Page 1

Valco Instruments Co. Inc.
Introduction
Description and Operating Principles............................................................1
Safety Notes and Information........................................................................2
Symbols
Installation Category
Safety
Components of the Detector System............................................................3
System Requirements
Components not Included with the Detector System....................................4
System Purity................................................................................................4
Gas Specifications........................................................................................5
Pulsed Discharge
Detector
Model D-4-I-VA38-R
Instruction Manual
Installation
General Precautions......................................................................................6
Mounting the Detector on the GC.................................................................6
Gas Connections...........................................................................................7
Installing and Purging the Gas Regulator..............................................7
Installing and Purging the Helium Purifier..............................................8
Connecting the Discharge Gas to the Detector.....................................8
Capillary Column Connection........................................................................9
Packed Column Connection..........................................................................9
Testing for Leaks.........................................................................................10
Pulser Module Installation...........................................................................11
Detector Electrical Connections..................................................................12
Initial Power-Up...........................................................................................13
Troubleshooting High Background Current..................................................13
Mode Selection and Setup
Helium Ionization Mode...............................................................................14
Selective Photoionization Mode...................................................................14
Warranty............................................................................................................16
d4_var.P65
Rev 5/12
Printed in USA
Valco Instruments Co. Inc.
800
·
367
·
·
688
·
688
8424 sales
·
9345 tech
·
8106 fax
713
713
valco@vici.com
Valco International
Schenkon, Switzerland
Int + 41 · 41 · 925
Int + 41 · 41 · 925
vici@vici.com
·
6200 phone
·
6201 fax
Page 2

