
Nextiva S1100w User
Guide
Firmware Release 4.12
October 2007


Nextiva S1100w
Firmware Release 4.12
User Guide
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions Revision: B

This document contains confidential and proprietary information of Verint Systems Inc. and
is protected by copyright laws and related international treaties. Unauthorized use,
duplication, disclosure or modification of this document in whole or in part without the
written consent of Verint Systems Inc. is strictly prohibited.
By providing this document, Verint Systems Inc. is not making any representations
regarding the correctness or completeness of its contents and reserves the right to alter
this document at any time without notice.
All marks referenced herein with the ® or TM symbol are registered trademarks or
trademarks of Verint Systems Inc. or its subsidiaries. All rights reserved. All other marks
are trademarks of their respective owners.
© 2007 Verint Systems Inc. All rights reserved.
www.verint.com/videosolutions
Publication date: October 10, 2007
Nextiva S1100w User Guide
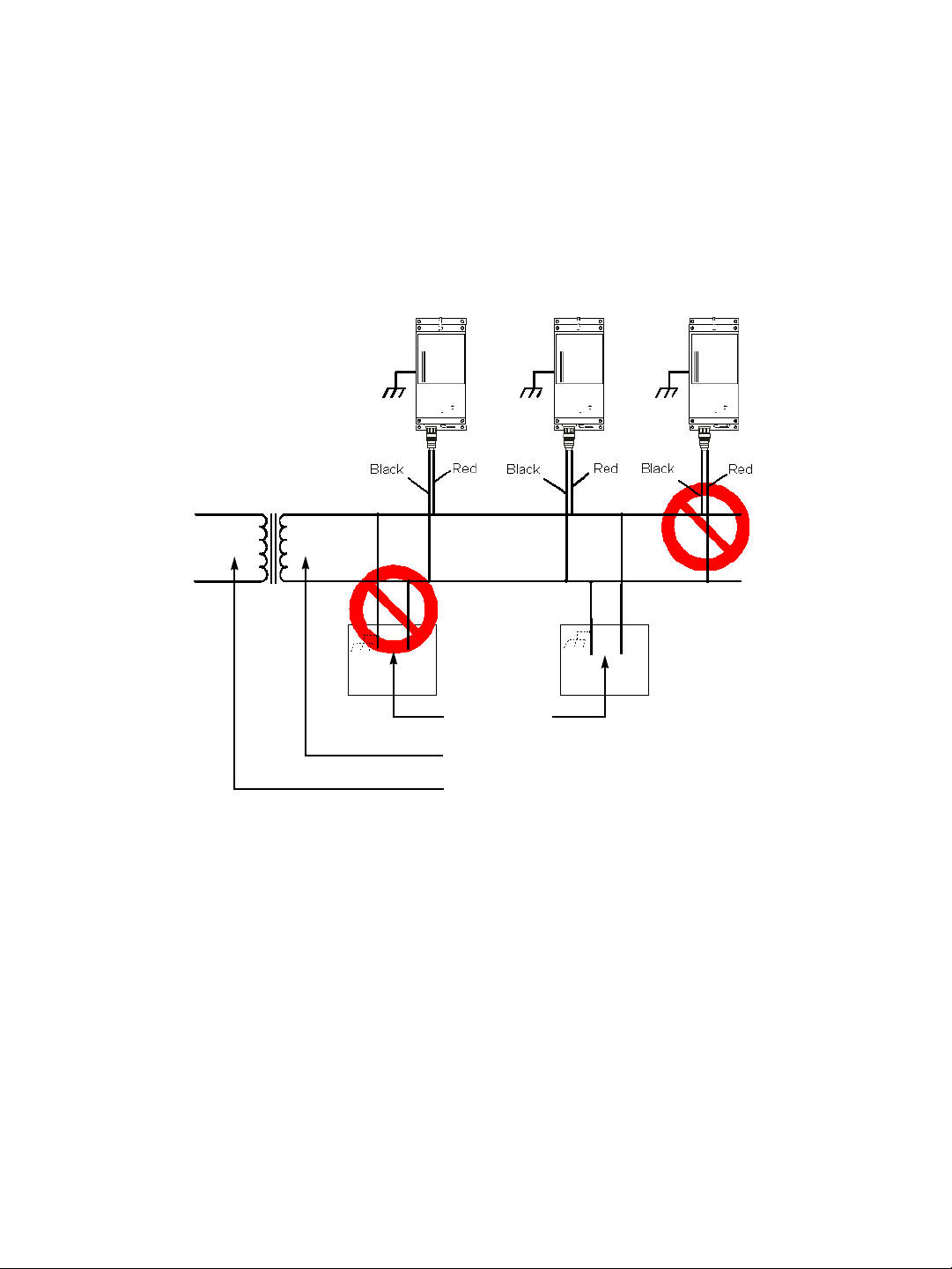
Warning: If you connect multiple devices on the same 24V AC power supply, always wire
them the same way: The red power wires of all devices must be on the same
power supply terminal. Since the black power wire of the device is internally
connected to its chassis (earth), swapping the power connection scheme from
device to device will short out the AC power supply.
