Page 1

Data Sheet
Apollo PLE133
North Bridge
Revision 1.86
April 22, 2005
VIA TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Page 2

Copyright Notice:
Copyright ©1998-2005 VIA Technologies Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. No part of this document may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language, in any form or by
any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or otherwise without the prior written
permission of VIA Technologies Incorporated. The material in this document is for information only and is subject to
change without notice. VIA Technologies Incorporated reserves the right to make changes in the product design
without reservation and without notice to its users.
Trademark Notices:
VT82C586B, VT82C596B, VT82C686A, VT82C686B, VT82C598, VT82C598MVP, VT8501, VT82C691, VT82C692,
VT82C693, VT82C693A, VT82C694, VT82C694A, VT82C694X, VT8601, VT8601A, VT8602, Mobile South, Super
South, Apollo MVP3, Apollo MVP4, Apollo Pro, Apollo ProPlus, Apollo Pro133, Apollo Pro133A, Apollo PM601, and
Apollo PLE133 may only be used to identify products of VIA Technologies.
VIA C3
PS/2
Celeron, Pentium
AMD6
Windows 95
PCI
All trademarks are the properties of their respective owners.
TM
is a registered trademark of VIA Technologies, Inc.
TM
is a registered trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
86TM, AMD-K6TM, and AMD-K6-2TM are registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices Corporation.
K
TM
is a registered trademark of the PCI Special Interest Group.
TM
, Pentium-IITM, Pentium-IIITM, MMXTM, and Intel are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
TM
, Windows 98TM, and Plug and PlayTM are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Disclaimer Notice:
No license is granted, implied or otherwise, under any patent or patent rights of VIA Technologies, Inc. VIA
Technologies makes no warranties, implied or otherwise, in regard to this document and to the products described in
this document. The information provided by this document is believed to be accurate and reliable as of the publication
date of this document. However, VIA Technologies assumes no responsibility for any errors in this document.
Furthermore, VIA Technologies assumes no responsibility for the use or misuse of the information in this document
and for any patent infringements that may arise from the use of this document. The information and product
specifications within this document are subject to change at any time, without notice and without obligation to notify
any person of such change.
Offices:
VIA Technologies Incorporated
Taiwan Office:
st
Floor, No. 531
1
Chung-Cheng Road, Hsin-Tien
Taipei, Taiwan ROC
Tel : (886-2) 2218-5452
Fax : (886-2) 2218-5453
Home page :
http ://www.via.com.tw
VIA Technologies Incorporated
USA Office :
940 Mission Court
Fremont, CA 94539
USA
Tel : (510) 683-3300
Fax : (510) 683-3301 or (510) 687-4654
Home Page :
http ://www.viatech.com
Page 3
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
REVISION HISTORY
Document Release Date Revision Initials
0.92 12/9/98 Initial internal release DH
0.93 12/16/98 Updated pinouts to match engineering rev 0.5 document dated 12/1/98 DH
0.94 1/20/99 Updated pinouts to match engineering rev 0.8 document dated 12/22/98 DH
1.0 6/4/99 Added 133 MHz Support to Feature Bullets
Updated / Fixed Pin Descriptions: Fixed description of strap options on MA2, MA8,
and MA11-14; Removed Auxiliary Memory Port; Added REQ/GNT[4-7]#;
Added GND & VCC3 pins to increase pin count to 510 (updated mech spec);
Fixed definitions of RESET# & CRSTI# and changed CRSTI# to CPURSTD#;
Removed PWRGD function from SERR#; Fixed definitions of SRAS#, SCAS#,
and SWE#; Added note to PLLTST description
Updated Device 0 Rx50-53, 68[4], 69, 6B[5-1], 6C[7-4], 70[3,0, 72[0], 76[7], 79[1-
0], 7A (added); Device 1 Rx41[0], 42[0]
1.1 6/23/99 Updated feature bullets & overview and fixed misc formatting problems
Fixed REQ/GNT4# pinouts and CKE & DQM naming polarity
Device 0 Bus 0 updated Rx2-3 Device ID, 69[7-6], 6D[6-5], 76[6]
Device 0 Bus 0 added Rx2C-D, 2E-F, 50[1], 51[5], 53[2], removed 6E-6F
Device 0 Bus 1 updated Rx0-3 Vendor & Device ID, Rx7-6[7]
Removed AC timing specs
1.11 7/8/99 Fixed pin descriptions of CPURSTD# and SUSP DH
1.2 8/23/99 Fixed typo in device 0 Rx50[7] description; added comment about default state
Fixed system freq divider settings (MA pin descriptions, Dev 0 Rx68[1-0])
1.3 9/8/99 Fixed strap options on MA2-6 and MA13 pin descriptions
Fixed Device 0 Rx52[7] strap option and removed (reserved) Device 0 Rx52[5]
Removed “VIA Confidential” watermark
1.4 2/2/00 Added DSTN modes to intro/overview panel interface section
Removed incorrect notes under CPU interface pin descriptions
Fixed MA11 strapping and VCC3/VSUS3 pin descriptions
Fixed Device 0 Bus 0 Rx50[1] and Rx51[1] defaults
Fixed Electrical Specs absolute max temp ratings
1.5 10/24/00 Changed product name to Apollo PLE133; Fixed typos in pinout table
Changed temp specs to be based on case instead of ambient; added power table
Changed orientation of pin 1 in mech diagram to match part marking
1.6 11/1/00 Fixed product name on cover page; Fixed strap descriptions
Fixed Rx50[7], Rx68[1-0], 6B[4], 6C[4], D0Bus1 Rx4[9], Graphics CR39[0]
1.7 12/1/00 Removed EDO, FP, VCM and PC66 DRAM support (no longer fully tested)
Added VIA Cyrix III CPU to supported CPUs list and changed 686A to 686B
Added PLLTST pin I/O type
Fixed table formatting errors introduced as a result of Word 2000 upgrade
Fixed Rx6B[4] and 6C[4]; Fixed spelling errors in Functional Description
1.71 4/26/01 Fixed various typographical and formatting errors DH
1.8 7/3/01 Updated company address; updated processors list
Removed LVDS and direct panel drive support; removed MA3-6 straps
Fixed SUSP pin description; Fixed Device 0 Rx6A; moved VGA regs intro
1.81 10/8/01 Clarified the difference between chipset name and north bridge part number
Changed “VIA Cyrix III” to “VIA C3”; Fixed max memory to be 1.5GB
Updated Device 0 Rx68[4], 69[7-6, 1], 6B[1]; Updated chip marking specs
1.82 10/22/01 Fixed strap pin definitions for MA14,12,11 & updated Rx50[7], 68[1-0] to match DH
1.83 4/22/02 Updated cover and page header logos; updated legal page addresses and phone #’s DH
1.84 7/22/02 Fixed Device 0 Rx50[7] DH
1.85 12/10/04 Added lead-free package in Mechanical Specifications VL
1.86 4/22/05 Revised top marking of Mechanical Specifications SV
DH
DH
DH
DH
DH
DH
DH
DH
DH
DH
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -i- Revision History
Page 4

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
TABLE OF CONTENTS
REVISION HISTORY .......................................................................................................................................................................I
TABLE OF CONTENTS.................................................................................................................................................................. II
LIST OF FIGURES .........................................................................................................................................................................IV
LIST OF TABLES ...........................................................................................................................................................................IV
PRODUCT FEATURES.................................................................................................................................................................... 1
SYSTEM OVERVIEW...................................................................................................................................................................... 6
APOLLO PLE133 CORE LOGIC OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................. 7
APOLLO PLE133 GRAPHICS CONTROLLER OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................. 8
Capability Overview............................................................................................................................................................... 8
System Capabilities................................................................................................................................................................. 9
High Performance 64-bit 2D GUI ......................................................................................................................................... 9
Highly Integrated RAMDACTM & Clock Synthesizer......................................................................................................... 9
Full Feature High Performance 3D Engine.......................................................................................................................... 9
Video Processor..................................................................................................................................................................... 10
Video Capture and DVD...................................................................................................................................................... 10
Versatile Frame Buffer Interface........................................................................................................................................ 10
Hi-Res and Hi-Ref Display Support.................................................................................................................................... 10
CRT Power Management (VESA DPMS).......................................................................................................................... 11
Flat Panel Monitor Interface............................................................................................................................................... 11
Video Capture Interface....................................................................................................................................................... 11
Complete Hardware Compatibility..................................................................................................................................... 11
PINOUTS.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 12
PIN DESCRIPTIONS....................................................................................................................................................................... 15
REGISTERS..................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
REGISTER OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................................................. 23
REGISTER SUMMARY TABLES..................................................................................................................................................... 23
MISCELLANEOUS I/O................................................................................................................................................................... 33
CONFIGURATION SPACE I/O ....................................................................................................................................................... 33
REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS ........................................................................................................................................................... 34
Device 0 Bus 0 Header Registers - Host Bridge ................................................................................................................. 34
Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers ................................................................................................................................. 36
CPU Interface Control........................................................................................................................................................................... 36
DRAM Control...................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
PCI Bus Control ....................................................................................................................................................................................44
GART / Graphics Aperture Control ......................................................................................................................................................48
AGP Control.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 50
Device 1 Bus 0 Header Registers - PCI-to-AGP Bridge .................................................................................................... 52
Device 1 Bus 0 PCI-to-AGP Bridge Registers.................................................................................................................... 54
AGP Bus Control................................................................................................................................................................................... 54
Device 0 Bus 1 Header Registers - Graphics Accelerator ................................................................................................. 55
Device 0 Bus 1 Graphics Accelerator Registers ................................................................................................................. 58
Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers ................................................................................................................................... 59
Capture / ZV Port Registers...................................................................................................................................................................64
DVD Registers ......................................................................................................................................................................................65
VGA Registers ...................................................................................................................................................................... 68
VGA Standard Registers - Introduction................................................................................................................................................. 68
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -ii- Table of Contents
Page 5

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Attribute Controller Registers (AR) ......................................................................................................................................................69
VGA Status / Enable Registers.............................................................................................................................................................. 69
VGA Sequencer Registers (SR)............................................................................................................................................................. 70
VGA RAMDAC Registers .................................................................................................................................................................... 70
VGA Graphics Controller Registers (GR)............................................................................................................................................. 71
VGA CRT Controller Registers (CR)................................................................................................................................................... 72
VGA Extended Registers ..................................................................................................................................................... 73
VGA Extended Registers – Non-Indexed I/O Ports ..............................................................................................................................73
VGA Extended Registers – Sequencer Indexed ....................................................................................................................................74
VGA Extended Registers – Graphics Controller Indexed .....................................................................................................................84
VGA Extended Registers – CRT Controller Indexed............................................................................................................................ 90
VGA Extended Registers – CRTC Shadow......................................................................................................................................... 104
3D Graphics Engine Registers........................................................................................................................................... 105
Operational Concept............................................................................................................................................................................ 105
Drawing............................................................................................................................................................................................... 106
Geometry Primitives............................................................................................................................................................................ 107
Synchronization................................................................................................................................................................................... 111
Functional Blocks................................................................................................................................................................................ 111
Bus Interface ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 111
Span Engine ........................................................................................................................................................................ 112
Graphics Engine Core........................................................................................................................................................ 113
Graphics Engine Organization.............................................................................................................................................................116
Setup Engine Registers........................................................................................................................................................................ 117
Vertex Registers .................................................................................................................................................................................. 118
Rasterization Engine Registers............................................................................................................................................................ 119
Pixel Engine Registers......................................................................................................................................................................... 126
Texture Engine Registers.....................................................................................................................................................................132
Memory Interface Registers ................................................................................................................................................................134
Data Port Area..................................................................................................................................................................................... 134
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTIONS................................................................................................................................................ 135
GRAPHICS CONTROLLER POWER MANAGEMENT.................................................................................................................... 135
Power Management States................................................................................................................................................. 135
Power Management Clock Control................................................................................................................................... 135
Power Management Registers ........................................................................................................................................... 135
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................................................................................ 136
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS ............................................................................................................................................... 136
DC CHARACTERISTICS.............................................................................................................................................................. 136
POWER CHARACTERISTICS ....................................................................................................................................................... 137
AC TIMING SPECIFICATIONS.................................................................................................................................................... 137
MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS........................................................................................................................................... 138
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -iii- Table of Contents
Page 6

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
LIST OF FIGURES
FIGURE 1. VT8601A BALL DIAGRAM (TOP VIEW) ............................................................................................................. 12
FIGURE 2. VT8601A PIN LIST (NUMERICAL ORDER)........................................................................................................ 13
FIGURE 3. VT8601A PIN LIST (ALPHABETICAL ORDER)................................................................................................. 14
FIGURE 4. GRAPHICS APERTURE ADDRESS TRANSLATION......................................................................................... 48
FIGURE 5. PHYSICAL REGION DESCRIPTOR TABLE FORMAT .................................................................................... 60
FIGURE 6. PCI BUS MASTER ADDRESS TRANSLATION................................................................................................... 60
FIGURE 7. FRAME BUFFER PARAMETERS.......................................................................................................................... 97
FIGURE 8. LIVE VIDEO DISPLAY PARAMETERS............................................................................................................... 97
FIGURE 9. MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS - 510-PIN BALL GRID ARRAY PACKAGE......................................... 138
FIGURE 10. LEAD-FREE MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS - 510-PIN BALL GRID ARRAY PACKAGE............... 139
LIST OF TABLES
TABLE 1. VT8601A PIN DESCRIPTIONS ................................................................................................................................. 15
TABLE 2. REGISTER SUMMARY ............................................................................................................................................. 23
TABLE 3. SYSTEM MEMORY MAP.......................................................................................................................................... 39
TABLE 4. MEMORY ADDRESS MAPPING TABLE ............................................................................................................... 39
TABLE 5. VGA/MDA MEMORY/IO REDIRECTION ............................................................................................................. 54
TABLE 6. SUPPORTED PCI COMMAND CODES .................................................................................................................. 55
TABLE 7. INTERRUPT SOURCES AND CONTROLS............................................................................................................ 57
TABLE 8. GRAPHICS CLOCK FREQUENCIES – 14.31818 MHZ REFERENCE............................................................... 76
TABLE 9. DPMS SEQUENCE - HARDWARE TIMER MODE............................................................................................... 87
TABLE 10. DPMS SEQUENCE - HARDWARE MODE IN SIMULTANEOUS DISPLAY MODE..................................... 87
TABLE 11. HARDWARE CURSOR PIXEL OPERATION ...................................................................................................... 94
TABLE 12. PCI POWER MANAGEMENT STATES.............................................................................................................. 135
TABLE 13. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS..................................................................................................................... 136
TABLE 14. DC CHARACTERISTICS....................................................................................................................................... 136
TABLE 15. DC CHARACTERISTICS....................................................................................................................................... 137
TABLE 16. AC TIMING MIN / MAX CONDITIONS.............................................................................................................. 137
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -iv- Table of Contents
Page 7

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
APOLLO PLE133 NORTH BRIDGE
133 / 100 / 66 MHz
Single-Chip Socket-370 PCI North Bridge,
With Integrated AGP 2D / 3D Graphics Accelerator
and Advanced Memory Controller
supporting PC133 / PC100 SDRAM
For Desktop PC Systems
PRODUCT FEATURES
• General
− 510 BGA Package (35mm x 35mm )
− 2.5 Volt core with 3.3V CMOS I/O
− Supports GTL+ I/O buffer Host interface
− Supports separately powered 5.0V tolerant interface to PCI bus and Video interface
− 2.5V, 0.25um, high speed / low power CMOS process
− PC98 / 99 compatible using VIA VT82C686B (352-pin BGA) south bridge chip for Desktop and Mobile
applications
− 133 / 100 / 66 MHz CPU Front Side Bus (FSB) Operation
• High Integration
− Single chip implementation for 64-bit Slot-1 and Socket-370 CPUs, 64-bit system memory, 32-bit PCI with
integrated 2D / 3D GUI accelerator
− Apollo PLE133 Chipset: VT8601A system controller and VT82C686B PCI to ISA bridge
− Chipset includes dual UltraDMA-100 / 66 / 33 EIDE, AC-97 link, 4 USB ports, integrated Super-I/O, hardware
monitoring, keyboard / mouse interfaces, and RTC / CMOS
• High Performance CPU Interface
− Supports VIA C3 and Intel Celeron
− 133 / 100 / 66 MHz CPU Front Side Bus (FSB)
− Built-in PLL (Phase Lock Loop) circuitry for optimal skew control within and between clocking regions
− Five outstanding transactions (four In-Order Queue (IOQ) plus one input latch)
− Supports WC (Write Combining) cycles
− Dynamic deferred transaction support
− Sleep mode support
− System management interrupt, memory remap and STPCLK mechanism
CPU DRAM GUI Core Internal AGP PCI Comments
133 MHz 133 MHz 100 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz Synchronous (DRAM uses CPU clock)
133 MHz 100 MHz 100 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz Pseudo-synchronous (DRAM uses GUI clock)
100 MHz 133 MHz 100 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz Pseudo-synchronous (DRAM uses GUI clock)
100 MHz 100 MHz 100 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz Synchronous (DRAM uses CPU clock)
100 MHz 66 MHz 66 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz Pseudo-synchronous (DRAM uses GUI clock)
66 MHz 100 MHz 100 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz Pseudo-synchronous (DRAM uses GUI clock)
66 MHz 66 MHz 66 MHz 66 MHz 33 MHz Synchronous (DRAM uses CPU clock)
TM
and Pentium IIITM processors
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -1- Product Features
Page 8

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
• Internal Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) Controller
− AGP v1.0 compliant
− Pipelined split-transaction long-burst transfers up to 533 MB/sec
− Eight level read request queue
− Four level posted-write request queue
− Thirty-two level (quadwords) read data FIFO (128 bytes)
− Sixteen level (quadwords) write data FIFO (64 bytes)
− Intelligent request reordering for maximum AGP bus utilization
− Supports Flush/Fence commands
− Graphics Address Relocation Table (GART)
− One level TLB structure
− Sixteen entry fully associative page table
− LRU replacement scheme
− Independent GART lookup control for host / AGP / PCI master accesses
− Windows 95 OSR-2 VXD and integrated Windows 98 / NT5 miniport driver support
• Concurrent PCI Bus Controller
− PCI bus is synchronous / pseudo-synchronous to host CPU bus
− 33 MHz operation on the primary PCI bus
− Supports up to five PCI masters
− Peer concurrency
− Concurrent multiple PCI master transactions; i.e., allow PCI masters from both PCI buses active at the same time
− Zero wait state PCI master and slave burst transfer rate
− PCI to system memory data streaming up to 132Mbyte/sec
− PCI master snoop ahead and snoop filtering
− Six levels (double-words) of CPU to PCI posted write buffers
− Byte merging in the write buffers to reduce the number of PCI cycles and to create further PCI bursting possibilities
− Enhanced PCI command optimization (MRL, MRM, MWI, etc.)
− Forty-eight levels (double-words) of post write buffers from PCI masters to DRAM
− Sixteen levels (double-words) of prefetch buffers from DRAM for access by PCI masters
− Supports L1/L2 write-back forward to PCI master read to minimize PCI read latency
− Supports L1/L2 write-back merged with PCI master post-write to minimize DRAM utilization
− Delay transaction from PCI master reading DRAM
− Read caching for PCI master reading DRAM
− Transaction timer for fair arbitration between PCI masters (granularity of two PCI clocks)
− Symmetric arbitration between Host/PCI bus for optimized system performance
− Complete steerable PCI interrupts
− PCI-2.2 compliant, 32 bit 3.3V PCI interface with 5V tolerant inputs
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -2- Product Features
Page 9

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
• Advanced High-Performance DRAM Controller
− DRAM interface synchronous or pseudosynchronous with CPU FSB speed of 133 / 100 / 66 MHz
− DRAM interface may be faster than CPU by 33 MHz to allow use of PC100 with 66 MHz Celeron CPU or use of
PC133 with 100 MHz VIA C3 or Intel Pentium II or Pentium III CPU
− DRAM interface may be slower than CPU by 33 MHz to allow use of older memory modules with a newer CPU
− Concurrent CPU, AGP, and PCI access
− Different DRAM timing for each bank
− Dynamic Clock Enable (CKE) control for SDRAM power reduction in high speed systems
− Mixed 1M / 2M / 4M / 8M / 16M / 32MxN DRAMs
− 6 banks DRAMs supported up to 1.5GB (256Mb DRAM technology)
− Flexible row and column addresses
− 64-bit data width only
− 3.3V DRAM interface with 5V-tolerant inputs
− Programmable I/O drive capability for MA, command, and MD signals
− Two-bank interleaving for 16Mbit SDRAM support
− Two-bank and four bank interleaving for 64Mbit SDRAM support
− Supports maximum 8-bank interleave (i.e., 8 pages open simultaneously); banks are allocated based on LRU
− Independent SDRAM control for each bank
− Seamless DRAM command scheduling for maximum DRAM bus utilization
(e.g., precharge other banks while accessing the current bank)
− Four cache lines (16 quadwords) of CPU to DRAM write buffers
− Four cache lines of CPU to DRAM read prefetch buffers
− Read around write capability for non-stalled CPU read
− Speculative DRAM read before snoop result
− Burst read and write operation
− x-1-1-1-1-1-1-1 back-to-back accesses for SDRAM from CPU or from DRAM controller
− BIOS shadow at 16KB increment
− Decoupled and burst DRAM refresh with staggered RAS timing
− CAS before RAS or self refresh
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -3- Product Features
Page 10

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
• General Graphic Capabilities
− 64-bit Single Cycle 2D/3D Graphics Engine
− Supports 2 to 8 Mbytes of Frame Buffer
− Real Time DVD MPEG-2 and AC-3 Playback
− Video Processor
2
− I
C Serial Interface
− Integrated 24-bit 230MHz True Color DAC
− Extended Screen Resolutions up to 1600x1200
− Extended Text Modes 80 or 132 columns by 25/30/43/60 rows
− DirectX 6 and OpenGL ICD API
• Graphics Performance
− Sustained 1M polygons/second and 100M pixels/second
− 30fps DVD playback of 9.8Mbps MPEG-2 video with 30% headroom
− Host Based AC-3 decode at only 8% utilization
• High Performance rCADE3D™ Accelerator
− 32 entry command queue, 32 entry data queue
− 4Kbyte texture cache with over 90% hit rates
− Pipelined Single Cycle Setup/Texturing/Rendering Engines
− DirectDraw™ acceleration
− Multiple buffering and page flipping
Setup Engine
− 32-bit IEEE floating point input data
− Slope and vertex calculations
− Back facing triangle culling
− 1/16 sub-pixel positioning
Rendering Engine
− High performance single pass execution
− Diffused and specula lighting
− Gouraud and flat shading
− Anti-aliasing including edge, scene, and super-sampling
− OpenGL compliant blending for fog and depth-cueing
− 16-bit Z-buffer
− 8/16/32 bit per pixel color formats
Texturing Engine
− 1/2/4/8-bits per pixel compact palletized textures
− 16/32-bits per pixel quality non-palletized textures
− Pallet formats in ARGB 565, 1555, or 444
− Tri-linear, bi-linear, and point-sampled filtering
− Mip-mapping with multiple Level-Of-Detail (LOD) calculations and perspective correction
− Color keying for translucency
2D GUI Engine
− 8/15/16/24/32-bits per pixel color formats
− 256 Raster Operations (ROPs)
− Accelerated drawing: BitBLTs, lines, polygons, fills, patterns, clipping, bit masking
− Panning, scrolling, clipping, color expansion, sprites
− 32x32 and 64x64 Hardware Cursor
− DOS graphics and text modes
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -4- Product Features
Page 11

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
• DVD
− Hardware-Assisted MPEG-2 Architecture for DVD with AC-3
− Simultaneous motion compensation and front-end processing (parsing, decryption and decode)
− Supports full DVD 1.0, VCD 2.0 and CD-Karaoke
− Microsoft DirectShow 3.0 native support, backward compatible to MCI
− No additional frame buffer requirements
− Sub-picture hardware eliminates Run-Length-Decoder and Alpha Blending overhead
− Dynamic frame and field de-interlace filtering for high quality playback on VGA monitors (Bob and Weave)
− Tamper-proof software CSS implementation
− Freeze, Fast-Forward, Slow Motion, Reverse
− Pan-and-Scan support for 16:9 sequence
• Video Processor
− On-chip Color Space Converter (CSC)
− Anti-tearing via two frame buffer based capture surfaces
− Minifier for video stream compression and filtering
− Horizontal/vertical interpolation with edge recovery
− Dual frame buffer apertures for independent memory access for graphics and video
− YUV 4:2:2/4:1:1/4:2:0 and RGB formats
− Video Module Interface (VMI) to MPEG and video decoder
− Vertical Blank Interval for Intercast™
− Overlay differing video and graphic color depths
− Minifier Video Module Interface (VMI) to MPEG and video decode
− Display two simultaneous video streams from both internal AGP and VMI
− Two scalers and Color Space Converters (CSC) for independent windows
• Digital Flat Panel (DFP) Interface
− 85 MHz Flat Panel Monitor interface supports 1024x768 panels
− Uses external TMDS transmitters for advanced panel interfaces
• Power Management Support
− Dynamic power down of SDRAM (CKE)
− Independent clock stop controls for CPU / SDRAM, AGP, and PCI bus
− PCI and AGP bus clock run and clock generator control
− VTT suspend power plane preserves memory data
− Suspend-to-DRAM and Self-Refresh operation
− EDO self-refresh and SDRAM self-refresh power down
− 8 bytes of BIOS scratch registers
− Low-leakage I/O pads
• Testability
− Build-in NAND-tree pin scan test capability
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -5- Product Features
Page 12
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
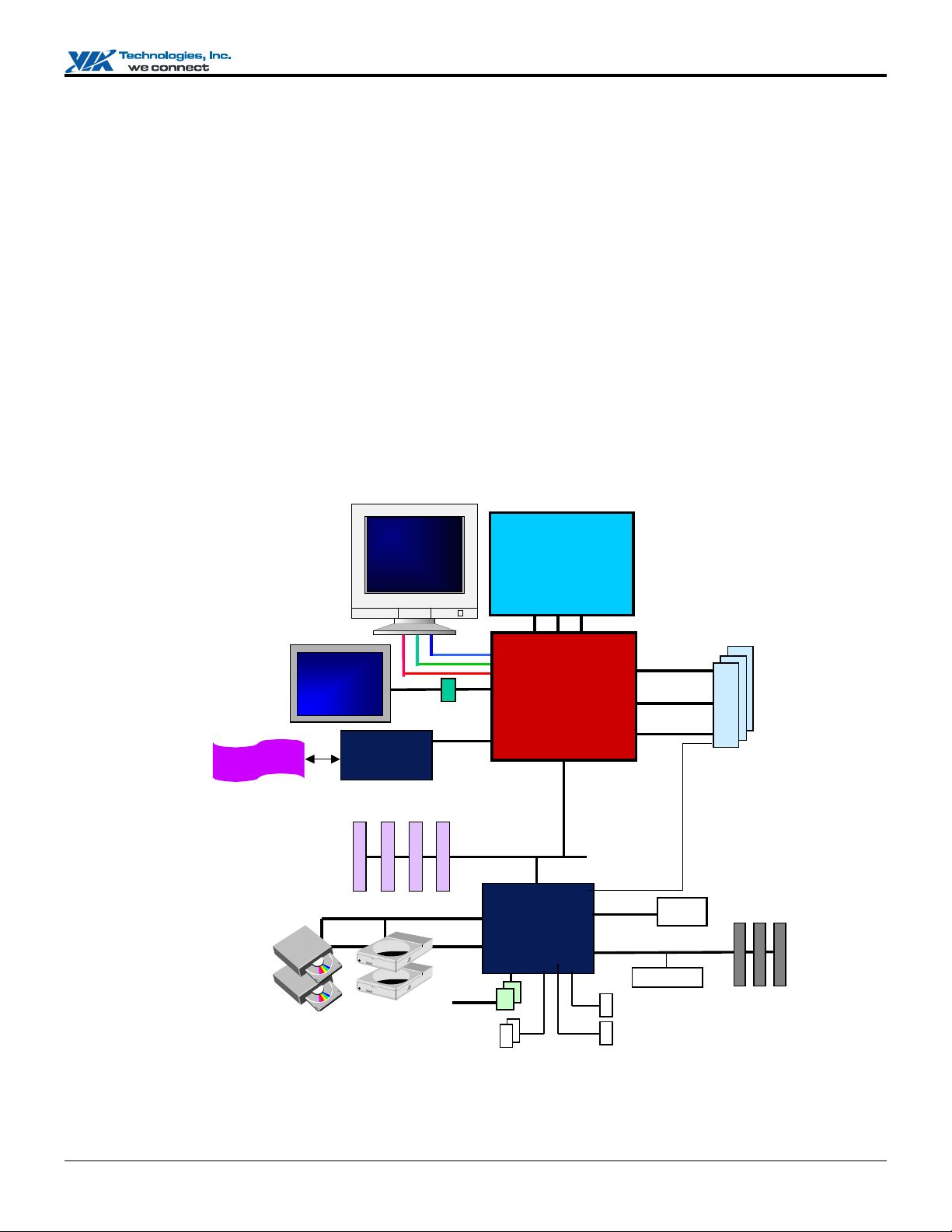
SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The Apollo PLE133 chipset consists of the VT8601A North Bridg e (described by this document) and the VT82C686B South
Bridge (described in a separate data sheet). The VT8601A is a PC system logic North Bridge for Socket-370 CPUs with
integrated 2D/3D Graphics accelerator. The core logic portion of the chip is based on the VIA Apollo Pro133 with integrated
graphics accelerator provided by an industry leading Graphics supplier. The combination of the two leading edge technologies
provides a stable, cost-effective, and high performance solution to both the Desktop and Mobile personal computer markets. As
shown in Figure 1 below, the Apollo PLE133 will interface to:
• Socket-370 Front-Side Bus (133, 100 and 66 MHz)
• PC133 / PC100 SDRAM Memory Interface
• PCI Bus (33 MHz)
• Analog RGB Monitor with DDC
• Digital Monitor Transmitters (TMDS)
• Video Capture / Playback CODECs
TV Signal
TV Encoder
PCI SLOTS
Dual-IDE
TMDS
VMI
4x USB
VIA C3 or Intel
Celeron /
Pentium III
Processor
VT8601A
North Bridge
510 BGA
PCI BUS
VT82C686B
South
Bridge
352 BGA
SMBUS
AC-Link
ISA Bus
Floppy Disk
CNTLs
MD[63:0]
MA[13:0]
AC-97
BIOS ROM
D
R
A
M
ISA SLOTS
Serial Ports
Parallel Port
Figure 1: Apollo PLE133 High Level System Diagram
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -6- System Overview
Page 13

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Apollo PLE133 Core Logic Overview
The Apollo PLE133 chipset is a high performance, cost-effective and energy efficient solution for the implementation of
Integrated 2D / 3D Graphics - PCI - ISA desktop and notebook personal computer systems from 66 MHz to 133 MHz based on 64bit Socket-370 VIA C3 / Intel Celeron and Pentium III processors. The complete solution consists of the VT8601A “System
Media Accelerator” (SMA) north bridge (510 BGA) and either the VT82C596B (324 BGA) or the VT82C686B (352 BGA) PCIto-ISA south bridge. Both south bridges are PC98 / PC99 compliant with integrated UltraDMA-66 / 33 IDE, 4 USB ports, and a
complete power management feature set. The VT82C686B also integrates HW monitoring, Super-I/O functions (floppy disk drive
interface and serial / parallel ports), and AC-97 link supporting digital audio and HSP modem functions.
Apollo PLE133 supports six banks of DRAMs up to 1.5GB. The DRAM controller supports PC133 and PC100 Synchronous
DRAM (SDRAM). The Synchronous DRAM interface allows zero wait state bursting between the DRAM and the data buffers at
100 or 133 MHz. The six banks of DRAM can be composed of an arbitrary mixture of 1M / 2M / 4M / 8M / 16M / 32MxN
DRAMs. The DRAM Controller is optimized to run synchronous with the CPU Front Side Bus (FSB) frequency of 100 or 133
MHz or pseudosynchronous to the Front Side Bus with the SDRAM and FSB frequencies differing by 33 MHz.
Apollo PLE133 also supports full AGP v1.0 capability with the internal 2D/3D Graphics Engine for maximum software
compatibility. An eight level request queue plus a four level post-write request queue with thirty-two and sixteen quadwords of
read and write data FIFO’s respectively are included for deep pipelined and split AGP transactio ns. A single-level GART TLB
with 16 full associative entries and flexible CPU/AGP/PCI remapping control is also provided for operation under protected mode
operating environments. Both Windows-95 VXD and Windows-98 / NT5 miniport drivers are supported.
Apollo PLE133 supports one 32-bit 3.3 / 5V system bus (PCI) that is synchronous to the CPU bus. The chip also contains a builtin AGP bus-to-PCI bus bridge to allow simultaneous con current operations on each bus. Five levels (doublewords) of post write
buffers are included to allow for concurrent CPU and PCI operation. For PCI master operation, forty-eight levels (doublewords)
of post write buffers and sixteen levels (doublewords) of prefetch buffers are included for concurrent PCI bus and DRAM/cache
accesses. The chip also supports enhanced PCI bus commands such as Memory-Read-Line, Memory-Read-Multiple and MemoryWrite-Invalid commands to minimize snoop overhead. In addition, advanced features are supported such as snoop ahead, snoop
filtering, L1 / L2 write-back forward to PCI master, and L1 / L2 write-back merged with PCI post write buffers to minimize PCI
master read latency and DRAM utilization. Delay transaction and read caching mechanisms are also implemented for further
improvement of overall system performance.
For sophisticated notebook implementations, the Apollo PLE133 north bridge provides independent clock stop control for the CPU
/ SDRAM, PCI, and AGP buses and Dynamic CKE control for powering down of the SDRAM. A separate suspend-well plane is
implemented for the SDRAM control signals for Suspend -to-DRAM operation. Coupled with the 324-pin Ball Grid Array VIA
VT82C596B south bridge chip, a complete notebook PC main board can be implemented with no external TTLs.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -7- System Overview
Page 14

