
IRF-633
RS-232/422/485 to 10/100Base-TX
Device Server/Managed Media
Converter
User Manual
(Dec 2007)

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
COPYRIGHT
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system,
or transmitted in any form or by any means, whether electronic, mechanical, photo copying,
recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher.
FCC WARNING
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class A device,
pursuant to part 15 of FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a commercial installation. This equipment generates, uses and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communication. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case, the user
will be required to correct the interference at the user’s own expense.
CE
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference
in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Take special note to read and understand all the content in the warning boxes:
Warning
i

RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 ABOUT THIS GUIDE..........................................................................1
1.1 Welcome............................................................................................................ 1
1.2 Purpose .............................................................................................................1
1.3 Terms/Usage .....................................................................................................1
1.4 Features.............................................................................................................1
1.5 Specifications ...................................................................................................2
1.6 Package Contents............................................................................................. 3
2 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION .............................................................4
2.1 Product Overview .............................................................................................4
2.2 Product Illustrations.........................................................................................4
3 INSTALLATION..................................................................................5
3.1 Location.............................................................................................................5
3.2 Wall Mount Installation..................................................................................... 5
3.3 Din Rail Mount Installation............................................................................... 5
3.4 Powering On Unit.............................................................................................. 6
3.5 DB9 Male Connector Pin Assignments........................................................... 7
3.6 Serial Connection .............................................................................................7
4 LED INDICATORS .............................................................................9
5 USER INTERFACE STARTUP.........................................................10
5.1 Console Port Access...................................................................................... 10
5.2 Telnet Access.................................................................................................. 12
5.3 Web Access..................................................................................................... 13
6 CONFIGURATION MANAGEMENT.................................................14
6.1 Menu-driven User Interface............................................................................14
6.1.1 System Information Menu...............................................................................................14
6.1.2 DHCP Configuration Menu..............................................................................................15
6.1.3 Serial Port Config Menu ..................................................................................................16
6.1.4 RS-232/422/485 UART Menu ...........................................................................................20
6.1.5 Connection Status ...........................................................................................................20
6.1.6 TFTP Firmware Upgrade .................................................................................................21
6.1.7 SNMP Configuration........................................................................................................21
6.1.8 System Restart Menu ......................................................................................................23
6.2 Command Line Interface................................................................................ 24
6.3 Web Graphic User Interface...........................................................................25
6.3.1 System Information .........................................................................................................25
6.3.2 Master Information ..........................................................................................................25
6.3.3 Serial Port Configuration ................................................................................................25

RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
iii
6.3.4 Serial Connect Status......................................................................................................30
6.3.5 User Configuration ..........................................................................................................31
6.3.6 Firmware Download ........................................................................................................31
6.3.7 Configuration File Backup and Restore........................................................................32
6.3.8 SNMP Community Configuration...................................................................................32
6.3.9 IP Trap...............................................................................................................................32
6.3.10 System Restart...............................................................................................................33
7 APPENDIX: RS-232 CABLE CONNECTION DIAGRAM.................34
8 CONTACT INFORMATION ..............................................................45

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
1
1 About This Guide
1.1 Welcome
Thank you for selecting the IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 to 10/100Base-TX Device Server
/ Managed Media Converter. This unit is designed to provide an RS-232/422/485
connection over twisted-pair cable where the connected devices have RS-232/422/485
interfaces. Enabling serial devices such as CNCs and PLCs to instantly connect to an
existing Ethernet/ Fast Ethernet network, the Serial-to-Ethernet Device Server /
Managed Media Converter represents a robust solution for devices controllers for MIS
personnel. This product can either be used as Device Server or Managed Media
Converter.
1.2 Purpose
This guide discusses how to install and configure your IRF-633 Device Server/
Managed Media Converter.
1.3 Terms/Usage
In this guide, the term “Device Server/Managed Media Converter” (first letter upper
case) refers to your IRF-633, and “device server / managed media converter” (first
letter lower case) refers to other device servers / managed media converter.
1.4 Features
• IRF-633 Device Server & Managed Media Converter Mode option
• Complies with EIA/TIA and IEEE standards
• Supports 4 wires full duplex asynchronous serial data transmission (RS-422/485)
• Supports 2 wires half-duplex asynchronous serial data transmission (RS-485)
• Supports serial port asynchronous data rates up to 115.2 Kbps
• Extended distances up to 1.2 km (24 AWG) using RS-422/485
• Auto-detecting 10/100 Mbps Ethernet interface
• Terminator feature improves signal quality and distance
• LEDs for ‘at-a-glance’ device status
• Wall mount or Din-Rail mountable installation
• Power range 9~32V DC
• FCC Class A & CE approved

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
2
1.5 Specifications
Standards:
IEEE 802.3 (10BASE-T Ethernet);
IEEE 802.3u (100BASE-TX/ Fast Ethernet); EIA/TIA RS232/422/485; EIA/TIA-5744
Ports:
1x UTP 100/120ohm; RJ-45 type
1x 9-pin serial connector; D-sub, Male
Max. Distance:
UTP: 100 meters (Cat 3/4/5.)
Serial: 15 meters (RS-232)
1,200 meters (RS-422, RS-485)
Data Rates:
UTP: 10 or 100 Mbps
Serial: 115.2 kbps (asynchronous)
Signals:
RS-232: TxD, RxD, CTS, RTS, DTR, DSR, RI, DCD, GND RS-422:
TxD+/-, RxD+/-, GND RS-485: Data+, Data-, GND
Configuration:
Bits Per Second: 38400
Parity: None
Data bits: 8
Stop bits: 1
Flow Control: None
(The console connection is only available once the DIP switch 1 is
ON)
Switches:
DIP 1: Enables / disables console / data communication mode
DIP 2: Enables / disables RS-232
DIP 3: Enables / disables RS- 422/485 (4-wire)
DIP 4: Enables / disables RS-485 (2-wire)
DIP 5: N/A
DIP 6: N/A
DIP 7: Enables / disables termination (TMR)
Power:
External power adapter; 9~32V DC @800mA
Frequency: 47Hz to 63Hz
Environment:
Temperature: Operating: 0°C to 50°C
Relative Humidity: 10% to 80%, non-condensing
Storage: -20°C to 80°C
Relative Humidity: 5% to 90%, non-condensing
Emissions:
FCC Part 15 of Class A & CE approved
Dimensions:
109.2 x 90 x 30mm (L x W x H)
Weight:
280 grams

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
3
1.6 Package Contents
The package should include the following:
• One IRF-633 Device Server / Managed Media Converter
• One power adapter (please check connector type and input power specification)
• Four self-adhesive pads
• DIN Rail Kit
• Screws for wall-mount installation
• Quick Installation Guide
• User’s Manual CD
• Serial IP Redirector software CD

