Page 1

Victor 900 Calculator
Teacher’s Guide
1
Page 2

Lesson 1: Learning the Victor 900 Calculator
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 1: Learning the Victor 900 Calculator
Overview Familiarize students with the calculator.
Teacher Materials “Learning the Victor 900 Calculator” transparency, red
transparency markers.
Student Materials Pencil, red crayons, “Victor 900 Calculator”
worksheet, calculator
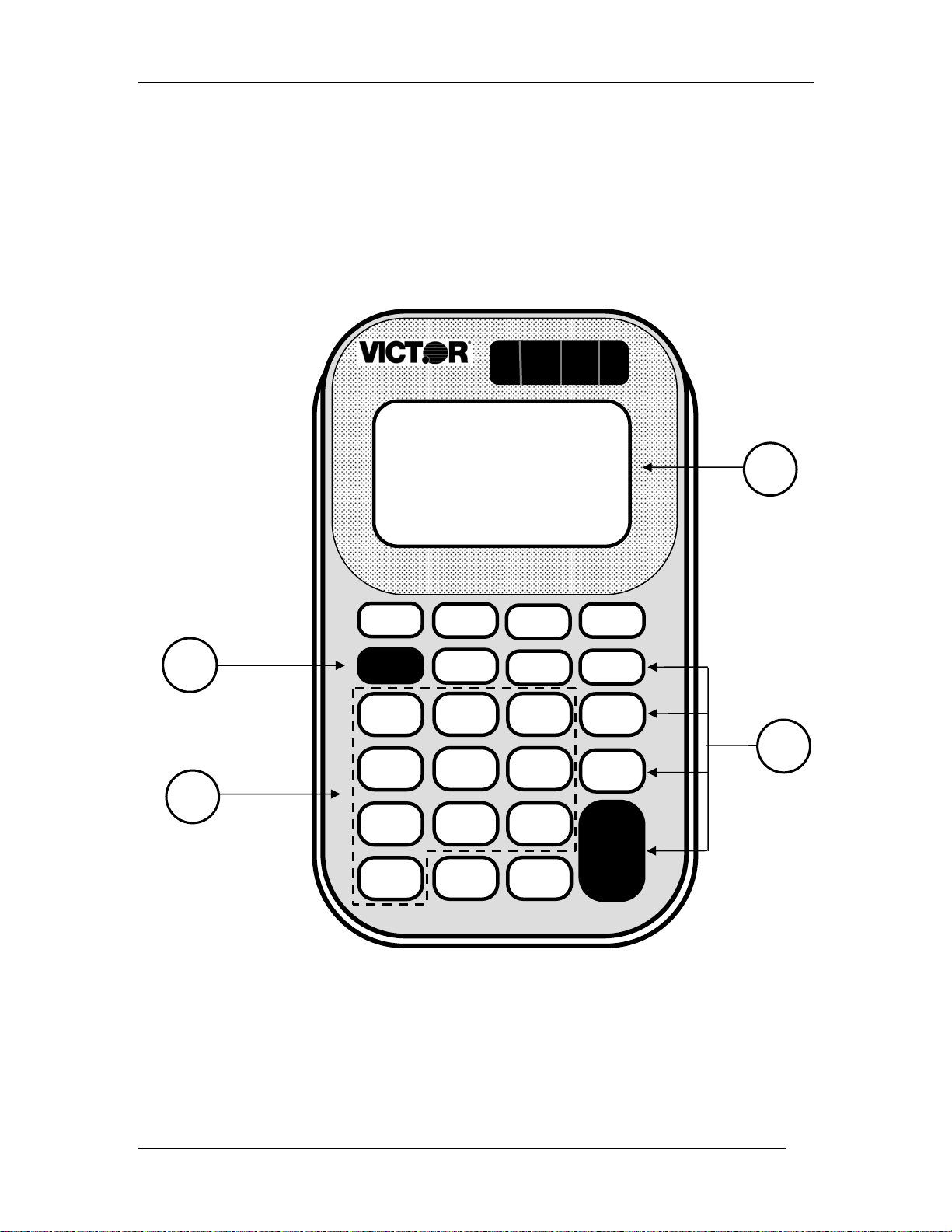
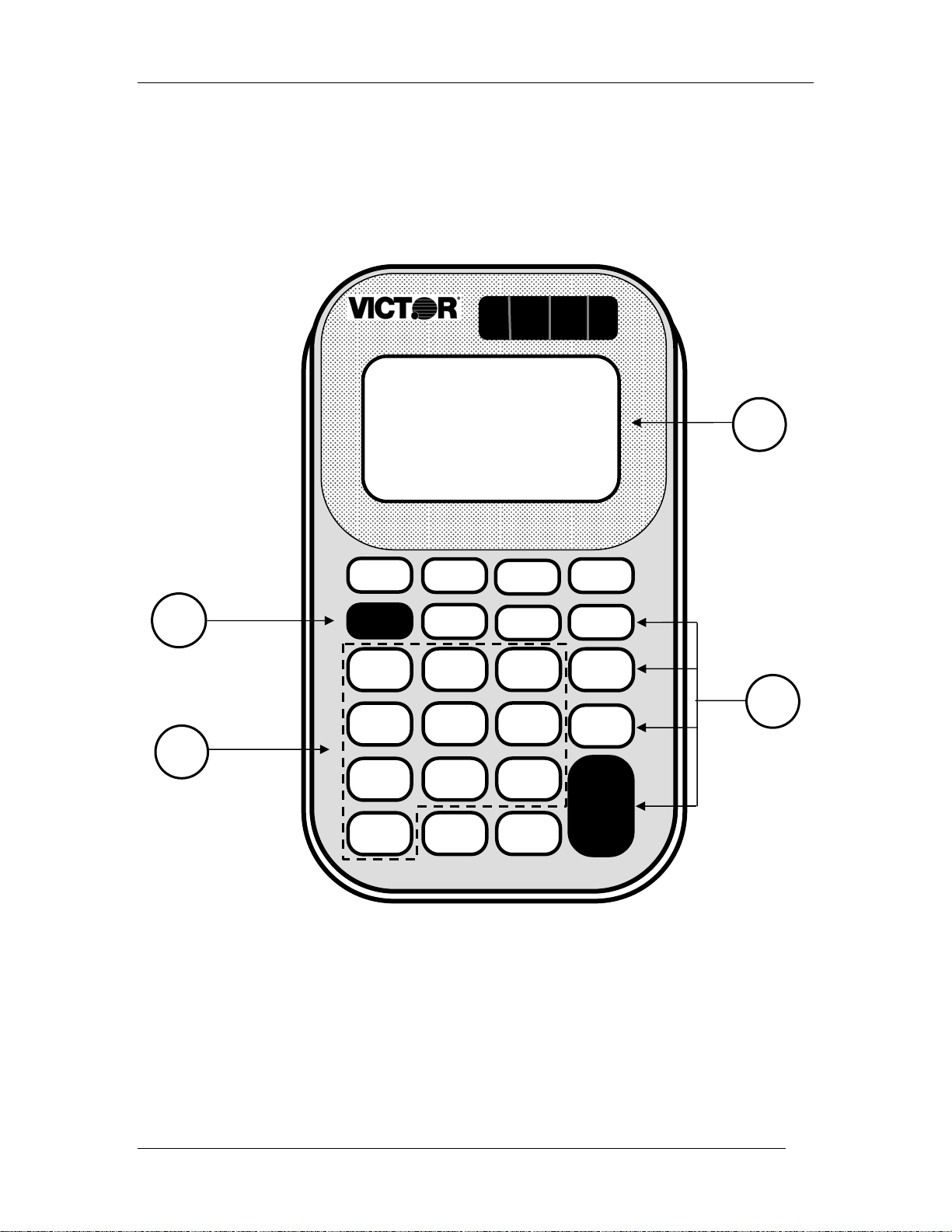
Key Introduced .ON/AC.
Teaching Notes Distribute the calculators.
Use the transparency to discuss the keys and display
of the Victor 900. Ask students to follow along on
their worksheet. The .ON/AC. key (1) turns the
calculator on and clears the display. Write “ON/AC”
on the appropriate key and ask the students to do the
same. Press the .ON/AC. key to turn the calculator
on.
Show the students the location of the display (2). Ask
what is showing in the display. Write a zero and a
decimal point in the display. Ask the students to do
the same.
Ask students to write the numbers on the number
keys (3) as you do the same. Press a number key to
show how the number shows on the display.
Ask students to write the math operations (÷, X, -, +)
on the math operation keys (4).
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
2
Page 3
Lesson 1: Learning the Victor 900 Calculator
TRANSPARENCY
Learning the Victor 900 Calculator
900
2
1
3
AntiMicrobial
4
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
3
Page 4