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller Overview
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller is a highly integrated display control device that incorporates a 64-bit 3D/2D graphic
engine and video accelerator with advanced DVD video and optional TV output capability. It provides a flexible and high
performance solution for graphics and video playback acceleration for various color depth and resolution modes.
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller supports a video capture port to import captured live MPEG 1 or MPEG 2 video streams,
or DVD decompressed video streams to be overlaid with a graphics stream of mixed color depth displays. In supporting dual live
videos, the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller offers independent dual video windows ready for videoconferencing and with
linear scaling capability.
Integrating the programmable phase lock loop with high speed LUT DACs, the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller is a true
price/performance solution for the modern multimedia based entertainment PC.
Capability Overview
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller is a fully integrated CRT and TV 64-bit 2D/3D Accelerator. The high performance
graphics engine offers high speed 3D image processing in full compliance and compatibility with IBM® VGA and VESA™
extended VGA. As an integrated controller, it allows unprecedented cost and performance advantages by eliminating the need for
an external frame buffer while at the same time gaining local access to a larger amount of memory. Many functions can now be
eliminated that previously consumed large amounts of bandwidth.
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller, equipped with a single-cycle 3D GUI Engine, pipelines 3D rendering process
architecture in hardware, providing real-time interactions with solid 3D models in CAD/CAM, 3D modeling, and 3D games. It
supports all key 3D rendering operations, including: Gouraud shading for smooth object surfaces, texture mapping for realistic
object textures, 16-bit hardware Z-buffering for fast 3D depth calculations, and Alpha Blending for transparency effects.
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller’s highly innovative design, a full 64-bit memory interface with a high performance
graphics engine which can support a RAMDAC™ running up to 230MHz, dramatically improves GUI functions and significantly
promotes overall system operation.
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller supports a full AGP implementation internally to remain compatible with existing
software and programming models. However, since the engine is integrated it enjoys a higher bandwidth and lower latency than is
possible with discrete solutions. AGP operations can include direct access of the system memory by the 2D/3D engine to provide
increased texture memory.
To meet the requirements of a PC99 graphics adapter in a multimedia PC, the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller supports planar
video format for MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and DVD-video playback. The dual video playback is capable of overlaying windows for
videoconferencing and multimedia displays. Advanced features of the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller, su ch as color space
conversion, video scaling, dual video windows, dual-view display, V ideo Module Interface (VMI), Vertical Blanking Interleave
(VBI), a 24-bit True Color DAC, and triple clock synthesizers allow performance at peak levels.
By using an extended 16-bit VMI port the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller can support DTV resolution . This port can op erate
as either an input for Video Capture or as an output for Video display. The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller is capable of
supporting three simultaneous displays: CRT, Flat Panel Monitor & Video, each with a different “window” or desktop.
The Apollo PLE133 integrated Graphics Controller supports a rich featured flat panel monitor interface that can be used with
external TMDS transmitters to support the latest DVI displays.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -8- System Overview
Page 15

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
System Capabilities
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller’s main system features include:
• High Performance single cycle GUI
• Highly Integrated RAMDAC™ and Triple Clock Synthesizer
• Full Feature High Performance 3D Graphics Engine
• High speed internal AGP Bus Mastering data bus supporting DVD video playback & 3D
• Hardware implementation of motion compensation
• Dual Video Windows for Videoconferencing
• TrueVideo
• DirectDraw
• Versatile Motion Video Capture/Overlay/Playback Support
• Flexible Frame Buffer Memory Interface
• Advanced Mobile Power Management
• CRT Power Management (VESA™ DPMS)
• PC99 Hardware Support
Processor
TM
and DirectVideoTM Hardware Support
High Performance 64-bit 2D GUI
The 64-bit graphics engine of the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller significantly improves graphics performance through
specialized hardware that accelerates the most frequently used GUI operations and matches the high-speed requirements of CPUs.
Functions directly supported in hardware include: BitBLTs, image and text transfer, line draw, short stroke vector draw, rectangle
fills, and clipping. The graphics engine supports 256 Raster Operations (ROPs) for up to 32-bit pack ed pix el graph ic modes. The
ROP3 Processor in the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller is able to perform Boolean functions which allow many additional
operations, including transparency, pattern masking, color expansion alignment, and pattern enhancement. Additionally, the
graphics engine features linear display memory addressing (up to 4GB memory space), accelerated color expansion modes for
graphics text procession, and memory-mapped I/O registers on the graphics engine for faster access time.
Graphic functions are optimized by a 64-bit internal data bus and a four-color hardware cursor/pop-up icon, operating up to a
128x128x2 pixel image, which offloads the CPU. The hardware cursor mechanism can also be used to display patterns stored in
the system memory. This pop-up icon is very useful to display user friendly information instantly through simple hot key
operations. This advanced function combination allows significant performance increases over standard Super VGA designs and
provides outstanding graphics acceleration on GUIs, such as Microsoft
Highly Integrated RAMDAC
TM
& Clock Synthesizer
Windows 98.
The highly integrated design of the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller offers a “no TTL” solution for cost-effective, highperformance multimedia subsystem designs for the PC and compatible notebooks. The 64-bit memory data bus supporting
SDRAM and SGRAM memory provides faster data transfer rates for improved system throughput. The Apollo PLE133 Graphics
Controller has a built-in, high speed RAMDAC
TM
. The RAMDACTM is composed of one 256x24 and one 256x18 color lookup
table and a triple loop frequency synthesizer, providing the read/write timing control for the Frame Buffer Memory and the refresh
of the TV/CRT display.
The integrated frequency synthesizer provides a 125MHz memory clock for high speed DRAM access and a 230MHz video clock
which supports various refresh rates up to 85Hz at 1280x1024.
Full Feature High Performance 3D Engine
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller is equipped with an advanced Graphics Drawing, Single Cycle 3D Graphics Engine that
performs premium 3D functions at a high level of more than 1M triangles per second. The 3D engine supports Microsoft
Direct3D. The 3D Engine is set up to off-load the CPU from major 3D tasks including slope calculation, sub-pixel positioning,
and Tri-striping. By balancing the 3D pipeline and reducing parameter passing, the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller provides
very high levels of performance. The 3D engine is integrated with a triangle set-up engine that sets up triangles according to
vertex input data and accomplishes various functions for 3D rendering. Gouraud shading provides smooth shading for colors
across surfaces, perspective correction texture mapping to correct texture data based on the perspective, bi-linear texture filtering
for interpolating, alpha blending to compensate colors for the opacity of two colors blended, Z-buffering (16-bit/24-bit), video
texturing to overlay 2D video play-back onto 3D images, fogging to simulate weather effects, palletized texture mapping (1-, 4-, or
8-bit) for memory and bandwidth reduction, and anti-aliasing to reduce or eliminate jaggies resulted from alias rendering. The 3D
engine also works with the APM system, conserving power while 3D operations are suspended.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -9- System Overview
Page 16

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Video Processor
Video processor features include: on-chip hardware Color Space Conversion (CSC) for faster data conversion on the fly,
Horizontal/Vertical (H/V) scaling with interpolation, edge recovery algorithm logic, gamma correction, and overlay control with
different color depths from graphics. The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller also includes a fully integrated GUI accelerator,
read cache, and command FIFO that optimize memory bandwidth and maximize graphics performance.
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller, with an integrated Video Display and a Capture Engine, supports dual apertures on the
PCI bus which enables independent graphic and video data to be transported simultaneously to and from different memory areas
and greatly accelerates the performance of both DirectDraw
provide dual video windows that display different images from different video sources (from the PCI bus and from the capture
port) on the same screen. The video image is stored in off-screen memory and is retrieved by the Video Display Processing block
for video processing. With the help of DirectDraw™ acceleration for sprites, page flipping, double buffering, and color keying,
video processing is performed by utilizing a proprietary edge recovery algorithm for sharper line visibility , de-interlacing, antitearing, multitap horizontal filtering, dithering, and scaling operations with b ilinear interpolation in both horizontal and vertical
directions. Linear scaling permits zoom in/out to any size without any restrictions. In addition, the on-chip hardware Color Space
Conversion (CSC) accelerates conversion for 16 bit YUV pixels into linear true color 32 bit RGB pixels on the fly. The additional
X and Y minifiers are capable of shrinking video images to any linear fractions, which saves bus bandwidth and memory space.
The YUV planar logic of the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller supports a YUV 420 format that can eliminate redundant video
stream decoding procedures. The load of the CPU is reduced while performing software MPEG or software video conferencing.
The color and luminance control provided by the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller offers color compensations to prevent color
distortion for display devices such as a CRT or TV with Gamma correction and hue adjustment control.
The Video Conferencing feature allows remote and local video images to be displayed simultaneously on the same screen.
TM
and DirectVideoTM. The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller can
Video Capture and DVD
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller has a Video Module Interface (VMI) and advanced hardware interface logic allowing it
to be directly connected to many MPEG and video decoders such as the C-Cube CL450 /480, SGS 3400/3500, Philips 7110/1 and
Brooktree BT819/817/827/829.
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller, integrated with a DVD video hardware block for motion compensation, gives existing
PCs the ability to play DVD video in MPEG-2 format at high bandwidths with very good video quality.
A new industry standard is being set for transmission of non-video data over a TV broadcast signal during vertical blanking dead
time. This technology is referred to as Intercast. The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller has the ab ility to take the entire video
stream over the video port, sending the visible video stream to the display memory for display in a window, stripping the VBI data
from the stream, and then sending this data to the CPU for processing using PCI Bus Mastering.
Versatile Frame Buffer Interface
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller features a versatile frame buffer interface aperture into main system memory. Optimized
performance can be achieved with the single cycle memory bus interface using programmable DRAM timing. The display queue
has been increased to reduce the frequency of memory bus requests, optimizing memory bus efficiency for the graphic controller.
With the support of the internal AGP aperture, the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller has access to system memory through the
GART. In the execute mode, the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller is able to use both the dedicated graphics portion and the
general portion of system memory for graphics operations. As a result, DVD and 3D rendering performance and quality are
greatly enhanced.
Hi-Res and Hi-Ref Display Support
Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller display enhancements dramatically improve CRT resolution. These enhancements include
support of non-interlaced 1280x1024x64K, 1024x768x16M, 800x600x16M, and 640x480x16M colors for “full spectrum” color.
Extended text modes of 80 or 132 columns by 25, 30, 43, or 60 rows provid e an extended graphics area frequently used in many
spreadsheet and database applications. Extended graphics and text modes are supported by software drivers that provide a “readyto-go” solution, minimizing the need for additional driver development.
A virtual screen can be created with the Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller . When this function is enabled, a selected portion of
a large image can be shown on a smaller display. The image can also be moved across the whole screen, either up or down.
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller is able to automatically detect DDC monitors with I
2
C signaling.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -10- System Overview
Page 17
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
CRT Power Management (VESA DPMS)
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller conforms to the standard power management schemes defined by VESA™ for CRTs.
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller supports four states of VESA™ Display Power Management Signaling (DPMS), which
decrease monitor power consumption after timeout periods. VESA™ DPMS power down states (ready, standby, suspend, and off)
specify HSYNC and VSYNC signals to control the monitor power down state.
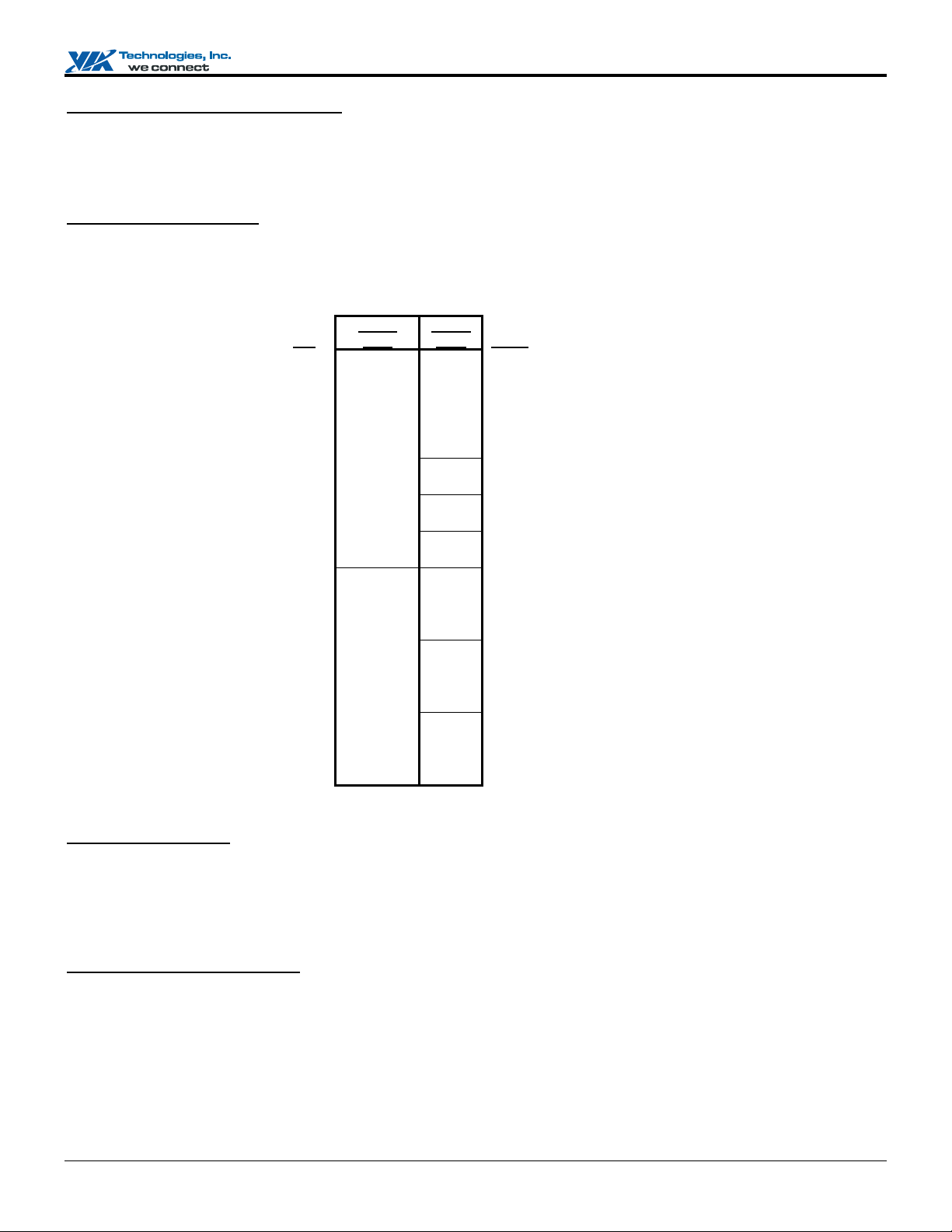
Flat Panel Monitor Interface
The Apollo PLE133 Flat Panel Monitor interface is designed to support industry standard TFT panel based Flat Panel Monitors via
external TMDS transmitters. The interface supports both 18-bit and 24-bit display modes. Optionally, an 18 +18 panel can be
supported utilizing external latches.
Pin
PD[23] B0 S2 S2 used for external 18+18
PD[22] B1 S1 S1 used for external 18+18
PD[21] G0
PD[20] G1
PD[19] R0
PD[18] R1
PD[17] B2 B0
PD[16] B3 B1
PD[15] G2 G0
PD[14] G3 G1
PD[13] R2 R0
PD[12] R3 R1
PD[11] B4 B2
PD[10] B5 B3
PD[9] B6 B4
PD[8] B7 B5
PD[7] G4 G2
PD[6] G5 G3
PD[5] G6 G4
PD[4] G7 G5
PD[3] R4 R2
PD[2] R5 R3
PD[1] R6 R4
PD[0] R7 R5
24 Bit
TFT
18 Bit
TFT Notes
Video Capture Interface
The Video Module Interface (VMI) is supported for video devices such as MPEG1 and MPEG2. Additionally, the zero-wait state
host write buffer, read cache, and memory mapped I/O increase operating speeds and contribute to peak performance levels. All
I/O interfaces are 5V tolerant, capable of interfacing with external devices operating at 5V, even though the Apollo PLE133
Graphics Controller runs at 2.5V. Graphics system throughput is further enhanced by a command FIFO, allowing maximum bus
transfer speed for applications such as Windows™ or AutoCAD™ that directly access video memory.
Complete Hardware Compatibility
The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller is fully compliant with the VESA™ DDC and VAFC standards. Th e Apollo PLE133
Graphics Controller is 100% VGA compatible at both the BIOS and Driver level, allowing full compatib ility with virtually any
VGA application software. The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller provides hardware support to DirectDraw™, offering high
speed game graphics on Windows 98
supporting a unique ID for each customer and a unique ID for each model.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -11- System Overview
. The Apollo PLE133 Graphics Controller meets the requirements of PC99 as well,
Page 18
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
ey
6 7 8
910
3
516
81920
3
526
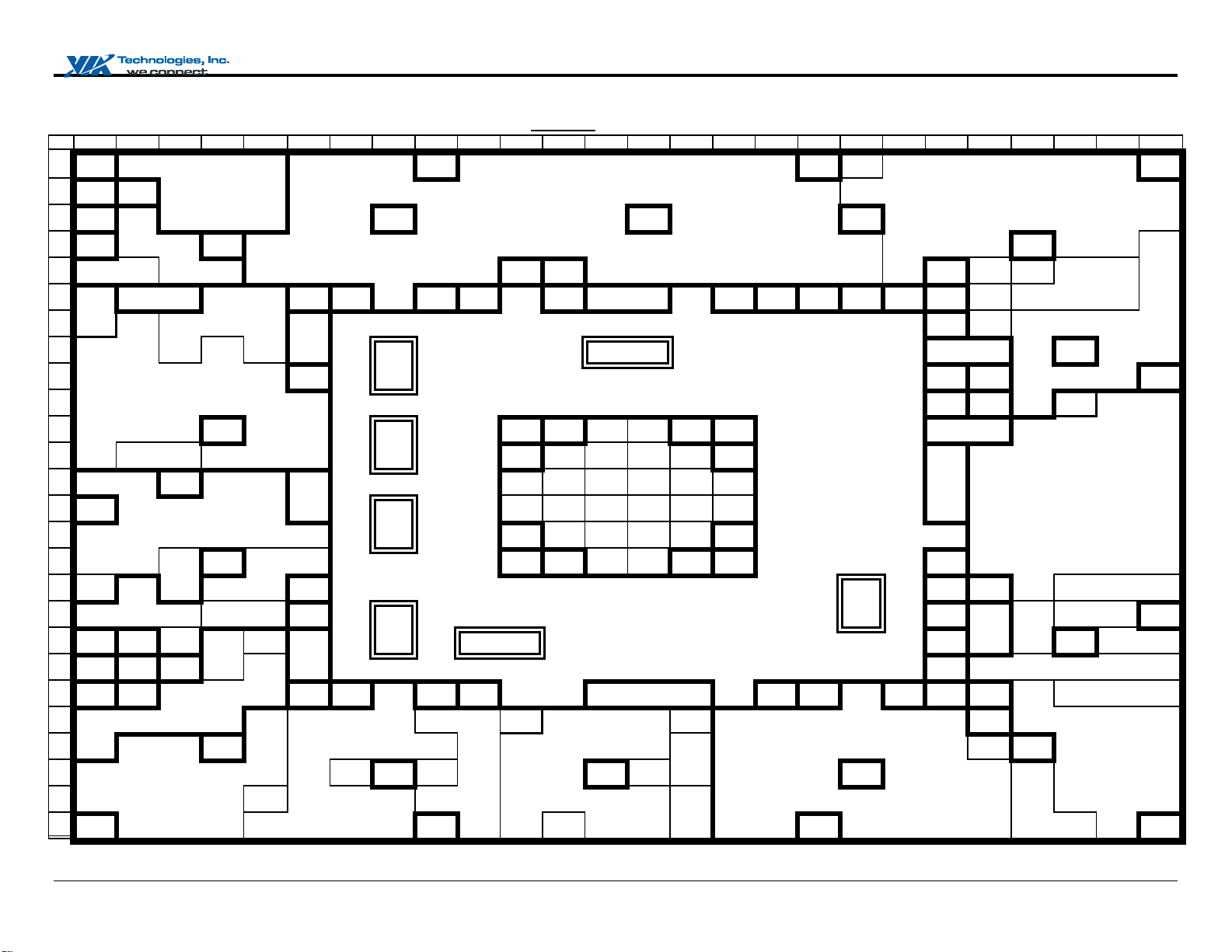
PINOUTS
Figure 1. VT8601A Ball Diagram (Top View)
K
1 2 3 4 5
GND
A
RGB
GND
B
VCC
C
VCC
D
VSYNC HSYNC IRSET COMP HD56 HD58 HD46 HD40 HD27 HD39 VTT
E
EVDD SDA SCL ETST# SUSP GND VCC3 HD52 VCCI VCC3 VCC3 GND GND GND VCC3 VCCI VTT VCC3 GND HA15
F
EBLT PD0 FLM SCLK LP VCC3 G7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 G20 VCC3 HCLK
G
H
J
PD12 PD10 PD13 PD20 PD16 PD6 K
K
PD17 PD15 PD18 VCC3 PD9 PD14 L
L
PD23 IMIO IMIIN PD21 PD22 PD19 M
M
NC NC NC NC HD62 HD57 HD63 GND HD45 HD38 HD34 HD31 HD16 HD13 HD3 HD12 GND
GND NC NC NC HD50 HD59 HD48 HD51 HD44 HD22 HD32 HD33 HD19 HD24 HD2 HD10 HD1 HA26 HA29 HA23 HA25 HA21 HA13 HA5 HA6
S
RED NC NC NC HD60 HD55 GND HD41 HD49 HD43 HD28 HD26 GND HD20 HD9 HD5 HD4 GND HA27 HA31 HA19 HA16 HA9 HA11 HA8
S
BLUE GRN GND HD61 HD53 HD54 HD47 HD42 HD37 HD36 HD29 HD25 HD23 HD7 HD11 HD8 HD6 HD15 HA30 HA17 HA12 GND HA4 HA14 BNR#
R
PD2 PD1 DE PD5 EVEE VCC3 H
PD4 PD3 PD8 PD7 PD11 VCCI J
CRT CPU Pins
Pins
Panel
Pins
11 12 1
GTL
REF
K10 11 12
L GND VCC3
M VCC3 GND
14 1
HD35 HD21 HD30 HD14 HD18 HD17 HD0 HA24
13 14 15 16 K17
GND GND VCC3 GND L
GND GND GND VCC3 M
171
CPU
HA18 HA20 HA22 HA10 HA28 HA3 GND
RST#
H VCCA VCCA RS0# GND RS2# DBSY#
J VCCI
K VCC3
L GNDA GNDA MD33 MD35 MD3 MD2
M GND MD34 MD0 MD5 MD36 MD4
21 22 2
GTL
CPU
REF
RSTD#
MCLK
O
MCLK
I
24 2
HREQ
HREQ
HA7
HREQ
LOCK#
DRDY# ADS#
RS1# PLLTST MD1 MD32
1#
0#
HREQ
2#
H
HIT#
4#
HREQ
3#
H
TRDY#
BREQ
0#
BPRI#
DE-
FER#
HITM#
GND
VD14 VD13 GND VD15 VD12 GND N
N
GND VD9 VD10 VD11 VD8 GND P
P
VD6 VD4 VD7 VD5 VD3 VD0 R
R
VD2 VD1 VHS VCC3 TVD4 TVD6 T
T
VVS TVD7 VCLK TVD5 TVD2 VCC5 U
U
TVD0 TVD1 TVD3 TVCK TVHS VCCI V
V
VCC D VCC
W
GND
Y
V1
GND
AA
V2
NC NC NC NC
AB
NC
AC
REQ
AD
7#
GNT
AE
7#
GND
AF
TVVS XTLO INTA# VCC3 W
V1
VCC
VLF1 XTLI NC VCC3 Y7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Y20 VCC3 CS4# CS3# CS2# CS1# CS0#
V2
VLF2 NC NC NC GND VCC3 AD16 VCCI VCC3 GND GND GND VCC3 VCCI MD58 VCC3 GND VSUS2 MA0
GNT
0#
REQ
5#
GNT
5#
GNT
4#
REQ
4#
REQ
6#
GNT
6#
GNT
3#
GNT
2#
REQ
GND
REQ
REQ
GNT
0#
REQ
3#
1#
LOCK# AD27 AD20 AD19 FRM# STOP# AD13 AD8 AD2 AD1
2#
AD31 AD26 AD22 AD18 GND SERR# AD12 CBE0# AD3 AD0
1#
Video
Pins
TVout Pins
Pins PCI Pins
AD30 AD25 AD21
AD29 AD24 AD23 AD17 IRDY# AD15 AD11 AD6 AD4 PREQ# MD31 MD60 MD25 MD23 MD52 MD49 SUST# GND MA7 MA6 MA5
AD28 CBE3# GND CBE2# TRDY# AD14 AD9 GND
DEV
SEL#
N GND GND GND GND GND GND N
P GND GND GND GND GND GND P
R VCC3 GND GND GND GND VCC3 R
T GND VCC3 GND GND VCC3 GND T
U10 11 12 13 14 15 16 U17
PAR CBE1# AD10 AD7 AD5 PCLK MD63 MD29 MD56 MD54 MD20 MD18 VSUS3 MA1 MA4 MA3 MA2
PWR
PGNT# MD61 MD27 MD57 GND MD21 MD50 MD16
OK
PCI
MD30 MD59 MD26 MD55 MD22 MD19 MD48
RST#
PCK
MD62 MD28 GND MD24 MD53 MD51 MD17
RUN#
Mem
N GND MD39 MD37 MD7 MD38 MD6
P GND MD12 MD8 MD41 MD9 MD40
R MD44 MD10 MD43 MD11 MD42
T GND MD15 MD13 MD46 MD14 MD45
U VCC3
V VCCI VSUS3
W CS5# VSUS3
SCAS
A#
MD47 SWEA#
DQM
0
DQM
1
DQM
6
DQM
3
DQM 7 DQM 2 MA14
SWEB#
SWEC#
CKE2
CKE0
SCASC#
SCASB#
CKE1
GND
SRASB#
SRAS
A#
MA11 MA9 MA8
MA12
GND
CKE3
DQM 5 DQM
SRASC#
CKE5
CKE4
MA13
MA10
BA0
GND
BA1
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -12- Pin Diagram
4
Page 19
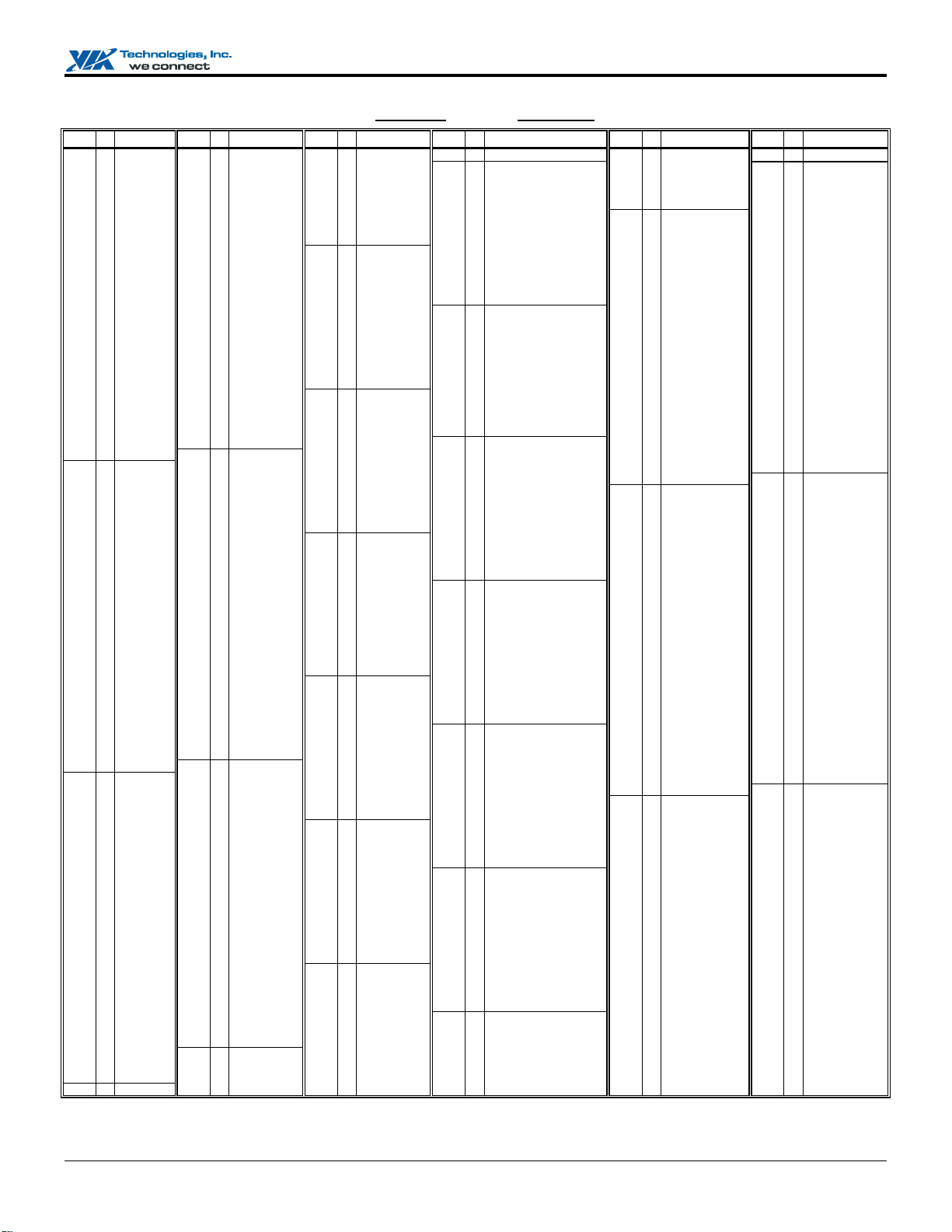
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
K
K
p
p
p
K
p
K
p
p
Q
p
K
Figure 2. VT8601A Pin List (Numerical Order)
Pin # Pin Name Pin # Pin Name Pin # Pin Name Pin # Pin Name Pin # Pin Names Pin # Pin Name
A03 IO NC
A04 IO NC D05 IO HD61 G22 I HCL
A05 IO NC D06 IO HD53 G23 I HLOCK# P04 IO VD11 Y26 O CS0# AD04 I REQ3#
A06 IO HD62 D07 IO HD54 G24 IO HIT# P05 IO VD08
A07 IO HD57 D08 IO HD47 G25 IO HTRDY#
A08 IO HD63 D09 IO HD42 G26 I HITM#
A09 P GND
A10 IO HD45 D11 IO HD36 H02 O PD01 P23 IO MD08 AA05 IO NC AD09 IO CBE2#
A11 IO HD38 D12 IO HD29 H03 O DE P24 IO MD41
A12 IO HD34 D13 IO HD25 H04 O PD05 P25 IO MD09
A13 IO HD31 D14 IO HD23 H05 O EVEE / P26 IO MD40 AA08 IO AD16 AD12 IO AD09
A14 IO HD16 D15 IO HD07
A15 IO HD13 D16 IO HD11
A16 IO HD03 D17 IO HD08
A17 IO HD12 D18 IO HD06 H23 IO RS0# R04 IO VD05
A18 P GND
A19 O CPURST# D20 IO HA30 H25 IO RS2# R06 IO VD00
A20 IO HA18 D21 IO HA17 H26 IO DBSY# R22 IO MD44
A21 IO HA20 D22 IO HA12 J01 O PD04 R23 IO MD10 AA19 IO MD58 AD20 IO MD21
A22 IO HA22
A23 IO HA10 D24 IO HA04 J03 O PD08 R25 IO MD11
A24 IO HA28 D25 IO HA14 J04 O PD07 R26 IO MD42
A25 IO HA03 D26 IO BNR# J05 O PD11 T01 IO VD02 AA23 O MA00 / strap AD24 O MA11 / stra
A26 P GND
B01 P GNDS
B02 P GND
B03 IO NC E04 A COMP J23 IO DRDY# T05 O TVD4 AB01 IO NC AE02 O GNT4#
B04 IO NC E05 IO HD56 J24 IO ADS# T06 O TVD6 AB02 IO NC AE03 O GNT3#
B05 IO NC E06 IO HD58 J25 O BREQ0#
B06 IO HD50 E07 IO HD46
B07 IO HD59 E08 IO HD40 K01 O PD12 T23 IO MD13 AB05 O GNT0# AE06 IO AD27
B08 IO HD48 E09 IO HD27 K02 O PD10 T24 IO MD46 AB06 IO AD30 AE07 IO AD20
B09 IO HD51 E10 IO HD39 K03 O PD13 T25 IO MD14 AB07 IO AD25 AE08 IO AD19
B10 IO HD44
B11 IO HD22
B12 IO HD32 E13 IO HD35 K06 O PD06 U02 O TVD7 AB10 IO PAR AE11 IO AD13
B13 IO HD33 E14 IO HD21
B14 IO HD19 E15 IO HD30 K22 I MCLKI U04 O TVD5 AB12 IO AD10 AE13 IO AD02
B15 IO HD24 E16 IO HD14 K23 IO RS1# U05 O TVD2 AB13 IO AD07 AE14 IO AD01
B16 IO HD02 E17 IO HD18 K24 I PLLTST
B17 IO HD10 E18 IO HD17 K25 IO MD01
B18 IO HD01 E19 IO HD00 K26 IO MD32 U22 O SCASA# AB16 IO MD63 AE17 IO MD59
B19 IO HA26 E20 IO HA24 L01 O PD17 U23 IO MD47 AB17 IO MD29 AE18 IO MD26
B20 IO HA29
B21 IO HA23 E22 O CPURSTD# L03 O PD18 U25 O SWEB#/ / CKE2 AB19 IO MD54 AE20 IO MD22
B22 IO HA25 E23 IO HA07
B23 IO HA21 E24 IO HREQ0# L05 O PD09 V01 O TVD0 AB21 IO MD18 AE22 IO MD48
B24 IO HA13 E25 IO HREQ4# L06 O PD14 V02 O TVD1
B25 IO HA05 E26 IO BPRI#
B26 IO HA06 F01 O EVDD
C01 P VCCS
C02 A RED F03 IO SCL L24 IO MD35
C03 IO NC F04 I ETST# L25 IO MD03
C04 IO NC F05 I SUSP L26 IO MD02
C05 IO NC
C06 IO HD60
C07 IO HD55 F08 IO HD52 M03 I IMIIN V25 O SCASB# / CKE3 AC05 I REQ0# AF06 IO AD26
C08 P GND F09 P VCCI
C09 IO HD41
C10 IO HD49
C11 IO HD43
C12 IO HD28
C13 IO HD26
C14 P GND F17 P VCC3
C15 IO HD20
C16 IO HD09
C17 IO HD05
C18 IO HD04
C19 P GND
C20 IO HA27 F23 IO HREQ1# N04 IO VD15 W26 O DQM4 AC18 IO MD25 AF19 IO MD24
C21 IO HA31 F24 IO HREQ2# N05 IO VD12
C22 IO HA19 F25 IO HREQ3#
C23 IO HA16 F26 IO DEFER#
C24 IO HA09 G01 O EBLT N22 IO MD39 Y04 I XLTI AC22 I SUST# AF23 O DQM7
C25 IO HA11 G02 O PD00 N23 IO MD37 Y05 IO NC
C26 IO HA08 G03 O FLM N24 IO MD07
D01 P VCCR
Center GND Pins (28 pins): L11, L13-14, L16, M12-15, N11-16, P11-16, R12-15, T11, T13-14, T16
Center VCC3 Pins (8 pins): L12, L15, M11, M16, R11, R16, T12, T15
D04 P GND G21 P VCC3
D10 IO HD37 H01 O PD02 P22 IO MD12 AA04 IO NC
H06 P VCC3
H21 P VCCA
H22 P VCCA
D19 IO HD15
D23 P GND
E01 O VSYNC
E02 O HSYNC
E03 A IRSET J22 O MCLKO
E11 P VTT
E12 P GTLREF
E21 P GTLREF
F02 IO SDA L23 IO MD33 V05 O TVHS AB25 O MA03 AE26 O MA10 / stra
F06 P GND
F07 P VCC3
F10 P VCC3
F12 P VCC3
F13 P GND M21 P GND
F14 P GND
F16 P GND
F18 P VCCI
F19 P VTT
F20 P VCC3
F21 P GND
F22 IO HA15
G04 O SCL
N25 IO MD38
H24 P GND
J02 O PD03 R24 IO MD43
J06 P VCCI
J21 P VCCI
J26 P GND
K04 O PD20 T26 IO MD45 AB08 IO AD21 AE09 IO FRAME#
K05 O PD16 U01 IO VVS AB09 IO DEVSEL# AE10 IO STOP#
K21 P VCC3
L02 O PD15 U24 O SWEA#/ AB18 IO MD56 AE19 IO MD55
L04 P VCC3
L21 P GNDA
L22 P GNDA
M01 O PD23 V23 O DQM0 AC03 IO REQ6# AF04 O GNT1#
M02 O IMIO V24 O SCASC# / CKE1
M04 O PD21
M05 O PD22
M06 O PD19
M22 IO MD34 W04 O XLTO AC10 IO IRDY# AF11 IO AD12
M23 IO MD00 W05 O INTA# AC11 IO AD15 AF12 IO CBE0#
M24 IO MD05
M25 IO MD36 W21 O CS5# AC13 IO AD06 AF14 IO AD00
M26 IO MD04
N01 IO VD14 W23 O DQM1 AC15 I PREQ# AF16 IO MD62
N02 IO VD13
N03 P GND
N06 P GND Y02 P VCCV2
N21 P GND
P02 IO VD09 Y24 O CS2# AD02 IO GNT5#
P03 IO VD10 Y25 O CS1# AD03 IO GNT6#
AA01 P GNDV2
P06 P GND
P21 P GND
R01 IO VD06
R02 IO VD04
R03 IO VD07
R05 IO VD03
T02 IO VD01 AA24 O SRASA# AD25 O MA09 / stra
T03 IO VHS AA25 O SRASB# / CKE5 AD26 O MA08 / stra
T04 P VCC3
T21 P GND
T22 IO MD15 AB04 IO NC AE05 IO LOCK#
U03 IO VCL
U06 P VCC5
U21 P VCC3
U26 O SWEC#/ / CKE0 AB20 IO MD20 AE21 IO MD19
V03 O TVD3 AB23 O MA01 / strap AE24 O MA12 / stra
V04 O TVCL
V06 P VCCI
V21 P VCCI
V22 P VSUS3
V26 P GND
W01 P VCCD
W02 P VCCV1
W03 O TVVS AC09 IO AD17 AF10 IO SERR#
W06 P VCC3
W22 P VSUS3
W24 P GND
W25 O D
Y01 P GNDV1
Y03 A VLF1 AC21 IO MD49 AF22 IO MD17
Y06 P VCC3
Y21 P VCC3
M5 AC17 IO MD60
AA02 A VLF2 AD06 IO AD28
AA03 IO NC AD07 IO CBE3#
AA06 P GND
AA07 P VCC3
AA09 P VCCI AD13 P GND
AA10 P VCC3
AA13 P GND
AA14 P GND
AA15 P GND
AA17 P VCC3
AA18 P VCCI AD19 P GND
AA20 P VCC3
AA21 P GND
AA22 P VSUS2
AA26 O SRASC# / CKE4 AE01 IO GNT7#
AB03 IO NC AE04 I REQ2#
AB11 IO CBE1# AE12 IO AD08
AB14 IO AD05 AE15 I RESET#
AB15 I PCLK AE16 IO MD30
AB22 P VSUS3
AB24 O MA04 AE25 O MA13 / stra
AB26 O MA02 / strap
AC01 IO NC AF02 I REQ4#
AC02 IO REQ5# AF03 O GNT2#
AC04 P GND
AC06 IO AD29 AF07 IO AD22
AC07 IO AD24 AF08 IO AD18
AC08 IO AD23
AC12 IO AD11 AF13 IO AD03
AC14 IO AD04 AF15 IO PCKRUN#
AC16 IO MD31 AF17 IO MD28
AC19 IO MD23 AF20 IO MD53
AC20 IO MD52 AF21 IO MD51
AC23 P GND
AC24 O MA07 / strap AF25 O MA14 / stra
AC25 O MA06
AD05 I REQ1#
AD08 P GND
AD10 IO TRDY#
AD11 IO AD14
AD14 I PWRO
AD15 O PGNT#
AD16 IO MD61
AD17 IO MD27
AD18 IO MD57
AD21 IO MD50
AD22 IO MD16
AD23 O DQM6
AE23 O DQM3
AF01 P GND
AF05 IO AD31
AF09 P GND
AF18 P GND
AF24 O DQM2
AF26 P GND
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -13- Pin Lists
Page 20
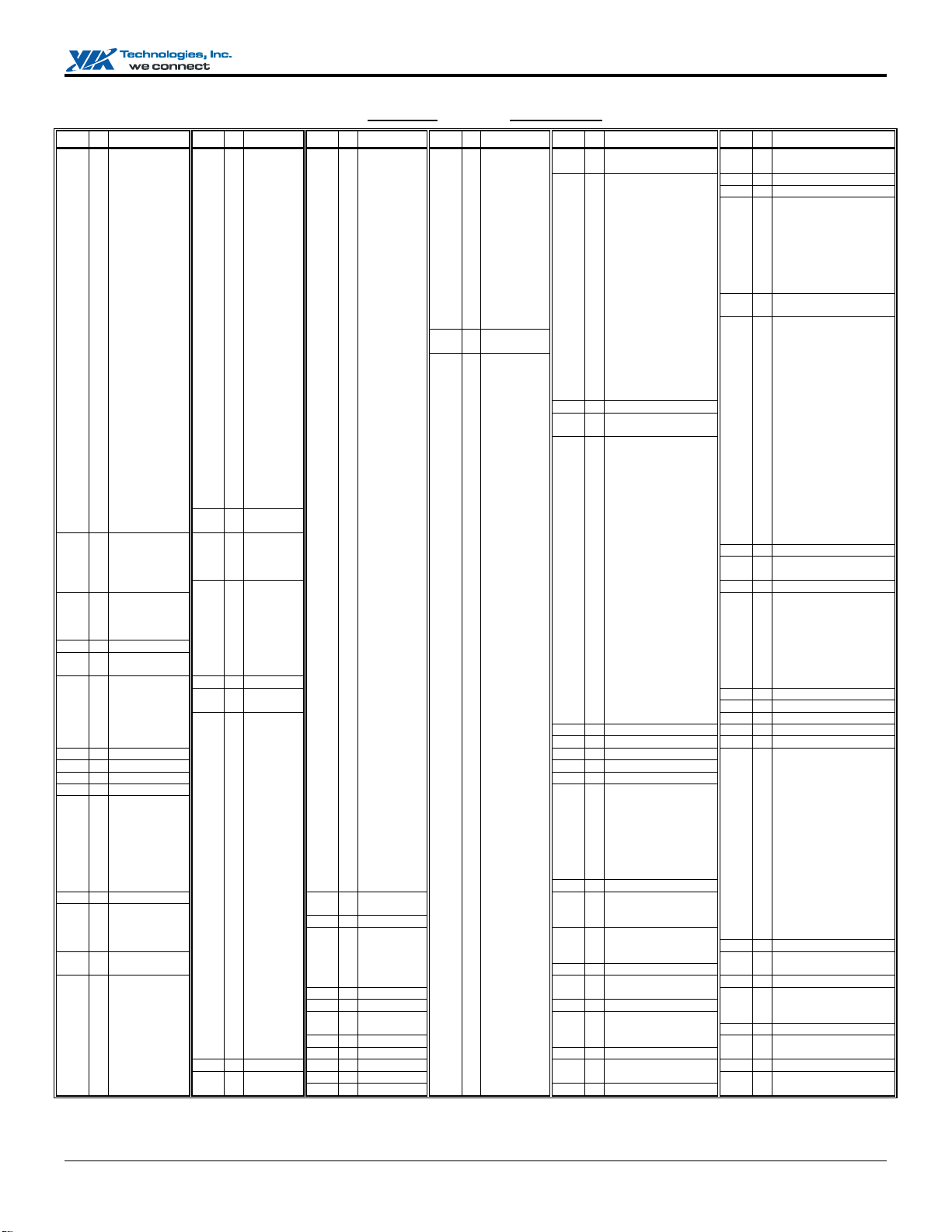
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
K
K
K
R
K
K
K
Q
K
Figure 3. VT8601A Pin List (Alphabetical Order)
Pin # Pin Name Pin # Pin Name Pin # Pin Name Pin # Pin Name Pin # Pin Names Pin # Pin Name
AE14 IO AD01
AE13 IO AD02
AF13 IO AD03
AC14 IO AD04
AB14 IO AD05
AC13 IO AD06
AB13 IO AD07
AE12 IO AD08
AD12 IO AD09
AB12 IO AD10
AC12 IO AD11
AF11 IO AD12
AE11 IO AD13
AD11 IO AD14
AC11 IO AD15
AA08 IO AD16
AC09 IO AD17
AF08 IO AD18
AE08 IO AD19
AE07 IO AD20
AB08 IO AD21
AF07 IO AD22
AC08 IO AD23
AC07 IO AD24
AB07 IO AD25
AF06 IO AD26
AE06 IO AD27
AD06 IO AD28
AC06 IO AD29
AB06 IO AD30
AF05 IO AD31
J24 IO ADS#
D02 A BLUE
D26 IO BNR#
E26 IO BPRI#
J25 O BREQ0# AB05 O GNT0# A11 IO HD38 AE21 IO MD19 K01 O PD12
AF12 IO CBE0# AF04 O GNT1# E10 IO HD39 AB20 IO MD20 K03 O PD13
AB11 IO CBE1# AF03 O GNT2# E08 IO HD40 AD20 IO MD21 L06 O PD14
AD09 IO CBE2# AE03 O GNT3# C09 IO HD41 AE20 IO MD22 L02 O PD15
AD07 IO CBE3# AE02 O GNT4# D09 IO HD42 AC19 IO MD23 K05 O PD16
E04 A COMP AD02 O GNT5# C11 IO HD43 AF19 IO MD24 L01 O PD17
A19 O CPURST# AD03 O GNT6# B10 IO HD44 AC18 IO MD25 L03 O PD18
E22 O CPURSTD# AE01 O GNT7# A10 IO HD45 AE18 IO MD26 M06 O PD19
Y26 O CS0# D03 A GRN E07 IO HD46 AD17 IO MD27 K04 O PD20
Y25 O CS1#
Y24 O CS2#
Y23 O CS3# A25 IO HA03 C10 IO HD49 AE16 IO MD30 M01 O PD23
Y22 O CS4# D24 IO HA04 B06 IO HD50 AC16 IO MD31 AD15 O PGNT#
W21 O CS5# B25 IO HA05 B09 IO HD51 K26 IO MD32 K24 I PLLTST U03 IO VCL
H26 IO DBSY# B26 IO HA06 F08 IO HD52 L23 IO MD33 AC15 I PREQ# R06 IO VD00
H03 O DE E23 IO HA07 D06 IO HD53 M22 IO MD34 AD14 I PWRO
F26 IO DEFER# C26 IO HA08 D07 IO HD54 L24 IO MD35 C02 A RED T01 IO VD02
AB09 IO DEVSEL# C24 IO HA09 C07 IO HD55 M25 IO MD36 AC05 I REQ0# R05 IO VD03
V23 O DQM0 A23 IO HA10 E05 IO HD56 N23 IO MD37 AD05 I REQ1# R02 IO VD04
W23 O DQM1 C25 IO HA11 A07 IO HD57 N25 IO MD38 AE04 I REQ2# R04 IO VD05
AF24 O DQM2 D22 IO HA12 E06 IO HD58 N22 IO MD39 AD04 I REQ3# R01 IO VD06
AE23 O DQM3 B24 IO HA13 B07 IO HD59 P26 IO MD40 AF02 I REQ4# R03 IO VD07
W26 O DQM4 D25 IO HA14 C06 IO HD60 P24 IO MD41 AC02 I REQ5# P05 IO VD08
W25 O DQM5 F22 IO HA15 D05 IO HD61 R26 IO MD42 AC03 I REQ6# P02 IO VD09
AD23 O DQM6 C23 IO HA16 A06 IO HD62 R24 IO MD43 AD01 I REQ7# P03 IO VD10
AF23 O DQM7 D21 IO HA17 A08 IO HD63 R22 IO MD44 AE15 I RESET# P04 IO VD11
J23 IO DRDY# A20 IO HA18 G24 IO HIT# T26 IO MD45 H23 IO RS0# N05 IO VD12
G01 O EBLT C22 IO HA19 G26 I HITM# T24 IO MD46 K23 IO RS1# N02 IO VD13
F04 I ETST# A21 IO HA20 G23 I HLOCK# U23 IO MD47 H25 IO RS2# N01 IO VD14
F01 O EVDD B23 IO HA21 E24 IO HREQ0# AE22 IO MD48 U22 O SCASA# N04 IO VD15
H05 O EVEE A22 IO HA22 F23 IO HREQ1# AC21 IO MD49 V25 O SCASB# / CKE3 T03 IO VHS
G03 O FLM B21 IO HA23 F24 IO HREQ2# AD21 IO MD50 V24 O SCASC# / CKE1 Y03 A VLF1
AE09 IO FRAME# E20 IO HA24 F25 IO HREQ3# AF21 IO MD51 G04 O SCL
A09 P GND
A18 P GND
A26 P GND
B02 P GND
C08 P GND
C14 P GND
C19 P GND
D04 P GND
D23 P GND
F06 P GND
Center GND Pins (28 pins): L11, L13-14, L16, M12-15, N11-16, P11-16, R12-15, T11, T13-14, T16
Center VCC3 Pins (8 pins): L12, L15, M11, M16, R11, R16, T12, T15
F14 P GND
F16 P GND
F21 P GND
H24 P GND
J26 P GND
M21 P GND
N03 P GND
N06 P GND
N21 P GND
P01 P GND
P06 P GND
P21 P GND
T21 P GND
V26 P GND
W24 P GND
AA06 P GND
AA13 P GND
AA14 P GND
AA15 P GND
AA21 P GND
AC04 P GND
AC23 P GND
AD08 P GND
AD13 P GND
AD19 P GND
AF01 P GND
AF09 P GND
AF18 P GND
AF26 P GND
L21 P GNDA
L22 P GNDA
A01 P GNDRGB
B01 P GNDS
Y01 P GNDV1
AA01 P GNDV2
E12 P GTLREF
E21 P GTLREF
B22 IO HA25 E25 IO HRE
B19 IO HA26 E02 O HSYNC AF20 IO MD53 F02 IO SDA
C20 IO HA27 G25 IO HTRDY# AB19 IO MD54 AF10 IO SERR#
A24 IO HA28 M02 O IMIO AE19 IO MD55 AA24 O SRASA#
B20 IO HA29 M03 I IMIIN AB18 IO MD56 AA25 O SRASB# / CKE5 E01 O VSYNC
D20 IO HA30 W05 O INTA# AD18 IO MD57 AA26 O SRASC# / CKE4
C21 IO HA31 AC10 IO IRDY# AA19 IO MD58 AE10 IO STOP#
G22 I HCL
E19 IO HD00 AE05 IO LOCK# AC17 IO MD60 AC22 I SUST# Y04 I XLTI
B18 IO HD01 G05 O LP AD16 IO MD61 U24 O SWEA# W04 O XLTO
A16 IO HD03 AB23 O MA01 / strapAB16 IO MD63 U26 O SWEC#/ / CKE0
C18 IO HD04 AB26 O MA02 / strapA02 - NC AD10 IO TRDY#
C17 IO HD05 AB25 O MA03 A03 - NC V04 O TVCL
D18 IO HD06 AB24 O MA04 A04 - NC V01 O TVD0
D15 IO HD07 AC26 O MA05 A05 - NC V02 O TVD1
D17 IO HD08 AC25 O MA06 B03 - NC U05 O TVD2
C16 IO HD09 AC24 O MA07 / strapB04 - NC V03 O TVD3
B17 IO HD10 AD26 O MA08 / strapB05 - NC T05 O TVD4
D16 IO HD11 AD25 O MA09 / strapC03 - NC U04 O TVD5
A17 IO HD12 AE26 O MA10 / strapC04 - NC T06 O TVD6
A15 IO HD13 AD24 O MA11 / strapC05 - NC U02 O TVD7
E16 IO HD14 AE24 O MA12 / strapY05 - NC V05 O TVHS
D19 IO HD15 AE25 O MA13 / strapAA03 - NC W03 O TVVS
A14 IO HD16 AF25 O MA14 / strapAA04 - NC
E18 IO HD17 K22 I MCLKI AA05 - NC
E17 IO HD18 J22 O MCLKO AB01 - NC
B14 IO HD19 M23 IO MD00 AB02 - NC
C15 IO HD20 K25 IO MD01 AB03 - NC
E14 IO HD21 L26 IO MD02 AB04 - NC
B11 IO HD22 L25 IO MD03 AC01 - NC
D14 IO HD23 M26 IO MD04 AB10 IO PAR
B15 IO HD24 M24 IO MD05 AF15 IO PCKRUN#
D13 IO HD25 N26 IO MD06 AB15 I PCL
C13 IO HD26 N24 IO MD07 G02 O PD00
E09 IO HD27 P23 IO MD08 H02 O PD01
C12 IO HD28 P25 IO MD09 H01 O PD02
D12 IO HD29 R23 IO MD10 J02 O PD03
E15 IO HD30 R25 IO MD11 J01 O PD04
A13 IO HD31 P22 IO MD12 H04 O PD05
B12 IO HD32 T23 IO MD13 K06 O PD06
B13 IO HD33 T25 IO MD14 J04 O PD07
A12 IO HD34 T22 IO MD15 J03 O PD08
E13 IO HD35 AD22 IO MD16 L05 O PD09
D11 IO HD36 AF22 IO MD17
D10 IO HD37 AB21 IO MD18 J05 O PD11
D08 IO HD47 AF17 IO MD28 M04 O PD21
B08 IO HD48 AB17 IO MD29 M05 O PD22
4# AC20 IO MD52 F03 IO SCL
E03 A IRSET AE17 IO MD59 F05 I SUSP U01 IO VVS
02 O PD10
F07 P VCC3
F10 P VCC3
F12 P VCC3
F17 P VCC3
F20 P VCC3
G06 P VCC3
G21 P VCC3
H06 P VCC3
K21 P VCC3
L04 P VCC3
T04 P VCC3
U21 P VCC3
W06 P VCC3
Y06 P VCC3
Y21 P VCC3
AA07 P VCC3
AA10 P VCC3
AA17 P VCC3
AA20 P VCC3
U06 P VCC5
H21 P VCCA
H22 P VCCA
W01 P VCCD
F09 P VCCI
F18 P VCCI
J06 P VCCI
J21 P VCCI
V06 P VCCI
V21 P VCCI
AA09 P VCCI
AA18 P VCCI
D01 P VCC
C01 P VCCS
W02 P VCCV1
Y02 P VCCV2
T02 IO VD01
AA02 A VLF2
AA22 P VSUS2
V22 P VSUS3
W22 P VSUS3
AB22 P VSUS3
E11 P VTT
F19 P VTT
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -14- Pin Lists
Page 21