This page is intentionally left blank for printing purposes
Page 3
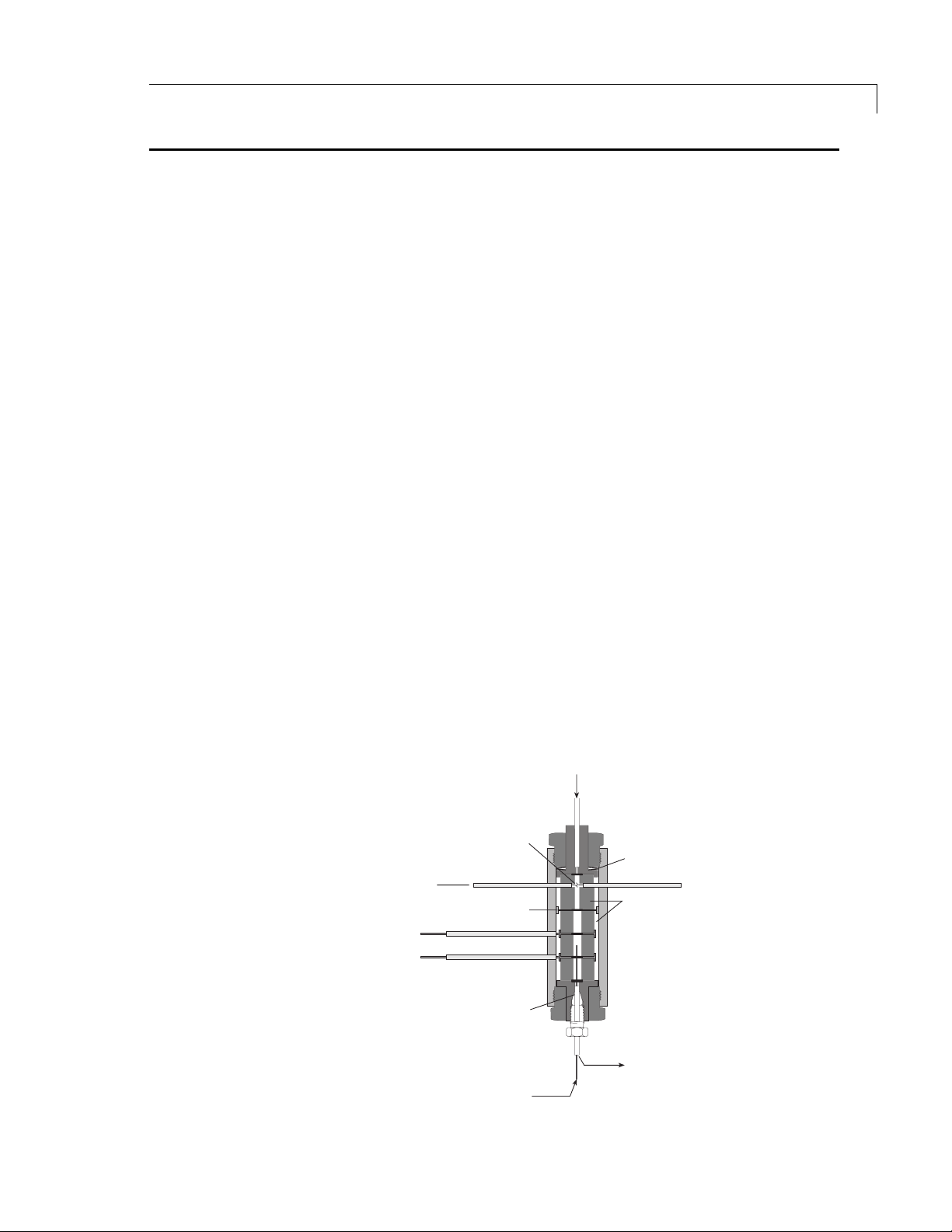
Introduction
Description and Operating Principle
1
The PD-D-4-I-V A38-R is a non-radioactive pulsed discharge ionization detector
(PDID) which is optimized for the Varian 3800 GC. A schematic representation
of the basic D4 detector is shown in Figure 1.
The D4 utilizes a stable, lo w pow er, pulsed DC discharge in helium as the
ionization source. Elutants from the column, flowing counter to the flow of
helium from the discharge zone, are ionized by photons from the helium
discharge above. Resulting electrons are focused toward the collector
electrode by the two bias electrodes.
The principal mode of ionization is photoionization by radiation arising from
the transition of diatomic helium
He
1
+
(
∑
)
A
u
2
to the dissociative 2He(1S
1
)
ground state. This is the well-known Hopfield emission. The photon energy
from the He2 continuum is in the range of 13.5 eV to 17.7 eV.
The D4 is essentially non-destructive (0.01 - 0.1% ionization) and highly
sensitive. The response to organic compounds is linear over fiv e orders
of magnitude with minimum detectable quantities (MDQs) in the low
picogram range. The response to fixed gases is positive (the standing
current increases), with MDQs in the low ppb range.
Detector response is universal except f or neon, which has an ionization
potential of 21.56 eV. Since this potential is close to the energy of the
He* metastable (19.8 eV) but greater than the photon energy from the
He2 continuum, neon exhibits a low ionization efficiency and low detector
response.
When a dopant is added to the discharge gas, the D4 also functions
as a selective photoionization detector . (Suitable dopants include Ar for
organic compounds, Kr for unsaturated compounds , or Xe f or polyn uclear
aromatics.)
HELIUM INLET
DISCHARGE ZONE
SPRING WASHERS
DISCHARGE ELECTRODES
GROUND
BIAS ELECTRODE
COLLECTOR ELECTRODE
CAPILLARY COLUMN
COLUMN INLET
INSULATOR
VENT
Figure 1: Schematic of the D4 detector
Page 4
Introduction
2
Helium Ionization (PDHID)
The PDHID is essentially non-destructive (0.01 - 0.1% ionization) and highly
sensitive. The response to organic compounds is linear over five orders of
magnitude with minimum detectable quantities (MDQs) in the low or sub
picogram range. The response to fixed gases is positive (the standing
current increases), with MDQs in the low ppb range.
The PDHID response is universal except f or neon, which has an ionization
potential of 21.56 eV. Since this potential is close to the energy of the He*
metastable (19.8 eV) but greater than the photon energy from the He
continuum, neon exhibits a low ionization efficiency and lo w detector
response.
2
Photoionization (PDPID)
Changing the discharge gas from pure helium to helium doped with argon,
krypton, or xenon changes the discharge emission profile, resulting in
resonance atomic and diatomic emissions of the rare gas added. Response
is limited to sample compounds with ionization potentials less than or equal
to the dopant gas emission energy. In this configuration, the detector is
essentially functioning as a specific photoionization detector for selective
determination of aliphatics, aromatics, and amines, as well as other species.
Since there is no lamp or window , sensitivity will not change with time.
Safety Notes and Information
CAUTION: During normal operation, the detector produces ultraviolet energy (UVA, UVB), some of which may
be emitted. Do not watch the arc without eye protection.
Symbols
HIGH VOL T A GE
V oltages presenting the risk of electric shock are present in
sever al places in the equipment. Avoid contact with hazardous live parts. Do not probe into openings or attempt to
defeat safety mechanisms .
HOT SURFACE
The surface of the detector body may be hot while in oper ation (possibly in excess of 250°C). Caution should be
observed.
A TTENTION
Refer to the manual.
PROTECTIVE EAR TH
This internal connection provides protection against electric
shock from mains voltages and should not be remov ed.
Page 5

