Vishay Semiconductors
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
GA200SA60SP
Ultralow V
CE(on)
, 342 A
FEATURES
• Standard: Optimized for minimum saturation
voltage and low speed up to 5 kHz
• Lowest conduction losses available
• Fully isolated package (2500 V
AC
)
• Very low internal inductance (5 nH typical)
• Industry standard outline
SOT-227
• UL approved file E78996
• Compliant to RoHS directive 2002/95/EC
PRODUCT SUMMARY
V
CES
V
(typical) at 200 A, 25 °C 1.33 V
CE(on)
I
at TC = 97 °C
C
Note
(1)
Maximum I
maximum temperature of terminals
RMS
(1)
current admitted 100 A to do not exceed the
600 V
200 A
• Designed and qualified for industrial level
BENEFITS
• Designed for increased operating efficiency in power
conversion: UPS, SMPS, TIG welding, induction heating
• Easy to assemble and parallel
• Direct mounting to heatsink
• Plug-in compatible with other SOT-227 packages
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS MAX. UNITS
Collector to emitter breakdown voltage V
Continuous collector current I
Pulsed collector current I
Clamped Inductive load current I
Gate to emitter voltage V
Reverse voltage avalanche energy E
RMS isolation voltage V
Maximum power dissipation P
Operating junction and storage
temperature range
Mounting torque 6-32 or M3 screw 12 (1.3) lbf in (N m)
Note
(1)
Maximum I
current admitted 100 A to do not exceed the maximum temperature of terminals
RMS
CES
TC = 25 °C 342
(1)
C
CM
LM
GE
ARV
ISOL
T
, T
J
T
= 97 °C 200
C
Repetitive rating; VGE = 20 V, pulse width limited
by maximum junction temperature
See fig. 15
VCC = 80 % (V
L = 10 μH, R
See fig. 14
Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by
maximum junction temperature
Any terminal to case, t = 1 minute 2500 V
TC = 25 °C 781
D
T
= 100 °C 312
C
Stg
), VGE = 20 V,
CES
= 2.0 ,
g
600 V
400
400
± 20 V
155 mJ
W
- 55 to + 150 °C
A
THERMAL AND MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS
PARAMETER SYMBOL TYP. MAX. UNITS
Junction to case R
Case to sink, flat, greased surface R
Weight of module 30 - g
Document Number: 94363 For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: www.vishay.com
Revision: 22-Jul-10 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com 1
thJC
thCS
-0.16
0.05 -
°C/W
GA200SA60SP
Vishay Semiconductors
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
Ultralow V
CE(on)
, 342 A
