Page 1

GPIB-VXI
User Manual
bus
April 1990 Edition
Part Number 320151-01
© Copyright 1983, 1991 National Instruments Corporation.
All Rights Reserved.
Page 2

National Instruments Corporation
6504 Bridge Point Parkway
Austin, TX 78730-5039
(512) 794-0100
(800) IEEE-488
Fax: (512) 794-8411
Page 3

Limited Warranty
The GPIB-VXI is warranted against defects in materials and workmanship for a period of one year from the date of
shipment, as evidenced by receipts or other documentation. National Instruments will, at its option, repair or
replace equipment that proves to be defective during the warranty period. This warranty includes parts and labor.
A Return Material Authorization (RMA) number must be obtained from the factory and clearly marked on the
outside of the package before any equipment will be accepted for warranty work. National Instruments will pay the
shipping costs of returning to the owner parts which are covered by warranty.
National Instruments believes that the information in this manual is accurate. The document has been carefully
reviewed for technical accuracy. In the event that technical or typographical errors exist, National Instruments
reserves the right to make changes to subsequent editions of this document without prior notice to holders of this
edition. The reader should consult National Instruments if errors are suspected. In no event shall National
Instruments be liable for any damages arising out of or related to this document or the information contained in it.
XCEPT AS SPECIFIED HEREIN, NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
E
AND SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. CUSTOMER'S RIGHT TO RECOVER DAMAGES CAUSED BY FAULT OR NEGLIGENCE ON THE PART
OF NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE AMOUNT THERETOFORE PAID BY THE CUSTOMER.
NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES RESULTING FROM LOSS OF DATA, PROFITS,
USE OF PRODUCTS, OR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
THEREOF. This limitation of the liability of National Instruments will apply regardless of the form of action,
whether in contract or tort, including negligence. Any action against National Instruments must be brought within
one year after the cause of action accrues. National Instruments shall not be liable for any delay in performance due
to causes beyond its reasonable control. The warranty provided herein does not cover damages, defects,
malfunctions, or service failures caused by owner's failure to follow the National Instruments installation, operation,
or maintenance instructions; owner's modification of the product; owner's abuse, misuse, or negligent acts; and
power failure or surges, fire, flood, accident, actions of third parties, or other events outside reasonable control.
Copyright
Under the copyright laws, this book may not be copied, photocopied, reproduced, or translated, in whole or in part,
without the prior written consent of National Instruments Corporation.
Trademarks
®
Turbo488
Product names listed are trademarks of their respective manufacturers. Company names listed are trademarks or
trade names of their respective companies.
is a trademark of National Instruments Corporation.
Page 4

FCC/DOC Radio Frequency Interference Compliance
This equipment generates and uses radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in strict
accordance with the instructions in this manual, may cause interference to radio and television
reception. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with (1) the limits for a Class A
computing device, in accordance with the specifications in Subpart J of Part 15 of U.S. Federal
Communications Commission (FCC) Rules, and (2) the limits for radio noise emissions from
digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of
Communication (DOC). These regulations are designed to provide reasonable protection against
interference from the equipment to radio and television reception in commercial areas.
There is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. However, the
chances of interference are much less if the equipment is used according to this instruction
manual.
If the equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment on and off, one or more of the following suggestions may
reduce or eliminate the problem.
• Operate the equipment and the receiver on different branches of your AC electrical system.
• Move the equipment away from the receiver with which it is interfering.
• Relocate the equipment with respect to the receiver.
• Reorient the receiver's antenna.
• Be sure that the equipment is plugged into a grounded outlet and that the grounding has not
been defeated with a cheater plug.
If necessary, consult National Instruments or an experienced radio/television technician for
additional suggestions. The following booklet prepared by the FCC may also be helpful: How
to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems. This booklet is available from the U.S.
Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402, Stock Number 004-000-00345-4.
Page 5

Preface
This manual contains information you will need to use the GPIB-VXI in your VXIbus system. It
describes the function and behavior of GPIB-VXI units configured with the standard firmware
option.
Organization of the GPIB-VXI User Manual
The GPIB-VXI User Manual is organized as follows:
• Chapter 1, General Description, gives an overview of the GPIB-VXI.
• Chapter 2, Configuration and Startup Procedures, gives configuration information and
describes the GPIB-VXI startup behavior.
• Chapter 3, Local Command Set, describes the GPIB-VXI local command set.
• Chapter 4, Nonvolatile Configuration, describes the method for editing the contents of the
GPIB-VXI configuration parameter memory.
• Chapter 5, Diagnostic Tests, describes the operation of the GPIB-VXI offline diagnostic
tests.
• Appendix A, Specifications, lists the specifications of the GPIB-VXI.
• Appendix B, Error Codes, lists the local command set error codes.
• Appendix C, Code Instrument Overview, describes the capabilities and implementation of
Code Instruments.
• Appendix D, Using the CDS-852 Adapter Code Instrument, contains instructions for
installing the Resident Code Instruments.
• Appendix E, GPIB-VXI Hardware and Software Configuration Form, contains a form that
you should complete in the event that you have a technical problem. Completing the form
before calling National Instruments will expedite your phone call and thus the solution to
your problem.
• The Glossary contains an alphabetical list of terms used in this manual and a description of
each.
• The Index contains an alphabetical list of key terms and topics used in this manual, including
the page where each one can be found.
© National Instruments Corporation v GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 6

Preface
Conventions Used in This Manual
Throughout this manual, the following conventions are used to distinguish elements of text:
italic Italic text denotes emphasis, a cross reference, or an introduction to a key
concept. In this manual, italics are also used to denote Word Serial
commands and queries.
monospace Text in this font denotes text or characters that are to be literally input
from the keyboard, sections of code, command or query syntax, console
responses, and syntax examples. This font is also used for the names of
all commands and queries used in the GPIB-VXI local command set.
<CR> Angle brackets enclosing a term in Times font denote a key on the
keyboard, or the equivalent ASCII character.
<hex value> Angle brackets enclosing a term in monospace denote a parameter.
Numbers in this manual are base 10 unless noted as follows:
• Binary numbers are indicated by a -b suffix (for example, 11010101b)
• Octal numbers are indicated by an -o suffix (for example, 325o),
• Hexadecimal numbers are indicated by an -h suffix (for example, D5h)
• ASCII character and string values are indicated by double quotation marks (for example,
"This is a string").
In this manual, the symbol <CR> is used to indicate the ASCII carriage return character. The
symbol <LF> is used to indicate the ASCII linefeed character. The symbol <CRLF> is used to
indicate a carriage return followed by a linefeed.
Terminology that is specific to a chapter or section is defined at its first occurrence.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are units of measure that are used in the text of this manual.
° degrees
A ampere
bytes/sec bytes per second
C Celsius
Hz hertz
in. inch
kbytes/sec 1,000 bytes per second
kHz kilohertz
GPIB-VXI User Manual vi © National Instruments Corporation
Page 7

Preface
K 1,024 bytes of memory
LSB least significant bit
m meter
mA milliampere
M 1,048,576 bytes of memory
MHz megahertz
MSB most significant bit
nsec nanosecond
sec second
VDC volts direct current
Related Documents
The following documents contain information that you may find helpful as you read this manual:
• IEEE Standard for a Versatile Backplane Bus: VMEbus, ANSI/IEEE Standard 1014-1987
• IEEE Standard Digital Interface for Programmable Instrumentation, ANSI/IEEE Standard
488.1-1987
• IEEE Standard Codes, Formats, Protocols, and Common Commands, ANSI/IEEE Standard
488.2-1987
• VXIbus System Specification, Revision 1.3, VXIbus Consortium
• 16/32-Bit Highly Integrated Microprocessor SCC68070 User Manual, Philips
Customer Communication
We appreciate communicating with the people who use our products. We are also very
interested in hearing about the applications you develop using our products. To make it easy for
you to communicate with us, we provide the Hardware and Software Configuration Form for
product-related technical comments, and the User Comment Form for documentation comments.
If you encounter any technical problems, please complete the Hardware and Software
Configuration Form in Appendix E and call National Instruments Corporation. Completing the
form before calling National Instruments will help solve your problem faster.
You can use the following toll-free number between the hours of 8:00 a.m. and 5:30 p.m.
(central time) to reach the National Instruments applications engineering department:
(512) 794-0100
(800) 433-3488 (toll-free U.S. and Canada)
For your documentation comments, we have included a User Comment Form at the back of the
manual. Please mail it to the address printed at the bottom of the form.
© National Instruments Corporation vii GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 8

Page 9

Contents
Chapter 1
General Description
Overview........................................................................................................................1-1
What Your Kit Should Contain...................................................................................... 1-2
Optional Equipment .......................................................................................................1-3
Unpacking ...................................................................................................................... 1-3
VXIbus and VMEbus Capabilities................................................................................. 1-3
GPIB Characteristics...................................................................................................... 1-4
Command Set................................................................................................................. 1-5
Code Instruments ...........................................................................................................1-5
Front Panel Indicators, Switches and Connectors..........................................................1-6
Power Consumption and Temperature Rating............................................................... 1-6
Chapter 2
Configuration and Startup Procedures
System Configuration ....................................................................................................2-1
GPIB-VXI Configuration............................................................................................... 2-2
Setting the Logical Address ...............................................................................2-4
Setting the GPIB Primary Address ....................................................................2-4
Setting the Servant Area Size ............................................................................2-5
Setting the Installed RAM Size..........................................................................2-5
Setting the Dual-Ported Memory Size ............................................................... 2-7
Setting the Front Panel Reset Operation............................................................ 2-7
Setting the VMEbus Requester Level................................................................2-8
Setting the VXI Interrupt Handler Levels.......................................................... 2-8
GPIB-VXI Startup Mode Configuration............................................................ 2-9
488-VXI System Operation ...........................................................................................2-10
System Startup Message Printing ......................................................................2-11
Slot 0 Resource Manager Configuration............................................................2-11
Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager Configuration ...................................................2-17
...........................................................................................................1-1
......................................................................2-1
488-VXI System Mode .......................................................................... 2-9
Diagnostics Mode ..................................................................................2-10
Nonvolatile Configuration Mode........................................................... 2-10
VXI pROBE Mode.................................................................................2-10
Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation ......................................................2-13
Front Panel LED Indications for RM Operation....................................2-13
Self-Test Operation................................................................................ 2-14
RM Operation ........................................................................................2-14
Static Configuration Operation ..............................................................2-15
Dynamic Configuration Operation ........................................................2-15
GPIB Secondary Address Assignment ......................................2-15
System Configuration Table ..................................................................2-16
Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation..............................................2-17
© National Instruments Corporation ix GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 10

Contents
Non-Slot 0 Message-Based Device Configuration ............................................2-18
Non-Slot 0 Message-Based Device Operation ......................................2-18
Front Panel LED Indications for Message-Based Device Operation ....2-19
Slot 0 Message-Based Device Configuration ....................................................2-19
Slot 0 Message-Based Device Operation............................................... 2-21
Chapter 3
Local Command Set
Command Set Access ....................................................................................................3-2
Command Syntax...........................................................................................................3-2
Command Line Termination..........................................................................................3-3
Command and Query Responses ...................................................................................3-3
Command Response Format ..........................................................................................3-4
Query Response Format.................................................................................................3-4
Error Reporting ..............................................................................................................3-4
The Help Query..............................................................................................................3-5
Help? ..................................................................................................................3-5
General Configuration Commands and Queries ............................................................3-6
ConsoleEna ........................................................................................................3-6
ConsMode ..........................................................................................................3-7
DPram?...............................................................................................................3-7
NVconf? .............................................................................................................3-8
OBram? ..............................................................................................................3-9
ProgMode...........................................................................................................3-9
WordSerEna.......................................................................................................3-10
RM Information Queries................................................................................................3-10
A24MemMap? ...................................................................................................3-11
A32MemMap? ...................................................................................................3-12
Cmdr?.................................................................................................................3-12
CmdrTable?........................................................................................................3-13
Laddrs?...............................................................................................................3-14
NumLaddrs?.......................................................................................................3-14
RmEntry? ...........................................................................................................3-15
Srvnts?................................................................................................................3-17
StatusState? ........................................................................................................3-17
Dynamic Configuration Commands and Queries ..........................................................3-18
DCBNOSend......................................................................................................3-19
DCGrantDev ......................................................................................................3-19
DCSystem?.........................................................................................................3-19
Dynamic Reconfiguration Queries ................................................................................3-20
Broadcast?..........................................................................................................3-21
GrantDev? ..........................................................................................................3-23
RelSrvnt?............................................................................................................3-24
VXI-Defined Common ASCII System Commands.......................................................3-25
DCON?...............................................................................................................3-25
DINF?.................................................................................................................3-27
DLAD?...............................................................................................................3-28
DNUM?..............................................................................................................3-29
DRES?................................................................................................................3-29
...........................................................................................................3-1
GPIB-VXI User Manual x © National Instruments Corporation
Page 11

Contents
RREG? ...............................................................................................................3-30
WREG................................................................................................................3-31
GPIB Address Configuration Commands and Queries .................................................3-31
LaSaddr ..............................................................................................................3-32
LaSaddr? ............................................................................................................3-32
Primary?.............................................................................................................3-33
SaddrLa? ............................................................................................................3-33
Saddrs?...............................................................................................................3-34
SaDisCon ...........................................................................................................3-35
VXIbus Interrupt Handler Configuration Commands and Queries ...............................3-35
AllHandlers? ......................................................................................................3-35
AssgnHndlr ........................................................................................................3-36
HandlerLine?......................................................................................................3-37
RdHandlers?.......................................................................................................3-37
IEEE-488.2 Common Commands and Queries .............................................................3-38
*CLS ..................................................................................................................3-38
*ESE...................................................................................................................3-39
*ESE?.................................................................................................................3-39
*ESR?.................................................................................................................3-39
*IDN?.................................................................................................................3-40
*OPC..................................................................................................................3-40
*OPC? ................................................................................................................3-40
*RST ..................................................................................................................3-41
*SRE ..................................................................................................................3-41
*SRE?.................................................................................................................3-41
*STB?.................................................................................................................3-42
*TRG..................................................................................................................3-42
*TST?.................................................................................................................3-42
*WAI..................................................................................................................3-43
VXIbus Access Commands and Queries .......................................................................3-43
A16.....................................................................................................................3-43
A16? ...................................................................................................................3-44
A24.....................................................................................................................3-44
A24? ...................................................................................................................3-45
SYSRESET ........................................................................................................3-45
TTL Trigger Access Commands....................................................................................3-46
SetTrigOutFP .....................................................................................................3-46
SetTrigSrc ..........................................................................................................3-47
SourceTrig..........................................................................................................3-47
Word Serial Communication Commands and Queries..................................................3-48
ProtErr? ..............................................................................................................3-49
RespReg? ...........................................................................................................3-49
WScmd...............................................................................................................3-50
WScmd?.............................................................................................................3-50
WSresp? .............................................................................................................3-50
WSstr..................................................................................................................3-52
WSstr?................................................................................................................3-53
CI Configuration Commands and Queries.....................................................................3-53
© National Instruments Corporation xi GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 12

Contents
CIAddr?..............................................................................................................3-54
CIArea................................................................................................................3-55
CIArea? ..............................................................................................................3-56
CIBlocks?...........................................................................................................3-56
CIDelete? ...........................................................................................................3-57
CIList?................................................................................................................3-58
DCIDownLdPI ...................................................................................................3-59
DCIDownLoad...................................................................................................3-60
DCISetup?..........................................................................................................3-61
DCISetupPI? ......................................................................................................3-62
Chapter 4
Nonvolatile Configuration
The GPIB-VXI Nonvolatile Configuration Main Menu................................................ 4-2
Read in Nonvolatile Configuration.................................................................... 4-2
Print Configuration Information ........................................................................ 4-2
Change Configuration Information....................................................................4-4
Set Configuration to Factory Settings................................................................4-5
Write Back (Save) Changes ...............................................................................4-5
Quit Configuration .............................................................................................4-5
Chapter 5
Diagnostic Tests
Configuration for Diagnostic Testing ............................................................................ 5-1
Diagnostic Test Structure............................................................................................... 5-1
Diagnostic Test Description........................................................................................... 5-2
Diagnostics Mode Selection ..........................................................................................5-3
Diagnostic Test Selection ..............................................................................................5-5
...................................................................................................................5-1
The EPROM Test...............................................................................................5-2
The RAM Test ...................................................................................................5-2
The 68070 CPU Test..........................................................................................5-2
The VXI Configuration Register Test................................................................5-2
The Local Interrupt Test ....................................................................................5-2
The GPIB Test ...................................................................................................5-2
The DIP Switch and Trigger Test ...................................................................... 5-2
The DMA Test ...................................................................................................5-2
The 68881 Coprocessor Test .............................................................................5-3
Appendix A
Specifications
........................................................................................................................A-1
Appendix B
Error Codes
...........................................................................................................................B-1
Appendix C
Code Instrument Overview
...............................................................................................4-1
.............................................................................................C-1
GPIB-VXI User Manual xii © National Instruments Corporation
Page 13

Contents
GPIB-VXI Operation without CIs .................................................................................C-2
CI Operation................................................................................................................... C-4
CI Characteristics...........................................................................................................C-5
Downloaded CIs and EPROMed CIs.............................................................................C-6
Resident CIs ................................................................................................................... C-6
Summary ........................................................................................................................C-6
Appendix D
Using the CDS-852 Adapter Code Instrument
Installing the 852 Adapter CI......................................................................................... D-1
Deleting a CI .................................................................................................................. D-4
Logical Address and A24 Address Assignment ............................................................D-4
852 Adapter CI Commands ...........................................................................................D-4
!!A ...................................................................................................................... D-5
!!B ......................................................................................................................D-5
!!D ...................................................................................................................... D-6
!!d....................................................................................................................... D-6
!!E.......................................................................................................................D-6
!!L.......................................................................................................................D-7
!!S....................................................................................................................... D-7
!!T.......................................................................................................................D-7
!!t........................................................................................................................ D-8
.........................................................D-1
Appendix E
GPIB-VXI Hardware and Software Configuration Form
..................................E-1
Glossary......................................................................................................................Glossary-1
Index ..................................................................................................................................Index-1
Figures
Figure 1-1. The GPIB-VXI Interface Module........................................................................1-1
Figure 2-1. GPIB-VXI Parts Locator Diagram ......................................................................2-3
Figure 2-2. Example Logical Address Switch Setting ...........................................................2-4
Figure 2-3. Example GPIB Primary Address Switch Setting ................................................2-4
Figure 2-4. Example Servant Area Size Switch Setting......................................................... 2-5
Figure 2-5. VMEbus Requester Jumper Settings ................................................................... 2-8
Figure 2-6. Startup Mode Switch Settings .............................................................................2-9
Figure 2-7. VXI System Startup Message Switch Settings....................................................2-11
Figure 2-8. CLK10 Jumper Settings for Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation ......................2-12
Figure 2-9. CLK10 Jumper Settings for Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation .............. 2-17
Figure 2-10. CLK10 Jumper Settings for Non-Slot 0 Message Based Device Operation ....... 2-18
Figure 2-11. CLK10 Jumper Settings for Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation ......................2-20
© National Instruments Corporation xiii GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 14

