Page 1

VMware vCenter Configuration Manager
Administration Guide
vCenter Configuration Manager 5.7
This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all
subsequent versions until the document is replaced by a new edition. To
check for more recent editions of this document, see
http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
EN-001187-00
Page 2

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at:
http://www.vmware.com/support/
The VMware Web site also provides the latest product updates.
If you have comments about this documentation, submit your feedback to:
docfeedback@vmware.com
© 2006–2013 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and
intellectual property laws. VMware products are covered by one or more patents listed at
http://www.vmware.com/go/patents.
VMware is a registered trademark or trademark of VMware, Inc. in the United States and/or other jurisdictions. All
other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
VMware, Inc.
3401 Hillview Ave.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
www.vmware.com
2
VMware, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
About This Book 9
Getting Started with VCM 11
Understanding User Access 11
Running VCM as Administrator on the Collector 12
Log In to VCM 12
Getting Familiar with the Portal 13
General Information Bar 13
Toolbar 14
Navigation Sliders 15
Customizing VCM for your Environment 16
Installing and Getting Started with VCM Tools 19
Install the VCM Tools Only 19
VCM Import/Export and Content Wizard Tools 20
Run the Import/Export Tool 20
Run the Content Wizard to Access Additional Compliance Content 21
Run the Deployment Utility 21
Package Studio 21
Foundation Checker 22
Configuring VMware Cloud Infrastructure 23
Virtual Environments Configuration 23
Managing Agents Virtual Environments 24
Managing vCenter Server Instances, Hosts, and Guest Virtual Machines 24
Managing Instances of vCloud Director and vApp Virtual Machines 25
Managing vShield Manager Instances 25
Configure Virtual Environments Collections 25
Configure Managing Agent Machines for Virtual Environment Management 26
Collect Machines Data From the Managing Agent Machines 26
Set the Trust Status for Managing Agent Machines 27
Configure HTTPS Bypass Setting for Virtual Environments 28
Enable Managing Agent Machines for Virtual Environments 28
Obtain the SSL Certificate Thumbprint 29
Configure vCenter Server Data Collections 29
Add vCenter Server Instances 30
Configure the vCenter Server Settings 31
Collect vCenter Server Data 32
vCenter Server Collection Results 33
Configure vCenter Server Scheduled Collections 34
Configure vCenter Server Virtual Machine Collections 35
Collect vCenter Server Virtual Machines Data 35
Manage vCenter Server Virtual Machines 36
Configure vCloud Director Collections 37
Add vCloud Director Instances 37
Configure the vCloud Director Settings 38
Collect vCloud Director Data 39
vCloud Director Collection Results 40
Configure vCloud Director vApp Virtual Machines Collections 41
Network Address Translation and vCloud Director vApp Discovery Rules 41
VMware, Inc.
3
Page 4

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Discover vCloud Director vApp Virtual Machines 43
Configure vShield Manager Collections 47
Configure ESX Service Console OS Collections 50
Configure the Collector as an Agent Proxy 51
Configure Virtual Machine Hosts 52
Copy Files to the ESX/ESXi Servers 54
Collect ESX Logs Data 55
Virtualization Collection Results 56
Configure the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In 56
Register the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In 56
Configuring the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In Integration Settings 57
Manage Machines from the vSphere Client 58
Running Compliance for the VMware Cloud Infrastructure 59
Create and Run Virtual Environment Compliance Templates 59
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups 60
Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Rules 61
Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Filters 62
Preview Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups 62
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Templates 63
Run Virtual Environment Compliance Templates 64
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Exceptions 65
Resolve Noncompliant Virtual Environments Template Results 66
Enforce Compliance Template Results by Using VCM Actions 66
Manually Enforce Compliance Template Results 67
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Exceptions 67
Configure Alerts and Schedule Virtual Environment Compliance Runs 68
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Alert Rules 69
Create Virtual Environments Compliance Alert Configurations 69
Schedule Virtual Environments Compliance Template Runs 70
Configuring vCenter Operations Manager Integration 73
VCM Registration in vCenter Operations Manager for Integration 73
Configure vCenter Operations Manager Change Events 73
Standards Compliance for vCenter Operations Manager 74
Configure vCenter Operations Manager Standards Compliance 74
Scoring Badges for vCenter Operations Manager Standards Compliance 80
Auditing Security Changes in Your Environment 85
Configuring Windows Machines 87
Configure Windows Machines 87
Verify Available Domains 88
Check the Network Authority 89
Assign Network Authority Accounts 89
Discover Windows Machines 90
License Windows Machines 90
Install the VCM Windows Agent on Your Windows Machines 91
Collect Windows Data 93
Windows Collection Results 94
Getting Started with Windows Custom Information 95
Prerequisites to Collect Windows Custom Information 96
Using PowerShell Scripts for WCI Collections 97
Guidelines in PowerShell Scripting for WCI 98
Challenges in PowerShell Scripting for WCI 98
PowerShell Script Signing Policies 101
Create an Example PowerShell Script for Scheduled Tasks 102
4
VMware, Inc.
Page 5

Contents
Windows Custom Information Change Management 107
Collecting Windows Custom Information 108
Create Your Own WCI PowerShell Collection Script 108
Verify that Your Custom PowerShell Script is Valid 109
Install PowerShell 110
Collect Windows Custom Information Data 110
Run the Script-Based Collection Filter 111
View Windows Custom Information Job Status Details 112
Windows Custom Information Collection Results 113
Run Windows Custom Information Reports 114
Troubleshooting Custom PowerShell Scripts 115
Configuring Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Machines 117
Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Machine Management 117
Linux, UNIX, or Mac OS X Installation Credentials 119
Configure Collections from Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Machines 120
Configure Installation Delegate Machines to Install Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Agents 121
Configure the HTTPS Bypass Setting for Linux Agent Installations 123
Enable Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Agent Installation 123
Add and License Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Machines for Agent Installation 124
Install the VCM Agent on Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Operating Systems 125
Collect Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Data 132
Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Collection Results 133
Configure Scheduled Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Collections 133
Create a Dynamic Machine Group for Linux, UNIX, or Mac OS X Machines 134
Schedule Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Collections 135
Patching Managed Machines 137
Patch Assessment and Deployment 137
Prerequisite Tasks and Requirements 138
General Requirements 138
Requirements to Patch Solaris Machines in Single-User Mode 140
Requirements to Patch Managed Machines Without Changing the Run Level 140
Requirements to Patch AIX Machines 141
Manually Patching Managed Machines 141
Getting Started with VCM Manual Patching 143
Getting Started with VCM Manual Patching for Linux and UNIX Managed Machines 143
Getting Started with VCM Manual Patching for Windows Managed Machines 150
Configuring An Automated Patch Deployment Environment 156
Configuring the Patching Repository Machine 158
(Optional) Configuring the Alternate Location Patch Repository Machines 161
Configuring VCM to Work with the Patching Repository and Alternate Locations 162
Deploying Patches with Automated Patch Assessment and Deployment 169
Configure VCM for Automatic Event-Driven Patch Assessment and Deployment 170
Generate a Patch Assessment Template 171
Run a Patch Assessment on Managed Machines 172
Add Exceptions for Patching Managed Machines 172
Configure the VCMAdministration Settings 173
Generate a Patch Deployment Mapping 175
Configure VCM for Automatic Scheduled Patch Assessment and Deployment 176
How the Linux and UNIX Patch Staging Works 177
How the Linux and UNIX Patching Job Chain Works 178
How the Deploy Action Works 178
Patch Deployment Wizards 179
Running Patching Reports 180
Running and Enforcing Compliance 181
VMware, Inc.
5
Page 6

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Running Machine Group Compliance 181
Getting Started with SCAP Compliance 194
Conduct SCAP Compliance Assessments 195
Provisioning Physical or Virtual Machine Operating Systems 199
Operating System Provisioning Components 199
How Operating System Provisioning Works 200
Configure Operating System Provisioning Servers 201
Add Operating System Provisioning Servers 202
Set the Trust Status for Operating System Provisioning Servers 202
Collect Operating System Distributions 203
Discover Provisionable Machines 203
Provision Machines with Operating System Distributions 204
Provision Windows Machines 204
Provision Linux Machines 208
Change Agent Communication 213
Provisioned Machines Results 213
Reprovision Machines 214
Provisioning Software on Managed Machines 217
Using Package Studio to Create Software Packages and Publish to Repositories 217
Software Repository for Windows 217
Package Manager for Windows 217
Software Provisioning Component Relationships 218
Install the Software Provisioning Components 218
Install Software Repository for Windows 219
Install Package Studio 220
Install Package Manager on Managed Machines 222
Using Package Studio to Create Software Packages and Publish to Repositories 223
Creating Packages 223
Using VCM Software Provisioning for Windows 225
Collect Package Manager Information from Machines 225
Collect Software Repository Data 226
Add Repository Sources to Package Managers 227
Install Packages 228
Related Software Provisioning Actions 229
Viewing Provisioning Jobs in the Job Manager 230
Create Compliance Rules Based on Software Provisioning Data 230
Create Compliance Rules Containing Software Provisioning Remediation Actions 231
Configuring Active Directory Environments 233
Configure Domain Controllers 233
Verify Available Domains 234
Check the Network Authority Account 234
Assign Network Authority Accounts 235
Discover Domain Controllers 235
License Domain Controllers 236
Install the VCM Windows Agent on Your Domain Controllers 237
Collect Domain Controller Data 238
Configure VCM for Active Directory as an Additional Product 239
Install VCM for Active Directory on the Domain Controllers 240
Run the Determine Forest Action 240
Run the Domain Controller Setup Action 241
Collect Active Directory Data 242
Active Directory Collection Results 242
Configuring Remote Machines 245
6
VMware, Inc.
Page 7

Contents
VCM Remote Management Workflow 245
Configuring VCM Remote Connection Types 245
Using Certificates With VCM Remote 246
Configure and Install the VCM Remote Client 246
Configure the VCM Remote Settings 246
Install the VCMRemote Client 249
Connect VCM Remote Client Machines to the Network 256
VCM Remote Collection Results 256
Tracking Unmanaged Hardware and Software Asset Data 259
Configure Asset Data Fields 259
Review Available Asset Data Fields 260
Add an Asset Data Field 260
Edit an Asset Data Field 261
Delete a VCM for Assets Data Field 262
Change the Order of Asset Data Columns 262
Refresh Dynamic Asset Data Fields 263
Configure Asset Data Values for VCM Machines 264
Configure Asset Data for Other Hardware Devices 264
Add Other Hardware Devices 265
Add Multiple Similar Other Hardware Devices 265
Edit Asset Data for Other Hardware Devices 265
Edit Asset Data Values for Other Hardware Devices 266
Delete Other Hardware Devices 266
Configure Asset Data for Software 267
Add Software Assets 267
Add Multiple Similar Software Assets 268
Edit Asset Data for Software 269
Edit Asset Data Values for Software 270
Delete Software Data 270
Managing Changes with Service Desk Integration 271
Configure Service Desk Integration 271
View Service Desk Integration in the Console 271
View Service Desk Integration in Job Manager 272
Index 273
VMware, Inc.
7
Page 8

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
8
VMware, Inc.
Page 9

About This Book
The VCM Administration Guide describes the steps required to configure VCM to collect and manage data
from your virtual and physical environment.
Read this document and complete the associated procedures to prepare for a successful implementation of
the components.
Intended Audience
This information is written for experienced Windows, Linux, UNIX, or Mac OS X, and virtual
environments system administrators who are familiar with managing network users and resources and
with performing system maintenance.
To use this information effectively, you must have a basic understanding of how to configure network
resources, install software, and administer operating systems. You also need to fully understand your
network topology and resource naming conventions.
Document Feedback
VMware welcomes your suggestions for improving our documentation. If you have comments, send
your feedback to docfeedback@vmware.com.
VMware VCM Documentation
The vCenter Configuration Manager (VCM) documentation consists of the VCM Installation Guide, VCM
Troubleshooting Guide, VCM online Help, and other associated documentation.
VMware, Inc.
9
Page 10

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Technical Support and Education Resources
The following technical support resources are available to you. To access the current version of this book
and other books, go to http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
Online and Telephone
Support
To use online support to submit technical support requests, view your
product and contract information, and register your products, go to
http://www.vmware.com/support.
Customers with appropriate support contracts should use telephone support
for priority 1 issues. Go to
http://www.vmware.com/support/phone_support.html.
Support Offerings To find out how VMware support offerings can help meet your business
needs, go to http://www.vmware.com/support/services.
VMware Professional
Services
VMware Education Services courses offer extensive hands-on labs, case study
examples, and course materials designed to be used as on-the-job reference
tools. Courses are available onsite, in the classroom, and live online. For
onsite pilot programs and implementation best practices, VMware Consulting
Services provides offerings to help you assess, plan, build, and manage your
virtual environment. To access information about education classes,
certification programs, and consulting services, go to
http://www.vmware.com/services.
10
VMware, Inc.
Page 11

Getting Started with VCM
When you use VCM, you must understand user access and how to start VCM from any physical or virtual
machine. You must also familiarize yourself with the VCM Web Console features.
This chapter includes the following topics:
Understanding User Access 11
Log In to VCM 12
Getting Familiar with the Portal 13
Customizing VCM for your Environment 16
Understanding User Access
User access determines who has access to VCM and with what roles. To manage your user access, create
rules that are assigned to roles. VCM assigns the roles to each user login you create. User access is
managed in the Administration User Manager node.
The user account that was used to install VCM is automatically granted access to VCM, placed in the roles
of ADMIN and USER, and placed into the Admin role. This user can log in to VCM using the Admin role.
The AD_Admin role allows full administration access to AD objects only.
1
VMware, Inc.
When a user is added to the Admin role in VCM or granted access to the Administration User Manager
node, that user is placed in the fixed machine roles Security Administrators and Bulk Insert Administrators
Groups. They are also added to the database roles of public, ADMIN, and User in the VCM Database.
Users who will not have access to the Administration User Manager node will be assigned to public.
Depending on the functions granted to a user, they might need additional or fewer privileges for their role
to function properly.
VCM provides a role named Change Restricted to limit users from making certain changes in your
environment. With this role, users can discover machines, collect data from machines, assess machines,
display bulletin and template details, check for updates, and view history. Users can add, edit, and delete
reports, compliance rules and rule groups, and compliance and patch assessment templates.Users with the
Change Restricted role can also install the VCM Agent, upgrade VCM, and uninstall VCM.
When you apply the Change Restricted role to a user’s VCM login, they cannot perform the following
actions.
11
Page 12

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
n
Remote command execution
n
Change actions against target managed machines
n
Change rollback
n
Compliance enforcement
n
Patch deployment
n
Software deployment
n
OS provisioning
n
Machine reboots
All VCM user accounts must have the following rights on the VCM Collector machine.
n
Ability to log on locally to access IIS
n
Read access to the System32 folder
n
Write access to the CMFiles$\Exported_Reports folder to export reports
n
If default permissions have been changed, read access to the C:\Program Files (x86)
\VMware\VCM\WebConsole directory and all subdirectories and files
Users who add machines to VCM using a file or the Available Machines Add Machines action must
have write access to CMFiles$\Discovery_Files.
Running VCM as Administrator on the Collector
By default for localhost, Internet Explorer on Windows Server 2008 R2 runs with Protected Mode enabled.
If you are logged in to VCM as an Administrator, because Protected Mode is enabled, problems can occur
with the SQLServer Reporting Service (SSRS) Web service interface components such as dashboards and
node summaries.
CAUTION Although you should not access VCM on the Collector using a Web console, to restore
the SSRS functionality you can run Internet Explorer as administrator or disable Protected Mode for
the zone of the Collector (localhost). If you perform this action, you must take additional precautions
to protect the Collector because of the increased exposure to attacks on the Collector through the
Web browser, such as cross-site scripting.
Log In to VCM
Access VCM from any physical or virtual machine in your network. The level of access is determined by
your VCM administrator.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the physical or virtual machines from which you are accessing VCM have a supported
version of Internet Explorer installed. For supported platforms, see the VCM Installation Guide.
n
Configure the Internet Explorer Pop-up Blocker settings to add your Collector to your list of allowed
Web sites, or disable Pop-up Blocker. Click Internet Explorer and select Tools > Pop-up Blocker > Pop-
up Blocker Settings and then add the path for your Collector in the allowable address field.
12
VMware, Inc.
Page 13
Procedure
1. To connect to VCM from a physical or virtual machine on your network, open Internet Explorer and
type http://<name-or-IP-address-of-Collector-machine>/VCM.
2. Type your user network credentials.
3. (Optional) Select Automatically log on using this role to have VCM log you in.
4. Click Log On.
Your VCM user account can have multiple roles. If you selected the Automatically log on using this role
option, VCM will automatically log you on as the User Role displayed on the Logon screen. To change
roles, you must use the Logoff button in the top right corner of the Console. This action will return you to
the Logon screen so that you can use the drop-down menu to select a different role.
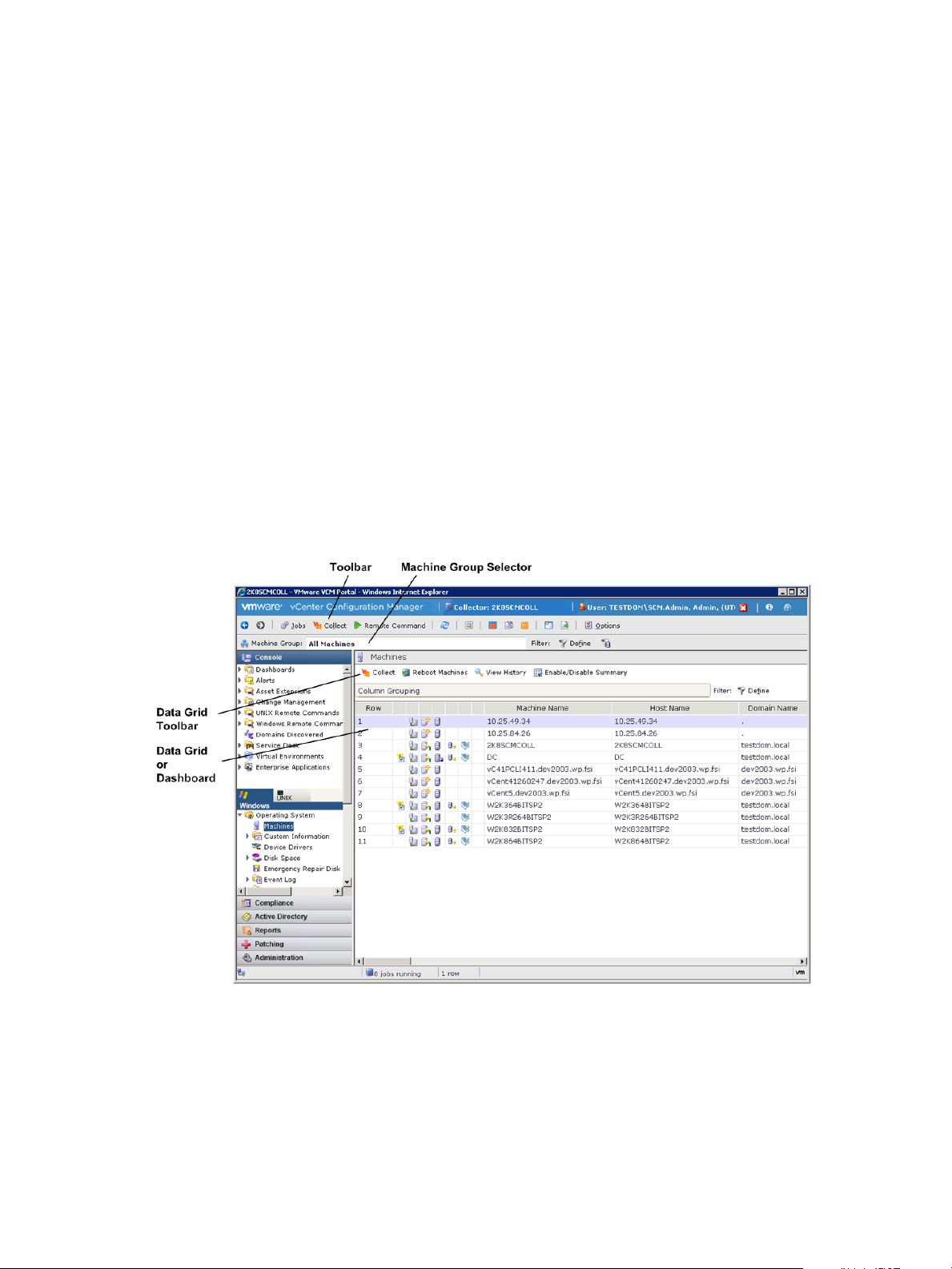
Getting Familiar with the Portal
The VCM Web Console provides access to all VCM features to manage your environment.
The Web Console uses a browser-based interface to run from any Windows machine that has access to the
server on which VCM is installed. The Windows machine must be running Internet Explorer or Mozilla
Firefox with the Internet Explorer tab plug-in installed.
The Web Console includes several major areas and controls.
Getting Started with VCM
Figure 1–1. VCM Portal
VMware, Inc.
General Information Bar
The general information bar displays the VCM Collector’s active SQL Server name, your VCM user name
and active Role, and the following buttons.
13
Page 14

