Page 1

Users Manual
Page 2

Technical Support
Visionman Computers, Inc.
3200 N. San Marcos Place
Chandler, AZ 85225
Telephone: 1-800-690-6771 extension 2665
Support e-mail:
For additional information, please visit the Visionman Web site:
support@visionman.com
www.visionman.com
Copyright © 2008 Visionman.com.
All Rights Reserved.
Visionman makes no warranty or representations, expressed, implied, or statutory, with respect to its products or the contents or use of this
documentation and all accompanying software, and specifically disclaims its quality, performance, merchantability or fitness for any particular
purpose. Visionman reserves the right to revise or update its products, software, or documentation without obligation to notify any individual or
entity.
GB means 1 billion bytes; actual formatted capacity varies with preloaded material and operating environment and will be less.
TB means 1 trillion bytes; actual formatted capacity varies with preloaded material and operating environment and will be less.
All product names and logos are the property of their respective owners.
ii
Page 3

Introduction _____________________________________________________________ 5
Front View __________________________________________________________________ 5
Rear View ___________________________________________________________________ 6
System Setup _____________________________________________________________ 7
Connecting Visionman VCM400/VCM200 to the Network___________________________ 7
Connecting the Ethernet cable and power: ________________________________________________ 7
Connecting a USB drive: _____________________________________________________________ 7
Connecting a USB printer: ____________________________________________________________ 8
Turning the System On_______________________________________________________________ 8
Turning the System Off ______________________________________________________________ 8
Resetting the System ________________________________________________________________ 8
System Configuration______________________________________________________ 9
Logging into the VCM400/VCM200 configuration utility____________________________ 9
Windows, Linux, and Mac ____________________________________________________________ 9
System Configuration ________________________________________________________ 10
General Setup Screen _______________________________________________________________ 12
Alerts Setup ______________________________________________________________________ 13
Change Admin Password ____________________________________________________________ 14
Firmware Update __________________________________________________________________ 15
Printer Management ________________________________________________________________ 16
Configuration Management __________________________________________________________ 17
Advanced Setup ___________________________________________________________________ 19
Network: LAN Setup Screen _________________________________________________________ 21
Network: Services _________________________________________________________________ 23
Workgroup/Domain Setup ___________________________________________________________ 25
Storage Screens _____________________________________________________________ 27
Disk Management Screen____________________________________________________________ 27
Volume Management _______________________________________________________________ 28
Manage RAID ____________________________________________________________________ 30
Share Management _________________________________________________________________ 33
USB Management _________________________________________________________________ 36
USB Backup______________________________________________________________________ 37
Access Control Section _______________________________________________________ 38
User Management _________________________________________________________________ 38
Group Management ________________________________________________________________ 42
Share Access______________________________________________________________________ 47
USB Access ______________________________________________________________________ 49
Using the Media Server _____________________________________________________________ 50
Using the Status Menu _______________________________________________________ 51
Logs ____________________________________________________________________________ 52
Product Support ____________________________________________________________ 56
Troubleshooting ___________________________________________________________________ 56
First Steps Checklist________________________________________________________________ 56
Specific Problems and Corrective Actions_______________________________________________ 56
Technical Specifications ______________________________________________________ 58
Page 4

iii
Page 5

Introduction
The Visionman VCM400/VCM200 storage appliance is a powerful and feature-rich
system designed as a flexible solution for storing and sharing your digital files
across a home or office network or across the Internet.
The VCM400/VCM200 makes remote management a simple task with its Webbased user interface. By using any Web-browser, network and operational
settings, such as monitoring the status of the network, installed disks, storage
space utilization and others; can be configured from any system on the network,
running any operating system.
The VCM400/VCM200’s Web-based & Internet style file sharing, in addition to its
industry standard network file sharing methods, allows you to store all of your
documents, pictures, music, and video files in a central storage location and share
files with other computers on your network, regardless of what software they are
running. No matter what computer system or style of network you are running,
chances are that he VCM400/VCM200 can significantly improve and simplify file
sharing, network storage, and backups for you.
Users Manual
Front View
Page 6

The functionality of the buttons and LED’s are the same between the VCM400 and the VCM200.
This manual will use examples for the VCM400, and exceptions for the VCM200 will be noted where
necessary.
Power Button: Press the power button to turn the VCM400/VCM200 on. The Green LED
under the button will indicate that the system is powered on. Press and hold the button to
power the system down. If the LED is off, then it indicates that either the system is still initializing
or the system is not powered on. A blinking LED indicates either the system is rebooting or the
RAID is rebuilding, and will be unavailable for file sharing or administration during this time.
Network Activity Indicator: The green LED under or next to this icon indicates a network
connection. The blinking of this LED indicates network traffic. When this LED is off, this
indicates there is no network connection.
HDD Status Indicator: The blinking green LED’s indicates formatting, accessing or
synchronization of the individual drives. The solid green light indicates that the system is
completely synchronized and is ready to use. And amber LED indicates a drive error or an old
HDD has been installed with data on it. When this LED is OFF, it means that the drive is not
installed correctly or has completely failed.
System Identification: This blue LED indicates that system identification is active. When this
LED is off it indicates that system identification is disabled. A blinking LED means there us a
critical condition.
USB Backup Status Indicator: This green LED lights to indicate that a USB hard drive is
attached, and the system is rebuilding, restoring, or transmitting files to the USB drive. A
blinking LED indicates that the system is backing up the USB hard disk or that the system is
formatting the drive.
Rear View
Page 7
The functionality of the connections on the back is the same between the VCM400 and the VCM200.
devices like a USB hard drive, a USB flash drive, or a USB printer.
Reset Switch: Press the Reset button to restore the VCM400/VCM200 to factory settings. The
button is recessed and located above the Ethernet port on the VCM400 and between the power
connector and Ethernet port on the VCM200.
Power Connector: Use this port to connect power the VCM400/VCM200. The VCM400 uses a
standard computer type AC power cord, whereas the VCM200 uses an AC to DC power adapter.
USB Port: The VCM400 has three USB ports, two in the back and one in the front. The
VCM200 has two USB ports in the back. These ports allow for the connection of USB
Ethernet Port: This port connects the VCM400/VCM200 to the local network.
System Setup
This section gives instructions on how to setup
the Visionman
VCM400/VCM200.
Connecting Visionman VCM400/VCM200 to the Network
Connecting the Ethernet cable and power:
Connect the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on the rear of
Connect the other end of the
Connect the power to the power connector on the rear of VCM400/VCM200.
Connect the other end of the power cable or adapter to the nearest power receptacle.
Connecting a USB drive:
Connect the USB cable of your USB hard drive or the USB flash drive to the USB port
the Ethernet port on the VCM400/VCM200.
Connect the other end of the USB cable to the USB drive, if necessary.
Connect the USB drive to power, if necessary.
Ethernet
cable to a switch or router.
Visionman
VCM400/VCM200.
next to
Page 8

