VITESSE VSC8163QR Datasheet
VITESSE
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION
Preliminary Data Sheet
VSC8163
OC-48 16:1 SONET/SDH
MUX with Clock Generator
Features
• 2.488Gb/s 16:1 Multiplexer
• Targeted for SONET OC-48 / SDH STM-16
Applications
• Differential LVPECL Low-Speed Interface
• On-Chip PLL-Based Clock Generator
• 128 Pin, 14x20mm PQFP Package
• Single +3.3V Supply
General Description
The VSC8163 is a 16:1 multiplexer with integrated clock generator for use in SONET/SDH systems operating at a 2.48832Gb/s data rate. The internal clock generator uses a Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) to multiply
either a 77.76MHz or 155.52MHz reference clock in order to provide the 2.48832GHz clock for internal logic
and output retiming. The 16-bit parallel interface inc orporates an on-board FIFO, elimina ting loop timing
design issues by providing a flexible paralle l timing arch itectur e. The devi ce operates usin g a +3.3V power supply, and is packaged in a thermally-enhanced plastic package. The thermal performance of the 128PQFP allows
the use of the VSC8163 without a heat sink under most thermal conditions.
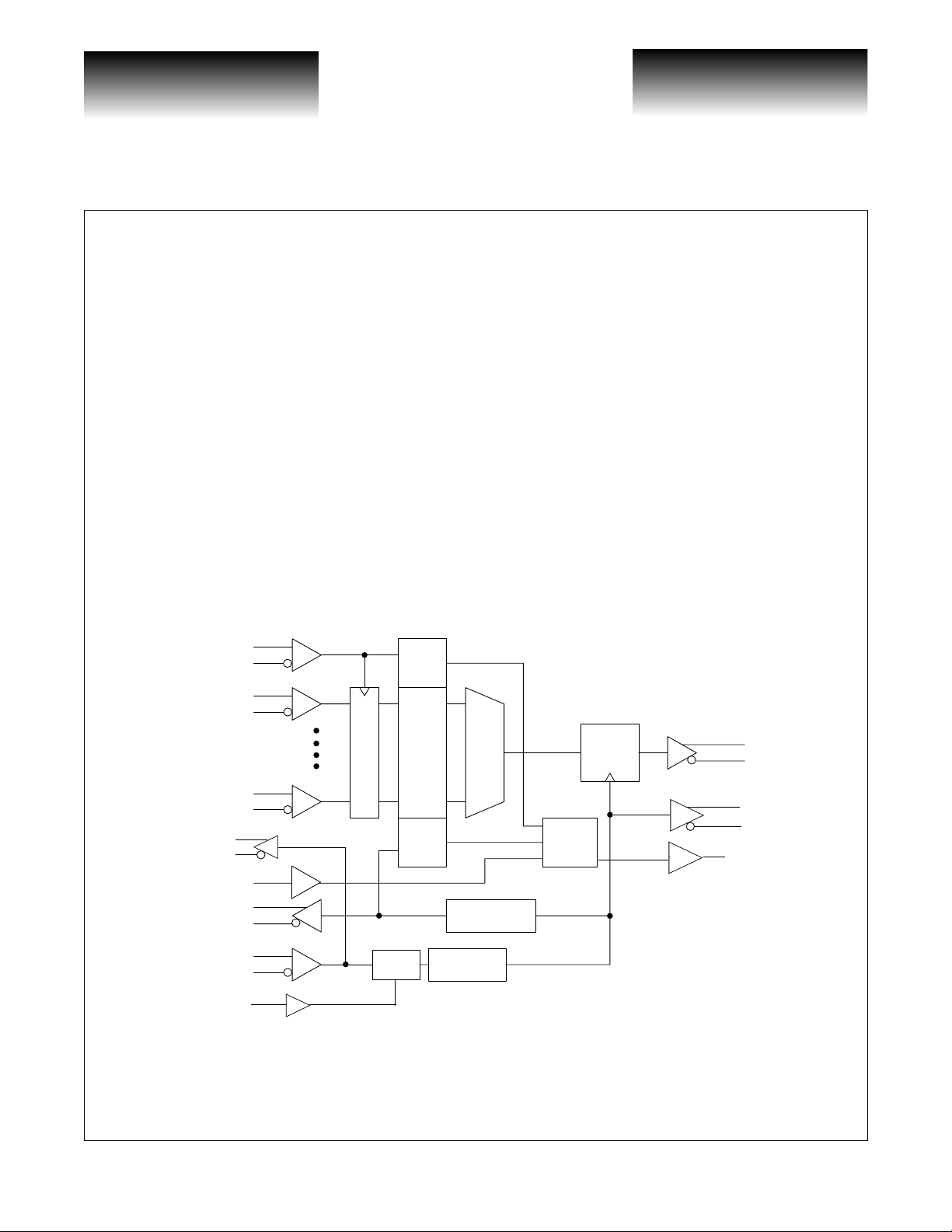
VSC8163 Block Diagram
CLK16I+
CLK16I-
D15+
D15-
REFCLKO+
REFCLKO-
Reset
CLK16O+
CLK16O-
REFCLK+
REFCLK
REF_FREQSEL
D0+
D0-
Write
Pointer
Input Register
16x5 FIFO
Read
Pointer
Divide
by 2