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
n
Log Out: Exits the Web Console. The Web Console closes and the VCM Logon screen appears.
n
About: Displays information about how to contact VMware Technical Support and version information
for VCM and all of its components. This information may be important when you contact VMware
Technical Support.
n
Help: Opens the online Help for the currently-active display.
Toolbar
The global toolbar provides you with easily-accessible options to enhance control of your environment
and data.
The left and right arrow buttons navigate to the previous or next page in the data
area.
The Jobs button opens the Jobs Running status window. This button provides
access to the Collector status and allows you to stop and restart the Collector
service.
The Collect button opens a wizard that allows you to define and initiate data
collections.
The Remote Commands button allows you to invoke the Remote Commands wizard
from the toolbar without having to access the node.
The Refresh data grid view button refreshes the data grid. Press F5 on the keyboard
as an alternative action.
The View row cells button displays a vertically scrolling view of a single row of
data, rather than the table-based data grid view in a separate window, and allows
you to move between records.
The Select all displayed data rows button selects all the rows in the data grid.
The Copy button copies information from the selected rows in the data grid to the
clipboard.
The Copy link to clipboard button copies the link of the content on-screen to the
clipboard.
The View data grid in separate window button displays the data grid in a separate
window.
The Export displayed d ata button exports data to a CSV formatted file. This file is
exported to
Reports
The Options button opens the User Options window. These s ettings pertain to the
User who is logged in to VCM. All VCM users can configure these settings to their
individual preferences.
\\<name_of_Collector_machine>\CMfiles$\Exported
.
14
VMware, Inc.
Page 15
Getting Started with VCM
Navigation Sliders
The navigation sliders on the left side of the Web Console include the items listed and described in the
following table. The individual items that you see in VCM vary depending on the components that you
have licensed.
n
Active Directory and AD objects based on your role.
n
Patching options are available based on your role.
n
Administration is visible only to users who have Administrative rights to VCM as part of their VCM
role.
For detailed instructions about any of these features, see the online Help.
Slider Actio n
Console
Compliance
n
View, export, or print enterprise-wide, summary information.
n
Review or acknowledge current alert notifications.
n
Manage VCM discovered and non-VCM discovered hardware and software
assets.
n
Review changes that occurred from one collection to the next.
n
Create, edit, or run remote commands on a VCM managed Windows or UNIX
machine.
n
View information about VCM discovered domains.
n
Navigate and manage integrated service desk events.
n
Manage virtual machines.
n
View your Windows NT Domain and Active Directory related data.
n
View information for enterprise-level applications.
n
Review non-security related UNIX machine-specific information.
n
Review UNIX security data to ensure consistent security configurations across
your environment.
n
Create and manage Compliance rule groups and templates based on AD
objects or machine group data.
VMware, Inc.
15
Page 16
vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Slider Actio n
Active
Directory
Reports
Patching
n
View, export, or print enterprise-wide, summary information for Active
Directory objects.
n
Review alert notifications for the selected AD location.
n
Review Active Directory-related changes that occurred from one collection to
the next.
n
View collected information about Active Directory objects such as Users,
Groups, Contacts, Computers, Printers, Shares, and Organizational Units.
n
Review Active Directory site lists, including Site Links, Site Link Bridges,
Subnets, Intersite Transports, Servers, Connections and Licensing.
n
View Active Directory Group Policy Container Settings.
n
View information about Active Directory Domains, DCs, and Trusts.
n
Track and display access control entries and security descriptor data on all
collected objects.
n
View Active Directory Schema information.
n
Run out-of-the-box reports against your collected data.
n
Write your own SQL and SSRS reports using VCM’s report wizard.
n
Review a list of bulletins available to VCM.
n
Create, run, or import VCM Patching templates to display the machines that
require the patches described in each bulletin.
n
Monitor VCM Patching jobs.
n
Deploy patches.
Administration
n
Manage basic configuration options for VCM.
n
Establish filters to limit the data you collect from machines in your
environment.
n
Review how your VCM licenses are being used.
n
Identify and manage your physical and virtual machines.
n
Manage VCM Logins and Roles.
n
Set options for assessment and deployment.
n
View the status of jobs that are currently running, scheduled to run, or
completed.
n
Configure VCM to notify you of certain conditions in your environment.
Customizing VCM for your Environment
Customization of your environment is essential to fine-tune the visibility of configuration information so
that the policies you develop and the actions you take are appropriate for your IT infrastructure.
16
VMware, Inc.
Page 17

Getting Started with VCM
Create a machine group structure that matches the organization of the machines in your environment.
With these machine groups, you can manage specific machines in your environment such as all SQL
Servers in a particular location. You can apply specific changes or create roles and rules for those machines
independently from other machines in your environment. This approach ensures that you can restrict
access to critical machines to the appropriate users with rights to VCM.
You can customize the following options for your environment.
n
Alerts: Define the objects and types of changes that you are alerted to when they are detected in VCM.
For example, you can set an alert to notify you if a registry setting changes in your environment.
n
Collection Filters and Filter Sets: Use collection filters to specify the data to collect from the VCM
managed machines. A default collection filter is provided for each data type. You can add custom
collection filters that are specific to your enterprise. You can apply filters during instant collections and
scheduled collections if the filters are included in a filter set. After you create collection filters, organize
them into filter sets. You can create specific filter sets or filter set groups for different machine groups.
You can apply filter sets during instant collections or scheduled collections.
n
Compliance Templates and Rule Groups: Use compliance templates and rule groups to define specific
settings and verify whether the machines match those criteria. VCM provides prepackaged templates
and rules to check the compliance of your machines with regulatory, industry, and vendor standards.
VMware provides additional compliance packages that you can import into VCM.
n
Reports: Create and print tailored reports of information that does not appear in VCM. VCM provides
prepackaged reports that you can run after you collect data from your VCM managed machines.
n
Roles and Rules: VCM roles and access rules work together to control user access to VCM. For
example, you can create a role that allows a user to view all data, but not make changes to the
environment. You can create a role to run certain reports or a role that allows unlimited access to a
single machine group.
The VCM Change Restricted role limits users from making certain changes in your environment. See
"Understanding User Access" on page 11.
VMware, Inc.
17
Page 18

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
18
VMware, Inc.
Page 19

Installing and Getting Started with VCM Tools
VCM Installation Manager installs several VCM components and tools on the Collector machine during
the installation.
This chapter includes the following topics:
Install the VCM Tools Only 19
VCM Import/Export and Content Wizard Tools 20
Run the Deployment Utility 21
Package Studio 21
Foundation Checker 22
Install the VCM Tools Only
You can install the VCM tools on a non-Collector Windows machine.
If you plan to install VCMon the non-Collector Windows machine later, you must uninstall the tools and
then install VCM.
Prerequisites
2
Perform the installation requirements for each tool in the Advanced Installation selection. For example,
you can install Import/Export (I/E) and Content Wizard only on a machine that is running VCM.
Procedure
1. On the non-Collector Windows machine on which you want to install the tools, insert the installation
CD.
2. In Installation Manager, click Run Installation Manager.
During the installation, follow the installation requirements that Installation Manager reports when
Foundation Checker runs.
3. Complete the initial installation pages, and click Next on subsequent pages to access the Select
Installation Type page.
a. Clear the VMware vCenter Configuration Manager check box.
b. Select Tools.
VMware, Inc.
19
Page 20
vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
c. To install a subset of tools, clear the Tools check box and select only the individual tools to install.
4. Click Next.
5. Complete the remaining instructions and click Next.
6. On the Installation Complete page, click Finish.
7. On the Installation Manager page, click Exit.
VCM Import/Export and Content Wizard Tools
Use the Import/Export Tool and the Content Wizard Tool to move or update VCM business objects. These
tools support the migration of any VCM Management Extension for Asset data that was added to VCM
manually, but does not import or export any collected data.
The Import/Export Tool supports the following scenarios.
n
Back up (export) and restore (import) business objects to the same machine.
n
Back up (export) and import (if needed) business objects during a VCM upgrade.
n
Export and migrate (import) business objects to additional machines in a multi-Collector environment
during setup or to move custom content.
n
Use the Content Wizard to download current Compliance Content from VMware and import it into an
existing database.
n
Using the Command Line Interface, automate the propagation of content to other machines in a multicollector environment with a “golden machine”.
n
Aid in disaster recovery by using the Command Line Interface to automate and schedule the backup of
VCM content and configuration parameters.
The Command Line Interface (CLI) is a powerful extension of the Import/Export graphic user interface
(GUI). In addition to supporting the scenarios noted above, the CLI allows content to be overwritten, as
opposed to “rename only”, and provides for automation through scripting suitable for customizations.
IMPORTANT Use of the CLI should be restricted to advanced users who exercise caution when testing
their scripts.
The Import/Export Tool and Content Wizard Tool were installed on your Collector machine during your
VCM installation.
Run the Import/Export Tool
Use the Import/Export Tool to back up your VCM database business objects and import them into a new
VCM database or into a recovered VCM database. This tool also supports the migration of any VCM
Management Extension for Asset data that was manually added to VCM.
Prerequisites
Install the Import/Export Tool. See "Installing and Getting Started with VCM Tools" on page 19.
Procedure
1. On the Collector, click Start.
2. Select All Programs > VMware vCenter Configuration Manager > Tools > Import Export Tool.
3. For importing and exporting procedures, click Help > Contents and use the online help.
20
VMware, Inc.
Page 21

Installingand Getting Started with VCM Tools
Run the Content Wizard to Access Additional Compliance Content
Use the Content Wizard to import additional VMware content such as VCM Compliance Content
Packages. These packages are not available in VCM until you download and import them. Check the VCM
Compliance Content Packages to determine if you need to import them.
Prerequisites
Install the Content Wizard. See "Installing and Getting Started with VCM Tools" on page 19.
Procedure
1. On the Collector, click Start.
2. Select All Programs > VMware vCenter Configuration Manager > Tools > Content Wizard Tool.
3. In the Content Wizard, select Get Updates from the Internet and click Next.
4. After the wizard identifies available content, click Next.
5. Select the updates to install on your Collector and click Install.
When the installation is finished, the Event Log Results window appears.
6. On the Event Log Results window, click Save and specify a location to save the logs.
7. Click Close.
8. On the Content Wizard page, click Exit.
What to do next
View the imported data in VCM. For example, click Compliance and select Machine Group Compliance >
Templates. You can now run any imported compliance template against your collected data.
Run the Deployment Utility
The Deployment Utility for UNIX/Linux and ESX/vSphere copies files to multiple target machines when
you configure Linux, UNIX, and ESX/vSphere machines for management in VCM.
Procedure
1. On the Collector, navigate to C:\Program Files (x86)\VMware\VCM\Tools.
2. Copy the DeployUtility-<version>.zip file from the Collector to your Windows machine.
3. Extract the files.
4. Double-click DeployUtil.exe to start the application.
What to do next
In the Deployment Utility, click Help and review the procedure for the type of machine you are
configuring.
Package Studio
Use Package Studio to create software packages that can be installed by VCM. It is one component of
VCM Software Provisioning that includes the Software Repository for Windows and the Package
Manager.
For procedures to run the Package Studio, see the Software Provisioning Components Installation and User's
Guide.
VMware, Inc.
21
Page 22

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Foundation Checker
Use the Foundation Checker tool to verify that a Windows machine designated as a VCM Collector meets
all of the prerequisites necessary to install VCM.
Installation Manager uses VCM Foundation Checker to check a machine’s viability for a successful VCM
deployment. Foundation Checker runs system checks that determine various conditions, settings, and
requirements, and displays a results file that displays the system checks that passed, failed, or generated
warnings.
If the checks run without error, you can install VCM. If the checks identify missing components or
incorrect configurations, Foundation Checker instructs you where to verify the component or
configuration and how to remedy the errors.
To run the Foundation Checker on a Windows machine on which you will install another instance of
VCM, see the Foundation Checker User's Guide.
22
VMware, Inc.
Page 23

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrastructure
VCM collects information from your instances of vCenter Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager
so that you can then use the information to manage and maintain your virtual environment.
The collected data appears in the Console under the Virtual Environments node. The information is
organized in logical groupings based on the information sources, including vCenter Server, vCloud
Director, and vShield Manager.
Based on the collected virtual environments data, you can manage the objects and data at an enterprise
and individual level, including running compliance rules and reports; running actions, such as changing
settings and taking virtual machine snapshots; and managing the guest operating systems as fully
managed VCM machines.
This chapter includes the following topics:
Virtual Environments Configuration 23
Configure Virtual Environments Collections 25
Configure Managing Agent Machines for Virtual Environment
Management 26
Obtain the SSL Certificate Thumbprint 29
Configure vCenter Server Data Collections 29
Configure vCenter Server Virtual Machine Collections 35
Configure vCloud Director Collections 37
Configure vCloud Director vApp Virtual Machines Collections 41
Configure vShield Manager Collections 47
Configure ESX Service Console OS Collections 50
Configure the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In 56
3
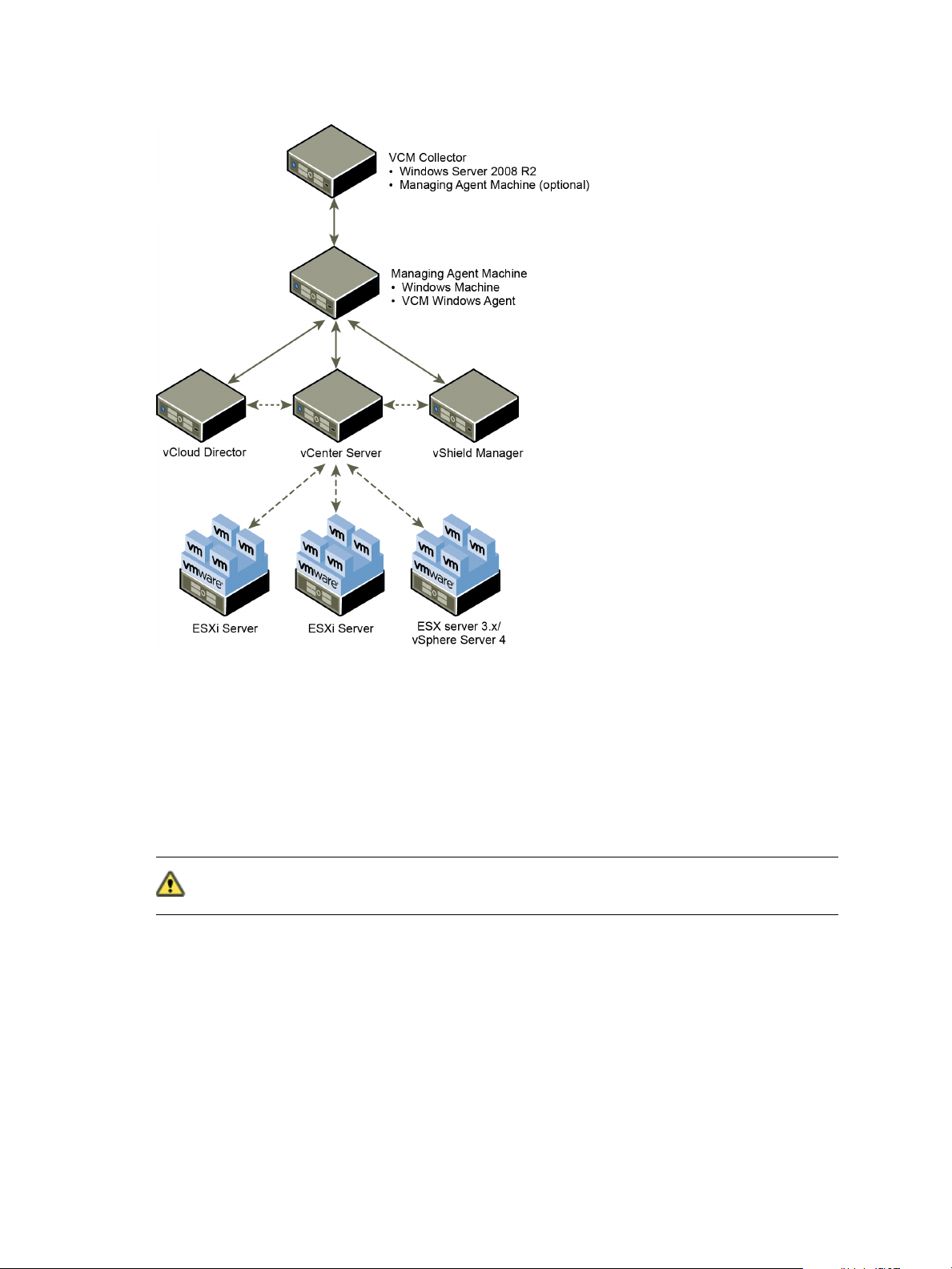
Virtual Environments Configuration
To manage your virtual environments, you collect vCenter Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager
data. To collect the data, you use one or more Managing Agent machines.
After configuring your Managing Agent machines, you add and configure your vCenter Server, vCloud
Director, and vShield Manager instances in VCMto use the Managing Agent for communication. For a
diagram illustrating how the components are configured together, see Figure 3–1. Virtual Environments
Configuration Diagram.
VMware, Inc.
23
Page 24
vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Figure 3–1. Virtual Environments Configuration Diagram
Managing Agents Virtual Environments
The Managing Agent machines must have the 5.5 Agent or later installed. They must also be configured to
manage the secure communication between the vCenter Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager
instances and the Collector. Depending on the size of your Cloud Infrastructure environment, you can use
your Collector as a Managing Agent or you can use another Windows machine. If your individual vCenter
Server instances manage no more than 1–30 hosts and a maximum of 1000 guests, then you can use the
Collector as your Managing Agent. If any of your vCenter Server instances exceed this amount, you must
use a Windows machine that is not your Collector as a Managing Agent.
CAUTION Do not use the Windows machines on which your vCenter Server instances are running
as Managing Agent machines.
Managing vCenter Server Instances, Hosts, and Guest Virtual Machines
You collect data from vCenter Server instances regarding resources managed by the vCenter Server, and
to identify and manage the host and guest machines. The host and guest machines are managed based on
configured vCenter Server instances. From VCM, you can run vCenter Server actions such as configuring
settings, turning the power on and off, or taking a snapshot. To fully manage the guest machines, install
the VCM Agent on the virtual machines and manage their operating system.
24
VMware, Inc.
Page 25
Managing Instances of vCloud Director and vApp Virtual Machines
You collect data from vCloud Director instances regarding their configurations, resources managed by
vCloud Director, and to identify and manage the vApp virtual machine guest operating systems. To fully
manage the guest machines, you install the VCM Agent on the virtual machines and manage their
operating system.
Managing vShield Manager Instances
You collect from vShield Manager instances to gather data regarding vShield App security groups. You
can run reports on the collected data.
Configure Virtual Environments Collections
To manage your virtual environments, configure your Managing Agent and then implement the
procedures that suit your environment.
Procedure
1. "Configure Managing Agent Machines for Virtual Environment Management" on page 26
The Managing Agents are one or more physical or virtual machines running a supported Windows
operating system that manages the communication between the Collector and your instances of
vCenter Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager.
Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
2. "Obtain the SSL Certificate Thumbprint" on page 29
When configuring the settings for your virtual environments systems, you can use an SSL certificate
thumbprint file to ensure secure communication between the Collector and your instances of vCenter
Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager.
3. "Configure vCenter Server Data Collections" on page 29
Collect data from your vCenter Server so that you can identify and manage your virtual
environments, including ESX and ESXi hosts, and guest virtual machines.
4. "Configure vCenter Server Virtual Machine Collections" on page 35
Configure virtual machine collections so that you can identify and manage the guest operating
systems on the vCenter Server virtual machines.
5. "Configure vCloud Director Collections" on page 37
Configure collections from your vCloud Director instances so that you can run compliance and
reports, and identify your vApp virtual machines.
6. "Configure vCloud Director vApp Virtual Machines Collections" on page 41
Collect vCloud Director data so that you can identify and manage the guest operating systems of the
vApp virtual machines.
7. "Configure vShield Manager Collections" on page 47
Configure collections from your vShield Manager instances so that you can run reports on the
collected data.
VMware, Inc.
8. "Configure ESX Service Console OS Collections" on page 50
The ESX Service Console OS Linux data type data and the ESXlogs are collected directly from the ESX
operating systems, not from vCenter Server. Configure the ESX servers so that you can collect the
25
Page 26

