Page 1

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
INARC-1000 I / 1250 I
Inverter Arc Welding Machines
OPERATING MANUAL
WARPP ENGINEERS PVT. LTD.
B-1005, Western Edge II, Near Metro Mall, Off. Western Express
Highway, Borivali (E), Mumbai-400 066.
Tel: 91-22-28542272 73/74. Fax: 91-22-28542275.
E-mail:sales@warpp.co.in Web Site: www.warpp.co.in
·26·
Page 2

Index
1. Safety Precautions……….……….………………………………..(1)
2. Principle &Technical data…………………………………………(7)
3. Features & Applications…………………………………………...(11)
4. Installation Guide………………………………………………….(12)
5. Operating Instruction …………...………………………………...(16)
6. Repair & Maintenance…………………………………………….(20)
Appendix A: EMC Suggestion for installation and use of welder…….(23)
Page 3

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
Safety Precautions
ARC WELDING CAN BE HAZARDOUS. PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE
SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH. KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS SHOULD
CONSULT WITH THEIR DOCTOR BEFORE OPERATING.
BE SURE THAT ONLY QUALIFIED INDIVIDUALS PERFORM ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION,
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR PROCEDURES
For Engine Powered equipments
1.a. Turn the engine off before troubleshooting and maintenance work unless the maintenance
work requires it to be running.
1.b. Operate engines in open, well-ventilated areas or vent the engine exhaust fumes outdoors.
1.c. Do not add the fuel near an open flame welding arc or when the engine is running. Stop the
engine and allow it to cool before refueling to prevent spilled fuel from vaporizing on
contact with hot engine parts and igniting. Do not spill fuel when filling tank. If fuel is
spilled, wipe it up and do not start engine until fumes have been eliminated.
1.d. Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and devices in position and in good repair. Keep
hands, hair, clothing and tools away from V-belts, gears, fans and all other moving parts
when starting, operating or repairing equipment.
1.e. In some cases it may be necessary to remove safety guards to perform required
maintenance. Remove guards only when necessary and replace them when the
maintenance requiring their removal is complete. Always use the greatest care when
working near moving parts.
1.f. Do not put your hands near the engine fan. Do not attempt to override the governor or idler
by pushing on the throttle control rods while the engine is running.
1.g. To prevent accidentally starting gasoline engines while turning the engine or welding
generator during maintenance work, disconnect the spark plug wires, distributor cap or
magnet wire as appropriate.
1.h. To avoid scalding, do not remove the radiator pressure cap when the engine is hot.
·1·
Page 4

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS may be dangerous
2.a. Electric current flowing through any conductor causes localized Electric and Magnetic
Fields(EMF). Welding current creates EMF fields around welding cables and welding
machines.
2.b. EMF fields may interfere with some pacemakers, and welders having a pacemaker should
consult their physician before welding.
2.c. Exposure to EMF fields in welding may have other health effects which are now not
known.
2.d. All welders should use the following procedures in order to minimize exposure to EMF
fields from the welding circuit:
2.d.1. Route the electrode and work cables together-Secure them with tape when possible.
2.d.2. Never coil electrode lead around your body.
2.d.3. Do not place your body between your electrode and work cables. If the electrode
cable is on your right side, the work cable should also be on your right side.
2.d.4. Connect the work cable to the work piece as close as possible to the area being
welded.
2.d.5. Do not work next to welding power source.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill
3.a. The electrode and work (or ground) circuits are electrically “hot” when the welder is on.
Do not touch these “hot” parts with your bare skin or wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free
gloves to insulate hands.
3.b. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation. Make certain the insulation is
large enough to cover your full area of physical contact with work and ground.
In addition to the normal safety precautions, if welding must be performed under
electrically hazardous conditions (in damp locations or wearing wet clothing; on metal
structures such as floors, gratings or scaffolds; when in cramped positions such as sitting,
·2·
Page 5