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
2 Hardware Description
2.1 Product Overview
The IRF-633 features complete Ethernet and TCP/IP network support that allows
devices in industry with RS-232/422/485 connectors such as milling machines,
measurement instruments, and robots to connect to LAN based automation. Other
devices typically found on campus networks such as card readers, code readers, lab
equipment, medical equipment, and other similar serial devices can now instantly
migrate to a TCP/IP network. Additionally, by deploying the device server mode, enable
users to monitor and manage up to 256 serial devices from single PC with the help of
Serial IP Redirector software for Device Server mode.
2.2 Product Illustrations
Front Panel
RS-232/422/485,
DB9 Male
RJ-45
LEDs
Rear Panel
DIP Switches Power LED Power Connector
4

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
5
3 Installation
To install your IRF-633, please see the following procedures:
• Location
• Din Rail Mounting
• Desktop Installation
• Powering On Unit
• Connecting Copper Cables
• DB9 Male Connector Pin Assignment
• Serial Connection
• Ethernet Connection
3.1 Location
The location selected for installing the IRF-633 may greatly affect its performance.
When selecting a site, we recommend considering the following rules:
1.
Install the IRF-633 in a fairly cool and dry place. See Technical Specifications for
the acceptable temperature and humidity operating ranges.
2.
Install the IRF-633 in a location free from strong electromagnetic field generators
(such as motors), vibration, dust, and direct exposure to sunlight.
3.
Leave at least 5cm of space at the front and rear of the unit for ventilation.
4.
Affix the provided rubber pads to the bottom of the IRF-633 for grip, and to protect
the case from scratching.
3.2 Wall Mount Installation
The Device Server/Managed Media Converter can also be installed by wall mounting.
The backside casing provides space for two screws each side. Identify the exact
location at wall by placing the IRF-633 and marking the screw positions. Use the screw
(include in the package) and snug them well to fix the IRF-633.
3.3 Din Rail Mount Installation
The aluminum DIN Rail attachment plate should already be affixed to the back panel of
the IRF-633. If you need to attach the DIN Rail plate, assure that the stiff metal spring
is situated towards the top. Attaching the IRF-633 to the DIN rail is easy, just align, and
attach the top rail, then press down and snap forward the IRF-633 to snap in the
bottom rail, as shown in the figures below.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
Use following steps set up the IRF-633:
• The surface must support at least 500 gm for the IRF-633.
• The power outlet should be within 1.82 meters (6 feet) of the IRF-633.
• Visually inspect the power adapter and make sure that it is properly connected.
Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation from and adequate ventilation around
the IRF-633. Do not place heavy objects on the product.
Warning Please exercise caution when using power tools. Also, install this
unit away from damp or wet locations, or in close proximity to very hot
surfaces. These types of environments can have a detrimental effect on the
unit and cables.
3.4 Powering On Unit
The IRF-633 uses external power supply 9~32V DC @ 0.8A 50~60 Hz.
1. Insert the power cable plug directly into the receptacle located at the back of the
device.
2. Plug the power adapter into an available socket.
3. Check the rear-panel LEDs as the device is powered on to verify that the Power
LED is lit. If not, check that the power cable is correctly and securely plugged in.
6
NOTE: The RJ-45 port accepts both ‘straight-through’ and ‘cross-over’ Ethernet cables
without the need to re-configure the port.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
3.5 DB9 Male Connector Pin Assignments
PIN
RS-232
(Full-duplex)
RS-422/485
4-wire
(Full-duplex)
RS-485
2-wire
(Half-duplex)
1 DCD
2 RX RX- **DATA B(-)
3 TX TX-
4 DTR
5 GND GND GND
6 DSR
7 RTS RX+ **DATA A(+)
8 CTS TX+
9 RI
NOTE: Bi-directional RS-485 BUS line.
For RS-232 cable connection, use cross-over cable when connecting to a DTE device,
and straight-through cable for connecting to a DCE device. See Appendix for
illustration.
3.6 Serial Connection
This IRF-633 features DIP switches on the rear panel that sets the unit to the correct
type of cable configuration to support connection with a RS-232 / 422 / 485 device.
Definition of DIP Switches
No Dip description Default
1 ON: Console / OFF: Data OFF
2 RS-232 ON
3 RS-422 / 485 (4W) OFF
4 RS-485 (2W) OFF
5 NA OFF
6 NA OFF
7 TMR (Terminator) OFF
For setting the control function of the serial port, see the table below:
DIP 1 Serial Connection
ON RS-232 Console
OFF Data Communication
NOTE:
1. If using console mode turn the DIP Switch 1 to ON position. For data
communication from the serial device keep the DIP switch 1 to OFF position. In
case of ON position data communication will be blocked and at OFF position
console port access blocked.
2. In RS-232 Condole mode (DIP Switch 1 = ON), all other DIP Switch settings are
ignored. In Data Communication mode (DIP Switch 1 = OFF), properly set other
DIP Switches for serial interface modes.
7
3. For some RS-422/485 devices, which may not be designed to provide DB-9
connection, please check the pin definition to connect the devices.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
8
4. For the first time installation, you have to use console mode to setup the IP and
TCP port configuration with RS-232 cable. Always use Cross Over cable, if using
Straight Through, you must use “Null Modem” to use Telnet option.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
9
4 LED Indicators
This device has LED indicators located at the front of the device. The LEDs have been
designed to give easy at-a-glance network status, and provides ‘real-time’ connectivity
information. Please see below for an interpretation of their functions:
LED Indicators
LED
Condition Status
On (Green) Unit is receiving power
PWR
Off Power off or failure
On (Green)
Illuminated when RJ-45 connector attached and
link signals received
LNK / ACT
(RJ-45)
Flashing (Green) Data traffic passing through RJ-45 port
Off No link established
100
On (Green) RJ-45 port in 100Base mode
Off Port is operating at full duplex
On (Green) Receiving data packets
ACT
Flashing
RS-232/422/485 data packets being transmitted
or received
Off No data packets received
POST
On (Green) Indicates normal operation

