
Avea
™
critical care ventilation
VENTILATION MODES USER GUIDE

The Avea™ ventilator user guide is not intended to replace the operator manual. You must become
completely familiar with the Avea ventilator operator manual before using the Avea ventilator.
Section 1: UIM navigation............................................ 1
Touch-Turn-Touch
™
/Touch-Turn-
Accept
™
techniques ��������������������������������������������������������2
Setting breath type and mode ��������������������������������3–4
Setting advanced settings �����������������������������������������5–6
Setting alarm limits ���������������������������������������������������������������7
Section 2: Breath types and modes .........................8
Breath types �����������������������������������������������������������������������������9
Mandatory breaths �������������������������������������������������������������10
Demand breaths �������������������������������������������������������������������11
Volume controlled ventilation ���������������������������������12–14
Volume SIMV mode ������������������������������������������������������������� 15
Pressure controlled ventilation �������������������������������16–17
Pressure SIMV �������������������������������������������������������������������������18
TCPL mode ��������������������������������������������������������������������� 19–20
TCPL SIMV mode ����������������������������������������������������������21–24
PRVC SIMV mode ���������������������������������������������������������������� 25
APRV/BiPhasic �������������������������������������������������������������� 26–28
CPAP/PSV �������������������������������������������������������������������������������29
Apnea Backup ventilation�������������������������������������� 30–31
CPAP/PSV ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������31
Table of contents
Nasal CPAP/IMV ������������������������������������������������������������������ 32
Standby ���������������������������������������������������������������������������33–34
Section 3: Advanced settings ................................. 35
Volume Limit ��������������������������������������������������������������������������36
Machine Volume ���������������������������������������������������������� 37–38
Inspiratory Rise ��������������������������������������������������������������������� 39
Flow Cycle ������������������������������������������������������������������������������39
Waveform �������������������������������������������������������������������������������40
Sigh ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������40
Bias Flow ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������41
Pres Trig �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������41
Vsync
®
�������������������������������������������������������������������������������42–43
Vsync Rise �������������������������������������������������������������������������������43
PSV Rise������������������������������������������������������������������������������������44
PSV Cycle ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������44
PSV Tmax ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������44
Volume Limit ��������������������������������������������������������������������������44
T High PSV�������������������������������������������������������������������������������45
T High Sync ����������������������������������������������������������������������������45
T Low Sync ������������������������������������������������������������������������������45
Avea ventilator modes ���������������������������������������������46–49