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Pin Descriptions
Table 1. VT8601A Pin Descriptions
CPU Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
HA[31:3]#
HD[63:0]#
ADS#
BNR#
BPRI#
DBSY#
DEFER#
DRDY#
HIT#
HITM#
HLOCK#
BREQ0#
HREQ[4:0]#
HTRDY#
RS[2:0]#
CPURST#
CPURSTD#
see pin list IO Host Address Bus. Connect to the address bus of the host CPU. These pins are inputs
during CPU cycles, but are driven by the VT8601A during cache snooping operations.
see pin list IO Host CPU Data. These signals are connected to the CPU data bus.
J24 IO Address Strobe. The CPU asserts ADS# in T1 of the CPU bus cycle.
D26 IO Block Next Request. Used to block the current request bus owner from issuing new
requests. This signal is used to dynamically control the processor bus pipeline depth.
E26 IO Priority Agent Bus Request. The owner of this signal will always be the next bus owner.
This signal has priority over symmetric bus requests and causes the current symmetric
owner to stop issuing new transactions unless the HLOCK# signal is asserted. The
VT82C693 drives this signal to gain control of the processor bus.
H26 IO Data Bus Busy. Used by the data bus owner to hold the data bus for transfers requiring
more than one cycle.
F26 IO Defer. The VT8601A uses a dynamic deferring policy to optimize system performance.
The VT8601A also uses the DEFER# signal to indicate a processor retry response.
J23 IO Data Ready. Asserted for each cycle that data is transferred.
G24 IO Hit. Indicates that a cacheing agent holds an unmodified version of the requested line.
Also driven in conjunction with HITM# by the target to extend the snoop window.
G26 I Hit Modified. Asserted by the CPU to indicate that the address presented with the last
assertion of EADS# is modified in the L1 cache and needs to be written back.
G23 I Host Lock. All CPU cycles sampled with the assertion of HLOCK# and ADS# until the
negation of HLOCK# must be atomic.
J25 O Bus Request 0. Bus request output to CPU.
E25, F25,
F24, F23,
E24
G25 IO Host Target Ready. Indicates that the target of the processor transaction is able to enter
H25, K23,
H23
A19 O CPU Reset. Reset output to CPU
E22 O CPU Reset Delayed. CPU Reset output delayed by 2T.
IO Request Command. Asserted during both clocks of the request phase. In the first clock,
the signals define the transaction type to a level of detail that is sufficient to begin a snoop
request. In the second clock, the signals carry additional information to define the
complete transaction type.
the data transfer phase.
IO Response Signals. Indicates the type of response per the table below:
RS[2:0]#
000 Idle State
001 Retry Response
010 Defer Response
011 Reserved
100 Hard Failure
101 Normal Without Data
110 Implicit Writeback
111 Normal With Data
Response type
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -15- Pin Descriptions
Page 22
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
DRAM Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
MD[63:0]
MA[14:0]
/ Strap Options
CKE5# / SRASB#,
CKE4# / SRASC#,
CKE3# / SCASB#,
CKE2# / SWEB#,
CKE1# / SCASC#,
CKE0# / SWEC#
CS[5-0]#
DQM[7:0]
SRASA#,
SRASB# / CKE5,
SRASC# / CKE4
SCASA#,
SCASB# / CKE3
SCASC# / CKE1
SWEA#,
SWEB# / CKE2,
SWEC# / CKE0
Note: Clocking of the memory subsystem uses memory clock (MCLK); see the clock pin group at the end of the pin descriptions
section for descriptions of the clock pins.
Note: Connect all memory interface pins except MD to the DRAM modules through 22Ω series resistors (see the Apollo PLE133
Design Guide” for more specific connection details and PCB layout recommendations).
see pin list IO
AF25, AE25, AE24,
AD24, AE26, AD25,
AD26, AC24, AC25,
AC26, AB24, AB25,
AB26, AB23, AA23
AA25,
AA26,
V25,
U25,
V24,
U26
W21, Y22, Y23,
Y24, Y25, Y26
AF23, AD23, W25,
W26, AE23, AF24,
W23, V23
AA24,
AA25,
AA26
U22,
V25,
V24
U24,
U25,
U26
Memory Data.
O / I Memory Address. DRAM address lines. These pins are also used for
power-up strapping options (sampled on the rising edge of RESET#):
MA14,12 Rx68[1-0] CPU FSB Freq (0=66, 1=100, 2=rsvd, 3=133)
MA13 Rx52[7] GTL I/O Buffer Pullup (L=Enable, H=Disable)
MA11 Rx50[7] In-Order Queue Depth (L=4-level, H=1-level)
MA10-9 North Bridge Clock Delay (0-3 Clocks)
MA8, 2 Graphics Clock Select (0=Normal, 1-3=Test)
MA7 Graphics Test Mode (L=Normal, H=Test)
MA1-0 Graphics Clock Delay (0-3 Clocks)
All pins have internal pull-downs for default low (L).
Strap high (H) using 4.7KΩ TO VCC3.
IO SDRAM Clock Enable. Clock enables 5-0 may be connected to the
DRAM modules in any order. Each DRAM module requires 2 clock
enables.
Note: These pins are powered by VSUS
O Chip Select. One per bank (powered by VSUS
O Data Mask. One per byte lane (powered by VSUS
O Row Address Command Indicator. For support of up to three
Synchronous DRAM DIMM slots (these are copies of the same logical
signal). “A” controls banks 0-1 (module 0), “B” controls banks 2-3
(module 1), and “C” controls banks 4-5 (module 2).
O Column Address Command Indicator. For support of up to three
Synchronous DRAM DIMM slots (these are copies of the same logical
signal). “A” controls banks 0-1 (module 0), “B” controls banks 2-3
(module 1), and “C” controls banks 4-5 (module 2).
O Write Enable Command Indicator. For support of up to three
Synchronous DRAM DIMM slots (these are copies of the same logical
signal). “A” controls banks 0-1 (module 0), “B” controls banks 2-3
(module 1), and “C” controls banks 4-5 (module 2). Note: These pins
are powered by VSUS.
)
)
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -16- Pin Descriptions
Page 23