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
kneeling or lying, if there is a high risk of unavoidable or accidental contact with the work
piece or ground) use the following equipment:
Semiautomatic DC Constant Voltage (Wire) Welder
DC Manual (Stick) Welder
AC Welder with Reduced voltage control
3.c. In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode, electrode reel, welding head,
nozzle or semiautomatic welding gun are also electrically “hot”.
3.d. Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical connection with the metal being
welded. The connection should be as close as possible to the area being welded.
3.e. Ground the work or metal to be welded to a good electrical (earth) ground.
3.f. Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and welding machine in good,
safe operating condition. Replace damaged insulation.
3.g. Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
3.h. Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of electrode holders connected to two
welders because voltage between the two can be the total of the open circuit voltage of
both welders.
3.i. When working above floor level, use a safety belt to protect yourself from a fall
ARC RAYS can burn.
4.a. Use a shield with the proper filter and cover plates to protect your eyes from sparks and the
rays of the arc when welding or observing open arc welding. Head shield and filter lens
should conform to standard.
4.b. Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant material to protect your skin and
that of your helpers from the arc rays.
4.c. protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable screening and/or warn them
not to watch the arc nor expose themselves to the arc rays or to hot spatter or material.
·3·
Page 6

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
FUMES AND GASES can be dangerous
5.a. Welding may produce fumes and gases hazardous to health. Avoid breathing these fumes
and gases. When welding, keep your head out of the fume. Use enough ventilation and/or
exhaust at the arc to keep fumes and gases away from the breathing zone. When welding
with electrodes which require special ventilation such as stainless or hard facing or on
lead or cadmium and plated steel and other materials or coatings which produce highly
toxic fumes, keep exposure as low as possible and below Threshold Limit Va lu es (T LV )
using local exhaust or mechanical ventilation. In confined spaces or in some
circumstances, outdoors, a respirator may be required. Additional precautions are also
required when welding on galvanized steel.
5.b. The operation of welding fume control equipment is affected by various factors including
proper use and positioning of the equipment, maintenance of the equipment and the
specific welding procedure and application involved. Worker exposure level should be
checked upon installation and periodically thereafter to be certain.
5.c. Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon vapors coming from degreasing,
cleaning or spraying operations. The heat and rays of the arc can react with solvent vapors
to form phosgene, a highly toxic gas, and other irritating products.
5.d. Shielding gases used for arc welding can displace air and cause injury or death. Always use
enough ventilation, especially in confined areas, to insure breathing air is safe.
5.e. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this equipment and the
consumables to be used,
5.f. Also see item 1.b.
·4·
Page 7

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
WELDING AND CUTTING SPARKS can cause fire or explosion.
6.a. Remove fire hazardous from the welding area. If this is not possible, cover them to prevent
the welding sparks from starting a fire. Remember that welding sparks and hot materials
from welding can easily go through small cracks and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid
welding near hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.
6.b. Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site, special precautions should be used
to prevent hazardous situations.
6.c. When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode circuit is touching the work or
ground. Accidental contact can cause overheating and create a fire hazard.
6.d. Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the proper steps have been taken
to insure that such procedures will not cause flammable or toxic vapors from substances
inside. They can cause an explosion even though they have been “cleaned”.
6.e. Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or welding. They may explode.
6.f. Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil free protective garments such
as leather gloves, heavy shirt, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear ear plugs when
welding out of position or in confined places. Always wear safety glasses with side shields
when in a welding area.
6.g. Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding area as practical. Work cables
connected to the building framework or other locations away from the welding area
increase the possibility of the welding current passing through lifting chains, crane cables
or other alternate circuits. This can create fire hazards or overheat lifting chains or cable
until they fail.
6.h. Also see item 1.c.
6.i. Do not use a welding power source for pipe thawing.
·5·
Page 8