Connecting a USB printer:
Connect the USB cable to the top USB port on the rear of the VCM400/VCM200.
Connect the other end of the USB cable to your USB printer.
Install the printer driver if it is not installed on the computer you are printing from.
Turning the System On
Power the system on after confirming that all the cables have been connected properly.
LED’s will flash and turn different colors.
After 30 seconds, verify LED’s are on and correct. The power button and hard drive LEDs
should be green. Network LED should be green and may flash.
The VCM400/VCM200 and the computers must be on the same subnet, and DHCP/DNS
must be enabled from either the router or a server. If you are uncertain what these terms
mean, contact your network administrator or the manufacturer of your router.
Turning the System Off
To power down the system, press and hold the power button down for about five seconds.
The green LED on the power button and hard drive LED will turn off, indicating the shutdown
is in progress.
The shutdown process will start and take about 10 to 15 seconds to complete.
Resetting the System
The storage solution has a reset button in the back. Pressing and holding the button
down will reset the IP Address, system name and the password for Administrator to factory
settings. After about 15 seconds, the hard drive LED’s will turn amber. This is an
indication that the system has been reset, and you can now release the button.
Factory default settings are as follows:
IP Address – This will reset the IP address to “DHCP Client”. The IP address will now be
received from the DHCP server or the router on the network.
System Name – The system name will now be VCM400 or VCM200, depending upon your
system.
Password – The password for the administrator will now be “admin”.
Page 9
System Configuration
The storage solution has a web interface for configuration and set up. This section will explain how
to access this configuration interface and what the various settings mean.
Logging into the VCM400/VCM200 configuration utility
Windows, Linux, and Mac
The web access to the configuration utility for Windows, Linux and Mac is the same.
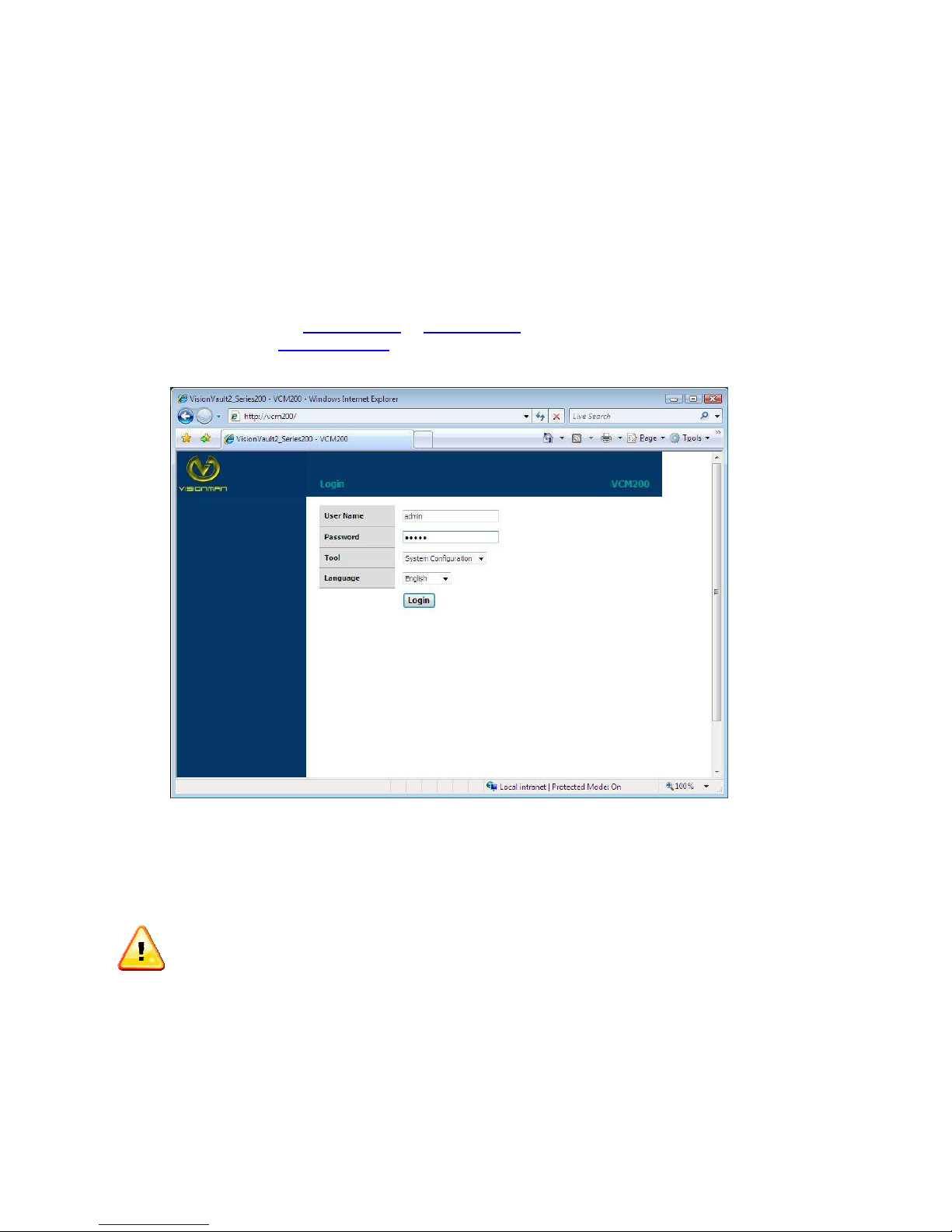
Launch the Internet browser on your PC or Mac.
Type the following:
the future, type
that is assigned by the DHCP server to the storage device.
http://vcm200/ or http://vcm400/, if you change the name of the device in
http://newname/ to access the device. You can also just type the IP address
The above screen will appear on your browser. If the page does not appear, please wait a
few minutes and try again. The default user name and password are: admin and admin
Please note that both the user name and the password are case sensitive.
In some cases it may be necessary to open the configuration file directly. You can do
this by clicking on Start, Run, and then typing in //VCM200 or //VCM400 depending on
which unit you have. You will be prompted for a username and password.
Page 10
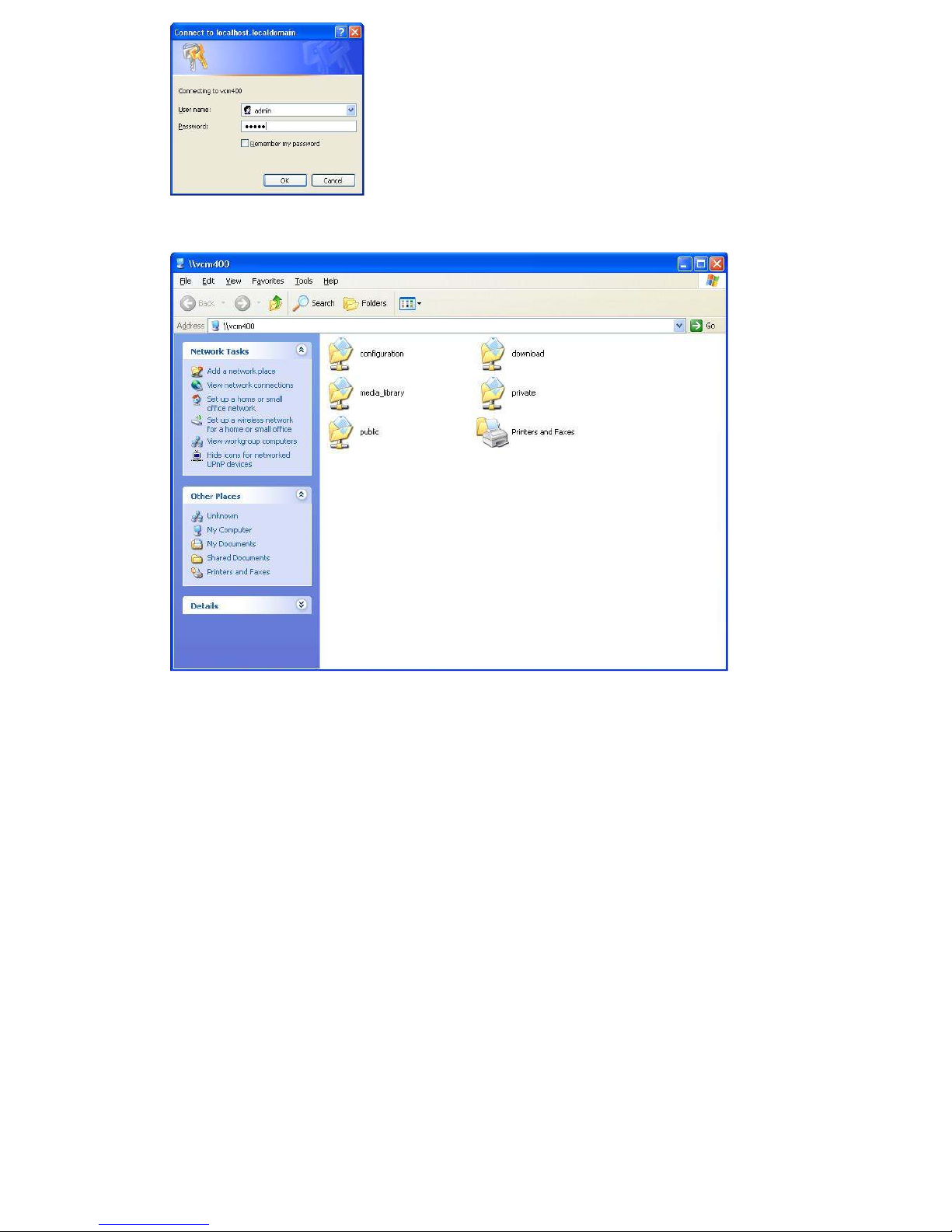
It will be the same as previously mentioned (admin/admin).
Once you have clicked on OK or hit ENTER, you will see the following screen:
Open the configuration folder by double-clicking on that folder’s icon. Once inside this folder, open
the Index file by double-clicking its icon. This will bring you to the configuration login screen in the
same way as typing the IP address or name directly into your browser.
System Configuration
The web screen will now show the display below. This will provide you with a high level status of
the storage system configuration.
On the left side is a list of configuration choices that you can select to change configurations. The
titles are self explanatory in what configuration choices will become available.
Page 11
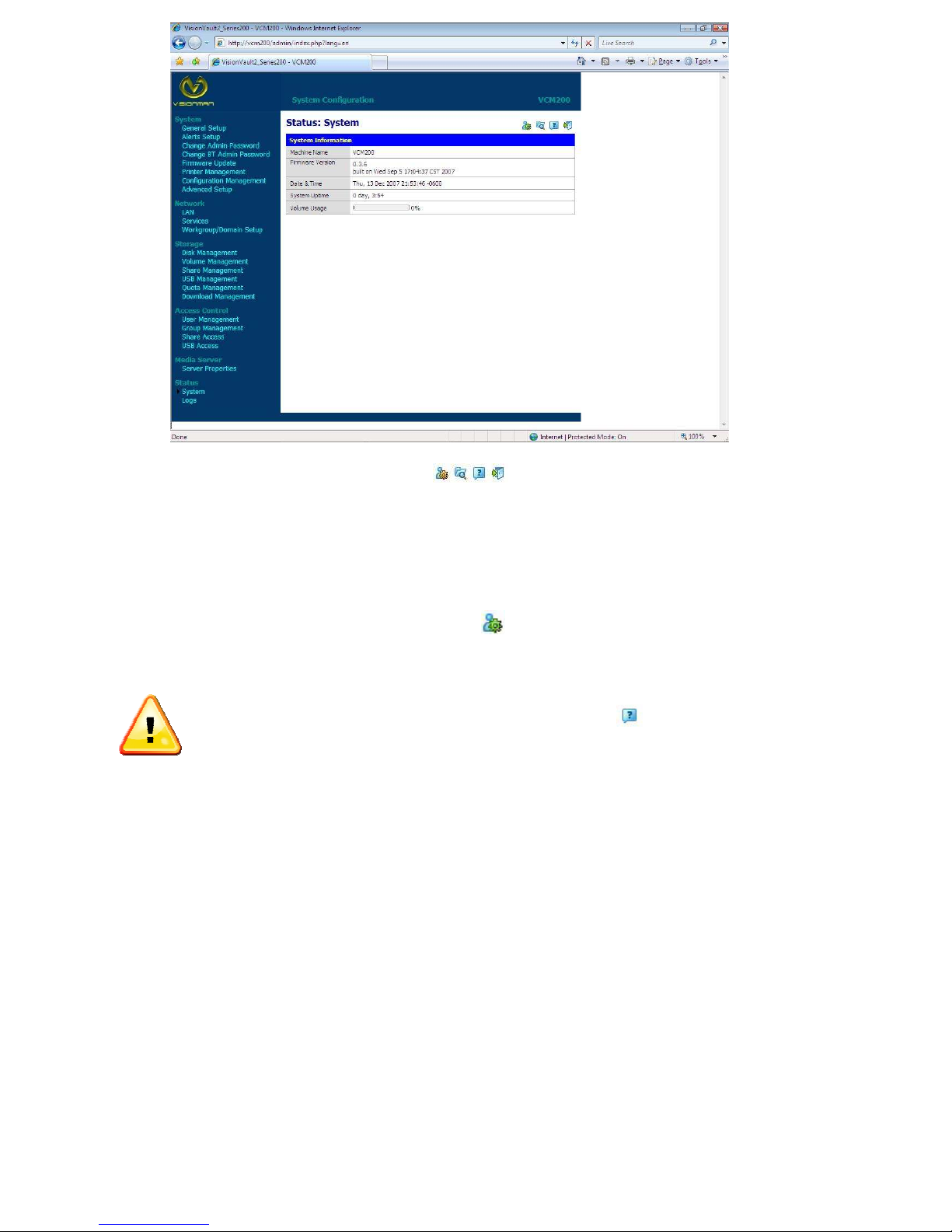
On the top right corner are four Icons , that can be selected for some more
detailed configuration choices:
The above is a simplified screen for set up and configuration. The choices are self explanatory for
configuration and setup.
To get to more detailed configuration screens, select
take you to the following configuration screen, with more detailed choices. Clicking it again will
simplify your choices.
NOTE: If at any time you have questions about any of the screens, when you are
configuring your VCM200/VCM400, you can just click on the
help screen will appear. This can be a source of good information for you and eliminate
the need to contact support in some cases.
icon from the top right corner. This will
button and on online
Page 12