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
PCI Bus Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
AD[31:0]
CBE[3:0]#
PAR
FRAME#
IRDY#
TRDY#
STOP#
DEVSEL#
LOCK#
SERR#
PREQ#
PGNT#
REQ[7:0]#
GNT[7:0]#
INTA#
Note: Clocking of the PCI interface is performed with PCLK; see the clock pin group at the end of the pin descriptions section for
descriptions of the clock input pins.
see pin list IO Address/Data Bus. The standard PCI address and data lines. The address is
driven with FRAME# assertion and data is driven or received in following
cycles.
AD7, AD9, AB11,
AF12
AB10 IO Parity. A single parity bit is provided over AD[31:0] and C/BE[3:0].
AE9 IO Frame. Assertion indicates the address phase of a PCI transfer. Negation
AC10 IO
AD10 IO
AE10 IO Stop. Asserted by the target to request the master to stop the current
AB9 IO Device Select. This signal is driven by the PLE133 when a PCI initiator is
AE5 IO
AF10 IO System Error. The PLE133 will pulse this signal when it detects a system
AC15 I South Bridge Request. This signal comes from the South Bridge. PREQ# is
AD15 O South Bridge Grant. This signal driven by the PLE133 to grant PCI access to
AD1, AC3, AC2, AF2,
AD4, AE4, AD5, AC5
AE1, AD3, AD2,
AE2, AE3, AF3, AF4,
AB5
W5 O PCI Interrupt Out. INTA# is an asynchronous active low output used to
IO Command/Byte Enables. Commands are driven with FRAME# assertion.
Byte enables corresponding to supplied or requested data are driven on
following clocks.
indicates that one more data transfer is desired by the cycle initiator. 10KΩ
pullup to VCC3.
Initiator Ready. Asserted when initiator is ready for data transfer. 10KΩ
pullup to VCC3.
Target Ready. Asserted when target is ready for data transfer. 10KΩ pullup to
VCC3.
transaction. 10KΩ pullup to VCC3.
attempting to access main memory. It is an input when the PLE133 is acting as
a PCI initiator. 10KΩ pullup to VCC3.
Lock. Used to establish, maintain, and release resource lock. 10KΩ pullup to
VCC3.
error condition (10KΩ pullup to VCC3).
the South Bridge request for the PCI bus. 10KΩ pullup to VCC3.
the South Bridge. 10KΩ pullup to VCC3.
I
PCI Master Request. PCI master requests for use of the PCI bus. 2.2KΩ
pullup to VCC5.
O PCI Master Grant. Permission is given to the master to use the PCI bus.
2.2KΩ pullup to VCC3.
signal an event that requires handling. It is driven by the integrated graphics
controller.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -17- Pin Descriptions
Page 24
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Clock / Reset Control
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
HCLK
MCLKI
MCLKO
PCLK
PCKRUN#
XLTI
XLTO
RESET#
CPURST#
CPURSTD#
PWROK
SUST#
SUSP
G22 I Host Clock. This pin receives the host CPU clock. This clock is used by all logic in
the host CPU domain. It is driven by the external clock synthesizer.
K22 I Memory Clock In. This clock is used by internal clock logic to maintain the proper
phase relationship with MCLKO. It is driven by the external clock synthesizer.
J22 O Memory Clock Out. Created on-chip from MCLKI and used by the memory
controller as a timing reference for creation of all memory timing sequences. It is
connected to the external clock chip for use in maintaining proper phase relationships.
AB15 I PCI Clock. This clock is used by all on-chip logic in the PCI clock domain. This input
must be 33 MHz maximum to comply with PCI specification requirements and must be
synchronous with the host CPU clock (HCLK) with an HCLK:PCLK frequency ratio of
2:1 (66MHz CPU clock) or 3:1 (100 MHz CPU clock). The PCI clock needs to be
controlled to within 1.5 ± 0.5 nsec relative to the host CPU clock (CPU leads).
AF15 IO PCI Clock Run. For implementation of PCI bus clock control for low-power PCI bus
operation. Refer to the “PCI Mobile Design Guidelines” and “Apollo PLE133 Design
Guide” documents for additional information.
Y4 I Crystal Input. 14.31818 MHz for the video clock synthesizer reference. Connect to a
14.31818 MHz clock source if a crystal not used. Connect to main ground plane GND
with 10Pf if using a crystal.
W4 O Crystal Output. 14.31818 MHz for the video clock synthesizer reference. Leave open
if a clock source is used instead of a crystal. Connect to main ground plane GND with
10Pf if using a crystal.
AE15 I Reset. Driven from the South Bridge PCIRST# signal. When asserted (low), this
signal resets the PLE133 and sets all register bits to the default value. This signal also
connects to the PCI bus (South Bridge RESET drives the ISA bus if implemented). The
rising edge of this signal is used to sample all power-up strap options (see memory
interface MA pins).
A19 O CPU Reset. CPU Reset output to the host CPU.
E22 O CPU Reset Delayed 2T. Alternate CPU Reset output to the host CPU
AD14 I Power OK. Connect to South Bridge and Power Good circuitry.
AC22 I Suspend Status. For implementation of the Suspend-to-DRAM feature. Input logic for
this pin is powered by VSUS. Connect to the South Bridge SUST# pin or to a 10KΩ
pullup to VSUS if not used.
F5 I Suspend. Used to put the integrated graphics controller into suspend state. Input logic
for this pin is powered by VCC3. Connect to South Bridge GPO pin or to a 10KΩ
pullup to VCC3 if not used.
Miscellaneous
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
ETST#
IMIO
IMIIN
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -18- Pin Descriptions
F4 I
M2 O IMI Out. Leave open.
M3 I
Test Mode Enable. 4.7KΩ pullup to VCC3 for normal operation.
IMI In. 4.7KΩ pullup to VCC3.
Page 25
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
CRT Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
RED
GRN
BLUE
HSYNC
VSYNC
SDA
SCL
C2 A
D3 A Green. Green analog output to the CRT. Connect same as RED.
D2 A Blue. Blue analog output to the CRT. Connect same as RED.
E2 O Horizontal Sync. Digital horizontal sync output to the CRT. Also used (with VSYNC)
E1 O Vertical Sync. Digital vertical sync output to the CRT. Also used (with HSYNC) to
F2 IO DDC Data/Address. Serial I
F3 IO DDC Clock. Serial I
Red. Red analog output to the CRT. Connect 75Ω load resistor to GNDR (RGB Return)
and connect to VGA connector through a series ferrite bead and 10pF capacitors to GNDR
on both input and output sides of the bead (see “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide”).
to signal power management state information to the CRT per the VESA™ DPMS™
standard. Connect to VGA connector through a series 47Ω resistor and 120pF capacitor
to ground (see “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide”).
signal power management state information to the CRT per the VESA™ DPMS™
standard. Connect to VGA connector through a series 47Ω resistor and 120pF capacitor
to ground (see “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide”).
Connect this pin to VCC5 through a 4.7KΩ pullup. Connect to the VGA connector only
(pin 12 of the connector). Connect through a ferrite bead and 120pF capacitor to ground
(on the output side of the bead). Refer to the “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide” for
additional information.
pin to VCC5 through a 4.7KΩ pullup. Connect to the VGA connector only (pin 15 of the
VGA connector). Connect through a ferrite bead and 120pF capacitor to ground (on the
output side of the bead). Refer to the “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide” for additional
information.
2
C protocol for VESA™ DDC2B signaling to the CRT. Connect this
2
C protocol for VESA™ DDC2B signaling to the CRT.
DFP Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
PD[23-0]
SCLK
DE
LP
FLM
EVDD
EVEE
EBLT
Note: Connect SHFCLK, DE, LP, and FLM to external TMDS transmitters through series 22Ω resistors. See the “Apollo PLE133
Design Guide” for DFP interface design examples and additional information.
(see pin list) O Panel Data. Digital pixel data outputs to the panel.
G4 O Shift Clock. Clock for transferring digital pixel data.
H3 O Data Enable. Indicates valid data on PD[23-0].
G5 O Line Pulse. Digital monitor equivalent of HSYNC.
G3 O First Line Marker. Digital monitor equivalent of VSYNC.
F1 O
H5 O
G1 O
Enable Panel VDD Power.
Enable Panel VEE Power.
Enable Panel Backlight.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -19- Pin Descriptions
Page 26
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
TV Input / Video Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
VD[15-0]
VHS
VVS
VCLK
Note: Refer to the “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide” for video interface design examples.
N4, N1, N2, N5, P4, P3, P2, P5,
R3, R1, R4, R2, R5, T1, T2, R6
T3 IO Video Horizontal Sync. Connect to TV decoder if used.
U1 IO Video Vertical Sync. Connect to TV decoder if used.
U3 IO
IO
Video Capture / Playback Data.
Video Clock. Connect to TV decoder through a series 22Ω resistor.
TV Output Interface
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
TVD[7-0]
TVHS
TVVS
TVCLK
Note: Refer to the “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide” for TV interface design examples.
U2, T6, U4, T5, V3, U5, V2, V1 O TV Output Data. Connect to TV encoder if used.
V5 O TV Horizontal Sync. Connect to TV encoder if used.
W3 O TV Vertical Sync. Connect to TV encoder if used.
V4 O
TV Clock. Connect to TV encoder through a series 22Ω resistor.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -20- Pin Descriptions
Page 27
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Clock Power / Ground and Filtering
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
VCCA
GNDA
VCCV1
GNDV1
VLF1
VCCV2
GNDV2
VLF2
PLLTST
H21, H22 P Power for North Bridge Clock Circuitry (2.5V ±5%). Connect to VCCI through a
ferrite bead and decouple to GNDA with 0.001Uf and 0.1Uf ceramic and 10Uf tantalum
capacitors (see “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide”).
L21, L22 P Ground for North Bridge Clock Circuitry. Connect to main ground plane GND
through a ferrite bead. (see “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide”).
W2 P Power for Video Clock Synthesizer 1 Analog Circuitry (2.5V ±5%). Connect to
VCCI through a ferrite bead and decouple to GNDV1 with 0.001Uf and 0.1Uf ceramic
and 10Uf tantalum capacitors (see “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide”).
Y1 P Ground for Video Clock Synthesizer 1. Connect to main ground plane through a
ferrite bead.
Y3 A Low Pass Filter Capacitor for Video Clock Synthesizer 1. Connect to GNDV1
through a 560Pf capacitor.
Y2 P Power for Video Clock Synthesizer 2 Analog Circuitry (2.5V ±5%). Connect to
VCCI through a ferrite bead and decouple to GNDV2 with 0.001Uf and 0.1Uf ceramic
and 10Uf tantalum capacitors (see “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide”).
AA1 P Ground for Video Clock Synthesizer 2. Connect to main ground plane through a
ferrite bead.
AA2 A Low Pass Filter Capacitor for Video Clock Synthesizer 2. Connect to GNDV2
through a 560Pf capacitor.
K24 I PLL Test. Pull down with 4.7K resistor for normal operation.
RAMDAC Output Power / Ground and Analog Control
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
VCCS
GNDS
COMP
IRSET
GNDRGB
Commonly Used Prefix / Suffix Letters in Signal Names:
I = Internal Logic A = North Bridge Clock Synthesizer
M = Memory (SDRAM) Interface V1 = Video Clock Synthesizer PLL1
H = Host CPU Interface V2 = Video Clock Synthesizer PLL2
P = PCI Bus Interface D = Video Clocks Digital Data Path
G = AGP Bus (internal in PLE133) R = RAMDAC Digital Data Path
GM = Graphics Memory Interface S = RAMDAC Current Source
U (or USB) = USB (Universal Serial Bus) RGB = Analog Video Out Return
H (or HWM) = Hardware Monitoring TV = TV Out
SUS = Suspend Power V = TV In / Video Capture
C1 P Power for RAMDAC Current Source Circuitry (2.5V ±5%). Connect to VCCI
through a ferrite bead and decouple to GNDS with 0.001uF and 0.1uF ceramic and
10uF tantalum capacitors (see “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide”).
B1 P Ground for RAMDAC Current Source Circuitry. Connect to main ground plane
through a ferrite bead.
E4 A Compensation Capacitor. RAMDAC analog control. Connect to VCCS using a 0.1
uF capacitor.
E3 A RAMDAC Current Set Point Resistor. RAMDAC analog control. Connect to
GNDS through a 360Ω 1% resistor.
A1 P RGB Video Output Return. Connection point for the RGB load resistors. Also used
as a shield for the RGB video output traces to the VGA display connector. Connects to
RGB return pins 6, 7, and 8 of the VGA connector. Connect to main ground plane
through a ferrite bead. Refer to the “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide” for more specific
connection and PCB layout details.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -21- Pin Descriptions
Page 28
Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Digital Power and Ground
Signal Name Pin # I/O Signal Description
VCC5
VCC3
VSUS3
VSUS2
VCCI
VCCD
VCCR
VTT
GTLREF
GND
NC
U6 P Power for Display / Video Interfaces (5V ±5%). Power for CRT
H/VSYNC, DFP interface, video interface, and TV interface. Used to
provide adequate output voltage swing for driving external video
devices. Also used to provide 5V input tolerance from those
interfaces.
F7, F10, F12, F17, F20, G6,
G21, H6, K21, L4, L12, L15,
M11, M16, R11, R16, T4, T12,
T15, U21, W6, Y6, Y21, AA7,
AA10, AA17, AA20
V22, W22, AB22 P Suspend Power (3.3V ±5%). Power for memory interface signals
AA22 P Suspend Power (2.5V ±5%). Connect to VCCI if suspend functions
F9, F18, J6, J21, V6, V21,
AA9, AA18
W1 P Power for Video Clock Synthesizer Digital Logic (2.5V ±5%).
D1 P Power for RAMDAC Video Output Digital Logic (2.5V ±5%).
E11, F19 P CPU Interface Termination Voltage (1.5V ±10%).
E12, E21 P CPU Interface GTL+ Voltage Reference. 2/3 VTT ±2%. Derived
A9, A18, A26, B2, C8, C14,
C19, D4, D23, F6, F13-F14,
F16, F21, H24, J26, L11, L13,
L14, L16, M12-M15, M21,
N3, N6, N11-N16, N21, P1, P6,
P11-P16, P21, R12-R15, T11,
T13, T14, T16, T21, V26,
W24, AA6, AA13-AA15,
AA21, AC4, AC23, AD8,
AD13, AD19, AF1, AF9,
AF18, AF26
A2-A5, B3-B5, C3-C5, Y5,
AA3-AA5, AB1-AB4, AC1
P Power for On-Board Interfaces (3.3V ±5%). Power for host CPU /
L2 Cache interface, PCI bus interface, and memory interface (except
pins listed below under VSUS).
SRASC#, SCASC#, SWEC#, SWEB#, RAS[5-0]#, CAS[7-0]#, and
SUST#. Connect to VCC3 if suspend functions are not implemented.
are not implemented.
P Power for On-Chip Internal Logic (2.5V ±5%).
Connect to VCCI through a ferrite bead and decouple to main ground
plane GND with 0.001uF and 0.1uF ceramic and 10uF tantalum
capacitors (see “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide”).
Connect to VCCI through a ferrite bead and decouple to main ground
plane GND with 0.001uF and 0.1uF ceramic and 10uF tantalum
capacitors (see “Apollo PLE133 Design Guide”).
from the termination voltage to the pullup resistors. Determines the
noise margin for the host CPU interface signals. Internally connects to
the GTL
P Ground. Connect to primary PCB ground plane.
-
No Connect.
+
sense amp on each GTL+ input or I/O pin.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -22- Pin Descriptions
Page 29

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
REGISTERS
Register Overview
The following tables summarize the configuration and I/O
registers of the PLE133. These tables also document the
power-on default value (“Default”) and access type (“Acc”)
for each register. Access type definitions used are RW
(Read/Write), RO (Read/Only), “—” for reserved / used
(essentially the same as RO), and RWC (or just WC) (Read /
Write 1’s to Clear individual bits). Registers indicated as RW
may have some read/only bits that always read back a fixed
value (usually 0 if unused); registers designated as RWC or
WC may have some read-only or read write bits (see
individual register descriptions following these tables for
details). All offset and default values are shown in
hexadecimal unless otherwise indicated.
Register Summary Tables
Table 2. Register Summary
I/O Ports
Port # I/O Port Default Acc
-
-
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -23- Register Summary Tables
Page 30

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
g
Device 0 Bus 0 Registers - Host Bridge
PCI Configuration Registers
Offset Confi
uration Header Default Acc
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Device-Specific Configuration Registers
Offset CPU Interface Control Default Acc
-
-
-
-
Offset DRAM Control Default Acc
-
-
-
-
-
Device-Specific Configuration Registers (continued)
Offset PCI Bus Control Default Acc
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Offset GART/TLB Control Default Acc
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Offset AGP Control Default Acc
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Offset BIOS Scratch Default Acc
F0-F7 BIOS Scratch 00 RW
Offset Miscellaneous Control Default Acc
F8 DRAM Arbitration Timer 1 00 RW
F9 DRAM Arbitration Timer 9 00 RW
FA CPU Direct Access FB Base Address 00 RW
FB Frame Buffer Conrol 00 RW
Offset Back Door Control Default Acc
FC Back Door Control 1 00 RW
FD BackDoor Control 2 00 RW
-
-
-
-
-
-
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -24- Register Summary Tables
Page 31

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 1 Bus 0 Registers - PCI-to-AGP Bridge
PCI Configuration Registers
Configuration Header Default Acc
Offset
1-0 Vendor ID
3-2 Device ID
5-4 Command
7-6 Status
8 Revision ID
9 Program Interface 00 RO
A Sub Class Code
B Base Class Code
C -reserved- (cache line size) 00 —
D Latency Timer 00
E Header Type
F Built In Self Test (BIST) 00 RO
10-17 -reserved- (base address registers) 00 —
18 Primary Bus Number 00
19 Secondary Bus Number 00
1A Subordinate Bus Number 00
1B -reserved- (secondary latency timer) 00 —
1C I/O Base
1D I/O Limit 00
1F-1E Secondary Status 0000 RO
21-20 Memory Base
23-22 Memory Limit (Inclusive) 0000
25-24 Prefetchable Memory Base
27-26 Prefetchable Memory Limit 0000
28-3D -reserved- (unassigned) 00 —
3F-3E PCI-to-AGP Bridge Control 00 RW
1106
8601
0007 RW
0220 WC
nn
04
06
01
F0 RW
FFF0 RW
FFF0 RW
RO
RO
RO
RO
RO
RW
RO
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Device-Specific Configuration Registers
Offset
43-4F -reserved- (unassigned) 00 —
AGP Control Default Acc
40 CPU-to-AGP Flow Control 1 00 RW
41 CPU-to-AGP Flow Control 2 00 RW
42 AGP Master Control 00 RW
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -25- Register Summary Tables
Page 32

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
g
Device 0 Bus 1 Registers - 2D / 3D Graphics Accelerator
PCI Configuration Registers
Configuration Header Default Acc
Offset
1-0 Vendor ID
3-2 Device ID
5-4 PCI Command
7-6 PCI Status
8 Revision ID
9 Register Level 00 R
A Sub Class Code 00 R
B Base Class Code
F-C -reserved- — —
13-10 Memory Base 0 (8MB display mem)
17-14 Memory Base 1 (128K mem map IO)
1B-18 Memory Base 2 (8MB video overlay)
2B-1C -reserved- — —
2D-2C Subsystem Vendor ID 0000
2F-2E Subsystem ID 0000
33-30 Expansion ROM Base
3B-34 -reserved- — —
3C Interrupt Line
3D Interrupt Pin
3E-3F -reserved- — —
Offset Device-Specific Configuration Default Acc
40-8F -reserved- — —
93-90 Power Management 1 — RW
97-94 Power Management 2 — RW
98-FF -reserved- — —
PCI Bus Master Registers (2204, 2300, 231x, 232x)
I/O Port PCI Bus Master Re
2207-2204 Master Status —
2303-2300 Master Control — RW
2313-2310 System Side Start Address — RW
2315-2314 Master Height — RW
2317-2316 Master Width — RW
231B-2318 FB Start Address & Pitch — RW
231D-231C System Side Pitch — RW
231F-231E -reserved- — —
2323-2320 Clear Data — RW
isters Default Acc
1023
8500
0003 RW
0220 RW
nn
03
E000 0000 RW
E080 0000 RW
E040 0000 RW
0000 0001 RW
0B RW
01
R
R
R
R
RW
RW
R
R
AGP Registers (2300-23FF)
I/O Port
2303-2300 (See PCI Bus Master Regs)
2307-2304 Capability List — RW
230F-2308 -reserved- — —
2323-2310 (See PCI Bus Master Regs)
2333-2324 -reserved- — —
2337-2334 Capability List Address — RW
233F-2338 -reserved- — —
I/O Port AGP Operation Registers Default Acc
2343-2340 FB Command List Start Addr — RW
2347-2344 FB Command List Size — RW
234B-2348 Ch 1 FB Start Addr / Pitch — RW
234F-234C Ch 1 Frame Buffer Size — RW
2353-2350 Ch 1 System Start Address — RW
2357-2354 Ch 1 & 2 System Side Pitch — RW
235B-2358 Ch 2 System Start Address — RW
235F-235C Ch 2 FB Start Addr / Pitch — RW
2363-2360 Ch 2 FB Size — RW
2367-2364 Ch Arb Counter Threshold — RW
236B-2368 Channel 1/0 Control — RW
236F-236C Global & Channel 2 Control — RW
2373-2370 Cmd List / Ch 0/1/2 Op Status — RW
237F-2374 -reserved- — —
I/O Port AGP Configuration Regs Default Acc
2383-2380 Capability Identifier — RW
2387-2384 AGP Status — RW
238B-2388 AGP Command — RW
23AF-238C -reserved- — —
I/O Port AGP Command Buffer Regs Default Acc
23B3-23B0 Command Buffer Start Addr — RW
23B7-23B4 Command Buffer End Addr — RW
23FF-23B8 -reserved- — —
AGP Configuration Regs Default Acc
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -26- Register Summary Tables
Page 33

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
p
g
Capture Registers (2200)
I/O Port Ca
2203-2200 Capture Command —
DVD Registers (2280-22FF)
I/O Port DVD Re
2280 MC ID —
2281 MC Control — RW
2282 MC Frame Buffer Config — RW
2283 -reserved- — —
2285-2284 MC Status — RW
2287-2284 MC Command Queue — RW
228B-2288 MC Y-Reference Address — RW
228F-228C MC U-Reference Address — RW
2293-2290 MC V-Reference Address — RW
2297-2294 MC Display Y-Addr Offset — RW
229B-2298 MC Display U-Addr Offset — RW
229F-229C MC Display V-Addr Offset — RW
22A0 MC H Macroblock Count — RW
22A1 -reserved- — —
22A2 MC V Macroblock Count — RW
22A3 -reserved- — —
22A5-22A4 MC Frame Buffer Y-Length — RW
22A7-22A6 -reserved- — —
22AB-22A8 Color Palette Entries — RW
22AF-22AC -reserved- — —
22B3-22B0 SP BUF0 Pixel Start Address — RW
22B7-22B4 SP BUF1 Pixel Start Address — RW
22BB-22B8 SP BUF0 Cmd Start Address — RW
22BF-22BC SP BUF1 Cmd Start Address — RW
22C1-22C0 SP Y Display Offset — RW
22CF-22C2 -reserved- — —
22D0 Digital TV Encoder Control — RW
22D3-22D1 Digital TV Encoder CFC — RW
22FF-22D4 -reserved- — —
ture Registers Default Acc
isters Default Acc
RW
R
Extended Registers – Non-Indexed I/O Ports
I/O Port
3D8 Alt Destination Segment Addr 00 RW
3D9 Alt Source Segment Address — RW
3xB Alt Clock Select — RW
Note: 3xB notation indicates that these registers are accessible
at either 3BB or 3DB depending on the setting of the color /
mono bit.
Extended Non-Indexed Regs Default Acc
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -27- Register Summary Tables
Page 34

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Standard VGA Registers
Port
Index VGA Registers Default Acc
3B4/5 0-18 CRT Controller (Mono Mode) — RW
3BA — Input Status 1 (Mono Mode) — R
3C0/1 0-14 Attribute Controller — RW
3C2 — Input Status 0 —
3C2 — Miscellaneous Output (Write) —
3C3 — Video Subsystem Enable — RW
3C4/5 0-4 Sequencer — RW
3C6 — RAMDAC Pixel Mask — RW
3C7 — RAMDAC Read Index —
3C8 — RAMDAC Write Index —
3C8 — RAMDAC Index Readback —
3C9 0-FF RAMDAC Palette Data — RW
3CC — Miscellaneous Output (Read) —
3CE/F 0-8 Graphics Controller — RW
3D4/5 0-18 CRT Controller (Color Mode) — RW
3DA — Input Status 1 (Color Mode) —
46E8 — Display Adapter Enable — RW
Note: CRTC registers are accessible at either 3B4 / 3B5 or
3D4 / 3D5 (shorthand notation 3x4 / 3x5) depending on the
setting of the color / mono bit.
Standard VGA Registers – Attribute Controller (AR)
Index Attribute Controller Regs Default Acc
Port
3C0 — Index — RW
3C0/1 0-F Color Palette — RW
3C0/1 10 Attribute Mode Control — RW
3C0/1 11 Overscan Color — RW
3C0/1 12 Color Plane Enable — RW
3C0/1 13 Horizontal Pixel Panning — RW
3C0/1 14 Color Select — RW
Standard VGA Registers – Sequencer (SR)
Index Sequencer Registers Default Acc
Port
3C4 — Index — RW
3C5 0 Reset — RW
3C5 1 Clocking Mode — RW
3C5 2 Map Mask — RW
3C5 3 Character Map Select — RW
3C5 4 Memory Mode — RW
R
W
W
W
R
R
R
Standard VGA Registers – Graphics Controller (GR)
Port
Index Graphics Controller Regs Default Acc
3CE — Index — RW
3CF 0 Set / Reset — RW
3CF 1 Enable Set / Reset — RW
3CF 2 Color Compare — RW
3CF 3 Data Rotate — RW
3CF 4 Read Map Select — RW
3CF 5 Graphics Mode 00 RW
3CF 6 Miscellaneous — RW
3CF 7 Color Don’t Care — RW
3CF 8 Bit Mask — RW
Standard VGA Registers – CRT Controller (CR)
Index CRT Controller Registers Default Acc
Port
3x4 — Index — RW
3x5 0 Horizontal Total 00 RW
3x5 1 Horizontal Display Ena End 00 RW
3x5 2 Horizontal Blanking Start 00 RW
3x5 3 Horizontal Blanking End 00 RW
3x5 4 Horizontal Retrace Start
3x5 5 Horizontal Retrace End 00 RW
3x5 6 Vertical Total 00 RW
3x5 7 Overflow 00 RW
3x5 8 Preset Row Scan 00 RW
3x5 9 Maximum Scan Line 00 RW
3x5 A Cursor Start 00 RW
3x5 B Cursor End 00 RW
3x5 C Start Address High 00 RW
3x5 D Start Address Low 00 RW
3x5 E Cursor Location High 00 RW
3x5 F Cursor Location Low 00 RW
3x5 10 Vertical Retrace Start 00 RW
3x5 11 Vertical Retrace End 00 RW
3x5 12 Vertical Display Enable End 00 RW
3x5 13 Offset 00 RW
3x5 14 Underline Location 00 RW
3x5 15 Vertical Blanking Start 00 RW
3x5 16 Vertical Blanking End 00 RW
3x5 17 CRTC Mode Control 00 RW
3x5 18 Line Compare 00 RW
Note: CRTC registers are accessible at either 3B4 / 3B5 or
3D4 / 3D5 (shorthand notation 3x4 / 3x5) depending on the
setting of the color / mono bit.
FF
RW
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -28- Register Summary Tables
Page 35

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Extended Registers – VGA Sequencer Indexed
Port
Index Extended Sequencer Regs Default Acc
3C5 8 Old-New Status 00
3C5 9 Graphics Controller Version
3C5 A -reserved- — —
3C5 B Version/Old-New Mode Ctrl
3C5 C Configuration Port 1
3C5 C Configuration Port 2 — RW
3C5 D Old Mode Control 2
3C5 D New Mode Control 2
3C5 E Old Mode Control 1
3C5 E New Mode Control 1
3C5 F Power-up Mode 2
3C5 10 VESA™ Big BIOS Control 00 RW
3C5 11 Protection 00 RW
3C5 12 Threshold
3C5 13-17 -reserved- — —
3C5 18 VCLK1 Frequency Control 0 00 RW
3C5 19 VCLK1 Frequency Control 1 00 RW
3C5 1A VCLK2 Frequency Control 0 00 RW
3C5 1B VCLK2 Frequency Control 1 00 RW
3C5 1C-1F -reserved- — —
3C5 20 Clk Syn / RAMDAC Setup 00 RW
3C5 21 Signature Control 00 RW
3C5 23-22 Signature Data —
3C5 24 Power Management Ctrl
3C5 25 Monitor Sense —
3C5 26-36 -reserved- — —
3C5 37 Video Key Mode 00 RW
3C5 38 Feature Connector Control 00 RW
3C5 39-4F -reserved- — —
3C5 52-50 Playback Color Key Data — RW
3C5 53 -reserved- — —
3C5 56-54 Playback Color Key Mask — RW
3C5 57 Playback Vid Key Mode Fun — RW
3C5 58-59 -reserved- — —
3C5 5A-5F Scratch Pad 0-5 — RW
3C5 62-60 2nd Playback Color Key Data — RW
3C5 63 -reserved- — —
3C5 66-64 2nd Playback ColorKey Mask — RW
3C5 67-7F -reserved- — —
58 R
F3
B7
20
10
A8
40
BF
21
0E
R
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
R
RW
R
Port
Index New Video Display Regs Default Acc
3C5 82-80 W1 U FB Start Address — RW
3C5 85-83 W1 V FB Start Address — RW
3C5 88-86 W2 FB Start Address — RW
3C5 8A-89 W2 H Scaling Factor — RW
3C5 8C-8B W2 V Scaling Factor — RW
3C5 90-8D W2 Live Video Start — RW
3C5 94-91 W2 Live Video End — RW
3C5 95 W2 Live Vid Line Buf Level — RW
3C5 96 New Live Video Win Ctrl 0 00 RW
3C5 97 New Live Video Win Ctrl 1 00 RW
3C5 98 New Live Video Win Ctrl 2 00 RW
3C5 99 New Live Video Win Ctrl 3 00 RW
3C5 9B-9A Vid Row Byte Off. (W1-UV) — RW
3C5 9D-9C Vid Row Byte Offset(W2-Y) — RW
3C5 9E Line Buf Req Threshold 00 RW
3C5 9F VBI Control — RW
3C5 A3-A0 VBI Frame Buffer Address — RW
3C5 A7-A4 VBI Capture Start — RW
3C5 AB-A8 VBI Capture End — RW
AD-AC
3C5
3C5 AF-AE Capture Row Byte Offset — RW
3C5 B1-B0 Window 1 HSB Control — RW
3C5 B3-B2 Window 2 HSB Control — RW
3C5 B6-B4 2nd Display Addr Select — RW
3C5 B7 Video Sharpness — RW
3C5 BA-B8 2nd Capture Addr Select — RW
3C5 BB -reserved- — —
3C5 BC Contrast Control — RW
3C5 BD Dual View MUX Control — RW
3C5 BE Miscellaneous Control Bits 00 RW
3C5 BF-CD -reserved- — —
3C5 CE Window 2 Live Video Ctrl 00 RW
3C5 CF -reserved- — —
3C5 D1-D0 Row Byte Offset (W2-UV) — RW
3C5 D4-D2 W2 U-Frame Start Address — RW
3C5 D7-D5 W2 V-Frame Start Address — RW
3C5 D9-D8 Digital TV Interface Control — RW
DB-DA
3C5
DD-DC
3C5
3C5 DF-DE W1 V Count Status —
Port
Index Reserved Registers Default Acc
3C5 E0-FF -reserved- — RW
VBI V Interrupt Position — RW
W2 V Count Status —
Dual View Control — RW
R
R
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -29- Register Summary Tables
Page 36

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Extended Registers – VGA Graphics Controller Indexed
Port
Index Extd Graphics Ctrlr Regs Default Acc
3CE/F E Old / New Src Segment Addr 00 RW
3CE/F F Misc Extended Function Ctrl 00 RW
3CE/F 10-1F -reserved- — —
3CE/F 20-2F
20 Standby Timer Control 0xxx0000b RW
21 Power Management Control 1 00 RW
22 Power Management Control 2 00 RW
23 Power Status — RW
24 Soft Power Control
25 Power Control Select
26 DPMS Control 00 RW
28-27 GPIO Control 0000 RW
29 -reserved- — —
2A Suspend Pin Timer 00 RW
2B -reserved- — —
2C Miscellaneous Pin Control 00 RW
2D-2E -reserved- — —
2F Miscellaneous Internal Ctrl 00 RW
3CE/F 30-5A -reserved- — —
3CE/F 5A-5F Scratch Pad 0-5 — RW
3CE/F 60-7F -reserved- — —
Power Management Regs
E0
FF
RW
RW
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -30- Register Summary Tables
Page 37

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
)
—
)
—
—
)
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
r
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Extended Registers – VGA CRT Controller Indexed
Port
Index Extended CRTC Registers Default Acc
3x5 0E CRT Module Test 00 RW
3x5 19 CRT Interlace Control — RW
3x5 1A Arbitration Control 1 00 RW
3x5 1B Arbitration Control 2 00 RW
3x5 1C Arbitration Control 3 00 RW
3x5 1D-1E -reserved3x5 1F Software Programming
3x5 20 Command FIFO 00 RW
3x5 21 Linear Addressing 00 RW
3x5 22 CPU Latch Readback
3x5 23 -reserved3x5 24 VGA Attribute State
3x5 25 RAMDAC RW Timing
3x5 26 -reserved3x5 27 CRT High Order Start 00 RW
3x5 28 -reserved3x5 29 RAMDAC Mode 00 RW
3x5 2A In terface Select
3x5 2B Horiz. Parameter Overflow 00 RW
3x5 2C -reserved3x5 2D GE Timing Control 00 RW
3x5 2E -reserved3x5 2F Performance Tuning
3x5 30-33 -reserved3x5 35-34 GE IO Linear Address Base 0000 RW
3x5 36 Graphics / Video Engine Ctrl 00 RW
3x5 37 I2C Control
3x5 38 Pixel Bus Mode 00 RW
3x5 39 PCI Interface Control 0000000nb RW
3x5 3A Physical Address Control 00 RW
3x5 3B Clock and Tuning 0n000001b RW
3x5 3C Misc Control 00 RW
3x5 3D-3F -reserved-
3x5 40-50 Hardware Cursor Registers
43-40 HW Cursor Position
45-44 HW Cursor Pattern Location
47-46 HW Cursor Offset
4F-48 HW Cursor Color
50 HW Cursor Control
3x5 51 Bus Grant Termination Ctrl — RW
3x5 52 Shared Frame Buffer Ctrl 000x0010b RW
3x5 53-54 -reserved3x5 55 PCI Retry Control
3x5 56 Display Pre-end Control 00 RW
3x5 57 Display Pre-end Fetch Param.
3x5 58-5D -reserved3x5 5E Capture / ZV Port Control x0000000b RW
3x5 5F Test Control 00 RW
3x5 60-61 -reserved3x5 62 Enhancement 0
3x5 63 Enhancement 1 00 RW
3x5 64 DPA Extra
3x5 65-7F -reserved-
0F
10
03
82
0F
04
RW
RO
RO
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Port
Index Extended CRTC Registers Default Acc
3x5 80-BF Video / Capture Engine
81-80 Horiz Scaling Factor (W1)
83-82 Vert Scaling Factor (W1)
85-84 -reserved89-86 Video Window Start (W1)
8D-8A Video Window End
8F-8E Video Display Engine Flag — RW
91-90 Row Byte Offset (W1, W1-Y
94-92 Vid Start Addr (W1-Y or W1
95 Vid Win Line Buffer Thresh
96 Line Buf Lev Ctl (W1-Y, W1
97 Video Display Engine Flag
9A-98 Capture Video Start Address
9B Video Display Status
9C Capture Control 1
9D Capture Control 2
9E Capture Control 3
9F Capture Control 4
A1-A0 Capture Vertical Total
A3-A2 Capture Horizontal Total
A5-A4 Capture Vertical Start
A7-A6 Capture Vertical End
A9-A8 Capture Horizontal Start
AB- Capture Horizontal End
AC Capture Vert Sync Pulse
AD Capture Horiz Sync Pulse
AE Capture CRTC Control
AF Capture CRTC Control
B1-B0 Capture Horiz Minify Facto
B3-B2 Capture Vert Minify Factor
B5-B4 DST Pixel Width Count
B7-B6 DST Pixel Height Count
B8 Capture FIFO Control 1
B9 Capture FIFO Control 2
BB- Chromakey Comp Data 0 Lo
BD- Chromakey Comp Data 0 Hi
BE Capture Control
BF Display Engine Flag 4
3x5 C0-CF -reserved- — —
3x5 D3-D0 VGA / Digital TV Sync Ctrl 1 — RW
3x5 D4-FF -reserved- — —
Extended Registers – CRTC Shadow
Index CRTC Shadow Registers Default Acc
Port
3x5 00 Horizontal Total
3x5 03 Horizontal Blanking End
3x5 04 Hoprizontal Retrace Start
3x5 05 Horizontal Retrace End
3x5 06 Vertical Total
3x5 07 Overflow
3x5 10 Vertical Retrace Start
3x5 11 Vertical Retrace End
3x5 16 Vertical Blanking End
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -31- Register Summary Tables
Page 38

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
3D Graphics Engine Registers
These registers are addressed at offsets from the Graphics
Engine Base Address (GEbase). All registers are 32-bit.
Offset
Span Engine Registers Default Acc
3-0 Parameter Source 1 — RW
7-4 Parameter Source 2 — RW
B-8 Parameter Destination 1 — RW
F-C Parameter Destination 2 — RW
Offset VGA Core Registers Default Acc
13-10 Right View Display Base Addresses — RW
17-14 Left View Display Base Addresses — RW
1B-18 Block Write Start Address — RW
1F-1C Block Write Area / End Address — RW
23-20 GE Status —
27-24 GE Control —
2B-28 GE Debug —
2F-2C Wait Mask — RW
Offset Rasterization & Setup Engine Regs Default Acc
33-30 Primitive Attribute — RW
37-34 -reserved- — —
3B-38 -reserved- — —
3F-3C Primitive Type —
3F-3C Setup Engine Status —
Offset Pixel Engine Registers Default Acc
43-40 -reserved- — —
47-44 Drawing Command — RW
4B-48 Raster Operation (ROP) — RW
4F-4C Z-Function — RW
53-50 Texture Function — RW
57-54 Clipping Window 0 — RW
5B-58 Clipping Window 1 — RW
5F-5C -reserved- — —
63-60 Color 0 — RW
67-64 Color 1 — RW
6B-68 Color Key — RW
6F-6C Pattern and Style — RW
73-70 Pattern Color — RW
77-74 Pattern Foreground Color — RW
7B-78 Pattern Background Color — RW
7F-7C Alpha — RW
83-80 Alpha Function — RW
87-84 Bit Mask — RW
8B-88 -reserved- — —
8F-8C -reserved- — —
93-90 -reserved- — —
97-94 -reserved- — —
9B-98 -reserved- — —
9F-9C -reserved- — —
R
W
R
W
R
Offset
A3-A0 Texture Control — RW
A7-A4 Texture Color — RW
AB-A8 Palette Data —
AF-AC Texture Boundary — RW
Offset Command List Control Registers Default Acc
B3-B0 -reserved- — —
B7-B4 -reserved- — —
Offset Memory Interface Registers Default Acc
BB-B8 Destination Stride & Buffer 0 — RW
BF-BC Destination Stride & Buffer 1 — RW
C3-C0 Destination Stride & Buffer 2 — RW
C7-C4 Destination Stride & Buffer 3 — RW
CB-C8 Source Stride & Buffer 0 — RW
CF-CC Source Stride & Buffer 1 — RW
D3-D0 Source Stride & Buffer 2 — RW
D7-D4 Source Stride & Buffer 3 — RW
DB-D8 Z Depth & Buffer — RW
DF-DC Texture Base Level 0 (1:1 Map) — RW
E3-E0 Texture Base Level 1 — RW
E7-E4 Texture Base Level 2 — RW
EB-E8 Texture Base Level 3 — RW
EF-EC Texture Base Level 4 — RW
F3-F0 Texture Base Level 5 — RW
F7-F4 Texture Base Level 6 — RW
FB-F8 Texture Base Level 7 — RW
FF-FC Texture Base Level 8 (mallest) — RW
Offset Data Port Area Default Acc
1xxxx Data Port Area —
Texture Engine Registers Default Acc
W
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -32- Register Summary Tables
Page 39

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Miscellaneous I/O
One I/O port is defined in the PLE133: Port 22.
Port 22 – PCI /AGP Arbiter Disable ...............................RW
7-2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1 AGP Arbiter Disable
0 Respond to GREQ# signal .....................default
1 Do not respond to GREQ# signal
0 PCI Arbiter Disable
0 Respond to all REQ# signals..................default
1 Do not respond to any REQ# signals,
including PREQ#
This port can be enabled for read/write access by setting bit-7
of Device 0 Configuration Register 78.
Configuration Space I/O
All registers in the PLE133 (listed above) are addressed via
the following configuration mechanism:
Mechanism #1
These ports respond only to double-word accesses. Byte or
word accesses will be passed on unchanged.
Port CFB-CF8 - Configuration Address......................... RW
31 Configuration Space Enable
0 Disabled................................................. default
1 Convert configuration data port writes to
30-24 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
23-16 PCI Bus Number
Used to choose a specific PCI bus in the system
15-11 Device Number
Used to choose a specific device in the system
10-8 Function Number
Used to choose a specific function if the selected
7-2 Register Number (also called the "Offset")
Used to select a specific DWORD in the
1-0 Fixed ........................................ always reads 0
configuration cycles on the PCI bus
(devices 0 and 1 are defined)
device supports multiple functions (only function 0 is
defined).
configuration space
Port CFF-CFC - Configuration Data.............................. RW
Refer to PCI Bus Specification Version 2.2 for further details
on operation of the above configuration registers.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -33- Register Summary Tables
Page 40