Introduction
Components of the Detector System
Components of the detector system are listed in the T able 1. Check the
contents of the packages to verify that everything is present. Contact the
factory if anything is missing or damaged. (NOTE: damaged shipments
must remain with the original packaging for freight company inspection.)
T ab le 2 lists additional required items which must be purchased from Varian.
Table 1: Components of the D-4-I-VA38-R system
Description Quantity Product number
Detector cell, PDHID 1 PD-D4-I-RU
Pulse supply module 1 PD-M2
Instruction manual 1 MAN-PDD4-VA
Varian fittings kit 1 PD-KIT-VA
Includes: 1/32" polyimide ferrule 5 ZF.5V
1/32" polyimide plug ferrule (no through hole) 1 ZF.5VX
1/16" gold-plated ferrule 5 ZF1GP
0.25 - 0.44 mm polyimide column ferrule 5 FS.4
0.4 - 0.5 mm polyimide column ferrule 5 FS.5
1/16" union, 316 SS 2 ZU1MS6
1/16" cross 1 ZX1
1/8" external to 1/16" internal adapter 2 EZR21
1/8" external to 1/16" internal reducing union 2 EZRU21
1/16" to 1/16"bulkhead union 2 ZBU1
1/32" external nut 1 EN.5KN
Fused silica adapter 1 IZERA1.5
Packed column adapter (installed) 1 I-23642-D4RU
Restrictor, 35 cc/min @ 80 psi He 1 TGA-R-35F80P
Clamp ring 1 CR1
Helium purifier 1 HP2
Electrometer cable assembly, Varian 1 I-23230
Bias cable assembly, Varian 1 I-23404-1
Pulser cable assembly, Varian 1 I-23628
Heater block, Varian 1 I-23755
3
Table 2: Components not supplied by Valco (may be obtained from Varian)
Description Quantity Varian Product number
Detector mounting base 1 03-925326-01
Mounting base screws 4 12-901163-00
Heater (depending on requirement) 1
120V 03-925396-01
220V 03-925396-02
101V 03-925396-03
Temperature probe 1 03-925374-01
Electrometer board 3800 FID 1 03-925021-01
Page 6

Introduction
4
System Requirements
Components Not Included with the Detector System
•Helium (99.999% purity) and other support gases
•Ultra high purity grade gas pressure regulator with stainless steel
diaphragm
•Any special adapters required for connection to the gas regulator
•SS tubing to go from gas supply to GC
•Flow measuring device
System Purity
Discharge/Carrier Gas Considerations
The performance of the detector is adversely affected by the presence
of any impurities in the gas streams (carrier, discharge, or dopant). We
recommend that a quality grade of helium 5.0 (99.999% pure or better)
be used at all times. Major gas suppliers off er research g rade helium
(99.9999% pure) which is particularly low in fixed gas impurities and should
give good results in a clean system, but even the highest quality carrier
gas may contain some water v apor and fixed gas impurities; hence a
helium purifier is included as part of the detector system.
must alwa ys flow through the helium purifier .
The discharge gas
Whenever a ne w batch of discharge gas is receiv ed, we recommend
performing a blank GC analysis of the gas in the PDHID mode to detect
and identify the presence of any impurities. Gas purity requirements
are specified on the next page.
T ubing
Standards of cleanliness that are suitable for many GC applications may
be totally inadequate for the sensitive PDHID/PDPID work. All surfaces that
contact the gas stream must be fused silica or stainless steel. Do not use
copper tubing or brass fittings. All tubes must be thoroughly cleaned and
baked before use.
Flow Controllers
The use of valves or flow controllers in which the gas stream is exposed
to any polymer-based packing or lubricating material is to be particularly
avoided.
Pressure Regulators
We recommend commercial “ultra-pure” g rade regulators with stainless steel
diaphragms. Regulators with diaphragms made of neoprene or other
elastomers should never be used.
Page 7

