TIG) with different specifications of rated current: 400A,
500A, 630A, etc., which are novelty high-efficient and energy-saving DC Arc welders,
not only are used in carbon steel and low alloy steel welding, but also used in stainless
steel, high alloy steel, copper, silver, molybdenum and titanium welding. As to its sound
static and dynamic characteristic and HF arc starting function, the series welders have
the following features:
¾ Invert technology can assured welding current high stability and arc length
consistency in fluctuating input primary power. Welding arc enjoys high
self-adjustability and mild strength.
¾ Low spatter
¾ Easy to start arc
¾ High deposit efficiency
¾ the machine can adjust its down- slope time while stopping arc. Weld formation are
pretty good.
¾ With remote control function, welding parameters can be adjusted in extended
distance.
¾ Light, small and portable.
¾ High power factor, high efficient and energy saving
Safety Precautions
General safety precaution:
z Please strictly comply with rules defined in this manual to avoid unexpected
accidents
z How to con nect to power supply, select working area and use pressure gas, please
comply with proper rules
z Not allow non-operator to ent er working area
z Welders’ installation, inspection, maintenance, and manipulation must be completed
by authorized person.
z Don’t use welding machine for unrelated purposes (Such as recharging, heating or
pipeline thaw, etc.)
z Must take safe precaution in case welder falling when it is put on the uneven ground
Avoid being electric shocked and burnt
z Never touch on the hot electrical units.
z Please instruct the authorized electrician to ground the welder frame by using
3
Page 4
proper-sized copper wire.
z Please instruct th e authorized electrician to connect the welder to power supply by
using proper- sized, well-insulated copper wire.
z When operating in the damp, space limited area, must ensure w ell-insulated betw een
body and work piece
z When operating in the high-rising location, must ensure safety by using safe net.
z Please power off the input voltage while no longer using.
Avoid breathing in hazardous welding fume or gas
z Please use specified ventilation to prevent being gas poisoned and asphyxiated
z Especially in the container where oxygen is depleted easily
Avoid being harmed by arc flash, hot spatter and slag
z Arc rays can injure your eyes and make your eyes feel uncomfortable.
z Hot spatter and slag can burn your skin. Please wear proper welding helmet, leather
gloves, long- sleeved suit, cap, apron and boot before welding.
Preventing from fire, explosion, container break accidents
z Don’t put flammable material in the working area. Hot spatter and hot weld can
easily start a fire.
z Cable must be connected the work piece firmly to ensure good conductivity in case
causing fire by resistance heat.
z Don’t weld in the flammable gas or weld container which contains flammable
material, otherwise it can cause explod e.
z Don’t weld encapsulated container, otherwise it can cause break.
z Ensuring a fire extinguisher at hand in case fire break out.
Avoid being hurt by moving parts.
z Never let the finger, hair, and cloth near the rotary cooling fan and wire feeder
rollers.
z When feeding wire, don’t let the bottom of gun near your eyes, face and body, to
prevent being harmed by wire.
Avoid gas bottle falling or gas regulator breaking
z Gas bottle must be firmly fixed on the ground, else if injure will exerts on.
z Never place bottle under high temperature or straight sun light.
z Never let y our face near gas outlet while turning on the gas valve to prevent from
being hurt by pressure gas.
z Customer should use the gas regulator provided by our company, and comply with
the proper instruction.
4
Page 5
O
Avoid being hurt by welding machine while in transport
z When moving the welding machine by fork-lift truck or crane, nobody can be
allowed for standing downright the route of the moving welder, in case being hurt
by the falling welding machine.
z The ropes or wires which used for hanging up the welding machine must be strong
enough to withstand corresponding tension strength. The rope or wire inclination
hanging on the tackle must be no more than 30°
Installation
1. Installing situation
1. Must place welding machine in the room where is no straight sunlight, no rain, less
dust, low humidity ,and temperature range of -10Ԩ~+40Ԩ
2. The gradient of ground must be no more than 15°
3. Ensure no wind at the welding position, or use screen to block the wind.
4. The distance between welder and wall must be more than 20cm, between welders
more than 10cm to ensure enough heat radiation.