General Setup Screen
This screen allows you to configure the basic information about the VCM400/VCM200 storage
appliance, such as give a name and brief description for the machine, select the web GUI protocol,
and set the time zone for your storage device. You can also set the date and time or enable
automatic time synchronization via NTP (Network Time Protocol) Service. You have to specify the
IP address of the NTP servers from which you want to synchronize.
If you want to change the name of the Storage System, you can assign a new machine
name for the VCM400/VCM200. The name can contain up to 15 characters, including
alphabetic, numeric, underscore, space, and most special characters. We suggest that
you keep it short and simple, so it is easier to remember. Please note that if you have
more then one storage solution, then they all need to have a unique name.
In the description box, enter the brief description for the storage appliance. The maximum
length of the description must not be more than 256 alphanumeric characters.
The difference between the two HTTP and HTTPS protocols is that HTTPS is secure web
access. You can select the protocol that makes the most sense on your particular network.
In the Time Zone drop-down menu, select the time zone for your location.
In the Date & Time drop-down menu, adjust the date and time manually.
You can set the date and time of the storage solution to automatically synchronize with an
Internet public NTP (Network Time Protocol) server. To set the date and time automatically,
select the Enable checkbox in NTP Service, then enter the IP address of the network time
servers from which you want to synchronize.
Click Submit.
Page 13