Contents
Figure 4-1. The GPIB-VXI Nonvolatile Configuration Main Menu .....................................4-2
Figure 4-2. The Nonvolatile Configuration Information Display .......................................... 4-3
Figure 4-3. The GPIB-VXI Nonvolatile Configuration Changer...........................................4-4
Figure 5-1. The Diagnostics Mode Menu ..............................................................................5-3
Figure 5-2. The Diagnostic Test Selection Menu...................................................................5-5
Figure C-1. GPIB-VXI Operation Without Code Instruments ...............................................C-3
Figure C-2. Code Instrument Operation .................................................................................C-4
Tables
Table 2-1. Serial Port Connector RS-232 Pinouts ................................................................2-1
Table 2-2. GPIB-VXI Factory Configuration....................................................................... 2-2
Table 2-3. Installed RAM Switch Settings ...........................................................................2-6
Table 2-4. GPIB-VXI CPU Local and A24 Memory Ranges...............................................2-6
Table 2-5. Dual-Ported Memory Size Configuration Switch Settings .................................2-7
Table 2-6. Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation Switch and Jumper Settings ......................2-12
Table 2-7. Front Panel LED Indications for RM Operation ................................................. 2-13
Table 2-8. Example Secondary Address Assignment........................................................... 2-16
Table 2-9. Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation Switch and Jumper Settings..............2-17
Table 2-10. Non-Slot 0 Message-Based Device Operation Switch and Jumper Settings ......2-18
Table 2-11. Front Panel LED Indications for Message-Based Device Operation.................. 2-19
Table 2-12. Slot 0 Message-Based Device Operation Switch and Jumper Settings............... 2-20
Table 3-1. Valid Ranges for Common Numeric Command Parameters...............................3-2
Table 3-2. Default Response Mode Configurations..............................................................3-3
Table 5-1. Diagnostic Tests .................................................................................................. 5-1
Table 5-2. Diagnostics Mode Menu Option Descriptions ....................................................5-4
Table B-1. Error Codes..........................................................................................................B-1
GPIB-VXI User Manual xiv © National Instruments Corporation
Page 15
Chapter 1
General Description
This chapter contains a brief overview of the GPIB-VXI and its VXIbus, VMEbus and GPIB
capabilities. This chapter also contains a description of the local command set, an introduction
to Code Instruments (CIs), and a description of the GPIB-VXI front panel indicators, switches
and connectors.
Overview
The GPIB-VXI is a C-sized interface module that links the industry standard IEEE-488 (GPIB)
bus and the VXIbus. The GPIB-VXI performs transparent conversion of the GPIB signals and
protocols to VXIbus signals and protocols, so that a GPIB Controller can control VXIbus
instruments in the same way that it controls GPIB instruments. Figure 1-1 shows the GPIB-VXI
interface module.
Product photo unavailable
Figure 1-1. The GPIB-VXI Interface Module
© National Instruments Corporation 1-1 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 16
General Description Chapter 1
The GPIB-VXI is factory configured as the system Resource Manager (RM). It performs the
VXIbus startup configuration, self-test, and initialization functions, as well as VXIbus Slot 0/
VMEbus Slot 1-related services.
The RM and Slot 0 functions can be defeated individually, so that the GPIB-VXI can coexist
with another RM and/or be located in any slot.
What Your Kit Should Contain
Your GPIB-VXI kit should contain the following components:
Kit Component Part Number
One GPIB-VXI module 180715-XYZ
One GPIB-VXI User Manual 320151-01
The GPIB-VXI part number and serial number are printed on the label affixed to its shield
casing.
If your kit is missing any of the listed items or if you received the wrong version, contact
National Instruments.
Note: The full part number of the GPIB-VXI is determined by configuration options
corresponding to the extension -XYZ in the part number shown in the previous table. The
options are described below.
X 68881 coprocessor option
0 without coprocessor
1 with coprocessor
Y ROM option
1 standard firmware
2 development firmware
Z RAM option
1 512K
2 1M
3 2M
4 4M
GPIB-VXI User Manual 1-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 17
Chapter 1 General Description
Optional Equipment
Item Part Number
Serial Port Cables:
GPIB-VXI to IBM-PC 9-pin - 2 m 181139-02
GPIB-VXI to 25-pin DTE terminal - 2 m 181138-02
Double-Shielded GPIB Cables:
Type X2 Cable - 1 m 763061-01
Type X2 Cable - 2 m 763061-02
Type X2 Cable - 4 m 763061-03
Unpacking
Follow these steps when unpacking your GPIB-VXI:
1. Verify that the pieces contained in the package you received match the kit parts list. Do not
remove the module from its plastic bag at this point.
2. Your GPIB-VXI module is shipped packaged in an antistatic plastic bag to prevent
electrostatic damage to the module. Several components on the module can be damaged by
electrostatic discharge. To avoid such damage while handling the module, touch the plastic
bag to a metal part of your VXIbus mainframe chassis before removing the module from the
bag.
3. Remove the module from the bag and inspect the module for loose components or any other
sign of damage. Notify National Instruments if the module appears damaged in any way.
Do not install a damaged module into your VXIbus mainframe.
VXIbus and VMEbus Capabilities
The GPIB-VXI has the following VXIbus and VMEbus capabilities:
• Fully compatible with VXIbus Specification Revisions 1.2 and 1.3
• VXIbus Resource Manager (RM) (defeatable)
• VXIbus Slot 0/VMEbus Slot 1 support (defeatable)
• VXIbus Message-Based commander and Message-Based servant
• VMEbus master and slave
© National Instruments Corporation 1-3 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 18

General Description Chapter 1
• Up to 4M of dual-ported (shared) memory
• Three programmable VXIbus interrupt handlers
• IEEE 488.1 and IEEE 488.2-compatible 488-VXIbus translator
GPIB Characteristics
The GPIB-VXI has the following GPIB characteristics:
• Communication with VXIbus Message-Based devices
- VXI logical addresses are mapped to GPIB secondary addresses
- Automatically configured at startup
- Programmable
• Interface
- NEC 7210 and National Instruments Turbo488 ASIC
- Full, transparent support of individual status bytes for each secondary address
- Buffered operation decouples GPIB and VXIbus operation
- Controller can address one VXIbus device to talk and other VXIbus devices to listen
• IEEE 488.1 capabilities
- SH1 (Source Handshake)
- AH1 (Acceptor Handshake)
- TE5 (Extended Talker)
- LE3 (Extended Listener)
- SR1 (Service Request)
- DC1 (Device Clear)
- DT1 (Device Trigger)
- RL0 (Remote Local)
• IEEE 488.2-compatible 488-VXIbus translation
The IEEE 488.1 capabilities are supported for all VXIbus devices associated with GPIB
secondary addresses. The IEEE 488.2 compatibility applies to 488.2-compatible VXIbus
devices associated with GPIB secondary addresses through the GPIB-VXI.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 1-4 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 19

Chapter 1 General Description
Command Set
The GPIB-VXI local command set supports the following types of operations:
• System configuration and control
- Help
- General configuration
- RM information extraction
- VXI-defined common ASCII system commands
- Dynamic system configuration and reconfiguration
- GPIB address configuration
- VXIbus interrupt handler configuration
- IEEE 488.2 common commands
• Instrument development and test
- VXIbus access
- Word Serial communication
• CI use and development
- CI configuration
You can access the command set from the GPIB port, the serial port, and through Word Serial
Protocol communication. You can also use separate programmable local command response
modes for interactive and control program operation.
Code Instruments
The GPIB-VXI can run software modules called Code Instruments or CIs that perform special
functions in the VXIbus environment. Typical applications of CIs include:
• Command language translation and interpretation
• Virtual (hierarchical) instrument creation
• Message-Based interface creation for Register-Based devices
• Message-Based interface for non-VXI devices
© National Instruments Corporation 1-5 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 20