Lesson 1: Learning the Victor 900 Calculator
TRANSPARENCY
Victor 900 Calculator
900
CE
ON/AC
7
4
1
0
AntiMicrobial
MRC
8 9
5 6
2 3
M-
%
=
M+
÷
X
+
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
4
Page 5
Lesson 1: Learning the Victor 900 Calculator
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Learning the Victor 900 Calculator
900
2
AntiMicrobial
1
4
3
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
5
Page 6

Lesson 2: Using the Victor 900 Calculator
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 2: Using the Victor 900 Calculator
Overview Use the calculator to enter and view numbers.
Teacher Materials “Victor 900 Calculator” transparency.
Student Materials Calculator, “Calculator Battle” worksheet, “Calculator
Battle Score Sheet”, pencil.
Keys Used 1 – 9, .ON/AC.
Teaching Notes Distribute the calculators.
Ask the students to press the .ON/AC. key.
Ask the students to press the “1” and “9” keys to enter
the number “19”. Ask “How do you clear the number
19 from the display”? Answer: press the .ON/AC.
key
To play “Calculator Battle”, pair up the students.
Explain the following game rules:
Cut out the Calculator Battle cards (one set for
each pair of students).
Mix the cards and place face down in one pile.
Student A draws a card and enters the number
on their calculator.
Student B draws a card and enters the number
on their calculator.
The students compare the displays. The
student with the largest number scores a hit
and enters “1” on the score sheet.
Both students press the .ON/AC. key.
The game continues until all cards are gone.
The player with the most hits wins.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
6
Page 7
Lesson 2: Using the Victor 900 Calculator
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Calculator Battle
2 5
7 6
8 4
1
9
3
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
7
Page 8
Lesson 2: Using the Victor 900 Calculator
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Calculator Battle Score Sheet
Student A Name:
Hits
Student B Name:
Hits
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
8
Page 9

Lesson 3: Addition
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 3: Addition
Overview Use the calculator to add numbers.
Teacher Materials “Addition” and “Correcting Wrong Entries”
transparencies.
Student Materials Pencil, Calculator, and “Calculator Connections”
worksheet.
Keys Introduced +, CE
Teaching Notes Display the “Addition” transparency. Ask the students
to press the buttons as illustrated.
Display the “Correcting Wrong Entries” transparency.
Ask the students to press the buttons as illustrated.
The “Calculator Connections” worksheet provides
additional practice. Ask students to solve each
addition problem with the calculator and connect the
box with the correct answer by drawing a line.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
9
Page 10

Lesson 3: Addition
Addition
1 + 2 = ?
1 + 3 + 5 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
TRANSPARENCY
.ON/AC.
1 +.
2.
=.
----------------------------- ------------------------------
.ON/AC.
1 +.
3.
+.
0.
1.
2.
3.
0.
1.
3.
4.
5.
=.
5.
9.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
10
Page 11

Lesson 3: Addition
TRANSPARENCY
Correcting Wrong Entries
6 + 3 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
.ON/AC.
6 +.
2.
.CE.
3.
=.
0.
6.
2.
0.
3.
9.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
11
Page 12

Lesson 3: Addition
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Calculator Connections
Add the numbers in the boxes on the left side of
the page. Draw a line to the box on the right side
with the correct answer.
34
+ 41
76
13
+ 12
1
+ 19
72
+ 21
67
+ 9
47
+ 33
3
+ 74
93
75
77
33
80
25
11
+ 22
20
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
12
Page 13

Lesson 4: Subtraction
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 4: Subtraction
Overview Use the calculator to subtract numbers.
Teacher Materials “Subtraction” transparency.
Student Materials Pencil, Calculator, and “Calculator Connections II”,
and “Big Number Math” worksheets.
Keys Introduced - (minus key)
Teaching Notes Display the “Subtraction” transparency.
The “Calculator Connections” worksheet provides
additional practice. Ask students to solve each
subtraction problem with the calculator and connect
the box with the correct answer by drawing a line.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
13
Page 14

Lesson 4: Subtraction
Subtraction
9 - 5 = ?
8 - 1 - 2 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
TRANSPARENCY
.ON/C.
9 -.
5.
=.
----------------------------- ------------------------------
.ON/C.
8 -.
1.
-.
0.
9.
5.
4.
0.
8.
1.
7.
2.
=.
2.
5.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
14
Page 15

Lesson 4: Subtraction
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Calculator Connections II
Subtract the numbers in the boxes on the left side
of the page. Draw a line to the box on the right
side with the correct answer.
186
- 22
121
54
- 51
99
- 11
222
- 11
677
- 556
69
- 42
32
- 18
88
164
211
3
27
26
55
- 29
14
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
15
Page 16
Lesson 4: Subtraction
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Big Number Math
Use your calculator to subtract the big numbers in
the boxes and write down the answers. Circle the
biggest answer.
72,456
-51,432
5,687
-3,216
98,744
-10,221
189,456
-10,432
984,300
-213,498
676,345
-99,999
780,780
-175,175
54,893
-55,221
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
16
Page 17