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
5 User Interface Startup
There are two separate methods for configuring this IRF-633 for use. In the first section
of this chapter, the Command line Interface (CLI) or Menu-driven interface via the
Console Port to set the device IP and TCP configuration to monitor/managed the
attached serial device via Serial IP Redirector software. The second section will
describe CLI or Menu-driven via Telnet configuration. Firstly, make the connection
below:
DIP Switch 1 set to ‘ON’ position
5.1 Console Port Access
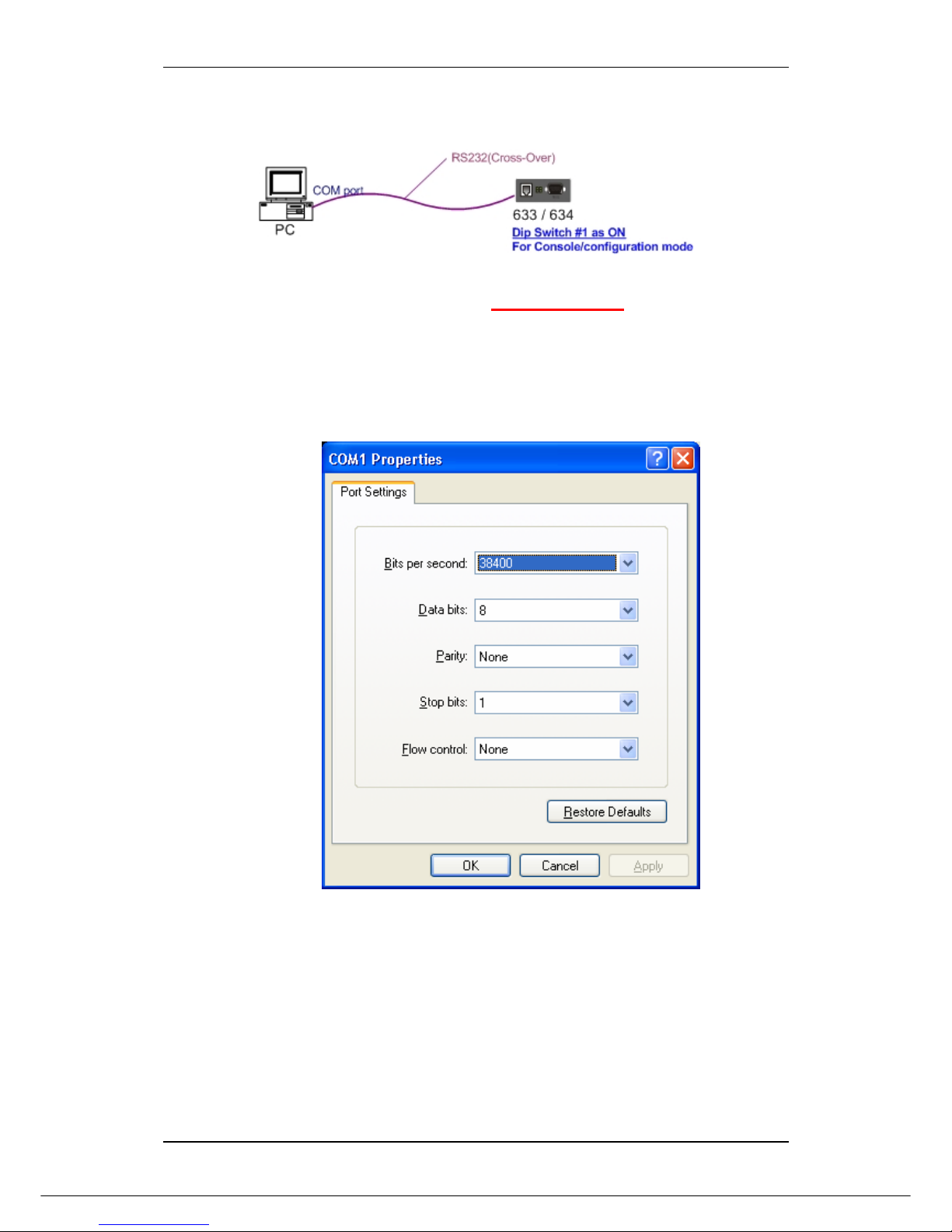
The IRF-633 is accessible via a terminal emulator attached to the RS-232 console port.
Please follow the step below.
1. Attaching the serial cable to COM port of computer and serial port of device server.
2. Select Hyper Terminal from (start menu Æ programs Æ Accessories Æ
communication) a window will appear, assign the connection name. Then select the
correct available COM port (COM1 or COM2). After this enter the port settings as
below.
Bits per seconds: 38400
Data bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flow Control: None
3. Once connection is established, you will see a log in screen.
10
Device
Serve
r
Female
Female
Compute
r
RS-232 Cable

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
Press ENTER and on the following screen, type the default username admin, leave the
password field blank since there is no default value and press ENTER to proceed.
4. Select either CLI User Interface or Menu-driven Interface option by using the
associated number key or using the TAB key and pressing ENTER. A relevant
Main Menu screen appears.
The IRF-633 is preset with a factory IP address (192.168.0.254) that must be
configured to the user’s individual IP address. It is important to do this so that the IRF633 doesn’t conflict with other devices with the same defaults.
NOTE:
Prior to following the instructions for HyperTerminal Configuration, ensure that a serial
cable connection between the IRF-633 and workstation exists.
Type the following command line to change the device IP address in CLI mode where
xxx’s represent values between 0 and 254 and the user should enter their own IP
address in this form.
11
a) set eth0 ip xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
If using the Menu-driven interface. Select the System Information from the Main Menu
and following screen will appear. Use TAB key to move the cursor and <Enter> to
change the value. Once change the value, select <SAVE> to apply the changes.
After entering the new IP address the system will confirm whether the operation is
successful.
NOTE:
Copy the new address down on a piece of paper. You will need the address when you
are going to use Telnet or set up data transfer/communication connection.
Warning
IP addresses are unique! If an address isn’t available, please contact the
appropriate authorities to apply for one.
5.2 Telnet Access
The IRF-633 is accessible via a Telnet. At the command prompt type telnet
192.168.0.254 (If connecting with default IP). You will be prompted to Enter user name
and password as mentioned and shown in the topic Console Port Access. Use CLI or
Menu-driven interface to perform the changes.
NOTE:
12
The only limitation of Telnet Access is that users can not assign new IP address to
device server. Please use Console Port Access or Web Access to assign new IP
address.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
5.3 Web Access
The IRF-633 is accessible via a web browser once connected to the network. Type the
IP address at web browser 192.168.0.254 (if connecting with default IP). A window will
be prompted to Enter user name and password.
(Note: We use IP 192.168.0.200 to write this manual)
After successful login, the main screen will appear.
13

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
6 Configuration Management
Users can manage the Device Server via menu-driven interface or command line
interface from Telnet or serial console, or Web graphic user interface.
6.1 Menu-driven User Interface
The figure below shows the Main Menu screen. From this screen the configuration
options available provide the user to quickly access and adjust the device server
settings as required.
Main Menu Screen
Use TAB key to move the cursor to different fields and press Enter to select/edit the
option.
6.1.1 System Information Menu
From this menu, the user can view system-related information and the default IP
address. The user should set up an appropriate IP address, subnet mask and Gateway
for his/her own network. After entering a new IP address, Telnet and data
communication will be based on the new address.
14