General Description Chapter 1
CIs can be implemented in three forms:
• As part of the National Instruments-supplied firmware (Resident CIs, or RCIs)
• As user-developed downloadable object code (Downloaded CIs, or DCIs)
• As user-add-on firmware (EPROMed CIs, or ECIs)
For more information about CI capabilities and applications, see Appendix C, Code Instrument
Overview.
Front Panel Indicators, Switches and Connectors
The GPIB-VXI has the following front panel features:
• Five front panel LEDs
- FAILED, TEST, and ONLINE LEDs indicate the self-test status of the GPIB-VXI.
- ACCESS LED indicates when the GPIB-VXI is accessed from GPIB or VXIbus.
- SYSFAIL LED indicates when any VXIbus device in the system fails.
• Five front panel connectors
- GPIB interface
- Serial port
- Trigger input and output (2 BNCs)
- External CLK10 I/O (BNC)
• System reset switch
Power Consumption and Temperature Rating
Current requirements and the temperature rating of the GPIB-VXI are printed on a label affixed
to its shield casing.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 1-6 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 21
Chapter 2
Configuration and Startup Procedures
This chapter contains information about the system configuration, GPIB-VXI configuration, and
startup operation.
System Configuration
The typical system includes the following components:
• A VXIbus system mainframe containing the GPIB-VXI and the target instrument modules
• A host computer with a GPIB interface module and associated driver software (available for
many computers from National Instruments) connected to the GPIB-VXI GPIB port
• A dumb terminal or host running a terminal emulator connected to the GPIB-VXI serial port
(optional)
The 9-pin serial port connector pinouts are listed in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1. Serial Port Connector RS-232 Pinouts
A three-wire connection to pins 2, 3, and 5 works well for most terminals and emulators. No
connections to pins 4, 7, or 8 are necessary. The serial port settings are 9600 baud, 8-bit data, no
parity, and one stop bit.
Warning: Do not make connections to pins 1 and 6. This could damage your GPIB-VXI.
Cables for connecting the GPIB-VXI serial port to an RS-232 terminal or COM1 port on an IBM
PC-compatible computer are available from National Instruments (see Optional Equipment in
Chapter 1).
Pin Signal GPIB-VXI I/O
2 Receive Data Input
3 Transmit Data Output
4 Data Terminal Ready Output
5 Signal Ground
7 Ready to Send Output
8 Clear to Send Input
© National Instruments Corporation 2-1 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 22
Configuration and Startup Procedures Chapter 2
GPIB-VXI Configuration
The GPIB-VXI factory configuration is shown in Table 2-2. The RAM, firmware and
coprocessor are configured according to the GPIB-VXI purchase options.
Table 2-2. GPIB-VXI Factory Configuration
Function Factory Configuration
Startup Mode VXIbus system
VXIbus characteristics
Resource Manager (RM) Enabled
Logical Address 0
Servant area size 0
Dual-ported memory 0% of installed memory
VXIbus Slot 0 services
CLK10 driver Enabled
CLK10 source Onboard clock
VMEbus Slot 1 services
SYSCLK driver Enabled
Priority Arbiter Enabled
VMEbus requester Level 3
VXI Interrupt handlers Unassigned
GPIB primary address 1
Serial Port
System startup messages Disabled
You do not have to change the GPIB-VXI factory configuration to use it as a Slot 0 Resource
Manager. This section is a guide to alternate configurations.
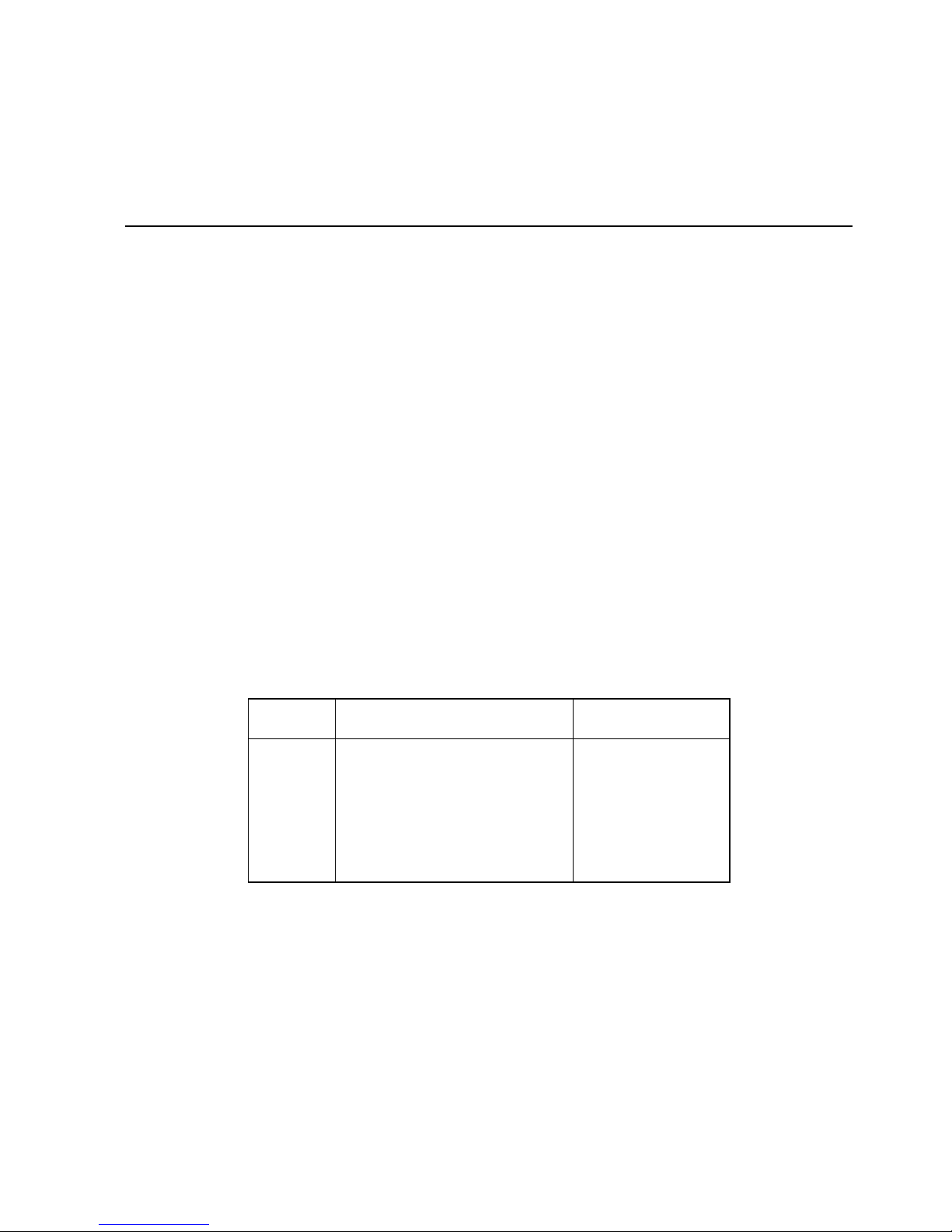
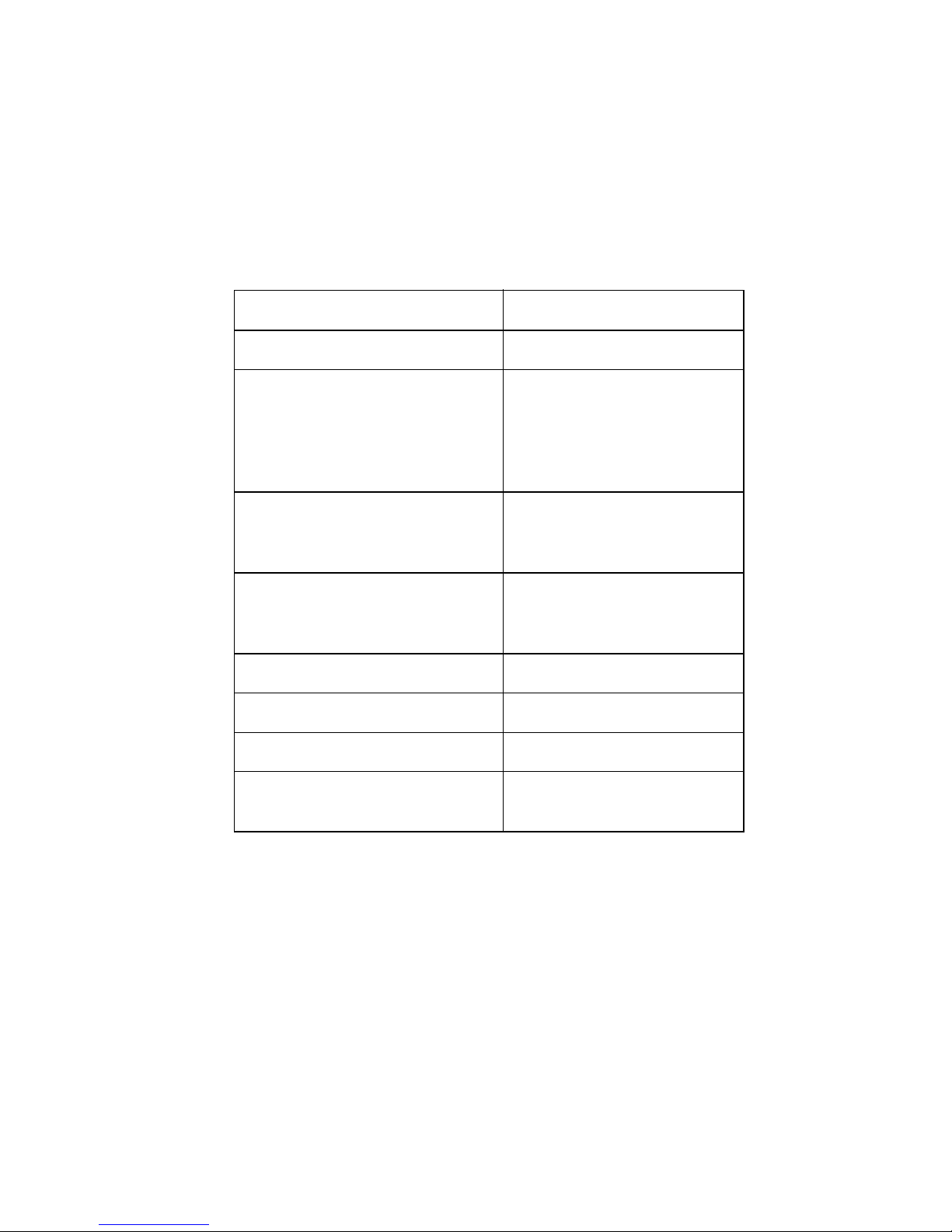
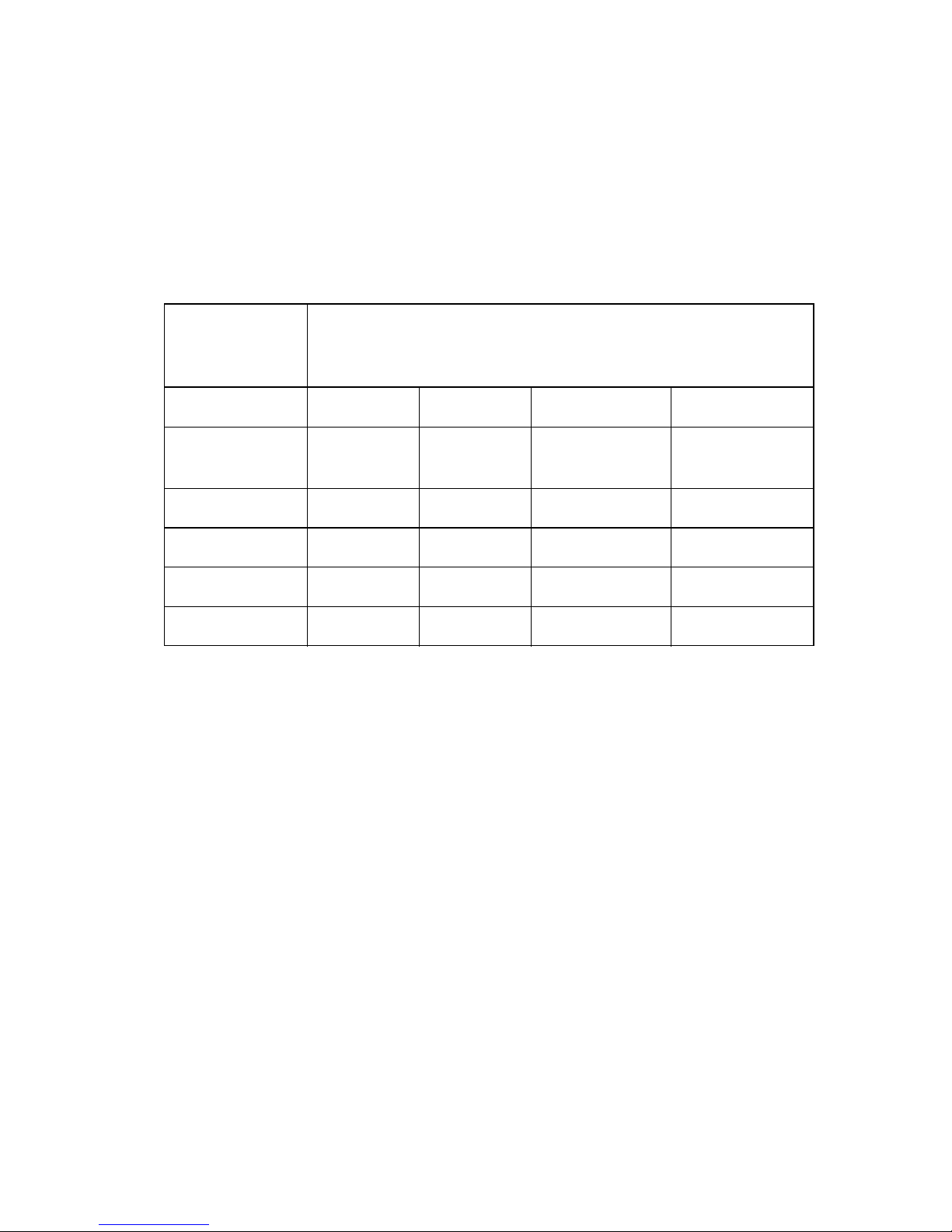
The location of the GPIB-VXI switches and jumpers is illustrated in Figure 2-1. The figures in
this section are illustrated according to the orientation of the GPIB-VXI as depicted in Figure
2-1.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 2-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 23
Chapter 2 Configuration and Startup Procedures
P1
P2
Detail of
2-Position
Switch
ON
OFF
•••
•••••••••••
•••
•
•
•
•
VMEbus Requester
Level Jumpers
S5
•••
S1
S12S11
68070
Reset
Enable
Jumper
S9
S8
W23
12345678
ON
OFF
Logical
Address
Switch
12345678
•
•
Servant
Area Size
Switch
RAM SIMM pair 1
RAM SIMM pair 2
•••••••
•••••••
•
•
CLK 10 Jumpers
ON
OFF
S2
S10
Startup
Mode
12345678
ON
OFF
GPIB
Primary
Turbo488
Address
Serial Port
Startup
EPROM
Expansion Board
Message
Printout
Enable
S24
GPIB Connector
TRG InTRG
Out
EXT
CLK
RS-232
Connector
Figure 2-1. GPIB-VXI Parts Locator Diagram
© National Instruments Corporation 2-3 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 24
Configuration and Startup Procedures Chapter 2
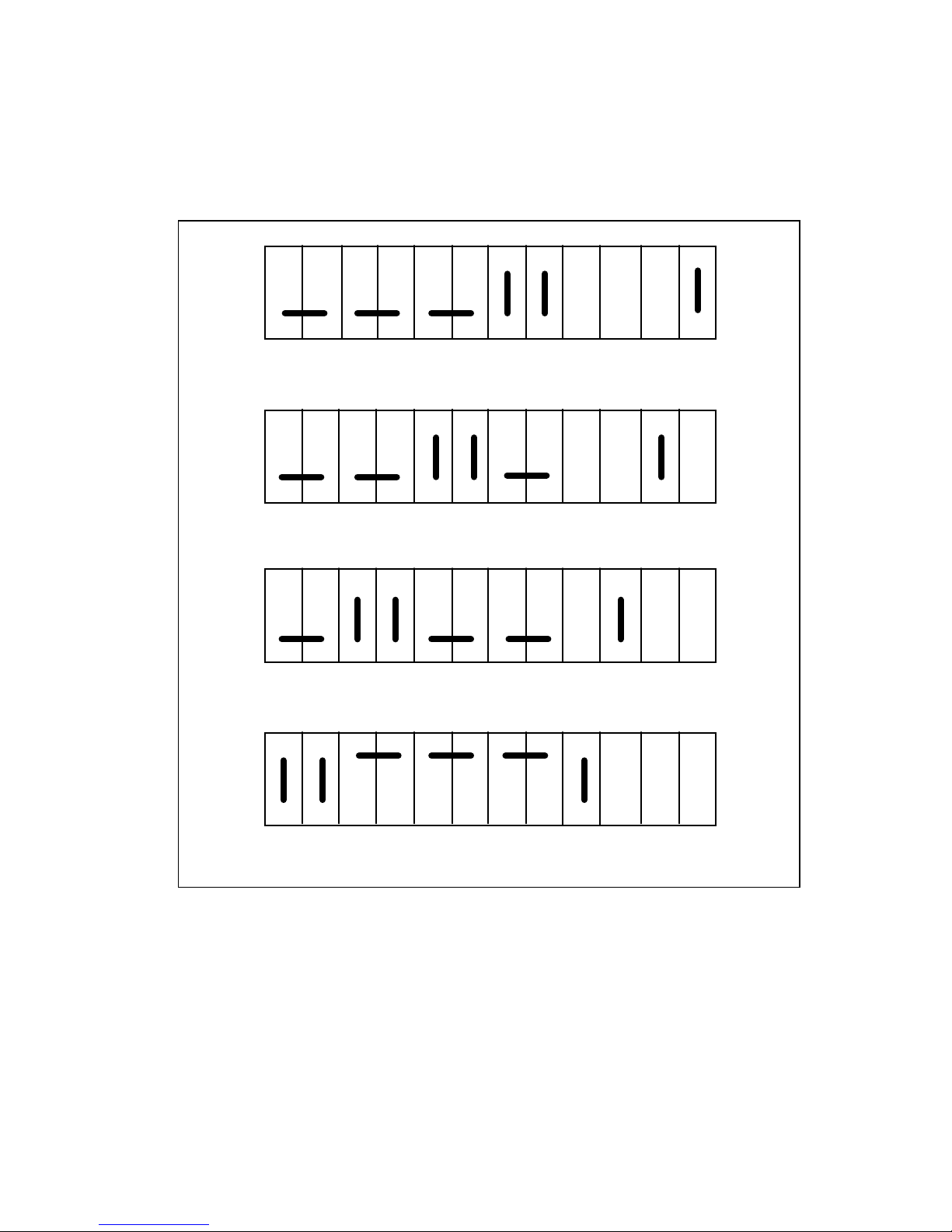
Setting the Logical Address
The logical address switches 8 through 1 correspond to the GPIB-VXI's logical address bits 7
through 0, respectively. The ON position corresponds to a bit value of 0, and OFF corresponds
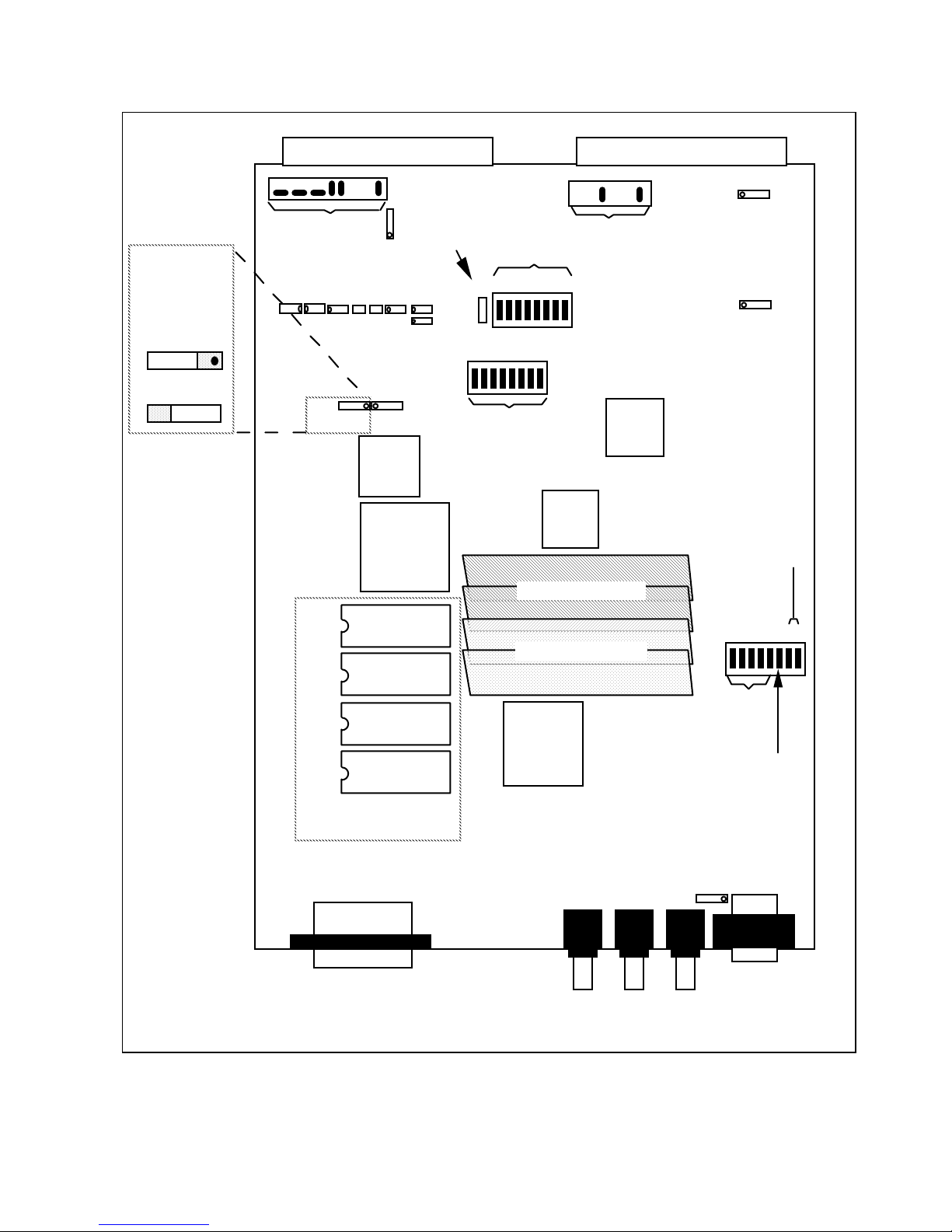
to a value of 1. For example, to set the logical address of the GPIB-VXI to 25 (19h), set the
switches as shown in Figure 2-2. Notice that setting the logical address to any setting but 0 will
disable the GPIB-VXI RM.
Key
Black = side you must press down
MSB
1 23456
O
N
O
F
F
Settings for Logical Address = 19h
7 8
Figure 2-2. Example Logical Address Switch Setting
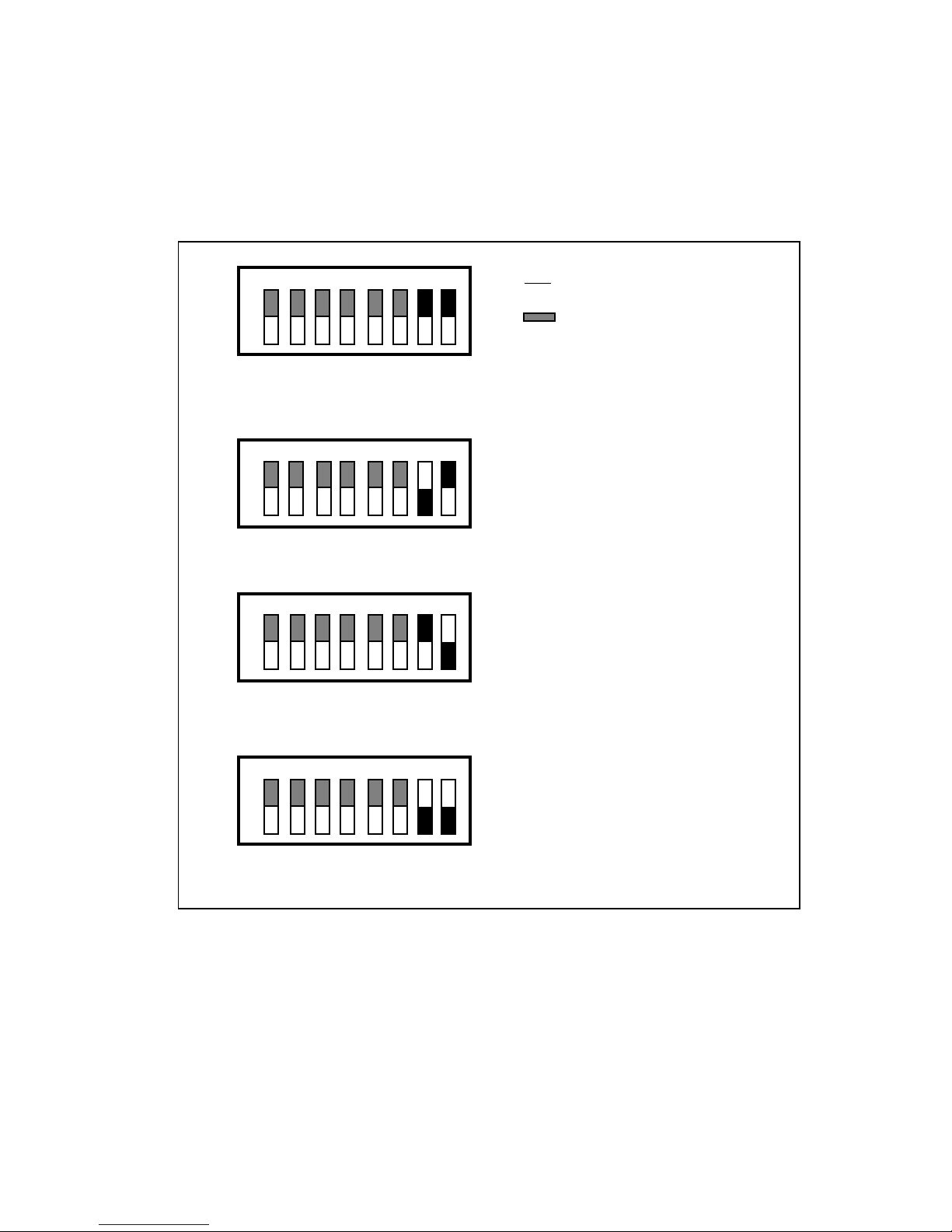
Setting the GPIB Primary Address
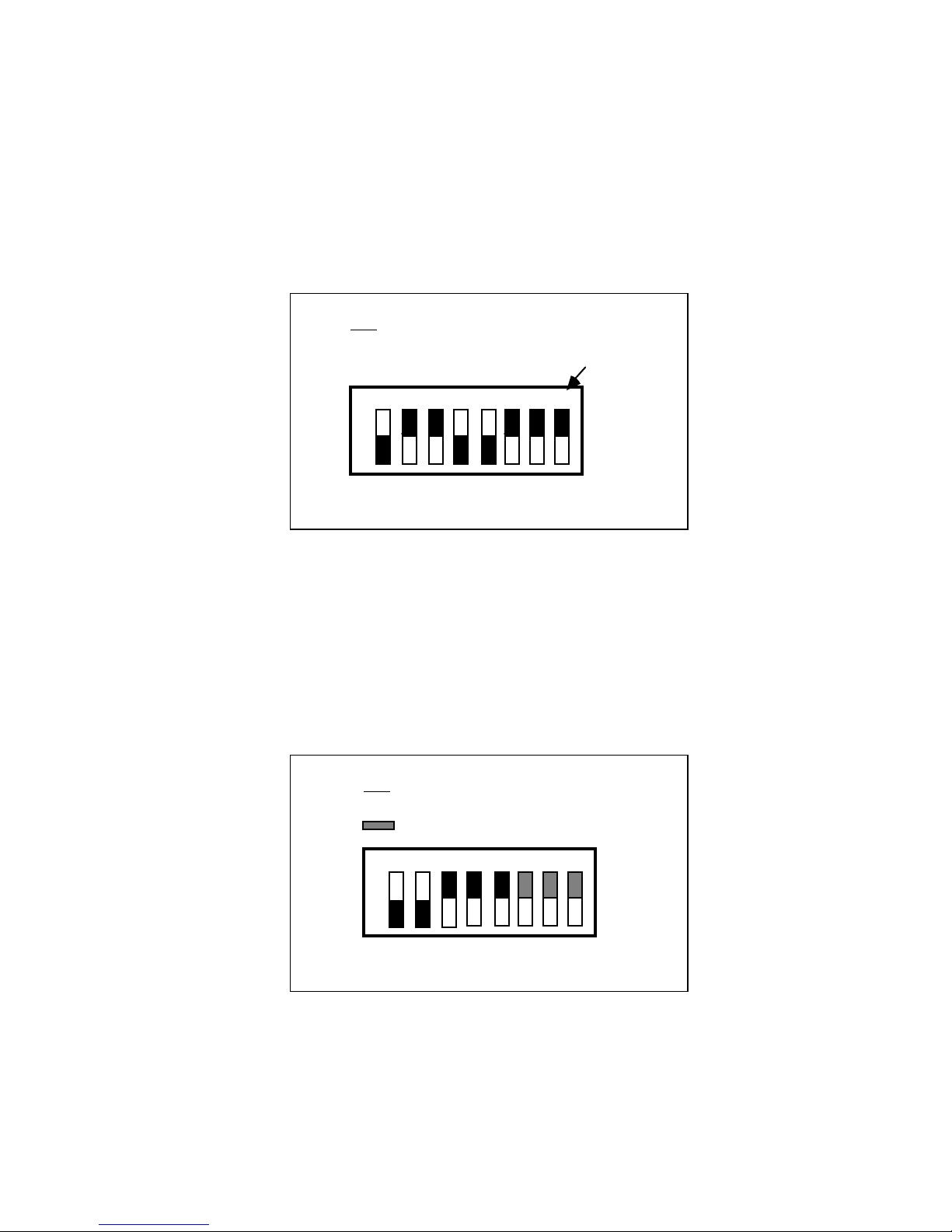
The GPIB switches 5 through 1 correspond to GPIB primary address bits 4 through 0,
respectively. The ON position corresponds to a bit value of 0, and OFF corresponds to a value
of 1. To set the primary address of the GPIB-VXI to 3 (03h), for example, set the switches as
shown in Figure 2-3.
Key
Black = side you must press down
= not used in this context
Figure 2-3. Example GPIB Primary Address Switch Setting
The primary address switches can be overridden by the nonvolatile memory configuration as
described in the Change Configuration Information section of Chapter 4, Nonvolatile
Configuration.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 2-4 © National Instruments Corporation
1 23456
O
N
O
F
F
Settings for GPIB Primary Address = 3
7 8
Page 25
Chapter 2 Configuration and Startup Procedures
Setting the Servant Area Size
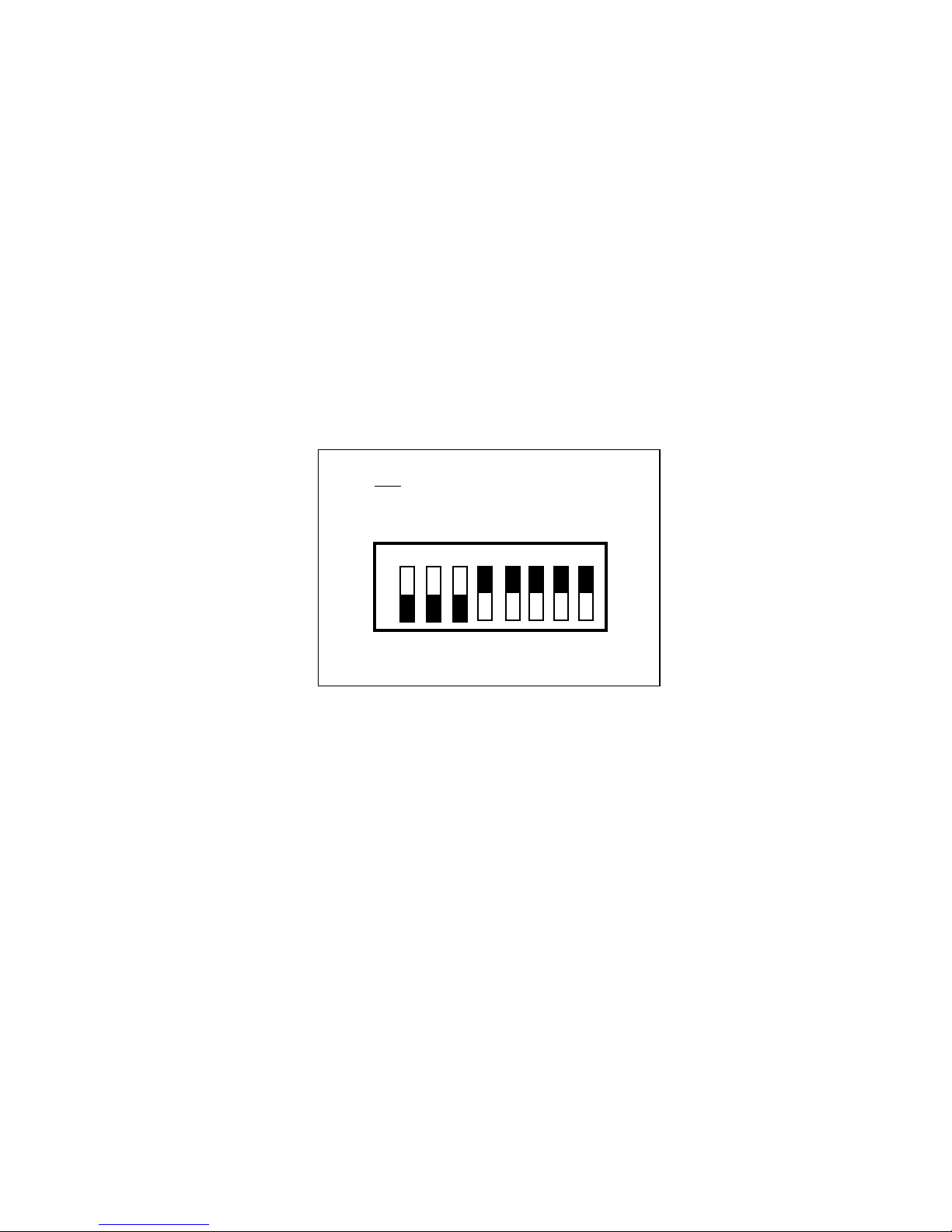
The servant area size is an 8-bit value (0 through 255) that indicates the GPIB-VXI servant area.
The servant area begins at the logical address following the GPIB-VXI's logical address, and
includes N contiguous logical addresses, where N is the value of the servant area size. The RM
uses the servant area of all commanders in the VXIbus system to configure the commander/
servant hierarchy, as described in the VXIbus specification. Notice that if the GPIB-VXI is RM,
the servant area size does not apply.
The servant area size switches 8 through 1 correspond to setting the GPIB-VXI servant area size
bits 7 through 0, respectively. The ON position corresponds to a bit value of 0, and OFF
corresponds to a value of 1. To set the servant area size to 7 (07h), for example, set the switches
as shown in Figure 2-4.
Key
Black = side you must press down
1 23 4 5 6
O
N
O
F
F
Settings for Servant Area Size = 7
7 8
Figure 2-4. Example Servant Area Size Switch Setting
The servant area size switch can be overridden by the nonvolatile memory configuration as
described in the Change Configuration Information section of Chapter 4, Nonvolatile
Configuration.
Setting the Installed RAM Size
You can install up to 4M of local RAM on the GPIB-VXI. The minimum amount of memory is
512K. You can install additional memory by inserting 256K by 8-bit (Texas Instruments part
number TMS41256GU8 or equivalent) or 1M by 8-bit (Texas Instruments part number
TMS024EAD9 or equivalent) DRAM SIMM modules into the SIMM sockets as illustrated in
Figure 2-1. You must install the RAM modules in pairs because the SIMM sockets
accommodate two SIMMs each. The allowed RAM configurations and their associated switch
settings are given in Table 2-3.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-5 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 26
Configuration and Startup Procedures Chapter 2
Note: Use only memory modules with an access time of 120 nsec or less. When installing the
memory modules, follow proper procedures for handling MOS ICs.
Remove any memory modules you have installed prior to returning the GPIB-VXI to
National Instruments for upgrades or repair.
Table 2-3. Installed RAM Switch Settings
Installed
Memory Switch S8 Switch S9 RAM SIMM RAM SIMM
Size Setting Setting Pair 1 Pair 2
512K OFF OFF 256K by 8-bit none
1M OFF ON 256K by 8-bit 256K by 8-bit
2M ON OFF 1M by 8-bit none
4M ON ON 1M by 8-bit 1M by 8-bit
The relationship between the amount of installed memory, the local address range occupied by
the memory, and range of VME A24 addresses accessible by the GPIB-VXI CPU is listed in
Table 2-4.
Table 2-4. GPIB-VXI CPU Local and A24 Memory Ranges
Installed Installed Memory Accessible
Memory Local Address VME A24
Size Range Address Range
Start End Start End
512K 000000h 07FFFFh 080000h E7FFFFh
1M 000000h 0FFFFFh 100000h E7FFFFh
2M 000000h 1FFFFFh 200000h E7FFFFh
4M 000000h 3FFFFFh 400000h E7FFFFh
GPIB-VXI User Manual 2-6 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 27
Chapter 2 Configuration and Startup Procedures
Setting the Dual-Ported Memory Size
The amount of installed memory that is dual-ported to the VMEbus can be set with switches S11
and S12. Table 2-5 gives the S11 and S12 switch settings for dual-porting various portions of
RAM with the VMEbus, for each possible installed memory configuration.
Table 2-5. Dual-Ported Memory Size Configuration Switch Settings
Installed Dual-Ported Portion of
Memory Installed Memory
Size
All One-Half One-Fourth None
Switch S12 ON S12 ON S12 OFF S12 OFF
Positions S11 ON S11 OFF S11 ON S11 OFF
512K 512K 256K 128K 0K
1M 1M 512K 256K 0K
2M 2M 1M 512K 0K
4M 4M 2M 1M 0K
The dual-ported memory VME A24 base address is held in the GPIB-VXI Offset Register, as
described in the VXIbus specification.
Setting the Front Panel Reset Operation
The Reset button on the front panel can be configured to reset the GPIB-VXI and drive
SYSRESET on the VXIbus backplane or just reset the GPIB-VXI. If jumper W23 is installed,
the GPIB-VXI is reset and SYSRESET is driven. If jumper W23 is not installed, only the GPIBVXI is reset.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-7 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 28
Configuration and Startup Procedures Chapter 2
Setting the VMEbus Requester Level
The VMEbus requester level of the GPIB-VXI is jumper-configurable as shown in Figure 2-5.
•
•••••
• •
• •
a. Level 3 Requester
• •
•••
•
•
•
b. Level 2 Requester
•
•
c. Level 1 Requester
d. Level 0 Requester
••
•
•
•
•••••
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
Figure 2-5. VMEbus Requester Jumper Settings
Setting the VXI Interrupt Handler Levels
The three default VXI interrupt handler levels are configured by the contents of the onboard
nonvolatile memory, as described in Chapter 4, Nonvolatile Configuration.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 2-8 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 29
Chapter 2 Configuration and Startup Procedures
GPIB-VXI Startup Mode Configuration
Startup mode switches 8 and 7 control the GPIB-VXI operation mode at system startup and
system reset, respectively. They select one of four modes, as shown in Figure 2-6.
1 23 4 5 6
O
N
O
F
F
a. 488-VXI Runtime System Mode
7 8
Key
Black = side you must press down
= not used in this context
1 23 4 5 6
O
N
O
F
F
b. Diagnostics Mode
1 23 4 5 6
O
N
O
F
F
c. Nonvolatile Configuration Mode
1 23 4 5 6
O
N
O
F
F
d. VXI pROBE Mode
7 8
7 8
7 8
Figure 2-6. Startup Mode Switch Settings
488-VXI System Mode
VXI system mode is the startup mode for normal operation in a VXI system. The GPIB-VXI
comes up as described in the 488-VXI System Operation section later in this chapter.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-9 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 30