Lesson 5: Repetitive Subtraction and Addition
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 5: Repetitive Subtraction and Addition
Overview Use the calculator to subtract or add repetitive
numbers using the constant function.
Teacher Materials “Repetitive Subtraction and Addition” and “Fastest
Fingers” transparencies.
Student Materials Pencil, Calculator, and “Constant Calculations”
worksheet.
Keys Introduced Constant function using the =. Key.
Teaching Notes Ask your students to enter 10 on the calculator and
add 10 to the total every time you snap your fingers.
Snap your fingers 4 times and compare the answers
from several students (the answer should be 50).
Tell the students how the calculator stores the last
command and number entered. This is called the
constant function. The constant function helps reduce
mistakes and save time when you must subtract, add,
divide, or multiply the same number many times.
Ask your students to again enter 10 on the calculator
and add 10 every time you snap your fingers. Snap
your fingers 4 times and compare the answers.
Note: The constant is removed from memory when
the ON/AC button is pushed.
Use the “Fastest Fingers” transparency to play a fun
game that reinforces the constant function.
Use the “Constant Calculations” worksheet for
practice.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
17
Page 18

Lesson 5: Repetitive Subtraction and Addition
TRANSPARENCY
Repetitive Subtraction and
Addition
15 - 3 - 3 - 3 = ?
6 + 2 + 2 + 2 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
.ON/AC.
15 -.
3. =.
=.
=.
----------------------------- ------------------------------
.ON/AC.
6 +.
2. =.
0.
15.
12.
9.
6.
0.
6.
8.
=.
=.
10.
12.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
18
Page 19

Lesson 5: Repetitive Subtraction and Addition
TRANSPARENCY
Fast Fingers
Enter 500 + 5 = on your calculator. When the teacher
says “Go” add one to your calculator as many times
as you can until the teacher says “stop”.
The student with the largest number has the fastest
fingers.
Winning total: ________________________
Name of Student with the Fastest Fingers
_________________________________
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
19
Page 20

Lesson 5: Repetitive Subtraction and Addition
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Constant Calculations
Use the =. key to work these constant
calculations.
1. 94 – 6 – 6 – 6 = ________
2. 945 + 12 + 12 + 12 = ________
3. 543 – 10 – 10 – 10 – 10 = ________
4. 345 + 22 + 22 + 22 + 22 = ________
5. 27 – 3 – 3 – 3 – 3 – 3 = ________
6. 45 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = ________
7. 1000 – 100 – 100 – 100 – 100 = ________
8. 2000 + 50 + 50 + 50 + 50 + 50 = ________
9. 948 – 8 – 8 – 8 – 8 – 8 – 8 = ________
10. 604 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = ________
11. 9987 – 3 – 3 – 3 – 3 – 3 – 3 = ________
12. 100 + 9 + 9 + 9 + 9 + 9 + 9 = ________
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
20
Page 21

Lesson 6: Multiplication
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 6: Multiplication
Overview Use the calculator to multiply numbers.
Teacher Materials “Multiplication” and “Multiplication Mountain Answer
Key”, “Multiplying Multiple Numbers”, and “Repetitive
Multiplication” transparencies.
Student Materials Pencil, Calculator, and “Multiplication Mountain”,
“Multiplication Calculator Battle”, and “Calculator
Connections III” worksheet.
Keys Introduced X.
Teaching Notes Display the “Multiplication” transparency. Ask the
students to follow along with you as you discuss the
exercise.
The “Multiplication Mountain” worksheet provides
additional practice. Ask students to solve each
multiplication problem with the calculator and fill in the
illustration.
To play “Multiplication Calculator Battle”, pair up the
students. Explain the following game rules:
Cut out the Multiplication Calculator Battle
cards (one set for each pair of students).
Mix the cards and place face down in one pile.
Student A draws two cards and multiplies the
numbers on their calculator.
Student B draws two cards and multiplies the
numbers on their calculator.
The students compare the displays. The
student with the largest number scores a hit
and enters “1” on the score sheet.
Both students press the .ON/AC. key.
The game continues until all cards are gone.
The player with the most hits wins.
To extend the game, mix the cards and start
again
The “Calculator Connections III” worksheet provides
additional practice. Ask students to solve each
multiplication problem with the calculator and connect
the box with the correct answer by drawing a line.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
21
Page 22

Lesson 6: Multiplication
TRANSPARENCY
Multiplication
6 X 8 = ?
43 X 5 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
.ON/AC.
6 X.
8.
=.
----------------------------- ------------------------------
.ON/AC.
43 X.
5.
=.
0.
6.
8.
48.
0.
43.
5.
215.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
22
Page 23