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
System Information menu
Once changes are made, move the cursor to <SAVE> by using the TAB key and press
Enter to save the settings. Changing the IP address will automatically restart the IRF-
633.
NOTE:
In Telnet mode you can’t change the IP address.
6.1.2 DHCP Configuration Menu
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) allows the IRF-633 to obtain an IP
address from the DHCP server automatically.
NOTE:
A DHCP server must exist and be available in your local network prior to enabling the
DHCP client.
DHCP Configuration menu
15
Use the Spacebar to enable/disable the DHCP Client settings. Select <SAVE> to
apply the settings and <ESC> to move to the previous menu. If you don’t want to save
the changes made, just select <ESC> and you will move to the previous menu without
making any changes.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
6.1.3 Serial Port Config Menu
This page offers the option for the communication model and operation mechanism of
Device Server. Please select the appropriate mode as required for your application.
The user can also monitor the serial port status and configure TCP port numbers from
this menu.
z The unit offers six modes (TCP Server / TCP Client / Converter Mode / UDP
Server / UDP Client / Device Server). Please restart the unit after selecting the
desired mode.
Note: In case of using Converter Mode Mode, we recommend you keep the Packet
Mode option set at Disable.
A detailed explanation of the setting choices are given underneath the following
screenshot:
16
EXPLANATION: Server/Client Mode Configuration
Operation Mode
TCP Server: the TCP Server mode of the Device Server allows
TCP connections from up to four Device Servers with TCP Client
mode or PC with Serial IP Redirector program running.
TCP Client: the TCP Client mode of the Device Server can
establish up to four TCP connections with Device Servers of TCP
Server mode.
UDP Server: the UDP Server mode of the Device Server allows
the communication initiated from up to four UDP Clients.
UDP Client: the UDP Client mode can communicate with up to
four UDP Servers in UDP communication model.
Device Server: the Device Server acts as Server role of RFC2217 COM Port Control Protocol.
Converter Mode: two Device Servers communicate with each
other through point-to-point architecture in TCP communication
model. The TCP Client and Server roles of two Device Server
peers are negotiated automatically.
Remote IP 1~4 IP addresses of the other end device or Serial IP Redirector
workstations.
Port The TCP port number corresponding to each remote IP that
the TCP Server is bound to.
Status Toggle between “Enable” and “Disable” for activating or
deactivating the second to the fourth remote IP/Port entries.
Connection Idle
Time
In seconds. The TCP Server or Client will disconnect the TCP
session if no packets are transmitted in the set period.
Packet mode
(serial)
Enabled – input data from the serial interface is treated as serial
packets.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
17
Disabled – input data from the serial interface is treated as bit
streams.
Packet mode
inter-packet
timeout
In milliseconds. The delimiter value for recognizing the timeout
gap between serial packets if Packet Mode is enabled.
Delimiter1(Hex)/
Status
Besides the inter-packet timeout, serial packets can be delimited
by one or two trailer bytes of specific values. Delimiter 1 is the
hexadecimal number of the first delimiter byte. Toggle to “Enable”
on the “Status” field for delimiting serial packets according to trailer
byte rather than inter-packet timeout.
Delimiter2(Hex)/
Status
The hexadecimal number of the second delimiter byte. If this byte
is “Disable” and the Delimiter 1 is “Enable”, the delimiter byte
length is one.
Delimiter Process Do Nothing: keep the delimiter bytes when transforming to IP
packets.
Strip Delimiter: Strip off the delimiter bytes when transforming to IP
packets.
NOTE:
For Device Server Mode, in case you are using a serial device with a 2-wire RS-485
application or Modbus RTU protocol, do not forget to “Enable” the “Packet” mode of
serial input. Also enter the appropriate inter-packet timeout value or delimiter byte
values to enable smooth data communication.
To set the timeout value via console mode, first “Enable” the packet mode and “Save”
the settings. Once settings are applied, you will be able to change the timeout or
delimiter values.
Next Page: More information on Operation Modes
Changes to the settings are saved to a system flash memory and do
NOT take effect until a system reset or reboot has occurred. This
action validates the new settings. Please note that you can’t change
the operation mode by using Telnet. Always use Web Interface or
Console access to change the Mode.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
Applications for Operation Modes:
Diagram 1 – Central Management Application (Device Server Mode)
Serial
Cable
IP Virtual COM port Software
IP
Network
TCP Connections
LAN
Serial
Cable
Serial
Cable
PLC
PLC
PLC
Device
Server
Device
Server
Device
Server
Device Server Mode: In this mode the Device Server acts in the Server role of the
RFC-2217 COM Port Control Protocol.
Diagram 2 – Peer-to-Peer Application (Converter Mode)
Serial
Cable
Serial
Cable
PC
IP
Network
TCP Connection
PLC
Device
Server
Device
Server
Converter Mode: In this mode the Device Server/Managed Media Converter acts like
an advanced media converter. Like a normal converter, the Device Server/Managed
Media Converter communicates with a remote Device Server/Managed Media
Converter in a peer-to-peer fashion. Also, the Device Servers communicate with each
other through an IP network in the TCP communication model. The TCP Client and
Server roles of the two Device Server peers are negotiated automatically.
18

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
Diagram 3 – Multi-host Application (TCP Server mode)
TCP client
A maximum of 4 remote devices can connect to a device server.
A maximum of 4 remote devices can connect to a device server.
TCP Server:
Local TCP port
TCP Server:
Local TCP port
Socket TCP call setup
Window XP
UNIX Linux
Device
Server
Device
Server
IP Network
TCP Server Mode: In this mode the Device Server/Managed Media Converter acts as
a device server and functions as a network agent for the serial device. For example,
when a serial device with a serial console port is connected to the Device
Server/Managed Media Converter while it is in TCP Server mode, the console port
becomes a network-accessible interface via the Device Server. In TCP Server Mode,
the Device Server can link the serial device and a TCP-operating control host by
providing two-way transmission between the two.
In TCP Server mode, the Device Server/Managed Media Converter waits for the
control host to initiate communication with the serial device. Conversely, in TCP Client
mode (next diagram) the Device Server/Managed Media Converter initiates
communication with one or up to four remote devices simultaneously – when the serial
device experiences a communication event and prompts the Device Server/Managed
Media Converter to initiate communication.
19
Diagram 4 – Multi-host Application (TCP Client mode)
TCP server
A device server can connect up to 4 remote devices.
A device server can connect up to 4 remote devices.
Socket TCP call setup
Window XP
UNIX Linux
TCP Client:
1. Local TCP port
2. Remote IP address, Port
TCP Client:
1. Local TCP port
2. Remote IP address, Port
Device
Server
Device
Server
IP Network
TCP Client Mode: This mode lets the Device Server/Managed Media Converter act as
a bridge for serial devices that must communicate with server hosts like the Linux, Unix