5. When using water cooled gun, must be care of not being frozen.
2. Requirement of input volt:
(1) Input volt must be standard sine wave, effective value 380V±10%, frequency
50Hz/60Hz
(2) Unbalance degree of 3- phase volt must be no more than 5%
(3) Power supply:
z The size of fuse and breaker in the table are for reference only.
Product type 400 500 630
Power supply 3 phase AC380V
Min. power capacity 28KVA 38KVA 51KVA
Input
protection
Min.
Cable
size
Fuse 50A 63A 63A
breaker 63A 100A 100A
2
Input side 4mm
6mm2 6mm2
utput side 50mm2 50mm2 70mm2
Earth lead 4mm2 6mm2 6mm2
5
Page 6
3. Installation
The machines are portably designed, can be effortlessly moved by operators without
fix-up. But it should be settled in even and dry places with well ventilation.
3.1 SMAW mode
(1) Ensure firmly connection to welding cable.
(2) Connect to remote controller( If needed)
(3) Adjust every knobs, and switches on the front panel to proper position in line
with selected mode.
(4) Turn on the air switch on the power source.
(5) Connect input 3 phase primary power cable to switch box.
3.2 TIG mode
(1) Ensure firmly connection to welding cable and TIG torch.
(2) Ensure firmly connection to gas hose and gas bottle and or water hose and
water supply as to using water-cooled welding torch.
(3) Connect to remote controller(If needed)
(4) Adjust every knobs, and switches on the front panel to proper position in line
with selected mode.
(5) Turn on air switch on the power source.
(6) Connect input 3 phase power cable to switch box and close it.
Attention: Before you plug the welding cable, please turn off the power and rightly
calibrate the plug key to the socket slot a t first, then insert and turn the plug clockwise until
it firmly seated. Make sure the plug and the socket are well-connected to be sound
conductivity in case that they are burnt out by over resistance heat.
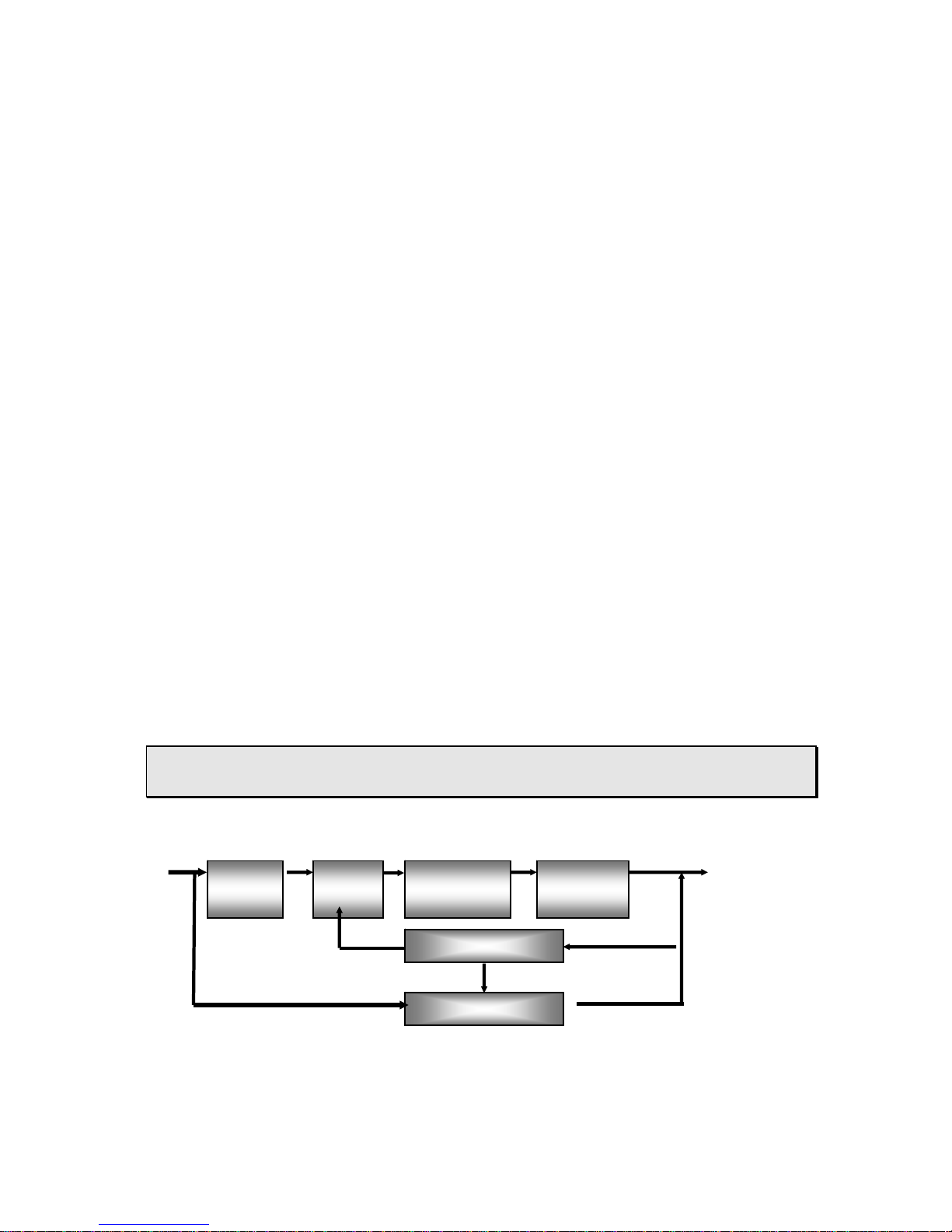
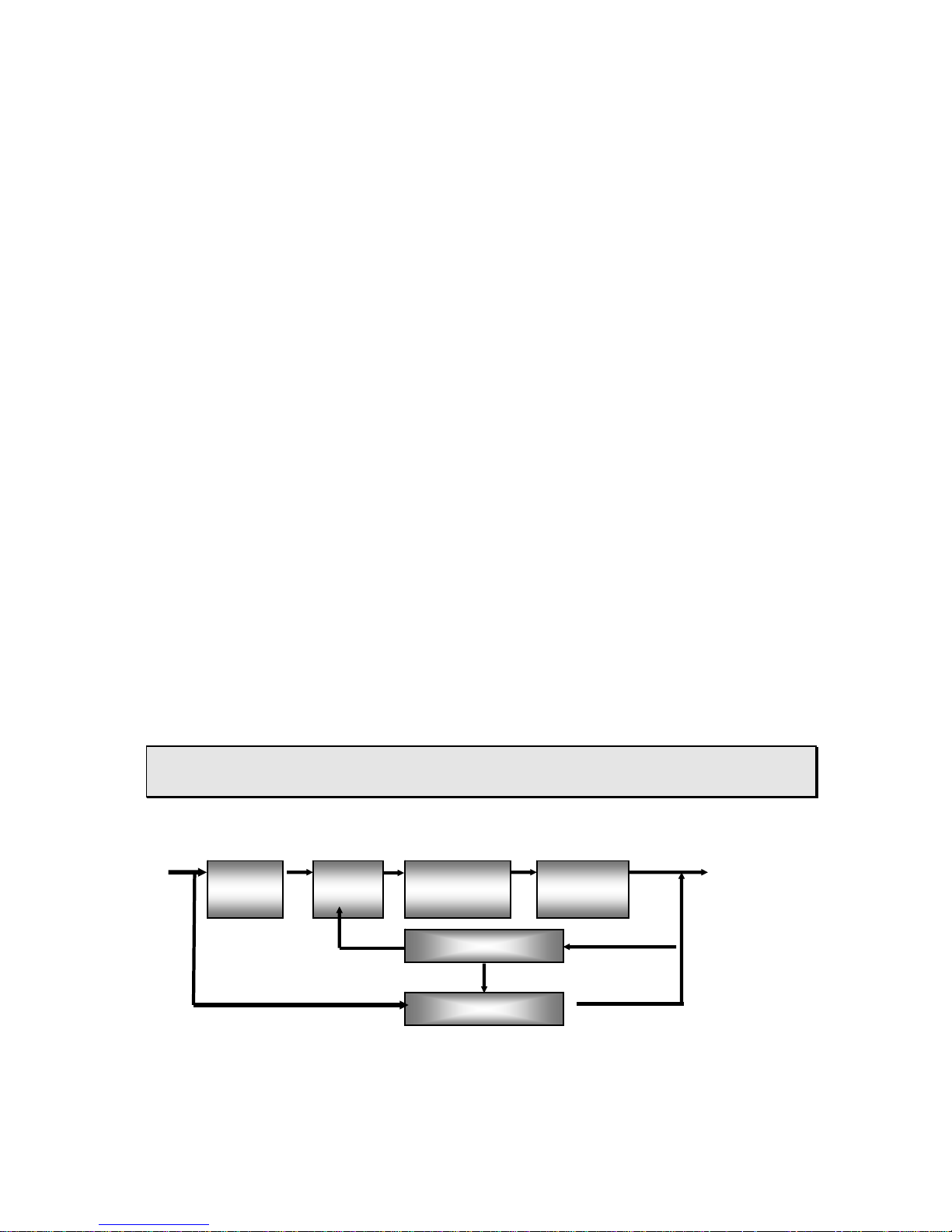
Block diagram of principle
3~380V/50Hz Output
3 phase
Rectifier
HF
Inverter
Transformer
High frequency arc start
HF
Control circuit
6
Principle in Brief
Rectifier &
Filter
Page 7
3. Installation
The machines are portably designed, can be effortlessly moved by operators without
fix-up. But it should be settled in even and dry places with well ventilation.
3.1 SMAW mode
(1) Ensure firmly connection to welding cable.
(2) Connect to remote controller( If needed)
(3) Adjust every knobs, and switches on the front panel to proper position in line
with selected mode.
(4) Turn on the air switch on the power source.
(5) Connect input 3 phase primary power cable to switch box.
3.2 TIG mode
(1) Ensure firmly connection to welding cable and TIG torch.
(2) Ensure firmly connection to gas hose and gas bottle and or water hose and
water supply as to using water-cooled welding torch.
(3) Connect to remote controller(If needed)
(4) Adjust every knobs, and switches on the front panel to proper position in line
with selected mode.
(5) Turn on air switch on the power source.
(6) Connect input 3 phase power cable to switch box and close it.
Attention: Before you plug the welding cable, please turn off the power and rightly
calibrate the plug key to the socket slot a t first, then insert and turn the plug clockwise until
it firmly seated. Make sure the plug and the socket are well-connected to be sound
conductivity in case that they are burnt out by over resistance heat.
Block diagram of principle
3~380V/50Hz Output
3 phase
Rectifier
HF
Inverter
Transformer
High frequency arc start
HF
Control circuit
6
Principle in Brief
Rectifier &
Filter
Page 8
(A)
This series welding machines apply IGBT soft switch inverter technology. 3- phase input
volt are rectified by rectifier, inverted into HF AC, reduced by HF transformer, rectified and
filtered by HF rectifier, then output DC power suitable for welding. After this process, the
welder’s dynamical responsive speed has been greatly increased, so the welder size and
weight are reduced noticeably result in energy saving. Power source enjoy sound
anti-fluctuating ability and high-quality performance during external context changes (As to
fluctuation in input power supply and extended welding cables).Easy to arc start, stable arc
length, pretty weld formation and capability of continuous regulation the current of welding,
arc-starting, arc force and time of down-slope as well as remote control availability add
significant values to customers. They can also perform down-slope, pre-gas flow and
post-gas flow function due to reasonable logic circuit design.
IN ARC Series arc welding machines output characteristic curve is as follows:
90–
20 –
0
U=20+0.04I
I
1. Functional introduction
Operating Instruction
7
Page 9