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Linux data type and ESX log data from the ESX service console operating system.
9. "Configure the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In" on page 56
The vSphere Client VCM Plug-In provides contextual access to VCM change, compliance, and
management functions. It also provides direct access to collected vCenter Server, virtual machine host,
and virtual machine guest data.
Configure Managing Agent Machines for Virtual Environment Management
The Managing Agents are one or more physical or virtual machines running a supported Windows
operating system that manages the communication between the Collector and your instances of vCenter
Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager.
The Managing Agent machines must have the 5.5 Agent or later installed. They must also be configured to
manage the secure communication between the vCenter Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager
instances and the Collector. Depending on the size of your Cloud Infrastructure environment, you can use
your Collector as a Managing Agent or you can use another Windows machine. If your individual vCenter
Server instances manage no more than 1–30 hosts and a maximum of 1000 guests, then you can use the
Collector as your Managing Agent. If any of your vCenter Server instances exceed this amount, you must
use a Windows machine that is not your Collector as a Managing Agent.
CAUTION Do not use the Windows machines on which your vCenter Server instances are running
as Managing Agent machines.
Procedure
1. "Collect Machines Data From the Managing Agent Machines" on page 26
Collect data from your Managing Agent machines to ensure that VCM identifies the Windows
machines as licensed and that the 5.5 Agent or later is installed.
2. "Set the Trust Status for Managing Agent Machines" on page 27
You can set the trusted status on machines where you have verified that the connection is legitimate.
When you set the trust status, you are marking the Agent certificate as trusted.
3. "Configure HTTPS Bypass Setting for Virtual Environments " on page 28
If your Collector is not configured to use HTTPS, you must configure the Collector to allow HTTP
communication when entering sensitive parameter values.
4. "Enable Managing Agent Machines for Virtual Environments" on page 28
Managing Agent machines must be enabled to perform the necessary communication with your
instances of vCenter Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager.
Collect Machines Data From the Managing Agent Machines
Collect data from your Managing Agent machines to ensure that VCM identifies the Windows machines
as licensed and that the 5.5 Agent or later is installed.
The Managing Agent is the Agent used to collect data from your instances of vCenter Server, vCloud
Director and vShield Manager.
26
VMware, Inc.
Page 27
Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
Prerequisites
Verify that the Windows machine that you designated as the Managing Agent is licensed and that it has
the VCM Agent 5.5 or later installed. See "Configure Windows Machines" on page 87.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Windows Machines.
3. Select the target machines and click Collect on the VCM toolbar.
4. Select Machine Data and click OK.
5. Verify that the Selected list includes the target machines and click Next.
6. Expand the Windows tree, select Machines, and click Next.
7. Resolve any conflicts and click Finish.
What to do next
n
When the job is finished, verify that the Agent Version value in the data grid is 5.5 or later.
n
Configure the trust status for the Managing Agents. See "Set the Trust Status for Managing Agent
Machines" on page 27.
Set the Trust Status for Managing Agent Machines
You can set the trusted status on machines where you have verified that the connection is legitimate.
When you set the trust status, you are marking the Agent certificate as trusted.
When you transmit sensitive information, such as credentials, between the Collector and virtual or
physical machines on which the Managing Agent is installed, the Agent certificate, including the Agent
certificate on the Collector, must be trusted.
If you do not use this level of security, you can set the Allow sensitive parameters to be passed
to agents not verified as Trusted option to Yes. To override the setting, click Administration
and select Settings > General Settings > Collector.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you collected the Machines data type from the Windows machines you are using as Managing
Agents. See "Collect Machines Data From the Managing Agent Machines" on page 26.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Certificates.
3. Select the target machines and click Change Trust Status.
4. Add any additional machines to trust to the lower data grid.
5. Select Check to trust or uncheck to untrust the selected machines and click Next.
VMware, Inc.
6. Review the number of machines affected and click Finish.
27
Page 28
vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
What to do next
n
If your Collector is not configured to use HTTPS, set the HTTPS bypass. See "Configure HTTPS Bypass
Setting for Virtual Environments " on page 28.
n
Identify the Windows machines as Managing Agents. See "Enable Managing Agent Machines for
Virtual Environments" on page 28.
Configure HTTPS Bypass Setting for Virtual Environments
If your Collector is not configured to use HTTPS, you must configure the Collector to allow HTTP
communication when entering sensitive parameter values.
If your Collector is configured to use HTTPS, you do not need to modify this setting.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Settings > General Settings > Collector.
3. Select Allow HTTP communication (HTTPS bypass) when entering sensitive parameter values and
click Edit Settings.
4. Select Yes and click Next.
5. Review the summary and click Finish.
What to do next
Identify the Windows machines as Managing Agents. See "Enable Managing Agent Machines for Virtual
Environments" on page 28.
Enable Managing Agent Machines for Virtual Environments
Managing Agent machines must be enabled to perform the necessary communication with your instances
of vCenter Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager.
Prerequisites
n
Ensure that the Managing Agent machines are trusted machines. See "Set the Trust Status for Managing
Agent Machines" on page 27.
n
If your Collector is not configured to use HTTPS, set the HTTPS bypass. See "Configure HTTPS Bypass
Setting for Virtual Environments " on page 28.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Administration > Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Windows Machines.
3. Select the Managing Agent machines and click Change Managing Agent Status.
4. Add any additional machines to the lower data grid.
5. Select Enable - allow the selected machines to be used as managing agents and click Next.
6. Review the number of machines affected and click Finish.
28
VMware, Inc.
Page 29

What to do next
n
To maintain secure communication, you need the SSLcertificates from your instances of vCenter
Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager. See "Obtain the SSL Certificate Thumbprint" on page 29.
n
Configure the collections from your instances of vCenter Server, vCloud Director, and vShield
Manager.
n
See "Configure vCenter Server Data Collections" on page 29.
n
See "Configure vCloud Director Collections" on page 37.
n
See "Configure vShield Manager Collections" on page 47.
Obtain the SSL Certificate Thumbprint
When configuring the settings for your virtual environments systems, you can use an SSL certificate
thumbprint file to ensure secure communication between the Collector and your instances of vCenter
Server, vCloud Director, and vShield Manager.
You can use this procedure to copy and save the thumbprint in advance of configuring the settings, or you
can follow the process while you are using the wizard.
This procedure applies when your certificates are not properly trusted. If your certificates are configured
and trusted, you must log onto the target machine to retrieve the thumbprint from the certificate store.
Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have network access to the target instances of vCenter Server, vCloud Director, and
vShield Manager from which you need the thumbprint string.
Procedure
1. Open Internet Explorer.
2. In the address bar, type https://<your vcenter server, vcloud director, or vshield
manager instance>.
3. On the certificate error page, click Continue to this website.
4. On the address bar, click Certificate Error and select View Certificates.
5. Click the Details tab.
6. In the list, select Thumbprint.
7. Copy the thumbprint string to your clipboard or to a file so that you can access it when needed.
Configure vCenter Server Data Collections
Collect data from your vCenter Server so that you can identify and manage your virtual environments,
including ESX and ESXi hosts, and guest virtual machines.
Prerequisites
VMware, Inc.
n
Configure your Managing Agent machines. See "Configure Managing Agent Machines for Virtual
Environment Management" on page 26.
n
To maintain secure communication, you need the SSLcertificates from your instances of vCenter
Server. See "Obtain the SSL Certificate Thumbprint" on page 29.
29
Page 30

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Procedure
1. "Add vCenter Server Instances" on page 30
Add the vCenter Server instances to VCM so that you can license and collect vCenter Server data
using the Managing Agent.
2. "Configure the vCenter Server Settings" on page 31
Configure the Managing Agent, communication, and vCenter Server access options so that VCM can
collect host and guest data from the vCenter Server instances.
3. "Collect vCenter Server Data" on page 32
Collect the vCenter Server, host, and guest data from the vCenter Server instances. The data is
displayed by detailed data type and appears in the VCM Console.
The collectedvCenter Server data appears in the Console in the Virtual Environments node. The collected
vCenter Server data helps you identify and manage vCenter Server, host, and guest objects. See " vCenter
Server Collection Results" on page 33.
Add vCenter Server Instances
Add the vCenter Server instances to VCM so that you can license and collect vCenter Server data using
the Managing Agent.
In addition to adding the vCenter Server instances, and you can also add the Windows machine on which
the vCenter Server is installed and manage the underlying Windows operating system.
Prerequisites
Know the names and domain information for the vCenter Server instances in your environment.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Available Machines.
3. Click Add Machines.
4. On the Add Machines page, select Basic: Name, Domain, Type, Automatically license machines, and
click Next.
5. On the Manually Add Machines - Basic page, configure these options to identify the vCenter Server
instances.
Option Descript ion
Machine Name of the vCenter Server.
Domain Domain to which the vCenter Server belongs.
Type Domain type.
Machine Type Select vCenter (Windows).
6. Click Add.
30
VMware, Inc.
Page 31

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
The machine information is added to the list.
7. (Optional) Add other vCenter Server instances as needed.
8. When all your vCenter Server are added to the list, click Next.
9. On the Information page, review the summary and click Finish.
What to do next
n
Configure the vCenter Server settings. See "Configure the vCenter Server Settings" on page 31.
n
Manage the Windows operating systems on which vCenter Server instances are running. See
"Configure Windows Machines" on page 87.
Configure the vCenter Server Settings
Configure the Managing Agent, communication, and vCenter Server access options so that VCM can
collect host and guest data from the vCenter Server instances.
Prerequisites
n
Collect Machines data from the Windows machine that you designated as your Managing Agent. See
"Collect Machines Data From the Managing Agent Machines" on page 26.
n
If you are using SSL Certificates to maintain secure communication, you must provide the certificate
thumbprint from the target system when configuring the settings. See "Obtain the SSL Certificate
Thumbprint" on page 29.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Virtual Environments.
3. Select the vCenter Server instances and click Configure Settings.
4. On the Virtual Environment page, verify that the vCenter Server instances appear in the lower pane
and click Next.
VMware, Inc.
31
Page 32

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
5. On the Managing Agent and Communication Settings page, configure the settings that are applied to
all selected vCenter Server instances and click Next.
Option Descriptio n
Managing Agent Select the Windows machine to manage
Port Type the port used by the VMware Infrastructure
User ID Type a vCenter Server instance user name.
communication between the Collector and the
vCenter Server instances.
This Windows machine must have the 5.5 Agent
or later installed.
You can use the Collector as your managing
agent.
SDK on the vCenter Server instances.
The default value is 443.
The user must have a vCenter Server
administrative role or an unrestricted read only
role.
Password Type the password for the vCenter Server
instance user ID.
Confirm Password Type the password again.
Ignore untrusted SSL Certificate Select one of the following certificate options.
n
Yes: Ignores the requirement for a valid signed
certificate.
n
No: Requires a valid signed certificate.
6. If you selected No on the Managing Agent and Communication Settings page, you must type or paste
the thumbprint string in the text box and click Next.
7. On the Important page, click Finish.
What to do next
Collect vCenter Server data. See "Collect vCenter Server Data" on page 32.
Collect vCenter Server Data
Collect the vCenter Server, host, and guest data from the vCenter Server instances. The data is displayed
by detailed data type and appears in the VCM Console.
Prerequisites
Configure the vCenter Server settings. See "Configure the vCenter Server Settings" on page 31.
32
VMware, Inc.
Page 33

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Virtual Environments.
3. Select the vCenter Server instances and click Collect on the VCM toolbar.
4. On the Collection Type page, select Machine Data and click OK.
5. On the Machines page, verify that the Selected list includes all the vCenter Server instances from which
you are collecting and click Next.
6. On the Data Types page, select the Virtualization vCenter Server data types that you want to collect
from the vCenter Server instances and click Next.
7. On the Important page, resolve any conflicts and click Finish.
What to do next
n
Review the collected virtualization data. Click Console and select Virtual Environments > vCenter.
n
(Optional) Schedule vCenter Server collections. See "Configure vCenter Server Scheduled Collections"
on page 34.
vCenter Server Collection Results
The collectedvCenter Server data appears in the Console in the Virtual Environments node. The collected
vCenter Server data helps you identify and manage vCenter Server, host, and guest objects.
Option Description
Console View the Virtual Environments dashboards. Click Click Console and select
Dashboards > Virtual Environments.
View the collected vCenter Server data. Click Console and select Virtual
Environments > vCenter to access the collected data.
View the change logs for the virtual environments. Click Console and select
Change Management to access the collected data.
Compliance Access compliance rules that you create based on the collected vCenter Server
data using the Virtual Environment Compliance node. You cannot create
enforceable compliance rules for vCenter Server data.
The compliance rules for the virtual machines you license and on which you
install the Agent are managed in the Machine Group Compliance node.
Reports Run configured Virtual Environments reports, including a vCenter Summary
report. Click Reports and select Machine Group Reports > Virtual
Environments.
Create reports based collected vCloud Director objects. Click Reports and
select Virtual Object Reports.
Administration Displays managed vCenter Server instances from which you are collecting
data.
Click Administration and select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines >
Licensed Virtual Environments to view licensed vCenter Server instances.
VMware, Inc.
Administration >
Machine Groups
Dynamic machine groups based on vCenter Server objects. These objects
include instances, hosts, and guest machines, and are used to limit the
displayed data.
33
Page 34

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Configure vCenter Server Scheduled Collections
Configure VCM to regularly collect vCenter Server data from your vCenter Server machine groups to
ensure that you are using current results when you are viewing the data and when running reports or
compliance.
This action is not required, but scheduling your collections improves your configuration management
efficiency.
Procedure
1. "Create vCenter Server Machine Groups" on page 34
Create a Windows machine group that contains your vCenter Server instances so that you can run
collections on the member machines.
2. "Schedule vCenter Server Collections" on page 34
Schedule the collection job to run against your vCenter Server machine group with the the Default
filter set applied so that you regularly collect the vCenter Server and Windows data from the vCenter
Server instances.
Create vCenter Server Machine Groups
Create a Windows machine group that contains your vCenter Server instances so that you can run
collections on the member machines.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Machine/Virtual Object Groups > All Windows Machines.
3. Click Add Group.
4. Type the name and description of the machine group and click Next.
For example, type the name vCenter Server Instances.
5. Select Static and click Next.
6. Add the Windows machines that are running vCenter Server to the Selected list and click Next.
7. Click Finish.
The group is added to the All Windows Machines list.
What to do next
Schedule the collection of the vCenter Server data types from the vCenter Server instances. See "Schedule
vCenter Server Collections" on page 34.
Schedule vCenter Server Collections
Schedule the collection job to run against your vCenter Server machine group with the the Default filter
set applied so that you regularly collect the vCenter Server and Windows data from the vCenter Server
instances.
Prerequisites
Create a Windows machine groups that includes the machines that are running vCenter Server. See
"Create vCenter Server Machine Groups" on page 34.
34
VMware, Inc.
Page 35

Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Job Manager > Scheduled.
3. Click Add.
4. Select Collection and click Next.
5. Type a job name and description and click Next.
For example, vCenter Server Collections.
6. Select Default filter set and click Next.
7. Select your vCenter Server machine group and click Next.
For example, vCenter Server Instances.
8. Configure when the collection job runs and click Next.
For example, every four hours starting today.
9. Resolve any conflicts and click Finish.
The collection job is added to your Scheduled Jobs list.
Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
What to do next
After a scheduled run time, verify that the job ran. The information is available in Job Manager history for
scheduled collections. Select the time and review the general status and success. View the machine detail
status if the collection was not 100% successful.
Configure vCenter Server Virtual Machine Collections
Configure virtual machine collections so that you can identify and manage the guest operating systems on
the vCenter Server virtual machines.
VCM manages virtual machines as guest machines and as Windows, Linux, or UNIX machines. To manage
the virtual machines as guest machines, you collect vCenter Guests data from your vCenter Server. To
manage the virtual machines based on operating system, you license, install the VCM Agent, and collect
data directly from the managed machines.
You can identify the virtual machines in your environment two ways.
n
Collect vCenter Guests data from you vCenter Servers and manage the virtual Windows, Linux, or
UNIX machines. See "Collect vCenter Server Virtual Machines Data" on page 35.
n
Manually discover Windows Machines or add Linux or UNIX machines. For Windows machines, see
"Discover Windows Machines" on page 90. For Linux or UNIX machines, see "Configure Collections
from Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Machines" on page 120.
Collect vCenter Server Virtual Machines Data
VMware, Inc.
Identify and license your virtual machines that are identified based on collected vCenter Guests data.
Prerequisites
Manage your vCenter Servers in VCM. See "Configure vCenter Server Data Collections" on page 29.
35
Page 36

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Available Machines > Licensed Virtual Environments.
3. Select the vCenter Servers and click Collect on the VCM toolbar.
4. On the Collection Type page, select Machine Data and click OK.
5. On the Machines page, verify that the Selected list includes all the vCenter Servers from which you are
collecting and click Next.
6. On the Data Types page select Virtualization > vCenter Guests and click Next.
7. On the Important page, resolve any conflicts and click Finish.
What to do next
License your virtual machines. See "Manage vCenter Server Virtual Machines " on page 36.
Manage vCenter Server Virtual Machines
Add and license the virtual machines identified based on a vCenter Guests collection from your vCenter
Servers. If you are managing Windows virtual machines, you can also install the VCM Agent.
Using the Manage Guests wizard, you can add the virtual machines to the appropriate Available Machines
data grid based on operating system, license the virtual machine based on operating system, or, for
Windows machines, license and install the Agent.
Prerequisites
Collect vCenter Guests data from your vCenter Servers. See "Collect vCenter Server Virtual Machines
Data" on page 35.
Procedure
1. Click Console.
2. Select Virtual Environments > vCenter > Guests > Summary.
3. Select either your Windows virtual machines or your Linux or UNIX virtual machines and click
Manage Guests.
4. On the Default Domain page, configure the options and click Next.
a. Specify the Domain in which the machines are running.
b. Select the Domain Type.
5. On the Edit VMGuest Machine Info page, review the list and update or remove virtual machines, and
click Next.
6. On the License VMGuests page, configure the options and click Next.
a. Select License the selected machines.
b. (Windows machines only) Select Install VCMagents for the selected Windows machines, and
click Next.
7. On the Confirm Your Changes page, review the changes and click Finish.
36
VMware, Inc.
Page 37

What to do next
n
For Windows operating system guest machines on which you installed the Agent, collect from the
Windows virtual machines. See "Collect Windows Data" on page 93. If you did not install the Agent, see
"Install the VCM Windows Agent on Your Windows Machines" on page 91.
n
For Linux or UNIX operating system guest machines you must install the Agent. See "Configure
Collections from Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Machines" on page 120.
Configure vCloud Director Collections
Configure collections from your vCloud Director instances so that you can run compliance and reports,
and identify your vApp virtual machines.
Prerequisites
n
Configure your Managing Agent machines. See "Configure Managing Agent Machines for Virtual
Environment Management" on page 26.
n
To maintain secure communication, you need the SSLcertificates from your instances of vCloud
Director. See "Obtain the SSL Certificate Thumbprint" on page 29.
Procedure
Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
1. "Add vCloud Director Instances" on page 37
Add the instances of vCloud Director to VCM so that you can license and collect vCloud Director data
using the Managing Agent.
2. "Configure the vCloud Director Settings" on page 38
Configure the Managing Agent, communication, and vCloud Director access options so that VCM can
collect virtual machine data from your instances of vCloud Director.
3. "Collect vCloud Director Data" on page 39
Collect the data from the instances of vCloud Director. The data is displayed by detailed data type and
appears in the VCM Console.
The collected vCloud Director data appears in the Console in the Virtual Environments node. The data
helps you identify and manage vApp virtual machines. See "vCloud Director Collection Results" on page
40.
Add vCloud Director Instances
Add the instances of vCloud Director to VCM so that you can license and collect vCloud Director data
using the Managing Agent.
In addition to adding the instances of vCloud Director, and you can also add the Red Hat machine on
which the vCloud Director instance is installed and manage the underlying Red Hat operating system.
Prerequisites
VMware, Inc.
Know the names and domain information for the instances of vCloud Director in your environment.
37
Page 38

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Available Machines.
3. Click Add Machines.
4. On the Add Machines page, select Basic: Name, Domain, Type, Automatically license machines, and
click Next.
5. On the Manually Add Machines - Basic page, configure these options to identify the instances of
vCloud Director.
Option Description
Machine Name of the vCloud Director instance.
Domain Domain to which the vCloud Director instance belongs.
Type Domain type.
Machine Type Select vCloud Director.
6. Click Add.
The machine information is added to the list.
7. (Optional) Add other instances of vCloud Director as needed.
8. When all your instances of vCloud Director are added to the list, click Next.
9. On the Information page, review the summary and click Finish.
What to do next
n
Configure the vCloud Director settings. See "Configure the vCloud Director Settings" on page 38.
n
Manage the Red Hat operating systems on which your vCloud Director instances are running. See
"Configure Collections from Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Machines" on page 120.
Configure the vCloud Director Settings
Configure the Managing Agent, communication, and vCloud Director access options so that VCM can
collect virtual machine data from your instances of vCloud Director.
Prerequisites
n
Collect Machines data from the Windows machine that you designated as your Managing Agent. See
"Collect Machines Data From the Managing Agent Machines" on page 26.
n
If you are using SSL Certificates to maintain secure communication, you must provide the certificate
thumbprint from the target system when configuring the settings. See "Obtain the SSL Certificate
Thumbprint" on page 29.
38
VMware, Inc.
Page 39