Divide by 16
2.488GHz
PLL
FIFO
Control
Output
Retime
DO+
DO-
CLKO+
CLKO-
FIFO_WARN
G52216-0, Rev 3.3 Page 1
01/05/01
© VITESSE SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION • 741 Calle Plano • Camarillo, CA 93012
Tel: (800) VITESSE • FAX: (805) 987-5896 • Email: prodinfo@vitesse.com
Internet: www.vitesse.com
VITESSE
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION
OC-48 16:1 SONET/ SDH
MUX with Clock Generator
Preliminary Data Sheet
VSC8163
Functional Description
Low-Speed Interface
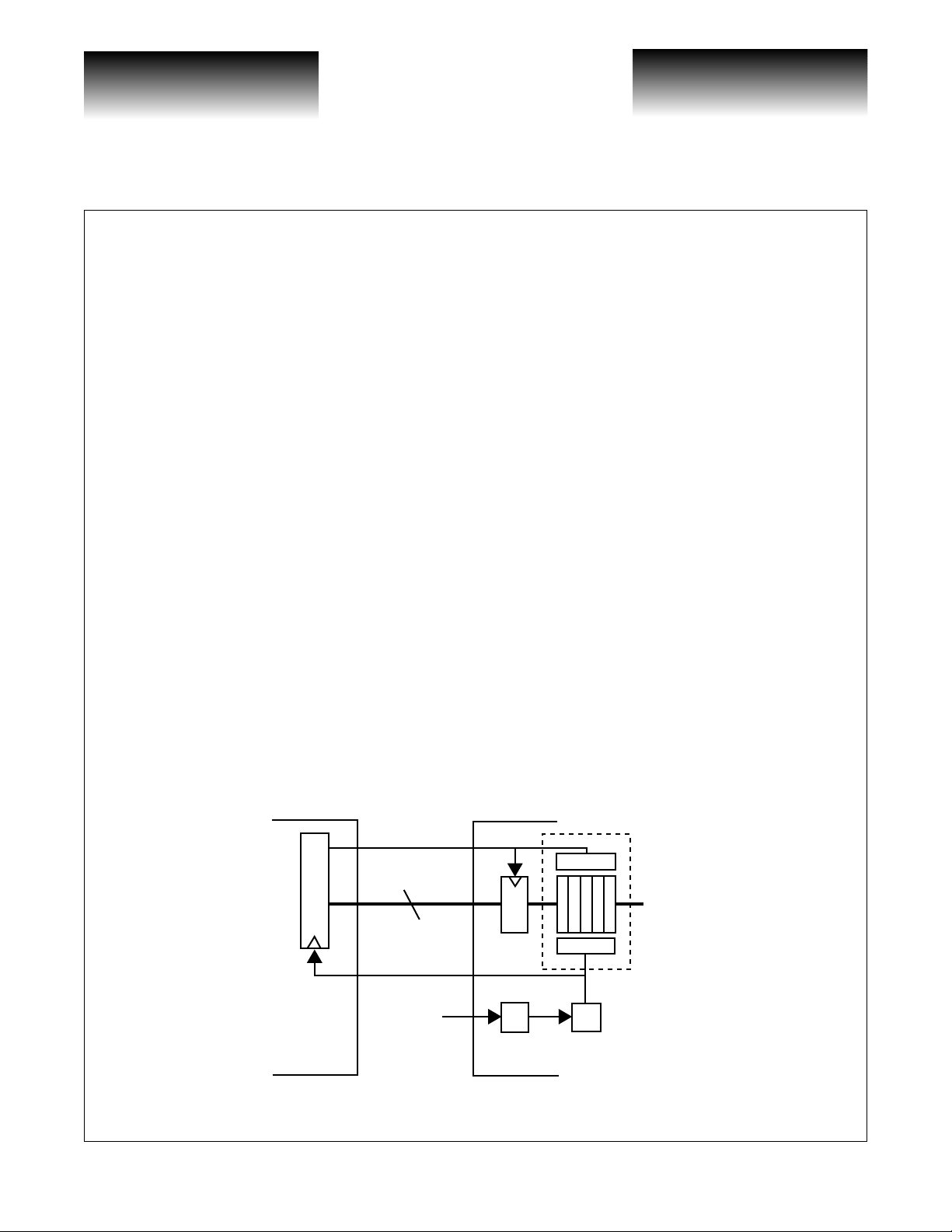
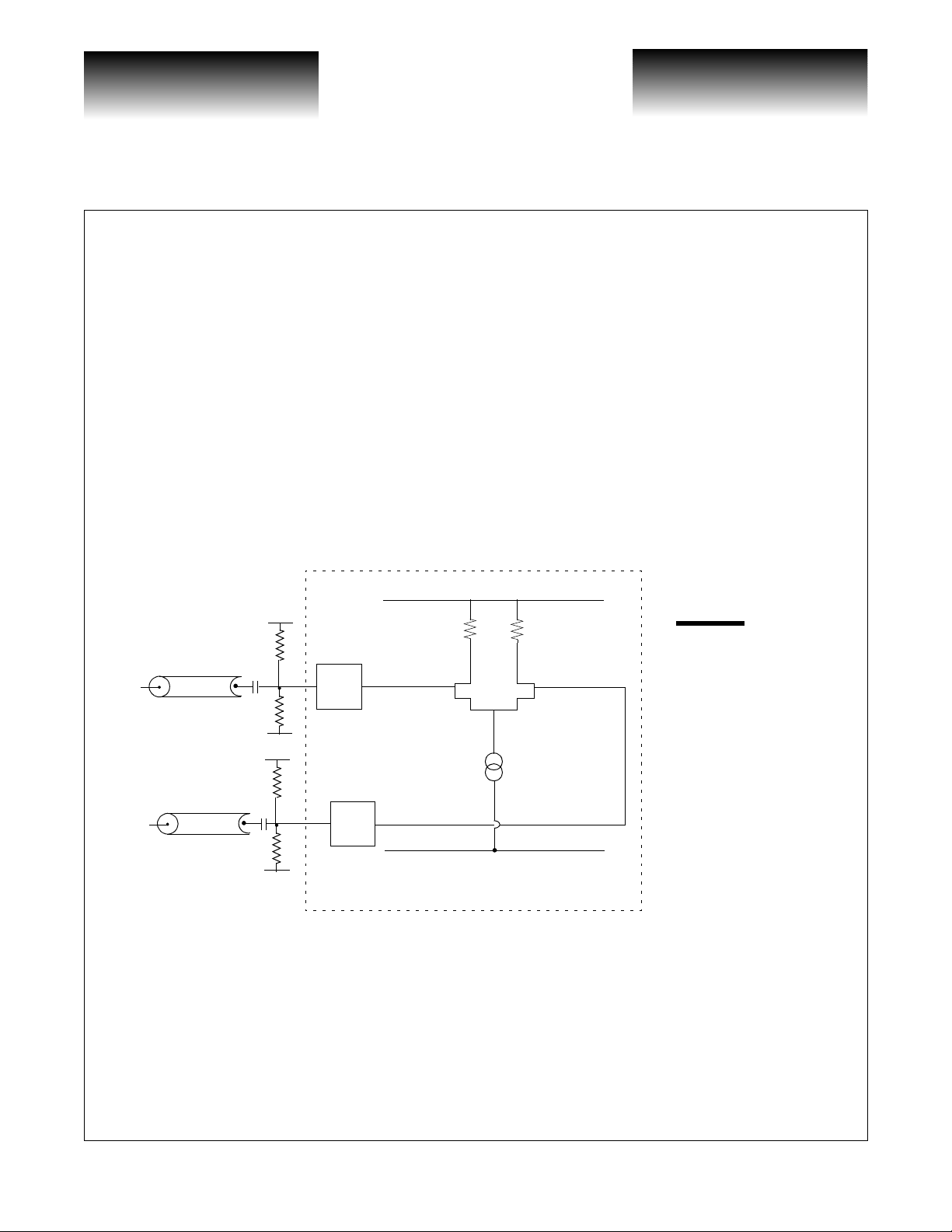
The Upstream Device should use the CLK16O as the timing source for its final output latch (see Figure 1).