Warning: You can install third-party equipment with an earth-referenced power input on
the same power source as the devices. To do so, you must connect the
earth-referenced terminal of the equipment to the same AC terminal as the black
wire of the devices. Failing to do so will short out the AC power supply.
Third-party
equipment
Isolated 24V AC
AC main
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions iii

iv Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Contents
Preface .............................................................................................................. vii
Who Should Read this Guide ............................................................................viii
How to Use this Guide .....................................................................................viii
Conventions .............................................................................................viii
Related Documentation ..............................................................................viii
Related Products ............................................................................................. ix
About Us ........................................................................................................ ix
Warranty .........................................................................................................x
Chapter 1
About the S1100w ............................................................................................ 2
Shipment ........................................................................................................3
Casing Description ......................... .. ........................... ......................................4
Chapter 2
Frequency Bands and Channels ..........................................................................6
Wireless Cells ....................................... .. ... .................................................... ..8
802.11 Support ..................................................................... .. .........................8
System Planning ..............................................................................................9
Colocated Cells .............................................................................................. 13
RF Planning ...................................................................................................18
Chapter 3
Cable for Power, Video, and Serial Data .............................................................22
Configuring the Wireless System ...................................................................... 23
Installing the Wireless System ......................................................................... 26
Overview ..........................................................................................1
Security .....................................................................................................2
Video ........................................................................................................2
System and RF Planning ...................................................................5
2.4 GHz Band .............................................................................................6
4.9 GHz Band .............................................................................................6
5 GHz Band ................................................................................................7
Point-to-Multipoint Application ....................................................................10
Compatibility Issues ..................................................................................10
Video Bit Rate and Data Throughput ............................................................11
TPC .........................................................................................................12
DFS ........................................................................................................13
Distance Limitations ....................................................... .. .........................13
4.9 GHz Band in North America ................................................................... 14
5 GHz Band in North America and 2.4 GHz ................................................... 15
5 GHz Band in Europe ................................................................................16
Location Evaluation ................................................................................... 18
Antenna Requirements ..............................................................................19
Interference ............................................................................................. 20
RF Exposure Considerations .......................................................................20
Configuring and Installing the Device ............................................. 21
Computer Requirements ............................................................................ 23
Setting Parameters ...................................................................................23
Point-to-Point Connection ...........................................................................24
Installing the Transmitter ........................................................................... 26
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions v

Contents
Installing an Antenna .................................................................................27
Performing the RS-422/485 Serial Connection ...............................................27
Configuring the I/Os ........................................................................................29
Audio .......................................................................................................29
Alarms ..................................................................................................... 30
Updating the Firmware ....................................................................................31
Performing a Hardware Reset ...........................................................................31
Red/Blue Display ............................................................................................32
Quality of Service ...........................................................................................32
Status LED .....................................................................................................32
Chapter 4
Setting Parameters with the CLI .....................................................35
Getting Started ..............................................................................................36
Serial Port .............................. .. .....................................................................37
Access Management ............................................................................ .. .. .. ......39
User Accounts .................................................................... .. .. .. .................39
Security ...................................................................................................39