Configuration and Startup Procedures Chapter 2
Diagnostics Mode
In diagnostics mode, you can perform extensive offline diagnostic tests on the GPIB-VXI. See
Chapter 5, Diagnostic Tests, for a description of the GPIB-VXI self-tests.
Nonvolatile Configuration Mode
In nonvolatile configuration mode, you can edit the contents of the nonvolatile configuration
parameter memory. See Chapter 4, Nonvolatile Configuration, for a description of how to edit
the GPIB-VXI nonvolatile memory.
VXI pROBE Mode
In VXI pROBE mode, you can use the enhanced pROBE debugger. This mode is available only
with the GPIB-VXI development firmware option. The VXI pROBE debugger is described in
the GPIB-VXI Software Reference Manual, part number 320152-01.
488-VXI System Operation
The GPIB-VXI is factory configured as a Slot 0 Resource Manager. The Slot 0 and Resource
Manager (RM) functions can be independently defeated, resulting in four modes of operation:
• Slot 0 Resource Manager
• Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager
• Non-Slot 0 Message-Based device
• Slot 0 Message-Based device
This section describes the GPIB-VXI configuration procedures and startup behavior for each
mode of operation.
Warning: Installation of a Non-Slot 0-configured GPIB-VXI in Slot 0 or a Slot 0-configured
GPIB-VXI in any slot other than Slot 0 is not allowed, and may result in damage to
the GPIB-VXI, the mainframe, or other modules.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 2-10 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 31

Chapter 2 Configuration and Startup Procedures
System Startup Message Printing
The serial port startup printout enable switch controls whether or not VXI system startup
messages are printed to the serial port, as shown in Figure 2-7.
1 23 4 5 6
O
N
O
F
F
a. Printing Disabled
7 8
Key
Black = side you must press down
= not used in this context
1 23 4 5 6
O
N
O
F
F
b. Printing Enabled
7 8
Figure 2-7. VXI System Startup Message Switch Settings
Slot 0 Resource Manager Configuration
You can configure the GPIB-VXI for Slot 0 Resource Manager operation by enabling the
VXIbus Slot 0 functions, setting the model code to 0FFh, and setting the logical address to 0, as
shown in Table 2-6.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-11 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 32

Configuration and Startup Procedures Chapter 2
Table 2-6. Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation Switch and Jumper Settings
Jumper/Switch Position Function
CLK10 jumpers See Figure 2-8 a. CLK10 sourcing for backplane is enabled
from onboard clock source. If S24 is OFF,
the GPIB-VXI will also source CLK10 at
the front panel BNC.
or
See Figure 2-8 b. CLK10 sourcing is enabled from external
source via front panel BNC (S24 must be
ON).
Switch S1 ON SYSCLK sourcing is enabled.
Switch S2 ON MODID pull up resistor is enabled.
Switch S5 ON Bus arbiter is enabled.
Switch S10 ON Model code is 0FFh.
Logical Address All ON Logical address is 0.
Switches 8 through 1
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
Figure 2-8. CLK10 Jumper Settings for Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation
GPIB-VXI User Manual 2-12 © National Instruments Corporation
a. CLK10 sourcing for backplane is enabled
from on-board clock source
• •
b. CLK10 sourcing is enabled from
• •
• •
external clock source
• •
• •
• •
Page 33

Chapter 2 Configuration and Startup Procedures
Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation
At startup, a GPIB-VXI configured as a Slot 0 Resource Manager performs its self-tests,
executes the RM functions, and then enters its normal mode of operation.
Front Panel LED Indications for RM Operation
The five front panel LEDs are SYSFAIL, FAILED, TEST, ONLINE, and ACCESS. The GPIBVXI uses the FAILED, TEST, and ONLINE LEDs to indicate the progress of its selfinitialization, self-test, and RM functions. The LED indications are shown in Table 2-7. A
successful system startup will sequence through the first five states. The probable cause of
failure shown for each combination of LEDs is valid if the FAILED LED is lit five seconds
following system startup. The LED indications are identical for Slot 0 Resource Manager and
Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager operation.
Table 2-7. Front Panel LED Indications for RM Operation
Sequence FAILED TEST ONLINE State Point of Failure
1 OFF OFF OFF No power
2 ON OFF OFF In self-initialization Failed before self-test
3 ON ON OFF In self-test Failed in self-test
4 OFF ON ON Performing RM
5 OFF OFF ON Online
ON ON ON Failed Failed while in RM
ON OFF ON Failed Failed while online
The SYSFAIL LED indicates the status of the VMEbus SYSFAIL signal. If any device in the
system is asserting SYSFAIL, the SYSFAIL LED is lit.
The ACCESS LED flashes whenever the GPIB-VXI is accessed from the GPIB or from the
VXIbus.
Self-Test Operation
The self-test sequence tests the basic functionality of many GPIB-VXI components, including
EPROM, RAM, I2C bus, RS-232 port, DMA channels, GPIB port, interrupt logic, timer, and
VXIbus registers. The five-second limitation imposed by the VXIbus specification does not
allow exhaustive tests to be executed at system startup. Full tests of the GPIB-VXI can be
executed in diagnostics mode, as described in Chapter 5, Diagnostic Tests.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-13 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 34

