Page 1

Data Sheet
VT82C686B
South Bridge
Revision 2.37
November 10, 2004
VIA TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Page 2
Copyright Notice:
Copyright © 2000 - 2004 VIA Technologies, Incorporated. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
No part of this document may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into
any language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or otherwise
without the prior written permission of VIA Technologies Incorporated.
VT82C686A, VT82C686B and Super South may only be used to identify products of VIA Technologies, Inc.
ia a registered trademark of VIA Technologies, Incorporated.
TM
PS/2
Pentium
Corporation.
Windows 95
Corporation.
PCI
All trademarks are the properties of their respective owners.
is a registered trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
TM
, Pentium-ProTM, Pentium-IITM, Pentium-IIITM, CeleronTM, and GTL+TM are registered trademarks of Intel
TM
, Windows 98TM, Windows NTTM, and Plug and PlayTM are registered trademarks of Microsoft
TM
is a registered trademark of the PCI Special Interest Group.
Disclaimer Notice:
No license is granted, implied or otherwise, under any patent or patent rights of VIA Technologies. VIA Technologies
makes no warranties, implied or otherwise, in regard to this document and to the products described in this document.
The information provided by this document is believed to be accurate and reliable as of the publication date of this
document. However, VIA Technologies assumes no responsibility for any errors in this document. Furthermore, VIA
Technologies assumes no responsibility for the use or misuse of the information in this document and for any patent
infringements that may arise from the use of this document. The information and product specifications within this
document are subject to change at any time, without notice and without obligation to notify any person of such change.
Offices:
USA Office: Taipei Office:
940 Mission Court 1th Floor, No. 529
Fremont, CA 94539 Chung-Cheng Road, Hsin-Tien
USA Taipei, Taiwan ROC
Tel: (510) 683-3300 Tel: (886-2) 218-5452
Fax: (510) 683-3301 or (510) 687-4654 Fax: (886-2) 218-5453
Web: http://www.viatech.com
Web: http://www.via.com.tw
Page 3
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
REVISION HISTORY
Document Release Date Revision Initials
1.72 6/15/00 Fixed SA pin description; fixed 686B part # in figures 1 & 7
Added 1.5V interface note to FERR# and APCD1-0
Removed RTC ports 72-73 and Rx75[6] (and fixed GPO6 description)
Fixed Func 1 Rx45[5-4] & default, PM I/O Rx20-25[5], 2A[10]
Added Func 2/3/4 Rx6[4]/Rx34, F4Rx68-6F power management capabilities
Added Func 4 SMB I/O Rx54, 90-93, D2-D6 and Func 5/6 Rx48[3]
Fixed mechanical drawing for proper orientation of marking relative to pin 1
1.8 8/1/00 Removed Super-I/O “high speed baud rate support”
Fixed VREF pin direction and voltage, Added F4 Rx55[3]
Removed ambient temp spec and added max power dissipation
1.9 12/8/00 Changed GPOWE# pin name to GPOWE; Updated VCCH/GNDH descriptions
Function 0 – Added Rx34 Capability Pointer, added note to Rx43
Function 1 – Fixed default values of Rx40, 41, 45, 54; Changed Rx4[7,1], 6[4],
10[2-0], 14[1-0], 18[2-0], 1C[1-0], 20[3-0], 40[3-2], 42[7-6], 44[7], 45[5]
Function 4 – Removed incorrect notes from Rx54[3-2]
1.91 1/2/01 Fixed typo in table of contents, Fixed Function 1 Rx43[3-0], 45[2] DH
1.92 2/2/01 Added EXTSMI#, ACSDIN, ACSDIN2 to suspend power; Fixed PMIO Rx10[10] DH
1.93 3/2/01 Removed ATEST/DTEST; Fixed F4 Rx4C[0] & PMIO Rx10[9], 2C[3] DH
2.0 3/19/01 Removed incorrect SMBus I/O Rx93-90 & D2-D6 and fixed reg summary table
Fixed SMB RxD2[1-0] bit descriptions
2.1 4/27/01 Removed temp sensor 3 (HWM Rx42[7],44[7-6],49[7-6],4B[5-4], & I/O Rx1D-1F) DH
2.2 7/2/01 Updated company address; Added changes for chip version “CE”
Updated F0Rx46[2],49[7],84[4]; F4Rx4C[1],55[3],57[1]; PMIO Rx20[7-6,4-2]
2.21 10/17/01 Added SuperIO Config RxD0-DB; Function 5 IO Base 3 Rx0-FF
Moved SB/Game port reg summary tables after other legacy regs
Added APIC reg summary table; Fixed F0 Rx46[2], 58, PMIO Rx20/22/24[2]
Moved APIC regs to before PCI config I/O, fixed Rx1, added Rx3
2.22 2/12/02 Updated logos and formatting; Fixed PMIO Rx21-20[7] DH
2.23 2/13/02 Fixed mech diagram & regenerated pdf to fix printing bug; changed page header DH
2.24 3/11/02 Updated Function 0 Rx5A[3] DH
2.25 12/19/02 Updated VIA logos on cover and page headers
Updated Port 61 (bits 7-6 and 3-2), Port 92 (bits 7-6 and 3), and Func 1 Rx54[1]
2.26 2/3/03 Updated VIA USA street address; Removed Function 0 Rx5A[3] DH
2.27 4/8/03 Fixed IDE Interrupt Pin default (Function 1 Rx3D)
Fixed incorrect JEDEC-specification reference in mechanical spec
2.28 6/9/03 Updated Func 0 Rx76[3], Func 4 Rx41[1], 4C[7-4], 4D[6-4], PMIO Rx10[3-0] DH
2.29 9/5/03 Re-added RTC ports 72-73 and updated PCI Function 0 Rx58[7] and 5B[1] AL
2.30 9/9/03 Fixed typographical errors and updated Function 0 Rx5B[1] AL
2.31 12/3/03
2.32 12/30/03 Updated pin description DRQ2 and DACK2# VL
2.33 3/26/04 Removed Power Characteristics in Electrical Spec section VL
2.34 7/9/04 Added lead-free package to mechanical specification section VL
2.35 8/17/04 Updated lead free package in mechanical specification section VL
2.36 10/06/04 Updated bit definition for Function 0 Rx85[5] and Function 4 Rx40[5]
2.37 11/10/04 Updated Rx69-68[1:0] bit definition VL
Removed FDCIRQ and FDCDRQ signals in pin G5, H3 and G1
Updated Miscellaneous / General Purpose IO Rx75[3]
Updated top marking in mechanical specification
Added Function 4 PMIO Rx5A-54
DH
DH
DH
DH
DH
DH
DH
DH
VL
VL
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -i- Revision History
Page 4

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
TABLE OF CONTENTS
REVISION HISTORY .......................................................................................................................................................................I
TABLE OF CONTENTS.................................................................................................................................................................. II
LIST OF FIGURES .........................................................................................................................................................................IV
LIST OF TABLES ...........................................................................................................................................................................IV
PRODUCT FEATURES ................................................................................................................................................................... 1
OVERVIEW....................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
PINOUTS............................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
PIN DIAGRAM ................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
PIN LISTS ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
PIN DESCRIPTIONS......................................................................................................................................................................... 9
REGISTERS..................................................................................................................................................................................... 27
REGISTER OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................................................. 27
REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS............................................................................................................................................................ 39
Legacy I/O Ports ................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Keyboard Controller Registers .............................................................................................................................................................. 40
DMA Controller I/O Registers .............................................................................................................................................................. 42
Interrupt Controller Registers................................................................................................................................................................ 43
Timer / Counter Registers .....................................................................................................................................................................43
CMOS / RTC Registers......................................................................................................................................................................... 44
Super-I/O Configuration Index / Data Registers............................................................................................................... 45
Keyboard / Mouse Controller Configuration Registers.................................................................................................... 45
Super-I/O Configuration Registers..................................................................................................................................... 46
Super-I/O I/O Ports.............................................................................................................................................................. 48
Floppy Disk Controller Registers .......................................................................................................................................................... 48
Parallel Port Registers ........................................................................................................................................................................... 49
Serial Port 1 Registers ........................................................................................................................................................................... 50
Serial Port 2 Registers ........................................................................................................................................................................... 51
SoundBlaster Pro Port Registers......................................................................................................................................... 52
FM Registers ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 52
Mixer Registers ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 52
Sound Processor Registers .................................................................................................................................................................... 52
Game Port Registers............................................................................................................................................................. 53
APIC Registers...................................................................................................................................................................... 54
Memory Mapped I/O APIC Registers ................................................................................................................................................... 54
Indexed I/O APIC 32-Bit Registers....................................................................................................................................................... 54
PCI Configuration Space I/O .............................................................................................................................................. 56
Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge .......................................................................................................................... 57
PCI Configuration Space Header ..........................................................................................................................................................57
ISA Bus Control .................................................................................................................................................................................... 57
Plug and Play Control............................................................................................................................................................................ 61
Distributed DMA / Serial IRQ Control .................................................................................................................................................63
Miscellaneous / General Purpose I/O .................................................................................................................................................... 64
Function 1 Registers - Enhanced IDE Controller.............................................................................................................. 70
PCI Configuration Space Header ..........................................................................................................................................................70
IDE-Controller-Specific Confiiguration Registers ................................................................................................................................ 72
IDE I/O Registers .................................................................................................................................................................................. 75
Function 2 Registers - USB Controller Ports 0-1............................................................................................................... 76
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -ii- Table of Contents
Page 5

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
PCI Configuration Space Header ..........................................................................................................................................................76
USB-Specific Configuration Registers.................................................................................................................................................. 77
USB I/O Registers................................................................................................................................................................................. 78
Function 3 Registers - USB Controller Ports 2-3............................................................................................................... 79
PCI Configuration Space Header ..........................................................................................................................................................79
USB-Specific Configuration Registers.................................................................................................................................................. 80
USB I/O Registers................................................................................................................................................................................. 81
Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM ............................................................................................. 82
PCI Configuration Space Header ..........................................................................................................................................................82
Power Management-Specific PCI Configuration Registers................................................................................................................... 83
Hardware-Monitor-Specific Configuration Registers............................................................................................................................ 90
System Management Bus-Specific Configuration Registers................................................................................................................. 90
Power Management I/O-Space Registers .............................................................................................................................................. 91
System Management Bus I/O-Space Registers ...................................................................................................................................100
Hardware Monitor I/O Space Registers............................................................................................................................................... 103
Function 5 & 6 Registers - AC97 Audio & Modem Codecs............................................................................................ 107
PCI Configuration Space Header – Function 5 Audio......................................................................................................................... 107
PCI Configuration Space Header – Function 6 Modem ...................................................................................................................... 108
Function 5 & 6 Codec-Specific Configuration Registers .................................................................................................................... 109
I/O Base 0 Registers –Audio/Modem Scatter/Gather DMA................................................................................................................ 111
I/O Base 1 Registers – Audio FM NMI Status Registers ....................................................................................................................115
I/O Base 2 Registers – MIDI / Game Port........................................................................................................................................... 115
I/O Base 3 Registers – Codec Register Shadow.................................................................................................................................. 115
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTIONS................................................................................................................................................ 116
POWER MANAGEMENT.............................................................................................................................................................. 116
Power Management Subsystem Overview.......................................................................................................................................... 116
Processor Bus States............................................................................................................................................................................ 116
System Suspend States and Power Plane Control ...............................................................................................................................117
General Purpose I/O Ports................................................................................................................................................................... 117
Power Management Events ................................................................................................................................................................. 118
System and Processor Resume Events ................................................................................................................................................118
Legacy Power Management Timers.................................................................................................................................................... 119
System Primary and Secondary Events ............................................................................................................................................... 119
Peripheral Events................................................................................................................................................................................. 119
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................................................................................ 120
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS ............................................................................................................................................... 120
DC CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................................................................................................................. 120
PACKAGE MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS...................................................................................................................... 121
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -iii- Table of Contents
Page 6

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
LIST OF FIGURES
FIGURE 1. PC SYSTEM CONFIGURATION USING THE VT82C686B ................................................................................ 5
FIGURE 2. VT82C686B BALL DIAGRAM (TOP VIEW) .......................................................................................................... 6
FIGURE 3. VT82C686B PIN LIST (NUMERICAL ORDER)..................................................................................................... 7
FIGURE 4. VT82C686B PIN LIST (ALPHABETICAL ORDER) .............................................................................................. 8
FIGURE 5. STRAP OPTION CIRCUIT...................................................................................................................................... 62
FIGURE 6. POWER MANAGEMENT SUBSYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM ........................................................................ 116
FIGURE 8. MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS – 352 PIN BALL GRID ARRAY PACKAGE........................................ 121
FIGURE 9. LEAD-FREE MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS – 352 PIN BALL GRID ARRAY PACKAGE................ 122
LIST OF TABLES
TABLE 1. PIN DESCRIPTIONS .................................................................................................................................................... 9
TABLE 2. SYSTEM I/O MAP....................................................................................................................................................... 27
TABLE 3. REGISTERS ................................................................................................................................................................. 28
TABLE 4. KEYBOARD CONTROLLER COMMAND CODES.............................................................................................. 41
TABLE 5. CMOS REGISTER SUMMARY ................................................................................................................................ 44
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -iv- Table of Contents
Page 7

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
VT82C686B PSIPC
PCI SUPER-I/O INTEGRATED PERIPHERAL CONTROLLER
PC99 COMPLIANT PCI-TO-ISA BRIDGE
WITH INTEGRATED SUPER-I/O (FDC, LPT, COM1/2, AND IR),
I
NTEGRATED HARDWARE SOUNDBLASTER/DIRECT SOUND AC97 AUDIO,
U
LTRADMA-33/66/100 MASTER MODE PCI-EIDE CONTROLLER,
USB C
D
ACPI, E
T
EMPERATURE, VOLTAGE, AND FAN-SPEED MONITORING
PRODUCT FEATURES
• Inter-operable with VIA and other Host-to-PCI Bridges
− Combine with VT82C598 for a complete Super-7 (66/75/83/100MHz) PCI / AGP / ISA system (Apollo MVP3)
− Combine with VT8501 for a complete Super-7 system with integrated 2D / 3D graphics (Apollo MVP4)
− Combine with VT82C693 for a complete 66 / 100 / 133 MHz Socket-370 or Slot-1 system (Apollo Pro133)
− Combine with VT8601 for a complete 66 / 100 / 133 MHz Socket-370 or Slot-1 system with integrated 2D / 3D
graphics (Apollo ProMedia)
− Inter-operable with Intel or other Host-to-PCI bridges for a complete PC99 compliant PCI / AGP / ISA system
• PCI to ISA Bridge
− Integrated ISA Bus Controller with integrated DMA, timer, and interrupt controller
− Integrated Keyboard Controller with PS2 mouse support
− Integrated DS12885-style Real Time Clock with extended 256 byte CMOS RAM and Day/Month Alarm for ACPI
− Integrated USB Controller with root hub and four function ports
− Integrated UltraDMA-33/66/100 master mode EIDE controller with enhanced PCI bus commands
− PCI-2.2 compliant with delay transaction and remote power management
− Eight double-word line buffer between PCI and ISA bus
− One level of PCI to ISA post-write buffer
− Supports type F DMA transfers
− Distributed DMA support for ISA legacy DMA across the PCI bus
− Serial interrupt for docking and non-docking applications
− Fast reset and Gate A20 operation
− Edge trigger or level sensitive interrupt
− Flash EPROM, 4Mb EPROM and combined BIOS support
− Supports positive and subtractive decoding
ONTROLLER, KEYBOARD CONTROLLER, RTC,
ISTRIBUTED DMA, SERIAL IRQ, PLUG AND PLAY,
NHANCED POWER MANAGEMENT, SMBUS, AND
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -1- Product Features
Page 8

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
• UltraDMA-100 / 66 / 33 Master Mode PCI EIDE Controller
− Dual channel master mode PCI supporting four Enhanced IDE devices
− Transfer rate up to 33MB/sec to cover PIO mode 4, multi-word DMA mode 2 drives, and UltraDMA-33 interface
− Increased reliability using UltraDMA-66 transfer protocols
− Increased performance using UltraDMA-100 mode 5
− Thirty-two levels (doublewords) of prefetch and write buffers
− Dual DMA engine for concurrent dual channel operation
− Bus master programming interface for SFF-8038I rev.1.0 and Windows-95 compliant
− Full scatter gather capability
− Support ATAPI compliant devices including DVD devices
− Support PCI native and ATA compatibility modes
− Complete software driver support
• Integrated Super IO Controller
− Supports 2 serial ports, IR port, parallel port, and floppy disk controller functions
− Two UARTs for Complete Serial Ports
− Programmable character lengths (5,6,7,8)
− Even, odd, stick or no parity bit generation and detection
− Programmable baud rate generator
− Independent transmit/receiver FIFOs
− Modem Control
− Plug and play with 96 base IO address and 12 IRQ options
− Infrared-IrDA (HPSIR) and ASK (Amplitude Shift Keyed) IR port multiplexed on COM2
− Multi-mode parallel port
− Standard mode, ECP and EPP support
− Plug and play with 192 base IO address, 12 IRQ and 4 DMA options
− Floppy Disk Controller
− 16 bytes of FIFO
− Data rates up to 1Mbps
− Perpendicular recording driver support
− Two FDDs with drive swap support
− Plug and play with 48 base IO address, 12 IRQ and 4 DMA options
• SoundBlaster Pro Hardware and Direct Sound Ready AC97 Digital Audio Controller
− Dual full-duplex Direct Sound channels between system memory and AC97 link
− PCI master interface with scatter / gather and bursting capability
− 32 byte FIFO of each direct sound channel
− Host based sample rate converter and mixer
− Standard v1.0 or v2.0 AC97 Codec interface for single or cascaded AC97 Codec’s from multiple vendors
− Loopback capability for re-directing mixed audio streams into USB and 1394 speakers
− Hardware SoundBlaster Pro for Windows DOS box and real-mode DOS legacy compatibility
− Plug and play with 4 IRQ, 4 DMA, and 4 I/O space options for SoundBlaster Pro and MIDI hardware
− Hardware assisted FM synthesis for legacy compatibility
− Direct two game ports and one MIDI port interface
− Complete software driver support for Windows-95/98/2000 and Windows-NT
• Voltage, Temperature, Fan Speed Monitor and Controller
− Five positive voltage (one internal), three temperature (one internal) and two fan-speed monitoring
− Programmable control, status, monitor and alarm for flexible desktop management
− External thermister or internal bandgap temperature sensing
− Automatic clock throttling with integrated temperature sensing
− Internal core VCC voltage sensing
− Flexible external voltage sensing arrangement (any positive supply and battery)
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -2- Product Features
Page 9

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
• Universal Serial Bus Controller
− USB v.1.1 and Intel Universal HCI v.1.1 compatible
− Eighteen level (doublewords) data FIFO with full scatter and gather capability
− Root hub and four function ports
− Integrated physical layer transceivers with optional over-current detection status on USB inputs
− Legacy keyboard and PS/2 mouse support
• System Management Bus Interface
Host interface for processor communications
−
− Slave interface for external SMBus masters
• Sophisticated PC99-Compatible Mobile Power Management
− Supports both ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) and legacy (APM) power management
− ACPI v1.0 Compliant
− APM v1.2 Compliant
− CPU clock throttling and clock stop control for complete ACPI C0 to C3 state support
− PCI bus clock run, Power Management Enable (PME) control, and PCI/CPU clock generator stop control
− Supports multiple system suspend types: power-on suspends with flexible CPU/PCI bus reset options,
suspend to DRAM, and suspend to disk (soft-off), all with hardware automatic wake-up
− Multiple suspend power plane controls and suspend status indicators
− One idle timer, one peripheral timer and one general purpose timer, plus 24/32-bit ACPI compliant timer
− Normal, doze, sleep, suspend and conserve modes
− Global and local device power control
− System event monitoring with two event classes
− Primary and secondary interrupt differentiation for individual channels
− Dedicated input pins for power and sleep buttons, external modem ring indicator, and notebook lid open/close for
system wake-up
− Up to 12 general purpose input ports and 23 output ports
− Multiple internal and external SMI sources for flexible power management models
− One programmable chip select and one microcontroller chip select
− Enhanced integrated real time clock (RTC) with date alarm, month alarm, and century field
− Thermal alarm on either external or any combination of three internal temperature sensing circuits
− Hot docking support
− I/O pad leakage control
• Plug and Play Controller
− PCI interrupts steerable to any interrupt channel
− Steerable interrupts for integrated peripheral controllers: USB, floppy, serial, parallel, audio, soundblaster, MIDI
− Steerable DMA channels for integrated floppy, parallel, and soundblaster pro controllers
− One additional steerable interrupt channel for on-board plug and play devices
− Microsoft Windows 98
TM
, Windows NTTM, Windows 95
TM
and plug and play BIOS compliant
• Integrated I/O APIC (Advanced Peripheral Interrupt Controller)
• Built-in NAND-tree pin scan test capability
• 0.35um, 3.3V, low power CMOS process
• Single chip 27x27 mm, 352 pin BGA
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -3- Product Features
Page 10

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
OVERVIEW
The VT82C686B PSIPC (PCI Super-I/O Integrated Peripheral Controller) is a high integration, high performance, power-efficient,
and high compatibility device that supports Intel and non-Intel based processor to PCI bus bridge functionality to make a complete
Microsoft PC99-compliant PCI/ISA system. In addition to complete ISA extension bus functionality, the VT82C686B includes
standard intelligent peripheral controllers:
a) Master mode enhanced IDE controller with dual channel DMA engine and interlaced dual channel commands. Dedicated
FIFO coupled with scatter and gather master mode operation allows high performance transfers between PCI and IDE
devices. In addition to standard PIO and DMA mode operation, the VT82C686B also supports the UltraDMA-33 standard
to allow reliable data transfer rates up to 33MB/sec throughput. The VT82C686B also supports the UltraDMA-66 and
UltraDMA-100 (ATA-100) standards. The IDE controller is SFF-8038I v1.0 and Microsoft Windows-family compliant.
b) Universal Serial Bus controller that is USB v1.1 and Universal HCI v1.1 compliant. The VT82C686B includes the root hub
with four function ports with integrated physical layer transceivers. The USB controller allows hot plug and play and
isochronous peripherals to be inserted into the system with universal driver support. The controller also implements legacy
keyboard and mouse support so that legacy software can run transparently in a non-USB-aware operating system
environment.
c) Keyboard controller with PS2 mouse support.
d) Real Time Clock with 256 byte extended CMOS. In addition to the standard ISA RTC functionality, the integrated RTC
also includes the date alarm, century field, and other enhancements for compatibility with the ACPI standard.
e) Notebook-class power management functionality compliant with ACPI and legacy APM requirements. Multiple sleep states
(power-on suspend, suspend-to-DRAM, and suspend-to-Disk) are supported with hardware automatic wake-up. Additional
functionality includes event monitoring, CPU clock throttling and stop (Intel processor protocol), PCI bus clock stop control,
modular power, clock and leakage control, hardware-based and software-based event handling, general purpose I/O, chip
select and external SMI.
f) Hardware monitoring subsystem for managing system / motherboard voltage levels, temperatures, and fan speeds
g) Full System Management Bus (SMBus) interface.
h) Two 16550-compatible serial I/O ports with infrared communications port option on the second port.
i) Integrated PCI-mastering dual full-duplex direct-sound AC97-link-compatible sound system. Hardware soundblaster-pro
and hardware-assisted FM blocks are included for Windows DOS box and real-mode DOS compatibility. Loopback
capability is also implemented for directing mixed audio streams into USB and 1394 speakers for high quality digital audio.
j) Two game ports and one MIDI port
k) ECP/EPP-capable parallel port
l) Standard floppy disk drive interface
m) Distributed DMA capability for support of ISA legacy DMA over the PCI bus. Serial IRQ is also supported for docking and
non-docking applications.
n) Plug and Play controller that allows complete steerability of all PCI interrupts and internal interrupts / DMA channels to any
interrupt channel. One additional steerable interrupt channel is provided to allow plug and play and reconfigurability of onboard peripherals for Windows family compliance.
o) Internal I/O APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller)
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -4- Overview
Page 11
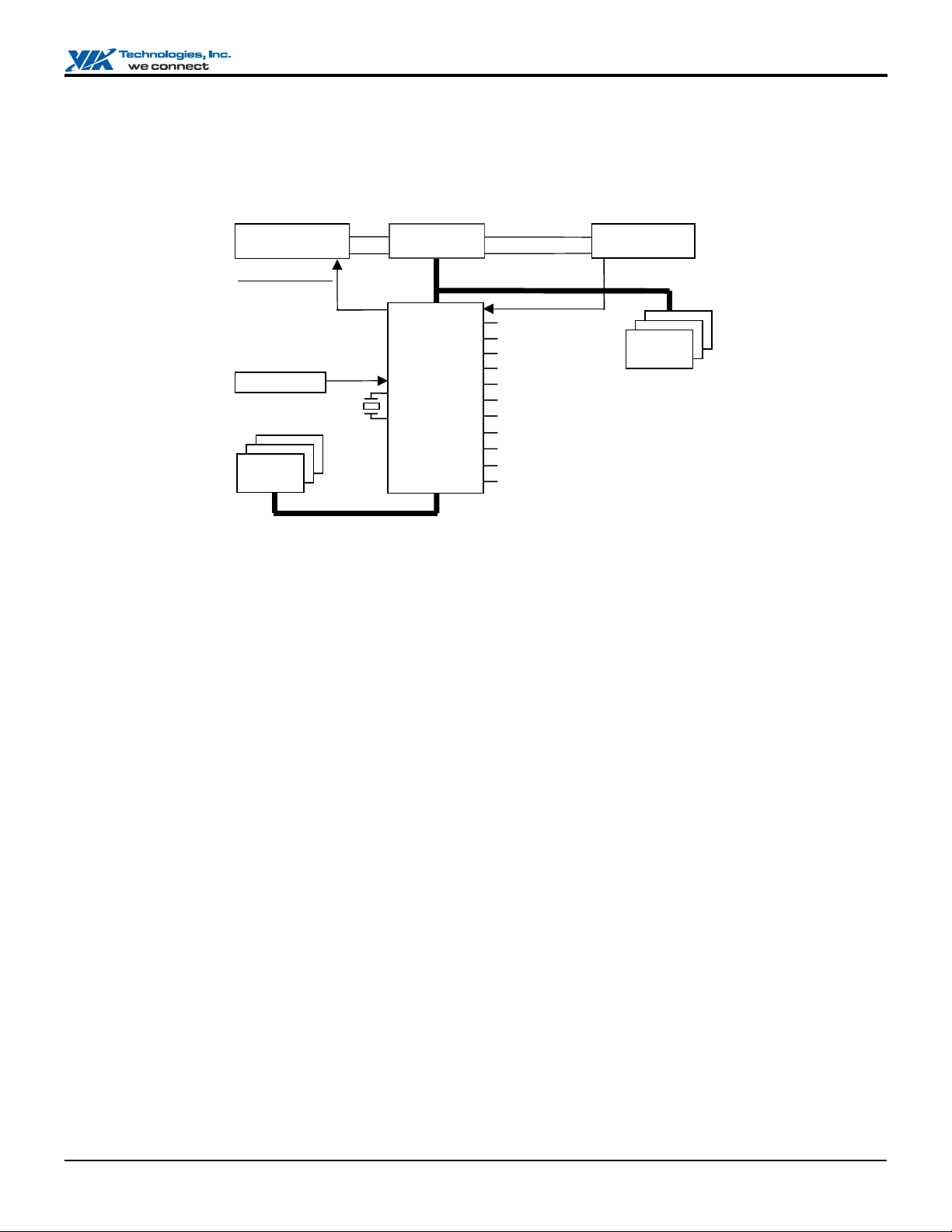
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
(
)
The VT82C686B also enhances the functionality of the standard ISA peripherals. The integrated interrupt controller supports
both edge and level triggered interrupts channel by channel. The integrated DMA controller supports type F DMA in addition to
standard ISA DMA modes. Compliant with the PCI-2.2 specification, the VT82C686B supports delayed transactions and remote
power management so that slower ISA peripherals do not block the traffic of the PCI bus. Special circuitry is built in to allow
concurrent operation without causing dead lock even in a PCI-to-PCI bridge environment. The chip also includes eight levels
(doublewords) of line buffers from the PCI bus to the ISA bus to further enhance overall system performance.
CPU / Cache
Sideband Signals:
Init / CPUreset
IRQ / NMI
SMI / StopClk
FERR / IGNNE
Slot-1
SLP#
Boot ROM
Expansion
Cards
RTC
Crystal
ISA
CA
CD
North Bridge
VT82C686B
352 BGA
MA/Command
MD
PCI
SMB
USB Ports 0-3
Keyboard / Mouse
MIDI / Game Ports
Parallel Port
Serial Ports 1 and 2
Infrared Comm Port
IDE Primary and Secondary
Floppy Disk Interface
AC97 Link
Hardware Monitor Inputs
GPIO, Power Control, Reset
System Memory
DIMM Module ID
Expansion
Cards
Figure 1. PC System Configuration Using the VT82C686B
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -5- Overview
Page 12
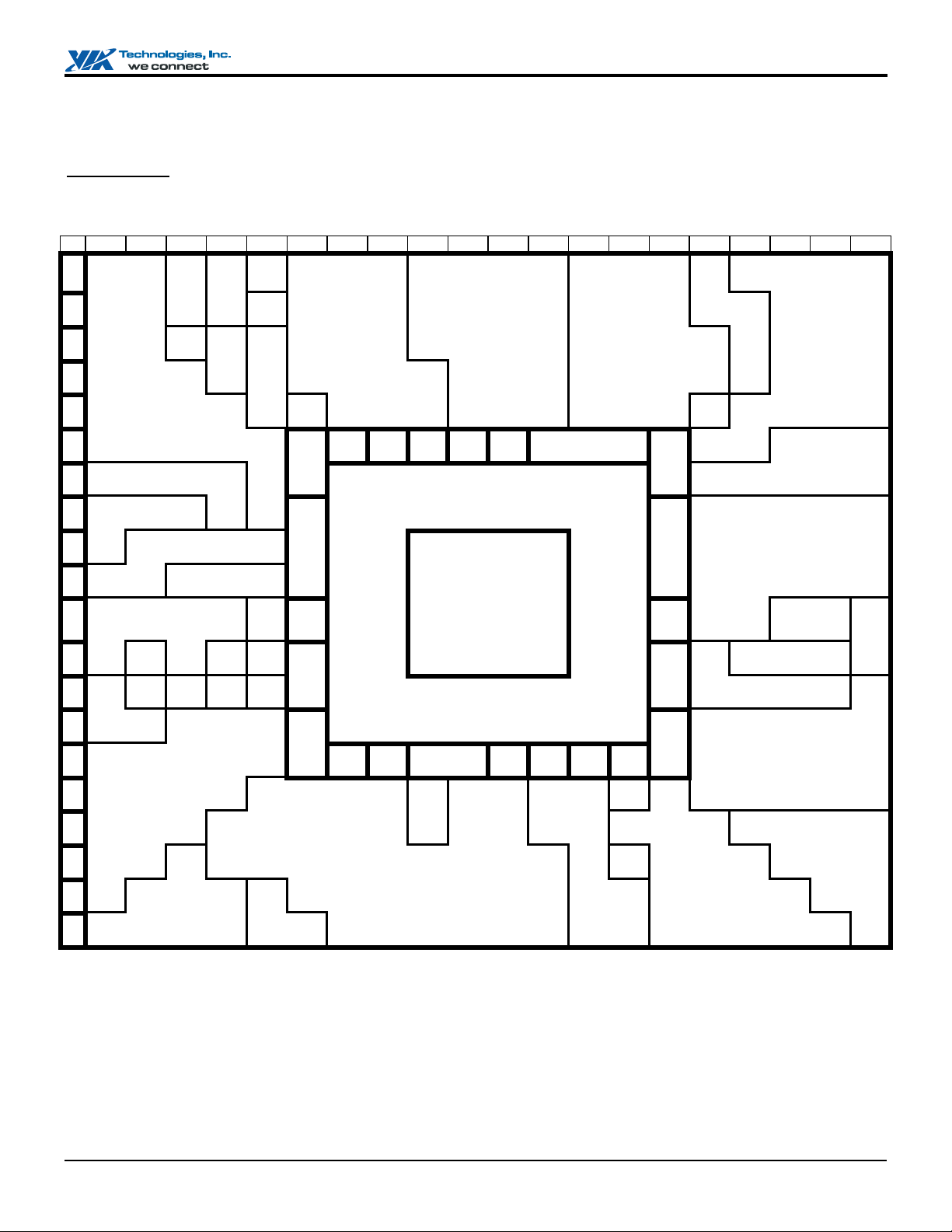
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
PINOUTS
Pin Diagram
Figure 2. VT82C686B Ball Diagram (Top View)
Key 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
W
DS
CTS
DCD
SMEM
IOCH
A
R#
SMEM
B
W#
ROM
C
CS#
IO
D
R#
DACK
E
1#
MCS
F
16# S BHE#
IRQ6
G
SLPB
TC BALE
H
RST
J
DRV
SA
K
19
IRQ
L
14
DRQ 5 SD 9 DACK
M
SD
N
11
SD
P
14
SA14
R
SDD14
SA9
T
SDD9
SA5
U
SDD5
SA2
V
SDD2
SA0
W
SDD0
SD 0 SD 1 SD 3 SD 6 RTC
Y
USB
RDY
P0+
USB
AEN
P0-
IO
USB
W#
CLK
DACK
DRQ 3 USB
3#
DRQ
RFSH# OSC
1
IOCS
16#
IRQ 5 IRQ 4 IRQ 3 DACK
DRQ2
SIRQ
LA
LA
23
22
SA
IRQ
18
10
DACK
DRQ 0 DACK
0#
6#
DACK
SDD13
SD
7#
12
SD
SA
15
17
SA13
SA12
SDD12
SA8
SA7
SDD8
SDD7
SA4
SA3
SDD4
SDD3
SA1
SD 5 MEM
SDD1
SD 2 SD 4 SD 7 RTC
USB
KB
P2+
DT
USB
USB
P2-
P3+
USB
MS
P1+
DT
MS
P1-
CK
KB
CK
IO
IRQ
CHK#
DRQ 7 SD
SA11
SDD11
SA6
SDD6
MEM
7
2#
IRQ 9 B
CLK
LA
LA
21
20
IRQ
IRQ
11
15
SD
5#
8
SD
DRQ
10
6
13
SA
SA15
SDD15
16
SA10
SDD10
XDIR INIT SLP#
SOE# SMI# NMI
R#
SPKR
W#
X2
X1
WRT
DATA#
PRT#
R
DATA# W GATE#
DSK
CHG#
SEL#
DRV
DEN1
DEX#
USB
P3-
GND VCC
GND
VCC H H VCC
VCC J GND GND GND GND J VCC
VCC K GND GND GND GND K VCC
GND L GND GND GND GND L GND
VCC M GND GND GND GND M VCC
VCC N N VCC
GND P7 8 9 10 11 12 13 P14 GND
GND VCC
RSM
FERR#
RST#
PWR
GD
CLK#
VBAT
1#
2#
DS
DTR
0#
2#
HD
MTR
IN
DIR#
TRK
STEP#
00#
GNDU VCC
G7 8 9 10 11 12 13 G14 GND
VCC
GPO 0 SMB
GPIOD SMB
CPU
RST#
STP
INTR
A20
M#
1#
IGN
NE#
RI
2#
DRV
DEN0
MTR
0#
U
VCCS VCC
DATA
CLK
SUS
A#
SUS
B#
ALRT#
SUS
C#
TXD 1 DCD
2#
RXD 2 RTS
DSR
TXD 2 DTR
VCC GND VCC VCC VCC GND
CLK
ST1#
SMB
EXT
SMI#
2#
RTS
2#
S
SUS
LID
SUS
1#
CTS
1#
1#
RI
1#
VCC
THRM
PME#
BAT
LOW#
RING#
IRQ8#
RUN#T SENS1V SENS3
PWR
BTN#
PD 7 PD
1#
RXD
ACK#
1
DSR
BUSY
1#
IR
RX
IR
SLCT
TX
VCCH GND
FAN
VREF
1
FAN 2 V
SENS1
PCI
STP#V SENS2
PCK
CPU
STP#T SENS2V SENS4
2
PD 3 PD 0 PCI
PD 4 P
PD 5 PD 1 STR
PE
PD 6 SLCT
VCC GND
H
GPIOA SDD10
JBX
GPI23
GPIOC JAX
PIRQ
ERR#
AUTO
INIT#
OBE#
IN# P CLK
JAB2
ACRS JBB2
SYNC SDI
GPO23
JBY
GPI22
JAY
GPO22
AD
A#
31
PIRQ
RST#
D#
PIRQ
FD#
C#
PIRQ
B#
AD
20
AD
C/BE
16
DEV
SEL#
AD
15
AD
10
AD 6 AD 5 AD 4 AD 3 AD
AD 1 AD
PD
CS3#
PD
RDY
PDD 0 PDD
PDD
12
PDD 5 PDD 9 PDD 6 PDD 8 PDD
JAB1 JBB1 BTCK
SDO SDI2 MSO MSI
FRM#
2#
STOP# SERR# PAR CBE1#
AD
14
AD 9 AD 8 C/BE
PREQ# PGNT
0
PD
A0
PD
IOR#
IOW#
PDD 1 PDD
14
PDD 3 PDD
SD
CS1#
CS3#
AD
28
AD
29
AD
30
AD
23
AD
19
AD
13
PD
A2
PD
11
SD
SD
A1
AD
AD
26
25
AD
AD
27
24
C/BE
RDY#T RDY#
DRQ
DACK#
IOR#
ID
3#
SEL
AD
AD
22
21
AD
AD
18
17
I
AD
AD
12
11
AD
0#
7
2
PD
CS1#
#
PD
PD
DACK#
A1
PD
PDD
15
PDD
13
2
PDD 4 PDD
10
7
SD
SD
A0
A2
SD
SD
RDY
SD
SD
IOW#
SD
DRQ
Note: Some of the pins above have alternate functions and alternate names. The table above contains only one name (usually the most often used function), but the
pin lists and pin descriptions contain all names.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -6- Pinouts
Page 13
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
)
K
)
K
Pin Lists
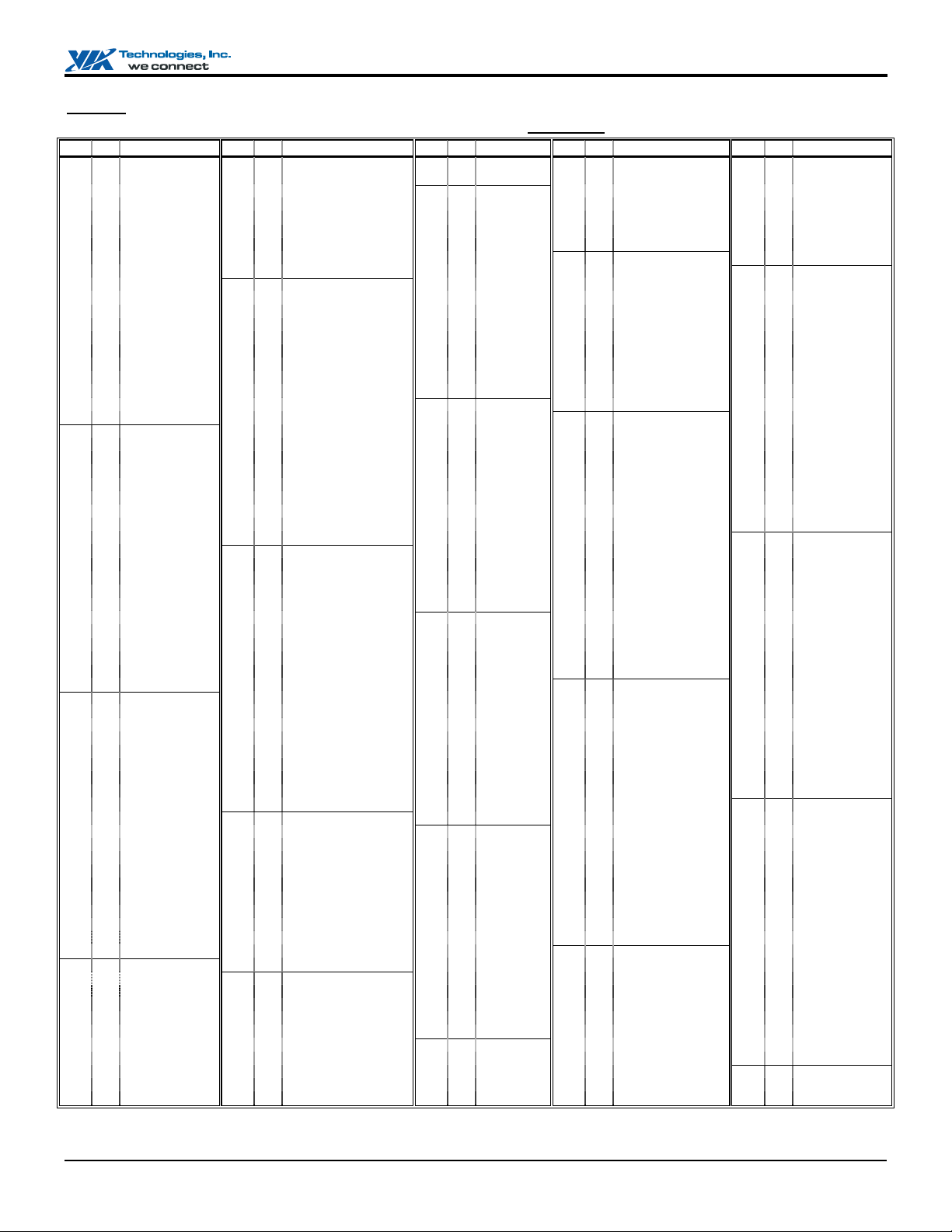
Figure 3. VT82C686B Pin List (Numerical Order)
Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name
A01 O SMEMR# D12 IO IRRX / GPO15 H19 IO AD12
A02 I IOCHRDY D13 I PE / WDATA# H20 IO AD11
A03 IO USBP0+ D14 IO PD5 J01 O RSTDRV N16 I PDRDY U15 O ACRST
A04 IO USBP2+ D15 IO PD1 / TRK00# J02 IO LA23 N17 O PDIOR# U16 I JBB2
A05 IO KBDT / KBRC D16 IO STROBE# J03 IO LA22 N18 O PDIOW# U17 O SDCS1#
A06 I WRTPRT# D17 I PIRQB# J04 IO LA21 N19 I PDDRQ U18 O SDCS3#
A07 O WDATA# D18 IO AD23 J05 IO LA20 N20 IO PDD15 U19 O SDA0
A08 O DS1# D19 IO AD22
A09 I CTS2# D20 IO AD21
A10 I DCD2# E01 O DACK1# / IDEIRQB
A11 O TXD1 E02 I DRQ1
A12 I DCD1# E03 IO RFSH#
A13 IO PD7 E04 I OSC
A14 IO PD2 / WRTPRT# E05 IO KBCK/A20GATE J16 IO AD10
A15 I ERROR#/HDSL# E06 IO USBP3- J17 IO AD09 P16 IO PDD00 V07 I FERR#
A16 I PIRQA# E07 I TRK00# J18 IO AD08 P17 IO PDD14 V08 OD CPURST
A17 IO AD31 E08 O STEP# J19 IO CBE0# P18 IO PDD01 V09 O SUSA#/O1/APD0
A18 IO AD28 E09 O MTR0# J20 IO AD07 P19 IO PDD13 V10 O SUSST1# / GPO3
A19 IO AD26 E10 O RTS2# K01 IO SA19 P20 IO PDD02 V11 I RING# / GPI7
A20 IO AD25 E11 I RI1# K02 IO SA18 R01 IO SA14 / SDD14 V12 O PCISTP#/GPO5
B01 O SMEMW# E12 O IRTX / GPO14 K03 I IRQ10 R02 IO SA13 / SDD13 V13 I VSENS2 (2.5V
B02 O AEN E13 I SLCT / WGATE# K04 I IRQ11 R03 IO SA12 / SDD12 V14 IO GPIOC(10)/CHAS
B03 IO USBP0- E14 IO PD6 K05 I IRQ15 R04 IO SA11 / SDD11 V15 I JAX / GPO23
B04 IO USBP2- E15 IO SLCTIN# / STEP#
B05 IO USBP3+ E16 I PCLK
B06 I RDATA# E17 IO AD20
B07 O WGATE# E18 IO AD19
B08 O DS0# E19 IO AD18
B09 O DTR2# E20 IO AD17
B10 I RXD2 F01 I MCS16# K16 IO AD06
B11 O RTS1# F02 IO SBHE# K17 IO AD05
B12 I RXD1 F03 I IOCS16# K18 IO AD04
B13 I ACK# / DS1# F04 I IOCHCK# / GPI0 K19 IO AD03
B14 IO PD3 / RDATA# F05 I IRQ7 K20 IO AD02
B15 IO PD0 / INDEX#
B16 O PCIRST#
B17 I PIRQD#
B18 IO AD29
B19 IO AD27
B20 IO AD24
C01 I ROMCS#/KBCS#
C02 IO IOW#
C03 I USBCLK
C04 IO USBP1+
C05 IO MSDT / IRQ12 F16 IO AD16
C06 I DSKCHG# F17 IO CBE2# L16 IO AD01 T07 OD SLP# / GPO7 W18 I ACBTC
C07 O HDSEL# F18 IO FRAME# L17 IO AD00 T08 O GPO0 / SLOWCLK W19 O SDIOR#
C08 O MTR1# F19 IO IRDY# L18 O PREQ# T09 IO SMBDATA W20 O SDIOW#
C09 I RI2# F20 IO TRDY# L19 I PGNT# T10 O SUSCLK / APICD1 Y01 IO SD00
C10 I DSR2# G01 I IRQ6/I4/SLPBTN# L20 O PDCS1# T11 I THRM / PME# / GI5 Y02 IO SD01
C11 I CTS1# G02 I IRQ5 M01 I DRQ5 T12 I FAN1 Y03 IO SD03
C12 I DSR1# G03 I IRQ4 M02 IO SD09
C13 I BUSY / MTR1# G04 I IRQ3 M03 O DACK6#/UA T14 IO GPIOA/8/GPOWE Y05 I RTCX1
C14 IO PD4 / DSKCHG# G05 O DACK2#/I13/O25/OC0# M04 IO SD10 T15 I JAB2
C15 IO PINIT# / DIR#
C16 IO AUTOFD#/DRV0
C17 I PIRQC# G16 IO DEVSEL#
C18 IO AD30 G17 IO STOP#
C19 IO CBE3# G18 I SERR#
C20 I IDSEL G19 IO PAR
D01 IO IOR# G20 IO CBE1#
D02 O DACK3#/ACIRQ H01 O TC M16 O PDCS3# U03 IO SA03 / SDD3 Y14 I VSENS4 (12V
D03 I DRQ3 H02 O BALE M17 O PDA0 U04 IO MEMR# Y15 I JAY / GPO22
D04 IO USBP1- H03 I DRQ2/I12/O24/SQ/OC1# M18 O PDA2 U05 O SOE#/O13/MCCS# Y16 O ACSDO
D05 IO MSCK / IRQ1 H04 I IRQ9 M19 O PDA1 U06 OD SMI# Y17 I ACSDI2
D06 O DRVDEN1 H05 O BCLK M20 O PDDACK# U07 OD NMI Y18 O MSO
D07 I INDEX#
D08 O DIR#
D09 O DRVDEN0 H16 IO AD15 N03 IO SD12 U10 I LID / GPI3 / WSC#
D10 O TXD2 H17 IO AD14 N04 I DRQ7 U11 I BATLOW#/GPI2
D11 O DTR1# H18 IO AD13 N05 IO SD13 U12 IO FAN2/GPIOB(9)
F06 P GND
F07 P VCC
F08 P GNDU
F09 P VCCU
F10 P VCC
F11 P GND L06 P GND
F12 P VCC L09 P GND
F13 P VCC L10 P GND
F14 P VCC L11 P GND
F15 P GND L12 P GND
G06 P GND
G15 P GND M06 P VCC
H06 P VCC
H15 P VCC
J06 P VCC
J09 P GND
J10 P GND
J11 P GND
J12 P GND
J15 P VCC P06 P GND
K06 P VCC
K09 P GND R06 P GND
K10 P GND R07 P VCC
K11 P GND R08 P VCC
K12 P GND R09 P VCCS
K15 P VCC R10 P VCCS
L01 I IRQ14 R16 IO PDD12 W07 OD STPCLK#
L02 O DACK0#/IA R17 IO PDD03 W08 OD INTR
L03 I DRQ0 R18 IO PDD11 W09 O SUSB# / GPO2
L04 O DACK5#/MI R19 IO PDD04 W10 I SMBALRT#/GPI6
L05 IO SD08 R20 IO PDD10 W11 I IRQ8#/GPI1
L15 P GND
M05 I DRQ6 T16 IO PDD05 Y07 OD A20M#
M09 P GND
M10 P GND
M11 P GND
M12 P GND
M15 P VCC
N01 IO SD11 U08 IO GPIOD/SO#/MCCS# Y19 I MSI
N02 O DACK7#/UB U09 IO SMBCL
N06 P VCC
N15 P VCC
P01 IO SD14 U20 O SDA2
P02 IO SD15 V01 IO SA02 / SDD2
P03 IO SA17 V02 IO SA01 / SDD1
P04 IO SA16 V03 IO SD05 / KBIN4
P05 IO SA15 / SDD15 V04 IO MEMW#
P15 P GND
R05 IO SA10 / SDD10 V16 O ACSYNC
R11 P VCC
R12 P VCCH
R13 P GNDH
R14 P VCC
R15 P GND
T01 IO SA09 / SDD9 W12 IO PCKRUN#
T02 IO SA08 / SDD8 W13 I TSENS1
T03 IO SA07 / SDD7 W14 I VSENS3 (5V)
T04 IO SA06 / SDD6 W15 I JBY / GPI22
T05 O XDIR/O12/PCS0# W16 I JAB1
T06 OD INIT W17 I JBB1
T13 O VREF
T17 IO PDD09 Y08 OD IGNNE#
T18 IO PDD06 Y09 O SUSC#
T19 IO PDD08 Y10 IOD EXTSMI#
T20 IO PDD07 Y11 I PWRBTN#
U01 IO SA05 / SDD5 Y12 O CPUSTP#/GPO4
U02 IO SA04 / SDD4 Y13 I TSENS2
U13 I VSENS1 (2.0V)
U14 I JBX / GPI23
V05 IO SPKR
V06 I RSMRST#
V17 I ACSDI
V18 O SDA1
V19 O SDDACK#
V20 I SDRDY
W01 IO SA00 / SDD0
W02 IO SD02
W03 IO SD04 / KBIN3
W04 IO SD07 / KBIN6
W05 O RTCX2
W06 I PWRGD
Y04 IO SD06 / KBIN5
Y06 P VBAT
Y20 I SDDRQ
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -7- Pinouts
Page 14