Section 1:
UIM navigation
Touch-Turn-Touch™/Touch-Turn-Accept™ techniques ��������������������2
Setting breath type and mode ������������������������������������������������������������ 3–4
Setting advanced settings ��������������������������������������������������������������������� 5–6
Setting alarm limits �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������7
1
2
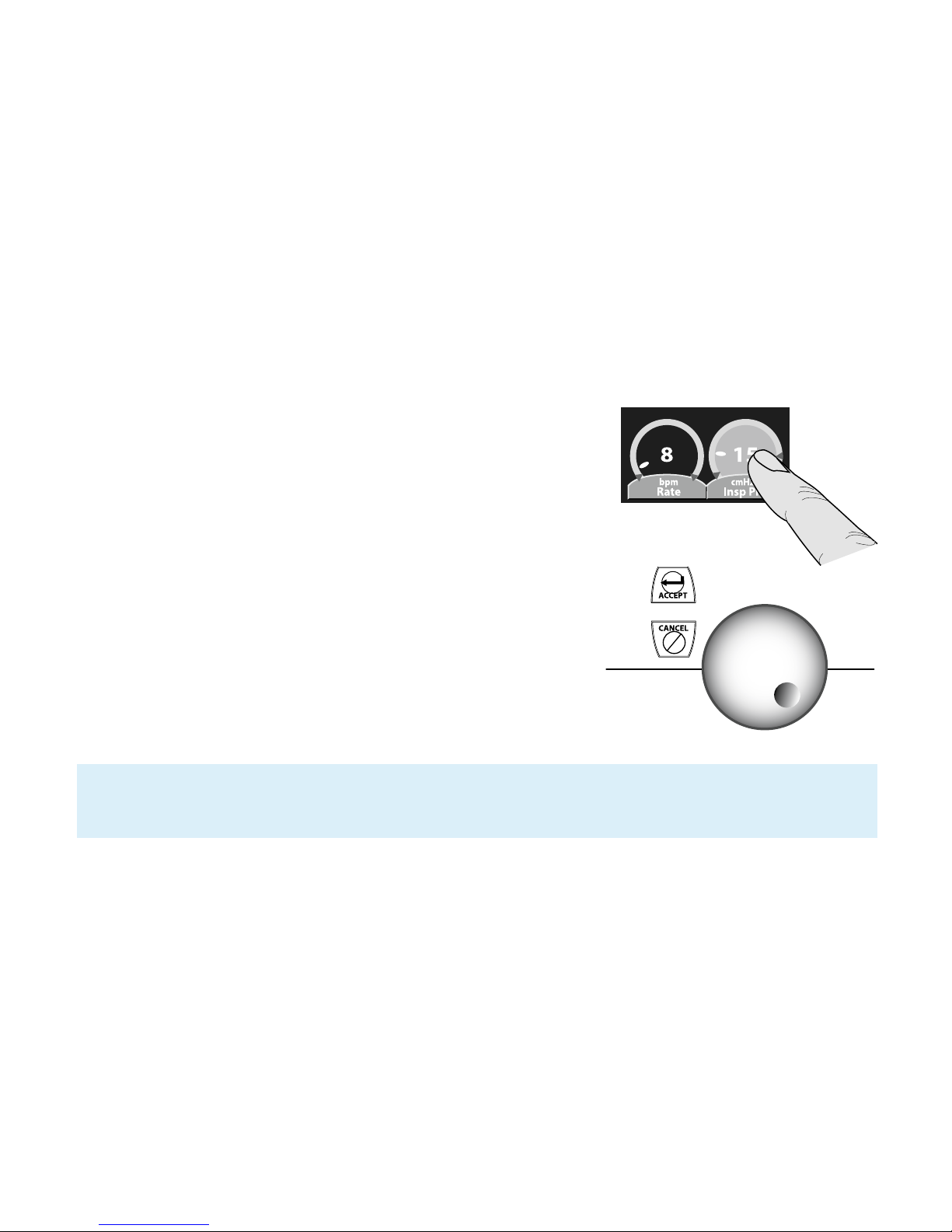
Touch-Turn-Touch™/Touch-Turn-Accept™ techniques
To change most controls on the Avea ventilator:
1. Touch the screen directly over the control to select it.
The control highlights (changes color), indicating that
it is active.
2. Turn the data dial clockwise to increase the selected
value, and turn the dial counter-clockwise to decrease
it. Turning the data dial quickly accelerates the rate
of change from one setting to another. Turning the
data dial slowly gradually changes the setting.
3. Touch the screen directly over the highlighted
control again, or press the ACCEPT membrane
button to the left of the data dial to accept your
new setting.
Note: If you press the CANCEL button or do not actively accept the new setting within
15 seconds, ventilation continues at the previous setting.
3
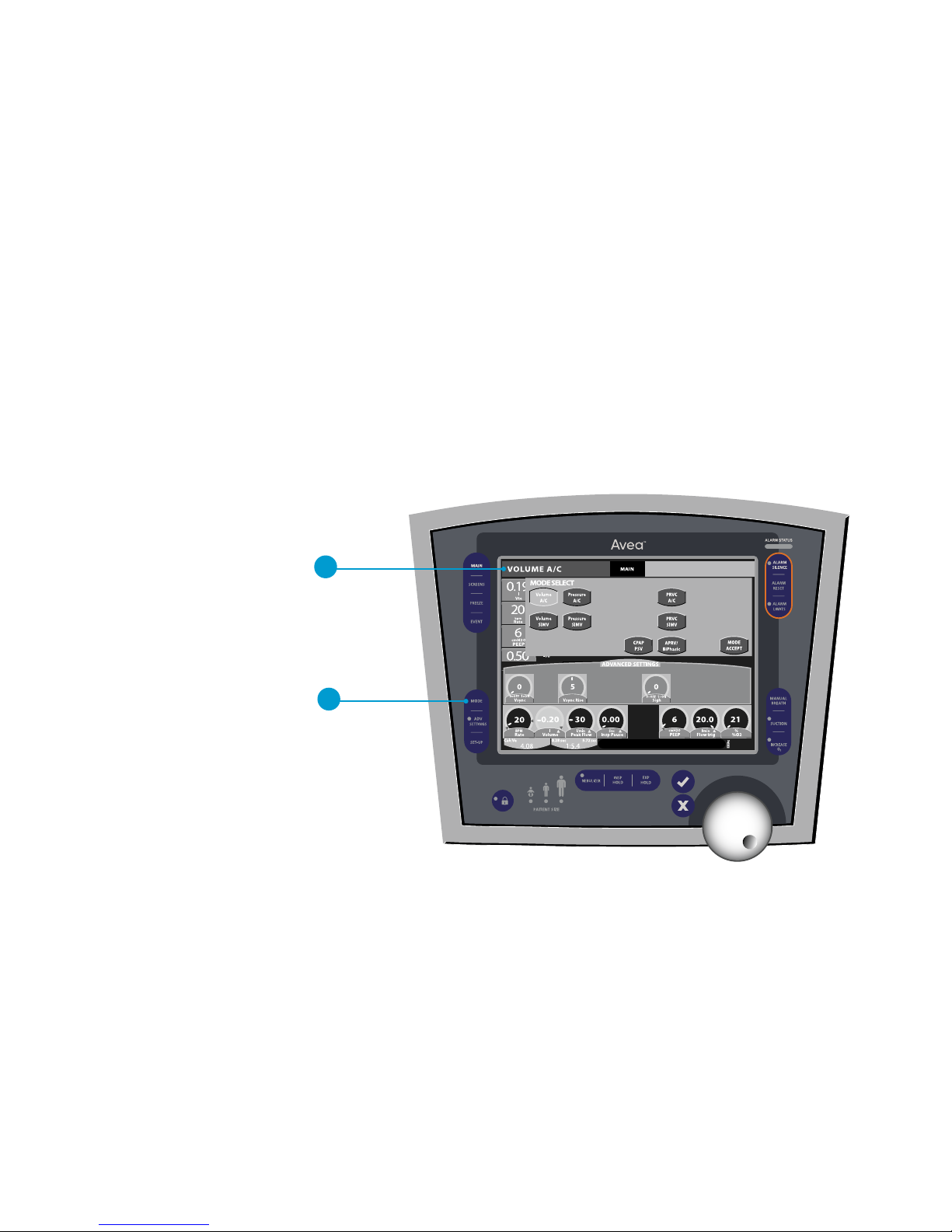
To access the MODE SELECT screen, press the MODE indicator on the touch screen
or the MODE button on the membrane panel.
A. MODE indicator
B. MODE button
Setting breath type and mode
A
B
4
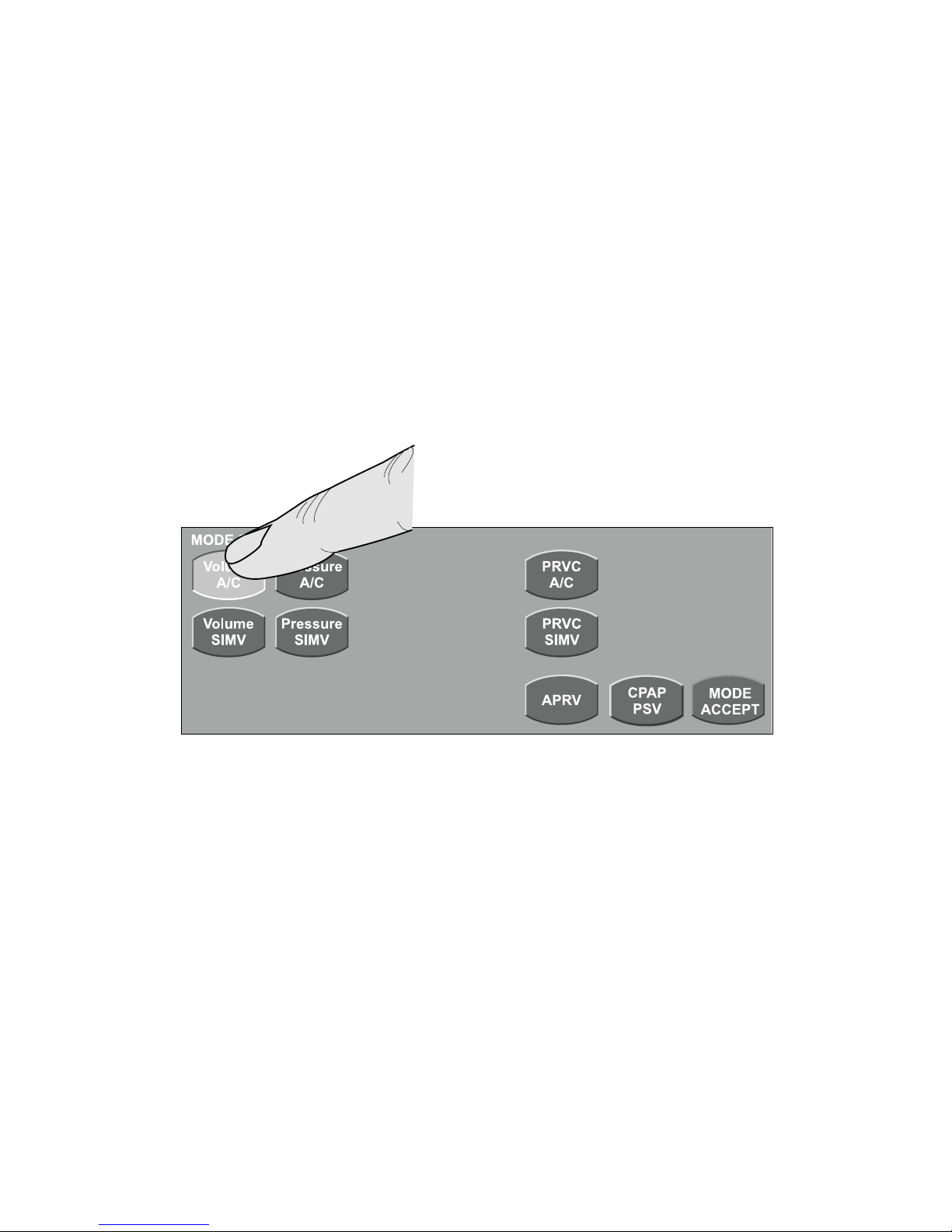
The MODE SELECT screen appears. Select the touch-screen button for the desired mode.
Primary controls for the proposed mode appear at the bottom of the touch screen. Use the
techniques described on page 3 to set these controls. Press MODE ACCEPT to accept the
new mode and primary control settings.
Setting breath type and mode (continued)
Selecting Volume A/C mode

5
To set advanced settings, press the ADV
SETTINGS button on the lower left of the
user interface. Advanced settings refine the
breath delivery beyond the primary breath
control settings. Press the ADV SETTINGS
button for the desired primary control.
Not all primary controls have advanced
settings. Primary controls with advanced
settings are marked with a yellow triangle.
Detailed descriptions of all advanced
settings are in section 3.
A. ADV SETTINGS button
Setting advanced settings
A

6
Setting advanced settings (continued)
Advanced settings for volume
Use the Touch-Turn-Touch or Touch-Turn-Accept technique to modify the advanced
settings (see page 3).