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Register Descriptions
Device 0 Bus 0 Header Registers - Host Bridge
All registers are located in PCI configuration space. They
should be programmed using PCI configuration mechanism 1
through CF8 / CFC with bus
device number equal to zero.
Device 0 Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID........................................RO
15-0 ID Code (reads 1106h to identify VIA Technologies)
Device 0 Offset 3-2 - Device ID..........................................RO
15-0 ID Code (reads 0601h to identify the VT8601A)
Device 0 Offset 5-4 - Command .......................................RW
15-10 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
9 Fast Back-to-Back Cycle Enable ........................ RO
0 Fast back-to-back transactions only allowed to
the same agent........................................default
1 Fast back-to-back transactions allowed to
different agents
8 SERR# Enable...................................................... RO
0 SERR# driver disabled...........................default
1 SERR# driver enabled
(SERR# is used to report parity errors if bit-6 is set).
7 Address / Data Stepping...................................... RO
0 Device never does stepping....................default
1 Device always does stepping
6 Parity Error Response........................................RW
0 Ignore parity errors & continue..............default
1 Take normal action on detected parity errors
5 VGA Palette Snoop.............................................. RO
0 Treat palette accesses normally..............default
1 Don’t respond to palette accesses on PCI bus
4 Memory Write and Invalidate Command ......... RO
0 Bus masters must use Mem Write..........default
1 Bus masters may generate Mem Write & Inval
3 Special Cycle Monitoring .................................... RO
0 Does not monitor special cycles.............default
1 Monitors special cycles
2 Bus Master .......................................................... RO
0 Never behaves as a bus master
1 Can behave as a bus master....................default
1 Memory Space...................................................... RO
0 Does not respond to memory space
1 Responds to memory space....................default
0 I/O Space .......................................................... RO
0 Does not respond to I/O space ..............default
1 Responds to I/O space
number, function number, and
Device 0 Offset 7-6 - Status ........................................... RWC
15 Detected Parity Error
0 No parity error detected......................... default
1 Error detected in either address or data phase.
This bit is set even if error response is disabled
(command register bit-6)...... write one to clear
14 Signaled System Error (SERR# Asserted)
........................................always reads 0
13 Signaled Master Abort
0 No abort received .................................. default
1 Transaction aborted by the master ...................
................................... write one to clear
12 Received Target Abort
0 No abort received .................................. default
1 Transaction aborted by the target .....................
....................................... write 1 to clear
11 Signaled Target Abort .......................always reads 0
0 Target Abort never signaled
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing
00 Fast
01 Medium ................................... always reads 01
10 Slow
11 Reserved
8 Data Parity Error Detected
0 No data parity error detected ................. default
1 Error detected in data phase. Set only if error
response enabled via command bit-6 = 1 and
VT8601A was initiator of the operation in
which the error occurred....... write one to clear
7 Fast Back-to-Back Capable ...............always reads 1
6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 66MHz Capable..................................always reads 0
4 Supports New Capability list.............always reads 1
3-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Device 0 Offset 8 - Revision ID......................................... RO
7-0 VT8601A Chip Revision Code
Device 0 Offset 9 - Programming Interface..................... RO
7-0 Interface Identifier ...........................always reads 00
Device 0 Offset A - Sub Class Code.................................. RO
7-0 Sub Class Code ....... reads 00 to indicate Host Bridge
Device 0 Offset B - Base Class Code................................. RO
7-0 Base Class Code.. reads 06 to indicate Bridge Device
Device 0 Offset D - Latency Timer.................................. RW
Specifies the latency timer value in PCI bus clocks.
7-3 Guaranteed Time Slice for CPU ...............default=0
2-0 Reserved (fixed granularity of 8 clks) .. always read 0
Bits 2-1 are writeable but read 0 for PCI specification
compatibility. The programmed value may be read
back in Offset 75 bits 5-4 (PCI Arbitration 1).
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -34- Device 0 Bus 0 Header Registers - Host Bridge
Page 41

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset E - Header Type.......................................RO
7-0 Header Type Code ........... reads 00: single function
Device 0 Offset F - Built In Self Test (BIST)....................RO
7 BIST Supported ......reads 0: no supported functions
6-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Device 0 Offset 13-10 - Graphics Aperture Base............ RW
31-28 Upper Programmable Base Address Bits ...... def=0
27-20 Lower Programmable Base Address Bits...... def=0
These bits behave as if hardwired to 0 if the
corresponding Graphics Aperture Size register bit
(Device 1 Offset 84h) is 0.
27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 (This Register)
7
RW RW RW RW RW RW RW RW 1M
RW RW RW RW RW RW RW 0 2M
RW RW RW RW RW RW 0 0 4M
RW RW RW RW RW 0 0 0 8M
RW RW RW RW 0 0 0 0 16M
RW RW RW 0 0 0 0 0 32M
RW RW 0 0 0 0 0 0 64M
RW 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 128M
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 256M
6 5 4 3 2 1 0 (Gr Aper Size)
Device 0 Offset 2D-2C – Subsystem Vendor ID............. RW
15-0 Subsystem Vendor ID ........................ default = 0000
Device 0 Offset 2F-2E – Subsystem ID ........................... RW
15-0 Subsystem ID ......................................default = 0000
Device 0 Offset 37-34 - Capability Pointer ...................... RO
Contains an offset from the start of configuration space.
31-0 AGP Capability List Pointer ........always reads A0h
19-0 Reserved ................................ always reads 00008
Note: The locations in the address range defined by this
register are prefetchable.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -35- Device 0 Bus 0 Header Registers - Host Bridge
Page 42

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
CPU Interface Control
Device 0 Offset 50 – Request Phase Control (02h) .........RW
7 CPU Hardwired IOQ (In Order Queue) Size
Default per the inverse of the strap on pin MA11
during reset. This register bit can be written to 0 to
restrict the chip to one level of IOQ.
0 1-Level
1 4-Level . default if no external strap resistor
6 Read-Around-Write
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Defer Retry When HLOCK Active
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
Note: always set this bit to 1
3-2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1 Fast Speculative Read
0 Disable
1 Enable ...................................................default
0 CPU / PCI Master Read DRAM Timing
0 Start DRAM read after
1 Start DRAM read before snoop complete
snoop complete.......def
Device 0 Offset 51 – Response Phase Control (02h) ...... RW
7 CPU Read DRAM 0WS for Back-to-Back Read
Transactions
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Setting this bit enables maximum read performance
by allowing continuous 0-wait-state reads for
pipelined line reads. If this bit is not set, there will be
at least 1T idle time between read transactions.
6 CPU Write DRAM 0WS for Back-to-Back Write
Transactions
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Setting this bit enables maximum write performance
by allowing continuous 0-wait-state writes for
pipelined line writes ands sustained 3T single writes.
If this bit is not set, there will be at least 1T idle time
between write transactions.
5 DRAM Read Request Rate
0 3T .................................................... default
1 2T
4 Fast Response (HIT/HITM Sampled 1T Earlier)
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 Non-Posted IOW
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 CPU Read DRAM Prefetch Buffer Depth
0 1-level prefetch buffer ........................... default
1 4-level prefetch buffer
1 CPU-to-DRAM Post-Write Buffer Depth
0 1-level post-write buffer
1 4-level post-write buffer ....................... default
0 Concurrent PCI Master / Host Operation
0 Disable – the CPU bus will be occupied (BPRI
asserted) during the entire PCI operation .... def
1 Enable – the CPU bus is only requested before
ADS# assertion
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -36- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 43

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset 52 – Dynamic Defer Timer (10h)...........RW
7 GTL I/O Buffer Pullup...........default = MA13 Strap
0 Disable
1 Enable
The default value of this bit is determined by a strap
on the MA13 pin during reset.
6 RAW Write Retire After 2 Writes
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4-0 Snoop Stall Count
00 Disable dynamic defer
01-1F Snoop stall count ........................ default = 10h
Device 0 Offset 53 – Miscellaneous (00h)........................ RW
7 HREQ Function
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6 DRAM Frequency Higher Than CPU FSB
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Setting this bit enables the DRAM subsystem to run at
a higher frequency than the CPU FSB frequency.
When setting this bit, register bit Rx69[6] must also be
set and only SDRAM memory type DIMM modules
may be installed. An EDO / SDRAM mix in the
DRAM subsystem is not supported in this case.
5 AGP/PCI-to-CPU Master / CPU-to-PCI Slave
Concurrency
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
4 HPRI Function
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 P6Lock Function
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 P6Lock
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -37- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 44

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset 55-54 - Non-Cacheable Region #1 .........RW
15-3 Base Address - A<28:16>........................... default=0
As noted below, the base address must be a multiple
of the region size.
2-0 Range (Region Size)
000 Disable ...................................................default
001 64K
010 128K (Base Address A16 must be 0)
011 256K (Base Address A16-17 must be 0)
100 512K (Base Address A16-18 must be 0)
101 1M (Base Address A16-19 must be 0)
110 2M (Base Address A16-20 must be 0)
111 4M (Base Address A16-21 must be 0)
Device 0 Offset 57-56 - Non-Cacheable Region #2......... RW
15-3 Base Address MSBs - A<28:16> ................ default=0
As noted below, the base address must be a multiple
of the region size.
2-0 Range (Region Size)
000 Disable................................................... default
001 64K
010 128K (Base Address A16 must be 0)
011 256K (Base Address A16-17 must be 0)
100 512K (Base Address A16-18 must be 0)
101 1M (Base Address A16-19 must be 0)
110 2M (Base Address A16-20 must be 0)
111 4M (Base Address A16-21 must be 0)
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -38- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 45

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
DRAM Control
These registers are normally set at system initialization time
and not accessed after that during normal system operation.
Some of these registers, however, may need to be programmed
using specific sequences during power-up initialization to
properly detect the type and size of installed memory (refer to
the VIA Technologies VT8601A BIOS porting guide for
details).
Table 3. System Memory Map
Space Start Size Address Range Comment
DOS 0 640K 00000000-0009FFFF Cacheable
VGA 640K 128K 000A0000-000BFFFF Used for SMM
BIOS 768K 16K 000C0000-000C3FFF Shadow Ctrl 1
BIOS 784K 16K 000C4000-000C7FFF Shadow Ctrl 1
BIOS 800K 16K 000C8000-000CBFFF Shadow Ctrl 1
BIOS 816K 16K 000CC000-000CFFFF Shadow Ctrl 1
BIOS 832K 16K 000D0000-000D3FFF Shadow Ctrl 2
BIOS 848K 16K 000D4000-000D7FFF Shadow Ctrl 2
BIOS 864K 16K 000D8000-000DBFFF Shadow Ctrl 2
BIOS 880K 16K 000DC000-000DFFFF Shadow Ctrl 2
BIOS 896K 64K 000E0000-000EFFFF Shadow Ctrl 3
BIOS 960K 64K 000F0000-000FFFFF Shadow Ctrl 3
Sys 1MB — 00100000-DRAM Top Can have hole
Bus D Top DRAM Top-FFFEFFFF
Init 4G-64K 64K FFFEFFFF-FFFFFFFF 000Fxxxx alias
Device 0 Offset 59-58 - DRAM MA Map Type...............RW
15-13 Bank 5/4 MA Map Type
0xx 16Mb SDRAM.......................................default
100 64/128Mb SDRAM (x4, x8, x16, 4-bank x32)
101 Reserved (Do Not Program)
110 Reserved (Do Not Program)
111 Reserved (Do Not Program)
12 Reserved (Do Not Program)...................... default=0
11-8 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
7-5 Bank 1/0 MA Map Type (see above)
4 Reserved (Do Not Program)...................... default=0
3-1 Bank 3/2 MA Map Type (see above)
0 Reserved (Do Not Program)...................... default=0
Device 0 Offset 5A-5F – DRAM Row Ending Address:
All of the registers in this group default to 01h:
Offset 5A – Bank 0 Ending (HA[30:23]).................... RW
Offset 5B – Bank 1 Ending (HA[30:23]) .................... RW
Offset 5C – Bank 2 Ending (HA[30:23]).................... RW
Offset 5D – Bank 3 Ending (HA[30:23]).................... RW
Offset 5E – Bank 4 Ending (HA[30:23]) .................... RW
Offset 5F – Bank 5 Ending (HA[30:23]) .................... RW
Note: BIOS is required to fill the ending address registers
for all banks even if no memory is populated. The
endings have to be in incremental order.
Device 0 Offset 60 – DRAM Type ................................... RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
5-4 DRAM Type for Bank 5/4
00 Reserved ................................................ default
01 Reserved
10 Reserved
11 SDRAM
3-2 DRAM Type for Bank 3/2 ......................... default=0
1-0 DRAM Type for Bank 1/0 ......................... default=0
Table 4. Memory Address Mapping Table
MA: 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
16Mb (0xx)
64Mb (100)
2/4 bank
x4, x8, x16;
4-bank x32
24
24
"PC" = "Precharge Control" (refer to SDRAM specifications)
16Mb 11x10, 11x9, and 11x8 configurations supported
64Mb x4: 12x10 4bank, 13x10 2bank
x8: 12x9 4bank, 13x9 2bank
x16: 12x8 4bank, 13x8 2bank
x32: 11x8 4bank
128Mb same as 64Mb
22PC212420
11
11
1313121222PC212620
23
25
19
18 9 17 8 16 7 156145134123Row Bits
10
19
18 9 17 8 16 7 15614
10
5114233
Col Bits
x4: 10 col
x8: 9 col
x16: 8 col
x32: 8 col
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -39- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 46

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset 61 - Shadow RAM Control 1 .................RW
7-6 CC000h-CFFFFh
00 Read/write disable..................................default
01 Write enable
10 Read enable
11 Read/write enable
5-4 C8000h-CBFFFh
00 Read/write disable..................................default
01 Write enable
10 Read enable
11 Read/write enable
3-2 C4000h-C7FFFh
00 Read/write disable..................................default
01 Write enable
10 Read enable
11 Read/write enable
1-0 C0000h-C3FFFh
00 Read/write disable..................................default
01 Write enable
10 Read enable
11 Read/write enable
Device 0 Offset 62 - Shadow RAM Control 2 .................RW
7-6 DC000h-DFFFFh
00 Read/write disable..................................default
01 Write enable
10 Read enable
11 Read/write enable
5-4 D8000h-DBFFFh
00 Read/write disable..................................default
01 Write enable
10 Read enable
11 Read/write enable
3-2 D4000h-D7FFFh
00 Read/write disable..................................default
01 Write enable
10 Read enable
11 Read/write enable
1-0 D0000h-D3FFFh
00 Read/write disable..................................default
01 Write enable
10 Read enable
11 Read/write enable
Device 0 Offset 63 - Shadow RAM Control 3................. RW
7-6 E0000h-EFFFFh
00 Read/write disable ................................. default
01 Write enable
10 Read enable
11 Read/write enable
5-4 F0000h-FFFFFh
00 Read/write disable ................................. default
01 Write enable
10 Read enable
11 Read/write enable
3-2 Memory Hole
00 None .................................................... default
01 512K-640K
10 15M-16M (1M)
11 14M-16M (2M)
1-0 SMI Mapping Control
00 Disable SMI Address Redirection ......... default
01 Allow access to DRAM Axxxx-Bxxxx for
both normal and SMI cycles
10 Reserved
11 Allow SMI Axxxx-Bxxxx DRAM access
Note: The A0000-BFFFF address range is reserved
for use by VGA controllers for system access to the
VGA frame buffer. Since frame buffer accesses are
normally directed to the system VGA controller (with
its separate memory subsystem), system DRAM
locations in the A0000-BFFFF range would normally
be unused. Setting the above bits appropriately
allows this block of system memory to be used by
directing Axxxx-Bxxxx accesses to corresponding
memory addresses in system DRAM instead of
directing those accesses to the PCI bus for VGA
frame buffer access.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -40- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 47

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset 64 - DRAM Timing for Banks 0,1 .........RW
Device 0 Offset 65 - DRAM Timing for Banks 2,3 .........RW
Device 0 Offset 66 - DRAM Timing for Banks 4,5 .........RW
Settings for Registers 64-66
7 Precharge Command to Active Command Period
0 T
1 T
RP = 2T
RP = 3T ................................................default
6 Active Command to Precharge Command Period
0 T
RAS = 5T
1 TRAS = 6T ..............................................default
5-4 CAS Latency
00 1T
01 2T
10 3T .....................................................default
11 Reserved
3 Reserved (Do Not Program).................... default = 0
2 ACTIVE Command to CMD Command Period
0 2T
1 3T .....................................................default
1-0 Bank Interleave
00 No Interleave..........................................default
01 2-way
10 4-way
11 Reserved
Device 0 Offset 68 - DRAM Control ............................... RW
7 Reserved (Do Not Program) ................... default = 0
6 Bank Page Control
0 Allow only pages of the same bank active .. def
1 Allow pages of different banks to be active
5 Reserved (Do Not Program) ................... default = 0
4 Internal Graphics Controller Frequency
0 66 / 100 MHz......................................... default
1 133 MHz
This bit must be set to 1 if the DRAM frequency is
133 MHz. If the DRAM frequency is set to 100 or 66
MHz this bit it ignored. (see also table under
Rx69[7-6]).
3 Reserved (Do Not Program) .................... default = 0
2 Burst Refresh
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable (burst 4 times)
1-0 System Frequency Divider...................................RO
00 CPU / PCI Frequency Ratio = 2x (66 MHz)
01 CPU / PCI Frequency Ratio = 3x (100 MHz)
10 -reserved 11 CPU / PCI Frequency Ratio = 4x (133 MHz)
These bits are latched from MA[14, 12] at the rising
edge of RESET#. Without external strapping
resistors, the default setting of these bits is 00 (66
MHz).
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -41- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 48

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset 69 – DRAM Clock Select (00h)..............RW
7-6 DRAM Operating Frequency Select ................. RW
Rx68[1-0]
00 00 x 66/66/66 (default)
00 01 x 66/100/100
01 00 x 100/100/100
01 10 x 100/66/66
01 01 1 100/133/133
10 00 1 133/133/133
10 10 x 133/100/100
All other combinations are reserved. The internal
graphics controller runs synchronous to the DRAM
and at the same frequency (if the DRAM controller
frequency is set to 133, Rx68[4] must also be set to
1).
5 256M bit DRAM Support
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable (DCLKRD becomes output)
4 DRAM Controller Command Register Output
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 Fast DRAM Precharge for Different Bank
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 DRAM 4K Pages (for 64Mbit DRAM)
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 Reserved (Do Not Program).................... default = 0
0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Rx69[7-6] Rx68[4] CPU/DRAM/VGA
Device 0 Offset 6A - Refresh Counter............................. RW
7-0 Refresh Counter (in units of 16 MCLKs)
00 DRAM Refresh Disabled ...................... default
01 32 MCLKs
02 48 MCLKs
03 64 MCLKs
04 80 MCLKs
05 96 MCLKs
… …
The programmed value is the desired number of 16-
MCLK units minus one.
Device 0 Offset 6B - DRAM Arbitration Control (01h) RW
7-6 Arbitration Parking Policy
00 Park at last bus owner............................ default
01 Park at CPU side
10 Park at AGP side
11 Reserved
5 Fast Read to Write Turnaround
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 MD Bus Second Level Strength Control
0 Normal slew rate control ....................... default
1 More slew rate control
2 CAS Second Level Strength Control
0 Normal slew rate control ....................... default
1 More slew rate control
1 Reserved (Do Not Program) ....................default = 0
0 Multi-Page Open
0 Disable (page registers marked invalid and no
page register update which causes non pagemode operation)
1 Enable.................................................... default
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -42- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 49

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset 6C - SDRAM Control.............................RW
7-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 CKE Configuration
0 RASA = CSA, RASB = CSB,
CKE0=CKE0, CKE1 = CKE1
1 RASA = CSA, RASB = CSB,
CKE3-2 = CSA7-6
CKE5-4 = CSB7-6
CKE1 = GCKE (Global CKE)
CKE0 = FENA (FET Enable)
3 Fast AGP TLB lookup
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Reduce the lookup time from 4T to 2T
2-0 SDRAM Operation Mode Select
000 Normal SDRAM Mode ..........................default
001 NOP Command Enable
010 All-Banks-Precharge Command Enable
(CPU-to-DRAM cycles are converted
to All-Banks-Precharge commands).
011 MSR Enable
CPU-to-DRAM cycles are converted to
commands and the commands are driven on
MA[13:0]. The BIOS selects an appropriate
host address for each row of memory such that
the right commands are generated on
MA[13:0].
100 CBR Cycle Enable (if this code is selected,
CAS-before-RAS refresh is used; if it is not
selected, RAS-Only refresh is used)
101 Reserved
11x Reserved
Rx6B[0] Rx64-66[1-0] Rx68[7-6] Remark
0 00 00 Non-page mode, every access starts
from precharge-active cmd
1 00 00 Only one page active at a time
(recommended setting)
1 01 or 10 00 Only allow sub-bank of a SDRAM
bank active at a time, # of subbank
depends on Rx64-66<1:0>
1 01 or 10 01 Allow mutliple sub-banks across
different SDRAM banks active, but
if EDO is accessed, all SDRAM
pages will be closed
1 01 or 10 11 Allow maximum 8 pages of
SDRAM, EDO opened
Device 0 Offset 6D - DRAM Drive Strength................... RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6-5 Delay DRAM Read Latch
00 Disable................................................... default
01 0.5 ns
10 1.0 ns
11 1.5 ns
4 MD Drive
0 6 mA .................................................... default
1 8 mA
3 SDRAM Command Drive Strength
(SRAS#, SCAS#, SWE#)
0 16mA .................................................... default
1 24mA
2 MA[2:13] / WE# Drive Strength
0 16mA .................................................... default
1 24mA
1 CAS# Drive Strength
0 8 mA .................................................... default
1 12 mA
0 RAS# Drive Strength
0 16mA .................................................... default
1 24mA
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -43- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 50

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
PCI Bus Control
These registers are normally programmed once at system
initialization time.
Device 0 Offset 70 - PCI Buffer Control .........................RW
7 CPU to PCI Post-Write
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 PCI Master to DRAM Post-Write
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 Reserved
4 PCI Master to DRAM Prefetch Disable
0 Enable ....................................................default
1 Disable
3 CPU-to-PCI Buffer Available Cycle Reduction
0 Normal operation ...................................default
1 Reduce 1 cycle when the CPU-to-PCI buffer
becomes available after being full (PCI and
AGP buses)
2 PCI Master Read Caching
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 Delay Transaction
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
0 Slave Device Stopped Idle Cycle Reduction
0 Normal Operation ..................................default
1 Reduce 1 PCI idle cycle when stopped by a
slave device (PCI and AGP buses)
Device 0 Offset 71 - CPU to PCI Flow Control 1 ........... RW
7 Dynamic Burst
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable (see note under bit-3 below)
6 Byte Merge
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 Reserved (do not program)........................ default = 0
4 PCI I/O Cycle Post Write
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 PCI Burst
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable (bit7=1 will override this option)
bit-7
0 0 Every write goes into the write buffer and no
0 1 If the write transaction is a burst transaction,
1 x Every write transaction goes to the write
2 PCI Fast Back-to-Back Write
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 Quick Frame Generation
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 1 Wait State PCI Cycles
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
bit-3 Operation
PCI burst operations occur.
the information goes into the write buffer and
burst transfers are later performed on the PCI
bus. If the transaction is not a burst, PCI write
occurs immediately (after a write buffer flush).
buffer; burstable transactions will then burst
on the PCI bus and non-burstable won’t. This
is the normal setting.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -44- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 51

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset 72 - CPU to PCI Flow Control 2......... RWC
7 Retry Status
0 Retry occurred less than retry limit ........default
1 Retry occurred more than x times (where x is
defined by bits 5-4) ................. write 1 to clear
6 Retry Timeout Action
0 Retry Forever (record status only) .........default
1 Flush buffer for write or return all 1s for read
5-4 Retry Limit
00 Retry 2 times ..........................................default
01 Retry 16 times
10 Retry 4 times
11 Retry 64 times
3 Clear Failed Data and Continue Retry
0 Flush the entire post-write buffer...........default
1 When data is posting and master (or target)
abort fails, pop the failed data if any, and keep
posting
2 CPU Backoff on PCI Read Retry Failure
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Backoff CPU when reading data from PCI and
retry fails
1 Reduce 1T for FRAME# Generation
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
0 Reduce 1T for CPU Read of PCI Slave
0 Disable ..................................................Default
1 Enable
Device 0 Offset 73 - PCI Master Control 1..................... RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6 PCI Master 1-Wait-State Write
0 Zero wait state TRDY# response........... default
1 One wait state TRDY# response
5 PCI Master 1-Wait-State Read
0 Zero wait state TRDY# response........... default
1 One wait state TRDY# response
4 Disable Prefetch when Doing Delay Transaction
0 Enable.................................................... default
1 Disable
3 Assert STOP# after PCI Master Write Timeout
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 Assert STOP# after PCI Master Read Timeout
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 LOCK# Function
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 PCI Master Broken Timer Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable. Force into arbitration when there is no
FRAME# 16 PCICLK’s after the grant. Does
not apply to south bridge PREQ# input
Device 0 Offset 74 - PCI Master Control 2..................... RW
7 PCI Master Read Prefetch by Enhance Command
0 Always Prefetch .................................... default
1 Prefetch only if Enhance command
6 PCI Master Write Merge
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Dummy Request Handling ...........Should be set to 1
0 As VP3 .................................................. default
1 Complete Fix
3 PCI Delay Transaction Time-Out
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 Backoff CPU Immediately on CPU to AGP Retry
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1-0 CPU/PCI Master Latency Timer Control
00 AGP Master Reloads MLT timer ..........default
01 Falling edge of AGP Master Request reloads
MLT timer
10 Rising Edge of AGP Master Request clears
MLT timer and falling edge reloads the timer
11 Reserved (illegal setting)
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -45- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 52

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset 75 - PCI Arbitration 1 ............................ RW
7 Arbitration Mechanism
0 PCI has priority ......................................default
1 Fair arbitration between PCI and CPU
6 Arbitration Mode
0 REQ-based (arbitrate at end of REQ#) ..default
1 Frame-based (arbitrate at FRAME# assertion)
5-4 Latency Timer........... read only, reads Rx0D bits 2:1
3-0 PCI Master Bus Time-Out
(force into arbitration after a period of time)
0000 Disable ...................................................default
0001 1x32 PCLKs
0010 2x32 PCLKs
0011 3x32 PCLKs
0100 4x32 PCLKs
... ...
1111 15x32 PCLKs
Device 0 Offset 76 - PCI Arbitration 2............................ RW
7 CPU-to-PCI Post-Write Retry Failed
0 Continue retry attempt........................... default
1 Go to arbitration
6 CPU Latency Timer Bit-0....................................RO
0 CPU has at least 1 PCLK time slot when CPU
has PCI bus............................................ default
1 CPU has no time slot
5-4 Master Priority Rotation Control
00 Disabled (arbitration per Rx75 bit-7) ....default
01 Grant to CPU after every PCI master grant
10 Grant to CPU after every 2 PCI master grants
11 Grant to CPU after every 3 PCI master grants
With setting 01, the CPU will always be granted
access after the current bus master completes, no
matter how many PCI masters are requesting. With
setting 10, if other PCI masters are requesting during
the current PCI master grant, the highest priority
master will get the bus after the current master
completes, but the CPU will be guaranteed to get the
bus after that master completes. With setting 11, if
other PCI masters are requesting, the highest priority
will get the bus next, then the next highest priority
will get the bus, then the CPU will get the bus. In
other words, with the above settings, even if multiple
PCI masters are continuously requesting the bus, the
CPU is guaranteed to get access after every master
grant (01), after every other master grant (10) or after
every third master grant (11).
3-2 High Priority REQ Select
00 REQ4 .................................................... default
01 REQ0
10 REQ1
11 REQ2
1 CPU-to-PCI QW High DW Read Access to PCI
Slave Allow Backoff
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 High Priority Request Support
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Device 0 Offset 77 - Chip Test Mode............................... RW
7-6 Reserved (no function).......................always reads 0
5-0 Reserved (do not use)................................. default=0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -46- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 53

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset 78 - PMU Control 1 ................................RW
7 I/O Port 22 Access
0 CPU access to I/O address 22h is passed on to
the PCI bus.............................................default
1 CPU access to I/O address 22h is processed
internally
6 Suspend Refresh Type
0 CBR Refresh ..........................................default
1 Self Refresh
5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Dynamic Clock Control
0 Normal (clock is always running)..........default
1 Clock to various internal functional blocks is
disabled when those blocks are not being used
3 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
2 AGPSTP# Control
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
0 Memory Clock Enable (CKE) Function
0 CKE Disable (pins used as MECC[2-0]) .....def
1 CKE Enable (pins used for CKE[2-0]#)
Device 0 Offset 79 – PMU Control 2................................RW
7 CPU Interface Controller Dynamic Clock
Stopping
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 DRAM Controller Dynamic Clock Stopping
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 AGP Controller Dynamic Clock Stopping
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 PCI Interface Controller Dynamic Clock Stopping
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 Pseudo Power Good
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 South Bridge has High Priority
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Device 0 Offset 7A – Miscellaneous Control .................. RW
7 No Time-Out Arbitration for Consecutive Frame
Accesses
0 Enable.................................................... default
1 Disable
6-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 Background PCI-to-PCI Write Cycle Mode
0 Enable.................................................... default
1 Disable
2-1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 South Bridge PCI Master Force Timeout When
PCI Master Occupancy Timer Is Up
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Device 0 Offset 7E – PLL Test Mode.............................. RW
7-6 Reserved (status) ..................................................RO
5-0 Reserved (do not use)................................. default=0
Device 0 Offset 7F – PLL Test Mode .............................. RW
7-0 Reserved (do not use)................................. default=0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -47- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 54

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
GART / Graphics Aperture Control
The function of the Graphics Address Relocation Table
(GART) is to translate virtual 32-bit addresses issued by an
AGP device into 4K-page based physical addresses for system
memory access. In this translation, the upper 20 bits (A31A12) are remapped, while the lower 12 address bits (A1 1-A0)
are used unchanged.
A one-level fully associative lookup scheme is used to
implement the address translation. In this scheme, the upper
20 bits of the virtual address are used to point to an entry in a
page table located in system memory. Each page table entry
contains the upper 20 bits of a physical address (a "physical
page" address). For simplicity, each page table entry is 4
bytes. The total size of the page table depends on the GART
range (called the "aperture size") which is programmable in
the VT8601A.
This scheme is shown in the figure below.
31 12 11 0
Virtual Page Address Page Offset
index
TLB Base
Page Table
31 12 11 0
Physical Page Address Page Offset
Since address translation using the above scheme requires an
access to system memory, an on-chip cache (called a
"Translation Lookaside Buffer" or TLB) is utilized to enhance
performance. The TLB in the 82C501 contains 16 entries.
Address "misses" in the TLB require an access of system
memory to retrieve translation data. Entries in the TLB are
replaced using an LRU (Least Recently Used) algorithm.
Addresses are translated only for accesses within the
"Graphics Aperture" (GA). The Graphics Aperture can be any
power of two in size from 1MB to 256MB (i.e., 1MB, 2MB,
4MB, 8MB, etc). The base of the Graphics Aperture can be
anywhere in the system virtual address space on an address
boundary determined by the aperture size (e.g., if the aperture
size is 4MB, the base must be on a 4MB address boundary).
The Graphics Aperture Base is defined in register offset 10 of
device 0. The Graphics Aperture Size and TLB Table Base
are defined in the following register group (offsets 84 and 88
respectively) along with various control bits.
Figure 4. Graphics Aperture Address Translation
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -48- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 55

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset 83-80 - GART/TLB Control...................RW
31-16 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
15-8 Reserved (test mode status)................................. RO
7 Flush Page TLB
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6-4 Reserved (always program to 0)........................ RW
3 PCI Master Address Translation for GA Access
0 Addresses generated by PCI Master accesses
of the Graphics Aperture will not
1 PCI Master GA addresses will be translated
2 AGP Master Address Translation for GA Access
0 Addresses generated by AGP Master accesses
of the Graphics Aperture will not
1 AGP Master GA addresses will
1 CPU Address Translation for GA Access
0 Addresses generated by CPU accesses of the
Graphics Aperture will not
1 CPU GA addresses will be translated
0 AGP Address Translation for GA Access
0 Addresses generated by AGP accesses of the
Graphics Aperture will not
1 AGP GA addresses will be translated
Note: For any master access to the Graphics Aperture range,
snoop will not be performed.
be translateddefault
be translateddefault
be translated
be translated......def
be translated......def
Device 0 Offset 84 - Graphics Aperture Size.................. RW
7-0 Graphics Aperture Size
11111111 1M
11111110 2M
11111100 4M
11111000 8M
11110000 16M
11100000 32M
11000000 64M
10000000 128M
00000000 256M
Offset 8B-88 - GA Translation Table Base..................... RW
31-12 Graphics Aperture Translation Table Base
Pointer to the base of the translation table in system
memory used to map addresses in the aperture range
(the pointer to the base of the "Directory" table).
11-3 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
2 One Cycle TLB Flush Command
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable................................... should be set to 1
1 Graphics Aperture Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable Graphics Aperture Address [31:28]
Note: To disable the Graphics Aperture, set this bit
to 0 and set all bits of the Graphics Aperture Size to
0. To enable the Graphics Aperture, set this bit to 1
and program the Graphics Aperture Size to the
desired aperture size.
0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Note: If TLB miss, the TLB table is fetched by the address:
Gr Ap Trans Table Base [31:12] + A[27:22], A[21:12], 2’b00
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -49- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 56

