Page 1
Reference
Manual
DOC. REV. 12/6/2013
Iguana
(VL-EPIC-25)
Intel® Atom-based SBC with
Ethernet, SATA, USB, eUSB,
CompactFlash, mSATA, Serial,
Industrial I/O, and SPX™
Page 2

WWW.VERSALOGIC.COM
12100 SW Tualatin Road
Tualatin, OR 97062-7341
(503) 747-2261
Fax (971) 224-4708
Copyright © 2013 VersaLogic Corp. All rights reserved.
Notice:
Although every effort has been made to ensure this document is error-free, VersaLogic makes no
representations or warranties with respect to this product and specifically disclaims any implied warranties
of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
VersaLogic reserves the right to revise this product and associated documentation at any time without
obligation to notify anyone of such changes.
PC/104 and the PC/104 logo are trademarks of the PC/104 Consortium.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual ii
Page 3
Product Revision Notes
VersaTech KnowledgeBase
Revsion 1.00 – Commercial release.
Support
The Iguana support page, at http://www.versalogic.com/private/iguanasupport.asp, contains additional
information and resources for this product including:
Reference Manual (PDF format)
Device drivers
Data sheets and manufacturers’ links for chips used in this product
Photograph of the circuit board
BIOS and PLD information and upgrades
This is a private page for Iguana users that can be accessed only by entering this address directly. It cannot
be reached from the VersaLogic homepage.
The VersaTech KnowledgeBase is an invaluable resource for resolving technical issues with your
VersaLogic product.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual iii
Page 4

Contents
Introduction ................................................................................................................... 1
Description .......................................................................................................................... 1
Features and Construction ..................................................................................... 1
Technical Specifications ..................................................................................................... 2
Block Diagram .................................................................................................................... 3
Thermal Considerations ...................................................................................................... 4
CPU Die Temperature ........................................................................................... 4
Model Differences ................................................................................................. 4
RoHS Compliance .............................................................................................................. 5
About RoHS ........................................................................................................... 5
Warnings ............................................................................................................................. 5
Electrostatic Discharge .......................................................................................... 5
Lithium Battery ...................................................................................................... 5
Handling Care ........................................................................................................ 6
Technical Support ............................................................................................................... 6
Repair Service ........................................................................................................ 6
Configuration and Setup ............................................................................................... 8
Initial Configuration ........................................................................................................... 8
Basic Setup ......................................................................................................................... 8
Operating System Installation ........................................................................................... 10
BIOS Setup Screens .......................................................................................................... 10
Physical Details ........................................................................................................... 11
Dimensions and Mounting ................................................................................................ 11
Iguana Dimensions .............................................................................................. 11
VL-CBR-5013 Dimensions ................................................................................. 12
VL-CBR-4004 Dimensions ................................................................................. 13
Hardware Assembly ............................................................................................. 14
Standoff Locations ............................................................................................... 14
External Connectors ......................................................................................................... 15
Iguana Connector Locations – Top...................................................................... 15
Iguana Connector Locations – Bottom ................................................................ 16
Iguana Connector Functions and Interface Cables .............................................. 17
VL-CBR-5013 Connector Locations ................................................................... 18
VL-CBR-5013 Connector Functions ................................................................... 18
VL-CBR-4004 Connector Locations ................................................................... 19
Jumper Blocks .................................................................................................................. 20
Jumpers As-Shipped Configuration ..................................................................... 20
Jumper Summary ................................................................................................. 21
System Features .......................................................................................................... 22
Power Supply .................................................................................................................... 22
Power Connectors ................................................................................................ 22
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual iv
Page 5

Contents
Power Requirements ............................................................................................ 22
Power Delivery Considerations ........................................................................... 23
Lithium Battery .................................................................................................... 23
CPU ................................................................................................................................... 24
System RAM ..................................................................................................................... 25
Clearing Non-volatile RAM (NVRAM) ........................................................................... 25
Real-Time Clock (RTC) ................................................................................................... 25
Setting the Clock.................................................................................................. 25
Clearing the Real-Time Clock ............................................................................. 26
Console Redirection ......................................................................................................... 26
Interfaces and Connectors ......................................................................................... 27
Expansion Buses ............................................................................................................... 27
PC/104-Plus (PCI + ISA) and PCI-104 (PCI Only) ............................................ 27
PC/104 ISA .......................................................................................................... 27
PC/104 I/O Support ............................................................................................. 28
PC/104 Memory Support ..................................................................................... 28
PC/104 IRQ Support ............................................................................................ 28
Ethernet Interface.............................................................................................................. 29
Ethernet Connectors ............................................................................................ 29
Ethernet Status LEDs ........................................................................................... 29
Status LED ........................................................................................................... 30
SATA Interface ................................................................................................................. 30
Serial Ports ........................................................................................................................ 31
COM Port Configuration ..................................................................................... 31
RS-485 Mode Line Driver Control ...................................................................... 31
Serial Port Connectors ......................................................................................... 32
USB Interface ................................................................................................................... 32
Flash Interfaces ................................................................................................................. 33
CompactFlash ...................................................................................................... 33
eUSB Socket ........................................................................................................ 33
PCIe Mini Card / mSATA Socket ....................................................................... 33
PCIe Mini Card Wireless Status LEDs ................................................................ 35
Video................................................................................................................................. 36
SVGA Output Connector ..................................................................................... 36
LVDS Flat Panel Display Connector ................................................................... 37
Audio ................................................................................................................................ 38
User I/O Connector ........................................................................................................... 39
Pushbutton Reset .............................................................................................................. 40
Power Button .................................................................................................................... 40
Supported Power States ....................................................................................... 40
External Speaker ............................................................................................................... 41
LEDs ................................................................................................................................. 41
Programmable LED ............................................................................................. 41
Power LED .......................................................................................................... 41
Digital I/O ......................................................................................................................... 42
Digital I/O Port Configuration Using the SPI Interface ...................................... 42
Analog Input ..................................................................................................................... 47
External Connections ........................................................................................... 47
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual v
Page 6

Contents
Analog Input Using the SPI Interface .................................................................. 47
Analog Output .................................................................................................................. 49
Counter / Timers ............................................................................................................... 50
SPX ................................................................................................................................... 51
VersaLogic SPX Expansion Modules ................................................................. 52
SPI Registers ........................................................................................................ 53
System Resources and Maps ..................................................................................... 56
Legacy Memory Map ........................................................................................................ 56
I/O Map ............................................................................................................................. 56
Special Registers ........................................................................................................ 57
PLED and Product Code Register .................................................................................... 57
PLD Revision and Type Register ..................................................................................... 58
BIOS and Jumper Status Register ..................................................................................... 59
Appendix A – References............................................................................................ 60
Appendix B – Custom Programming ......................................................................... 61
PLD Interrupts .................................................................................................................. 61
Interrupt Control Register .................................................................................... 61
Interrupt Status Register ...................................................................................... 62
8254 Timer Control Register ............................................................................................ 63
A/D and D/A Control/Status Register .............................................................................. 64
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual vi
Page 7
Intel Atom D425 Single Core or D525
Dual Core processor with ICH8M I/O
hub
Up to 2GB of DDR3 via a single SO-
DIMM
Dual Gigabit Ethernet
PC/104-Plus expansion
Eight USB 1.1/2.0 channels: two
(Type A) on-board, four (Type A) on
the paddleboard, one to the PCIe Mini
Card, and one to the eUSB interface
Industrial I/O
Eight 12-bit analog inputs
Four 12-bit analog outputs
Sixteen digital I/O lines
Three SATA 2.5 ports: two on-board
vertical latching connectors, one port
to the mSATA port
Four serial ports: RS-232/422/485
Flash interfaces: eUSB, PCIe Mini
Card/mSATA SSD, CompactFlash
RoHS-compliant
Extended temperature options
Integrated high performance video with
simultaneous, independent analog and
FPD output capability
Intel 3rd generation graphics core
24-bit VGA up to 2048x1536
18-bit LVDS up to 1366x768
SPX interface supports up to four
external SPI devices either of user
design or any of the SPX™ series of
expansion boards, with clock
frequencies from 1-8 MHz
Two 16-bit counter/timers (standard);
three 8254 Programmable Interval
Timers (custom)
TVS devices for ESD protection
Watchdog timer
Field upgradeable UEFI BIOS with
OEM enhancements
Customization available
1 1
Description
FEATURES AND CONSTRUCTION
The Iguana (VL-EPIC-25) is a feature-packed single board computer (SBC). It is designed for
OEM control projects requiring compact size, high reliability, and longevity (product lifespan).
Its features include:
Introduction
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 1
The Iguana is compatible with popular operating systems such as Windows CE, Windows XP
Professional/XP Embedded (SP3), Linux, VxWorks, and QNX (see the VersaLogic OS
Compatibility Chart). Note: Windows 7 will not install with less than 512 MB RAM.
The Iguana features high reliability design and construction, including voltage sensing reset
circuits and self-resetting fuses on the power supplies to the user I/O connectors.
Iguana boards are subjected to 100% functional testing and are backed by a limited two-year
warranty. Careful parts sourcing and US-based technical support ensure the highest possible
quality, reliability, service, and product longevity for this exceptional SBC.
Page 8

Technical Specifications
Board Size:
4.5" x 6.5" (EPIC standard)
Storage Temperature:
-40° to +85°C
Operating Temperature:
VL-EPIC-25SA, SB, with heatsink: 0° to +60°C
VL-EPIC-25EA, RA1, RB1 with fan, heatsink:
-40° to +85°C
Power Requirements: at +25°C with +5V supply
running Windows XP with 2 GB RAM, LVDS display,
SATA, GbE, and USB keyboard/mouse
VL-EPIC-25SA: 1.68A (8.40W) idle,1.82A
(9.1W) typical, 1.94A (9.7W) max.
VL-EPIC-25SB: 2.08A (10.40W) idle, 2.34A
(11.7W) typical,2.58A (12.9W) max
VL-EPIC-25EA, RA: 1.88A (9.40W) idle, 2.02A
(10.1W) typical, 2.14A (10.7W) max.
VL-EPIC-25RB: 2.28A (11.4W) idle, 2.54A
(12.7W) typical, 2.78A (13.9W) max.
+3.3V or ±12V may be required by some
expansion modules
System Reset:
Input power sensing, resets below 4.70V typ.
Watchdog timeout (warm/cold reset)
DRAM:
One SO-DIMM socket, up to 2GB of DDR3
DRAM
Video Interface:
Intel 3rd generation graphic core, 400 MHz
18-bit LVDS interface
VGA – 2048x1536 with 24-bit color
LVDS – 1355x768 with 18-bit color
SATA Interface:
Three SATA 2.5 ports: two on-board vertical
latching connectors, one port to the mSATA port
Flash Storage:
eUSB site
PCIe Mini Card/mSATA site
CompactFlash socket
Ethernet Interface:
Two Intel 82574IT based 10BaseT / 100BaseTX
/ 1000BaseT Ethernet Controllers
USB:
Eight host USB channels: two on-board Type A
connectors, four Type A connectors on VL-CBR5013 paddleboard, one on Mini PCIe connector,
1 on eUSB header
Serial Ports 0-1:
RS-232/422/485, 16C550 compatible, 460 Kbps
max., 4-wire RS-232 (CTS and RTS
handshaking), DB-9 connector on VL-CBR-5013
paddleboard
Serial Ports 2-3:
RS-232/422/485, 16C550 compatible, 460 Kbps
max., 4-wire RS-232 (CTS and RTS
handshaking), terminal block on VL-CBR-5013
paddleboard
Analog Input:
8-channel, 12-bit, single-ended, 100 Ksps,
channel independent input range: bipolar ±5,
±10, or unipolar 0 to +5V or 0 to +10V
Analog Output:
4-channel, 12-bit, single-ended, 100 Ksps
0V to 4.096V
Digital Interface:
16-channel, ±24 mA outputs, 3.3V signaling
SPX:
Supports four external SPI chips of user design
or any SPX series expansion board
Audio:
Stereo HD audio line in/out
BIOS:
AMI UEFI BIOS with OEM enhancements, field
programmable.
Bus Speed:
PC/104-Plus (PCI): 33.33 MHz
PC/104 (ISA): 8.33 MHz
Compatibility:
PC/104 - Full compliance
Weight:
VL-EPIC-25SA - 0.645 lbs (0.293 kg)
VL-EPIC-25SB - 0.662 lbs (0.300 kg)
VL-EPIC-25EA - 0.701 lbs (0.318 kg)
Specifications are typical at 25°C with +5V supply unless otherwise noted. Specifications are
subject to change without notification.
Introduction
1. Special order. Ruggedized Ethernet and user I/O connectors.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 2
Page 9
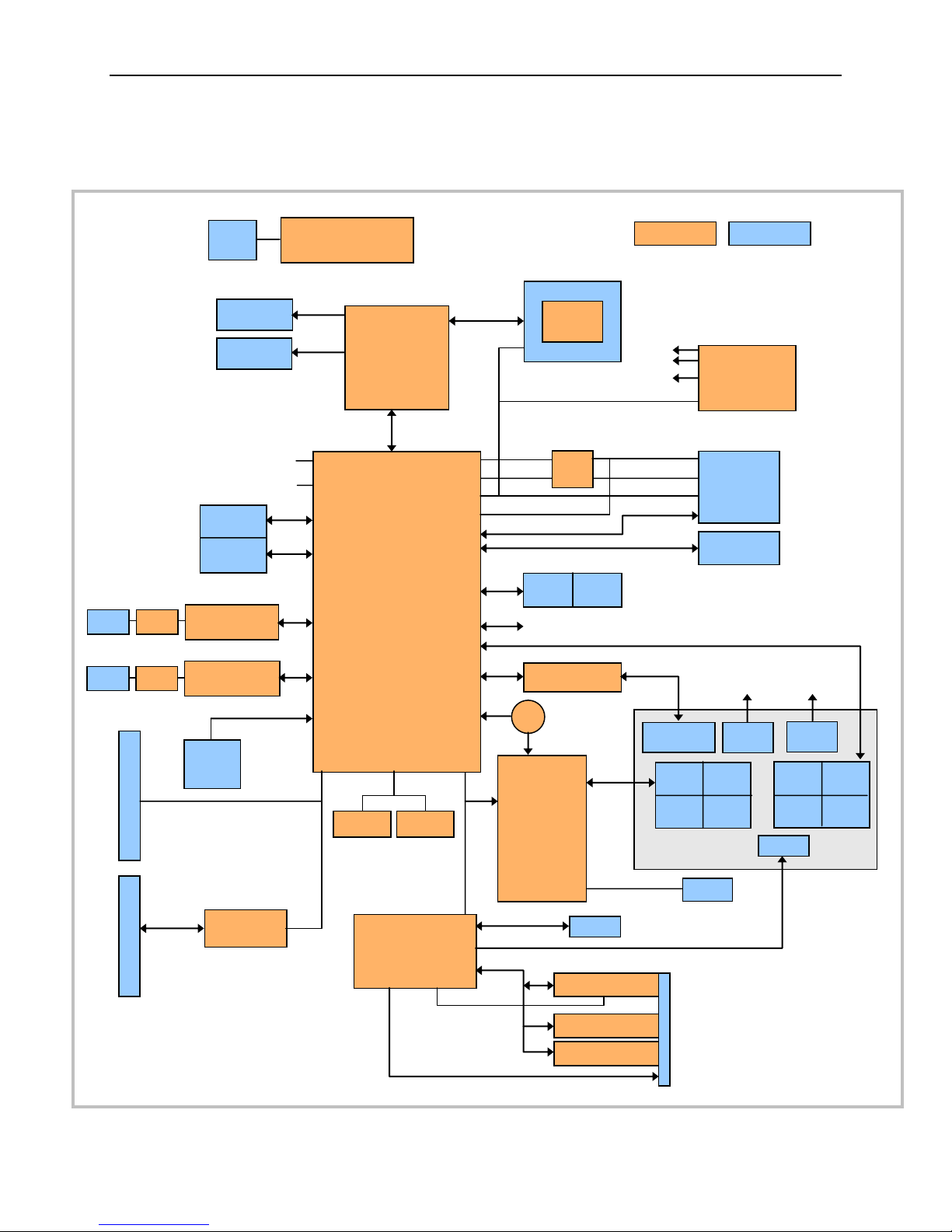
Block Diagram
Power
Input
Regulators
Includes Power Mgt &
Sequencing Logic
18-bit LVDS
Panel
VGA
On-Board
Peripheral
Intel Atom
Processor
D425 (1 core)
D525 (2 core)
DDR3
SO-DIMM
CK505 Clock
Generation
E-Mux
PCIe Mini
Card or
mSATA
eUSB Flash
Module
Conn.
Mag
Conn.
Mag
Ethernet 0
GigE MAC/PHY
Ethernet 1
GigE MAC/PHY
Compact
Flash
Socket
PC/104-Plus (PCI)
PC/104 (ISA)
ITE PCI-ISA
Bridge
Pri.
Sec.
LPC-SPI Bridge
& 8254 Timers
(Actel FPGA)
Digital I/O (16)
Analog Input (8)
Analog Output (4)
SPX
Fan
Super I/O
Tach
HD Audio &
Audio Jacks
& Speaker
Reset
Button
Power
Button
PLED
LVDS
RGB
Key:
DDR3
SMB
Electronic Mux
SMB
PCIe/SATA
SMB
USB 2.0
RTC
Monitor
Serial
SPI SS0/1/2/3
LPC
LPC
4 Timer I/Os (CTC)
SPI Boot Flash
PC/104
PCI
Intel 82574IT
Intel 82574IT
PCIe x1 [6]
PCIe x1 [4,5]
SATA 0
SATA 1
PCIe x1 [1]
PCIe x1 [2]
IDE I/F
PCI32
SATA 2
PCIe x1 [3]
SMB
GPIO
USB 8
USB 9
USB 0-1
USB 2-3
USB 4-7
HDA
LPC
Intel 82801HM
I/O Controller
(ICH8M)
4xDMI Gen 1
(FSB)
N/C
RST_BTN# PWR_BTN#
(on heat sink)
Batt
USB0 USB2
2.0 2.0
X
Serial Serial
COM0 COM2
Serial Serial
COM1 COM3
USB4 USB6
2.0 2.0
USB5 USB7
2.0 2.0
SATA0
Connector
SATA1
Connector
X
X
N/C
N/C
SPI
VL-CBR-4004
VL-CBR-5013
SPI I/F
Introduction
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 3
Page 10