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Virtual Environments.
3. Select the vCloud Director instances and click Configure Settings.
4. On the Virtual Environment page, verify that the vCloud Director instances appear in the lower pane
and click Next.
5. On the Managing Agent and Communication Settings page, configure the settings that are applied to
all selected vCloud Director instances and click Next.
Option Descriptio n
Managing Agent Select the Windows machine to manage
communication between the Collector and the
vCloud Director instances.
This Windows machine must have the 5.5 Agent
or later installed.
You can use the Collector as your managing
agent.
Port Type the port used by the API on the vCloud
Director instance.
The default value is 443.
User ID Type a vCloud Director instance user name.
The user must have a vCloud Director
administrative role or an unrestricted read only
role. Use a full vCloud Director administrative
user, such as administrator@system.
Password Type the password for the vCloud Director
instance user ID.
Confirm Password Type the password again.
Ignore untrusted SSL Certificate Select one of the following certificate options.
n
Yes: Ignores the requirement for a valid signed
certificate.
n
No: Requires a valid signed certificate.
6. If you selected No on the Managing Agent and Communication Settings page, you must type or paste
the thumbprint string in the text box and click Next.
7. On the Important page, click Finish.
VMware, Inc.
What to do next
Collect vCloud Director data. See "Collect vCloud Director Data" on page 39.
Collect vCloud Director Data
Collect the data from the instances of vCloud Director. The data is displayed by detailed data type and
appears in the VCM Console.
39
Page 40

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Prerequisites
Configure the vCloud Director settings. See "Configure the vCloud Director Settings" on page 38.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Virtual Environments.
3. Select the vCloud Director instances and click Collect on the VCM toolbar.
4. On the Collection Type page, select Machine Data and click OK.
5. On the Machines page, verify that the Selected list includes all the vCloud Director instances from
which you are collecting and click Next.
6. On the Data Types page, select the Virtualization vCloud Director data type that you want to collect
from the vCloud Director instances and click Next.
7. On the Important page, resolve any conflicts and click Finish.
What to do next
Review the collected virtualization data. Click Console and select Virtual Environments > vCloud
Director.
Discover the vApp virtual machines created by the vCloud Director and make them available in VCM. See
"Discover vCloud Director vApp Virtual Machines" on page 43.
vCloud Director Collection Results
The collected vCloud Director data appears in the Console. The discovered virtual machines appear on
Administration. After you license the virtual machines and install the Agent, you manage them based on
their operating system.
The displayed data is only as current as the last time you collected data from your vCloud Director
instances and from your managed machines.
Option Description
Console View collected vCloud Director instance data. Click Console and
selectVirtual Environments > vCloud Director.
View the change logs for the virtual environments. Click Console and
select Change Management to access the collected data.
Compliance Access compliance rules that you create based on the collected vCloud
Director data using the Virtual Environment Compliance node. You
cannot create enforceable compliance rules for vCloud Director data.
The compliance rules for the virtual machines that you license and on
which you install the Agent are managed in the Machine Group
Compliance node.
40
VMware, Inc.
Page 41

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
Option Description
Reports Run a configured vCloud Director report. Click Reports and select
Machine Group Reports > Virtual Environments > vCloud Director
Managed VMs. The report includes the vCloud Director Instance,
Organization, Organization virtual datacenter, vApp Name, the VC
Machine Name, and the related networking data.
Create reports based collected vCloud Director objects. Click Reports
and select Virtual Object Reports.
Administration Displays managed vCloud Director instances from which you are
collecting data. Click Administration and select Machines Manager >
Licensed Machines > Licensed Virtual Environments.
Displays the discovered virtual machines with a machine name that is
based on your configuration options in the discovery rule.
For example, OrgName:vAppName:VirtualMachineName.
Click Administration and select Machines Manager.
n
If the machines are not licensed and the Agent is not installed, the
machines appear in the Available Machines data grid based on the
operating system.
n
If the machines are licensed and the Agent is installed, the machines
appear in the Licensed Machines data grid based on the operating
system.
Administration >
Machine Groups
Dynamic machine groups based on vCloud Director objects, including
instances and guest machines, are used to limit the displayed data.
Configure vCloud Director vApp Virtual Machines Collections
Collect vCloud Director data so that you can identify and manage the guest operating systems of the
vApp virtual machines.
To accommodate how vCloud Director manages vApps, which can include duplicate names, IP addresses,
and MAC addresses, VCM collects and displays internal and external IP address information, internal
machine name information, and vCenter machine name information collected directly from vCloud
Director. Based on the collected data, you determine how VCM constructs a unique virtual machine name
and specify which IP address to use based on the network address translation (NAT) mapping level.
To identify the vCloud Director virtual machines, you configure discovery rules that analyze data collected
from the vCloud Director REST API and use the vApp virtual machine information to add new virtual
machines to VCM. After installing the Agent and licensing the virtual machines, you manage the new
machines based on their operating systems. The machines appear in VCM based on your configured
naming convention.
Network Address Translation and vCloud Director vApp Discovery Rules
VMware, Inc.
To configure the connection string when creating a vCloud Director virtual machines discovery rule, you
must know how network address translation (NAT) is implemented in your vCloud Director instances.
The vCloud Director administrator configures the NATmapping. How the virtual machines are
configured with NATand where VCM is in the network determines the connection string that VCM uses
to communicate with the virtual machines.
41
Page 42

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
vCloud Director 1.0 and 1.5 support a variety of vApp network configurations. VCM supports these
scenarios.
n
VCM is located in the vApp with the virtual machines that it is managing.
n
The vApp has a direct connection to the org network.
n
The vApp has a direct connection to the external network.
n
The vApp has a one-to-one IP address NAT connection to the organization network with direct
connection to the external network.
n
The vApp has a one-to-one IP address NAT connection to the organization network with a one one-toone IP address NAT connection to the external network.
n
The vApp has a direct connection to the organization network with one IP address to one IP address
NAT connection to the external network.
VCM does not support one to many IP addresses NAT mapping for vCloud Director vApp virtual
machines.
To determine the connection string to use when discovering the vCloud Director virtual machines, you
must know where VCM is located in the network and how NAT is implemented.
Table 3–1. Determining the Connection String Based on Network Configuration
Location of
VCM or the
Proxy Server
on the
Network
External Network Organization Network Discovery
Rule
Con nection
String
In the
NA NA Internal IP
managed
vApp
On Org
Network
NA Direct connection. None (use
DNS) or
Internal IP
On Org
Network
On External
NA NATat vApp level. vApp
External IP
Direct Connection Not connected or direct connection. Internal IP
Network
On External
Network
On External
Network
Direct from
NAT at vApp level. vApp
Organization
NAT at Org level The vApp level IPis collected from
vCloud Director, but it is not used for
External IP
Org External
IP
the VCM connection.
After you collect the vCloud Director data, you can view the internal and external IP addresses in network
information for the virtual machines.
Best Practice
VCM cannot use DCOM to communicate with vCloud Director vApp virtual machines across NAT
mapped networks.
42
VMware, Inc.
Page 43

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
In a NATmapped network environment, your best practice is to install the Agent on the vApp template
machines. You must manually install the Agent with the HTTP mode enabled, but you must not collect
data from these template machines. Collecting from the template machines generates machine-specific
information that will cause the virtual machines created from the template to run incomplete collections.
If you discovered NAT mapped vApp virtual machines that do not have the Agent preinstalled on the
templates from which they were created, you must manually install the Agent. The Agent must be
installed with the HTTP protocol enabled. See Manually Install the Windows Agent in the online Help.
Discover vCloud Director vApp Virtual Machines
To begin managing the vCloud Director vApp virtual machines, create and run a VCM discovery rule. The
rule runs against the collected vCloud Director data in the VCM database.
Prerequisites
n
Collect vCloud Director data. You can run the discovery only on the collected data. See "Collect vCloud
Director Data" on page 39.
n
Determine how NATis used in your vCloud Director network and where VCM is located in
relationship to the network. See "Network Address Translation and vCloud Director vApp Discovery
Rules" on page 41.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Discovery Rules.
3. On the data grid toolbar, click Add.
4. On the Discovery Rules page, type a Name and Description, and click Next.
5. On the Discovery Method page, select By DB Discovery and click Next.
6. On the Discovery Query page, in the Discovery Query drop-down menu, select vCloud Director
Managed VMs and click Next.
7. On the Discovery Query Parameters page, configure the options to use when discovering and adding
the data to VCM and click Next.
VMware, Inc.
43
Page 44

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Option Description
Machine
Name
Format
Select the format used to display the virtual machine name.
You can select the vCenter name for the virtual machine or select a combination
of names for the virtual machine that includes the vApp that contains the virtual
machine, the vCloud Director organization, and the vCloud Director instance.
With these formats, you can easily sort, group, and display the data in VCM.
The composite name is limited to 128 characters.
n
VCName: Name of the virtual machinein vCenter. vCloud Director creates the
virtual machine and generates the name of the virtual machine, which includes
the machine's host name and the 10-digit identification number of the virtual
machinein vCenter. This name is unique in a single vCloud Director instance.
n
vApp:VCName: Name of the vApp that contains the virtual machine and the
name of the virtual machinein vCenter.
n
vDC:vApp:VCName: Name of the virtual datacenter with the vApp name and
the name of the virtual machinein vCenter.
n
Org:vDC:vApp:VCName: Name of the vCloud Director organization with the
virtual datacenter name, the name of the vApp that contains the virtual
machine, and the name of the virtual machinein vCenter.
n
Cloud:Org:vDC:vApp:VCName: Name of the vCloud Director instance with
the name of the vCloud Director organization, the virtual datacenter name, the
name of the vApp that contains the virtual machine, and the name of the
virtual machinein vCenter.
Machine
Name
Select a character to separate the elements of the vCloud Director hierarchy that
you use as the machine name.
Delimiter
Domain
Type or select the domain in which you are managing the virtual machines.
Name
Domain
Select the type of domain to which you are adding the virtual machines.
Type
Protocol Select the protocol by which the Collector will communicate with the Agent.
If the virtual machines in the vApp uses NAT mapping, you must select HTTP. If
the virtual machines do not use NAT, you can use HTTP or DCOM.
HTTPPort If you selected the HTTP protocol, you must specify the port used to communicate
with the Collector.
Uses the HTTP Listener on the target machine. The listener is configured to listen
on the designated port. Port 26542 is the default setting. Accepted port values
range from 1–65535. Other applications should not use this port.
44
VMware, Inc.
Page 45

Option Description
Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
Use a
proxy
server
Connection
String
Select Yes if you use a proxy server for communication between the Collector and
the Agents on the virtual Windows machines.
Select No if you do not use a proxy server or if you are managing Linux or UNIX
machines.
If the machines you add are Windows machines, you can select a proxy server for
communication between the Collector and the Agents on managed machines that
are located on the other side of a proxy server. The proxy server routes requests
from the Collector to the Agents on managed machines. A proxy server can only
be used with Windows HTTP agents.
Select the IP address to use when communicating with the virtual machines.
This address can differ from the address that resolves by machine name from
DNS or other name resolution systems. Use this address when VCM must contact
a vApp virtual machine through a Network Address Translation (NAT) address,
or when DNS available to the Collector cannot resolve the vApp virtual machines.
If the virtual machines that appear in the console as part of your vCloud Director
collections are not added as part of your database discovery of vCloud Director
data, ensure that the internal or external connection string is valid for the virtual
machines. If the connection string is set to External IP, you will discover only
machines with external IP addresses.
The connection string depends on the type and level at which NAT mapping is
configured.
Cloud
Name
Filter
Org Name
Filter
n
None (use DNS): The Collector resolves the IP address to the virtual machine
based on the configured name resolution mechanisms. For example, DNS or
Hosts.
n
Internal IP: The IP address that the virtual machine has in the vApp.
n
vApp External IP: The IP address external to the vApp addresses of the virtual
machines that are configured with NAT at the vApp level.
n
Org External IP: The IP address external to the organization addresses of the
virtual machines that are configured with NAT at the organization level or at
the organization and vApp level. If NATis implemented at the vApp and
organization level, select this option.
To run the query against all system resources in a vCloud Director instance, type
the name of the vCloud Director instance.
SQL wildcard expressions are allowed.
Discovers all virtual machines managed by the vCloud Director instance.
To run the query against an organization in a vCloud Director instance, type the
name of the organization.
SQL wildcard expressions are allowed.
Discovers all virtual machines in the organization.
VMware, Inc.
45
Page 46

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Option Description
vDC Name
Filter
vApp
Name
Filter
VM Name
Filter
Network
Name
Filter
IP Address
Filter
Include
rule in post
collection
IPupdate
To run the query against a virtual datacenter in a vCloud Director instance, type
the name of the virtual datacenter.
SQL wildcard expressions are allowed.
Discovers all virtual machines in the virtual datacenter.
To run the query against a vApp, type the name of the vApp.
SQL wildcard expressions are allowed.
Discovers all virtual machines in the vApp.
To run the query to add a specific virtual machine, type the name of the machine.
SQL wildcard expressions are allowed.
Discovers the virtual machine.
To run the query against resources on a particular network, type the name of the
network.
SQL wildcard expressions are allowed.
Discovers all virtual machines on the network.
To run the query to add virtual machines with a particular IP address, type the
address.
SQL wildcard expressions are allowed.
Discovers all virtual machines with that IPaddress.
Select Yes to include the properties of this discovery rule to update the connection
string information for the discovered machines when new vCloud Director data is
collected.
Select No to not update the connection string information.
8. On the Important page, select the options and click Finish.
Option Description
Would you like to run this
Select Yes.
Discovery Rule now?
License and Install Agent on
Discovered Machines
If you do not use NAT mapping, select the option to install
the Agent.
If you use NATmapping, you must manually install the
Agent on the discovered machines.
What to do next
n
Review the discovery jobs to determine if your job finished. Click Administration and select Job
Manager > History > Other Jobs.
n
Review the collected vCloud Director vApp virtual machine data. Click Administration and select
Machines Manager. In Available Machines and Licensed Machines, select the operating system type
and review the list for the added virtual machines.
n
If the discovered machines are listed only in the Available Machines list and the virtual machines use
NAT mapping, you must manually install the Agent appropriate for the operating system. See the
online Help for the manual installation procedures.
46
VMware, Inc.
Page 47

Configure vShield Manager Collections
Configure collections from your vShield Manager instances so that you can run reports on the collected
data.
Prerequisites
n
Configure your Managing Agent machines. See "Configure Managing Agent Machines for Virtual
Environment Management" on page 26.
n
To maintain secure communication, you need the SSLcertificates from your instances of vShield
Manager. See "Obtain the SSL Certificate Thumbprint" on page 29.
Procedure
1. "Add vShield Manager Instances" on page 47
Add the instances of vShield Manager to VCM so that you can license and collect vShield Manager data
using the Managing Agent.
2. "Configure the vShield Manager Settings" on page 48
Configure the Managing Agent, communication, and vShield Manager access options so that VCM can
collect group and group member data from your instances of vShield Manager.
Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
"Collect vShield Manager Data" on page 49
3.
Collect the data from the instances of vShield Manager. The data is displayed by detailed data type and
appears in the VCM Console.
The collected vShield Manager data appears in the Console in the Virtual Environments node. See "vShield
Manager Collection Results" on page 50.
Add vShield Manager Instances
Add the instances of vShield Manager to VCM so that you can license and collect vShield Manager data
using the Managing Agent.
Most vShield Manager instances are discovered, added, and licensed. Use this procedure if they are not
added to VCM.
Prerequisites
n
Ensure that the vCenter Server that each instance of vShield Manager is managing is added to VCM.
See "Add vCenter Server Instances" on page 30.
n
Know the names and domain information for the instances of vShield Manager in your environment.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Available Machines.
VMware, Inc.
3. Click Add Machines.
4. On the Add Machines page, select Basic: Name, Domain, Type, Automatically license machines, and
click Next.
5. On the Manually Add Machines - Basic page, configure these options to identify the instances of
vShield Manager.
47
Page 48

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Option Description
Machine Name of the instance of vShield Manager.
Domain Domain to which the instance of vShield Manager belongs.
Type Domain type.
Machine Type Select vShield.
6. Click Add.
The machine information is added to the list.
7. (Optional) Add other instances of vShield Manager as needed.
8. When all your instances of vShield Manager are added to the list, click Next.
9. On the Information page, review the summary and click Finish.
What to do next
Configure the vShield Manager settings. See "Configure the vShield Manager Settings" on page 48.
Configure the vShield Manager Settings
Configure the Managing Agent, communication, and vShield Manager access options so that VCM can
collect group and group member data from your instances of vShield Manager.
Prerequisites
n
Collect Machines data from the Windows machine that you designated as your Managing Agent. See
"Collect Machines Data From the Managing Agent Machines" on page 26.
n
If you are using SSL Certificates to maintain secure communication, you must provide the certificate
thumbprint from the target system when configuring the settings. See "Obtain the SSL Certificate
Thumbprint" on page 29.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Virtual Environments.
3. Select the instances of vShield Manager and click Configure Settings.
4. On the Virtual Environment page, verify that the vShield Manager instances appear in the lower pane
and click Next.
48
VMware, Inc.
Page 49

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
5. On the Managing Agent and Communication Settings page, configure the settings that are applied to
all selected vShield Manager instances and click Next.
Option Descriptio n
Managing Agent Select the Windows machine to manage
communication between the Collector and the
vShield Manager instances.
This Windows machine must have the 5.5 Agent
or later installed.
You can use the Collector as your managing
agent.
Port Type the port used by the API on the vShield
Manager instances.
The default value is 443.
User ID Type a vShield Manager instance user name.
The user must have a vShield Manager
administrative role or an unrestricted read only
role.
Password Type the password for the vShield Manager
instance user ID.
Confirm Password Type the password again.
Ignore untrusted SSL Certificate Select one of the following certificate options.
n
Yes: Ignores the requirement for a valid signed
certificate.
n
No: Requires a valid signed certificate.
Select vCenter for vShield Select the vCenter Server instance managed by this
vShield Manager instance.
6. If you selected No on the Managing Agent and Communication Settings page, you must type or paste
the thumbprint string in the text box and click Next.
7. On the Important page, click Finish.
What to do next
Collect vCloud Director data. See "Collect vShield Manager Data" on page 49.
Collect vShield Manager Data
Collect the data from the instances of vShield Manager. The data is displayed by detailed data type and
appears in the VCM Console.
VMware, Inc.
Prerequisites
Configure the vShield Manager settings. See "Configure the vShield Manager Settings" on page 48.
49
Page 50

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Virtual Environments.
3. Select the vShield Manager instances and click Collect on the VCM toolbar.
4. On the Collection Type page, select Machine Data and click OK.
5. On the Machines page, verify that the Selected list includes all the vShield Manager instances from
which you are collecting and click Next.
6. On the Data Types page, select the Virtualization that you want to collect from the vShield Manager
instances and click Next.
7. On the Important page, resolve any conflicts and click Finish.
What to do next
Review the collected virtualization data. Click Console and select Virtual Environments > vCloud
Director.
Discover the vApp virtual machines created by the vCloud Director and make them available in VCM. See
"Discover vCloud Director vApp Virtual Machines" on page 43.
vShield Manager Collection Results
The collected vShield Manager data appears in the Console and is available to generate reports.
The displayed data is only as current as the last time you collected data from your vShield Manager
instances.
Option Description
Console Displays collected vShield Manager instance data.
Click Console and selectVirtual Environments > vCloud Director.
Reports Create and run configured vShield Manager reports.
Administration Displays managed vShield Manager instances from which you are
collecting data.
Click Administration and select Machines Manager > Licensed
Machines > Licensed Virtual Environments to view licensed vShield
Manager instances.
Administration >
Machine Groups
Dynamic machine groups based on vShield App instances security group
membership and are used to limit the displayed data.
Configure ESX Service Console OS Collections
The ESX Service Console OS Linux data type data and the ESXlogs are collected directly from the ESX
operating systems, not from vCenter Server. Configure the ESX servers so that you can collect the Linux
data type and ESX log data from the ESX service console operating system.
To collect the data, VCM uses an Agent Proxy rather than a VCM Agent installed directly on the ESX and
ESXi machines. To support the Agent Proxy, you must copy required files and certificates on the ESX and
ESXi servers to manage the data collection from those machines.
Perform the required tasks first for ESX servers, and then for ESXi servers.
50
VMware, Inc.
Page 51