Configuration and Startup Procedures Chapter 2
RM Operation
The RM waits until all devices have stopped driving the VME SYSFAIL signal, or until five
seconds have elapsed after the VMEbus SYSRESET signal is negated. During this period, all of
the VXIbus devices in the system should have completed their self-tests.
The RM then scans logical addresses 1 through 254 for static configuration devices (SC devices).
For each SC device found, it reads the device class and manufacturer's ID code from the ID
Register, and the model code from the Device Type Register. If the device is an extended
device, the RM reads its Subclass Register. The RM then performs slot associations for each
static configuration device by reading its Status Register while asserting each MODID line.
The RM then looks for dynamic configuration devices (DC devices) at logical address 255 by
asserting each MODID line and reading the device's ID Register. DC devices initially have a
logical address of 255. The RM subsequently assigns each DC device a different logical
address. For each DC device found, it reads the device's configuration registers, as with SC
devices, but also assigns each device the next unused logical address by writing the appropriate
value to the device's Logical Address Register. The starting logical address to begin assigning
DC devices may be configured in the nonvolatile configuration, as described in Chapter 4,
Nonvolatile Configuration.
If any device has not passed its self-test, the RM forces that device offline by setting the Sysfail
Inhibit and Reset bits in that device's Control Register.
The RM then determines the address space of each device by reading its ID Register. If the
device's address space is A16/A24 or A16/A32, the RM allocates a section of A24 or A32
memory space to the device according to the memory requirements indicated by the content of
its Device Type Register, and writes the appropriate value to the device's Offset Register.
The RM configures the initial commander/servant hierarchy according to each commander's
servant area size, using the algorithm described in the VXIbus specification. The RM issues the
appropriate Read Servant Area and Device Grant commands to each SC commander. The RM
retains all devices not assigned to other commanders as its immediate servants. Regardless of
where DC device logical addresses are assigned, they are never granted to an SC commander.
DC commander/servant hierarchy creation is done through the use of the GPIB-VXI Local
Command Set, as described in the DC Commands and Queries section of Chapter 3, Local
Command Set.
The RM then sends the Word Serial Query Read Protocols to all Message-Based devices. The
response to the query is saved internally for later use in interrupt handler and GPIB
configuration.
The RM configures the VXI interrupter and interrupt handlers using a seven entry table
contained in nonvolatile configurations. During the VXI interrupt configuration, all
Programmable Handlers (PH) and Programmable Interrupters (PI) are assigned interrupt levels.
Each entry in the table represents the logical address of the handler that handles the
corresponding level (1 through 7). If the handler is static, PI servants are assigned to the level.
If the device is a PH device, both it and any PI servants are assigned to the corresponding level.
Notice that if the table entry is FFh, the level is free to be assigned to any PH device. If only PH
and PI devices are in a system, all entries may contain FFh. See Chapter 4, Nonvolatile
Configurations, for more complete details.
The remainder of the RM procedure depends upon whether the RM found any DC devices in the
system.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 2-14 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 35

Chapter 2 Configuration and Startup Procedures
Static Configuration Operation
When all of the previous operations are complete and successful, the RM sends the Word Serial
command Identify Commander to all immediate Message-Based servants with the master
capability. At this point, the RM is ready to bring the system into the Normal Operation substate. This is accomplished by sending the Word Serial query Begin Normal Operation to all
top-level commanders and immediate Message-Based servants.
Dynamic Configuration Operation
If the system is a DC system (at least one DC device was found), the GPIB-VXI RM does not
send Identify Commander or Begin Normal Operation to any devices. The outside controller (or
embedded CI) can then create the DC commander/servant hierarchy without having to
dynamically reconfigure the system. Use the GPIB-VXI local command DCGrantDev to
create the DC hierarchy. When the system is configured and ready to make a transition to the
Normal Operation sub-state, send the GPIB-VXI local command DCBNOSend. DCBNOSend
sends the Identify Commander and Begin Normal Operation commands to Message-Based
devices as described in Static Configuration Operation. See the DC Commands and Queries
section of Chapter 3, Local Command Set for further information about dynamic configuration
operation.
The GPIB-VXI then performs general configuration operations. The GPIB-VXI creates GPIB
secondary address links for its immediate Message-Based SC servants. After this, the GPIBVXI RM and general configuration operations are complete.
GPIB Secondary Address Assignment
The GPIB-VXI automatically assigns a GPIB secondary address to itself and to each of its
immediate Message-Based SC servants. If the Message-Based device does not support minimal
Word Serial[I] or VXIbus 488.2[I4] capabilities, no GPIB secondary address link is created. The
GPIB-VXI assigns a secondary address to each device according to the top five bits of its logical
address. For example, the secondary address of a device with logical address 96 (01100000b)
would be 12 (01100b).
If two or more devices have logical addresses with the same top five bits, the GPIB-VXI assigns
secondary addresses to devices in order of the least significant three bits. Conflicting devices are
given the next available secondary address. For example, if the GPIB-VXI and its MessageBased servants have logical addresses 0, 24, 27, and 33, the GPIB-VXI assigns secondary
addresses as shown in Table 2-8.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-15 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 36

Configuration and Startup Procedures Chapter 2
Table 2-8. Example Secondary Address Assignment
Upper Secondary
Logical Address Logical Address 5 Bits Address
3 LSB Group Decimal Binary Decimal
(Order of
Assignment)
000 0 00000000h 00000h 0
24 00011000h 00011h 3
001 33 00100001h 00100h 4
010 none
011 27 00011011h 00011h 5
100 none
101 none
110 none
111 none
In the example shown in Table 2-8, the device at logical address 27 was assigned secondary
address 5 because addresses 3 and 4 were previously assigned. Spacing the GPIB-VXI's
Message-Based servants at intervals of eight logical address locations is recommended in order
to avoid situations in which removing or adding one device changes the secondary address of
another device.
The self-assigned default secondary address of the GPIB-VXI can be overridden by the
nonvolatile memory configuration as described in the Change Configuration Information section
of Chapter 4, Nonvolatile Configuration.
System Configuration Table
During the execution of the RM and general configuration operations, the GPIB-VXI builds up a
table of system configuration information. Each device has an entry in the table containing the device's logical
address, its commander's logical address, its secondary address, slot number, device class, manufacturer ID number, model code, memory space requirement, memory base address, and memory size. The GPIB-VXI retains this table after the RM and general configuration operations are complete. The information in the table is accessible through the GPIB-VXI local command set. T
he secondary address entry is only meaningful for immediate
Message-Based servants of the GPIB-VXI.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 2-16 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 37

Chapter 2 Configuration and Startup Procedures
Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager Configuration
You can configure the GPIB-VXI for Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager operation by disabling the
VXIbus Slot 0 functions, setting the model code 8FFh, and setting the logical address to 0, as
shown in Table 2-9.
Table 2-9. Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation Switch and Jumper Settings
Jumper/Switch Position Function
CLK10 jumpers See Figure 2-9. CLK10 receiving from backplane is
enabled.
If S24 is OFF, the GPIB-VXI will source
CLK10 at the front panel BNC.
Switch S1 OFF SYSCLK sourcing is disabled.
Switch S2 OFF MODID pull-down resistor is disabled.
Switch S5 OFF Bus arbiter is disabled.
Switch S10 OFF Model code is 8FFh.
Logical Address All ON Logical address is 0.
Switches 8 through 1
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
Figure 2-9. CLK10 Jumper Settings for Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation
Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation
The startup sequence for a GPIB-VXI configured for Non-Slot 0 Resource Manager operation is
identical to the Slot 0 Resource Manager operation, except that the GPIB-VXI controls the Slot 0
resources remotely.
A VXIbus Slot 0 device must be in the system. It must be either a Register-Based device that
implements the MODID Register, or a Message-Based device that supports the Word Serial
commands Read MODID, Set Lower MODID, and Set Upper MODID. VXIbus Specification
Revision 1.2 Word Serial Slot 0 devices are not supported.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-17 GPIB-VXI User Manual
CLK10 receiving from backplane is enabled
Page 38

Configuration and Startup Procedures Chapter 2
Non-Slot 0 Message-Based Device Configuration
You can configure the GPIB-VXI for Non-Slot 0 Message-Based device operation by disabling
the VXIbus Slot 0 functions, setting the model code to 8FFh, and setting the logical address to a
non-zero value, as shown in Table 2-10.
Table 2-10. Non-Slot 0 Message-Based Device Operation Switch and Jumper Settings
Jumper/Switch Position Function
CLK10 jumpers See Figure 2-10. CLK10 receiving from backplane is
enabled.
If S24 is OFF, the GPIB-VXI will source
CLK10 at the front panel BNC.
Switch S1 OFF SYSCLK sourcing is disabled.
Switch S2 OFF MODID pull-down resistor is disabled.
Switch S5 OFF Bus arbiter is disabled.
Switch S10 OFF Model code is 8FFh.
Logical Address At least one is Logical address is not equal to 0.
Switches 8 through 1 OFF
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
Figure 2-10. CLK10 Jumper Settings for Non-Slot 0 Message-Based Device Operation
Non-Slot 0 Message-Based Device Operation
Setting the logical address to FFh causes the GPIB-VXI to participate in dynamic configuration.
At startup, a GPIB-VXI configured as a Non-Slot 0 Message-Based device performs its selftests, then waits until it receives its Device Grant and Begin Normal Operation Word Serial
commands. When it responds to the Begin Normal Operation command, the GPIB-VXI enters
its normal mode of operation.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 2-18 © National Instruments Corporation
CLK10 receiving from backplane is enabled
Page 39

Chapter 2 Configuration and Startup Procedures
Front Panel LED Indications for Message-Based Device Operation
The GPIB-VXI indicates the progress of its self-test with the FAILED, TEST, and ONLINE
LEDs. The LED indications are shown in Table 2-11. A successful system startup sequences
through the first five states. The probable cause of failure shown for each combination of LEDs
is valid if the FAILED LED is lit five seconds following system startup. The LED indications
are identical for Non-Slot 0 Message-Based device and Slot 0 Message-Based device operation.
Table 2-11. Front Panel LED Indications for Message-Based Device Operation
Sequence FAILED TEST ONLINE State Point of Failure
1 OFF OFF OFF No power
2 ON OFF OFF In self-initialization Failed before self-test
3 ON ON OFF In self-test Failed self-test
4 OFF ON ON Waiting for BNO
5 OFF OFF ON Online
ON OFF ON Failed Failed while online
Slot 0 Message-Based Device Configuration
The GPIB-VXI is configured for Slot 0 Message-Based device operation by enabling the
VXIbus Slot 0 functions, setting the model code to 0FFh, and setting the logical address to a
non-zero value, as shown in Table 2-12.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-19 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 40

Configuration and Startup Procedures Chapter 2
Table 2-12. Slot 0 Message-Based Device Operation Switch and Jumper Settings
Jumper/Switch Position Function
CLK10 jumpers See Figure 2-11 a. CLK10 sourcing for backplane is enabled
from onboard clock source. If S24 is OFF,
the GPIB-VXI will also source CLK10 at
the front panel BNC.
or
See Figure 2-11 b. CLK10 sourcing is enabled from external
clock source via front panel BNC
(S24 must be ON).
Switch S1 ON SYSCLK sourcing is enabled.
Switch S2 ON MODID pull-up resistor is enabled.
Switch S5 ON Bus arbiter is enabled.
Switch S10 ON Model code is 0FFh.
Logical Address At least one is Logical address is not equal to 0.
Switches 8 through 1 OFF
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• •
Figure 2-11. CLK10 Jumper Settings for Slot 0 Resource Manager Operation
GPIB-VXI User Manual 2-20 © National Instruments Corporation
a. CLK10 sourcing for backplane is enabled
from on-board clock source
• •
b. CLK10 sourcing is enabled from
• •
• •
external clock source
• •
• •
• •
Page 41

Chapter 2 Configuration and Startup Procedures
Slot 0 Message-Based Device Operation
At startup, a GPIB-VXI configured as a Slot 0 Message-Based device performs its self-tests,
then waits until it receives its Device Grant (if any) and Begin Normal Operation Word Serial
commands. When the GPIB-VXI responds to the Begin Normal Operation command, it enters
the normal mode of operation.
After the GPIB-VXI Passed bit is set, the RM can manipulate or read the MODID lines by
sending the Word Serial queries Read MODID, Set Lower MODID, or Set Upper MODID to the
GPIB-VXI.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-21 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 42

Page 43

Chapter 3
Local Command Set
This chapter contains descriptions of the GPIB-VXI local command set. The descriptions of the
commands and queries include syntax, format and error handling information, as well as
examples of the use of the commands and queries. The local command set supports the
following types of operations:
• System configuration and control
– Help
– General configuration
– Resource Manager (RM) information extraction
– Dynamic system configuration and reconfiguration
– VXI-defined Common ASCII System Commands
– GPIB address configuration
– VXIbus interrupt handler configuration
– IEEE-488.2 common commands
• Instrument development and test
– VXIbus access
– TTL Trigger access
– Word Serial communication
• Code Instrument (CI) use and development
– CI configuration
The GPIB-VXI command set consists of commands and queries. Commands cause the GPIBVXI to take some action. A query may also cause the GPIB-VXI to take some action, but it also
returns a response containing data or other information.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-1 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 44

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Command Set Access
The local commands can be executed from the following ports:
• RS-232
• GPIB
• VXI Word Serial communication
The three ports are active when the GPIB-VXI is in the Normal Operation sub-state and operate
independently of one another. The GPIB-VXI returns query responses only to the port
originating the query. The GPIB-VXI also maintains a separate status state for each port. You
can use local commands to disable and re-enable each port's access to the local command set.
The RS-232 port prompts you to enter a local command with the
GPIB-VXI> prompt.
Command Syntax
The local command set parser is syntactically compatible with the IEEE-488.2 standard. It will
accept numeric parameters in the 488.2 binary, octal, decimal, or hexadecimal formats. 488.2
binary parameters are prefixed with #b. Octal parameters are prefixed with #q, and hexadecimal
parameters are prefixed with #h. The most common numeric parameter types are listed in Table
3-1. The ranges given in Table 3-1 apply unless otherwise specified.
Table 3-1. Valid Ranges for Common Numeric Command Parameters
Parameter 488.2 Decimal 488.2 Hexadecimal
<logical address> 0 to 254 #h0 to #hFE
<secondary address> 0 to 30 #h0 to #h1E
<handler> 1 to 3 #h1 to #h3
<level> 0 to 7 #h0 to #h7
<A16 address> 0 to 65535 #h0 to #hFFFF
<A24 address> 2097152 to 14680062 #h200000 to #hDFFFFE
<word value> 0 to 65535 #h0 to #hFFFF
<byte value> 0 to 255 #h0 to #hFF
<boolean> 0 or 1 #h0 or #h1
The logical value of a <boolean> parameter is FALSE for the numeric value 0, and TRUE for
the numeric value 1.
The first parameter is delimited from the command name by a space ( ). Additional parameters
are delimited from one another by a comma (,). The command names are not case-sensitive.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 45

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
In the command descriptions, parameters are enclosed in angle brackets (< >), and optional
parameters are also enclosed in square brackets ([ ]). Do not enter the brackets as part of the
command.
Multiple commands may be concatenated in a single command line if they are separated with
semicolons (for example, OBRAM?; DPRAM?<CR>).
Command Line Termination
The serial port command line termination is a carriage return, shown in the subsequent function
descriptions as <CR> (ASCII 0Dh). If the command contains a trailing linefeed, shown in the
subsequent function descriptions as <LF> (ASCII 0Ah), it is ignored. The GPIB termination is
EOI. Commands issued to the GPIB-VXI via VXI Word Serial Protocol are terminated by
setting the END bit in the last Byte Available command. Responses are terminated by setting the
END bit in response to the last Byte Request query.
Command and Query Responses
The local commands and queries have two response formats–program mode and console mode.
Program mode responses have a terse data-only format that is intended for a control program to
read and parse. Console responses are returned in the form of readable sentences, which are
better suited for interactive command entry.
You can enable or disable each mode independently, except that one response mode must be
enabled at all times. If both modes are simultaneously enabled, the program response is returned
first, followed by the console response.
The response mode configuration is independent for each command source. The default
(startup/reset) response mode configurations are given in Table 3-2.
Table 3-2. Default Response Mode Configurations
Port Response Mode
RS-232 Console mode enabled, program mode disabled
GPIB Program mode enabled, console mode disabled
VXI Word Serial Program mode enabled, console mode disabled
© National Instruments Corporation 3-3 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 46

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Command Response Format
Commands do not have program mode responses. They do not return a response to a port
configured for console mode response only, unless the GPIB-VXI detects an error condition.
Console mode command responses are self-explanatory, and are not described in this manual.
Query Response Format
Queries have both program and console mode responses. Program mode query responses are
fixed-field formatted, with commas delimiting the fields. For example, the list of logical
addresses returned by the Laddrs? query is returned as groups of three characters (to allow the
field to accommodate the valid range of 0 to 254) separated by commas. The values are rightjustified and padded with the ASCII space character ( ) (20h). For example, the logical address
45 would be returned as ( )45. Unless otherwise noted, all returned values are decimal.
Console mode query responses are self-explanatory, and are not described in this manual.
The query response line termination sequence, shown in the query descriptions as <CRLF>,
indicates an ASCII 0Dh followed by 0Ah.
Error Reporting
Command syntax and execution errors are reported to the port where the command originated.
If the program response mode is enabled, the GPIB-VXI returns an error message in the
following format:
$ <error code><CRLF>
The distinguishing characteristic of a program mode error message is the leading dollar sign
character ($). A list of error code descriptions is given in Appendix B, Error Codes.
If the console response mode is enabled, the GPIB-VXI returns an error message in the
following format:
<error description><CRLF>
If both response modes are enabled, the program mode error message is returned first, followed
by the console mode message.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-4 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 47

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
The Help Query
The Help? query is a quick online reference to the syntax and functionality of the GPIB-VXI
local command set.
Help?
Purpose: List syntax and descriptions of local command set.
Query
Syntax: Help? [<type>[,<type>,....]]
Help [<type>[,<type>,....]]
<type> is the category of command information requested, as follows:
he Help ci Code Instruments
al All sa GPIB secondary address
gc General configuration ih Interrupt handler configuration
dc Dynamic configuration ba VXIbus access
rc Dynamic reconfiguration ws Word Serial communication
rm Resource Manager tr TTL Trigger access
cc Common commands
The default type is All.
Response: The local command set is displayed in the following format:
Command/Query Format Description<CRLF>
<Command Syntax> <Command description><CRLF>
<Command Syntax> <Command description><CRLF>
<Command Syntax> <Command description><CRLF>
• •
• •
• •
Example: List syntax and descriptions of general configuration and secondary address
Help? gc,sa
or
GPIB-VXI Local Command Set<CRLF>
commands.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-5 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 48