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
K
K
K
)
(
)
(
)
Q
Q
K
Figure 4. VT82C686B Pin List (Alphabetical Order)
Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name Pin Pin Name
Y07 OD A20M# N04 I DRQ7 K05 I IRQ15 A16 I PIRQA# T07 OD SLP# / GPO7
B13 I ACK# / DS1# D09 O DRVDEN0 D12 IO IRRX / GPO15 D17 I PIRQB# W10 I SMBALRT# / GPI6
W18 I ACBTCK D06 O DRVDEN1 E12 O IRTX / GPO14 C17 I PIRQC# U09 IO SMBCL
U15 O ACRST B08 O DS0# W16 I JAB1 B17 I PIRQD# T09 IO SMBDATA
V17 I ACSDI A08 O DS1# T15 I JAB2 L18 O PREQ# A01 O SMEMR#
Y17 I ACSDI2 C06 I DSKCHG# V15 I JAX / GPO23 Y11 I PWRBTN# B01 O SMEMW#
Y16 O ACSDO C12 I DSR1# Y15 I JAY / GPO22 W06 I PWRGD U06 OD SMI#
V16 O ACSYNC C10 I DSR2# W17 I JBB1 B06 I RDATA# U05 O SOE#/GPO13/MCCS#
L17 IO AD00 D11 O DTR1# U16 I JBB2 E03 IO RFSH# V05 IO SPKR
L16 IO AD01 B09 O DTR2# U14 I JBX / GPI23 E11 I RI1# E08 O STEP#
K20 IO AD02 A15 I ERROR#/HDSEL# W15 I JBY / GPI22 C09 I RI2# G17 IO STOP#
K19 IO AD03 Y10 IOD EXTSMI# E05 IO KBCK / A20G V11 I RING# / GPI7 W07 OD STPCLK#
K18 IO AD04 T12 I FAN1 A05 IO KBDT / KBRC C01 O ROMCS#/KBCS# D16 IO STROBE#
K17 IO AD05 U12 IO FAN2/GPIOB(9) J05 IO LA20 V06 I RSMRST# V09 O SUSA# / O1 / APICD0
K16 IO AD06 V07 I FERR# J04 IO LA21 J01 O RSTDRV W09 O SUSB# / GPO2
J20 IO AD07 F18 IO FRAME# J03 IO LA22 Y05 I RTCX1 Y09 O SUSC#
J18 IO AD08
J17 IO AD09
J16 IO AD10
H20 IO AD11
H19 IO AD12
H18 IO AD13
H17 IO AD14
H16 IO AD15
F16 IO AD16
E20 IO AD17
E19 IO AD18
E18 IO AD19
E17 IO AD20
D20 IO AD21
D19 IO AD22
D18 IO AD23
B20 IO AD24
A20 IO AD25
A19 IO AD26
B19 IO AD27
A18 IO AD28
B18 IO AD29
C18 IO AD30
A17 IO AD31
B02 O AEN
C16 IO AUTOFD#/DR0
H02 O BALE
U11 I BATLOW#/GPI2
H05 O BCLK
C13 I BUSY / MTR1# T14 IO GPIOA(8)/GPOWE L20 O PDCS1# Y03 IO SD03
J19 IO CBE0# V14 IO GPIOC(10)/CHAS M16 O PDCS3# W03 IO SD04 / KBIN3
G20 IO CBE1# U08 IO GPIOD(11)/MCCS# P16 IO PDD00 V03 IO SD05 / KBIN4
F17 IO CBE2# T08 O GPO0 / SLOWCLK P18 IO PDD01 Y04 IO SD06 / KBIN5
C19 IO CBE3# C07 O HDSEL# P20 IO PDD02 W04 IO SD07 / KBIN6
V08 OD CPURST C20 I IDSEL R17 IO PDD03 L05 IO SD08
Y12 O CPUSTP#/GPO4 Y08 OD IGNNE# R19 IO PDD04 M02 IO SD09
C11 I CTS1# D07 I INDEX# T16 IO PDD05 M04 IO SD10
A09 I CTS2# T06 OD INIT T18 IO PDD06 N01 IO SD11
L02 O DACK0#/IDEA W08 OD INTR T20 IO PDD07 N03 IO SD12
E01 O DACK1#/IDEB F04 I IOCHCK# / GPI0 T19 IO PDD08 N05 IO SD13
G05 O DAK2#/I13/O25 A02 I IOCHRDY T17 IO PDD09 P01 IO SD14
D02 O DACK3#/AIRQ F03 I IOCS16# R20 IO PDD10 P02 IO SD15
L04 O DACK5#/MIRQ D01 IO IOR# R18 IO PDD11 U19 O SDA0
M03 O DACK6#/USBIA C02 IO IOW# R16 IO PDD12 V18 O SDA1
N02 O DACK7#/USBIB F19 IO IRDY# P19 IO PDD13 U20 O SDA2 U13 I VSENS1 (2.0V
A12 I DCD1# G04 I IRQ3 P17 IO PDD14 U17 O SDCS1# V13 I VSENS2
A10 I DCD2# G03 I IRQ4 N20 IO PDD15 U18 O SDCS3# W14 I VSENS3 (5V)
G16 IO DEVSEL# G02 I IRQ5 M20 O PDDACK# V19 O SDDACK# Y14 I VSENS4
D08 O DIR# G01 I IRQ6/I4/SLPBTN# N19 I PDDR
L03 I DRQ0 F05 I IRQ7 N17 O PDIOR# W19 O SDIOR# B07 O WGATE#
E02 I DRQ1 W11 I IRQ8# / GPI1 N18 O PDIOW# W20 O SDIOW# A06 I WRTPRT#
H03 I D2/I12/O24/SQ H04 I IRQ9 N16 I PDRDY V20 I SDRDY T05 O XDIR/GPO12/PCS0#
D03 I DRQ3
M01 I DRQ5 K04 I IRQ11 L19 I PGNT# E13 I SLCT / WGATE#
M05 I DRQ6 L01 I IRQ14 C15 IO PINIT# / DIR# E15 IO SLCTIN#/STEP#
F06 P GND
F11 P GND
F15 P GND
G06 P GND
G15 P GND
J09 P GND
J10 P GND
J11 P GND
J12 P GND
K09 P GND
K10 P GND
K11 P GND
K12 P GND
L06 P GND
L09 P GND
L10 P GND
L11 P GND
L12 P GND
L15 P GND
M09 P GND
M10 P GND
M11 P GND
M12 P GND
P06 P GND
P15 P GND
R06 P GND
R15 P GND
R13 P GNDH
F08 P GNDU
03 I IRQ10 D13 I PE / WDATA# G18 I SERR#
J02 IO LA23 W05 O RTCX2 T10 O SUSCLK / APICD1
U10 I LID/GPI3/WSC# B11 O RTS1# V10 O SUSST1# / GPO3
F01 I MCS16# E10 O RTS2# H01 O TC
U04 IO MEMR# B12 I RXD1 T11 I THRM / PME# / GI5
V04 IO MEMW# B10 I RXD2 F20 IO TRDY#
D05 IO MSCK / IRQ1 W01 IO SA00 / SDD0 E07 I TRK00#
C05 IO MSDT / IRQ12 V02 IO SA01 / SDD1 W13 I TSENS1
Y19 I MSI V01 IO SA02 / SDD2 Y13 I TSENS2
Y18 I MSO U03 IO SA03 / SDD3 A11 O TXD1
E09 O MTR0# U02 IO SA04 / SDD4 D10 O TXD2
C08 O MTR1# U01 IO SA05 / SDD5 C03 I USBCL
U07 OD NMI T04 IO SA06 / SDD6 B03 IO USBP0E04 I OSC T03 IO SA07 / SDD7 A03 IO USBP0+
G19 IO PAR T02 IO SA08 / SDD8 D04 IO USBP1-
W12 IO PCKRUN# T01 IO SA09 / SDD9 C04 IO USBP1+
E16 I PCL
B16 O PCIRST# R04 IO SA11 / SDD11 A04 IO USBP2+
V12 O PCISTP#/GPO5 R03 IO SA12 / SDD12 E06 IO USBP3B15 IO PD0 / INDEX# R02 IO SA13 / SDD13 B05 IO USBP3+
D15 IO PD1 / TRK00# R01 IO SA14 / SDD14
A14 IO PD2 / WRTPRT# P05 IO SA15 / SDD15
B14 IO PD3 / RDATA# P04 IO SA16
C14 IO PD4 / DSKCHG# P03 IO SA17
D14 IO PD5 K02 IO SA18
E14 IO PD6 K01 IO SA19
A13 IO PD7 F02 IO SBHE#
M17 O PDA0 Y01 IO SD00
M19 O PDA1 Y02 IO SD01
M18 O PDA2 W02 IO SD02
R05 IO SA10 / SDD10 B04 IO USBP2-
Y06 P VBAT
F07 P VCC
F10 P VCC
F12 P VCC
F13 P VCC
F14 P VCC
H06 P VCC
H15 P VCC
J06 P VCC
J15 P VCC
K06 P VCC
K15 P VCC
M06 P VCC
M15 P VCC
N06 P VCC
N15 P VCC
R07 P VCC
R08 P VCC
R11 P VCC
R14 P VCC
R12 P VCCH
R09 P VCCS
R10 P VCCS
F09 P VCCU
T13 O VREF
Y20 I SDDR
A07 O WDATA#
2.2V
12V
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -8- Pinouts
Page 15
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
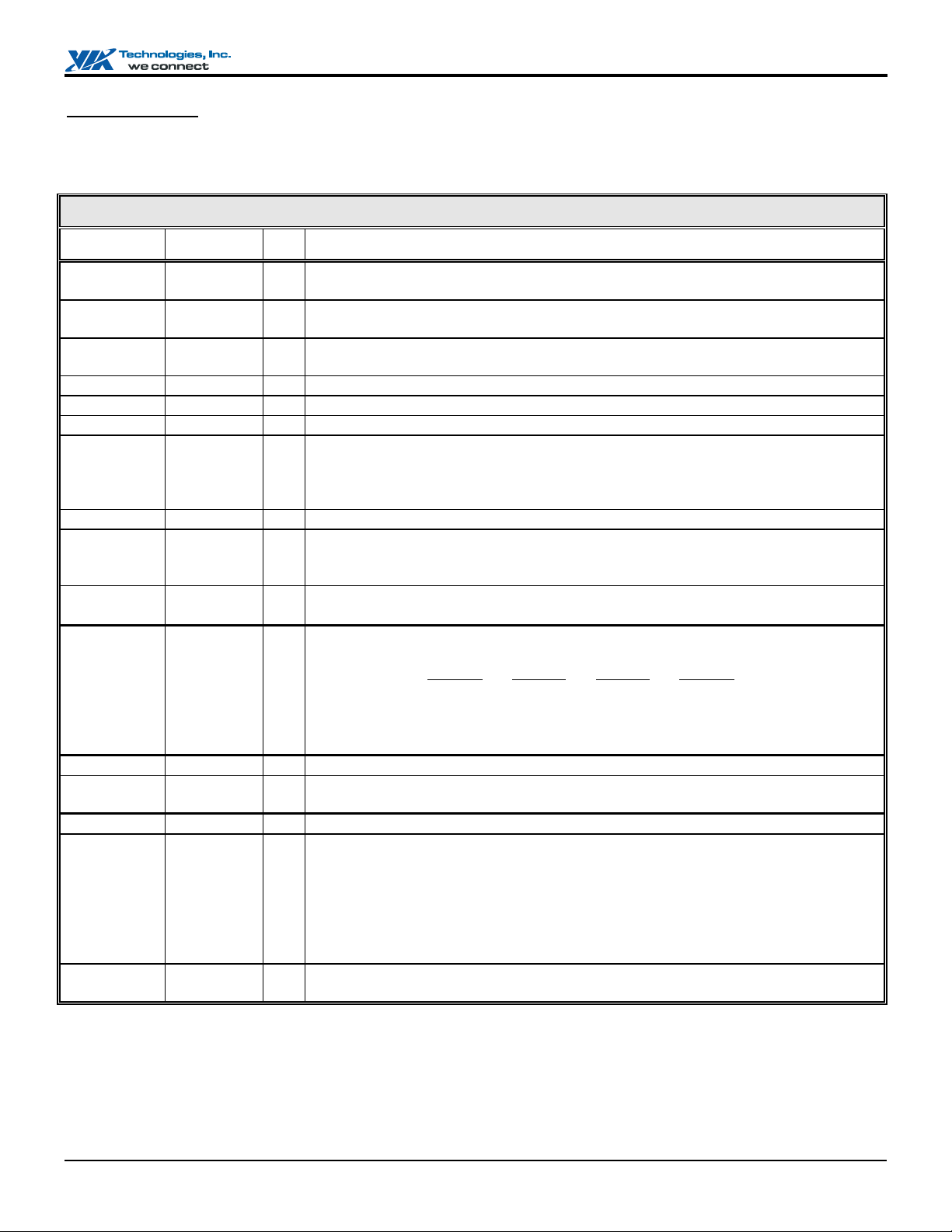
Pin Descriptions
Table 1. Pin Descriptions
PCI Bus Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
AD[31:0]
C/BE[3:0]#
FRAME#
IRDY#
TRDY#
STOP#
DEVSEL#
PAR
SERR#
IDSEL
PIRQA-D#
PREQ#
PGNT#
PCLK
PCKRUN#
PCIRST#
(see pin list) IO
C19, F17,
G20, J19
F18 IO
F19 IO
F20 IO
G17 IO
G16 IO
G19 IO
G18 I
C20 I
A16, D17,
C17, B17
L18 O
L19 I
E16 I
W12 IO
B16 O
IO
I
Address/Data Bus. The standard PCI address and data lines. The address is driven with
FRAME# assertion and data is driven or received in following cycles.
Command/Byte Enable. The command is driven with FRAME# assertion. Byte enables
corresponding to supplied or requested data are driven on following clocks.
Frame. Assertion indicates the address phase of a PCI transfer. Negation indicates that
one more data transfer is desired by the cycle initiator.
Initiator Ready. Asserted when the initiator is ready for data transfer.
Target Ready. Asserted when the target is ready for data transfer.
Stop. Asserted by the target to request the master to stop the current transaction.
Device Select. The VT82C686B asserts this signal to claim PCI transactions through
positive or subtractive decoding. As an input, DEVSEL# indicates the response to a
VT82C686B-initiated transaction and is also sampled when decoding whether to
subtractively decode the cycle.
Parity. A single parity bit is provided over AD[31:0] and C/BE[3:0]#.
System Error. SERR# can be pulsed active by any PCI device that detects a system
error condition. Upon sampling SERR# active, the VT82C686B can be programmed to
generate an NMI to the CPU.
Initialization Device Select. IDSEL is used as a chip select during configuration read
and write cycles. Connect this pin to AD18 using a 100 Ω resistor.
PCI Interrupt Request. These pins are typically connected to the PCI bus INTA#INTD# pins as follows:
PIRQA#
PCI Slot 1 INTA# INTB# INTC# INTD#
PCI Slot 2 INTB# INTC# INTD# INTA#
PCI Slot 3 INTC# INTD# INTA# INTB#
PCI Slot 4 INTD# INTA# INTB# INTC#
PCI Request. This signal goes to the North Bridge to request the PCI bus.
PCI Grant. This signal is driven by the North Bridge to grant PCI access to the
VT82C686B.
PCI Clock. PCLK provides timing for all transactions on the PCI Bus.
PCI Bus Clock Run. This signal indicates whether the PCI clock is or will be stopped
(high) or running (low). The VT82C686B drives this signal low when the PCI clock is
running (default on reset) and releases it when it stops the PCI clock. External devices
may assert this signal low to request that the PCI clock be restarted or prevent it from
stopping. Connect this pin to ground using a 100 Ω resistor if the function is not used.
Refer to the “PCI Mobile Design Guide” and the VIA “Apollo MVP4 Design Guide” for
more details.
PCI Reset. Active low reset signal for the PCI bus. The VT82C686B will assert this pin
during power-up or from the control register.
PIRQB# PIRQC# PIRQD#
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -9- Pinouts
Page 16
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
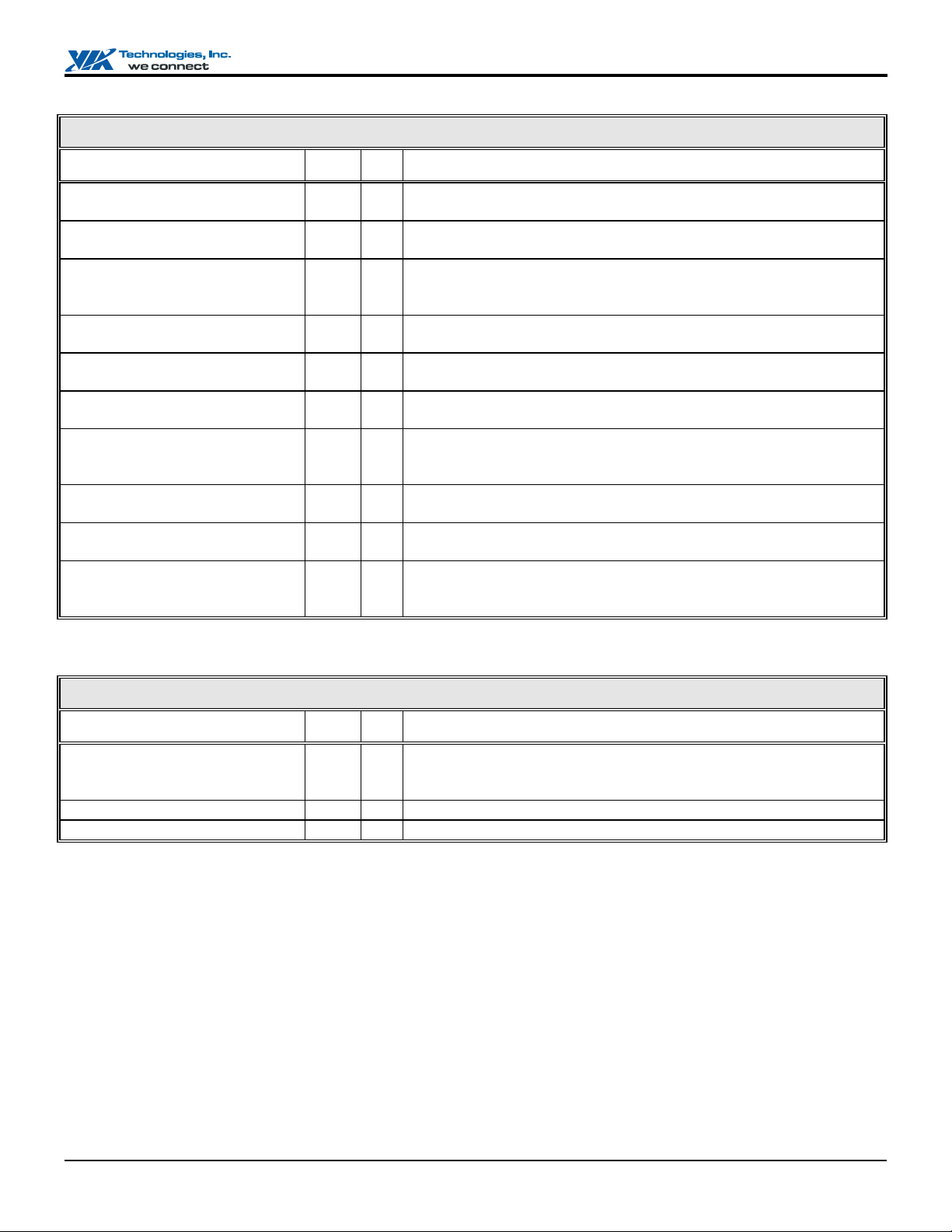
CPU Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
CPURST
INTR
NMI
INIT
STPCLK#
SMI#
FERR#
IGNNE#
SLP# / GPO7
A20M#
Note: Connect each of the above signals to 4.7K Ω pullup resistors to VCC3.
V8 OD
W8 OD
U7 OD
T6 OD
W7 OD
U6 OD
V7 I
Y8 OD
T7 OD
Y7 OD
CPU Reset. The VT82C686B asserts CPURST to reset the CPU during
power-up.
CPU Interrupt. INTR is driven by the VT82C686B to signal the CPU
that an interrupt request is pending and needs service.
Non-Maskable Interrupt. NMI is used to force a non-maskable interrupt
to the CPU. The VT82C686B generates an NMI when either SERR# or
IOCHK# is asserted.
Initialization. The VT82C686B asserts INIT if it detects a shut-down
special cycle on the PCI bus or if a soft reset is initiated by the register
Stop Clock. STPCLK# is asserted by the VT82C686B to the CPU to
throttle the processor clock.
System Management Interrupt. SMI# is asserted by the VT82C686B to
the CPU in response to different Power-Management events.
Numerical Coprocessor Error. This signal is tied to the coprocessor
error signal on the CPU. Internally generates interrupt 13 if active. 1.5V
interface.
Ignore Numeric Error. This pin is connected to the “ignore error” pin
on the CPU.
Sleep (Rx75[7] = 0). Used to put the CPU to sleep. Used with slot-1
CPUs only. Not currently used with socket-7 CPUs.
A20 Mask. Connect to A20 mask input of the CPU to control address
bit-20 generation. Logical combination of the A20GATE input (from
internal or external keyboard controller) and Port 92 bit-1 (Fast_A20).
Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC)
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
WSC# / GPI3 / LID
APICD0 / GPO1 / SUSA#
APICD1 / SUSCLK
For programming information, refer to Function 0 Rx74, 77, Function 4 Rx54[3-2], and Memory Mapped / Indexed APIC
registers.
Rx77[4] is “Internal APIC Enable”.
The clock source used by the chip to clock the internal I/O APIC is OSC (14.31818 MHz), so OSC must be externally connected
to the CPU I/O APIC clock input.
U10 I
V9 IO
T10 IO
Write Snoop Complete. Asserted by the north bridge to indicate that all
snoop activity on the CPU bus initiated by the last PCI-to-DRAM write
is complete and that it is safe to perform an APIC interrupt.
APIC Data 0. 1.5V interface.
APIC Data 1. 1.5V interface.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -10- Pinouts
Page 17
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
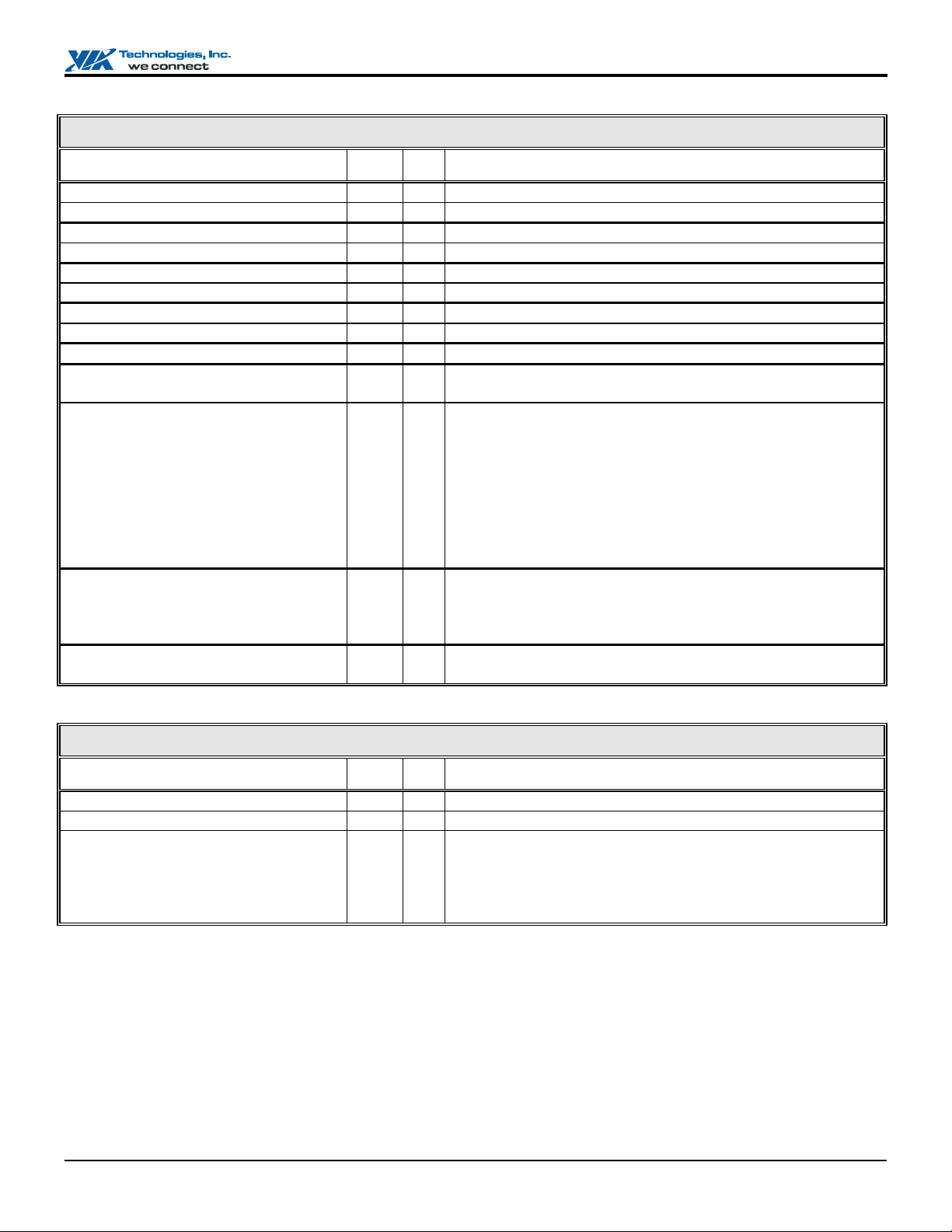
Universal Serial Bus Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
USBP0+
USBP0USBP1+
USBP1USBP2+
USBP2USBP3+
USBP3USBCLK
USBOC0# / GPO25 / DACK2#
USBOC1# / GPO24 / DRQ2 / SERIRQ
USBOC0# (SD2 & RFSH#)
USBOC1# (SD1 & RFSH#)
USBOC2# (SD0 & RFSH#)
USBOC3# (SD3 & RFSH#)
USBIRQA / DACK6#
USBIRQB / DACK7#
A3 IO
B3 IO
C4 IO
D4 IO
A4 IO
B4 IO
B5 IO
E6 IO
C3 I
G5 I
H3 I
(W2) I
(Y2) I
(Y1) I
(Y3) I
M3 O
N2 O
USB Port 0 Data +
USB Port 0 Data USB Port 1 Data +
USB Port 1 Data USB Port 2 Data +
USB Port 2 Data USB Port 3 Data +
USB Port 3 Data USB Clock. 48MHz clock input for the USB interface
USB Port 0 Over Current Detect. Port 0 is disabled if low.
USBOC0# if Rx76[7] = 1 and Rx76[6] = 0
USB Port 1 Over Current Detect. Port 1 is disabled if this input
is low. Direct inputs are provided for overcurrent protection for
ports 0 and 1 which may be used if the alternate functions of these
two pins are not required. If overcurrent protection is desired on all
four ports (or it is desired to use the alternate functions of these two
pins), an external buffer may be used to drive the state of
USBOC[3-0]# onto SD[3-0] during ISA bus refresh cycles (i.e.,
while ISA bus RFSH# is low, so that RFSH# may be used as the
buffer enable). USCOC1# if Rx76[7] = 1 and Rx76[6] = 0.
USB Port 0 Over Current Detect
USB Port 1 Over Current Detect
USB Port 2 Over Current Detect
USB Port 3 Over Current Detect
USB Interrupt Request A. Output of internal block.
USB Interrupt Request B. Output of internal block.
System Management Bus (SMB) Interface (I2C Bus)
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
SMBCLK
SMBDATA
SMBALRT# / GPI6
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -11- Pinouts
U9 IO
T9 IO
W10 I
SMB / I2C Clock.
SMB / I2C Data.
SMB Alert. (System Management Bus I/O space Rx08[3] = 1)
When the chip is enabled to allow it, assertion generates an IRQ or
SMI interrupt or a power management resume event. The same pin
is used as General Purpose Input 6 whose value is reflected in
Rx48[6] of function 4 I/O space
Page 18
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
UltraDMA-33 / 66 / 100 Enhanced IDE Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
PDRDY /
PDDMARDY /
PDSTROBE
SDRDY /
SDDMARDY /
SDSTROBE
PDIOR# /
PHDMARDY /
PHSTROBE
SDIOR# /
SHDMARDY /
SHSTROBE
PDIOW# /
PSTOP
SDIOW# /
SSTOP
PDDRQ
SDDRQ
PDDACK#
SDDACK#
IRQ14
IRQ15
N16 I
V20 I
N17 O
W19 O
N18 O
W20 O
N19 I
Y20 I
M20 O
V19 O
L1 I
K5 I
EIDE Mode: Primary I/O Channel Ready. Device ready indicator
UltraDMA Mode: Primary Device DMA Ready. Output flow control. The device
Primary Device Strobe. Input data strobe (both edges). The
EIDE Mode: Secondary I/O Channel Ready. D
UltraDMA Mode: Secondary Device DMA Ready. O
Secondary Device Strobe. Input data strobe (both edges). The
EIDE Mode: Primary Device I/O Read.
UltraDMA Mode: Primary Host DMA Ready. Primary
Primary Host Strobe. Output data strobe (both edges). The
EIDE Mode: Secondary Device I/O Read.
UltraDMA Mode: Secondary Host DMA Ready. Input flow control. The host
Host Strobe B. Output strobe (both edges). The host may stop
EIDE Mode: Primary Device I/O Write. Device write strobe
UltraDMA Mode: Primary Stop. Stop transfer: Asserted by the host prior to
EIDE Mode: Secondary Device I/O Write. Device write strobe
UltraDMA Mode: Secondary Stop. Stop transfer: Asserted by the host prior to
Primary Device DMA Request. Primary channel DMA request
Secondary Device DMA Request. Secondary channel DMA request
Primary Device DMA Acknowledge. Primary channel DMA acknowledge
Secondary Device DMA Acknowledge. Secondary channel DMA acknowledge
Primary Channel Interrupt.
Secondary Channel Interrupt.
may assert DDMARDY to pause output transfers
device may stop DSTROBE to pause input data transfers
evice ready indicator
utput flow control. The
device may assert DDMARDY to pause output transfers
device may stop DSTROBE to pause input data transfers
Device read strobe
channel input flow
control. The host may assert HDMARDY to pause input
transfers
host may stop HSTROBE to pause output data transfers
Device read strobe
may assert HDMARDY to pause input transfers
HSTROBE to pause output data transfers
initiation of an UltraDMA burst; negated by the host before data
is transferred in an UltraDMA burst. Assertion of STOP by the
host during or after data transfer in UltraDMA mode signals the
termination of the burst.
initiation of an UltraDMA burst; negated by the host before data
is transferred in an UltraDMA burst. Assertion of STOP by the
host during or after data transfer in UltraDMA mode signals the
termination of the burst.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -12- Pinouts
Page 19
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
UltraDMA-33 / 66 / 100 Enhanced IDE Interface (continued)
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
PDCS1#
PDCS3#
SDCS1#
SDCS3#
PDA[2-0]
SDA[2-0]
PDD[15-0]
SDD[15-0] / SA[15-0]
IDEIRQA / DACK0#
IDEIRQB / DACK1#
L20 O
M16 O
U17 O
U18 O
M18, M19, M17 O
U20, V18, U19 O
N20, P17, P19, R16,
R18, R20, T17, T19,
T20, T18, T16, R19,
R17, P20, P18, P16
P5, R1-R5, T1-T4,
U1-U3, V1, V2, W1
L2 O
E1 O
Primary Master Chip Select. This signal corresponds to CS1FX# on
the primary IDE connector.
Primary Slave Chip Select. This signal corresponds to CS3FX# on the
primary IDE connector.
Secondary Master Chip Select. This signal corresponds to CS17X# on
the secondary IDE connector.
Secondary Slave Chip Select. This signal corresponds to CS37X# on
the secondary IDE connector.
Primary Disk Address. PDA[2:0] are used to indicate which byte in
either the ATA command block or control block is being accessed.
Secondary Disk Address. SDA[2:0] are used to indicate which byte in
either the ATA command block or control block is being accessed.
IO
Primary Disk Data
IO
Secondary Disk Data muxed with ISA Bus Address.
IDE Interrupt Request A. Output of internal block.
IDE Interrupt Request B. Output of internal block.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -13- Pinouts
Page 20
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
MIDI Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
MSI
MSO
Y19 I
Y18 O
MIDI Serial In
MIDI Serial Out
AC97 Audio / Modem Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
ACRST
ACSDOUT
ACSYNC
ACSDIN2
ACSDIN
ACBTCK
AC97IRQ / DACK3#
MC97IRQ / DACK5#
/ SERIRQ / GPO19
U15 O
Y16 O
V16 O
Y17 I
V17 I
W18 I
D2 O
L4 O
AC97 Reset
AC97 Serial Data Out
AC97 Sync
AC97 Serial Data In 2
AC97 Serial Data In
AC97 Bit Clock
AC97 Interrupt Request. Output of internal block.
MC97 Interrupt Request. Output of internal block. Rx77[7] = 1, Rx77[3] = 1,
Rx74[6] = 0.
Game Port Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
JAB1
JAB2
JBB1
JBB2
JAX / GPO23
JAY / GPO22
JBX / GPI23
JBY / GPI22
See Function 0 Rx77[6]
W16 I
T15 I
W17 I
U16 I
V15 I
Y15 I
U14 I
W15 I
Joystick A Button 1
Joystick A Button 2
Joystick B Button 1
Joystick B Button 2
Joystick A X-axis
Joystick A Y-axis
Joystick B X-axis
Joystick B Y-axis
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -14- Pinouts
Page 21
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Floppy Disk Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
DRVDEN0
DRVDEN1
MTR0#
MTR1#
DS0#
DS1#
DIR#
STEP#
INDEX#
HDSEL#
TRK00#
RDATA#
WDATA#
WGATE#
DSKCHG#
WRTPRT#
D9 O
D6 O
E9 O
C8 O
B8 O
A8 O
D8 O
E8 O
D7 I
C7 O
E7 I
B6 I
A7 O
B7 O
C6 I
A6 I
Drive Density Select 0.
Drive Density Select 1.
Motor Control 0. Select motor on drive 0.
Motor Control 1. Select motor on drive 1
Drive Select 0. Select drive 0.
Drive Select 1. Select drive 1
Direction. Direction of head movement (0 = inward motion, 1 = outward motion)
Step. Low pulse for each track-to-track movement of the head.
Index. Sense to detect that the head is positioned over the beginning of a track
Head Select. Selects the side for R/W operations (0 = side 1, 1 = side 0)
Track 0. Sense to detect that the head is positioned over track 0.
Read Data. Raw serial bit stream from the drive for read operatrions.
Write Data. Encoded data to the drive for write operations.
Write Gate. Signal to the drive to enable current flow in the write head.
Disk Change. Sense that the drive door is open or the diskette has been changed
since the last drive selection.
Write Protect. Sense for detection that the diskette is write protected (causes write
commands to be ignored)
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -15- Pinouts
Page 22
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Parallel Port Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
PINIT# / DIR#
STROBE# / nc
AUTOFD# / DRVEN0
SLCTIN# / STEP#
SLCT / WGATE#
ACK# / DS1#
ERROR# / HDSEL#
BUSY / MTR1#
PE / WDATA#
PD7 / nc,
PD6 / nc,
PD5 / nc,
PD4 / DSKCHG#,
PD3 / RDATA#,
PD2 / WRTPRT#,
PD1 / TRK00#,
PD0 / INDEX#
As shown by the alternate functions above, in mobile applications the parallel port pins can optionally be selected to function as a
floppy disk interface for attachment of an external floppy drive using the parallel port connector (see Super I/O Configuration
Index F6[5]).
C15 IO / O
D16 IO / C16 IO / O
E15 IO / O
E13 I / O
B13 I / O
A15 I / O
C13 I / O
D13 I / O
A13,
E14,
D14,
C14,
B14,
A14,
D15,
B15
IO / IO / IO / IO / I
IO / I
IO / I
IO / I
IO / I
Initialize. Initialize printer. Output in standard mode, I/O in ECP/EPP mode.
Strobe. Output used to strobe data into the printer. I/O in ECP/EPP mode.
Auto Feed. Output used to cause the printer to automatically feed one line after
each line is printed. I/O pin in ECP/EPP mode.
Select In. Output used to select the printer. I/O pin in ECP/EPP mode.
Select. Status output from the printer. High indicates that it is powered on.
Acknowledge. Status output from the printer. Low indicates that it has received
the data and is ready to accept new data
Error. Status output from the printer. Low indicates an error condition in the
printer.
Busy. Status output from the printer. High indicates not ready to accept data.
Paper End. Status output from the printer. High indicates that it is out of paper.
Parallel Port Data.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -16- Pinouts
Page 23
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Serial Ports and Infrared Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
TXD1
TXD2
IRTX / GPO14
RXD1
RXD2
IRRX / GPO15
RTS1#
RTS2##
CTS1#
CTS2#
DTR1#
DTR2#
DSR1#
DSR2#
DCD1#
DCD2#
RI1#
RI2#
A11 O
D10 O
E12 O
B12 I
B10 I
D12 IO
B11 O
E10 O
C11 I
A9 I
D11 O
B9 O
C12 I
C10 I
A12 I
A10 I
E11 I
C9 I
Transmit Data 1. Serial port 1 transmit data out.
Transmit Data 2. Serial port 2 transmit data out.
Infrared Transmit. IR transmit data out (Rx76[5] = 0) from serial port 2.
General Purpose Output 14 if Rx76[5] = 1
Receive Data 1. Serial port 1 receive data in.
Receive Data 2. Serial port 2 receive data in.
Infrared Receive. IR receive data in (Rx76[5] = 0) to serial port 2. General
Purpose Output 15 if Rx76[5] = 1
Request To Send 1. Indicator that serial output port 1 is ready to transmit data.
Typically used as hardware handshake with CTS1# for low level flow control.
Designed for direct input to external RS-232C driver.
Request To Send 2. Indicator that serial output port 2 is ready to transmit data.
Typically used as hardware handshake with CTS2# for low level flow control.
Designed for direct input to external RS-232C driver.
Clear To Send 1. Indicator to serial port 1 that external communications device
is ready to receive data. Typically used as hardware handshake with RTS1# for
low level flow control. Designed for input from external RS-232C receiver.
Clear To Send 2. Indicator to serial port 2 that external communications device
is ready to receive data. Typically used as hardware handshake with RTS2# for
low level flow control. Designed for input from external RS-232C receiver.
Data Terminal Ready 1. Serial port 1 indicator that port is powered, initialized,
and ready. Typically used as hardware handshake with DSR1# for overall
readiness to communicate. Designed for direct input to external RS-232C driver.
Data Terminal Ready 2. Serial port 2 indicator that port is powered, initialized,
and ready. Typically used as hardware handshake with DSR2# for overall
readiness to communicate. Designed for direct input to external RS-232C driver.
Data Set Ready 1. Indicator to serial port 1 that external serial communications
device is powered, initialized, and ready. Typically used as hardware handshake
with DTR1# for overall readiness to communicate. Designed for direct input
from external RS-232C receiver.
Data Set Ready 2. Indicator to serial port 2 that external serial communications
device is powered, initialized, and ready. Typically used as hardware handshake
with DTR2# for overall readiness to communicate. Designed for direct input
from external RS-232C receiver.
Data Carrier Detect 1. Indicator to serial port 1 that external modem is detecting
a carrier signal (i.e., a communications channel is currently open). In direct
connect environments, this input will typically be driven by DTR1# as part of the
DTR/DSR handshake. Designed for direct input from external RS-232C receiver.
Data Carrier Detect 2. Indicator to serial port 2 that external modem is detecting
a carrier signal (i.e., a communications channel is currently open). In direct
connect environments, this input will typically be driven by DTR2# as part of the
DTR/DSR handshake. Designed for direct input from external RS-232C receiver.
Ring Indicator 1. Indicator to serial port 1 that external modem is detecting a
ring condition. Used by software to initiate operations to answer and open the
communications channel. Designed for direct input from external RS-232C
receiver (whose input is typically not connected in direct connect environments).
Ring Indicator 2. Indicator to serial port 2 that external modem is detecting a
ring condition. Used by software to initiate operations to answer and open the
communications channel. Designed for direct input from external RS-232C
receiver (whose input is typically not connected in direct connect environments).
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -17- Pinouts
Page 24
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
ISA Bus Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
SA[19:16],
SA[15-0] /
SDD[15-0]
LA[23:20]
SD[15:0]
SBHE#
IOR#
IOW#
MEMR#
MEMW#
SMEMR#
SMEMW#
BALE
IOCS16#
MCS16#
IOCHCK# /
GPI0
IOCHRDY
AEN
K1, K2, P3, P4,
P5, R1, R2, R3,
R4, R5, T1, T2,
T3, T4, U1, U2,
U3, V1, V2,
W1
J2, J3, J4, J5 IO
P2, P1, N5, N3,
N1, M4, M2,
L5, W4, Y4,
V3, W3, Y3,
W2, Y2, Y1
F2 IO
D1 IO
C2 IO
U4 IO
V4 IO
A1 O
B1 O
H2 O
F3 I
F1 I
F4 I
A2 I
B2 O
IO
System Address Bus. SA[19-16] are connected to ISA bus SA[19-16] directly.
IO
SA[19-17] are also connected to LA[19-17] of the ISA bus. SA[15-0] are
multiplexed with the IDE Secondary Data Bus. SA[15-0] may be connected to both
SDD[15-0] and ISA bus SA[15-0], however if ISA address bus loading is a concern,
74F245 transceivers may be used to externally drive ISA address bus pins SA[15-0].
In this case, these pins would connect directly to the IDE secondary data bus and to
the transceiver “A” pins and the ISA address bus would connect to the transceiver
“B” pins. SOE# would be used to control the transceiver output enables and the
ISA bus MASTER# signal would drive the transceiver direction controls.
System “Latched” Address Bus: The LA[23:20] address lines are bi-directional.
These address lines allow accesses to physical memory on the ISA bus up to
16Mbytes. LA[19-17] on the ISA bus are connected to SA[19-17] (see notes
above).
IO
System Data. SD[15:0] provide the data path for devices residing on the ISA bus.
X-Bus data signals XD[7:0] may be derived if needed from SD[7:0] using an
external 74F245-type transceiver (see the XDIR pin description for transceiver
connection details).
SD7:4 are strap options for keyboard inputs 6:3 (see Function 0 Rx5A)
System Byte High Enable. SBHE# indicates, when asserted, that a byte is being
transferred on the upper byte (SD[15:8]) of the data bus. SBHE# is negated during
refresh cycles.
I/O Read. IOR# is the command to an ISA I/O slave device that the slave may
drive data on to the ISA data bus.
I/O Write. IOW# is the command to an ISA I/O slave device that the slave may
latch data from the ISA data bus.
Memory Read. MEMR# is the command to a memory slave that it may drive data
onto the ISA data bus.
Memory Write. MEMW# is the command to a memory slave that it may latch data
from the ISA data bus.
Standard Memory Read. SMEMR# is the command to a memory slave, under
1MB, which indicates that it may drive data onto the ISA data bus
Standard Memory Write. SMEMW# is the command to a memory slave, under
1MB, which indicates that it may latch data from the ISA data bus.
Bus Address Latch Enable. BALE is an active high signal asserted by the
VT82C686B to indicate that the address (SA[19:0], LA[23:17] and the SBHE#
signal) is valid
16-Bit I/O Chip Select. This signal is driven by I/O devices on the ISA Bus to
indicate that they support 16-bit I/O bus cycles.
Memory Chip Select 16. ISA slaves that are 16-bit memory devices drive this line
low to indicate they support 16-bit memory bus cycles.
I/O Channel Check (Rx74[0] = 1). When this signal is asserted, it indicates that a
parity or an uncorrectable error has occurred for an I/O or memory device on the
ISA Bus. The same pin may optionally be used as General Purpose Input 0.
I/O Channel Ready (Rx74[0] = 1). This signal is normally high. Devices on the
ISA Bus assert IOCHRDY low to indicate that additional time (wait states) is
required to complete the cycle.
Address Enable. AEN is asserted during DMA cycles to prevent I/O slaves from
misinterpreting DMA cycles as valid I/O cycles.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -18- Pinouts
Page 25
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
ISA Bus Interface (continued)
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
RFSH#
IRQ0 / GPI10 / GPO10
/ GPIOC / CHAS
IRQ1 / MSCK
IRQ3
IRQ4
IRQ5
IRQ6 / GPI4 / SLPBTN#
IRQ7
IRQ8# / GPI1
IRQ9
IRQ10
IRQ11
IRQ12 / MSDT
IRQ14
IRQ15
DRQ7 / GPI21,
DRQ6 / GPI20,
DRQ5 / GPI19,
DRQ3 / GPI18,
DRQ2 / SERIRQ / GPO24
/ USBOC1#
DRQ1 / GPI17,
DRQ0 / GPI16
DACK7# / USBIRQB / GPO21
/ THRM#,
DACK6# / USBIRQA / GPO20,
DACK5# / MC97IRQ / GPO19
/ SERIRQ,
DACK3# / AC97IRQ / GPO18,
DACK2# / USBOC0# / GPO25
DACK1# / IDEIRQB / GPO17,
DACK0# / IDEIRQA / GPO16
TC
SPKR
SOE# (default pin function)
/ GPO13
/ MCCS#
E3 IO
V14 I
D5 I
G4 I
G3 I
G2 I
G1 I
F5 I
W11 I
H4 I
K3 I
K4 I
C5 I
L1 I
K5 I
N4,
M5,
M1,
D3,
H3,
E2,
L3
N2,
M3,
L4,
D2,
G5,
E1,
L2
H1 O
V5 O
U5 O
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
Refresh. Indicates when a refresh cycle is in progress. Also driven by 16bit ISA Bus masters to indicate a refresh cycle.
Interrupt Request 0. (Rx77[3] = 1)
Interrupt Request 1. (Rx5A[1] = 0) (used for external KBC interrupt)
Interrupt Request 3. (typically used for COM2 serial port interrupt)
Interrupt Request 4. (typically used for COM1 serial port interrupt)
Interrupt Request 5.
Interrupt Request 6. (typically used for FDC floppy ctrlr interrupt)
Interrupt Request 7. (typically used for LPT parallel port interrupt)
Interrupt Request 8 from ext RTC if int RTC disabled (Rx5A[2] = 0)
Interrupt Request 9.
Interrupt Request 10.
Interrupt Request 11.
Interrupt Request 12. (Rx5A[1] = 0)
Interrupt Request 14. (typically used for IDE primary chan interrupt)
Interrupt Request 15. (typically used for IDE secondary ch interrupt)
DMA Request. Used to request DMA services from the internal DMA
controller.
DRQ2: Rx68[3] = 0 & Rx75[3] = 0 & Rx75[1] = 0
See also Function 0 Rx77[7]
Acknowledge. Used by the internal DMA controller to indicate that a
request for DMA service has been granted.
DACK5#: Rx77[7] = 0
DACK2#: Rx68[3] = 0 & Rx75[3] = 0 & Rx75[2] = 0
See also Function 0 Rx77[7], Rx77[3], and Rx58
Terminal Count. Terminal count indicator asserted to DMA slaves.
Speaker Drive. Output of internal timer/counter 2.
ISA Address (SA) Output Enable. Asserted low when ISA address (SA)
is valid (deasserted when SDD is valid) when SA and SDD are multiplexed
on SA pins 15-0 (i.e., when SPKR is strapped low to enable the audio
interface pins). SOE# is tied directly to the output enable of 74F245
transceivers that buffer IDE Secondary Bus data and ISA-address (see SA
pins for more information).
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -19- Pinouts
Page 26
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
XD Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
XDIR / PCS0# / GPO12
T5 O
X-Bus Data Direction. (Rx76[1]=0) Asserted low for all I/O read cycles and for
memory read cycles to the programmed BIOS address space. XDIR is tied
directly to the direction control of a 74F245 transceiver that buffers the X-Bus
data and ISA-Bus data. The transceiver output enable may be grounded. SD0-7
connect to the “A” side of the transceiver and XD0-7 connect to the “B” side.
XDIR high indicates that SD0-7 drives XD0-7.
Serial IRQ
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
SERIRQ / DRQ2
/ GPO24 / USBOC1#
SERIRQ / DACK5#
/ GPO19 / MC97IRQ
H3 I
L4 I
Serial IRQ (Rx68[3] = 1, Rx74[6] = 0 and Rx75[3] = 1)
Serial IRQ (Rx68[3] = 1 and Rx74[6] = 1)
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -20- Pinouts
Page 27
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Internal Keyboard Controller
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
MSCK / IRQ1
MSDT / IRQ12
KBCK / A20GATE
KBDT / KBRC
KBCS# / ROMCS# / strap
KBIN[6-3] / SD[7-4]
D5 IO / I
C5 IO / I
E5 IO / I
A5 IO / I
C1 O / O / I
W4,
Y4,
V3,
W3
I / IO
MultiFunction Pin (Internal mouse controller enabled by Rx5A[1])
Rx5A[1]=1 Mouse Clock. From internal mouse controller.
Rx5A[1]=0 Interrupt Request 1. Interrupt input 1.
MultiFunction Pin (Internal mouse controller enabled by Rx5A[1])
Rx5A[1]=1 Mouse Data. From internal mouse controller.
Rx5A[1]=0 Interrupt Request 12. Interrupt input 12.
MultiFunction Pin (Internal keyboard controller enabled by Rx5A[0])
Rx5A[0]=1 Keyboard Clock. From internal keyboard controller
Rx5A[0]=0 Gate A20. Input from external keyboard controller.
MultiFunction Pin (Internal keyboard controller enabled by Rx5A[0])
Rx5A[0]=1 Keyboard Data. From internal keyboard controller.
Rx5A[0]=0 Keyboard Reset. From external keyboard controller (KBC)
for CPURST# generation
Keyboard Chip Select (Rx5A[0]=0). To external keyboard controller chip.
Power-Up Configuration Strap (Sampled At Reset):
4.7K to GND = Socket-7, 4.7K to VCC3 = Socket-370 / Slot-1
Keyboard Inputs 6-3. Sampled at reset on SD[7-4] and latched into
Rx5A[7-4].
Chip Selects
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
ROMCS# / KBCS# / strap
PCS0# / GPO12 / XDIR
MCCS# / GPO13 / SOE#
MCCS# / GPI11 / GPO11
/ GPIOD
C1 O
T5 O
U5 O
U8 O
ROM Chip Select (Rx5A[0]=1). Chip Select to the BIOS ROM.
Power-Up Configuration Strap (Sampled At Reset):
4.7K to GND = Socket-7, 4.7K to VCC3 = Socket-370 / Slot-1
Programmable Chip Select 0 (Rx76[1] = 1 and Rx8B[0] = 1). Asserted
during I/O cycles to programmable read or write ISA I/O port ranges.
Addressed devices drive data to the SD pins (XDIR is disabled and the XBus is not implemented). See also Rx59[3] and Rx77[2].
Microcontroller Chip Select (Rx76[3] = 1, Rx76[4] = 0, Rx77[0] = 1).
Asserted during read or write accesses to I/O ports 62h or 66h.
Microcontroller Chip Select (Alternate Pin) (Rx76[4] = 0 selects MCCS#
on pin U8, Rx76[4] = 1 selects MCCS# on pin U5). Rx76[3] = 1 enables
MCCS# output on the selected pin.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -21- Pinouts
Page 28
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
General Purpose Inputs
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
GPI0 / IOCHCK#
GPI1 / IRQ8#
GPI2 / BATLOW#
GPI3 / LID / WSC#
GPI4 / IRQ6 / SLPBTN#
GPI5 / THRM / PME#
GPI6 / SMBALRT#
GPI7 / RING#
GPI8 / GPO8 / GPIOA / GPOWE
GPI9 / GPO9 / GPIOB / FAN2
GPI10 / GPO10 / GPIOC / CHAS / IRQ0
GPI11 / GPO11 / GPIOD / MCCS#
GPI16 / DRQ0
GPI17 / DRQ1
GPI18 / DRQ3
GPI19 / DRQ5
GPI20 / DRQ6
GPI21 / DRQ7
GPI22 / JBY
GPI23 / JBX
GPI[23-16] (SD[7-0] & RFSH#)
See also Function 0 Rx77[7-6]
F4 I
W11 I
U11 I
U10 I
G1 I
T11 I
W10 I
V11 I
T14 I
U12 I
V14 I
U8 I
L3 I
E2 I
D3 I
M1 I
M5 I
N4 I
W15 I
U14 I
n/a I
General Purpose Input 0 (Rx74[0] = 0)
General Purpose Input 1 (Rx5A[2] = 1)
General Purpose Input 2
General Purpose Input 3 (see Rx74[7] and Rx77[3])
General Purpose Input 4
General Purpose Input 5 (Read pin state at PMU IO Rx48[5])
General Purpose Input 6
General Purpose Input 7
General Purpose Input 8 (Rx74[2] = 0)
General Purpose Input 9 (Rx74[3] = 0)
General Purpose Input 10 (Rx74[4] = 0)
General Purpose Input 11 (Rx74[5] = 0)
General Purpose Input 16 (Rx77[7] = 1). Read at PMU IO
44[2]
General Purpose Input 17 (Rx77[7] = 1). Read at PMU IO
44[3]
General Purpose Input 18 (Rx77[7] = 1)
General Purpose Input 19 (Rx77[7] = 1)
General Purpose Input 20 (Rx77[7] = 1)
General Purpose Input 21 (Rx77[7] = 1)
General Purpose Input 22 (Rx77[6] = 1, game disa)
General Purpose Input 23 (Rx77[6] = 1, game disa)
General Purpose Inputs 16-23 (enabled on SD by RFSH# active)
GPI if Rx77[7] = 0 , SD if Rx77[7] = 1
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -22- Pinouts
Page 29
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
General Purpose Outputs
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
GPO0 (H) / SLOWCLK
GPO1 (H) / SUSA# / APICACK#
GPO2 (H) / SUSB# / APICCS#
GPO3 / SUSST1# (H)
GPO4 / CPUSTP# (L)
GPO5 / PCISTP# (L)
GPO6
GPO7 / SLP# (OD)
GPO8 / GPI8 / GPIOA / GPOWE
GPO9 / GPI9 / GPIOB / FAN2
GPO10 / GPI10 / GPIOC/CHAS/IRQ0
GPO11 / GPI11 / GPIOD / MCCS#
GPO12 / XDIR (H) / PCS0#
GPO13 / SOE# (L) / MCCS#
GPO14 / IRTX (L)
GPO15 / IRRX (L)
GPO16 / DACK0#
GPO17 / DACK1#
GPO18 / DACK3#
GPO19 / DACK5#
/ SERIRQ / MC97IRQ
GPO20 / DACK6#
GPO21
/DACK7#/THRM#/USBIRQB
GPO22 / JAY
GPO23 / JAX
GPO24 / DRQ2 (H)
/ USBOC1# / SERIRQ
GPO25 / DACK2# (H)
/ USBOC0#
GPO[23-16] (latched from SD[7-0])
GPOWE# / GPIOA / GPI8 / GPO8
Default pin functions are underlined in table above (with default level following in parentheses)
See also Function 0 Rx77[7-6]
T8 O
V9 O
W9 O
V10 O
Y12 O
V12 O
T7 O
T14 O
U12 O
V14 O
U8 O
T5 O
U5 O
E12 O
D12 O
L2 O
E1 O
D2 O
L4 O
M3 O
N2 O
Y15 O
V15 O
H3 O
G5 O
n/a O
T14 O
General Purpose Output 0 (Function 4 Rx54[1-0] = 00). Output value
determined by PMU I/O Rx4C[0]
General Purpose Output 1 (Rx74[7] = 0 and Function 4 Rx54[2] = 1)
General Purpose Output 2 (Rx74[7] = 0 and Function 4 Rx54[3] = 1)
General Purpose Output 3 (Function 4 Rx54[4] = 1)
General Purpose Output 4 (Rx75[4] = 1)
General Purpose Output 5 (Rx75[5] = 1)
General Purpose Output 6
General Purpose Output 7 (Rx75[7] = 1)
General Purpose Output 8 (Rx74[2] = 1 and Rx76[0] = 0)
General Purpose Output 9 (Rx74[3] = 1)
General Purpose Output 10 (Rx74[4] = 1 and Rx76[2] = 0)
General Purpose Output 11 (Rx74[5] = 1 and Rx76[3] = 0)
General Purpose Output 12 (Rx76[1] = 1 and Rx76[4] = 0)
General Purpose Output 13 (Rx77[0] = 1) see also Rx76[4-3]
General Purpose Output 14 (Rx76[5] = 1)
General Purpose Output 15 (Rx76[5] = 1)
General Purpose Output 16 (Rx77[7] = 1 and Rx77[3] = 0)
General Purpose Output 17 (Rx77[7] = 1 and Rx77[3] = 0)
General Purpose Output 18 (Rx77[7] = 1 and Rx77[3] = 0)
General Purpose Output 19 (Rx77[7] = 1, Rx77[3] = 0 and Rx74[6] = 0)
General Purpose Output 20 (Rx77[7] = 1 and Rx77[3] = 0)
General Purpose Output 21 (Rx77[7] = 1, Rx77[3] = 0, F4Rx57[0] = 0)
General Purpose Output 22 (Rx77[6] = 1, game disabled)
General Purpose Output 23 (Rx77[6] = 1, game disabled)
General Purpose Output 24 (Rx75[3] = 1 & Rx75[1]=1 & Rx68[3]=0)
General Purpose Output 25 (Rx75[3] = 1 & Rx75[2]=1 & Rx68[3]=0)
General Purpose Output 23-16 (Rx74[7]=0) latched by GPOWE# rising
General Purpose Output Write Enable (Rx74[2] = 1 and Rx76[0] = 1).
General Purpose I/Os
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
GPIOA / GPI8 / GPO8 / GPOWE
GPIOB / GPI9 / GPO9 / FAN2
GPIOC / GPI10 / GPO10 / CHAS / IRQ0
GPIOD / GPI11 / GPO11 / MCCS#
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -23- Pinouts
T14 IO
U12 IO
V14 IO
U8 IO
General Purpose I/O A / 8 (Rx76[0] = 0). GPOWE if Rx76[0] = 1.
See also Rx74[2]
General Purpose I/O B / 9. See also Rx74[3]
General Purpose I/O C / 10. (Rx76[2] = 0). See also Rx74[4]
General Purpose I/O D / 11. (Rx76[3] = 0). See also Rx74[5]
Page 30
VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Hardware Monitoring
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
VSENS1
VSENS2
VSENS3
VSENS4
VREF
TSENS1
TSENS2
FAN1
FAN2 / GPIOB / 9
CHAS / GPIOC / 10 / IRQ0
U13 I
V13 I
W14 I
Y14 I
T13 O
W13 I
Y13 I
T12 I
U12 I
V14 I
Voltage Sense 2.0V. Monitor for CPU core voltage.
Voltage Sense 2.5V. Monitor for North Bridge core voltage.
Voltage Sense 5V.
Voltage Sense 12V. Connect +12V through a resistive voltage divider to insure 5V
max to the input pin (see MVP4 Design Guide for details).
Voltage Reference for Thermal Sensing (2.48V ±5%)
Temperature Sense 1.
Temperature Sense 2.
Fan Speed Monitor 1. (3.3V only)
Fan Speed Monitor 2.
Chassis Intrusion Detect (Func 0 Rx76[2] = 1). Used for system security purposes.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -24- Pinouts
Page 31