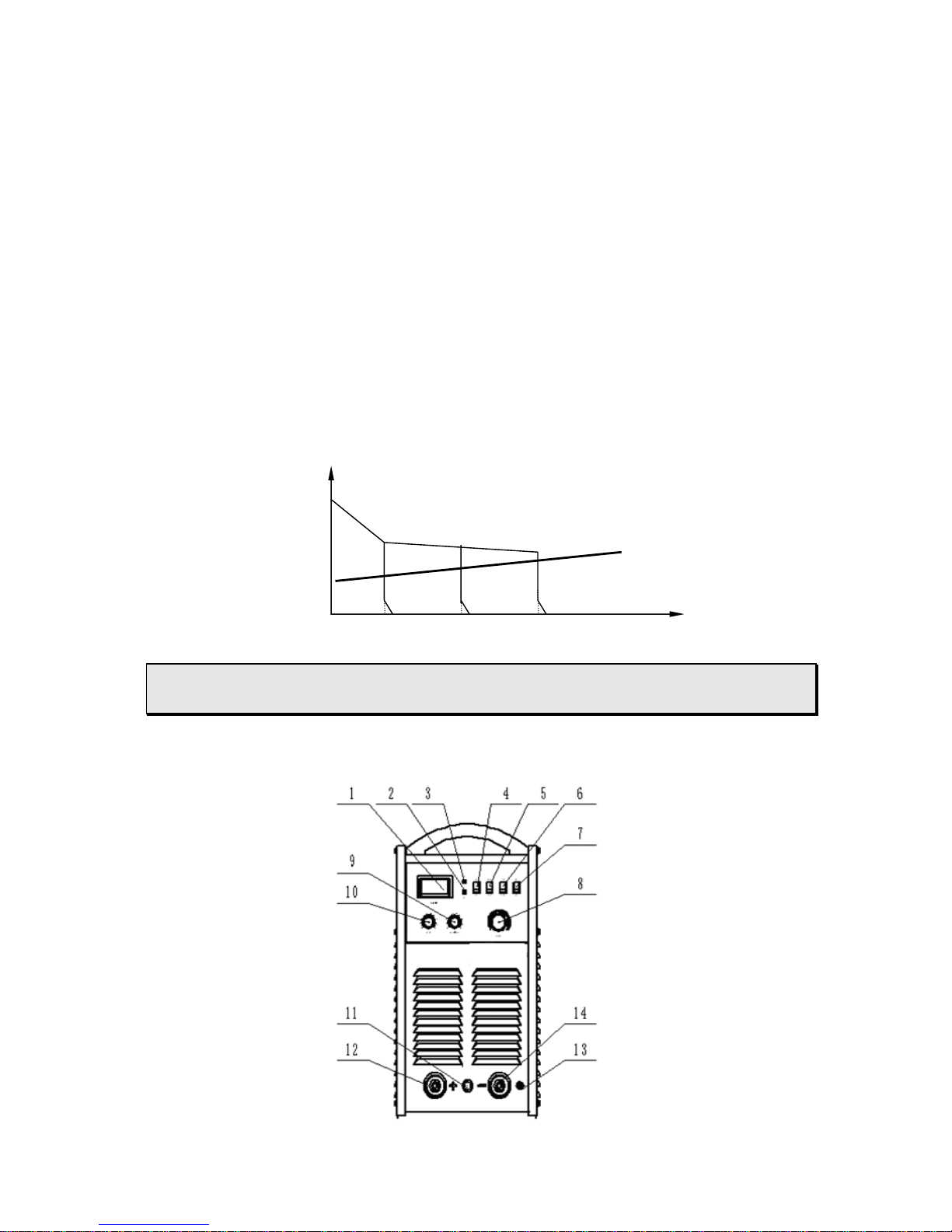
Front panel illustration and parts number reference
1.1
(1) “ Amp/volt ” meter
When meter mode switch indicates to “Amp”, the meter display s preset value while
in open load, and display practical value of welding current while in actual working.
To “Volt”, display practical value while in welding.
(2) “Protection” indicator lamp
Welding machine will automatically stop working when it is overheat, and the lamp
will be light on.
(3) “Power” indicator lamp
Lamp indicating whether power source is effectively connected to power supply
(4) “Amp/Volt” meter mode switch
(5)”SMAW/TIG” Switch (Only in IN TIG Series).
When it is indicated to “SMAW”, the machine is to work on SMAW;
When it is on “TIG”, the machine is to work on TIG
4-step/ 2-step switch (Only in IN TIG Series).
(6) “Remote/ Panel control” switch ((200 series only equipped with Panel control)
When it is on “Panel control”, you can adjust current of welding, arc force or
down-slope time through the knobs and switches on the panel; when it is on “Remote
control’, you can adjust the above parameters through remote control box in a
extended distance from the welding areas
(8) “Welding current” regulation knob
Used to adjust welding current on panel control mode
(9) “Arc force current/ down-slope time” regulation knob
Used to adjust arc force current under SMAW or stop-arc time under TIG
(10) “Arc-starting current “regulation knob used to adjust arc starting current
(11) “Remote control/ TIG” cable socket
It is used to connect with remote control cable to adjust welding current, arc force
current or down-slope time through remote control box when it is on the “Remote
control” mode, used to weld in extended distance.
To weld in normal distance on TIG, it is used to connect TIG torch's control cable
directly.
(12)Welding cable (+) quick plug socket
It is used to connect with stick holder on SMAW mode. Connect to work leads on
TIG mode.
(13)Gas outlet (S series not equipped with it)
Connect to TIG torch gas hose.
(14)Welding cable (-) quick plug socket
It is connected to work lead on SMAW mode and connected to TIG torch welding
cable on TIG mode.
.
8
Page 10
(11) “Remote control/ TIG” cable socket
It is used to connect with remote control cable to adjust welding current, arc force
current or down-slope time through remote control box when it is on the “Remote
control” mode, used to weld in extended distance.
To weld in normal distance on TIG, it is used to connect TIG torch's control cable
directly.
(12)Welding cable (+) quick plug socket
It is used to connect with stick holder on SMAW mode. Connect to work leads on
TIG mode.
(13)Gas outlet (S series not equipped with it)
Connect to TIG torch gas hose.
(14)Welding cable (-) quick plug socket
It is connected to work lead on SMAW mode and connected to TIG torch welding
cable on TIG mode.
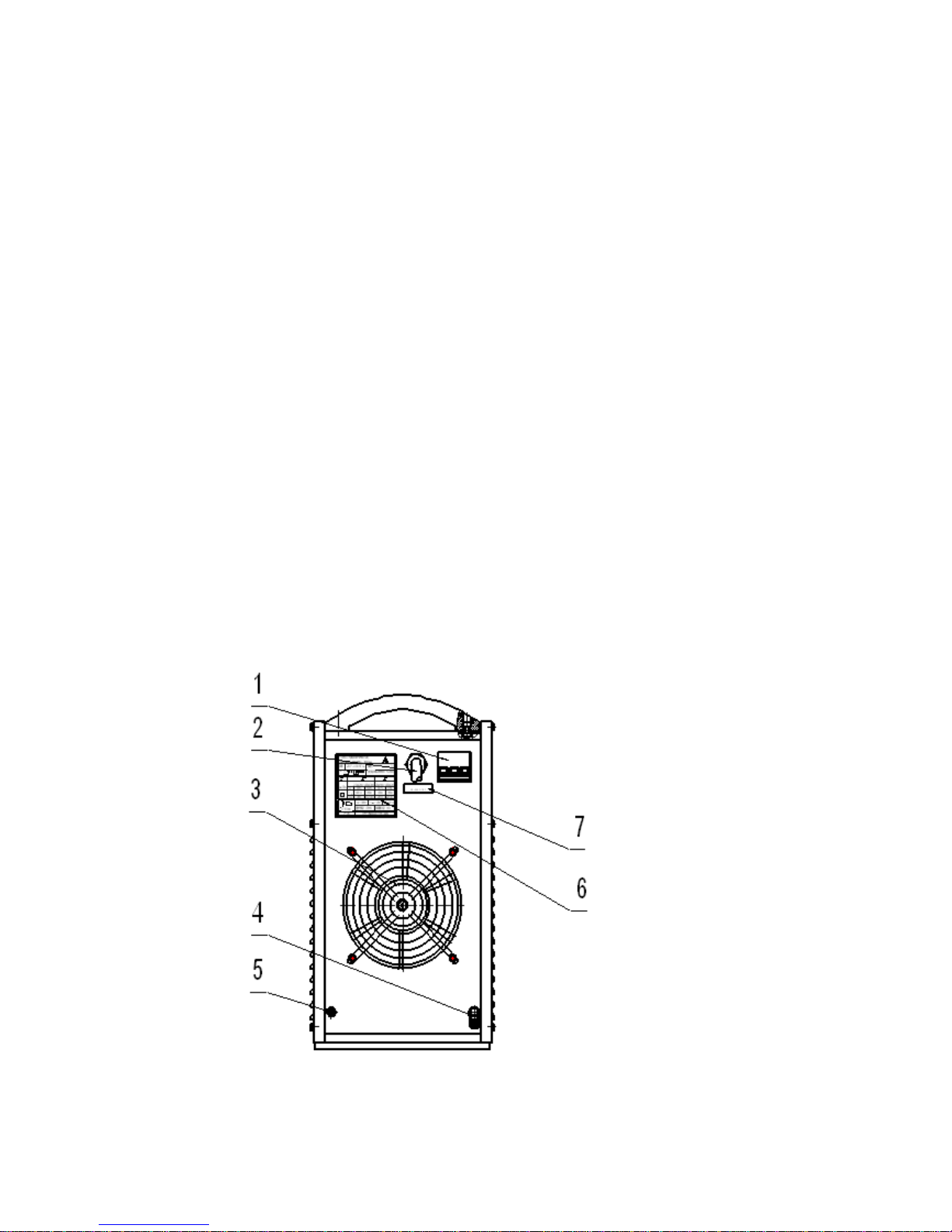
1.2 The rear panel and parts number reference
(1) Air switch
The function of air switch is to protect welding machine by automatic trip to turn-off
power supply while in machine overload or failure. Normally, the switch flipped to
upward means power-on. Use switch on the switch box to start or stop welding
machine, avoiding using the breaker.
(2) Input power cable
It is 4-pin cable. The mixed-colored wire must be firmly grounded, the rest wires
connect to corresponding 3-phase power supply (380v/50Hz).
8
Page 11