Local Command Set Chapter 3
General Configuration Commands and Queries
The general configuration commands and queries are described on the following pages.
• ConsoleEna
• ConsMode
• DPRAM?
• NVconf?
• OBRAM?
• ProgMode
• WordSerEna
The ConsMode and ProgMode commands enable and disable the console and program
response modes for the port originating the command.
The NVconf? query returns the contents of the onboard nonvolatile memory.
The ConsoleEna and WordSerEna commands control access to the local command set from
the RS-232 and VXI Word Serial ports.
The OBRAM? query can be used to determine the amount of GPIB-VXI installed RAM, and the
DPRAM? query returns the amount of the installed RAM that is dual-ported to VME A24 space.
ConsoleEna
Purpose: Enable or disable the RS-232 port as the console. When the RS-232 port is
disabled as the console, a CI can take control of the serial port.
Command
Syntax: ConsoleEna <boolean>
Action: If <boolean> is TRUE, ConsoleEna sets the RS-232 port to be a local
command set input.
If <boolean> is FALSE, ConsoleEna disables the RS-232 port connection to
the local command set. Notice that once the console has been disabled, it must be
re-enabled from another command source (such as the GPIB port).
Examples: Disable console.
ConsoleEna 0
Enable console.
ConsoleEna 1
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-6 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 49

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
ConsMode
Purpose: Enable or disable the console data mode.
Command
Syntax: ConsMode <boolean>
Action: If <boolean> is TRUE, ConsMode enables console format responses for the
command source issuing the command.
If <boolean> is FALSE, ConsMode disables console format responses for the
command source issuing the command.
The console response mode applies only to the response path connected to the
ConsMode command source. For example, disabling the console response mode
from the GPIB port does not affect the response mode on the serial port.
Example: Disable console format responses.
ConsMode 0
Enable console format responses.
ConsMode 1
DPram?
Purpose: Get the A24 starting address and the size of dual-ported RAM.
Query
Syntax: DPram?
Response: Program response:
<A24 starting address>, <dual-ported RAM size><CRLF>
Console response:
This GPIB-VXI has <dual-ported RAM size>K bytes Dual-Ported to A24
Address <A24 hex starting address><CRLF>
where <A24 starting address> is the dual-ported RAM base address in
decimal integer format.
<dual-ported RAM size> is in K bytes.
<A24 hex starting address> is in C language hexadecimal format.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-7 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 50

Local Command Set Chapter 3
NVconf?
Purpose: Display the contents of the nonvolatile (NV) configuration parameter memory.
Query
Syntax: NVconf?
Response: The contents of the onboard EEPROM are displayed in the following format:
=============== Nonvolatile Configuration Information ===============
Serial Number : 0x68
Region 1 Size : 0x70000 Number Procs : 32
Number Exchgs : 32 Number Msgs : 384
VXI Interrupt Level to Handler Logical Address (0xFF = free to assign):
1:0xFF 2:0xFF 3:0xFF 4:0xFF 5:0xFF 6:0xFF 7:0xFF
DC Starting LA : 0x01 For FAILED DEV : DO set Reset bit
A24 Assign Base: 0x200000 A32 Assign Base: 0x20000000
OverRide Srvnt : NO Servant Area : N/A
OverRide Prim : NO GPIB Primary : N/A
GPIB Sec Addr : Default GPIB Flags : DMA 7210
CI Block Base : 0x80000 CI Num Blocks : 128
------ Resident Code Instrument Locations -----# 0: 0 # 1: 0 # 2: 0
# 3: 0 # 4: 0 # 5: 0
# 6: 0 # 7: 0 # 8: 0
# 9: 0 # a: 0 # b: 0
------ CI Nonvolatile User Configuration Variables -----# 0: 0 # 1: 0 # 2: 0 # 3: 0
# 4: 0 # 5: 0 # 6: 0 # 7: 0
# 8: 0 # 9: 0 #10: 0 #11: 0
#12: 0 #13: 0 #14: 0 #15: 0
#16: 0 #17: 0 #18: 0 #19: 0
#20: 0 #21: 0 #22: 0 #23: 0
#24: 0 #25: 0 #26: 0 #27: 0
#28: 0 #29: 0 #30: 0 #31: 0
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-8 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 51

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
OBram?
Purpose: Get the amount of RAM installed onboard the GPIB-VXI.
Query
Syntax: OBram?
Response: Program response:
<memsize><CRLF>
where <memsize> is the amount of installed RAM, in K.
Console response:
This GPIB-VXI has <expression> of RAM installed onboard.<CRLF>
where <expression> is the amount of installed RAM.
ProgMode
Purpose: Enable or disable the program data mode.
Command
Syntax: ProgMode <boolean>
Action: If <boolean> is TRUE, ProgMode enables program format responses for the
command source issuing the command.
If <boolean> is FALSE, ProgMode disables program format responses for the
command source issuing the command.
The program response mode applies only to the response path connected to the
ProgMode command source. For example, disabling the program response
mode from the GPIB port does not affect the response mode on the serial port.
Examples: Disable program format responses.
ProgMode 0
Enable program format responses.
ProgMode 1
© National Instruments Corporation 3-9 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 52

Local Command Set Chapter 3
WordSerEna
Purpose: Assign control of the GPIB-VXI physical Word Serial registers to an onboard
logical address (GPIB-VXI command interpreter or code instrument).
Command
Syntax: WordSerEna <logical address>
Action: Control of the physical Word Serial registers is passed to <logical
address>.
The default control of the physical registers is given to the GPIB-VXI local
command set parser.
Examples: Pass control of the physical registers to code instrument at logical address 5.
WordSerEna 5
Pass control of the physical registers back to GPIB-VXI local command parser at
logical address 0.
WordSerEna 0
RM Information Queries
The RM information queries are described on the following pages.
• A24MemMap?
• A32MemMap?
• Cmdr?
• CmdrTable?
• Laddrs?
• NumLaddrs?
• RmEntry?
• Srvnts?
• StatusState?
The Numladdrs? query is used to find out how many devices there are in the system. The
number of devices could then be used by a control program to determine the allocation size for
an array that is to hold the logical addresses of each device.
The Laddrs? query returns a list of logical addresses for devices in the system.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-10 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 53

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
The RmEntry?, Srvnts?, Cmdr?, and StatusState? queries return RM information for a
particular device.
The CmdrTable? query returns the system hierarchy table.
The A24MemMap? and A32MemMap? queries return the A24 and A32 memory configuration
lists.
The system information commands (NumLaddrs?, Laddrs?, CmdrTable?, A24MemMap?,
and A32MemMap?) return information about the known system. If the GPIB-VXI is the system
RM, it can access information about the entire system. If it is not the RM, it has information
only about itself and its immediate servants.
A24MemMap?
Purpose: Get the A24 address space allocation for the system.
Query
Syntax: A24MemMap?
Response: Program response:
<la1>,<A24 memory base>,<A24 memory size><CRLF>
<la2>,<A24 memory base>,<A24 memory size><CRLF>
•
•
<la
where <la1> through <laN> are logical addresses containing A24 address
Console response:
A24 Memory Map is as follows:<CRLF>
Logical Address <la1> has <A24 memory size>K
(<A24 memory size> bytes) at A24 Address<A24 memory base><CRLF>
•
•
Logical Address <la
(<A24 memory size> bytes) at A24 Address<A24 memory base><CRLF>
Example: Get A24 address map for the system.
A24MemMap?
N
>,<A24 memory base>,<A24 memory size><CRLF>
space.
N
> has <A24 memory size>K
© National Instruments Corporation 3-11 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 54

Local Command Set Chapter 3
A32MemMap?
Purpose: Get the A32 address space allocation for the system.
Query
Syntax: A32MemMap?
Response: Program response:
<la1>,<A32 memory base>,<A32 memory size><CRLF>
<la2>,<A32 memory base>,<A32 memory size><CRLF>
•
•
<la
where <la1> through <la
Console response:
A32 Memory Map is as follows:<CRLF>
Logical Address <la1> has <A32 memory size>K
(<A32 memory size> bytes) at A32 Address<A32 memory base><CRLF>
•
•
Logical Address <la
(<A32 memory size> bytes) at A32 Address<A32 memory base><CRLF>
Example: Get A32 address map for the system.
A32MemMap?
N
>,<A32 memory base>,<A32 memory size><CRLF>
N
> are logical addresses containing A32 address
space.
N
> has <A32 memory size>K
Cmdr?
Purpose: Get the logical address of a device's commander.
Query
Syntax: Cmdr? <logical address>
where <logical address> is the logical address of the device.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-12 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 55

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
Response: Program response:
<commander's logical address><CRLF>
Console response:
The Commander of Logical Address <logical address> is Logical
Address <commander's logical address><CRLF>
Example: Get the commander's logical address for logical address 15.
Cmdr? 15
CmdrTable?
Purpose: Get the known system hierarchy table.
Query
Syntax: CmdrTable?
Response: Program response:
<cla0>,<cla1>,<cla2>,<cla3>,<cla4>, . . .,<cla254><CRLF>
where <claN> is either the commander's logical address for logical address N, or
0 for top-level commanders and unused logical addresses. Notice that no value is
returned for logical address 255.
Console response:
Logical address <la1> has servants: <sa1,1>,...,<sa1,M> <comment><CRLF>
Logical address <la2> has servants: <sa2,1> ,...,<sa2,M> <comment><CRLF>
•
•
Logical address <laN> has servants: <saN,1> ,...,<saN,M> <comment><CRLF>
where <la
<saX,1> through <sa1,M>.
The <comment> field indicates any relevant information about the status and/or
Known Hierarchy is as follows:<CRLF>
X
> is a valid logical address with servant addresses
capabilities of the device at logical address <laX>.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-13 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 56

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Laddrs?
Purpose: Get a list of the known logical addresses.
Query
Syntax: Laddrs?
Response: Program response:
<la1>,<la2>,..., <la
where <la1> through <laN> are the known logical addresses.
Console response:
Known logical addresses are <la1>,<la2>,..., <la
CI logical addresses are terminated with an asterisk (*) in the console mode
response.
N
><CRLF>
N
><CRLF>
NumLaddrs?
Purpose: Get the number of known logical addresses.
Query
Syntax: NumLaddrs?
Response: Program response:
<num las><CRLF>
where <num las> is the number of known logical addresses.
Console response:
There are <num las> known Logical Addresses<CRLF>
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-14 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 57

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
RmEntry?
Purpose: Return RM information about a device or all devices. RmEntry? does not return
the servant list.
Query
Syntax: RmEntry? [<logical address>]
(If <logical address> is omitted, RmEntry? returns the RM information
for all devices.)
Response: Program response:
<la>,<cla>,<sa>,<slot>,<devclass>,<subclass>,<manID>,<modelcode>,
<memspace>,<membase>,<memsize>,<state>,<line status><CRLF>
Console response:
Resource manager entry for logical address <logical address>:
<CRLF>
<CRLF>
Commander's Logical Address :<cla><CRLF>
Secondary Address :<sa><CRLF>
Slot :<slot><CRLF>
Device class :<device class> (class)<CRLF>
Extended Sub Class :<subclass><CRLF>
Manufacturer's ID :<manID> (manufacturer's name)<CRLF>
Model code :<modelcode><CRLF>
Memory space :<memspace> (memory space)<CRLF>
Memory Base :<membase><CRLF>
Memory Size :<memsize>K (<memsize> bytes)<CRLF>
Status State :<state> (state)<CRLF>
Forced Offline? :<line status> (yes/no)<CRLF>
The mnemonics have the following meanings:
la device's logical address
cla
commander's logical address
sa device's secondary address
(255 if not assigned secondary address)
slot slot number
(255 if unknown, such as if the device does not have MODID
capability)
© National Instruments Corporation 3-15 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 58

Local Command Set Chapter 3
devclass device class; the following values may be used:
0 = Memory
1 = Extended
2 = Message-Based
3 = Register-Based
subclass extended device subclass
manID manufacturer's ID number
modelcode device's manufacturer-assigned model code
memspace memory space requirement:
0 = A16 only
1 = A16/A24
2 = A16/A32
membase memory base address
memsize memory size in bytes
state status state:
0 = Failed and not Ready
1 = Passed and not Ready
2 = Failed and Ready
3 = Passed and Ready
line status online/offline status:
0 = online
1 = forced offline
The program mode response format is the same for all devices. However, the console mode
response returns only the lines that are relevant. For example, memory base address and
memory size lines are not returned for A16-only memory space devices.
Example: Get RM information for a device at logical address 78.
RmEntry? 78
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-16 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 59

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
Srvnts?
Purpose: Get a list of a device's servants.
Query
Syntax: Srvnts? <logical address>
<logical address> is the device's logical address.
Response: Program response:
<sla1>,<sla2>,...,<sla
where <sla1> through <slaN> are the servant device logical addresses.
Console response:
Logical Address <logical address> has servants:
<sla1>, <sla2>,..., <sla
if the device has servants, or
Logical Address <logical address> has servants:
none <comment><CRLF>
if the device has no servants.
The <comment> field indicates any relevant information about the status and/or
capabilities of the device.
Example: Get a list of logical address 15's servants.
Srvnts? 15
N
><CRLF>
N
> <comment><CRLF>
StatusState?
Purpose: Get a device's current self-test status.
Query
Syntax: StatusState? <logical address>
<logical address> is the logical address for the device.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-17 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 60

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Response: Program response:
<val><CRLF>
The value of <val> is equivalent to the value of the field in the device's status
register containing the Ready and Passed bits. <val> can be interpreted as
follows:
0 The device is Failed and not Ready.
1 The device is Passed and not Ready.
2 The device is Failed and Ready.
3 The device is Passed and Ready.
Console response:
Device at logical address <logical address> is FAILED and not Ready<CRLF>
or
Device at logical address <logical address> is PASSED and not Ready<CRLF>
or
Device at logical address <logical address> is FAILED and Ready<CRLF>
or
Device at logical address <logical address> is PASSED and Ready<CRLF>
Example: Get logical address 48's self-test status.
StatusState? 48
Dynamic Configuration Commands and Queries
The dynamic configuration (DC) commands and queries are described on the following pages.
• DCBNOSend
• DCGrantDev
• DCSystem?
The DC commands are used to configure the VXI system when all of these conditions are
present:
• The GPIB-VXI is the RM.
• At least one DC device is present in the system.
• The system is still in the startup Configure sub-state.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-18 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 61

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
The DCSystem? query response indicates whether the system contains a DC device. If the
system is found to be a DC system, the DCGrantDev command is used to configure the
commander/servant hierarchy. The DCBNOSend command is used to end the DC phase and to
cause the system to enter normal operation.
DCBNOSend
Purpose: Cause a DC system to exit the Configure sub-state and enter the Normal
Operation sub-state.
Command
Syntax: DCBNOSend
Action: Send the Begin Normal Operation command to all top-level commanders.
DCGrantDev
Purpose: Grant a device to a Message-Based commander in a DC system. DCGrantDev
can be used only to configure the initial commander/servant hierarchy of a DC
system, and before DCBNOSend is used to cause the system to enter the Normal
Operation sub-state.
Command
Syntax: DCGrantDev <commander's logical address>,
<servant's logical address>
Action: DCGrantDev sends the Device Grant command to the commander at
<commander's logical address>, granting it the device at
<servant's logical address>.
Example: Grant servant at logical address 7 to commander at logical address 5.
DCGrantDev 5,7
DCSystem?
Purpose: Determine if the system is a DC system. A system is DC if it has at least one DC
device.
Query
Syntax: DCSystem?
© National Instruments Corporation 3-19 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 62

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Response: Program response:
1 <CRLF>
if it is a DC system, or
0 <CRLF>
if it is not a DC system, or if it is no longer dynamically configurable because the
Begin Normal Operation command has already been sent to the top-level
commanders through the DCBNOSend local command.
Console response:
This IS a Dynamic Configured system.<CRLF>
if it is a DC system, or
This is NOT a Dynamic Configured system.<CRLF>
if it is not a DC system.
Dynamic Reconfiguration Queries
The dynamic reconfiguration queries are described on the following pages.
• Broadcast?
• GrantDev?
• RelSrvnt?
The dynamic reconfiguration commands are used to reconfigure the GPIB-VXI's servant subtree
after the system has entered the Normal Operation sub-state. If the GPIB-VXI is RM, these
commands can be used to reconfigure the entire system.
The Broadcast? query can be used to make the system or subtree enter the Configure substate by broadcasting the End Normal Operation Word Serial query, or the Clear Word Serial
command followed by the Abort Normal Operation Word Serial query.
The RelSrvnt? and GrantDev? queries can then be used to restructure the
commander/servant hierarchy. Dynamic reconfiguration could be directly performed by using
the WSCmd and WSCmd? local commands, but the GPIB-VXI's RM table would not be updated.
By using the RelSrvnt? and GrantDev? queries to reconfigure the system, you ensure that
the GPIB-VXI's system hierarchy and secondary address link records do not become corrupted.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-20 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 63

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
The system or subtree can be returned to the Normal Operation sub-state by using the
Broadcast? query to broadcast the Identify Commander and Begin Normal Operation Word
Serial commands.
Broadcast?
Purpose: Broadcast dynamic reconfiguration initialization or termination Word Serial
commands to the GPIB-VXI's Message-Based servants or to all top-level
commanders in the system.
Query
Syntax: Broadcast? <boolean>,<ws cmd>
If <boolean> is 1, the GPIB-VXI broadcasts <ws cmd> to all top-level
commanders. If <boolean> is 0, it broadcasts <ws cmd> to its Message-Based
servants. Notice that the GPIB-VXI should only broadcast to top-level
commanders when it is RM.
<ws cmd> is a mnemonic as follows:
The Broadcast? query can fail due to inability to complete a Word Serial
Response: Program response:
<la>,<cmd val>,<ws response>,<ws error code>
if the command failed.
Console response:
name>.
<ws cmd> Word Serial Command Name Type
ANO Abort Normal Operation Query
BNO Begin Normal Operation Query
CLR Clear Command
ENO End Normal Operation Query
IDN Identify Commander Command
operation, or because an invalid code was returned from a device in response to
ANO or ENO.
<CRLF>
if the command was successful, or
Done broadcasting Word Serial command: <Word Serial command
© National Instruments Corporation 3-21 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 64