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
p
Power Management
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
THRM / GPI5 / PME#
THRM# / GPO21 / DACK7#
PWRBTN#
SLPBTN# / IRQ6 / GPI4
RSMRST#
EXTSMI#
PME# / GPI5 / THRM
SMBALRT# / GPI6
LID / GPI3 / WSC#
RING# / GPI7
BATLOW# / GPI2
CPUSTP# / GPO4
PCISTP# / GPO5
SUSA# / GPO1 / APICD0
SUSB# / GPO2
SUSC#
SUSST1# / GPO3
SUSCLK / APICD1
T11 I
N2 O
Y11 I
G1 I / I /
I
V6 I
Y10 IOD
T11 I
W10 I
U10 I
V11 I
U11 I
Y12 O
V12 O
V9 O
W9 O
Y9 O
V10 O
T10 O
Thermal Alarm Monitor Input. (Rx74[1] = 1)
Internal Thermal Alarm Output. (F4 Rx57[0] = 1)
Power Button. Used by the Power Management subsystem to monitor an
external system on/off button or switch. The VT82C686B performs a 200us
debounce of this input if Function 4 Rx40[5] is set to 1. (3.3V only)
Sleep Button. Used by the Power Management subsystem to monitor an
external system sleep button or switch. (Function 4 Rx40[6]=1) (10K PU to
VCC if not used)
Resume Reset. Resets the internal logic connected to the VCCS power plane
and also resets portions of the internal RTC logic.
External System Management Interrupt. When enabled to allow it, a
falling edge on this input causes an SMI# to be generated to the CPU to enter
SMI mode. (10K PU to VCCS if not used) (3.3V only)
Power Management Event. (Rx74[1]=0) (1K PU to VCCS if not used)
SMB Alert (System Management Bus I/O space Rx08[3] = 1). When the
chip is enabled to allow it, assertion generates an IRQ or SMI or power
management event. (10K PU to VCCS if not used)
Notebook Computer Display Lid Open / Closed Monitor. Used by the
Power Management subsystem to monitor the opening and closing of the
display lid of notebook computers. Can be used to detect either low-to-high
and/or high-to-low transitions to generate an SMI#. The VT82C686B
erforms a 200 usec debounce of this input if Function 4 Rx40[5] is set to 1.
(10K PU to VCCS if not used)
Ring Indicator. May be connected to external modem circuitry to allow the
system to be re-activated by a received phone call. (10K PU to VCCS if not
used)
Battery Low Indicator. (10K PU to VCCS if not used) (3.3V only)
CPU Clock Stop (Rx75[4] = 0). Signals the system clock generator to
disable the CPU clock outputs. Not connected if not used. See also PMU I/O
Rx2C[3].
PCI Clock Stop (Rx75[5] = 0). Signals the system clock generator to
disable the PCI clock outputs. Not connected if not used.
Suspend Plane A Control (Rx74[7]=0 and Function 4 Rx54[2]=0).
Asserted during power management POS, STR, and STD suspend states.
Used to control the primary power plane. (10K PU to VCCS if not used)
Suspend Plane B Control (Rx74[7]=0 and Function 4 Rx54[3]=0). Asserted
during power management STR and STD suspend states. Used to control the
secondary power plane. (10K PU to VCCS if not used)
Suspend Plane C Control. Asserted during power management STD
suspend state. Used to control the tertiary power plane. Also connected to
ATX power-on circuitry.
Suspend Status 1 (Func4 Rx54[4] = 1 for GPO3). Typically connected to
the North Bridge to provide information on host clock status. Asserted when
the system may stop the host clock, such as Stop Clock or during POS, STR,
or STD suspend states. Connect 10K PU to VCCS.
Suspend Clock. 32.768 KHz output clock for use by the North Bridge (e.g.,
Apollo MVP3 or MVP4) for DRAM refresh purposes. Stopped during
Suspend-to-Disk and Soft-Off modes. Connect 10K PU to VCCS.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -25- Pinouts
Page 32