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
CYLINDER may explode if damaged.
7.a. Use only compressed gas cylinders containing the correct shielding gas for the process
used and properly operating regulators designed for the gas and pressure used. All hoses,
fittings, etc. should be suitable for the application and maintained in good condition.
7.b. Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely chained to an undercarriage or fixed
support.
7.c. Cylinders should be located:
Away from areas where they may be struck or subjected to physical damage, A safe
distance from arc welding or cutting operations and any other source of heat, sparks, or
flame.
7.d. Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other electrically “hot” parts to touch a
cylinder.
7.e. Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet when opening the cylinder
valve.
7.f. Valve protection caps should be always be in place and hand tight expect when the cylinder
is in use or connected for use.
FOR ELECTRICALLY powered equipment
8.a. Turn off input power using the disconnect switch at the fuse box before working on the
equipment.
8.b. Install equipment in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
8.c. Ground the equipment in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
·6·
Page 9
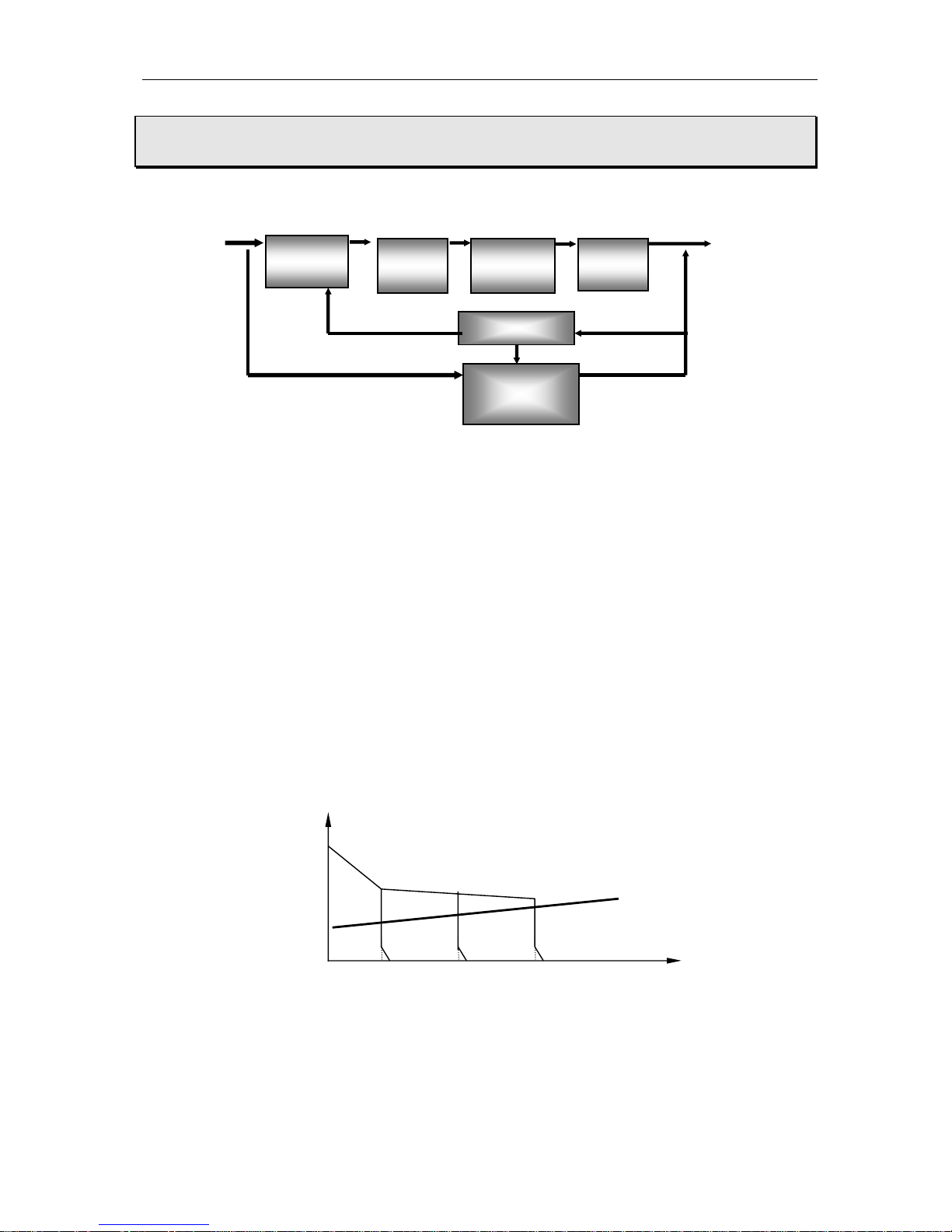
INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
(A)
Principle & Technical data
INARC-1000 I series Block diagram of principle
3 phase
Rectifier
HF
Inverter
Figure 1: Block diagram of principle
This series welding machines apply IGBT soft switch inverter technology. 3- Phase input are
HF
Transforme
Control circuit
HF Arc-starting
Device
Rectifier
& Filter
rectified by rectifier, inverted into HF AC, reduced by HF transformer, rectified and filtered by
HF rectifier, then output DC power suitable for welding. After this process, the welder’s
dynamical responsive speed has been greatly increased, so the welder size and weight are
reduced noticeably result in energy saving.
Power source enjoy sound anti-fluctuating ability and high-quality performance during external
context changes (As to fluctuation in input power supply and extended welding cables). Easy
to arc start, stable arc length, pretty weld formation and capability of continuous regulation the
welding current and arc-force current.
90–
20 –
0
U=20+0.04I
I
Figure 2: Volt-Ampere curve
·7·
Page 10