Network ........................................................................................................40
Wireless Communication .................................. ........................... .. .. .................41
Basic Parameters .................................... .. ........................... .. .. .................42
Advanced Parameters ................................................................................46
System Status ................................................................................................47
Advanced ......................................................................................................48
Identifying a Device ...................................................................................48
Setting the VSIP Port ......................................... .. ............................ .. .. .. ....48
Conducting Site Surveys .............................. .. ........................... ... .. .. ..........49
Load Default Configuration ........................... .. ........................... .. .. ...................49
Reboot System ...............................................................................................50
Appendix A
Appendix B
Factory Default Configuration........................................................51
Cable Connections .........................................................................53
CAB9P ...........................................................................................................54
CAB8P ...........................................................................................................55
Appendix C
Appendix D
Appendix E
Appendix F
DHCP Support and APIPA...............................................................57
DTE and DCE Connections..............................................................59
Surge Protection............................................................................63
Separation Between Devices Using Adjacent Channels ..................65
Performing a Site Survey .................................................................................66
Minimum Distances .........................................................................................69
Appendix G DFS and False Radar Detection ......................................................73
Appendix H
S1100w Technical Specifications...................................................75
Glossary ............................................................................................................. 77
Index .................................................................................................................83
Compliance ........................................................................................................89
vi Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Preface
The Nextiva S1100w User Guide presents the information and procedures for installing,
configuring, and using the Nextiva
TM
S1100w wireless video transmitters.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions vii

Preface
Who Should Read this Guide
This guide is intended for managers, IT system administrators, engineers, and technicians
who will use the S1100w edge devices. It provides conceptual information on how to
configure, install, and operate the devices.
This guide assumes that you are familiar with:
Installation and manipulation of electronic equipment
General use of computers
Local area networks (LANs) and basic IP data communication concepts and practices
Radio frequency (RF) platforms
801.11 networks if the 802.11 MAC mode is used
Pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) platforms (cameras and keyboards)
Microsoft Windows operating systems
How to Use this Guide
This guide contains all the information needed to install, configure, and use an S1100w
device.
Conventions
The following typographic conventions are used throughout this guide:
Visual cue Meaning
Connect The name of an interface element you have to act on. A key to press. The
value of an interface element.
connection_name Text that must be replaced by a user-supplied value. Text representing
SConfigurator.exe
variable content.
The name of a command, file, or directory. Text th at appears on the screen.
Examples of user-supplied values.
Related Documentation
In addition to this guide, the following documentation is also available:
Nextiva S1100w Installation Guide
SConfigurator User Guide
Release Notes
All these documents are contained on the Utilities CD shipped with the device.
Furthermore, a paper copy of the installation guide is included with your order.
viii Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Related Products
Nextiva S1100w User Guide
You use the S1100w devices with the Nextiva S3100 multipurpose outdoor access point.
You may also use them with the nDVR
solutions. For more details about any of these products, visit our web site. For pricing
information, call your dealer.
TM
and Nextiva enterprise management and storage
About Us
Verint® Systems Inc. (NASDAQ: VRNT) is a leading global provider of analytic
software-based solutions for security and business intelligence. Verint solutions help
organizations make sense of the vast voice, video , and data available to them, tr ansforming
this information into actionable intelligence for better decisions and highly effective
performance.
Since 1994, Verint has been committed to developing innovative solutions that help global
organizations achieve their most important objectives. Today, organizations in over
50 countries use Verint solutions to enhance security, boost operational efficiency, and fuel
profitability.
Web Site
For information about the Nextiva line of products, visit www.verint.com/videosolutions.
To request the latest versions of firmware and software or to download other
product-related documents, you need access to the Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
partner extranet. To register, go to http://vvs.verint.com
.
Support
If you encounter any type of problem after reading this guide, contact your local distributor
or Verint representative. You can also use the following sections on the partner extranet to
find the answers to your questions:
Knowledge Base
FAQ
My Account
For assistance with the Nextiva edge devices and the related software, contact the
customer service team:
By phone: 1 888 747-6246 or 631 962-9202
By email: vvssupport@verint.com
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions ix

Preface
Warranty
Each product manufactured by Verint Systems is warranted to meet all published
specifications and to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of
two (2) years from date of delivery as evidenced by the Verint Systems packing slip or
other transportation receipt. Products showing damage by misuse or abnormal conditions of
operation, or which have been modified by Buyer or repaired or altered outside Verint
Systems factory without a specific authorization from Verint Systems shall be excluded
from this warranty. Verint Systems shall in no event be responsible for incidental or
consequential damages including without limitation, personal injury or property damage.
