Page 1
VISHAY SEMICONDUCTORS
Rectifiers
PowerTab
TM
Mounting Guidelines
Application Note
3.0 MECHANICAL CONSIDERATIONS
3.1 TYPE OF FIXINGS
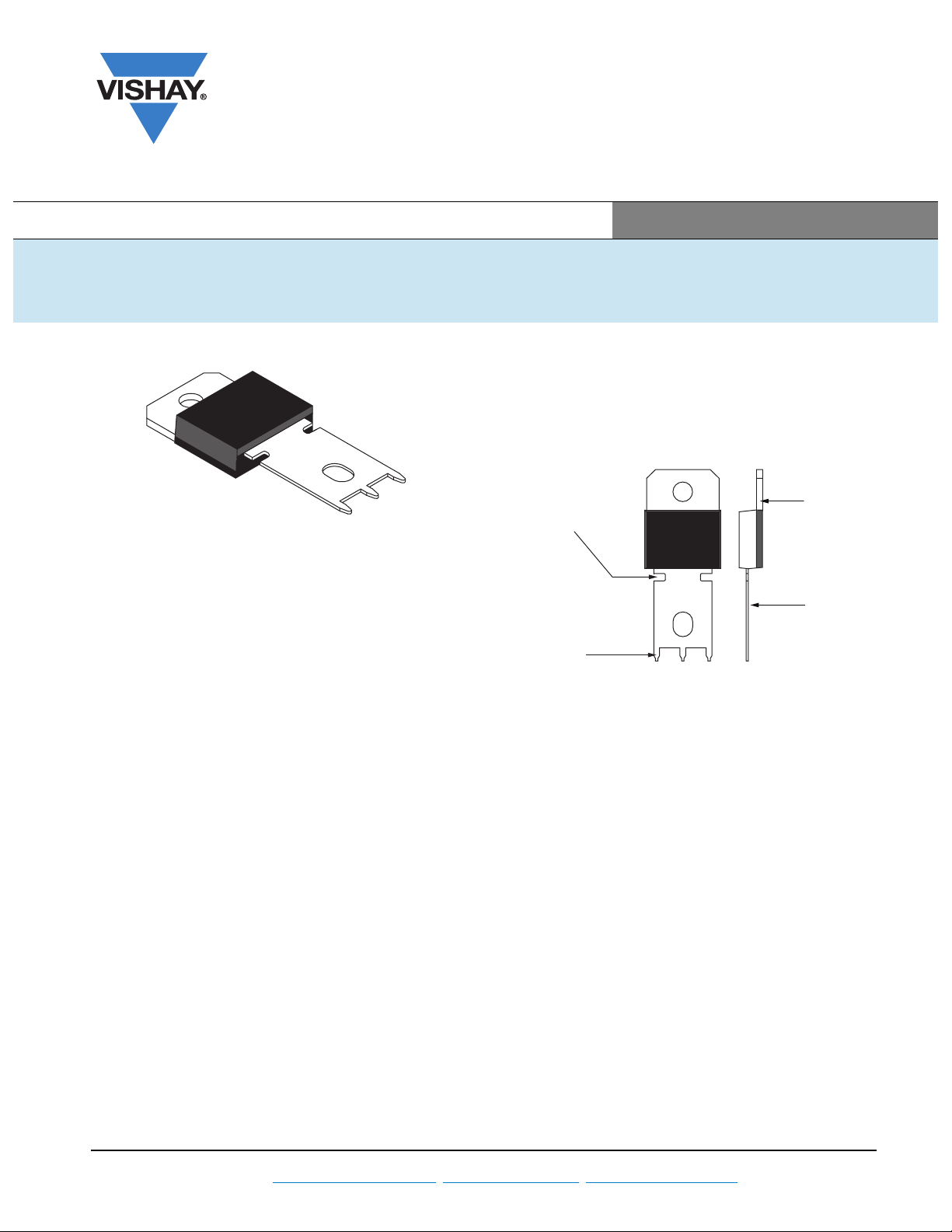
The PowerTab possesses mounting holes in the tab and
lead for electrically connecting the device to heatsinks or
busbars. The lead also carries PCB insertion pins so that the
lead end may be soldered into a board.