Alerts Setup
In the Alerts setup screen, you can configure the system to automatically send e-mails or pop-up
messages for event notification, to the administrator to monitor the functionality of the storage
device. These messages can be warnings or errors related to Fan, temperature, Hard Drive
functionality, Volume, Network, USB, Users and Groups.
Configuring the email:
Select the Enable checkbox
Enter the SMTP server name or an IP address to be used for sending email.
In the SMTP Port box, enter the port number to be used when connected for SMTP
sending of e-mail. The default port number for standard SMTP is 25, and 465 for
secure SMTP.
In the Email Recipients box, enter the email address of the persons you wish to send
an event email message to. Up to five emails can be on this list.
Select Send Test Mail to send a test alert and confirm your settings are correct.
Select Submit.
Configure the pop-up message alert settings:
Select the Enable checkbox.
Enter the name of the computer you wish to send a pop-up message to, when an
event occurs. Up to five computer names can be added to this list. (This requires that
messenger service is enabled on the computers that you wish to send pop up
messages.)
Select Send Test Pop-up to send a test alert and confirm your settings are correct.
Click Submit.
Page 14

Change Admin Password
Change the administrator password:
E
nter the old password.
Enter the new password. The maximum length of the password must not be more than
15 alphanumeric characters. Password is case sensitive and should be entered exactly
in the same way each time.
Re-enter the new password.
Click Submit.
Page 15

Firmware Update
This screen provides information about the current firmware version and allows you to perform a
firmware upgrade. Check on our web site to see if a newer version of the firmware is available.
To upgrade the firmware:
Download a copy of the new firmware from our Website to your computer.
The firmware image filename should have the following format: <firmware version>.IMG;
for example VCM200_V0_1_6.IMG. When you download the firmware image file from
the site, please be sure that the filename is correct, and do not rename the file.
Select Browse to locate the file that you downloaded and select the correct IMG file
(e.g. VCM200_V0_1_6.img).
Select Submit to transfer the firmware file from your computer to the VCM400/VCM200
storage appliance. Do not interrupt the firmware upgrade process. This may
cause the system to become disabled, and unable to function.
The update process might take a few minutes to complete.
After your firmware has been updated, the system will reboot to initialize the new firmware. The Web
GUI will redirect you to the System Information page after the update is completed.
Page 16

Printer Management
The Printer Management screen allows you to manage the USB printers
connected to the storage device, as well as manage print queues and
print jobs across the network.
Install the printer drivers on the PC’s that will use this printer.
For Windows:
Connect the USB printer to the storage device.
Open My Network Places > Entire Network > Microsoft Windows Network > Workgroup
Name > Machine Name (where Machine Name is the name of the VCM400/VCM200
storage appliance), then right-click on the printer icon and select Connect.
Select your printer model from the list and click OK.
Managing print jobs:
To pause or resume printing of a document, click the Pause/Continue icon.
To cancel printing of a document, click the Cancel icon.
Page 17