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Resets and Clocks
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
PWRGD
PCIRST#
RSTDRV
BCLK
OSC
RTCX1
RTCX2
SLOWCLK /
GPO0
W6 I
B16 O
J1 O
H5 O
E4 I
Y5 I
W5 O
T8 O
Power Good. Connected to the PWRGOOD signal on the Power Supply.
PCI Reset. Active low reset signal for the PCI bus. The VT82C686B will
assert this pin during power-up or from the control register.
Reset Drive. Reset signal to the ISA bus. Connect through an inverter to the
chipset north bridge RESET# input and to PCI bus RESET#.
Bus Clock. ISA bus clock.
Oscillator. 14.31818 MHz clock signal used by the internal Timer.
RTC Crystal Input: 32.768 KHz crystal or oscillator input. This input is
used for the internal RTC and for power-well power management logic.
RTC Crystal Output: 32.768 KHz crystal output
Slow Clock. .Frequency selectable if PMU function 4 Rx54[1-0] is nonzero
(set to 01, 10, or 11).
Power and Ground
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
VCC
GND
VCCS
VBAT
VCCH
GNDH
VCCU
GNDU
F7, F10, F12-F14,
H6, H15, J6, J15,
K6, K15, M6,
M15, N6, N15,
R7-R8, R11, R14
F6, F11, F15, G6,
G15, J9-J12, K9-
K12, L6, L9-L12,
L15, M9-M12,
P6, P15, R6, R15
R9-R10 P
Y6 P
R12 P
R13 P
F9 P
F8 P
P
Core Power. 3.3V nominal (3.15V to 3.45V). This supply is turned on only
when the mechanical switch on the power supply is turned on and the
PWRON signal is conditioned high. This pin should be connected to the
same voltage as the CPU I/O circuitry. Internally connected to hardware
monitoring system voltage detection circuitry for 3.3V monitoring.
P
Ground. Connect to primary motherboard ground plane.
Suspend Power. Always available unless the mechanical switch of the
power supply is turned off. If the “soft-off” state is not implemented, then
this pin can be connected to VCC. Signals powered by or referenced to this
plane are: PWRGD, RSMRST#, EXTSMI#, PWRBTN#, SMBCLK,
SMBDATA, SUSCLK, SUSA# / GPO1, SUSB# / GPO2, SUSC#, SUSST1#
/ GPO6, GPI1 / IRQ8#, GPI2 / BATLOW#, GPI3 / LID, GPI5 / PME#, GPI6
/ SMBALRT#, GPI7 / RING#, GPO0, ACSDIN, ACSDIN2
RTC Battery. Battery input for internal RTC (RTCX1, RTCX2)
Hardware Monitor / UDMA66 / Game Port Power. Power for hardware
monitoring subsystem (voltage monitoring, temperature monitoring, and fan
speed monitoring), internal IDE controller UDMA66 PLL, and Game Port
pins. Connect to VCC through a ferrite bead.
Hardware Monitor / UDMA66 / Game Port Ground. Connect to GND
through a ferrite bead.
USB Differential Output Power. Power for USB differential outputs
(USBP0+, P0-, P1+, P1-, P2+, P2-, P3+, P3-). Connect to VCC through a
ferrite bead.
USB Differential Output Ground. Connect to GND through a ferrite bead.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -26- Pinouts
Page 33

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
REGISTERS
Register Overview
The following tables summarize the configuration and I/O
registers of the VT82C686B. These tables also document the
power-on default value (“Default”) and access type (“Acc”)
for each register. Access type definitions used are RW
(Read/Write), RO (Read/Only), “—” for reserved / used
(essentially the same as RO), and RWC (or just WC) (Read /
Write 1’s to Clear individual bits). Registers indicated as RW
may have some read/only bits that always read back a fixed
value (usually 0 if unused); registers designated as RWC or
WC may have some read-only or read write bits (see
individual register descriptions for details).
Detailed register descriptions are provided in the following
section of this document. All offset and default values are
shown in hexadecimal unless otherwise indicated
Table 2. System I/O Map
Port Function Actual Port Decoding
00-1F Master DMA Controller 0000 0000 000x nnnn
20-3F Master Interrupt Controller 0000 0000 001x xxxn
40-5F Timer / Counter 0000 0000 010x xxnn
60-6F Keyboard Controller 0000 0000 0110 xnxn
(60h) KBC Data 0000 0000 0110 x0x0
(61h) Misc Functions & Spkr Ctrl 0000 0000 0110 xxx1
(64h) KBC Command / Status 0000 0000 0110 x1x0
70-77 RTC/CMOS/NMI-Disable 0000 0000 0111 0nnn
78-7F -available for system use- 0000 0000 0111 1xxx
80 -reserved- (debug port) 0000 0000 1000 0000
81-8F DMA Page Registers 0000 0000 1000 nnnn
90-91 -available for system use- 0000 0000 1001 000x
92 System Control 0000 0000 1001 0010
93-9F -available for system use- 0000 0000 1001 nnnn
A0-BF Slave Interrupt Controller 0000 0000 101x xxxn
C0-DF Slave DMA Controller 0000 0000 110n nnnx
E0-FF -available for system use- 0000 0000 111x xxxx
100-CF7 -available for system use*
CF8-CFB PCI Configuration Address 0000 1100 1111 10xx
CFC-CFF PCI Configuration Data 0000 1100 1111 11xx
D00-FFFF -available for system use-
* On-Chip Super-I/O Functions – PC-Standard Port Addresses
200-20F Game Port
2E8-2EF COM4
2F8-2FF COM2
378-37F Parallel Port (Standard & EPP)
3E8-3EF COM3
3F0-3F1 Configuration Index / Data
3F0-3F7 Floppy Controller
3F8-3FF COM1
778-77A Parallel Port (ECP Extensions) (Port 378+400)
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -27- Register Overview
Page 34

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Table 3. Registers
Legacy I/O Registers
Port Master DMA Controller Registers Default Acc
00 Channel 0 Base & Current Address RW
01 Channel 0 Base & Current Count RW
02 Channel 1 Base & Current Address RW
03 Channel 1 Base & Current Count RW
04 Channel 2 Base & Current Address RW
05 Channel 2 Base & Current Count RW
06 Channel 3 Base & Current Address RW
07 Channel 3 Base & Current Count RW
08 Status / Command RW
09 Write Request
0A Write Single Mask
0B Write Mode
0C Clear Byte Pointer FF
0D Master Clear
0E Clear Mask
0F Read / Write Mask RW
Master Interrupt Controller Regs Default Acc
Port
20 Master Interrupt Control — *
21 Master Interrupt Mask — *
20 Master Interrupt Control Shadow —
21 Master Interrupt Mask Shadow —
* RW if shadow registers are disabled
Timer/Counter Registers Default Acc
Port
40 Timer / Counter 0 Count RW
41 Timer / Counter 1 Count RW
42 Timer / Counter 2 Count RW
43 Timer / Counter Control
Keyboard Controller Registers Default Acc
Port
60 Keyboard Controller Data RW
61 Misc Functions & Speaker Control RW
64 Keyboard Ctrlr Command / Status RW
CMOS / RTC / NMI Registers Default Acc
Port
70 CMOS Memory Address & NMI Disa
71 CMOS Memory Data (128 bytes) RW
72 CMOS Memory Address
73 CMOS Memory Data
74 CMOS Memory Address
75 CMOS Memory Data (256 bytes) RW
NMI Disable is port 70h (CMOS Memory Address) bit-7.
RTC control occurs via specific CMOS data locations (0-Dh).
Ports 74-75 may be used to access CMOS if the internal RTC
is disabled.
WO
WO
WO
WO
WO
WO
RW
RW
WO
WO
RW
RW
RW
Legacy I/O Registers (continued)
Port DMA Page Registers Default Acc
87 DMA Page – DMA Channel 0 RW
83 DMA Page – DMA Channel 1 RW
81 DMA Page – DMA Channel 2 RW
82 DMA Page – DMA Channel 3 RW
8F DMA Page – DMA Channel 4 RW
8B DMA Page – DMA Channel 5 RW
89 DMA Page – DMA Channel 6 RW
8A DMA Page – DMA Channel 7 RW
System Control Registers Default Acc
Port
92 System Control RW
Slave Interrupt Controller Regs Default Acc
Port
A0 Slave Interrupt Control — *
A1 Slave Interrupt Mask — *
A0 Slave Interrupt Control Shadow —
A1 Slave Interrupt Mask Shadow —
* RW accessible if shadow registers are disabled
Slave DMA Controller Registers Default Acc
Port
C0 Channel 0 Base & Current Address RW
C2 Channel 0 Base & Current Count RW
C4 Channel 1 Base & Current Address RW
C6 Channel 1 Base & Current Count RW
C8 Channel 2 Base & Current Address RW
CA Channel 2 Base & Current Count RW
CC Channel 3 Base & Current Address RW
CE Channel 3 Base & Current Count RW
D0 Status / Command RW
D2 Write Request
D4 Write Single Mask
D6 Write Mode
D8 Clear Byte Pointer FF
DA Master Clear
DC Clear Mask
DE Read / Write Mask RW
WO
WO
WO
WO
WO
WO
RW
RW
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -28- Register Overview
Page 35

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
y
Super-I/O Configuration Index (I/O Space)
Port Super-I/O Configuration Registers Default Acc
3F0 Super-I/O Config Index (Rx85[1]=1) 00 RW
3F1 Super-I/O Config Data (Rx85[1]=1) 00 RW
Super-I/O Configuration Regs (Indexed via Port 3F0/1)
Offset Ke
-
D1 Keyboard Scan Code Ref 0
D2 Keyboard Scan Code Ref 1 00
D3 Keyboard Scan Code Ref 2 00
D4 Keyboard Scan Code Ref 3 00
D5 Keyboard Scan Code Ref 4 00
D6 Keyboard Scan Code Ref 5 00
D7 Keyboard Scan Code Ref 6 00
D8 Keyboard Scan Code Ref 7 00
D9 PS/2 Mouse Scan Code Ref 1
DA PS/2 Mouse Scan Code Ref 2 00
DB PS/2 Mouse Scan Code Mask 00
DC-DF
Offset
E0 Super-I/O Device ID
E1 Super-I/O Device Revision 00
E2 Function Select
E3 Floppy Ctrlr Base Addr (def = 3F0-7)
E4-E5 -reserved- 00 RO
E6 Parallel Port Base Addr (def = 378-F)
E7 Serial Port 1 Base Addr (def = 3F8-F)
E8 Serial Port 2 Base Addr (def = 2F8-F)
E9-ED -reserved- 00 RO
EE Serial Port Configuration 00
EF Power Down Control 00
F0 Parallel Port Control 00
F1 Serial Port Control 00
F2 Test Mode (Do Not Program) 00
F3 -reserved- 00 RO
F4 Test Mode (Do Not Program) 2 00
F5 -reserved- 00 RO
F6 Floppy Controller Configuration 00
F7 -reserved- 00 RO
F8 Floppy Controller Drive Select 00
F9-FB -reserved- 00 RO
FC General Purpose I/O 00
FD-FF -reserved- 00 RO
board / Mouse (CE Only) Default Acc
-
-reserved- 00 RO
Super-I/O Control Default Acc
-
F0 RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
09 RW
RW
RW
3C RW
RW
03 RW
FC RW
DE RW
FE RW
BE RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Super-I/O I/O Ports
Offset Floppy Disk Controller (Base = E3) Default Acc
00-01 -reserved- 00 –
02 FDC Command – RW
03 -reserved- 00 –
04 FDC Main Status –
04 FDC Data Rate Select 02
05 FDC Data – RW
06 -reserved- 00 –
07 Disk Change Status –
Offset
Offset
Offset
Parallel Port (Base = E6) Default Acc
00 Parallel Port Data – RW
01 Parallel Port Status –
02 Parallel Port Control
03 EPP Address RW
04 EPP Data Port 0 RW
05 EPP Data Port 1 RW
06 EPP Data Port 2 RW
07 EPP Data Port 3 RW
400h ECP Data / Configuration A RW
401h ECP Configuration B RW
402h ECP Extended Control RW
Serial Port 1 (Base = E7) Default Acc
0 Transmit (Wr) / Receive (Rd) Buffer RW
1 Interrupt Enable RW
2 FIFO Control
2 Interrupt Status
3 UART Control RW
4 Handshake Control RW
5 UART Status RW
6 Handshake Status RW
7 Scratchpad RW
9-8 Baud Rate Generator Divisor RW
A-F -undefined- –
Serial Port 2 (Base = E8) Default Acc
0 Transmit (Wr) / Receive (Rd) Buffer RW
1 Interrupt Enable RW
2 FIFO Control
2 Interrupt Status
3 UART Control RW
4 Handshake Control RW
5 UART Status RW
6 Handshake Status RW
7 Scratchpad RW
9-8 Baud Rate Generator Divisor RW
A-F -undefined- –
E0
RO
WO
RO
RO
RW
WO
RO
WO
RO
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -29- Register Overview
Page 36

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
I/O Registers – SoundBlaster Pro
Offset SB Pro Registers (220 or 240h typ) Default Acc
0 FM Left Channel Index / Status RW
1 FM Left Channel Data
2 FM Right Channel Index / Status RW
3 FM Right Channel Data
4 Mixer Index
5 Mixer Data RW
6 Sound Processor Reset
7 -reserved- 00 –
8 FM Index / Status (Both Channels) RW
9 FM Data (Both Channels)
A Sound Processor Data
B -reserved- 00 –
C Sound Processor Command / Data
Sound Processor Buffer Status
D -reserved- 00 –
E Snd Processor Data Available Status
F -reserved- 00 –
SB Pro Regs (same as offsets 8 & 9) Default Acc
Port
388h FM Index / Status RW
389h FM Data
The above group of registers emulates the “FM”, “Mixer”,
and “Sound Processor” functions of the SoundBlaster Pro.
WO
WO
WO
WO
WO
RO
WR
RD
RO
WO
Memory Mapped I/O Registers – APIC
Offset APIC Default Acc
FEC0 0000 APIC Index (8-bit) 00 RW
FEC0 0010 APIC Data (32-bit) 0000 0000 RW
FEC0 0020 APIC IRQ Pin Assertion (8-bit) undefined
FEC0 0040 APIC EOI (8-bit) undefined
Indexed I/O Registers – APIC
Offset APIC Default Acc
0 APIC Identification 0000 0000 RW
1 APIC Version CD: 0017 0011
CE: 0017 8002
2 APIC Arbitration 0000 0000
3 Boot Configuration (CE Only) 0000 0000 RW
WO
WO
RO
RO
RO
I/O Registers – Game Port
Offset Game Port (200-20F typical) Default Acc
0 -reserved- 00 –
1 Game Port Status
1 Start One-Shot
2-F -reserved- 00 –
RO
WO
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -30- Register Overview
Page 37

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
g
g
g
PCI Function 0 Registers – PCI-to-ISA Bridge
Configuration Space PCI-to-ISA Bridge Header Registers
Offset PCI Confi
1-0 Vendor ID
3-2 Device ID
5-4 Command
7-6 Status
8 Revision ID
9 Programming Interface 00 RO
A Sub Class Code
B Base Class Code
C -reserved- (cache line size) 00 —
D -reserved- (latency timer) 00 —
E Header Type
F Built In Self Test (BIST) 00 RO
10-27 -reserved- (base address registers) 00 —
28-2B -reserved- (unassigned) 00 —
2F-2C Subsystem ID Read 00 RO
30-33 -reserved- (expan. ROM base addr) 00 —
34 Power Management Capability Ptr
35-3B -reserved- (unassigned) 00 —
3C -reserved- (interrupt line) 00 —
3D -reserved- (interrupt pin) 00 —
3E -reserved- (min gnt) 00 —
3F -reserved- (max lat) 00 —
Configuration Space PCI-to-ISA Bridge-Specific Registers
Offset ISA Bus Control Default Acc
40 ISA Bus Control 00 RW
41 ISA Test Mode 00 RW
42 ISA Clock Control 00 RW
43 ROM Decode Control 00 RW
44 Keyboard Controller Control 00 RW
45 Type F DMA Control 00 RW
46 Miscellaneous Control 1 00 RW
47 Miscellaneous Control 2 00 RW
48 Miscellaneous Control 3
49 Port 70 / 74 Access Status (CE Only) 00
4A IDE Interrupt Routing
4B -reserved- 00 —
4C DMA / Master Mem Access Control 1 00 RW
4D DMA / Master Mem Access Control 2 00 RW
4F-4E DMA / Master Mem Access Control 3
Offset Plu
50 PnP DMA Request Control
51 PnP Routing for LPT / FDC IRQ 00 RW
52 PnP Routing for COM2 / COM1 IRQ 00 RW
53 -reserved- 00 —
uration Space Header Default Acc
1106
0686
0087 RW
0200 WC
nn
01
06
80
C0
01
04
0300
and Play Control Default Acc
2D
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RW
RO
RW
RW
RW
Offset Plu
54 PCI IRQ Edge / Level Select 00 RW
55 PnP Routing for PCI INTA 00 RW
56 PnP Routing for PCI INTB-C 00 RW
57 PnP Routing for PCI INTD 00 RW
58 APIC IRQ Output Control 00 RW
59 -reserved5A KBC / RTC Control
5B Internal RTC Test Mode 00 RW
5C DMA Control 00 RW
5D-5E -reserved- 00 —
5F -reserved- (do not program)
† Bit 7-4 power-up default depends on external strapping
Offset Distributed DMA Default Acc
61-60 Channel 0 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
63-62 Channel 1 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
65-64 Channel 2 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
67-66 Channel 3 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
69-68 Serial IRQ Control 0000 RW
6B-6A Channel 5 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
6D-6C Channel 6 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
6F-6E Channel 7 Base Address / Enable 0000 RW
Offset Miscellaneous Default Acc
70 Subsystem ID Write 00 WO
71-73 -reserved- 00 —
74 GPIO Control 1 00 RW
75 GPIO Control 2 00 RW
76 GPIO Control 3 00 RW
77 GPIO Control 4
79-78 PCS0# I/O Port Address 0000 0000 RW
7B-7A PCS1# I/O Port Address 0000 0000 RW
7D-7C PCI DMA Channel Enable 0000 RW
7F-7E 32-Bit DMA Control 0000 RW
80 Programmable Chip Select Mask 00 RW
81 ISA Positive Decoding Control 1 00 RW
82 ISA Positive Decoding Control 2 00 RW
83 ISA Positive Decoding Control 3 00 RW
84 ISA Positive Decoding Control 4 CD: 00
85 Extended Function Enable 00 RW
86-87 PnP IRQ/DRQ Test (do not program) 00 RW
88 PLL Test 00 RW
89 PLL Control 00 RW
8A PCS2/3 I/O Port Address Mask 00 RW
8B PCS Control 00 RW
8D-8C PCS2# I/O Port Address 0000 RW
8F-8E PCS3# I/O Port Address 0000 RW
90-FF -reserved- 00 —
and Play Control (cont’d) Default Acc
04
x4†
04
10
CE: 10
—
RW
RW
RW
RW
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -31- Register Overview
Page 38

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
g
g
g
PCI Function 1 Registers – IDE Controller
Configuration Space IDE Header Registers
Offset PCI Confi
1-0 Vendor ID
3-2 Device ID
5-4 Command
7-6 Status
8 Revision ID
9 Programming Interface
A Sub Class Code
B Base Class Code
C -reserved- (cache line size) 00 —
D Latency Timer 00
E Header Type 00 RO
F Built In Self Test (BIST) 00 RO
13-10 Base Address – Pri Data / Command
17-14 Base Address – Pri Control / Status
1B-18 Base Address – Sec Data / Command
1F-1C Base Address – Sec Control / Status
23-20 Base Address – Bus Master Control
24-2F -reserved- (unassigned) 00 —
30-33 -reserved- (expan ROM base addr) 00 —
34 Capability Pointer
35-3B -reserved- (unassigned) 00 —
3C Interrupt Line
3D Interrupt Pin
3E Minimum Grant 00 RO
3F Maximum Latency 00 RO
Configuration Space IDE-Specific Registers
Offset Confi
40 IDE Chip Enable
41 IDE Configuration 1
42 IDE Configuration 2
43 IDE FIFO Configuration
44 IDE Miscellaneous Control 1
45 IDE Miscellaneous Control 2 00 RW
46 IDE Miscellaneous Control 3
4B-48 IDE Drive Timing Control
4C IDE Address Setup Time
4D -reserved- (do not program) 00
4E-4F -reserved- 00 —
uration Space Header Default Acc
uration Space IDE Registers Default Acc
1106
0571
0080
0280 RW
nn
85 RW
01
01
000001F0
000003F4
00000170
00000374
0000CC01 RW
C0
0E RW
01
08
02
09 RW
0A
68
C0
A8A8A8A8
FF
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RW
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Configuration Space IDE-Specific Registers (continued)
Offset Confi
53-50 UltraDMA Extended Timing Control
54 UltraDMA FIFO Control
55-5F -reserved- 00 —
61-60 IDE Primary Sector Size
62-67 -reserved- 00 —
69-68 IDE Secondary Sector Size
69-6F -reserved- 00 —
70 IDE Primary Status 00 RW
71 IDE Primary Intrpt Control 00 RW
72-77 -reserved- 00 —
78 IDE Secondary Status 00 RW
79 IDE Secondary Intrpt Control 00 RW
7A-7F -reserved- 00 —
83-80 IDE Primary S/G Descriptor Address 0000 0000 RW
84-87 -reserved- 00 —
8B-88 IDE Secondary S/G Descriptor Addr 0000 0000 RW
8C-BF -reserved- 00 —
C3-C0 PCI PM Block 1
C7-C4 PCI PM Block 2 0000 0000 RW
C8-FF -reserved- 00 —
I/O Registers – IDE Controller (SFF 8038 v1.0 Compliant
Offset
0 Primary Channel Command 00 RW
1 -reserved- 00 —
2 Primary Channel Status 00
3 -reserved- 00 —
4-7 Primary Channel PRD Table Addr 00 RW
8 Secondary Channel Command 00 RW
9 -reserved- 00 —
A Secondary Channel Status 00
B -reserved- 00 —
C-F Secondary Channel PRD Table Addr 00 RW
uration Space IDE Registers Default Acc
07070707
04
0200
0200
0002 0001 RO
IDE I/O Registers Default Acc
RW
RW
RW
RW
WC
WC
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -32- Register Overview
Page 39

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
g
g
g
f
g
PCI Function 2 Registers – USB Controller Ports 0-1
Configuration Space USB Header Registers
Offset PCI Confi
1-0 Vendor ID
3-2 Device ID
5-4 Command 0000
7-6 Status
8 Revision ID
9 Programming Interface 00 RO
A Sub Class Code
B Base Class Code
C Cache Line Size 00 RO
D Latency Timer
E Header Type 00 RO
F BIST 00 RO
10-1F -reserved- 00 —
23-20 USB I/O Register Base Address
24-33 -reserved- 00 —
34 USB Power Management Capabilities
35-3B -reserved- 00 —
3C Interrupt Line 00
3D Interrupt Pin
3E-3F -reserved- 00 —
uration Space Header Default Acc
1106
3038
0210 WC
nn
03
0C
16 RW
00000301 RW
80
04
RO
RO
RW
RO
RO
RO
RO
RW
RO
PCI Function 3 Registers – USB Controller Ports 2-3
Configuration Space USB Header Registers
Offset PCI Confi
1-0 Vendor ID
3-2 Device ID
5-4 Command 0000
7-6 Status
8 Revision ID
9 Programming Interface 00 RO
A Sub Class Code
B Base Class Code
C Cache Line Size 00 RO
D Latency Timer
E Header Type 00 RO
F BIST 00 RO
10-1F -reserved- 00 —
23-20 USB I/O Register Base Address
24-33 -reserved- 00 —
34 USB Power Management Capabilities
35-3B -reserved- 00 —
3C Interrupt Line 00
3D Interrupt Pin
3E-3F -reserved- 00 —
uration Space Header Default Acc
1106
3038
RW
0210 WC
nn
03
0C
16 RW
00000301 RW
80
RW
04
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
Configuration Space USB-Specific Registers
Offset USB Control Default Acc
40 USB Miscellaneous Control 1 00
41 USB Miscellaneous Control 2
42 USB FIFO Control 00
43 -reserved- 00 —
44-45 -reserved- (test, do not program)
46-47 -reserved- (test) RO
48-5F -reserved- 00 —
60 USB Serial Bus Release Number
61-7F -reserved- 00 —
83-80 PM Capability
84 PM Capability Status 00
85-BF -reserved- 00 —
C1-C0 USB Legacy Support
C2-FF -reserved- 00 —
I/O Registers – USB Controller
Offset USB I/O Re
1-0 USB Command 0000 RW
3-2 USB Status 0000
5-4 USB Interrupt Enable 0000 RW
7-6 Frame Number 0000 RW
B-8 Frame List Base Address 00000000 RW
C Start Of Frame Modify
11-10 Port 0 Status / Control
13-12 Port 1 Status / Control
14-1F -reserved- 00 —
isters Default Acc
10 RW
10
0002 0001
2000 RW
40
0080 WC
0080 WC
RW
RW
RW
RO
RO
RW
WC
RW
Configuration Space USB-Specific Registers
Offset USB Control De
40 USB Miscellaneous Control 1 00
41 USB Miscellaneous Control 2
42 USB FIFO Control 00
43 -reserved- 00 —
44-45 -reserved- (test only, do not program)
46-47 -reserved- (test) RO
48-5F -reserved- 00 —
60 USB Serial Bus Release Number
61-7F -reserved- 00 —
83-80 PM Capability
84 PM Capability Status 00
85-BF -reserved- 00 —
C1-C0 USB Legacy Support
C2-FF -reserved- 00 —
I/O Registers - USB Controller
Offset USB I/O Re
1-0 USB Command 0000 RW
3-2 USB Status 0000
5-4 USB Interrupt Enable 0000 RW
7-6 Frame Number 0000 RW
B-8 Frame List Base Address 00000000 RW
C Start Of Frame Modify
11-10 Port 2 Status / Control
13-12 Port 3 Status / Control
14-1F -reserved- 00 —
isters Default Acc
ault Acc
10 RW
10
0002 0001
2000 RW
40
0080 WC
0080 WC
RW
RW
RW
RO
RO
RW
WC
RW
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -33- Register Overview
Page 40

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
g
O
O
O
7
O
9
OA Sub Class Code
O
Code
O
C Cache
O
O
ype
O
O
eserved
—
de
d Capab
O
35-3
eserved
00
—
g
PCI Function 4 Registers - Power Management
Configuration Space Pwr Management Header Registers
Offset PCI Confi
1-0 Vendor ID
3-2 Device ID
5-4 Command 0000 R
-6 Status
8 Revision ID
Programming Interface
B Base Class
D Latency Timer 00 R
E Header T
F BIST 00 R
10-33 -r
34 Pwr Mgmt Exten
F -r
† The default values for these registers may be changed by
writing to offsets 61-63h (see below).
Configuration Space Power Management Registers
Offset Power Mana
40 General Configuration 0 00 RW
41 General Configuration 1 00 RW
42 ACPI Interrupt Select 00 RW
43 Internal Timer Read Test
45-44 Primary Interrupt Channel 0000 RW
47-46 Secondary Interrupt Channel 0000 RW
4B-48 Power Mgmt I/O Base (256 Bytes)
4C Host Bus Power Management Control 00 RW
4D Throttle / Clock Stop Control 00 RW
4E-4F -reserved- 00
53-50 GP Timer Control 0000 0000 RW
54 Power Well Control 00 RW
55 USB Wakeup Control 00 RW
56 -reserved- 00
57 Miscellaneous Control 00 RW
58 GP2 / GP3 Timer Control 00 RW
59 GP2 Timer 00 RW
5A GP3 Timer 00 RW
5B-60 -reserved- 00
61 Read value for Offset 9 (Prog Intfc) 00
62 Read value for Offset A (Sub Class) 00
63 Read value for Offset B (Base Class) 00
64-67 -reserved- 00
6B-68 Power Management Capabilities I
6F-6C Power Management Capabilities II 0000 0000
70-7F -reserved- 00
uration Space Header Default Acc
Line Size 00 R
00 R
- 00
ilities Ptr
-
ement Default Acc
— RO
0000 0001
0002 0001 RO
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
RW
—
—
—
WO
WO
WO
—
RO
—
Configuration Space Hardware Monitor Registers
Offset System Management Bus Default Acc
71-70 Hardware Mon IO Base (128 Bytes)
72-73 -reserved- 00
74 Hardware Monitor Control 00 RW
75-8F -reserved- 00
Configuration Space SMBus Registers
Offset
System Management Bus Default Acc
93-90 SMBus I/O Base (16 Bytes)
94-D1 -reserved- 00
D2 SMBus Host Configuration 00 RW
D3 SMBus Host Slave Command 00 RW
D4 SMBus Slave Address Shadow Port 1 00 RW
D5 SMBus Slave Address Shadow Port 2 00 RW
D6 SMBus Revision ID
D7-FF -reserved- 00
0001
0000 0001
nn RO
RW
—
—
RW
—
—
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -34- Register Overview
Page 41

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
g
g
p
g
p
y
I/O Space Power Management - Registers
Offset Basic Control / Status Re
1-0 Power Management Status 0000
3-2 Power Management Enable 0000 RW
5-4 Power Management Control 0000 RW
6-7 -reserved- 00
B-8 Power Management Timer 0000 0000 RW
C-F -reserved- 00
Offset Processor Re
13-10 Processor and PCI Bus Control 0000 0000 RW
14 Processor LVL2 00
15 Processor LVL3 00
16-1F -reserved- 00
Offset General Pur
21-20 General Purpose Status 0000
23-22 General Purpose SCI Enable 0000 RW
25-24 General Purpose SMI Enable 0000 RW
26-27 -reserved- 00
Offset Generic Re
29-28 Global Status 0000
2B-2A Global Enable 0000 RW
2D-2C Global Control
2E -reserved- 00
2F SMI Command 00 RW
33-30 Primary Activity Detect Status 0000 0000
37-34 Primary Activity Detect Enable 0000 0000 RW
3B-38 GP Timer Reload Enable 0000 0000 RW
3C-3F -reserved- 00
Offset General Pur
40 Extended I/O Trap Status 00
41 -reserved- 00
42 Extended I/O Trap Enable 00 RW
43 -reserved- 00
44 External SMI / GPI Input Value
45 SMI / IRQ / Resume Status 00
46-47 -reserved- 00
4B-48 GPI Port Input Value
4F-4C GPO Port Output Value
50-FF -reserved- 00
isters Default Acc
ose Registers Default Acc
isters Default Acc
ose I/O Registers Default Acc
isters Default Acc
WC
—
—
RO
RO
—
WC
—
WC
0010
input RO
input RO
03FF FFFF
RW
—
WC
—
WC
—
—
RO
—
RW
—
I/O Space System Management Bus Registers
Offset S
0 SMBus Host Status 00
1 SMBus Slave Status 00 RW
2 SMBus Host Control 00 RW
3 SMBus Host Command 00 RW
4 SMBus Host Address 00 RW
5 SMBus Host Data 0 00 RW
6 SMBus Host Data 1 00 RW
7 SMBus Block Data 00 RW
8 SMBus Slave Control 00 RW
9 SMBus Shadow Command 00
A-B SMBus Slave Event 0000 RW
C-D SMBus Slave Data 0000
0E-53 -reserved- 00
54 SMBus Clock Select 00 RW
55-FF -reserved- 00
stem Management Bus Default Acc
WC
RO
RO
—
—
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -35- Register Overview
Page 42

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
I/O Space Hardware Monitor Registers
Offset Hardware Monitor Default Acc
00-3F Value RAM
00-12 -reserved- 00
13 Analog Data 15-8 00 RW
14 Analog Data 7-0 00 RW
15 Digital Data 7-0 00 RW
16 Channel Counter 00 RW
17 Data Valid & Channel Indicators 00 RW
18-1F -reserved- 00
20 TSENS1 (W13) Temp Reading 00 RW
21 TSENS2 (Y13) Temp Reading 00 RW
22 VSENS1 (U13) Voltage Reading 00 RW
23 VSENS2 (V13) Voltage Reading 00 RW
24 Internal Core VCC Voltage Reading 00 RW
25 VSENS3 (W14) Voltage Reading 00 RW
26 VSENS4 (Y14) Voltage Reading 00 RW
27 -reserved- (-12V Voltage Reading) 00
28 -reserved- (-5V Voltage Reading) 00
29 FAN1 (T12) Count Reading 00 RW
2A FAN2 (U12) Count Reading 00 RW
2B VSENS1 (CPU) Voltage High Limit 00 RW
2C VSENS1 (CPU) Voltage Low Limit 00 RW
2D VSENS2 (NB) Voltage High Limit 00 RW
2E VSENS2 (NB) Voltage Low Limit 00 RW
2F Internal Core VCC High Limit 00 RW
30 Internal Core VCC Low Limit 00 RW
31 VSENS3 (5V) Voltage High Limit 00 RW
32 VSENS3 (5V) Voltage Low Limit 00 RW
33 VSENS4 (12V) Voltage High Limit 00 RW
34 VSENS4 (12V) Voltage Low Limit 00 RW
35 -reserved- (-12V Sense High Limit) 00
36 -reserved- (-12V Sense Low Limit) 00
37 -reserved- (-5V Sense High Limit) 00
38 -reserved- (-5V Sense Low Limit) 00
39 TSENS1 Hot High Limit 00 RW
3A TSENS1 Hot Hysteresis Lo Lim 00 RW
3B FAN1 Fan Count Limit 00 RW
3C FAN2 Fan Count Limit 00 RW
3D TSENS2 Hot High Limit 00 RW
3E TSENS2 Hot Hysteresis Lo Lim 00 RW
3F Stepping ID Number 00 RW
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Offset Hardware Monitor (continued) Default Acc
40 Hardware Monitor Configuration
41 Hardware Monitor Interrupt Status 1 00
42 Hardware Monitor Interrupt Status 2 00
43 Hardware Monitor Interrupt Mask 1 00 RW
44 Hardware Monitor Interrupt Mask 2 00 RW
45-46 -reserved- 00
47 Hardware Monitor Fan Configuration
48 -reserved- 00
49 HW Mon Temp Value Lo-Order Bits 00 RW
4A -reserved- 00
4B Temperature Interrupt Configuration
4C-FF -reserved- 00
08
50
15
RW
RO
RO
—
RW
—
—
RW
—
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -36- Register Overview
Page 43