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (TJ = 25 °C unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNITS
Collector to emitter breakdown voltage V
Emitter to collector breakdown voltage
Temperature coeff. of breakdown voltage V
Collector to emitter saturation voltage V
Gate threshold voltage V
Temperature coeff. of threshold voltage V
Forward transconductance g
Zero gate voltage collector current I
Gate to emitter leakage current I
Notes
(1)
Pulse width 80 μs; duty factor 0.1 %
(2)
Pulse width 5.0 μs, single shot
(BR)CES
V
(BR)ECS
/TJVGE = 0 V, IC = 1.0 mA - 0.62 - V/°C
(BR)CES
CE(on)
GE(th)
/T
GE(th)
(2)
fe
CES
GES
VGE = 0 V, IC = 250 μA 600 - -
(1)
VGE = 0 V, IC = 1.0 A 18 - -
IC = 100 A
V
= 15 V
I
= 200 A - 1.33 -
C
I
= 100 A, TJ = 150 °C - 1.02 -
C
GE
See fig. 2, 5
- 1.10 1.3
VCE = VGE, IC = 250 μA 3.0 - 6.0
VCE = VGE, IC = 2 mA - - 10 - mV/°C
J
VCE = 100 V, IC = 100 A 90 150 - S
VGE = 0 V, VCE = 600 V - - 1.0
V
= 0 V, VCE = 10 V, TJ = 150 °C - - 10
GE
VGE = ± 20 V - - ± 250 nA
V
V
mA
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS (TJ = 25 °C unless otherwise specified)
PARAMETER SYMBOL TEST CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNITS
Total gate charge (turn-on) Q
Gate collector charge (turn-on) Q
Turn-on delay time t
Rise time t
Turn-off delay time t
Fall time t
Turn-on switching loss E
Total switching loss E
Turn-on delay time t
Rise time t
Turn-off delay time t
Fall time t
Total switching loss E
Internal emitter inductance L
Input capacitance C
Reverse transfer capacitance C
ge
gc
d(on)
r
d(off)
f
on
off
ts
d(on)
r
d(off)
f
ts
ies
oes
res
g
IC = 100 A
= 400 V
V
CC
= 15 V; See fig. 8
V
GE
TJ = 25 °C
= 100 A
I
C
= 480 V
V
CC
= 15 V
V
GE
= 2.0
R
g
Energy losses include “tail”
See fig. 9, 10, 13
TJ = 150 °C
= 100 A, VCC = 480 V
I
C
= 15 V, Rg = 2.0
V
GE
Energy losses include “tail”
See fig. 10, 11, 13
E
Between lead, and center of
the die contact
VGE = 0 V
= 30 V
V
CC
f = 1.0 MHz; See fig. 7
- 770 1200
- 100 150
nCGate emitter charge (turn-on) Q
- 260 380
-78-
-56-
- 890 1300
ns
- 390 580
-0.98-
- 17.4 -
mJTurn-off switching loss E
- 18.4 25.5
-72-
-60-
-1500-
ns
-660-
- 35.7 - mJ
-5.0 - nH
- 16 250 -
-1040-
pFOutput capacitance C
-190-
www.vishay.com For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: Document Number: 94363
2 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com Revision: 22-Jul-10
For both:
Duty cycle: 50 %
T
J
= 125 °C
T
sink