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
1. Main technical parameters
Parameters
Description
INARC-1000 I INARC-1250 I
Primary power voltage /
frequency
Three Phase 380V±10% / 50HZ
Rated output capacity 44KW 55KW
Rated input current 83A 120A
Rated duty cycle 100%
Range of output current 60-1000A 60-1250A
Output voltage of open load 80±8V
Full-load efficiency 92%
Power factor(full-load)
Welding electrode diameter
3~6mm 3~8mm
0.88
Carbon rod diameter
Weight (kg) 95 100
Dimension (mm3) 767×352×757 767×352×802
Insulation class
Table1: Parameter Specification
3~10mm
Main transformer H
Transformer for ZKB/QDB,
Output reactor
·8·
B
Page 11

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
2. Main circuit diagram
z INARC-1000 / 1250 I
Figure 3: Main Circuit Diagram for INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
·9·
Page 12

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
3. Components List
z INARC-1000 I / 1250 I
No. Tab Item Model Quantity Remark
1 QF1 Circuit Breaker
2 AB1, AB2 Three Phase Rectifier
Module
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
L3~4
L10~11
C7~8
C9~10
V1~4
R1~2
C53~54
C31~32
Power Inductor
Resonance Inductor MZ-1000.6.1.0 2
Polypropylene Capacitor CBB65-50uF/500VAC 8
Polypropylene Capacitor MFD-DA01 20uF/1400VDC 4
IGBT Module
Varistor MYL1-625/5 2
Capacitor CT81-3KV-0.01uF-K 2
Polypropylene Capacitor
JD158-100D(100A/3P)
MDS100A/1200V 2
MZ-1000Ⅲ .6.1.0
SKM100GB123D(1000)
SKM150GB123D(1250)
MFD-DA01 5uF/500VAC(For
1000)
1
2
4
2
MFD-DA01 6uF/500VAC(For
1250)
11 T2, T3 Main Transformer MZ-1000.5.1.0 1
12
V5~10,
Fast Recovery Diode
Module
DKR200AB60 6 (For 1000)
8 (For 1250)
V15~20
13 T1 Transformer for
ZX7-1000S.3.1-1 1
ZKB/QDB
14
L7~8
Output Reactor
ZX7-1000S.4-2(For 1000)
2
ZX7-1000S.5-2(For 1250)
15 FU1 Fuse 3A (6×30) 1
16
EV1~2
Fan 200FZY8-S
2
(380V single phase)
17 Digital Display XL5139GV-2 1
18
ST1~3
Thermal Switch
JUC-079F/70±5℃-1D-A
3
19 Potentiometer WH118-1A-2W/4.7K±10% 2
20 Potentiometer POC20-2W-4.7K 1
21 AP1 Main Control Board ZX7-1000S.6.0 1
22 AP2 Drive Board
ZX7-400Ⅲ .7.0
2
23 AP3 Current Test Board ZX7-1000S.7.0 1
·10·
Page 13