7
Setting alarm limits
Alarm Limits window with Volume A/C mode selected on MODE SELECT window
Use the Touch-Turn-Touch or Touch-Turn-Accept technique to modify the alarm limits
settings (see page 3).
Press the ALARM LIMITS membrane button
(to the upper right of the UIM) to open or
close the window.
A. ALARM LIMITS button
A

Section 2:
Breath types and modes
Breath types ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������9
Mandatory breaths �����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������10
Demand breaths �����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������11
Volume controlled ventilation �������������������������������������������������������������12–14
Volume SIMV mode ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 15
Pressure controlled ventilation ����������������������������������������������������������� 16–17
Pressure SIMV ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 18
TCPL mode ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������19–20
TCPL SIMV mode ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������21–24
PRVC SIMV mode �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 25
APRV/BiPhasic ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������26–28
CPAP/PSV ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 29
Apnea Backup ventilation�������������������������������������������������������������������30–31
CPAP/PSV ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������31
Nasal CPAP/IMV ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 32
Standby �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������33–34
8

9
Section 2: Breath types and modes
This section describes the breath types and ventilation mode combinations available
for adult, pediatric and neonatal patients using the Avea ventilator.
Breath types
There are two basic breath types:
• Mandatory breaths (delivered according to the set ventilator parameters)
• Demand breaths (triggered by the patient)
All breaths are defined by four variables:
1
• Trigger (initiates the breath)
• Control (controls the delivery)
• Limit (terminates the breath)
• Cycle (initiates the frequency of delivery)
10
Mandatory breaths
Mandatory breaths can be triggered by the machine, patient or operator. The Avea
ventilator can deliver five mandatory breath types:
1. Volume breaths
2. Pressure breaths
3. Time cycled pressure limited (TCPL) breaths (neonatal patients only)
4. Pressure regulated volume control (PRVC/Vsync
®
) breaths
(adult and pediatric patients only)
5. Volume Guarantee (VG) breaths (neonatal patients only)
Note: The volume controlled breath is the default breath type for adult and pediatric
patients. The TCPL breath type is only available for neonates and the default breath
type for neonate patients.

11
Demand breaths
All demand breaths are patient triggered, pressure controlled and flow or time cycled.
Demand breaths can be either pressure supported (PSV) or spontaneous. All demand
breaths are accompanied by the yellow patient demand indicator, which flashes in the
upper left of the touch screen. The Avea ventilator delivers two demand breath types:
1. PSV: Active when CPAP/PSV, synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV)
and airway pressure release ventilation (APRV)/BiPhasic modes are selected.
2. Spontaneous breath: For adult and pediatric patients during a spontaneous demand
breath, inspiratory pressure is pre-set at positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) + 2
cmH
2
O. For neonatal patients, a spontaneous breath is a demand flow breath delivered
at the pre-set PEEP.

12
Volume controlled ventilation
Avea ventilator intra-breath demand system
The Avea ventilator features a unique intra-breath demand system in volume controlled
ventilation designed to provide additional flow to the patient during periods of demand.
The Avea ventilator measures the peak inspiratory pressure (Ppeak) every 2 ms throughout
the breath cycle and sets a virtual pressure support target at the greater of PEEP +
2 cmH
2
O or Ppeak–2 cmH2O.
The minimum virtual pressure support level is set PEEP + 2 cmH
2
O, and the maximum is
two times the set PEEP. Simultaneously, the ventilator monitors and compares the Ppeak
measurement to its previous value. If the Ppeak decreases by 2 cmH2O, the ventilator
recognizes the patient demand and automatically switches over to deliver a pressure
support breath at the virtual pressure support target. This allows flow to exceed the set
peak flow, thereby meeting patient demand.
Once the set tidal volume has been delivered, the ventilator looks at the inspiratory flow.
Should the peak inspiratory flow be greater than set peak flow, the ventilator determines
that the patient continues to demand flow. The breath then cycles when inspiratory flow
falls to 25% of the peak inspiratory flow. If the peak inspiratory flow is equal to the set flow,
the ventilator determines the patient is not demanding flow and ends the breath as a
volume control breath.
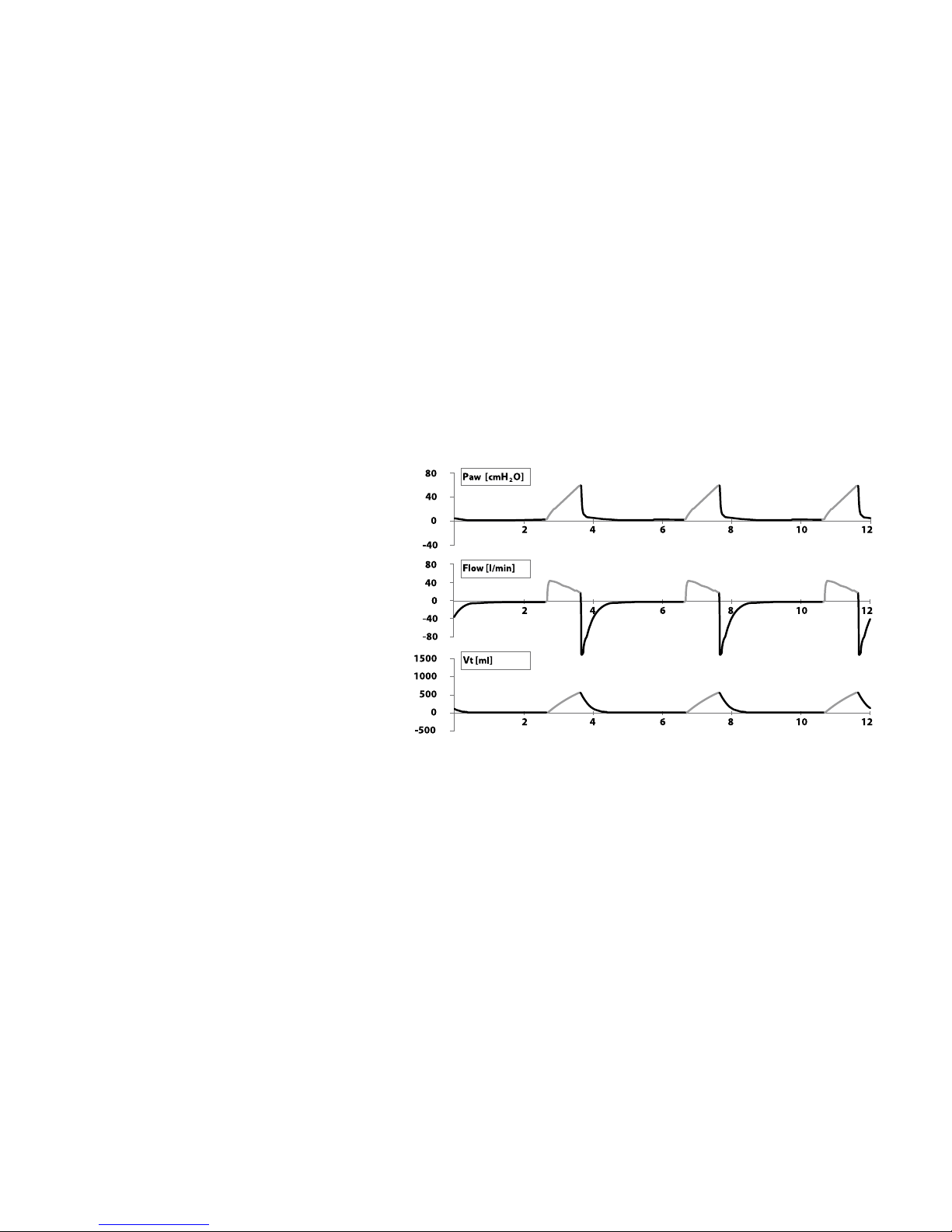
13
Volume breaths are controlled by inspiratory flow, limited by a pre-set volume or maximum
inspiratory pressure and cycled by volume or time. During mandatory breaths, the demand
system can provide additional flow if needed. The mode for this breath type is Volume
Assist Control (A/C) mode.
All breaths are mandatory breaths
at the set tidal volume. Breaths
are triggered when a patient
eort is detected, the breath
interval elapses when no
patient eort is detected
or the MANUAL BREATH key
is activated. The initiation of
a breath by any means resets
the breath interval. The patient
may initiate all breaths. Without
patient eort, breaths deliver
at the set breath rate.
Volume A/C with decelerating flow pattern

14
In a volume breath, airway pressure increases until the set tidal volume delivers. Flow
delivers at the set flow rate for the duration of the inspiratory time (with a square waveform
selected) or can decelerate to 50% of the set peak flow during the inspiratory phase of the
breath (with a decelerating waveform selected).
Primary controls: Active in Volume A/C mode are Rate, Volume, Peak Flow, Inspiratory
Pause, PEEP, Flow Trigger and %O
2
.
Advanced settings: Available in Volume A/C mode are Vsync*, Vsync Rise*, Volume Limit++,
Demand Flow, Flow Cycle++, Sigh*, Waveform, Bias Flow and Pressure Trigger.
*Available for adult and pediatric patients only.
++Only available when Vsync is active.
15
Volume SIMV mode
In synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV), mandatory and demand breath
types can deliver. Mandatory breaths deliver when the SIMV Time window is open as a
patient eort is detected, the breath interval elapses when no patient eort is detected or
the MANUAL BREATH key is activated.
Primary controls: Active in Volume
SIMV mode are Rate, Volume, Peak
Flow, Inspiratory Pause, PSV, PEEP,
Flow Trigger and %O
2
.
Advanced settings: Available in
Volume SIMV mode are Vsync*,
Vsync Rise*, Volume Limit, Sigh*,
Waveform, PSV Rise, PSV Cycle,
PSV Tmax, Demand Flow, Bias
Flow, Flow Cycle++, Waveform
and Pressure Trigger.
* Available for adult and pediatric
patients only.
++Only available when Vsync is active.
Volume SIMV with mandatory (1) and
assisted (2) breaths