= 90 °C
Gate drive as specified
Power dissipation = 140 W
0
250
0.1
f - Frequency (kHz)
Load Current (A)
1 10 100
200
150
100
50
Clamp voltage:
80 % of rated
Triangular wave:
I
60 % of rated
voltage
Ideal diodes
Square wave:
I
1
10
100
1000
0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
VCE - Collector to Emitter Voltage (V)
I
C
- Collector to Emitter Current (A)
VGE = 15 V
20 µs pulse width
TJ = 150 °C
TJ = 25 °C
0
80
120
160
40
20
100
140
60
0 50 100 150 250200 300 350
T
C
- Case Temperature (°C)
Maximum DC Collector Current (A)
DC
1
2
3
- 60 - 40 - 20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
TJ - Junction Temperature (°C)
V
CE
- Collector to Emitter Voltage (V)
VGE = 15 V
80 µs pulse width
IC = 400 A
IC = 200 A
IC = 100 A
GA200SA60SP
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
Ultralow V
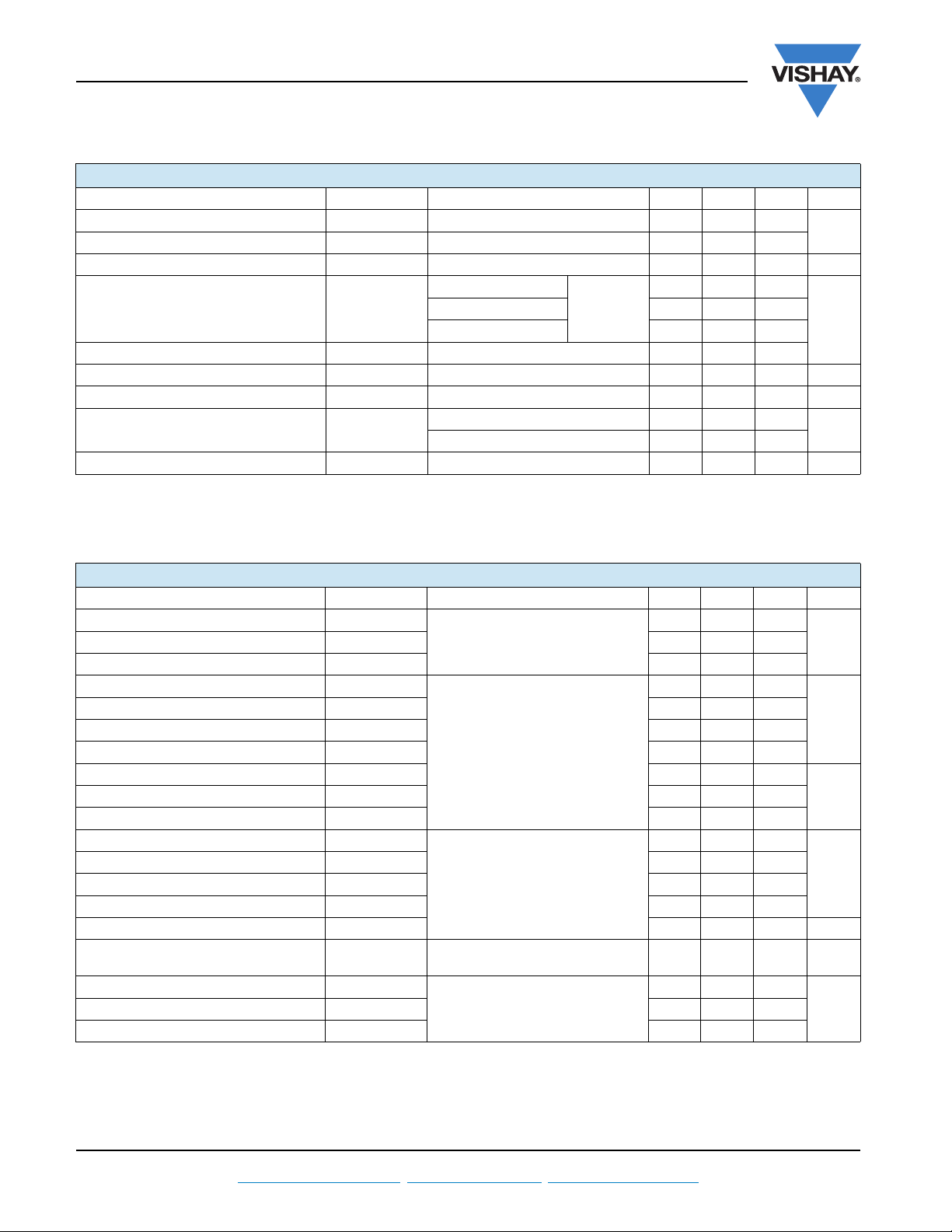
Fig. 1 - Typical Load Current vs. Frequency
(Load Current = I
CE(on)
RMS
, 342 A
of Fundamental)
Vishay Semiconductors
Fig. 2 - Typical Output Characteristics
1000
100
- Collector to Emitter Current (A)
C
I
10
567
VGE - Gate to Emitter Voltage (V)
Fig. 3 - Typical Transfer Characteristics
Document Number: 94363 For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: www.vishay.com
Revision: 22-Jul-10 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
Fig. 4 - Maximum Collector Current vs. Case Temperature
TJ = 150 °C
TJ = 25 °C
VCC = 50 V
5 µs pulse width
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com 3
Fig. 5 - Typical Collector to Emitter Voltage vs.
Junction Temperature

GA200SA60SP
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 100 10
t1 - Rectangular Pulse Duration (s)
Z
thJC
-
Thermal Response
D = 0.75
D = 0.50
D = 0.25
D = 0.10
D = 0.05
D = 0.02
D = 0.01
Single pulse
(thermal resistance)
0 200 400 600 800
0
4
8
12
16
20
QG - Total Gate Charge (nC)
V
GE
- Gate to Emitter Voltage (V)
VCC = 400 V
I
C
= 100 A
Vishay Semiconductors
Fig. 6 - Maximum Effective Transient Thermal Impedance, Junction to Case
30 000
24 000
18 000
C
ies
VGE = 0 V, f = 1 MHz
= Cge + Cgc, Cce shorted
C
ies
= C
C
res
gc
C
= Cce + C
oes
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
Ultralow V
gc
CE(on)
, 342 A
25
VCC = 480 V
V
24
GE
T
J
= 200 A
I
C
23
22
= 15 V
= 25 °C
C
12 000
C - Capacitance (pF)
6000
0
1 10 100
oes
C
res
VCE - Collector to Emitter Voltage (V)
Fig. 7 - Typical Capacitance vs.