The Upstream Device should then generate a CLK16I phase aligned with the data. The VSC8163 will latch
D[15:0]
T able 2) . In addition to the CLK16O clock output , there also exis ts a utility REFCL KO output signal , which is a
clock with the same rate as that presented at the REFCLK input.
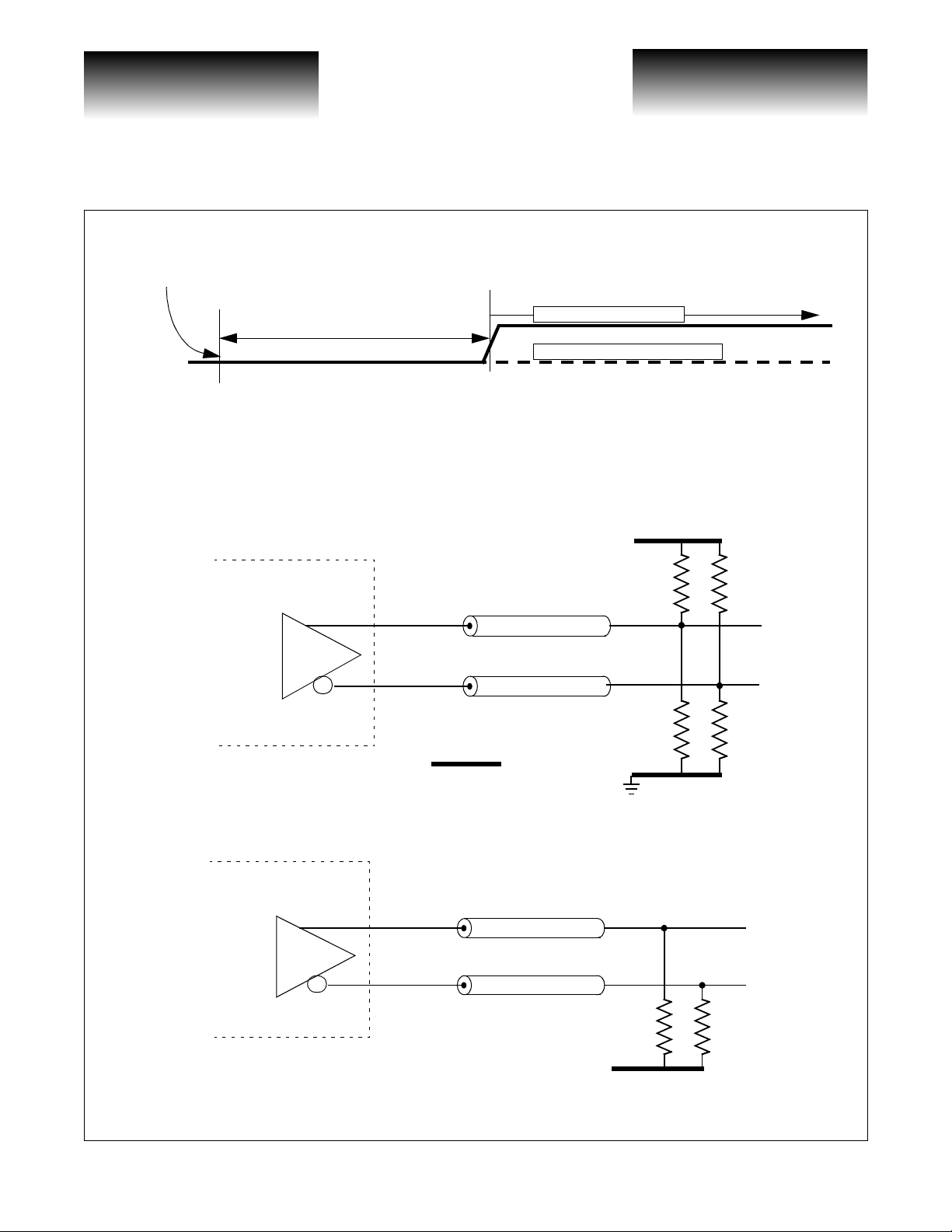
locked to the reference clock, RESET must be held low for a minimum of five CLK16 cycles ( > 32ns) to initialize the FIFO, then RESET should be set high and held constant for continuous FIFO operation. For the
transparent mode of operation (no FIFO), simply hold RESET at a constant low state (see Figure 2).