Gas Specifications
Introduction
5
edoMrotceteD
DIHDPDIPDP-rADIPDP-rKDIPDP-eX
sagegrahcsiD
sagreirraC
Any gas including He which has an ionization potential greater than 12 eV
**
Any gas including He which has an ionization potential greater than 11 eV
**
muileHeHnirA%2eHnirK%5.1eHnieX%8.0
muileH*****
Purity Specifications
•Helium (discharge and carrier gas) must have a minimum purity of
99.999%, with < 20 ppm Ne impurity . For trace analysis of fixed gases,
we strongly recomment 99.9999% purity He with < 0.5 ppm Ne.
•Ar-PDPID mode: 2% ± 0.2% Ar in 99.999% He balance
•Kr-PDPID mode: 1.5% ± 0.1% Kr in 99.999% He balance
•Xe-PDPID mode: 0.8% ± 0.2% Xe in 99.999% He balance
Page 8

6
Installation
General Precautions
• Do not use plastic/polymer or copper tubes for gas handling and inter-
connectons. Use only stainless steel tubing with Valco gold-plated ferrules.
• Do not turn the unit on until helium discharge gas is flowing through the
detector.
• Do not shut off or disconnect the discharge gas when the detector is hot,
even if the unit is turned off. Turn off the discharge power switch and
allow the detector to cool down naturally before disconnecting or shutting
off the discharge gas.
• Do not cover the unit with anything which could restrict air circulation.
• Position the controller unit where the mains switch on the rear panel can
be reached easily.
Mounting the Detector on the GC
1. Remove the heater bloc k from the detector b y loosening the clamping
screw.
2. Remove the detector mounting base (V arian #03-925326-01) from the GC
by removing the four mounting base scre ws (Varian #12-901163-00).
3. Using the two 8-32 x 1" screws provided, install the heater block on the
underside of the detector mounting base. Be sure to orient it so that the
cut-out slot on the top of the heater block will be facing the rear of the GC.
4. Insert the detector into the heater block with the bias, electrometer, and
high voltage connectors facing the rear of the GC . Tighten the clamping
screw in the heater block to secure the detector.
5. Insert the heater (Varian #03-925396-01, -02, or -03) and temperature
probe (V arian #03-925374-01) into the detector’s heater b loc k.
6. Using the four mounting screws, install the detector mounting base with
heater block/detector assembly on the GC .
TEMPERATURE
PROBE
HEATER
CABLE
HEATER BLOCK
SCREWS (2)
HEATER BLOCK
MOUNTING BASE
SCREWS (4)
DETECTOR MOUNTING BASE
Figure 3: Mounting the detector on the GC
Page 9

Gas Connections
Remember these three points discussed earlier: (1) all surfaces that contact
the gas stream must be fused silica or stainless steel; (2) do not use copper
tubing or brass fittings; and (3) all tubes m ust be thoroughly cleaned and
baked before use . The installation instructions below assume that the
detector discharge gas will be supplied from a nearby cylinder of helium
of the proper purity . If your installation is different, you ma y need to modify
the instructions appropriately . A number of Valco fittings have been supplied
in the fittings kit to handle different situations.
Figure 4 illustrates gas connections for the D-4-I-VA38-R detector system.
Since the distance from the helium supply to the GC varies from installation
to installation, we do not supply tubing for that purpose.
VENT
COLUMN
INLET
CONNECT TO “SAMPLE IN”
FOR BLANK RUN”
TGA-R-35F80P
RESTRICTOR
(35 mL/min minimum)
DISCHARGE GAS
INLET
SAMPLE IN
(or blank)
EPC
HPM
CROSS
(ZX1)
HELIUM
PURIFIER
ELECTRONIC
PNEUMATIC
CONTROL
VICI
MINIATURE
HELIUM
PURIFER
(recommended)
VENT
Installation
DISCHARGE GAS
(99.999% He)
7
COLUMN
GAS CHROMATOGRAPH
Figure 4: Gas connections for a D-4-I-VA38-R system
Installing and Purging the Gas Regulator
1. Make sure the on/off valve on the helium cylinder is completely closed.
Screw the CGA fitting nut of the regulator into the helium cylinder . Go
beyond finger-tight, but do not tighten the n ut all the way – some leakage
is required for the purging operation.
2. Turn the output pressure regulating knob completely counterclockwise.
3. Open the cylinder on/off valve
4. Adjust the tightness of the regulator connecting nut to allow a pressure
reduction of ~690 kPa/sec (100 psi/sec). With a new bottle, the gauge
should start out at about 14 MPa (2000 psi).
5. When the pressure drops into the 1.4 - 3.4 MPa (200 - 500 psi) range,
open the cylinder on/off valve slightly and quic kly close it again.
6. Repeat Step 5 eight or ten times to be certain that all the air is purged.
On the final purge, tighten the regulator connecting nut very securely as
the pressure approaches the 2.1 - 3.4 MPa (300 - 500 psi) range.
slightly
and quickly close it again.
Page 10

