Page 1
User’s Manual
EPIA-M
Mini-ITX Mainboard
P/N: 99-51-012561-14
Version 1.40
December 11, 2003
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright by VIA Technologies Inc. (“VIA”). No part of this manual may be
reproduced or transmitted in any form without express written authorization
from VIA.
Trademarks
All trademarks are the property of their respective holders.
PS/2 is a registered trademark of IBM Corporation.
Windows 95/98/98SE/ME/2000/NT and Windows XP are registered
trademarks of Microsoft.
AwardBIOS is a registered trademark of Phoenix Technologies Ltd.
Data protection
All data should be backed-up prior to the installation of any drive unit or
storage peripheral. VIA will not be responsible for any loss of data resulting
from the use, disuse or misuse of this or any other VIA product.
No Warranty
VIA has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the content of this
manual. However, it is possible that it may contain technical inaccuracies or
typographical or other errors. Our products are under continual improvement
and we reserve the right to make changes without notice. VIA will assume
no liability for any inaccuracy found in this publication, nor for damages,
direct, indirect, incidental, consequential or otherwise, that may result from
such an inaccuracy, including without limitation loss of data or profits.
VIA provides this manual “as is”, and does not issue a warranty of any kind,
express or implied, including without limitation implied warranties of
merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
The information provided in this manual is subject to change without notice.
VIA reserves the right to alter product designs, layouts or drivers without
notification.
ii
Page 3

FCC-B Radio Frequency Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case the user
will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Notice 1
The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the
equipment.
Notice 2
Shielded interface cables and A.C. power cord, if any, must be used in order
to comply with the emission limits.
iii
Page 4

Safety Instructions
1. Always read the safety instructions carefully.
2. Keep this User’s Manual for future reference.
3. Keep this equipment away from humidity.
4. Lay this equipment on a reliable flat surface before setting it up.
5. The openings on the enclosure are for air convection hence protects the
equipment from overheating. DO NOT COVER THE OPENINGS.
6. Make sure the voltage of the power source and adjust properly 110/220V
before connecting the equipment to the power inlet.
7. Place the power cord in such a way that people cannot step on it. Do not
place anything over the power cord.
8. Always unplug the power cord before inserting any add-on card or
module.
9. All cautions and warnings on the equipment should be noted.
10. Never pour any liquid into the opening. Liquid can cause damage or
electrical shock.
11. If any of the following situations arises, get the equipment checked by a
service personnel:
• The power cord or plug is damaged
• Liquid has penetrated into the equipment
• The equipment has been exposed to moisture
• The equipment has not work well or you can not get it work according
to User’s Manual.
• The equipment has dropped and damaged
• If the equipment has obvious sign of breakage
12. DO NOT LEAVE THIS EQUIPMENT IN AN ENVIRONMENT
UNCONDITIONED, STORAGE TEMPERATURE ABOVE 60
0
(140
F), IT MAY DAMAGE THE EQUIPMENT.
0
C
CAUTION: Explosion or serious damage may occur if the battery is
incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or equivalent type
recommended by the manufacturer.
iv
Page 5

Box Contents
• 1 x VIA Mainboard
• 1 x User’s Manual
• 1 x Floppy Ribbon Cable
• 1 x ATA-33/66/100 IDE Ribbon Cable
• 1 x Combo Module (2 port USB 2.0 and 2 port IEEE1394)
• 1 x Driver Utilities CD
v
Page 6

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Specifications ........................................1-1
Mainboard Specifications.......................................................... 1-2
Mainboard Layout ..................................................................... 1-4
Back Panel Ports ...................................................................... 1-5
Slots ..........................................................................................1-5
Onboard Connectors and Jumpers........................................... 1-6
Chapter 2: Installation..............................................2-1
CPU Installation ........................................................................2-2
Memory Module Installation ...................................................... 2-4
Connecting the Power Supply...................................................2-6
Back Panel Ports ...................................................................... 2-7
Connectors.............................................................................. 2-11
Jumpers ..................................................................................2-19
Slots ........................................................................................2-20
Chapter 3: BIOS Setup .............................................3-1
Entering Setup .......................................................................... 3-2
Control Keys ............................................................................. 3-2
Gettings Help ............................................................................3-3
The Main Menu ......................................................................... 3-4
Standard CMOS Features ........................................................3-6
Advanced BIOS Features .........................................................3-8
Advanced Chipset Features.................................................... 3-12
Integrated Peripherals.............................................................3-14
Power Management Setup ..................................................... 3-18
PNP / PCI Configurations ....................................................... 3-23
PC Health Status .................................................................... 3-26
Frequency / Voltage Control ...................................................3-27
Load Fail-Safe Defaults .......................................................... 3-30
Load Optimized Defaults.........................................................3-31
Set Supervisor / User Password .............................................3-32
Save & Exit Setup ................................................................... 3-34
Exit Without Saving ................................................................. 3-35
Chapter 4: Driver Installation ..................................4-1
Driver Utilities............................................................................ 4-2
CD Content ............................................................................... 4-3
vi
Page 7

Appendix A: Smart 5.1 ............................................ A-1
Intelligent 6-Channel Audio...................................................... A-2
vii
Page 8
Chapter
1
Specifications
The ultra-compact and highly intergrated VIA
EPIA-M Mini-ITX Mainboard is the smallest form
factor mainboard specification available today,
developed by VIA Technologies, Inc. as part of the
company’s open industry-wide total connectivity
initiative. The mainboard enables the creation of an
exciting new generation of small, ergonomic,
innovative and affordable embedded systems.
Through high level of integration, mini-ITX only
occupy 66% of the size of FlexATX mainboard
form factor. The mainboard comes with an
embedded VIA Processor, boasting ultra low power
consumption and cool, quiet operation.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Mainboard Specifications 1-2
Mainboard Layout 1-4
Back Panel Ports 1-5
Slots 1-5
Connectors / Jumpers 1-6
1-1
Page 9

Chapter 1
Mainboard Specifications
CPU
• VIA C3 / EDEN EBGA Processor (on board)
• Enhanced Ball Grid Array Package (EBGA)
• Internal L1 128KB and L2 64KB cache memory
Chipset
• VIA CLE266 North Bridge
• VT8235 South Bridge
Graphics
• Integrated UniChrome graphics with MPEG-2 decoder
Audio
• VT1616 six channel AC’97 Codec
• 3 Audio jacks: Line-in, Line-out and Mic-in; switched to 6-channel
output during 6-channel operations with Smart 5.1 (See Appendix A)
Main Memory
• 1 DDR266 DIMM socket
• Up to 1GB memory size
PCI Bus & IDE
• 1 PCI slot
• 2 X UltraDMA 66 / 100 / 133 Connector
LAN
• VIA VT6103 10 / 100 Base-T Ethernet PHY
USB
• USB v2.0 / v1.1
Firewire
• IEEE 1394; VIA VT6307S 2-port Firewire
TV-Out (optional)
• VIA VT1622/M (Macrovision) TV-Out Controller
• Supports 640 x 480, 800 x 600, and 1024 x 768 NTSC/PAL TV
1-2
Page 10