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
and Windows systems. In this Client mode, the Device Server establishes a temporary
TCP connection with the servers automatically after powering up. All the data received
from the serial device is then sent to remote servers. The servers can also send data
back to the serial device while the connection is active. The Device Server/Managed
Media Converter automatically ends the connection when all information is sent and
the connection becomes idle for a specified length of time. It will reestablish the
connection when it receives data from the serial device.
In TCP Server mode (previous section), the Device Server/Managed Media Converter
waits for the control host to initiate communication with the serial device. Conversely,
in TCP Client mode the Device Server/Managed Media Converter initiates
communication with one or up to four remote devices simultaneously – when the serial
device experiences a communication event and prompts the Device Server/Managed
Media Converter to initiate communications.
6.1.4 RS-232/422/485 UART Menu
This window will show you the serial port configuration.
The screenshot below shows the different configuration options (the screenshot is
followed by a detailed explanation of the different options):
RS232/422/485 UART Configuration (Serial Port Configuration)
Operation Mode A read-only attribute. It shows the RS232/422/485 mode set by the
DIP switch.
Baud Rate The speed of the serial interface.
Parity Select or disable the parity checking method
Word Length The length of data in bits
Stop Bits The bit length of stop bits
Flow Control The flow control method for informing the correspondent
6.1.5 Connection Status
20
This screen provides at-a-glance system status information.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
6.1.6 TFTP Firmware Upgrade
From this menu, the user can upgrade the existing firmware to newer firmware
available from a TFTP server. Simply enter the file name of the updated firmware in the
file name field and
enter the IP address of the TFTP server in the IP address field to
perform the upgrade. Selecting <update> will start downloading the newer firmware
and system will restart to apply the firmware. For ensuring correct parameter values for
Device to be functioning after firmware upgrade from a prior version with different
configuration structure and data format, please Restore Factory Default Settings in
System Restart Menu.
TFTP Firmware Upgrade menu
6.1.7 SNMP Configuration
Use the SNMP Configuration screen to display and modify parameters for the Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP). The product includes an onboard SNMP
agent that monitors the status of its hardware as well as the traffic passing through its
ports. A computer attached to the network, called a Network Management Station
(NMS), can be used to access this information. Community strings control access
rights to the agent module. To communicate with the IRF-633, the NMS must first
submit a valid community string for authentication.
21

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
The options for configuring community strings and related trap functions are described
as below.
Use the <Tab> and <Enter> keys as previously. Enter the IP address of computers for
when abnormalities on a connection occur and an alarm to be sent. Enter their
community names and disable or enable their alarm function accordingly. See
descriptions below:
Parameter Description
Index
Status
IP Address
Community
Number assigned to each trap
Disable or enable their alarm function accordingly
Enter the IP address of computers for when abnormalities on
a connection occur and an alarm to be sent. Enter their
community names and disable or enable their alarm function
accordingly
Enter their community names
22
You can use an external SNMP-based application to configure and manage the IRF-
633. This management method requires the SNMP agent on the IRF-633 and the
SNMP Network Management Station to use the same community string. This
management method, in fact, uses two community strings: the get community string
and the set community string. If the SNMP Network Management Station only knows
the set community string, it can read and write to the MIBs. However, if it only knows
the get community string, it can only read MIBs. The default Get and Set community
strings for the product are public.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
6.1.8 System Restart Menu
This menu allows users to restore the factory default setting for the IRF-633 and/or to
reset the system manually. Selecting this option will lead to another window with the
following two options to select.
Restore Factory Default Settings
Selecting this option will lead to restore factory default settings to the IRF-633.
Highlight the field and hit the <ENTER> key to execute.
System Restart
The System Restart allows a user to perform a ‘warm’ restart and validate newly saved
configuration to the IRF-633. Highlight the System Restart field and hit the <ENTER>
key to reset the unit.
23
After each configuration session, be sure to set DIP switch 1 to the
‘OFF’ position. Otherwise, the unit will not transmit any data.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
6.2 Command Line Interface
Once you logged in and select the option of Command Line Interface, a window with
command prompt will appear. Type ? or help and it will show you the command list.
Command List
Command Definitions
backup: Use this command to save configuration settings
to file.
exit: Type exit or logout and press ENTER to quit the program.
help: To access help commands list.
logout: To logout from the device server.
ping: Type ping followed by a space, and then the IP address of the device to
send a test signal. If a response is received, then the device is connected. To
view a full list of ping options, type ping and press ENTER.
reset: Type reset config and press ENTER to load factory default settings, or type
reset system and press ENTER to restart the system.
show: Type show to display variety of device server settings.
set: To configure the management settings, type the commands below, followed
by the ENTER key.
NOTE: Separate each port of the command line with a space.
set admin - follow the prompts to change user name and password
set eth0 - the command is for factory setting use set eth0 ip (new IP address)
network mask (new network mask) gateway (new gateway). Use this
command to set new Ethernet settings.
24
IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
set idle - (time in seconds) – set automatic logout. when the program or
communication is idle
set xfer - the command is for RS-232 configuration and data communication
setting. The command syntax is as below.
set xfer [arg_1 data_1] [arg_2 data_2] ...
[arg_n data_n]
[Argument List]
Port........... Set TCP port number
statistics..... Clear statistics
upgrade - Use this command to upgrade the firmware.
i.e upgrade firmware xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx Soft2.bin
set snmp - Use this command to set SNMP settings of the device server.
After each configuration session, be sure to set DIP switch 1 to the
‘OFF’ position. Otherwise, the unit will not transmit any data.
6.3 Web Graphic User Interface
Please see previous chapter to log-in the IRF-633 via web browser.
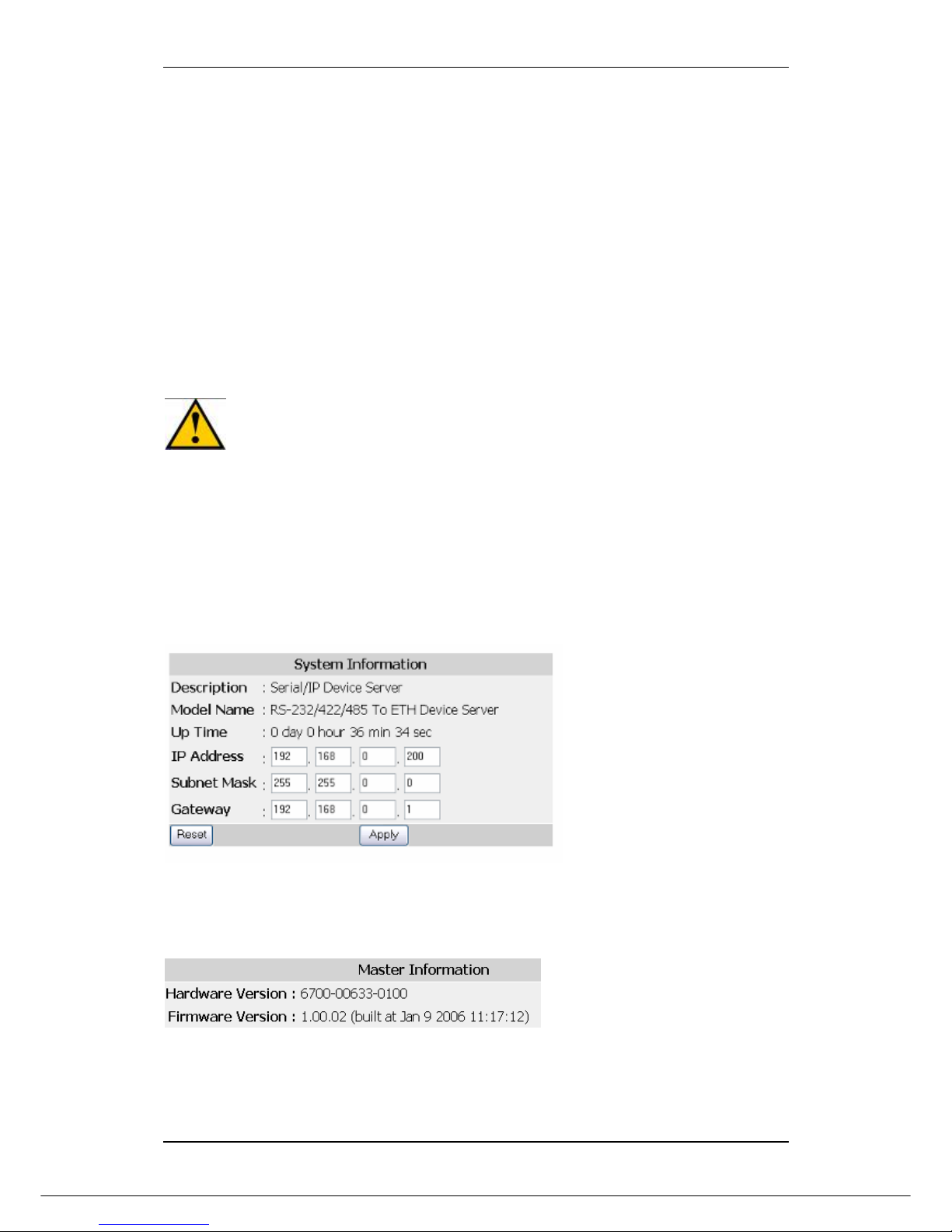
6.3.1 System Information
System information will show IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway settings. After
editing the setting press Apply to implement the settings.
6.3.2 Master Information
Master Info will show the hardware and firmware version.
6.3.3 Serial Port Configuration
25
This page lets you configure the communication model and operation mechanism of
the Device Server. Please select the appropriate mode as required for your