Tab (header)
Stress relief slots
1.0 INTRODUCTION
The PowerTabTM package has been designed to fill the gap
in the market between the TO-247, more expensive metal
case devices and non-isolated power modules. It is the
natural replacement for metal case outlines such as
DO-203AA and DO-203AB, but it is also suitable for new
innovative solutions, thanks to a package outline that
combines low profile, excellent die to footprint ratio and
sturdy connectivity. It utilises a large lead for high current
connection, carrying both a mounting hole and PCB insertion
pins. The body is compatible with a TO-218 outline, with an
exposed heatsink and non-isolated mounting hole.
It is anticipated that the devices would find typical
applications in busbar assemblies or finned heatsinks,
reducing component count and cost of ownership.
2.0 SCOPE
This application note covers the various fixment methods
that are possible with this device, and the associated thermal
properties resulting from their use:
a. Optimum mounting torque
b. Type of fixings
c. Effect of torque on thermal resistance (“wet” and “dry”)
d. Effect of pressure on contact thermal resistance (“wet”
and “dry”)
Document Number: 95179 For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: www.vishay.com
Revision: 11-Jun-10 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com 1
3.2 TAB CONNECTION
Using the mounting hole in the tab allows a designer to
attach the PowerTab to a heatsink. The tab of a PowerTab
acts as one of the terminals. There is no common additional
lead, so the mounting hole contact must be very good, with
the heatsink forming part of the circuit. For the best results
the surface of the heatsink must be as smooth and flat as
possible to maximise the contact area of the tab. A good
flatness specification would be 0.02 mm (0.0007") maximum
per 10 mm (0.393"). Ensure also that the heatsink mounting
hole has been deburred.
The mounting hole in the tab is designed to accept a M4
screw, No. 6-32 screw or 6-40 screw. A self tapping type
screw may also be used. However, only a certain type of
screw and washer may be used to attach the tab to the