16
Pressure breaths are controlled by pressure (inspiratory + PEEP), limited by pressure
(inspiratory + PEEP) and cycled by time or flow. The mode for this breath type is
Pressure Assist Control (A/C) mode.
All breaths are mandatory
breaths. Breaths may be triggered
when a patient eort is detected,
the breath interval times out when
no patient eort is detected or the
MANUAL BREATH key is activated.
The initiation of a breath resets
the breath interval. Patients
may initiate all breaths. Without
patient eort, breaths deliver
at the set breath rate. During
mandatory breaths, the demand
system can provide additional
flow if needed.
Pressure A/C, mandatory breaths
Pressure controlled ventilation

17
In a pressure breath, a variable flow delivers to reach the set inspiratory pressure above
baseline. Once the set pressure level is achieved, flow is regulated to maintain this pressure
for the duration of the set inspiratory time. The monitored peak pressure is equal to the sum
of the inspiratory pressure and PEEP settings.
Primary controls: Active in Pressure A/C mode are Rate, Inspiratory Pressure, Inspiratory
Time, PEEP, Flow Trigger and %O
2
.
Advanced settings: Available in Pressure A/C mode are Machine Volume, Volume Limit,
Inspiratory Rise, Flow Cycle, Bias Flow and Pressure Trigger.
Volume Guarantee breaths* (neonatal patients only): When Volume Guarantee is
selected, the control Insp Pres becomes an advanced setting, the Volume setting displays
as a primary control and the ventilator delivers a test breath at the set inspiratory pressure.
The inspiratory pressure for subsequent breaths adjusts breath-to-breath. The pressure
adjusts separately for time triggered breaths, patient triggered breaths, apnea backup
breaths and manual breaths to maintain monitored expired tidal volume close to the
set target.
*Requires wye flow sensor.

18
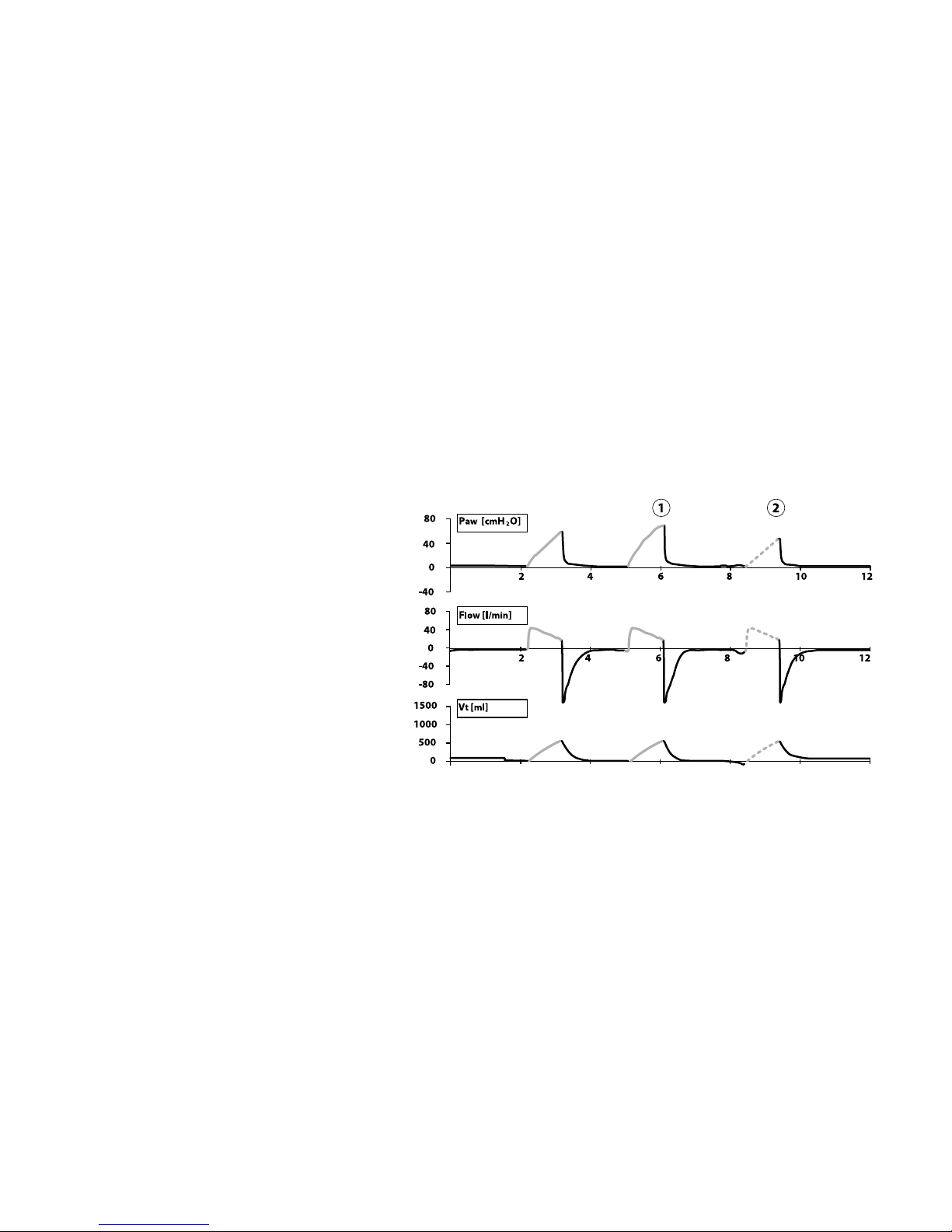
Pressure SIMV
In SIMV mode, the ventilator can deliver mandatory and demand breath types. Mandatory
breaths deliver when the SIMV Time window is open as a patient eort is detected, the
breath interval has elapsed when no patient eort is detected or the MANUAL BREATH key
is activated.
Primary controls: Active in Pressure
SIMV mode are Rate, Inspiratory
Pressure, Inspiratory Time, Pressure
Support, PEEP, Flow Trigger
and %O
2
.
Advanced settings: Available in
Pressure SIMV mode are Machine
Volume, Volume Limit, Inspiratory
Rise, Flow Cycle, Pressure Support
Rise, Pressure Support Cycle,
Pressure Support Tmax, Bias Flow
and Pressure Trigger.
Pressure SIMV with mandatory (1) and assisted
(2) breaths
19
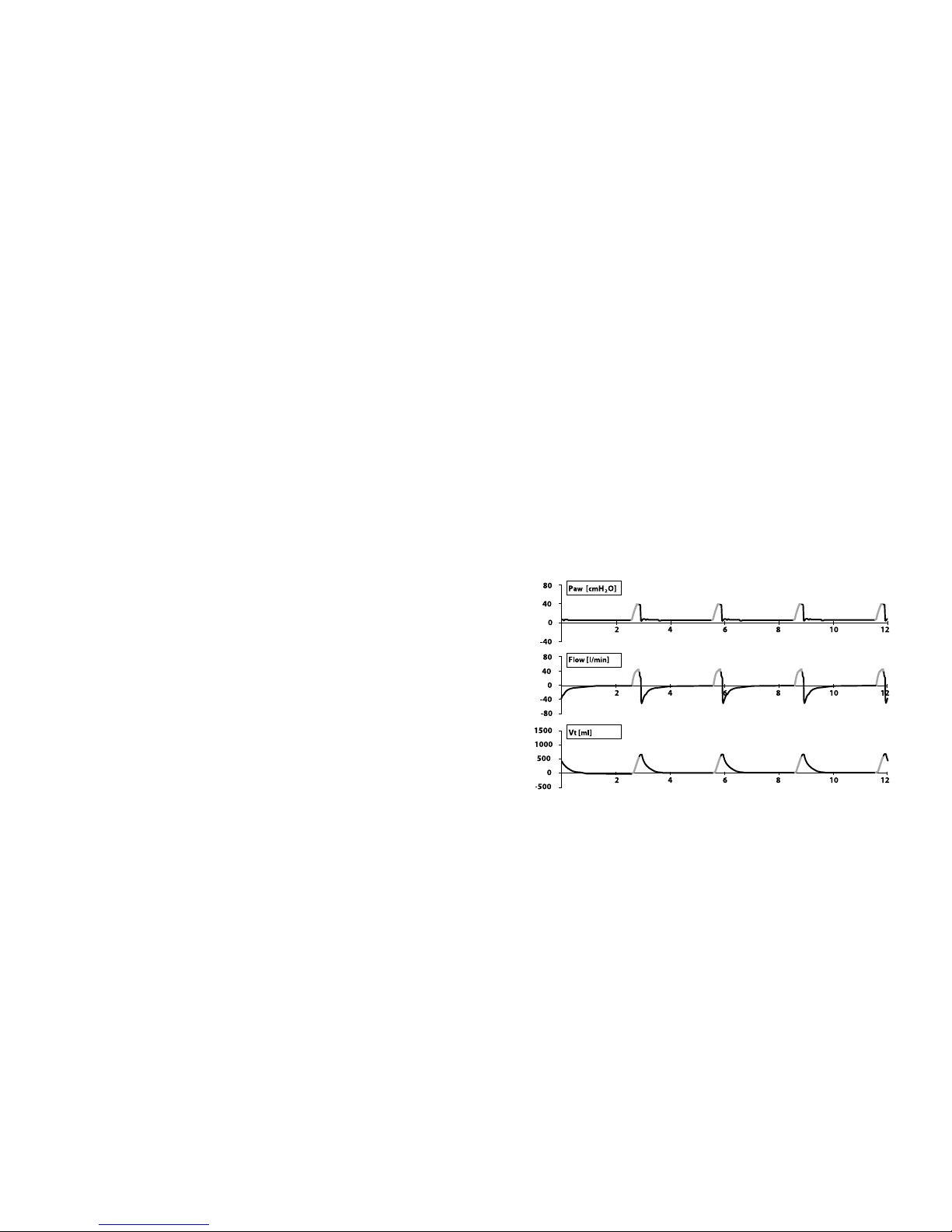
TCPL breaths are controlled by inspiratory
flow, limited by pressure (inspiratory + PEEP)
and cycled by time, inspiratory flow or volume
(Volume Limit). The mode for this breath type is
TCPL Assist Control (A/C) mode.**
All breaths are mandatory breaths. Breaths can
be triggered when a patient eort is detected,
the breath interval times out when no patient
eort is detected or the MANUAL BREATH key
is activated.
TCPL A/C, mandatory breaths
Volume Guarantee breaths (neonatal patients only):* When Volume Guarantee is
selected, the control Insp Pres becomes an advanced setting, the Volume setting displays
as a primary control and the ventilator delivers a test breath at the set inspiratory pressure.
The inspiratory pressure for subsequent breaths is adjusted breath-to-breath. The pressure
adjusts separately for time triggered breaths, patient triggered breaths, apnea backup breaths
and manual breaths to maintain monitored expired tidal volume close to the set target.
TCPL mode
*Requires wye flow sensor.
**Available for neonatal patients only.