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
application. The user can also monitor the serial port status and configure TCP port
numbers from this menu.
A. The unit offers six modes (TCP Server / TCP Client / Converter / UDP Server /
UDP Client / Device Server). Please restart the unit after selecting the desired
mode.
Note: If you use Converter Mode, we recommend that you Disable the Packet Mode
option.
A detailed explanation of the setting choices is given underneath the following
screenshot – this is followed by diagrams and descriptions of the different network
setups and operating modes.
26
EXPLANATION: Server/Client Mode Configuration
Operation Mode
TCP Server: the TCP Server mode of the Device Server allows
TCP connections from up to four Device Servers with TCP Client
mode or PC with Serial IP Redirector program running.
TCP Client: the TCP Client mode of the Device Server can
establish up to four TCP connections with Device Servers of TCP
Server mode.
UDP Server: the UDP Server mode of the Device Server allows the
communication initiated from up to four UDP Clients.
UDP Client: the UDP Client mode can communicate with up to four
UDP Servers in UDP communication model.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
27
Device Server: the Device Server acts as Server role of RFC-2217
COM Port Control Protocol.
Converter Mode: two Device Servers communicate with each
other through point-to-point architecture in TCP communication
model. The TCP Client and Server roles of two Device Server
peers are negotiated automatically.
Remote IP 1~4 IP addresses of the other end device or Serial IP Redirector
workstations.
Port The TCP port number corresponding to each remote IP that
the TCP Server is bound to.
Status Toggle between “Enable” and “Disable” for activating or
deactivating the second to the fourth remote IP/Port entries.
Connection Idle
Time
In seconds. The TCP Server or Client will disconnect the TCP
session if no packets are transmitted in the set period.
Packet mode
(serial)
Enabled – input data from the serial interface is treated as serial
packets.
Disabled – input data from the serial interface is treated as bit
streams.
Packet mode
inter-packet
timeout
In milliseconds. The delimiter value for recognizing the timeout gap
between serial packets if Packet Mode is enabled.
Packet length of
serial output
In bytes. The length of a serial packet for Device Server to delimit
among data stream from IP network.
Packet length
timeout
In milliseconds. When the accumulated bytes do not exceed the
“Packet length of serial output” and the specified “Packet length
timeout” value is reached, a serial packet is formed and sent out.
Delimiter1(Hex)/
Status
Besides the inter-packet timeout, serial packets can be delimited by
one or two trailer bytes of specific values. Delimiter 1 is the
hexadecimal number of the first delimiter byte. Toggle to “Enable”
on the “Status” field for delimiting serial packets according to trailer
byte rather than inter-packet timeout.
Delimiter2(Hex)/
Status
The hexadecimal number of the second delimiter byte. If this byte is
“Disable” and the Delimiter 1 is “Enable”, the delimiter byte length is
one.
Serial Port Configuration
DIP Switch Mode Enable: use software management interface to set serial interface
configurations.
Disable: use DIP Switch to set serial interface configurations.
Operation Mode A read-only attribute. It shows the RS232/422/485 mode set by the
DIP switch.
Baud Rate The speed of the serial interface.
Parity Select or disable the parity checking method
Word Length The length of data in bits
Stop Bits The bit length of stop bits
Flow Control The flow control method for informing the correspondent