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
1. "Configure the Collector as an Agent Proxy" on page 51
The Agent Proxy machine is a Windows machine configured to communicate with ESX and ESXi
servers and to remotely collect data from those servers. The Collector automatically meets the Agent
Proxy requirements. You license the Collector and then collect the Machines data type.
2. "Configure Virtual Machine Hosts" on page 52
License virtual machine hosts to generate a file containing machine names and settings. You use the
generated file to configure the ESX machines for management in VCM.
3. "Copy Files to the ESX/ESXi Servers" on page 54
To import target machine information and copy the required files from VCM, you use the
UNIX/ESX/vSphere Deployment Utility on your Agent Proxy machines.
4. "Collect ESX Logs Data" on page 55
An initial collection of Virtual Environments data identifies your virtual machine hosts and their guest
machines.
You have several options for reviewing and using ESX Logs data in VCM. The data used is only as current
as the last collection, and the amount of time it takes for the data to display is based on the volume or
complexity of the data requested. See "Virtualization Collection Results" on page 56.
Configure the Collector as an Agent Proxy
The Agent Proxy machine is a Windows machine configured to communicate with ESX and ESXi servers
and to remotely collect data from those servers. The Collector automatically meets the Agent Proxy
requirements. You license the Collector and then collect the Machines data type.
NOTE If you manage more than fifty host machines, you must use a separate Windows machine as your
Agent Proxy. Moving the Agent Proxy activity to the separate machine optimizes performance. See
"Configuring Standalone Agent Proxy Machines" in the online Help.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Windows Machines.
3. Determine whether the Collector machine name appears in the data grid.
If it is listed in the data grid, the machine is licensed. If it is not listed, continue with the licensing
process.
VMware, Inc.
51
Page 52

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
4. License the Collector.
a. Select Machines Manager > Available Machines.
b. Select the Collector in the data grid and click License
c. On the Machines page of the Available Machines License wizard, verify that the Collector machine
name appears in the Selected list and click Next.
d. Review the Product License Details page and click Next.
e. Review the Important page and click Finish.
f. Select Administration > Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Windows Machines
to verify that the Collector is now licensed.
g. Click Refresh on the Console toolbar to update the data.
5. Run a collection for machines data to identify the Collector as an available Windows machine.
a. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Windows Machines, select the Collector in the data grid, and
click Collect on the Console toolbar.
b. On the Collection Type page, click Machine Data and click OK.
c. On the Machines page, verify that the Collector machine name appears in the Selected list.
d. Click Select Data Types to collect from these machines and click Next.
e. On the Data Types page, expand the Windows tree and select Machines.
f. Select Use default filters and click Next.
g. Review the Important page and click Finish.
The collection job starts. You can use the Job Manager to determine when the collection is finished.
What to do next
n
When the collection is completed, verify that the Collector machine Agent Proxy State equals Current
Agent. Click Administration and select Machines Manager > Agent Proxies and review the data grid.
n
License and configure the target virtual machine hosts. See "Configure Virtual Machine Hosts" on page
52.
Configure Virtual Machine Hosts
License virtual machine hosts to generate a file containing machine names and settings. You use the
generated file to configure the ESX machines for management in VCM.
All Virtualization data types are collected through Web Services communication except for the VM Logs,
which are collected through SSH and only from ESX machines.
Prerequisites
Verify that at least one Agent Proxy machine is configured. See "Configure the Collector as an Agent
Proxy" on page 51.
52
VMware, Inc.
Page 53

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed ESX/ESXi Hosts.
3. Select the ESX host and click Configure Settings.
4. Add the machines to be configured to the lower grid and click Next.
The selected machines will use the same Agent Proxy and the same SSHand Web Services settings.
5. Configure the settings on the Agent Proxy and Communication Setting page.
Option Description
Agent
Proxy
SSH
Settings
Web
Services
Settings
The configured Agent Proxy used to manage the selected virtual machine host
machines.
This option is required when you are licensing host machines, but it is optional if you
are modifying the settings.
Select the check box to configure the settings for your ESX machines. Configure these
settings so that you can collect ESX Logs data from the managed host machines.
n
Port: Used by VMware Web Services SDK for the ESX server on which SSH
listening. The Agent Proxy communicates with the ESX server using this port. The
default port (22) is set to the default value for SSH on ESX.
n
User ID: Used by the Agent Proxy to communicate with the ESX server through
SSH. This account must have certain permissions, for example, sudoers, defined
in the installation process. Authentication for this account uses public key
cryptography that was setup during the installation process.
(Optional) Select the check box to configure the settings for your ESX and ESXi
machines. Configure the settings to collect virtual environment data from a host
machine.
n
Port: The port on the ESXserver used by the Agent Proxy to communicate with
the VMware web services interface.
n
User ID: The account that has access to the VMware Web services interface. If you
are using ESX, this account must have Administrator access to Web services on the
ESX server. This user ID may be different from the user ID for SSH
communication, depending on whether you created different accounts during the
ESX installation process.
VMware, Inc.
n
Password: The password for the Web services User ID specified above. This
password is encrypted in the VCM database.
n
Confirm Password: Retype the password.
n
Ignore untrusted SSL Certificate: Connection allowed even when certificates are
not verified as trusted.
6. On the Important page, record the .xml file name.
The file is saved to the location configured for CMFiles$\VMHosts_Config. The default location is
\Program Files (x86)\VMware\VCM\WebConsole\L1033\Files\VMHosts_Config.
7. Click Finish.
53
Page 54

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
What to do next
Copy the copy SSH public key file, the csiprep.py file, and the csiprep.config file to the target ESX
machines. See "Copy Files to the ESX/ESXi Servers" on page 54.
Copy Files to the ESX/ESXi Servers
To import target machine information and copy the required files from VCM, you use the
UNIX/ESX/vSphere Deployment Utility on your Agent Proxy machines.
For ESX machines, you import target machine information from VCM and copy the SSH public key file,
the csiprep.py file, and the csiprep.config file to the target ESX machines.
For ESXi machines, you import machine information and copy the necessary Web Services settings to the
target machines.
Prerequisites
n
License the ESX and ESXi machines. See "Configure Virtual Machine Hosts" on page 52.
n
Locate the UNIX/ESX/vSphere Deployment Utility file in C:\Program Files (x86)
\VMware\VCM\Tools\DeployUtility-<version number>. Consult the Deployment Utility online
help when using the tool.
Procedure
1. Copy the UNIX/ESX/vSphere Deployment Utility file to the Agent Proxy machine, either a standalone
Windows machine or the Collector, and unzip the file.
2. Double-click DeployUtil.exe to start the Deployment Utility.
3. Click the ESX/vSphere Configuration tab.
4. Click File > Open.
5. Browse to the location of the virtual machine hosts configuration file generated when you licensed and
configured the virtual machine hosts.
The default location on the Collector is \Program Files (x86)
\VMware\VCM\WebConsole\L1033\Files\VMHosts_Config.
6. Select the .xml file and click Open.
The machine information in the .xml file is imported into the ESX Server Settings table on the
ESX/vSphere Configuration tab with the settings that you defined in VCM.
7. Select a configuration option.
Option Descriptio n
Configure ESX 3.x
Servers
Configures the SSH certificate, the csiprep.py file, the
csiprep.config file, and passes the SSH and Web Services user
information to the target ESX machines.
Configure
Passes the Web Services to the target ESXmachines
ESXiServers
54
VMware, Inc.
Page 55

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
8. (Optional) Configure the default server location.
The following settings are automatically configured to the default server locations. If you need to
change the paths, click the ellipsis button.
n
SSH Public Key file (ESX 3.x only)
n
Log Files Location
n
csiprep.py File (ESX 3.x only)
n
csiprep.config File (ESX 3.x only)
9. (Optional) Configure the VCM user name and password.
To modify the settings in VCM, use the following options or manually change the values in the ESX
Server Settings table. For more information about the settings, see the Deployment Utility online Help.
n
Use the same user name for both SSH and Web Services collections (ESX 3.x only).
n
Use the same password for all WebServices users.
n
Apply the same user names and passwords to all ESX servers.
10. Click Configure.
All the machines where the Configure check box is selected now have the same version of the files
copied to the location specified in the Remote Path field in the table. If no path is specified, the files are
copied to the /tmp directory.
What to do next
Collect data from the target virtual machine hosts. See "Collect ESX Logs Data" on page 55.
Collect ESX Logs Data
An initial collection of Virtual Environments data identifies your virtual machine hosts and their guest
machines.
Procedure
1. On the Portal toolbar, click Collect.
2. Select your ESX Servers.
To avoid configuration conflicts, do not select both for one action. The selected machines appear in the
Selected list.
3. Click Select Data Types to collect from these machines and click Next.
4. Expand the UNIX node and select the Machines - General data type.
5. Expand the Virtualization node and select the ESX Logs data types.
6. Click Use default filters and click Next.
7. Click Finish.
Monitor the collection job in Job Manager. When the collection is completed, the data appears is available
for reports and compliance assessments.
VMware, Inc.
What to do next
Review the collected data in the Console, run reports, configure alerts, and use the machine groups. See
"Virtualization Collection Results" on page 56.
55
Page 56

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Virtualization Collection Results
You have several options for reviewing and using ESX Logs data in VCM. The data used is only as current
as the last collection, and the amount of time it takes for the data to display is based on the volume or
complexity of the data requested.
Option Description
Console View ESX logs.
Click Console and select Virtual Environments > ESX Logs.
Configure the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In
The vSphere Client VCM Plug-In provides contextual access to VCM change, compliance, and
management functions. It also provides direct access to collected vCenter Server, virtual machine host, and
virtual machine guest data.
When using the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In, the virtual machine host name in vCenter must match the
virtual machine host name in VCM.
CAUTION Anyone accessing VCM and the vSphere Client must have a unique login. Do not share
vSphere Client logins between VCM users. Do not share vSphere Client logins between VCM users
and non-VCM users.
Procedure
1. "Register the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In" on page 56
The registration process configures the URL in the VMware vSphere Client to the VCM Collector and
makes the VCM Summary and VCM Actions tabs available in the vSphere Client.
2. "Configuring the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In Integration Settings" on page 57
Configure integration settings in VCM for your vSphere Client VCM Plug-In users. The settings
enable users to view the VCM reports.
3. "Manage Machines from the vSphere Client" on page 58
vSphere Client-managed machines are available in the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In when they
licensed and have the VCM Agent installed. The available actions include collecting new data and
running compliance, patching, and reports for the selected machines.
Register the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In
The registration process configures the URL in the VMware vSphere Client to the VCM Collector and
makes the VCM Summary and VCM Actions tabs available in the vSphere Client.
The plug-in is installed with VCM. To unregister a previous version of the plug-in, see the online Help.
IMPORTANT The account that you use to register the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In should be a local
administrator on the vSphere instance. The account must connect to a machine that has a valid SSL
certificate or must register an invalid certificate (for example, a development certificate) when that user
logs into the vSphere Client.
56
VMware, Inc.
Page 57

Configuring VMware Cloud Infrast ructure
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you are using VMware vCenter 4 Server.
n
Verify that the VMware vSphere Client is installed.
n
Verify that the VMware Tools is installed on the virtual machines.
Procedure
1. On the VCM Collector, browse to [path]\VMware\VCM\Tools\vSphere Client VCM
Plugin\bin and double-click VCVPInstaller.exe.
2. In the VCVP Plug-in Registration dialog box, configure the following options.
Option Description
Register Select the option to register the URL for the plug-in.
Select Unregister only if you are discontinuing the use
of the plug-in on the target vSphere Client.
Server URL Type the http or https path, where <server> is your
vSphere Client server.
Administrator User Name Type the name of a user with Administrator privileges
in the vSphere Client.
Administrator Password Type the associated password.
URLto vSphereClientVCMPlugin.xml Type the http path, where <VCMserver> is the name or
IP address for the VCM Collector. The xml file is
located in
\VMware\VCM\WebConsole\L1033\VCVPAnon\Xml\
vSphereClientVCMPlugin.xml
3. Click OK.
4. Start VCM.
5. On the login screen, select the role that you are using to log into the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In.
6. Select the Automatically log in using this role check box.
7. Start the vSphere Client.
8. Select a Guest machine.
What to do next
n
Confirm that you can access the VCM Summary and VCM Actions tabs.
n
Configure the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In integration settings in VCM. See "Configuring the vSphere
Client VCM Plug-In Integration Settings" on page 57.
Configuring the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In Integration Settings
VMware, Inc.
Configure integration settings in VCM for your vSphere Client VCM Plug-In users. The settings enable
users to view the VCM reports.
57
Page 58

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Prerequisites
Verify that the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In is registered. See "Register the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In"
on page 56.
Procedure
1. Select Administration > Settings > Integrated Products > VMware > vSphere Client VCM Plug-In.
2. Select the setting that you want to configure and click Edit Settings.
3. On the Settings Wizard page for each setting, configure the options.
Option Description
Machine group against which the external
reports will be run
Type the name of the machine group.
The default value is All Machines.
Role to use for external report access Type the name of the user role to be used to
access the reports.
The default value is Read-Only. Users other
than Admin must have the role selected
here in order to see reports in the vSphere
Client.
User name to use for assessments Type the name of the user who will run
assessments to obtain data for generating
reports.
4. Click Next.
5. Verify your settings and click Finish.
What to do next
You manage machines by running compliance, patching, and reports. See "Manage Machines from the
vSphere Client" on page 58.
Manage Machines from the vSphere Client
vSphere Client-managed machines are available in the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In when they licensed
and have the VCM Agent installed. The available actions include collecting new data and running
compliance, patching, and reports for the selected machines.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the integration settings are configured. See "Configuring the vSphere Client VCM Plug-In
Integration Settings" on page 57.
n
Configure your virtual machines for VCM management. See "Configure Windows Machines" on page
87 and "Configure Collections from Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X Machines" on page 120.
Procedure
1. Start the vSphere Client.
2. Click the VCM Actions tab.
What to do next
Click help on the VCMActions tab for more information about the actions.
58
VMware, Inc.
Page 59

Running Compliance for the VMware Cloud Infrastructure
Compliance templates evaluate the virtual environment object data to determine if the objects meet the
criteria in the rules. If the property values on an object do not meet the criteria, and if there is no exception
defined, then the object is flagged as noncompliant. When an object is non compliant, the template results
provide the details of the settings or configurations that do not match the rules. You can use this
information to resolve the issue.
Compliance templates include the following components:
n
Rule Groups: The rule groups comprise rules and filters.
n
Rules: The rules define the optimal configuration standard.
n
Filters: The filters limit the objects on which the template runs to only the objects that meet the filter
criteria. If filters are not defined, the rules are run against all objects in the virtual objects group.
n
Exceptions: The exceptions are optional temporary or permanent exceptions to the template results.
The defined exception indicates that a specific result is compliant or noncompliant even though it does
not match the requirements of the rules.
After you configure your compliance templates, you can optimize how VCM monitors the compliance of
objects in your environment using alerts and scheduling regular compliance template runs on your
collected virtual environment data.
4
This chapter includes the following topics:
Create and Run Virtual Environment Compliance Templates 59
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups 60
Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Rules 61
Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Filters 62
Preview Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups 62
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Templates 63
Run Virtual Environment Compliance Templates 64
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Exceptions 65
Resolve Noncompliant Virtual Environments Template Results 66
Configure Alerts and Schedule Virtual Environment Compliance Runs 68
Create and Run Virtual Environment Compliance Templates
Create compliance templates that evaluate your virtual environment object data to determine if the
objects meet the criteria in the rules that define objects as compliant or noncompliant.
VMware, Inc.
59
Page 60

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
The example used in this procedure is whether VMware Tools is running on guest virtual machines on all
vCenter Server instances, but excluding vCenter_Dev.
Prerequisites
Collect virtual environments data. See "Configure Virtual Environments Collections" on page 25.
Procedure
1. "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups" on page 60
Rule groups contain compliance rules and filters. You must create rule groups that you then assign to
compliance templates.
2. "Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Rules" on page 61
You create rules that define the ideal values that objects should have to be considered compliant.
3. "Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Filters" on page 62
You can create filters that limit the objects on which the templates run to only the objects that meet the
filter criteria.
4. "Preview Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups" on page 62
You use the rules preview action, with the filters turned off and then turned on, to determine if a rule
group is returning the expected results.
5. "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Templates" on page 63
You can create compliance templates that include one or more rule groups that assess your selected
object group to determine which objects are compliant and noncompliant.
6. "Run Virtual Environment Compliance Templates" on page 64
You run templates against your collected data to determine which objects are compliant or
noncompliant.
7. "Resolve Noncompliant Virtual Environments Template Results" on page 66
The results for the compliance templates indicate whether the virtual or physical machine are
compliant or noncompliant. If the machine is noncompliant, you can enforce noncompliant results
manually or using VCM, or you can add an exception for expected noncompliant results.
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups
Rule groups contain compliance rules and filters. You must create rule groups that you then assign to
compliance templates.
Templates can include one or more rule groups. Rule groups comprise rules and filters.
The example used in this procedure is whether VMware Tools is running on guest virtual machines on all
vCenter Server instances, but excluding vCenter_Dev.
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select Virtual Environment Compliance > Rule Groups.
3. Click Add.
4. Type the Rule Group Name and Description in the text boxes and click OK.
For example, Guest Tools Running and a description.
60
VMware, Inc.
Page 61

Running Compliance f or the VMware C loud Infrast ructure
What to do next
Add a rule to the rule group. See "Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Rules" on page 61.
Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Rules
You create rules that define the ideal values that objects should have to be considered compliant.
The data types correspond to the collected virtual environments data that is displayed in the Console. To
identify the values you are configuring for compliance, review the data grids so that you can locate the
correct data type in the rule wizard.
The example used in this procedure is whether VMware Tools is running on guest virtual machines on all
vCenter Server instances, but excluding vCenter_Dev.
Prerequisites
Create a rule group. See "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups" on page 60.
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select Virtual Environment Compliance > Rule Groups > rule group name > Rules.
Guest Tools Running is the rule group in this example.
3. Click Add.
4. Type the Name and Description in the text boxes and click Next.
For example, Tools Running.
5. Expand Virtualization, select vCenter - Guests - Summary, and click Next.
The collected guest summary data includes whether the VMware Tools is installed and running on the
guest virtual machines.
6. Select Basic and click Next.
7. Click Add and configure the rules with the ideal values.
n
In the properties drop-down menu, select Tools Running Status.
n
Select = as the rule operator.
n
Click the ellipsis button and select guestToolsRunning and click OK.
n
Click Next.
8. Select the Severity of a failure in the drop-down menu and click Next.
9. Review the changes and click Finish.
The rule is added to the data grid.
10. Select your new rule and click Preview.
11. Select Do not apply machine filters to preview and click OK.
12. Review the data in the Non-compliant results window to verify that your rule is behaving as expected.
VMware, Inc.
When you test a rule, test first without the filter to ensure that the rule returns the expected results.
What to do next
Add a filter to the rule group. See "Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Filters" on page 62.
61
Page 62

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Filters
You can create filters that limit the objects on which the templates run to only the objects that meet the
filter criteria.If filters are not defined, the rules are run against all objects in the selected virtual objects
group.
The example used in this procedure is whether VMware Tools is running on guest virtual machines on all
vCenter Server instances, but excluding vCenter_Dev.
Prerequisites
n
Create a rule group. See "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups" on page 60.
n
Create a rule. See "Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Rules" on page 61.
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select Virtual Environment Compliance > Rule Groups > rule group name > Filters.
Guest Tools Running is the rule group in this example.
3. Click Add.
4. Type the Name and Description in the text boxes and click Next.
For example, Not vCenter_Dev
5. Expand Virtualization, select vCenter - Guest - Summary, and click Next.
The collected guest summary data includes vCenter names.
6. Select Basic and click Next.
7. Click Add and configure the filter with the values to limit assessed objects or to exclude objects from
assessment.
n
In the properties drop-down menu, select vCenter.
n
Select <> as the filter operator.
n
Click the ellipsis and select vCenter_Dev and click OK.
n
Click Next.
8. Review the changes and click Finish.
The filter is added to the data grid.
9. Select your new filter and click Preview.
10. Review the data in the Machines window to verify that your filter is behaving as expected.
What to do next
Test your rule and filter together. See "Preview Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups" on page
62.
Preview Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups
You use the rules preview action, with the filters turned off and then turned on, to determine if a rule
group is returning the expected results.
62
VMware, Inc.
Page 63