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
g
g
PCI Function 5 & 6 Registers – AC97 / MC97 Codecs
Function 5 Configuration Space AC97 Header Registers
Offset PCI Confi
1-0 Vendor ID
3-2 Device ID
5-4 Command 0000
7-6 Status
8 Revision ID
9 Programming Interface 00 RO
A Sub Class Code
B Base Class Code
C Cache Line Size 00 RO
D Latency Timer 00
E Header Type 00 RO
F BIST 00 RO
13-10 Base Address 0 - SGD Control/Status
17-14 Base Address 1 - FM NMI Status
1B-18 Base Address 2 - MIDI Port 0000 0000
1F-1C Base Address 3 (reserved) 0000 0000 —
23-20 Base Address 4 (reserved) 0000 0000 —
27-24 Base Address 5 (reserved) 0000 0000 —
28-29 -reserved- 00 —
2F-2C Subsys ID / SubVendor ID 0000 0000
33-30 Expansion ROM (reserved) 0000 0000 —
34 Capture Pointer 00
35-3B -reserved- 00 —
3C Interrupt Line 00
3D Interrupt Pin
3E-3F -reserved- 00 —
uration Space Header Default Acc
1106
3058
0210 WC
nn
01
04
0000 0001 RW
0000 0001 RW
03
RO
RO
RW
RO
RO
RO
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RO
Function 6 Configuration Space MC97 Header Registers
Offset PCI Confi
1-0 Vendor ID
3-2 Device ID
5-4 Command 0000
7-6 Status
8 Revision ID
9 Programming Interface 00 RO
A Sub Class Code
B Base Class Code
C Cache Line Size 00 RO
D Latency Timer 00
E Header Type 00 RO
F BIST 00 RO
13-10 Base Address 0 - SGD Control/Status
17-14 Base Address 1 - FM NMI Status
1B-18 Base Address 2 - MIDI Port 0000 0000
1F-1C Base Address 3 (reserved) 0000 0000 —
23-20 Base Address 4 (reserved) 0000 0000 —
27-24 Base Address 5 (reserved) 0000 0000 —
28-29 -reserved- 00 —
2F-2C Subsys ID / SubVendor ID 0000 0000
33-30 Expansion ROM (reserved) 0000 0000 —
34 Capture Pointer 00
35-3B -reserved- 00 —
3C Interrupt Line 00
3D Interrupt Pin
3E-3F -reserved- 00 —
uration Space Header Default Acc
1106
3068
0200 WC
nn
80
07
0000 0001 RW
0000 0001 RW
03
RO
RO
RW
RO
RO
RO
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RO
Configuration Space Audio Codec-Specific Registers
Offset Audio Codec Link Control Default Acc
40 AC-Link Interface Status 00
41 AC-Link Interface Control 00 RW
42 Function Enable 00 RW
43 Plug and Play Control
44 MC97 Interface Control 00
45-47 -reserved- 00 —
48 FM NMI Control 00
49 -reserved- 00 —
4B-4A Game Port Base Address 0000 RW
4C-FF -reserved- 00 —
Note that these registers are the same as function 6 except for
offset 44 (Read / Write in function 6)
1C
RO
RW
RO
RO
Configuration Space Modem Codec-Specific Registers
Offset Modem Codec Link Control Default Acc
40 AC-Link Interface Status 00
41 AC-Link Interface Control 00 RW
42 Function Enable 00 RW
43 Plug and Play Control
44 MC97 Interface Control 00 RW
45-47 -reserved- 00 —
48 FM NMI Control 00
49 -reserved- 00 —
4B-4A Game Port Base Address 0000
4C-FF -reserved- 00 —
Note that these registers are the same as function 5 except for
offset 44 (Read Only in function 5)
1C
RO
RW
RO
RO
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -37- Register Overview
Page 44

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
g
g
g
g
g
Function 5 I/O Base 0 Registers – AC97 Audio S/G DMA
Offset AC97 SGD I/O Re
0 SGD Read Channel Status 00
1 SGD Read Channel Control 00 RW
2 SGD Read Channel Type 00 RW
3 -reserved- 00 —
7-4 SGD Read Chan Table Pointer Base
SGD Read Channel Current Address
B-8 Reserved (Test) 0000 0000
F-C SGD Read Chan Current Count 0000 0000
10 SGD Write Channel Status 00
11 SGD Write Channel Control 00 RW
12 SGD Write Channel Type 00 RW
13 -reserved- 00 —
17-14 SGD Write Chan Table Pointer Base
SGD Write Channel Current Address
1B-18 Reserved (Test) 0000 0000
1F-1C SGD Write Channel Current Count 0000 0000
20 SGD FM Channel Status 00
21 SGD FM Channel Control 00 RW
22 SGD FM Type 00 RW
23 -reserved- 00 —
27-24 SGD FM Channel Table Pointer Base
SGD FM Channel Current Address
2B-28 Reserved (Test) 0000 0000
2F-2C SGD FM Channel Current Count 0000 0000
30-7F -reserved- 00 —
Offset AC97 / Audio Codec I/O Registers Default Acc
83-80 AC97 Controller Command / Status 0000 0000 RW
87-84 SGD Status Shadow 0000 0000
88-FF -reserved- 00 —
isters Default Acc
WC
0000 0000 WR
RD
RO
RO
WC
0000 0000 WR
RD
RO
RO
WC
0000 0000 WR
RD
RO
RO
RO
Function 6 I/O Base 0 Registers – MC97 Modem S/G
DMA
Offset MC97 SGD I/O Re
40 SGD Read Channel Status 00
41 SGD Read Channel Control 00 RW
42 SGD Read Channel Type 00 RW
43 -reserved- 00 —
47-44 SGD Read Chan Table Pointer Base
SGD Read Channel Current Address
4B-48 -reserved- (Test) 0000 0000
4F-4C SGD Read Chan Current Count 0000 0000
50 SGD Write Channel Status 00
51 SGD Write Channel Control 00 RW
52 SGD Write Channel Type 00 RW
53 -reserved- 00 —
57-54 SGD Write Chan Table Pointer Base
SGD Write Channel Current Address
5B-58 Reserved (Test) 0000 0000
5F-5C SGD Write Channel Current Count 0000 0000
60-7F -reserved- 00 —
Offset AC97 / Modem Codec I/O Registers Default Acc
83-80 AC97 Controller Command / Status 0000 0000 RW
87-84 SGD Status Shadow 0000 0000
8B-88 Modem Codec GPI Intr Status / GPIO 0000 0000
8F-8C Modem Codec GPI Interrupt Enable 0000 0000 RW
90-FF -reserved- 00 —
isters Default Acc
WC
0000 0000 WR
RD
RO
RO
WC
0000 0000 WR
RD
RO
RO
RO
WC
Function 5 I/O Base 1 Registers – FM NMI Status
Offset FM NMI Status Re
0 FM NMI Status 00
1 FM NMI Data 00
2 FM NMI Index 00
3 -reserved- 00 —
Function 5 I/O Base 2 Registers – MIDI / Game Port
Offset FM NMI Status Re
1-0 MIDI Port Base 0330 RW
3-2 Game Port Base 0200 RW
Function 5 I/O Base 3 Registers – Codec Register Shadow
Offset FM NMI Status Re
0-7F Primary Codec Shadow RW
80-FF Secondary Codec Shadow RW
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -38- Register Overview
isters Default Acc
RO
RO
RO
isters Default Acc
isters Default Acc
Page 45

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Register Descriptions
Legacy I/O Ports
This group of registers includes the DMA Controllers,
Interrupt Controllers, and Timer/Counters as well as a number
of miscellaneous ports originally implemented using discrete
logic on original PC/AT motherboards. All of the registers
listed are integrated on-chip. These registers are implemented
in a precise manner for backwards compatibility with previous
generations of PC hardware. These registers are listed for
information purposes only. Detailed descriptions of the
actions and programming of these registers are included in
numerous industry publications (duplication of that
information here is beyond the scope of this document). All
of these registers reside in I/O space.
Port 61 - Misc Functions & Speaker Control ................ RW
7 SERR# Status .......................................................RO
0 SERR# has not been asserted ................ default
1 SERR# was asserted by a PCI agent
Note: This bit is set when the PCI bus SERR# signal
is asserted. Once set, this bit may be cleared
by setting bit-2 of this register. Bit-2 should
be cleared to enable recording of the next
SERR# (i.e., bit-2 must be set to 0 to enable
this bit to be set).
6 IOCHK# Status ....................................................RO
0 IOCHK# has not been asserted ............. default
1 IOCHK # was asserted by an ISA agent
Note: This bit is set when the ISA bus IOCHCK#
signal is asserted. Once set, this bit may be
cleared by setting bit-3 of this register. Bit-3
should be cleared to enable recording of the
next IOCHCK# (i.e., bit-3 must be set to 0 to
enable this bit to be set). IOCHCK# generates
NMI to the CPU if NMI is enabled.
5 Timer/Counter 2 Output .....................................RO
This bit reflects the output of Timer/Counter 2
without any synchronization.
4 Refresh Detected ..................................................RO
This bit toggles on every rising edge of the ISA bus
REFRESH# signal.
3 IOCHK# Enable
0 Enable (see bit-6 above) ........................ default
1 Disable (force IOCHCK# inactive and clear
any “IOCHCK# Active” condition in bit-6)
2 SERR# Enable
0 Enable (see bit-7 above) ........................ default
1 Disable (force SERR# inactive and clear any
“SERR# Active” condition in bit-7)
1 Speaker Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable Timer/Ctr 2 output to drive SPKR pin
0 Timer/Counter 2 Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable Timer/Counter 2
Port 92h - System Control ............................................... RW
7-2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1 A20 Address Line Enable
0 A20 disabled / forced 0 (real mode)...... default
1 A20 address line enabled
0 High Speed Reset
0 Normal
1 Briefly pulse system reset to switch from
protected mode to real mode
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -39- Register Descriptions - Legacy I/O Ports
Page 46

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Keyboard Controller Registers
The keyboard controller handles the keyboard and mouse
interfaces. Two ports are used: port 60 and port 64. Reads
from port 64 return a status byte. Writes to port 64h are
command codes (see command code list following the register
descriptions). Input and output data is transferred via port 60.
A “Control” register is also available. It is accessable by
writing commands 20h / 60h to the command port (port 64h);
The control byte is written by first sending 60h to the
command port, then sending the control byte value. The
control register may be read by sending a command of 20h to
port 64h, waiting for “Output Buffer Full” status = 1, then
reading the control byte value from port 60h.
Traditional (non-integrated) keyboard controllers have an
“Input Port” and an “Output Port” with specific pins dedicated
to certain functions and other pins available for general
purpose I/O. Specific commands are provided to set these
pins high and low. All outputs are “open-collector” so to
allow input on one of these pins, the output value for that pin
would be set high (non-driving) and the desired input value
read on the input port. These ports are defined as follows:
Input Port Lo Code Hi Code
Bit
0 P10 - Keyboard Data In B0 B8
1 P11 - Mouse Data In B1 B9
2 P12 - Turbo Pin (PS/2 mode only) B2 BA
3 P13 - user-defined B3 BB
4 P14 - user-defined B6 BE
5 P15 - user-defined B7 BF
6 P16 - user-defined – –
7 P17 - undefined – –
Output Port Lo Code Hi Code
Bit
0 P20 - SYSRST (1=execute reset) – –
1 P21 - GATEA20 (1=A20 enabled) – –
2 P22 - Mouse Data Out B4 BC
3 P23 - Mouse Clock Out B5 BD
4 P24 - Keyboard OBF Interrupt (IRQ1) – –
5 P25 - Mouse OBF Interrupt (IRQ 12) – –
6 P26 - Keyboard Clock Out – –
7 P27 - Keyboard Data Out – –
Bit Test Port
0 T0 - Keyboard Clock In – –
1 T1 - Mouse Clock In – –
Note: Command code C0h transfers input port data to the
output buffer. Command code D0h copies output port values
to the output buffer. Command code E0h transfers test input
port data to the output buffer.
Port 60 - Keyboard Controller Input Buffer ..................WO
Only write to port 60h if port 64h bit-1 = 0 (1=full).
Port 60 - Keyboard Controller Output Buffer ................RO
Only read from port 60h if port 64h bit-0 = 1 (0=empty).
Lo Code Hi Code
Port 64 - Keyboard / Mouse Status.................................. RO
7 Parity Error
0 No parity error (odd parity received) .... default
1 Even parity occurred on last byte received
from keyboard / mouse
6 General Receive / Transmit Timeout
0 No error ................................................. default
1 Error
5 Mouse Output Buffer Full
0 Mouse output buffer empty ................... default
1 Mouse output buffer holds mouse data
4 Keylock Status
0 Locked
1 Free
3 Command / Data
0 Last write was data write....................... default
1 Last write was command write
2 System Flag
0 Power-On Default ................................. default
1 Self Test Successful
1 Input Buffer Full
0 Input Buffer Empty ............................... default
1 Input Buffer Full
0 Keyboard Output Buffer Full
0 Keyboard Output Buffer Empty ............ default
1 Keyboard Output Buffer Full
KBC Control Register..........(R/W via Commands 20h/60h)
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6 PC Compatibility
0 Disable scan conversion
1 Convert scan codes to PC format; convert 2-
byte break sequences to 1-byte PC-compatible
break codes............................................ default
5 Mouse Disable
0 Enable Mouse Interface......................... default
1 Disable Mouse Interface
4 Keyboard Disable
0 Enable Keyboard Interface .................... default
1 Disable Keyboard Interface
3 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
2 System Flag ................................................default=0
This bit may be read back as status register bit-2
1 Mouse Interrupt Enable
0 Disable mouse interrupts ....................... default
1 Generate interrupt on IRQ12 when mouse data
comes in output bufer
0 Keyboard Interrupt Enable
0 Disable Keyboard Interrupts ................. default
1 Generate interrupt on IRQ1 when output
buffer has been written.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -40- Register Descriptions - Legacy I/O Ports
Page 47

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Port 64 - Keyboard / Mouse Command ..........................WO
This port is used to send commands to the keyboard / mouse
controller. The command codes recognized by the
VT82C686B are listed n the table below.
Note: The VT82C686B Keyboard Controller is compatible
with the VIA VT82C42 Industry-Standard Keyboard
Controller except that due to its integrated nature, many of the
input and output port pins are not available externally for use
as general purpose I/O pins (even though P13-P16 are set on
power-up as strapping options). In other words, many of the
commands below are provided and “work”, but otherwise
perform no useful function (e.g., commands that set P12-P17
high or low). Also note that setting P10-11, P22-23, P26-27,
and T0-1 high or low directly serves no useful purpose, since
these bits are used to implement the keyboard and mouse ports
and are directly controlled by keyboard controller logic.
Table 4. Keyboard Controller Command Codes
Code Keyboard Command Code Description
20h Read Control Byte (next byte is Control Byte)
21-3Fh Read SRAM Data (next byte is Data Byte)
60h Write Control Byte (next byte is Control Byte)
61-7Fh Write SRAM Data (next byte is Data Byte)
9xh Write low nibble (bits 0-3) to P10-P13
A1h Output Keyboard Controller Version #
A4h Test if Password is installed
(always returns F1h to indicate not installed)
A7h Disable Mouse Interface
A8h Enable Mouse Interface
A9h Mouse Interface Test (puts test results in port 60h)
(value: 0=OK, 1=clk stuck low, 2=clk stuck high,
3=data stuck lo, 4=data stuck hi, FF=general error)
AAh KBC self test (returns 55h if OK, FCh if not)
ABh Keyboard Interface Test (see A9h Mouse Test)
ADh Disable Keyboard Interface
AEh Enable Keyboard Interface
AFh Return Version #
B0h Set P10 low
B1h Set P11 low
B2h Set P12 low
B3h Set P13 low
B4h Set P22 low
B5h Set P23 low
B6h Set P14 low
B7h Set P15 low
B8h Set P10 high
B9h Set P11 high
BAh Set P12 high
BBh Set P13 high
BCh Set P22 high
BDh Set P23 high
BEh Set P14 high
BFh Set P15 high
Keyboard Command Code Description
Code
C0h Read input port (read P10-17 input data to
the output buffer)
C1h Poll input port low (read input data on P11-13
repeatably & put in bits 5-7 of status
C2h Poll input port high (same except P15-17)
C8h Unblock P22-23 (use before D1 to change
active mode)
C9h Reblock P22-23 (protection mechanism for D1)
CAh Read mode (output KBC mode info to port 60
output buffer (bit-0=0 if ISA, 1 if PS/2)
D0h Read Output Port (copy P10-17 output port values
to port 60)
D1h Write Output Port (data byte following is written to
keyboard output port as if it came from keyboard)
D2h Write Keyboard Output Buffer & clear status bit-5
(write following byte to keyboard)
D3h Write Mouse Output Buffer & set status bit-5 (write
following byte to mouse; put value in mouse input
buffer so it appears to have come from the mouse)
D4h Write Mouse (write following byte to mouse)
E0h Read test inputs (T0-1 read to bits 0-1 of resp byte)
Exh Set P23-P21 per command bits 3-1
Fxh Pulse P23-P20 low for 6usec per command bits 3-0
All other codes not listed are undefined.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -41- Register Descriptions - Legacy I/O Ports
Page 48

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
DMA Controller I/O Registers
Ports 00-0F - Master DMA Controller
Channels 0-3 of the Master DMA Controller control System
DMA Channels 0-3. There are 16 Master DMA Controller
registers:
I/O Address Bits 15-0
Register Name
0000 0000 000x 0000 Ch 0 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 000x 0001 Ch 0 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 000x 0010 Ch 1 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 000x 0011 Ch 1 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 000x 0100 Ch 2 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 000x 0101 Ch 2 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 000x 0110 Ch 3 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 000x 0111 Ch 3 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 000x 1000 Status / Command RW
0000 0000 000x 1001 Write Request WO
0000 0000 000x 1010 Write Single Mask WO
0000 0000 000x 1011 Write Mode WO
0000 0000 000x 1100 Clear Byte Pointer F/F WO
0000 0000 000x 1101 Master Clear WO
0000 0000 000x 1110 Clear Mask WO
0000 0000 000x 1111 R/W All Mask Bits RW
Ports C0-DF - Slave DMA Controller
Channels 0-3 of the Slave DMA Controller control System
DMA Channels 4-7. There are 16 Slave DMA Controller
registers:
I/O Address Bits 15-0
Register Name
0000 0000 1100 000x Ch 4 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 1100 001x Ch 4 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 1100 010x Ch 5 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 1100 011x Ch 5 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 1100 100x Ch 6 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 1100 101x Ch 6 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 1100 110x Ch 7 Base / Current Address RW
0000 0000 1100 111x Ch 7 Base / Current Count RW
0000 0000 1101 000x Status / Command RW
0000 0000 1101 001x Write Request WO
0000 0000 1101 010x Write Single Mask WO
0000 0000 1101 011x Write Mode WO
0000 0000 1101 100x Clear Byte Pointer F/F WO
0000 0000 1101 101x Master Clear WO
0000 0000 1101 110x Clear Mask WO
0000 0000 1101 111x Read/Write All Mask Bits WO
Note that not all bits of the address are decoded.
The Master and Slave DMA Controllers are compatible with
the Intel 8237 DMA Controller chip. Detailed description of
8237 DMA controller operations can be obtained from the
Intel Peripheral Components Data Book and numerous other
industry publications.
Ports 80-8F - DMA Page Registers
There are eight DMA Page Registers, one for each DMA
channel. These registers provide bits 16-23 of the 24-bit
address for each DMA channel (bits 0-15 are stored in
registers in the Master and Slave DMA Controllers). They are
located at the following I/O Port addresses:
I/O Address Bits 15-0
Register Name
0000 0000 1000 0111 Channel 0 DMA Page (M-0).........RW
0000 0000 1000 0011 Channel 1 DMA Page (M-1).........RW
0000 0000 1000 0001 Channel 2 DMA Page (M-2).........RW
0000 0000 1000 0010 Channel 3 DMA Page (M-3).........RW
0000 0000 1000 1111 Channel 4 DMA Page (S-0) ..........RW
0000 0000 1000 1011 Channel 5 DMA Page (S-1) ..........RW
0000 0000 1000 1001 Channel 6 DMA Page (S-2) ..........RW
0000 0000 1000 1010 Channel 7 DMA Page (S-3) .........RW
DMA Controller Shadow Registers
The DMA Controller shadow registers are enabled by setting
function 0 Rx77 bit 0. If the shadow registers are enabled,
they are read back at the indicated I/O port instead of the
standard DMA controller registers (writes are unchanged).
Port 0 –Channel 0 Base Address ...................................... RO
Port 1 –Channel 0 Byte Count.......................................... RO
Port 2 –Channel 1 Base Address ...................................... RO
Port 3 –Channel 1 Byte Count.......................................... RO
Port 4 –Channel 2 Base Address ...................................... RO
Port 5 –Channel 2 Byte Count.......................................... RO
Port 6 –Channel 3 Base Address ...................................... RO
Port 7 –Channel 3 Byte Count.......................................... RO
st
Port 8 –1
Port 8 –2
Port 8 –3
Port 8 –4
Port 8 –5
Port 8 –6
Read Channel 0-3 Command Register.......... RO
nd
Read Channel 0-3 Request Register ............. RO
rd
Read Channel 0 Mode Register..................... RO
th
Read Channel 1 Mode Register..................... RO
th
Read Channel 2 Mode Register..................... RO
th
Read Channel 3 Mode Register..................... RO
Port F –Channel 0-3 Read All Mask................................ RO
Port C4 –Channel 5 Base Address ................................... RO
Port C6 –Channel 5 Byte Count....................................... RO
Port C8 –Channel 6 Base Address ................................... RO
Port CA –Channel 6 Byte Count...................................... RO
Port CC –Channel 7 Base Address .................................. RO
Port CE –Channel 7 Byte Count ...................................... RO
st
Port D0 –1
Port D0 –2
Port D0 –3
Port D0 –4
Port D0 –5
Port D0 –6
Read Channel 4-7 Command Register....... RO
nd
Read Channel 4-7 Request Register .......... RO
rd
Read Channel 4 Mode Register.................. RO
th
Read Channel 5 Mode Register .................. RO
th
Read Channel 6 Mode Register .................. RO
th
Read Channel 7 Mode Register .................. RO
Port DE –Channel 4-7 Read All Mask............................. RO
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -42- Register Descriptions - Legacy I/O Ports
Page 49

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Interrupt Controller Registers
Ports 20-21 - Master Interrupt Controller
The Master Interrupt Controller controls system interrupt
channels 0-7. Two registers control the Master Interrupt
Controller. They are:
I/O Address Bits 15-0
Register Name
0000 0000 001x xxx0 Master Interrupt Control RW
0000 0000 001x xxx1 Master Interrupt Mask RW
Note that not all bits of the address are decoded.
The Master Interrupt Controller is compatible with the Intel
8259 Interrupt Controller chip. Detailed descriptions of 8259
Interrupt Controller operation can be obtained from the Intel
Peripheral Components Data Book and numerous other
industry publications.
Ports A0-A1 - Slave Interrupt Controller
The Slave Interrupt Controller controls system interrupt
channels 8-15. The slave system interrupt controller also
occupies two register locations:
I/O Address Bits 15-0
Register Name
0000 0000 101x xxx0 Slave Interrupt Control RW
0000 0000 101x xxx1 Slave Interrupt Mask RW
Note that not all address bits are decoded.
The Slave Interrupt Controller is compatible with the Intel
8259 Interrupt Controller chip. Detailed descriptions of 8259
Interrupt Controller operation can be obtained from the Intel
Peripheral Components Data Book and numerous other
industry publications.
Interrupt Controller Shadow Registers
The following shadow registers are enabled by setting
function 0 Rx47[4]. If the shadow registers are enabled, they
are read back at the indicated I/O port instead of the standard
interrupt controller registers (writes are unchanged).
Port 20 - Master Interrupt Control Shadow................... RO
Port A0 - Slave Interrupt Control Shadow ..................... RO
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6 OCW3 bit 2 (POLL)
5 OCW3 bit 0 (RIS)
4 OCW3 bit 5 (SMM)
3 OCW2 bit 7 (R)
2 ICW4 bit 4 (SFNM)
1 ICW4 bit 1 (AEOI)
0 ICW1 bit 3 (LTIM)
Port 21 - Master Interrupt Mask Shadow....................... RO
Port A1 - Slave Interrupt Mask Shadow ........................ RO
7-5 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
4-0 T7-T3 of Interrupt Vector Address
Timer / Counter Registers
Ports 40-43 - Timer / Counter Registers
There are 4 Timer / Counter registers:
I/O Address Bits 15-0
Register Name
0000 0000 010x xx00 Timer / Counter 0 Count RW
0000 0000 010x xx01 Timer / Counter 1 Count RW
0000 0000 010x xx10 Timer / Counter 2 Count RW
0000 0000 010x xx11 Timer / Counter Cmd Mode WO
Note that not all bits of the address are decoded.
The Timer / Counters are compatible with the Intel 8254
Timer / Counter chip. Detailed descriptions of 8254 Timer /
Counter operation can be obtained from the Intel Peripheral
Components Data Book and numerous other industry
publications.
Timer / Counter Shadow Registers
The following shadow registers are enabled for readback by
setting function 0 Rx47[4]. If the shadow registers are
enabled, they are read back at the indicated I/O port instead of
the standard timer / counter registers (writes are unchanged).
st
Port 40 – Counter 0 Base Count Value (LSB 1
Port 41 – Counter 1 Base Count Value (LSB 1
Port 42 – Counter 2 Base Count Value (LSB 1
MSB 2nd)RO
st
MSB 2nd)RO
st
MSB 2nd)RO
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -43- Register Descriptions - Legacy I/O Ports
Page 50

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
CMOS / RTC Registers
Port 70 - CMOS Address..................................................RW
7 NMI Disable ........................................................ RW
0 Enable NMI Generation. NMI is asserted on
encountering IOCHCK# on the ISA bus or
SERR# on the PCI bus.
1 Disable NMI Generation........................default
6-0 CMOS Address (lower 128 bytes) ...................... RW
Port 71 - CMOS Data .......................................................RW
7-0 CMOS Data (128 bytes)
Note: Ports 70-71 may be accessed if Rx5A bit-2 is set to
one to select the internal RTC. If Rx5A bit-2 is set to
zero, accesses to ports 70-71 will be directed to an
external RTC.
Port 72- CMOS Address...................................................RW
7-0 CMOS Address (256 bytes) ................................ RW
Port 73 - CMOS Data .......................................................RW
7-0 CMOS Data (256 bytes)
Note: Ports 72-73 may be accessed if Rx5A bit-2 is set to
one to select the internal RTC. If Rx5A bit-2 is set to
zero, accesses to ports 72-73 will be directed to an
external RTC.
Port 74 - CMOS Address..................................................RW
7-0 CMOS Address (256 bytes) ................................ RW
Port 75 - CMOS Data .......................................................RW
7-0 CMOS Data (256 bytes)
Note: Ports 74-75 may be accessed only if Function 0
Rx5A bit-2 is set to zero to disable the internal RTC
and if Rx48 bit-3 (Port 74/75 Access Enable) is set to
one to enable port 74/75 access.
Note: Ports 70-71 are compatible with PC industry-
standards and may be used to access the lower 128
bytes of the 256-byte on-chip CMOS RAM. Ports
72-73 may be used to access the full-extended 256byte space. Ports 74-75 may be used to access the
full on-chip extended 256-byte space in cases where
the on-chip RTC is disabled.
Note: The system Real Time Clock (RTC) is part of the
“CMOS” block. The RTC control registers are
located at specific offsets in the CMOS data area (00Dh and 7D-7Fh). Detailed descriptions of CMOS /
RTC operation and programming can be obtained
from the VIA VT82887 Data Book or numerous
other industry publications. For reference, the
definition of the RTC register locations and bits are
summarized in the following table:
Offset
00 Seconds 00-3Bh 00-59h
01 Seconds Alarm 00-3Bh 00-59h
02 Minutes 00-3Bh 00-59h
03 Minutes Alarm 00-3Bh 00-59h
04 Hours am 12hr: 01-1Ch 01-12h
pm 12hr: 81-8Ch 81-92h
24hr: 00-17h 00-23h
05 Hours Alarm am 12hr: 01-1Ch 01-12h
pm 12hr: 81-8Ch 81-92h
24hr: 00-17h 00-23h
06 Day of the Week Sun=1: 01-07h 01-07h
07 Day of the Month 01-1Fh 01-31h
08 Month 01-0Ch 01-12h
09 Year 00-63h 00-99h
0A Register A
7 UIP Update In Progress
6-4 DV2-0 Divide (010=ena osc & keep time)
3-0 RS3-0 Rate Select for Periodic Interrupt
0B Register B
7 SET Inhibit Update Transfers
6 PIE Periodic Interrupt Enable
5 AIE Alarm Interrupt Enable
4 UIE Update Ended Interrupt Enable
3 SQWE No function (read/write bit)
2 DM Data Mode (0=BCD, 1=binary)
1 24/12 Hours Byte Format (0=12, 1=24)
0 DSE Daylight Savings Enable
0C Register C
7 IRQF Interrupt Request Flag
6 PF Periodic Interrupt Flag
5 AF Alarm Interrupt Flag
4 UF Update Ended Flag
3-0 0 Unused (always read 0)
0D Register D
7 VRT Reads 1 if VBAT voltage is OK
6-0 0 Unused (always read 0)
0E-7C Software-Defined Storage Registers (111 Bytes)
Offset
7D Date Alarm 01-1Fh 01-31h
7E Month Alarm 01-0Ch 01-12h
7F Century Field 13-14h 19-20h
80-FF Software-Defined Storage Registers (128 Bytes)
Description Binary Range BCD Range
Extended Functions Binary Range BCD Range
Table 5. CMOS Register Summary
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -44- Register Descriptions - Legacy I/O Ports
Page 51

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Super-I/O Configuration Index / Data Registers
Super-I/O configuration registers are accessed by performing
I/O operations to / from an index / data pair of registers in
system I/O space at port addresses 3F0h and 3F1h. The
configuration registers accessed using this mechanism are
used to configure the Super-I/O registers (parallel port, serial
ports, IR port, and floppy controller).
Super I/O configuration is accomplished in three steps:
1) Enter configuration mode (set Function 0 Rx85[1] = 1)
2) Configure the chip
a) Write index to port 3F0
b) Read / write data from / to port 3F1
c) Repeat a and b for all desired registers
3) Exit configuration mode (set Function 0 Rx85[1] = 0)
Port 3F0h – Super-I/O Configuration Index ..................RW
7-0 Index value
Function 0 PCI configuration space register Rx85[1] must be
set to 1 to enable access to the Super-I/O configuration
registers.
Port 3F1h – Super-I/O Configuration Data....................RW
7-0 Data value
This register shares a port with the Floppy Status Port (which
is read only). This port is accessible only when Rx85[1] is set
to 1 (the floppy status port is accessed if Rx85[1] = 0).
Keyboard / Mouse Controller Configuration Registers
These registers are accessed via the port 3F0 / 3F1 index / data
register pair using the indicated index values below
Index D0 – KBC Wakeup Enable (08h) ......................... RW
7-5 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
4 Keyboard / Mouse Pin Swap
0 Disable .................................................. default
1 Enable
3 Win98 Keyboard Power Key Wake-up
0 Disable
1 Enable................................................... default
2 Password Wake-up
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 PS/2 Mouse Wake-up
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Keyboard Wake-up
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Index D1 – Keyboard Scan Code Reference Set 0 (F0h)RW
7-0 Keyboard First Reference Scan Code ..... def = F0h
Index D2 – Keyboard Scan Code Reference Set 1 (00h)RW
7-0 Keyboard Second Reference Scan Code ..def = 00h
Index D3 – Keyboard Scan Code Reference Set 2 (00h)RW
7-0 Keyboard Third Reference Scan Code ....def = 00h
Index D4 – Keyboard Scan Code Reference Set 3 (00h)RW
7-0 Keyboard Fourth Reference Scan Code ..def = 00h
Index D5 – Keyboard Scan Code Reference Set 4 (00h)RW
7-0 Keyboard Fifth Reference Scan Code......def = 00h
Index D6 – Keyboard Scan Code Reference Set 5 (00h)RW
7-0 Keyboard Sixth Reference Scan Code......def = 00h
Index D7 – Keyboard Scan Code Reference Set 6 (00h)RW
7-0 Keyboard Seventh Reference Scan Code. def = 00h
Index D8 – Keyboard Scan Code Reference Set 7 (00h)RW
7-0 Keyboard Eighth Reference Scan Code... def = 00h
Index D9 – PS2 Mouse Scan Code Ref Set 1 (09h) ........ RW
7-0 PS2 Mouse Scan Code Ref Set 1 .............. def = 09h
Index DA – PS2 Mouse Scan Code Ref Set 2 (00h) ....... RW
7-0 PS2 Mouse Scan Code Ref Set 2 ...............def = 00h
Index DB – PS2 Mouse Scan Code Mask (00h) ............. RW
7-0 PS2 Mouse Scan Code Mask..................... def = 00h
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -45- Register Descriptions - Super-I/O I/O Ports
Page 52

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Super-I/O Configuration Registers
These registers are accessed via the port 3F0 / 3F1 index / data
register pair using the indicated index values below
Index E0 – Super-I/O Device ID (3Ch) ............................RO
7-0 Super-I/O ID ........................................default = 3Ch
Index E1 – Super-I/O Device Revision (00h) ...................RO
7-0 Super-I/O Revision Code ........................ default = 0
Index E2 – Super-I/O Function Select (03h)................... RW
7-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Floppy Controller Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 Serial Port 2 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 Serial Port 1 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1-0 Parallel Port Mode / Enable
00 Unidirectional mode
01 ECP
10 EPP
11 Parallel Port Disable ..............................default
Index E3 – Floppy Controller I/O Base Address (00h)..RW
7-2 I/O Address 9-4........................................ default = 0
1-0 Must be 0 .............................................. default = 0
Index E6 – Parallel Port I/O Base Address (00h)........... RW
7-0 I/O Address 9-2........................................ default = 0
If EPP is not enabled, the parallel port can be set to 192
locations on 4-byte boundaries from 100h to 3FCh. If EPP is
enabled, the parallel port can be set to 96 locations on 8-byte
boundaries from 100h to 3F8h.
Index E7 – Serial Port 1 I/O Base Address (00h) ........... RW
7-1 I/O Address 9-3........................................ default = 0
0 Must be 0 .............................................. default = 0
Index E8 – Serial Port 2 I/O Base Address (00h) ........... RW
7-1 I/O Address 9-3........................................ default = 0
0 Must be 0 .............................................. default = 0
Index EE – Serial Port Configuration (00h) .................. RW
7 Serial Port 2 High Speed Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6 Serial Port 1 High Speed Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5-3 Serial Port 2 Mode
000 Standard ................................................ default
001 IrDA (HIPSIR)
010 Amplitude shift keyed IR @ 500KHz
011 -reserved 1xx -reserved 2 Serial Port 2 Half Duplex
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 Serial Port 2 TX Output Inversion
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Serial Port 2 RX Input Inversion
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Index EF – Power Down Control (00h) .......................... RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
5 Clock Power Down
0 Normal operation................................... default
1 Power Down
4 Parallel Port Power Down
0 Normal operation................................... default
1 Power Down
3 Serial Port 2 Power Down
0 Normal operation................................... default
1 Power Down
2 Serial Port 1 Power Down
0 Normal operation................................... default
1 Power Down
1 FDC Power Down
0 Normal operation................................... default
1 Power Down
0 All Power Down
0 Normal operation................................... default
1 Power Down All
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -46- Register Descriptions - Super-I/O I/O Ports
Page 53

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Index F0 – Parallel Port Control (00h) ...........................RW
7 PS2 Type BiDirectionl Parallel Port
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 EPP Direction by Register not by IOW
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 EPP+ECP
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 EPP Version
0 Version 1.9.............................................default
1 Version 1.7
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Index F1 – Serial Port Control (00h)...............................RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 IR Loop Back
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 Serial Port 2 Power-Down State
0 Normal ...................................................default
1 Tristate output in power down mode
3 Serial Port 1 Power-Down State
0 Normal ...................................................default
1 Tristate output in power down mode
2 IR Dedicated Pin (IRTX/IRRX) Select
0 IRTX / IRRX Output from Serial Port 2......def
1 Function 0 Rx76[5] = 0:
IRRX output from dedicated pin D12
IRTX output from dedicated pin E12
1-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Index F2 – Test Mode (Do Not Program) .......................RW
Index F4 – Test Mode (Do Not Program) .......................RW
Index F6 – Floppy Controller Configuration................. RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
5 Floppy Drive On Parallel Port
0 Parallel Port (SPP) Mode ...................... default
1 FDC Mode
This bit is used in notebook applications to allow
attachment of an external floppy drive using the
parallel port I/O connector:
SPP Mode
STROBE# I/O - n/a
PD0 I/O INDEX# I
PD1 I/O TRK00# I
PD2 I/O WRTPRT# I
PD3 I/O RDATA# I
PD4 I/O DSKCHG# I
PD5 I/O - n/a
PD6 I/O - n/a
PD7 I/O - n/a
ACK# I DS1# O
BUSY I MTR1# O
PE I WDATA# O
SLCT I WGATE# O
AUTOFD# I/O DRVEN0 O
ERROR# I HDSEL# O
PINIT# I/O DIR# O
SLCTIN# I/O STEP# O
4 3-Mode FDD
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
2 Four Floppy Drive Option
0 Internal 2-Drive Decoder....................... default
1 External 4-Drive Decoder
1 FDC DMA Non-Burst
0 Burst .................................................... default
1 Non-Burst
0 FDC Swap
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Pin Type FDC Mode Pin Type
Index F8 – Floppy Drive Control.................................... RW
7-6 Floppy Drive 3 (see table below)
5-4 Floppy Drive 2 (see table below)
3-2 Floppy Drive 1 (see table below)
1-0 Floppy Drive 0 (see table below)
DRVEN1
00 DRATE0 DENSEL
01 DRATE0 DRATE1
10 DRATE0 DENSEL#
11 DRATE1 DRATE0
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -47- Register Descriptions - Super-I/O I/O Ports
DRVEN0
Page 54