2.1.1 Shift between two working styles:
(1) Shift from down-slope to non-down-slope
Switch to “TIG” mode, pull TIG torch trigger, then loose it, open load voltage of
power source will disappear to indicate working style being shifted to
non-down-slope.
(2) Shift from non-down-slope to down-slope
Switch to “SMAW” mode from “TIG”, then back to “TIG” to complete shift.
2.1.2 Scratch arc-start with down-slope working style
Reference to 2.2.2 operation procedure
2.1.3 Scratch arc-start with non-down-slope working style
Reference to 2.2.3 operation procedure
2.2 Working styles on TIG mode of type STG series
Can be divided into 2 working styles: scratch arc-start and high frequency arc-start.
2.2.1 Shift between two working styles:
Shift scratch arc-start to high frequency arc-start
(1)Switch to “TIG” mode, then pull TIG torch trigger, then loose it, open load
voltage of power source will disappear to indicate working style is shifted to HF
arc-start.
(2)Shift HF arc-start to scratch arc-start
Switch to “SMAW” mode from “TIG”, then back to “TIG” to complete shift.
2.2.2 High frequency arc-start
Procedure flow sheet shows below :( Next page)
In principle, welders’ maintenance and repair should be co mpleted by us or our authorized
distributors. Customers can also solve the problems instructed by us or our authorized
distributors.
1. Attention:
(1) Rivet equipment name tag on the specified area of the case, otherwise the inside
parts will be damaged.
(2) Connect welding cable to terminal lug firmly, otherwise the terminal lug will be
burn out which will lead to welding process instability.
(3) Prevent jointer of welding cable and terminal lug from contacting with other
metals on the ground to avoid short circuit.
(4) Operating carefully not to make welding and control cable to be worn out or
Repair and Maintenance
11
Page 12