Specifications
Onboard I/O Connectors
• Two 1394 connectors for two 1394 ports
• Front-panel audio connectors (Mic and Line Out)
• CD Audio-in connector
• 1 FIR connector; 1 PS2 connector
• Wake-on-LAN
• CPU / System Fan / FAN3
2
• 1 I
C connector
• 1 Connector for LVDS module (Optional)
• Serial port connector for second COM port
Back Panel I/O Ports
• 1 PS2 mouse port; 1 PS2 keyboard port
• 1 Parallel port; 1 RJ-45 LAN port; 1 Serial port
• 2 USB 2.0 ports; 1 VGA port
• 1 RCA port (SPDIF or TV out); 1 S-Video port
• 3 Audio jacks: line-out, line-in and mic-in; can be switched to 6 channel
output with Smart 5.1 (See Appendix A)
BIOS
• AwardBIOS with 2 / 4Mbit flash memory
Form Factor
• 17 cm X 17 cm Mini-ITX (4 layers)
1-3
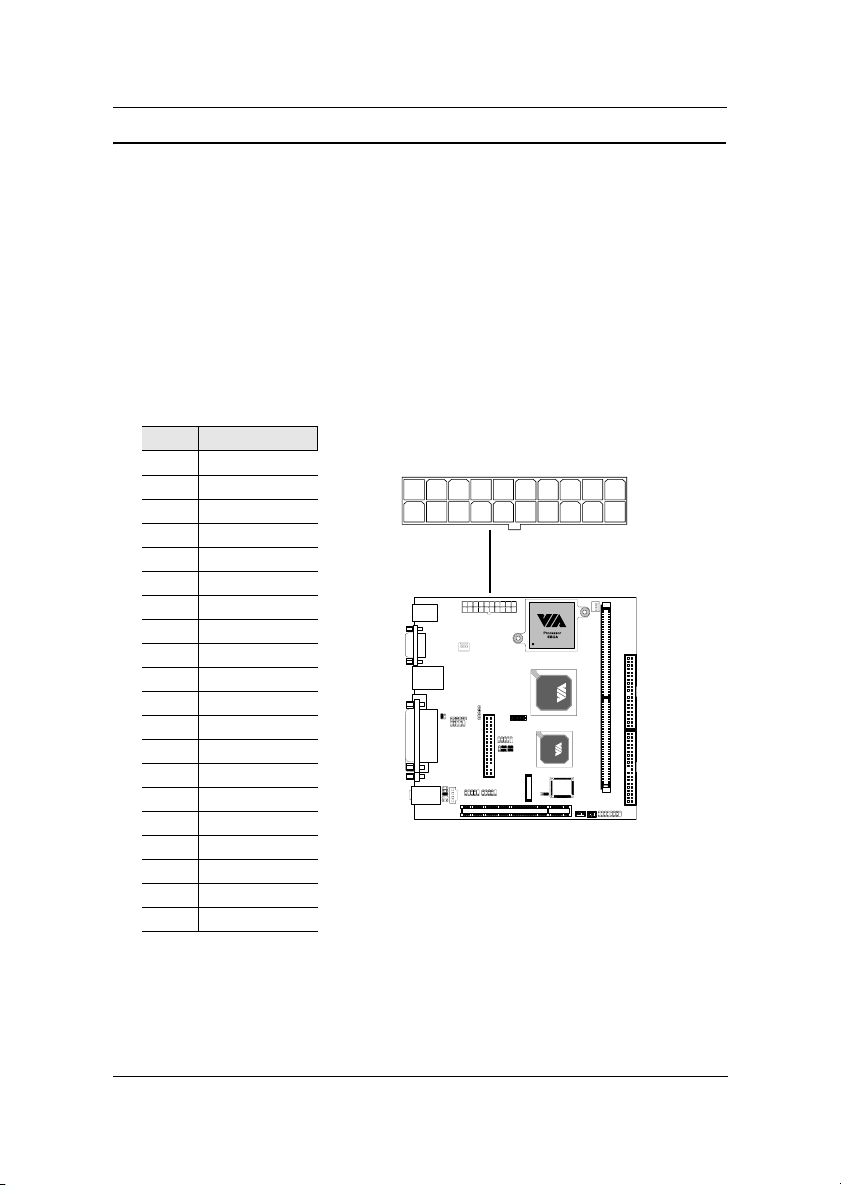
Page 11
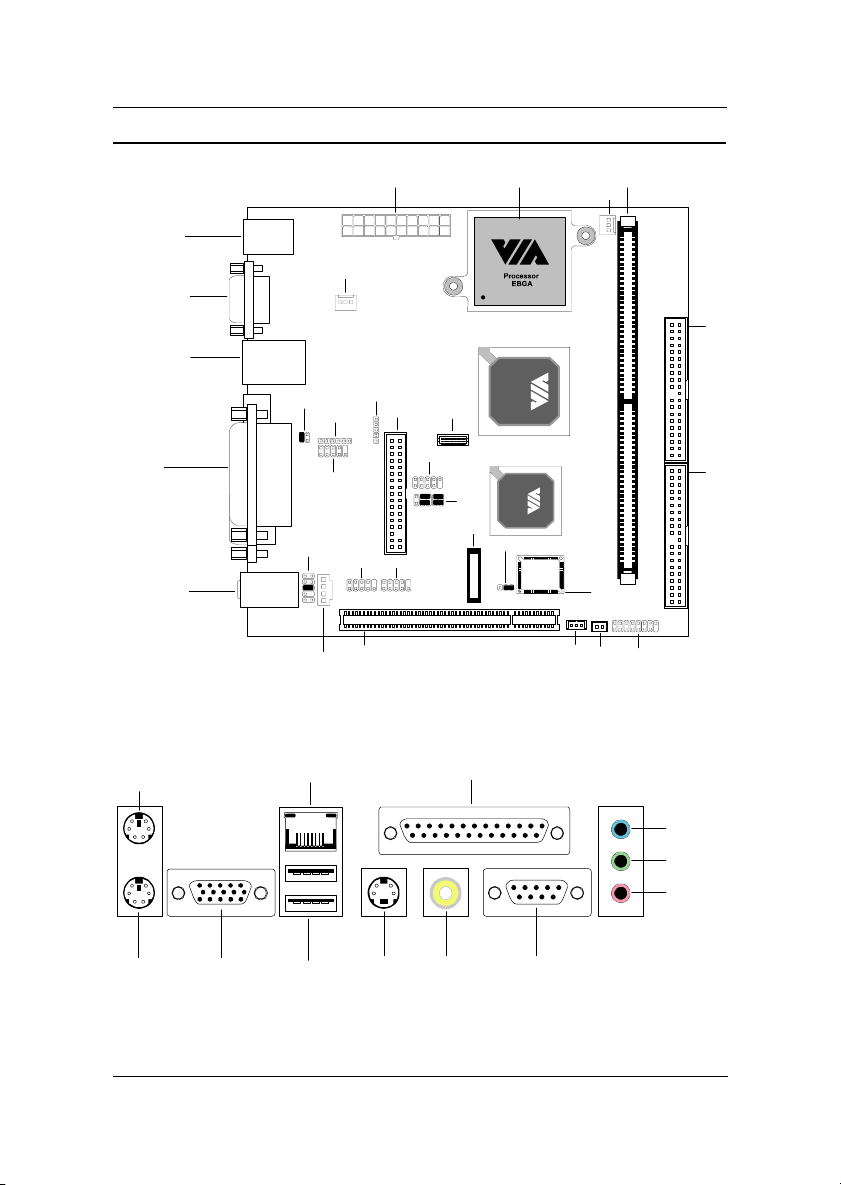
Chapter 1
Mainboard Layout
Top: Mouse
Bottom: Keyboard
VGA-Out
Top: RJ45
Bottom: USB
Top: Parallel
Bottom (L): S-Video
Bottom (M): RCA/SPDIF
Bottom (R): COM1
Top: Line-In
Middle: Line-Out
Bottom: Microphone
Back Panel
PS2_MS
SPDIF_SEL
F_AUDIO
C
RJ45
D
SYSFAN
I2C
COM2
I
N
_
FIR
FDD
1394_1 1394_2
PCI1
LVDS
USB 3/4
Parallel (LPT1)
CIR
CMOS
BATTERY
CPU
CLEAR_CMOS
WOL
CPUFAN
BIOS Socket
FAN3
DIMMATXPWR
IDE1
IDE2
F_PANEL
PS2_KB
VGA Out
USB
S-Video
RCA / SPDIF
1-4
Line-In
Line-Out
Microphone
COM1
Page 12
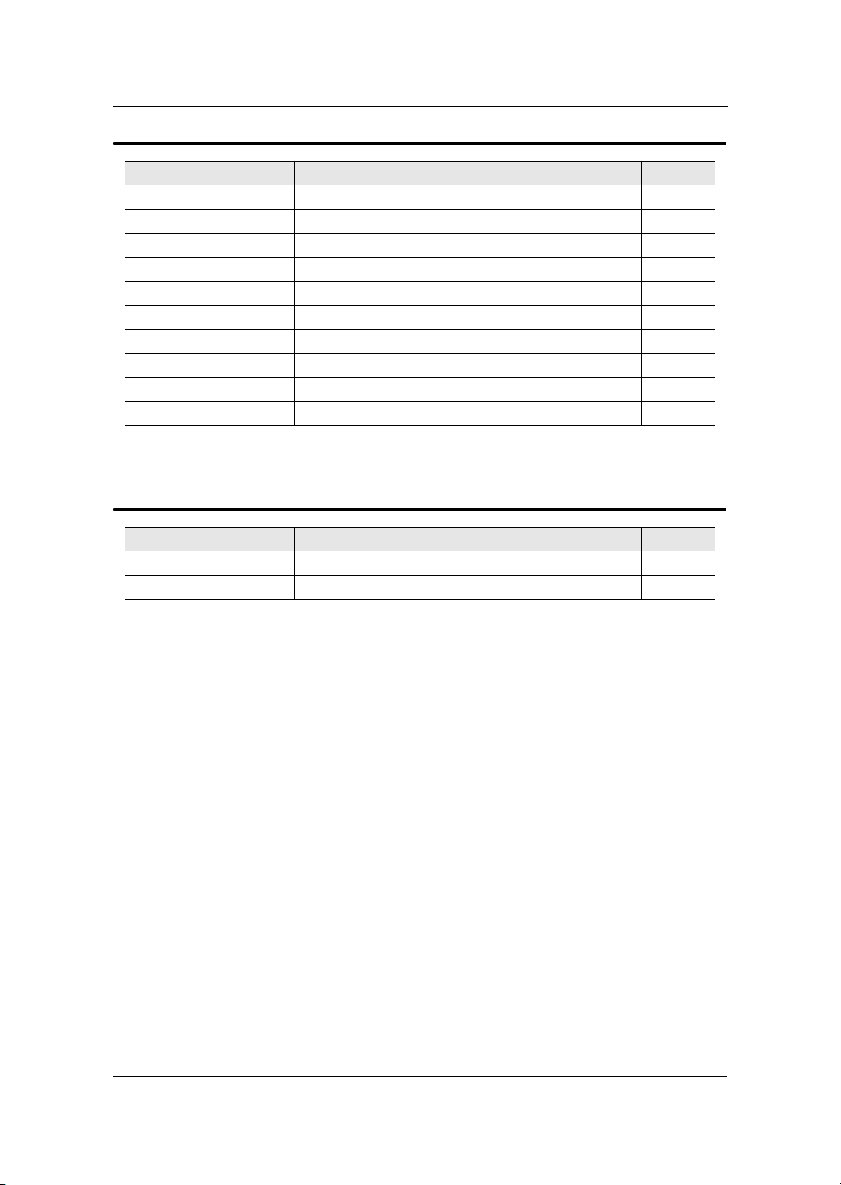
Specifications
Back Panel Ports
Port Description Page
Audio Jacks Line-Out, Line-In, Microphone 2-10
COM 1 Serial port 2-10
LPT1 Parallel port 2-9
PS2-MS PS2 mouse port 2-7
PS2-KB PS2 keyboard port 2-7
RCA_JACK RCA Video or SPDIF jack 2-8
RJ45 10/100 NIC port 2-8
S-VIDEO S-Video Port 2-8
USB 1-2 Universal Serial Bus ports 1 - 2 2-8
VGA Out VGA out port 2-8
Slots
Slot Description Page
DIMM Memory module slot 2-4
PCI Expansion card slot 2-20
1-5
Page 13
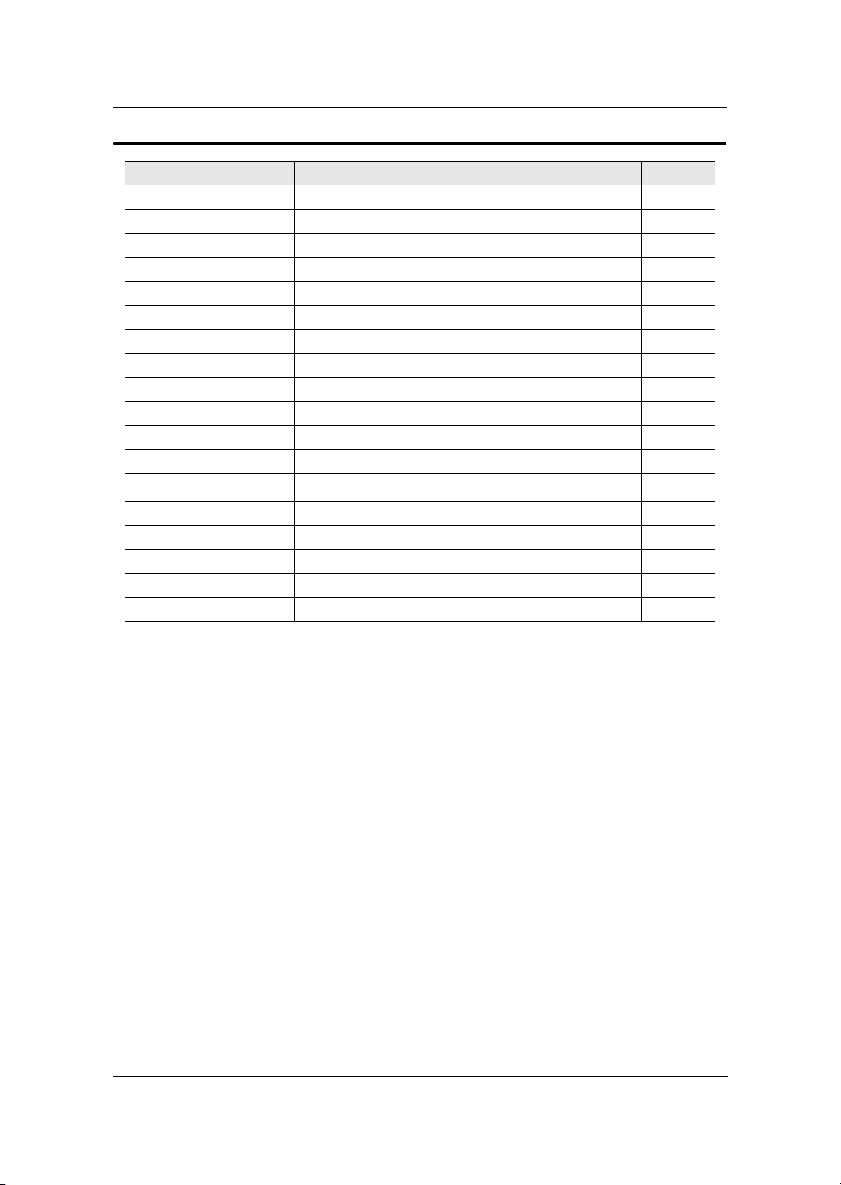
Chapter 1
Onboard Connectors and Jumpers
Connecter/Jumper Description Page
1394_1 Connector for first 1394 port 2-15
1394_2 Connector for second 1394 port 2-15
ATXPWR ATX power cable connector 2-6
CD_IN Onboard CD audio cable connector 2-16
CIR Consumer IR connector 2-13
CLEAR_CMOS Jumper to reset CMOS settings to default 2-19
COM2 Second serial port connector 2-15
F_AUDIO Connectors for optional front audio panel 2-17
F_PANEL Case connectors 2-12
Fans CPU, System, Fan3 2-2
FDD Floppy disk drive connector 2-16
FIR Fast Infrared Radiation connector 2-13
2
CI
I
IDE 1-2 IDE hard disk drive connectors 2-11
LVDS LVDS connector 2-18
SPDIF_SEL Sony Philips Digital Interface jumper 2-19
USB 3/4 Universal Serial Bus connectors 3 - 4 2-14
WOL Wake On LAN connector 2-14
2
C connector
2-17
1-6
Page 14
Chapter
2
Installation
This chapter provides you with information about
hardware setup procedures. While installing the
mainboard, carefully hold the components and
closely follow the installation procedures. Some
components may be damaged if they are installed
incorrectly.
It is recommended to use a grounded wrist strap
before handling computer components. Static
electricity can damage some components.
This chapter includes the following sections:
CPU 2-2
Memory Module Installation 2-4
Connecting the Power Supply 2-6
Back Panel Ports 2-7
Connectors 2-11
Jumpers 2-19
Slots 2-20
2-1
Page 15
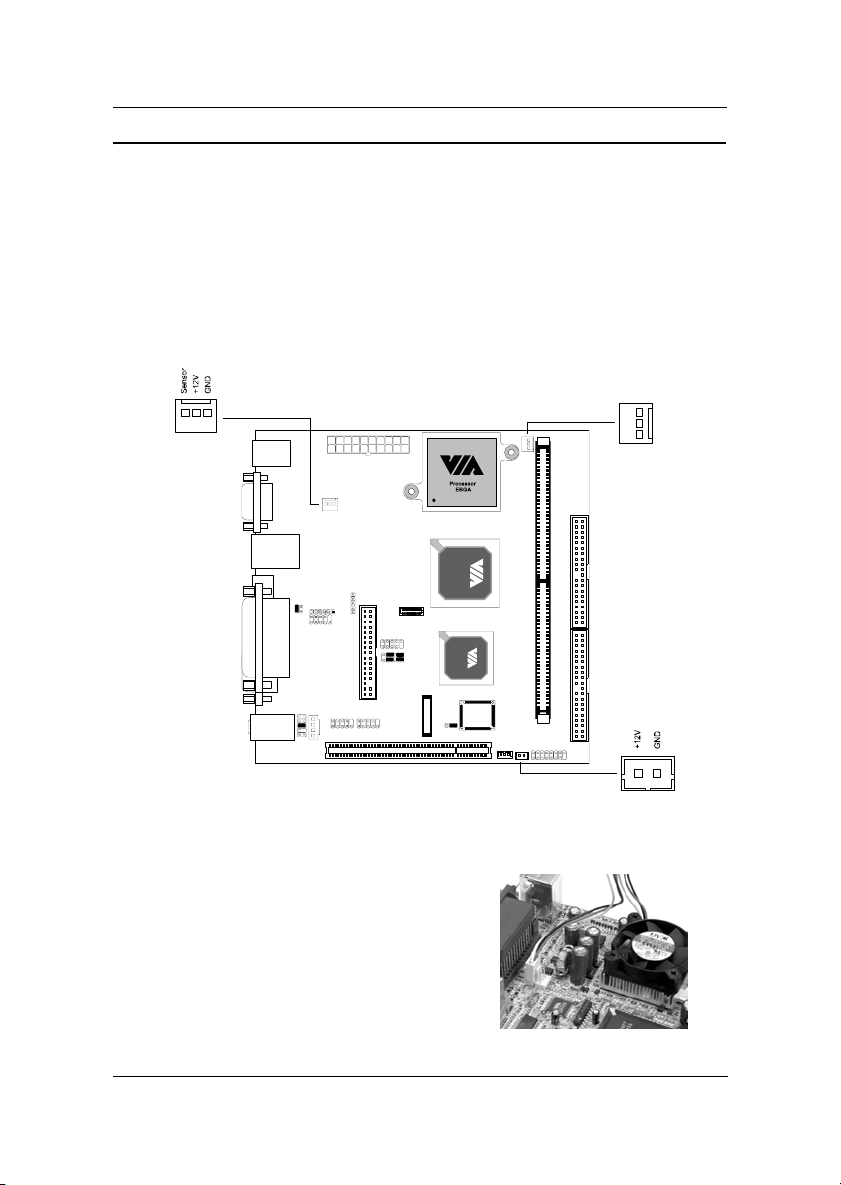
Chapter 2
CPU
The VIA EPIA-M Mini-ITX Mainboard includes an embedded VIA Eden
Processor or VIA C3
TM
E-Series Processor. The CPUFAN (CPU fan) and
SYSFAN (system fan) run on +12V and maintain system cooling. When
connecting the wire to the connectors, always be aware that the red wire is
the Positive and should be connected to the +12V. The black wire is Ground
and should be connected to GND. Both CPU and System fan connectors
have sensors to detect fan speed, but the power fan does not have a sensor.
FAN3 is an additional FAN connector.
CPUFAN
Sensor
+12V
SYSFAN
GND
The VIA C3TM E-Series Processor
With low power consumption and advanced
thermal dissipation properties, the embedded
VIA C3
guarantee performance and reliability. Ensure
that the CPU Fan Connector is correctly
installed as shown.
TM
E-Series requires only a small fan to
2-2
FAN3
Page 16