Lesson 6: Multiplication
_
Multiplication Mountain
69
510
411
312
213
114
STUDENT WORKSHEET
78
Across Down
1 10 X 10 = __________ 2 5 X 4 = __________
2 6 X 4 = __________ 3 47 X 20 = __________
3 3 X 3,201 = __________ 4 19 X 4 = __________
4 25 X 3,161,825 = __________ 5 16 X 1,193 = __________
5 156 X 921 = ____________ 6 27 X 89 = __________
6 48 X 56 = __________ 7 2 X 4,817 = __________
7 11 X 9 = __________ 8 1,973 X 5 = __________
14 19 X 40 = __________ 9 32 X 274 = __________
10 2,503 X 25 = _________
11 27 X 2 = __________
12 11 1 X 7 = __________
13 13 X 2 = __________
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
23
Page 24

Lesson 6: Multiplication
Multiplication Mountain
Answer Key
99
2688
143676
79045625
9603 8547
24 8 7 72
TRANSPARENCY
1008 5760
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
24
Page 25

Lesson 6: Multiplication
TRANSPARENCY
Multiplying Multiple Numbers
6 X 8 X 2 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
.ON/AC.
6 X.
8.
X.
2.
=.
0.
6.
8.
48.
2.
96.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
25
Page 26

Lesson 6: Multiplication
Repetitive Multiplication
4 X 2 = ?
4 X 4 = ?
4 X 6 = ?
4 X 8 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
TRANSPARENCY
.ON/AC.
4 X.
2.
=.
4.
=.
6.
=.
8.
0.
4.
2.
8.
4.
16.
6.
24.
8.
=.
32.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
26
Page 27

Lesson 6: Multiplication
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Multiplication Calculator Battle
12 51
23
48
37 38
17
9
39
65
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
42
15
27
Page 28

Lesson 6: Multiplication
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Multiplication Calculator Battle
Score Sheet
Student A Name:
Hits
Student B Name:
Hits
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
28
Page 29

Lesson 6: Multiplication
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Calculator Connections III
Multiply the numbers in the boxes on the left side
of the page. Draw a line to the box on the right
side with the correct answer.
32
X 4
160
12
X 35
8
X 20
57
X 11
72
X 2
81
X 4
110
X 5
627
128
144
420
2,816
324
64
X 44
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
550
29
Page 30

Lesson 7: Division
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 7: Division
Overview Use the calculator to divide numbers.
Teacher Materials “Two Methods for Writing Division Problems”,
“Division”, and “Repetitive Division“ transparencies.
Student Materials Pencil, Calculator, and “Calculator Connections IV”
worksheet.
Keys Introduced ÷.
Teaching Notes Display the transparencies. Ask the students to follow
along with you as you discuss the exercise.
The “Calculator Connections IV” worksheet provides
additional practice. Ask students to solve each
division problem with the calculator and connect the
box with the correct answer by drawing a line.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
30
Page 31

Lesson 7: Division
TRANSPARENCY
Two Methods for Writing Division
Problems
Hand Written Method
Quotient
8
)
48 6
Divisor
Dividend
Calculator Method
Divisor
48 ÷ 6 = 8
Dividend Quotient
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
31
Page 32

Lesson 7: Division
TRANSPARENCY
Division
48 ÷ 6 = ?
81 ÷ 3 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
.ON/AC.
48 ÷.
6.
=.
----------------------------- ------------------------------
.ON/AC.
81 ÷.
3.
=.
0.
48.
6.
8.
0.
81.
3.
27.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
32
Page 33

Lesson 7: Division
Repetitive Division
100 ÷ 4 = ?
40 ÷ 4 = ?
88 ÷ 4 = ?
52 ÷ 4 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
TRANSPARENCY
.ON/AC.
100 ÷.
4.
=.
40.
=.
88.
=.
52.
0.
100.
4.
25.
40.
10.
88.
22.
52.
=.
13.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
33
Page 34

Lesson 7: Division
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Calculator Connections IV
Divide the numbers in the boxes on the left side of
the page. Draw a line to the box on the right side
with the correct answer.
125
÷ 25
100
49
÷ 7
1000
÷10
66
÷ 11
72
÷ 2
888
÷ 4
550
÷ 5
6
5
7
36
110
222
147
÷ 21
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
7
34
Page 35

Lesson 8: Division with Remainders
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 8: Division with Remainders
Overview Use the calculator to divide numbers with remainders.
Teacher Materials “Two Methods for Writing Division with Remainders”,
“Division with Remainders”, “Repetitive Division with
Remainders”, and “Calculating the Remainder” ,
transparencies.
Student Materials Pencil, Calculator, and “Calculator Connections V”
worksheet.
Keys Introduced ÷.
Teaching Notes Display the transparencies. Ask the students to follow
along with you as you discuss the exercise.
Inform the students how the calculator displays the
“remainder” as digits to the right of the decimal point.
Use the “Calculating the Remainder” transparency to
show how to determine the remainder. To find the
remainder, multiply the number to the left of the
decimal point by the divisor. Then subtract the result
from the dividend to get the remainder.
The “Calculator Connections V” worksheet provides
additional practice. Ask students to solve each
division problem with the calculator and connect the
box with the correct answer by drawing a line.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
35
Page 36