(1) “Amp” meter
It displays preset value while in open load, and displays practical value of
welding current while in actual working.
(2) “Welding current” regulation knob
(3) “Arc force current/ down-slope” regulation knob
(4) Socket 1
Connect to remote control cable.
(5) Socket 2
Connect to welding torch control cable which has a plug. There are 2 control wires
welded to lug 1 and lug 2 respectively on the plug
2. Operating instruction
Turn on the air switch on the switch box, the “Normal” indication lamp will light
on and cooling fan rotate. Before welding normally, set up parameters by adjusting
knobs and switches on the control box and front panel according to the selected
mode. Customer should refer to parameters defined in table 1 and table 2 showing
below:
Table 1 SMAW welding parameters
Work piece thickness
(mm)
<1
2 3
4~5 6~12
≥13
Electrode diameter
(mm)
Welding current(A) 20~40 40~50 90~110 90~130 160~250 250~400
1.5 2 3.2
10
3.2~4 4~5 5~6
Page 13

Table 2 TIG welding parameters
Welding current
(A)
40~50
50~80
80~120
120~160
160~200
200~300
Tungsten electrode
diameter(mm)
1~2
2~4
Max Argon gas
flow rate(L/min)
Work piece
thickness(mm)
1~3
3~6
6~9 300~400 4~6
Attention: On SMAW, when welding current is low and cable length of stick holder is
short(no more than 40m), arc force current should be adjusted in the range of 1-7 .
As to large welding current and long cable of stick holder, where volt potential
difference is very high between the two ends of cable, arc force current should be
adjusted in the range of 7- 10.
2.1 Working styles on TIG mode of ST series
Can be divided into 2 working styles: scratch arc-start with down-slope and
scratch arc-start without down-slope.
2.1.1 Shift between two working styles:
(1) Shift from down-slope to non-down-slope
Switch to “TIG” mode, pull TIG torch trigger, then loose it, open load voltage of
power source will disappear to indicate working style being shifted to
non-down-slope.
(2) Shift from non-down-slope to down-slope
Switch to “SMAW” mode from “TIG”, then back to “TIG” to complete shift.
2.1.2 Scratch arc-start with down-slope working style
Reference to 2.2.2 operation procedure
2.1.3 Scratch arc-start with non-down-slope working style
Reference to 2.2.3 operation procedure
4
6
7
8
9
10
12
11
Page 14