Installation
The VIA Eden Processor
Providing ultra-low power consumption
and advanced thermal dissipation
properties, the VIA Eden Processor
features a fanless design. The VIA Eden
Processor requires only a heatsink as
shown.
Warning: This motherboard is not designed to support overclocking. Any attempt to
operate beyond product specifications is not recommended. We do not guarantee
the damages or risks caused by operation beyond product specifications.
2-3
Page 17
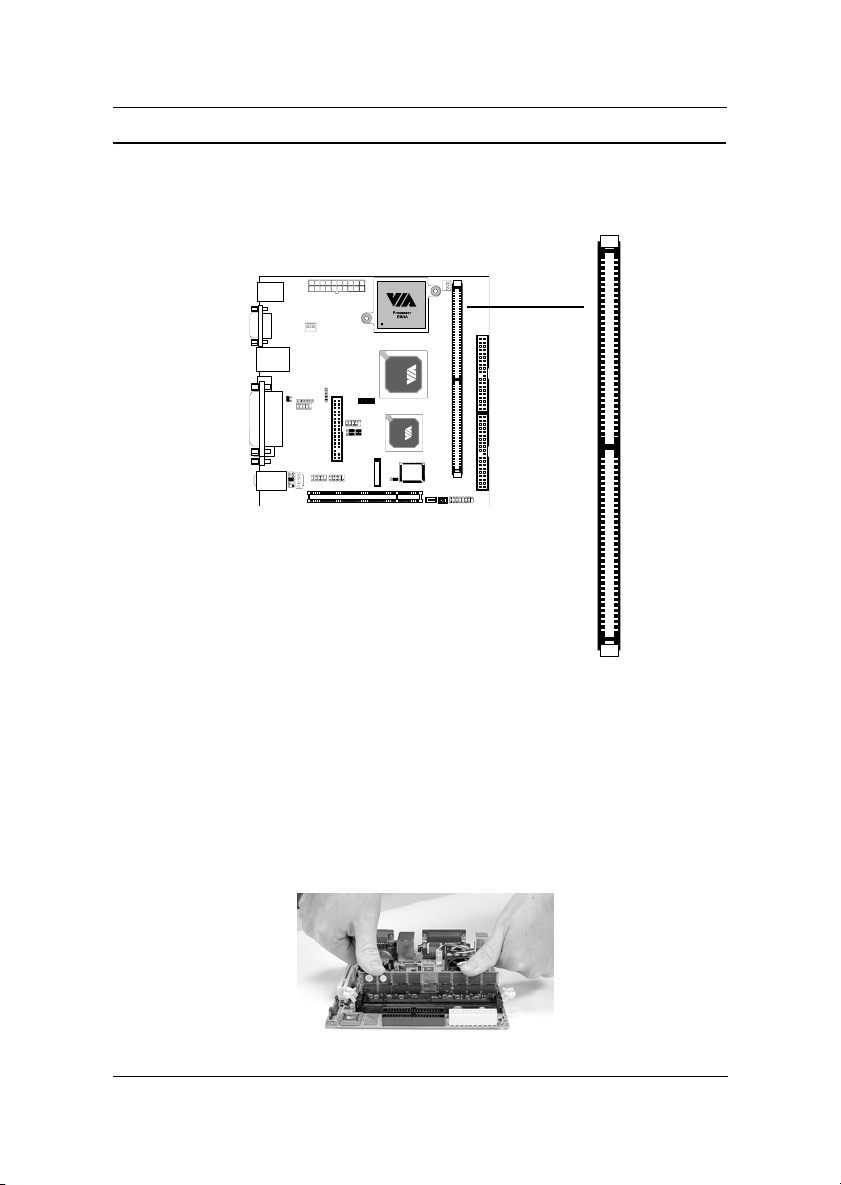
Chapter 2
Memory Module Installation
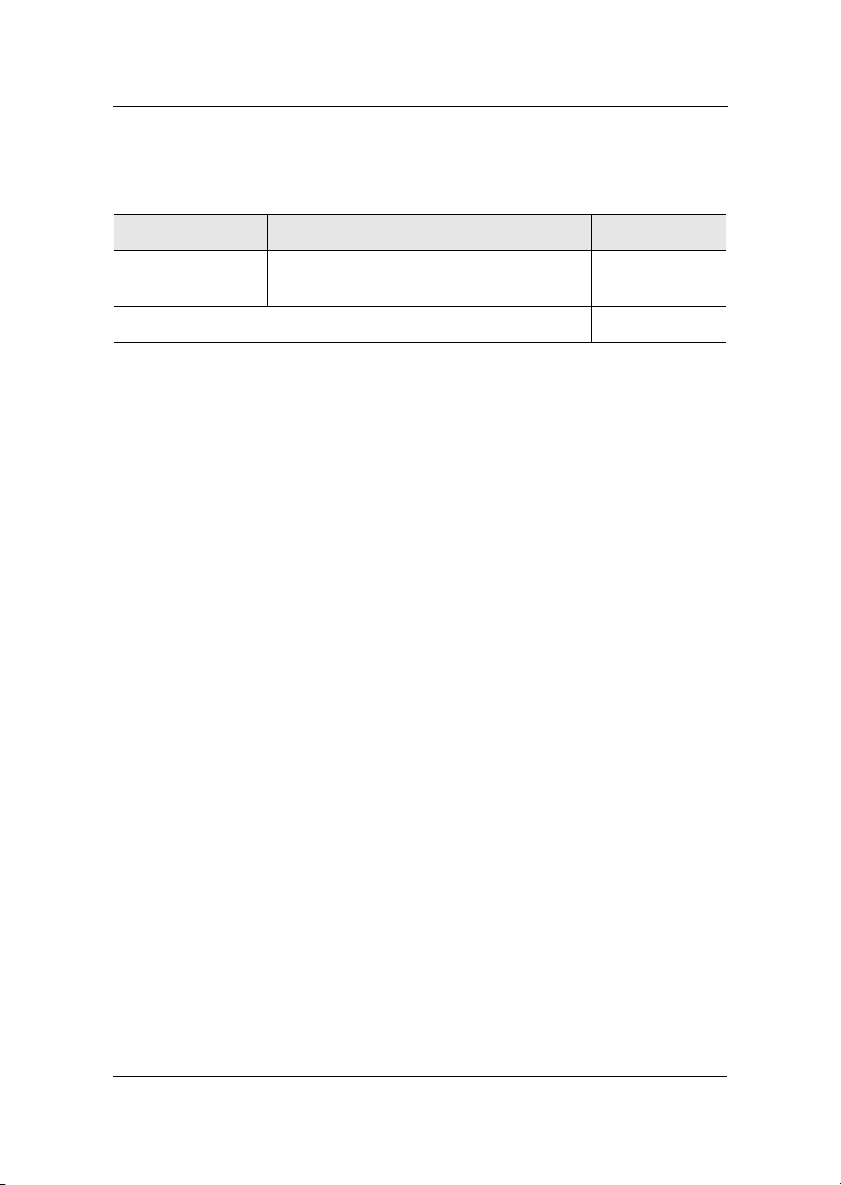
The VIA EPIA-M Mini-ITX Mainboard provides one 184-pin DIMM slot
for DDR266 SDRAM memory modules.
DDR SDRAM Module Installation Procedures
1. Push the white retaining latches at either end of the DIMM slot outwards.
2. Align the DDR SDRAM module with the corresponding notches on the
DIMM slot. The modules will only fit if placed in the correct position.
3. With both hands, press the DDR SDRAM module down into the DIMM
slot so that the white retaining latches rotate up and secure the module in
place (see picture below).
2-4
Page 18
Installation
Available DDR SDRAM Configurations
Refer to the table below for available DDR SDRAM configurations on the
mainboard.
Slot Memory Module Total Memory
DIMM
(Bank 0 & 1)
64MB, 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1GB 64 MB - 1 GB
Maximum System Memory Supported 64 MB - 1 GB
2-5
Page 19
Chapter 2
Connecting the Power Supply
The VIA EPIA-M Mini-ITX Mainboard requires an ATX power supply to be
connected. Before inserting the power supply connector, always make sure
that all components are installed correctly to ensure that no damage will be
caused.
ATX 20-Pin Power Connector
To connect the ATX power supply, make sure the plugs of the power supply
are inserted in the proper orientation and the pins are correctly aligned.
Then, push down the power supply plug firmly into the connector.
Pin Signal
13.3V
23.3V
3GND
45V
5GND
65V
7GND
8PW_OK
9 5V_SB
10 12V
11 3.3V
12 -12V
13 GND
14 PS_ON
15 GND
16 GND
17 GND
18 NC
19 5V
20 5V
110
2011
2-6
Page 20
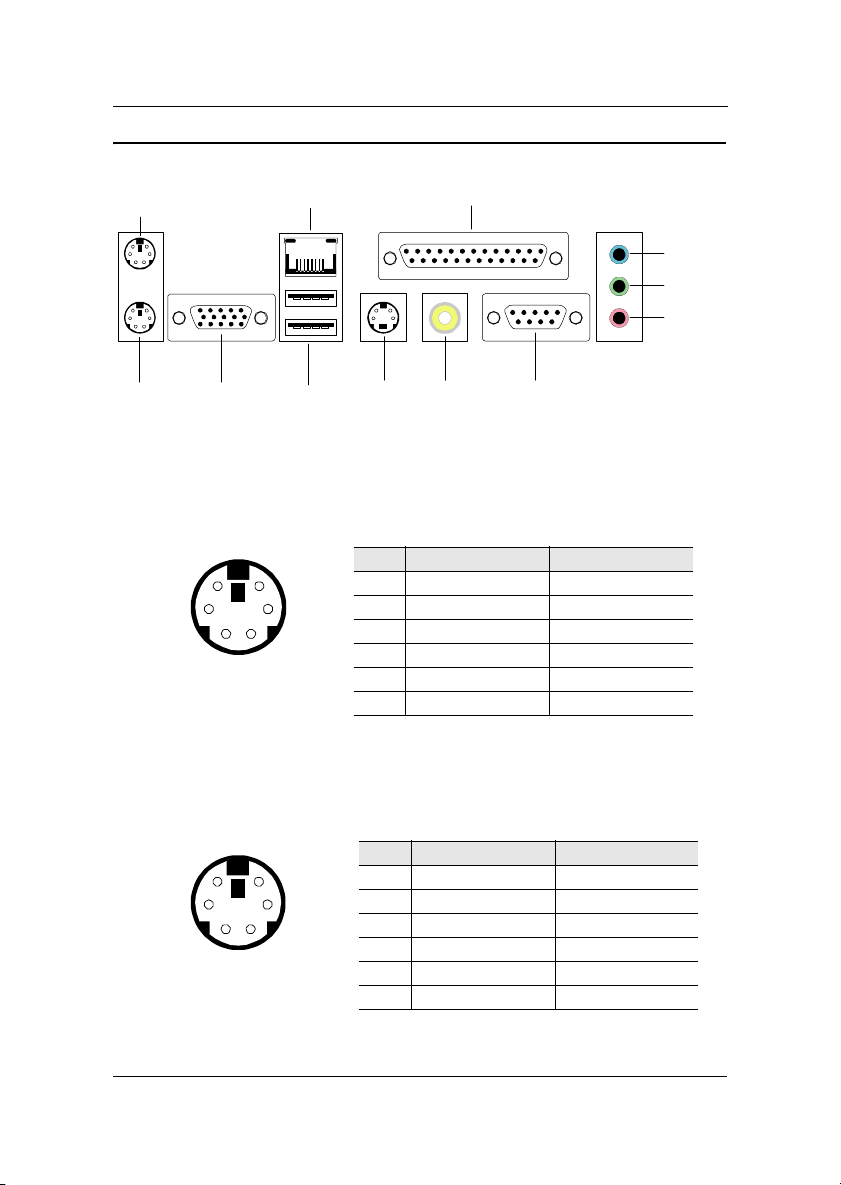
Back Panel Ports
The back panel has the following ports:
PS2_MS
RJ45
Installation
Parallel (LPT1)
Line-In
Line-Out
Microphone
PS2_KB
VGA Out
USB
S-Video
RCA / SPDIF
COM1
Mouse Port: PS2_MS
The mainboard provides a standard PS/2 mouse connector for attaching a
PS/2 mouse. You can plug a PS/2 mouse directly into this connector. The
connector location and pin assignments are as follows.
Pin Signal Description
6
4
2
5
3
1
PS2 Mouse (6-pin female)
1 Mouse DATA Mouse data
2 NC No connection
3 GND Ground
4VCC +5V
5 Mouse Clock Mouse clock
6 NC No connection
Keyboard Port: PS2_KB
The mainboard provides a standard PS/2 keyboard connector for attaching a
PS/2 keyboard. You can plug a PS/2 keyboard directly into this connector.
Pin Signal Description
6
4
2
5
3
1
PS2 Keyboard (6-pin female)
1 Keyboard DATA Keyboard data
2 NC No connection
3 GND Ground
4VCC +5V
5 Keyboard Clock Keyboard clock
6 NC No connection
2-7
Page 21
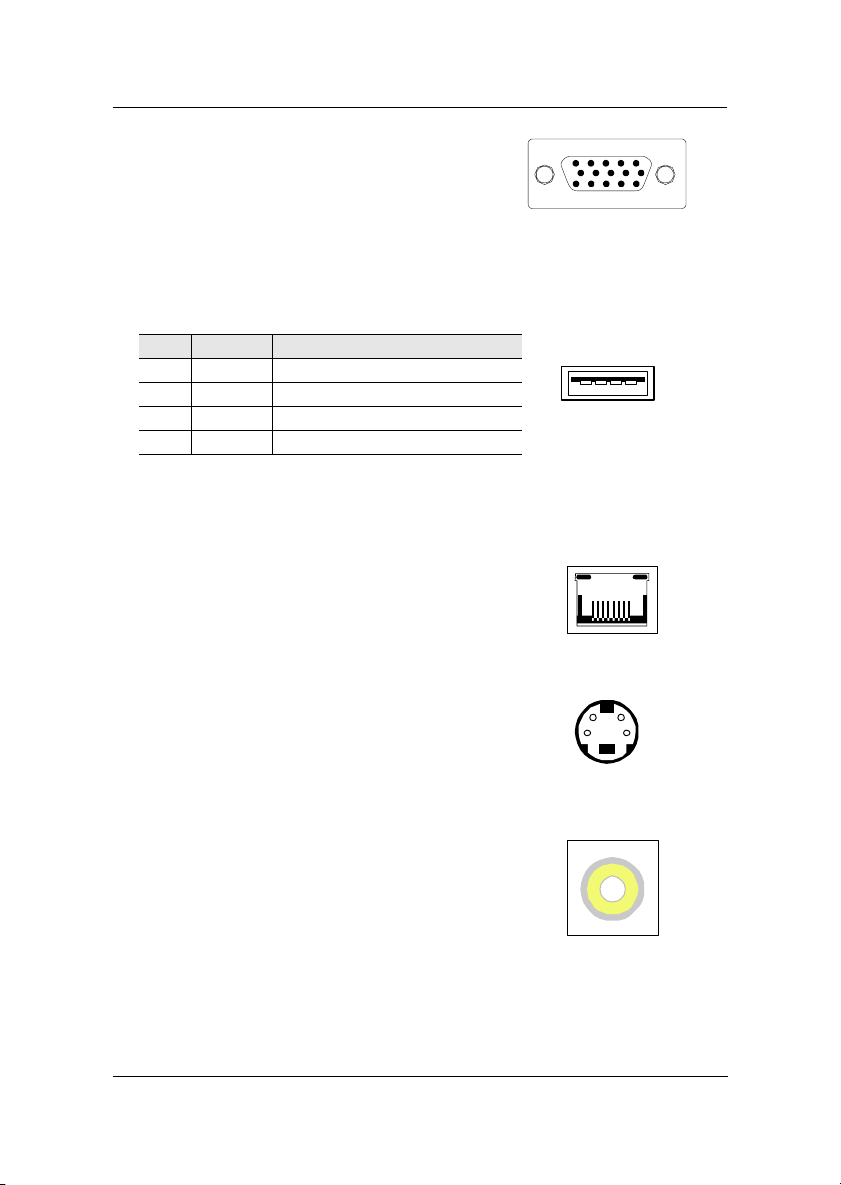
Chapter 2
VGA Out
A DB-15 pin female connector that connects to a
VGA monitor.
USB Ports
The mainboard provides 2 USB 2.0 ports. USB-compatible devices can be
plugged directly into these ports.
Pin Signal Description
1VCC + 5V
2 - DATA Negative data channel