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
Features & Applications
This series machines are MMA/TIG machines with different specifications of rated current:
1000A and 1250A, which are novelty high-efficient and energy-saving DC Arc welders. It can
perform MMA, TIG welding, and air arc gouging, not only used in carbon steel and low alloy
steel welding, but also used in stainless steel welding, air arc gouging for all kinds of metals. It
can perform metal cutting, bevel welding, open groove, clean-up welding roots, remove the
seam and fly-casting, such as burr.
Features and benefits:
◆ Inverter technology ensures stable welding voltage, high adjustability for arc regulation.
◆ Low spatter
Easy to arc-starting and molten pool control with Smooth, consistent arc
2 cycle / 4cycle operating modes provided
High duty cycle
Wide range of current adjustment
Non-source power factor compensation technology, high PF (power factor)
Extendable cable provided. It is suitable for long distance welding
Soft switch technology, high efficiency
Applications:
Suitable for carbon steel, stainless steels and alloy steels.
Electric power, petrochemical Construction.
Maintenance shop.
Light and heavy industries.
Boiler pressure container manufacture.
Shipyards.
·11·
Page 14

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
Installation Guide
1. Pre-installation
1.1 Installation Environment
The INARC-1000 I series is designed for use in adverse environments. Examples
of environments with increased adverse conditions are:
z In locations in which freedom of movement is restricted, so that the operator is
forced to perform the work in a cramped (kneeling, sitting or lying) position with
physical contact with conductive parts;
z In locations which are fully or partially limited by conductive elements, and in
which there is a high risk of unavoidable or accidental contact by the operator;
z In wet or damp hot locations where humidity or perspiration considerably reduces
the skin resistance of the human body and the insulation properties of accessories.
z Environments with adverse conditions do not include places where electrically
conductive parts, in the near vicinity of the operator, which can cause increased
hazard, have been insulated.
z The gradient of ground must be no more than 10°
z Ensure no wind at the welding position, or use screen to block the wind.
z When using water-cooled torch, must be care of not being frozen.
z Welding power sources with degree of protection IP21S may be stored, but are not
intended to be used outside during precipitation unless sheltered.
1.2. Installation Location
Be sure to locate the welder according to the following guidelines:
z In areas, free from moisture and dust.
z Ambient temperature between 0 degrees C to 40 degrees C.
z In areas, free from oil, steam and corrosive gases.
z In areas, not subjected to abnormal vibration or shock.
z In areas, not exposed to direct sunlight or rain.
·12·
Page 15

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
z Place at a distance of 12" (304.79mm) or more from walls or similar boundaries
that could restrict natural airflow for cooling.
1.3 Power Source Connections
Warning
Thermal Arc advises that this equipment be electrically connected by a qualified
electrician.
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill; SIGNIFICANT DC VOLTAGE is present after
removal of input power.
DO NOT TOUCH live electrical parts.
z SHUT DOWN welding power source, disconnect input power employing
lockout/tagging procedures.
z Lockout/tagging procedures consist of padlocking line disconnect switch in open
position.
z Removing fuses from fuse box, or shutting off and red-tagging circuit breaker or
other disconnecting device.
1.4.Power Supply Requirements
z Input volt must be standard sine wave, effective value 380V, and frequency
50Hz/60Hz.
z Unbalance degree of 3- phase volt must be no more than 5%.
z Power supply:
·13·
Page 16