2.2 Working styles on TIG mode of type STG series
Can be divided into 2 working styles: scratch arc-start and high frequency arc-start.
2.2.1 Shift between two working styles:
Shift scratch arc-start to high frequency arc-start
(1)Switch to “TIG” mode, then pull TIG torch trigger, then loose it, open load
voltage of power source will disappear to indicate working style is shifted to HF
arc-start.
(2)Shift HF arc-start to scratch arc-start
Switch to “SMAW” mode from “TIG”, then back to “TIG” to complete shift.
2.2.2 High frequency arc-start
Procedure flow sheet shows below :( Next page)
Repair and Maintenance
In principle, welders’ maintenance and repair should be co mpleted by us or our authorized
distributors. Customers can also solve the problems instructed by us or our authorized
distributors.
1. Attention:
(1) Rivet equipment name tag on the specified area of the case, otherwise the inside
parts will be damaged.
(2) Connect welding cable to terminal lug firmly, otherwise the terminal lug will be
burn out which will lead to welding process instability.
(3) Prevent jointer of welding cable and terminal lug from contacting with other
metals on the ground to avoid short circuit.
(4) Operating carefully not to make welding and control cable to be worn out or
Broken
12
Page 15

Auto-lock Non-Auto lock
Release trigger
Hold on trigger
Pull TIG torch trigger
Pre-gas flow , HF/ scratch arc-start
Hold on trigger
Welding Welding
Release trigger
Down -slope
Down-slope
Release
Until crater fill
Until crater fill
Push trigger
Post-gas flow
Post-gas flow
Up -slope
Release trigger
Up-slope
Reset power source
Fig. HF arc-start procedure flow sheet
(5) Never let welding machine be bumped into or stacked up by heavy objects.
(6) Ensure good ventilation
(7) Temperature of cooling water is no more than 3 0 and no less than 0. The water
must be clean without impurity for fear of blocking water circulation which will
result in torch damage.
The machines can halt automatically, when work with large current for a long time.
Overheat protection lamp will light on. The machines will recovery after running up several
minutes in open load.
13
Page 16

(8) If the air switch on rear panel trips when the machine has worked with large
current for a long time, operator should power off the switch, then start the
machine in 5 minutes. Remember before starting the machine, turn on the air
switch on the rear panel, power on the switch box. The machine will be ready after
running under open load for several minutes.
(9) Be sure to turn off argon and water as well as power source when finish welding.
2. Periodic inspection and maintenance
(1) Removes dust from power resource with pressure air by authorized maintainer
every 3-6 months. Check if the bolt is loose.
(2) Check frequently if control cables are worn out, adjusting knobs are loose, and
components of panel are damaged.
(3) Check output cable periodically, if jointers are loose or plugs are distortion, please
repair in time, otherwise the sockets will burn out.
(4) Clear up or change contact tips and tungsten electrodes timely.
3. Trouble shooting
3.1. Checking procedure prior to maintenance
(1) Check if the panel switches and potentiometers are on the proper position
(2) Check if the input volt has phase missing, and range are between 340-420V.
(3) Check if the input cable connects correctly and firmly with the power source.
(4) Check if the welding cables connect correctly and firmly.
(5) Check if water circulation and CO2 flows out smoothly.
Warning:
Don’t open up case uninstructed, the max volt inside mach ine is 600V. Take safe
precautions to prevent from being electric shocked while in maintenance.
Never discharge high voltage to welder case with welding torch! Shut down power
source before changing or repairing welding cable or torch
14
Page 17

Technical data
Main technical parameters
Description
400 500 630
Primary power voltage/frequency 3 phase 380V±10%/50Hz
Rated output capacity 14.4KW 20KW 27.7KW
Rated input current 28A 38A 52A
Rated duty cycle 60%
Parameters
Range of output current
20~400A 20~500A 50~630A
Output voltage of open load 80±8V
Full-load efficiency 89%
Power factor(full-load)
Welding electrode diameter
Tungsten electrode diameter
2~6mm 2~6mm 2~6mm
1~6mm 1~6mm 1~6mm
0.95
Weight 43Kg 47Kg 55Kg
Dimension 636×322×582 mm 576×297×557 mm
Max argon flow rate 25L/min
Main transformer H
Insulation grade
Power source transformer、
B
output reactance
15
Page 18

z IN ARC / IN TIG-400 I
No. Tab Item Qua. Memo
1 K1 Air switch 1
2 D1 3-phase rectifier module 1 Small
3 L1 Polypropylene capacitor 1
4 C30 Polypropylene capacitor 1
5 C4 IGBT module 1
6
M1、M2
Voltage sensitive resistance 2
7 R1 Ceramic dielectric capacitor 1
8
C8~C17
Ceramic dielectric capacitor 10
9 T1 Main transformer 1
10 T4 Power source transformer 1
11 T5 Insulation transformer (IN TIG) 1
12
D1~D4
13 L2
Fast recovery diode module 2
Current exchange inductor (IN
TIG)
1
14 F1 Fuse size 1
15 YHB
Arc-start board components (IN
TIG)
1
16 T3 Stray transformer (IN TIG) 1
17 M axial airflow fan 1
18 Switch 4
19 Digital displayer 1
20 SW Thermal relay 1
21 Potentiometer 1
Current
adjustment
22 Potentiometer 2
23 Electromagnet valve (IN TIG) 1
24 Main control board 1
25 Driving board 1
Force
arc-starting
adjustment
16
Page 19