Collector to Emitter Voltage
Fig. 8 - Typical Gate Charge vs. Gate to Emitter Voltage
www.vishay.com For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: Document Number: 94363
4 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com Revision: 22-Jul-10
21
20
19
Total Switching Losses (mJ)
18
0 1020304050
Rg - Gate Resistance (Ω)
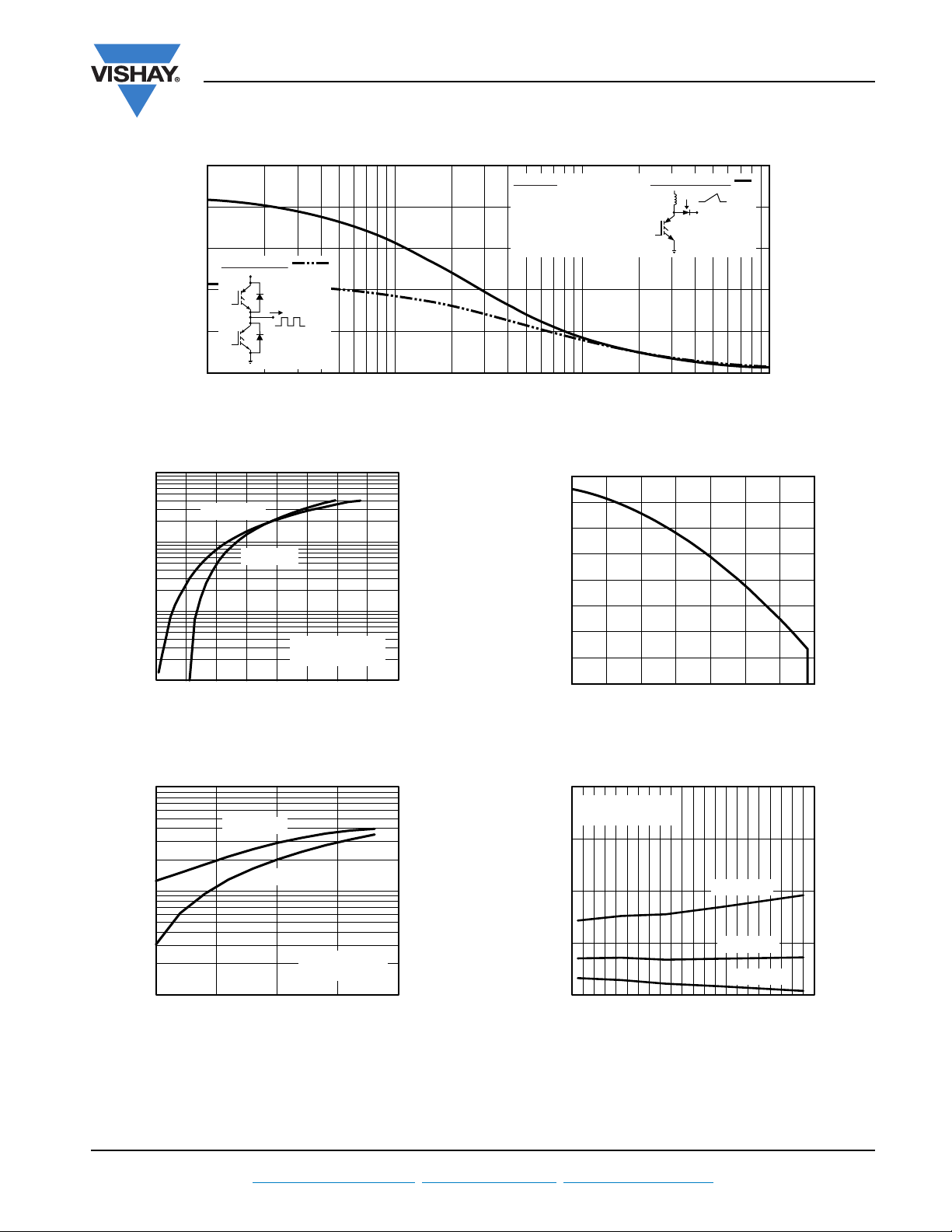
Fig. 9 - Typical Switching Losses vs. Gate Resistance
1000
RG = 2.0 Ω
= 15 V
V
GE
= 480 V
V
CC
IC = 350 A
100
IC = 200 A
IC = 100 A
Total Switching Losses (mJ)
10
- 60 - 40 - 20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
TJ - Junction Temperature (°C)
Fig. 10 - Typical Switching Losses vs.
Junction Temperature

Total Switching Losses (mJ)
100 150 200 250 300 350
0
40
80
120
160
IC - Collector Current (A)
RG = 2.0 Ω
T
J
= 150 °C
V
CC
= 480 V
V
GE
= 15 V
I
C
- Collector Current (A)
1
10
100
1000
1 10 100 1000
Safe operating area
VCE - Collector to Emitter Voltage (V)
VGE = 20 V
T
J
= 125 °C
D.U.T.
50
V
L
V
C
*
* Driver same type as D.U.T.; V
C
= 80 % of VCE (max)
Note: Due to the 50 V power supply, pulse width and inductor
will increase to obtain rated I
d
1000 V
121
2
50 V
Driver*
1000 V
D.U.T.