heatsink because of the proximity of the mounting hole to the
plastic body.
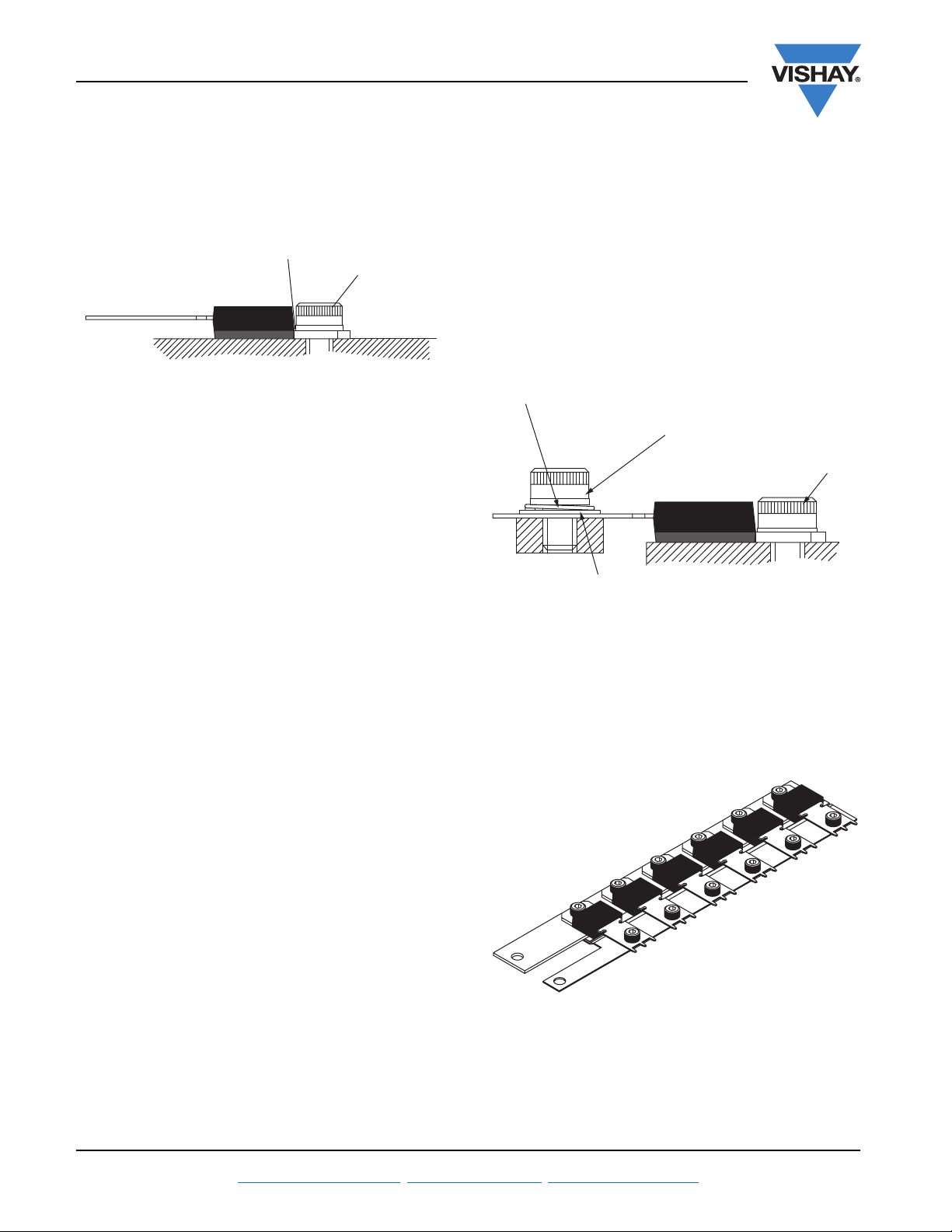
The recommended method of attachment is a socket headed
M4 screw, with a plain washer, as shown in the figure 2. The
washer used must be no larger than the diameter of the
socket head. If a larger washer is used, it can bear directly on
the edge of the plastic body, causing the body to crack when
the screw is tightened. The largest possible diameter washer
that may be used is 7.2 mm (0.283"). An alternative is a
suitably sized rectangular washer.
PCB insertion
pins
Fig. 1
Lead
APPLICATION NOTE
Page 2
Application Note
Vishay Semiconductors
PowerTabTM Mounting Guidelines
Small clearance
between washer and
plastic body
M4 socket
headed bolt
the back of the heatsink and the back of the lead is nominally
3.0 mm. This means that in busbar configurations, the lead
will either need forming down to the same level as the
heatsink, or the lead busbar will need to be raised by 3.0 mm
to the same level as the back of the lead. A typical busbar
configuration is shown in Figure 3.
Care must be taken when tightening the fixing to prevent
distortion of the lead. The lead fixing can be typically
tightened to 3.00 Nm (2.21 lbf · ft) without distortion.
Fig. 2
Similarly, M4 nuts cannot be used (on the plastic side) for the
tab connection, since there is inadequate clearance between
the hole and plastic body to rotate the nut. Using the plastic
body to prevent the nut rotating will inevitably crack the
plastic and is not recommended.
Rivets may be used but the following precautions must be
noted:
The diameter of the hole in the heatsink must be of a smaller
diameter than that of the PowerTab mounting hole, the
crimping force is controlled to give a slow pressure build-up
and the rivet used must be of a soft material. Too high a
crimping speed and pressure is likely to damage the die
inside the package and deform the header, lifting it away
from the heatsink.
Wherever possible, the use of heatsink compound is
recommended to mount the package to improve the heat
dissipation.