Running Compliance f or the VMware C loud Infrast ructure
The example used in this procedure is whether VMware Tools is running on guest virtual machines on all
vCenter Server instances, but excluding vCenter_Dev.
Prerequisites
n
Create a rule group. See "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Rule Groups" on page 60.
n
Create a rule. See "Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Rules" on page 61.
n
Create compliance filters. See "Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Filters" on page 62.
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select Virtual Environment Compliance > Rule Groups.
Guest Tools Running is the rule group in this example.
3. Select your new rule group and click Preview.
4. Select Do not apply machine filters to preview and click OK.
When you test a rule, test first without the filter to ensure that the rule returns the expected results.
5. Review the data in the Non-compliant results window to verify that your rule is behaving as expected.
6. Close the window.
7. Select your new rule group and click Preview.
8. Select Apply machine filters to preview and click OK.
9. Review the data in the Non-compliant results window to verify that your rule is behaving as expected.
If the results are incorrect, adjust your rules and filters until they work correctly when you preview
them.
What to do next
n
If you have more than one rule that you must run in a particular order, set the order. The Set Order
option is located on the toolbar.
n
Create a template. See "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Templates" on page 63.
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Templates
You can create compliance templates that include one or more rule groups that assess your selected object
group to determine which objects are compliant and noncompliant.
The example used in this procedure is whether VMware Tools is running on guest virtual machines on all
vCenter Server instances, but excluding vCenter_Dev.
VMware, Inc.
63
Page 64

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Prerequisites
Create a rule group. See "Create and Test Virtual Environment Compliance Rules" on page 61.
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select Virtual Environment Compliance > Templates.
3. Click Add.
4. Type the Name and Description in the text boxes and click Next.
For example, Tools Running Not vCenter_Dev and a description.
5. Move the rule group, for this example, Guest Tools Running, to the list on the right and click Next.
6. Select Return both compliant and non-compliant and click Next.
Returning complaint and noncompliant results will help you determine whether your template is
returning the correct results.
7. Review your changes and click Finish.
What to do next
Run the template. See "Run Virtual Environment Compliance Templates" on page 64.
Run Virtual Environment Compliance Templates
You run templates against your collected data to determine which objects are compliant or noncompliant.
When a compliance template is run, the results appear in a report format and a data grid format.
The example used in this procedure is whether VMware Tools is running on guest virtual machines on all
vCenter Server instances, but excluding vCenter_Dev.
Prerequisites
Create a template. See "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Templates" on page 63.
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select Virtual Environment Compliance > Templates.
3. Select your template in the data grid and click Run.
In this example, select Tools Running Not vCenter_Dev.
4. Click OK.
5. When the template run is finished, click Close.
6. Double-click the template name in the data grid.
Unless you turned off the summary view, the Virtual Environments Compliance Results report
appears. The report includes the number of objects that are compliant and the number that are
noncompliant.
7. To view the results in the data grid, click View data grid.
64
VMware, Inc.
Page 65

Running Compliance f or the VMware C loud Infrast ructure
What to do next
n
If you find results that you want to temporarily make compliant or noncompliant, create an exception.
See "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Exceptions" on page 67.
n
Evaluate the results and resolve any issues on the noncompliant objects.
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Exceptions
To temporarily or permanently override the specific template results, use exceptions rather than explicitly
resolve noncompliant results.
The exceptions are defined against the template results and indicate that a specific result is compliant or
noncompliant even though it does not match the requirements of the rules.
You can add exceptions only to existing templates.
The example used in this procedure is whether VMware Tools is running on guest virtual machines on all
vCenter Server instances, but excluding vCenter_Dev.
To create an exception in this example, a virtual machine, RHEL_60_ProdDev, is approved to be excluded
from the noncompliant results because you never require VMware Tools to be running on this machine.
Prerequisites
Create a template. See "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Templates" on page 63.
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select Virtual Environment Compliance > Templates > template name.
3. In the data grid, select the noncompliant result on which you are basing the exception and click Add
Exception.
In this example, the noncompliant result is the RHEL_60_ProdDev guest machine.
4. Type the Name, Short Description, Description, and Sponsor in the text boxes and click Next.
5. Select the template to which you are applying the exception in the drop-down menu and click Next.
For this example, select Tools Running Not vCenter_Dev.
6. Select the object group to which you are applying the exception and click Next.
For this example, select All Virtual Objects.
7. Select the override options and the expiration date.
a. Select Override non-compliant results to compliant.
b. Select No Expiration.
c. Click Next.
VMware, Inc.
65
Page 66

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
8. To define the exception values, modify, delete, or add to the properties, operators, and values for the
selected results.
In this example, you are specifying the RHEL_60_ProdDev as the exception.
a. Click Add.
b. In the properties drop-down menu, select Object.
c. Select = as the rule operator.
d. Click the ellipsis button and select RHEL_60_ProdDev in the property values dialog box and click
OK.
9. Click Finish.
What to do next
n
Run the template. See "Run Virtual Environment Compliance Templates" on page 64.
n
Create alerts and schedule regular runs of your compliance templates. See "Configure Alerts and
Schedule Virtual Environment Compliance Runs" on page 68
Resolve Noncompliant Virtual Environments Template Results
The results for the compliance templates indicate whether the virtual or physical machine are compliant or
noncompliant. If the machine is noncompliant, you can enforce noncompliant results manually or using
VCM, or you can add an exception for expected noncompliant results.
These procedures provide a variety of examples that apply to virtual environments compliance.
Procedure
1. "Enforce Compliance Template Results by Using VCM Actions" on page 190
You can resolve noncompliant results using VCM actions on the data grids to change settings when
the action is not available for enforceable compliance.
2. "Manually Enforce Compliance Template Results" on page 191
You can resolve noncompliant results by directly accessing the virtual or physical machine, or by
accessing the object in vCenter Server, to change the noncompliant configuration setting.
3. "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Exceptions" on page 67
To temporarily or permanently override the specific template results, use exceptions rather than
explicitly resolve noncompliant results.
Enforce Compliance Template Results by Using VCM Actions
You can resolve noncompliant results using VCM actions on the data grids to change settings when the
action is not available for enforceable compliance.
For this example, a template includes a rule that requires virtual machines to be powered on. If a virtual
machine is powered off, the object is noncompliant. The compliance remediation action is to power it on.
66
VMware, Inc.
Page 67

Running Compliance f or the VMware C loud Infrast ructure
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select Virtual Environments Compliance > Templates > {template name}.
3. In the Status column, identify the rule results that are noncompliant.
4. Identify the affected physical or virtual machines or virtual objects, and determine the expected value
of the property.
For example, click and drag the Status column heading and the Rule column heading to the filter.
Expand the noncompliant results and the rule related to the power state. The noncompliant object
appears in the object column.
5. To resolve the noncompliant results, click Console and select Virtual Environments, the Windows tab,
or the UNIX tab, and browse to the data grid where the action is available.
For example, click Console and select Virtual Environments > vCenter > Guests > Summary.
6. Select the machines or objects that you identified as noncompliant and click the applicable action
button on the data grid.
For example, select the virtual machines that are powered off that should be powered on to be
compliant and click Power VM On.
7. Follow the prompts to configure the options, select Run action now, and click Finish.
What to do next
Collect the appropriate data from the physical or virtual machines or objects and run compliance against
the collected data. The objects should now be compliant.
Manually Enforce Compliance Template Results
You can resolve noncompliant results by directly accessing the virtual or physical machine, or by accessing
the object in vCenter Server, to change the noncompliant configuration setting.
Procedure
n
Using your allowed methods, change the noncompliant setting value on the machine or object to the
required compliant value.
What to do next
Collect the appropriate data from the virtual or physical machines or objects and run compliance against
the collected data. The objects should now be compliant.
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Exceptions
To temporarily or permanently override the specific template results, use exceptions rather than explicitly
resolve noncompliant results.
VMware, Inc.
The exceptions are defined against the template results and indicate that a specific result is compliant or
noncompliant even though it does not match the requirements of the rules.
You can add exceptions only to existing templates.
The example used in this procedure is whether VMware Tools is running on guest virtual machines on all
vCenter Server instances, but excluding vCenter_Dev.
67
Page 68

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
To create an exception in this example, a virtual machine, RHEL_60_ProdDev, is approved to be excluded
from the noncompliant results because you never require VMware Tools to be running on this machine.
Prerequisites
Create a template. See "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Templates" on page 63.
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select Virtual Environment Compliance > Templates > template name.
3. In the data grid, select the noncompliant result on which you are basing the exception and click Add
Exception.
In this example, the noncompliant result is the RHEL_60_ProdDev guest machine.
4. Type the Name, Short Description, Description, and Sponsor in the text boxes and click Next.
5. Select the template to which you are applying the exception in the drop-down menu and click Next.
For this example, select Tools Running Not vCenter_Dev.
6. Select the object group to which you are applying the exception and click Next.
For this example, select All Virtual Objects.
7. Select the override options and the expiration date.
a. Select Override non-compliant results to compliant.
b. Select No Expiration.
c. Click Next.
8. To define the exception values, modify, delete, or add to the properties, operators, and values for the
selected results.
In this example, you are specifying the RHEL_60_ProdDev as the exception.
a. Click Add.
b. In the properties drop-down menu, select Object.
c. Select = as the rule operator.
d. Click the ellipsis button and select RHEL_60_ProdDev in the property values dialog box and click
OK.
9. Click Finish.
What to do next
n
Run the template. See "Run Virtual Environment Compliance Templates" on page 64.
n
Create alerts and schedule regular runs of your compliance templates. See "Configure Alerts and
Schedule Virtual Environment Compliance Runs" on page 68
Configure Alerts and Schedule Virtual Environment Compliance Runs
To optimize how VCM monitors the compliance of objects in your environment, configure alerts and
schedule regular compliance template runs on your collected virtual environment data.
68
VMware, Inc.
Page 69

Running Compliance f or the VMware C loud Infrast ructure
Prerequisites
Create at least on virtual environments compliance template. See "Create and Run Virtual Environment
Compliance Templates" on page 59.
Procedure
1. "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Alert Rules" on page 69
Alert rules are the conditions you define that determine when an alert is generated. Virtual
environment alert rules are based on virtual environment compliance templates.
2. "Create Virtual Environments Compliance Alert Configurations" on page 69
Virtual environment compliance alert configurations are created for virtual object groups to generate
alerts when a virtual environment compliance template returns noncompliant results during scheduled
runs of the template.
3. "Schedule Virtual Environments Compliance Template Runs" on page 70
You can schedule a regular run of your virtual environments compliance templates to ensure that the
collected data is regularly assessed for adherence to the defined compliance rules.
Create Virtual Environment Compliance Alert Rules
Alert rules are the conditions you define that determine when an alert is generated. Virtual environment
alert rules are based on virtual environment compliance templates.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have virtual environment compliance templates. See "Create and Run Virtual
Environment Compliance Templates" on page 59.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Alerts > Rules.
3. Click Add.
4. Type the alert name and description in the text boxes and click Next.
5. Select VE Compliance Results Data and click Next.
6. Select a compliance template and click Next.
7. Review the configured actions and click Finish.
What to do next
Create a virtual environments configuration that includes this rule. See "Create Virtual Environments
Compliance Alert Configurations" on page 69.
VMware, Inc.
Create Virtual Environments Compliance Alert Configurations
Virtual environment compliance alert configurations are created for virtual object groups to generate
alerts when a virtual environment compliance template returns noncompliant results during scheduled
runs of the template.
You must have at least one unused rule to add to the alert configuration parameters.
69
Page 70

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have virtual environment alert rules. See "Create Virtual Environment Compliance
Alert Rules" on page 69.
n
Review the automated response options, which you configure in this procedure, in the online Help.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Alerts > Virtual Environments Configurations.
3. In the middle pane, select the virtual objects group for which you want to generate an alert if one or
more rules in the template fail.
4. Click Add.
5. Select a virtual environments compliance results alert rule and click Next.
6. Select the alert severity and click Next.
You can select Critical, Important, Moderate, or Low.
7. Select and configure one or more automated responses that are performed when an alert is generated
and click Next.
Depending on the automated responses you selected, the pages will vary. See the online Help for
configuration details.
8. Review the alert configuration and click Finish.
What to do next
Schedule a job to run your the virtual environments compliance templates on a timetable of your
choosing. See "Schedule Virtual Environments Compliance Template Runs" on page 70.
Schedule Virtual Environments Compliance Template Runs
You can schedule a regular run of your virtual environments compliance templates to ensure that the
collected data is regularly assessed for adherence to the defined compliance rules.
Compliance templates are run against collected data, so you should also schedule collections for the data
types and virtual objects that you are assessing.
Prerequisites
n
Schedule a regular collection of the virtual environments data types for the virtual object groups
against which you are running the virtual environments compliance templates.
n
Create Virtual Environments Compliance Template. See "Create and Run Virtual Environment
Compliance Templates" on page 59.
n
Create Virtual Environments Compliance Alerts. See "Create Virtual Environment Compliance Alert
Rules" on page 69.
70
VMware, Inc.
Page 71

Running Compliance f or the VMware C loud Infrast ructure
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Job Manager > Scheduled.
3. Click Add.
4. Select Compliance and click Next.
5. Type a name and description in the text boxes and click Next.
6. Select the virtual environment template and click Next.
7. Select the virtual objects against which to run the template assessment and click Next.
8. Configure frequency, time of day, and duration for the job and click Finish.
9. To test whether the job is producing the expected results, click Run Now on the data grid toolbar.
The job runs at the scheduled time.
What to do next
If you a configured virtual environments compliance alert for this template and non-compliant rules were
found, you can review any alerts in the Alerts node in the Console.
VMware, Inc.
71
Page 72

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
72
VMware, Inc.
Page 73

Configuring vCenter Operations Manager Integration
Integration of VCM with vCenter Operations Manager reports VCM configuration change events and
standard compliance results in vCenter Operations Manager.
This chapter includes the following topics:
Configure vCenter Operations Manager Change Events 73
Standards Compliance for vCenter Operations Manager 74
VCM Registration in vCenter Operations Manager for Integration
Integration between VCM and vCenter Operations Manager uses an adapter to manage the connection.
When you register the VCM adapter in the vCenter Operations Manager Administration portal, ensure
that the user account used for the integration meets the following criteria:
n
The account is used only by the adapter login. The account must not be one used as an interactive user
login. The adapter account frequently logs in and out of VCM. If you use it as an interactive account,
you will need to regularly refresh the connection, which affects your VCM experience.
n
The account has permission in VCM to access the virtual object groups and machine groups that
correspond to the objects managed by your vCenter Operations Manager instance.
5
For more information about registering the VCM adapter, see the vCenter Operations Manager
Administration portal online Help.
Configure vCenter Operations Manager Change Events
Configure the data types to report to vCenter Operations Manager as change events and the threshold
reporting level used to roll up the configuration changes. VCM records configuration changes in the
change log regardless of whether you report the data in vCenter Operations Manager. From vCenter
Operations Manager, you can navigate to VCM to view the details.
You can report on UNIX and Windows configuration change data and VCM initiated reboot changes.
VCM reports change data to vCenter Operations Manager. vCenter Operations Manager polls VCM for
configuration changes every five minutes.
For example, you can configure VCM to report a UNIXdata type to vCenter Operations Manager and set
the threshold reporting level to roll up a defined number of configuration changes into a single reporting
icon to report the changes in the vCenter Operations Manager console.
Prerequisites
Ensure that the VCM adapter is registered with the correct user account in vCenter Operations Manager.
See "VCM Registration in vCenter Operations Manager for Integration" on page 73.
VMware, Inc.
73
Page 74

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Procedure
1. In VCM, click Administration.
2. Select Settings > Integrated Products > VMware > vCenter Operations Manager > Change Events.
3. Configure VCM to report a UNIXdata type, such as UNIX Patch Assessment, to vCenter Operations
Manager.
a. Select UNIXPatch Assessment - Report to vCenter Operations Manager, and click Edit Setting.
b. Click Yes to report the data.
c. Click Next and click Finish.
4. Set the threshold reporting level to roll up the configuration changes in the vCenter Operations
Manager console.
a. Select UNIXPatch Assessment - Rollup Threshold, and click Edit Setting.
b. Type the number of configuration changes for the collection to roll up to a single reporting icon to
report in vCenter Operations Manager.
c. Click Next and click Finish.
For details about the reporting settings, see the VCM online help.
Standards Compliance for vCenter Operations Manager
The integration between vCenter Operations Manager and VCM includes using the VCM compliance
template results to contribute to the Risk badge score in vCenter Operations Manager.
The compliance templates are included in badge mappings that are run in VCM against objects in vCenter
Server instances that are managed by both VCM and vCenter Operations Manager. These objects include
virtual machines, host systems, clusters, vCenter Server instances, and data stores. The compliance
mapping results determine the compliance score. vCenter Operations Manager then pulls the scores into
the formulas used to calculate the Risk badge scores.
When you review the standards compliance in vCenter Operations Manager, you can navigate back to
VCM to view the detailed results and identify any configuration changes that you must make to bring an
object that is noncompliant back to compliance.
The correct correlation of the scores requires the following conditions:
n
VCM is configured to collect data from the same vCenter Server instances that are managed by
vCenter Operations Manager. See "Configure vCenter Server Data Collections" on page 29.
n
You must collect the required virtualization data types from the shared vCenter Server instances. The
data types are vCenter Guests, vCenter Hosts, vCenter Inventory, and vCenter Settings. See "Collect
vCenter Server Data" on page 32.
Configure vCenter Operations Manager Standards Compliance
Create vCenter Operations ManagerCompliance badge scores that are based on the results of VCM
compliance template mapping runs. The badge scores are values that appear in vCenter Operations
Manager for vCenter Server instances, datacenters, clusters, virtual machine hosts, and virtual machines
managed by your vCenter Operations Manager and VCM.
74
VMware, Inc.
Page 75

Configuring vCenter Operations Manager Integration
Prerequisites
n
Ensure that the VCM adapter is registered with the correct user account in vCenter Operations
Manager. See "VCM Registration in vCenter Operations Manager for Integration" on page 73.
n
Verify that VCM is configured to collect data from the same vCenter Server instances thatvCenter
Operations Manager manages. See "Configure vCenter Server Data Collections" on page 29.
n
Collect the required virtualization data types from the shared vCenter Server instances. The data types
are vCenter Guests, vCenter Hosts, vCenter Inventory, vCenter Settings. See "Collect vCenter Server
Virtual Machines Data" on page 35.
n
Create compliance templates to include in the mappings. You can use Machine Group Compliance
templates and Virtual Environments Compliance templates. See "Create and Run Virtual Environment
Compliance Templates" on page 59.
n
Review how the badge scores are calculated based on your compliance badge settings and compliance
mapping options. See "Scoring Badges for vCenter Operations Manager Standards Compliance" on
page 80.
Procedure
1. "Create Compliance Badge Mappings" on page 75
Create badge mappings that contribute to the Risk badge score in vCenter Operations Manager. When
you configure the mappings, you specify the templates to include, the badge to which it is assigned,
and how the score is calculated.
2. "Run Compliance Badge Mappings " on page 77
When you run the compliance badge mapping, the included templates are run against the collected
data and a score is calculated based on the selected options and settings for the badge to which it is
assigned.
3. "Review Mapping Scores in the Dashboard Report" on page 78
The roll up scores appear in the Compliance Badge Rollup dashboard. Review the dashboard to ensure
that the scores are calculated as expected.
4. "Schedule Compliance Badge Mapping Runs" on page 78
Schedule the compliance badge mapping runs so that you have consistently current scores that are
pulled into vCenter Operations Manager.
5. "View Compliance Badges in vCenter Operations Manager" on page 79
The standards compliance score in VCM contributes a compliance score to the Risk badge score in
vCenter Operations Manager. If the Risk score indicates distress for the object, you can view the
compliance breakdown to determine which of the noncompliant templates are contributing to the
score and determine what action to take to resolve the noncompliant results.
Create Compliance Badge Mappings
Create badge mappings that contribute to the Risk badge score in vCenter Operations Manager. When
you configure the mappings, you specify the templates to include, the badge to which it is assigned, and
how the score is calculated.
VMware, Inc.
75
Page 76

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Prerequisites
n
Use the Content Wizard tool to download compliance templates created by VMware,for example, the
vSphere Hardening Guides and other standards. The Content Wizard is available from the Start menu
on the Collector machine.
n
Create compliance templates that are specific to your environment to include in the mappings. The
template names should not include the | character. You can use Machine Group Compliance templates
and Virtual Environments Compliance templates. See "Create and Run Virtual Environment
Compliance Templates" on page 59.
n
Review how the scores are calculated before configuring the mappings. See "Scoring Badges for
vCenter Operations Manager Standards Compliance" on page 80.
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select vCenter Operations Manager Badge Mapping > Mappings.
3. Click Add.
4. Configure the basic settings for the mapping, select the machine group or virtual objects group
context, and click Next.
Option Description
Name Mapping name.
Do not use the | character in the mapping name.
Description Mapping description
Badge Select the badge to which the mapping applies.
n
Risk - Compliance: Mapped to the vCenter Operations Manager Risk badge.
n
VCM Only: Not mapped to a vCenter Operations Manager badge.
This option allows you to test mapping configurations before assigning them
to vCenter Operations Manager. Does not appear in vCenter Operations
Manager.
76
VMware, Inc.
Page 77