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
Product type
Power Supply
INARC-1000 I INARC-1250 I
3 phase AC 380V
Min. capacity 83KVA 120KVA
Input volt
protection
Cable size
Fuse 90A 130A
Circuit Breaker 120A 160A
Input volt
25mm
35mm2
2
Output volt 70mm2×2 95mm2×2
Ground lead 16mm2 16mm2
Table 4: Power supply connection
Please note: The size of fuse and breaker in the table are for reference only.
2. Installation:
This series of welding machine does not need fixed installation. Ensure the location where
the machine is to be placed is even, dry, and with good ventilation.
2.1 MMA mode
(1) Ensure firmly connection to welding cable.
(2) Adjust every switches and potentiometers on the front panel to proper position in
line with selected mode.
(3) Turn on the circuit breaker on the power source.
(4) Connect input 3 phase power cable to switch box.
2.2 Air arc gouging mode
(1) Ensure firmly connection to ground cable and air arc gouging torch.
(2) Ensure firmly connection to gas hose and gas cylinder
(3) Adjust every switches and potentiometers on the front panel to proper position in
line with selected mode.
(4) Turn on the circuit breaker on the power source.
(5) Connect input 3 phase power cable to switch box.
·14·
Page 17

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
2.3 TIG mode
(1) Ensure firmly connection to ground cable and TIG torch.
(2) Ensure firmly connection to gas hose and gas cylinder if it is gas cooled;
Ensure firmly connection to water hose and water cooling machine if it is water cooled.
(3) Adjust every switches and potentiometers on the front panel to proper position in
line with selected mode.
(4) Turn on the circuit breaker on the power source.
(5) Connect input 3 phase power cable to switch box.
Attention:Cut off the power supply before connecting the welding cable.
Ensure the good connection between welding cable and connection terminal.
·15·
Page 18

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
Operating Instruction
1. Functional introduction
1.1 Front panel illustration and parts number reference
Figure 5: Front Panel
(1) Protection on LED
Lights up and stops welding automatically while in overheat, but will not light up
when normally welding.
(2) Fault on LED
Lights up and stops welding automatically while machine is in breakdown.
(3) Current / Voltage displayer
z When the switch is on “Current”, display the preset current during the open-load;
display the welding current during the welding.
z When the switch is on “Current”, display the output voltage value.
(4) Down-slope time adjustment knob
Adjust the crater-filling time in TIG mode.
(5) Current / Voltage switch
Transfer between current and voltage
·16·
Page 19

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
(6) MMA / TIG / Air arc gouging switch
Transfer among MMA / TIG / Air arc gouging
(7) 4-step / 2-step switch
Used in TIG mode. It is auto-lock when in 4-step, and non-auto-lock when in 2-step
(8) Arc length switch
z In MMA mode:
Long: Output cable length is more than 25m, less than 40m.
Short: Output cable length is less than 10m.
Middle: Output cable length is more than 10m, less than 25m.
z It is on “Long” position when in air arc gouging welding.
(9) Arc-force current adjustment knob
Adjust arc-force current
(10) Welding current adjustment knob
Adjust welding current
(11) Output terminal (+)
z In MMA welding, it is connected to welding cable
z In air arc gouging, it is connected to the torch
z In TIG welding, it is connected to the workpiece
(12) Output terminal (+)
z In MMA welding or in air arc gouging, it is connected to the workpiece
z In TIG welding, it is connected to the torch
(13) Gas outlet (S series machine does not have this one)
Connect the gas hose of the torch
(14) Socket P20
Control switch of the torch
·17·
Page 20

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
1.2 The rear panel and parts number reference
Figure 6: Rear panel
(1) Specification Plate
(2) Input cable connection box
(3) Circuit Breaker
The function of Circuit Breaker is to protect welding machine by automatic trip to
turn-off power supply while in machine overload or failure. Normally, the Breaker
flipped to upward means power-on. Switch on from the switch box to start or stop
welding machine, avoiding using the breaker.
(4)Ground bolt
To ensure operators not to be harmed and welding machine to be working normally,
make sure the ground bolt is grounded firmly by ground cable.
5) Fan
Cool down the heat components in the welding machine.
(6) Gas inlet (S series machine does not have this one)
Connect to gas regulator with gas hose.
·18·
Page 21