Lesson 8: Division with Remainders
Q
)
d
Q
TRANSPARENCY
Two Methods for Writing Division
with Remainder Problems
Hand Written
uotient
Divisor
9.6
48 5
Dividen
Remainder
Calculator Method
Divisor
Remainder
48 ÷ 5 = 9.6
Dividend
uotient
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
36
Page 37

Lesson 8: Division with Remainders
TRANSPARENCY
Division with Remainders
48 ÷ 5 = ?
74 ÷ 6 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
.ON/AC.
48 ÷.
5.
=.
----------------------------- ------------------------------
.ON/AC.
74 ÷.
6.
=.
0.
48.
5.
9.6
0.
74.
6.
12.3333333
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
37
Page 38

Lesson 8: Division with Remainders
TRANSPARENCY
Repetitive Division with
Remainders
100 ÷ 6 = ?
40 ÷ 6 = ?
88 ÷ 6 = ?
52 ÷ 6 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
.ON/AC.
100 ÷.
6.
=.
40.
=.
88.
=.
52.
0.
100.
6.
16.666666
40.
6.6666666
88.
14.666666
52.
=.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
8.6666666
38
Page 39

Lesson 8: Division with Remainders
TRANSPARENCY
Calculating the Remainder
76 ÷ 8 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
.ON/AC.
76 ÷.
8.
=.
----------------------------- ------------------------------
9 X.
8.
=.
----------------------------- ------------------------------
0.
76.
8.
9.5
9
8.
72
76 -.
72
═.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
55.
4.
76.
The
remainder
is 4.
39
Page 40

Lesson 8: Division with Remainders
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Calculator Connections V
Divide the numbers in the boxes on the left side of
the page. Draw a line to the box on the right side
with the correct answer.
164
÷ 5
36.571428
32
÷ 9
256
÷7
23
÷ 12
231
÷ 26
20
÷ 8
51
÷ 4
8.8846153
12.75
3.5555555
2.5
32.8
1.9166666
147
÷ 21
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
7.
40
Page 41

Lesson 9: Decimals
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 9: Decimals
Overview Use the calculator to add and subtract numbers with
decimals.
Teacher Materials “Decimals” transparency
Student Materials Pencil, Calculator, “Calculator Connections VI”
worksheet, “Estimation Exploration” worksheet, and “I
Love Decimals” worksheet.
Keys Introduced ● .
Teaching Notes The “Calculator Connections VI” worksheet provides
additional practice. Ask students to solve each math
problem with the calculator and connect the box with
the correct answer by drawing a line.
The “Estimation Exploration” worksheet, is an
additional way to have a fun time with decimals. It
shows the difference between estimated and exact
answers. It is another way to improve skills and learn
more about decimals and using the calculator.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
41
Page 42

Lesson 9: Decimals
TRANSPARENCY
Decimals
2.5 + 5.3 = ?
7.4 - 6.1 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
.ON/AC.
2.5 +.
5.3.
=.
----------------------------- ------------------------------
.ON/AC.
7.4 -.
6.1.
=.
0.
2.5
5.3
7.8
0.
7.4.
6.1
1.3
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
42
Page 43

Lesson 9: Decimals
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Calculator Connections VI
Add the Decimals in the boxes on the left side of
the page. Draw a line to the box on the right side
with the correct answer.
16.4
+ 5.3
1.5
3.2
- 1.7
2.5
+7.1
2.3
+ 1.2
23.1
- 2.6
9.7
+ 4.1
5.1
- 1.4
3.5
21.7
20.5
13.8
12.5
9.6
14.7
- 2.2
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
3.7
43
Page 44

Lesson 9: Decimals
STUDENT WORKSHEET
I Love Decimals
Estimate the answer for the math problems then use your calculator
to check the answers. Write your estimates in the left arc of the
hearts and the calculator answers in the right arcs.
Example:
Estimate
8.0 8.1 Calculator
5.7 + 2.4 =
4.5 + 6.7 = 3.8 - 9.2 = 5.9 - 8.1 =
3.7 + 5.6 = 6.3 - 9.0 = 7.5 - 6.6 =
7.7 + 4.3 = 9.1 + 7.8 = 9.3 + 5.6 =
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
44
Page 45