Thermal Considerations
CPU DIE TEMPERATURE
The CPU die temperature is affected by numerous conditions, such as CPU utilization, CPU
speed, ambient air temperature, air flow, thermal effects of adjacent circuit boards, external heat
sources, and many others.
The CPU is protected from over-temperature conditions by two mechanisms.
The CPU will automatically slow down by 50% whenever its die temperature exceeds +100°C.
When the temperature falls back below +100°C, the CPU resumes full-speed operation.
As a failsafe, if the CPU die temperature climbs above +105°C, the CPU will turn itself off to
prevent damage to the chip.
MODEL DIFFERENCES
VersaLogic offers both commercial and industrial temperature models of the VL-EPIC-25. The
basic operating temperature specification for both models is shown below.
Introduction
VL-EPIC-25SA and SB: 0°C to +60°C free air, no airflow, heatsink, no fan
VL-EPIC-25EA, RA, and RB: -40°C to +85°C free air, heatsink, fan
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 4
Page 11

RoHS Compliance
The Iguana is RoHS-compliant.
ABOUT ROHS
In 2003, the European Union issued Directive 2002/95/EC regarding the Restriction of the use of
certain Hazardous Substances (RoHS) in electrical and electronic equipment.
The RoHS directive requires producers of electrical and electronic equipment to reduce to
acceptable levels the presence of six environmentally sensitive substances: lead, mercury,
cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and the presence of polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) and
polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) flame retardants, in certain electrical and electronic
products sold in the European Union (EU) beginning July 1, 2006.
VersaLogic Corp. is committed to supporting customers with high-quality products and services
meeting the European Union’s RoHS directive.
Introduction
Warnings
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE
Warning! Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage circuit boards, disk drives, and other
After removing the board from its protective wrapper, place the board on a
Note: The exterior coating on some metallic antistatic bags is sufficiently conductive to
LITHIUM BATTERY
components. The circuit board must only be handled at an ESD workstation. If an
approved station is not available, some measure of protection can be provided by
wearing a grounded antistatic wrist strap. Keep all plastic away from the board,
and do not slide the board over any surface.
grounded, static-free surface, component side up. Use an antistatic foam pad if
available.
The board should also be protected inside a closed metallic antistatic envelope
during shipment or storage.
cause excessive battery drain if the bag comes in contact with the bottom side of
the Iguana.
Warning! To prevent shorting, premature failure, or damage to the lithium battery, do not
place the board on a conductive surface such as metal, black conductive foam, or
the outside surface of a metalized ESD protective pouch. The lithium battery may
explode if mistreated. Do not recharge, disassemble, or dispose of in fire. Dispose
of used batteries promptly and in an environmentally suitable manner.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 5
Page 12
HANDLING CARE
Iguana Support Page
http://www.versalogic.com/private/iguanasupport.asp
VersaTech KnowledgeBase
Warning! Care must be taken when handling the board not to touch the exposed circuitry
with your fingers. Though it will not damage the circuitry, it is possible that small
amounts of oil or perspiration on the skin could have enough conductivity to cause
the Real Time Clock to become corrupted through careless handling.
Technical Support
If you are unable to solve a problem after reading this manual, please visit the Iguana product
support Web page below. The support page provides links to component datasheets, device
drivers, and BIOS and PLD code updates.
Introduction
The VersaTech KnowledgeBase contains a wealth of technical information about VersaLogic
products, along with product advisories. Click the link below to see all KnowledgeBase articles
related to the VL-EPIC-25.
If you have further questions, contact VersaLogic Technical Support at (503) 747-2261.
VersaLogic support engineers are also available via e-mail at Support@VersaLogic.com.
REPAIR SERVICE
If your product requires service, you must obtain a Returned Material Authorization (RMA)
number by calling (503) 747-2261.
Please provide the following information:
Your name, the name of your company, your phone number, and e-mail address
The name of a technician or engineer that can be contacted if any questions arise
Quantity of items being returned
The model and serial number (barcode) of each item
A detailed description of the problem
Steps you have taken to resolve or recreate the problem
The return shipping address
Warranty Repair All parts and labor charges are covered, including return shipping
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 6
charges for UPS Ground delivery to United States addresses.
Page 13

Introduction
Non-warranty Repair All approved non-warranty repairs are subject to diagnosis and labor
charges, parts charges, and return shipping fees. Please specify the
shipping method you prefer and provide a purchase order number for
invoicing the repair.
Note: Please mark the RMA number clearly on the outside of the box before
returning.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 7
Page 14

2 2
Initial Configuration
The following components are recommended for a typical development system with the Iguana:
ATX power supply
DDR3 DRAM module
USB keyboard and mouse
SATA hard drive
USB CD-ROM drive
LVDS or VGA display
The following VersaLogic cables are recommended:
VL-CBR-2022 – Power adapter cable
VL-CBR-5013 – Paddleboard
VL-CBR-0701 – SATA data cable
LVDS or VGA video adapter cable
Configuration and Setup
You will also need an operating system (OS) installation CD-ROM.
Basic Setup
The following steps outline the procedure for setting up a typical development system. The
Iguana should be handled at an ESD workstation or while wearing a grounded antistatic wrist
strap.
Before you begin, unpack the Iguana and accessories. Verify that you received all the items you
ordered. Inspect the system visually for any damage that may have occurred in shipping. Contact
Support@VersaLogic.com immediately if any items are damaged or missing.
Gather all the peripheral devices you plan to attach to the Iguana and their interface and power
cables.
It is recommended that you attach standoffs to the board (see Hardware Assembly) to stabilize
the board and make it easier to work with.
Figure 1 shows a typical start-up configuration.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 8
Page 15
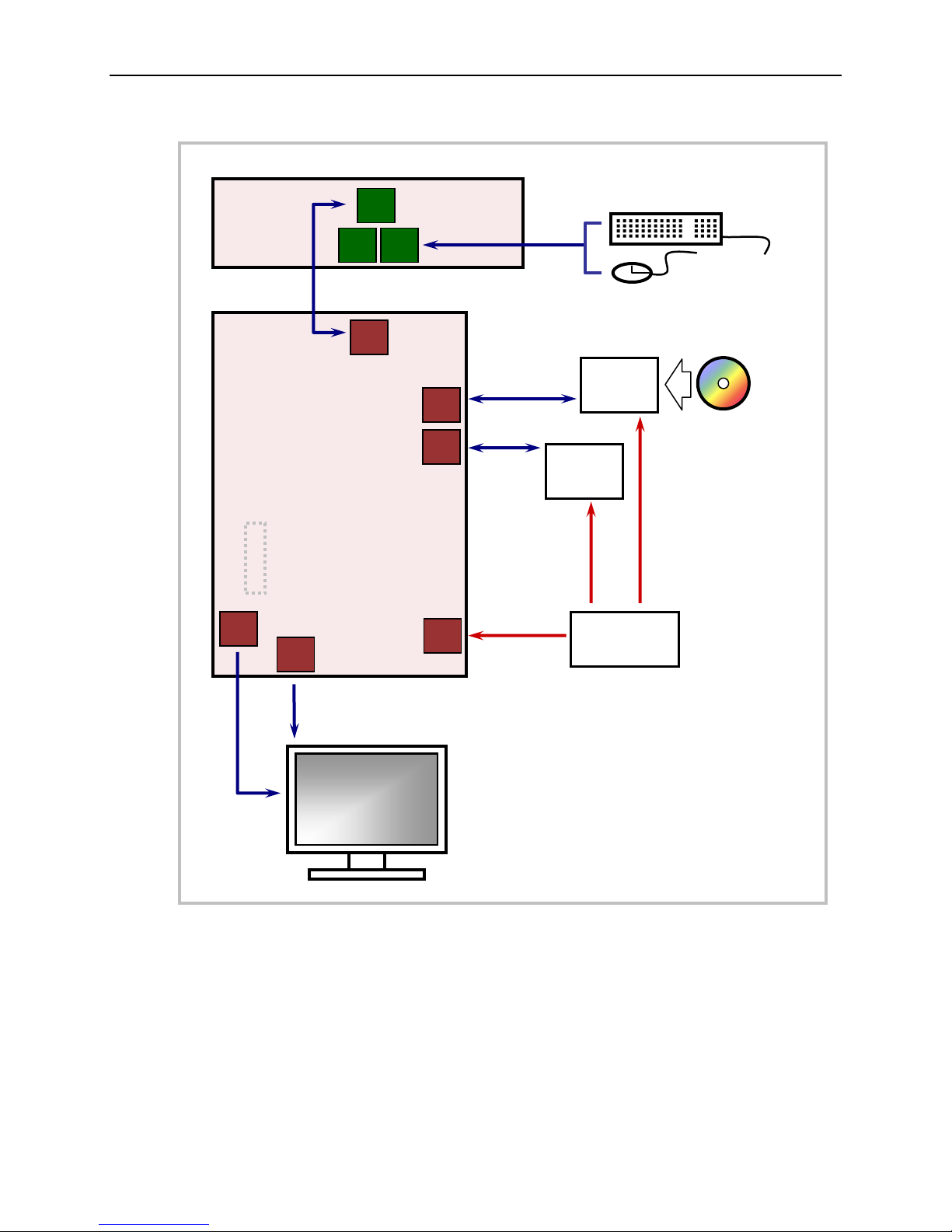
Configuration and Setup
ATX
Power Supply
SVGA or LVDS
USB Keyboard
and USB Mouse
USB CD-
ROM Drive
OS Installation
CD-ROM
IGUANA
VL-EPIC-25
VL-CBR-2022
J29
VL-CBR-0701
VL-CBR-5013B
J4
J19
J7
J1
J3
J16
J17
J11
J12
VL-CBR-2010 or
VL-CBR-2011
VL-CBR-5013A
SATA
Hard Drive
VL-CBR-0401
J1
J2
VL-CBR-1201
SVGA
or
LVDS
1. Install Memory
Insert a DDR3 DRAM module into SO-DIMM socket J1 on the bottom of the board and
latch it into place.
2. Attach Cables and Peripherals
Plug the appropriate video cable into the LVDS connector (J3) or the VGA connector
(J2) and attach the monitor.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 9
Figure 1. Typical Start-up Configuration
Page 16