The warranty becomes void if the product is altered in any way.
Verint Systems responsibility under this warr anty shall be to repair or replace, at its option,
defective work or returned parts with transportation charges to V erint Systems factory paid
by Buyer and return paid by Ve rint Sy stems. If Verint Systems determines that the Product
is not defective within the terms of the warranty, Buyer shall pay all handling and
transportation costs. Verint Systems may, at its option, elect to correct any warranty
defects by sending its supervisory or technical representative, at its expense, to customer’s
plant or location.
Since Verint Systems has no control ov er conditions of use, no warr anty is made or implied
as to suitability for customer’s intended use. There are no warranties, expressed or implied,
except as stated herein. This limitation on warranties shall not be modified by verbal
representations.
Equipment shipped ex works Verint Systems factory shall become the property of Buyer,
upon transfer to the common carrier. Buyer shall communicate directly with the carrier by
immediately requesting carrier’s inspection upon evidence of damage in shipment.
Buyer must obtain a return materials authorization (RMA) number and shipping instructions
from Verint Systems prior to returning any product under warranty. Do not return any
Verint Systems product to the factory until RMA and shipping instructions are received.
x Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Overview
The S1100w allows digital video transmission over license-free and licensed bands. It
delivers high-quality MPEG-4-based video at 30 frames per second in NTSC (25 in PAL) over
local and wide area networks (LANs and WANs). This wireless edge device is built on open
standards to provide long-term investment protection.
Combined with a Nextiva S3100 multipurpose outdoor wireless device or a commercial
802.11 access point, the S1100w enables analog CCTV extension over the enterprise’s
network at a cost lower than that of laying new cables. The S1100w also allows the
migration of analog CCTV cameras to an IP network.
Note: The S1100w edge devices require professional installation.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 1

1: Overview
About the S1100w
The S1100w devices come as transmitters only. You can buy 12V DC or 24V AC devices.
The S1100w covers the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands in North America and Europe.
It also covers the 4.9 GHz public safety band in North America.
Unless otherwise specified, the word S1100w refers to any of these devices.
Each device is configured to operate, right out of the box, with the most popular camera
data port configuration (4800 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit).
Security
Every S1100w device comes with the following security features:
SSL —Every edge device is shipped with a unique SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate
for securing its IP link. SSL is a commonly used protocol for managing the security of IP
message transmission. Therefore, the connections with another device or the
SConfigurator tool can be secured.
If enabled, the SSL protocol secures the VSIP communication data. It does not apply to
audio and video transmission.
Once a device is in secure mode, you cannot access it anymore with Telnet and you
cannot perform firmware updates through the IP network on it. However, you can
configure it with SConfigurator.
For more information about this security feature, refer to the SConfigurator User
Guide.
SPCF (SmartSight Point Coordination Function)—This proprietary MAC (Media Access
Control) protocol using AES encryption (with key rotation) over the wireless link to
secure communication between the devices and resolve “hidden node,” quality of
service, range, and problems inherent to 802.11 wireless networking products. SPCF
secures VSIP communication as well as the audio and video data.
Video
The S1100w has one video input with two encoders.
The video frame rate of the edge device can be:
NTSC—1 to 7, 10, 15, or 30 frames per second (fps)
PAL—1 to 6, 8, 12, or 25 fps
2 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
The S1100w devices can have the following video resolutions and maximum frame rates (in
frames per second), using the NTSC (PAL) format:
Resolution Number of columns Number of lines Maximum frame rate
NTSC/PAL NTSC PAL NTSC PAL
QCIF 176 128 144 30 25
CIF 352 240 288 30 25
2CIF 352 384 448 30 25
2CIFH 704 240 288 30 25
4CIF 704 480 576 15 12
All lines 352 480 576 30 25
2/3 D1 480 480 576 15/30 * 12/25 *
VGA 640 480 576 15/30 * 12/25 *
* Without noise, I/Os, and other factors affecting quality, the device can achieve the
highest frame rate.
For more information about these video parameters, refer to the SConfigurator User
Guide.