3 + DATA Positive data channel
4 GND Ground
1234
RJ45 10/100 NIC Port
The mainboard provides one standard RJ-45 port for
connection to the Local Area Network (LAN). You can
connect a network cable to the LAN port.
S-Video Port
This port allows S-Video output in NTSC and PAL
modes.
RCA Video or S/PDIF Port
This dual function port may be used either as a RCA
Video port or as a S/PDIF port. See SPDIF_SEL in the
Jumpers section for more details.
2-8
Page 22
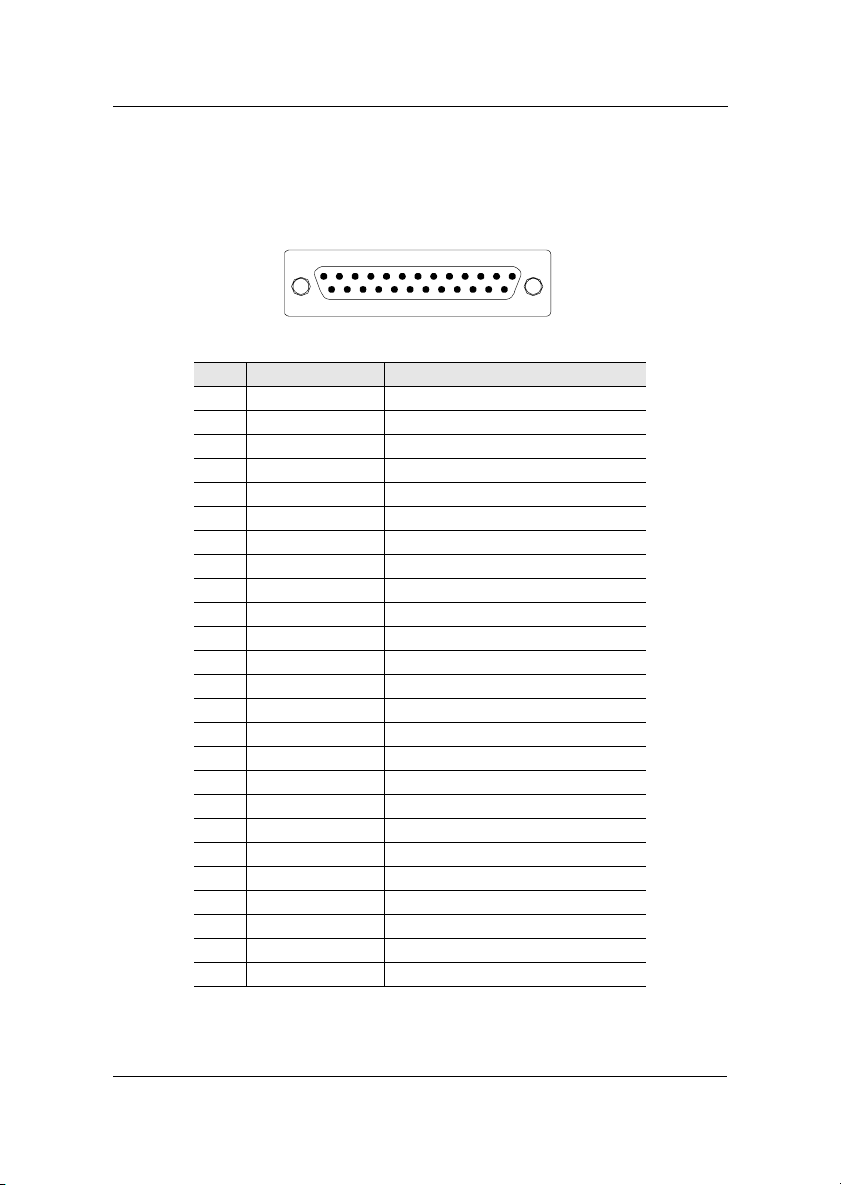
Installation
Parallel Port: LPT1
The mainboard provides a 25-pin female connector for LPT (parallel port). A
parallel port is a standard printer port that supports Enhanced Parallel Port
(EPP) and Extended Capabilities Parallel Port (ECP) modes.
13
Pin Signal Description
1 STROBE Strobe
2DATA0 Data 0
3DATA1 Data 1
4DATA2 Data 2
5DATA3 Data 3
6DATA4 Data 4
7DATA5 Data 5
8DATA6 Data 6
9DATA7 Data 7
10 ACK# Acknowledge
11 BUSY Busy
12 PE Paper End
13 SELECT Select
14 AUTOFEED# Automatic Feed
15 ERR# Error
16 INIT# Initialize Printer
17 SLIN# Select In
18 GND Ground
19 GND Ground
20 GND Ground
21 GND Ground
22 GND Ground
23 GND Ground
24 GND Ground
25 GND Ground
1
1425
2-9
Page 23
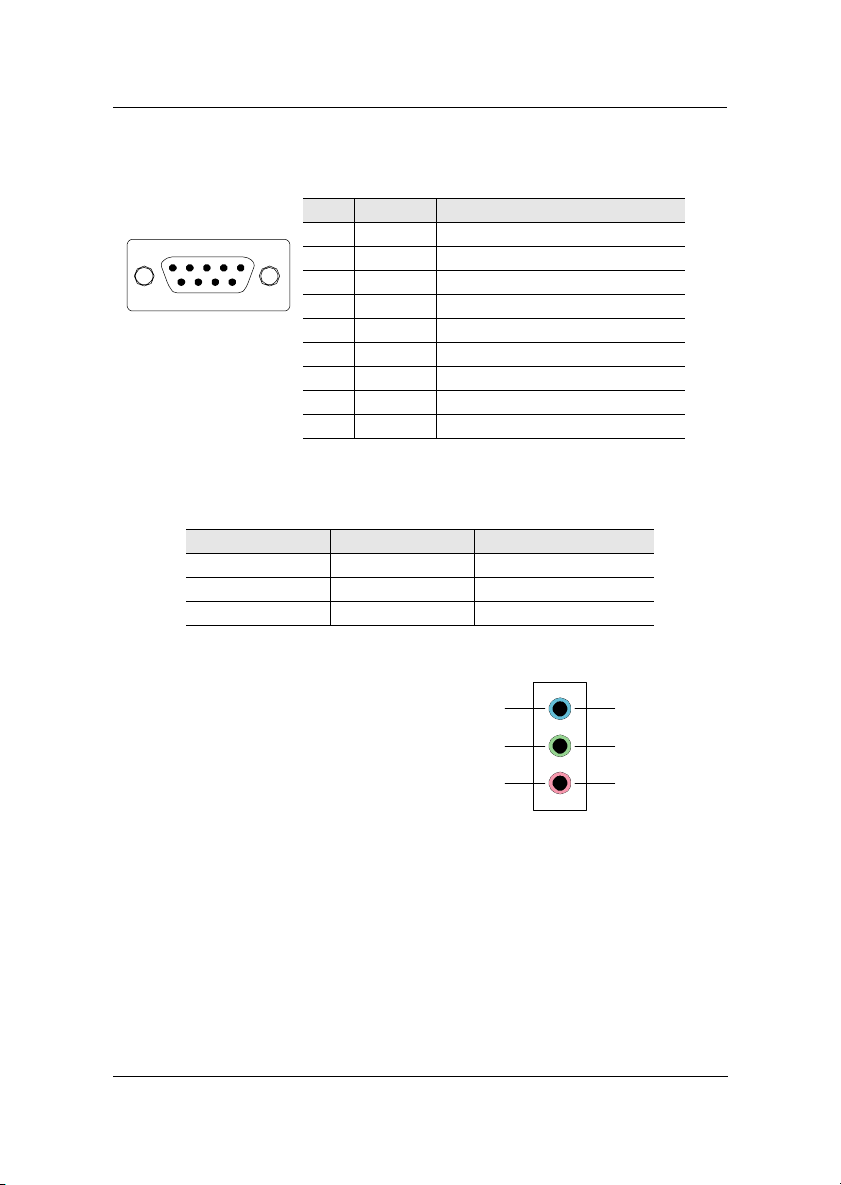
Chapter 2
Serial Ports: COM1
The mainboard offers two 9-pin male Serial Port connectors COM1. You can
attach a serial mouse or other serial devices directly to these ports.
15
6
9
9-Pin Serial Port
Pin Signal Description
1 DCD Data Carry Detect
2 SIN Serial In or Receive Data
3 SOUT Serial Out or Transmit Data
4 DTR Data Terminal Ready
5 GND Ground
6 DSR Data Set Ready
7 RTS Request To Send
8 CTS Clear To Send
9 RI Ring Indicate
Audio Jacks: Line-In, Line-Out, Microphone
Jack 2-Channel 6-Channel
Line-In Line in Rear (Left / Right)
Line-Out Line out Front (Left / Right)
Mic Microphone Center / Subwoofer
The Line-Out jack is for connecting
to external speakers or headphones.
2-Channel 6-Channel
The Line-In jack is for connecting to
an external audio device such as a CD
Line-In
Line-Out
Rear (L/R)
Front (L/R)
player, tape player, etc....
Microphone
Center/Sub
The Mic jack is for connecting to a
microphone.
When 6-channel applications are used, all three jacks become output
connectors with Smart 5.1 (See Appendix A) In order for the 6-channel
audio to function, the operating system and multimedia application must be
properly configured. Please note that Windows 98 only supports 4-channel
audio.
2-10
Page 24
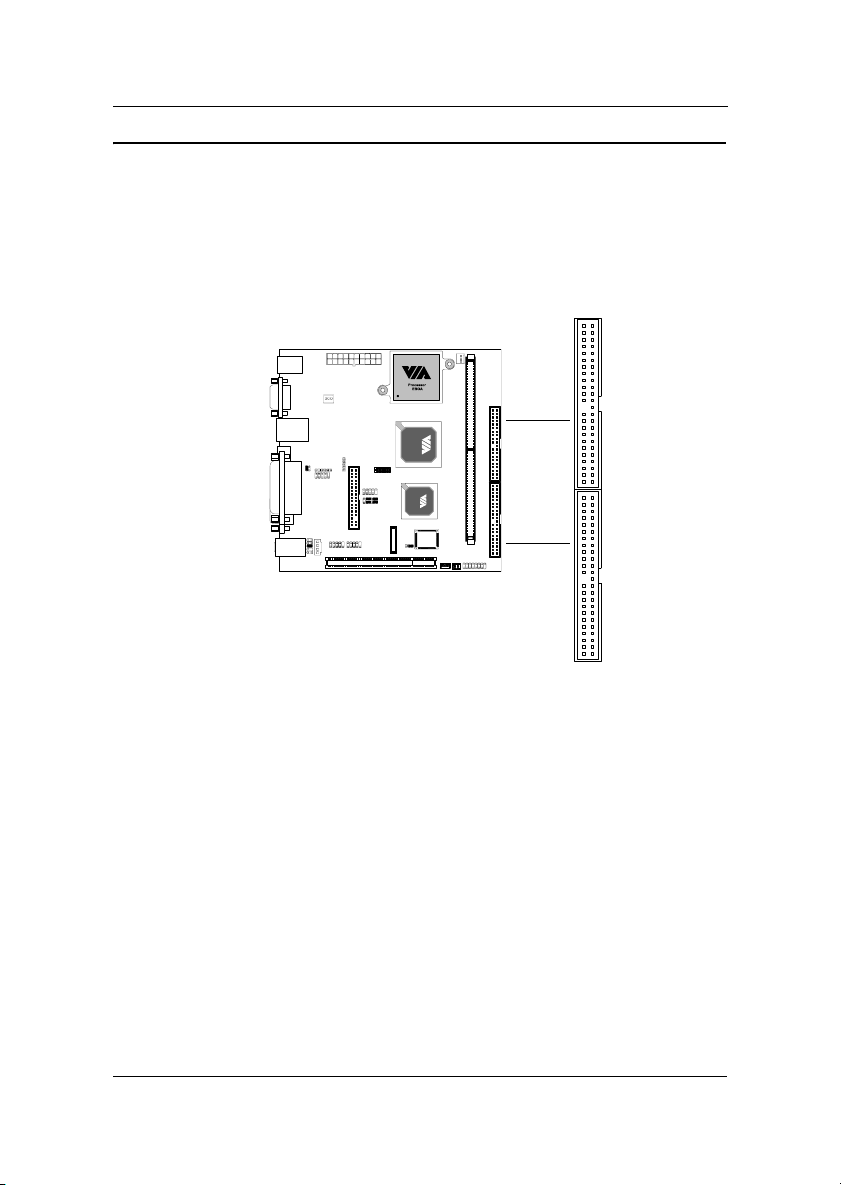
Installation
Connectors
Hard Disk Connectors: IDE1 & IDE2
The mainboard has a 32-bit Enhanced PCI IDE and Ultra DMA 33/66/100/
133 controller that provides PIO mode 0~4, Bus Master, and Ultra DMA 33/
66/100/133 functions. You can connect up to four hard disk drive, CD-ROM,
LS-120 and other devices. These connectors utilize the provided IDE hard
disk cable.
IDE 1
IDE 2
IDE1 (Primary IDE Connector)
The first hard drive should always be connected to IDE1. IDE1 can connect
a Master and a Slave drive. You must configure the second hard drive to
Slave mode by setting the jumper accordingly.
IDE2 (Secondary IDE Connector)
IDE2 can also connect a Master and a Slave drive.
If you install two hard disks on a single cable, you must set the jumper on the
second hard disk drive to slave mode. Please refer to the hard disk
documentation supplied by hard disk vendor for the jumper settings.
2-11
Page 25