Configuration and Setup
Plug the VL-CBR-5013A cable into the user I/O connector (J19) on the Iguana and the
VL-CBR-5013B paddleboard (the cable is shipped attached to the paddleboard).
Plug a USB keyboard and mouse into USB sockets J1 or J7 of the paddleboard.
Plug the SATA data cable VL-CBR-0701 into socket J11 or J12. Attach a hard drive to
the cable.
Attach the ATX SATA power cable (VL-CBR-0401) to the ATX power supply and the
SATA hard drive.
Plug a USB CD-ROM drive into a USB socket J16 or J17.
Attach an ATX power cable to any 3.5” drive that is not already attached to the power
supply (hard drive or CD-ROM drive).
3. Attach Power
Plug the power adapter cable VL-CBR-2022 into socket J29. Attach the motherboard
connector of the ATX power supply to the adapter.
4. Review Configuration
Before you power up the system, double check all the connections. Make sure all cables
are oriented correctly and that adequate power will be supplied to the Iguana and
peripheral devices.
5. Power On
Turn on the ATX power supply and the video monitor. If the system is correctly
configured, a video signal should be present. (There might be a delay of several seconds
before the video signal becomes present.) If video does not appear, press the Power
Button on the paddleboard.
6. Install Operating System
Install the OS according to the instructions provided by the OS manufacturer.
Note: If you intend to operate the Iguana under Windows XP or Windows XP
Embedded, be sure to use Service Pack 3 (SP3) for full support of the latest device
features.
Operating System Installation
The standard PC architecture used on the Iguana makes the installation and use of most of the
standard x86-based operating systems very simple. The operating systems listed on the
VersaLogic OS Compatibility Chart use the standard installation procedures provided by the
maker of the OS. Special optimized hardware drivers for a particular OS, or a link to the drivers,
are available at the Iguana Product Support web page.
BIOS Setup Screens
See KnowledgeBase article VT1701 - BIOS Setup Reference for complete information on how to
configure the Iguana BIOS.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 10
Page 17
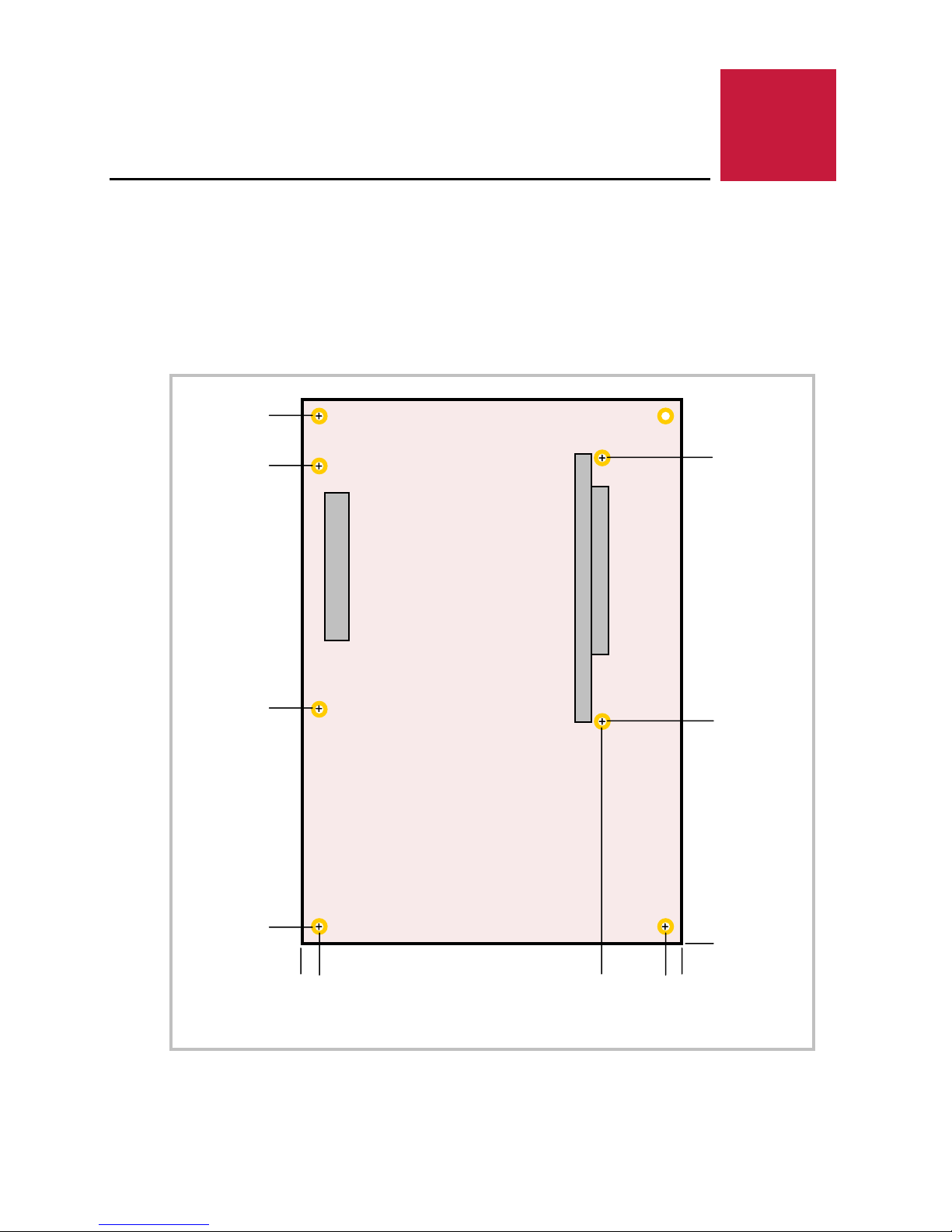
3 3
6.096
4.128
4.328
2.596
5.496
-0.200
5.596
2.446
0.000
3.375
-0.200
0.000
Dimensions and Mounting
IGUANA DIMENSIONS
The VL-EPIC-25 complies with EPIC dimensional standards. Dimensions are given below to
help with pre-production planning and layout.
Physical Details
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 11
Figure 2. Iguana Dimensions and Mounting Holes
(Not to scale. All dimensions in inches.)
Page 18
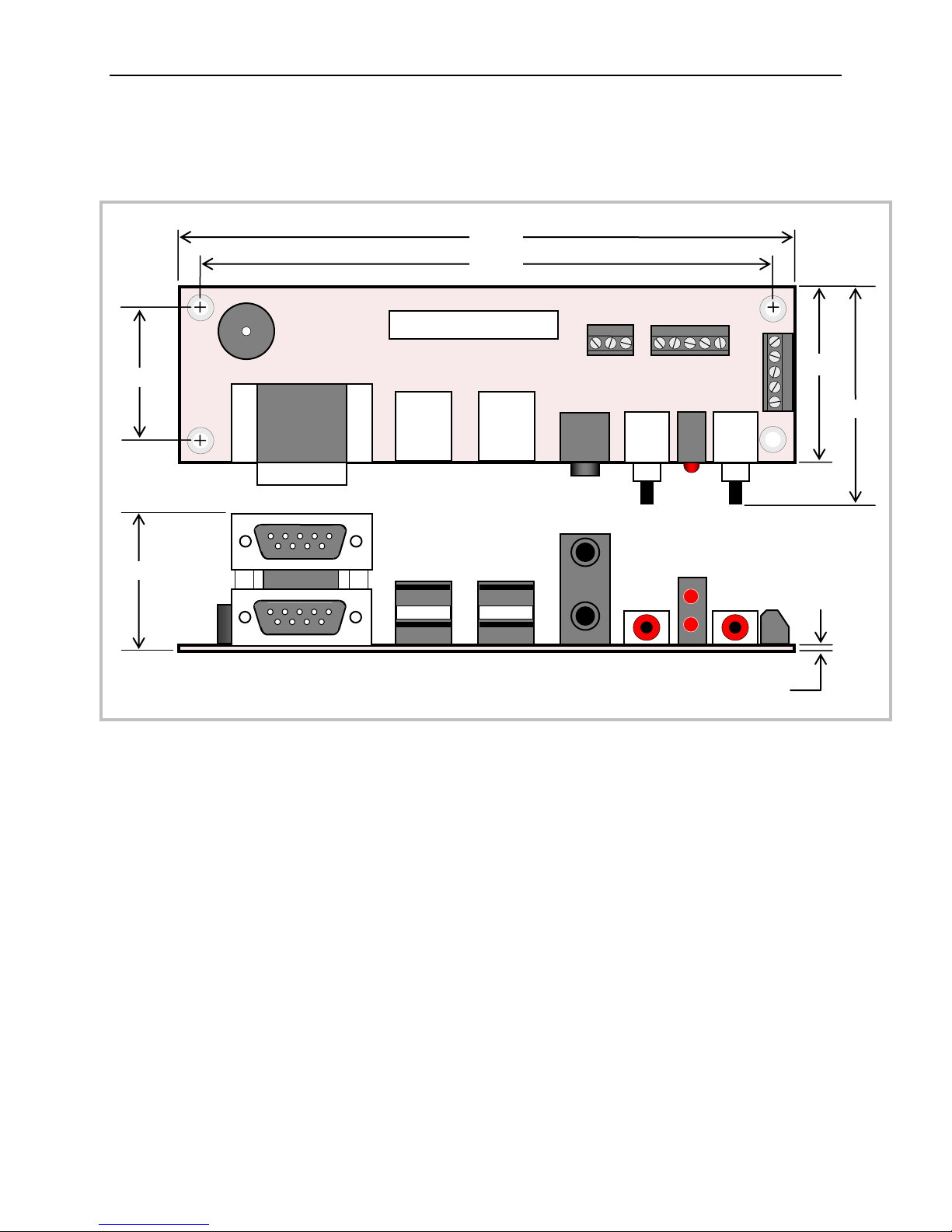
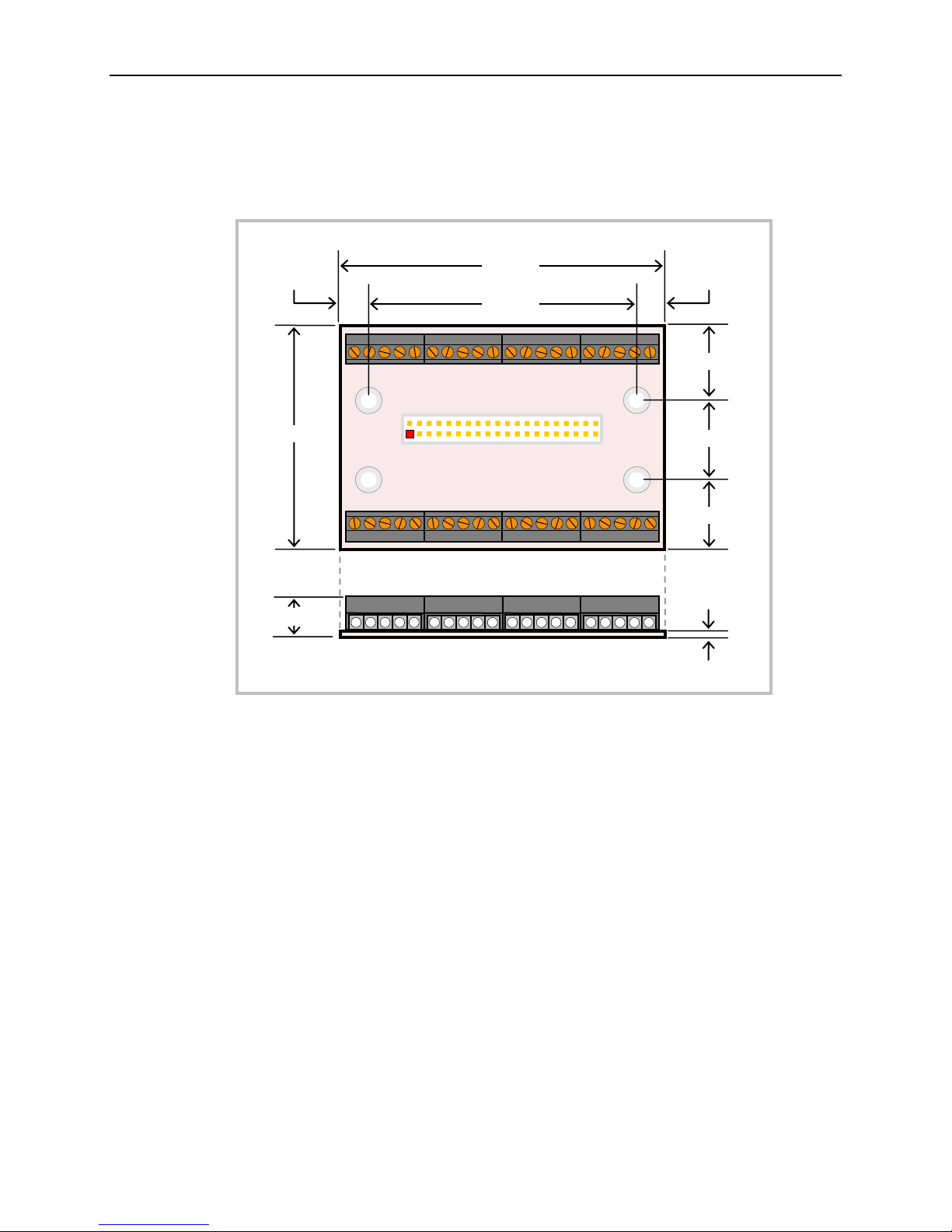
VL-CBR-5013 DIMENSIONS
1.95
1.57
5.50
5.10
1.17
1.24
0.065
Physical Details
Figure 3. VL-CBR-5013 Dimensions and Mounting Holes
(Not to scale. All dimensions in inches.)
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 12
Page 19
VL-CBR-4004 DIMENSIONS
J1 J2 J3 J4
J6 J7 J8 J9
J5
+ + +
+
2.38
2.87
0.25
0.25
0.40
1.95
0.70
0.63
0.62
0.06
Physical Details
Figure 4. VL-CBR-4004 Dimensions and Mounting Holes
(Not to scale. All dimensions in inches.)
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 13
Page 20
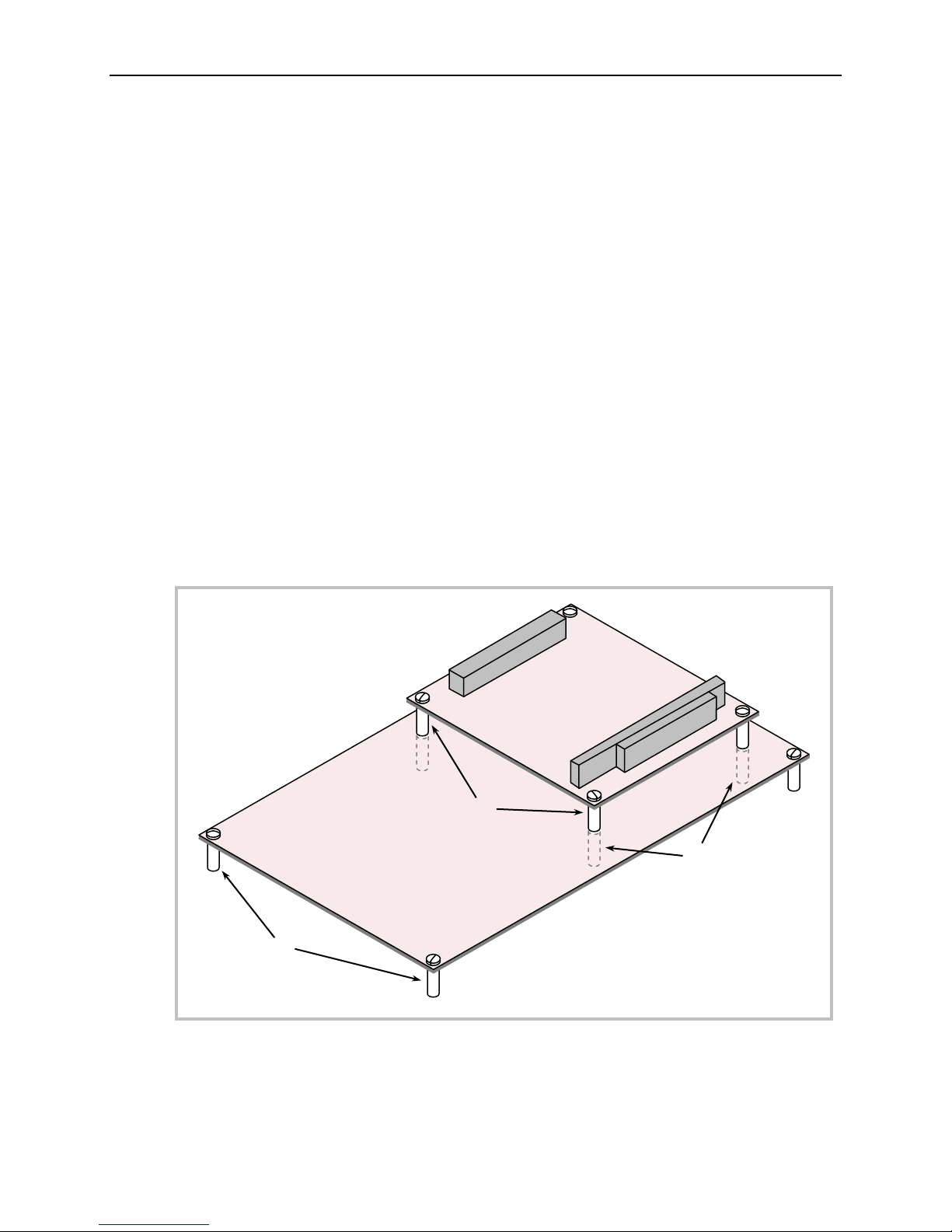
Physical Details
A
B
C
HARDWARE ASSEMBLY
The Iguana uses PC/104 and PC/104-Plus connectors so that expansion modules can be added to
the top of the stack. PC/104 (ISA) modules must not be positioned between the Iguana and any
PC/104-Plus (PCI) modules on the stack.
The entire assembly can sit on a table top or be secured to a base plate. When bolting the unit
down, make sure to secure all eight standoffs (A and B) to the mounting surface to prevent
circuit board flexing. Four standoffs (B) must be used under the stack. These are secured with
four male-female standoffs (C), threaded from the top side, which also serve as mounting struts
for the PC/104 stack. Standoffs are secured to the top circuit board using pan head screws. Four
standoffs and screws are available as part number VL-HDW-106.
Note: A minimum height clearance of 8.5mm is required beneath the board to avoid
contacting the tallest component (the CompactFlash socket) with the enclosure or
other components.
An extractor tool is available (part number VL-HDW-203) to separate the PC/104 modules from
the stack. Use caution when using the extractor tool not to damage any board components.
STANDOFF LOCATIONS
Figure 5. Stack Arrangement Example
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 14
Page 21
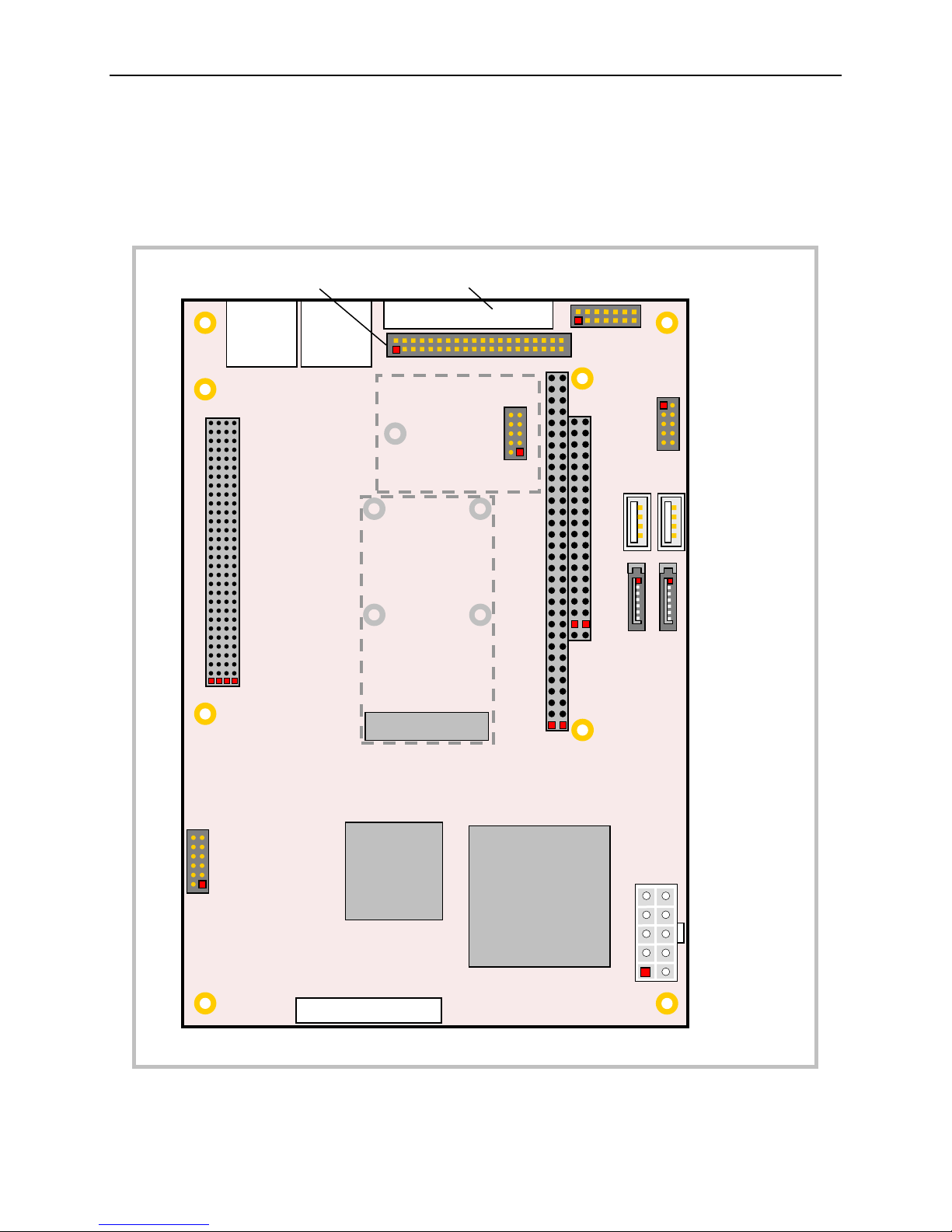
External Connectors
J27 - SPX
J28
External
Ethernet LED
J3 – LVDS
J22
Ethernet 1
J7-J8
ISA
J6
PCI
J16 J17
J16 - USB0
J17 - USB1
J19 – User I/O
J29
Power
J25 – Digital, Analog, Timers
ICH8M
J13
PCIe Mini Card
or mSATA
J20
Ethernet 0
J11 - SATA0
J12 - SATA1
J2
VGA
J18
eUSB
J11 J12
DCBA
B A
C D
Atom
CPU
IGUANA CONNECTOR LOCATIONS – TOP
Physical Details
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 15
Figure 6. Connector Locations (Top)
Page 22