and CLK16I. Once RESET is asserted and the FIFO initialized, the delay betw een CLK16O and CLK16I can
decrease or increase up to one period of the low-speed clock (6.4ns). Should this delay drift exceed one period,
the write pointer and the read pointer could point to the same word in the FIFO, resulting i n a loss of transmitted
data (a FIFO overflow). In the event of a FIFO overflow, an active low FIFO_WARN signal is asserted (for a
minimum of 5 CLK16I cycles) which can be used to initiate a reset signal from an external controller.
transmission line can be DC terminated with a split-end termin ation scheme (see Fig ure 3), or DC terminated by
50
substituted for the traditional 50
ods. Figure 5 illustrates an example AC-coupling method for the occasion when the downstream device provides the bias point for AC-coupling. If the do wnstream dev ice were to have inter nal termination, the line-toline 100
± on the rising edge of CLK16I +. The data must meet setup and hold times with r esp ect to CLK16I ( see
A FIFO exists within the VS C8163 to elimina te difficult system loop timing issues . Once the PLL h as
The use of a FIFO permits the system designer to tolerate an arbitrary amount of delay between CLK16O
The CLK16O
Ω to V
CC
Ω resistor may not be necessary.
± output driver is a LVPECL output driver designed to drive a 50Ω transmission line. The
-2V on each line (see Figure 4). At any time, the equivalent split-end termination technique can be
Ω to V
-2V on each line. AC-coupling can be achieved by a number of meth-
CC
Figure 1: Low-Speed Systems Interface
CLK16I
x16
Upstream
Device
CLK16O
REFCLK
2.488GHz
PLL
Page 2 G52216-0, Rev 3.3
© VITESSE SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION • 741 Calle Plano • Camarillo, CA 93012
Tel: (800) VITESSE • FAX: (805) 987-5896 • Email: prodinfo@vitesse.com
Internet: www.vitesse.com
Write
Read
16 x 5 FIFO
VSC8163
Divide by 16
01/05/00
VITESSE
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION
Preliminary Data Sheet
VSC8163
PLL locked to reference clock.
Minimum 5 CLK16 cycles (32ns)
RESET
Holding RESET “low” for a minimum of five CLK16 cycles, then setting “high” enables FIFO operation.
Holding RESET constantly “low” bypasses the FIFO for transparent mode operation.
Figure 3: Split-End DC Termination of CLK16O+/-, REFCLKO+/-
VSC8163