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
While using as Device Server mode, in case you are using a serial device with a 2-wire
RS-485 application or Modbus RTU protocol, do not forget to “Enable” the “Packet”
mode of serial input. Also enter the appropriate inter-packet timeout or delimiter byte
values to enable smooth data communication.
Note: You will not be able to change the serial port settings (Baud Rate, Parity, Stop
bits etc) while working in Device Server mode; they are managed through IP Serial
Redirector software.
Applications for Operation Modes:
Diagram 1 – Central Management Application (Device Server Mode)
Serial
Cable
IP Virtual COM port Software
IP
Network
TCP Connections
LAN
Serial
Cable
Serial
Cable
PLC
PLC
PLC
Device
Server
Device
Server
Device
Server
Device Server Mode: In this mode the Device Server acts in the Server role of the
RFC-2217 COM Port Control Protocol.
Diagram 2 – Peer-to-Peer Application (Converter Mode)
Serial
Cable
Serial
Cable
PC
IP
Network
TCP Connection
PLC
Device
Server
Device
Server
Converter Mode: In this mode the Device Server/Managed Media Converter acts like
an advanced media converter. Like a normal converter, the Device Server/Managed
Media Converter communicates with a remote Device Server/Managed Media
Converter in a peer-to-peer way. Also, the Device Servers communicate with each
28

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
other through an IP network in the TCP communication model. The TCP Client and
Server roles of the two Device Server peers are negotiated automatically.
Diagram 3 – Multi-host Application (TCP Server mode)
TCP client
A maximum of 4 remote devices can connect to a device server.
A maximum of 4 remote devices can connect to a device server.
TCP Server:
Local TCP port
TCP Server:
Local TCP port
Socket TCP call setup
Window XP
UNIX Linux
Device
Server
Device
Server
IP Network
TCP Server Mode: In this mode the Device Server/Managed Media Converter acts as
a device server and functions as a network agent for the serial device. For example,
when a serial device with a serial console port is connected to the Device
Server/Managed Media Converter while it is in TCP Server mode, the console port
becomes a network-accessible interface via the Device Server/Managed Media
Converter device server. In TCP Server Mode, the Device Server/Managed Media
Converter device server can link the serial device and a TCP-operating control host by
providing two-way transmission between the two.
In TCP Server mode, the Device Server/Managed Media Converter waits for the
control host to initiate communication with the serial device. Conversely, in TCP Client
mode (next diagram) the Device Server/Managed Media Converter initiates
communication with one or up to four remote devices simultaneously – when the serial
device experiences a communication event and prompts the Device Server/Managed
Media Converter to initiate communication.
29
Diagram 4 – Multi-host Application (TCP Client mode)
TCP server
A device server can connect up to 4 remote devices.
A device server can connect up to 4 remote devices.
Socket TCP call setup
Window XP
UNIX Linux
TCP Client:
1. Local TCP port
2. Remote IP address, Port
TCP Client:
1. Local TCP port
2. Remote IP address, Port
Device
Server
Device
Server
IP Network

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
TCP Client Mode: This mode lets the Device Server/Managed Media Converter act as
a bridge for serial devices that must communicate with server hosts like the Linux, Unix
and Windows systems. In this Client mode, the Device Server establishes a temporary
TCP connection with the servers automatically after powering up. All the data received
from the serial device is then sent to remote servers. The servers can also send data
back to the serial device while the connection is active. The Device Server/Managed
Media Converter automatically ends the connection when all information is sent and
the connection becomes idle for a specified length of time. It will reestablish the
connection when it receives data from the serial device.
In TCP Server mode (previous section), the Device Server/Managed Media Converter
waits for the control host to initiate communication with the serial device. Conversely,
in TCP Client mode the DEVICE SERVER/MANAGED MEDIA CONVERTER initiates
communication with one or up to four remote devices simultaneously – when the serial
device experiences a communication event and prompts the DEVICE
SERVER/MANAGED MEDIA CONVERTER to initiate communications.
6.3.4 Serial Connect Status
Serial Connect Status will show the serial port connection to the serial device. Serial
port settings can only be changed when using Media Converter mode.
User can get the instant information about the connectivity.
Connect Status: Server or Client
Peer IP Address: IP of remote PC access the serial device via Device Server
Dest/Srce Port Number: Showing the destination and source Port numbers. Source
port number will be as configured.
Byte Counts From UART: Displaying the number of bytes transmitted from serial
device.
Byte Counts to Network: Displaying the number of bytes received to TCP/IP network.
Byte Counts From Network: Displaying the number of bytes transmitted from Network.
Byte Counts to UART: Displaying the number of bytes received to serial device.
Mgmt. Configuration
30
This category offers multiple management options.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
6.3.5 User Configuration
This option will allow user to change the “username” and “user password” for the IRF633 management.
Type the new user name in the “User Name” and password to “User Password”.
Selecting Apply will implement the new user name and password, which will be
required to manage the IRF-633.
It is recommended to keep a written record in a safe place for the
User Name and Password. In case, you lost the both or either one,
you need to reset the system to default setting. This can be done by
pressing a button at S1 location of PCB (near to capacitor) after
removing the casing.
6.3.6 Firmware Download
The user can download the newer/latest firmware to upgrade the IRF-633 once
available. The user has two options, either they can upgrade via HTTP with browse
option to select the firmware file.
If using TFTP method, user must provide the valid IP address of TFTP server and the
file name, i.e. VK413.bin.
31
Once enter the parameters press “Start Upgrade by HTTP / TFTP” to upgrade the
firmware. The window will appear to show the time to before restarting the device
server to implement the upgraded firmware. For ensuring correct parameter values for
Device to be functioning after firmware upgrade from a prior version with different
configuration structure and data format, please Restore Factory Default Settings in
System Restart Menu.

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
6.3.7 Configuration File Backup and Restore
The user can backup configuration settings in a file or restore the settings saved in file
to device server.
For backup system configurations, click the button “Backup Setting” and then choose
the file path and file name. For restore system configurations, click the button
“Browse…” to choose the backup file for restoring and then click the button “Restore
Setting” to start the configuration restoring.
6.3.8 SNMP Community Configuration
You can use an external SNMP-based application to configure and manage the IRF-
633. This management method requires the SNMP agent on the IRF-633 and the
SNMP Network Management Station to use the same community string. This
management method, in fact, uses two community strings: the Get community string
and the Set community string. If the SNMP Network Management Station only knows
the Set community string, it can read and write to the MIBs. However, if it only knows
the Get community string, it can only read MIBs. The default Get and Set community
strings for the IRF-633 are public and private respectively.
If needed, assign the new parameters and press Save to implement the settings.
6.3.9 IP Trap
The following figure and table describe how to specify management stations that will
receive authentication failure messages or other trap messages from the IRF-633. Up
to 5 trap managers may be assigned.
32