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Super-I/O I/O Ports
Floppy Disk Controller Registers
These registers are located at I/O ports which are offsets from
“FDCBase” (index E3h of the Super-I/O configuration
registers). FDCBase is typically set to allow these ports to be
accessed at the standard floppy disk controller address range
of 3F0-3F7h.
Port FDCBase+2 – FDC Command ................................RW
7 Motor 3 (unused in VT82C686B: no MTR3# pin)
6 Motor 2 (unused in VT82C686B: no MTR2# pin)
5 Motor 1
0 Motor Off
1 Motor On
4 Motor 0
0 Motor Off
1 Motor On
3 DMA and IRQ Channels
0 Disable
1 Enable
2 FDC Reset
0 Execute FDC Reset
1 FDC Enable
1-0 Drive Select
00 Select Drive 0
01 Select Drive 1
1x -reserved-
Port FDCBase+4 – FDC Main Status...............................RO
7 Main Request
0 Data register not ready
1 Data register ready
6 Data Input / Output
0 CPU => FDC
1 FDC => CPU
5 Non-DMA Mode
0 FDC in DMA mode
1 FDC not in DMA mode
4 FDC Busy
0 FDC inactive
1 FDC active
3-2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1 Drive 1 Active
0 Drive inactive
1 Drive performing a positioning change
0 Drive 0 Active
0 Drive inactive
1 Drive performing a positioning change
Port FDCBase+4 – FDC Data Rate Select...................... WO
7 Software Reset
0 Normal operation................................... default
1 Execute FDC reset (this bit is self clearing)
6 Power Down
0 Normal operation................................... default
1 Power down FDC logic
5 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
4-2 Precompensation Select
Selects the amount of write precompensation to be
used on the WDATA output:
000 Default................................................... default
001 41.7 ns
010 93.3 ns
011 125.0 ns
100 166.7 ns
101 208.3 ns
110 250.0 ns
111 0.0 ns (disable)
1-0 Data Rate
MFM
00 500K 250K bps 1.2MB 5” or 1.44 MB 3”
01 300K 150K bps 360KB 5”
10 250K 125K bps 720KB 3” ................ default
11 1M illegal bps
Note: these bits are not changed by software reset
Port FDCBase+5 – FDC Data ......................................... RW
Port FDCBase+7 – FDC Disk Change Status ................ RW
7 Disk Change......................................................... RO
0 Floppy not changed ............................... default
1 Floppy changed since last instruction
6-2 Undefined ..................................... always reads 1’s
1-0 Data Rate ........................................................ WO
00 500 Kbit/sec (1.2MB 5” or 1.44 MB 3” drive)
01 300 Kbit/sec (360KB 5” drive)
10 250 Kbit/sec (720KB 3” drive)
11 1 Mbit/sec
FM Drive Type
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -48- Register Descriptions - Super-I/O I/O Ports
Page 55

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Parallel Port Registers
These registers are located at I/O ports which are offsets from
“LPTBase” (index E6h of the Super-I/O configuration
registers). LPTBase is typically set to allow these ports to be
accessed at the standard parallel port address range of 37837Fh.
Port LPTBase+0 – Parallel Port Data............................. RW
7-0 Parallel Port Data
Port LPTBase+1 – Parallel Port Status............................RO
7 BUSY#
0 Printer busy, offline, or error
1 Printer not busy
6 ACK#
0 Data transfer to printer complete
1 Data transfer to printer in progress
5 PE
0 Paper available
1 No paper available
4 SLCT
0 Printer offline
1 Printer online
3 ERROR#
0 Printer error
1 Printer OK
2-0 Reserved ...................................always read 1 bits
Port LPTBase+2 – Parallel Port Control........................RW
7-5 Undefined ................................. always read back 1
4 Hardware Interrupt
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 Printer Select
0 Deselect printer ......................................default
1 Select printer
2 Printer Initialize
0 Initialize Printer .....................................default
1 Allow printer to operate normally
1 Automatic Line Feed
0 Host handles line feeds ..........................default
1 Printer does automatic line feeds
0 Strobe
0 No data transfer......................................default
1 Transfer data to printer
Port LPTBase+3 – Parallel Port EPP Address .............. RW
Port LPTBase+4 – Parallel Port EPP Data Port 0 ........ RW
Port LPTBase+5 – Parallel Port EPP Data Port 1 ........ RW
Port LPTBase+6 – Parallel Port EPP Data Port 2 ........ RW
Port LPTBase+7 – Parallel Port EPP Data Port 3 ........ RW
Port LPTBase+400h – Parallel Port ECP Data / Cfg A RW
Port LPTBase+401h – Parallel Port ECP Config B ...... RW
Port LPTBase+402h – Parallel Port ECP Extd Ctrl ..... RW
7-5 Parallel Port Mode Select
000 Standard Mode ...................................... default
001 PS/2 Mode
010 FIFO Mode
011 ECP Mode
100 EPP Mode
101 -reserved 110 -reserved 111 Configuration Mode
4 Parallel Port Interrupt Disable
0 Enable an interrupt pulse to be generated on
the high to low edge of the fault. An interrupt
will also be generated if the fault condition is
asserted and this bit is written from 1 to 0.
1 Disable the interrupt generated on the
asserting edge of the fault condition
3 Parallel Port DMA Enable
0 Disable DMA unconditionally
1 Enable DMA
2 Parallel Port Interrupt Pending
0 Interrupt not pending
1 Interrupt pending (DMA & interrupts
disabled)
This bit is set to 1 by hardware and must be written
to 0 to re-enable interrupts
1 FIFO Full ......................................................... RO
0 FIFO has at least 1 free byte
1 FIFO full or cannot accept byte
0 FIFO Empty......................................................... RO
0 FIFO contains at least 1 byte of data
1 FIFO is completely empty
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -49- Register Descriptions - Super-I/O I/O Ports
Page 56

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Serial Port 1 Registers
These registers are located at I/O ports which are offsets from
“COM1Base” (index E7h of the Super-I/O configuration
registers). COM1Base is typically set to allow these ports to
be accessed at the standard serial port 1 address range of 3F83FFh.
Port COM1Base+0 – Transmit / Receive Buffer............RW
7-0 Serial Data
Port COM1Base+1 – Interrupt Enable...........................RW
7-4 Undefined ..........................................always read 0
3 Interrupt on Handshake Input State Change
2 Intr on Parity, Overrun, Framing Error or Break
1 Interrupt on Transmit Buffer Empty
0 Interrupt on Receive Data Ready
Port COM1Base+1-0 – Baud Rate Generator Divisor ..RW
15-0 Divisor Value for Baud Rate Generator
Baud Rate = 115,200 / Divisor
(e.g., setting this register to 1 selects 115.2 Kbaud)
Port COM1Base+2 – Interrupt Status .............................RO
7-3 Undefined ..........................................always read 0
2-1 Interrupt ID (0=highest priority)
00 Priority 3 (Handshake Input Changed State)
01 Priority 2 (Transmit Buffer Empty)
10 Priority 1 (Data Received)
11 Priority 0 (Serialization Error or Break)
0 Interrupt Pending
0 Interrupt Pending
1 No Interrupt Pending
Port COM1Base+2 – FIFO Control ................................WO
Port COM1Base+3 – UART Control ..............................RW
7 Divisor Latch Access
0 Access xmit / rcv & int enable regs at 0-1
1 Access baud rate generator divisor latch at 0-1
6 Break
0 Break condition off
1 Break condition on
5-3 Parity
000 None
001 Odd
011 Even
101 Mark
111 Space
2 Stop Bits
0 1
1 2
1-0 Data Bits
00 5
01 6
10 7
11 8
Port COM1Base+4 – Handshake Control...................... RW
7-5 Undefined ......................................... always read 0
4 Loopback Check
0 Normal operation
1 Loopback enable
3 General Purpose Output 2 (unused in 82C686B)
2 General Purpose Output 1 (unused in 82C686B)
1 Request To Send
0 Disable
1 Enable
0 Data Terminal Ready
0 Disable
1 Enable
Port COM1Base+5 – UART Status ................................ RW
7 Undefined ......................................... always read 0
6 Transmitter Empty
0 1 byte in transmit hold or transmit shift
register
1 0 bytes transmit hold and transmit shift regs
5 Transmit Buffer Empty
0 1 byte in transmit hold register
1 Transmit hold register empty
4 Break Detected
0 No break detected
1 Break detected
3 Framing Error Detected
0 No error
1 Error
2 Parity Error Detected
0 No error
1 Error
1 Overrun Error Detected
0 No error
1 Error
0 Received Data Ready
0 No received data available
1 Received data in receiver buffer register
Port COM1Base+6 – Handshake Status ........................ RW
7 DCD Status (1=Active, 0=Inactive)
6 RI Status (1=Active, 0=Inactive)
5 DSR Status (1=Active, 0=Inactive)
4 CTS Status (1=Active, 0=Inactive)
3 DCD Changed (1=Changed Since Last Read)
2 RI Changed (1=Changed Since Last Read)
1 DSR Changed (1=Changed Since Last Read)
0 CTS Changed (1=Changed Since Last Read)
Port COM1Base+7 – Scratchpad.................................... RW
7 Scratchpad Data
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -50- Register Descriptions - Super-I/O I/O Ports
Page 57

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Serial Port 2 Registers
These registers are located at I/O ports which are offsets from
“COM2Base” (index E8h of the Super-I/O configuration
registers). COM2Base is typically set to allow these ports to
be accessed at the standard serial port 2 address range of 2F82FFh.
Port COM2Base+0 – Transmit / Receive Buffer............RW
7-0 Serial Data
Port COM2Base+1 – Interrupt Enable...........................RW
7-4 Undefined ..........................................always read 0
3 Interrupt on Handshake Input State Change
2 Intr on Parity, Overrun, Framing Error or Break
1 Interrupt on Transmit Buffer Empty
0 Interrupt on Receive Data Ready
Port COM2Base+1-0 – Baud Rate Generator Divisor ..RW
15-0 Divisor Value for Baud Rate Generator
Baud Rate = 115,200 / Divisor
(e.g., setting this register to 1 selects 115.2 Kbaud)
Port COM2Base+2 – Interrupt Status .............................RO
7-3 Undefined ..........................................always read 0
2-1 Interrupt ID (0=highest priority)
00 Priority 3 (Handshake Input Changed State)
01 Priority 2 (Transmit Buffer Empty)
10 Priority 1 (Data Received)
11 Priority 0 (Serialization Error or Break)
0 Interrupt Pending
0 Interrupt Pending
1 No Interrupt Pending
Port COM2Base+2 – FIFO Control ................................WO
Port COM2Base+3 – UART Control ..............................RW
7 Divisor Latch Access
0 Access xmit / rcv & int enable regs at 0-1
1 Access baud rate generator divisor latch at 0-1
6 Break
0 Break condition off
1 Break condition on
5-3 Parity
000 None
001 Odd
011 Even
101 Mark
111 Space
2 Stop Bits
0 1
1 2
1-0 Data Bits
00 5
01 6
10 7
11 8
Port COM2Base+4 – Handshake Control...................... RW
7-5 Undefined ......................................... always read 0
4 Loopback Check
0 Normal operation
1 Loopback enable
3 General Purpose Output 2 (unused in 82C686B)
2 General Purpose Output 1 (unused in 82C686B)
1 Request To Send
0 Disable
1 Enable
0 Data Terminal Ready
0 Disable
1 Enable
Port COM2Base+5 – UART Status ................................ RW
7 Undefined ......................................... always read 0
6 Transmitter Empty
0 1 byte in transmit hold or transmit shift
register
1 0 bytes transmit hold and transmit shift regs
5 Transmit Buffer Empty
0 1 byte in transmit hold register
1 Transmit hold register empty
4 Break Detected
0 No break detected
1 Break detected
3 Framing Error Detected
0 No error
1 Error
2 Parity Error Detected
0 No error
1 Error
1 Overrun Error Detected
0 No error
1 Error
0 Received Data Ready
0 No received data available
1 Received data in receiver buffer register
Port COM2Base+6 – Handshake Status ........................ RW
7 DCD Status (1=Active, 0=Inactive)
6 RI Status (1=Active, 0=Inactive)
5 DSR Status (1=Active, 0=Inactive)
4 CTS Status (1=Active, 0=Inactive)
3 DCD Changed (1=Changed Since Last Read)
2 RI Changed (1=Changed Since Last Read)
1 DSR Changed (1=Changed Since Last Read)
0 CTS Changed (1=Changed Since Last Read)
Port COM2Base+7 – Scratchpad.................................... RW
7 Scratchpad Data
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -51- Register Descriptions - Super-I/O I/O Ports
Page 58

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
SoundBlaster Pro Port Registers
These registers are located at offsets from “SBPBase”
(defined in Rx43 of Audio Function 5 PCI configuration
space). SBPBase is typically set to allow these ports to be
accessed at the standard SoundBlaster Pro port address of
220h or 240h.
FM Registers
Port SBPBase+0 – FM Left Channel Index / Status ......RW
7-0 FM Right Channel Index / Status
Port SBPBase+1 – FM Left Channel Data .....................WO
7-0 Right Channel FM Data
Port SBPBase+2 – FM Right Channel Index / Status.... RW
7-0 FM Right Channel Index / Status
Port SBPBase+3 – FM Right Channel Data ...................WO
7-0 Right Channel FM Data
Port 388h or SBPBase+8 – FM Index / Status................ RW
7-0 FM Index / Status (Both Channels)
Writing to this port programs both the left and right channels
(the write programms port offsets 0 and 2 as well)
Port 389h or SBPBase+9 – FM Data ...............................WO
7-0 FM Data (Both Channels)
Writing to this port programs both the left and right channels
(the write programms port offsets 1 and 3 as well)
Mixer Registers
Port SBPBase+4 – Mixer Index .......................................WO
7-0 Mixer Index
Port SBPBase+5 – Mixer Data......................................... RW
7-0 Mixer Data
Register Summary - FM
Index
20-35 AM VIB EGT KSR Multi
40-55 KSL Total Level (TL)
60-75 Attack Rate (AR) Decay Rate (DR)
80-95 Sustain Level (SL) Release Rate (RR)
A0-A8 F-Number
B0-B8 Key Block F-Number
C0-C8 Feedback FM
E0-F5 WS
MFC=Mask Fast Counter SSFC=Start / Stop Fast Counter
MSC=Mask Slow Counter SSSC=Start / Stop Slow Counter
Register Summary – Mixer
Index
Finp = Input Filter
Fout = Output Filter
TFIL = Input Filter Type
ST = Stereo / Mono Mode
Select = Input Choices (0=Microphone, 1=CD, 3=Line)
Command Summary – Sound Processor (see next page)
Bit-7 Bit-6 Bit-5 Bit-4 Bit-3 Bit-2 Bit-1 Bit-0
01 Test
02 Fast Counter (80 usec)
03 Slow Counter (320 usec)
04 IRQ MFC MSC SSSC SSFC
08 CSMSEL
BD Int AM VIB Ryth Bass Snare Tom Cym HiHat
Bit-7 Bit-6 Bit-5 Bit-4 Bit-3 Bit-2 Bit-1 Bit-0
00 Data Reset
02 SP Volume L SP Volume R
0A Mic Vol
0C Finp TFIL Select
0E Fout ST
22 General Volume General Volume
26 FM Volume L FM Volume R
28 CD Volume L CD Volume R
2E Line Volume L Line Volume R
Sound Processor Registers
Port SBPBase+6 – Sound Processor Reset......................WO
0 1 = Sound Processor Reset
Port SBPBase+A – Sound Processor Read Data .............RO
7-0 Sound Processor Read Data
Port SBPBase+C – Sound Processor Command / Data.WO
7-0 Sound Processor Command / Write Data
Port SBPBase+C – Sound Processor Buffer Status ........RO
7 1 = Sound Processor Command / Data Port Busy
Port SBPBase+E – Sound Processor Data Avail Status .RO
7 1 = Sound Processor Data Available
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -52- Register Descriptions - Super-I/O I/O Ports
Page 59

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Command Summary – Sound Processor
Type Command
#
10 Play 8 bits directly
14 Play 8 bits via DMA
91 Play High-speed 8 bits via DMA
16 Play 2-bit compressed via DMA
17 Play 2-bit compressed via DMA with reference
74 Play 4-bit compressed via DMA
75 Play 4-bit compressed via DMA with reference
76 Play 2.6-bit compressed via DMA
77 Play 2.6-bit compressed via DMA with reference
20 Record Direct
24 Record Via DMA
99 Record High-speed 8 bits via DMA
D1 Speaker Turn on speaker connection
D3 Speaker Turn off speaker connection
D8 Speaker Get speaker setting
40 Misc Set sample rate
48 Misc Set block length
80 Misc Set silence block
D0 Misc Stop DMA
D4 Misc Continue DMA
E1 Misc Get version
30 MIDI Direct MIDI input
31 MIDI MIDI input via interrupt
32 MIDI Direct MIDI input with time stamp
33 MIDI MIDI input via interrupt with time stamp
34 MIDI Direct MIDI UART mode
35 MIDI MIDI UART mode via interrupt
36 MIDI Direct MIDI UART mode with time stamp
37 MIDI MIDI UART mode via interrupt with time stamp
38 MIDI Send MIDI code
Game Port Registers
These registers are fixed at the standard game port address of
201h.
I/O Port 201h – Game Port Status ................................... RO
7 Joystick B Button 2 Status
6 Joystick B Button 1 Status
5 Joystick A Button 2 Status
4 Joystick A Button 1 Status
3 Joystick B One-Shot Status for Y-Potentiometer
2 Joystick B One-Shot Status for X-Potentiometer
1 Joystick A One-Shot Status for Y-Potentiometer
0 Joystick A One-Shot Status for X-Potentiometer
I/O Port 201h – Start One-Shot....................................... WO
7-0 (Value Written is Ignored)
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -53- Register Descriptions - Super-I/O I/O Ports
Page 60

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
APIC Registers
Memory Mapped I/O APIC Registers
Memory Address FEC00000 – APIC Index ...................RW
7-0 APIC Index .......................................... default = 00h
8-bit pointer to APIC registers.
Memory Address FEC00013-10 – APIC 32-bit Data.....RW
31-0 APIC 32-bit Data .................... default = 0000 0000h
Data for the APIC register pointed to by the APIC
index
Memory Address FEC00020 – APIC IRQ Pin AssertionWO
7-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4-0 APIC IRQ Number........................default undefined
IRQ # for this interrupt. Valid values are 0-23 only.
Memory Address FEC00040 – APIC EOI......................WO
7-0 Redirection Entry Clear................default undefined
When a write is issued to this register, the APIC will
check this field and compare it with the vector field
for each entry in the I/O redirection table. When a
match is found, the “Remote_IRR” bit for that I/O
Redirection Entry will be cleared.
Indexed I/O APIC 32-Bit Registers
Offset 0 – APIC Identification (0000 0000h).................. RW
31-28 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
27-24 APIC Identification.................................. default = 0
Software must program this value before using the
23-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Offset 1 – APIC Version (CD: 0017 0011h, CE: 0017
8002) ................................................................................... RO
31-24 Reserved .................................... always reads 00h
23-16 Maximum Redirection...................always reads 17h
Equal to the number of APIC interrupt pins minus
15 CD: Reserved..................................... always reads 0
CE: PRQ ........................................always reads 1
Indicates that this APIC version implements the IRQ
14-8 Reserved ....................................always reads 00h
7-0 APIC Version......................... CD: always reads 11h
............................CE: always reads 02h
These bits read back the implementation version for
APIC.
one. For this APIC, this value is 17h (23 decimal).
Assertion Register and allows PCI devices to write to
it to cause interrupts.
this APIC.
Offset 2 – APIC Arbitration (0000 0000h) ...................... RO
31-28 Reserved .................................... always reads 00h
27-24 APIC Arbitration ID......................always reads 00h
23-0 Reserved ....................................always reads 00h
Offset 3 – Boot Configuration (0000 0000h) ................... RO
31-1 Reserved ....................................always reads 00h
0 Interrupt Delivery Type
0 Interrupt delivery via the APIC bus ...... default
1 Interrupt delivery mechanism is a FSB
message
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -54- Register Descriptions – Memory Mapped I/O APIC
Page 61

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 3F-10 – I/O Redirection Table
This table contains 24 registers, with one dedicated table entry
for each of the 24 APIC interrupt signals. Each 64-bit register
consists of two 32-bit values at consecutive index locations,
with the low 32 bits at the even index and the upper 32 bits at
the odd index. The default value for all registers is xxx1 xxxx
xxxx xxxxh.
Offset 11-10 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ0................. RW
Offset 13-12 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ1................. RW
Offset 15-14 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ2................. RW
Offset 17-16 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ3................. RW
Offset 19-18 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ4................. RW
Offset 1B-1A – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ5 ...............RW
Offset 1D-1C – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ6 ............... RW
Offset 1F-1E – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ7................ RW
Offset 21-20 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ8................. RW
Offset 23-22 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ9................. RW
Offset 25-24 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ10............... RW
Offset 27-26 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ11............... RW
Offset 29-28 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ12............... RW
Offset 2B-2A – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ13 .............RW
Offset 2D-2C – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ14 ............. RW
Offset 2F-2E – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ15.............. RW
Offset 31-30 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ16............... RW
Offset 33-32 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ17............... RW
Offset 35-34 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ18............... RW
Offset 37-36 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ19............... RW
Offset 39-38 – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ20............... RW
Offset 3B-3A – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ21 .............RW
Offset 3D-3C – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ22 ............. RW
Offset 3F-3E – I/O Redirection – APIC IRQ23.............. RW
Offset 42 – SMI on BIOS Write.......................................RW
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
Offset 4B-48 – General Purpose Input............................RW
31-0 GPI 31-0
Offset 4F-4C – General Purpose Output ........................RW
31-0 GPO 31-0
Format for Each I/O Redirection Table Entry:
Physical Mode (bit-11=0)
63-60 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
59-56 APIC ID ................................default = undefined
Logical Mode (bit-11=1)
63-56 Destination ................................ default = undefined
55-17 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
16 Interrupt Masked
0 Not masked............................................ default
1 Masked
15 Trigger Mode
0 Edge Sensitive ....................................... default
1 Level Sensitive
14 Remote IRR (Level Sensitive Interrupts Only) RO
0 EOI message with a matching interrupt vector
received from a local APIC
1 Level sensitive interrupt sent by IOAPIC
accepted by local APIC(s)
13 Interrupt Input Pin Polarity
0 Active High ........................................... default
1 Active Low
12 Delivery Status..................................................... RO
Contains the current status of the delivery of this
interrupt.
0 Idle (no activity)
1 Send Pending (the interrupt has been injected
but its delivery is temporarily delayed either
because the APIC bus is busy or because the
receiving APIC unit cannot currently accept
the interrupt)
11 Destination Mode
Determines the interpretation of bits 56-63.
0 Physical Mode ....................................... default
1 Lowest Priority
10-8 Delivery Mode
Specifies how the APICs listed in the destination
field should act upon reception of this signal
000 Fixed .................................................... default
001 Logical Mode
010 SMI
011 -reserved 100 NMI
101 INIT
110 -reserved 111 External INT
7-0 Interrupt Vector
Contains the interrupt vector for this interrupt.
Vector values range from 10h to FEh.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -55- Register Descriptions – Memory Mapped I/O APIC
Page 62

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
PCI Configuration Space I/O
PCI configuration space accesses for functions 0-6 use PCI
configuration mechanism 1 (see PCI specification revision 2.2
for more details). The ports respond only to double-word
accesses. Byte or word accesses will be passed on unchanged.
Port CFB-CF8 - Configuration Address.........................RW
31 Configuration Space Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Convert configuration data port writes to
configuration cycles on the PCI bus
30-24 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
23-16 PCI Bus Number
Used to choose a specific PCI bus in the system
15-11 Device Number
Used to choose a specific device in the system
10-8 Function Number
Used to choose a specific function if the selected
device supports multiple functions
7-2 Register Number
Used to select a specific DWORD in the device’s
configuration space
1-0 Fixed ........................................ always reads 0
Port CFF-CFC - Configuration Data..............................RW
There are 7 “functions” implemented in the VT82C686B:
Function #
0 PCI to ISA Bridge
1 IDE Controller
2 USB Controller Ports 0-1
3 USB Controller Ports 2-3
4 Power Management, SMBus & Hardware
5 AC97 Audio Codec Controller
6 MC97 Modem Codec Controller
The following sections describe the registers and register bits
of these functions.
Function
Monitor
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -56- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 63

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
All registers are located in the function 0 PCI configuration
space of the VT82C686B. These registers are accessed
through PCI configuration mechanism #1 via I/O address
CF8/CFC.
PCI Configuration Space Header
Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID = 1106h.........................................RO
Offset 3-2 - Device ID = 0686h ..........................................RO
Offset 5-4 - Command ......................................................RW
15-8 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
7 Address / Data Stepping
0 Disable
1 Enable ...................................................default
6-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 Special Cycle Enable .....Normally RW†, default = 0
2 Bus Master ........................................ always reads 1
1 Memory Space.................. Normally RO†, reads as 1
0 I/O Space ...................... Normally RO†, reads as 1
† If the Rx46[4] test bit is set, access to bits 0, 1, and 3 above
is reversed: bit-3 becomes read only (reading back 1) and bits
0-1 become read / write (with a default of 1).
Offset 7-6 - Status........................................................... RWC
15 Detected Parity Error.................... write one to clear
14 Signalled System Error ..................... always reads 0
13 Signalled Master Abort ................. write one to clear
12 Received Target Abort .................. write one to clear
11 Signalled Target Abort.................. write one to clear
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing .................... fixed at 01 (medium)
8 Data Parity Detected ......................... always reads 0
7 Fast Back-to-Back.............................. always reads 0
6-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 8 - Revision ID = nn................................................RO
7-0 Revision ID
0x VT82C686
1x VT82C686A
4x VT82C686B
Offset 9 - Program Interface = 00h ..................................RO
Offset A - Sub Class Code = 01h.......................................RO
Offset B - Class Code = 06h...............................................RO
Offset E - Header Type = 80h ...........................................RO
7-0 Header Type Code.........80h (Multifunction Device)
Offset F - BIST = 00h.........................................................RO
Offset 2F-2C - Subsystem ID ............................................RO
Use offset 70-73 to change the value returned.
Offset 34 – Power Management Capability Ptr = C0h ...RO
ISA Bus Control
Offset 40 - ISA Bus Control............................................. RW
7 ISA Command Delay
0 Normal................................................... default
1 Extra
6 Extended ISA Bus Ready
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 ISA Slave Wait States
0 4 Wait States.......................................... default
1 5 Wait States
4 Chipset I/O Wait States
0 2 Wait States.......................................... default
1 4 Wait States
3 I/O Recovery Time
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 Extend-ALE
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 ROM Wait States
0 1 Wait State ........................................... default
1 0 Wait States
0 ROM Write
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Offset 41 - ISA Test Mode ............................................... RW
7 Bus Refresh Arbitration (do not program) default=0
6 I/O Recovery Time
0 Normal (13 BCLKs).............................. default
1 Medium (8 BCLKs)
5 Port 92 Fast Reset
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
4 A20G Emulation (do not program) ............default=0
3 Double DMA Clock
0 Disable (DMA Clock = ½ ISA Clock) .. default
1 Enable (DMA Clock = ISA Clock)
This function can be enabled for external ISA
devices (e.g., advanced Super-IO or FIR controllers)
which support 8MHz DMA channels. However, if
this bit is set to 1, then all
MHz. If this bit is set to 1 and
then ISA DMA channel ‘n’ will be 16 MHz.
Therefore, typically this bit is set to 0 and the
appropriate bits of Rx45 should be set to 1 to enable
8 MHz DMA clock only for specific channels that
support the higher rate.
2 SHOLD Lock During INTA (do not program) def=0
1 Refresh Request Test Mode (do not program) def=0
0 ISA Refresh
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
This bit should be set to 1 for ISA compatibility.
DMA channels will be 8
Rx45[n] is set to 1,
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -57- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 64

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 42 - ISA Clock Control.......................................... RW
7 Latch IO16#
0 Enable (recommended setting)...............default
1 Disable
6 MCS16# Output
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 Master Request Test Mode (do not program)
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 Reserved (Do Not Program) .................. default = 0
3 ISA Clock (BCLK) Select Enable
0 BCLK = PCICLK / 4 .............................default
1 BCLK selected per bits 2-0
2-0 ISA Bus Clock Select (if bit-3 = 1)
000 BCLK = PCICLK / 3 .............................default
001 BCLK = PCICLK / 2
010 BCLK = PCICLK / 4
011 BCLK = PCICLK / 6
100 BCLK = PCICLK / 5
101 BCLK = PCICLK / 10
110 BCLK = PCICLK / 12
111 BCLK = OSC / 2
Note: Procedure for ISA Clock switching:
1) Set bit 3 to 0; 2) Change value of bit 2-0; 3) Set bit 3 to 1
Offset 43 - ROM Decode Control.................................... RW
Setting these bits enables the indicated address range to be
included in the ROMCS# decode:
7 FFFE0000h-FFFEFFFFh .......................... default=0
6 FFF80000h-FFFDFFFFh........................... default=0
5 FFF00000h-FFF7FFFFh ...........................default=0
4 000E0000h-000EFFFFh............................. default=0
3 000D8000h-000DFFFFh ............................ default=0
2 000D0000h-000D7FFFh............................. default=0
1 000C8000h-000CFFFFh ............................ default=0
0 000C0000h-000C7FFFh............................. default=0
Note: ROMCS# is always active when ISA addresses
FFF80000-FFFFFFFF and 000E0000-000FFFFF are
decoded
Offset 44 - Keyboard Controller Control....................... RW
7 KBC Timeout Test (do not program) .......default = 0
6-4 Reserved (do not program)........................ default = 0
3 Mouse Lock Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2-1 Reserved (do not program)........................ default = 0
0 Reserved (no function).............................. default = 0
Offset 45 - Type F DMA Control .................................... RW
7 ISA Master / DMA to PCI Line Buffer
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6 DMA type F Timing on Channel 7 ...........default=0
5 DMA type F Timing on Channel 6 ...........default=0
4 DMA type F Timing on Channel 5 ...........default=0
3 DMA type F Timing on Channel 3 ...........default=0
2 DMA type F Timing on Channel 2 ...........default=0
1 DMA type F Timing on Channel 1 ...........default=0
0 DMA type F Timing on Channel 0 ...........default=0
Note: For bits 0-6 above, see also Rx41[3]
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -58- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 65

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 46 - Miscellaneous Control 1 ................................RW
7 PCI Master Write Wait States
0 0 Wait States ..........................................default
1 1 Wait State
6 Gate INTR
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 Flush Line Buffer for Int or DMA IOR Cycle
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 Config Command Reg Rx04 Access (Test Only)
0 Normal: Bits 0-1=RO, Bit 3=RW .........default
1 Test Mode: Bits 0-1=RW, Bit-3=RO
3 Reserved (do not program) ....................... default = 0
2 CD: Reserved (no function) .................... default = 0
CE: Internal ISA Cycle Arbitration
0 All ISA cycles arbitrate w/ secondary IDE..def
1 Internal ISA cycles don’t arbitrate with sec
IDE
1 PCI Burst Read Interruptability
0 Allow burst reads to be interrupted by ISA
master or DMA ......................................default
1 Don’t allow PCI burst reads to be interrupted
0 Posted Memory Write Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
The Posted Memory Write function is automatically
enabled when Delay Transaction (see Rx47 bit-6) is
enabled, independent of the state of this bit.
Offset 47 - Miscellaneous Control 2................................ RW
7 CPU Reset Source
0 Use CPURST as CPU Reset.................. default
1 Use INIT as CPU Reset
6 PCI Delay Transaction Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
The "Posted Memory Write" function is
automatically enabled when this bit is enabled,
independent of the state of Rx46 bit-0.
5 EISA 4D0/4D1 Port Enable
0 Disable (ignore ports 4D0-1)................. default
1 Enable (ports 4D0-1 per EISA specification)
4 Interrupt Controller Shadow Register Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable (for test purposes, enable readback of
interrupt controller internal functions on I/O
reads from ports 20-21, A0-A1, A8-A9, and
C8-C9) (Contact VIA Test Engineering
department)
3 Reserved (always program to 0) .............default = 0
Note: Always mask this bit. This bit may read back
as either 0 or 1 but must always be
programmed with 0.
2 Write Delay Transaction Time-Out Timer
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 Read Delay Transaction Time-Out Timer
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Software PCI Reset ......write 1 to generate PCI reset
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -59- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 66

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 48 - Miscellaneous Control 3 ................................RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 Extra RTC Port 74/75 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 Integrated USB Controller Disable
0 Enable ....................................................default
1 Disable
1 Integrated IDE Controller Disable
0 Enable ....................................................default
1 Disable
0 512K PCI Memory Decode
0 Use Rx4E[15-12] to select top of PCI memory
1 Use contents of Rx4E[15-12] plus 512K as top
of PCI memory.......................................default
Offset 49 – Port 70/74 Access Status (Version CE Only)RO
7 CD: Reserved .................................... always reads 0
CE: Port 70 / 74 Access Status...........................RO
0 Last access was to Port 70
1 Last access was to Port 74
6-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 4A - IDE Interrupt Routing..................................RW
7 Wait for PGNT Before Grant to ISA Master /
DMA
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 Bus Select for Access to I/O Devices Below 100h
0 Access ports 00-FFh via XD bus ...........default
1 Access ports 00-FFh via SD bus (applies to
external devices only; internal devices such as
the mouse controller are not effected)
5-4 Reserved (do not program)..................... default = 0
3-2 IDE Second Channel IRQ Routing
00 IRQ14
01 IRQ15.....................................................default
10 IRQ10
11 IRQ11
1-0 IDE Primary Channel IRQ Routing
00 IRQ14.....................................................default
01 IRQ15
10 IRQ10
11 IRQ11
Offset 4C - ISA DMA/Master Memory Access Ctrl 1... RW
7-0 PCI Memory Hole Bottom Address
These bits correspond to HA[23:16]............ default=0
Offset 4D - ISA DMA/Master Memory Access Ctrl 2... RW
7-0 PCI Memory Hole Top Address (HA[23:16])
These bits correspond to HA[23:16]............ default=0
Note: Access to the memory defined in the PCI memory
hole will not be forwarded to PCI. This function is
disabled if the top address is less than or equal to the
bottom address.
Offset 4F-4E - ISA DMA/Master Mem Access Ctrl 3 ... RW
15-12 Top of PCI Memory for ISA DMA/Master accesses
0000 1M .................................................... default
0001 2M
... ...
1111 16M
Note: All ISA DMA / Masters that access addresses higher
than the top of PCI memory will not be directed to
the PCI bus.
11 Forward E0000-EFFFF Accesses to PCI .......def=0
10 Forward A0000-BFFFF Accesses to PCI .......def=0
9 Forward 80000-9FFFF Accesses to PCI ........ def=1
8 Forward 00000-7FFFF Accesses to PCI ........ def=1
7 Forward DC000-DFFFF Accesses to PCI ......def=0
6 Forward D8000-DBFFF Accesses to PCI ...... def=0
5 Forward D4000-D7FFF Accesses to PCI ...... def=0
4 Forward D0000-D3FFF Accesses to PCI ...... def=0
3 Forward CC000-CFFFF Accesses to PCI ..... def=0
2 Forward C8000-CBFFF Accesses to PCI ...... def=0
1 Forward C4000-C7FFF Accesses to PCI ...... def=0
0 Forward C0000-C3FFF Accesses to PCI ...... def=0
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -60- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 67