The recommended mounting torques, with and without
heatsink compound, may found under section 4.1 of this
application note - “Contact thermal resistance as a function
of torque on the mounting screw” and also in summary form
in Section 5.0.
3.3 CLIP MOUNTING
If desired, use may be made of a clip to attach the package
to a heatsink. The recommended point for the placement of
the clip is directly over the die, ie in the middle of the plastic
body. This will give the best contact thermal resistance. Also
refer to section 4.2 and 5.0 of this application note for the
optimum clip force.
Sprung washer
Busbar connection to lead
Heatsink connection
washer
Plain
Fig. 3
Another solution is a laminated busbar, as supplied by the
Rogers Mektron Busbar Division. Here a single busbar is
stamped to the step height of the package and an isolating
laminate and second busbar added. The PowerTab
TM
packages can then be bolted (or rivetted) down to this strip
to form a single assembly, with two large single outputs. A
typical example is shown below in Figure 4.
3.4 LEAD CONNECTION
The mounting hole in the lead of the PowerTab is oval in
shape. This slotted hole allows for some movement between
the two mounting holes in an assembly, and for any
assembly tolerances. Any M4 screw, No. 6-32 or 6-40 screw
Fig. 4
or nut combination may be used to secure the lead. The use
of a plane and spring washer is recommended to allow for
movement of the lead due to thermal expansion or vibration.
This will also, along with the stress relief slots, minimize
the possibility of the plastic body cracking under
tension/compression stresses. The step difference between
APPLICATION NOTE
www.vishay.com For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: Document Number: 95179
2 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com Revision: 11-Jun-10
Page 3

Vishay Semiconductors
PowerTabTM Mounting Guidelines
Application Note
3.5 LEADFORMING
In some applications, forming or bending the lead to an angle
of 90° is desirable (Figure 5). This could facilitate connection
to a PCB situated above the package. The minimum
recommended distance of the bend point from the plastic
body is 2.50 mm (0.098"). This will produce a leadform as
shown in Figure 5.
The form occurs at the lower edge of the stress relief slots in
the lead. The vertical height of the lead, measured from the
underside of the unformed section of lead is typically
16.6 mm (0.653"). The stress relief slots, as well as making
the leadforming operation simpler, help to reduce the
stresses imposed on the plastic body caused by differential
expansion at higher operating temperatures. During the
leadforming operation, it is very important that the area of
lead between the plastic and the bend is securely clamped,
to ensure that the plastic is not cracked by this operation.
The physical source of the contact resistance is a result of
the fact that surfaces are never perfectly flat. Even for two
well prepared surfaces contact only actually occurs at
several points separated by large air gaps. As air is a very
good thermal insulator this is undesirable and increases the
thermal resistance. There are two ways of reducing the
volume of air trapped between the surfaces. One is to
increase the force holding the two surfaces together and the
other is to improve the quality of the contact area by filling in
the gaps. In the case of the former this can be done by either
applying a force above the die with a clip or by increasing the
torque on the screw which mounts the tab to the heatsink.
The second technique requires the use of a heatsinking
compound. This is usually a silicone grease loaded with
electrically insulating, thermally conductive material such as
alumina. The purpose of the grease is to fill the gaps without
increasing the distance between the two surfaces. If the layer
of grease is too thick then the thermal resistance will be
increased. When using heatsinking compound in conjunction
with a PowerTab it is important to remember that electrical
contact to the drain can only be made through the mounting
tab. In addition to this, care must be taken to avoid getting
any compound in the screw threads or mounting holes as this
will affect the accuracy of the torque measurement.
For the purpose of this application note the contact thermal
resistance has been measured as a function of both the
torque on the mounting screw and the force above the die. In
PowerTabTM with 90° leadform
Fig. 5
Care must also be taken not flex or bend the lead over sharp
angles repeatedly. If the lead is bent through 30° and back
both cases measurements have been performed with and
without heatsinking compound.