Chapter 2
Case Connectors: F_PANEL
The F_PANEL connector block allows you to connect to the power switch,
reset switch, power LED, HDD LED, SLED and the Speaker on the case.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 PWR LED+ 2 HDD LED+
3 PWR LED+ 4 HDD LED-
5PWR LED- 6PW_BN+
7 SPEAKER+ 8 PW_BN-
9 NC 10 RESET+
11 NC 12 RESET-
13 SPEAKER- 14 SLED+
15 NC 16 SLED-
Power Switch (PW_BN)
Connect to a 2-pin push button switch. Pressing this button will turn the
system power on or off.
Reset Switch (RESET)
The Reset Switch is used to reboot the system rather than turning the power
ON/OFF. Avoid rebooting while the HDD is working. You can connect the
Reset Switch from the system case to this pin.
216
151
Power LED (PWR LED)
The LED is lit when the system is power on. If the system is in S1 (POS Power On Suspend) or S3 (STR - Suspend To RAM) state, the LED will
blink.
HDD LED
HDD LED shows the activity of a hard disk drive. Avoid turning the power
off while HDD LED is lit. Connect the HDD LED from the system case to
this pin.
SLED
The SLED is lit when the system is in the S1 (POS - Power On Suspend)
state.
Speaker
The speaker from the system case is connected to this pin
2-12
Page 26