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
AGP Control
Device 0 Offset A3-A0 - AGP Capability Identifier ........RO
31-24 Reserved ...................................... always reads 00
23-20 Major Specification Revision ..... always reads 0001
Major revision # of AGP spec device conforms to
19-16 Minor Specification Revision ..... always reads 0000
Minor revision # of AGP spec device conforms to
15-8 Pointer to Next Item ....... always reads 00 (last item)
7-0 AGP ID .. (always reads 02 to indicate it is AGP)
Device 0 Offset A7-A4 - AGP Status.................................RO
31-24 Maximum AGP Requests................ always reads 07
Max # of AGP requests the device can manage (8)
23-10 Reserved .......................................always reads 0s
9 Supports SideBand Addressing ........ always reads 1
8-2 Reserved .......................................always reads 0s
1 2X Rate Supported
Value returned can be programmed by writing to
RxAC[3] ........................................ always reads 1
0 1X Rate Supported ............................ always reads 1
Device 0 Offset AB-A8 - AGP Command........................RW
31-24 Request Depth (reserved for target) ..always reads 0s
23-10 Reserved .......................................always reads 0s
9 SideBand Addressing Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
8 AGP Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
7-2 Reserved .......................................always reads 0s
1 2X Mode Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
0 1X Mode Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
Device 0 Offset AC - AGP Control.................................. RW
7 Reserved ...................................... always reads 0s
6 AGP Read Synchronization
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable (the CPU to AGP cycle will be delayed
if the CMFIFO contains a GART access)
5 AGP Read Snoop CMFIFO
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable (AGP read address will snoop the
CMFIFO; if hit, AGP read will be started after
the write is retired)
4 AGP Master Request has Higher Priority if AGP
Controller is Parking at AGP Master
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 2X Rate Supported (read also at RxA4[1])
0 Not supported ........................................ default
1 Supported
2 LPR In-Order Access (Force Fence)
0 Fence/Flush functions not guaranteed. AGP
read requests (low/normal priority and high
priority) may be executed before previously
issued write requests.............................. default
1 Force all requests to be executed in order
(automatically enables Fence/Flush functions).
Low (i.e., normal) priority AGP read requests
will never be executed before previously
issued writes. High priority AGP read
requests may still be executed prior to
previously issued write requests as required.
1 AGP Arbitration Parking
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable (GGNT# remains asserted until either
GREQ# de-asserts or data phase ready)
0 2T AGP to DRAM Request Generation
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Device 0 Offset AD – AGP Latency Register ................. RW
7-4 Reserved ...................................... always reads 0s
3-0 AGP Latency Timer(units of 16 GCLKs)
0000 Free Run ................................................ default
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -50- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 57

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Offset F7-F0 – BIOS Scratch Register ............. RW
7-0 No Hardware Function
Device 0 Offset F8 – DRAM Arbitration Timer 1..........RW
7-4 AGP Timer (units of 4 DRAM Clocks)
3-0 Host Timer (units of 4 DRAM Clocks)
Device 0 Offset F9 – DRAM Arbitration Timer 2..........RW
7-4 VGA High Priority Timer (units of 16 DRAM
Clocks)
3-0 VGA Timer (units of 16 DRAM Clocks)
Device 0 Offset FA – CPU Direct Access Frame Buffer
Base Address A[28:21]...................................................... RW
7-0 A[28:21]
Device 0 Offset FB – Frame Buffer Control ...................RW
7 VGA Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 VGA Reset ................................. (Write 1 to Reset)
5-4 Frame Buffer Size
00 None .....................................................default
01 2M
10 4M
11 8M
3 CPU Direct Access Frame Buffer
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2-0 CPU Direct Access Frame Buffer Base Address
<31:29>
Device 0 Offset FC – Back Door Control 1..................... RW
7-2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1 Back-Door Max # of AGP Requests Allowed
0 Read RXA7 will return 7....................... default
1 Read RxXA7 will have number programmed
at RxFD
0 Back-Door Device ID Enable
0 Use Rx3-2’s value for Rx3-2 read......... default
1 Use the value in RxFE-FF
Device 0 Offset FD – Back Door Control 2..................... RW
7-3 Reserved
2-0 Back-Door Max # of AGP Requests the Device can
Handle
000 1-Request............................................... default
001 2-Requests
… …
111 8-Requests
Device 0 Offset FF-FE – Back Door Device ID .............. RW
15-0 Back-Door Device ID ...............................default = 0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -51- Device 0 Bus 0 Host Bridge Registers
Page 58

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 1 Bus 0 Header Registers - PCI-to-AGP Bridge
All registers are located in PCI configuration space. They
should be programmed using PCI configuration mechanism 1
through CF8 / CFC with bus
equal to zero
Device 1 Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID........................................RO
15-0 ID Code (reads 1106h to identify VIA Technologies)
Device 1 Offset 3-2 - Device ID..........................................RO
15-0 ID Code (reads 8601h to identify the VT8601A PCI-
Device 1 Offset 5-4 - Command .......................................RW
15-10 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
9 Fast Back-to-Back Cycle Enable ........................ RO
0 Fast back-to-back transactions only allowed to
1 Fast back-to-back transactions allowed to
8 SERR# Enable...................................................... RO
0 SERR# driver disabled...........................default
1 SERR# driver enabled
(SERR# is used to report parity errors if bit-6 is set).
7 Address / Data Stepping...................................... RO
0 Device never does stepping....................default
1 Device always does stepping
6 Parity Error Response........................................RW
0 Ignore parity errors & continue..............default
1 Take normal action on detected parity errors
5 VGA Palette Snoop.............................................. RO
0 Treat palette accesses normally..............default
1 Don’t respond to palette writes on PCI bus
4 Memory Write and Invalidate Command ......... RO
0 Bus masters must use Mem Write..........default
1 Bus masters may generate Mem Write & Inval
3 Special Cycle Monitoring .................................... RO
0 Does not monitor special cycles.............default
1 Monitors special cycles
2 Bus Master .........................................................RW
0 Never behaves as a bus master
1 Enable to operate as a bus master on the
1 Memory Space.....................................................RW
0 Does not respond to memory space
1 Enable memory space access ................default
0 I/O Space .........................................................RW
0 Does not respond to I/O space
1 Enable I/O space access ........................default
and device number equal to one.
to-PCI Bridge device)
the same agent........................................default
different agents
(10-bit decode of I/O addresses 3C6-3C9 hex)
primary interface on behalf of a master on the
secondary interface ...............................default
number and function number
Device 1 Offset 7-6 - Status (Primary Bus).................. RWC
15 Detected Parity Error ........................always reads 0
14 Signaled System Error (SERR#).......always reads 0
13 Signaled Master Abort
0 No abort received .................................. default
1 Transaction aborted by the master with
Master-Abort (except Special Cycles)..............
....................................... write 1 to clear
12 Received Target Abort
0 No abort received .................................. default
1 Transaction aborted by the target with Target-
Abort ....................................... write 1 to clear
11 Signaled Target Abort .......................always reads 0
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing
00 Fast
01 Medium ................................... always reads 01
10 Slow
11 Reserved
8 Data Parity Error Detected ............... always reads 0
7 Fast Back-to-Back Capable ...............always reads 0
6 User Definable Features..................... always reads 0
5 66MHz Capable..................................always reads 1
4 Supports New Capability list.............always reads 0
3-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Device 1 Offset 8 - Revision ID......................................... RO
7-0 VT8601A Chip Revision Code (00=First Silicon)
Device 1 Offset 9 - Programming Interface..................... RO
This register is defined in different ways for each Base/SubClass Code value and is undefined for this type of device.
7-0 Interface Identifier ...........................always reads 00
Device 1 Offset A - Sub Class Code.................................. RO
7-0 Sub Class Code .reads 04 to indicate PCI-PCI Bridge
Device 1 Offset B - Base Class Code................................. RO
7-0 Base Class Code.. reads 06 to indicate Bridge Device
Device 1 Offset D - Latency Timer................................... RO
7-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Device 1 Offset E - Header Type ...................................... RO
7-0 Header Type Code.......... reads 01: PCI-PCI Bridge
Device 1 Offset F - Built In Self Test (BIST) ................... RO
7 BIST Supported...... reads 0: no supported functions
6 Start Test .......... write 1 to start but writes ignored
5-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3-0 Response Code..........0 = test completed successfully
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -52- Device 1 Bus 0 Header Registers - PCI-to-AGP Bridge
Page 59

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 1 Offset 18 - Primary Bus Number......................RW
7-0 Primary Bus Number .............................. default = 0
This register is read write, but internally the chip always uses
bus 0 as the primary.
Device 1 Offset 19 - Secondary Bus Number ..................RW
7-0 Secondary Bus Number........................... default = 0
Note: PCI#2 must use these bits to convert Type 1 to Type 0.
Device 1 Offset 1A - Subordinate Bus Number ..............RW
7-0 Primary Bus Number .............................. default = 0
Note: PCI#2 must use these bits to decide if Type 1 to Type 1
command passing is allowed.
Device 1 Offset 1C - I/O Base ........................................... RW
7-4 I/O Base AD[15:12].......................... default = 1111b
3-0 I/O Addressing Capability ...................... default = 0
Device 1 Offset 1D - I/O Limit .........................................RW
7-4 I/O Limit AD[15:12] ................................ default = 0
3-0 I/O Addressing Capability ...................... default = 0
Device 1 Offset 1F-1E - Secondary Status........................RO
15-0 Reserved .................................. always reads 0000
Device 1 Offset 3F-3E – PCI-to-PCI Bridge Control..... RW
15-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 VGA-Present on AGP
0 Forward VGA accesses to PCI Bus ....... default
1 Forward VGA accesses to AGP Bus
Note: VGA addresses are memory A0000-BFFFFh
and I/O addresses 3B0-3BBh, 3C0-3CFh and 3D03DFh (10-bit decode). "Mono" text mode uses
B0000-B7FFFh and "Color" Text Mode uses B8000-
2 Block / Forward ISA I/O Addresses
0 Forward all I/O accesses to the AGP bus if
.................................................... default
1 Do not forward I/O accesses to the AGP bus
1-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
BFFFFh. Graphics modes use Axxxxh. Mono VGA
uses I/O addresses 3Bx-3Cxh and Color VGA uses
3Cx-3Dxh. If an MDA is present, a VGA will not
use the 3Bxh I/O addresses and B0000-B7FFFh
memory space; if not, the VGA will use those
addresses to emulate MDA modes.
they are in the range defined by the I/O Base
and I/O Limit registers (device 1 offset 1C-
1D)
that are in the 100-3FFh address range even if
they are in the range defined by the I/O Base
and I/O Limit registers.
Device 1 Offset 21-20 - Memory Base.............................. RW
15-4 Memory Base AD[31:20] ................. default = 0FFFh
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Device 1 Offset 23-22 - Memory Limit (Inclusive) .........RW
15-4 Memory Limit AD[31:20] ....................... default = 0
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Device 1 Offset 25-24 - Prefetchable Memory Base .......RW
15-4 Prefetchable Memory Base AD[31:20].def = 0FFFh
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Device 1 Offset 27-26 - Prefetchable Memory Limit...... RW
15-4 Prefetchable Memory Limit AD[31:20] ...................
.............................................. default = 0
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -53- Device 1 Bus 0 Header Registers - PCI-to-AGP Bridge
Page 60

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 1 Bus 0 PCI-to-AGP Bridge Registers
AGP Bus Control
Device 1 Offset 40 - CPU-to-AGP Flow Control 1 .........RW
7 CPU-AGP Post Write
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 CPU-AGP Dynamic Burst
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 CPU-AGP One Wait State Burst Write
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 AGP to DRAM Prefetch
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 AGP Master Allowed Before CPU-to-AGP Post
Write Buffer is Not Flushed
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
This option is always enabled for PCI
2 MDA Present on AGP
0 Forward MDA accesses to AGP ............default
1 Forward MDA accesses to PCI
Note: Forward despite IO / Memory Base / Limit
Note: MDA (Monochrome Display Adapter)
addresses are memory addresses B0000h-B7FFFh
and I/O addresses 3B4-3B5h, 3B8-3BAh, and 3BFh
(10-bit decode). 3BC-3BE are reserved for printers.
Note: If Rx3E bit-3 is 0, this bit is a don't care
(MDA accesses are forwarded to the PCI bus).
1 AGP Master Read Caching
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
0 AGP Delay Transaction
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
Table 5. VGA/MDA Memory/IO Redirection
3E[3]
VGA
Pres.
0 - PCI PCI PCI PCI PCI PCI
1 0 AGP AGP AGP AGP AGP AGP
1 1 AGP PCI AGP PCI AGP PCI
40[2]
MDA
Pres.
VGA
is
on
MDA
is
on
Axxxx,
B8xxx
Access
B0000
-B7FFF
Access
3Cx,
3Dx
I/O
3Bx
I/O
Device 1 Offset 41 - CPU-to-AGP Flow Control 2...... RWC
7 Retry Status
0 No retry occurred................................... default
1 Retry Occurred ........................write 1 to clear
6 Retry Timeout Action
0 No action taken except to record status ....... def
1 Flush buffer for write or return all 1s for read
5-4 Retry Count
00 Retry 2, backoff CPU ............................ default
01 Retry 4, backoff CPU
10 Retry 16, backoff CPU
11 Retry 64, backoff CPU
3 Post Write Data on Abort
0 Flush entire post-write buffer on target-abort
or master abort....................................... default
1 Pop one data output on target-abort or master-
abort
2 CPU Backoff on AGP Read Retry Timeout
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Device 1 Offset 42 - AGP Master Control ...................... RW
7 Read Prefetch for Enhance Command
0 Always Perform Prefetch ...................... default
1 Prefetch only if Enhance Command
6 AGP Master One Wait State Write
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 AGP Master One Wait State Read
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
4 Extend AGP Internal Master for Efficient
Handling of Dummy Request Cycles
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
This bit is normally set to 1.
3 AGP Delay Transaction Timeout
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 Prefetch During Delay Transaction
0 Enable.................................................... default
1 Disable
1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 Reserved (do not use)............................... default = 0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -54- Device 1 Bus 0 PCI-to-AGP Bridge Registers
Page 61

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Bus 1 Header Registers - Graphics Accelerator
The Apollo PLE133 2D / 3D Graphics Accelerator is fully
compliant with PCI bus interface protocol revision 2.2. The
controller implements slave functions of PCI to accept cycles
initiated by PCI masters targeted for its internal registers,
RAMDAC™, frame buffer, and/or BIOS. It will accept only
one data transaction for non-memory type transfers; however
burst read/write transfers for frame buffer accesses are also
implemented for performance enhancement. Bursting is
disabled when accessing memory mapped I/O. Data parity
will be generated for read cycles.
To support the PC AT architecture, palette snooping is
supported. There are two different palette snooping modes:
(1) snooping due to PCI retry, and (2) snooping due to master
abort. Both modes are supported. The video BIOS will
automatically determine the correct snooping mode in a PCI
based system during power up. The PLE133 follows the PCI
2.2 specification running at 33 MHz or lower system clock
frequencies. For packed pixel modes, if the first data TRDY is
not generated within 16 clocks, a retry will be issued. During
bursting, if successful data is not generated within 8 clocks, a
retry will also be issued.
The table below lists the commands implemented by the
PLE133 graphics controller PCI interface. Note that codes not
listed (0000 interrupt acknowledge, 0001 special cycle, 0100,
0101, 1000, 1001 reserved, and 1101 dual address cycle) are
not decoded and DEVSEL# is not generated. No action takes
place inside the chip for these codes.
Table 6. Supported PCI Command Codes
Command Code Command
0010 I/O Read
0011 I/O Write
0110 Memory Read
0111 Memory Write
1010 Configuration Read
1011 Configuration Write
1100 Memory Read Multiple
(treated as simple memory read)
1110 Memory Read Line
(treated as simple memory read)
1111 Memory Write and Invalid
(treated as simple memory write)
The PCI configuration space is fully implemented. Due to the
second memory base register, all I/O registers can be memory
mapped; which allows more than one graphics co ntroller to b e
installed within a system by mapping memory and I/O to
different locations.
All configuration registers are located in PCI configuration
space and should be programmed using PCI configuration
mechanism 1 through CF8 / CFC with bus
one
and function number and device number equal to zero.
There are three memory base registers. The first defines the
memory base location for the graphics frame buffer. The
second defines the memory base for the memory mapped I/O
locations. The third defines the memory base for the second
video aperture. With this second aperture, graphics data and
video data can be sent to the PLE133 simultaneously.
The PLE133 supports the PCI Bus Master mode which can
send captured video data directly to system memory for
processing. The registers to control the PCI Bus Master are
defined in following sections (they are all in PCI configuration
space).
Offset 1-0 - Vendor ID (1023h)......................................... RO
15-0 ID Code ................................always reads 1023h
Offset 3-2 - Device ID (8500h) .......................................... RO
15-0 ID Code ................................always reads 8500h
number equal to
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -55- Device 0 Bus 1 Header Registers - Graphics Accelerator
Page 62

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Offset 5-4 - Command.......................................................RW
15-10 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
9 Fast Back-to-Back Cycle Enable ........................ RO
0 Fast back-to-back transactions only allowed to
the same agent
1 Fast back-to-back transactions allowed to
different agents
8 SERR# Enable...................................................... RO
0 SERR# driver disabled...........................default
1 SERR# driver enabled
(SERR# is used to report parity errors if bit-6 is set).
7 Address / Data Stepping...................................... RO
0 Device never does stepping....................default
1 Device always does stepping
6 Parity Error Response......................................... RO
0 Ignore parity errors & continue..............default
1 Take normal action on detected parity errors
5 VGA Palette Snoop.............................................RW
0 Treat palette accesses normally..............default
1 Don’t respond to palette accesses on PCI bus
4 Memory Write and Invalidate Command ......... RO
0 Bus masters must use Mem Write..........default
1 Bus masters may generate Mem Write & Inval
3 Special Cycle Monitoring .................................... RO
0 Does not monitor special cycles.............default
1 Monitors special cycles
2 Bus Master .........................................................RW
0 Never behaves as a bus master...............default
1 Can behave as a bus master
1 Memory Space.....................................................RW
0 Does not respond to memory space
1 Responds to memory space....................default
0 I/O Space .........................................................RW
0 Does not respond to I/O space
1 Responds to I/O space ...........................default
Offset 7-6 - Status .......................................................... RWC
15 Detected Parity Error
0 No parity error detected......................... default
1 Error detected in either address or data phase.
This bit is set even if error response is disabled
(command register bit-6)...... write one to clear
14 Signaled System Error (SERR# Asserted)
........................................always reads 0
13 Signaled Master Abort (Bus Master Only)
0 No abort received .................................. default
1 Transaction aborted by the master ...................
................................... write one to clear
12 Received Target Abort (Bus Master Only)
0 No abort received .................................. default
1 Transaction aborted by the target .....................
....................................... write 1 to clear
11 Signaled Target Abort .......................always reads 0
0 Target Abort never signaled
10-9 DEVSEL# Timing
00 Fast
01 Medium ................................... always reads 01
10 Slow
11 Reserved
8 Data Parity Error Detected (Bus Master Only)
0 No data parity error detected .....always reads 0
1 Error detected in data phase
7 Fast Back-to-Back Capable
0 Not capable............................................ default
1 Capable
6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 66MHz Capable..................................always reads 1
4 Supports New Capability list.............always reads 0
3-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -56- Device 0 Bus 1 Header Registers - Graphics Accelerator
Page 63

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Offset 8 - Revision ID.........................................................RO
8-0 VT8601A Graphics Controller Revision Code
Offset 9 - Programming Interface.....................................RO
7-0 Interface Identifier........................... always reads 00
Offset A - Sub Class Code .................................................RO
7-0 Sub Class Code................................. always reads 00
Offset B - Base Class Code ................................................RO
7-0 Base Class Code
Reads 03 to indicate Graphics Controller
Offset 13-10 - Graphics Memory Base 0 .........................RW
31-0 Graphics Memory Base 0 .........default = E000 0000
Defines an 8MB space for display memory
Offset 17-14 - Graphics Memory Base 1 .........................RW
31-0 Graphics Memory Base 0 .........default = E080 0000
Defines a 128KB space for memory mapped I/O
Offset 1B-18 - Graphics Memory Base 2.........................RW
31-0 Graphics Memory Base 0 .........default = E040 0000
Defines an 8MB space for off-screen video overlay
Offset 2D-2C – Subsystem Vendor ID.............................RW
15-0 Subsystem Vendor ID............................ default = 00
Offset 2F-2E - Subsystem ID............................................RW
15-0 Subsystem ID.......................................... default = 00
Offset 3C – Interrupt Line............................................... RW
7-0 Interrupt Line...................................... default = 0Bh
Offset 3D – Interrupt Pin.................................................. RO
7-0 Interrupt Pin....................always reads 01h (INTA#)
Interrupts
There are several interrupt sources and their corresponding
controls in the PLE133 as shown in the following table:
Table 7. Interrupt Sources and Controls
Source Mask Clear Status
Capture3 CR9B[7] CR9B[6]1CR9B[4]
Capture VSYNC
Capture Even Field
Capture Odd Field
Capture Blank
GE4 2122[7] 2122[7] 2120[4]
VGA5 CR11[5] CR11[4]
1) Write 0 to clear.
2) Selected by CR9E[7:6]
3) Video capture logic can generate an interrupt which is
selected from one of four sources determined by
CR9E.[7:6]. This interrupt is enabled by CR9B[7]. To
clear this bit write 0 to CR9B[6]. Whether an interrupt is
generated can be determined from CR9B[4].
4) The GE interrupt is similar to the capture interrupt.
5) The VGA interrupt is similar to the capture interrupt
except that there is no status bit.
2
2
2
2
Offset 33-30 –Graphics ROM Base..................................RW
31-0 Graphics ROM Base................. default = 0000 0001
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -57- Device 0 Bus 1 Header Registers - Graphics Accelerator
Page 64

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Device 0 Bus 1 Graphics Accelerator Registers
Offset 93-90 – Power Management 1................................RO
31-27 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
PME# not supported
26 D2 State (Suspend) Supported.......... always reads 1
The D2 state is supported
25 D1 State (Standby) Supported .......... always reads 1
The D1 state is supported
24-22 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
21 Device Specific Initialization............. always reads 1
Special DSI is required from the video BIOS
20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Auxiliary power source not supported
19 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
PME# generation not supported
18-16 PCI PM Version #........................ always reads 001b
15-8 Next Item Pointer............................... always reads 0
7-0 PCI PM Capable ............................ always reads 01h
This device is PCI PM capable
Offset 97-94 – Power Management 2 .............................. RW
31-24 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Power dissipation reporting not supported
23-16 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
15 D3 Cold Supported............................. always reads 0
D3 cold not supported
14-13 Data Scale ........................................always reads 0
Power dissipation reporting not supported
12-9 Power Consumed / Dissipated...........always reads 0
Power dissipation reporting not supported
8 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
PME# for D3 cold not supported
7-2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1-0 Power State
00 Fully On................................................. default
01 Standby
10 Suspend
11 D3hot, similar to suspend
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -58- Device 0 Bus 1 Graphics Accelerator Registers
Page 65

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers
The PLE133 PCI Bus Master controller supports both
read/write and scatter/gather. Software can take advantage of
this feature to transfer data between system memory and the
frame buffer. After software sets the proper registers and
commands, the PCI master begins to transfer data
automatically between system memory and the frame buffer.
This allows the CPU to do other jobs at the same time, thus
increasing performance.
Software should use the PCI Bus Master functionality to
transfer big chunks of data such as video capture data for
video conferencing applications or texture data for 3-D
applications. For small chunks of data, direct CPU access to
the Frame Buffer is the preferred method.
The software sequence used to control bus master operation is
as follows: Software first sets registers such as the system
memory starting address, page table starting address / height /
width, and frame buffer starting address and line offset.
Software finally sets the bus master control register where
either bit 1 (for reads) or bit 2 (for writes) is set as the
command bit. After the command bit is set, the hardware will
begin to transfer data automatically based on the parameters
specified. After the transfer is finished, the hardware will
issue an interrupt. Software can then poll the status bit to get
the transfer status. The hardware will clear the command bit
after the transfer is finished. Software cannot issue new
commands until the previous command is completed.
All Registers are memory mapped. The memory address base
is defined in PCI configuration register “Memory Base 1”
(offset 17h-14h).
Port 2204 – Graphics Bus Master Status .........................RO
31-3 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
2 Bus Master Interrupt Status
1 End of Transfer
0 Still processing.......................................default
1 End of Transfer (Idle)
0 Bus Master Error Status
0 Normal ...................................................default
1 Error Detected
This error is ususlly detected because the total page
table size is less than the size defined in the
“Graphics Bus Master Height” register at index
2314h.
Port 2300 – Graphics Bus Master Control..................... RW
31-16 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
15 PCI Master Read Data to GE SRCQ
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
14-11 Bytes in DW to be Cleared
When enabling block transfer with clear, one bits
define which byte(s) in the DW will be cleared
10 Enable Bit with Clear
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
9 Invert C / Z Position
0 Hardware assumes C is located in bits 15:0
and Z in bits 31:16................................. default
1 Hardware assumes C is located in bits 31:16
and Z in bits 15:0
8 Enable Z Stripping
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
7-5 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
4 Bus Master Interrupt
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 Master Latency
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 Write Command........................................ default =0
Writing this bit to 1 will trigger the hardware to begin
a write operation. After finishing the operation,
hardware will automatically clear this bit.
1 Read Command ........................................default =0
Writing this bit to 1 will trigger the hardware to begin
a read operation. After finishing the operation,
hardware will automatically clear this bit.
0 Scatter / Gather
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -59- Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers
Page 66

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Port 2310 – Graphics Bus Master System Start Addr...RW
31-0 System Start Address
If scatter / gather is enabled, bits 31:12 point to the
physical region translation table (the page starting
address must be aligned on 4KB address boundaries)
and bits 11:0 are the offset within a page.
Physical Region Descriptor Table
While system memory is allocated in a non-contiguous space,
software needs to provide a physical region description table
in system memory and pass the table's starting address to
hardware.
The table size must less than or equal to 4K bytes and the table
cannot cross the 4K boundary.
Figure 5. Physical Region Descriptor Table Format
BYTE3 | BYTE2 | BYTE1 | BYTE0
Page 0 physical address |EOT
Page 1 physical address |EOT
......
Page n physical address |EOT
EOT = End of Table
Port 2314 – Graphics Bus Master Height....................... RW
15-10 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
9-0 Source Data Height
Port 2316 – Graphics Bus Master Width ....................... RW
15-12 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
11-0 Source Data Width (in bytes)
Port 2318 – Graphics Bus Master FB Start Addr/Pitch RW
31-22 Frame Buffer Line Offset (FB pitch) in quadwords
21-20 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
19-0 Frame Buffer Start Address (quadword aligned)
Port 231C – Graphics Bus Master System Pitch ........... RW
15-12 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
11-0 System Row Byte Offset (pitch) in bytes
Port 2320 – Graphics Bus Master Clear Data................ RW
31-0 Clear Data Value
Used as the “clear” value for “block transfer with
clear”
Each table entry is 4 bytes in length. Hardware assumes that
the physical page is always 4K. Bits 31:2 indicate the
physical page starting address. Bit 0 of the first byte indicates
the end of the table. Bus Master operation terminates when
the last descriptor has been retired.
Figure 6. PCI Bus Master Address Translation
System Start Address
Register at 2210
31 ................ 12 11 ...... 0
Physical Region
Description Table
Physical Memory
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -60- Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers
Page 67

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Graphics Accelerator AGP Registers
The default base I/O address for the AGP registers is 2300h.
The AGP control unit has 3 channels. These channels can
work independently and in parallel. Each channel has its own
capabilities:
Channel 0: Execution mode texture access.
Channel 1: Command List Operation. Executes command
lists from AGP memory.
Channel 2: Data Move. Moves data from AGP memory to
frame buffer or to the Capture/MPEG2 FIFO.
Also moves data from the frame buffer to AGP
memory.
Graphics AGP Configuration Registers
Port 2304 – Graphics AGP Capability List.....................RW
31-0 xx
Port 2334 – Graphics AGP Capability List Address......RW
31-0 xx
Graphics AGP Operation Registers
Port 2340 – Graphics AGP FB Command List Start.....RW
31-19 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
18-0 Frame Buffer Command List Start Address
Command List Format
The command list is stored in AGP memory in groups. Each
group has the following format:
Bit Bit
QuadWord
0 Data 0 Header
1 Data 2 Data 1
2 Data 4 Data 3
… … …
n / 2 + 1 Pad/Data n-1 Data n – 1/2
The header is a 32-bit word that contains information about
this group, such as the amount of useful data in the group. A
group is always padded to a quadword boundary. Padding
DWORDs are discarded by the channel. The format of the
header is as follows:
31 Consecutive Addressing
0 Disabled (all data in this group will be written
1 Enabled (All data in this group will be written
30 Wait
0 Don’t Wait (send data to the Graphics Engine
1 Wait (until the GE is idle, then send data)
29-8 Register Address of the First Data (ADDR)
15-0 Number of DWORDs of Data in this Group (LEN)
63 48 32 31 16 0
to the register with the destination address
specified in the “ADDR” field in bits 29-8)
to registers ADDR, ADDR+4, … ADDR+4 *
(LEN-1) sequentially
as long as it can receive it)
Port 2344 – Graphics AGP FB Command List Size.......RW
31-19 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
18-3 Frame Buffer Command List Size (in quadwords)
Value programmed is the desired size minus one
2-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -61- Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers
Page 68

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Port 2348 – Graphics AGP Channel 1 FB Start/Pitch...RW
31-22 Frame Buffer Line Offset (in quadwords)
21-19 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
18-0 Frame Buffer Starting Address
Port 234C – Graphics AGP Channel 1 FB Size..............RW
31-13 X Direction (in quadwords minus one)
12-10 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
9-0 Y Direction (in pixels minus one)
Port 2350 – Graphics AGP Channel 1 System Start...... RW
31-3 Channel 1 System Memory Start Address
(quadword aligned)
2-1 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
0 Command List Operation Trigger
This bit is the same as bit-19 of register 2368h
(Channel 1 Read Enable). It is used to trigger
command list operation and force bit-17 of register
2368h (Channel 1 Destination Select) to 1 (to select
the GE Command FIFO).
Port 2354 – Graphics AGP Chan 1/2 System Pitch........RW
31-27 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
26-16 Ch 2 System Memory Line Offset (in quadwords)
15-11 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
10-0 Ch 1 System Memory Line Offset (in quadwords)
Port 2358 – Graphics AGP Channel 2 System Start...... RW
31-3 Channel 2 System Memory Start Address
(quadword aligned)
2-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
Port 2364 –Channel Arbitration Counter Threshold.... RW
31-28 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
26-24 Channel 2 System Arbitration Threshold
23-20 Channel 2 System Arbitration Threshold
19-16 Channel 2 System Arbitration Threshold
15-12 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
11-8 ??
7-0 ??
Port 2368 – Graphics AGP Channel I/O Control.......... RW
31-27 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
26 Reserved (Do not Program)....................... must be 0
25 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
24 Reserved (Do not Program)....................... must be 0
23-22 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
21-20 Reserved (Do not Program).....................must be 01
19 Channel 1 Read Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
18 Channel 1 Interrupt Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
17 Channel 1 Destination Select
0 Frame Buffer ......................................... default
1 GE Command FIFO
16 Channel 1 Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
15-1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 Channel 0 Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
Port 235C – Graphics AGP Channel 2 FB Start/Pitch . RW
31-22 Frame Buffer Line Offset (in quadwords)
21-19 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
18-0 Frame Buffer Starting Address
Port 2360 – Graphics AGP Channel 2 FB Size...............RW
31-27 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
26-16 Ch 2 System Memory Line Offset (in quadwords)
15-11 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
10-0 Ch 1 System Memory Line Offset (in quadwords)
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -62- Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers
Page 69

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Port 236C – Graphics AGP Global & Chan 2 Control .. RW
31-26 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
25-24 Sideband Address (SBA) Standby Latency Timer
23 High Priority Command Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
22 Long Read Command Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
21 System Side Channel 2 Priority
20 System Side Channel 1 Priority
19 System Side Channel 0 Priority
18 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
17 Frame Buffer Channel 2 Priority
16 Frame Buffer Channel 1 Priority
15-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4-3 Channel 2 Read Operation Select
00 Disabled .................................................default
01 Read from Frame Buffer to AGP
10 Write from AGP to Capture / MPEG / FB
11 -reserved 2 Channel 2 Interrupt Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1-0 Channel 2 Write Target Select
00 Write to Frame Buffer............................default
01 Write to Capture / MPEG / FB
1x -reserved-
Port 2370 –AGP Status .................................................... RW
31-18 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
17 Channel 2 Interrupt Status
0 No interrupt pending.............................. default
1 Interrupt Pending
16 Channel 2 Busy Status
0 Idle .................................................... default
1 Busy
15-10 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
9 Channel 1 Interrupt Status
0 No interrupt pending.............................. default
1 Interrupt Pending
8 Channel 1 Busy Status
0 Idle .................................................... default
1 Busy
7-2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1 Channel 0 Interrupt Status
0 No interrupt pending.............................. default
1 Interrupt Pending
0 Channel 0 Busy Status
0 Idle .................................................... default
1 Busy
Graphics AGP Configuration Registers
Port 2380 – Graphics AGP Capability Identifier .......... RW
31-0 xx
Port 2384 – Graphics AGP Status................................... RW
31-0 xx
Port 2388 – Graphics AGP Command............................ RW
31-0 xx
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -63- Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers
Page 70