20
The initiation of a breath resets the breath interval. Patients may initiate all breaths.
Without patient eort, breaths deliver at the set breath rate. During mandatory breaths,
the demand system can provide additional flow if needed.
In a TCPL breath, the inspiratory flow is used to achieve a set inspiratory pressure. During
the inspiratory phase of the breath, inspiratory pressure maintains while flow is allowed
to decelerate.
Primary controls: Active in TCPL A/C mode are Rate, Inspiratory Pressure, Peak Flow,
Inspiratory Time, PEEP, Flow Trigger and %O
2
.
Advanced settings: Available in TCPL mode are Volume Limit*, Flow Cycle, Bias Flow
and Pressure Trigger.
Volume Guarantee breaths (neonatal patients only):* When Volume Guarantee is
selected, the control Insp Pres becomes an advanced setting, the Volume setting displays
as a primary control and the ventilator delivers a test breath at the set inspiratory pressure.
The inspiratory pressure for subsequent breaths is adjusted breath-to-breath. The pressure
adjusts separately for time triggered breaths, patient triggered breaths, apnea backup
breaths and manual breaths to maintain monitored expired tidal volume.
*Requires wye flow sensor.
21
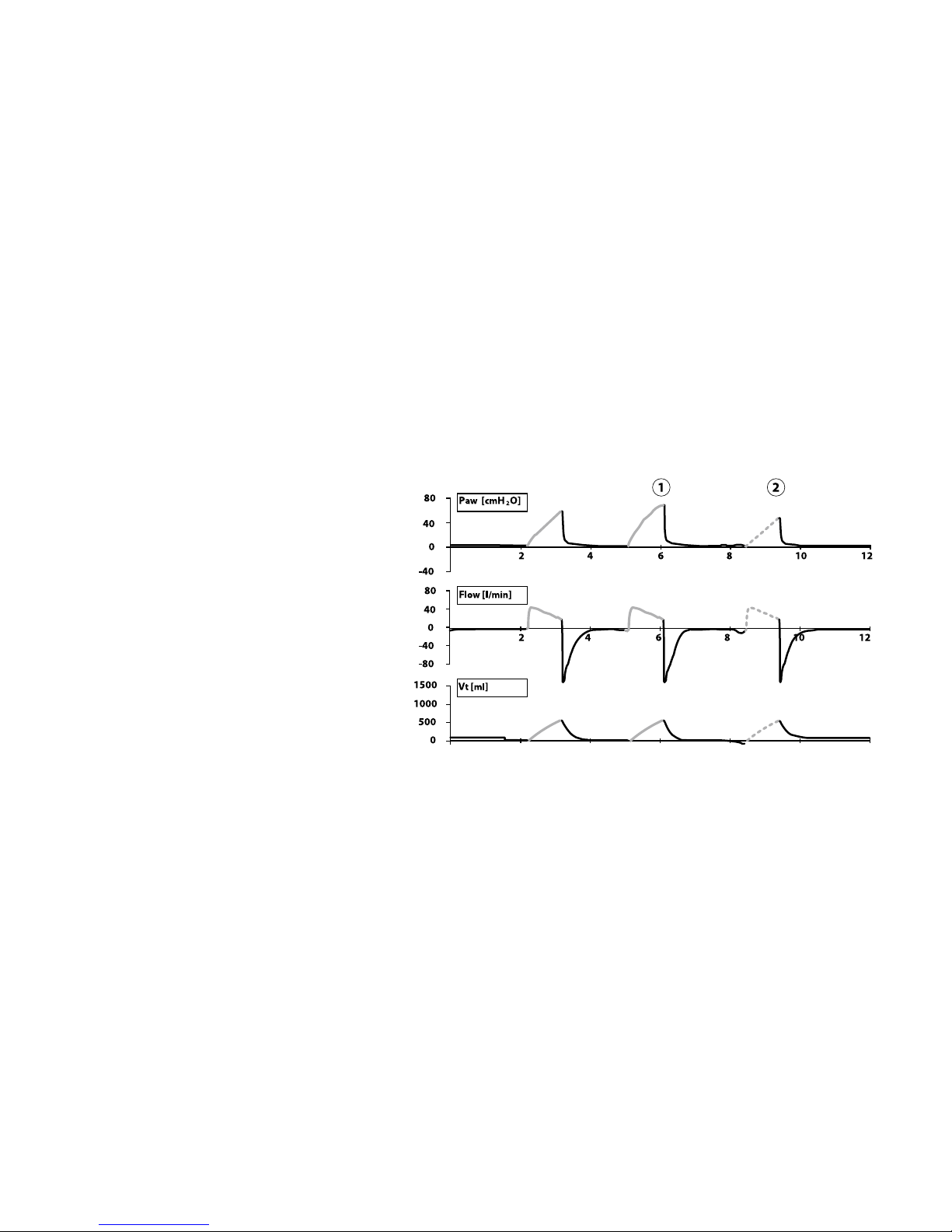
TCPL SIMV mode*
In SIMV mode, the ventilator can deliver mandatory and demand breath types. Mandatory
breaths deliver when the SIMV Time window is open as a patient eort is detected, the
breath interval has elapsed when no patient eort is detected or the MANUAL BREATH
key is activated.
Primary controls: Active in TCPL
SIMV mode are Rate, Inspiratory
Pressure, Peak Flow, Inspiratory
Time, PEEP, Flow Trigger and %O
2
.
Advanced settings: Available in
TCPL SIMV mode are Volume
Limit, Flow Cycle, Bias Flow and
Pressure Trigger.
Volume Guarantee breaths
(neonatal patients only):**
When Volume Guarantee is
selected, the control Insp Pres
becomes an advanced setting, the Volume setting displays as a primary control and the
ventilator delivers a test breath at the set inspiratory pressure.
*Available for neonatal patients only.
**Requires wye flow sensor.
TCPL SIMV with mandatory (1) and assisted (2) breaths