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Plug and Play Control
Offset 50 – PNP DMA Request Control.......................... RW
7-4 Reserved .............................................. default = 0
3-2 PnP Routing for Parallel Port DRQ.....def = DRQ3
1-0 PnP Routing for Floppy DRQ .............. def = DRQ2
DRQ Mapping: 00=DRQ0, 01=DRQ1, 10=DRQ2, 11=DRQ3
Offset 51 - PNP IRQ Routing 1........................................RW
7-4 PnP Routing for Parallel Port IRQ (see PnP IRQ
routing table)
3-0 PnP Routing for Floppy IRQ (see PnP IRQ routing
table)
Offset 52 - PNP IRQ Routing 2........................................RW
7-4 PnP Routing for Serial Port 2 IRQ (see PnP IRQ
routing table)
3-0 PnP Routing for Serial Port 1 IRQ (see PnP IRQ
routing table)
Offset 54 - PCI IRQ Edge / Level Select .........................RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
The following bits all default to “level” triggered (0)
3 PIRQA# Invert (edge) / Non-invert (level) ......(1/0)
2 PIRQB# Invert (edge) / Non-invert (level) ......(1/0)
1 PIRQC# Invert (edge) / Non-invert (level) ......(1/0)
0 PIRQD# Invert (edge) / Non-invert (level) ......(1/0)
Note: PIRQA-D# normally connect to PCI interrupt pins
INTA-D# (see pin definitions for more information).
Offset 55 - PNP IRQ Routing 4........................................RW
7-4 PIRQA# Routing (see PnP IRQ routing table)
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 56 - PNP IRQ Routing 5........................................RW
7-4 PIRQC# Routing (see PnP IRQ routing table)
3-0 PIRQB# Routing (see PnP IRQ routing table)
Offset 57 - PNP IRQ Routing 6........................................RW
7-4 PIRQD# Routing (see PnP IRQ routing table)
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 58 – External APIC IRQ Output Control........... RW
CD:
7 RTC High Bank Access (80-FFh)
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6-5 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
4 ACPI IRQ to APIC[23:16] with Rx42[2:0]
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 MC97 IRQ to APIC[23:16] with Rx3C[2:0]
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 AC97 IRQ to APIC[23:16] with Rx3C[2:0]
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 USB Port 1 IRQ to APIC[23:16] with Rx3C[2:0]
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 USB Port 0 IRQ to APIC[23:16] with Rx3C[2:0]
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
CE:
7 RTC High Bank Access (80-FFh)
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Note: In chip version CE, when using the APIC, the
internal IRQ routing is:
INTA ...............IRQ16
INTB ...............IRQ17
INTC ...............IRQ18
INTD ...............IRQ19
IDE..................IRQ20
USB.................IRQ21
AC97/MC97....IRQ22
PnP IRQ Routing Table
0000 Disable ...................................................default
0001 IRQ1
0010 Reserved
0011 IRQ3
0100 IRQ4
0101 IRQ5
0110 IRQ6
0111 IRQ7
1000 Reserved
1001 IRQ9
1010 IRQ10
1011 IRQ11
1100 IRQ12
1101 Reserved
1110 IRQ14
1111 IRQ15
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -61- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 68

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 5A – KBC / RTC Control......................................RW
Bits 7-4 of this register are latched from pins SD7-4 at powerup but are read/write accessible so may be changed after
power-up to change the default strap setting:
7 Keyboard RP16........................... latched from SD7†
6 Keyboard RP15 .......................... latched from SD6†
5 Keyboard RP14 .......................... latched from SD5†
4 Keyboard RP13 .......................... latched from SD4†
3 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
2 Internal RTC Enable
0 Disable
1 Enable ...................................................default
1 Internal PS2 Mouse Enable
0 Disable ..................................................default
1 Enable
0 Internal KBC Enable
0 Disable ..................................................default
1 Enable
†Note: External straps may be set by connecting the
indicated pin to a 4.7K ohm pullup (for 1) or driving
it low during reset with a 7407 or equivalent open
collector (OC) buffer (for 0) as shown in the example
circuit below. The OC buffer provides a valid strap
value of 0 during reset but after reset the buffer does
not drive so the strap circuit therefore does not effect
normal operation of the pin.
VCC
7407
RESET#
VCC
4.7K
strap
pin
Offset 5B - Internal RTC Test Mode .............................. RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 Map RTC Rx32 to Rx3F
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 RTC Reset Enable (do not program)
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 Reserved (do not program).......................... default=0
0 RTC Test Mode Enable (do not program). default=0
Offset 5C - DMA Control ................................................ RW
7 PCS0# & PCS1# 16-Bit I/O
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6 Passive Release
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 Internal Passive Release
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
4 Dummy PREQ
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
2 APIC Connection
0 APIC on SD Bus ................................... default
1 APIC on XD Bus
1 Reserved (Do Not Program).................... default = 0
0 DMA Line Buffer Disable
0 DMA cycles can be to/from line buffer....... def
1 Disable DMA Line Buffer
Figure 5. Strap Option Circuit
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -62- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 69

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Distributed DMA / Serial IRQ Control
Offset 61-60 - Distributed DMA Ch 0 Base / Enable .....RW
15-4 Channel 0 Base Address Bits 15-4 .......... default = 0
3 Channel 0 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 63-62 - Distributed DMA Ch 1 Base / Enable .....RW
15-4 Channel 1 Base Address Bits 15-4 .......... default = 0
3 Channel 1 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 65-64 - Distributed DMA Ch 2 Base / Enable .....RW
15-4 Channel 2 Base Address Bits 15-4 .......... default = 0
3 Channel 2 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 67-66 - Distributed DMA Ch 3 Base / Enable .....RW
15-4 Channel 3 Base Address Bits 15-4 .......... default = 0
3 Channel 3 Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 6B-6A - Distributed DMA Ch 5 Base / Enable ... RW
15-4 Channel 5 Base Address Bits 15-4 ..........default = 0
3 Channel 5 Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Offset 6D-6C - Distributed DMA Ch 6 Base / Enable... RW
15-4 Channel 6 Base Address Bits 15-4 ..........default = 0
3 Channel 6 Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Offset 6F-6E - Distributed DMA Ch 7 Base / Enable.... RW
15-4 Channel 7 Base Address Bits 15-4 ..........default = 0
3 Channel 7 Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Offset 69-68 – Serial IRQ Control...................................RW
15-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 ISA IRQ Asserted Via Serial IRQ (Pin H3 or L4)
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 Serial IRQ Mode
0 Continuous Mode...................................default
1 Quiet Mode
1-0 Serial IRQ Start-Frame Width
00 4 PCI Clocks ..........................................default
01 6 PCI Clocks
10 8 PCI Clocks
11 10 PCI Clocks
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -63- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 70

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Miscellaneous / General Purpose I/O
Offset 73-70 - Subsystem ID.............................................WO
31-0 Subsystem ID / Vendor ID ................ always reads 0
Contents may be read at offset 2C.
Offset 74 – GPIO Control 1..............................................RW
7 Reserved (Do Not Program) ................... default = 0
6 SERIRQ Pin
0 SERIRQ input from DRQ2 (Pin H3) .....default
1 SERIRQ input from DACK5# (Pin L4)
5 GPIOD Direction (Pin U8)
0 Input .....................................................default
1 Output (GPO11)
4 GPIOC Direction (Pin V14)
0 Input .....................................................default
1 Output
3 GPIOB Direction (Pin U12)
0 Input .....................................................default
1 Output
2 GPIOA Direction (Pin T14)
0 Input .....................................................default
1 Output
1 THRM Enable (Pin T11)
0 PME# / GPI5 (see Func 4 Rx48[5]).......default
1 THRM
0 GPI0 / IOCHCK# Select
0 GPI0 .....................................................default
1 IOCHCK#
Offset 75 – GPIO Control 2............................................. RW
7 GPO7 Enable (Pin T7)
0 Pin defined as SLP# .............................. default
1 Pin defined as GPO7
6 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
5 GPO5 Enable (Pin V12)
0 Pin defined as PCISTP# ........................ default
1 Pin defined as GPO5
4 GPO4 Enable (Pin Y12)
0 Pin defined as CPUSTP#....................... default
1 Pin defined as GPO4
3 FDC External IRQ / DRQ Via DACK2# / DRQ2
Enable
0 Enable Pin G1 is IRQ6, Pin H3 is DRQ2, Pin
G5 is DACK2#
1 Disable Pin G1 is IRQ6, Pin H3 is DRQ2, Pin
G5 is DACK2#
2 GPO25 Enable (Pin G5)
0 See bit-3 & Rx76[7-6] for G5 pin function. def
1 Pin G5 defined as GPO25
1 GPO24 Enable (Pin H3)
0 See bit-3 & Rx68[3] for H3 pin function ....def
1 Pin H3 defined as GPO24
0 Positive Decode
0 Subtractive Decode................................ default
1 Positive Decode
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -64- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 71

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 76 – GPIO Control 3 (00)......................................RW
7 Over-Current (OC) Input
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable (pins G5 and H3 are USBOC0# and
USBOC1# if bit-6 = 0)
6 OC[3:0] From SD[3:0] By Scan
0 Disable (pins G5 & H3 are USBOC0# and
USBOC1# if bit-7 = 1)...........................default
1 Enable
5 GPO14 / GPO15 Enable (Pins E12 / D12)
0 Pins used for IRTX and IRRX ...............default
1 Pins used for GPO14 and GPO15
4 MCCS# Pin Select
0 MCCS# is on Pin U5..............................default
1 MCCS# is on Pin U8
3 MCCS# Function
0 Disable MCCS# function .......................default
1 Enable MCCS# function (Decode port 62/66h)
(see bit-4 for select of U5 or U8 for MCCS#)
2 CHAS Enable (Pin V14)
0 Pin is defined as GPIOC ........................default
1 Pin is defined as CHAS
1 GPO12 Enable (Pin T5)
0 Pin is defined as XDIR ..........................default
1 Pin is defined as GPO12
0 GPOWE (GPO[23-16]) Enable (Pin T14)
0 Pin is defined as GPIOA ........................default
1 Pin is defined as GPOWE (Rx74[2] also must
be set to 1)
Offset 77 – GPIO Control 4 Control (10h)..................... RW
7 DRQ / DACK# Pins are GPI / GPO
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6 Game Port XY Pins are GPI / GPO
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Internal APIC Enable
0 Disable
1 Enable (U10 = WSC#, V9 = APICD0, T10 =
APICD1)................................................ default
3 IRQ0 Output
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable IRQ0 output to GPIOC
2 RTC Rx32 Write Protect
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 RTC Rx0D Write Protect
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 GPO13 Enable (Pin U5)
0 Pin defined as SOE#.............................. default
1 Pin defined as GPO13
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -65- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 72

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 79-78 – PCS0# I/O Port Address..........................RW
15-0 PCS0# I/O Port Address [15-0]
Offset 7B-7A – PCS1# I/O Port Address ........................RW
15-0 PCS1# I/O Port Address [15-0]
Offset 7D-7C – PCI DMA Channel Enable ....................RW
15-9 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
8-5 Reserved (Do Not Program) ................... default = 0
4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-0 Reserved (Do Not Program) ................... default = 0
Offset 7F-7E – 32-Bit DMA Control............................... RW
15-3 32-Bit DMA High Page (A31-24) Registers IOBase
2-1 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
0 32-Bit DMA
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Offset 80 – Programmable Chip Select Mask................ RW
7-4 PCS1# I/O Port Address Mask [3-0]
3-0 PCS0# I/O Port Address Mask [3-0]
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -66- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 73

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 81 – ISA Positive Decoding Control 1..................RW
7 On-Board I/O Port Positive Decoding
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 Microsoft-Sound System I/O Port Positive
Decoding
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5-4 Microsoft-Sound System I/O Decode Range
00 0530h-0537h ..........................................default
01 0604h-060Bh
10 0E80-0E87h
11 0F40h-0F47h
3 APIC Positive Decoding
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 BIOS ROM Positive Decoding
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
0 PCS0 Positive Decoding
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
Offset 83 – ISA Positive Decoding Control 3 ................. RW
7 COM Port B Positive Decoding
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6-4 COM-Port B Decode Range
000 3F8h-3FFh (COM1)............................ default
001 2F8h-2FFh (COM2)
010 220h-227h
011 228h-22Fh
100 238h-23Fh
101 2E8h-2EFh (COM4)
110 338h-33Fh
111 3E8h-3EFh (COM3)
3 COM Port A Positive Decoding
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2-0 COM-Port A Decode Range
000 3F8h-3FFh (COM1)............................ default
001 2F8h-2FFh (COM2)
010 220h-227h
011 228h-22Fh
100 238h-23Fh
101 2E8h-2EFh (COM4)
110 338h-33Fh
111 3E8h-3EFh (COM3)
Offset 82 – ISA Positive Decoding Control 2..................RW
7 FDC Positive Decoding
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 LPT Positive Decoding
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5-4 LPT Decode Range
00 3BCh-3BFh, 7BCh-7BEh ......................default
01 378h-37Fh, 778h-77Ah
10 278h-27Fh, 678h-67Ah
11 -reserved-
3 Game Port Positive Decoding
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 MIDI Positive Decoding
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1-0 MIDI Decode Range
00 300h-303h ..............................................default
01 310h-313h
10 320h-323h
11 330h-333h
Offset 84 – ISA Positive Decoding Control 4 ................. RW
7-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 CD: Reserved.....................................always reads 0
CE: Port CF9 Positive Decoding
0 Disable
1 Enable................................................... default
3 FDC Decoding Range
0 Primary .................................................. default
1 Secondary
2 Sound Blaster Positive Decoding
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1-0 Sound Blaster Decode Range
00 220h-22Fh, 230h-233h .......................... default
01 240h-24Fh, 250h-253h
10 260h-26Fh, 270h-273h
11 280h-28Fh, 290h-293h
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -67- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 74

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 85 – Extended Function Enable............................RW
7-6 PCI Master Grant Timeout Select
00 Disable ...................................................default
01 32 PCI Clocks
10 64 PCI Clocks
11 96 PCI Clocks
5 Keyboard Controller Configuration
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 Function 3 USB Ports 2-3
0 Enable ....................................................default
1 Disable
3 Function 6 Modem / Audio
0 Enable ....................................................default
1 Disable
2 Function 5 Audio
0 Enable ....................................................default
1 Disable
1 Super-I/O Configuration
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
0 Super-I/O
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
Offset 86 – PNP IRQ/DRQ Test 1 (Do Not Program)... RW
Offset 87 – PNP IRQ/DRQ Test 2 (Do Not Program)... RW
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -68- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 75

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 88 – PLL Test ......................................................... RW
7 PCS0# Access Status
6 RTC Rx32 / Rx7F Write Protect
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 MC IRQ Test (Do Not Program)
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 PLL PU (Do Not Program)
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 PLL Test Mode (Do Not Program)
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 PLL Test Mode Select
Offset 89 – PLL Control................................................... RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-2 PLL PCLK Input Delay Select
1-0 PLL CLK66 Feedback Delay Select
Offset 8A – PCS2/3 I/O Port Address Mask .................. RW
7-4 PCS3# I/O Port Address Mask 3-0
3-0 PCS2# I/O Port Address Mask 3-0
Offset 8B – PCS Control.................................................. RW
7 PCS3# For Internal I/O
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6 PCS2# For Internal I/O
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 PCS1# For Internal I/O
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
4 PCS0# For Internal I/O
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 PCS3#
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 PCS2#
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 PCS1#
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 PCS0#
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Offset 8D-8C – PCS2# I/O Port Address........................ RW
15-0 PCS2# I/O Port Address
Offset 8F-8E – PCS3# I/O Port Address ........................ RW
15-0 PCS3# I/O Port Address
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -69- Function 0 Registers - PCI to ISA Bridge
Page 76

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Function 1 Registers - Enhanced IDE Controller
This Enhanced IDE controller interface is fully compatible
with the SFF 8038i v.1.0 specification. There are two sets of
software accessible registers -- PCI configuration registers and
Bus Master IDE I/O registers. The PCI configuration registers
are located in the function 1 PCI configuration space of the
VT82C686B. The Bus Master IDE I/O registers are defined
in the SFF8038i v1.0 specification.
PCI Configuration Space Header
Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID (1106h=VIA)................................RO
Offset 3-2 - Device ID (0571h=IDE Controller) ..............RO
Offset 5-4 - Command ......................................................RW
15-10 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
9 Fast Back to Back Cycles ....... default = 0 (disabled)
8 SERR# Enable......................... default = 0 (disabled)
7 Address Stepping ....................default = 1 (enabled)
A value of 1 provides additional address decode time
to IDE devices.
6 Parity Error Response............ default = 0 (disabled)
5 VGA Palette Snoop....................fixed at 0 (disabled)
4 Memory Write & Invalidate .....fixed at 0 (disabled)
3 Special Cycles .............................fixed at 0 (disabled)
2 Bus Master ............................. default = 0 (disabled)
S/G operation can be issued only when the “Bus
Master” bit is enabled.
1 Memory Space......................... default = 0 (disabled)
0 I/O Space ............................. default = 0 (disabled)
When the “I/O Space” bit is disabled, the device will
not respond to any I/O addresses for both compatible
and native mode.
Offset 9 - Programming Interface................................... RW
7 Master IDE Capability .......... fixed at 1 (Supported)
6-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 Programmable Indicator - Secondary...... fixed at 1
Supports both modes (may be set to either mode by
writing bit-2)
2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1 Programmable Indicator - Primary ......... fixed at 1
Supports both modes (may be set to either mode by
writing bit-0)
0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Compatibility Mode (fixed IRQs and I/O addresses):
Command Block Control Block
Channel
Pri 1F0-1F7 3F6 14
Registers Registers IRQ
Sec 170-177 376 15
Native PCI Mode (registers are programmable in I/O space)
Command Block Control Block
Channel
Registers Registers
Pri BA @offset 10h BA @offset 14h
Sec BA @offset 18h BA @offset 1Ch
Command register blocks are 8 bytes of I/O space
Control registers are 4 bytes of I/O space (only byte 2 is used)
Offset A - Sub Class Code (01h=IDE Controller) .......... RO
Offset B - Base Class Code (01h=Mass Storage Ctrlr)... RO
Offset C – Cache Line Size (00h) ..................................... RO
Offset D - Latency Timer (Default=0) ............................ RW
Offset E - Header Type (00h) ........................................... RO
Offset 7-6 – Status ..............................................................RO
Offset F - BIST (00h)......................................................... RO
15 Detected Parity Error........................ always reads 0
14 Signalled System Error ..................... always reads 0
13 Received Master Abort ..................... always reads 0
12 Received Target Abort ...................... always reads 0
11 Signalled Target Abort...................... always reads 0
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing ............always reads 01 (medium)
8 Data Parity Detected ......................... always reads 0
7 Fast Back to Back .............................always reads 1
6-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Power Management Capabilty Ptr.. always reads 1
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 8 - Revision ID (06).................................................RO
0-7 Revision Code for IDE Controller Logic Block
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -70- Function 1 Registers - Enhanced IDE Controller
Page 77

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 13-10 - Pri Data / Command Base Address.........RW
Specifies an 8 byte I/O address space.
31-16 Reserved ..........................................always read 0
15-3 Port Address....................................... default=01F0h
2-0 Fixed at 001b (Native Mode)............................ fixed
Fixed at 000b (Compatibility Mode)
Offset 17-14 - Pri Control / Status Base Address ...........RW
Specifies a 4 byte I/O address space of which only the third
byte is active (i.e., 3F6h for the default base address of 3F4h).
31-16 Reserved .......................................... always read 0
15-2 Port Address....................................... default=03F4h
1-0 Fixed at 01b (Native Mode).............................. fixed
Fixed at 00b (Compatibility Mode)
Offset 1B-18 - Sec Data / Command Base Address........RW
Specifies an 8 byte I/O address space.
31-16 Reserved ..........................................always read 0
15-3 Port Address ...................................... default=0170h
2-0 Fixed at 001b (Native Mode)............................ fixed
Fixed at 000b (Compatibility Mode)
Offset 1F-1C - Sec Control / Status Base Address .........RW
Specifies a 4 byte I/O address space of which only the third
byte is active (i.e., 376h for the default base address of 374h).
Offset 34 - Capability Pointer (C0h)................................ RO
Offset 3C - Interrupt Line (0Eh)...................................... RO
Offset 3D - Interrupt Pin (01h) ........................................ RO
7-0 Interrupt Routing Mode
01h Legacy mode interrupt routing.............. default
01h Native mode interrupt routing
Offset 3E - Min Gnt (00h)................................................. RO
Offset 3F - Max Latency (00h) ......................................... RO
31-16 Reserved ..........................................always read 0
15-2 Port Address ...................................... default=0374h
1-0 Fixed at 01b (Native Mode).............................. fixed
Fixed at 00b (Compatibility Mode)
Offset 23-20 - Bus Master Control Regs Base Address .RW
Specifies a 16 byte I/O address space compliant with the SFF-
8038i rev 1.0 specification.
31-16 Reserved ..........................................always read 0
15-4 Port Address ....................................... default=CC0h
3-0 Fixed at 0001b (Native Mode).......................... fixed
Fixed at 0000b (Compatibility Mode)
See Rx42[7-6] for Native / Compatibility mode select for the
above registers
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -71- Function 1 Registers - Enhanced IDE Controller
Page 78

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
IDE-Controller-Specific Confiiguration Registers
Offset 40 - Chip Enable (08h) ..........................................RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-2 Reserved (Do Not Program) ......R/W, default = 10b
1 Primary Channel Enable ....... default = 0 (disabled)
0 Secondary Channel Enable.... default = 0 (disabled)
Offset 41 - IDE Configuration I (02h) ............................. RW
7 Primary IDE Read Prefetch Buffer
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 Primary IDE Post Write Buffer
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 Secondary IDE Read Prefetch Buffer
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 Secondary IDE Post Write Buffer
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3-2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1 Reserved (Do Not Program) ..................... default=1
0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 42 - IDE Configuration II (09h) ...........................RW
7 Primary Channel PIO Operation Mode
0 Compatibility Mode
1 Native Mode ..........................................default
6 Secondary Channel PIO Operation Mode
0 Compatibility Mode
1 Native Mode ..........................................default
5-2 Reserved (Do Not Program) ....... default = 000010b
1-0 DEVSEL# Timing Select..................... default = 01b
(also reflected in Rx07)
Offset 43 - FIFO Configuration (0Ah) ............................RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-2 Threshold for Primary Channel
00 1/4
01 1/2
10 3/4 .....................................................default
11 1
1-0 Threshold for Secondary Channel
00 1/4
01 1/2
10 3/4 .....................................................default
11 1
Offset 44 - Miscellaneous Control 1 (68h) ...................... RW
7 IDE Controller Max Speed
0 UDMA100............................................. default
1 UDMA66
6 Master Read Cycle IRDY# Wait States
0 0 wait states
1 1 wait state............................................. default
5 Master Write Cycle IRDY# Wait States
0 0 wait states
1 1 wait state............................................. default
4 PIO Read Prefetch Byte Counter
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 Bus Master IDE Status Register Read Retry
Retry bus master IDE status register read when
master write operation for DMA read is not complete
0 Disable
1 Enable.................................................... default
2 Packet Command Prefetching
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 UltraDMA Host Must Wait for First Strobe
Before Termination
0 Enable.................................................... default
1 Disable
Offset 45 - Miscellaneous Control 2 (00h) ...................... RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6 Interrupt Steering Swap
0 Don’t swap channel interrupts............... default
1 Swap interrupts between the two channels
5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Rx3C Write Protect
0 Enable.................................................... default
1 Disable
3 Memory Read Multiple Command
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 Memory Write and Invalidate Command
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Offset 46 - Miscellaneous Control 3 (C0h) ..................... RW
7 Primary Channel Read DMA FIFO Flush
0 Disable
1 Enable FIFO flush for Read DMA when
interrupt asserts primary channel........... default
6 Secondary Channel Read DMA FIFO Flush
0 Disable
1 Enable FIFO flush for Read DMA when
interrupt asserts secondary channel....... default
5-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -72- Function 1 Registers - Enhanced IDE Controller
Page 79

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 4B-48 - Drive Timing Control (A8A8A8A8h) .....RW
The following fields define the Active Pulse Width and
Recovery Time for the IDE DIOR# and DIOW# signals:
31-28 Primary Drive 0 Active Pulse Width...... def=1010b
27-24 Primary Drive 0 Recovery Time ............ def=1000b
23-20 Primary Drive 1 Active Pulse Width...... def=1010b
19-16 Primary Drive 1 Recovery Time ............ def=1000b
15-12 Secondary Drive 0 Active Pulse Width .. def=1010b
11-8 Secondary Drive 0 Recovery Time ......... def=1000b
7-4 Secondary Drive 1 Active Pulse Width.. def=1010b
3-0 Secondary Drive 1 Recovery Time......... def=1000b
The actual value for each field is the encoded value in the
field plus one and indicates the number of PCI clocks.
Offset 4C - Address Setup Time (FFh)............................RW
7-6 Primary Drive 0 Address Setup Time........ def = 11
5-4 Primary Drive 1 Address Setup Time ....... def = 11
3-2 Secondary Drive 0 Address Setup Time ... def = 11
1-0 Secondary Drive 1 Address Setup Time ... def = 11
For each field above:
00 1T
01 2T
10 3T
11 4T .....................................................default
Offset 53-50 - UltraDMA Extended Timing Control .... RW
31 Pri Drive 0 UltraDMA-Mode Enable Method
0 Enable by using “Set Feature” command.... def
1 Enable by setting bit-30 of this register
30 Pri Drive 0 UltraDMA-Mode Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable UltraDMA-Mode Operation
29 Pri Drive 0 Transfer Mode
0 DMA or PIO Mode .............................. default
1 UltraDMA Mode
28 Pri Drive 0 Cabal Type Reporting
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
27 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
26-24 Pri Drive 0 Cycle Time (T = 10nsec)
000 2T
001 3T
010 4T
011 5T
100 6T
101 7T
110 8T
111 9T .................................................... default
23 Pri Drive 1 UltraDMA-Mode Enable Method
22 Pri Drive 1 UltraDMA-Mode Enable
21 Pri Drive 1 Transfer Mode
20 Pri Drive 1 Cabal Type Reporting
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
19 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
18-16 Pri Drive 1 Cycle Time ......... (see above for default)
15 Sec Drive 0 UltraDMA-Mode Enable Method
14 Sec Drive 0 UltraDMA-Mode Enable
13 Sec Drive 0 Transfer Mode
12 Sec Drive 0 Cabal Type Reporting
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
11 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
10-8 Sec Drive 0 Cycle Time ......... (see above for default)
7 Sec Drive 1 UltraDMA-Mode Enable Method
6 Sec Drive 1 UltraDMA-Mode Enable
5 Sec Drive 1 Transfer Mode
4 Sec Drive 1 Cabal Type Reporting
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
2-0 Sec Drive 1 Cycle Time......... (see above for default)
Each byte defines UltraDMA operation for the indicated
drive. The bit definitions are the same within each byte.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -73- Function 1 Registers - Enhanced IDE Controller
Page 80

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 54 – UltraDMA FIFO Control (04h).................... RW
7-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 One Frame For Each PCI Request For IDE PCI
Master Cycles
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
2 Change Drive to Clear All FIFO & Internal States
0 Disable
1 Enable ....................................................default
1 Select Internal Bus Request for FRAME Request
to Enter PCI Address Phase
0 Select internal bus request .....................default
1 Select internal FRAME request
0 Complete DMA Cycle with Transfer Size Less
Than FIFO Size
0 Enable ....................................................default
1 Disable
Offset 61-60 - Primary Sector Size (0200h) ....................RW
15-12 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
11-0 Number of Bytes Per Sector... def=200h (512 bytes)
Offset 69-68 - Secondary Sector Size (0200h).................RW
15-12 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
11-0 Number of Bytes Per Sector... def=200h (512 bytes)
Offset 70 – Primary IDE Status ...................................... RW
7 Interrupt Status
6 Prefetch Buffer Status
5 Post Write Buffer Status
4 DMA Read Prefetch Status
3 DMA Write Prefetch Status
2 S/G Operation Complete
1 FIFO Empty Status
0 Response to External DMAREQ
Offset 71 – Primary Interrupt Control........................... RW
7-1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 Flush FIFO Before Generating IDE Interrupt
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Offset 78 – Secondary IDE Status................................... RW
7 Interrupt Status
6 Prefetch Buffer Status
5 Post Write Buffer Status
4 DMA Read Prefetch Status
3 DMA Write Prefetch Status
2 S/G Operation Complete
1 FIFO Empty Status
0 Response to External DMAREQ
Offset 79 - Secondary Interrupt Control........................ RW
7-1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 Flush FIFO Before Generating IDE Interrupt
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Offset 83-80 – Primary S/G Descriptor Address ........... RW
Offset 8B-88 – Secondary S/G Descriptor Address ....... RW
Offset C3-C0 – PCI PM Block 1....................................... RO
31-0 PCI PM Block 1 ................. always reads 0002 0001h
Offset C7-C4 – PCI PM Block 2....................................... RO
31-2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1-0 Power State
00 On .................................................... default
01 Off
1x -reserved-
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -74- Function 1 Registers - Enhanced IDE Controller
Page 81

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
IDE I/O Registers
These registers are compliant with the SFF 8038I v1.0
standard. Refer to the SFF 8038I v1.0 specification for
further details.
I/O Offset 0 - Primary Channel Command
I/O Offset 2 - Primary Channel Status
I/O Offset 4-7 - Primary Channel PRD Table Address
I/O Offset 8 - Secondary Channel Command
I/O Offset A - Secondary Channel Status
I/O Offset C-F - Secondary Channel PRD Table Address
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -75- Function 1 Registers - Enhanced IDE Controller
Page 82

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
e
Function 2 Registers - USB Controller Ports 0-1
This Universal Serial Bus host controller interface is fully
compatible with UHCI specification v1.1. There are two sets
of software accessible registers: PCI configuration registers
and USB I/O registers. The PCI configuration registers are
located in the function 2 PCI configuration space of the
VT82C686B. The USB I/O registers are defined in UHCI
specification v1.1. The registers in this function control USB
ports 0-1 (see function 3 for ports 2-3).
PCI Configuration Space Header
Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID .......................................................RO
0-7 Vendor ID ................. (1106h = VIA Technologies)
Offset 3-2 - Device ID.........................................................RO
0-7 Device ID (3038h = VT82C686B USB Controller)
Offset 5-4 – Command (0000h)........................................RW
15-8 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
7 Address Stepping ...................... default=0 (disabled)
6 Reserved (parity error response)..................fixed at 0
5 Reserved (VGA palette snoop) ....................fixed at 0
4 Memory Write and Invalidate. default=0 (disabled)
3 Reserved (special cycle monitoring)............fixed at 0
2 Bus Master ............................... default=0 (disabled)
1 Memory Space........................... default=0 (disabled)
0 I/O Space ............................... default=0 (disabled)
Offset 7-6 – Status (0210h) ............................................RWC
15 Reserved (detected parity error) ......... always reads 0
14 Signalled System Error ............................. default=0
13 Received Master Abort ............................. default=0
12 Received Target Abort .............................. default=0
11 Signalled Target Abort.............................. default=0
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing
00 Fast
01 Medium ...................................... default (fixed)
10 Slow
11 Reserved
8-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Pwr Mgmt Extended Capabilties ..... always reads 1
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 8 - Revision ID (nnh).............................................. RO
7-0 Silicon Revision Code (0 indicates first silicon)
06h Corresponds to Chip Revision D
Offset 9 - Programming Interface (00h).......................... RO
Offset A - Sub Class Code (03h=USB Controller).......... RO
Offset B - Base Class Code (0Ch=Serial Bus Controller)RO
Offset C – Cache Line Size (00h) ..................................... RO
Offset D - Latency Timer................................................. RW
7-0 Timer Value ............................................................... d
Offset E - Header Type (00h) ........................................... RO
Offset F - BIST (00h)......................................................... RO
Offset 23-20 - USB I/O Register Base Address .............. RW
31-16 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
15-5 USB I/O Register Base Address. Port Address for
the base of the 32-byte USB I/O Register block,
corresponding to AD[15:5]
4-0 00001b
Offset 34 – USB Power Management Capabilities (80h) RO
Offset 3C - Interrupt Line (00h) ..................................... RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3-0 USB Interrupt Routing........................ default = 16h
0000 Disable................................................... default
0001 IRQ1
0010 Reserved
0011 IRQ3
0100 IRQ4
0101 IRQ5
0110 IRQ6
0111 IRQ7
1000 IRQ8
1001 IRQ9
1010 IRQ10
1011 IRQ11
1100 IRQ12
1101 IRQ13
1110 IRQ14
1111 Disable
Offset 3D - Interrupt Pin (04h) ........................................ RO
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -76- Function 2 Registers - USB Controller Ports 0-1
Page 83

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
USB-Specific Configuration Registers
Offset 40 - Miscellaneous Control 1 ................................RW
7 PCI Memory Command Option
0 Support Memory-Read-Line, Memory-Read-
Multiple, & Memory-Write-&-Invalidate....def
1 Only support Mem Read, Mem Write Cmds
6 Babble Option
0 Automatically disable babbled port when EOF
babble occurs .........................................default
1 Don’t disable babbled port
5 PCI Parity Check Option
0 Disable PERR# generation ....................default
1 Enable parity check and PERR# generation
4 Frame Interval Select
0 1 ms frame..............................................default
1 0.1 ms frame
3 USB Data Length Option
0 Support TD length up to 1280 ...............default
1 Support TD length up to 1023
2 USB Power Management
0 Disable USB power management ..........default
1 Enable USB power management
1 DMA Option
0 8 DW burst access with better FIFO latencydef
1 16 DW burst access (original performance)
0 PCI Wait States
0 Zero wait ................................................default
1 One wait
Offset 41 - Miscellaneous Control 2................................ RW
7 USB 1.1 Improvement for EOP
0 USB Specification 1.1 Compliant ......... default
If a bit stuffing error occurs before EOP, the
receiver will accept
1 USB Specification 1.0 Compliant
If a bit stuffing error occurs before EOP, the
receiver will ignore
6-5 Reserved (Do Not Program).................... default = 0
4 Hold PCI Request for Successive Accesses
0 Disable
1 Enable.................................................... default
Setting this bit to “enable” causes the system to treat
the USB request as higher priority
3 Frame Counter Test Mode
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 Trap Option
0 Set trap 60/64 status bits only when trap 60/64
enable bits are set. ................................ default
1 Set trap 60/64 status bits without checking
enable bits
1 A20gate Pass Through Option
0 Pass through A20GATE command sequence
defined in UHCI .................................... default
1 Don’t pass through Write I/O port 64 (ff)
0 USB IRQ Test Mode
0 Normal Operation.................................. default
1 Generate USB IRQ
the packet
the packet
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -77- Function 2 Registers - USB Controller Ports 0-1
Page 84

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 42 - FIFO Control..................................................RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-2 Reserved (Do Not Program) ................... default = 0
1-0 Release Continuous REQ After “N” PCICLKs
00 Do Not Release ......................................default
01 N = 32 PCICLKs
10 N = 64 PCICLKs
11 N = 96 PCICLKs
Offset 60 - Serial Bus Release Number ............................RO
7-0 Release Number ............................. always reads 10h
Offset 83-80 – PM Capability............................................RO
31-0 PM Capability .................... always reads 00020001h
Offset 84 – PM Capability Status ....................................RW
7-0 PM Capability Status .......................... default = 00h
Supports 00h (Off) and 11h (On) only
Offset C1-C0 - Legacy Support ........................................RO
15-0 UHCI v1.1 Compliant................ always reads 2000h
USB I/O Registers
These registers are compliant with the UHCI v1.1 standard.
Refer to the UHCI v1.1 specification for further details.
I/O Offset 1-0 - USB Command
I/O Offset 3-2 - USB Status
I/O Offset 5-4 - USB Interrupt Enable
I/O Offset 7-6 - Frame Number
I/O Offset B-8 - Frame List Base Address
I/O Offset 0C - Start Of Frame Modify
I/O Offset 11-10 - Port 0 Status / Control
I/O Offset 13-12 - Port 1 Status / Control
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -78- Function 2 Registers - USB Controller Ports 0-1
Page 85

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
e
Function 3 Registers - USB Controller Ports 2-3
This Universal Serial Bus host controller interface is fully
compatible with UHCI specification v1.1. There are two sets
of software accessible registers: PCI configuration registers
and USB I/O registers. The PCI configuration registers are
located in the function 3 PCI configuration space of the
VT82C686B. The USB I/O registers are defined in UHCI
specification v1.1. The registers in this function control USB
ports 2-3 (see function 2 for ports 0-1).
PCI Configuration Space Header
Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID .......................................................RO
0-7 Vendor ID ................. (1106h = VIA Technologies)
Offset 3-2 - Device ID.........................................................RO
0-7 Device ID (3038h = VT82C686B USB Controller)
Offset 5-4 – Command (0000h)........................................RW
15-8 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
7 Address Stepping ...................... default=0 (disabled)
6 Reserved (parity error response)..................fixed at 0
5 Reserved (VGA palette snoop) ....................fixed at 0
4 Memory Write and Invalidate. default=0 (disabled)
3 Reserved (special cycle monitoring)............fixed at 0
2 Bus Master ............................... default=0 (disabled)
1 Memory Space........................... default=0 (disabled)
0 I/O Space ............................... default=0 (disabled)
Offset 7-6 – Status (0210h) ............................................RWC
15 Reserved (detected parity error) ......... always reads 0
14 Signalled System Error ............................. default=0
13 Received Master Abort ............................. default=0
12 Received Target Abort .............................. default=0
11 Signalled Target Abort.............................. default=0
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing
00 Fast
01 Medium ...................................... default (fixed)
10 Slow
11 Reserved
8-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Pwr Mgmt Extended Capabilties ..... always reads 1
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 8 - Revision ID (nnh).............................................. RO
7-0 Silicon Revision Code (0 indicates first silicon)
Offset 9 - Programming Interface (00h).......................... RO
Offset A - Sub Class Code (03h=USB Controller).......... RO
Offset B - Base Class Code (0Ch=Serial Bus Controller)RO
Offset C – Cache Line Size (00h) ..................................... RO
Offset D - Latency Timer................................................. RW
7-0 Timer Value ............................................................... d
Offset E - Header Type (00h) ........................................... RO
Offset F - BIST (00h)......................................................... RO
Offset 23-20 - USB I/O Register Base Address .............. RW
31-16 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
15-5 USB I/O Register Base Address. Port Address for
the base of the 32-byte USB I/O Register block,
corresponding to AD[15:5]
4-0 00001b
Offset 34 – USB Power Management Capabilities (80h) RO
Offset 3C - Interrupt Line (00h) ..................................... RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3-0 USB Interrupt Routing........................ default = 16h
0000 Disable................................................... default
0001 IRQ1
0010 Reserved
0011 IRQ3
0100 IRQ4
0101 IRQ5
0110 IRQ6
0111 IRQ7
1000 IRQ8
1001 IRQ9
1010 IRQ10
1011 IRQ11
1100 IRQ12
1101 IRQ13
1110 IRQ14
1111 Disable
Offset 3D - Interrupt Pin (04h) ........................................ RO
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -79- Function 3 Registers - USB Controller Ports 2-3
Page 86