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
2. Operating instruction
Turn on the circuit breaker on the switchboard, the Power on LED light, up, and the fan runs.
Before welding, set up parameters by adjusting knobs and switches on the front panel
according to the selected mode. Customer should refer to parameters defined in table 5 and
table 6 showing below:
Workpiece thickness
(mm)
Electrode diameter
(mm)
Welding current (A)
Workpiece thickness
(mm)
1~4
4~7
7~10
<1
1.5 2 3.2
2 3
4~5 6~12
3.2~4 4~5 5~6
≥13
20~40 40~50 90~110 90~130 160~250 250~400
Table 5: MMA welding parameters
Carbon rod diameter
Welding current (A)
(mm)
150~200
3~4
200~250
250~300
300~350
5~7
350~400
450~500
7~8
500~550
≥10 ≥600
9~10
Table 6: Air arc gouging parameters
·19·
Page 22

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
Repair & Maintenance
WARNING: Have a qualified electrician do the maintenance and trouble shooting work.
Turn the input power off, using the disconnect switch at the fuse box before working
inside the machine.
1. Cautions:
• Rivet equipment name tag on the specified area of the case, otherwise the inside parts
will possibly be damaged.
• Connect welding cable to terminals firmly, otherwise the terminals will be burn out
which will cause the instability of welding process.
• Avoid welding cable and control cable being broken, and prevent welding machine
from being short circuit.
• Never let welding machine be bumped into or stacked up by heavy objects.
• Ensure good ventilation
• Under high temperature, if work with large current for long period, welder may shut
down automatically due to thermal protection acts .At this point, let the machine runs
under open-load for a few minutes, and it will be automatically recover.
• Under high temperature, if work with large current for long period, welder may shut
down automatically due to air switcher trips. Cut off the power supply to the electricity
switchboard on frame, and wait for 5 minutes to turn on the air switcher on the power
source fist then connect the power supply to the electricity switchboard on frame. And
leave the machine runs under open-load condition for a while.
• After welding, cut off the Argon gas supply and the power supply.
·20·
Page 23

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
2. General maintenance
• Remove dust from power resource with pressure air by qualified individuals every 3-6
months. Check if the jointers are loose.
• Check regularly if cables are worn out, knobs are loose, and components of panel are
damaged.
• Check regularly if cables are tightly connected to cable connecting terminals in case of
terminals being burnt out.
• Clean and replace Contact Tip and Tungsten Electrode in time.
3. Procedure for regular checking prior to maintenance
• Check if all front panel switches are on the proper positions.
• Check if the input volt has the phase missing, and range are between 340~420V.
• Check if the input cable is connected correctly and firmly with the power source.
• Check if the ground lead is connected correctly and firmly.
• Check if the welding cables are connected correctly and firmly.
• Check if gas regulator is in good situation and gas flows out normally.
WARNING: Have a qualified electrician do the maintenance and trouble shooting work.
Turn the input power off, using the disconnect switch at the fuse box before working
inside the machine. Don’t open up case uninstructed, the max volt inside machine is 600V,
Never discharge high voltage to welder case with welding torch! Shut down power source
before changing or repairing welding cable or torch
·21·
Page 24

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
№ TROUBLE CAUSES WHAT TO DO
After power on, it
1
doesn’t work.
Circuit Breaker on
Rear Panel trips
2
while the machine is
working normally.
Welding current is
3
instable.
1) Phase missing in power
source
2) Fuse(3A)in welder is
broken.
3) Cable is broken
1) The following components
may be damaged: IGBT
Module, 3-phase Rectify
Module, or other devices
2) Drive Board is damaged.
3) Short circuit between cables.
1) Phase missing
2) The following devices may
be damaged: Potentiometers
or switches on front panel
3) Main Control Board is
1) Check power source
2) Check if the Fan,
Transformer for ZKB/QDB
and Main Control Board are
good or not.
3) Check the connection
1) Check and replace.
2) When IGBT Module is
damaged, please check
the devices on Drive Board
1) Check power source.
2) Check and replace.
Welding current is
4
not adjustable.
damaged
4) Current Sensor is damaged
1) Welding Current
Potentiometer is damaged.
2) Main Control Board is
damaged
3) Current Sensor is damaged
Table 7: Trouble Shooting Table
Check and replace
·22·
Page 25