22
The inspiratory pressure for subsequent breaths is adjusted breath-to-breath. The pressure
adjusts separately for time triggered breaths, patient triggered breaths, apnea backup
breaths and manual breaths to maintain monitored expired tidal volume.
PRVC Mode
In pressure regulated volume control (PRVC) breaths, the pressure level modulates up or
down to achieve a pre-set tidal volume. Breaths are controlled by pressure (inspiratory +
PEEP) and volume, limited by pressure (inspiratory + PEEP) and cycled by time.
When PRVC is selected, the ventilator delivers a decelerating flow, volume controlled test
breath to the set tidal volume with a 40 msec pause. It sets the target pressure at the end
inspiratory pressure for the first pressure control breath. The next breath and all subsequent
breaths deliver as pressure control breaths.
Inspiratory pressure adjusts automatically to maintain the target volume based on the
dynamic compliance of the previous breath. The maximum step change between two
consecutive breaths is 3 cm of water pressure. The maximum tidal volume delivered
in a single breath is determined by the Volume Limit setting.
The test breath sequence initiates when:
• Entering the PRVC mode
• Changing the set tidal volume while in PRVC

23
• Reaching the Volume Limit setting
• Reaching a delivered tidal volume > 1.5 times the set volume
• Terminating the flow of the test breath
• Activating the:
- High Peak Pressure alarm
- Low Peak Pressure alarm
- Low PEEP alarm
- Patient Circuit Disconnect alarm
- I-Time Limit
- I:E Limit
- When exiting Standby

24
The mode for the PRVC breath type is PRVC Assist Control (A/C) mode.*
All breaths are mandatory breaths. A breath can be triggered by the detection of a
patient eort, the breath interval timing out or the MANUAL BREATH key being activated.
The initiation of a breath resets the breath interval. A patient may initiate all breaths.
Without patient eort, breaths deliver at the set breath rate. During mandatory breaths,
the demand system can provide additional flow if needed.
Primary controls: Active in PRVC
A/C mode are Rate, Volume,
Inspiratory Time, PEEP, Flow
Trigger and %O
2
.
Advanced settings: Available in
PRVC A/C mode are Volume Limit,
Inspiratory Rise, Flow Cycle, Bias
Flow, PSV Rise, PSV Cycle, PSV
Tmax and Pressure Trigger.
* Available for adult and
pediatric patients only.
PRVC A/C with test breath (1) and step changes (2–4)
to achieve target volume

25
PRVC SIMV mode*
In SIMV mode, the ventilator can deliver mandatory and demand breath types. Mandatory
breaths deliver when the SIMV Time window is open as a patient eort is detected, the
breath interval has elapsed when no patient eort is detected or the MANUAL BREATH
key is activated.
Primary controls: Active in PRVC
SIMV mode are Rate, Volume,
Inspiratory Time, Pressure Support,
PEEP, Flow Trigger and %O
2
.
Advanced settings: Available in
PRVC SIMV mode are Volume Limit,
Pressure Support Rise, Pressure
Support Cycle, Pressure Support
Tmax, Bias Flow, Flow Cycle and
Pressure Trigger.
* Available for adult and
pediatric patients only.
PRVC SIMV with mandatory (1) and assisted
(2–4) breaths

26
APRV/BiPhasic mode*
Airway pressure release ventilation (APRV)/BiPhasic is a time cycled pressure mode that
cycles between two dierent baseline pressures based on time, which can be synchronized
with patient eort. Controlled ventilation can be maintained by time cycling the transitions
between baseline pressures. Pressure support can be added to improve comfort for the
spontaneously breathing patient.
In this mode, the patient can breathe spontaneously at two pre-set pressure levels. These
are set using the Pres High and Pres Low controls. The maximum duration at each pressure
during time cycling is set with the Time High and Time Low controls. The operator can also
adjust the length of the respective trigger (Sync) windows with the Time High and Time Low
Sync controls, which are advanced settings of Time High and Time Low. The Sync windows
are adjustable from 0% to 50%, in 5% increments of set Time High and Time Low. The
change synchronizes from Pressure Low to Pressure High with the detection of inspiratory
flow or first inspiratory eort within the T Low Sync window. Transition from Pressure High
to Pressure Low occurs with the first end of inspiration detected after the T High Sync
window opens.

27
Note: Time High and Time Low are the maximum time settings for a time cycled
transition. Actual times may vary depending on the patient’s spontaneous breathing
pattern and Sync window setting. Setting the Sync to 0% cycles the transition
between pressure levels on time only and does not synchronize with patient eorts.
The MANUAL BREATH button is not active in APRV/BiPhasic.
APRV/BiPhasic mode features
adjustable PSV. The PSV delivers
above the current phase baseline
pressure. PSV breaths are
available during Time High and by
activating T High PSV, which is an
advanced setting of Time High. If
activated, the same PSV level for
both Pressure Low and Pressure
High delivers during Time High.
1 - Time High, Pressure High
2 - Time Low, Pressure Low APRV/BiPhasic mode

28
Apnea ventilation is available in APRV/BiPhasic mode. If the patient does not initiate a
spontaneous eort or the ventilator does not time cycle between pressure levels before the
apnea interval has elapsed, the ventilator alarms for apnea and begins apnea ventilation
at the apnea ventilation settings. A spontaneous eort from the patient or a transition in
baseline pressure resets the apnea alarm and timer and returns the ventilator to APRV/
BiPhasic ventilation.
Primary controls: Active in APRV/BiPhasic mode are Time High, Pressure High, Time Low,
Pressure Low, Pressure Support, Flow Trigger and %O
2
.
Advanced settings: Available in APRV/BiPhasic mode are T High PSV, T High Sync,
T Low Sync, Volume Limit, Pressure Support Rise, Pressure Support Cycle, Pressure Support
Tmax, Bias Flow and Pressure Trigger.
*APRV/BiPhasic mode is available for adult and pediatric patients only.

29
CPA P/PSV*
Continuous positive airway pressure with pressure support ventilation (CPAP/PSV) breaths
are demand breaths with the pressure level during inspiration equal to the pre-set PSV
level plus PEEP. This breath type is controlled by pressure (pre-set PSV level + PEEP), limited
by pressure (pre-set PSV level + PEEP) and cycled by time (PSV Tmax) or flow (PSV cycle).
All breaths are patient-initiated
demand breaths unless the MANUAL
BREATH key is pressed. When the
MANUAL BREATH key is pressed in
CPAP/PSV, a single breath delivers at
the apnea backup control settings.
Primary controls: Active in CPAP/PSV
mode are Pressure Support, PEEP,
Flow Trigger and %O
2
.
Advanced settings: Available in
CPAP/PSV are Volume Limit, Pressure
Support Rise, Pressure Support Cycle,
Pressure Support Tmax, Bias Flow
and Pressure Trigger.
CPAP/PSV

30
Apnea Backup ventilation
Apnea Backup ventilation is available in Assist Control (A/C), SIMV, APRV/BiPhasic
and CPAP/PSV modes.
Apnea Backup in Assist Control or SIMV
The set mandatory breath rate or the Apnea Interval setting (whichever provides the
highest respiratory rate) determines the apnea backup rate.
When the Apnea Interval setting (found in the Alarm Limits window) determines the backup
rate, the ventilator continues to ventilate at this rate until the apnea has been resolved. All
other controls for apnea ventilation in Assist Control (A/C) and SIMV are the current active
primary controls.
Apnea ventilation ends when a patient initiates a spontaneous breath, a manual breath
is delivered or the rate control is increased above the Apnea Interval setting.