Lesson 10: Memory
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 10: Memory
Overview Use the calculator to add and subtract numbers and
store the numbers in the calculator’s memory
Teacher Materials “Calculator Memory”, “Adding Products with Memory”,
and “Find the Total Cost Using Memory”,
transparencies.
Student Materials Pencil, Calculator, and “Million Memory Magic”
worksheet.
Keys Introduced MRC . M+. M-.
Teaching Notes Talk to the students about memory, and how it works
on a calculator. The memory icon will appear on the
calculator screen when a number has been stored.
To view the stored number, press the MRC button
once. MRC stands for “Memory Recall & Clear”. If
the MRC key is pressed twice, the memory is cleared.
M+. Adds the displayed number to the memory of the
calculator
M-. Subtracts the displayed number from the memory
of the calculator
MRC. Displays the number from the memory onto
the screen of the calculator
MRC. MRC. Clears the memory
The Million Memory Magic worksheet is for students
to practice using the memory function of the
calculator. It is to be done individually to test the skills
learned in the lesson. Understanding this worksheet
will show fulfillment and accomplishment with this
lesson.
You should ask students to press the MRC key twice
before the exercise … to make sure everyone starts
with a clear memory.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
45
Page 46

Lesson 10: Memory
TRANSPARENCY
Calculator Memory
M+. Adds the displayed
number to the memory of
the calculator
M-. Subtracts the displayed
number from the memory
of the calculator
MRC. Recalls and displays the
number in memory
MRC. MRC. Clears the memory
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
46
Page 47

Lesson 10: Memory
TRANSPARENCY
Adding Products with Memory
What is the total of the three equations below?
2 x .86 = ?
3 x 1.49 = ?
4 x .52 = ?
Press these buttons:
ON/AC MRC MRC
ON/AC
0.
The calculator shows:
2 x . 99 =.
M+.
3 x. 1 . 49 =.
.M+.
4 x. . 52 =.
M+.
1.98
MEMORY 1.98
MEMORY 4.47
MEMORY 4.47.
MEMORY 2.08
MEMORY 2.08
MRC.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
MEMORY 8.53
47
Page 48

Lesson 10: Memory
TRANSPARENCY
Find the Total Cost Using Memory
3 $5 Items
6 $2 Items
$13 Discount = ?
Press these buttons:
ON/AC MRC MRC
ON/AC
0.
The calculator shows:
3 x 5 =
M+.
6 x 2 =
M+.
MRC.
-. 13 =
15.
MEMORY 15
MEMORY 12
MEMORY 12
MEMORY 27
MEMORY 14
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
48
Page 49

Lesson 10: Memory
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Million Memory Magic
Use the Memory function to quickly divide 1,000,000 by 1 through 10.
Enter 1,000,000 into memory. Use the MRC key to recall the
1,000,000 value instead of re-entering 1,000,000 for each equation.
1,000,000 ÷ 1 ═
1,000,000 ÷ 3 ═
1,000,000 ÷ 5 ═
1,000,000 ÷ 7 ═
1,000,000 ÷ 2 ═
1,000,000 ÷ 4 ═
1,000,000 ÷ 6 ═
1,000,000 ÷ 8 ═
1,000,000 ÷ 9 ═
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
1,000,000 ÷ 10 ═
49
Page 50

Lesson 11: Percents
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 11: Percents
Overview Use the calculator for situations involving sales taxes,
discounts, or other percent problems.
Teacher Materials “Percents” and “More Percents” transparencies.
Student Materials Pencil, Calculator, and ”Would You Like To Own an
Amusement Park?” worksheet.
Keys Introduced %.
Teaching Notes Remember the %. key acts like the =. key so =.
does not need to be pressed at any point when doing
percents
For the game where the students have to make up an
Amusement Park and have to figure out what the
discounted price with tax will be, is a way for the
students to look at a real life situation. They use their
new knowledge of percents to figure out the discounts
that they one day might be using and then they will
know how much money they are saving.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
50
Page 51

Lesson 11: Percents
TRANSPARENCY
Percents
$3.70 - 12% discount =?
$7.50 + 6% sales tax= ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
ON/AC ON/AC
3.70 –
12 %
------------------------------ -----------------------------------
7.50 +
6. %
0.
3.70
3.256
7.50
7.95
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
51
Page 52

Lesson 11: Percents
TRANSPARENCY
More Percents
$4.90 - 15% discount=?
$8.20 + 7% sales tax
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
ON/AC ON/AC
4.90 -
15.
------------------------------- ------------------------------------
8.20 +
%. 4.165
%. 8.774
7.
0.
4.90
8.20
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
52
Page 53