z IN ARC / IN TIG-500 I
No. Tab Item Qua. Memo
1 K1 Air switch 1
2 D1 3-phase rectifier module 1 big
3 L1 Polypropylene capacitor 1
4 C30 Polypropylene capacitor 1
5
6
C4~5
M1、M2
IGBT module 2
Voltage sensitive resistance 2
7 R1 Ceramic dielectric capacitor 1
8
C8~C19
Ceramic dielectric capacitor 12
9 T1 Main transformer 1
10 T4 Power source transformer 1
11 T5 Insulation transformer (IN TIG) 1
12
D1~D6
13 L2
Fast recovery diode module 3
Current exchange inductor (IN
TIG)
1
14 F1 Fuse size 1
15 YHB
Arc-start board components (IN
TIG)
1
16 T3 Stray transformer (IN TIG) 1
17 M axial airflow fan 1
18 Switch 4
19 Digital displayer 1
20 SW Thermal relay 1
21 Potentiometer 1
Current
adjustment
Force
22 Potentiometer 2
arc-starting
adjustment
23 Electromagnet valve (IN TIG) 1
24 Main control board 1
25 Driving board 1
17
Page 20

z IN ARC / IN TIG-630 I
No. Tab Item Qua. Memo
1 K1 Air switch 1
2 D1 3-phase rectifier module 1
3 L1 Polypropylene capacitor 1
4 C30 Polypropylene capacitor 1
5
C4~5
IGBT module 2
6
M1、M2
Voltage sensitive resistance 2
7 R1 Ceramic dielectric capacitor 1
8
C8]~C21
Ceramic dielectric capacitor 14
9 T1 Main transformer 1
10 T3 Power source transformer 1
11 T5 Insulation transformer (IN TIG) 1
12
D3~D8
13 L2
Fast recovery diode module 4
Current exchange inductor (IN
TIG)
1
14 F1 Fuse size 1
15 YHB
Arc-start board components (IN
TIG)
1
16 T3 Stray transformer (IN TIG) 1
17 M1 axial airflow fan 1
18 Switch 4
19 Digital displayer 1
20 SW Thermal relay 1
21 Potentiometer 1 Current adjustment
22 Potentiometer 2
23 Electromagnet valve (IN TIG) 1
24 Main control board 1
24 Driving board 1
Force arc-starting
adjustment
18
Page 21

Appendix A: common failures, probable cause & countermeasures
№ Phenomena Reason Solving methods
1 After power on, it
doesn’t work.
2 Air switch on
back panel trips
while the
machine is
working
normally.
3 Welding current
is unstable.
Phase missing power source, in
Fuse(2A)in welder is broken.
Cable is broken
The following components may be
damaged: IGBT module, 3-phase
rectify module, outputting diode
module, or other components, Driving
board is damaged.
Short circuit between lines.
Phase missing
The following components may be
Check power source
Check if cooling fan,
power source transformer
and main control board are
good or not.
Check connection
Check and replace.
When IGBT module is
damaged, please check
12Ω, 5.1Ω resistance or
SR160 on driving board is
damaged or not.
Check power source.
Check and replace.
4 Welding current
is not adjustable.
5 TIG welding is
abnormal.
damaged: Potentiometers, switches
on front panel and remote control
cable, potentiometer on remote
controller.
Main control board is damaged
Potentiometer of welding current
adjustment is damaged.
Remote control cable is broken.
Main control board is damaged
The switch on the front panel is
damaged
TIG torch switch is damaged.
Remote control cable is broken.
The tungsten electrode in welder is in
the wrong position.
Main control board is damaged
Check and replace.
Check and replace.
19
Page 22

Page 23

Page 24

Page 25

Front Panel of ARC series
Remote /
Protection on LED (LED2)
Power on LED (LED1)
Panel Control
Switch (KD1)
Digital Display
(DSP001)
Arc-starting Current
Potentiometer (W3)
A
mp / Volt
Switch (KD2)
Arc-force Current /
Down-slo
p
e Time
Welding Current
Potentiometer (W1)
p
Potentiometer (W2)
Control Socket
Output Terminal (-)
(
OUTN
)
(P20)
Output T erminal
()
(+) (OUTP)
Page 26

Front Panel
VOLTAGE/AMPERE
SMAW/TIG SELECTION
SWITCH (PSW01)
SWITCH (PSW01)
LED YELLOW
(LED Y01)
2 / 4 TRACK
SELECTION SWITCH
(PSW01)
Digital Display
Meter (DSP001)
LED RED (LED R01
)
REMOTE/PANEL
SELECTION SWITCH
(PSW01)
()
POTENTIOMETER
FOR CURRENT
(POT001)
POTENTIOMETER FOR
STRIKING CURRENT
(POT001)
POTENTIONMETER
FOR ARC FORCE
(POT001)
Output T erminal (+)
(OUTP)
7 PIN CONNECTOR
MALE (CON7PNM)
OUTPUT
TERMINAL (-)
(OUTN)
Page 27

Left
View
Fan (FAN
Main
(
002)
Transformer
Thrust Coil
Output
Choke (CHK
001)
Snubber PCB
Isolation
PCB
(
PSB-
For O/P FRM
(PCB-SNB-
OUT-01)
(
ISO-01)
Output Rectifier
Module (FRM001)
Page 28

Right View
-
g
Thermal Cut
Out
SNUBBER CARD
Over Current
Protection
PCB
HF PCB (PCB-
HF-01)
HF T
ransformer
(CTRAX007)
Resonant Coil
IGBT
Input Bridge
AC Capacitor
Module
Fan Capacitor
p
(CAP05)
Solonaid Valve
Shunt
MOV (MOV001)
DC Capacitor
(CAP001)
(SV001)
Insulation
Transformer
(INSTRX001)
Page 29

Top View
p
Drive CARD
(PCB-DRV-01)
CONTROL
TRANSFORMER
(CTRAX001)
Input Surge
Suppressor (ISS
01)
Main PCB
Fuse (F1)
Page 30