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
Appendix A
1. General
The user is responsible for installing and using the arc welding equipment according to the
manufacturer’s instructions. If electromagnetic disturbances are detected, then it shall be the
responsibility of the user of the arc welding equipment to resolve the situation with the
technical assistance of the manufacturer. In some cases this remedial action may be as
simple as earthling the welding circuit, see note. In other cases it could involve constructing
an electromagnetic screen enclosing the welding power source and the word complete with
associated input filters. In all cases electromagnetic disturbances shall be reduced to the
point, where they are no longer troublesome.
NOTE: The welding circuit may not be earthed for safety reasons. Changing the
earthling arrangements should only be authorized by a person who is
competent to assess whether the changes will increase the risk of injury.
2. Assessment of area
Before installing arc welding equipment the user shall make an assessment of potential
electromagnetic problems in the surrounding area. The following shall be taken into account:
1) Other supply cables, control cables, signaling and telephone cables, above, below and
adjacent to the arc welding equipment;
2) Radio and television transmitters and receivers;
3) Computer and other control equipment;
4) Safety critical equipment, for example guarding of industrial equipment;
5) The health of the people around, for example the use of pacemakers and hearing aids;
6) Equipment used for calibration or measurement;
7) The immunity of other equipment in the environment is compatible. The user shall ensure
that other equipment being used in the environment is compatible. This may require
additional protection measures;
8) The time of day that welding or other activities are to be carried out.
·23·
Page 26

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
3. Methods of reducing emissions
1) Public supply system
Arc welding equipment should be connected to the public supply system according to the
manufacturer’s recommendations. If interference occurs, it may be necessary to take
additional precautions such as filtering of the public supply system. Consideration should
be given to shielding the supply cable of permanently installed arc welding equipment, in
metallic conduit or equivalent. Shielding should be electrically continuous its length. The
shielding should be connected to the welding power source so that good electrical contact
is maintained between the conduit and the welding power source enclosure.
2) Maintenance of the arc welding equipment
The arc welding equipment should be routinely maintained according to the
manufacturer’s recommendations. All access and service doors and covers should be
closed and properly fastened when the arc welding equipment is in operation. The arc
welding equipment should not be modified in any way, except for those changes and
adjustments covered in the manufacturer’s instructions. In particular, the spark gaps of arc
striking and stabilizing devices should be adjusted and maintained according to the
manufacturer’s recommendations.
3) Welding cables
The welding cables should be kept as short as possible and should be positioned close
together, running at or close to the floor level.
4) Equipotent bonding
Bonding of all metallic components in the welding installation and adjacent to it should be
considered. However, metallic components bonded to the word piece will increase the risk
that the operator could receive an electric shock by touching these metallic components
and the electrode at the same time. The operator should be insulated from all such bonded
metallic components.
·24·
Page 27

INARC-1000 I/ 1250 I
5) Earthling of the work piece
Where the work piece is nor bonded to earth for electrical safety, nor connected to earth
because of its size and position, for example ships hull or building steelwork, a connection
bonding the work piece to earth may reduce emissions in some, but not all instances. Care
should be taken to prevent the earthling of the work piece increasing the risk of injury to
users, or damage to other electrical equipment. Where necessary, the connection of the
work piece to earth should be made by a direct connection to the work piece, but in some
countries where direct connection is not permitted, the bonding should be achieved by
suitable capacitance, selected according to national regulations.
6) Screening and shielding
Selective screening and shielding of other cables and equipment in the surrounding area
may alleviate problems of interference. Screening of the entire welding installation may
be considered for special applications.
·25·
 Loading...
Loading...