Local Command Set Chapter 3
if the command was successful, or
Logical address <la> returned <ws response> from ENO (Unable to
halt)
or
Logical address <la> returned <ws response> from ANO (Invalid
response)
Error sending logical address <la> word serial command <hex cmd
or
val><CRLF><space><space><ws error><CRLF>
if the command failed.
<la> is the logical address of the device to which the broadcast failed.
<cmd val> is the value of the Word Serial command, in decimal. <hex cmd
val> is the value in hexadecimal.
For Word Serial queries, <ws response> is the Word Serial response of the
device at logical address <la>. For Word Serial commands <ws response>
is 0.
<Word Serial command name> is the name of the command name as
shown in the previous table.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-22 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 65

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
<ws error code> is a decimal value that can be interpreted by converting it
to a binary bit pattern. A value of 1 in the bit positions shown in the following
table indicates that an error occurred during the attempt to broadcast the Word
Serial command:
Bit Word Serial Error
0 Word Serial command completed successfully
(no Word Serial error)
1 Timeout waiting to send Word Serial command
to device at <la>
2 Timeout waiting for Word Serial response from
device at <la>
3 Device at <la> did not recognize the command
6 Multiple query error
10 Read Protocol error not supported
13 Read Ready (RR) violation
14 Write Ready (WR) violation
None of the other bits has significance in this context.
<ws error> is a string explaining the Word Serial error as shown in the
previous table.
Example: Broadcast the Identify Commander Word Serial command to all top-level
commanders.
broadcast? 1,IDN
GrantDev?
Purpose: Grant a servant to a commander.
Query
Syntax: GrantDev? <commander's logical address>, <servant's
logical address>
Action: Grants the device at <servant's logical address> to device at
<commander's logical address>.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-23 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 66

Local Command Set Chapter 3
The GPIB-VXI must own the device at <servant's logical address>.
The GPIB-VXI can get ownership of any device with the RelSrvnt? command.
Notice that before the GrantDev? query is used, the Word Serial End Normal
Operation query, or a Clear command followed by the Abort Normal Operation
query should have been broadcast with the Broadcast? query.
Response: Program response:
0<CRLF>
indicates that the command was successful.
Console response:
Logical Address <commander's logical address> granted device at
Logical Address <servant's logical address>.
Example: Grant device 16 to commander at logical address 8.
Grantdev? 8,16
RelSrvnt?
Purpose: Recover a servant from a commander.
Query
Syntax: RelSrvnt? <commander's logical address>, <servant's
logical address>
Action: Commands device at <commander's logical address> to release
ownership of the device at <servant's logical address>. The GPIBVXI assumes ownership of the device.
Response: Program response:
254<CRLF>
if the commander released the servant. Any other response indicates that an error
occurred.
Console response:
Logical Address <commander's logical address> released device at
Logical Address <servant's logical address>.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-24 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 67

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
Example: Recover servant at logical address 16 from commander at logical address 8.
Relsrvnt? 8,16
VXI-Defined Common ASCII System Commands
The VXI-defined Common ASCII System Commands and Queries are described on the
following pages.
• DCON?
• DINF?
• DLAD?
• DNUM?
• DRES?
• RREG?
• WREG
These commands and queries can be used to retrieve device information/configuration, perform
a soft reset, and peek/poke a device's registers.
The DNUM? query is used to find out how many devices are in the system. The DLAD? query
returns a list of logical addresses for devices in the system.
The DINF? query returns static information about a device. The DCON? query returns
configuration information about a device.
The DRES? query is used to perform a soft-reset sequence on a device.
The RREG? query and WREG command are used to peek and poke registers on a VXI device.
DCON?
Purpose: Return system configuration information about a device or all devices.
Query
Syntax: DCON? [<logical address>]
(If <logical address> is omitted, DCON? returns the configuration
information for all devices.)
© National Instruments Corporation 3-25 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 68

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Response: Program response:
<la1>,<cla>,<IHANS>,<INTS>,<status>,<sstate>,<com><CRLF>
Console response:
Device configuration at Logical Address <la>:<CRLF>
<CRLF>
Commander's Logical Address :<cla><CRLF>
Interrupt Handlers :<IHANS><CRLF>
Interrupters :<INTS><CRLF>
Passed/Failed/Ready :<status><CRLF>
Device Substate :<sstate><CRLF>
Manufacturer Specific Comment :<com><CRLF>
The mnemonics have the following meanings:
la device's logical address
cla
commander's logical address
IHANS
Interrupt handler levels used by this device where IHANS is
a 7-digit binary representing the seven VXI interrupt levels
and a one in each position, meaning Interrupt Handler
present
INTS
Interrupter levels used by this device where INTS is a 7-digit
binary representing the seven VXI interrupt levels and a one
in each position, meaning Interrupter present.
status
the status state of the device:
PASS
FAIL
IFAIL
READY
sstate
the substate of the device
NOP
CONF
NONE
com
not used; always returns ""
Example: Get device configuration information for logical address 6.
DCON? 6
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-26 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 69

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
DINF?
Purpose: Return static system information about a device.
Query
Syntax: DINF? [<logical address>]
(If <logical address> is omitted, DINF? returns static information for all
devices.)
Response: Program response:
<la1>,<manID>,<modelcode>,<devclass>,<memspace>,<membase>,
<memsize>,<slot>,<slot0>,<ext>,<attr>,<com><CRLF>
Console response:
Device configuration at Logical Address <la>:<CRLF>
<CRLF>
Manufacturer ID Number :<manid> (manufacturer name)<CRLF>
Model Code :<modelcode><CRLF>
Device Class :<devclass><CRLF>
A16/A24/A32 Memory Space :<memspace><CRLF>
A16/A24/A32 Memory Base :<membase><CRLF>
A16/A24/A32 Memory Size :<memsize><CRLF>
Slot :<slot><CRLF>
Slot 0 Logical Address :<slot0><CRLF>
Extended Subclass :<ext><CRLF>
Attribute :<attr><CRLF>
Manufacturer Specific Comment :<com><CRLF>
The mnemonics have the following meanings:
la device's logical address
manid
devclass
MSG = Message-Based device
EXT = Extended-Class device
MEM = Memory-Based device
memspace
A16/A24
A16/A32
membase
manufacturer's ID number
device class; the following values may be used:
REG = Register-Based device
memory space requirement
A16
memory-based address for A16, A24, A32
© National Instruments Corporation 3-27 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 70

Local Command Set Chapter 3
"HHHH, HHHHHH, HHHHHHHH"
memsize
slot
slot0
ext
attr
com
memory sizes for A16, A24, A32
"HHHH, HHHHHH, HHHHHHHH"
slot number (-1 if unknown)
slot 0 Logical Address (-1 if unknown)
extended device's subclass
memory device's attributes
not used, always ""
DLAD?
Purpose: Get a list of the known logical addresses.
Query
Syntax: DLAD?
Response: Program response:
<la1>,<la2>,..., <la
where <la1> through <laN> are the known logical addresses.
Console response:
Known logical addresses are <la1>,<la2>,..., <la
CI logical addresses are terminated with an asterisk (*) in the console mode
response.
Example: Get a list of the known logical addresses.
DLAD?
N
><CRLF>
N
><CRLF>
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-28 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 71

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
DNUM?
Purpose: Get the number of the known logical addresses.
Query
Syntax: DNUM?
Response: Program response:
<num las><CRLF>
where <num las> is the number of known logical addresses.
Console response:
There are <num las> known Logical Addresses.<CRLF>
Example: Get the number of the known logical addresses.
DNUM?
DRES?
Purpose: Perform a soft-reset sequence on a device.
Query
Syntax: DRES? <logical address> [, <sysfail flag>]
Note: If the device stays failed for five seconds after the soft-reset sequence,
<sysfail flag> determines whether or not the device is kept
sysfail-inhibited.
Response: Program response:
<status><CRLF>
Console response:
Logical Address <logical address> is <status>. SYSFAIL Inhibit is
<state>.<CRLF>
where <status> is one of the following:
PASS
FAIL
© National Instruments Corporation 3-29 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 72

Local Command Set Chapter 3
IFAIL
READY
and <state> is one of the following:
ON
OFF
Example: Soft-reset device at logical address 3.
DRES? 3
RREG?
Purpose: Read a 16-bit VXI register from a device.
Query
Syntax: RREG? <logical address>, <reg offset>
where <logical address> is the device to read from and <reg offset>
is the number of bytes to offset from the base of the VXI registers for that device.
Response: Program response:
<hex word value><CRLF>
Console response:
Value 0x<hex word value> (<word value>) read from Logical Address
<logical address>, Register offset 0x<reg offset><CRLF>
Example: Read Device Type register from logical address 12.
RREG? 12,2
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-30 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 73

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
WREG
Purpose: Write a 16-bit VXI register on a particular device.
Query
Syntax: WREG <logical address>, <reg offset>, <value>
where <logical address> is the device to write, <reg offset> is the
register offset to write to, and <value> is the 16-bit value to write.
Action: Write <value> to <logical address>, register offset <reg offset>.
Example: Write the Data Low register for logical address 4 with the value 65535.
WREG 4,14,65535
GPIB Address Configuration Commands and Queries
The GPIB address configuration commands are described on the following pages.
• LaSaddr
• LaSaddr?
• Primary?
• SaddrLa?
• Saddrs?
• SaDisCon
These commands and queries configure and report the relationships between VXI logical
addresses and GPIB addresses.
The GPIB-VXI's primary address can be determined by using the Primary? query from the
serial port. The relationships between GPIB secondary addresses and VXI logical addresses can
be determined by using the Saddrs? query followed by SaddrLa? queries, or by using the
RM information query Laddrs? followed by LaSaddr? queries.
Secondary address links to Message-Based servants of the GPIB-VXI can be assigned with the
LaSaddr command. The SaDisCon command deletes all secondary address links except the
link to the GPIB-VXI local commands.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-31 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 74

Local Command Set Chapter 3
LaSaddr
Purpose: Attach or detach a secondary address to a logical address.
Command
Syntax: LaSaddr <logical address>, <secondary address>
Action: If <secondary address> is not equal to 255, attach <secondary
address> to <logical address>.
If <secondary address> is equal to 255, release <secondary
address> currently attached to <logical address>.
Attaching a secondary address to a logical address that already has a secondary
address will cause the first secondary address to be replaced by the new
secondary address.
Attempting to release or change a secondary address will result in a Delete I/O
Link error if any of the following conditions is true:
• The secondary address does not exist.
• The secondary address is addressed to talk or listen.
• There is still data in the secondary address input or output queue.
Examples: Attach secondary address 6 to logical address 4.
LaSaddr 4,6
Release secondary address currently attached to logical address 8.
LaSaddr 8,255
LaSaddr?
Purpose: Get the secondary address attached to a logical address.
Query
Syntax: LaSaddr? <logical address>
Response: Program response:
<secondary address><CRLF>
where <secondary address> is the secondary address attached to the
logical address. A value of 255 indicates that no secondary address is attached to
the logical address.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-32 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 75

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
Console response:
Logical Address <logical address> is attached to GPIB
Secondary Address <secondary address><CRLF>
for logical addresses with attached secondary addresses, or
Logical Address <logical address> is NOT attached to a
GPIB Secondary Address<CRLF>
for logical addresses without attached secondary addresses.
Example: Get the secondary address attached to logical address 9.
LaSaddr? 9
Primary?
Purpose: Get a GPIB primary address.
Query
Syntax: Primary?
Response: Program response:
<primary address><CRLF>
where <primary address> is the GPIB primary address of GPIB-VXI.
Console response:
The GPIB primary address of the GPIB-VXI is <primary
address><CRLF>
SaddrLa?
Purpose: Get the logical address that a secondary address is attached to.
Query
Syntax: SaddrLa? <secondary address>
© National Instruments Corporation 3-33 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 76

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Response: Program response:
<logical address><CRLF>
where <logical address> is the logical address that the secondary address
is attached to. A value of 255 indicates that the secondary address is not attached
to a logical address.
Console response:
GPIB Secondary Address <secondary address> is attached
to Logical Address <logical address><CRLF>
for a secondary address that is attached to a logical address, or
GPIB Secondary Address <secondary address> is NOT
attached to a Logical Address<CRLF>
for a secondary address that is not attached to any logical address.
Example: Get the logical address attached to secondary address 9.
SaddrLa? 9
Saddrs?
Purpose: Get a list of used secondary addresses.
Query
Syntax: Saddrs?
Response: Program response:
<sa1>,<sa2>, . . .,<sa
where <sa1> through <saN> are the secondary addresses currently attached to
logical addresses.
Console response:
Current Secondary Addresses used:
Secondary Address <sa1>: connected to Logical Address <la1>.
Secondary Address <sa2>: connected to Logical Address <la2>.
•
•
Secondary Address <sa
<la
N
><CRLF>
N
><CRLF>
N
>: connected to Logical Address
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-34 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 77

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
SaDisCon
Purpose: Detach all secondary address links except the secondary address link to the GPIB-
VXI command set.
Command
Syntax: SaDisCon
Action: Detaches all secondary address links from servants of the GPIB-VXI.
VXIbus Interrupt Handler Configuration Commands and
Queries
The interrupt handler configuration commands and queries are described on the following pages.
• AllHandlers?
• AssgnHndlr
• HandlerLine?
• RdHandlers?
The interrupt handler commands and queries configure and report the relationships between the
GPIB-VXI interrupt handlers and VXIbus interrupt levels.
The GPIB-VXI has three programmable interrupter handlers. An application program can
confirm this with the RdHandlers? query. The AllHandlers? and HandlerLine?
queries return the current VXI interrupt level assignments for the handlers. The AssgnHndlr
command can be used to change the level assignments.
AllHandlers?
Purpose: Get the VXIbus interrupt level assigned to all GPIB-VXI interrupt handlers.
Query
Syntax: AllHandlers?
Response: Program response:
where <level1> is the interrupt level assigned to handler 1, <level2> is the
<level1>,<level2>,<level3><CRLF>
interrupt level assigned to handler 2, and <level3> is the interrupt level
assigned to handler 3.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-35 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 78

Local Command Set Chapter 3
If <levelN> equals 0, then interrupt handler <handlerN> is not assigned to
an interrupt level.
Console response:
VXI interrupt Handler 2 assigned to interrupt level
VXI interrupt Handler 3 assigned to interrupt level
VXI interrupt Handler 1 assigned to interrupt level
<level1><CRLF>
<level2><CRLF>
<level3><CRLF>
if all handlers are assigned to levels, or
VXI interrupt Handler <handler> NOT assigned to any interrupt
level.<CRLF>
if <handlerN> is not assigned to a level.
Example: Get the interrupt level assigned to all interrupt handlers.
AllHandlers?
AssgnHndlr
Purpose: Assign a VXIbus interrupt level to a GPIB-VXI interrupt handler.
Command
Syntax: AssgnHndlr <handler>, <level>
where <handler> is a numeric integer quantity in the range 1 to 3, and
<level> is a numeric integer quantity in the range 0 to 7.
Action: If <level> is in the range 1 to 7, VXIbus interrupt line <level> is assigned to
interrupt handler <handler>.
If <level> is 0, then the current VXIbus interrupt line held by interrupt handler
<handler> is released.
Examples: Assign the interrupt level 6 to the GPIB-VXI interrupt handler 2.
AssgnHndlr 2,6
Release the interrupt level currently held by the GPIB-VXI interrupt handler 1.
AssgnHndlr 1,0
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-36 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 79

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
HandlerLine?
Purpose: Get the level assigned to a GPIB-VXI interrupt handler.
Query
Syntax: HandlerLine? <handler>
Response: Program response:
<level><CRLF>
Console response:
VXI interrupt handler <handler> assigned to interrupt level
<level><CRLF>
<level> is the interrupt level assigned to handler <handler>. If <level>
equals 0, then the interrupt handler <handler> is not assigned an interrupt
level.
Example: Get the interrupt level assigned to interrupt handler 3.
HandlerLine? 3
RdHandlers?
Purpose: Get the number of assignable GPIB-VXI interrupt handlers.
Query
Syntax: RdHandlers?
Response: Program response:
Console response:
This GPIB-VXI has 3 configurable VXI interrupt handlers.<CRLF>
Example: Get the number of assignable GPIB-VXI interrupt handlers.
RdHandlers?
3 <CRLF>
© National Instruments Corporation 3-37 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 80

Local Command Set Chapter 3
IEEE-488.2 Common Commands and Queries
The IEEE-488.2 commands and queries are as follows:
• *CLS
• *ESE
• *ESE?
• *ESR?
• *IDN?
• *OPC
• *OPC?
• *RST
• *SRE
• *SRE?
• *STB?
• *TRG
• *TST?
• *WAI
These commands provide minimal conformance to the 488.2 requirements for a DT1 device.
Many of these 488.2 commands have limited meaning in the VXI environment, but are included
for compatibility.
*CLS
488.2
Intent: Clear the device status data structures, and force it to the Operation Complete
Query Idle state.
Command
Syntax: *CLS
Action: None.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-38 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 81

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
*ESE
488.2
Intent: Set the GPIB-VXI's Standard Event Status Enable (ESE) Register bits.
Command
Syntax: *ESE <byte value>
where <byte value> is the new value of the ESE register.
Action: Sets ESE to <byte value>.
Example: Set the ESE register to 45.
*ESE 45
*ESE?
488.2
Intent: Get the contents of the ESE Register.
Query
Syntax: *ESE?
Response: <ESE val><CRLF>
where <ESE val> is the current value of the ESE register. The default value is
FFh.
*ESR?
488.2
Intent: Read and clear the Standard Event Status Register (ESR).
Query
Syntax: *ESR?
Response:
<ESR val> is the current value of the ESR.
<ESR val><CRLF>
© National Instruments Corporation 3-39 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 82

Local Command Set Chapter 3
*IDN?
488.2
Intent: Get the GPIB-VXI's manufacturer, model, serial number, and firmware level.
Query
Syntax: *IDN?
Response: "National Instruments","GPIB-VXI",<serial number>,<firmware
version><CRLF>
*OPC
488.2
Intent: Cause the GPIB-VXI to generate the operation complete message in the ESR
when all pending selected device operations have been finished.
Command
Syntax: *OPC
Action: None.
Notice that since the GPIB-VXI only parses and routes commands, there are
never any pending commands on the GPIB-VXI.
*OPC?
488.2
Intent: Cause the GPIB-VXI to place an ASCII 1 in its output queue when all pending
operations have completed.
Query
Syntax: *OPC?
Response: 1 <CRLF>
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-40 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 83