Installation
8
7. Open the cylinder valve to pressurize the regulator once again. Close the
valve and observe the needle of the high pressure gauge f or 15 minutes.
If it doesn’t move, there is no critical leak on the high pressure side of the
regulator.
CAUTION: Never use leak detecting fluids on any part
of this system.
Installing and Purging the Helium Purifier
EZR21
1. If the pressure regulator has a 1/8"
the Valco 1/8" external to 1/16" internal reducer (EZR21); if it has a
1/4"
male
cone-type outlet port, install the V alco 1/4" e xternal to 1/16"
internal reducer (EZR41). For other regulator outlet fittings , a wide
variety of Valco adapters is availab le.
2. Remove the cap from the inlet tube of the Valco helium purifier and insert
the tube fitting into the 1/16" reducer port. (Keep the outlet tube capped.)
Use a 1/4" wrench to turn the nut one-quarter turn past the point where
the ferrule first starts to grab the tubing. Do not remov e the fitting. When
made up properly , it should be leak-tight.
3. Turn the output pressure regulating knob clockwise until the gauge
registers 345 KPA (50 psi).
4. Allow five minutes for equilibration, then turn the regulating knob all the
way counterclockwise .
5. Observe the needle of the output pressure gauge for 15 minutes. There
will be a slight initial drop, but if it doesn’t mo v e after that, consider that all
the connections are tight.
6. If necessary, use an electronic leak detector to locate any leaks. If a
leak detector is not availab le, tighten all the fittings (including the output
pressure guage), and repressurize the system for another test.
7. Upcap the outlet tube of the purifier and purge the system for
15 to 30 minutes at 60 - 80 mL/min to eliminate air from the purifier
getter material.
male
cone-type outlet port, install
Connecting the Discharge Gas to the Detector
1. If you are supplying the GC from the helium purifier, use the Valco
ZX1 cross. (The cross supplies an extra port for a blank helium run.)
Otherwise, use one of the Valco 1/16" unions (ZU1) to connect the
outlet tube of the purifier to the inlet of the supplied discharge gas
restrictor (TGA-R-35F80P).
2. Connect the outlet end of the restrictor to a flow measuring device. Adjust
the helium pressure to 80 psi to obtain a continuous flow of ~35 mL/min.
3. After setting the flow rate, connect the outlet of the restrictor to the
discharge gas inlet tube (labelled “INLET”) which comes out the side
of the detector.
Page 11