Installation
Fast IrDA Infrared Module Connector: IR
This connector allows you to connect an IrDA Infrared module. You must
configure the setting through the BIOS setup to activate the IR function.
Pin Signal
1VCC
2 IRRX1
3 IRRX
4GND
5IRTX
FIR
1
5
Consumer Infrared Module,
PS2 Header: CIR / EXT_KBMS
When the header is not in use, please short pin 3&5, pin 4&6, pin 7&9, and
pin 8&10.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1+5V 2GND
3 KB_CLK 4 KB_DATA
5 EXT_KBCLK 6 EXT_KBDATA
7MS_CLK 8MS_DATA
9 EXT_MSCLK 10 EXT_MSDATA
2-13
210
1
CIR / EXT_KBMS
9
Page 27

Chapter 2
USB pin-header: USB3/4
The mainboard provides 1 front USB pin-header connector, allowing up to 2
additional USB ports. Please plug the USB 2-port module onto this pinheader.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 VCC 2 VCC
3 USB2 - 4 USB 3 -
5 USB2 + 6 USB 3 +
7GND 8GND
9NC 10GND
2
10
19
USB 3/4
Wake-on LAN: WOL
This connector allows you to connect a network card with the Wake-On
LAN function. The connector will power up the system when a signal is
received through the network card. Please note that the function of ACPI
WOL may be disabled when users unplug the power cord or turn off the
power button manually.
2-14
WOL
Page 28

Installation
FireWire: IEEE1394
FireWire is a serial I/O interface that provides you fast data transfer rates.
There are 2 FireWire ports available.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 TPA0+ 2 T PA0-
3GND 4GNF
5 TPB0+ 6 TPB0-
7 1394_VDD 8 1394_VDD
9GND 10
1394_21394_1
2
2
19
COM2
COM2: The Second Serial Port
COM2 is a pin header for second serial port.
Pin Signal Description
1 DCD Data Carry Detect
2 SIN Serial In or Receive Data
3 SOUT Serial Out or Transmit Data
4 DTR Data Terminal Ready
5 GND Ground
6 DSR Data Set Ready
7 RTS Request To Send
8 CTS Clear To Send
9 RI Ring Indicate
2-15
19129
Page 29

Chapter 2
Floppy Disk Drive Connector: FDD
The floppy disk drive connector supports 360K, 720K, 1.2M. 1.44M, and
2.88M floppy disk types.
FDD
CD Audio Connector: CD_IN
This connector is for the CD-ROM audio connector.
CD_IN
2-16
Page 30

Installation
I2C Connector: I2C
This is for connecting a I2C device.
Pin Signal
1 +3.3V
2 +3.3V
3EL-ON
4SMBCK
5SMBDT
6GND
I2C
16
Front Audio Panel: F_AUDIO
This connector allows you to connect a front audio panel to the mainboard.
Only the line-out and microphone functions are available for use on the front
panel. To connect the front audio cable, first remove the two red plastic
jumpers.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 FRN_MIC 2 AGND
3 AUD_MIC_BIAS 4 +5V
5LINE_OUT_R6Next_R
7NC 8 Keypin
9 LINE_OUT_L 10 Next_L
F-AUDIO
12
109
2-17
Page 31

Chapter 2
LVDS Module Connector: LVDS (Optional)
This connector allows you to connect to a LVDS module. The LVDS
connector may not be available on your mainboard. This is an option that is
added during the manufacturing process. If you would like a mainboard with
the LVDS connector, please contact your vendor or sales contact for more
information.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 GFPDE 2 GFPD3
3 GFPD0 4 GFPD4
5 GFPD1 6 GFPD5
7 GFPD2 8 GFPCLK
9GFPHS 10GFPD6
11 GFPVS 12 GFPD7
13 GFPD11 14 GFPD8
15 GFPD12 16 GFPD9
17 ENPVDD 18 GFPD10
19 ENPVEE 20 GFPD13
21 FPBKLP 22 GFPD14
23 PWRGD_SB 24 GFPD15
25 SPCLK2 26 GFPD16
27 SPD2 28 GFPD17
29 GND 30 GFPD18
31 GND 32 GFPD19
33 3.3V 34 GFPD20
35 GND 36 GFPD21
37 5V 38 GFPD22
39 5V 40 GFPD23
LVDS
2-18
Page 32

Installation
Jumpers
The mainboard provides jumpers for setting the mainboard’s functions. This
section will explain how to change settings for your mainboard’s functions
through the use of the jumpers.
Clear CMOS: CLEAR_CMOS
The onboard CMOS RAM stores system configuration data and has an
onboard battery power supply. The long-life battery has a lifetime of at least
5 years. If you want to clear the system configuration data from the CMOS
RAM, use the CLEAR_CMOS (Clear CMOS jumper). You can clear the
CMOS by shorting 1-2 pin while the system is off. Then return it to the 2-3
pin position. Shorting the jumper while the system is on will damage the
mainboard.
Setting 1 2 3
Clear ON ON OFF
Keep OFF ON ON
123
CLEAR_CMOS
24
SPDIF_SEL
13
RCA Video or S/PDIF Select: SPDIF_SEL
Users can select either RCA Video or S/PDIF as the enabled function on the
dual-purpose port. For SPDIF, please short pins 1 and 2. For RCA, short pins
3 and 4 (default). .
Setting 1 2 3 4
SPDIF ON ON OFF OFF
RCA OFF OFF ON ON
2-19
Page 33

Chapter 2
Slots
Peripheral Component Interconnect: PCI
The PCI slot allows you to insert PCI expansion card. When adding or
removing expansion cards, make sure that you unplug the power supply first.
Meanwhile, read the documentation for the expansion card to make any
necessary hardware or software settings for the expansion card, such as
jumpers, switches or BIOS configuration.
PCI Interrupt Request Routing
The IRQ, abbreviation of interrupt request line and pronounced I-R-Q, are
hardware lines over which devices can send interrupt signals to the
microprocessor. The “PCI & LAN” IRQ pins are typically connected to the
PCI bus INT A# ~ INT D# pins as follows:
Order 1 Order 2 Order 3 Order 4
PCI Slot INT B# INT C# INT D# INT A#
IEEE 1394 INT B#
2-20
Page 34

Chapter
3
BIOS Setup
This chapter gives you detailed explaination of each
BIOS setup functions.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Entering Setup 3-2
Control Keys 3-2
Gettings Help 3-3
The Main Menu 3-4
Standard CMOS Features 3-6
Advanced BIOS Features 3-8
Advanced Chipset Features 3-12
Integrated Peripherals 3-14
Power Management Setup 3-18
PNP / PCI Configurations 3-23
PC Health Status 3-26
Frequency / Voltage Control 3-27
Load Fail-Safe Defaults 3-30
Load Optimized Defaults 3-31
Set Supervisor / User Password 3-32
Save & Exit Setup 3-34
Exit Without Saving 3-35
3-1
Page 35

Chapter 3
Entering Setup
Power on the computer and press Delete straight away to enter the BIOS
setup menu. If you missed the BIOS setup entry point, you may restart the
system and try again.
Control Keys
Keys Description
Up Arrow Move to the previous item
Down Arrow Move to the next item
Left Arrow Move to the item in the left side
Right Arrow Move to the item in the right side
Enter Select the item
Escape Jumps to the Exit menu or returns to the main menu
from a submenu
Page Up / + Increase the numeric value or make changes
Page Down / - Decrease the numeric value or make changes
F1 General help, only for Status Page Setup Menu and
Option Page Setup Menu
F5 Restore the previous CMOS value from CMOS, only
for Option Page Setup Menu
F6 Load the default CMOS value from Fail-Safe default
table, only for Option Page Setup Menu
F7 Load Optimized defaults
F9 Jumps to the Main Menu
F10 Save all the CMOS changes and exit
3-2
Page 36

BIOS Setup
Getting Help
Main Menu
The main menu displays all BIOS setup categories. Use the control keys
Up/Down Arrow Keys to select any item/sub-menu. Description of the
selected/highlighted category is displayed at the bottom of the screen.
Sub-Menu
If you find a right pointer symbol (as shown in
the right view) appears on the left of certain
fields, this means a sub-menu is available. The
sub-menu contains additional options. You
can use control keys Up/Down Arrow
Keys to highlight the field and press Enter
to enter the sub-menu. To return from the sub-menu press Esc.
General Help: F1
The BIOS setup program provides a General Help screen. You can call up
this screen from any menu/sub-menu by pressing F1. The help screen
displays the keys for use and navigate the BIOS setup. Press Esc to exit the
help screen.
IDE Primary Master
IDE Primary Slave
IDE Secondary Master
IDE Secondary Slave
3-3
Page 37

Chapter 3
The Main Menu
The Main Menu contains twelve setup functions and two exit choices. Use
arrow keys to select the items and press Enter to accept or enter the submenu.
Standard CMOS Features
Use this menu to set basic system configurations.
Advanced BIOS Features
Use this menu to set the advanced features available on your system.
Advanced Chipset Features
Use this menu to set chipset specific features and optimize system
performance.
Integrated Peripherals
Use this menu to set onboard peripherals features.
Power Management Setup
Use this menu to set onboard power management functions.
PnP/PCI Configurations
Use this menu to set the PnP and PCI configurations.
PC Health Status
This menu shows the PC health status.
3-4
Page 38

BIOS Setup
Frequency/Voltage Control
Use this menu to set the system frequency and voltage control.
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Use this menu option to load the BIOS default settings for minimal and
stable system operations.
Load Optimized Defaults
Use this menu option to load BIOS default settings for optimal and high
performance system operations.
Set Supervisor Password
Use this menu option to set the BIOS supervisor password.
Set User Password
Use this menu option to set the BIOS user password.
Save & Exit Setup
Save BIOS setting changes and exit setup.
Exit Without Saving
Abandon all BIOS setting changes and exit setup.
3-5
Page 39

Chapter 3
Standard CMOS Features
Date
The date format is <Day><Month><Date><Year>.
Day - day of the week, for example Friday. Read-only.
Month - the month from Jan to Dec.
Date - the date from 1 to 31.
Year - the year, range from 1999 to 2098.
Time
The time format is <Hour><Minute><Second>.
Drive A/B
Set the type of floppy drive installed. Settings: None, 360K (5.25 in.), 1.2M
(5.25 in.), 720K (3.5 in.), 1.44M (3.5 in.), 2.88M (3.5 in.)
Halt On
Determine the system behaviour if an error is detected at boot. Settings are:
All Errors System halts when any error is detected.
No Errors System does not halt for any error.
All, But Keyboard System halts for all non-key errors.
All, But Diskette System halts for all non-disk errors.
All, But Disk/Key System halts for all non-key and non-disk errors.
3-6
Page 40

BIOS Setup
IDE Primary Master/Slave, Secondary Master/Slave
Press Enter to enter the sub-menu and the following screen appears:
The specifications of your drive must match with the drive table. The hard
disk will not work properly if you enter improper information for this
category. Select
information provided is from your hard disk vendor or system manufacturer.
IDE <Primary
Master>
Access Mode The settings are
Capacity The formatted size of the storage device.
Cylinder Number of cylinders.
Head Number of heads.
Precomp Write precompensation.
Landing Zone Cylinder location of the landing zone.
Sector Number of sectors.
PIO Mode The settings are
Ultra DMA Mode The settings are
Auto whenever possible. If you select Manual, make sure the
The name of this menu item will match the
name of the menu. The settings are
Auto, Manual.
CHS, LBA, Large, Auto.
Mode 0/1/2/3/4, Auto.
Disabled and Auto.
None,
3-7
Page 41

Chapter 3
Advanced BIOS Features
Virus Warning
Set the Virus Warning feature for IDE Hard Disk boot sector protection. If
the function is enabled, any attempt to write data into this area will cause a
beep and warning message display on screen. Settings:
CPU L2 Cache ECC Checking
Set the ECC (Error-Correcting Code) feature for Level 2 cache. Facilitates
error detection/correction when data passes through Level 2 cache. Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
Disabled and Enabled
Quick Power On Self Test
Shorten Power On Self Test (POST) cycle and enable shorter bootup time.
Allow BIOS to skip some check items during POST. Settings:
Disabled
3-8
Enabled and
Page 42

BIOS Setup
First/Second/Third Boot Device
Set the boot device sequence as BIOS attempts to load the disk operating
system. The settings are:
Floppy The system will boot from floppy drive.
LS120 The system will boot from LS-120 drive.
HDD-0 The system will boot from first HDD.
SCSI The system will boot from SCSI.
CD-ROM The system will boot from CD-ROM.
HDD-1 The system will boot from second HDD.
HDD-2 The system will boot from third HDD.
HDD-3 The system will boot from fourth HDD.
ZIP100 The system will boot from ATAPI ZIP drive.
USB-FDD The system will boot from USB floppy drive.
USB-ZIP The system will boot from USB ZIP drive.
USB-CDROM The system will boot from USB CDROM.
USB-HDD The system will boot from USB HDD.
LAN The system will boot from network drive.
Disabled Disable this sequence.
Boot Other Device
Enable the system to boot from other devices if the system fails to boot from
the First/Second/Third boot device. Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
Swap Floppy Drive
If the system has two floppy drives, choose Enabled to assign physical drive
B to logical drive A and vice versa. Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
Boot Up Floppy Seek
Set floppy seek during POST, BIOS will determine whether the floppy is 40
or 80 tracks. Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
3-9
Page 43