Shipment
Your S1100w shipment contains the following items:
The requested transmitter, which comes with an integrated patch antenna (with a gain
of 8.5 dBi in the 2.4 GHz band or 13 dBi in the 4.9 and 5 GHz bands)
A wall mount bracket set, already installed on the device
A pole mount bracket set, including stainless steel clamps
A cable assembly for video, power, and serial port (CAB9P)
The Utilities CD containing the release notes and documentation for the device as well
as the SConfigurator application
The Nextiva S1100w Ins t a l l a t i o n G u id e
The shipment may also contain the following options:
A high-gain antenna
Warning: When choosing an antenna, you must ensure that the combined transmission
power of the device and antenna does not exceed the maximum value
established by your country’s regulations. For more information, see
page 19.
A junction box (JBOX)
An alarm/audio cable assembly (CAB8P)
A power supply
Note: If you are using a power supply other than those supplied by Verint, you need to
ensure that they have a minimum capacity of 1A (for 12V DC) or 30 VA (for
24V AC).
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 3
1: Overview
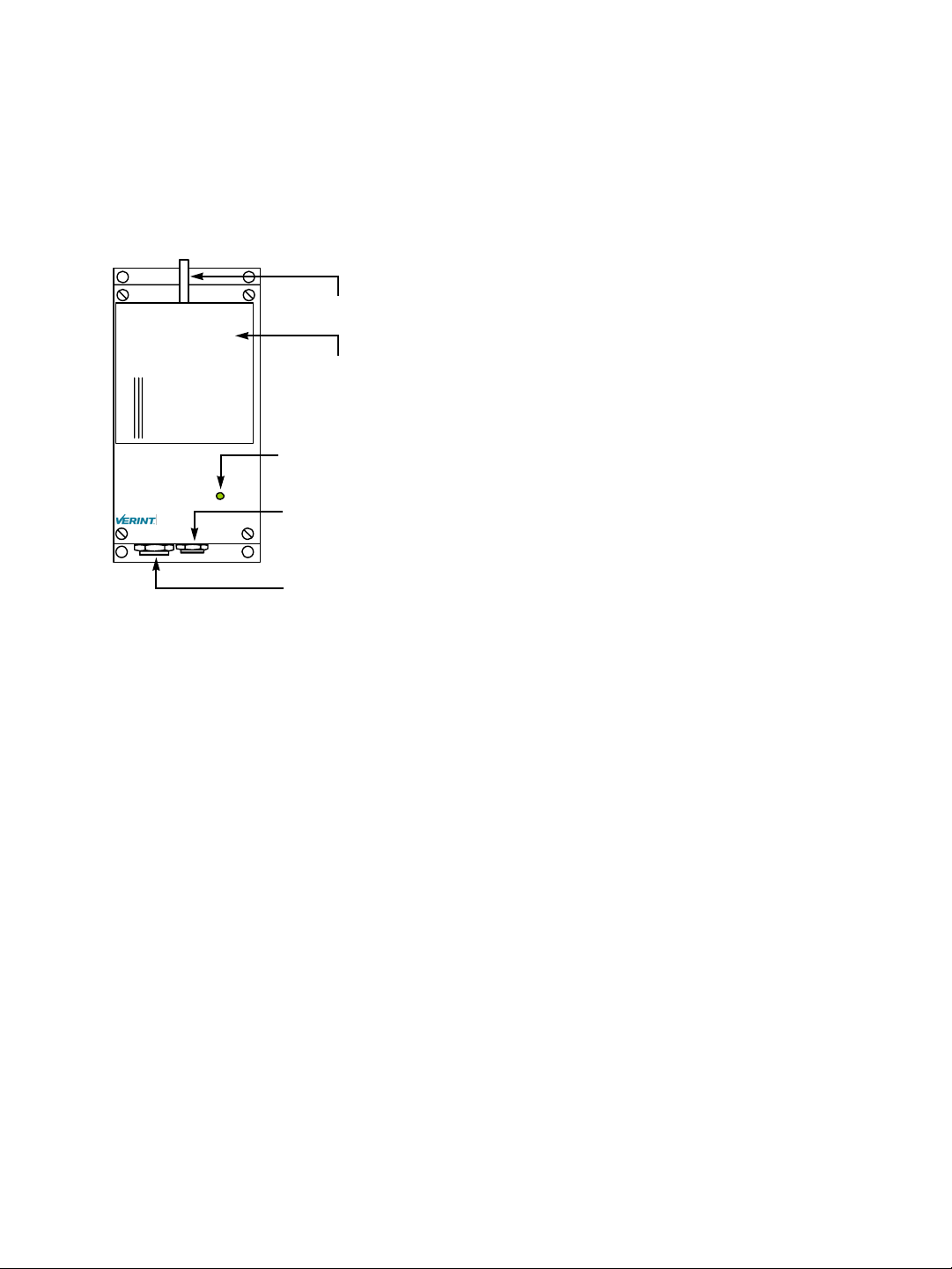
Casing Description
The S1100w electronics are enclosed in a weather-tight cast aluminum module. All cable
entries are mounted on the underside of the module to maintain its weatherproof
properties. The front panel integrates one bicolor visual indicator that illustrates the
operational state of the device.