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Command List Operation
The PLE133 implements an internal block called the
“Command List Control Unit” to process command lists.
Command list operation is invisible to software. After
initialization of the Command List Control Unit, software can
set registers as if there is no Command List Control Unit. If
an engine is idle and there are no pending commands in the
command buffer, data will be passed to the corresponding
register directly. Otherwise, address and data will be stored
into the command buffer to be processed later. When the
engine is idle, the Command List Control Unit will fetch
commands from the command buffer which is located in video
memory and send it to the engine. There are two registers that
determine the lower and upper bounds of the command buffer,
the Command Buffer Start and Command Buffer End
registers. The Command List Control Unit uses the command
buffer in a round robin fashion, i.e., the address is wrapped
around when it passes the end of the buffer.
Registers in the Setup Engine, Rasterization Engine, Pixel
Engine, Memory Interface, and data from the host CPU and
the drawing environment can be buffered by the Command
List Control Unit. Command List Control registers and VGA
extension registers cannot be buffered. Every entry in the
command buffer is 64-bit with the lower 32 bits for the
register address and the higher 32 bits for register data. In
order to optimize memory bandwidth usage, the Command
List Control Unit maintains one read and one write FIFO in its
interface to memory in order to burst information from the
read/write command list.
Capture / ZV Port Registers
Port 2200 – Capture / ZV Port Command ..................... RW
31-28 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
27-24 Address 1
23-20 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
19-16 Address 0
15-8 Data 1
7-0 Data 0
Port 23B0 –Command Buffer Start Address.................. RW
31-30 Command List Mode
00 Disable Command Buffer ......................default
01 Enable Command Buffer
10 Flush Command Buffer Then Disable (after
first completing any commands in the existing
command buffer)
11 -reserved-
29-24 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
23-0 Command Buffer Start Address
Starting address of the command buffer in bytes
(quadword aligned). Writing to this register will set
the internal buffer start and end pointers to this
address.
Port 23B0 –Command Buffer End Address....................RW
31-24 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
23-0 Command Buffer End Address
End address of the command buffer in bytes
(quadword aligned). This address should be
programmed to one more than the address of the last
byte of the command buffer.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -64- Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers
Page 71

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
DVD Registers
Port 2280 – MC Version ID...............................................RO
7-0 Version ID
Port 2281 – MC Control ...................................................RW
7 Debug Mode
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 MC Completion Interrupt
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 VO Completion Interrupt
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 Host Bus Identification
0 AGP .....................................................default
1 PCI
3 Decode Overwrite
0 Enable ....................................................default
1 Disable
2-1 IDCT Data Format
00 -reserved- ...............................................default
01 9 bits
10 8 bits
11 16 bits
0 MC Mode
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
Port 2282 – MC Frame Buffer Configuration................ RW
7 Interlaced Display
6 TV Flicker Filter Bypass
0 Use TV CRTC ....................................... default
1 Use VGA CRTC
5 Request Threshold of Display Command Queue
4 Request Threshold of PBF
3 Request Threshold of PFF
2 Hardware SP RL-Decode Disable
0 Enable.................................................... default
1 Disable
1-0 Frame Buffer Configuration
00 4-frame .................................................. default
01 3.5-frame
10 3.5-frame HHR
11 3-frame
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -65- Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers
Page 72

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Port 2287-2284 – MC Command Queue ......................... RW
31-12 Page Table Address
11 SP Command Present
0 SP Command is Absent..........................default
1 SP Command is Present
10-9 Video Output Display Fields
00 -reserved- ...............................................default
01 Top
10 Bottom
11 Both
8-6 Video Output Display Buffer
000 F0 .....................................................default
001 F1
010 F2
011 F3
100 H0
101 H1
110 H2
111 -reserved-
5-4 MC Buffer 2
Bit-1 = 1
00 H0 top
01 H1 bottom
10 H2 both
11 No Buf 2 n/a
3-2 MC Buffer 1
Bit-1 = 1
00 H0 F0
01 H1 F1
10 H2 F2
11 n/a F3
1 MC Buffer is Field
0 Not Field ................................................default
1 Field
0 MC Command in Queue
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
This register changes definition when written with bit-0 = 1.
This address then becomes “MC Status” with the definition of
the bits matching the following bit definitions until MC-Status
bit-0 is cleared by hardware.
Bit-1 = 0
Bit-1 = 0
Port 2285-2284 – MC Status............................................ RW
15 Task Pop Out Done Status
14-12 FIFO Status
11 MC Decode Done Status
10-9 Video Output Display Fields
00 -reserved-............................................... default
01 Top
10 Bottom
11 Both
8-6 Video Output Display Buffer
000 F0 .................................................... default
001 F1
010 F2
011 F3
100 H0
101 H1
110 H2
111 -reserved-
5-4 MC Buffer 2
Bit-1 = 1
00 H0 top
01 H1 bottom
10 H2 both
11 No Buf 2 n/a
3-2 MC Buffer 1
Bit-1 = 1
00 H0 F0
01 H1 F1
10 H2 F2
11 n/a F3
1 MC Buffer is Field
0 Not Field................................................ default
1 Field
0 MC Status
0 Not in progress ...................................... default
1 In Progress
The bit definitions above are valid only when bit-0 is equal to
1. When hardware clears bit-0, bit definitions revert to those
defined by the “MC Command Queue” register defined in the
left hand column of this page.
Bit-1 = 0
Bit-1 = 0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -66- Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers
Page 73

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Port 228B-2288 – MC Y-Reference Address ..................RW
31-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 Y-Reference Start Address (quadword aligned)
Port 228F-228C – MC U-Reference Address.................. RW
31-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 U-Reference Start Address (quadword aligned)
Port 2293-2290 – MC V-Reference Address ...................RW
31-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 V-Reference Start Address (quadword aligned)
Port 2297-2294 – MC Display Y-Address Offset............RW
31-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 Y Address Offset
Y address offset (quadword aligned) of first display
pixel relative to the first pixel (top left hand corner)
of the picture.
Port 229B-2298 – MC Display U-Address Offset ...........RW
31-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 U Address Offset
U address offset (quadword aligned) of first display
pixel relative to the first pixel (top left hand corner)
of the picture.
Port 22AB-22A8 – Color Palette Entries........................ RW
Port 22B3-22B0 – SP BUF0 Pixel Start Address ........... RW
Port 22B7-22B4 – SP BUF1 Pixel Start Address ........... RW
Port 22BB-22B8 – SP BUF0 Command Start Address . RW
Port 22BF-22BC – SP BUF1 Command Start Address. RW
Port 22C1-22C0 – SP Y Display Offset........................... RW
Port 22D0 – Digital TV Encoder Control....................... RW
Port 22D3-22D1 – Digital TV Encoder CFC.................. RW
Port 229F-229C – MC Display V-Address Offset...........RW
31-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 V Address Offset
V address offset (quadword aligned) of first display
pixel relative to the first pixel (top left hand corner)
of the picture.
Port 22A0 – MC H Macroblock Count ...........................RW
7-0 Number of Horizontal Macroblocks
Port 22A2 – MC V Macroblock Count............................RW
7-0 Number of Vertical Macroblocks
Port 22A5-22A4 – MC Frame Buffer Y Length ............. RW
15-0 Number of Pixels in a Y Frame
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -67- Graphics Accelerator PCI Bus Master Registers
Page 74

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
VGA Registers
VGA Standard Registers - Introduction
The standard VGA register set consists of five sets of indexed
registers plus several individually addressed registers. All
VGA registers are addressed at specific I/O port addresses
defined by the VGA legacy standard.
The non-indexed registers (also called the “Status / Enable”
registers) are:
Input Status Register 0 Read at 3C2
Input Status Register 1 Read at 3BA or 3DA
Miscellaneous Register Read at 3CC, Write at 3C2
Video Subsystem Enable Read/Write at 3C3
Display Adapter Enable Read/Write at 46E8
The indexed register sets each control different functional
blocks inside the hardware VGA logic. These register sets
are:
Attribute Controller 21 registers (0-14h) at 3C0/1
Sequencer 5 registers (0-4h) at 3C4/5
Graphics Controller 9 registers (0-8h) at 3CE/F
CRT Controller 25 registers (0-18h) at 3x4/5
RAMDAC 256 24-bit registers at 3C7-3C9
Indexed registers typically require two sequential port
addresses, the first of which is the index and the second of
which is the data. In other words, the index is written to the
first port address and then the data corresponding to that
indexed register is read from or written to the second port
address. The exceptions to this are the Attribute Controller
and the RAMDAC. For the Attribute Controller, the index is
written at 3C0 as expected. Data reads (but not writes) can be
performed from port 3C1 in the standard way. However,
generally most data read and all data write operations use the
same 3C0 port as used for the index. Data and address are
accessed on alternate operations to 3C0 with an internal flag to
keep track of where the next operation is to be performed
(reads from 3BA or 3DA reset the flag to point at the index
register). The other exception to the 2-port index/data
structure is the RAMDAC which uses three port addresses. In
this case, there are two locations provided for the index, 3C7
and 3C8, with the data at 3C9. There is actually only one
index register, but automatic pre / post incrementation is
performed differently depending on whether the index is
written at the “Read” address (3C7) or the “Write” address
(3C8). The current index value may be read at 3C8. Refer to
the RAMDAC register group for further explanation of the
operation of the index registers and sequential access to the
three data bytes of each indexed data location.
where extended functions are provided in all indexed register
groups except the Attribute Controller (due to the unusual
nature of Attribute Controller indexing using a single I/O port
which makes access to this register group more cumbersome).
This document will detail the functions of all the standard
VGA registers first. All extended functions will then be
separately documented in following sections.
Regarding notation used in this document, indexed registers
(including extended registers) may be referenced using a 2letter mnemonic from the following table followed by the
index number:
Attribute Controller AR
Graphics Controller GR
CRT Controller CR
Sequencer SR
For example, index register 26h of the 3CE / 3CFh indexed
register group could also be referred to as GR26. Bit-7 if this
register, using this notation, would be GR26[7].
Register groups, for the most part, are included in this
document in order by I/O port address. Some registers are
included out of order with other registers in the same
functional block. Refer to the table of contents and the
register summary tables at the beginning of the register section
of this document for further information and help in finding
descriptive information for a specific register.
For standard VGA registers, primarily only the bit definitions
are provided here. Since the operation of these bits was
standardized long ago, full explanation of the operation of
these bits is not provided in this document. Detailed
explanation of these bits is provided by many fine indiustry
publications (check your local computer book store or the
internet for further information).
The number of registers listed above for each indexed register
group is the number of registers defined by the VGA standard.
The operation of these “base” registers will always be exactly
the same from one vendor’s implementation of the VGA to
another. Typically, however, there are additional nonstandard / extended functions implemented in higher
numbered index values. That is the case for this chip as well,
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -68- VGA Registers
Page 75

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Attribute Controller Registers (AR)
For this indexed register group, the index is accessed at 3C0 as
expected. However, although data operations can be
performed using port 3C1 in the standard way, data is
generally accessed at 3C0 as well. In other words, data and
address are accessed on alternate operations to 3C0 with an
internal flag to keep track of where the next operation is to be
performed. The state of the internal flag may be read back in
the extended registers (see CR24). To set the internal flag to
select the index (i.e., to set the flag so that the next access to
port 3C0h points to the index register), read port 3BAh or
3DAh (depending on the state of the color / mono bit in the
Miscellaneous Output Register at 3C2[0]). Attribute
Controller register data may be read at 3C1 (the internal flag is
not toggled) but must be written at 3C0.
Port 3C0 – VGA Attribute Controller Index.................. RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 Palette Address Source
4-0 Attribute Controller Index
Only the lower 5 bits are implemented to allow
access to Attribute Controller registers 0-14h.
Port 3C0/3C1 Index 0-F – Attr Ctrlr Color Palette .......RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5-0 Color Value
Port 3C0/3C1 Index 10 – Attr Ctrlr Mode Control........RW
7 P5 / P4 Select
6 Pixel Width
5 Pixel Panning Compatibility
4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 Select Background Intensity or Enable Blink
2 Enable Line Graphics Character Mode
1 Display Type
0 Graphics / Text Mode
Port 3C0/3C1 Index 11 – Attr Ctrlr Overscan Color.....RW
7-0 Overscan Color
Port 3C0/3C1 Index 12 – Attr Ctrlr Color Plane Ena ...RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5-4 Video Status Mux
3-0 Color Plane Enable for Color Planes 3-0
VGA Status / Enable Registers
Port 3C2 – VGA Input Status 0........................................ RO
7 Vertical Retrace Interrupt Pending
6-5 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
4 Switch Sense
3-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Port 3xA – VGA Input Status 1........................................ RO
This register is accessible at either 3BA or 3DA (shorthand
notation 3xA) depending on the setting of Miscellaneous
Output Register at 3C2[0].
7-6 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
5-4 Diagnostic
3 Vertical Retrace
2-1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 Display Enable (Inverted)
Port 3C2 – VGA Miscellaneous Output Register (Write)WO
Port 3CC – VGA Miscellaneous Output Register (Read)RO
7 Vertical Sync Polarity
6 Horizontal Sync Polarity
5 Page Bit for Odd / Even
4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3-2 Clock Select
1 Enable RAM
0 I/O Address Select
0 CRTC registers at 3Bx, Input Status 1 at 3BA
1 CRTC registers at 3Dx, Input Status 1 at 3DA
Port 3C3 – VGA Video Subsystem Enable..................... RW
7-1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 Video Subsystem Enable
Port 46E8h – VGA Display Adapter Enable.................. RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 Display Adapter Enable
2-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
Port 3C0/3C1 Index 13 – Attr Ctrlr H Pixel Panning....RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-0 Horizontal Pixel Pan
Port 3C0/3C1 Index 14 – Attr Ctrlr Color Select...........RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-0 Color Select Bits 7-4
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -69- VGA Registers
Page 76

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
VGA Sequencer Registers (SR)
Port 3C4 – VGA Sequencer Index...................................RW
7-0 Sequencer Index
Only the lower 3 bits are implemented in a standard
VGA to point to Sequencer registers 0-4. However,
all 8 bits are implemented here to allow for extended
registers up to index FF.
Port 3C5 Index 0 – Sequencer Reset................................RW
7-2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1 Synchronous Reset
0 Asynchronous Reset
Port 3C5 Index 1 – Sequencer Clocking Mode...............RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 Screen Off
4 Shift 4
3 Dot Clock
2 Shift Load
1 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
0 8/9 Dot Clocks
Port 3C5 Index 2 – Sequencer Map Mask ......................RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 Enable Map 3
2 Enable Map 2
1 Enable Map 1
0 Enable Map 0
Port 3C5 Index 3 – Sequencer Character Map Select....RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 Character Map Select A
4 Character Map Select B
3-2 Character Map Select A
1-0 Character Map Select B
Port 3C5 Index 4 – Sequencer Memory Mode................RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 Chain 4
2 Odd / Even
1 Extended Memory
0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
VGA RAMDAC Registers
Port 3C6 – VGA RAMDAC Pixel Mask......................... RW
7-0 Palette Address Mask
Port 3C6 – VGA RAMDAC Command.......................... RW
This register is a non-standard VGA register (“extension
register”) located at the same port address as the VGA
RAMDAC Pixel Mask register. In order to maintain
compatibility with standard VGA operations, access to this
register is restricted: access is enabled by performing four
successive accesses to the Pixel Mask register at 3C6 (i.e.,
read 3C6 four times).
7-4 Color Mode Select
0000 Pseudo-Color Mode............................... default
0001 Hi-Color Mode (15-bit direct interface)
0010 Muxed Pseudo-Color Mode (16-bit pixel bus)
0011 XGA Color Mode (16-bit direct interface)
01xx -reserved 10xx -reserved 1100 -reserved 1101 True Color Mode (24-bit direct interface)
111x -reserved-
3 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
2 DAC Disable
0 DAC On (if SR20[0] = 1)...................... default
1 DAC Off
1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 RAMDAC Enable
0 Disable (Bypass) RAMDAC ................. default
1 Enable RAMDAC
Port 3C7 – VGA RAMDAC Read Index ........................ WO
Port 3C8 – VGA RAMDAC Write Index....................... WO
Port 3C8 – VGA RAMDAC Index Readback................. RO
7-0 RAMDAC Index
Port 3C9 Index 0-FF – RAMDAC Color Palette ........... RW
7-0 RAMDAC Color Data
There are 768 data entries in the palette consisting of 256
three-byte entries. R, G, and B 8-bit values are accessed on
successive operations to this port with the index
autoincremented after every 3 accesses. Refer to a VGA
programmers guide for further information.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -70- VGA Registers
Page 77

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
VGA Graphics Controller Registers (GR)
Port 3CE – VGA Graphics Controller Index .................RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6-0 Graphics Controller Index
Only the lower 4 bits are implemented in a standard
VGA to allow access to Graphics Controller registers
0-8. However, 7 bits are implemented here to allow
for extended registers up to index 7F.
Port 3CF Index 0 – Graphics Controller Set / Reset......RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-0 Set / Reset Planes 3-0
Port 3CF Index 1 – Graphics Controller Set / Reset EnaRW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-0 Enable Set / Reset Planes 3-0
Port 3CF Index 2 – Graphics Controller Color CompareRW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-0 Color Compare Planes 3-0
Port 3CF Index 3 – Graphics Controller Data Rotate ... RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 Function Select
2-0 Rotate Count
Port 3CF Index 5 – Graphics Controller Mode............. RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6 256 Color Mode ........................................default = 0
5 Shift Register ............................................default = 0
4 Odd / Even .............................................. default = 0
3 Read Mode ..............................................default = 0
2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1-0 Write Mode .............................................. default = 0
Port 3CF Index 6 – Graphics Controller MiscellaneousRW
7-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3-2 Memory Map
1 Chain Odd Maps to Even
0 Graphics Mode
Port 3CF Index 7 – Graphics Ctrlr Color Don’t Care .. RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3-0 Color Don’t Care Planes 3-0
Port 3CF Index 8 – Graphics Controller Bit Mask ....... RW
7-0 Bit Mask
Port 3CF Index 4 – Graphics Ctrlr Read Map Select....RW
7-2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1-0 Map Select
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -71- VGA Registers
Page 78

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
VGA CRT Controller Registers (CR)
CRTC registers are accessible at either 3B4 / 3B5 or 3D4 /
3D5 (shorthand notation 3x4 / 3x5) depending on the setting
of Miscellaneous Output Register 3C2 bit-0
Port 3x4 – VGA CRT Controller Index ..........................RW
7-0 CRT Controller Index
Only the lower 5 bits are implemented in a standard
VGA to allow access to CRTC registers 0-18h.
However, all 8 bits are implemented here to allow for
extended registers up to index FF.
Port 3x5 Index 0 – VGA CRTC – H Total ......................RW
7-0 Horizontal Total....................................... default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 1 – VGA CRTC – H Display Ena End...RW
7-0 Horizontal Display Enable End.............. default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 2 – VGA CRTC – H Blank Start ...........RW
7-0 Horizontal Blanking Start....................... default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 3 – VGA CRTC – H Blank End............. RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6-5 Display Enable Skew ............................... default = 0
4-0 Horizontal Blanking End ........................ default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 4 – VGA CRTC – H Retrace Start ........RW
7-0 Horizontal Retrace Pulse Start.........default = 0FFh
Port 3x5 Index 5 – VGA CRTC – H Retrace End..........RW
7 Horizontal Blanking End ........................ default = 0
6-5 Horizontal Retrace Delay........................ default = 0
4-0 Horizontal Retrace Pulse End................. default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 6 – VGA CRTC – V Total ......................RW
7-0 Vertical Total .......................................... default = 0
Port 3x5 Index A – VGA CRTC – Cursor Start............ RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
5 Cursor On/Off ..........................................default = 0
4-0 Cursor Row Scan Start............................ default = 0
Port 3x5 Index B – VGA CRTC – Cursor End.............. RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6-5 Cursor Skew .............................................default = 0
4-0 Cursor Row Scan End ............................. default = 0
Port 3x5 Index C / D – VGA CRTC Start Addr Hi/Lo . RW
.............................................. default = 0
Port 3x5 Index E / F – VGA CRTC Cursor Loc Hi/Lo . RW
.............................................. default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 10 – VGA CRTC – V Retrace Start ...... RW
7-0 Vertical Retrace Pulse Start.................... default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 11 – VGA CRTC – V Retrace End........ RW
7 CR0-7 Write Protect ................................default = 0
6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 Vertical Interrupt Enable........................ default = 0
4 Vertical Interrupt Clear ..........................default = 0
3-0 Vertical Retrace Pulse End......................default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 12 – VGA CRTC – V Display Ena End RW
7-0 Vertical Display Enable End................... default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 13 – VGA CRTC – Offset ...................... RW
7-0 Display Screen Logical Line Width ........default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 14 – VGA CRTC – Underline Location RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6 Double Word Mode.................................. default = 0
5 Count By 4 ............................................. default = 0
4-0 Underline Location...................................default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 7 – VGA CRTC – Overflow ...................RW
7 Vertical Retrace Start Bit-9 .................... default = 0
6 Vertical Display Enable End Bit-9 ......... default = 0
5 Vertical Total Bit-9 .................................. default = 0
4 Line Compare Bit-8 ................................. default = 0
3 Vertical Blank Start Bit-8 ....................... default = 0
2 Vertical Retrace Start Bit-8 ................... default = 0
1 Vertical Display Enable End Bit-8 ......... default = 0
0 Vertical Total Bit-8 .................................. default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 8 – VGA CRTC – Preset Row Scan.......RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6-5 Byte Panning ............................................ default = 0
4-0 Preset Row Scan....................................... default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 9 – VGA CRTC – Max Scan Line..........RW
7 200 to 400 Line Conversion..................... default = 0
6 Line Compare Bit-9 ................................. default = 0
5 Vertical Blank Start Bit-9 ....................... default = 0
4-0 Maximum Scan Line................................ default = 0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -72- VGA Registers
Port 3x5 Index 15 – VGA CRTC – V Blank Start......... RW
7-0 Vertical Blanking Start............................ default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 16 – VGA CRTC – V Blank End........... RW
7-0 Vertical Blanking End .............................default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 17 – VGA CRTC – Mode Control......... RW
7 Hardware Rese .........................................default = 0
6 Word / Byte Mode .................................... default = 0
5 Address Wrap........................................... default = 0
4 VSYNC Update Select (VGA Extended Capability)
0 Base may only
1 Base address may be updated during Hsync
3 Count By 2 ..............................................default = 0
2 Horizzontal Retrace Select ...................... default = 0
1 Select Row Scan Counter......................... default = 0
0 Compatibility Mode Support ..................default = 0
Port 3x5 Index 18 – VGA CRTC – Line Compare........ RW
7-0 Line Compare ........................................... default = 0
be updated during Vsync ....def
Page 79

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
VGA Extended Registers
VGA Extended Registers – Non-Indexed I/O Ports
Port 3D8 – Alternate Destination Segment Addr...........RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6-0 Alternative Destination Segment Address .def = 00
Read / write of this register is enabled by GRF[2].
This register becomes active when GR6[3-2] are not 00.
Port 3D9 – Alternate Source Segment Address..............RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6-0 Alternative Source Segment Address......... def = 00
Read / write of this register is enabled by GRF[2].
This register becomes active when GR6[3-2] are not 00.
Port 3xB – Alternate Clock Select................................... RW
3xB notation indicates that this register is accessible at either
3BB or 3DB depending on the setting of the color / mono bit.
7-5 New Mode Control Register Bits 3-1 ..........def = 00
These bits have the same function as SRD[3-1]
4-2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1-0 Video Clock Select........................................ def = 00
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -73- VGA Extended Registers
Page 80

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
VGA Extended Registers – Sequencer Indexed
SR8 – Old / New Status......................................................RO
7 Old / New Status (see SRB, SRC, SRD, SRE, GRE)
0 Old .....................................................default
1 New
6 Interlace Scan Field
0 Odd .....................................................default
1 Even
5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Command FIFO Empty
0 Empty .....................................................default
1 Not Empty
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
SR9 – Graphics Controller Version..................................RO
7-0 Version Number............................. always reads 58h
SRB – Version / Old-New Mode Control ........................RW
7-0 Graphics Controller Version # .....always reads F3h
A write to this register will change the Old / New Mode
Control registers (SRD, SRE, and GRE) to the “old”
definition. A read from this register will change the Old /
New Mode Control registers to the “new” definition.
SRC – Configuration Port 1.............................................RW
Access to this register is enabled by SRE_Old[5] = 1 (“Select
Configuration Port 1”) and writes are enabled by SRE_New[7]
= 1 (“Configuration Port Write Enable”).
7 Reserved .......................................always reads 1
6 Memory Bus Width
0 32-bit Memory Bus ................................default
1 64-bit Memory Bus
Note: Although the PLE133 integrated graphics
controller does not control memory directly (the
system memory controller is used to access graphics
memory as a portion of system memory), some
functional blocks in the graphics controller (such as
video) use this bit to manage their data bus widths.
5 Reserved .......................................always reads 1
4 Video Subsystem Enable
0 46E8
1 3C3 .....................................................default
3 Video BIOS Size
0 64K .....................................................default
1 32K
2-0 Reserved .................................always reads 111b
SRD – Mode Control 2 (Old)........................................... RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
5 Reserved ...................................... always reads 1
4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 CPU Bandwidth Select
0 Normal................................................... default
1 Non-interrupted CPU access during VBLANK
2-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
SRD – Mode Control 2 (New).......................................... RW
7-4 Display FIFO Memory Request Threshold Ctrl
0000 Empty 0 level
0001 Empty 4 level......................................... default
0010 Empty 8 lrevel
0011 Empty 12 level
0100 Empty 16 level
0101 Empty 20 level
0110 Empty 24 level
0111 Empty 28 level
1000 Empty 32 level
1001 Empty 36 level
1010 Empty 40 level
1011 Empty 44 level
1100 Empty 48 level
1101 Empty 52 level
1110 Empty 56 level
1111 Empty 60 level
3 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
2-1 Video Clock Divide
00 Divide by 1 ............................................ default
01 Divide by 2
10 Divide by 4
11 Divide by 1.5
0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
SRC – Configuration Port 2.............................................RW
Access to this register is enabled by SRE_Old[5] = 0 (“Select
Configuration Port 2”) and writes are enabled by SRE_New[7]
= 1 (“Configuration Port Write Enable”).
7-0 Reserved for BIOS
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -74- VGA Extended Registers
Page 81

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
SRE – Mode Control 1 (Old)............................................ RW
7 Reserved .......................................always reads 1
6 IRQ Polarity Select
0 Active High............................................default
1 Active Low
5 Configuration Port (SR0C) Select
0 Select Port 2
1 Select Port 1..........................................default
4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 Memory Bus.........................................................RO
0 8-bit
1 16-bit ....................................... always reads 1
2-1 256K Bank Select
00 Bank 0....................................................default
01 Bank 1
10 Bank 2
11 Bank 3
Note: an inverted value will be written to bit-1
These bits (and 3C2[5]) are write enabled when
GR06[3-2] = 00. 3C2[5] is used as a page select to
select one of the two 64KB pages.
0 RAMDAC Pixel Clock Invert
0 Normal ...................................................default
1 Invert pixel clock to RAMDAC
SRE – Mode Control 1 (New)...........................................RW
7 Configuration Port Write Enable........... default = 0
0 Write Protect
1 Write Enable
Ports effected: SRC, SRF, CR28-2A, SRE_New[6-4]
(this register), and SR10[0]
6 CPU Bandwidth Select for Text Mode
0 132-Column Text
1 Other Text ............................................. default
5-0 64K Bank Select ....................................... default = 0
Bit-1 should be inverted when performing writes
These bits are enabled when GR06[3-2] are written
with any value other than 00.
SRF – Power-up Mode 2 .................................................. RW
This register is write protected by SRE_New[7].
7 Reserved ...................................... always reads 1
6 BIOS Control
0 Disabled................................................. default
1 Enabled
5 Palette Mode
0 Master Abort Mode
1 Intel Retry Mode .................................. default
4 Linear / Bank Addressing Control
0 Linear Only
1 Linear / Bank ........................................ default
3-0 Reserved for BIOS ............................default = 1111
SR10 – VESA™ Big BIOS Control................................. RW
7 Extended VESA™ Big BIOS Enable
0 Disabled ................................................ default
1 Enabled
6-5 Video Address Select ........................................... RO
00 A0000-A7FFF ....................................... default
01 -reserved 10 B0000-B7FFF
11 B8000-BFFFF
These bits are decoded from GR6[3-2]
4-1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 Page Select
0 Select the original C0000-C7FFF access..... def
1 Select extended access defined by bits 6-5
Bit-0 of this register is write protected by SRE_New[7].
SR11 – Protection ........................................................ RW
7-0 Register Protection Enable.................... default = 00
87 Unprotect all extended registers except those
which may still be protected by SRE_New[7]
92 Unprotect all extended registers independent
of SRE_New[7]
If any value other than the ones listed above is
programmed into this register, all extended registers
will be write protected.
SR12 – Threshold ........................................................ RW
7-4 Queue Threshold Playback and
Capture ..... def = 2
Threshold of the display queue when both playback
and capture are enabled (for definition see SRD.new).
3-0 Queue Threshold Playback or
Capture........ def = 1
Threshold of the display queue when either playback
or capture are enabled (for definition see SRD.new)
The old threshold is used when neither playback nor capture is
enabled. All three thresholds cannot be set to 0. Other
definitions are the same as the original.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -75- VGA Extended Registers
Page 82

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Graphics Clock Synthesizer Control
SR18 – VCLK1 Frequency Control 0..............................RW
7-0 VCLK1 Frequency Generator Numerator.... def=0
SR19 – VCLK1 Frequency Control 1..............................RW
7-6 VCLK1 Frequency Generator K-Factor ....... def=0
5-0 VCLK1 Frequency Generator Denominator def=0
SR1A – VCLK2 Frequency Control 0.............................RW
7-0 VCLK2 Frequency Generator Numerator.... def=0
SR1B – VCLK2 Frequency Control 1.............................RW
7-6 VCLK2 Frequency Generator K-Factor ....... def=0
5-0 VCLK2 Frequency Generator Denominator def=0
SR20 – Clock Synthesizer / RAMDAC Setup ................ RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6 Multiplex Mode Sync Mechanism
0 Normal Mode ........................................ default
1 Enable synchronization in multiplexed mode
for high VCLK tracking
5 Simultaneous VAFC and Playback
0 Simultaneous VAFC / playback display default
1 Playback only
4 VAFC and Playback Display Overlay
0 VAFC is on top...................................... default
1 Playback is on top
3 DAC Test Mode
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 Video Mode
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1-0 Video Mode Select
x0 5-5-5 Hi-color.................................. default = 0
x1 5-6-5 XGA-color
0x Video Playback, True-color
1x Video Playback, 256-color
Table 8. Graphics Clock Frequencies – 14.31818 MHz Reference
Denominator
Value
88 3E 62 8 2 25.057 25.175 -0.0047
89 4F 79 9 2 28.311 28.322 -0.0004
88 5D 93 8 2 36.153 36.000 0.0043
83 30 48 3 2 40.091 40.000 0.0023
85 4A 74 5 2 41.932 42.000 -0.0016
84 42 66 4 2 44.148 44.000 0.0034
84 43 67 4 2 44.744 44.900 -0.0035
84 48 72 4 2 47.727 48.000 -0.0057
43 1B 27 3 1 50.114 50.350 -0.0047
46 33 51 6 1 52.798 52.800 0.0000
42 18 24 2 1 57.273 57.270 0.0000
43 21 33 3 1 58.705 58.800 -0.0016
43 23 35 3 1 61.568 61.600 -0.0005
4A 63 99 10 1 63.835 64.000 -0.0026
48 53 83 8 1 65.148 65.000 0.0023
46 43 67 6 1 67.116 67.200 -0.0012
44 33 51 4 1 70.398 70.400 0.0000
44 34 52 4 1 71.591 72.000 -0.0057
42 22 34 2 1 75.170 75.000 0.0023
44 39 57 4 1 77.557 77.000 0.0072
44 3B 59 4 1 79.943 80.000 -0.0007
44 42 66 4 1 88.295 88.000 0.0034
44 44 68 4 1 90.682 90.000 0.0076
44 4A 74 4 1 97.841 98.000 -0.0016
04 22 34 4 0 100.227 100.000 0.0023
07 3C 60 7 0 108.182 108.000 0.0017
02 19 25 2 0 118.125 118.000 0.0011
03 22 34 3 0 120.273 120.000 0.0023
05 3A 58 5 0 135.000 135.000 0.0000
05 4B 75 5 0 169.773 170.000 -0.0013
Numerator
Value
N
M K
Actual
Frequency
Expected
Frequency
Frequency
Error %
The clock frequency can be derived by multiplying the reference frequency times (N+8) / [(M+2) x 2K]
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -76- VGA Extended Registers
Page 83

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Graphics Signature Analyzer Registers
SR21 – Signature Control.................................................RW
7 Signature Generator Enable
0 Disable (readback 0 indicates done).......default
1 Enable (readback 1 indicates busy)
6 Signature Source Select
0 TV / CRT ...............................................default
1 LCD
5-0 Bit Select .............................................. default = 0
SR23-22 – Signature Data .................................................RO
15-0 Signature Data
Graphics Power Management Control Registers
SR24 – Power Management Control...............................RW
7 RAMDAC Clock During RAMDAC Powerdown
0 14.318 MHz ..........................................default
1 14.31818 MHz divided by 2
6 Enable VCLK2 VCO Directly
(without warmup sequence)
0 Enable
1 Don’t Enable ..........................................default
5-4 Clock Input Divisor
Divisor for 14.318 MHz clock input to MCLK to
drive DRAM refresh cycles in power managed
modes.
00 1 .....................................................default
01 2
10 4
11 8
3 Power Management Slow MCLK
0 Use divided MCLK during standby &
suspend
1 Use MCLK during standby & suspend ....... def
2 Enable MCLK VCO Directly
(without warmup sequence)
0 Enable
1 Don’t Enable .........................................default
1 Enable MCLK VCO Directly
(without warmup sequence)
0 Enable
1 Don’t Enable .........................................default
0 DAC Power
0 Off .....................................................default
1 On
Graphics Connector Control Registers
SR25 – Monitor Sense ....................................................... RO
7-3 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
2-0 Monitor Sense Result: [red, green, blue]
SR37 – Video Key Mode .................................................. RW
7 Feature Connector Input Clock Polarity
0 Normal................................................... default
1 Inverted
6 Signal Output (AFC Processing)
0 Signal output is sent before AFC processingdef
1 Signal output is sent after AFC processing
5-4 Feature Connector Input Pixel Clock Tuning
00 0 ns .................................................... default
01 4 ns
10 8 ns
11 12 ns delay of pixel clock with respect to data
3-0 Overlay Key Type
0000 VGA Port Only...................................... default
0001 Color Key & Video Key
0010 Color Key & not Video Key
0011 Color Key
0100 Not Color Key & Video Key
0101 Video Key
0110 Color Key XOR Video Key
0111 Color Key | Video Key
1000 Not Color Key & Not Video Key
1001 Color Key XNOR Video Key
1010 Not Video Key
1011 Color Key | Not Video Key
1100 Not Color Key
1101 Not Color Key | Video Key
1110 Not Color Key | Not Video Key
1111 Video Port Only
SR38 – Advanced Feature Connector (AFC) Control... RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6 DCLK Rate (set after other bits for syncronization)
0 PCLK .................................................... default
1 PCLK / 2
5 DCLK Phase Select (if bit-6 = 1)
0 180 degree phase shift ........................... default
1 In phase
4 DCLK Output Polarity
0 Normal when bit-6 = 0 .......................... default
1 Inverted
3 VCLK Input Polarity
0 Normal................................................... default
1 Inverted
2-1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 Pixel Data Bus Output Enable Control
0 Disable Output Drive............................. default
1 Disable drive only when EVIDEO# is low
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -77- VGA Extended Registers
Page 84