Chapter 3
Boot Up NumLock Status
Set the NumLock status when the system is powered on. On will turn key
pad into number keys, and
and
Off
Off will turn key pad into arrow keys. Settings: On
Typematic Rate Setting
When Enabled, you can set the Typematic Rate and Typematic Delay.
Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
When Typematic Rate Setting is enabled, this item allows you to set the rate
(characters/second) at which the keys are accelerated. Settings:
15, 20, 24
and 30
6, 8, 10, 12,
Typematic Delay (Msec)
When Typematic Rate Setting is enabled, this item allows you to select the
delay between when the key was first pressed and when the acceleration
begins. Settings:
250, 500, 750 and 1000
Security Option
If you have set a password, select whether the password is required every
time the System boots, or only when you enter Setup. Settings are described
below:
Setup The password prompt appears only when end users
try to run Setup.
System A password prompt appears every time when the
computer is powered on or when end users try to
run Setup.
Display Full Screen Logo
Show full screen logo during BIOS bootup process. Settings: Enabled and
Disabled
3-10
Page 44

BIOS Setup
Show Summary Information
Show the summary information during the BIOS boot process. Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
Display Small Logo
Show small energy star logo during BIOS bootup process. Settings: Enabled
and
Disabled
3-11
Page 45

Chapter 3
Advanced Chipset Features
The Advanced Chipset Features menu is used for optimizing the chipset
functions.
WARNING: Do not change these settings unless you are familiar with the chipset.
AGP Aperture Size
This setting controls how much memory space can be allocated to AGP for
video purposes. The aperture is a portion of the PCI memory address range
dedicated to graphics memory address space. Host cycles that hit the
aperture range are forwarded to the AGP without any translation. Settings:
4MB, 8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB, 128MB, and 256MB
AGP Mode (Internal)
This mainboard supports the AGP 4x interface. AGP 4x can transfer video
data at 1066MB/s and is backward-compatible with AGP2x and AGP1x.
CPU to PCI POST Write
When Enabled, CPU can write up to four words of data to the PCI write
buffer before CPU must wait for PCI bus cycle to finish. If
must wait after each write cycle until PCI bus signals that it is ready to
receive more data. Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
3-12
Disabled, CPU
Page 46

BIOS Setup
Select Display Device
This setting refers to the type of display being used with the system.
Settings:
CRT, TV, CRT + TV, LCD and CRT + LCD
Panel Type
This setting refers to the native resolution of the display being used with the
system. Settings:
and
640x480
1600x1200, 1400.1050, 1280,1024, 1280x768,1024x768, 800x600
TV Type
This setting refers to the native resolution of the display being used with the
system. Settings:
NTSC and PA L
CPU Direct Access FB
Enable the CPU to directly access the frame buffer. Settings: Enabled and
Disabled
3-13
Page 47

Chapter 3
Integrated Peripherals
Onboard IDE Channel 1/2
The integrated peripheral controller contains an IDE interface with support
for two IDE channels. Choose
Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
IDE Prefetch Mode
This allows your hard disk controller to use the fast block mode to transfer
data to and from the hard disk drive. Block mode is also called block
transfer, multiple commands or multiple sector read/write.
IDE controller to use block mode;
standard mode. Settings:
Enabled to activate each channel separately.
Enabled enables
Disabled allows the controller to use
Enabled and Disabled
Display Card Priority
This setting specifies which VGA card is your primary graphics adapter.
Settings:
PCI Slot and AGP
Frame Buffer Size
This setting instructs the BIOS to reserved the specified amount of memory
for the internal video controller. Settings:
16M, 32M, 64M
3-14
Page 48

BIOS Setup
AC97 Audio
Auto allows the mainboard to detect whether an audio device is used. If the
device is detected, the onboard VIA AC’97 (Audio Codec’97) controller will
be enabled; if not, it is disabled. Disable the controller if you want to use
other controller cards to connect to an audio device. Settings:
Disabled
Auto and
MC97 Modem
Auto allows the mainboard to detect whether a modem is used. If the device
is detected, the onboard VIA MC’97 (Modem Codec’97) controller will be
enabled; if not, it is disabled. Disable the controller if you want to use other
controller cards to connect to a modem. Settings:
Auto and Disabled
VIA OnChip LAN
This setting allows you to make VIA OnChip LAN enabled or disabled.
Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
USB Keyboard Support
Enable USB Keyboard Support for DOS and Windows. Settings: Enabled and
Disabled
Onboard Lan Boot ROM
Enable Onboard Lan Boot ROM for DOS and Windows. Settings: Enabled
and
Disabled
Onboard Fast IR
Enable Onboard Fast IR functions. Settings: Enabled and Disabled
Fast IR IRQ
Set this field to reserve an IRQ for the Fast IR port. This field is only
available if Onboard Fast IR is enabled. Settings:
Fast IR DMA
Set this field to choose the DMA channel. This field is only available if
Onboard Fast IR is enabled. Settings:
6, 5
3-15
3, 4
Page 49

Chapter 3
SuperIO Device
Press Enter to enter the sub-menu and the following screen appears:
Onboard FDC Controller
Enable the onboard floppy controller. Select
installed a floppy disk drive. Settings:
Onboard Serial Port 1/2
Set the base I/O port address and IRQ for the onboard serial port A/serial
port B. Selecting
Auto allows BIOS to automatically determine the
correct base I/O port address. Settings:
Port Settings
Disabled 3F8/IRQ4 2F8/IRQ3 3E8/IRQ4 2E8/IRQ3 Auto
1
Disabled 3F8/IRQ4 2F8/IRQ3 3E8/IRQ4 2E8/IRQ3 Auto
2
Enabled when you have
Enabled, Disabled
Onboard Parallel Port
This specifies the I/O port address and IRQ of the onboard parallel port.
Settings:
Disabled, 378/IRQ7, 278/IRQ5, 3BC/IRQ7
Parallel Port Mode
Set the parallel port mode. To operate the onboard parallel port as
Standard Parallel Port, choose
in the EPP mode, choose
will operate in ECP mode. Choosing
SPP. To operate the onboard parallel port
EPP. By choosing ECP, the onboard parallel port
ECP + EPP will allow the onboard
parallel port to support both the ECP and EPP modes simultaneously.
Settings:
SPP, EPP, ECP, ECP + EPP
3-16
Page 50

BIOS Setup
EPP Mode Select
EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port) comes in two modes: 1.9 and 1.7. EPP 1.9
is the newer version of the protocol and is backwards compatible with
most EPP devices. If your EPP device does not work with the EPP 1.9
setting, try changing the setting to EPP 1.7.
Settings:
EPP 1.9, EPP 1.7
ECP Mode Use DMA
ECP (Extended Capabilities Port) has two DMA channels that it can use.
The default channel is 3. However, some expansion cards may use
channel 3 as well. To solve this conflict, change the ECP channel to 1.
Select a DMA channel for the port. Settings:
1, 3
3-17
Page 51

Chapter 3
Power Management Setup
The Power Management Setup menu configures the system to most
effectively save energy while operating in a manner consistent with your
own style of computer use.
ACPI Function
Activate the ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Management)
Function. If your operating system is ACPI-aware (i.e. Windows 98/98SE/
ME/2000/XP) select Enabled. Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
ACPI Suspend Type
Set the power saving mode for ACPI function. Settings are:
S1(POS) S1/Power On Suspend (POS) is a low power state. In
this state, no system context (CPU or chipset) is lost
and hardware maintains all system context.
S3(STR) S3/Suspend To RAM (STR) is a power-down state. In
this state, power is supplied only to essential
components such as main memory and wakeup-
capable devices. The system context is saved to
main memory, and context is restored from the
memory when a “wakeup” event occurs.
S1 & S3 Depends on OS to select S1 or S3.
3-18
Page 52

BIOS Setup
HDD Power Down
Set the time to power down HDD after hard disk inactivity. Settings: Disabled
and
1~15 (minutes)
Power Management Timer
Set the idle time before system enters power saving mode. ACPI OS such as
Windows XP will override this option. Settings:
(minutes) and 1 (hour)
30/40
Disabled and 1/2/4/6/8/10/20/
Video Off Option
Select whether or not to turn off the screen when system enters power saving
mode, ACPI OS such as Windows XP will override this option. Settings are:
Always On The screen is always on even when system
enters power saving mode.
Suspend -> Off The screen is turned off when system enters
power saving mode.
Power Off by PWRBTN
This field configures the power button function. Settings are:
Delay 4 Sec The system is turned off if power button is pressed
for more than four seconds.
Instant-Off The power button functions as a normal power-on/-
off buttton.
Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume
Select whether to run VGA BIOS if resumed from S3 state. This is only
necessary for older VGA drivers, select
and
No
Auto if in doubt. Settings: Auto, Yes
3-19
Page 53

Chapter 3
Peripheral Activities
Press Enter to enter the sub-menu and the following screen appears:
VGA Event
Decide whether or not the power management unit should monitor VGA
activities. Settings:
LPT & COM Event
Decide whether or not the power management unit should monitor
parallel port (LPT) and serial port (COM) activities. Settings:
and LPT/COM
COM
Off and On
None, LPT,
HDD & FDD Event
Decide whether or not the power management unit should monitor hard
disks and floppy drives activities. Settings:
Off and On
PCI Master Event
Decide whether or not the power management unit should monitor PCI
master activities. Settings:
Off and On
PS2KB Wakeup Select
When select
change
Password, please press Page Up or Page Down key to
Password, 8 characters maximum. Please note that PS2MS
Wakeup from suspend and PS2KB Wakeup from suspend will be
disabled while changing the passward. Settings:
3-20
Hot key and Password
Page 54

BIOS Setup
PS2KB Wakeup from suspend
Select which Hot-Key to wake-up the system from power saving mode.
Settings:
Ctrl+F8, Ctrl+F9, Ctrl+F10, Ctrl+F11, Ctrl+F12, Power, Wake
Disabled, Ctrl+F1, Ctrl+F2, Ctrl+F3, Ctrl+F4, Ctrl+F5, Ctrl+F6, Ctrl+F7,
and Any Key
USB Resume
Decide whether or not USB devices can wake the system from suspend
state. Settings:
Disabled and Enabled
PowerOn by PCI Card
Decide whether or not any PCI card can power up the system or resume
from suspend state. Such PCI cards include LAN, onboard USB ports,
etc. Settings:
Disabled and Enabled
Wake On LAN/Ring Connector
Decide whether or not any Ring-In signals from the modem can wake up
the system or resume from suspend state. Settings:
Disabled and Enabled
RTC Alarm Resume
The field is used to enable or disable the feature of booting up the system
on a scheduled time/date. Settings:
Disabled and Enabled
Date (of Month)
This field can only be set if RTC Alarm Resume is enabled. The field
specifies the date for
RTC Alarm Resume.
Resume Time (hh:mm:ss)
This field can only be set if RTC Alarm Resume is enabled. The field
specifies the time for
RTC Alarm Resume.
3-21
Page 55

Chapter 3
IRQs Activities
Press Enter to enter the sub-menu and the following screen appears:
Primary INTR
Selecting
if activity is detected from any enabled IRQ channels. Settings:
IRQ3~IRQ15
Enables or disables the monitoring of the specified IRQ line. If set to
Enabled, the activity of the specified IRQ line will prevent the system
from entering power saving modes or awaken it from power saving
modes. These fields are only available if Primary INTR is on. Settings:
Enabled and Disabled
On will cause the system to wake up from power saving modes
Off, On
Note: IRQ (Interrupt Request) lines are system resources allocated to I/O devices.
When an I/O device needs to gain attention of the operating system, it signals this
by causing an IRQ to occur. After receiving the signal, when the operating system is
ready, the system will interrupt itself and perform the service required by the IO
device.
3-22
Page 56