Figure 2: Enabling FIFO Operation
FIFO Mode Operation
Transparent Mode Operation
Split-end equivalent termination is Z0 to V
R1 = 125Ω R2 = 83Ω, Zo=50Ω, V
Z
o
TERM
TERM
= VCC-2V
OC-48 16:1 SONET/SDH
MUX with Clock Generator
V
CC
R1
R1
Z
o
R1||R2 = Z
VCCR2 + VEER1
R1+R2
0
= V
TERM
V
EE
R2
Figure 4: Traditional DC Termination of CLK16O+/-, REFCLKO+/-
VSC8163
Z
0
Z
0
50Ω
VCC-2V
R2
50Ω
G52216-0, Rev 3.3 Page 3
01/05/01
© VITESSE SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION • 741 Calle Plano • Camarillo, CA 93012
Tel: (800) VITESSE • FAX: (805) 987-5896 • Email: prodinfo@vitesse.com
Internet: www.vitesse.com
VITESSE
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION
OC-48 16:1 SONET/ SDH
MUX with Clock Generator
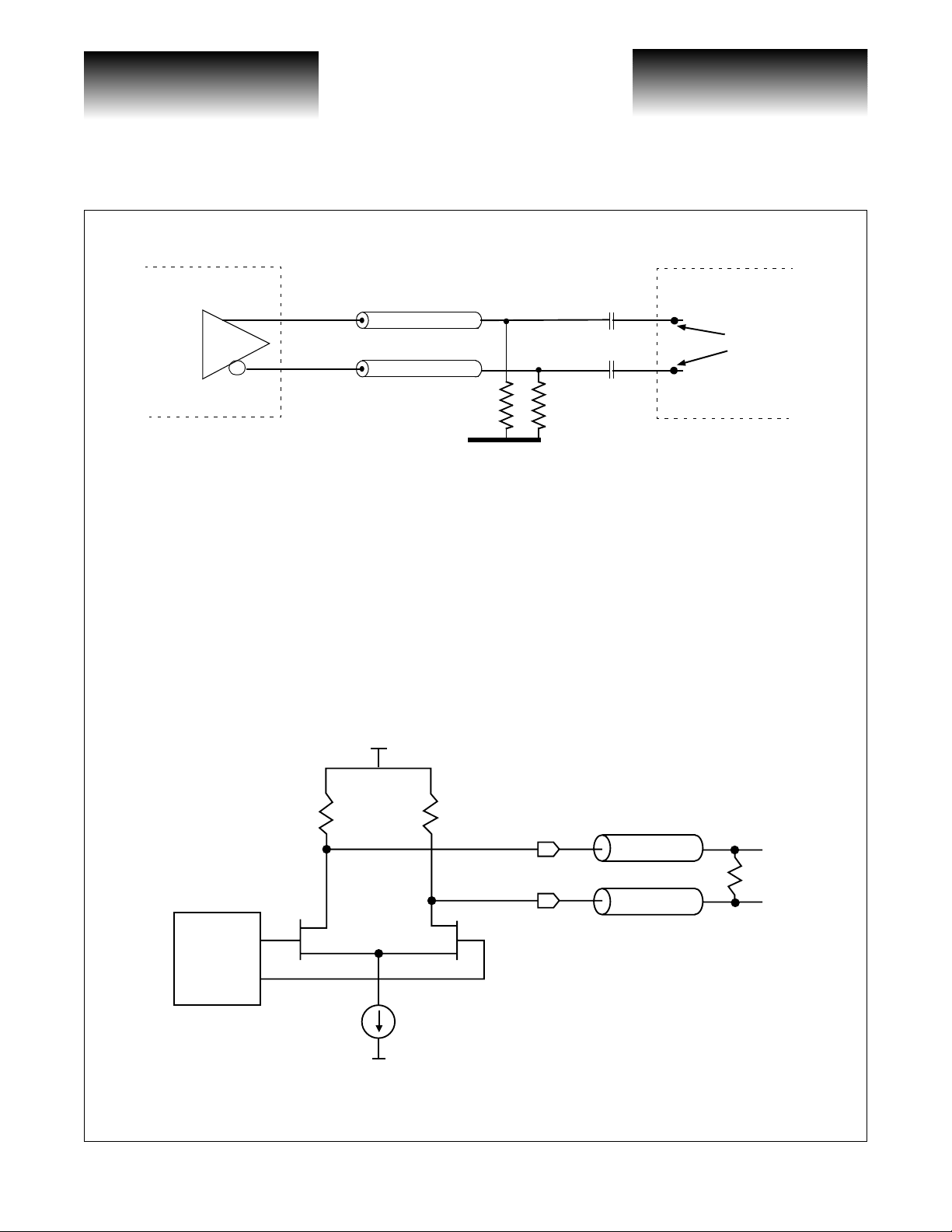
Figure 5: AC Termination of CLK16O+/-, REFCLKO+/-
VSC8163
High-Speed Data and Clock Output
The high-speed data and clock outpu t driver s consist of a dif f erenti al pair desi gned to dri ve a 50Ω tran s mis-
sion line. The transmission line should be terminated with a 100
ment outputs (see Figure 6). Connection to a termination voltage is not required. The output driver is back
terminated to 50
driver must still be terminated differentially at the load with a 100
puts. The high-speed clock output can be powered down for additi onal power savi ngs. To power down the highspeed clock, tie the associated pins to V
Ω on-chip, providing a snubbing of any refl ect ion s . If used sin gle- ended , the high-speed output
Z
0
Z
0
50Ω
Ω resistor at the load between true and comple-
(see Table 3, Package Pin Descriptions, pins 5,6,7).
CC
100nF
100nF
50Ω
-2V
V
CC
Ω resistor between true and complement out-
Preliminary Data Sheet
VSC8163
downstream
bias point
generated
internally
Pre-Driver
50Ω
Figure 6: High-Speed Output Termination
V
CC
50Ω
V
EE
100Ω
Z0 = 50Ω
Page 4 G52216-0, Rev 3.3
© VITESSE SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION • 741 Calle Plano • Camarillo, CA 93012
Tel: (800) VITESSE • FAX: (805) 987-5896 • Email: prodinfo@vitesse.com
Internet: www.vitesse.com
01/05/00
VITESSE
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION
Preliminary Data Sheet
VSC8163
OC-48 16:1 SONET/SDH
MUX with Clock Generator
Clock Generator
An on-chip PLL generates the 2.48832GHz transmit clock from the externally provided REF CLK input.