IGUANA CONNECTOR LOCATIONS – BOTTOM
J9
CompactFlash
J1
SODIMM
Physical Details
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 16
Figure 7. Connector Locations (Bottom)
Page 23

Physical Details
Connector1
Function
Mating
Connector
Transition
Cable
Cable
Description
Page
Pin 1 Location
X Coord. Y Coord.2
J1
204-pin SO-DIMM 1.5V
DDR3 Socket
(DDR3 RAM)
— — 25
0.656
1.226
J2
SVGA Video Output
FCI 89361-712LF or
FCI 89947-712LF
VL-CBR-1201
12" 12-pin 2 mm IDC to
15-pin HD D-Sub VGA
36
-0.033
1.079
J3
LVDS
20-pin, PanelMate
1.25mm
VL-CBR-2010;
VL-CBR-2011;
VL-CBR-2012
(24-bit)
18-bit TFT FPD using
20-pin Hirose
18-bit TFT FPD using
20-pin JAE
37
1.399
-0.081
J6
PCI
AMP 1375799-1
— — 27
0.236
2.896
J7, J8
ISA
AMP 1375795-2
— — 27
3.1753
2.496
J9
CompactFlash
Type I & II
— — —
33
2.009
2.736
J11
SATA
Standard SATA
VL-CBR-0701;
VL-CBR-0401
500 mm (19.75”) 7-pin,
straight-to-straight
SATA data; ATX to
SATA power adapter
30
3.793
3.793
J12
SATA
Standard SATA
VL-CBR-0701;
VL-CBR-0401
500 mm (19.75”) 7-pin,
straight-to-straight
SATA data; ATX to
SATA power adapter
30
4.187
3.793
J13
PCIe Mini Card
mSATA
— — —
33
1.514
2.533
J16
USB 1
Standard USB Type A
— — 32
3.805
4.120
J17
USB 2
Standard USB Type A
— — 32
4.128
4.120
J18
eUSB Flash Drive
— — —
33
2.809
5.102
J19
COM ports, USB,
PLED, power LED,
push-button reset,
power button, audio
jacks, PC speaker
Oupiin 1204-50G00B2A
VL-CBR-5013A
18" 1.27 mm IDC 50-pin
to 50-pin
39
2.371
6.176
J20
Ethernet 0
RJ45
— — 29
1.060
6.024
J22
Ethernet 1
RJ45
— — 29
0.362
6.024
J25
Digital I/O, Analog I/O,
Timer I/O
FCI 89361-340LF
VL-CBR-4004
12” 2 mm 40-pin to 40pin IDC to
VL-CBR-4004 board
42,
47,
49, 50
1.722
5.831
J26
Fan (model AE)
— — — — 4.175
1.176
J27
SPX
FCI 89361-714LF
VL-CBR-1401
or VL-CBR-1402
2mm 14-pin IDC, 2 or 4
SPX device cable
51
3.364
6.126
J28
External Ethernet LED
— — —
30
4.159
5.295
J29
Main power input
Molex 39-01-2100
Molex 39-00-0059 (10ea.)
VL-CBR-2022
6” ATX to EPIC power
cable
22
3.946
0.289
IGUANA CONNECTOR FUNCTIONS AND INTERFACE CABLES
Table 1 provides information about the function, mating connectors, and transition cables for
Iguana connectors. Page numbers indicate where a detailed pinout or further information is
available.
Table 1: Connector Functions and Interface Cables
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 17
1. Connectors J4, J5 (XDP Debug), J10 (SPI Programming), J14, J15, J21 & J23 (ruggedized Ethernet), J24 (JTAG), J26
are either not assigned, not installed, or for factory use only.
2. The PCB Origin is the mounting hole to the lower left as shown in Figure 3. Coordinates in inches.
3. Pin A1.
Page 24

VL-CBR-5013 CONNECTOR LOCATIONS
Connector
Function
PCB Connector
Description
J1
USB3, USB4
USB Type A
USB Host
J2
COM0, COM1
Kycon K42-E9P/P-A4N
Dual DB-9 male
J3
Audio In/Out
3.5 mm dual audio jack
–
J4
High Density Connector
FCI 98414-F06-50ULF
2 mm, 50-pin, keyed header
J5
COM2
Conta-Clip 10250.4
5-pin screw terminal
J6
COM3
Conta-Clip 10250.4
5-pin screw terminal
J7
USB1, USB2
USB Type A
USB Host
J8
External Reset and Power Buttons
Conta-Clip 10250.4
3-pin screw terminal
D1
PLED (Top), Power LED (Bottom)
LED – S1
Power Button
Pushbutton
–
S2
Reset Button
Pushbutton
–
SP1
Speaker
Piezo speaker
–
J7
USB1 (Top)
USB2
(Bottom)
J3
Audio
In (Top)
Out (Bottom)
S1
Power
D1
Programmable
LED (Top)
Power LED
(Bottom)
S2
Reset
J1
USB3 (Top)
USB4
(Bottom)
J2
COM0 (Top)
COM1
(Bottom)
J6
COM3
SP1
Speaker
J4
Paddleboard Adapter
J5
COM2
J8
Ext. Pushbutton
Controls
Physical Details
Figure 8. VL-CBR-5013 Connector Locations
VL-CBR-5013 CONNECTOR FUNCTIONS
Table 2: VL-CBR-5013 Connector Functions and Interface Cables
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 18
Page 25

VL-CBR-4004 CONNECTOR LOCATIONS
2 1 40
39
J1 J2 J3 J4
J6 J7 J8 J9
5 1 5 1 5 1 5 1
1 5 1 5 1 5 1 5
= Pin 1
J5
Physical Details
Figure 9. VL-CBR-4004 Connectors
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 19
Page 26

Jumper Blocks
V4
V5
V1
V1
V7
V2
V6
V4
V5
1
2
3
V6
V3
V2
V3
1
2
3
2 4 6 8
1 3 5 7
1 2
2 1
2 1
3 4
V7
2 1
JUMPERS AS-SHIPPED CONFIGURATION
Physical Details
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 20
Figure 10. Jumper Block Locations
Page 27

JUMPER SUMMARY
Jumper
Block
Description
As
Shipped
Page
V1[1-2-3]
Factory Use Only. Jumper may be installed or removed.
V1[1-2] In
—
V2[1-2]
SPI Flash Write-Protect
In – Writable
Out – Write Protected
In
33
V3[1-2-3]
Real-Time Clock (RTC) Reset
[1-2] In – Normal operation (jumper storage)
[2-3] In – Reset RTC
[1-2] In
25
V4[1-2]
COM0 configuration
In — RS-485 (Rx endpoint termination)
Out — RS-232
Out
31
V4[3-4]
COM1 configuration
In — RS-485 (Rx endpoint termination)
Out — RS-232
Out
31
V4[5-6]
COM2 configuration
In — RS-485 (Rx endpoint termination)
Out — RS-232
Out
31
V4[7-8]
COM3 configuration
In — RS-485 (Rx endpoint termination)
Out — RS-232
Out
31
V5[1-2]
BIOS Select
In — Secondary BIOS
Out — Primary BIOS
Out
59
V5[3-4]
General Purpose Input Bit 1
In — Bit D7 in GPI register reads as 1
Out — Bit D7 in GPI register reads as 0
In
59
V6[1-2]
Clear Non-volatile RAM (NVRAM)
In — Resets BIOS settings to factory defaults.
Out — Normal
Out
25
V7[1-2]
Factory Use Only — Jumper must not be installed.
Out
—
Physical Details
Table 3: Jumper Summary
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 21
Page 28

J29
Pin
Signal
Name
Description
1*
GND
Ground
2
GND
Ground
3
GND
Ground
4
+12VDC
Power Input
5
+3.3VDC
Power Input
6**
NC
Not connected
7
+5VDC
Power Input
8
+5VDC
Power Input
9
-12VDC
Power Input
10
GND
Ground
4 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10
Power Supply
POWER CONNECTORS
Main power is applied to the Iguana through an EPIC-style 10-pin polarized connector at location
J29.
Warning! To prevent severe and possibly irreparable damage to the system, it is critical that
the power connectors are wired correctly. Make sure to use both +5VDC pins and
all ground pins to prevent excess voltage drop.
System Features
Table 4: Main Power Connector Pinout
* Pin 1 is typically used in EPIC-style power cables as a PS-ON signal. Since the EBX-11 does not support
soft-off, pin 1 is internally connected to ground.
** Pin 6 is typically used in EPIC style power cables as a 5VSB (5V Stand By) signal. Since the EBX-11
does not support soft-off, pin 6 is an internal no connect.
Note: The +3.3 VDC, +12 VDC and -12 VDC inputs are necessary for expansion
modules that require these voltages.
POWER REQUIREMENTS
The Iguana requires only +5V (±5%) for proper operation. (Initial power up typically requires >
+4.85V due to 0.1V of input voltage monitoring hysteresis.) The higher voltages required for the
RS-232 ports and analog inputs are generated as needed on-board. Variable low-voltage supply
circuits provide the many power rails required by the CPU and other on-board devices.
The exact power requirement of the Iguana depends on several factors, including memory
configuration, CPU speed, peripheral connections, type and number of expansion modules and
attached devices.For example, driving long RS-232 lines at high speed can increase power
demand, and supplying 4.85V input voltage would meet the load requirements for on-board USB
ports, but 5V would be needed to meet the load requirements on the VL-CBR-5013 USB ports.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 22
Page 29

System Features
POWER DELIVERY CONSIDERATIONS
Using the VersaLogic approved power supply (VL-PS200-ATX) and power cable (VL-CBR-
2022) will ensure high quality power delivery to the board. Customers who design their own
power delivery methods should take into consideration the guidelines below to ensure good
power connections.
Also, the specifications for typical operating current do not include any off-board power usage
that may be fed through the VL-EPIC-25 power connector. Expansion boards and USB devices
plugged into the board will source additional power through the VL-EPIC-25 power connector.
Do not use wire smaller than 18 AWG. Use high quality UL 1007 compliant stranded
wire.
The length of the wire should not exceed 18".
Avoid using any additional connectors in the power delivery system.
The power and ground leads should be twisted together, or as close together as possible
to reduce lead inductance.
A separate conductor must be used for each of the power pins.
All power input pins and all ground pins must be independently connected between the
power source and the power connector.
Implement the remote sense feature on your power supply if it has one. Connect the
remote sense lines in tandem with one of the power input and ground pins. This is done
at the connector to compensate for losses in the power wires.
Use a high quality power supply that can supply a stable voltage while reacting to widely varying
current draws.
LITHIUM BATTERY
Warning! To prevent shorting, premature failure, or damage to the lithium battery, do not
place the board on a conductive surface such as metal, black conductive foam, or
the outside surface of a metalized ESD protective pouch. The lithium battery may
explode if mistreated. Do not recharge, disassemble or dispose of in fire. Dispose
of used batteries promptly.
Normal battery voltage should be at least +3V. If the voltage drops below +2V, contact the
factory for a replacement (part number HB3/0-1). The life expectancy under normal use is
approximately 10 years. Battery voltage can be monitored on the H/W Monitor BIOS setup
screen.
Storage temperature affects the life of the battery. The on-board Real-Time Clock (RTC)
continues to draw power even when the Iguana is powered off. The following graph shows that
battery life improves when the board is stored at a lower temperature.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 23
Page 30

Figure 11. Battery Life vs. Storage Temperature
System Features
CPU
Intel® Atom™ D425 and D525 processors include the following key features:
On die, primary 32-kB instructions cache and 24-kB write-back data cache
Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology 2-threads per core
On die 2 x 512-kB, 8-way L2 cache for D500 dual-core processor, 1 x 512-kB, 8-way L2
cache for D400 single-core processor
Processor memory features include:
Support for DDR3 at data transfer rate of 800 MT/s
I/O Voltage of 1.5 V for DDR3
Integrated graphics features include:
The GPU contains a refresh of the 3rd generation graphics core
Intel® Dynamic Video Memory Technology support 4.0
Directx 9 compliant Pixel Shader v2.0
400 MHz render clock frequency
Two display ports: LVDS and RGB
Intel® Clear Video Technology
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 24
Page 31

System RAM
The Iguana accepts one 204-pin DDR3 SO-DIMM memory module with the following
characteristics:
Size Up to 2GB (1GB or 2GB recommended)
Voltage +1.5V
Type DDR3, 800 MT/s (400 MHz clock)
Clearing Non-volatile RAM (NVRAM)
You can clear NVRAM and reset the BIOS settings to factory defaults by following the
instructions below.
1. Power off the Iguana.
2. Install a jumper on V6[1-2].
3. Power on the Iguana and wait 10 seconds or more.
4. Power off the Iguana.
System Features
5. Remove the jumper from V6[1-2]. The board will not boot if you do not remove this
jumper.
6. Power on the Iguana.
Real-Time Clock (RTC)
The Iguana features a battery-backed real-time clock/calendar chip. Under normal battery
conditions, the clock maintains accurate timekeeping functions when the board is powered off.
The accuracy of the RTC clock is ± 20 ppm (parts per million) at 25° C, which equates to
approximately ± 1.7 seconds per day of clock drift error (± 20 ppm is the crystal frequency
accuracy). The RTC accuracy varies with temperature. The approximate clock accuracy at any
temperature T (in C) can be calculated as follows:
ppm = [1 – 0.04(T-25)2] ± 20 (in ppm)
clock drift error = 0.0864 x ppm (in seconds per day)
For example, at -40° C the ppm = -168 ± 20 ppm. For the worst case crystal accuracy of -20 ppm,
the ppm = -188 ppm, which equates to -16.2 seconds per day.
SETTING THE CLOCK
The Main BIOS setup screen (accessed by pressing the Delete key during the early boot cycle, or
F4 if operating in terminal mode) can be used to set the time and date of the real-time clock.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 25
Page 32

CLEARING THE REAL-TIME CLOCK
You can move the V3 jumper to position [2-3] for a minimum of two seconds to clear the RTC.
When clearing the RTC:
1. Power off the Iguana.
2. Move the jumper from V3[1-2] to V3[2-3] and leave it for two or more seconds.
3. Return the jumper to V3[1-2]. (The board will not boot if the jumper is not returned to
this position.)
4. Power on the Iguana.
This procedure sets the RTC date to Sat 01/01/2011. The time is not reset by this
procedure; however, the time is reset to 00:00:00 if battery power is lost.
Console Redirection
The Iguana can be configured for remote access by redirecting the console to a serial
communications port. The BIOS setup utility and some operating systems such as DOS can use
this console for user interaction.
System Features
Console redirection settings are configured in the Serial Port Console Redirection BIOS setup
screen. Console redirection is disabled by default.
Console redirection can be disabled or redirected to one or more COM ports that will share the
video console. The default settings for the redirected console are 115.2 kbps, 8 data bits, 1 stop
bit, no parity, and no flow control.
Null Modem
The following figure illustrates a typical DB9 to DB9 RS-232 null modem adapter.
Figure 12. Null Modem with Loop-back Handshaking
Pins 1, 4, and 6 are shorted together on each connector.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 26
Page 33