I
C
V
C
L
* Driver same type as D.U.T., VC = 480 V
3
1
2
GA200SA60SP
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
Ultralow V
Fig. 11 - Typical Switching Losses vs. Collector Current
CE(on)
Vishay Semiconductors
, 342 A
Fig. 13a - Clamped Inductive Load Test Circuit
Fig. 12 - Turn-Off SOA
Document Number: 94363 For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: www.vishay.com
Revision: 22-Jul-10 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
V
0 V to 480 V
480 µF
960 V
RL ==
4 x I
480
at 25 °C
C
Fig. 13b - Pulsed Collector Current Test Circuit
Fig. 14a - Switching Lost Test Circuit
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com 5

GA200SA60SP
t = 5 µs
t
d (on)
t
f
t
r
90 %
t
d (off)
10 %
90 %
10 %
5 %
V
C
I
C
E
on
E
off
Ets = (Eon + E
off
)
1
2
3
1 - Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
2 - Generation 4, IGBT silicon, DBC construction
3 - Current rating (200 = 200 A)
4 - Single switch, no diode
5 - SOT-227
6 - Voltage rating (60 = 600 V)
8 - None = Standard production
P = Lead (Pb)-free
7 - Speed/type (S = Standard speed)
Device code
51324678
G A 200 S A 60 S P
Vishay Semiconductors
ORDERING INFORMATION TABLE
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
Ultralow V
Fig. 14b - Switching Loss Waveforms
CE(on)
, 342 A
www.vishay.com For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: Document Number: 94363
6 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com Revision: 22-Jul-10

GA200SA60SP
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
Ultralow V
CE(on)
, 342 A
Vishay Semiconductors
CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION
3 (C)
Lead assignment
E
C
4
2 (G)
1, 4 (E)
N-channel
LINKS TO RELATED DOCUMENTS
Dimensions www.vishay.com/doc?95036
Packaging information www.vishay.com/doc?95037
1
E
3
2
G
Document Number: 94363 For technical questions within your region, please contact one of the following: www.vishay.com
Revision: 22-Jul-10 DiodesAmericas@vishay.com
, DiodesAsia@vishay.com, DiodesEurope@vishay.com 7
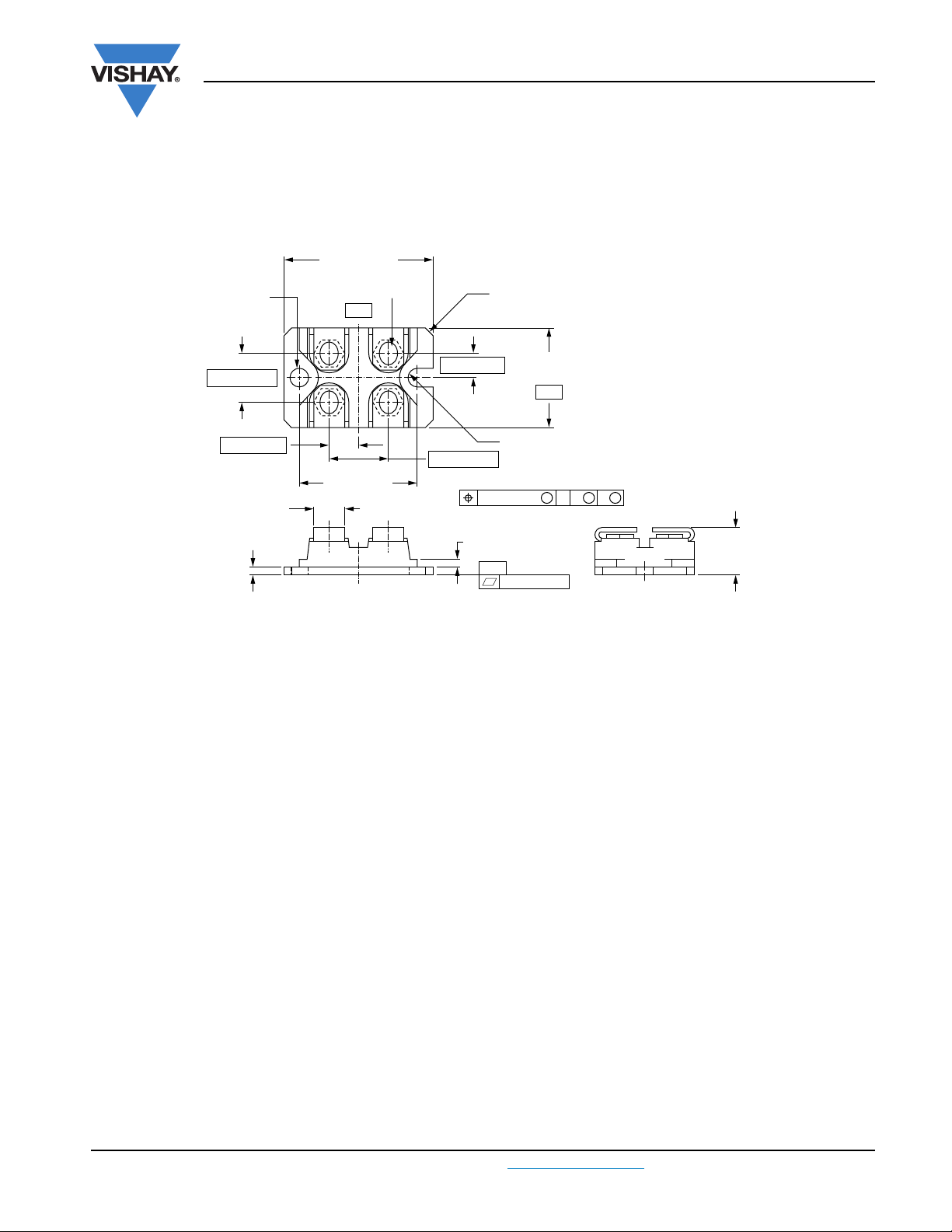
DIMENSIONS in millimeters (inches)
38.30 (1.508)
37.80 (1.488)
-A-
4
12
3
12.50 (0.492)
7.50 (0.295)
Ø 4.40 (0.173)
Ø 4.20 (0.165)
30.20 (1.189)
29.80 (1.173)
15.00 (0.590)
6.25 (0.246)
25.70 (1.012)
25.20 (0.992)
-B-
R full
Chamfer
2.00 (0.079) x 45°
2.10 (0.082)
1.90 (0.075)
8.10 (0.319)
7.70 (0.303)
4 x
2.10 (0.082)
1.90 (0.075)
-C-
0.12 (0.005)
12.30 (0.484)
11.80 (0.464)
MMM
0.25 (0.010)
CA B
4 x M4 nuts
Outline Dimensions
Vishay Semiconductors
SOT-227
Notes
• Dimensioning and tolerancing per ANSI Y14.5M-1982
• Controlling dimension: millimeter
Document Number: 95036 For technical questions, contact: indmodules@vishay.com
Revision: 28-Aug-07 1
www.vishay.com

Legal Disclaimer Notice
Vishay
Disclaimer
ALL PRODUCT, PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS AND DATA ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE TO IMPROVE