4.1 CONTACT THERMAL RESISTANCE AS A FUNCTION
OF TORQUE ON THE MOUNTING SCREW
again more than twice, it will be considerably weakened and
liable to breakage.
4.0 THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
One of the major considerations when mounting all power
semiconductor packages is the dissipation of heat. This is
because the performance of the device is limited by the
junction temperature of the die and the glass transition
temperature of the plastic. Indeed there are maximum
allowable temperatures above which the device is not
functional. The way in which a device is mounted can have a
large effect on the thermal contact between the header and
the heatsink and hence on the ability of the package to
dissipate heat. This is often referred to as the contact thermal
resistance and is quoted in datasheets. In the present note
we shall concentrate on the thermal resistance between the
case and the heatsink as this is the most dependent on the
mounting technique.
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
Thermal Resistance (°C/W)
0.2
0
0 0.5 1.0 1.5
Dry mounting
With heatsink compound
Torque (Nm)
Fig. 6
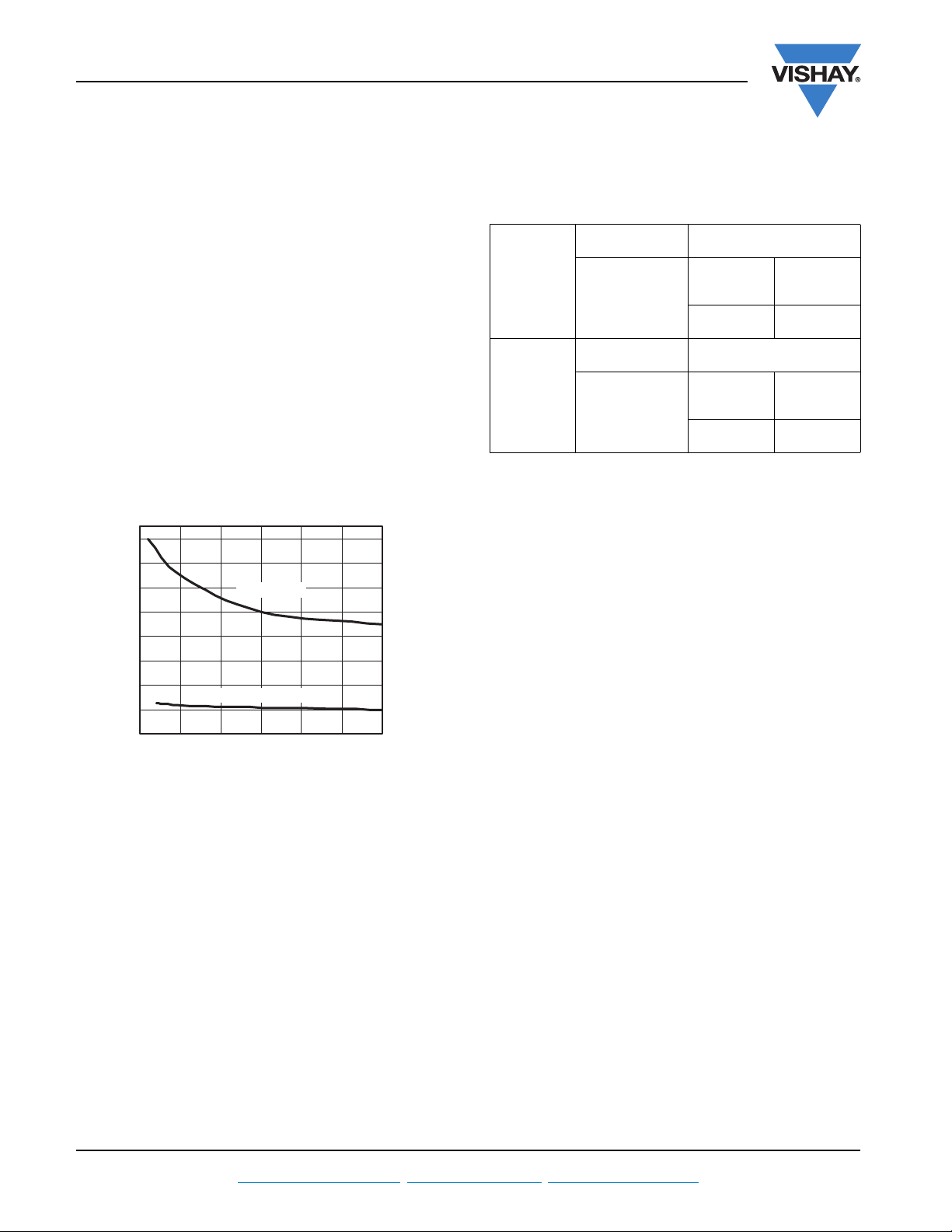
Figure 6 shows the contact thermal resistance as a function
of torque with and without heatsink compound. The package
was mounted using a M4 screw in accordance with the
mounting instructions described in this application note. It
can be seen from the graph that in the case of a dry mounted
Document Number: 95179 For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: www.vishay.com
Revision: 11-Jun-10 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com 3
APPLICATION NOTE
Page 4
Application Note
Vishay Semiconductors
PowerTabTM Mounting Guidelines
device the contact thermal resistance can be reduced to a
minimum of 1 °C/W by increasing the torque up to an
optimum value of 1.1 Nm. Further increasing the torque is not
beneficial since the header/mounting tab becomes
deformed, lifting the package away from the heatsink and
hence increasing the thermal resistance. The use of heatsink