31
Apnea Backup in APRV/BiPhasic and CPAP/PSV
When these modes are selected, you must:
1. Set the primary and advanced settings for CPAP/PSV or APRV/BiPhasic.
2. Select the breath type for Apnea Backup mode (Volume or Pressure in adult and
pediatric patients or Volume, Pressure or TCPL in neonatal patients) by pressing the
Apnea Settings button.
3. Set the primary controls appearing at the bottom of the touch screen, for the selected
apnea breath type before pressing the MODE ACCEPT button.
Note: The controls for apnea backup ventilation are not visible once the MODE
ACCEPT button has been pressed. Only the controls that are active and required
for the selected mode display on the main screen once the MODE ACCEPT button
is pressed.

32
nCPAP/IMV
Nasal CPAP (nCPAP) is a spontaneous ventilation. In this mode, no mechanical positive
pressure breaths deliver. Nasal IMV is a time triggered, time cycled mode of pressure
control ventilation provided via nasal prongs as an enhancement to the nCPAP mode.
When a rate is set greater than zero, time triggered, time cycled mandatory breaths
deliver. Each breath comprises an inspiratory phase, during which the delivered pressure
increases from baseline (PEEP) to PEEP + Inspiratory Pressure, and an expiratory phase,
during which the delivered pressure returns to PEEP.
Nasal IMV breaths are:
• Controlled by pressure
• Limited by pressure
• Cycled by time
Primary controls: nCPAP level, Inspiratory Pressure, Inspiratory Time, FiO
2
% and Rate
Advanced settings: Inspiratory Rise*
*No advanced settings appear when Rate is set to o.
nCPAP/IMV is only available in the neonatal patient size setting.

33
Standby
When activated, Standby retains the primary
controls, advanced settings and alarm limits when
the patient is away from the ventilator. To initiate
Standby, press the screen’s membrane button.
The Standby Check message appears, asking
you to confirm your intent to stop ventilation.
The patient should be disconnected from the
ventilator prior to the user initiating Standby.
If YES is selected, ventilation stops, the safety
valve closes and the ventilator supplies 2 L/min
of gas continuously to the circuit. This supply
reduces the risk of an overheated circuit if an
active humidifier is in use and left on.

34
Standby (continued)
Note: The patient wye must be blocked for this flow to be directed through the full
length of the patient circuit.
The STANDBY NOT VENTILATING message
displays. Press Resume to restart ventilation
at the current settings.

Section 3:
Advanced settings
Volume Limit ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������36
Machine Volume �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 37–38
Inspiratory Rise ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 39
Flow Cycle ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 39
Waveform �����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������40
Sigh ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������40
Bias Flow ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������41
Pres Trig ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 41
Vsync® �����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������42–43
Vsync Rise �����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������43
PSV Rise����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������44
PSV Cycle ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������44
PSV Tmax �������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������44
Volume Limit ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������44
T High PSV�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������45
T High Sync ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������45
T Low Sync ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������45
Avea ventilator modes ������������������������������������������������������������������������� 46–49
35
36
Volume Limit
The Volume Limit (Vol Limit) setting sets the volume limit for a pressure limited breath.
When the volume delivered to the patient meets or exceeds the pre-set volume limit,
the inspiratory phase of the breath terminates.
The volume limit is active for Pressure, PRVC/Vsync, TCPL and PSV breaths only. In
neonatal applications, the volume limit requires a wye flow sensor. Whenever a proximal
flow sensor is used (neonatal, pediatric or adult applications), the volume limit activates
by the inspiratory tidal volume measured by the wye flow sensor. In adult and pediatric
applications that do not use a wye flow sensor, the volume limit is determined by the
calculated inspiratory wye flow. When the volume limit threshold has been reached, the
ventilator alarm status indicator changes to yellow and displays Volume Limit. The alarm
status indicator cannot be reset until the ventilator has delivered a breath, which does
not meet the volume limit threshold. To reset the alarm status window, use the
ALARM RESET button.
Note: Excessive inspiratory flow rates or highly compliant ventilator circuits may
allow tidal volume delivery that exceeds the Volume Limit setting. This is due to
the ventilator circuit recoiling and providing additional tidal volume to the patient.
Delivered tidal volumes should be closely monitored to ensure volume limit accuracy.

37
Machine Volume
The Machine Volume (Mach Vol) control sets the minimum tidal volume delivered as the
control is activated in a pressure control breath. This control is always used with the time
cycling criterion in pressure control ventilation. The machine volume is circuit compliance
compensated in adult and pediatric applications.
Once you set the machine volume, the ventilator calculates the decelerating inspiratory
flow required to deliver the machine volume in the set inspiratory time. When a pressure
control breath delivers and peak flow decelerates to this calculated peak inspiratory
flow, if the machine volume has not been met, the ventilator automatically transitions to
a continuous flow until the machine volume has been delivered. Once the set machine
volume has been delivered, the ventilator cycles into exhalation. Upon meeting or
exceeding the machine volume or pressure control breath delivery, the ventilator
completes the breath as a normal pressure control breath.

38
During this transition in flow, the inspiratory time remains constant and the Ppeak increases
to reach the set machine volume. The maximum Ppeak is determined by the High Peak
Pressure alarm setting.
Note: Pmax disables when the machine volume is set. If flow cycling is active in pressure
control, the ventilator does not cycle the flow until meeting the machine volume. The
machine volume is circuit compliance compensated in adult and pediatric applications.
To set the machine volume in adult and pediatric applications (with circuit compliance
compensation active), simply set the minimum desired tidal volume.
In neonatal applications with proximal flow sensor in use:
1. Adjust the peak inspiratory pressure to reach the desired tidal volume.
2. Select Vdel as one of the monitored parameters. Read the Vdel (uncorrected tidal volume
delivered from the machine) during a pressure control breath.
3. Set the machine volume to or slightly below the Vdel measurement. This sets the machine
volume to provide more consistent tidal volume delivery for slight decreases in lung
compliance.
Note: To protect against larger changes in lung compliance, the machine volume
should be set higher and volume limit should be added.

39
Inspiratory Rise
The Inspiratory Rise (Insp Rise) setting controls the slope of the pressure rise during a
mandatory breath. This control is a relative control with fast at a setting of 1 and slow
at a setting of 9. The Insp Rise control is not active for TCPL breaths.
Flow Cycle
The Flow Cycle setting sets the percentage of the peak flow that terminates the inspiratory
phase of a pressure control or TCPL breath. Flow cycling is active for pressure or TCPL
breaths only.
Note: If flow cycling is active during a pressure control breath, monitored airway
pressures (inspiratory) are higher than active automatic airway compensation (AAC).
An Inspiratory Pressure setting of zero AAC still provides an elevated airway pressure,
which compensates for the resistance of the endotracheal tube.

40
Waveform
During the delivery of a volume breath, flow can be delivered in one of two userselectable waveforms: Square Wave or Decelerating Wave. The default waveform
is Decelerating Wave.
Square Wave (Square)
With this waveform selected, the ventilator delivers gas at the set peak flow for the
duration of the inspiration.
Decelerating Wave (Decel)
With this waveform selected, the ventilator delivers gas starting at the peak flow and
decreasing until the flow reaches 50% of the set peak flow.
Sigh
The ventilator delivers sigh volume breaths when this setting is on. A sigh volume breath
delivers every 100th breath in place of the next normal volume breath.
Sigh breaths are only available for volume breaths in Assist and SIMV modes for adult
and pediatric patients.

41
Bias Flow
The Bias Flow control sets the background flow available between breaths. Additionally,
this control establishes the base flow for flow triggering.
Note: To ensure adequate bias flow for inspiratory triggering, the Bias Flow setting
should be at least 0.5 L per minute greater than the flow trigger threshold. Consult the
ventilator circuit manufacturer to ensure the Bias Flow setting can suciently prevent
overheating the ventilator circuit.
Pressure Trigger
The Pressure Trigger (Pres Trig) control sets the level below PEEP that activates the
inspiratory trigger mechanism. When the pressure in the patient circuit falls below PEEP by
the set pressure trigger level, the ventilator cycles to inspiration. Pres Trig is also used to
activate the inter-breath demand system in volume controlled ventilation.
Note: Setting the Pres Trig to excessively high levels can impair the patient’s ability
to activate the inter-breath demand system in volume controlled ventilation.