Configuring vCenter Operations Manager Integration
Option Description
Roll Up Type Select the method used to calculate how the score for the templates in a
mapping is determined. Scores are always between 0 and 100. A score of 0
indicates the that all the rules are noncompliant. A score of 100 indicates that all
the rules are compliant.
n
Simple Percentage: Percentage of the template results that are compliant.
n
Weighted Percentage: Percentage of the template results that are compliant
where the Critical severity rule results are weighted more heavily than the
Low severity rules results.
n
Simple Rule Percentage: Percentage of compliance rules in the templates that
passed as compliant. If any of the results are non-compliant, the rule is
noncompliant.
n
Weighted Rule Percentage: Percentage of the compliance rules in the
templates where the Critical severity rule results are weighted more heavily
than the Low severity rules results.
Select Group
Context
Select compliance template context for which you are creating this mapping.
n
Machine Group Compliance: Select this option to add machine group
templates to the mapping. The virtual machines and host machines must also
be managed as virtual objects in VCM in order for the machine object IDs to
correlate to the objects in vCenter Operations Manager.
n
Virtual Object Group Compliance:Select this option to add virtual
environments templates to the mapping.
5. Select the Machine Group or Virtual Objects Group from which to build the mapping and click Next.
6. Select one or more templates to include in the mapping and click Next.
The list of available templates is based on the selected machine or virtual object group. Templates used
in compliance mappings should not include the | character.
7. Click Finish.
What to do next
Run the compliance badge mappings to determine if they are scoring as expected. See "Run Compliance
Badge Mappings " on page 77.
Run Compliance Badge Mappings
When you run the compliance badge mapping, the included templates are run against the collected data
and a score is calculated based on the selected options and settings for the badge to which it is assigned.
VMware, Inc.
Prerequisites
n
Collect the data from the machine or virtual object groups. Ensure that you collect the vCenter Guests,
vCenter Hosts, vCenter Inventory, and vCenter Settings from your vCenter Server instances. See
"Collect vCenter Server Data" on page 32.
n
Create compliance badge mappings that include one or more templates. See "Create Compliance Badge
Mappings" on page 75.
77
Page 78

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Procedure
1. Click Compliance.
2. Select vCenter Operations Manager Badge Mapping > Mappings.
3. Select a mapping and click Run.
4. Click OK.
All templates included in the mapping are run and the score calculated. The template results are in the
individual template results data grid and the score is available in the vCenter Operations Manager
Compliance Rollup dashboard.
What to do next
Review the scores in the vCenter Operations Manager Compliance Rollup dashboard. See "Review
Mapping Scores in the Dashboard Report" on page 78.
Review Mapping Scores in the Dashboard Report
The roll up scores appear in the Compliance Badge Rollup dashboard. Review the dashboard to ensure
that the scores are calculated as expected.
The current roll up scores are also available in the Machine Group Compliance Badge Rollup Detail and
Summary report.
Prerequisites
Run the Compliance Badge Mappings. See "Run Compliance Badge Mappings " on page 77.
Procedure
1. Click Console.
2. Select Dashboards > Compliance > Compliance Badge Rollup.
3. Review the scores and modify the settings as needed.
What to do next
n
To ensure that the scores that are pulled into vCenter Operations Manager are always current, schedule
the mappings to run at a regular time. See "Schedule Compliance Badge Mapping Runs" on page 78.
n
(Optional) To change how the mappings are scored, modify the Standards Compliance Settings. Do not
modify the scores unless you understand how the scores are calculated. See "Scoring Badges for
vCenter Operations Manager Standards Compliance" on page 80.
Schedule Compliance Badge Mapping Runs
Schedule the compliance badge mapping runs so that you have consistently current scores that are pulled
into vCenter Operations Manager.
Prerequisites
Schedule the collections for the vCenter Server instances on which you are running templates to complete
the collections before you run the compliance mappings against the collected data. See "Configure vCenter
Server Scheduled Collections" on page 34.
78
VMware, Inc.
Page 79

Configuring vCenter Operations Manager Integration
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Job Manager > Scheduled and click Add.
3. Select vCenter Operations Manager Compliance Badge Mapping Run and click Next.
4. Type a name and description and click Next.
5. Select one mapping and click Next.
6. Use the scheduling options to schedule when the mapping runs.
Schedule the job to run at the frequency at which you want refreshed results to be available to pull into
vCenter Operations Manager. Schedule the compliance badge mapping to run after your scheduled
collection.
7. Click Finish.
What to do next
View the mapped badges in vCenter Operations Manager. See "View Compliance Badges in vCenter
Operations Manager" on page 79.
View Compliance Badges in vCenter Operations Manager
The standards compliance score in VCM contributes a compliance score to the Risk badge score in vCenter
Operations Manager. If the Risk score indicates distress for the object, you can view the compliance
breakdown to determine which of the noncompliant templates are contributing to the score and
determine what action to take to resolve the noncompliant results.
Prerequisites
Verify the following requirements.
n
VCM adapter is installed.
n
VCM adapter is registered.
n
Internet Explorer is installed.
n
You have a vCenter Operations Manager user name and password from the vCenter Operations
Manager administrator.
Procedure
1. In vCenter Operations Manager, select an object in the inventory pane.
2. Click Dashboard.
3. Click Why is Risk {score}? and review the Compliance score.
4. Click the Compliance badge to view the template scores associated with the overall score.
5. On the Views tab, the score for each template appears in the Details section.
VMware, Inc.
6. To view the template results in VCM, click View details in VCM for the template you are
investigating.
7. If necessary, copy the URL provided in the Info dialog box into the Internet Explorer address bar.
The template results appear in VCM.
79
Page 80

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
What to do next
Resolve the noncompliant results. See "Resolve Noncompliant Virtual Environments Template Results" on
page 66.
Scoring Badges for vCenter Operations Manager Standards Compliance
Badge scores are values that appear in a vCenter Operations Manager Compliance badge, and which also
contribute to the dashboard values for the Risk badge.
The badge score pulled into vCenter Operations Manager is a calculated value that is based on your
compliance mapping options and on the compliance badge settings configured in VCM and run against
collected VCM data.
A compliance mapping is one or more compliance templates that run against a machine group or virtual
object group and calculate scores based on the selected options and the defined settings. When the VCM
adapter is configured in vCenter Operations Manager, the score appears as a Compliance badge for the
Risk badge.
Scoring Calculation Process
The badge calculations are based on mapping options and standards compliance settings. The options and
the settings interact in the following workflow:
n
Scoring based on mapping options.
n
Select the compliance standard badge to which the mapping contributes a score.
n
Select the roll up type that determines the initial score calculation. If you select weighted
percentages, the weight values are configured in the standards compliance settings.
n
Setting detail level aggregation of scores based on the standards compliance options.
n
Refining the badge scores as they appear in vCenter Operations Manager using the midpoint and
magnitude settings.
n
Scoring the Risk badge in vCenter Operations Manager.
Scoring Based on Mapping Options
You specify the badge name and the roll up types for each mapping you create in VCM.
Standards Compliance Badges
When you create a mapping in VCM, you select the vCenter Operations Manager badge with which it is
associated.
The Compliance subbadges are aligned with the following vCenter Operations Manager badge and VCMonly roll up.
n
Risk - Compliance scores are included in the Risk badge.
The Risk badge indicates potential problems that might eventually degrade the performance of the
managed environment. Risk does not necessarily imply a current problem. Risk indicates problems that
might require your attention in the near future, but not immediately. The overall Risk score for an
object ranges between 0 (no risk) to 100 (serious risk).
80
VMware, Inc.
Page 81

Configuring vCenter Operations Manager Integration
Compliance mappings should include templates that evaluate your environment in a way that helps to
identify performance issues. For example, you have an object setting that should be addressed if it is
found to be noncompliant from the configuration standard, but it does not require immediate
attention.
n
VCM Only scores are available only in VCM.
The VCM Only mapping scores are not pulled into vCenter Operations Manager. The scores are
intended to provide mapping of multiple templates and scores only in VCM. For example, you can use
this mapping to test a new mapping in VCMbefore you begin reporting the scores in vCenter
Operations Manager.
The roll up type calculations for each badge determine the initial score.
Roll Up Types
The roll up types determine how the template results are initially scored.
When you create a compliance template, each template includes one or more rules, and you assign each
rule a severity level of Low, Moderate, Important, and Critical. Each rule includes one or more individual
checks that return one or more results for each check. The results for the individual checks that are made
on the target machine or object determine if the object is compliant or noncompliant.
For the Weighted Percentage and Weighted Rule Percentage roll up types, you can apply a weighted
value. The weighting is the value by which the result or rule is multiplied to give the different severity
levels more or less weight when calculating the scores. The weighting of the severity levels is configured in
the Standards Compliance Settings. The default values are Low=1, Moderate=2, Important=4, and
Critical=8.
Simple Percentage is the percentage of the template results that are compliant. This option does not weight
the results based on severity. For example, the simple percentage score for the results is 73. This score is
calculated based on 11 compliant results out of a total of 15 results.
Table 5–1. Simple Percentage Template Results
Severity Compliant Results Noncompli ant Results
Critical 1 4
Important 2 0
Moderate 3 0
Low 5 0
Total 11 4
Weighted Percentage is the percentage of the template results that are compliant where the Critical
severity rule results are weighted more heavily than the Low severity rules results. For example, the
weighted percentage score for the results is 46. This score is calculated based on a weighted value of 27
compliant results out of a total of 59 results.
Table 5–2. Weighted Percentage Template Results
Severity Severity
Weight
Critical 8 1 8*1=8 8 4 8*4=32 32
Important 4 2 4*2=8 8 0 4*0=0 0
Compliant
Results
Weighting
Calculations
Weighted
Compliant
Results
Noncompliant
Results
Weighting
Calculations
Weighted
Noncompliant
Results
VMware, Inc.
Moderate 2 3 2*3=6 6 0 2*0=0 0
Low 1 5 1*5=5 5 0 1*0=0 0
Total 27 32
81
Page 82

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Simple Rule Percentage is the percentage of compliance rules in the templates that passed as compliant. If
any of the results are non-compliant, the rule is non-compliant. This option does not weight the rules
based on severity. For example, the simple rule percentage is 40. This score is calculated based on two
compliant rules out of a total of five rules.
Table 5–3. Simple Rule Percentage Based on Template Rules
Rule/ Severity Compliant Results Noncompliant Results Simple Compliant Rule Simple Noncompl iant Rul e
Rule 1/ Critical 1 0 1
Rule 2/ Important 5 6 1
Rule 3/ Important 15 1 1
Rule 4/ Moderate 1 0 1
Rule 5/ Low 0 9 1
Total 2 3
You might choose scoring by rule rather than by results when some rule groups return significantly more
rules than other rules in the same rule group. For example, a rule that checks user accounts returns one
result per user account on an object, but a rule that checks a password policy returns only one result for an
entire system.
Weighted Rule Percentage is the percentage of the compliance rules in the templates where the Critical
severity rule are weighted more heavily than the Low severity rules. For example, the weighted rule
percentage is 53. This score is calculated based on a weighted value of 10 compliant rules out of a total of
19 rules.
Table 5–4. Weighted Rule Percentage Based on Template Rules
Rule/
Severity
Rule 1/
Critical
Rule 2/
Important
Rule 3/
Important
Rule 4/
Moderate
Rule 5/
Low
Total 10 9
Severity
Weight
Compliant
Results
Noncompliant
Results
Simple
Compliant
Rule
Simple
Noncompliant
Rule
Weighted
Compliant Rule
Value
8 1 0 1 8
4 5 6 1 4
4 15 1 1 4
2 1 0 1 2
1 0 9 1 1
Weighted
Noncompliant Rule
Value
Detail Level Score Aggregation
After the initial scoring, the Standards Compliance Settings determine the badge scores that are calculated
for the vCenter Operations Manager badges, based first on the Detail Level aggregation, and then on the
midpoint and magnitude.
The level from which to roll up the badge scores that are generated for each mapping.
Use the Standards Compliance badge settings to select the level of detail at which to roll up the scores, and
the midpoint and magnitude used to adjust the scores that are reported in vCenter Operations Manager.
82
VMware, Inc.
Page 83

Configuring vCenter Operations Manager Integration
Table 5–5. Detail Level Score Aggregation Example Values
Templates i n Mappi ngs Score Results
Mapping 1 Template 1 80 10,000
Mapping 1 Template 2 50 5
Mapping 1 Template 3 100 1
Mapping 2 Template 4 30 100
Mapping 2 Template 5 75 500
n
Compliance Result: To roll up at the compliance result level means that the scores for the templates
assigned to the mapping, times the number of compliance results for each score divided by the total
number of compliance results.
For example, Mapping 1 has three templates using the scores and results provided in the Scoring table.
The scoring is calculated as (80*10,000)+(50*5)+(100*1)/(10,000+5+1)=80, where 80 is the score.
n
Template: To roll up at the template level means that each template's scores are averaged when rolled
up to the badge level.
For example, Mapping 1 has three templates using the scores provided in the Scoring table. The score is
calculated as (80+50+100)/3=77, where 77 is the score.
n
Mapping: To roll up at the mapping level means that the score for each mapping associated with a
badge is averaged when rolled up to the badge level.
For example, Mapping 1 and Mapping 2 are assigned to the same badge. The score is calculated as
(77+53)/2=65, where 77 is the Mapping 1 average, 53 is the Mapping 2 average, and 65 is the average of
the two mappings included in the badge.
Midpoint and Magnitude Score Calculations
Use midpoint and magnitude to refine how the badge scores are ultimately calculated for vCenter
Operations Manager.
n
Midpoint: The score that triggers the magnitude to increase or decrease the returned score.
n
Magnitude: The percentage by which any score that is above or below the midpoint is calculated.
The calculation is {detail level score}-{midpoint}={difference}; {difference}*{magnitude}={adjusted
magnitude factor}; {detail level score}+{adjusted magnitude factor}={adjusted score}.
Detail level scores can differ even where the midpoint and magnitude remain the same.
Table 5–6. Static Midpoint and Magnitude Values
Detail Level Score Midpoin t Magnitude Calculation Adjusted Score
20 50 10 20-50=-30
-30*10%=-3
20-3=17
40 50 10 40-50=-10
-10*10%=-1
40-1=39
17
39
VMware, Inc.
70 50 10 70-50=20
20*10%=2
70+2=72
72
83
Page 84

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Detail Level Score Midpoin t Magnitude Calculation Adjusted Score
100 50 10 100-50=50
100
50*10%=5
100+5=105
Table 5–7. Different Magnitude Values
Detail Level Score Midpoin t Magnitude Calculation Adjusted Score
70 50 20 70-50=20
74
20*20%=4
70+4=74
70 50 50 70-50=20
80
20*50%=10
70+10=80
70 50 80 70-50=20
86
20*80%=16
70+16=86
The adjusted score is the score that is pulled by the vCenter Operations Manager VCM Adapter and
appears as part of the Risk badge score.
You modify the midpoint and magnitude to give the Compliance subbadge scores a stronger or weaker
influence on the Risk parent badge. For example, if the compliance mappings score is configured so that it
normally scores 100 and you want any deviation to clearly degrade the score, you can set the midpoint to
99 and the magnitude to a high value. The resulting adjusted score lowers the value of the compliance
score and the Risk score when any noncompliance is found.
If you do not want to apply midpoint and magnitude calculations, set the magnitude to 0.
Scoring in vCenter Operations Manager
The standards compliance scores are pulled from VCM into vCenter Operations Manager and added to
the Risk badge score using the following calculation:
n
Risk: 100 - GeometricMean(badge|time_remaining, badge|capacity_remaining, 100 - badge|stress,
badge|riskcompliance)
84
VMware, Inc.
Page 85

Auditing Security Changes in Your Environment
The VCM Auditing capability tracks all changes in the security aspects of VCM. Security-related events are
written to the Windows Event Log, which is stored on the Collector, and is independent of the VCM
application. The format of the event log prohibits any modifications to the recorded entries, which makes
it a secure and tamper-proof auditing record of changes in security.
When you perform an action in VCM that affects security, and the auditing setting that corresponds to
that change is enabled, the event is written to the event log.
Examples of VCM actions that cause events to be written to the event log include user log on and log off,
session timeouts, changes in managing users, changes to passwords and administration settings, changes
in network accounts and authority, collection requests, and service and registry changes.
VCM supports the ability to create numerous audit records.
Figure 6–1. VCM Auditing
6
VMware, Inc.
Prerequisites
Log in as a user who has the Admin role assigned.
85
Page 86

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Procedure
1. To view the VCM Auditing settings, click Administration.
2. Select Settings > General Settings > Auditing.
3. To change an auditing setting, highlight a setting and click Edit Setting.
When you change an auditing setting, the VCM Auditing data grid displays the user’s name in the Last
Modified By column.
What to do next
For details about the Auditing settings and the Windows Event Log, see the online help.
86
VMware, Inc.
Page 87

Configuring Windows Machines
To manage your virtual and physical Windows machines, you must verify domains and accounts, discover
and license those machines, install the VCM Agent, and collect Windows data from those machines. You
can also collect Windows Custom Information.
This chapter includes the following topics:
Configure Windows Machines 87
Windows Collection Results 94
Getting Started with Windows Custom Information 95
Prerequisites to Collect Windows Custom Information 96
Using PowerShell Scripts for WCI Collections 97
Windows Custom Information Change Management 107
Collecting Windows Custom Information 108
Create Your Own WCI PowerShell Collection Script 108
Verify that Your Custom PowerShell Script is Valid 109
Install PowerShell 110
Collect Windows Custom Information Data 110
Run the Script-Based Collection Filter 111
View Windows Custom Information Job Status Details 112
Windows Custom Information Collection Results 113
Run Windows Custom Information Reports 114
Troubleshooting Custom PowerShell Scripts 115
7
Configure Windows Machines
To manage Windows machines, you must configure the environmental components and machine options
in VCM.
VMware, Inc.
87
Page 88

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Procedure
1. Verify Available Domains
Allow VCM access to each domain so that the VCM Collector can interact with the Windows machines
in your environment.
2. Check the Network Authority
Verify that at least one domain account with administrator privileges is available to act as a network
authority account for VCM.
3. Assign Network Authority Accounts
Select and assign the network authority account that you identified for VCM access to the Windows
machines.
4. Discover Windows Machines
In your network, identify the Windows machines that you are managing with VCM.
5. License Windows Machines
To manage Windows machines, you must license them in VCM.
6. Install the VCM Windows Agent on Your Windows Machines
Install the VCM Windows Agent on each Windows machine so that you can collect data and manage
the virtual or physical machines.
7. Collect Windows Data
Start managing the Windows machines by performing an initial collection, which adds Windows
machine data to VCM.
Continuous Windows machine management is based on the latest data you collect from target machines.
You can view data and run actions, such as reports or compliance, based on the collected data. See
"Windows Collection Results" on page 94.
Verify Available Domains
Allow VCM access to each domain so that the VCM Collector can interact with the Windows machines in
your environment.
During installation, VCM discovered all domains to which the network authority account had access. If the
Windows machines belong to a domain that is not listed, you must add that domain manually.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have the fully-qualified names of the domains to manage.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Settings > Network Authority > Available Domains.
3. If the domain does not appear Available Domains view, add the domain.
a. Click Add.
b. Type the domain name and select the domain type as NetBios or AD, depending on your domain.
c. Click OK.
4. Verify that the domain appears in the data grid.
88
VMware, Inc.
Page 89

Configuring Windows Machines
What to do next
Verify that a network authority account is available and create other necessary domain accounts. See
"Check the Network Authority" on page 89.
Check the Network Authority
Verify that at least one domain account with administrator privileges is available to act as a network
authority account for VCM.
Although you specified an initial default network authority account when you installed VCM, you can add
different administrator accounts if you do not assign the default account.
Prerequisites
Verify the presence of domains. See "Verify Available Domains" on page 88.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Settings > Network Authority > Available Accounts.
3. To add a new domain account, click Add.
4. Type the domain name, user name, and password, and click Next.
5. Click Finish to add the account.
What to do next
Assign the network authority account to the domain so that VCM can access the Windows machines in the
domain. See "Assign Network Authority Accounts" on page 89.
Assign Network Authority Accounts
Select and assign the network authority account that you identified for VCM access to the Windows
machines.
You can assign a single account to all domains and machine groups, or assign a unique account or multiple
accounts to each domain and machine group.
In this procedure, NetBios is used as the example.
Prerequisites
Verify or add the necessary network authority account. See "Check the Network Authority" on page 89.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Settings > Network Authority > Assigned Accounts > By Domain > NetBios.
VMware, Inc.
3. Select an assigned account.
4. Click Edit Assigned Accounts.
5. Select the account to receive authority to the domain and click Next.
6. Confirm the accounts to include in the authority list for the domain and click Finish.
What to do next
Discover the Windows machines in your environment. See "Discover Windows Machines" on page 90.
89
Page 90