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
*RST
488.2
Intent: Return a device to a known initial state.
Command
Syntax: *RST
Action: None.
Other than the response mode configuration, the GPIB-VXI does not depart from
its initial state.
*SRE
488.2
Intent: Set the device's Service Request Enable (SRE) Register bits.
Command
Syntax: *SRE <byte value>
where <byte value> is the new value of the SRE register.
Action: Sets the SRE to <byte value>.
Example: Set the SRE register to 120.
*SRE 120
*SRE?
488.2
Intent: Get the contents of the SRE Register.
Query
Syntax: *SRE?
Response:
<SRE val> is the current value of the SRE Register. The default value is FFh.
<SRE val><CRLF>
© National Instruments Corporation 3-41 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 84

Local Command Set Chapter 3
*STB?
488.2
Intent: Get the contents of a device's Status Byte.
Query
Syntax: *STB?
Response: <STB value><CRLF>
where <STB value> is the current status of the path to the GPIB-VXI local
command parser.
*TRG
488.2
Intent: Cause a device to execute a stored trigger sequence.
Command
Syntax: *TRG
Action: None.
*TST?
488.2
Intent: Perform self-test and return passed or failed status.
Query
Syntax: *TST?
Response:
Failure to complete the self-test is indicated by a failure to respond to this query.
0 <CRLF>
If the response is received, the self-test was successful.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-42 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 85

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
*WAI
488.2
Intent: Prevent device from executing any further commands until the No-Operation
Pending flag is TRUE.
Command
Syntax: *WAI
Action: None.
VXIbus Access Commands and Queries
The VXIbus access commands and queries are described on the following pages.
• A16
• A16?
• A24
• A24?
• SYSRESET
The A16 and A24 commands can be used to poke, or write, locations in VME A16 and A24
memory space. The A16? and A24? queries can be used to peek, or read, locations in VME
A16 and A24 memory space.
The SYSRESET command can be used to remotely reset the system.
A16
Purpose: Write a 16-bit value into VXI A16 space.
Command
Syntax: A16 <A16 address>, <word value>
Action: Write <word value> to <A16 address>.
Example: Write A502h to VXI A16 address 4305h.
A16 #h4305, #hA502
© National Instruments Corporation 3-43 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 86

Local Command Set Chapter 3
A16?
Purpose: Read word value from VXI A16 address space.
Query
Syntax: A16? <A16 address>
Response: Program response:
<word value><CRLF>
Console response:
Value <hex word value> (<word value>) read from A16 address <A16
hex address> (<A16 address>)<CRLF>
where <word value> is in decimal integer format, <hex word value> is
in C language hexadecimal format, <A16 hex address> is in C language
hexadecimal format, and <A16 address> is in decimal integer format.
Example: Read the ID register of logical address 16.
A16? #hc400
A24
Purpose: Write a 16-bit value into VXI A24 space.
Command
Syntax: A24 <A24 address>, <word value>
Notice that <A24 address> has a valid range of 2097152 to 14680062
(#h200000 to #hDFFFFE).
Action: Write <word value> to <A24 address>.
Example: Write the value A502h to VXI A24 address 504305h.
A24 #h504305, #hA502
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-44 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 87

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
A24?
Purpose: Read a word value from VXI A24 address space.
Query
Syntax: A24? <A24 address>
Response: Program response:
<word value><CRLF>
Console response:
Value <hex word value> (<word value>) read from A24 address <A42
hex address (<A24 address>)<CRLF>
where <word value> is in decimal integer format, <hex word value> is
in C language hexadecimal format, <A24 hex address> is in C language
hexadecimal format, and <A24 address> is in decimal integer format.
Example: Read the word at A24 address 205634h.
A24? #h205634
SYSRESET
Purpose: Remotely reset system.
Command
Syntax: SysReset
Action: Asserts the VME backplane signal SYSRESET.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-45 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 88

Local Command Set Chapter 3
TTL Trigger Access Commands
The TTL Trigger Access commands are described on the following pages.
• SetTrigOutFP
• SetTrigSrc
• SourceTrig
These commands can be used to directly manipulate the VXI TTL Trigger lines and the front
panel Trigger connectors of the GPIB-VXI.
The SetTrigSrc command is used to set up the trigger line and protocol to use.
SetTrigOutFP routes sourced triggers out the GPIB-VXI's front panel. SourceTrig is
used to generate a TTL trigger.
SetTrigOutFP
Purpose: Set up GPIB-VXI trigger output on the front panel.
Command
Syntax: SetTrigOutFP <enable>
where <enable> is a boolean value.
Action: If <enable> is TRUE (1), the GPIB-VXI is set up to source Trigger out the
front panel. If <enable> is FALSE (0), the GPIB-VXI Trigger output is
disabled.
Example: SetTrigOutFP 1
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-46 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 89

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
SetTrigSrc
Purpose: Set up a trigger line to source on.
Command
Syntax: SetTrigSrc <enable>, <line>, <protocol>
where <enable> is a boolean value, <line> is 0-7 corresponding to TTL lines
0-7, and <protocol> is 0-4 where:
0: External In from front panel
1: Start/Stop
2: Sync
3: Semi-Sync
4: Asynch
Action: GPIB-VXI is set up to source on TTL Trigger line <line> using protocol
<protocol>.
Example: Set up to source Sync protocol on TTL line 3.
SetTrigSrc 1, 3, 2
SourceTrig
Purpose: Source a TTL trigger.
Command
Syntax: SourceTrig
Action: Source a TTL trigger on VXIbus backplane and/or our front panel depending
upon current configuration by SetTrigSrc and SetTrigOutFP commands.
Example: SourceTrig
© National Instruments Corporation 3-47 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 90

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Word Serial Communication Commands and Queries
The Word Serial communication commands and queries are described on the following pages.
• ProtErr?
• RespReg?
• WScmd
• WScmd?
• WSresp?
• WSstr
• WSstr?
These commands can be used to directly generate Word Serial communication operations with
any Message-Based device, including the GPIB-VXI itself, regardless of whether or not it is the
GPIB-VXI's servant.
Note: The Word Serial communication commands and queries are intended for debugging
purposes. National Instruments does not guarantee that these commands will work
when other Word Serial paths are open, such as the GPIB Secondary Address link.
Some of the Word Serial commands as defined in the VXIbus specification require a response
from the Message-Based device, while other commands do not. To distinguish between the two
types of Word Serial commands, and to avoid confusion between Word Serial commands and
GPIB-VXI local commands and queries, the following terminology will be used in this section:
Word Serial command–A VXI-defined Word Serial command that does not require a response
from the Message-Based device.
Word Serial query–A VXI-defined Word Serial command that requires a response from the
Message-Based device.
Command–A GPIB-VXI command, as defined in this chapter.
Query–A GPIB-VXI query, as defined in this chapter.
The WScmd command is used to send a Word Serial command to a Message-Based device. The
WScmd? query is used to send a Word Serial query to the Message-Based device, and to
automatically read and return the device's response.
WScmd can also be used to send a Word Serial query to a Message-Based device. Because
WScmd does not read the query response, the intermediate state of the device can be examined
using the RespReg? query, after which the response can be read using the WSresp? query.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-48 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 91

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
The WSstr command can be used to send device-dependent commands and queries to a device.
If the string sent to the device was a device-dependent query, the WSstr? query can be used to
read the device's response.
The ProtErr? query sends a Read Protocol Error Word Serial query to a device and reports
the error response. The RespReg? query returns the value of a device's response register.
ProtErr?
Purpose: Send a Read Protocol Error Word Serial query to a Message-Based device.
Query
Syntax: ProtErr? <log addr>
Action: Read Protocol Error query is sent to a Message-Based device. Response is read
and reported.
Response: Program response:
<hex value><CRLF>
where <hex value> is the hexadecimal value of the Data Low Register
response.
Console response:
Example: ProtErr? 3
Read Protocol Error for Logical Address <log addr> returned 0x<hex
value>:
<description>
where <description> is text explaining the error response.
RespReg?
Purpose: Get the Response Register contents of a Message-Based device.
Query
Syntax: RespReg? <log addr>
Action: Returns the contents of the device's Response Register at logical address <log
addr>.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-49 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 92

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Response: Program response:
<hex value><CRLF>
where <hex value> is the hexadecimal value of the Response Register
contents.
Console response:
Logical Address <log addr>'s Response register:<CRLF>
[0x<hex value>]: <dor> <dir> <err> <rr> <wr> <fhs>
<locked><CRLF>
where <dor>, <dir>, <err>, <rr>, <wr>, <fhs>, and <locked> are text
flags that interpret the state of the Response Register bit flags. Capitalized text in
a text flag indicates that the corresponding bit flag is in the logic TRUE state.
Lowercase text indicates that the corresponding bit flag is in the logic FALSE
state.
WScmd
Purpose: Send a 16-bit Word Serial command or query to a Message-Based device.
Command
Syntax: WScmd <log addr>, <WS cmd>
Action: Sends the Word Serial command <WS cmd> to the device at <log addr>.
Example: Write the Begin Normal Operation Word Serial query (FCFFh) to a device at
logical address 3.
WScmd 3, #hFCFF
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-50 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 93

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
WScmd?
Purpose: Send a 16-bit Word Serial query to a Message-Based device.
Query
Syntax: WScmd? <log addr>, <WS cmd>
Action: Sends the Word Serial query <WS cmd> to the device at <log addr>. Reads
and returns the device's response.
Response: Program response:
where <hex value> is the hexadecimal value of the Data Low Register
Console response:
Example: Write the Read Servant Area Word Serial query (CEFFh) to a device at logical
WScmd? 4, #hCEFF
<hex value><CRLF>
response.
Logical Address <log addr> Word Serial Query 0xceff returned
0x<hex value>.<CRLF>
address 4.
WSresp?
Purpose: Read a 16-bit Word Serial response to a previously sent query.
Query
Syntax: WSresp? <log addr>
Action: Reads and returns the response of the device at <log addr>.
Response: Program response:
where <hex value> is the hexadecimal value of the Data Low Register
<hex value><CRLF>
response.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-51 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 94

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Console response:
Logical Address <log addr> returned response 0x<hex value><CRLF>
Example: Read the 16-bit response to a previously sent Word Serial query from logical
address 3.
WSresp? 3
WSstr
Purpose: Send a device-dependent command string to a Message-Based device.
Command
Syntax: WSstr <log addr>, <string>
where <string> is an ASCII character sequence enclosed by double quotation
marks (").
The following sequences of characters within the <string> parameter are
special cases and will be interpreted as follows:
\n line feed (LF)
\r carriage return (CR)
\\ backslash (\)
\xHH any binary 8-bit value where HH is the ASCII hexadecimal
representation of that value
Action: Writes the string <string> to the device at <log addr> as a series of Byte
Available commands.
Example: Write the string "start" to a device at logical address 8.
WSstr 8, "start"
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-52 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 95

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
WSstr?
Purpose: Read a device-dependent response string from a Message-Based device.
Query
Syntax: WSstr? <log addr>, <max cnt>
Action: Reads and returns a string, up to a maximum character count of <max cnt>,
using a series of Byte Request commands.
Response: Program response:
<resp string>
where <resp string> is the response string returned by the device.
Console response:
Logical address <log addr> read <# bytes> (<hex # bytes>) through
word serial: <CRLF><CRLF> <resp string>
where <# bytes> and <hex # bytes> are the number of bytes in <resp
string>, in decimal and hexadecimal, respectively.
Example: Read a device-dependent response up to 20 characters long from a device at
logical address 10.
WSstr? 10, 20
CI Configuration Commands and Queries
The CI configuration commands and queries are described on the following pages.
• CIAddr?
• CIArea
• CIArea?
• CIBlocks?
• CIDelete?
• CIList?
• DCIDownLdPI
• DCIDownLoad
© National Instruments Corporation 3-53 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 96

Local Command Set Chapter 3
• DCISetup?
• DCISetupPI?
These commands and queries manipulate CIs and their related resources, and extract information
about the CI configuration.
The query CIList? returns the list of code instrument logical addresses. The RM information
queries that access information for physical devices (Cmdr?, RmEntry?, Srvnts?,
StatusState?) can be used to retrieve the equivalent information for a CI. The CIDelete
query deletes a CI.
The amount of RAM reserved for all CIs is set by the GPIB-VXI, depending upon its nonvolatile
configuration, the amount of RAM installed, and the use of the command CIArea. The CI
RAM area is partitioned into blocks of 4K. The current location and size of the CI RAM area
can be determined by using the CIArea? query. The CIBlocks? query returns the allocation
state of each block in the CI RAM area. The base address of a particular CI's RAM area can be
determined by using the CIAddr? query.
Static Downloaded CIs (DCIs) are downloaded to the GPIB-VXI and initialized with the local
commands DCISetUp? and DCIDownLoad.
Position Independent DCIs are downloaded to the GPIB-VXI and initialized with the local
commands DCISetupPI? and DCIDownLdPI.
CIAddr?
Purpose: Get the local base RAM address of a CI.
Query
Syntax: CIAddr? <logical address>
Response: Program response:
<base address><CRLF>
where <base address> is the CI's base address in decimal.
Console response:
CI at Logical Address <logical address> base Local Address is <hex
base address><CRLF>
where <hex base address> is the CI's base address in C language
hexadecimal notation.
Example: Get the local address of the CI at logical address 9.
CIAddr? 9
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-54 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 97

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
CIArea
Purpose: Change the location and size of the CI RAM area.
Command
Syntax: CIArea <Base Address>, <Number of blocks>
Action: Sets the CI global RAM to start at <Base Address>, and span
<Number of blocks> blocks of 4096 bytes each.
The default base address and size of the CI RAM area are set by the nonvolatile
configuration parameters CI Block Base and CI Num Blocks.
<Base Address> is the new base address of the CI RAM area. It must be a
multiple of 4096 decimal (1000h), and must be in the region above the top of
pSOS Region 1 and below the top of memory. pSOS Region 1 starts at 10000h,
and its size is determined by the nonvolatile configuration parameter Region 1
Size. For example, if Region 1 Size = 60000h, then the lowest allowed
value for <Base Address> is as follows:
10000h + 600000h = 70000h
<Number of blocks> is the number of 4096 (1000h) byte blocks in the CI
RAM area. The size of the CI RAM area is limited by the amount of physical
RAM on the GPIB-VXI, so the maximum allowed value for <Number of
blocks> is as follows:
(<RAM size> - <Base Address>) / 1000h
For example, if the GPIB-VXI is configured with 512K (80000h) of RAM, and
<New Base Address> is 70000h, the maximum allowed value for <Number
of blocks> is given by the following formula:
(80000h - 70000h)/ 1000h = 10h = 16
If <Number of blocks> is set to 0, CI's are disabled.
Example: Set the base of CI RAM area to 80000h, and the size to 128 blocks of 4K.
CIArea #h80000, 128
© National Instruments Corporation 3-55 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 98

Local Command Set Chapter 3
CIArea?
Purpose: Return the base address and size of CI global memory area.
Query
Syntax: CIArea?
Response: Program response:
<base address>, <number of blocks><CRLF>
where <base address> and <number of blocks> are the current base
address and size of the CI RAM area in blocks of 4K, respectively.
Console response:
CI Global Base is local Address <hex base address> with <number of
blocks> 4K blocks<CRLF>
<hex base address> is the base address of the CI RAM area in C language
hexadecimal notation. <number of blocks> is the size of the CI RAM area
(in blocks of 4K) in decimal.
CIBlocks?
Purpose: Return a listing of used and unused CI memory area blocks.
Query
Syntax: CIBlocks?
Response: Program response:
where <bJ> is a boolean value that indicates whether the Jth block is unused (0)
Console response:
<r0start> - <r0stop>, <r1start> - <r1stop>, . . .,<r
where <rMstart> and <rMstop> are the start and stop block numbers for the
<b0>, <b1>, . . ., <bL-1><CRLF>
or used (1). L is the number of blocks of 4K in the CI global memory area.
Blocks Used of the <L> Blocks of CI Global Memory: <CRLF>
N
-1start> -
<r
N
-1stop><CRLF>
Mth occupied memory region.
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-56 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 99

Chapter 3 Local Command Set
CIDelete?
Purpose: Delete a CI.
Query
Syntax: CIDelete? <code instrument logical address>
<code instrument logical address> is the logical address of the CI
to be deleted.
Response: Program response:
<error code><CRLF>
where <error code> is a decimal value that indicates the result of the attempt
to delete the CI. If <error code> is equal to 0, the attempt was successful.
Console response:
Code Instrument at Logical Address <code instrument logical
address> successfully deleted<CRLF>
if the attempt was successful, or
Error Deleting Code Instrument (Error code = <hex error code>)
if the attempt was unsuccessful.
<hex error code> is a value in C language hexadecimal format that
indicates the result of the attempt to delete the CI.
<error code> and <hex error code> can be interpreted by converting
them to a binary bit pattern. A value of 1 in any bit position indicates that the
error shown in the following table occurred during the attempt to delete the CI:
© National Instruments Corporation 3-57 GPIB-VXI User Manual
Page 100

Local Command Set Chapter 3
Bit Error condition
0 The GPIB-VXI was unable to delete the CI's
secondary address link.
1 The GPIB-VXI was unable to delete the CI's
message exchange.
2 The GPIB-VXI was unable to delete the CI's
Async process.
3 The GPIB-VXI was unable to delete the CI's
Worker process.
4 The GPIB-VXI was unable to delete the CI's
Word Serial I/O structures.
5 The GPIB-VXI was unable to free the PI CI's
dynamic memory.
Any error encountered is unrecoverable in the sense that the CI is not restored.
Any further attempts to communicate with it will have undetermined results, and
may adversely affect the behavior of the GPIB-VXI.
CIList?
Purpose: Get a list of logical addresses for CIs running on the GPIB-VXI.
Query
Syntax: CIList?
Response: Program response:
where <ci laJ> is the logical address of the Jth local CI. N is the total number
Console response:
<ci la1>,<ci la2>, . . .,<ci laN><CRLF>
of local CIs.
Local CI Logical Addresses are: <ci la1>,<ci la2>, . . .,
N
<ci la
><CRLF>
GPIB-VXI User Manual 3-58 © National Instruments Corporation
 Loading...
Loading...