11.4 cm/
Capillary Column Connection
If the capillary column adapter is installed in the column inlet:
1. Make a mark on the column 11.4 cm from the end.
COLUMN
INLET
CAPILLARY
COLUMN
ADAPTER
(IZERA1.5)
COLUMN
FERRULE
NUT
CAPILLARY
COLUMN
2. Remove the knurled nut and plug from the capillary column adapter in the
column inlet at the bottom of the detector. Slide the nut over the end of
the column, followed b y the appropriate column ferrule (FS.4 or FS .5, or
ZF.5V for megabore).
3. Seat the ferrule in the detail of the column adapter and begin sliding the
column through the capillary column adapter and into the column inlet.
4. Get the nut started on the threads and tighten it until you feel it contact
the ferrule, then back off half a turn. Slide the column into the column
inlet until the mark is flush with the surface of the knurled nut, and secure
the column in the adapter by tightening the knurled nut
If the capillary column adapter has been removed, reinstall it:
1. Unscrew the liner as far as it will go, then screw the fitting body into the
column inlet fingertight.
Installation
finger tight only
9
.
9.8 cm/
2. While using a 1/8" wrench to prevent rotation of the liner (the part with the
seat for the column ferrule), use a 1/4" wrench to tighten the body of the
adapter until the ferrule has sealed. The liner
3. Proceed to Step 1 above.
Packed Column Connection
T o pre vent detector contamination, we strongly
recommend disconnecting the column from the
detector during column bakeout procedures.
COLUMN
INLET
The D4 is optimized for pack ed columns . The column tubing must be
thoroughly cleaned and baked before the column is pac ked. Even when
the best care is taken in column tubing cleaning and in the support and
stationary phase selection, a new column will often bleed compounds,
PACKED
COLUMN
ADAPTER
(I-23642-D4RU)
resulting in a considerable increase in the detector baseline. This initial
bleed will usually be reduced to acceptable levels after the column is
conditioned with clean carrier gas flow for sev er al hours at the
recommended bakeout temperature.
1. Loosen and remove the knurled nut and plug of the capillary column
adapter, (or remov e the column ferrule and the column if one has been
installed).
will deform
if it rotates.
PACKED
COLUMN
2. Use a 1/8" wrench to hold the liner – that part of the adapter in which the
column ferrule sits. While the 1/8" wrench k eeps the liner from rotating,
use a 1/4" wrench on the fitting body to loosen the adapter 1/2 turn.
Page 12

Installation
10
3. Set aside the 1/8" wrench and completely remove the adapter from the
column inlet.
4. Screw the packed column adapter into the column inlet by hand.
caution
, as the tip of the adapter is very fragile. Then tighten the adapter
with a 1/4" wrench, using an additional wrench on the flats of the column
inlet to support the detector.
5. Connect the 1/8" column to the packed column adapter with the EZRU21
reducing union supplied in the fittings kit.
Testing for Leaks
It is critical for the system to be leak-tight, and an additional check at this
point can save many headaches later on. To test for leaks:
1. Cap the tube and pressurize the entire system with helium to 138 kPa
(20 psi).
2. If the system does not hold pressure, check all the fittings with an
electronic helium leak detector. DO NOT use leak detecting liquids.
3. Tighten fittings as required.
Exercise
TO DETECTOR
PULSER MODULE
TO PUSH BUTTON
SWITCH
TO POWER BOARD
Figure 5: Mounting the pulser module in the pneumatics area of the GC
Page 13

SWITCH MOUNTING NUT
+
-
Pulser Module Installation
GREEN
BLACK
RED
RED
BLACK
BLACK
BLACK
BLACK
Figure 6: Pulser cable assembly
1. Mount the pulser module in the pneumatics area of the GC, using existing
slotted screw holes. (Figure 5)
2. Pow er to the pulser module is provided through cable assembly I-23628.
Drill a 12.0 mm diameter hole in the front panel of the GC to mount the
on/off switch.
3. Unscrew the switch mounting nut and remove it from the cable assembly
by sliding it over all the wiring.
Installation
11
PIN 3
PIN 4
PIN 2
PIN 1
4. Feed the wiring through the 12 mm hole from the front of the GC until the
threaded portion of the switch follows the wiring through the mounting hole.
5. Slide the switch mounting nut back over all the wiring, and tighten the nut
onto the threads.
6. Install the 4-pin connector by
inserting Pins 1-4 of the cable
assembly into the connector as
shown in Figures 6 and 7. (Once a
pin is snapped into the connector,
BLACK 4
BLACK 2
3 GREEN
1 BLACK
Figure 7: 4-pin connector
it cannot be removed.)
7. Plug the 4-pin connector into the pulser module.
8. Figure 8 is a schematic of a portion of the V arian GC pow er board.
Connect the red wire (+) of the I-23628 cable to pin 14 of “External
Events” connector J43, and the black wire (-) to pin 13.
J42
12345678
9 1011121314
J43
EXTERNAL
91011121314
BLACK
RED
EVENTS
CHASSIS FAN
JACK
TRANSFORMER
HARNESS JACK
JACK
MAIN POWER
COLUMN OVEN
HEATER JACK
Figure 8: Connections f or 24 VDC for the pulser module
Page 14