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Discover Windows Machines
In your network, identify the Windows machines that you are managing with VCM.
To discover the available Windows machines, VCM uses general discovery rules to identify many
Windows machines or uses specific discovery rules to identify particular Windows machines.
The time required to perform an initial discovery depends on the size and composition of your network. If
all Windows machines are not available during initial discovery, such as systems that are disconnected
from the network, the first discovery will not find all Windows machines. If the discovery does not
identify all Windows machines, you might need to run additional discoveries after the other Windows
machines become available.
NOTE You can use the Discovered Machines Import Tool (DMIT), which imports machines discovered by
the Network Mapper (Nmap), to import many physical and virtual machines at one time into the VCM
database. Download DMIT from the VMware Web site.
The following procedure is based on Active Directory.
Prerequisites
Assign a Network Authority Account that VCM can use for access. See "Assign Network Authority
Accounts" on page 89.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Discovery Rules.
3. Click Add to create a discovery rule.
4. On the Discovery Rules page, type a name and description and click Next.
5. On the Discovery Method page, select By Active Directory and click Next.
6. On the AD Domain page, specify the AD Domain, select Discover machines only from the selected
domain, and click Next.
7. On the Discovery Filters page, select Discover all machines in <domain_name> Domain.
8. (Optional) Create a filter to discover Windows machines based on a limited criteria and click Next.
9. On the Important page, click Yes and click Finish.
To avoid exceeding your license count, do not select License and Install Agent on Discovered
Machines.
10. On the toolbar, click Jobs to track current discovery job status.
What to do next
n
Verify that the jobs finished running. Click Administration and select Job Manager > History > Other
Jobs > Past 24 Hours.
n
Verify that the Windows machines are available. Click Administration and select Machines Manager >
Available Machines.
n
License the Windows machines in your environment. See "License Windows Machines" on page 90.
License Windows Machines
To manage Windows machines, you must license them in VCM.
90
VMware, Inc.
Page 91

Configuring Windows Machines
The number of discovered Windows, UNIX, or Linux machines might exceed the number of your
available licenses. If that happens, the number available goes negative and appears in red to indicate that
you do not have enough licenses.
For servers and workstations, exceeding the limit on your license key produces warnings but does not
restrict VCM operation. License key counts that are over the limit are recorded and maintained for
auditing purposes. Suite license keys support unlimited licenses, provided that the suite edition includes
VCM and the component that you are managing is part of the suite. If a component is not part of the suite,
it counts against the nonsuite server or workstation key.
Prerequisites
Verify that the Windows machines you license are listed with a machine type of workstation or server in
the Available Machines node. If the discovered or added type is not workstation or server, VCM cannot
license the machines.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Available Machines.
3. Select the Windows machines to license.
4. Click License.
5. Verify that the Windows machines to license appear in the Selected list.
Use the arrows to move the Windows machines.
6. Click Next to view your Product License Details.
The licensed Windows machine count increases by the number of licensed machines.
7. Click Next.
VCM confirms that the licenses you requested will be applied to the selected Windows machines.
8. Click Finish.
What to do next
Install the Windows Agent. See "Install the VCM Windows Agent on Your Windows Machines" on page 91
Install the VCM Windows Agent on Your Windows Machines
Install the VCM Windows Agent on each Windows machine so that you can collect data and manage the
virtual or physical machines.
Before you can collect data from Windows machines, you must install the VCM Windows Agent on the
licensed Windows machines in your environment to enable communication between the Collector and the
target machines.
You can use VCM to install the Agent or you can install the Agent manually. This procedure uses VCM to
install the Agent. For information about manually installing the Agent see the online Help.
VMware, Inc.
The Agent is installed on Collector when you install VCM, and locked. It cannot be unlocked, uninstalled,
or upgraded.
91
Page 92

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Locking the VCM Agent on VCM managed machines is typically done in environments that have multiple
VCM Collectors, to help prevent these Agents from being unintentionally upgraded or removed. The
VCM Agent on the VCM Collector is locked, because it is installed as part of the VCM installation and is
required for VCM Collector operations. The version of the VCM Agent on the Collector must also match
the version of VCM installed.
Use the UNLOCK option only when you intend to upgrade or uninstall a locked Agent on a VCM
managed machine. Never use the UNLOCK option on the VCM Collector. If the VCM Agent is uninstalled
from the Collector, the Collector service cannot run. If the VCM Agent is accidentally uninstalled from a
Collector, you must reinstall it and restart the Collector service to re-enable the Collector functionality. If
the VCM Agent is unintentionally reinstalled on a Collector, you must restart the Collector service.
Standardized Windows configurations such as Federal Desktop Core Configuration (FDCC) or United
States Government Configuration Baseline (USGCB) include strict security group policy settings. The
Windows Firewall: Do not Allow Exceptions group policy configures Windows Firewall to block all
unsolicited incoming messages, including configured exceptions. This setting overrides all configured
exceptions. For VCM to communicate properly with the VCM Agent on managed machines in strict,
secure environments, disable the Windows Firewall: Do not Allow Exceptions group policy on the
managed machines. For more information, see support.microsoft.com.
Prerequisites
n
License the Windows machines on which you install the Agent. See "License Windows Machines" on
page 90.
n
Verify that you know the communication protocols and ports that are used by the Collector and the
Agents.
Procedure
1. Click Administration.
2. Select Machines Manager > Licensed Machines > Licensed Windows Machines.
3. In the data grid, select one or more Windows machines on which to install the Agent and click Install.
4. On the Machines page, verify that the target machines appear in the Selected list and click Next.
5. On the Install Options page, select the installation options and click Next.
Option Description
Share Location to install the Agent. The default location is ADMIN$.
Path Path for the Agent files. The default path includes CMAgent.
Install From VCM Collector from which to install the Agent.
DCOM Communication protocol for the Agent. The default setting is
DCOM.
HTTP Secure communication protocol for the Agent. Use HTTP, which
installs the HTTP Listener on the target machine and configures it
to listen on the designated port.
Port Designated port for the HTTP Listener.
92
VMware, Inc.
Page 93

Configuring Windows Machines
Option Description
Install using a proxy server For Windows Proxies and Windows Agents only. If the target
machine is separated from the Collector by a proxy server, this
option instructs the installation process to check for available
proxy servers.
Lock the machine after
installation
Ensures that VCMwill not uninstall the Agent or replace it with a
different version.
Reinstall Agent Overwrites an installed Agent.
6. On the Schedule page, select Run Action now and click Next.
You can schedule subsequent Agent installations to run later.
7. Review the summary information and click Finish.
What to do next
n
Verify that the jobs finished running. Click Administration and select Job Manager > History > Other
Jobs > Past 24 Hours.
n
Collect Windows data from VCM managed machines in your environment. See "Collect Windows
Data" on page 93.
Locate the Enterprise Certificate
Locate the Enterprise Certificate before you install the VCM Agent on the managed Windows machine.
VCM must access the Enterprise Certificate during the Agent installation.
If your Collector is operating in a full Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), and the target machine can validate
the Collector root certificate (Enterprise Certificate), the .pem file is not required.
Procedure
1. Locate the Enterprise Certificate .pem file in the Collector's c:\Program Files (x86)
\VMware\VCM\CollectorData folder.
2. If the certificate files are not in the default location, you must confirm the path to the files.
a. Click Administration.
b. Select Settings > General Settings > Collector.
c. Select Root directory for all collector files.
d. Confirm the file path in the Value column.
Collect Windows Data
Start managing the Windows machines by performing an initial collection, which adds Windows machine
data to VCM.
Use the default filter set to collect a general view of the Windows machines in your environment. The first
time that you use the default filter to collect data, the Windows Agent returns all of the data specified in
the filter and stores the data in the VCM database. All subsequent collections will return a delta against the
data previously collected.
VMware, Inc.
93
Page 94

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
A delta collection includes only the differences between the data on the target machine and the data stored
in the VCM database. If you need a full collection, you can specify that VCM collect all data again. A full
collection can take a significant amount of time depending on the number of VCM managed Windows
machines from which you are collecting.
When you perform a full collection from your entire environment, run the collection during nonworking
hours so that users do not notice any performance impact on managed machines. After the initial
collection is finished, subsequent delta collections will most likely not impact performance.
Prerequisites
n
Collect the Accounts and Groups data types from the primary domain controller (PDC) in each domain
to increase the performance of initial collections that require a SID lookup.
n
To collect data from Windows XP SP2 or Vista machines that use DCOM communication, you must
enable ICMP pings in the firewall settings or disable ICMP pings in VCM.
n
Verify that DCOM is enabled on the managed machine. Run dcomcnfg and select Enable Distributed
COM on this computer.
Procedure
1. On the VCM toolbar, click Collect.
2. On the Collection Type page, select and click OK.
3. On the Machines page, select the Windows machines from which to collect data and click Next.
To move all visible Windows machines to the selection window, 500 at a time, use the double arrow.
4. On the Data Types page, configure the collection and click Next.
a. Expand Windows and select the data types.
At a minimum, you must collect Machines data. If you are managing data using compliance,
change, or running reports, you must collect the data types that are included in the other actions or
that you want to view in the appropriate data grids.
b. Select Use default filters.
5. On the Important page, resolve any conflicts and click Finish.
6. Click Administration and select Job Manager > History > Instant Collections > Past 24 Hours to
determine if the collection finished.
The amount of time the collection requires is determined by the number of machines and network
connectivity.
What to do next
n
Verify that the jobs finished running. Click Administration and select Job Manager > History > Other
Jobs > Past 24 Hours.
n
Review the collection results. See "Windows Collection Results" on page 94.
Windows Collection Results
Continuous Windows machine management is based on the latest data that you collect from target
machines. You can view data and run actions, such as reports or compliance, based on the collected data.
Windows data appears in VCM and is available for several management actions, including Console
dashboards and reports, Compliance views, and VCMPatching. The displayed data is only as current as
the last time you collected the data.
94
VMware, Inc.
Page 95

Configuring Windows Machines
After the initial discovery is finished, perform a weekly discovery to update the list of available Windows
machines. To schedule a VCM discovery job, click Administration, select Job Manager > Scheduled, and
follow the wizard.
Option Descriptio n
Console Displays dashboards and reports based on collected data. Use the Console to view
data that is relevant to day-to-day operations, troubleshooting, and analysis.
n
To view the dashboards, click Console and select Dashboards > Windows >
Operating Systems.
n
To view the summary reports, click Console and select Windows > Operating
System > Machines. You can view the data in a summary report or data grid
format.
Compliance Determines if the data collected from VCM managed Windows machines meets
specified compliance values, and allows you to run compliance remediation
actions.
n
To run a compliance check, click Compliance and select Machine Group
Compliance.
n
To create rule groups, rules, filters, and templates, see the online help.
Reports Runs preconfigured reports or you can create custom reports. VCM runs reports
against the latest collected data. Depending on the data volume or complexity of
the requested report, it might take time to generate the report. You can also
schedule and disseminate reports.
n
To use the reporting options, click Reports and select Machine Group Reports
> Windows.
Patching Assesses target machines to determine if the patching status of the Windows
machines is up-to-date. You can install the latest patches on target machines.
n
To assess and patch Windows machines, click Patching and select Windows.
n
To run assessments and patch your Windows machines, see the online help.
Getting Started with Windows Custom Information
Windows Custom Information (WCI) is data collected from VCM managed machines that is created by
PowerShell or Python scripts. WCI supplements and extends the data collected by VCM from managed
Windows machines using other VCM data types.
You can create or modify WCI scripts to collect almost any data type that is accessible from VCM
managed machines. VCM supports PowerShell and Python scripting, and XML output to collect Windows
Custom Information.
VMware, Inc.
95
Page 96

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Figure 7–1. Windows Custom Information Collection Process
To extend the data collected by VCM from managed Windows machines using other VCM data types,
collect Windows Custom Information. The example used to get you started collecting WCI data is for
Powershell. Follow the same basic procedures to configure and run Python scripts.
Configure the prerequisites and create and validate your script.
Prerequisites
To collect Windows Custom Information from VCM managed machines, you must configure the
prerequisites. See "Prerequisites to Collect Windows Custom Information" on page 96.
Procedure
n
"Collecting Windows Custom Information" on page 108
To collect Windows Custom Information (WCI) using script-based filters, you create and verify your
custom PowerShell scripts, install PowerShell on the VCM managed machines, and use VCM to collect
the WCI data.
Prerequisites to Collect Windows Custom Information
To collect Windows Custom Information from VCM managed machines, you must configure the
prerequisites.
These prerequisites use PoweShell as the example script. VCM supports PowerShell and Python scripts to
configure WCI collections.
96
VMware, Inc.
Page 97

Configuring Windows Machines
Prerequisites
n
Write your own PowerShell script to return data in a VCM compatible, element-normal XML format,
or obtain PowerShell scripts from VMware Professional Services or another source. See "Using
PowerShell Scripts for WCI Collections" on page 97.
n
Understand the script signing policies if you use PowerShell 2.0. See "PowerShell Script Signing Policies"
on page 101.
n
Set the PowerShell execution policy on the VCM managed machine. See "Built-In PowerShell Policy
Settings" on page 102.
n
Understand how to write and run PowerShell scripts. See "References on PowerShell and Script Signing"
on page 102.
n
Verify that your PowerShell script is accessible when you paste the script content into the Script area of
the collection filter on the VCM Collector.
n
Confirm that the VCM Collector includes PowerShell 2.0 if the Collector is a client for WCI collections.
n
Understand how VCM manages Windows Custom Information data changes. See "Windows Custom
Information Change Management" on page 107.
n
Confirm that PowerShell 2.0 is installed on each VCM managed machine that will be used for WCI
collections. See "Install PowerShell" on page 110.
n
Upgrade older VCMAgents on the VCM managed machines from which you collect Windows Custom
Information, and then install the VCM 5.3 Agent or later on these machines.
n
Confirm or update the Agent Thread Administration settings on the VCM Collector. The default value
is set to below normal thread priority, and the Agent Data Retention default is set to a 15-day change
log.
Using PowerShell Scripts for WCI Collections
Windows Custom Information (WCI) uses PowerShell as the scripting engine and the element-normal
XML format as the output that is inserted into the VCM database.
WCI supports PowerShell 2.0 and works with later versions of PowerShell.
n
PowerShell 2.0 is the base requirement for WCI in VCM because of its ability to set the execution policy
at the process level.
n
You can run WCI PowerShell collection scripts against Windows machines that have PowerShell 1.0
installed if needed, although this usage is not supported or tested. If the collection scripts do not use
PowerShell 2.0 commands, your WCI filters that use the in-line method to pass a WCI script to
PowerShell will operate correctly.
The WCI data type uses extensions to the VCM Windows Agent. The extensions allow the Agent to
invoke PowerShell scripts. Using the script-based collection filter, VCM passes the PowerShell scripts to a
VCM managed machine, and the VCM Agent parses the resulting XML output. The default WCI filter
returns the PowerShell version information from the managed machines.
VMware, Inc.
WCIdata type extensions are flexible because they use filter parameters that the command line uses to
invoke the scripting engine. The WCI extensions use a COM class name to specify the parser required for
the Agent to parse the script output, and allow new types of parsers to be added at the Agent. This
approach extends the support of multiple scripting engines, languages, and output formats.
97
Page 98

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Guidelines in PowerShell Scripting for WCI
When you develop custom PowerShell scripts to collect the Windows Custom Information (WCI)data
type from VCM managed Windows machines, follow these guidelines.
n
Make XML element names unique at the same level.
For example, you can specify two child nodes that are not siblings.
n
Make attributes unique at the same level.
n
Use unique XMLelement names to generate valid VCM XML. The XML elements are code blocks that
include the element's start and end tags. The element can contain other elements, text, attributes, or a
combination of them.
n
Use repeatable identifiers to prevent false indications of changes at the Collector. If your element labels
(identifiers) are not the same for every collection of the same item, you will see false additions, changes,
and deletions in the VCM change log.
n
Confirm that the script returns valid XMLelement names and attribute names.
If the data to be returned is an element name or an attribute name that is not valid for XML, you can
encode the name using the [ToCMBase64String] function. A VCM Collector job, called the inserter, is
executed during each collection. The inserter recognizes the names that are encoded with this function
and decodes them in the raw insertion process.
The inserter parses the resulting XML file and inserts the data into a new raw database table named
VCM_Raw by default. The XML process transforms the raw data into data that appears in VCM.
The function is defined as follows.
function ToCMBase64String([string]$input_string)
{
return [string]("cmbase64-" +
[System.Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::UNICODE.GetBytes
($input_string))).replace("=","-")
}
n
Include a comment block and configurable parameter entries near the start of the script so that when
you clone a WCI collection filter you can see the parameters and set them when you edit the collection
filter. To view and edit the collection filters, click Administration and select Collection Filters > Filters.
n
Redirect any variable declarations in the script to out-null, along with any other tasks that generate
output that is not part of the XML result set. For example, you can use the following command.
[reflection.assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("Microsoft.SqlServer.Smo") > out-
null
n
Do not include any formatting, white space, carriage returns, or line feeds at the end of elements,
nodes, or attributes.
Challenges in PowerShell Scripting for WCI
When you develop custom collection scripts, understand the challenges that you might encounter while
scripting in PowerShell to collect the Windows Custom Information (WCI)data type from VCM managed
Windows machines.
PowerShell scripts can use the split method of PowerShell strings, which separates the columns of the rows
into separate values in arrays. For example, Windows provides the schtasks.exe utility to manage
scheduled tasks on a local or remote computer and report on the scheduled tasks.
98
VMware, Inc.
Page 99

Configuring Windows Machines
The split method of PowerShell strings in the $schtasks script separates the columns of the $schtasks
rows into separate values in arrays.
n
Column names row provides the names to use for attributes.
n
Corresponding data from the scheduled task rows provides the values to use for these attributes.
The top-level name of <schtasks> is an arbitrary name that you apply to distinguish the results of this
script from other results. The XML script returns the parsed data, which resembles the following structure.
<schtasks>
<taskname1>
<attribute1>Value1</attribute1>
<attribute2>Value2</attribute2>
</taskname1>
<taskname2>
<attribute1>Value1</attribute1>
<attribute2>Value2</attribute2>
</taskname2>
</schtasks>
The returned data can include the following problems with content.
n
White space, such as tabs or spaces, is not allowed in returned data.
n
Column names include spaces.
n
Specific task entries do not include a unique and repeatable identifier.
n
Values can contain XML syntax in functions, which you must enclose in CDATA.
VMware, Inc.
99
Page 100

vCenter Configuration Manager Administration Guide
Column Names Include Spaces
Running the schtasks command without any options displays a column name of Next Run Time.
Because this name includes spaces, you cannot use it as an attribute name in an XML document. Running
the schtasks command verbosely generates other column names that include spaces. Although you
cannot use these invalid names as attribute names, you can preserve the names by using VCM encoding
standards.
To preserve these column names in the form that schtasks returns and allow for XML handling, VCM
encodes the column names with the ToCMBase64String function. To create a valid XML form of an
element name or attribute name, this function uses Unicode Base64 encoding and character substitution,
such as using a dash instead of an equal sign, as shown in the following example.
function ToCMBase64String([string]$input_string)
{
return [string]("cmbase64-" +
[System.Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::
UNICODE.GetBytes($input_string))).replace("=","-")
}
Using this function corrects the invalid column name data.
VCM prefaces the string with cmbase64- so that the VCM inserter can decode the data and load the
decoded data into the VCM database.
The valid XML appears as follows.
<cmbase64-TgBlAHgAdAAgAFIAdQBuACAAVABpAG0AZQA->
12:32:00, 5/26/2010
</cmbase64-TgBlAHgAdAAgAFIAdQBuACAAVABpAG0AZQA->
Invalid XML omits the encoding function as follows.
<Next Run Time>
12:32:00, 5/26/2010
</Next Run Time>
Task Entries Do Not Include a Unique and Repeatable Identifier
Use repeatable identifiers to prevent false indications of changes at the Collector. If your element labels
(identifiers) are not the same for every collection of the same item, you will see false additions, changes,
and deletions in the VCM change log.
The Windows schtasks command does not include a unique and repeatable identifier for specific task
entries. Because unique element names are a requirement for valid VCM XML and repeatable identifiers
help prevent false indications of changes at the VCM Collector, you must code the task names correctly in
your script.
100
To create unique and repeatable element names, create a task entry name based on a hash of the data in
the row. You can use this method for data that does not have a name-type attribute, where the task name
exists but is not guaranteed to be unique. When the task name is user-friendly and useful, you must
attempt to preserve the name and use it in the collection script.
VMware, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...