Voltage
Max. Current
+5V
8A
+3.3V
4A
+12V
1A
-12V
0.5A
5
Expansion Buses
Note Some information in this section may change as the BIOS continues in
development.
PC/104-PLUS (PCI + ISA) AND PCI-104 (PCI ONLY)
PC/104-Plus and PCI-104 modules can be secured directly to the top of the Iguana. Make sure to
correctly configure the slot position jumpers on each PC/104-Plus module appropriately. PC/104
(ISA only) modules must not be positioned between the Iguana and any PC/104-Plus or PCI-104
modules in the stack.
The VL-EPIC-25 is compliant with revision 2.0 of the PC/104-Plus specification and can support
four bus master capable PC/104-Plus modules.
Interfaces and Connectors
The BIOS automatically allocates I/O and memory resources. However, manual PCI Interrupt
routing is used.
The following table shows the maximum PC/104-Plus slot power on the Iguana.
Table 5: Maximum PC/104-Plus Slot Power
PC/104 ISA
The Iguana provides full support of the PC/104 bus, with the following exceptions:
-5.0V power is not supplied on J7 pin B5. This pin is not connected.
The ISA bus cannot be mastered by an external module. The Iguana is always the bus
master. The MASTER signal on pin D17 of J8 is not connected.
DMA not supported.
Most PC/104 cards will work, but be sure to check the requirements of your PC/104 card against
the list above.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 27
Page 34

Interfaces and Connectors
0x019 – 0x01E
0x062 – 0x063
0x0D2 – 0x0DD
0x3F7
0x022 – 0x023
0x065 – 0x070
0x0E0 – 0x0EF
0x400 – 0x47F
0x026 – 0x027
0x078 – 0x07F
0x0F1 – 0x16F
0x4C0 – 0x4CF
0x02A – 0x02B
0x0A2 – 0x0A3
0x178 – 0x1EF
0x4D2 – 0x7FF
0x032 – 0x033
0x0A6 – 0x0A7
0x1F8 – 0x2E7
0x880 – 0xBFF
0x036 – 0x037
0x0AA – 0x0AB
0x2F0 – 0x2F7
0xCC0 – 0xCF8
0x03A – 0x03B
0x0AE – 0x0AF
0x300 – 0x375
0xCFA – 0xCFB
0x03E – 0x03F
0x0B6 – 0x0B7
0x377 – 0x3BF
0xD00
0x043 – 0x04D
0x0BA –0x0BB
0x3E0 – 0x3E7
0x053 – 0x05F
0x0BE – 0x0BF
0x3F0 – 0x3F5
PC/104 I/O SUPPORT
The following I/O ranges are available on the ISA bus unless there is a device claiming the range
on the LPC bus (COM and LPT ports). Be sure to configure the ISA I/O ranges and the onboard
serial ports in BIOS setup to avoid conflicts with one another. (An OS will not allocate I/O in the
legacy ISA range.)
Available base I/O addresses for COM ports are: 2E8h, 2F8h, 3E8h, 3F8h.
PC/104 MEMORY SUPPORT
The following memory addresses are available on the ISA bus:
0xA0000 – 0xB7FFF
0xD0000 – 0xDFFFF
PC/104 IRQ SUPPORT
Interrupts are routed automatically, though manual routing control may be added in future BIOS
releases. First the COM ports are assigned IRQs according to the Serial Port Configuration
settings. Next the PCI devices are assigned IRQs. After an OS loads and transitions from 8259 to
APIC mode, these PCI IRQs will be freed and available for legacy use. In the 1.00 BIOS,
VersaLogic recommends IRQ6 for ISA bus use in a OS using the legacy 8259 interrupt
controller.
Because ISA IRQ sharing is not supported, IRQs may not be available to the ISA bus due to
operating system limitations.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 28
Page 35

Ethernet Interface
LED
State
Description
Green/Yellow
(Link Speed)
Yellow
1 Gbps speed
Green
100 Mbps speed
Off
10 Mbps speed or cable not
connected
Yellow (Activity)
On
Cable connected (intermittent with
activity)
Off
Cable not connected
The Iguana features two on-board Intel 82574IT Gigabit Ethernet controllers. The controllers
provide a standard IEEE 802.3 Ethernet interface for 1000Base-T, 100Base-TX, and 10Base-T
applications. RJ45 connectors are located at locations J22 (Ethernet 1) and J20 (Ethernet 0).
While these controllers are not NE2000-compatible, they are widely supported. Drivers are
readily available to support a variety of operating systems. These interfaces are protected against
ESD damage.
ETHERNET CONNECTORS
Two board-mounted RJ45 connectors are provided to make connection with Category 5 or 6
Ethernet cables. The 82574IT Ethernet controller auto-negotiates connection speed. These
interfaces use IEC 61000-4-2-rated TVS components to help protect against ESD damage.
ETHERNET STATUS LEDS
On-board status LEDs are provided at locations D7 (single yellow) and D8 (dual green/yellow)
for Ethernet 0, and D9 (single yellow) and D10 (dual green/yellow) for Ethernet 1. These LEDs
provide an indication of the Ethernet status as shown in the following table.
Interfaces and Connectors
Table 6: On-board Ethernet Status LEDs
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 29
Page 36

Interfaces and Connectors
J28
Pin
Signal
Name
Function
On-Board LED
Equivalent
1
+3.3V
Protected Power Supply
—
2
YEL1
Yellow LED - Ethernet 0
D7 – Yellow
3
ORN1
Orange LED - Ethernet 0
D8 – Yellow
4
GRN1
Green LED - Ethernet 0
D8 – Green
5
+3.3V
Protected Power Supply
D9 – Yellow
6
YEL2
Yellow LED - Ethernet 1
D10 – Yellow
7
ORN2
Orange LED - Ethernet 1
D10 – Green
8
GRN2
Green LED - Ethernet 1
— 9
GND
Ground
— 10
W_DISABLE#
PCIe Mini Card Disable*
—
J11 or
J12 Pin
Signal Name
Function
1
GND
Ground
2
TX+
Transmit +
3
TX-
Transmit -
4
GND
Ground
5
RX-
Receive -
6
RX+
Receive +
7
GND
Ground
STATUS LED
Connector J28 provides an additional on-board Ethernet status LED interface. The +3.3V power
supplied to this connector is protected by a 1 Amp fuse.
Table 7: Ethernet Status LED Pinout
* This pin can be connected to the Disable signal on the PCIe Mini Card
(pin 20) on custom models.
SATA Interface
The Iguana provides two serial ATA (SATA) ports, which communicate at a rate of up to 3.0
GB/s (SATA 2). The SATA connectors at locations J11 and J12 are standard 7-pin straight
SATA connectors with friction latching. Power to SATA drives is supplied by the ATX power
supply. Note that the standard SATA drive power connector is different than the common 4-pin
Molex connector used on IDE drives. Most current ATX power supplies provide SATA
connectors, and many SATA drives provide both types of power connectors. If the power supply
you are using does not provide SATA connectors, adapters are available.
Table 8: SATA Port Pinout
The blue LED at location D11 (upper right corner of the board as shown in Figure 7) lights with
disk activity on the SATA ports.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 30
Page 37

Serial Ports
The Iguana features four on-board 16550-based serial communications channels located at
standard PC I/O addresses. All serial ports can be operated in RS-232 4-wire, RS-422, or RS-485
modes. IRQ lines are chosen in BIOS setup. Each COM port can be independently enabled,
disabled, or assigned a different I/O base address in BIOS setup.
COM PORT CONFIGURATION
Use the BIOS setup screens to select between RS-232 and RS-422/485 operating modes.
Jumper block V4 is used to configure serial ports for RS-422/485 operation. See “Jumper
Summary” for details. The termination resistor should be enabled for RS-422 and the RS-485
endpoint stations. It should be disabled for RS-232 and RS-485 intermediate stations.
If RS-485 mode is used, the differential twisted pair (TxD+/RxD+ and TxD-/RxD-) is formed by
connecting both transmit and receive pairs together. For example, on CBR-5013 connectors J6
and J5, the TxD+/RxD+ signal is formed by connecting pins 3 and 5, and the TxD-/RxD- signal
is formed by connecting pins 2 and 4.
Interfaces and Connectors
RS-485 MODE LINE DRIVER CONTROL
The TxD+/TxD– differential line driver is automatically turned on and off based on data
availability in the UART output FIFO.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 31
Page 38

Interfaces and Connectors
COM0
COM1
Top DB9
J2 Pin
Bottom DB9
J2 Pin
RS-232
RS-422
RS-485
1 1 — — — 2 2
RXD*
RxD-
RxD- 3 3
TXD*
TxD-
TxD- 4 4 — — — 5 5 Ground
Ground
Ground 6 6 — — — 7 7 RTS
TxD+
TxD+ 8 8
CTS
RxD+
RxD+ 9 9 — —
—
COM2
COM3
J5 Pin
J6 Pin
RS-232
RS-422
RS-485
1 1 Ground
Ground
Ground
2 2 RXD
RxD-
RxD- 3 3
CTS
RxD+
RxD+
4 4 TXD
TxD-
TxD- 5 5
RTS
TxD+
TxD+
SERIAL PORT CONNECTORS
The pinouts of the DB9M connectors apply to the serial connectors on the VersaLogic breakout
board VL-CBR-5013.
These connectors use IEC 61000-4-2-rated TVS components to help protect against ESD
damage.
Table 9: COM0-1 Pinout – VL-CBR-5013 Connector J2
USB Interface
The USB interface on the Iguana is UHCI (Universal Host Controller Interface) and EHCI
(Enhanced Host Controller Interface) compatible, which provides a common industry
software/hardware interface. The Iguana provides six Type A USB host connectors at locations
J16 and J17 on the motherboard, and dual connectors J1 and J7 on the VL-CBR-5013
paddleboard. Two more USB channels are available through the PCIe Mini Card connector at
J13 and the eUSB connector at J18.
Table 10: COM2-3 Pinout – VL-CBR-5013 Connectors J5-6
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 32
Page 39

Flash Interfaces
J18
Pin
Signal
Name
Function
1
+5V
+5V Power Supply
2
NC
Not connected
3
D-
Data –
4
NC
Not connected
5
D+
Data +
6
NC
Not connected
7
GND
Ground
8
NC
Not connected
9
Key
Physical key
10
LED
SSD LED
COMPACTFLASH
Connector J9 provides a socket for a Type I or Type II CompactFlash (CF) module. The CF
interface supports operation in DMA mode. Contact VersaLogic Sales to order CF modules that
have been tested and qualified as bootable devices.
After installing the OS on the CF, you may configure the module to be the first boot device,
which will reduce boot time.
The blue LED at location D11 (upper right corner of the board as shown in Figure 7) lights with
disk activity on the CF port.
EUSB SOCKET
The Iguana includes an eUSB port. The VersaLogic VL-F15 Series of eUSB SSD modules are
available in sizes of 2 GB or 4 GB. Contact VersaLogic Sales to order. eUSB modules are
secured to the on-board standoff using M2.5 x 6mm pan head Philips nylon screws. These screws
are available in quantities of 10 in the VL-HDW-108 hardware kit from VersaLogic.
Interfaces and Connectors
Table 11: eUSB Port Locations
The blue LED at location D6 (upper right corner of the board as shown in Figure 7) lights with
activity on the eUSB port, if supported by the eUSB module.
PCIE MINI CARD / MSATA SOCKET
The socket at location J13 accepts a full-height PCI Express Mini Card or an mSATA module.
The PCIe Mini Card interface includes one PCIe x1 lane, one USB 2.0 channel, and the SMBus
interface. The socket is compatible with plug-in Wi-Fi modems, GPS receivers, flash data
storage, and other cards for added flexibility. An Intel WiFi Link 5300 PCI Express Mini Card
(VL-WD10-CBN) is available from VersaLogic. A WiFi antenna (VL-CBR-ANT01) and a 12"
WiFi card to bulkhead RP-SMA transition cable (VL-CBR-0201) are also available. For more
information, contact Sales@VersaLogic.com.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 33
Page 40

Interfaces and Connectors
J13
Pin
PCIe Mini Card
Signal Name
PCIe Mini Card
Function
mSATA
Signal Name
mSATA
Function
1 WAKE#
Wake
Reserved
Not connected
2 3.3VAUX
3.3V auxiliary source
+3.3V
3.3V source
3 NC
Not connected
Reserved
Not connected
4 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
5 NC
Not connected
Reserved
Not connected
6 1.5V
1.5V power
+1.5V
1.5V power
7 CLKREQ#
Reference clock request
Reserved
Not connected
8 NC
Not connected
Reserved
Not connected
9 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
10 NC
Not connected
Reserved
Not connected
11 REFCLK-
Reference clock input –
Reserved
Not connected
12 NC
Not connected
Reserved
Not connected
13 REFCLK+
Reference clock input +
Reserved
Not connected
14 NC
Not connected
Reserved
Not connected
15 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
16 NC
Not connected
Reserved
Not connected
17 NC
Not connected
Reserved
Not connected
18 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
19 NC
Not connected
Reserved
Not connected
20 W_DISABLE#
Wireless disable 1
Reserved
Not connected
21 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
22 PERST#
Card reset
Reserved
Not connected
23 PERn0
PCIe receive –
+B
Host receiver diff. pair +
24 3.3VAUX
3.3V auxiliary source
+3.3V
3.3V source
25 PERp0
PCIe receive +
-B
Host receiver diff. pair –
26 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
27 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
28 1.5V
1.5V power
+1.5V
1.5V power
29 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
30 SMB_CLK
SMBus clock
Two Wire I/F
Two wire I/F clock
31 PETn0
PCIe transmit –
-A
Host transmitter diff. pair –
32 SMB_DATA
SMBus data
Two Wire I/F
Two wire I/F data
33 PETp0
PCIe transmit +
+A
Host transmitter diff. pair +
34 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
35 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
36 USB_D-
USB data –
Reserved
Not connected
37 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
38 USB_D+
USB data +
Reserved
Not connected
39 3.3VAUX
3.3V auxiliary source
+3.3V
3.3V source
40 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
The VL-MPEs-F1E series of mSATA modules provide flash storage of 4 GB, 16 GB, or 32 GB.
To secure a Mini Card or mSATA module to the on-board standoffs, use two M2.5 x 6mm pan
head Philips nylon screws. These screws are available in quantities of 10 in the VL-HDW-108
hardware kit from VersaLogic.
Table 12: PCIe Mini Card / mSATA Pinout
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 34
Page 41

Interfaces and Connectors
J13
Pin
PCIe Mini Card
Signal Name
PCIe Mini Card
Function
mSATA
Signal Name
mSATA
Function
41 3.3VAUX
3.3V auxiliary source
+3.3V
3.3V source
42 LED_WWAN#
Wireless WAN LED
Reserved
Not connected
43 GND
mSATA Detect 2
GND/NC
Ground/Not connected 3
44 LED_WLAN#
Wireless LAN LED
Reserved
Not connected
45 NC
Not connected
Vendor
Not connected
46 LED_WPAN#
Wireless PAN LED
Reserved
Not connected
47 NC
Not connected
Vendor
Not connected
48 1.5V
1.5V power
+1.5V
1.5V power
49 Reserved
Reserved
DA/DSS
Device activity 4
50 GND
Ground
GND
Ground
51 Reserved
Reserved
GND
Ground 5
52 3.3VAUX
3.3V auxiliary source
+3.3V
3.3V source
Notes:
1. This signal can be driven by GPIO24 from the ICH8M or as a custom option from Pin 10 on the
Ethernet LED connector at location J28.
2. This pin is not grounded on the Iguana since it can be used to detect the presence of an mSATA
module versus a PCIe Mini Card. Grounding this pin is available as an option on custom boards.
3. This pin is not grounded on the Iguana to make it available for mSATA module detection.
4. This signal drives the blue LED activity indicator at location D11 (upper right corner of the board
as shown in Figure 6). This LED lights with mSATA disk activity, if supported by the mSATA
module.
5. Some PCIe modules use this signal as a second Mini Card wireless disable input. On the
Iguana, this signal is available for use for mSATA versus PCIe Mini Card detection. There is an
option on the VersaLogic Features BIOS setup screen for setting the mSATA detection method.
PCIE MINI CARD WIRELESS STATUS LEDS
Three wireless status LEDs are provided on the Iguana at locations D4 and D5:
D4 Yellow – Wireless WAN
D5 Green – Wireless LAN
D5 Yellow – Wireless PAN
These LEDs light when the associated device is installed and capable of transmitting.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 35
Page 42