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
Click on each parameter field to modify the desired setting, then click on Undo to
restore previously saved configurations or click on Save to retain newly entered
information. See descriptions below:
Parameter Description
IP Address
Community Name
Status
Enter the IP address of terminals for when abnormalities on a
connection occur and an alarm to be sent. Enter their
community names and disable or enable their alarm function
accordingly
Enter their community names
Disable or enable their alarm function
6.3.10 System Restart
Users can restart/reset the system via software from a remote location.
Restart Options
Clicking on the Restore button will set the IRF-633 back to factory
defaults. All saved configurations will be lost.
33

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
7 Appendix: RS-232 Cable Connection Diagram
Part 1.
Connection Diagram
Case i. PC connect to Device by
Straight-through RS232 cable
After connection with one paired 633 / 634 converters mode
Case ii. PC connect to Device by Cross-over RS232 cable
After connection with one paired 633 / 634 converters mode
34

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
Part 2. Configure 633/634 in Converter-mode by using the Console Port
0. Parameters of 633
Example for 633-A
i. Local(Source) IP address
IP address : 192.168.0.10 / 255.255.255.0
Gateway : 192.168.0.1
ii. Remote(Target) IP address
Remote IP address : 192.168.0.20
iii. Data mode and transmission parameters
Mode : RS232
baud : 38,400
data bit : 8
parity check : none
stop bit : 1
flow control : No
35
IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
Connection diagram
1. Set 633 dip switch #1 as ON for the “Console Mode”
2. Connect PC and 633 with an RS232
Cross-Over cable
3. Setup HyperTerminal parameters as below
baud : 38,400
data bit : 8
parity check : none
stop bit : 1
flow control : No
36

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
4. Enter username “admin” and press [enter] for password
5. Press 2 to select “Menu-Driven Interface”
37

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
6. Select “System Information Menu”
7. Assign an IP address (192.168.0.10) for 633/634 and save it.
38

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
***** After saving the IP address the device will re-boot
8. Select “Operation Mode Menu”
39
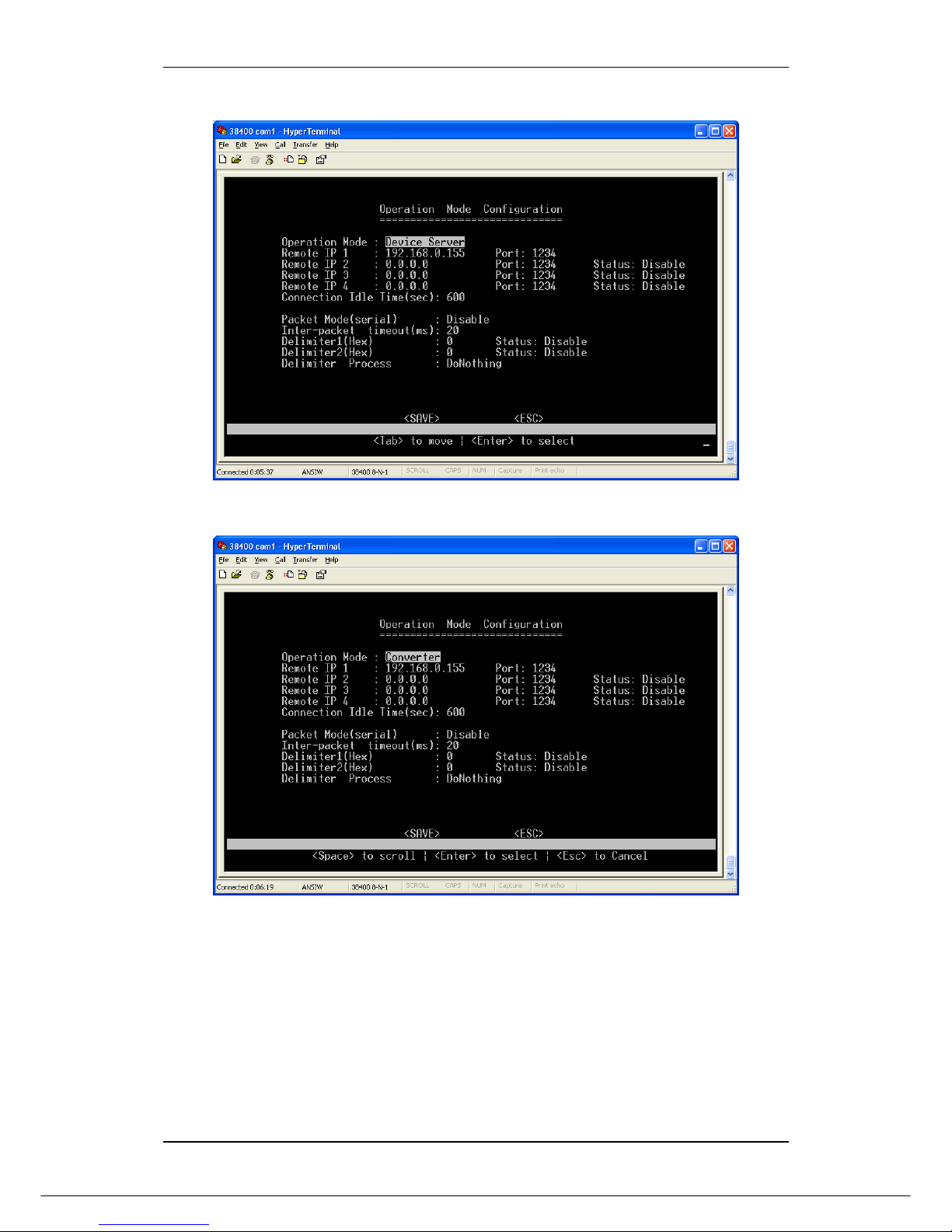
IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
The default setting of Operation Mode is ‘Device Mode’
9. Change the Operation Mode to ‘Converter’
40

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
10. Change Remote IP for 192.168.0.20
***** After saving this setting, the system needs to re-boot for it to take effect
41

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
10. choose “RS232/422/485 UART Menu”
11. Assign the serial parameters
42

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
13. After saving this setting, the system needs to re-boot for it to take
effect
43

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
14. After finishing these settings, the DIP switch #1 has to be changed back
to ‘Data Communications’ mode as required.
Ex: If position 2 is set as ON it means the serial port is set to RS232 mode.
44

IRF-633 RS-232/422/485 TO 100BASE-TX DEVICE SERVER
45
8 Contact Information
VOLKTEK CORPORATION
4F, No. 192 Lian-Cheng Road
Chung-Ho, Taipei 235, Taiwan ROC
TEL: +886 (2) 8242-1000
FAX: +886 (2) 8242-3333
ISO 9001 Certified
 Loading...
Loading...