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
USB-Specific Configuration Registers
Offset 40 - Miscellaneous Control 1 ................................RW
7 PCI Memory Command Option
0 Support Memory-Read-Line, Memory-Read-
Multiple, & Memory-Write-&-Invalidate....def
1 Only support Mem Read, Mem Write Cmds
6 Babble Option
0 Automatically disable babbled port when EOF
babble occurs .........................................default
1 Don’t disable babbled port
5 PCI Parity Check Option
0 Disable PERR# generation ....................default
1 Enable parity check and PERR# generation
4 Frame Interval Select
0 1 ms frame..............................................default
1 0.1 ms frame
3 USB Data Length Option
0 Support TD length up to 1280 ...............default
1 Support TD length up to 1023
2 USB Power Management
0 Disable USB power management ..........default
1 Enable USB power management
1 DMA Option
0 8 DW burst access with better FIFO latencydef
1 16 DW burst access (original performance)
0 PCI Wait States
0 Zero wait ................................................default
1 One wait
Offset 41 - Miscellaneous Control 2................................ RW
7 USB 1.1 Improvement for EOP
0 USB Specification 1.1 Compliant ......... default
If a bit stuffing error occurs before EOP, the
receiver will accept
1 USB Specification 1.0 Compliant
If a bit stuffing error occurs before EOP, the
receiver will ignore
6-5 Reserved (Do Not Program).................... default = 0
4 Hold PCI Request for Successive Accesses
0 Disable
1 Enable.................................................... default
Setting this bit to “enable” causes the system to treat
the USB request as higher priority
3 Frame Counter Test Mode
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 Trap Option
0 Set trap 60/64 status bits only when trap 60/64
enable bits are set. ................................ default
1 Set trap 60/64 status bits without checking
enable bits
1 A20gate Pass Through Option
0 Pass through A20GATE command sequence
defined in UHCI .................................... default
1 Don’t pass through Write I/O port 64 (ff)
0 USB IRQ Test Mode
0 Normal Operation.................................. default
1 Generate USB IRQ
the packet
the packet
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -80- Function 3 Registers - USB Controller Ports 2-3
Page 87

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 42 - FIFO Control..................................................RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-2 Reserved (Do Not Program) ................... default = 0
1-0 Release Continuous REQ After “N” PCICLKs
00 Do Not Release ......................................default
01 N = 32 PCICLKs
10 N = 64 PCICLKs
11 N = 96 PCICLKs
Offset 60 - Serial Bus Release Number ............................RO
7-0 Release Number ............................. always reads 10h
Offset 83-80 – PM Capability............................................RO
31-0 PM Capability .................... always reads 00020001h
Offset 84 – PM Capability Status ....................................RW
7-0 PM Capability Status ..... supports 00h and 11h only
Offset C1-C0 - Legacy Support ........................................RO
15-0 UHCI v1.1 Compliant................ always reads 2000h
USB I/O Registers
These registers are compliant with the UHCI v1.1 standard.
Refer to the UHCI v1.1 specification for further details.
I/O Offset 1-0 - USB Command
I/O Offset 3-2 - USB Status
I/O Offset 5-4 - USB Interrupt Enable
I/O Offset 7-6 - Frame Number
I/O Offset B-8 - Frame List Base Address
I/O Offset 0C - Start Of Frame Modify
I/O Offset 11-10 - Port 0 Status / Control
I/O Offset 13-12 - Port 1 Status / Control
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -81- Function 3 Registers - USB Controller Ports 2-3
Page 88

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
e
Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM
This section describes the ACPI (Advanced Configuration and
Power Interface) Power Management system of the
VT82C686B which includes a System Management Bus
(SMBus) interface controller and Hardware Monitoring
(HWM) subsystem. The power management system of the
VT82C686B supports both ACPI and legacy power
management functions and is compatible with the APM v1.2
and ACPI v1.0 specifications.
PCI Configuration Space Header
Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID .......................................................RO
0-7 Vendor ID ................. (1106h = VIA Technologies)
Offset 3-2 - Device ID.........................................................RO
0-7 Device ID ................(3057h = ACPI Power Mgmt)
Offset 5-4 - Command ......................................................RW
15-8 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
7 Address Stepping ........................................fixed at 0
6 Reserved (parity error response)..................fixed at 0
5 Reserved (VGA palette snoop) ....................fixed at 0
4 Memory Write and Invalidate...................fixed at 0
3 Reserved (special cycle monitoring)............fixed at 0
2 Bus Master .................................................fixed at 0
1 Memory Space.............................................fixed at 0
0 I/O Space .................................................fixed at 0
Offset 7-6 - Status........................................................... RWC
15 Detected Parity Error........................ always reads 0
14 Signalled System Error ..................... always reads 0
13 Received Master Abort ..................... always reads 0
12 Received Target Abort ...................... always reads 0
11 Signalled Target Abort...................... always reads 0
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing
00 Fast
01 Medium .....................................default (fixed)
10 Slow
11 Reserved
8 Data Parity Detected ......................... always reads 0
7 Fast Back to Back Capable ............... always reads 1
6-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Pwr Mgmt Extended Capabilities .... always reads 1
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Offset 8 - Revision ID (nnh).............................................. RO
7-0 Silicon Revision Code
Offset 9 - Programming Interface (00h).......................... RO
The value returned by this register may be changed by writing
the desired value to PCI Configuration Function 4 offset 61h.
Offset A - Sub Class Code (00h)....................................... RO
The value returned by this register may be changed by writing
the desired value to PCI Configuration Function 4 offset 62h.
Offset B - Base Class Code (00h)...................................... RO
The value returned by this register may be changed by writing
the desired value to PCI Configuration Function 4 offset 63h.
Offset 0D - Latency Timer............................................... RW
7-0 Timer Value ............................................................... d
Offset 0E - Header Type (00h) ......................................... RO
Offset 34 –Pwr Mgmt Extended Capabilities Ptr (68h) . RO
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -82- Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM
Page 89

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Power Management-Specific PCI Configuration Registers
Offset 40 – General Configuration 0 ...............................RW
7 Thermal Alarm Source Select
0 From pin T11 (Function 0 Rx74[1] must be set
to define the pin as THRM#) .................default
1 From any of the three internal temperature
sensing circuits (see Rx43 and Rx44 of
Hardware Monitoring configuration space)
6 Sleep Button
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Sleep Button is on IRQ6 pin (pin G1)
5 Debounce LID and PWRBTN# Inputs for 16ms
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 Microsoft Sound Monitor in Audio Access
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 Game Port Monitor in Audio Access
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 SoundBlaster Monitor in Audio Access
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
0 MIDI Monitor in Audio Access
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
Offset 41 - General Configuration 1 ............................... RW
7 I/O Enable for ACPI I/O Base
0 Disable access to ACPI I/O block ......... default
1 Allow access to Power Management I/O
Register Block (see offset 4B-48 to set the
base address for this register block). The
definitions of the registers in the Power
Management I/O Register Block are included
later in this document, following the Power
Management Subsystem overview.
6 ACPI Timer Reset
0 Normal Timer Operation ....................... default
1 Reset Timer
5-4 PMU Timer Test Mode (Do Not Program)....def = 0
3 ACPI Timer Count Select
0 24-bit Timer........................................... default
1 32-bit Timer
2 RTC Enable Signal Gated with PSON (SUSC#) in
Soft-Off Mode
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 Clock Throttling Clock Select (STPCLK#)
This bit controls the timer tick base for the throttle
timer.
0 30 usec (480 usec cycle time when using a 4-
bit timer)................................................ default
1 1 msec (16 msec cycle time when using a 4-bit
timer)
The timer tick base can be further lowered to 7.5 usec
(120 usec cycle time when using a 4-bit timer) by
setting Rx4D[4] = 1. When Rx4D[4] = 1, the setting
of this bit is ignored.
0 DEVSEL# Test Mode (Do Not Program) ......def = 0
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -83- Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM
Page 90

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 42 - ACPI Interrupt Select....................................RW
7 ATX / AT Power Indicator ................................. RO
0 ATX
1 AT
6 SUSC# State ......................................................... RO
5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 SUSC# AC-Power-On Default Value................. RO
This bit is written at RTC Index 0D bit-7.
3-0 SCI Interrupt Assignment
0000 Disable ...................................................default
0001 IRQ1
0010 Reserved
0011 IRQ3
0100 IRQ4
0101 IRQ5
0110 IRQ6
0111 IRQ7
1000 IRQ8
1001 IRQ9
1010 IRQ10
1011 IRQ11
1100 IRQ12
1101 IRQ13
1110 IRQ14
1111 IRQ15
Offset 43 – Internal Timer Read Test ..............................RO
7-0 Internal Timer Read Test
Offset 45-44 - Primary Interrupt Channel (0000h) ....... RW
15 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ15 as Primary Intrpt Channel
14 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ14 as Primary Intrpt Channel
13 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ13 as Primary Intrpt Channel
12 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ12 as Primary Intrpt Channel
11 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ11 as Primary Intrpt Channel
10 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ10 as Primary Intrpt Channel
9 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ9 as Primary Intrpt Channel
8 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ8 as Primary Intrpt Channel
7 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ7 as Primary Intrpt Channel
6 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ6 as Primary Intrpt Channel
5 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ5 as Primary Intrpt Channel
4 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ4 as Primary Intrpt Channel
3 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ3 as Primary Intrpt Channel
2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ1 as Primary Intrpt Channel
0 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ0 as Primary Intrpt Channel
Offset 47-46 - Secondary Interrupt Channel (0000h) ... RW
15 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ15 as Secondary Intr Channel
14 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ14 as Secondary Intr Channel
13 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ13 as Secondary Intr Channel
12 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ12 as Secondary Intr Channel
11 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ11 as Secondary Intr Channel
10 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ10 as Secondary Intr Channel
9 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ9 as Secondary Intr Channel
8 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ8 as Secondary Intr Channel
7 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ7 as Secondary Intr Channel
6 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ6 as Secondary Intr Channel
5 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ5 as Secondary Intr Channel
4 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ4 as Secondary Intr Channel
3 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ3 as Secondary Intr Channel
2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ1 as Secondary Intr Channel
0 1/0 = Ena/Disa IRQ0 as Secondary Intr Channel
Offset 4B-48 – Power Management I/O Base................. RW
31-16 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
15-7 Power Management I/O Register Base Address.
Port Address for the base of the 128-byte Power
Management I/O Register block, corresponding to
AD[15:7]. The "I/O Space" bit at offset 41 bit-7
enables access to this register block. The definitions
of the registers in the Power Management I/O
Register Block are included in the following section
this document.
6-0 0000001b
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -84- Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM
Page 91

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 4C – Host Bus Power Management Control .......RW
7-4 Thermal Duty Cycle
This field determines the duty cycle of STPCLK#
when the THRM# pin is asserted. The STPCLK#
duty cycle when THRM# is NOT asserted is
controlled by PMIO Rx10[3:0]. The duty cycle
indicates the percentage of performance (the lower
the percentage, the lower the performance and the
higher the power savings). If the Throttling Timer
Width (Function 0 Rx4D[6-5]) is set to 3-bit width,
bit-0 of this field should be set to 0 (and the
performance increment will be 12.5%). If the
Throttling Timer Width is set to 2-bit width, bits 1-0
of this field should be set to 0 (and the performance
increment will be 25%).
Throttling Timer Width
4-Bit
0000 -reserved- -reserved- -reserved 0001 6.25% -reserved- -reserved 0010 12.50% 12.50% -reserved 0011 18.75% -reserved- -reserved 0100 25.00% 25.00% 25.00%
0101 31.25% -reserved- -reserved 0110 37.50% 37.50% -reserved 0111 43.75% -reserved- -reserved 1000 50.00% 50.00% 50.00%
1001 56.25% -reserved- -reserved 1010 62.50% 62.50% -reserved 1011 68.75% -reserved- -reserved 1100 75.00% 75.00% 75.00%
1101 81.25% -reserved- -reserved 1110 87.50% 87.50% -reserved 1111 93.75% -reserved- -reserved 3 THRM Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 Frame Input as Resume Event in C3
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 CD: APIC IRQ1 / IRQ12 is Primary IRQ
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
If the internal APIC is enabled (Func 0 Rx77[4] = 1)
and this bit is enabled, the PS2 mouse / keyboard can
wake the system from the S1 state
CE: Reserved..................................... always reads 0
PS2 mouse / keyboard wake-up is supported without
this bit
3-Bit 2-Bit
0 CPU Stop Grant Cycle Select
0 From Halt and Stop Grant Cycle ........... default
1 From Stop Grant Cycle
This bit is combined with I/O space Rx2C[3] for
controlling the start of STPCLK# assertion during
system suspend mode (set PMIO Rx13-10[9] = 0):
Rx2C[3] Rx4C[0]
Function 4 Function 4
I/O Space
0 x Immediate
1 0 Wait for CPU Halt
/ Stop Grant cycle
1 1 Wait for CPU
Stop Grant cycle
Offset 4D – Throttle / Clock Stop Control ..................... RW
7 Throttle Timer Reset...................................... def = 0
6-5 Throttle Timer
This field determines the number of bits used for the
throttle timer, which in conjunction with the throttle
timer tick determines the cycle time of STPCLK#.
For example, if a 2-bit timer and a 7.5 usec timer tick
are selected, the STPCLK# cycle time would be 30
usec (2**2 x 7.5). If a 4-bit timer and a 7.5 usec
timer tick is selected, the cycle time would be 120
usec (2**4 x 7.5).
0x 4-Bit .................................................... default
10 3-Bit
11 2-Bit
(see also Rx4C[7-4] and PMIO Rx10[3-0])
4 Fast Clock (7.5us) as Throttle Timer Tick
This bit controls whether the throttle timer tick uses
7.5 usec as its time base (120 usec cycle time when
using a 4-bit timer).
0 Timer Tick is selected by Rx41[1] ........ default
1 Timer Tick is 7.5 usec (Rx41[1] is ignored)
3 SMI Level Output (Low)
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable (set this bit for socket-370 coppermine)
2 Internal Clock Stop for PCI Idle
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 Internal Clock Stop During C3
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Internal Clock Stop During Suspend
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Cfg Space STPCLK# Assertion
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -85- Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM
Page 92

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 53-50 - GP Timer Control (0000 0000h) .............. RW
31-30 Conserve Mode Timer Count Value
00 1/16 second ............................................default
01 1/8 second
10 1 second
11 1 minute
29 Conserve Mode Status
This bit reads 1 when in Conserve Mode
28 Conserve Mode Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
27-26 Secondary Event Timer Count Value
00 2 milliseconds ........................................default
01 64 milliseconds
10 ½ second
11 by EOI + 0.25 milliseconds
25 Secondary Event Occurred Status
This bit reads 1 to indicate that a secondary event has
occurred (to resume the system from suspend) and
the secondary event timer is counting down.
24 Secondary Event Timer Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
23-16 GP1 Timer Count Value (base defined by bits 5-4)
Write to load count value; Read to get current count
15-8 GP0 Timer Count Value (base defined by bits 1-0)
Write to load count value; Read to get current count
7 GP1 Timer Start
On setting this bit to 1, the GP1 timer loads the value
defined by bits 23-16 of this register and starts
counting down. The GP1 timer is reloaded at the
occurrence of certain peripheral events enabled in the
GP Timer Reload Enable Register (Power
Management I/O Space Offset 38h). If no such event
occurs and the GP1 timer counts down to zero, then
the GP1 Timer Timeout Status bit is set to one (bit-3
of the Global Status register at Power Management
Register I/O Space Offset 28h). Additionally, if the
GP1 Timer Timeout Enable bit is set (bit-3 of the
Global Enable register at Power Management
Register I/O Space Offset 2Ah), then an SMI is
generated.
6 GP1 Timer Automatic Reload
0 GP1 Timer stops at 0 .............................default
1 Reload GP1 timer automatically after counting
down to 0
5-4 GP1 Timer Base
00 Disable ...................................................default
01 1/16 second
10 1 second
11 1 minute
3 GP0 Timer Start
On setting this bit to 1, the GP0 timer loads the value
defined by bits 15-8 of this register and starts
counting down. The GP0 timer is reloaded at the
occurrence of certain peripheral events enabled in the
GP Timer Reload Enable Register (Power
Management I/O Space Offset 38h). If no such event
occurs and the GP0 timer counts down to zero, then
the GP0 Timer Timeout Status bit is set to one (bit-2
of the Global Status register at Power Management
Register I/O Space Offset 28h). Additionally, if the
GP0 Timer Timeout Enable bit is set (bit-2 of the
Global Enable register at Power Management
Register I/O Space Offset 2Ah), then an SMI is
generated.
2 GP0 Timer Automatic Reload
0 GP0 Timer stops at 0 ............................ default
1 Reload GP0 timer automatically after counting
down to 0
1-0 GP0 Timer Base
00 Disable................................................... default
01 1/16 second
10 1 second
11 1 minute
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -86- Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM
Page 93

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 54 – Power Well Control.......................................WO
7 SMBus Clock Select
0 SMBus Clock from 14.31818 MHz Dividerdef
1 SMBus Clock from RTC 32.768 KHz
6 STR Power Well Output Gating
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 SUSC# = 0 for STR
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 SUSST1# / GPO3 Select (Pin V10)
0 SUSST1# ...............................................default
1 GPO3
3 GPO2 / SUSB# Select (Pin W9)
0 SUSB# ...................................................default
1 GPO2
2 GPO1 / SUSA# Select (Pin V9)
0 SUSA# ...................................................default
1 GPO1
1-0 GPO0 (SLOWCLK) Output Selection (Pin T8)
00 From GPO0 (PMU I/O Rx4C[0]) ..........default
01 1 Hz
10 4 Hz
11 16 Hz
Offset 55 – USB Wakeup ................................................. RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 CD: CPUSTP# to SUSST# Delay
0 1 ~ 2 ms ................................................. default
1 125 ~ 250 us
CE: Resume Timing for CPUSTP# / PCISTP# /
SUSST# De-asserted
0 Extend (16 ms, 1 ms minimum) ............ default
1 Reduce (1 ms, 128 us minimum)
2 Deassert SUSST1# Before PWRGD Rising for S5
Wakeup
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
0 USB Wakeup for STR/STD/Soff
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Offset 57 – Miscellaneous Control .................................. RW
7-2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1 CD: Reserved ................................... always reads 0
CE: GPI Status Toggle / Edge Select
(see PMIO Rx20[7:6,4:2])
0 Toggle.................................................... default
1 Falling Edge
0 Internal THRM# Output on GPO21
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -87- Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM
Page 94

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 58 – GP2 / GP3 Timer Control............................. RW
7 GP3 Timer Start
On setting this bit to 1, the GP3 timer loads the value
defined by Rx5A and starts counting down. The GP3
timer is reloaded at the occurrence of certain events
enabled in the GP Timer Reload Enable Register
(Power Management I/O Space Offset 38h). If no
such event occurs and the GP3 timer counts down to
zero, then the GP3 Timer Timeout Status bit is set to
one (bit-13 of the Global Status register at Power
Management Register I/O Space Offset 28h).
Additionally, if the GP3 Timer Timeout Enable bit is
set (bit-13 of the Global Enable register at Power
Management Register I/O Space Offset 2Ah), then an
SMI is generated.
6 GP3 Timer Automatic Reload
0 GP3 Timer stops at 0 .............................default
1 Reload GP3 timer automatically after counting
down to 0
5-4 GP3 Timer Tick Select
00 Disable ...................................................default
01 1/16 second
10 1 second
11 1 minute
3 GP2 Timer Start
On setting this bit to 1, the GP2 timer loads the value
defined by Rx59 and starts counting down. The GP2
timer is reloaded at the occurrence of certain events
enabled in the GP Timer Reload Enable Register
(Power Management I/O Space Offset 38h). If no
such event occurs and the GP2 timer counts down to
zero, then the GP2 Timer Timeout Status bit is set to
one (bit-12 of the Global Status register at Power
Management Register I/O Space Offset 28h).
Additionally, if the GP2 Timer Timeout Enable bit is
set (bit-12 of the Global Enable register at Power
Management Register I/O Space Offset 2Ah), then an
SMI is generated.
2 GP2 Timer Automatic Reload
0 GP2 Timer stops at 0 .............................default
1 Reload GP2 timer automatically after counting
down to 0
1-0 GP2 Timer Tick Select
00 Disable ...................................................default
01 1/16 second
10 1 second
11 1 minute
Offset 59 – GP2 Timer ..................................................... RW
7 Write: GP2 Timer Load Value ..............default = 0
Read: GP2 Timer Current Count
Offset 5A – GP3 Timer .................................................... RW
7 Write: GP3 Timer Load Value ..............default = 0
Read: GP3 Timer Current Count
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -88- Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM
Page 95

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Offset 61 – Program Interface Read Value ....................WO
7-0 Rx09 Read Value
The value returned by the register at offset 9h (Programming
Interface) may be changed by writing the desired value to this
location.
Offset 62 - Sub Class Read Value ....................................WO
7-0 Rx0A Read Value
The value returned by the register at offset 0Ah (Sub Class
Code) may be changed by writing the desired value to this
location.
Offset 63 - Base Class Read Value...................................WO
7-0 Rx0B Read Value
The value returned by the register at offset 0Bh (Base Class
Code) may be changed by writing the desired value to this
location.
Offset 6B-68 – Power Management Capabilities I..........RO
31-16 Power Mgmt Capabilities.......... always reads 0002h
15-8 “Next” Pointer................................ always reads 00h
7-0 Capability ID.................................. always reads 01h
Offset 6F-6C – Power Management Capabilities II........RO
31-24 PM Capabilities.................................. always reads 0
23-16 PM CSR P2P Support Extensions.... always reads 0
15-0 PM Control / Status ........................... always reads 0
(D0/D3 only)
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -89- Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM
Page 96

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Hardware-Monitor-Specific Configuration Registers
Offset 71-70 – Hardware Monitor I/O Base ...................RW
15-7 I/O Base (128-byte I/O space) ................. default = 0
6-0 Fixed .......................... always reads 0000001b
Offset 74 –Hardware Monitor Control ........................... RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 Hardware Monitoring Interrupt
0 SMI .....................................................default
1 SCI
2-1 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
0 Hardware Monitoring I/O Enable
0 Disable hardware monitor functions ......default
1 Enable hardware monitor functions
System Management Bus-Specific Configuration Registers
Offset 93-90 – SMBus I/O Base ....................................... RW
31-16 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
15-4 I/O Base (16-byte I/O space) ............... default = 00h
3-0 Fixed ................................always reads 0001b
Offset D2 – SMBus Host Configuration ......................... RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 SMBus Interrupt Select
0 SMI .................................................... default
1 SCI
2 SMBus Clock Select
0 Divide down from 14.31818 MHz ........ default
1 64 KHz derived from 32.768 KHz RTC clock
1 SMBus Host Interface SCI Interrupt
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 SMBus Host Controller Functions
0 Disable SMB controller functions ......... default
1 Enable SMB controller functions
Offset D3 – SMBus Host Slave Command ..................... RW
7-0 SMBus Host Slave Command Code .........default=0
Offset D4 – SMBus Slave Address for Port 1................. RW
7-0 SMBus Slave Address for Port 1...............default=0
Bit-0 must be set to 0 for proper operation
Offset D5 – SMBus Slave Address for Port 2................. RW
7-0 SMBus Slave Address for Port 2...............default=0
Bit-0 must be set to 0 for proper operation
Offset D6 – SMBus Revision ID ....................................... RO
7-0 SMBus Revision Code
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -90- Function 4 Regs - Power Management, SMBus and HWM
Page 97

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Power Management I/O-Space Registers
Basic Power Management Control and Status
I/O Offset 1-0 - Power Management Status................. RWC
The bits in this register are set only by hardware and can be
reset by software by writing a one to the desired bit position.
15 Wakeup Status (WAK_STS) ................... default = 0
This bit is set when the system is in the suspend state
and an enabled resume event occurs. Upon setting
this bit, the system automatically transitions from the
suspend state to the normal working state (from C3 to
C0 for the processor).
14-12 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
11 Abnormal Power-Off (APO_STS) .......... default = 0
10 RTC Status (RTC_STS)........................... default = 0
This bit is set when the RTC generates an alarm (on
assertion of the RTC IRQ signal).
9 Sleep Button Status (SB_STS) ................ default = 0
This bit is set when the sleep button (SLPBTN# /
IRQ6 / GPI4) is pressed.
8 Power Button Status (PB_STS)............... default = 0
This bit is set when the PWRBTN# signal is asserted
LOW. If the PWRBTN# signal is held LOW for
more than four seconds, this bit is cleared and the
system will transition into the soft off state.
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 Global Status (GBL_STS) ....................... default = 0
This bit is set by hardware when BIOS_RLS is set
(typically by an SMI routine to release control of the
SCI/SMI lock). When this bit is cleared by software
(by writing a one to this bit position) the BIOS_RLS
bit is also cleared at the same time by hardware.
4 Bus Master Status (BM_STS) ................. default = 0
This bit is set when a system bus master requests the
system bus. All PCI master, ISA master and ISA
DMA devices are included.
3-1 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
0 ACPI Timer Carry Status (TMR_STS).. default = 0
The bit is set when the 23
rd
(31st) bit of the 24 (32)
bit ACPI power management timer changes.
I/O Offset 3-2 - Power Management Enable.................. RW
The bits in this register correspond to the bits in the Power
Management Status Register at offset 1-0.
15 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
14-12 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
11 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
10 RTC Enable (RTC_EN) ........................... default = 0
This bit may be set to trigger either an SCI or an SMI
(depending on the setting of the SCI_EN bit) to be
generated when the RTC_STS bit is set.
9 Sleep Button Enable (SB_EN) .................default = 0
This bit may be set to trigger either an SCI or SMI
when the SB_STS bit is set.
8 Power Button Enable (PB_EN) ...............default = 0
This bit may be set to trigger either an SCI or an SMI
(depending on the setting of the SCI_EN bit) to be
generated when the PB_STS bit is set.
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 Global Enable (GBL_EN) ........................ default = 0
This bit may be set to trigger either an SCI or an SMI
(depending on the setting of the SCI_EN bit) to be
generated when the GBL_STS bit is set.
4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-1 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
0 ACPI Timer Enable (TMR_EN)..............default = 0
This bit may be set to trigger either an SCI or an SMI
(depending on the setting of the SCI_EN bit) to be
generated when the TMR_STS bit is set.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -91- Power Management I/O-Space Registers
Page 98

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
I/O Offset 5-4 - Power Management Control .................RW
15 Soft Resume
14 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
13 Sleep Enable (SLP_EN) ..................... always reads 0
This is a write-only bit; reads from this bit always
return zero. Writing a one to this bit causes the
system to sequence into the sleep (suspend) state
defined by the SLP_TYP field.
12-10 Sleep Type (SLP_TYP)
000 Normal On
001 Suspend to RAM (STR)
010 Suspend to Disk (STD) (also called Soft Off).
The VCC power plane is turned off while the
VCCS and VBAT planes remain on.
011 Reserved
100 Power On Suspend without Reset
101 Power On Suspend with CPU Reset
110 Power On Suspend with CPU/PCI Reset
111 Reserved
In any sleep state, there is minimal interface between
powered and non-powered planes so that the effort
for hardware design may be well managed.
9 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
8 STD Command Generates System Reset Only
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
7-3 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
2 Global Release (GBL_RLS)............ WO, default = 0
This bit is set by ACPI software to indicate the
release of the SCI / SMI lock. Upon setting of this
bit, the hardware automatically sets the BIOS_STS
bit. The bit is cleared by hardware when the
BIOS_STS bit is cleared by software. Note that the
setting of this bit will cause an SMI to be generated if
the BIOS_EN bit is set (bit-5 of the Global Enable
register at offset 2Ah).
1 Bus Master Reload (BMS_RLD)
0 Bus master requests are ignored by power
management logic ..................................default
1 Bus master requests transition the processor
from the C3 state to the C0 state
0 SCI Enable (SCI_EN)
Selects the power management event to generate
either an SCI or SMI (for Power / Sleep Buttons &
RTC only)
0 Generate SMI .........................................default
1 Generate SCI
Note that certain power management events can be
programmed individually to generate an SCI or SMI
independent of the setting of this bit (refer to the
General Purpose SCI Enable and General Purpose
SMI Enable registers at offsets 22 and 24). Also,
TMR_STS & GBL_STS always generate SCI and
BIOS_STS always generates SMI.
I/O Offset 0B-08 - Power Management Timer............... RW
31-24 Extended Timer Value (ETM_VAL)
This field reads back 0 if the 24-bit timer option is
selected (Rx41 bit-3).
23-0 Timer Value (TMR_VAL)
This read-only field returns the running count of the
power management timer. This is a 24/32-bit counter
that runs off a 3.579545 MHz clock, and counts
while in the S0 (working) system state. The timer is
reset to an initial value of zero during a reset, and
then continues counting until the 14.31818 MHz
input to the chip is stopped. If the clock is restarted
without a reset, then the counter will continue
counting from where it stopped.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -92- Power Management I/O-Space Registers
Page 99

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
Processor Power Management Registers
I/O Offset 13-10 - Processor & PCI Bus Control ...........RW
31-12 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
11 PCI Stop (PCISTP# asserted) when PCKRUN# is
Deasserted (PCI_STP)
0 Enable ....................................................default
1 Disable
10 PCI Bus Clock Run Without Stop (PCI_RUN)
0 PCKRUN# is always asserted................default
1 PCKRUN# will be de-activated after the PCI
bus is idle for 26 clocks
9 Host Clock Stop Enable (HOST_STP)
0 STPCLK# will be asserted in C3 state...default
1 CPUSTP# will be asserted in C3 and S1 state
8 Assert SLP# for Processor Level 3 Read
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
Used in Slot-1 systems only.
7-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Throttling Enable
Setting this bit starts clock throttling (modulating the
STPCLK# signal) regardless of the CPU state. The
throttling duty cycle is determined by bits 3-0 of this
register.
3-0 Throttling Duty Cycle
This field determines the duty cycle of the STPCLK#
signal when the system is in throttling mode
("Throttling Enable" bit of this register set to one).
The duty cycle indicates the percentage of
performance (the lower the percentage, the lower the
performance and the higher the power savings). If
the Throttling Timer Width (Function 0 Rx4D[6-5])
is set to 3-bit width, bit-0 of this field should be set to
0 (and the performance increment will be 12.5%). If
the Throttling Timer Width is set to 2-bit width, bits
1-0 of this field should be set to 0 (and the
performance increment will be 25%).
Throttling Timer Width
4-Bit
3-Bit 2-Bit
0000 -reserved- -reserved- -reserved 0001 6.25% -reserved- -reserved 0010 12.50% 12.50% -reserved 0011 18.75% -reserved- -reserved 0100 25.00% 25.00% 25.00%
0101 31.25% -reserved- -reserved 0110 37.50% 37.50% -reserved 0111 43.75% -reserved- -reserved 1000 50.00% 50.00% 50.00%
1001 56.25% -reserved- -reserved 1010 62.50% 62.50% -reserved 1011 68.75% -reserved- -reserved 1100 75.00% 75.00% 75.00%
1101 81.25% -reserved- -reserved 1110 87.50% 87.50% -reserved 1111 93.75% -reserved- -reserved-
I/O Offset 14 - Processor Level 2 ..................................... RO
7-0 Level 2 ........................................ always reads 0
Reads from this register put the processor into the
Stop Grant state (the VT82C686B asserts STPCLK#
to suspend the processor). Wake up from Stop Grant
state is by interrupt (INTR, SMI, and SCI).
Reads from this register return all zeros; writes to this register
have no effect.
I/O Offset 15 - Processor Level 3 ..................................... RO
7-0 Level 3 ........................................ always reads 0
Reads from this register put the processor in the C3
clock state with the STPCLK# signal asserted. If
Rx10[9] = 1 then the CPU clock is also stopped by
asserting CPUSTP#. Wakeup from the C3 state is by
interrupt (INTR, SMI, and SCI).
Reads from this register return all zeros; writes to this register
have no effect.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -93- Power Management I/O-Space Registers
Page 100

VT82C686B "Super South" South Bridge
General Purpose Power Management Registers
I/O Offset 21-20 - General Purpose Status (GP_STS) RWC
15 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
14 USB Wake-Up Status (UWAK_STS)
For STR / STD / SoftOff
13 AC97 Wake-Up Status (AWAK_STS)
Can be set only in suspend mode
12 Battery Low Status (BL_STS)
This bit is set if the BATLOW# input is asserted low.
11 Notebook Lid Status (LID_STS)
This bit is set if the LID input detects the edge
selected by Rx2C bit-7 (0=rising, 1=falling).
10 Thermal Detect Status (THRM_STS)
This bit is set if the THRM input detects the edge
selected by Rx2C bit-6 (0=rising, 1=falling).
9 USB Resume Status (USB_STS)
This bit is set if a USB peripheral generates a resume
event.
8 Ring Status (RING_STS)
This bit is set if the RING# input is asserted low.
7 GPI18 Status (GPI18_STS)
This bit is set if the GPI18 pin is asserted low.
6† GPI6 / EXTSMI6 Toggle Status (GPI6_STS)
This bit is set if the GPI6 pin is toggled†.
5 GPI5 / PME# Toggle Status (PME_STS)
This bit is set if the GPI5 pin is toggled.
4† GPI4 / EXTSMI4 Toggle Status (GPI4_STS)
This bit is set if the GPI4 pin is toggled†.
3† GPI17 Toggle Status (GPI17_STS)
This bit is set if the GPI17 pin is toggled†.
2† CD: GPI16 Toggle Status (GPI16_STS)
CE: Internal KBC PME Status (KPME_STS)
This bit is set if the GPI16 pin is toggled†.
1 GPI1 Toggle Status (GPI1_STS)
This bit is set if the GPI1 pin is toggled.
0 EXTSMI# Status (EXT_STS)
This bit is set if the EXTSMI# pin is asserted low.
Note that the above bits correspond one for one with the bits
of the General Purpose SCI Enable and General Purpose SMI
Enable registers at offsets 22 and 24: an SCI or SMI is
generated if the corresponding bit of the General Purpose SCI
or SMI Enable registers, respectively, is set to one.
The above bits are set by hardware only and can only be
cleared by writing a one to the desired bit.
†In chip version CE, if Function 4 Rx57[1] = 0, bits 6 and 4-2
will be set if the corresponding GPI pin is toggled
same function as in chip version CD). However, if Function 4
Rx57[1] = 1, these bits will be set if the corresoponding GPI
pin sees a falling
version CD).
edge (this function is not available in chip
(this is the
I/O Offset 23-22 - General Purpose SCI Enable............ RW
15 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
14 Enable SCI on setting of the UWAK_STS bit def=0
13 Enable SCI on setting of the AWAK_STS bit def=0
12 Enable SCI on setting of the BL_STS bit ......def=0
11 Enable SCI on setting of the LID_STS bit ....def=0
10 Enable SCI on setting of the THRM_STS bit def=0
9 Enable SCI on setting of the USB_STS bit ... def=0
8 Enable SCI on setting of the RING_STS bit .def=0
7 Enable SCI on setting of the GPI18_STS bit .def=0
6 Enable SCI on setting of the GPI6_STS bit ... def=0
5 Enable SCI on setting of the PME_STS bit ...def=0
4 Enable SCI on setting of the GPI4_STS bit ... def=0
3 Enable SCI on setting of the GPI17_STS bit .def=0
2 CD: Ena SCI on setting of GPI16_STS bit ....def=0
CE: Ena SCI on setting of KPME_STS bit.... def=0
1 Enable SCI on setting of the GPI1_STS bit ... def=0
0 Enable SCI on setting of the EXT_STS bit .... def=0
These bits allow generation of an SCI using a separate set of
conditions from those used for generating an SMI.
I/O Offset 25-24 - General Purpose SMI Enable........... RW
15-14 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
13 Enable SMI on setting of the AWAK_STS bit def=0
12 Enable SMI on setting of the BL_STS bit .....def=0
11 Enable SMI on setting of the LID_STS bit ...def=0
10 Enable SMI on setting of the THRM_STS bit def=0
9 Enable SMI on setting of the USB_STS bit .. def=0
8 Enable SMI on setting of the RING_STS bit def=0
7 Enable SMI on setting of the GPI18_STS bit def=0
6 Enable SMI on setting of the GPI6_STS bit ..def=0
5 Enable SMI on setting of the PME_STS bit ..def=0
4 Enable SMI on setting of the GPI4_STS bit ..def=0
3 Enable SMI on setting of the GPI17_STS bit def=0
2 CD: Ena SMI on setting of GPI16_STS bit ..def=0
CE: Ena SMI on setting of KPME_STS bit.. def=0
1 Enable SMI on setting of the GPI1_STS bit ..def=0
0 Enable SMI on setting of the EXT_STS bit ...def=0
These bits allow generation of an SMI using a separate set of
conditions from those used for generating an SCI.
Revision 2.37, November 10, 2004 -94- Power Management I/O-Space Registers
 Loading...
Loading...