Installation
12
Detector Electrical Connections
CAUTION: Do not use a wrench to tighten the SMC
connectors on the bias and electrometer cables.
Connections should be finger tight only.
1. Referring to Figure 9 as necessary, connect the BIAS cable to the top
electrode and the electrometer cable (ELECT) to the bottom electrode.
2. Connect the high-voltage cable from the detector to the pulse supply.
3. Connect the heater cable from the detector to the power board.
(Figure 8)
BIAS CABLE
P/N: I-23404-1
PUSH BUTTON
SWITCH
PULSER CABLE
PULSER
MODULE
P/N: I-23628
ELECTROMETER CABLE
P/N: I-23230
VARIAN
HEATER CABLE
ELECTROMETER
VARIAN
POWER
BOARD
Figure 9: Schematic of electrical connections
VARIAN
BOARD
Page 15

Initial Power-Up
1. Set the discharge gas flow as specified in Figure 4 on page 7.
2. Apply power to the helium purifier.
3. Turn on the pulser with the toggle switch. The discharge should start
within five minutes. (Once a system has been up and running, the discharge will start within a few seconds.) In a clean system the discharge
will have a peach/pink color. A purple discharge is an indication of
impurities and/or leaks in the discharge gas stream.
4. Set the desired detector temperature.
5. Check the detector standing/background current. For optimum performance, detector background current should be < 10 mV. The initial value
may be higher , b ut as the system bak es out at its operating temper ature ,
the background current should decrease to the optimum v alue.
Installation
13
CAUTION: Always make sure that discharge gas is
flowing before powering up the detector.
If the standing current reaches an acceptable lev el, the detector is ready
for use. Follow the Varian instruction manual for operation as an FID .
Troubleshooting High Background Current
If the background current does not drop below 50 mV e v en after a 12 hour
bakeout, there is either a leak in the system or the column effluent is not
clean. To see if the high background current is due to the column:
1. With a capillary column:
Loosen the knurled nut and pull the column out ~20 mm. Secure the n ut.
With a packed column:
Completely disconnect the column from the column inlet tube, leaving the
inlet open.
2. Watch the detector standing/backg round current.
If the current remains high:
Either the system has a leak in the discharge gas supply line or the
discharge gas has impurities in it. Re vie w “T esting for Leaks” on page 10.
If the current decreases dramatically:
Either the carrier gas supply has leaks and/or contaminants, or the
column is the source of contamination and needs a bakeout.
Page 16

14
Mode Selection and Setup
Helium Ionization Mode
If the instructions of Step 1 at the top of page 9 were properly executed,
the column should already be properly positioned. Since there ma y be
some variation in the flow rate f or the diff erent types of capillary columns, the
user may want to optimize the column position within this suggested r ange.
DO NOT insert the column more than 11.6 cm.
With this flow configuration, only pure helium passes through the discharge
region, minimizing the chance of discharge electrode contamination through
contact with the eluting sample. How e ver, if very high concentrations of
organic compounds are introduced for extended periods of time, the y could
diffuse into the discharge region and contaminate the electrodes. Under
normal chromatographic use with capillary columns, such contamination is
negligible even o v er extended periods.
Selective Photoionization Mode
Since the pulsed discharge detector is essentially a windowless helium
photoionization detector, changing the discharge gas from pure helium
to helium doped with argon, krypton, or xenon changes the discharge
emission profile. This results in a change in the photon energy due to
additional resonance atomic emissions and diatomic emissions from the
rare gas added. Thus a single detector can be operated in any of the
three photoionization detector (PID) modes: Ar-, Kr-, or Xe-PID.
Doped helium is used rather than other pure gases in order to retain the
benefits of the helium: namely, its transparency for Ar, Kr, an Xe resonance
radiation and its efficient cooling of the electrodes. An y prob lems associated
with the presence of a window between the photon source and the ionization
chamber are eliminated. In most applications in v olving current commercial
PIDs, analyte condensation and decomposition on the window attenuate the
lamp energy , necessitating frequent cleaning and recalibr ation.
Custom gas blends for the pulsed discharge detector are a v ailab le from
leading gas suppliers at special prices. Alternatively, they ma y be f ormulated on the spot by using appropriate fixed restrictors to mix appropriate
amounts of pure helium and pure dopant through a tee. Since all gas
streams must pass through a Valco purifier, the second option requires
an additional purifier for each dopant. This may still be more cost effective
than requesting a custom blend of the more expensiv e Kr or Xe; since the
typical flow rate required for the pure dopant rare gas is about 0 . 3 - 1 mL/min,
a small lecture bottle can last for a long time. In either case, the total discharge gas flow rate should be the same as specified in “Gas Connections”
on page 7.
Page 17