Configuration Management
Configuration Management screen allows administrators to easily perform backup or restore
operation of the storage systems settings or revert system to factory default settings.
To backup your current configuration settings:
On the Configuration Management page, click Configuration Download.
Click Open and specify a file name and location where you want to save the file and
select save.
To restore your configuration settings:
On the Configuration Management page, click Browse.
Select the previously saved system configuration file, and select General Restore or
Full Restore.
Selecting General Restore restores all features except the settings for data volume and
shares to its previously saved settings. While Full Restore erases all data on the
VCM400/VCM200 and revert the data volume and shares to its previously saved
settings.
Page 18

To restore VCM400/VCM200 to factory defaults:
Performing a factory default reset will erase all settings in VCM400/VCM200. System
settings such as the IP address, machine name, admin user name, password, RAID
reconstructs, and media files stored in VCM400/VCM200 are lost.
On the Configuration Management page, click Factory Default Restore and click OK.
It is important to backup all critical data and files before undertaking any
restore operations.
Page 19

Advanced Setup
This screen allows you to configure the system identification LED, setup a system for a secure
connection by generating an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate and a key, and perform a
reboot or shutdown for the VCM400/VCM200.
To turn on the system identification LED:
Click the Turn LED ON button to enable the system identification LED, and select
Submit.
This will turn the System Identification LED on, and this could be useful in identifying a
particular storage system if you have multiple units.
To generate an SSL certificate and an RSA key:
SSL is a protocol for managing the security of passing data back and forth between a
client computer and VCM400/VCM200 over the network. SSL uses two keys — a public
and a private key, to encrypt data and to ensure a scalable, efficient, and secure filesharing over the Internet.
Administrators can generate an SSL certificate and an RSA key using this screen.
You can generate an SSL certificate and RSA key by using the System Configuration
Utility.
On this screen, select the highlighted word “HERE”.
Page 20

Enter the necessay information for generating an SSL certificate, then click Submit.
To use the “extend disk mode” feature:
By default, your storage system will place the installed disks in what is called a “span”
configuration. This utilizes all available disk space for networked storage. If your
storage system does not have all the disk slots used you may want to add more
capacity later. If that is the case, you may want to enable the storage system’s
“Extend” mode.
Click on the drop down menu and select “Enabled” and then click on Submit.
Page 21

Network: LAN Setup Screen
This screen allows access to all network configuration options; such as setting the connection
method, changing the IP address, netmask, gateway, DNS (Domain Name Service) server IP
address, and the ability to configure the optional jumbo frame size.
DHCP is the default network IP setting for the storage device. When this option is selected, the
system automatically acquires its IP address and IP settings from the DHCP server on the network.
A jumbo frame size support is also included for switch or routers that support jumbo frames. The
storage device supports jumbo Ethernet frames to enhance networking performance.
By default, the jumbo frame option is disabled.
To manually configure the IP settings:
You may want to manually configure the IP settings on your storage system if you are
using a static IP address.
On the Network Mode drop-down menu, select Static.
In the IP address box, enter a valid IP address and network prefix.
In the Default Gateway box, enter the IP address of the gateway or router.
In the DNS Servers box, enter the DNS server IP address.
In the MTU Size (Bytes) box, enter the appropriate MTU size.
Page 22

Click Submit.
You must restart the system for these changes to take effect.
Page 23

Network: Services
The Network services screen allows you to set up and manage file services for different types of
clients, such as Mac, Windows, Linux, Unix, on your network using the FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
or NFS (Network File System) protocols.
Computers can access files and shared folders on your storage system, without requiring any
special software.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) services allow you to share files securely, between Storage System and
other computers, over the Internet.
To enable the FTP file service on the storage system:
On the Services page, click the FTP service Enable checkbox.
Click the Yes or No button to enable or disable anonymous access to the FTP server.
Public file sharing is easily accessed by enabling anonymous and selecting Submit.
To access VCM400/VCM200 through an FTP:
After you enable FTP files services, you can connect to the storage system via any FTP client.
For example if your VCM400/VCM200’s IP address is set to 11.45.57.82, entering
in a browser or Windows Explorer address bar will access the VCM400/VCM200’s public contents.
NFS services allow you to share files with other Linux or UNIX clients or clients who have the NFS
ftp://11.45.57.82
Page 24

client software.
To enable the NFS file service on VCM400/VCM200:
On the Services page, click the NFS service Enable checkbox.
The IP Allowed box appears. Enter the IP filters that are allowed for NFS service, then
click Add to add the new IP filter, and select Submit.
Page 25

Workgroup/Domain Setup
This screen allows you to setup the storage system as a workgroup or domain member. Both
workgroup and domain are ways of grouping computers on the network. By default, the storage
system is set as a Workgroup. Unlike workgroups, domains are controlled from a central location
(domain controller) and require central authentication before you can join them.
Workgroups, in contrast, are much simpler to control. As long as you know the workgroup name,
you can add any computer to a workgroup.
To setup a workgroup name:
On the Workgroup/Domain Setup page, select the Workgroup button.
In the Workgroup Name box, enter a name for your workgroup, and select Submit.
The storage system will become a member of that workgroup.
Domain Setup
If your network uses a domain (i.e., has Windows Active Directory Services), you may wish to
connect the VCM400/VCM200 as a domain member.
When configured as a domain member, the storage system requests are coordinated by the domain
controller on your network to authenticate users. Domain mode has more restrictive security levels,
as network users must enter appropriate passwords before gaining access to VCM400/VCM200.
When joining a domain, VCM400/VCM200 needs the authorization of the domain’s administrator.
You must enter the Domain Name, Administrator and Administrator Password for the authorization.
Page 26

To join a domain as a member:
Select the Domain Member button.
In the Domain Name box, enter the domain name.
In the Domain Controller IP Address box, enter the domain controller’s IP address.
In the Administrator box, enter the administrator’s user name.
In the Administrator Password box, enter the administrator’s password.
Click Submit.
Page 27