42
Vsync*
When Vsync is selected, a decelerating flow, volume test breath to the set tidal volume
with a 40 msec pause delivers to the patient. The ventilator sets the target pressure at
the end inspiratory pressure for the first pressure control breath. The next breath and
all subsequent breaths deliver as pressure control breaths. Inspiratory pressure adjusts
automatically to maintain the target volume based on the dynamic compliance of the
previous breath. The maximum step change between two consecutive breaths is 3 cm of
water pressure. The maximum tidal volume delivered in a single breath is determined by
the Volume Limit setting.
This test breath sequence initiates when:
• Entering the mode (Vsync)
• Changing the set tidal volume while in Vsync
• Reaching the Volume Limit setting
• Reaching a delivered tidal volume > 1.5 times the set volume

43
Vsync* (continued)
• Terminating the flow the test breath
• Activating the:
- High Peak Pressure alarm
- Low Peak alarm
- Low PEEP alarm
- Patient Circuit Disconnect alarm
- I-Time Limit
- I:E Limit
*Vsync is only available for adult and pediatric patients.
Note: The Peak Flow control sets the flow rate, which is used for the test breath only.
The ventilator uses the Peak Flow setting and inspiratory pause to determine the
maximum inspiratory time during Vsync ventilation.
Vsync Rise
With Vsync active, this control sets the slope of the pressure rise during the PRVC/Vsync
breath. It is a relative control ranging from fast at a setting of 1 to slow at a setting of 9.

44
PSV Rise
The PSV Rise setting sets the slope of the pressure rise during a pressure-supported breath.
It is a relative control with a range from fast at a setting of 1 to slow at a setting of 9.
PSV Cycle
The PSV Cycle setting sets the percentage of peak inspiratory flow that terminates
the inspiratory phase of a PSV breath.
PSV Tmax
The PSV Tmax setting controls the maximum inspiratory time of a pressure-supported
breath.
Note: PSV Rise, PSV Cycle and PSV Tmax are active even if the PSV level is zero.
Volume Limit
The Vol Lim setting sets the volume limit for a pressure limited breath. When the volume
delivered to the patient meets or exceeds the pre-set volume limit, the inspiratory phase
of the breath terminates.

45
T High PSV
The T High PSV setting sets the volume limit for a pressure limited breath. When the volume
delivered to the patient meets or exceeds the pre-set volume limit, the inspiratory phase
of the breath terminates.
T High Sync
The T High Sync setting sets the length of the Time High trigger (Sync) window. The Sync
window adjusts from 0% to 50%, in 5% increments of set Time High, and synchronizes the
change from Pressure High to Pressure Low with the first end of inspiration detected after
the T High Sync window opens. If no patient eort detected, the transition occurs when the
set Time High has elapsed. Setting the T High Sync window to 0% provides time cycling only.
T Low Sync
The T Low Sync setting sets the length of the Time Low trigger (Sync) window. The Sync
window adjusts from 0% to 50%, in 5% increments of the set Time Low, and synchronizes
the change from Pressure Low to Pressure High when detecting inspiratory flow or the
first inspiratory eort within the T Low Sync window. If no patient eort is detected, the
transition occurs when the set Time Low has elapsed. Setting the T Low Sync window to
0% provides time cycling only. The Volume Limit setting sets the volume limit for a pressure
limited breath. When the volume delivered to the patient meets or exceeds the pre-set
volume limit, the inspiratory phase of the breath terminates.

46
Avea ventilator modes, primary controls and advanced settings
Breath type and mode Vol A/C Vol SIMV Pres A/C Press SIMV
Primary controls
Rate BPM * * * *
Volume mL * *
Insp Pres cmH
2
O * *
Peak flow L/min * *
Insp time sec * *
Insp pause sec * *
PSV cmH
2
O * *
PEEP cmH
2
O * * * *
Flow trig L/min * * * *
% oxygen %O
2
* * * *
Pres High cmH
2
O
Time High sec
*Available with Vsync activated for adult or pediatric patients only.
**Available for adult and pediatric patients only.
47
Avea ventilator modes, primary controls and advanced settings
(continued)
Breath type and mode Vol A/C Vol SIMV Pres A/C Pressure SIMV
Time Low sec
Pres Low cmH
2
O
Advanced settings available
within each mode
• Vsync*
• Vsync Rise*
• Sigh**
• Waveform
• Bias Flow
• Pres Trig
• Vol Limit (when
Vsync = On)
• Flow Cycle (when
Vsync = On)
• Demand Flow
• Vsync*
• Vsync Rise*
• Sigh**
• Waveform
• Vol Limit
• PSV Rise
• PSV Cycle
• PSV Tmax
• Bias Flow
• Pres Trig
• Flow Cycle (when
Vsync = On)
• Demand Flow
• Mach Vol
• Vol Limit
• Insp Rise
• Flow Cycle
• Bias Flow
• Pres Trig
• Mach Vol
• Vol Limit
• Insp Rise
• Flow Cycle
• PSV Rise
• PSV Cycle
• PSV Tmax
• Bias Flow
• Pres Trig
VG breaths N/A N/A Available
in neonatal
patient type
Available in
neonatal patient
type
*Available with Vsync activated for adult or pediatric patients only.
**Available for adult and pediatric patients only.

48
Avea ventilator modes, primary controls and advanced settings
(continued)
Breath type
and mode
PRCV A/C PRVC SIMV CPAP/PSV APRV/
BiPhasic
TCPL A/C TCPL SIMV
Primary controls
Rate BPM * * Apnea mode* Apnea mode* * *
Volume mL * * Apnea mode* Apnea mode*
Insp Pres cmH
2
O Apnea mode* Apnea mode* * *
Peak flow L/min Apnea mode* Apnea mode* * *
Insp time sec * * Apnea mode* Apnea mode* * *
Insp pause sec Apnea mode* Apnea mode*
PSV cmH
2
O * * * * *
PEEP cmH
2
O * * * * * *
Flow trig L/min * * * * * *
% oxygen %O
2
* * * * * *
Pres High cmH
2
O *
Time High sec *
*Available with Vsync activated for adult or pediatric patients only.
**Available for adult and pediatric patients only.

49
Breath type
and mode
PRCV
A/C
PRVC
SIMV
CPAP/
PSV
APRV/
BiPhasic
TCPL A/C TCPL
SIMV
nCPAP/
IMV
Time Low sec *
Pres Low
cmH2O
*
Advanced
settings
available
within
each mode
• Insp Rise
• Bias Flow
• Pres Trig
• Vol Limit
• Flow
Cycle
• Vol Limit
• PSV Rise
• PSV Cycle
• PSV Tmax
• Bias Flow
• Pres Trig
• Flow Cycle
• Insp Rise
• Vol Limit
• PSV Rise
• PSV Cycle
• PSV Tmax
• Bias Flow
• Pres Trig
• Vol Limit
• PSV Rise
• PSV Cycle
• PSV Tmax
• Bias Flow
• Pres Trig
• T High
Sync
• T High PSV
• T Low Sync
• Vol Limit
• Flow Cycle
• Bias Flow
• Pres Trig
• Vol Limit
•
Flow
Cycle
• PSV Rise
• PSV Cycle
• PSV Tmax
• Bias Flow
• Pres Trig
• Insp
Rise***
VG breaths N/A N/A N/A N/A
Available
in neonatal
patient
type
Available
in neonatal
patient
type
N/A
Avea ventilator modes, primary controls and advanced settings
(continued)
*Available with Vsync activated for adult or pediatric patients only.
**Available for adult and pediatric patients only.
***Not available when rate is set to OFF.

50
Notes

51
Notes

REFERENCES
1. Branson, R., Chatbum, R. Proceedings of consensus conference on the essentials of mechanical ventilators, Cancun, Mexico, February 1992.
GLOBAL
HEADQUARTERS
Vyaire Medical, Inc.
26125 North Riverwoods Blvd
Mettawa, IL 60045, USA
Vyaire Medical, Inc.
22745 Savi Ranch Parkway
Yorba Linda, CA 92887, USA
WARNING—U.S. Federal Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
©2018 Vyaire. Vyaire, the Vyaire Logo and Avea are trademarks of Vyaire Medical, Inc. | 32116-001 Version A (0218)
vyaire�com
 Loading...
Loading...