compound reduces the thermal resistance by a factor of
78 % to 0.22 °C/W. The dependence on torque is also
reduced. This measurement was acheived using a device
with 60 W power applied for 100 s, on an “infinite” heatsink.
Recommended torque:
Without heatsink compound: 1.1 Nm (0.81 lbf · ft) to give a
thermal resistance, case to sink, of 1 °C/W.
With heatsink compound: 0.8 Nm (0.59 lbf · ft) to give a
thermal resistance, case to sink, of 0.22 °C/W.
4.2 CONTACT THERMAL RESISTANCE AS A FUNCTION
OF FORCE ABOVE THE DIE (CLIP MOUNTING)
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
Thermal Resistance (°C/W)
0.2
0
0 100 20050 150 250 300
With heatsink compound
Dry mounting
Force (N)
Fig. 7
Figure 7 shows the contact thermal resistance as a function
of force above the die with and without heatsink. It can be
seen from the graph that when heatsink compound is not
used the contact resistance decreases with increasing force.
However there is a point beyond which the advantage gained
by increasing the force is offset by the additional cost
required to do so. The use of heatsink compound reduces
the thermal resistance by a factor of 85 % and also makes
the thermal resistance less dependent on the applied force.
This measurement was acheived using a device with 60 W
power applied for 100 s, on an “infinite” heatsink.
Recommended force:
Without heatsink compound: 20 N (4.5 lbf) minimum to give
a thermal resistance, case to sink, of 1.5 °C/W.
With heatsink compound: 20 N (4.5 lbf) minimum to give a
thermal resistance, case to sink, of 0.23 °C/W.
5.0 SUMMARY TABLE
Maximum
allowable torque
Screw
Mounting
Clip
Mounting
2.4 Nm
(21.24 lbf · in)
Maximum
allowable force
250 N
(56.21 lbf)
Thermal mounting
Without
heatsink
compound
1 °C/W
at 1.1 Nm
Thermal mounting
Without
heatsink
compound
1.5 °C/W
at 20 N
With heatsink
With heatsink
compound
0.22 °C/W
at 0.8 Nm
compound
0.23 °C/W
at 20 N
APPLICATION NOTE
www.vishay.com For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: Document Number: 95179
4 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com Revision: 11-Jun-10
 Loading...
Loading...