The on-chip PLL uses a low phase noise reactance-based Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) with an on-chip
loop filter. The loop bandwidth of the PLL is within the SONET specified limit of 2MHz.
The customer can select to provide either a 77.76MHz reference (recommen ded), or the 2x of that reference, 155.52MH z. REF_FR EQSEL is us ed to select t he desire d refere nce frequen cy. REF_FREQSEL = “0”
designates REFCLK
input as 77.76MHz, REF_FREQSEL = “1” designates REFCLK input as 155.52MHz.
The REFCLK should be of high quality since noise on the REFCLK below the loop band width of the PLL
will pass through the PLL and appear as jitter on the output. Preconditioning of the REFCLK signal with a
VCXO may be required to avoid passing REFCLK noise with greater than 2ps of RMS jitter to the output. The
VSC8163 will output the REFC LK noise in add ition to the intr insic jitte r from the VSC816 3 itself duri ng such
conditions.
Figure 7: AC Termination of Low-Speed LVPECL REFCLK, D[15:0] Inputs
Split-end equivalent te r m ination is Z0 to V
Chip Boundary
VCC = 3.3V
V
CC
R1
Z
O
C
IN
R1 = 83Ω R2 = 125Ω, Z0=50Ω, V
R1||R2 = Z
VCCR2 + VEER1
R1+R2
TERM
o
= V
TERM
= VCC-2V
BIAS
EE
CC
C
EE
R2
R1
IN
R2
= 0V
V
EE
V
V
Z
O
V
CIN typ = 100nF
for AC operation
Low-Speed Inputs
The incoming low-speed data and reference clock input are received by LVPECL inputs D[15:0] and REFCLK. Off-chip termination of these inputs is required. For AC -coupling, a bias voltage suitable for AC-coupling needs to be provided (see Figure 7 for external biasing resistor scheme).
In most situations these inputs will have high transition density and little DC offset. However, in cases
where this does not hol d, d irect DC con nect io n i s possi bl e. Al l ser ia l d at a i nputs have the same circuit topology,
as shown in Figure 7. If the input signal is dri ven dif feren tial ly and DC-cou pled to the part, t he mid-poi nt of the
G52216-0, Rev 3.3 Page 5
01/05/01
© VITESSE SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION • 741 Calle Plano • Camarillo, CA 93012
Tel: (800) VITESSE • FAX: (805) 987-5896 • Email: prodinfo@vitesse.com
Internet: www.vitesse.com
VITESSE
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION
OC-48 16:1 SONET/ SDH
MUX with Clock Generator
input signal swing should be cente red about this c ommon-mode reference voltag e (V
Preliminary Data Sheet
VSC8163
) and not exceed the
CMI
maximum allowable amplitude. For single -ended , DC-coupli ng operati ons, it is recommend ed that th e user provides an external reference voltage. The external reference should have a nominal value equivalent to the common mode switch point of the DC-coupled signal, and can be connected to either side of the differential gate.
Power Supplies
This device is specified as a LVPECL device with a single positive 3.3V supply. Should the user desire to
use the device in an ECL environment with a negative 3.3V supply, then V
-3.3V. If used with V
tied to -3.3V, the TTL control signals are still referenced to VEE.