Antenna port
Integrated antenna
Status indicator
Status
Auxiliary connector (alarm, audio)
Main connector (video, power, serial port)
4 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

System and RF Planning
To allow optimal configuration, you must properly plan your network, especially RF (radio
frequency) and configuration layout.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 5
2: System and RF Planning
Frequency Bands and Channels
The S1100w supports communications in the following frequency bands, in North America
and Europe:
2.4 GHz OFDM, also known as 802.11g
4.9 GHz OFDM, a public safety band available in North America only
5 GHz OFDM, also known as 802.11a
2.4 GHz Band
The 2.4 GHz band provides 11 channels in North America and 13 in Europe. In these two
regions, only channels 1, 6, and 11 are independent (that is, non-overlapping). All these
channels are for indoor or outdoor use. The center frequencies of the channels are:
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Frequency (GHz)
1 2.412 8 2.447
2 2.417 9 2.452
3 2.422 10 2.457
4 2.427 11 2.462
5 2.432 12 2.467 (Europe only)
6 2.437 13 2.472 (Europe only)
7 2.442
4.9 GHz Band
The 4.9 GHz band is a licensed band for entities providing public safety services focused on
the protection of life, health, or property in North America. This band provides license
holders with an interference-free, secure channel for robust and secure broadband
technologies, including wireless video surveillance systems.
For more detailed information concerning the regulations governing licensing and use of
frequencies in the 4.9 GHz band, see Subpart Y of the FCC document, Memorandum
Opinion and Order and Third Report and Order at:
http://hraunfoss.fcc.gov/edocs_public/attachmatch/FCC-03-99A1.pdf
The 4.9 GHz band has a width of 50 MHz (4940 to 4990 MHz). Since the standard channel
width is 20 MHz, only two independent channels can co-exist in the band. However, the
S1100w supports channel fragmentation, allowing narrower channels of 5 MHz and 10 MHz.
You can have up to four independent channels with a 10 MHz width, and up to 10 with a
5 MHz width. All these channels are for indoor or outdoor use. For more information about
channel fragmentation, see page 45.
6 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
The available channels are:
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel width
3 4.9425 5 MHz
6 4.9475 5 MHz
7 4.9525 5 MHz or 10 MHz
7 4.950 20 MHz
8 4.9575 5 MHz
9 4.9625 5 MHz or 10 MHz
10 4.9675 5 MHz
11 4.9725 5 MHz or 10 MHz
11 4.970 20 MHz
12 4.9775 5 MHz
13 4.9825 5 MHz or 10 MHz
16 4.9875 5 MHz
5 GHz Band
In the 5 GHz band, the number of available channels and sub-bands vary depending on the
country of operation.
Most European countries adhere to the DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection) and TPC
(Transmit Power Control) regulations established by the European Telecommunications
Standards Institute (ETSI); these regulations apply to the 5 GHz frequency band only. To
know which bands are available in your country of operation and whether your country
adheres to DFS and TPC, refer to the Wireless Frequency Plan document located on the
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions extranet (Technical Support, then Downloads, then
Utilities and Tools).
In North America, five channels are available in the 5 GHz band, all independent and for
indoor or outdoor use. The center frequencies of these channels are:
Channel Frequency (GHz)
149 5.745
153 5.765
157 5.785
161 5.805
165 5.825
In Europe, the 11 independent channels, for indoor or outdoor use, are:
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Frequency (GHz)
100 5.50 124 5.62
104 5.52 128 5.64
108 5.54 132 5.66
112 5.56 136 5.68
116 5.58 140 5.70
120 5.60
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 7
2: System and RF Planning
Wireless Cells
A wireless network is designed such that information can travel back and forth between two
points without the need for wires. For the S1100w, this information consists of digitized
video, audio, and PTZ data sent to and from the wired network via an outdoor wireless
access point—either the Nextiva S3100 device or a commercial 802.11 access point.