RELIABILITY, FUNCTION OR DESIGN OR OTHERWISE.
Vishay Intertechnology, Inc., its affiliates, agents, and employees, and all persons acting on its or their behalf (collectively,
“Vishay”), disclaim any and all liability for any errors, inaccuracies or incompleteness contained in any datasheet or in any other
disclosure relating to any product.
Vishay makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of the products for any particular purpose or
the continuing production of any product. To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, Vishay disclaims (i) any and all
liability arising out of the application or use of any product, (ii) any and all liability, including without limitation special,
consequential or incidental damages, and (iii) any and all implied warranties, including warranties of fitness for particular
purpose, non-infringement and merchantability.
Statements regarding the suitability of products for certain types of applications are based on Vishay’s knowledge of typical
requirements that are often placed on Vishay products in generic applications. Such statements are not binding statements
about the suitability of products for a particular application. It is the customer’s responsibility to validate that a particular
product with the properties described in the product specification is suitable for use in a particular application. Parameters
provided in datasheets and/or specifications may vary in different applications and performance may vary over time. All
operating parameters, including typical parameters, must be validated for each customer application by the customer’s
technical experts. Product specifications do not expand or otherwise modify Vishay’s terms and conditions of purchase,
including but not limited to the warranty expressed therein.
Except as expressly indicated in writing, Vishay products are not designed for use in medical, life-saving, or life-sustaining
applications or for any other application in which the failure of the Vishay product could result in personal injury or death.
Customers using or selling Vishay products not expressly indicated for use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree
to fully indemnify and hold Vishay and its distributors harmless from and against any and all claims, liabilities, expenses and
damages arising or resulting in connection with such use or sale, including attorneys fees, even if such claim alleges that Vishay
or its distributor was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Please contact authorized Vishay personnel to
obtain written terms and conditions regarding products designed for such applications.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document or by
any conduct of Vishay. Product names and markings noted herein may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Document Number: 91000 www.vishay.com
Revision: 11-Mar-11 1
 Loading...
Loading...