Rear
Panel
FAN
MCB
Page 31

List for the spares of INTIG I Series machines
DESCRIPTION INTIG-315 INTIG-400 I INTIG-500 I INTIG-630 I
MAIN PCB
DRIVE CARD
IGBT
INPUT BRIDGE MODULE
OUTPUT RECTIFIER MODULE
FAN
DC CAPACITOR
AC CAPACITOR
SNUBBER CARD
MCB
DIGITAL DISPLAY METER
INPUT SURGE SUPPRESSOR
SNUBBER CAPACITOR
CONTROL TRANSFORMER
OUTPUT CHOKE
HF PCB
HF PCB CAPACITOR
SOLONAID VALVE
INSULATION TRANSFORMER
MOV
ISOLATION PCB
SNUBBER PCB FOR OUTPUT
FRM
POTENTIOMETER FOR
KNOB FOR THE POT
OVERCURRENT PROTECTION
PCB
MAIN TRANSFORMER
FAN CAPACITOR
TWO POLE SWITCH FOR
OUT PUT CONNECTOR
MACHINE SIDE
OUT PUT CONNECTOR
CABLE SIDE
7 PIN CONNECTOR MALE
SHUNT
LED RED
LED YELLOW
Part Code Part Code Part Code Part Code
PCB-TIG-315I PCB-TIG-400I PCB-500I PCB-TIG-630I
PCB-DRV-01 PCB-DRV-01 PCB-DRV-01L PCB-DRV-01L
IGBT7512 IGBT7512 IGBT10012 IGBT15012
IBDG003 IBDG003 IBDG004 IBDG004
FRM001 FRM001 FRM001 FRM001
FAN002 FAN002 FAN003 FAN003
CAP001 CAP001 CAP001 CAP001
CAP002 CAP003 CAP003 CAP04
PCB-SNB-01 PCB-SNB-01 PCB-SNB-02 PCB-SNB-02
MCB001 MCB001 MCB002 MCB003
DSP001 DSP001 DSP001 DSP001
ISS001 ISS001 ISS001 ISS001
SCAP001 SCAP001 SCAP001 SCAP001
CTRAX001 CTRAX001 CTRAX001 CTRAX001
CHK001 CHK001 CHK001 CHK001
PCB-HF-01 PCB-HF-01 PCB-HF-01 PCB-HF-01
PCB22.01 PCB22.01 PCB22.01 PCB22.01
SV001 SV001 SV001 SV001
INSTRX001 INSTRX001 INSTRX001 INSTRX001
MOV001 MOV001 MOV001 MOV001
PCB-ISO-01 PCB-ISO-01 PCB-ISO-01 PCB-ISO-01
PCB-SNB-OUT-01 PCB-SNB-OUT-01 PCB-SNB-OUT-01 PCB-SNB-OUT-01
POT001 POT001 POT001 POT001
KNOB001 KNOB001 KNOB001 KNOB001
PCB-OC-315 PCB-OC-400 PCB-OC-500 PCB-OC-630
MTRX001 MTRX002 MTRX003 MTRX004
CAP05 CAP05 CAP05 CAP05
PSW001 PSW001 PSW001 PSW001
FST-PLG-F-01 FST-PLG-F-01 OUT-CON-01 OUT-CON-01
FST-PLG-M-01 FST-PLG-M-01 NA NA
CON7PNM CON7PNM CON7PNM CON7PNM
SHUNT001 SHUNT001 SHUNT002 SHUNT002
LEDR01 LEDR01 LEDR01 LEDR01
LEDY01 LEDY01 LEDY01 LEDY01
Page 32

DESCRIPTION INARC-315 INARC-400 I INARC-500 I INARC-630 I
/
/A
Part Code Part Code Part Code Part Code
MAIN PCB PCB-ARC-315I PCB-ARC-400I PCB-ARC-500I PCB-ARC-630I
DRIVE CARD PCB-DRV-01 PCB-DRV-01 PCB-DRV-01L PCB-DRV-01L
IGBT IGBT7512 IGBT7512 IGBT10012 IGBT15012
INPUT BRIDGE MODULE IBDG003 IBDG003 IBDG004 IBDG004
OUTPUT RECTIFIER
MODULE
FRM001 FRM001 FRM001 FRM001
FAN FAN002 FAN002 FAN003 FAN003
DC CAPACITOR CAP001 CAP001 CAP001 CAP001
AC CAPACITOR CAP002 CAP003 CAP003 CAP004
SNUBBER CARD PCB-SNB-01 PCB-SNB-01 PCB-SNB-02 PCB-SNB-02
MCB MCB001 MCB001 MCB002 MCB003
DIGITAL DISPLAY METER DSP001 DSP001 DSP001 DSP001
INPUT SURGE
SUPPRESSOR
ISS001 ISS001 ISS001 ISS001
SNUBBER CAPACITOR SCAP001 SCAP001 SCAP001 SCAP001
CONTROL TRANSFORMER CTRAX001 CTRAX001 CTRAX001 CTRAX001
MOV MOV001 MOV001 MOV001 MOV001
ISOLATION PCB PCB-ISO-01 PCB-ISO-01 PCB-ISO-01 PCB-ISO-01
SNUBBER PCB FOR
OUTPUT FRM
PCB-SNB-OUT-01 PCB-SNB-OUT01 PCB-SNB-OUT-02 PCB-SNB-OUT-02
POTENTIOMETER FOR
CURRENT/STRIKING
POT001 POT001 POT001 POT001
CURRENT/ARC FORCE
KNOB FOR THE POT KNOB001 KNOB001 KNOB001 KNOB001
OVERCURRENT
PROTECTION PCB
PCB-OC-315 PCB-OC-400 PCB-OC-500 PCB-OC-630
MAIN TRANSFORMER MTRX001 MTRX002 MTRX003 MTRX004
FAN CAPACITOR CAP05 CAP05 CAP05 CAP05
TWO POLE SWITCH FOR
REMOTE & V
PANEL
OUT PUT CONNECTOR
MACHINE SIDE
OUT PUT CONNECTOR
CABLE SIDE
PSW001 PSW001 PSW001 PSW001
FST-PLG-F-01 FST-PLG-F-01 OUT-CON-01 OUT-CON-01
FST-PLG-M-01 FST-PLG-M-01 NA NA
7 PIN CONNECTOR MALE CON7PNM CON7PNM CON7PNM CON7PNM
 Loading...
Loading...