Storage Screens
The Storage screens provide all the necessary options required for individual storage disk
configuration and maintenance. You can also change RAID configuration, set shared
folder names, format and disconnect USB hard drives that are connected to the system.
The above screen shows a screen shot from the VCM200, which has two drives. The
VCM400 screens will actually show up to four drives, and different RAID configurations.
Beyond these two things, the screens will be very similar.
Disk Management Screen
The Disk Management screen provides a detailed summary of the hard drives, installed on
VCM400/VCM200. Again, on a VCM400, you will see up to four drives listed, unlike the
two drives on the VCM200.
The drive status allows you to monitor hard drive fault conditions and activity.
Good - Indicates the hard drive is accessible and functioning normally.
Failed - Indicates a fatal error has occurred, such as the hard drive partition has been
deleted, corrupted, or damaged, which could result in data loss.
Foreign - Indicates VCM400/VCM200 has detected an old hard drive or a hard drive
containing other data has been installed. A Clean disk icon appears on disks that
display the “Foreign” status. Unless the user performs a clean disk operation, the hard
drive cannot be accessed. After performing a clean disk operation, the hard drive appears
on the Disk Management table.
Page 28

Volume Management
The Manage Volume tab contains a table that shows all volumes currently defined on the
VCM400/VCM200’s hard drives and provides access to configuration details relating to how
the disks are partitioned and how RAID volumes are created on these partitions.
These volumes are the ones used for creating shares.
Manage Volume
The Manage Volume tab in the Volume Management submenu lists all the volumes
available, and provides detailed summary about each volume, such as the name of the
volume, description, RAID type (Stripe, Mirror, or Span), volume space used, total drive
capacity, and status of the volume.
A volume is a portion of one or more hard disks that are configured to store data. On the
Manage volume table, the volume status that appears in the Status column includes the
following values:
Good - Indicates the volume is accessible and hard drive is functioning normally.
Failed - Indicates a volume cannot be started automatically, the disk is damaged or
the file system is corrupt.
Re-synching - Occurs when creating a mirror or when a mirrored volume is being
resynchronized so both mirrors contain identical data. With the four drive system
and a RAID 5 volume, this could indicate the creation or recovery of the RAID set.
Formatting - Indicates volume is being formatted or system is creating an ext3 (third
extended) file system for a Linux operating system.
Page 29

Degraded - A drive is missing or contains corrupted data for the existing volume.
Recovering - Occurs when the system detects a spare drive that was inserted into a
degraded RAID volume.
Page 30

WARNING: CHANGING THE RAID TYPE WILL ERASE ALL DATA. PLEASE BACKUP
YOUR FILES BEFORE CHANGING THE RAID SETTINGS.
Manage RAID
The Manage RAID screen allows you to configure the SATA hard drives into different RAID
types.
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disk Drives) refers to an array of multiple
independent hard drives that provide high performance and reliability. RAID function
depends on the number of drives present and the RAID level you selected.
VCM200 supports the following RAID levels:
Stripe (RAID 0) - All data are distributed evenly to all existing drives. The two drives
work in unison to maximize system performance. However, RAID 0 has high risks
of data security. If one drive fails then all the data in both drives is lost.
Mirror (RAID 1) - Two hard drives are required. Data written to one hard drive is
simultaneously duplicated to another hard drive. If one drive fails, the other drive
continues to function as a single drive until the failed drive is replaced. To create a
mirror you must select unallocated space on another hard drive and the unallocated
space must be the same size or larger than the source drive you want to mirror that
data. Data on a mirrored drive is secured, if one hard drive fails, VCM200
administers a warning and the failed drive must be replaced immediately.
Span - Also known as a Linear array. Two hard drives are required. Several hard
drives are configured as a single volume with a size equal to the total of all the
Page 31

member disks. However, span does not increase system performance or data
security.
Default RAID configuration - The default RAID configuration for each hard drive
installed on VCM200 is as follows:
• If one drive is installed to an empty drive bay, the default RAID
configuration is mirror and the volume status is degraded.
• If system has one hard drive and a new hard drive is added, the
default RAID configuration is mirror and the volume status is good.
• If two hard drives are installed to an empty drive bay, the default
RAID configuration is span.
VCM400 supports the following RAID levels:
Stripe (RAID 0) - All data are distributed evenly to all existing drives. The two drives
work in unison to maximize system performance. However, RAID 0 has high risks
of data security. If one drive fails then all the data in both drives is lost.
Mirror (RAID 1) - Two hard drives are required. Data written to one hard drive is
simultaneously duplicated to another hard drive. If one drive fails, the other drive
continues to function as a single drive until the failed drive is replaced.
Span - Also known as a Linear array. Two hard drives are required. Several hard
drives are configured as a single volume with a size equal to the total of all the
member disks. However, span does not increase system performance or data
Page 32

security.
RAID 5 – A minimum of three hard disks is required for this array type. This is a
striped array with distributed parity, forming a redundant array. This type of array
gives good performance and protects the data against any single drive failure.
Default RAID configuration: The default RAID configuration for each hard drive installed
on VCM400 is as follows:
• If one drive is installed to an empty drive bay, the default RAID configuration
is mirror and the volume status is degrade.
• If system has one hard drive and a new hard drive is added, the default RAID
configuration is mirror and the volume status is good.
• If two or more hard drives are installed, the default RAID configuration is span.
Page 33

Share Management
This screen provides access to configuration details relating to how shares are made available by
the VCM400/VCM200. This menu contains a table that shows all the shares, logical volumes, and
protocols currently defined on the VCM400/VCM200 system.
Page 34

VCM400/VCM200 comes preconfigured with two shared folders: public and private.
To create a new share on a logical volume:
Click on the Create icon
Assign a share name. The share name can contain up to 32 characters, including
alphabetic, numeric, or underscore.
Enter a brief description, if desired.
Select file sharing protocol. The VCM400/VCM200 supports the following file
sharing protocols:
CIFS (Common Internet File System) - A standard way that clients share
files across intranets. CIFS allows Windows, Mac, or Linux clients to
access folders and files stored on your VCM400/VCM200. The access
control for CIFS is set to each shared folder. You can define access rights
for each user/group where the user will need to enter his/her password for
accessing that share. When the client browses the shares via Windows
Explorer, he can only see the shares which he has been granted access
rights (Read Only or Full Access) to.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - Allows access to files on VCM400/VCM200
from most computers whether they are inside or outside your local network.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) - Allows access to folders and files on
your VCM400/VCM200 using a Web browser. This method of access is
unique, as most NAS boxes will not allow you to access the files in this way.
You can, quite literally, access the files on the VCM400/VCM200 from any
system with a web browser regardless, including some PDA’s and cell
phones.
NFS (Network File System) - Allows Linux clients or clients who have
TCP/IP installed to remotely access folders and files on your
VCM400/VCM200.
Using NFS protocol, the client can access all or a portion of the shared file
directory on the network. The portion of the file directory can be accessed
with the privileges (read only or full access) designated to each file.
Click Submit.
To modify the share properties:
Click on the Modify icon.
Page 35