Video
J2
Pin
Signal
Name
Function
Mini DB15
Pin
1
GND
Ground 6
2
RED
Red Video
1 3
GND
Ground 7
4
GREEN
Green Video
2 5
GND
Ground 8
6
BLUE
Blue Video
3 7
GND
Ground 5
8
HSYNC
Horizontal Sync
13
9
GND
Ground 10
10
VSYNC
Vertical Sync
14
11
SCL
DDC Serial Data Line Clock
15
12
SDA
DDC Serial Data Line
12
An on-board video controller integrated into the chipset provides high-performance video output
for the Iguana. The controller supports dual, simultaneous, independent video output. The Iguana
can also be operated without video attached (see Console Redirection).
The Iguana supports two types of video output, SVGA and LVDS Flat Panel Display.
SVGA OUTPUT CONNECTOR
An adapter cable, part number VL-CBR-1201, is available to translate J2 into a standard 15-pin
D-Sub SVGA connector. This connector is protected against ESD damage.
Interfaces and Connectors
Table 13: Video Output Pinout
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 36
Page 43

Interfaces and Connectors
J3
Pin
Signal
Name
Function
1
GND
Ground
2
NC
Not Connected
3
NC
Not Connected
4
NC
Not Connected
5
GND
Ground
6
LVDSCLK0
Differential Clock (+)
7
LVDSCLK0#
Differential Clock (-)
8
GND
Ground
9
LVDSA2
Diff. Data 2 (+)
10
LVDSA2#
Diff. Data 2 (-)
11
GND
Ground
12
LVDSA1
Diff. Data 1 (+)
13
LVDSA1#
Diff. Data 1 (-)
14
GND
Ground
15
LVDSA0
Diff. Data 0 (+)
16
LVDSA0#
Diff. Data 0 (-)
17
GND
Ground
18
GND
Ground
19
+3.3V
+3.3V (Protected)
20
+3.3V
+3.3V (Protected)
LVDS FLAT PANEL DISPLAY CONNECTOR
The integrated LVDS Flat Panel Display in the VL-EPIC-25 is an ANSI/TIA/EIA-644-1995
specification-compliant interface. It can support up to 18 bits of RGB pixel data plus 3 bits of
timing control (HSYNC/VSYNC/DE) on the 4 differential data output pairs. The LVDS clock
frequency ranges from 25 MHz to 112 MHz.
Iguana has one LVDS connector at location J3.
BIOS setup provides several options for standard LVDS flat panel types. If these options do not
match the requirements of the panel you are attempting to use, contact Support@VersaLogic.com
for a custom video BIOS.
Table 14: LVDS Flat Panel Display Pinout
The +3.3V power provided to pins 19 and 20 of J3 is protected by a software-controllable power
switch (1 Amp max.). This switch is controlled by the LVDD_EN signal from the LVDS
interface controller in the CPU.
Note: A +5V power option is available on custom models.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 37
Page 44

Audio
J3
Pin
Signal
Name
Function
1
LINE_INL
Line-In Left
2
LINE_INR
Line-In Right
3
HDA_GND
HDA Ground
4
LINE_OUTL
Line-Out Left
5
LINE_OUTR
Line-Out Right
6
HDA_GND
HDA Ground
The audio interface on the Iguana is implemented using an Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
92HD87B1X5 Audio Codec. This interface is Intel High Definition Audio compatible. Drivers
are available for most Windows-based and Linux operating systems. To obtain the most current
versions, consult the Iguana product support page.
The J19 main I/O connector provides the line-level stereo input and line-level stereo output
connection points. The outputs will drive most amplified PC speaker sets.
The following table shows the pinout of the audio connector J3 on the VL-CBR-5013 breakout
board.
Interfaces and Connectors
Table 15: VL-CBR-5013 J3 Audio Connector Pinout
Note: In Windows, the rear line-in audio input is configured by default as a microphone
input. To configure it for audio input, disable the microphone boost to eliminate
audio distortion.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 38
Page 45

User I/O Connector
J19
Pin
CBR-5013
Connector
Signal
J19
Pin
CBR-5013
Connector
Signal
RS-232
RS-422/485
25
USB 4
USB4-5 +5.0V
1
COM0
Ground
Ground
26 Data +
2
J2
RXD
RxD- 27 Data -
3
Top DB9
CTS
RxD+ 28
USB 5
USB4-5 +5.0V
4 Ground
Ground
29 Data + 5
TXD
TxD- 30 Data - 6
RTS
TxD+ 31
USB 6
USB6-7 +5.0V
7
COM1
Ground
Ground
32 Data +
8
J2
RXD
RxD- 33 Data -
9
Bottom DB9
CTS
RxD+ 34
USB 7
USB6-7 +5.0V
10 Ground
Ground
35 Data +
11 TXD
TxD- 36 Data -
12 RTS
TxD+ 37 +5.0V (Protected)
13
COM2
Ground
Ground
38
D1
Programmable LED
14
J5
RXD
RxD- 39
SP1
Speaker
15 CTS
RxD+ 40
S2, J8 Pin 1
Pushbutton Reset
16 Ground
Ground
41
S1, J8 Pin 3
Power Button
17 TXD
TxD- 42 Ground
18 RTS
TxD+ 43
Audio In
Audio In Left
19
COM3
Ground
Ground
44
J3 Top
HDA ground (isolated)
20
J6
RXD
RxD- 45 Audio In Right
21 CTS
RxD+ 46 HDA ground (isolated)
22 Ground
Ground
47
Audio Out
Audio Out Left
23 TXD
TxD- 48
J3 Bottom
HDA ground (isolated)
24 RTS
TxD+ 49 Audio Out Right
50 HDA ground (isolated)
The 50-pin user I/O connector (J19) incorporates the COM ports, four USB ports, programmable
LED, power LED, pushbutton reset, power button, audio line in/out, and speaker interfaces. The
table below illustrates the function of each pin.
Interfaces and Connectors
Table 16: User I/O Connector Pinout
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 39
Page 46

Pushbutton Reset
Connector J19 includes an input for a pushbutton reset switch. Shorting J19 pin 40 to ground
causes the Iguana to reboot. This must be a mechanical switch or an open-collector or open-drain
active switch with less than a 0.5V low-level input when the current is 1 mA. There must be no
pull-up resistor on this signal.
This connector uses IEC 61000-4-2-rated TVS components to help protect against ESD damage.
A reset button is provided on the VL-CBR-5013 breakout board. Terminal block J8 on the
breakout board also provides a reset signal on pin 1 and ground on pin 2.
Power Button
Connector J19 includes an input for a power button. Shorting J19 pin 41 to ground causes the
board to enter an S5 power state (similar to the Windows Shutdown state). Shorting it again will
return the board to the S0 power state and reboot the board. The button can be configured in
Windows to enter an S3 power state (Sleep, Standby, or Suspend-to-RAM), an S4 power state
(Hibernate or Suspend-to-Disk), or an S5 power state (Shutdown or Soft-Off).
Interfaces and Connectors
This connector uses IEC 61000-4-2-rated TVS components to help protect against ESD damage.
A power button is provided on the VL-CBR-5013 breakout board. Terminal block J8 also
provides a power button signal on pin 3 and ground on pin 2.
In configurations where a power button is not connected to the board, if the system is put into an
S5 state, power can be restored by turning off the power supply and turning it back on. This
behavior is set by default by the BIOS. The behavior can be changed using the Restore AC
Power Loss parameter on the Chipset > South Bridge menu of the BIOS setup screens.
SUPPORTED POWER STATES
The Iguana supports the following power states:
S0 (G0): Working.
S1 (G1-S1): All processor caches are flushed, and the CPUs stop executing instructions.
Power to the CPUs and RAM is maintained. Devices that do not indicate they must
remain on may be powered down.
S3 (G1-S3): Commonly referred to as Standby, Sleep, or Suspend-to-RAM. RAM
remains powered.
S4 (G1-S4): Hibernation or Suspend-to-Disk. All content of main memory is saved to
non-volatile memory, such as a hard drive, and is powered down.
S5 (G2): Soft Off. Almost the same as G3 Mechanical Off, except that the power supply
still provides power, at a minimum, to the power button to allow return to S0. A full
reboot is required. No previous content is retained. Other components may remain
powered so the computer can "wake" on input from the keyboard, clock, modem, LAN,
or USB device.
G3: Mechanical off (ATX supply switch turned off).
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 40
Page 47

External Speaker
Connector J19 includes a speaker output signal at pin 39. The VL-CBR-5013 breakout board
provides a Piezo electric speaker.
LEDs
PROGRAMMABLE LED
Connector J19 includes an output signal for a programmable LED. Connect the cathode of the
LED to J19 pin 38; connect the anode to +5V. A 332Ω on-board resistor limits the current to 15
mA when the LED is shorted. A programmable LED is provided on the VL-CBR-5013 breakout
board. The programmable LED is the top LED at position D1.
To turn the LED on and off, set or clear bit D7 in I/O port CA0h. When changing the register,
make sure not to alter the value of the other bits.
The following code examples show how to turn the LED on and off.
LED On LED Off
MOV DX,CA0H MOV DX,CA0H
IN AL,DX IN AL,DX
OR AL,80H AND AL,7FH
OUT DX,AL OUT DX,AL
Interfaces and Connectors
POWER LED
The power LED on the VL-CBR-5013 indicates that the paddle board is being powered by the
5V supply (though it does not indicate that all S0 power supplies are good). The LED is lit only
on when the board is in the S0 power state. If the board enters a Sleep or Hibernate mode, the
LED will not be lit.
There is also an on-board green "Power-OK" LED (at location D4). This will illuminate when all
power rails are good, and indicates that the board is in the S0 power state. If any power rail is not
good, the LED will not illuminate. It also goes out when the board enters a sleep or hibernate
power mode.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 41
Page 48

Digital I/O
J25
Pin Signal
VL-CBR-4004
Connector
VL-CBR-4004
Pin (Label)
16
Digital I/O 1
J4
5 (IO13)
17
Digital I/O 2
4 (IO14)
18
Digital I/O 3
3 (IO15)
19
Digital I/O 4
2 (IO16)
20
Ground
1 (GND2)
21
Digital I/O 5
J6
1 (IO17)
22
Digital I/O 6
2 (IO18)
23
Digital I/O 7
3 (IO19)
24
Digital I/O 8
4 (IO20)
25
Ground
5 (GND3/PBRST#)
26
Digital I/O 9
J7
1 (IO21)
27
Digital I/O 10
2 (IO22)
28
Digital I/O 11
3 (IO23)
29
Digital I/O 12
4 (IO24)
30
Ground
5 (GND3)
31
Digital I/O 13
J8
1 (IO25)
32
Digital I/O 14
2 (IO26)
33
Digital I/O 15
3 (IO27)
34
Digital I/O 16
4 (IO28)
35
Ground
5 (GND4)
The 40-pin I/O connector (J25) incorporates 16 digital I/O lines. Table 17 shows the function of
each pin. The digital I/O lines are controlled using the SPI registers. See "SPI Registers" for a
complete description of the registers.
The digital lines are grouped into two banks of 16-bit bi-directional ports. The direction of each
8-bit port is controlled by software. The digital I/O lines are powered up in the input mode. The
24 mA source/sink drive and short protected outputs are an excellent choice for industrial
LVTTL interfacing. All I/O pins use +3.3V signaling.
Warning! Damage may occur if the I/O pins are connected to +5V logic.
Interfaces and Connectors
Table 17: J25 I/O Connector Pinout
Note: Connector J6 pin 5 on the CBR-4004 is labeled "GND3/PBRST#" for
compatibility with other VersaLogic CPU boards. When connected to the Iguana,
this pin is GND3.
DIGITAL I/O PORT CONFIGURATION USING THE SPI INTERFACE
Digital I/O channels 0-15 are accessed via SPI slave select 6 (writing 6h to the SS field in
SPICONTROL). Each pair of I/O ports is configured by a set of paged I/O registers accessible
through SPI. These registers control settings such as signal direction, input polarity, and interrupt
source.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 42
Page 49

Interfaces and Connectors
Digital I/O Interrupt Generation Using the SPI Interface
Digital I/O can be configured to issue hardware interrupts on the transition (high to low or low to
high) of any digital I/O pin. IRQ assignment is made in SPI control register SPISTATUS. This
IRQ is shared among all SPI devices connected to the Iguana (the ADC and DAC devices on the
SPI interface do not have interrupts). Digital I/O chip interrupt configuration is achieved through
I/O port register settings. Please refer to the Microchip MCP23S17 datasheet for more
information.
The on-board digital I/O chips must be configured for open-drain and mirrored interrupts in order
for any SPI device to use hardware interrupts. The following code example illustrates how to do
this for device #0 on channels 0-15. Normally, the BIOS initializes the on-board digital I/O chips
at boot time.
MOV DX, CA8h
MOV AL, 26h ;SPICONTROL: SPI Mode 00, 24bit, auto SPI 6
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CA9h
MOV AL, 30h ;SPISTATUS: 8MHz, no IRQ, left-shift
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CABh
MOV AL, 44h ;SPIDATA1: Mirror & Open-Drain interrupts
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CACh
MOV AL, 0Ah ;SPIDATA2: MCP23S17 address 0x0A
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CADh
MOV AL, 40h ;SPIDATA3: MCP23S17 write command
OUT DX, AL
BUSY: MOV DX, CA9h
IN AL, DX ;Get SPI status
AND AL, 01h ;Isolate the BUSY bit
JNZ BUSY ;Loop back if SPI transaction is not complete
MOV DX, CA8h
MOV AL, 27h ;SPICONTROL: SPI Mode 00, 24bit, auto SPI 6
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CA9h
MOV AL, 30h ;SPISTATUS: 8MHz, no IRQ, left-shift
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CABh
MOV AL, 44h ;SPIDATA1: Mirror & Open-Drain interrupts
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CACh
MOV AL, 0Ah ;SPIDATA2: MCP23S17 address 0x0A
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CADh
MOV AL, 40h ;SPIDATA3: MCP23S17 write command
OUT DX, AL
Writing to a Digital I/O Port Using the SPI Interface
The following code example initiates a write of 55h to Digital I/O port bits DIO15-DIO8.
;Write 44h to configure MCP23S17 register IOCON
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 43
Page 50

Interfaces and Connectors
MOV DX, CA8h
MOV AL, 26h ;SPICONTROL: SPI Mode 00, 24bit, SPI 6
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CA9h
MOV AL, 30h ;SPISTATUS: 8MHz, no IRQ, left-shift
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CABh
MOV AL, 44h ;SPIDATA1: mirror and open-drain interrupts
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CACh
MOV AL, 0Ah ;SPIDATA2: MCP23S17 IOCON register address 0Ah
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CADh
MOV AL, 40h ;SPIDATA3: MCP23S17 write command
OUT DX, AL
CALL BUSY ;Poll busy flag to wait for SPI transaction
;Configure MCP23S17 register IODIRA for outputs
MOV DX, CABh
MOV AL, 00h ;SPIDATA1: 00h for outputs
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CACh
MOV AL, 00h ;SPIDATA2: MCP23S17 register address 00h
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CADh
MOV AL, 40h ;SPIDATA3: MCP23S17 write command
OUT DX, AL
CALL BUSY ;Poll busy flag to wait for SPI transaction
;Write 55h to MCP23S17 register GPIOA
MOV DX, CABh
MOV AL, 55h ;SPIDATA1: data to write
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CACh
MOV AL, 14h ;SPIDATA2: MCP23S17 register address 14h
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX, CADh
MOV AL, 40h ;SPIDATA3: MCP23S17 write command
OUT DX, AL
CALL BUSY ;Poll busy flag to wait for SPI transaction
BUSY: MOV DX, CA9h
IN AL, DX ;Get SPISTATUS
AND AL, 01h ;Isolate the BUSY flag
JNZ BUSY ;Loop if SPI transaction not complete
Reading a Digital I/O Port Using the SPI Interface
The following code example reads the DIO15-DIO8 input lines.
'REGISTER ASSIGNMENT
'--------------------CONST SPICONTROL1 = &HCA8
CONST SPICONTROL2 = &HCA9
CONST SPISTATUS = &HCA9
CONST SPIDATA1 = &HCAB
CONST SPIDATA2 = &HCAC
CONST SPIDATA3 = &HCAD
'INITIALIZE SPI CONTROLLER
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 44
Page 51