Mode Selection and Setup
Ar-PDPID
Changing the discharge gas from helium to a mixture of 2% argon in
helium changes the photon energy level from the 17 - 13.5 eV r ange to the
11.8 - 9.8 eV range. The argon emission consists of resonance radiation
at 11.8 eV and 11.6 eV and the diatomic Ar2 emission in the range of
9.2 - 10.3 eV. Except for fixed gases and a few organic compounds like
CH4 (IP = 12.5 eV), CH3CN (IP = 12.2 eV) and some fluro-chloro hydrocarbons, the majority of organic compounds have ionization potentials
lower than 11.8 eV. Thus the Ar-PDPID is nearly universal, like the flame
ionization detector, b ut without the risks associated with the presence of
an open flame and hydrogen.
Kr-PDPID
The recommended proportion is 1.4% Kr in He as the discharge gas.
The krypton emission consists principally of resonance lines at 10.6 eV
and 10.1 eV. The Kr-PDPID can detect compounds with IP < 10.6 eV ,
which includes unsaturated and cyclic hydrocarbons, alcohols, aldeh ydes ,
organic acids, esters, etc.
15
Xe-PDPID
The recommended proportion is 0.8% Xe in He as the discharge gas. The
xenon emission consists principally of resonance lines at 9.6 eV and 8.4 eV,
and can detect compounds with IP < 9.6, like aromatics, ethers, alcohols ,
aldehydes, etc.
In addition to the specific compounds named in the three paragraphs
above, certain important inorganic compounds like ammonia, hydrogen
peroxide, arsenic trichloride, h ydrogen sulfide, arsine, phosphine , nitric
oxide, carbon disulfide etc. can be selectively detected using the
appropriate photoionization mode.
Each dopant gas requires an additional helium purifier, which must be
purged and conditioned in the same manner as the purifier installed on
the discharge gas supply. If you are using more than one dopant, we
recommend use of a Valco multiposition stream selection valve so that no
fittings have to be disconnected. Not only is this convenient, it keeps the
system closed, minimizing chances of contamination. When changing from
one dopant to another, allo w at least one hour f or the old gas to be purged
from the system.
Page 18

16
Warranty
This Limited W arranty giv es the Buy er specific legal rights, and a Buy er
may also hav e other rights that vary from state to state. For a period of 365
calendar days from the date of shipment, Valco Instruments Company , Inc.
(hereinafter Seller) warrants the goods to be free from defect in material
and workmanship to the original purchaser. During the warranty period,
Seller agrees to repair or replace defective and/or nonconforming goods or
parts without charge for material or labor, or, at the Seller’s option, demand
return of the goods and tender repayment of the price. Buyer’s exclusive
remedy is repair or replacement of defective and nonconforming goods, or,
at Seller’s option, the repayment of the price.
Seller excludes and disclaims any liability for lost profits, personal
injury, interruption of service, or for consequential incidental or
special damages arising out of, resuiting from, or relating in any
manner to these goods
This Limited Warranty does not cover defects, damage, or nonconfor mity
resulting from abuse, misuse, neglect, lack of reasonable care, modification,
or the attachment of improper devices to the goods. This Limited Warranty
does not cover expendable items. This warranty is VOID when repairs are
performed by a nonauthorized service center or representative. For information about authorized service centers or representatives, write Customer
Repairs, Valco Instruments Company, Inc, P.O . Box 55603, Houston, Te xas
77255, or phone (713) 688-9345. At Seller’s option, repairs or replacements
will be made on site or at the factory. If repairs or replacements are to be
made at the factory, Buyer shall return the goods prepaid and bear all the
risks of loss until delivered to the factory. If Seller returns the goods, they
will be delivered prepaid and Seller will bear all risks of loss until delivery to
Buyer. Buyer and Seller agree that this Limited Warranty shall be governed
by and construed in accordance with the laws of the State of Texas.
The warranties contained in this agreement are in lieu of all
other warranties expressed or implied, including the warranties
of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose.
This Limited W arranty supercedes all prior proposals or representations oral
or written and constitutes the entire understanding regarding the warranties
made by Seller to Buyer. This Limited Warranty may not be expanded or
modified except in writing signed by the parties hereto.
 Loading...
Loading...