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Graphics Playback Control Registers
SR52-50 – Playback Color Key Data...............................RW
23-16 Playback Color Key for True Color Mode
15-8 Playback Color Key for High Color Mode
7-0 Playback Color Key for 256 Color Mode
SR56-54 – Playback Color Key Mask .............................RW
23-16 Playback Color Key Mask for True Color Mode
15-8 Playback Color Key Mask for High Color Mode
7-0 Playback Color Key Mask for 256 Color Mode
SR57 – Playback Video Key Mode Function..................RW
7-0 Overlay Key Type
Defines all 256 defferent types of mixing among
VGA Color Key, Playback Window Key, and Video
Chroma Key (very similar to ROP3 code). Below
are some common combinations:
00 VGA Port Only
F0 Color Key Only
CC Playback Key Only
AA Chromakey Only
88 Playback Key & Chromakey
C0 Colorkey & Playback Key
80 Colorkey & Playback key & Chromakey
FF Video Port Only
Graphics Second Playback Control Registers
SR62-60 – 2
nd
Playback Color Key Data ........................ RW
23-16 Playback Color Key for True Color Mode
15-8 Playback Color Key for High Color Mode
7-0 Playback Color Key for 256 Color Mode
SR66-64 – 2
nd
Playback Color Key Mask....................... RW
23-16 Playback Color Key Mask for True Color Mode
15-8 Playback Color Key Mask for High Color Mode
7-0 Playback Color Key Mask for 256 Color Mode
Graphics BIOS Scratch Pad Registers
SR5A – Scratch Pad 0....................................................... RW
SR5B – Scratch Pad 1....................................................... RW
SR5C – Scratch Pad 2....................................................... RW
SR5D – Scratch Pad 3....................................................... RW
SR5E – Scratch Pad 4....................................................... RW
SR5F – Scratch Pad 5 .......................................................RW
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -78- VGA Extended Registers
Page 85

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Graphics Video Display Registers
SR82-80 – Window 1 U-Plane FB Start Address............RW
23-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 W1 U-Plane FB Start Address
When operating in planar mode, this field defines the
frame buffer starting address for the U-plane for the
first live video window
SR85-83 – Window 1 V-Plane FB Start Address............RW
23-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 W1 V-Plane FB Start Address
When operating in planar mode, this field defines the
frame buffer starting address for the V-plane for the
first live video window
SR88-86 – Window 2 Frame Buffer Start Address ........RW
23-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 Window 2 Frame Buffer Start Address
Frame buffer starting address for the second live
video window (packed YUV format only)
SR8A-89 – Window 2 Horizontal Scaling Factor...........RW
15 W2 Horizontal Minify / Zoom Select
0 Zoom .....................................................default
1 Minify
Zoom Selected (Bit-15 = 0)
14 Reserved
13-0 W2 Horizontal Zoom Factor
Same format as for the first live video window as
defined in CR80 and CR81
Minify Selected (Bit-15 = 1)
14-13 W2 Tap
12-10 W2 Horizontal Minify Integer (Inverter)
9-0 W2 Horizontal Minify Factor
SR8C-8B – Window 2 Vertical Scaling Factor .............. RW
15 W2 Vertical Minify / Zoom Select
0 Zoom .................................................... default
1 Minify
14 W2 Vertical Filtering
0 Off .................................................... default
1 On
Zoom Selected (Bit-15 = 0)
13-0 W2 Vertical Zoom Factor
Same format as for the first live video window as
defined in CR82 and CR83
Minify Selected (Bit-15 = 1)
13-10 Reserved
9-0 W2 Vertical Minify Factor
SR90-8D – Window 2 Live Video Start .......................... RW
31-28 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
27-16 W2 Vertical Starting Point
15-12 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
11-0 W2 Horizontal Starting Point
SR94-91 – Window 2 Live Video End............................. RW
31-30 W2 Line Buffer Level Bits 8-7 (see SR95)
29-28 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
27-16 W2 Vertical Ending Point
15-12 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
11-0 W2 Horizontal Ending Point
SR95 – Window 2 Live Video Line Buffer Level........... RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6-0 W2 Line Buffer Level Bits 6-0 (see SR91[31-30])
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -79- VGA Extended Registers
Page 86

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
SR96 – New Live Video Window Control 0.................... RW
7 W2 Horizontal Interpolation
0 Interpolation...........................................default
1 Duplication
6 W1 Vertical Interpolation U and V Components
0 Enable ....................................................default
1 Disable
This bit is effective only if window 1 vertical Y
interpolation is enabled (CR8E[12] = 1)
5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 656
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 W2 Color Space Converter (CSC) Bypass
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1 MC Even / Odd Inverter
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
0 MC Interlace Display
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
SR97 – New Live Video Window Control 1.................... RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6 Planar Mode X (Horizontal) Y/UV Ratio
0 2x .....................................................default
1 4x
5-4 Planar Mode Y (Vertical) Y/UV Ratio
00 2x (Yp420).............................................default
01 4x (Yp410)
1x 1x (Yp422)
3 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
2-0 Window Mode .................................... default = 000b
Format
000 YUV422 H-V (96+48) x 64
001 Planar H-V (96+48) x 64
01x YUV FIFO H 96 x 64
100 MPEG2 YUV422 H-V 2x(96+48)x64
101 MPEG2 Planar H-V 2x(96+48)x64
11x YUV422 H-V (V-YUV) 2x(96+48)x64
For 1xx, only one h/w overlay window is supported
Interpolation Line Buffers
SR98 – New Live Video Window Control 2 ................... RW
7-6 Two Live Window Chroma Key Select
00 Chroma key only ................................... default
01 Window 1 & chroma key
10 Window 2 & chroma key
11 (Window 1 | Window 2) & chroma key
5-4 W1 Anti-Flicker Removal
00 Disable................................................... default
01 One field is shifted up 1 line
10 One field is shifted up 2 lines
11 One field is shifted up 3 lines
3 W1 Anti-Flicker Removal Field Selection
0 Odd field is shifted up ........................... default
1 Even field is shifted up
2-1 W2 Anti-Flicker Removal
00 Disable................................................... default
01 One field is shifted up 1 line
10 One field is shifted up 2 lines
11 One field is shifted up 3 lines
0 W2 Anti-Flicker Removal Field Selection
0 Odd field is shifted up ........................... default
1 Even field is shifted up
SR99 – New Live Video Window Control 3 ................... RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6 Capture Addres Swap Enable
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 Capture Address Swap
0 No swap................................................. default
1 Swap
4-2 W2 HDE Delay Adjust............................. default = 0
1-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
SR9B-9A – Window 1 UV Video Row Byte Offset ........ RW
15-14 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
13-0 W1 UV Plane Video Row Byte Offset (the bytes in
a row)
SR9D-9C – Window 2 Y Video Row Byte Offset........... RW
15-14 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
13-0 W2 Y Plane Video Row Byte Offset (the bytes in a
row)
SR9E – Line Buffer Request Threshold ......................... RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6-0 Line Buffer Request Threshold Level ..........def = 0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -80- VGA Extended Registers
Page 87

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
SR9F – VBI Control .........................................................RW
7 VBI Interrupt Status ...........................................RO
6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 VBI Bit-8
4 VBI IV Bit-8
3 VBI Interrupt
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 VBI Enable
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1-0 VBI Data Format in Frame Buffer
00 Every field data overwrite ......................default
01 Data in even/odd format
10 Every two field data write contiguous
11 -reserved-
SRA3-A0 - VBI Frame Buffer Address...........................RW
31-20 VBI Row Byte Offset
19-0 VBI Start Address
SRA7-A4 – VBI Capture Start.........................................RW
31-27 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
26-16 VBI Vertical Start
15-11 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
10-0 VBI Horizontal Start
SRAD-AC – VBI Vertical Interrupt Position ................ RW
15 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
14-12 Dithering Mode
000 Bypass dithering .................................... default
001 -reserved 010 24 bpp dither to 16 bpp
011 24 bpp chop to 16 bpp
100 24 bpp dither to 15 bpp
101 24 bpp chop to 15 bpp
110 24 bpp dither to RGB8
111 24 bpp chop to RGB8
11 Capture CSC
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
10-0 VINST[10-0]
SRAB-A8 – VBI Capture End .........................................RW
31-27 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
26-16 VBI Vertical End
15-11 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
10-0 VBI Horizontal End
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -81- VGA Extended Registers
Page 88

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
SRAF-AE – Capture Row Byte Offset ............................RW
15 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
14 Capture Address Initial Control
13-0 Capture Row Byte
SRB1-B0 – Window 1 HSB Control ................................RW
15-10 Brightness
9-5 Sin(Hue) * Saturation * 8 (bit-9 is the sign bit)
4-0 Cos(Hue) * Saturation * 8 (bit-4 is the sign bit)
Hue range is 0-360 degrees (default = 0)
Saturation range is 0-1.875 (default = 1)
SRB3-B2 – Window 2 HSB Control ................................RW
15-10 Brightness
9-5 Sin(Hue) * Saturation * 8 (bit-9 is the sign bit)
4-0 Cos(Hue) * Saturation * 8 (bit-4 is the sign bit)
Hue range is 0-360 degrees (default = 0)
Saturation range is 0-1.875 (default = 1)
SRB6-B4 – Second Display Address Select .....................RW
23-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 Second Display Address for Double Buffering
Second display address for double buffering instead
of capture address
SRB7 – Video Sharpness ..................................................RW
7-0 Video Sharpness Factor
SRBA-B8 – Second Capture Address Select...................RW
23-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 Second Capture Address for Double Buffering
Second capture address for double buffering instead
of display address
SRBC – Contrast Control.................................................RW
7-4 Window 2 Contrast
3-0 Window 1 Contrast
SRBD – Dual View Mux Control .................................... RW
7-3 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
2-0 CRT / TV View Multiplexing Control
00x Color key 1 determines top window (1=W1)def
010 Video window 1 overlay
011 Video window 2 overlay
10x Window key defines window 1 on top
11x Window key defines window 2 on top
SRBE – Miscellaneous Control Bits................................ RW
7 Planar Capture
0 Off .................................................... default
1 On
6-5 Capture Start Address W/R Control (CR98[19-
0])
0x W/R Y address ...................................... default
10 W/R U address
11 W/R V address
4 Video Engine Power Saving Mode
0 On .................................................... default
1 On
3 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
2 Interpolation Bypass
0 Interpolation .......................................... default
1 Bypass
1 Window 2 HSCB Enable
0 Bypass ................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Window 1 HSCB Enable
0 Bypass ................................................... default
1 Enable
SRCE – Window 2 Live Video Control .......................... RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6 W2 Vertical Interpolation
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
5 Planar Mode X (Horizontal) Y/UV Ratio
0 2x .................................................... default
1 4x
4-3 Planar Mode Y (Vertical) Y/UV Ratio
00 2x (Yp420) ............................................ default
01 4x (Yp410)
1x 1x (Yp422)
2-0 Window Mode ....................................default = 000b
Format
000 YUV422 H-V (96+48) x 64
001 Planar H-V (96+48) x 64
01x YUV FIFO H 96 x 64
100 MPEG2 YUV422 H-V 2x(96+48)x64
101 MPEG2 Planar H-V 2x(96+48)x64
11x YUV422 H-V (V-YUV) 2x(96+48)x64
For 1xx, only one h/w overlay window is supported
Interpolation Line Buffers
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -82- VGA Extended Registers
Page 89

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
SRD1-D0 – Window 2 UV Row Byte Offset....................RW
15-14 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
13-0 W2 UV Plane Video Row Byte Offset (the bytes in
a row)
SRD4-D2 – Window 2 U-Frame Start Address .............. RW
23-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 W2 U-Frame Start Address
SRD7-D5 – Window 2 V-Frame Start Address .............. RW
23-20 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
19-0 W2 V-Frame Start Address
SRD9-D8 – Digital TV Interface Control........................RW
(see also CRD0, VGA / Digital TV Sync Control)
15-14 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
13 DIVS I/O Control
12 DTVI Signal Output Control, except DIVS
(Vsync)
11 Dual View Clock Inversion Control
10 Dual View Clock Control for DTVI
9 DICLK Inversion Control
8 DIVS Inversion Control
7 DIHS Inversion Control
6-5 YUV Order Inversion Control
4, 1 Data Out Control
00 VGA / Video Overlay Data
x1 TV Data
10 Data Direct from Video Engine
3-0 HS / VS / CLK Control
0000 VGAHS, VGAVS, and PCLK
x100 VGAHS, VGAVS, and SPKTV
1000 VGAHS, VGAVS, and PCLK x 2
xxx1 DVHS, DVVS, and LCDCLK
xx10 TVHS, TVVS, and TVCLK
SRDB-DA – Window 2 V-Count Status .......................... RO
15-0 W2 V Count Status
SRDD-DC – Dual View Control...................................... RW
15-11 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
10-9 Dual View Control - SHIF
8 Dual View Control – G Window Enable
7 Dual View Control – W2 Double Buffer Enable
6 Dual View Control – W1 Double Buffer Enable
5 Dual View Control – W2 Address Trans Enable
4 Dual View Control – W1 Address Trans Enable
3 Dual View Control – Digital TV Enable
2 Dual View Control – Digital Video LUT Write
1 Dual View Control – Digital Video LUT Read
0 Dual View Control – Digital Video CRT
SRDF-DE – Window 1 V-Count Status........................... RO
15-13 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
12 DVV Sync
11-0 W1 V Count Status
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -83- VGA Extended Registers
Page 90

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
VGA Extended Registers – Graphics Controller Indexed
GRE – Old Source Segment Address ..............................RW
7-3 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
2-1 Source Segment Address Select .............. default = 0
0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
GRE – New Source Segment Address .............................RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6-0 Source Segment Address Select .............. default = 0
Bit-1 is written inverted
GRF – Miscellaneous Extended Function Control........ RW
7 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
6 Character Clock Division Control Bit-1 (see bit-3)
00 No division ............................................ default
01 Divide by 2
10 Divide by 3
11 -reserved-
5 Symmetric / Asymmetric DRAM Address
0 Symmetric ............................................. default
1 Asymmetric
4 Compressed Chain 4 Mode for CPU Path
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 Character Clock Division Control Bit-0 (see bit-6)
2 Alternate Bank & Clock Select
0 Disable 3D8, 3D9, and 3xB................... default
1 Enable 3D8, 3D9, and 3xB
1 Compressed Chain 4 Mode Display Path
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Source Segment Address Register Enable
0 Disable GRE.......................................... default
1 Enable GRE
All bits except 2 and 0 are write protected by SRE_New[7]
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -84- VGA Extended Registers
Page 91

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Power Management Registers
GR20 – Standby Timer Control.......................................RW
7 Timer Initialize & Enable
0 Enable Timer..........................................default
1 Initialize and hold standby and DPMS timer
6-4 Timer Testing .......................................................RO
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
GR21 – Power Management Control 1 ........................... RW
7 Power Management Pin Polarity
0 Active High............................................default
1 Active Low
6 PCI Power Management
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5 Suspend Mode
0 Normal mode .........................................default
1 Enter Suspend Mode
4 Suspend Input Pin
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 D3 to D0 Reset
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 Standby Input Pin
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 CLKRUN# Mechanism
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
0 Consistent Standby / Suspend
0 The bits in the PCI PM configuration registers
will be OR’ed with bits 5 and 3 of this register
for connection to the internal PM state
machine..................................................default
1 The bits in the PCI PM configuration registers
will be the same as bits 5 and 3 of this register
to allow software coherency
GR22 – Power Management Control 2........................... RW
7 Timer Test Mode
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6 Refresh Clock Select
0 Crystal input or external clock (XMCLK)
provides refresh clock during suspend .. default
1 REFCLK is used as refresh clock during
suspend for 64ms refresh (ignore “Suspend
DRAM Refresh Mode” bits 5-4 below)
5-4 Suspend DRAM Refresh Mode
00 No refresh.............................................. default
01 Self refresh
10 Crystal clock provides rate for 8ms refresh
11 Crystal clock provides rate for 64ms refresh
3 Disable GPIO
0 Allow GPIO 7-0 pins to drive data in.... default
1 Disable GPIO 7-0 pins (and their shared
functions) from driving data. Tristates input
buffers on pins so no power is consumed if
GPIO pins are set to input mode.
2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1 Hardware / Software Oscillator Select
0 Software controls oscillator off with bit-0
(prevents automatic oscillator shutdown
without direct software control of the
“Oscillator Disable” bit).............................. def
1 Hardware controls oscillator off (allow
oscillator shutdown when power states are
entered using hardware mechanisms)
0 Oscillator Disable
0 Enable normal function ......................... default
1 Disable (oscillator off)
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -85- VGA Extended Registers
Page 92

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
GR23 – Power Status ........................................................ RW
7 Power Management Pin Polarity (see GR21[7])
6-5 Chip Power Status
00 Ready
01 Standby
10 Suspend
11 -reserved-
4 LCD Power Sequence Status
0 LCD power sequencing is not occurring at
this time
1 LCD power sequencing is occurring at this
time
3-2 Panel Power Sequencing
00 Fast panel power sequencing .................default
01 -reserved 10 -reserved 11 Slow panel power sequencing
1-0 DPMS Power Status
00 On Mode (CRT interface is active and
RAMDAC is full on)..............................default
01 Standby Mode (Hsync disabled, Vsync active,
DAC off, RAMDAC color palette lookup
table (LUT) video data path is off but LUT
I/O is allowed)
10 Suspend Mode (Vsync disabled, Hsync
active, RAMDAC is off but contents are
retained)
11 Off Mode (Hsync and Vsync disabled, DAC
LUT is full off)
In hardware
CRT Hsync and Vsync as well as the internal
RAMDAC power state (the “off” mode state can be
read only in CRT only mode). In software
these bits control the state of the CRT Hsync and
Vsync signals but not
RAMDAC. In simultaneous display modes, the
power state of the RAMDAC is not controlled by the
DPMS Power State (bits 1-0), but by the Chip Power
State (bits 6-5).
mode, these bits indicate the status of
mode,
the power state of the internal
GR24 – Software Power Control..................................... RW
7 VCLK
0 Disable
1 Enable................................................... default
6 MCLK
0 Disable
1 Enable................................................... default
5 CPU & DRAM Data Bus
0 Disable
1 Enable................................................... default
4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 ENPBLT (Panel and/or Backlight Enable)
Control
Software Power Control
0 Drive ENPBLT Low ............................. default
1 Drive ENPBLT High
Hardware Power Control
0 ENPBLT is active low........................... default
1 ENPBLT is active high
2 Panel VDD
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 Panel Interface Signals
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Panel VEE
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
GR25 – Power Control Select.......................................... RW
When any of bits 7-6 or 3-0 are set to 1, the corresponding
power control bit reads back the logic state of the internal
power management engine. For all bits below, 0 selects
hardware power control and 1 selects software power control.
7 Power Control for VCLK.............................. def = 1
6 Power Control for MCLK ............................def = 1
5 Power Control for the Data Bus ................... def = 1
4 Power Control for the RAMDAC ................def = 1
The RAMDAC is software enabled in GR26[7-6]
3 Power Control for Panel Enable / Backlight def = 1
(see GR24[3])
2 Power Control for Panel VDD ..................... def = 1
1 Power Control for Panel Interface Signals .def = 1
0 Power Control for Panel VEE ...................... def = 1
(timers, pin, register bit)
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -86- VGA Extended Registers
Page 93

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
GR26 – DPMS Control.....................................................RW
7-6 RAMDAC Internal Power Control
00 Normal ...................................................default
01 DAC off (used in LCD only mode)
10 Standby (DAC off, LUT in low power mode,
I/O allowed to LUT). May be used in LUT
bypass mode.
11 Suspend (DAC off, LUT access disallowed
but LUT contents are preserved)
5-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 DPMS Control
0 Software Control Mode: DPMS controlled by
GR23[1-0] in simultaneous display and CRTonly modes (may be used to decouple the
power modes of the CRT and LCD during
simultaneous display) ..........................default
1 Hardware Control Mode: DPMS controlled
by internal power states.
2-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
DPMS Control Modes
DPMS Software Control Mode
In simultaneous display mode, the software control mode can
be used to control DPMS low power states independent of the
chip power states. In CRT display mode, software mode
gives total DPMS control to software. Pseudo-standby may
be controlled by bits 7 and 6, as well as BLANK# timing.
DPMS Hardware Control Mode
Table 9. DPMS Sequence - Hardware Timer Mode
Power Level DPMS Mode
High - Activity detected On
Moderate - 16 min inactivity Standby
Low - 32 min inactivity Suspend
Lowest - 64 min inactivity Off
DPMS hardware timer mode is defined as CRT only mode
with the DPMS control mode bit set to hardware (bit 3 =1).
Activity detection is set by register GR21[2:0]. Status is
indicated in bits 1 and 0. The timer may be controlled by
software from GR20[7].
Table 10. DPMS Sequence - Hardware Mode in
Simultaneous Display Mode
Power Level DPMS Mode
High - Chip on state On
Moderate - Chip standby Off
Low - Chip suspend Off
Lowest - Chip off state Off
In simultaneous display mode with hardware DPMS
set, DPMS states are sequenced by the timer, pin, and
register bits that control the chip power states.
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -87- VGA Extended Registers
Page 94

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
GR28-27 – GPIO Control................................................. RW
15-8 GPIO Direction 7-0
0 Read .....................................................default
1 Write
7-0 GPIO Data 7-0.......................................... default = 0
GR2A – Suspend Pin Timer.............................................RW
7 Motion Video Port Suspend
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
GR2C – Miscellaneous Pin Control................................. RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6 Use PDINV pin as GPIO5
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
5-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3 Use INT# pin as PSTATUS
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 Tristate P35-0, DE, SFCLK, LP, FLM
0 Tristate ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 Tristate ENPVEE, ENPVDD, ENPBLT
0 Tristate ...................................................default
1 Enable
0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
GR2F – Miscellaneous Internal Control......................... RW
7 PCLK Control
0 VGA Compatible................................... default
1 PCLK equals VCLK
6 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
5 Hsync Skew Control
0 One skew in graphics, two skew in text default
1 No skew
4-3 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
2 Double Logical Line Width
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1 Text Mode Display FIFO Prefetch Cycles Select
0 Multiple of 8.......................................... default
1 Multiple of 4
0 Enable Display FIFO Threshold Control
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable (can also be enabled by AR10[0])
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -88- VGA Extended Registers
Page 95

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Scratch Pad Registers
These registers are reserved for use by software.
GR5A – Scratch Pad 0......................................................RW
GR5B – Scratch Pad 1 ......................................................RW
GR5C – Scratch Pad 2......................................................RW
GR5D – Scratch Pad 3......................................................RW
GR5E – Scratch Pad 4 ......................................................RW
GR5F – Scratch Pad 5 ......................................................RW
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -89- VGA Extended Registers
Page 96

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
VGA Extended Registers – CRT Controller Indexed
CRE – CRT Module Test .................................................RW
7 Extended Memory Access Above 256KB
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
6 VGA Misc Output Register (3C2) Write Protect
0 Writes to 3C2 Allowed ..........................default
1 Write Protect 3C2
5 CRT Start Address Bit-16
4-3 Reserved ....................................... alwatys reads 0
2 Interlaced Mode
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1-0 Reserved for Test (Do Not Program) .... default = 0
CR19 – CRT Interlace Control........................................ RW
7-0 Interlaced Vsync Adjust Value
CR1A – Arbitration Control 1 ........................................ RW
7-0 Display Queue Kill Counter .................... default = 0
Controls how many requests can be accepted by the
arbiter before changing the owner to another agent
(00 disables the counter).
CR1B – Arbitration Control 2......................................... RW
7-0 High Priority Arbiter Kill Counter ........ default = 0
Controls how many requests can be accepted by the
arbiter before changing the owner to another agent
(00 disables the counter).
CR1C – Arbitration Control 3 ........................................ RW
7-0 Low Priority Arbiter Kill Counter .........default = 0
Controls how many requests can be accepted by the
arbiter before changing the owner to another agent
(00 disables the counter).
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -90- VGA Extended Registers
Page 97

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
CR1F – Software Programming ......................................RW
7-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-0 Display Memory Size
0011 1MB
0111 2MB
1111 4MB
0100 8MB
All other codes are reserved
Memory size is automatically detected during system setup.
CR20 – Command FIFO ..................................................RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 Write Buffer
0 Disable ....................................................defaul
1 Enable
4 16-Bit Planar Mode
0 Disable ....................................................defaul
1 Enable
3-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
CR21 – Linear Addressing............................................... RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 Linear Memory Access
0 Disable ....................................................defaul
1 Enable
4-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
This register is write protected by SRE_New[7].
CR29 – RAMDAC Mode ................................................. RW
7 External DAC
0 Disable.................................................... defaul
1 Enable
6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5-4 CRTC Offset[9:8] for High or True Color Modes
3 GE I/O Decode
0 Disable.................................................... defaul
1 Enable
2 RAMDAC
0 External .................................................. defaul
1 Internal
1-0 RS[3-2] for RAMDAC (if register access definition
is selected)
This register is write protected by SRE_New[7]
CR2A – Interface Select................................................... RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6 Internal Data Path Width
0 8/16-bit ................................................... defaul
1 32-bit
5 Reserved .......................................always reads 1
4 Power Down Mode Using ROMCS#
0 Enable..................................................... defaul
1 Disable
3-0 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
This register is write protected by SRE_New[7]
CR22 – CPU Latch Readback...........................................RO
7-0 Latched Data
Pointed to by GR4 (VGA Read Map Select Register
)
CR24 – VGA Attribute State ............................................RO
7 VGA Attribute State
0 Index ......................................................defaul
1 Data
6-0 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
CR25 – RAMDAC Read/Write Timing ..........................RW
7 PCLK / P[7-0] BufferTristate Control
0 Enable .....................................................defaul
1 Disable
6-4 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
3-0 RAMDAC Read / Write Wait States..... def =1111b
CR27 – CRT High Order Start Address......................... RW
7 Vertical Total Bit-10 ................................ default = 0
6 Vertical Blanking Start Bit-10 ............... default = 0
5 Vertical Retrace Start Bit-10 ................. default = 0
4 Vertical Display Enable End Bit-10 ...... default = 0
3 Line Compare Bit-10 .............................. default = 0
2-0 Start Address Bits 19-17 ......................... default = 0
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -91- VGA Extended Registers
Page 98

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
CR2B – Horizontal Parameter Overflow........................ RW
7-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4 Horizontal Blank Start Bit-8................... default = 0
3 Horizontal Retrace Start Bit-8 ............... default = 0
2 Horizontal Interlace Parameter Bit-8 ... default = 0
1 Horizontal Display Enable Bit-8 ............ default = 0
0 Horizontal Total Bit-8 ............................ default = 0
CR2D – GE Timing Control.............................................RW
7-5 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
4-3 GE Sample Clock Delay Selection.......... default = 0
2-0 GE Frame Buffer Read Delay Cycles..... default = 0
CR2F – Performance Tuning........................................... RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6 DRAM Refresh Cycle Control Bit-1
(Bit-0 is CR11[6])
00 3 refresh cycles per horizontal line
01 5 refresh cycles per horizontal line
10 1 refresh cycles per horizontal line
11 2 refresh cycles per horizontal line
5 Blank TimingSelect
0 Normal blank .........................................default
1 Blank is the inverse of display enable
4 Display FIFO Depth Control
0 32 deep...................................................default
1 8 deep
3-2 Memory Read Ready Control
00 -reserved.................................................default
01 Fast read cycle (same as 10)
10 Fast read cycle (same as 01)
11 Normal read cycle
1 Clock Source
0 VCLK2
1 VCLK1 ..................................................default
0 Pin Scan (Test Only) ................................ default = 1
CR35-34 – Graphics Engine I/O Linear Address Base . RW
15-0 Graphics Engine Linear Address Base... default = 0
CR36 – Graphics Engine / Video Engine Control ......... RW
7 Graphics Engine
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
6 PCI Video Minifier
0 Bypass ................................................... default
1 Go through minifier
5 Video Aperture
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
4 Graphics Engine Software Reset
Writing a one to this bit resets the graphics engine
3 Graphics Engine I/O
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
2 String Write
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
1-0 Graphics Engine Register Mapping
00 I/O mapped at 21xxh ............................. default
01 Memory mapped at B7Fxxh
10 Memory mapped at BFFxxh
11 Memory mapped using the GE base register
CR37 – I
7 SMBCLK Buffer is Open Drain .......always reads 1
6 I
5-4 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
3 I
2
C / SMB Control .............................................. RW
2
C SMBCLK Status............................................RO
2
C Operation
0 Read .................................................... default
1 Write
2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1 I
2
C SMBCLK Signal
0 Low
1 High ................................................... default
0 I
2
C SMBDAT Signal
0 Low .................................................... default
1 High
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -92- VGA Extended Registers
Page 99

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
CR38 – Pixel Bus Mode ....................................................RW
7-6 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
5 Packed 24-Bit True-Color Mode
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
4 Standard VGA Mode in 64-Bit Configuration
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
3 True Color Mode
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
2 High Color Mode
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
0 16-Bit Pixel Bus
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
This register is protected by SRE_New[7]
CR39 – PCI Interface Control .........................................RW
7 Pixel Data Format
0 Little Endian...........................................default
1 Big Endian
6-5 Memory Data with Big Endian Format
00 Pass Through (PT) .................................default
01 Word Swap (WS)
10 Half Swap (HS)
11 Full Swap (FS)
4-3 BE[3-0]# With Big Endian Format
00 Pass Through (PT) .................................default
01 Word Swap (WS)
10 Half Swap (HS)
11 Full Swap (FS)
2 PCI Burst Write
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
1 PCI Burst Read
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable
0 MMIO Control
0 Disable ...................................................default
1 Enable (64KB VGA I/O space can be
memory mapped within the 4GB memory
space)
This register is protected by SRE_New[7]
CR3A – Physical Address Control.................................. RW
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6 AGP / PCI Select
0 PCI .................................................... default
1 AGP
5 Both IO
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
4 Memory Address Linearization
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
2 AGP Software Reset
0 Normal................................................... default
1 Reset
1 PCI Configuration Subsystem ID Write
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
0 Enhanced Register I/O Scheme
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
CR3B – Clock and Tuning............................................... RW
7 Observe Clock Source
0 VCLK1.................................................. default
1 VCLK2
6-4 Clock Source Mode Select
0xx Internal Clock Chip
000 V/MCLK test mode, observe MCLK
001 V/MCLK test mode, observe VCLK1
010 V/MCLK test mode, observe VCLK2
011 Normal operation
1xx External Clock Chip
Bit 6 default is set from MA7
Bits 5-4 default is set from MA8,2 inverted
3 Clock Control
0 When bits 6-4 = 00x, clock is normal.... default
1 When bits 6-4 = 00x, clock is divided by 2
2-1 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
0 Vertical Retrace Memory Refresh
0 Disable
1 Enable................................................... default
This register is protected by SRE_New[7]
CR3C – Miscellaneous Control ....................................... RW
7-3 Same Definition as GRF[7-3] ..................default = 0
2 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
1 Same Definition as GRF[1]...................... default = 0
0 Mode Select 1 ............................................ default = 0
0 This register has no function ................. default
The original GRF[7-0] bits are used
1 GRF[7-3, 1] accessed via this register only
GRF[2, 0] accessed at original register only
Original GRF[3] is R/W but has no function
This register is protected by SRE_New[7]
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -93- VGA Extended Registers
Page 100

Apollo PLE133 Data Sheet
Hardware Cursor Registers
The PLE133 supports a Windows® compatible hardware
cursor. The hardware cursor operates only in extended planar
and packed pixel modes. The cursor size can be selected
between 32x32 and 64x64. Two 2-bits-per-pixel images
define the cursor shape. The table below shows how these
two bits operate on each pixel. The hardware cursor pattern
is stored in off-screen memory.
Table 11. Hardware Cursor Pixel Operation
Plane 0
(AND)
CR43-40 – Hardware Cursor Position ............................RW
31-28 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
27-16 Hardware Cursor Position Y Dimension
15-12 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
11-0 Hardware Cursor Position X Dimension
Plane 1
(XOR)
1 0 Transparent Cursor BG Color
1 1 VGA Data Inversion Cursor FG Color
0 1 Cursor FG Color Transparent
0 0 Cursor BG Color Transparent
Pixel Operation
(Windows®)
Pixel Operation
(X11)
CR50 – Hardware Cursor Control ................................. RW
7 Hardware Cursor Enable
0 Disable .................................................. default
1 Enable
6 Hardware Cursor Mode
0 MS Windows™ Compatible ................ default
1 X11 Compatible
5 Hardware Cursor Color Control 3
0 Disable .................................................. default
1 Enable
4 Hardware Cursor Color Control 2
0 Disable................................................... default
1 Enable
3-2 Reserved ........................................always reads 0
1-0 Hardware Cursor Size
00 128x128 ................................................ default
01 64x64
10 32x32
11 -reserved-
CR45-44 – Hardware Cursor Pattern Location .............RW
15-12 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
11-0 Hardware Cursor Map Mask Storage Location
1KB aligned in the frame buffer
CR47-46 – Hardware Cursor Offset................................RW
15 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
14-8 Hardware Cursor Position Y-Offset
7 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
6-0 Hardware Cursor Position X-Offset
CR4F-48 – Hardware Cursor Color................................RW
63-56 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
55-32 Hardware Cursor Background Color
31-24 Reserved ........................................ always reads 0
23-0 Hardware Cursor Foreground Color
Revision 1.86, April 22, 2005 -94- VGA Extended Registers
 Loading...
Loading...