Lesson 11: Percents
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Would you like to own an Amusement Park?
Decide what rides to offer and set the ticket price for
each ride. Offer a 10% discount. Use 5% for the Tax
rate and calculate the final price.
___________________’s Park
Name of
Ride
Twister
Original
Cost of
Ride
% discount
Sale Price
Sales Tax
%
$10.00
10%
$9.00
5%
Final Cost
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
$9.45
53
Page 54

Lesson 12: Interest
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 12: Interest
Overview Use the % key to determine interest amounts for a
loan.
Teacher Materials “Simple Interest” and “Total with Interest”
transparencies.
Student Materials Pencil, Calculator, and ”Interesting Ride” worksheet.
Keys Introduced %.
Teaching Notes Remember the %. key acts like the =. key so =.
does not need to be pressed at any point when doing
percents
The worksheet “Interesting Ride” is fun and
interesting to students. Word problems that portray
real life situations can better focus the mind and show
how interest will one day affect the student.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
54
Page 55

Lesson 12: Interest
TRANSPARENCY
Simple Interest
$750.00 at 13% =?
$299.00 at 3% =?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
ON/AC ON/AC
750 x
13 %
------------------------------ -----------------------------------
299 x
3. %
0.
750.
97.5
299.
8.97
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
55
Page 56

Lesson 12: Interest
TRANSPARENCY
Total with Interest
$490 + 15% =?
$820 + 7% =?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
ON/AC ON/AC
490 +
15.
------------------------------- ------------------------------------
820 +
%. 563.5
%. 877.4
7.
0.
490.
820.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
56
Page 57

Lesson 12: Interest
INTERESTing Ride
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Hop aboard and get ready for the
INTERESTing ride!!
Below are a few problems that are fun. Come along and enjoy the
ride.
☺ Mr. Bob has a piggy bank that has $300.00 in it. The piggy pays
Mr. Bob 3% per year. How much interest will piggy pay Mr. Bob in
the first year?
☺ Mrs. Bob has a jar full of $3,500.00 all in pennies that is 350,000
pennies. Every year the jar pays Mrs. Bob 9% interest. How much
money will the jar pay Mrs. Bob at the end of the year?
☺ Mr. and Mrs. Bob have a bank account for Little Bob their son. At
the start of the year, they put a deposit of $2,500.00. The bank
pays a yearly interest of 6%. How much will Mr. and Mrs. Bob
have at the end of the year?
☺ Sam, Little Bob’s friend asks Little Bob for $50 to buy ice cream for
a month. Little Bob is smart and gives Sam the money with a fee
of 2% interest. How much money total will Sam have to pay Little
Bob at the end of the month?
☺ Mr. Smith works with Mr. Bob, and they both need lunch, but Mr.
Bob does not have money with him. Mr. Smith pays $15 for Mr.
Bob’s lunch and says to pay him back in 4 days with 2% interest
for everyday until he pays. How much money will Mr. Bob have to
pay Mr. Smith total in 4 days?
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
57
Page 58

Lesson 13: Square Roots and Squares
TEACHER’S GUIDE
Lesson 13: Square Roots and Squares
Overview Use the calculator to determine the square and
square root of numbers.
Teacher Materials “Why Call it the “Square”, “Square Roots”, and
“Squares” transparencies.
Student Materials Crayons, Calculator, and ”Square Grid” worksheet.
Keys Introduced √.
Teaching Notes Remember to explain that Square roots and Squares
are inverses of each other.
Write the following equation on the board:
10 X 10 = 100
Show how 100 is the square of 10. Explain that 10 is
the square root of 100.
Provide copies of the “Square Grid” worksheet to
students. Ask the students to draw colored boxes
representing the Square of 1, 2, and 4.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
58
Page 59

Lesson 13: Square Roots and Squares
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Why Call it the “Square”?
When small squares are used to make a larger
square you can see why we use the term “Square”.
3 high
═
9
3 wide
9 is the
“Square” of 3.
3 is the “Square
Root” of 9.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
59
Page 60

Lesson 13: Square Roots and Squares
TRANSPARENCY
Square Roots
√ 121 = ?
√ 225 = ?
√ 36 = ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
ON/AC ON/AC
121
----------------------------
225
----------------------------- ----------------------------------
36.
.√.
.√.
.√.
0.
11.
----------------------------------
15.
6.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
60
Page 61

Lesson 13: Square Roots and Squares
TRANSPARENCY
Squares
2
12
= ?
2
4
= ?
Press these buttons:
The calculator shows:
ON/AC ON/AC
12 x 12
------------------------------- ------------------------------------
4 x 4
0.
144.
16.
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
61
Page 62

Lesson 13: Square Roots and Squares
STUDENT WORKSHEET
Square Grid
Victor 900 Calculator Teacher’s Guide
62
 Loading...
Loading...