Interfaces and Connectors
'================================
'SPICONTROL1 Register
'--------------------------'D7 CPOL = 0 SPI Clock Polarity (SCLK idles low)
'D6 CPHA = 0 SPI Clock Phase (Data read on rising edge)
'D5 SPILEN1 = 1 SPI Frame Length (24-Bit)
'D4 SPILEN0 = 0 " " " "
'D3 MAN_SS = 0 SPI Slave Select Mode (Automatic)
'D2 SS2 = 1 SPI Slave Select (On-Board DIO 0-15)
'D1 SS1 = 1 " " " " "
'D0 SS0 = 0 " " " " "
OUT SPICONTROL1, &H26
'SPICONTROL2 Register
'--------------------------'D7 IRQSEL1 = 0 IRQ Select (IRQ3)
'D6 IRQSEL0 = 0 " " "
'D5 SPICLK1 = 1 SPI SCLK Frequency (8.333 MHz)
'D4 SPICLK0 = 1 " " " "
'D3 HW_IRQ_EN = 0 Hardware IRQ Enable (Disabled)
'D2 LSBIT_1ST = 0 SPI Shift Direction (Left Shifted)
'D1 0 = 0 This bit has no function
'D0 0 = 0 This bit has no function
OUT SPICONTROL2, &H30
'INITIALIZE MCP23S17
'===================
'MCP23S17 IOCON Register
'----------------------'D7 BANK = 0 Registers in same bank (addresses are sequential)
'D6 MIRROR = 1 The INT pins are internally connected
'D5 SEQOP = 0 Sequential op disabled. Addr ptr does not increment.
'D4 DISSLW = 0 Slew rate control for SDA output (enabled)
'D3 HAEN = 0 Hardware address enable (addr pins disabled)
'D2 ODR = 1 INT pin is open-drain
'D1 INTPOL = 0 Polarity of INT output pin (ignored when ODR=1)
'D0 0 = 0 This bit has no function
OUT SPIDATA1, &H44
'MCP23S17 IOCON Register Address
'------------------------------OUT SPIDATA2, &HA
'MCP23S17 SPI Control Byte (Write)
'--------------------------------'D7 SLAVEFA3 = 0 Slave Address (Fixed Portion)
'D6 SLAVEFA2 = 1 " " " "
'D5 SLAVEFA1 = 0 " " " "
'D4 SLAVEFA0 = 0 " " " "
'D3 SLAVEHA2 = 0 Slave Address Bits (Hardware Address Bits)
'D2 SLAVEHA1 = 0 " " " "
'D1 SLAVEHA0 = 0 " " " "
'D0 READWRITE = 0 Read/Write Bit = Write
OUT SPIDATA3, &H40
WHILE (INP(SPISTATUS) AND &H1) = &H1: WEND
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 45
Page 52

'INITIALIZE DIRECTION OF DIO LINES D15-D8 AS INPUTS
'==================================================
'Direction = All Inputs
OUT SPIDATA1, &HFF
'MCP23S17 IODIRA Register Address
OUT SPIDATA2, &H0
'MCP23S17 SPI Control Byte (Write)
OUT SPIDATA3, &H40
WHILE (INP(SPISTATUS) AND &H1) = &H1: WEND
'Repeat until ESC key is pressed
WHILE INKEY$ <> CHR$(27)
'READ DIO INPUT DATA FROM MCP23S17
'---------------------------------
'MCP23S17 GPIOA Register Address
OUT SPIDATA2, &H12
'MCP23S17 SPI Control Byte (Read)
OUT SPIDATA3, &H41
WHILE (INP(SPISTATUS) AND &H1) = &H1: WEND
'DIO Input Data
PRINT HEX$(INP(SPIDATA1))
WEND
SYSTEM
Interfaces and Connectors
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 46
Page 53

Analog Input
J25
Pin Signal
VL-CBR-4004
Connector
VL-CBR-4004
Pin (Label)
1
Analog Input 1
J1
5 (IO1)
2
Analog Input 2
Analog Input
4 (IO2)
3
Analog Input 3
3 (IO3)
4
Analog Input 4
2 (IO4)
5
Ground
1 (GND1)
6
Analog Input 5
J2
5 (IO5)
7
Analog Input 6
Analog Input
4 (IO6)
8
Analog Input 7
3 (IO7)
9
Analog Input 8
2 (IO8)
10
Ground
1 (GND1)
The Iguana uses a multi-range, 12-bit Linear Technology LTC1857 A/D converter with eight
single-ended input signals (even and odd analog channels, for example inputs 1 and 2, can also
be combined as differential inputs). The converter has a 100 kilo-samples-per-second (Ksps)
sampling rate, with a 4 µs acquisition time, with per-channel input ranges of 0 to +5V or 0 to
+10V unipolar, and ±5V or ±10V bipolar
The Iguana A/D converter is controlled using the SPI registers. The A/D converter is accessed
via SPI slave select 5 (writing 5h to the SS field in SPICONTROL).
See "SPI Registers" for a complete description of the registers.
See the Linear Technology LTC1857 A/D Converter Datasheet for programming information.
Warning! Application of analog voltages greater than +25V or less than -25V can damage
EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS
Interfaces and Connectors
the converter.
Single-ended analog voltages are applied to connectors J1 and J2 of the VL-CBR-4004 board
(connected to J25 of the Iguana) as shown in the following table.
Table 18: Analog Input Connector
ANALOG INPUT USING THE SPI INTERFACE
See "SPI Registers" for a description of the SPI interface and registers.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 47
Page 54

Interfaces and Connectors
Initiating an Analog Conversion Using the SPI Interface
The following procedure can be used to initiate an analog conversion using the SPI interface.
1. Write 15h to the SPICONTROL register (I/O address CA8h) – This value configures the
SPI port to select the on-board A/D converter, 16-bit frame length, low SCLK idle state,
rising edge SCLK edge, and automatic slave select.
2. Write 10h to the SPISTATUS register (I/O address CA9h) – This value selects 2 MHz
SCLK speed, hardware IRQ disable, and left-shift data. A 2 MHz clock is used to avoid
having to insert a delay after the SPI cycle to wait for the end of the 4 µs A/D signal
acquisition interval. If a 4 MHz SPI clock is used then there must be a delay of 1.5 µs
after the SPI cycle ends before starting an A/D conversion; if an 8 MHz SPI clock is
used then there must be a delay of 2.75 µs after the end of the SPI cycle.
3. Write any value to SPIDATA2 (I/O address CACh) – This data will be ignored by the
A/D converter.
4. Write bit 0 of the analog input channel number to bit 6, bits 2-1 of the analog input
channel number to bits 5-4, and a 2-bit input range code to bits 3-2 of SPIDATA3 (I/O
address CADh). Any write operation to this register triggers an SPI transaction. The 2-bit
input-range codes are 0 (±5V), 1 (±10V), 2 (0 to +5V) or 3 (0 to +10V). Set bit 7 if you
wish your conversion to be for a single-ended channel. For example, if converting the 4th
A/D channel (channel number 3) with a 0 to +5V range as a single channel then
SPIDATA3 is set to d8h.
5. Poll the SPI BUSY bit in the SPISTATUS register until the conversion is completed.
6. Write a ‘1’ to ADCONVST0 Bit 0 of the FPGA ADC, DAC control/status register (I/O
address CAFh) to start a conversion
7. Poll the the ADCBUSY0 Bit 2 of the FPGA ADC/DAC control/status register (I/O
address CAFh) until this bit is a ‘0’ (not busy) to indicate a conversion is completed (a
conversion takes a maximum of 5 µs).
8. Read the conversion data from SPIDATA3 (upper 8 bits of the 12-bit conversion) and
SPIDATA2 (lower 4 bits of the 12-bit conversion are in the upper 4 bits of this byte).
The data read is from the previous conversion not the one for the SPI values written in
Steps 1–5. Another conversion cycle is required to retrieve that data. Typically a number
of channels are sampled at one time so this conversion delay is not significant.
Anytime an SPI command is written to the A/D device a conversion must be issued for that
command. Another command will not be accepted until a conversion is performed.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 48
Page 55

Analog Output
J25
Pin Signal
VL-CBR-4004
Connector
VL-CBR-4004
Pin (Label)
11
Analog Output 1
J3
5 (IO9)
12
Analog Output 2
Analog Output
4 (IO10)
13
Analog Output 3
3 (IO11)
14
Analog Output 4
2 (IO12)
15
Ground
1 (GND2)
The Iguana uses a 12-bit Linear Technology LTC2634 D/A converter with four (4) single-ended
output signals. The converter has 5 µs per-channel update rate with a 0 to 4.096V output voltage
range.
The Iguana D/A converter is controlled using the SPI registers. The D/A converter is accessed
via SPI slave select 7 (writing 7h to the SS field in SPICONTROL). See "SPI Registers" for a
complete description of the registers.
See the Linear Technology LTC2634 D/A Converter Datasheet for programming information.
Interfaces and Connectors
Table 19: Analog Output Pinout
Analog Output Using the SPI Interface
The following procedure can be used to set an analog output using the SPI interface.
1. Write 27h to the SPICONTROL register (I/O address CA8h) – This value configures the
SPI port to select the D/A converter, 24-bit frame length, low SCLK idle state, rising
edge SCLK edge, and automatic slave select.
2. Write 30h to the SPISTATUS register (I/O address CA9h) – This value selects 8 MHz
SCLK speed, hardware IRQ disable, and left-shift data.
3. Write the LS 4-bits of the 12-bit output value into the MS 4-bits of SPIDATA1 (I/O
address CABh). For example, if writing a 12-bit value of 123h the value of 30h is written
to SPIDATA1.
4. Write the MS 8-bits of the 12-bit output value to SPIDATA2 (I/O address CACh). For
example, if writing a 12-bit value of 123h the value of 12h is written to SPIDATA2.
5. Write the analog output channel number (0 to 3) to Bits 3-0 and the write-and-update-
channel command 3h to Bits 7-4 of SPIDATA3 (I/O address CADh) – Any write
operation to this register triggers an SPI transaction. For example, if writing to the third
DAC channel (channel number 2) the value written to SPIDATA3 is 32h.
6. Poll the SPI BUSY bit in the SPISTATUS register until the conversion is completed.
7. The D/A output will be stable in no more than 5 µs.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 49
Page 56

Counter / Timers
J25
Pin
Signal
Direction*
Signal
Name
Function
VL-CBR-4004
Connector
VL-CBR-4004
Pin (Label)
36
Output
OCTC3
Timer 3 Counter Output
J9
1 (IO29)
37
Input
ICTC3
Timer 3 Clock Input
2 (IO30)
38
Output
OCTC4
Timer 4 Counter Output
3 (IO31)
39
Input
ICTC4
Timer 4 Clock Input
4 (IO32)
40 — GND
Ground
5 (GND4)
Register
Read/Write
Address
Name
IRQCTRL
R/W
CA3h
Interrupt Control Register
IRQSTAT
R-Status/Write-Clear
CA4h
Interrupt Status Register
TMCNTRL
R/W
CA5h
Timer Control Register
The Iguana includes two uncommitted 8254 type counter/timer channels for general program use.
External control signals for the two channels are available on connector J25.
* Relative to VL-EPIC-25
The Custom Programming appendix discusses how to use and configure these timers using the
following registers.
Interfaces and Connectors
Table 20: Counter Timer Pinout
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 50
Page 57

SPX
J27
Pin
Signal
Name
Function
1
V5_0
+5V (Protected)
2
SCLK
Serial Clock
3
GND
Ground
4
MISO
Serial Data In
5
GND
Ground
6
MOSI
Serial Data Out
7
GND
Ground
8
SS0#
Chip Select 0
9
SS1#
Chip Select 1
10
SS2#
Chip Select 2
11
SS3#
Chip Select 3
12
GND
Ground
13
SINT#
Interrupt Input
14
V5_0
+5V (Protected)
Interfaces and Connectors
Up to four serial peripheral expansion (SPX) devices can be attached to the Iguana at connector
J27 using the VL-CBR-1401 or VL-CBR-1402 cable. The SPX interface provides the standard
serial peripheral interface (SPI) signals: SCLK, MISO, and MOSI, as well as four chip selects,
SS0# to SS3#, and an interrupt input, SINT#.
The +5V power provided to pins 1 and 14 of J27 is protected by a 1 Amp resettable fuse.
Table 21: SPX Expansion Bus Pinout
SPI is, in its simplest form, a three wire serial bus. One signal is a Clock, driven only by the
permanent Master device on-board. The others are Data In and Data Out with respect to the
Master. The SPX implementation adds additional features, such as chip selects and an interrupt
input to the Master. The Master device initiates all SPI transactions. A slave device responds
when its Chip Select is asserted and it receives Clock pulses from the Master.
The SPI clock rate can be software configured to operate at speeds between 1 MHz and 8 MHz.
Please note that since this clock is divided from a 33 MHz PCI clock, the actual generated
frequencies are not discrete integer MHz frequencies. All four common SPI modes are supported
through the use of clock polarity and clock idle state controls.
This SPX interface is also used as a manufacturing test interface to output data from the internal
LPC bus (primarily for I/O Port 80 codes). When there is no SPX module installed, there will be
signal activity on this SPX connector (for example, the 33 MHz LPC clock will be on the SCLK
pin 2). This mode can be disabled by grounding pin 5 on J27, and the interface will function
normally as an SPX interface. It can also be permanently disabled by adding stuffing resistors on
the board.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 51
Page 58

Interfaces and Connectors
VERSALOGIC SPX EXPANSION MODULES
VersaLogic offers a number of SPX modules that provide a variety of standard functions, such as
analog input, digital I/O, CANbus controller, and others. These are small boards (1.2” x 3.78”)
that can mount on the PC/104 stack, using standard standoffs, or up to two feet away from the
baseboard. For more information, contact VersaLogic at info@VersaLogic.com.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 52
Page 59

Interfaces and Connectors
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
CPOL
CPHA
SPILEN1
SPILEN0
MAN_SS
SS2
SS1
SS0
Bit
Mnemonic
Description
D7
CPOL
SPI Clock Polarity – Sets the SCLK idle state.
0 = SCLK idles low
1 = SCLK idles high
D6
CPHA
SPI Clock Phase – Sets the SCLK edge on which valid data will be
read.
0 = Data read on rising edge
1 = Data read on falling edge
D5-D4
SPILEN
SPI Frame Length – Sets the SPI frame length. This selection works in
manual and auto slave select modes.
SPILEN1 SPILEN0 Frame Length
0 0 8-bit
0 1 16-bit
1 0 24-bit
1 1 32-bit
D3
MAN_SS
SPI Manual Slave Select Mode – This bit determines whether the
slave select lines are controlled through the user software or are
automatically controlled by a write operation to SPIDATA3 (CADh). If
MAN_SS = 0, then the slave select operates automatically; if MAN_SS
= 1, then the slave select line is controlled manually through
SPICONTROL bits SS2, SS1, and SS0.
0 = Automatic, default
1 = Manual
D2-D0
SS
SPI Slave Select – These bits select which slave select will be asserted. The
SSx# pin on the baseboard will be directly controlled by these bits when
MAN_SS = 1.
SS2 SS1 SS0 Slave Select
0 0 0 None, port disabled
0 0 1 SPX Slave Select 0, J27 pin-8
0 1 0 SPX Slave Select 1, J27 pin-9
0 1 1 SPX Slave Select 2, J27 pin-10
1 0 0 SPX Slave Select 3, J27 pin-11
1 0 1 A/D Converter (on-board)
1 1 0 Digital I/O (on-board)
1 1 1 D/A Converter (on-board)
SPI REGISTERS
A set of control and data registers are available for SPI transactions. The following tables
describe the SPI control registers (SPICONTROL and SPISTATUS) and data registers
(SPIDATA3-0).
SPICONTROL (READ/WRITE) CA8h
Table 22: SPI Control Register 1 Bit Assignments
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 53
Page 60