Assign a new share name. The share name can contain up to 32 characters,
including alphabetic, numeric, or underscore.
Enter a brief description, if desired.
Select a file sharing protocol.
Click Submit to save your changes.
To delete existing shares:
Select the share you want to delete.
Click the Delete icon.
A warning dialog box will appear.
Click on OK to delete the share.
Page 36

USB Management
The Storage Appliance supports USB external hard disk drives and USB Flash drives. It does not
support USB CD/DVD/CDRW/DVDRW Drives.
To format a USB hard drive: (Remember, formatting a drive erases all data from the
drive, including any partitions, volumes…etc.)
Connect a USB hard drive to VCM400/VCM200.
On the USB Management page, select the USB Disk tab.
Select the USB hard drive you want to format and click the Format icon.
A dialog box appears warning that all data will be erased.
Click OK.
To disconnect a USB hard drive from VCM400/VCM200:
On the USB Disk tab, select the device you wish to remove.
Click the Safely Remove Disk icon.
Click OK.
Page 37

USB Backup
USB port number one, which is next to the Ethernet port on the VCM200 and on the front for the
VCM400, has been configured to handle the automatic backup of the contents of a USB drive
attached to the VCM200/VCM400. You can use the other USB port(s) for transferring data to and
from the storage system, but only USB port one can be used for automatic backup.
To set a destination share name for the USB hard drive:
On the USB Management page, select the USB Backup tab.
Select a share to be used as a default backup share from the Destination Share
drop-down menu. This is where all the files will be copied to from the USB drive.
A folder within this share will be automatically created based on the volume name of
the USB hard disk.
Click Submit.
Page 38

Access Control Section
The Access Control screens allow you to configure access to files and folder in the Storage
Appliance.
User Management
The User Management screen allows the system administrator to create, edit, and delete user
accounts on the system. Administrators can create Public or Private user accounts and further
customize these accounts with privilege levels.
To create a user account:
Click the Create icon.
And the following screen will come up:
In the User name box, enter the user name.
Click the Grant Administration Rights checkbox to allow user to have
administrative rights and to access and configure the System Configuration Utility.
In the Full Name box, enter the user’s full name.
To secure the shared folder so that users must use a password to access it, enter a
Page 39

password in the Password box. The user name and passwords are case
sensitive, and can contain up to 15 characters, including alphabet, numbers,
underscore, and some special characters.
In the Confirm Password box, re-enter the password for confirmation.
In the Group List select a previously created Group for the user to join in. Click
the >> button.
Select the Yes button in the Create User Private Share if you want to create a
private folder for this user. Select an appropriate file sharing protocol to allow this
share to be accessed by the user. The share will have the same name as the
user’s name.
Click Submit.
Page 40

The above screen shows the new user has been added successfully.
To modify a user account:
Select the user account you want to modify.
Click the Modify icon.
The following screen will come up:
Page 41

Make the changes you want, then click Submit.
To delete a user:
Select the user account you want to delete.
Click the Delete icon.
Page 42

You will get a warning about deleting of the user. Click on OK, and the user will be deleted.
Group Management
The Group Management submenu allows administrators to create, edit, and delete
a group of users on the system.
Page 43

To create a new local group:
Click the Create icon.
And the following screen will come up:
Page 44

Assign a new group name for the new group. As before, the name can be up to
32 characters long.
Enter a description for the new group.
In the User List, add the users that you want to have access to the group.
And Click Submit.
The following screen will show up to confirm that you have successfully created a new
group.
To modify a local group:
Select the group you want to modify.
Click the Modify icon.
Page 45

Make the changes you want, and then click Submit.
To delete a local group:
Select the group you want to delete.
Click the Delete icon.
Page 46

You will get a warning to confirm the deletion of the user group.
You will get the above screen to confirm that the group has been deleted.
Page 47

Share Access
The Share Access screen allows administrators to set the access control for each user or group in
the Access list. Each user or group defined in User Management must have an assigned privilege
level for every shared folder on the storage appliance.
There are three privilege levels assigned to a user or group.
Full Access
When there is a conflict in the access rights of the user and group, VCM400/VCM200 uses the
following rule to handle the conflict:
If the access control is assigned to a user or group, the full access, read only, and no access icons
appear on the Share Access page. You can move your mouse over the icon to view the user or
group list.
Read Only
No Access
No Access has the highest priority.
Read Write + Read Only = Full Access.
Page 48

To assign privilege levels for users or groups:
Select a user or group, then click the Edit icon.
The upper section of the page contains an information table that lists the share folder’s logical
volume name and supported file service protocol. Each defined user or group must have a privilege
level for every shared folder you create.
Click the Enable Public Access checkbox if you want to enable any user or group to
have access to the shared folder.
In NFS Access, you can set a privilege level for a Linux or Unix client.
In the Not Assigned Users list, select the users you want to grant full access, read only
permission, or no access to the logical volume.
Click the >> button.
In the Not Assigned Groups list, select the local groups you want to grant full access,
ready only permission, or no access to the logical volume.
Click the >> button.
Page 49

Click Submit.
USB Access
The USB Access submenu allows you to set the access control for the two USB ports on the rear of
VCM200, and the one additional USB port in the front of the VCM400. There are three privilege
levels that you can assign to a user or group are Full Access, Read Only, or No Access.
When there is a conflict in the access rights of the user and group, VCM400/VCM200 uses the
following rule to handle the conflict:
No Access has the highest priority.
Read Write + Read Only = Full Access.
If the access control is set, a small icon appears on User/Group permission box, the administrator
can move the mouse cursor over the icon to see the user/group list.
To configure the privilege levels for a USB share:
Select a USB share, then click the Edit icon.
Make the changes you want, then click Submit.
Page 50

Using the Media Server
This feature allows the Storage appliance to automatically sort media files into Music, Photo and
Video categories and make them available on the network.
Enable the Media Service by selecting the Enable button.
You can also decide if you want the media files sorted in alphabetical order or by the date
the file was created.
Select Submit, for the system to sort the media content in the system and save your
changes.
Page 51