EE
will be ground and VEE will be
CC
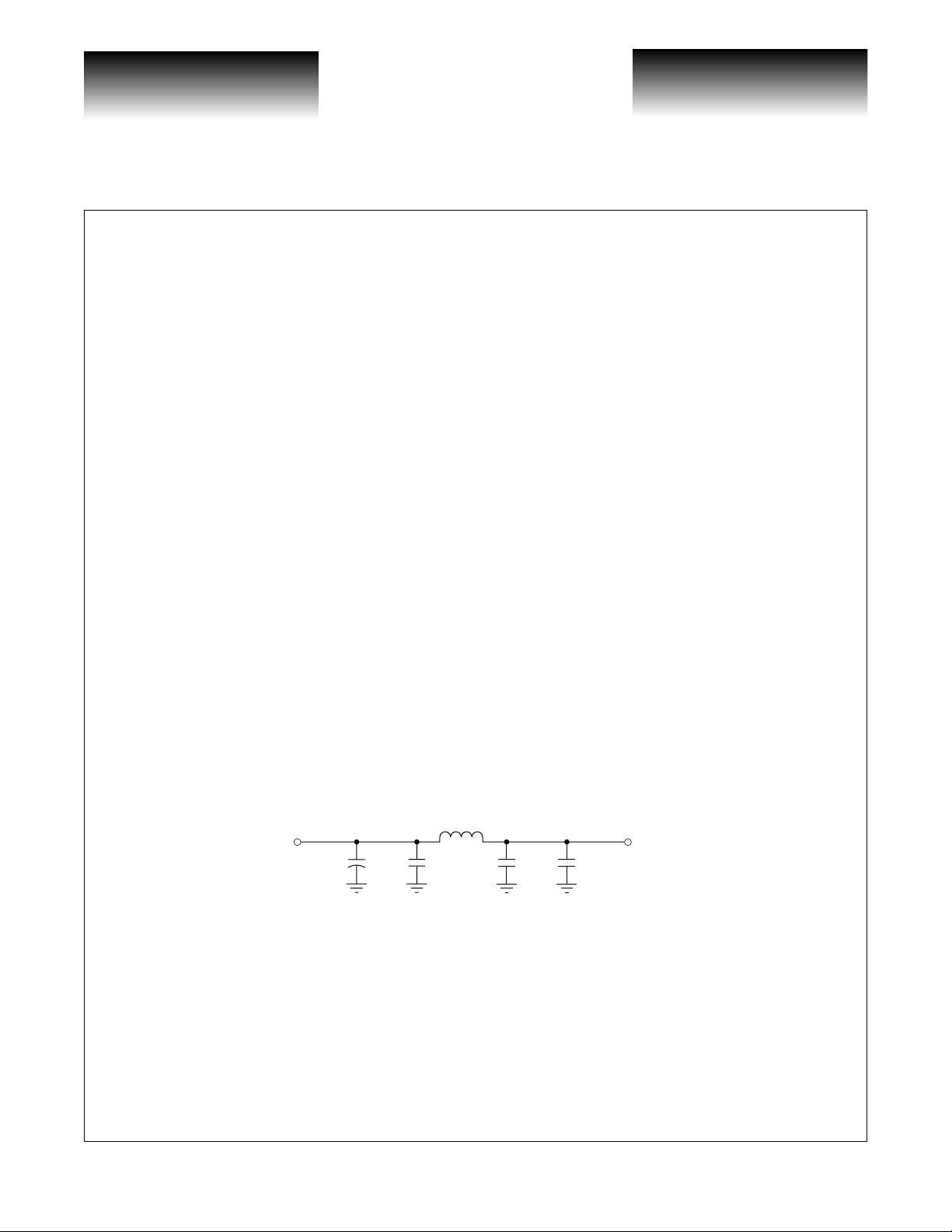
Decoupling of the power supplies is a critical element in maintaining the proper operation of the part. It is
recommended that the V
on each V
power supply pin as close to the package as possible. If room permits, a 0.001µF capacitor should
CC
also be placed in parallel with the 0.1
low inductance ceramic SMT X7R devices. For the 0.1
0.01
µF and 0.001µF capacitors can be either 0603 or 0402 packages.
Extra care needs to be take n when decoup ling the analog power supp ly pi ns (V
power supply be decoupled using a 0.1µF and 0.01µF capacitor placed in parallel
CC
µF and 0.01µF capacitors mentioned above. Recommended capacitors are
µF capacitor, a 0603 package should be used. The
). In order to maintain
CCANA
the optimal jitter and loop bandwidth ch aracteristics of the PLL co ntained in the V SC8163, the an alog power
supply pins should be filtered from the ma in power supply with a 10
bead may be used to provide the isolation. The 0. 1
µF and 0.01µF decoupling capacitors are sti ll required and
µH C-L-C pi filter. If preferred, a ferrite
must be connected to the supply pins between the device and the C-L-C pi filter (or ferrite bead).
For low frequency decoupling, 47
µF tantalum low inductance SMT caps are sprinkled over the board’s
main +3.3V power supply and placed close to the C-L-C pi filter.
If the device is being used in an ECL environment with a -3.3V supply, then all references to decoupling
V
must be changed to VEE, and all references to decoupling 3.3V must be changed to -3.3V.
CC
Figure 8: PLL Power Supply Decoupling Scheme
10µH
V
CC
10µF
Page 6 G52216-0, Rev 3.3
© VITESSE SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION • 741 Calle Plano • Camarillo, CA 93012
Tel: (800) VITESSE • FAX: (805) 987-5896 • Email: prodinfo@vitesse.com
0.1µF
V
EE
V
EE_ANA
Internet: www.vitesse.com
0.01µF0.1µF
V
CC_ANA
01/05/00
 Loading...
Loading...