BIOS Setup
PNP/PCI Configurations
This section describes the BIOS configuration of the PCI bus system. This
section covers some very technical items and it is strongly recommended
that only experienced users should make any changes to the default settings.
PNP OS Installed
When set to Yes, BIOS will only initialize the PnP cards used for booting
(VGA, IDE, SCSI). The rest of the cards will be initialized by the PnP
operating system like Windows
initialize all the PnP cards. Set to Ye s the operating system is Plug & Play
capable. Settings:
No and Yes
®
95 or 98/98SE. When set to No, BIOS will
Reset Configuration Data
Normally, you leave this field Disabled. Select Enabled to reset Extended
System Configuration Data (ESCD) when you exit Setup if you have
installed a new add-on and the system reconfiguration has caused such a
serious conflict that the operating system can not boot. Settings:
Disabled
Enabled and
Resource Controlled By
The BIOS can automatically configure all the boot and Plug and Play
compatible devices. Choose
automatically assign IRQ, DMA and memory base address fields. Settings:
Auto (ESCD) and Manual
Auto(ESCD) if unsure, the BIOS will
3-23
Page 57

Chapter 3
Assign IRQ For VGA/USB
Assign IRQ for VGA and USB devices. Settings: Disabled and Enabled
3-24
Page 58

BIOS Setup
IRQ Resources
The items are adjustable only when Resources Controlled By is set to Manual.
Press Enter and you will enter the sub-menu of the items.
IRQ Resources list IRQ 3/4/5/7/9/10/11/12/14/15 for users to set each IRQ a
type depending on the type of device using the IRQ. Settings:
PCI Device For Plug & Play compatible devices designed for PCI
bus architecture.
Reserved The IRQ will be reserved for further request.
3-25
Page 59

Chapter 3
PC Health Status
This section shows the status of your CPU, fan, warning for overall system
status.
The PC Health Status displays the current status of all of the monitored
hardware devices/components such as CPU voltages, temperatures and fan
speeds.
3-26
Page 60

BIOS Setup
Frequency / Voltage Control
DRAM Clock
The chipset supports synchronous and asynchronous mode between host
clock and DRAM clock frequency. Settings:
By SPD
DRAM Timing
The value in this field depends on the memory modules installed in your
system. Changing the value from the factory setting is not recommended
unless you install new memory that has a different performance rating than
the original modules. Settings:
Manual and By SPD
66 MHz, 100 MHz, 133 MHz, and
DRAM CAS Latency
This item adjusts the speed it takes for the memory module to complete a
command. Generally, a lower setting will improve the performance of your
system. However, if your system becomes less stable, you should change it
to a higher setting. This field is only available when DRAM Timing is set to
Manual. Settings:
2, 2.5
3-27
Page 61

Chapter 3
Bank Interleave
Set the interleave mode of the SDRAM interface. Interleaving allows banks
of SDRAM to alternate their refresh and access cycles. One bank will
undergo its refresh cycle while another is being accessed. This improves
performance of the SDRAM by masking the refresh time of each bank. This
field is only available when DRAM Timing is set to Manual. Settings:
Disabled, 2 Bank, 4 Bank
Precharge to Active (Trp)
This field controls the length of time it takes to precharge a row in the
memory module before the row becomes active. Longer values are safer but
may not offer the best performance. This field is only available when DRAM
Timing is set to Manual. Settings:
2T, 3T
Active to Precharge (Tras)
This field controls the length of time it a row stays active before precharging.
Longer values are safer buy may not offer the best performance. This field is
only available when DRAM Timing is set to Manual. Settings:
5T, 6T
Active to CMD (Trcd)
This field is only available when DRAM Timing is set to Manual. Settings:
2T, 3T
DRAM Command Rate
This field controls how fast the memory controller sends out commands.
Lower setting equals faster command rate. Please note that some memory
modules may not be able to handle lower settings. Settings:
Command
2T Command, 1T
DRAM Burst Len
This field sets the length of time for one burst of data during a read/write
transaction. Longer settings equals better memory performance. Settings:
8
3-28
4,
Page 62

BIOS Setup
DRAM Voltage
This field sets the voltage for the memory module. Settings: 2.9V, 2.8V, 2.6V,
2.5V
Spread Spectrum
When the mainboard’s clock generator pulses, the extreme values (spikes) of
the pulses creates EMI (Electromagnetic Interference). The Spread Spectrum
function reduces the EMI generated by modulating the pulses so that the
spikes of the pulses are reduced to flatter curves.
3-29
Page 63

Chapter 3
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
This option on the main menu allows users to restore all the BIOS settings to
the default Fail Safe values. These values are set by the mainboard
manufacturer to provide a minimal and stable system.
When you select Load-Fail Safe Defaults, a message as below appears:
Entering
system configuration.
Y loads the default BIOS values that provide a minimal and stable
3-30
Page 64

BIOS Setup
Load Optimized Defaults
This option on the main menu allows users to restore all the BIOS settings to
the default Optimized values. The Optimized Defaults are the default values
also set by the mainboard manufacturer for both optimized and stable
performance of the mainboard.
When you select Load Optimized Defaults, a message as below appears:
Entering
stable system performance.
Y loads the default values that are factory settings for optimal and
3-31
Page 65

Chapter 3
Set Supervisor / User Password
When you select this function, a message as below will appear on the screen:
Type the password, up to eight characters in length, and press Enter. The
password typed now will clear any previously set password from CMOS
memory. You will be prompted to confirm the password. Re-type the
password and press Enter. You may also press Esc to abort the selection
and not enter a password.
To clear a set password, just press Enter when you are prompted to enter
the password. A message will show up confirming the password will be
disabled. Once the password is disabled, the system will boot and you can
enter Setup without entering any password.
When a password has been set, you will be prompted to enter it every time
you try to enter Setup. This prevents an unauthorized person from changing
any part of your system configuration.
There are two types of passwords you can set. A Supervisor password and a
User password. When a Supervisor password is used, the user can start
BIOS Setup program and change the settings of the setup menus. When a
User password is used, the user can start the BIOS Setup program but does
not have the right to change the settings of the setup menus.
3-32
Page 66

BIOS Setup
Additionally, when a password is enabled, you can also have BIOS to
request a password each time the system is booted. This would prevent
unauthorized use of your computer. The setting to determine when the
password prompt is required is the Security Option of the Advanced BIOS
Features menu. If the Security Option is set to
required both at boot and at entry to Setup. If set to
System, the password is
Setup, password prompt
only occurs when trying to enter Setup.
3-33
Page 67

Chapter 3
Save & Exit Setup
When you want to quit the Setup menu, you can select this option to save the
changes and quit. A message as below will appear on the screen:
Entering
Y will allow you to quit the Setup Utility and save the user setup
changes to RTC CMOS.
Entering
N will return to the Setup Utility.
3-34
Page 68

BIOS Setup
Exit Without Saving
When you want to quit the Setup menu, you can select this option to abandon
the changes. A message as below will appear on the screen:
Entering
Y will allow you to quit the Setup Utility without saving any
changes to RTC CMOS.
Entering
N will return to the Setup Utility.
3-35
Page 69

Chapter
4
Driver Installation
This chapter gives you brief descriptions of each
mainboard drivers and applications. You must
install VIA chipset drivers first before installing
other drivers such as audio or VGA drivers. The
applications will only function correctly if the
necessary drivers are already installed.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Driver Utilities 4-2
CD Content 4-3
4-1
Page 70

Chapter 4
Driver Utilities
Getting Started
The mainboard includes a Driver Utilities CD which contains driver utilities
and software to enhance the performance of the mainboard. Please check
that you have this CD in your retail box. If the CD is missing in your retail
box, please contact your local dealer for the CD.
Note: The driver utilities and software are updated from time to time. Please visit our
website (http://www.viaembedded.com/) for the latest updated mainboard
driver and utilities.
Running the Driver Utilities CD
To start using the CD, just simply insert the CD into your local CD-ROM or
DVD-ROM drive. The CD should run automatically when you close your
CD-ROM or DVD-ROM drive. The driver utilities and software menu
screen should then appear on your desktop. If the CD does not run
automatically, you can run the CD manually by typing “D:\Setup.exe” at
Start\Run.
(Please note that D: might not be your CD-ROM/DVD-ROM drive letter. Make sure
you type the correct letter of CD-ROM/DVD-ROM drive on your system).
4-2
Page 71

Driver Installation
CD Content
The driver utilities and software in this CD are:
• VIA 4in1 Drivers: Contains VIA ATAPI Vendor Support Driver
(enables the performance enhancing bus mastering functions on ATAcapable Hard Disk Drives and ensures IDE device compatibility), AGP
VxD Driver (provides service routines to your VGA driver and
interface directly to hardware, providing fast graphical access), IRQ
Routing Miniport Driver (sets the system’s PCI IRQ routing sequence)
and VIA INF Driver (enables the VIA Power Management function).
• VIA Graphics Driver: Enhance the onboard VIA graphic chip.
• VIA Audio Driver: Enhance the onboard VIA audio chip.
• VIA USB 2.0 Driver: Enhance VIA USB 2.0 ports.
• VIA LAN Driver: Enhance the onboard VIA LAN chip.
• VIA FIR Driver: Support for FIR.
4-3
Page 72

Appendix
A
Smart 5.1
This chapter gives you brief description of how
Smart 5.1 is enabled.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Intelligent 6-Channel Audio A-2
A-1
Page 73

Appendix A
Intelligent 6-Channel Audio
Enabling Smart 5.1 Intelligent 6 Channel Audio
Smart5.1 allows the user to output 6 channel audio directly from the audio
jacks on the mainboard, using the traditional line-in and microphone jacks as
output jacks. For it to work properly, both the OS and the software
application used need to support 6 channel audio. Win98 supports 4 channel
only.Please follow the example A and B to enable the Smart 5.1 function,
and the examples are based on Windows XP. Start the settings in Control
Panel of your computer.
Example A
1. Double click [Sounds and Audio Devices] icon in Control Panel.
A-2
Page 74

Smart 5.1
2. The panel of [Sounds and Audio Devices Properties] appears and select
[Audio] tab. Then press [Advanced] as shown in the picture.
3. Choose [5.1 surround sound speakers] to support the 6 channel function.
A-3
Page 75

Appendix A
Example B
1. Double click [Sounds and Audio Devices] icon in Control Panel and then
select [Audio] tab on the panel as shown below. Press [Volume] button in
the [Sound playback] column.
2. [Front Speaker] panel appears and then select [Options] menu to check
the item [Advanced Controls].
A-4
Page 76

Smart 5.1
3. Then [Front Speaker] panel displays [Advanced] button and press it.
4. Check the item [Smart5.1 Enable] in the panel below.
A-5
Page 77

Appendix A
After completing the previous settings, you need to connect your speakers to
the audio jacks as shown below.
PS2_MS
PS2_KB
VGA Out
RJ45
USB
S-Video
Parallel (LPT1)
RCA / SPDIF
Line-In
Line-Out
Microphone
COM1
2-Channel 6-Channel
Line-In
Line-Out
Microphone
Rear (L/R)
Front (L/R)
Center/Sub
Following the system setup, users need to install software for playing DVD.
Currently the two main DVD-playing applications are WIN-DVD v4.0 and
Power DVD XP v4.0. Both of them are able to support 5.1 channel. Please
follow the instructions below to do the proper settings for Smart 5.1.
WIN-DVD v4.0
1. Open the application and click on the right arrow icon shown as the
picture below. Then select [Audio Effect].
A-6
Page 78

Smart 5.1
2. The panel of Audio Effect appears and click on the lower right corner
button as shown in the picture below.
3. The [Setup] panel appears and select [Audio] tab. Then choose the item
[6 Channel (5.1 Home Theater)] in the column of [Audio Speaker
Configuration]. Finally users can click [Test] button to verify the channel
output. You will hear sound of flowing water from different speakers if
each setup has been completed successfully.
A-7
Page 79

Appendix A
Power-DVD XP v4.0
1. Open the application and click on the [Configuration] icon shown as the
picture below.
2. The panel of Configuration appears and select [Audio] tab. Then choose
[6 Speaker] in the column of [Audio Output] and click [Ok].
Through the system operation and software settings, users can take
advantage of Smart 5.1 6-channel output with ease!
A-8
 Loading...
Loading...