The above screen will show that media content in the storage system has been identified and sorted.
Using the Status Menu
The Status menu displays general information about the system, such as machine name, firmware
version, current date/time, machine up-time, and volume of the storage space that is being used.
Page 52

Logs
Logs screen includes five tabs — System, CIFS, FTP, Printer, Settings. It displays a record of
activity that has occurred on storage device. Each activity displays a time and date associated with
the event and a description of the activity that took place.
Settings Tab
Page 53

In the settings tab, you can decide the sequence that the log should be showed and the size of the
log.
System
In the System tab, you will view information about the system, file and services requested, Web
pages transferred from VCM400/VCM200 to a client computer, or print events.
Page 54

The above is an example of the display from the system logs screen.
The System Logs records significant problems that occur in the system. You can obtain information
from the following conditions or errors that may occur in the system components, hardware or
software components.
System shutdown
System reboot
Fan failed or defective fan
System temperature exceeds a threshold value
Disk SMART failure
Volume failed or does not exist
Volume space is full or close to 100%
Unsafe removal of a USB mass storage device
Each event is classified into following types:
Critical - An event such as fan failed, system temperature has exceeded the threshold level,
Disk SMART failed, volume space is full or close to 100%. When a critical event occurs,
the system status LED lights up and the system records the events in the System Log.
Warning - An event that is not necessarily significant, but may indicate a possible future
problem. An email or pop-up message alert is sent to notify user of the problem that
occurred in the system.
Information - An event that describes the successful operation of an application, driver, or
service.
Page 55

The CIFS, FTP and Printer tabs track the logs for their respective functions.
CIFS
The CIFS (Common Internet File System) tab displays the file and print services log
of CIFS clients.
FTP
The FTP (File Transfer Protocol) tab displays file transfer sessions to and from the
VCM400/VCM200.
Printer
The Printer tab displays the print services log.
Page 56

Product Support
To get the latest firmware, please visit Visionman.com web site to find the latest firmware version,
and instructions on how to download and update the firmware on your Visionman
VCM400/VCM200.
Troubleshooting
For any issue, first ensure that you are using the latest firmware for the Visionman VCM400/VCM200.
If you are unable to resolve your server problems on your own, contact your dealer or Visionman for
assistance.
First Steps Checklist
Is power being supplied to the unit?
Are all cables correctly connected and secured?
Turn the power on by pressing the switch. The Power LED should light up and be
steady on (not flashing).
Specific Problems and Corrective Actions
The following contains specific problems that may arise during the use of your
server. Possible solutions are listed for each problem.
HDD activity indicator does not light.
If the drives are pre-installed (came with the system), contact technical support for
assistance.
If you installed the drives, make sure that the drives are seated securely and
properly in their respective slots. The front drive latch should click when it is
correctly in the slot and be almost flush with the front of the unit (with the door
open).
System cannot connect to a network and network status indicator does not light.
Make sure the network cable is securely attached to the correct connector at the
system rear panel.
Confirm that the network is functional, by checking other devices on the network to
confirm that network access is working properly.
Page 57

Try a different network cable.
Cannot view System Configuration Utility in the Web browser.
Make sure JavaScript is enabled in your browser. The following describes how to
enable JavaScript using Internet Explorer 6.0 and Mozilla Firefox (1.0 and 1.5) for
Windows.
To enable JavaScript in Internet Explorer 6.0:
From the Internet Explorer menu, go to Tools, then select Internet Options.
Choose the Security tab, then click Custom Level.
Scroll down to Active Scripting, then select Enable.
Click OK.
To enable JavaScript in Mozilla Firefox 1.0:
From the Mozilla Firefox browser, select Tools.
Click Options, then select Web Features.
Select the Enable JavaScript check box, then click OK.
To enable JavaScript in Mozilla Firefox 1.5:
From the Mozilla Firefox browser, select Tools.
Click Content.
Select the Enable JavaScript check box, then click OK.
How do I manually create a pair of SSL certificate and key on a Linux system?
Generate a RSA private key by typing the following commands:
/usr/bin/openssl genrsa 1024 > server.key/bin/cat server.key
From the Mozilla Firefox browser, select Tools.
Copy and paste to the Key field of the SSL Certificate/Key on the Advanced Setup
page.
Create a self-signed certificate by typing the following commands:
/usr/bin/openssl req -new -key server.key -x509 -out server.crt/bin/cat server.crt
Copy and paste to the Certificate field of the SSL Certificate/Key on the Advanced
Setup page.
Page 58

Technical Specifications
The table below lists the technical specifications for the Visionman
VCM400/VCM200 storage appliance.
Model Name Visionman VCM400/VCM200
Form Factor 4-bay for the VCM400
2-bay for the VCM200
Processor Marvell 5281 500 MHz AMR9 SOC for the VCM400
Memory 128 MB DDR333 SDRAM for application storage
Storage Capacity 320 GBs - 2 TBs
Hard Drives Supported 3.5” SATA II 7200 RPM Hard
Drive Buffer Size 8 MB cache and above
RAID Constructs RAID 0 (Stripe), 1 (Mirror), 5 (Parity), Linear (Span)
USB interface 3 (VCM400) and 2 (VCM200) x USB 2.0 ports for
Ethernet (10/100/1000) Gigabit Ethernet port
IP DHCP (Auto IP, changes), Static (Manual, constant)
Marvell 5182 500 MHz ARM9 SOC for the VCM200
16 MB flash ROM for firmware storage
USB device extension and file backup
Protocols HTTP, HTTPS, CIFS, NFS, FTP, SMB
Operating Systems Windows Vista, Windows 2000 SP4,
Windows XP, Windows 2003, Red Hat
File Systems NTFS, FAT
W x H x D (in) 9.5 x 11.5 x 11 in (VCM200)
6 x 7.5 x 11 in (VCM400)
Weight (lbs) 6 lbs (VCM200)
16 lbs (VCM400)
Power Requirement 100-240 V 50/60 Hz
Consumption 150 W max
Operating Temperature 0 to -40 deg C
Operating Humidity 0% to 80% (non-condensing)
Operating Shock 3.5 G. 3 ms
Non-Operating Shock 30 G, 1 ms
Operating Vibration 0.25 G at 2 Hz to 200 Hz
Safety and Agency FCC Class A / CE / UL / CB
Enterprise Linux 2.6.7, MAC OS 10.1
 Loading...
Loading...