Interfaces and Connectors
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
IRQSEL1
IRQSEL0
SPICLK1
SPICLK0
HW_IRQ_EN
LSBIT_1ST
HW_INT
BUSY
Bit
Mnemonic
Description
D7-D6
IRQSEL
IRQ Select – These bits select which IRQ will be asserted when a
hardware interrupt from a connected SPI device occurs. The
HW_IRQ_EN bit must be set to enable SPI IRQ functionality.
IRQSEL1 IRQSEL0 IRQ
0 0 IRQ3
0 1 IRQ4
1 0 IRQ5
1 1 IRQ10
D5-D4
SPICLK
SPI SCLK Frequency – These bits set the SPI clock frequency.
SPICLK1 SPICLK0 Frequency
0 0 1.042 MHz
0 1 2.083 MHz
1 0 4.167 MHz
1 1 8.333 MHz
D3
HW_IRQ_E
N
Hardware IRQ Enable – Enables or disables the use of the selected
IRQ (IRQSEL) by an SPI device.
0 = SPI IRQ disabled, default
1 = SPI IRQ enabled
Note: The selected IRQ is shared with PC/104 ISA bus devices. CMOS
settings must be configured for the desired ISA IRQ.
D2
LSBIT_1ST
SPI Shift Direction – Controls the SPI shift direction of the SPIDATA
registers. The direction can be shifted toward the least significant bit or
the most significant bit.
0 = SPIDATA data is left-shifted (MSbit first), default
1 = SPIDATA data is right-shifted (LSbit first)
D1
HW_INT
SPI Device Interrupt State – This bit is a status flag that indicates
when the hardware SPX signal SINT# is asserted.
0 = Hardware interrupt on SINT# is deasserted
1 = Interrupt is present on SINT#
This bit is read-only and is cleared when the SPI device’s interrupt is
cleared.
D0
BUSY
SPI Busy Flag – This bit is a status flag that indicates when an SPI
transaction is underway.
0 = SPI bus idle
1 = SCLK is clocking data in and out of the SPIDATA registers
This bit is read-only.
SPISTATUS (READ/WRITE) CA9h
Table 23: SPI Control Register 2 Bit assignments
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 54
Page 61

Interfaces and Connectors
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
MSbit
LSbit
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
MSbit
LSbit
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
MSbit
LSbit
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
MSbit
LSbit
SPIDATA0 (READ/WRITE) CAAh
SPIDATA1 (READ/WRITE) CABh
SPIDATA2 (READ/WRITE) CACh
SPIDATA3 (READ/WRITE) CADh
SPIDATA3 contains the most significant byte (MSB) of the SPI data word. A write to this
register will initiate the SPI clock and, if the MAN_SS bit = 0, will also assert a slave select to
begin an SPI bus transaction. Increasing frame sizes from 8-bit uses the lowest address for the
least significant byte of the SPI data word; for example, the LSB of a 24-bit frame would be
SPIDATA1. Data is sent according to the LSBIT_1ST setting. When LSBIT_1ST = 0, the MSbit
of SPIDATA3 is sent first, and received data will be shifted into the LSbit of the selected frame
size set in the SPILEN field. When LSBIT_1ST = 1, the LSbit of the selected frame size is sent
first, and the received data will be shifted into the MSbit of SPIDATA3.
Data returning from the SPI target will normally have its most significant data in the SPIDATA3
register. An exception will occur when LSBIT_1ST = 1 to indicate a right-shift transaction. In
this case the most significant byte of an 8-bit transaction will be located in SPIDATA0, a 16-bit
transaction’s most significant byte will be located in SPIDATA1, and a 24-bit transaction’s most
significant byte will be located in SPIDATA2.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 55
Page 62

Start
Address
End
Address
Comment
F0000h
FFFFFh
System BIOS Area
E0000h
EFFFFh
Extended System BIOS Area
D0000h
DFFFFh
ISA Expansion Area
C0000h
CFFFFh
Video BIOS Area
A0000h
BFFFFh
Legacy Video Area
00000h
9FFFFh
Legacy System (DOS) Area
I/O Device
Standard
I/O Addresses
Reserved
CB4h-CBFh
PLD Internal 8254 Timers
CB0h-CB3h
ADC/DAC Control/Status Register
CAFh
mSATA/PCIe Mux Control Register
CAEh
SPI Data Register 3
CADh
SPI Data Register 2
CACh
SPI Data Register 1
CABh
SPI Data Register 0
CAAh
SPI Status Register
CA9h
SPI Control Register
CA8h
Reserved
CA6h-CA7h
Timer Control Register
CA5h
Interrupt Status Register
CA4h
Interrupt Control Register
CA3h
BIOS and Jumper Status Register
CA2h
Revision Indicator Register
CA1h
PLED and Product ID Register
CA0h
Reserved
C80h-C9Fh
Super I/O Runtime Registers
C00h-C80h
COM1 Serial Port Default
3F8h– 3FFh
COM2 Serial Port Default
2F8h– 2FFh
Primary IDE Controller for Compact Flash
1F0h– 1F7h
6 6
System Resources and Maps
Legacy Memory Map
The lower 1 MB memory map of the Iguana is arranged as shown in the following table. Various
blocks of memory space between A0000h and FFFFFh are shadowed.
Table 24: Memory Map
I/O Map
The following table lists the common I/O devices in the Iguana I/O map. User I/O devices should
be added using care to avoid the devices already in the map as shown below.
Table 25: On-Board I/O Devices
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 56
Page 63

D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
PLED
PC6
PC5
PC4
PC3
PC2
PC1
PC0
Bit
Mnemonic
Description
D7
PLED
Light Emitting Diode — Controls the programmable LED on connector J7.
0 = Turns LED off
1 = Turns LED on
D6-D0
PC
Product Code — These bits are hard-coded to represent the product type. The
Iguana always reads as 0000011. Other codes are reserved for future products.
PC6 PC5 PC4 PC3 PC2 PC1 PC0 Product Code
0 0 0 1 0 1 1 VL-EPIC-25
These bits are read-only.
7 7
Special Registers
PLED and Product Code Register
PLEDPC (Read/Write) CA0h
Table 26: PLED and Product Code Register Bit Assignments
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 57
Page 64

PLD Revision and Type Register
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
PLD4
PLD3
PLD2
PLD1
PLD0
TEMP
CUSTOM
BETA
Bit
Mnemonic
Description
D7-D3
PLD
PLD Code Revision Level — These bits are hard-coded and represent the PLD
code revision.
PLD4 PLD3 PLD2 PLD1 PLD0 Revision
0 0 0 0 0 Rev. 0.10B
0 0 0 0 1 Rev. 0.10B
0 0 0 1 0 Rev. 0.20A
0 0 0 1 1 Rev. 1.00A
0 0 1 0 0 Rev. 1.01A
These bits are read-only. Note: For beta boards, the Revision Level is set to 1.00A,
but the Production Level is set to Beta.
D2
Reserved
This bit is reserved.
D1
CUSTOM
PLD Class — This bit indicates whether the PLD code is standard or customized.
0 = Standard PLD code
1 = Custom PLD code
This bit is read-only.
D0
BETA
Production Level — This bit indicates if the PLD code is at the beta or production
level.
0 = Production level PLD
1 = Beta level PLD
This bit is read-only.
REVTYP (Read Only) CA1h
This register is used to indicate the revision level of the Iguana.
Table 27: Revision and Type Register Bit Assignments
Interfaces and Connectors
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 58
Page 65

BIOS and Jumper Status Register
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
BIOS_JMP
BIOS_OR
BIOS_SEL
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
GPI_JMP
Bit
Mnemonic
Description
D7
BIOS_JMP
System BIOS Selector Jumper Status — Indicates the status of the system
BIOS selector jumper at V5[1 -2].
0 = Jumper installed – backup system BIOS selected
1 = No jumper installed – primary system BIOS selected
This bit is read-only.
D6
BIOS_OR
BIOS Jumper Override — Overrides the system BIOS selector jumper and
selects the BIOS with BIOS_SEL.
0 = No BIOS override
1 = BIOS override
D5
BIOS_SEL
BIOS Select — Selects the system BIOS when BIOS_OR is set.
0 = Backup BIOS selected
1 = Primary BIOS selected
D4-D2
Reserved
These bits are reserved. Only write 0 to these bits and ignore all read values.
D1
GPI_JMP
General Purpose Jumper Status – Indicates the status of the general purpose
jumper at V5[3-4].
D0
Reserved
This bit is reserved. Only write 0 to this bit and ignore all read values.
BIOSJSR (Read/Write) CA2h
Table 28: Special Control Register Bit Assignments
Special Registers
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 59
Page 66

CPU
Intel Atom D425/D525 Dual Core
Intel Atom Datasheet Vol. 1 and
Vol. 2
Chipset
Intel ICH8
Intel ICH8 Datasheet
Super I/O Chip
SMSC SCH3114
SCH3114 Datasheet
Ethernet Controller
Intel 82574IT Ethernet Controller
Intel 8257IT Datasheet
PC/104 Interface
PC/104 Specification
PC/104-Plus Interface
PC/104-Plus Specification
A
Appendix A – References
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 60
Page 67

D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
IRQEN
IRQSEL2
IRQSEL1
IRQSEL0
reserved
IMSK_TC5
IMSK_TC4
IMSK_TC3
Bit
Mnemonic
Description
D7
IRQEN
IRQ Enable — Enables or disables an interrupt.
0 = Disable interrupt
1 = Enable interrupt
D6-D5
IRQSEL(2:0)
Specifies the interrupt mapping (this setting is ignored when IRQEN = 0 …
interrupts are disabled):
"000" IRQ3 (default)
"001" IRQ4
"010" IRQ5
"011" IRQ10
"100" IRQ6
"101" IRQ7
"110" IRQ9
"111" IRQ11
D4
Reserved
These bits are reserved. Only write 0 to these bits and ignore all read values.
D2
IMASK_TC5
Mask for the 8254 Timer #5 output (terminal count) Interrupt.
0 = Disable interrupt
1 = Enable interrupt
D1
IMASK_TC4
Mask for the 8254 Timer #4 output (terminal count) Interrupt.
0 = Disable interrupt
1 = Enable interrupt
D0
IMASK_TC3
Mask for the 8254 Timer #3 output (terminal count) Interrupt.
0 = Disable interrupt
1 = Enable interrupt
B B
Appendix B – Custom Programming
PLD Interrupts
The PLD can generate interrupts for the internal 8254 timers and the external SPI interrupt
(which includes the DIO device interrupt). The SPI interrupt settings are discussed in the section
on “SPX Expansion Bus.” This section covers the interrupt settings for the 8254 timers.
INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER
This register enables interrupts.
IRQCTRL (Read/Write) CA3h
Table 29: Interrupt Control Register Bit Assignments
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 61
Note: IRQ3, IRQ4, IRQ5, IRQ10 are also defined for the SPX interface interrupts. If one of these interrupts
is selected for the SPX interface and also enabled here for the timer interrupts, then the interrupt sources
are combined (i.e., logically OR’d).
Page 68

INTERRUPT STATUS REGISTER
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
ISTAT_TC5
ISTAT_TC4
ISTAT_TC3
Bit
Mnemonic
Description
D7-D3
Reserved
These bits are reserved. Only write 0 to these bits and ignore all read values.
D2
ISTAT _TC5
Status for the 8254 Timer #5 output (terminal count) Interrupt when read.
0 = Timer output (terminal count) has not transitioned from 0 to a 1 level
1 = Timer output (terminal count) has transitioned from a 0 to a 1 level
This bit is read-status and a write-1-to-clear.
D1
ISTAT _TC4
Status for the 8254 Timer #4 output (terminal count) Interrupt when read.
0 = Timer output (terminal count) has not transitioned from 0 to a 1 level
1 = Timer output (terminal count) has transitioned from a 0 to a 1 level
This bit is read-status and a write-1-to-clear.
D0
ISTAT _TC3
Status for the 8254 Timer #3 output (terminal count) Interrupt when read.
0 = Timer output (terminal count) has not transitioned from 0 to a 1 level
1 = Timer output (terminal count) has transitioned from a 0 to a 1 level
This bit is read-status and a write-1-to-clear.
This register is used for reading the status of interrupts generated by the PLD.
IRQSTAT (Read-Status/Write-Clear) CA4h
Table 30: Interrupt Status Register Bit Assignments
Special Registers
The interrupt status register is valid whether the interrupt mask is set or not for the interrupt (that
is, it can be used for polled status). An interrupt status is acknowledged (cleared to a 0) by
writing a ‘1’ to the status bit.
The PLD implements an 8254 timer (consisting of three individual timers). The outputs of these
timers can generate interrupts when they transition from a 0 level to a 1 level (edge sensitive).
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 62
Page 69

8254 Timer Control Register
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
TIM5GATE
TIM4GATE
TIM3GATE
TM4MODE
TM4SEL
TM3SEL
Reserved
Reserved
Bit
Mnemonic
Description
D7
TIM5GATE
Sets the level on the Gate input for the 8254 Timer #5.
0 = GCTC5 Gate is disabled (set to a logic 0)
1 = GCTC5 Gate is enabled (set to a logic 1)
D6
TIM4GATE
Sets the level on the Gate input for the 8254 Timer #4.
0 = GCTC4 Gate is disabled (set to a logic 0)
1 = GCTC4 Gate is enabled (set to a logic 1)
D5
TIM3GATE
Sets the level on the Gate input for the 8254 Timer #3.
0 = GCTC3 Gate is disabled (set to a logic 0)
1 = GCTC3 Gate is enabled (set to a logic 1)
D4
TM4MODE
Configure how the 8254 Timer #4 and #5 are used.
0 – Timer #4 is cascaded with Timer #5 for a 32-bit timer
1 – Timer #4 operates in normal 16-bit mode
D3
TM4SEL
Configure the clock source for 8254 Timer #4.
0 – Timer #4 input clock is 4.167 MHz internal clock (PCI clock divided by 8)
1 – Timer #4 input clock is from User I/O connector Input ICTC4
D2
TM3SEL
Configure the clock source for 8254 Timer #3.
0 – Timer #3 input clock is 4.167 MHz internal clock (PCI clock divided by 8)
1 – Timer #3 input clock is from User I/O connector Input ICTC3
D1-D0
Reserved
These bits are reserved. Only write 0 to these bits and ignore all read values.
This register is used to set modes related to the inputs on the 8254 Timers.
TIMCNTRL (Read/Write) CA5h
Table 31: 8254 Timer Control Register Bit Assignments
Special Registers
An 8254 timer is implemented in the PLD (see Table 25: On-Board I/O Devices for I/O
addresses). It contains three independent 16-bit timers. It is fully software compatible with the
Intel 8254, except that only binary counting modes are implemented (the BCD control bit is
implemented but ignored). See the Intel 82C54 Programmable Interval Timer Datasheet for
register definitions and programming information.
There is an option to cascade two of the timers together in a 32-bit mode. The timers are
identified as Timer 3, 4, and 5. When Timers 4 and 5 are cascaded, Timer 4 is the LS 16-bits and
Timer 5 is the MS 16-bits. In this 32-bit cascade mode the timer output of Timer 4 feeds the
clock input of Timer 5. In this mode Timer 4 would normally be set so that it generates a clock
after counting the full 16-bit range, but there is no requirement to do this.
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 63
Page 70

The 32-bit cascade mode is set in TM4MODE in the Timer Control Register. There are also
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
DACLDA0
Reserved
ADCBUSY0
Reserved
ADCONVST0
Bit
Mnemonic
Description
D7-D6
Reserved
These bits are reserved. Only write 0 to these bits and ignore all read values.
D5
Reserved
This bit is reserved. Only write 0 to this bit and ignore read values.
D4
DACLDA0
This is a write-only (pulsed) bit. When a ‘1’ is written it will strobe the LDAC signal
on the LTC2634 D/A Converter. Writing a ‘0’ is ignored.
D3
Reserved
This bit is reserved. Only write 0 to this bit and ignore read values.
D2
ADCBUSY0
This read-only status bit returns the A/D conversion status.
0 – A/D is not busy doing a conversion.
1 – A/D is busy doing a conversion.
D1
Reserved
This bit is reserved. Only write 0 to this bit and ignore read values.
D0
ADCONVST0
This is a write-only (pulsed) bit. When a ‘1’ is written it will start a conversion on
the LTC1857 A/D converter. Writing a ‘0’ is ignored.
internal or external clock selections for the timers in this register using the external clocks ICTC3
and ICTC4 signals on the connector at J25. The internal clock is the PCI clock divided by 8
(33.33 MHz / 8 = 4.167 MHz). ICTC3 can only be used with Timer 3. ICTC4 can only be used
with Timer 4. The clock for Timer 5 is always the internal clock except in the 32-bit cascade
mode when the output from Timer 4 is the clock for Timer 5.
The timer outputs can generate interrupts. When a timer output transitions from a 0 to a 1 then an
interrupt status bit is set and can generate an interrupt. This bit sticks until cleared.
By default there are two external timer input clocks (ICTC3, ICTC4) and two timer outputs
(OCTC3, OCTC4) on connector J25. To use all three of the 16-bit timers, timers 4 and 5 are
configured in 32-bit mode by default. Custom options are available that can expand the external
controls to allow for three clock inputs and four, timer outputs as well as three timer gate inputs
for all three 16-bit timers by using some of the digital I/O signal pins on J25.
A/D and D/A Control/Status Register
This register is used to control A/D and D/A conversion.
Special Registers
ADCONSTAT (Read/Write) CAFh
Table 32: A/D, D/A Control/Status Register Bit Assignments
VL-EPIC-25 Reference Manual 64
 Loading...
Loading...