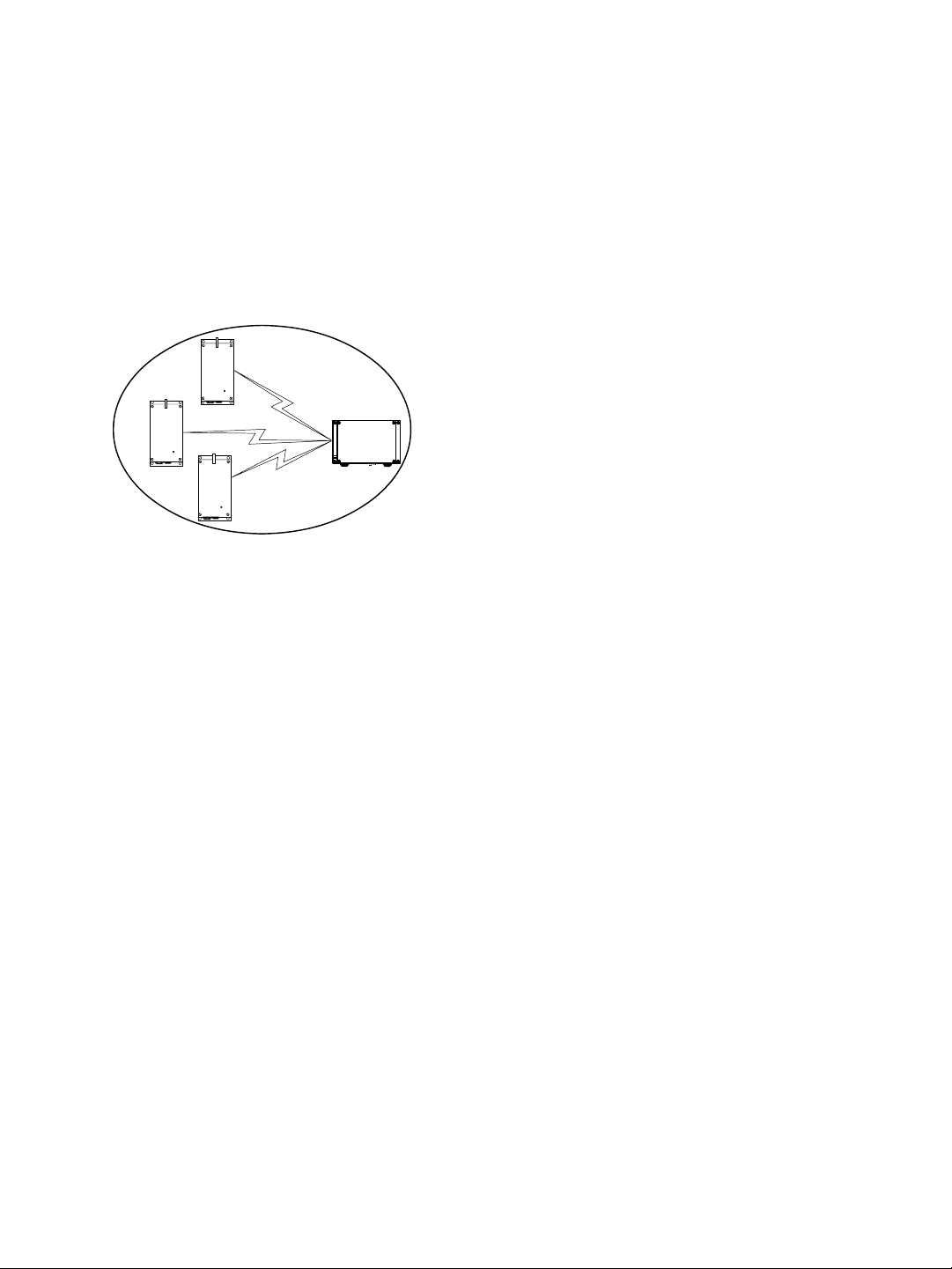
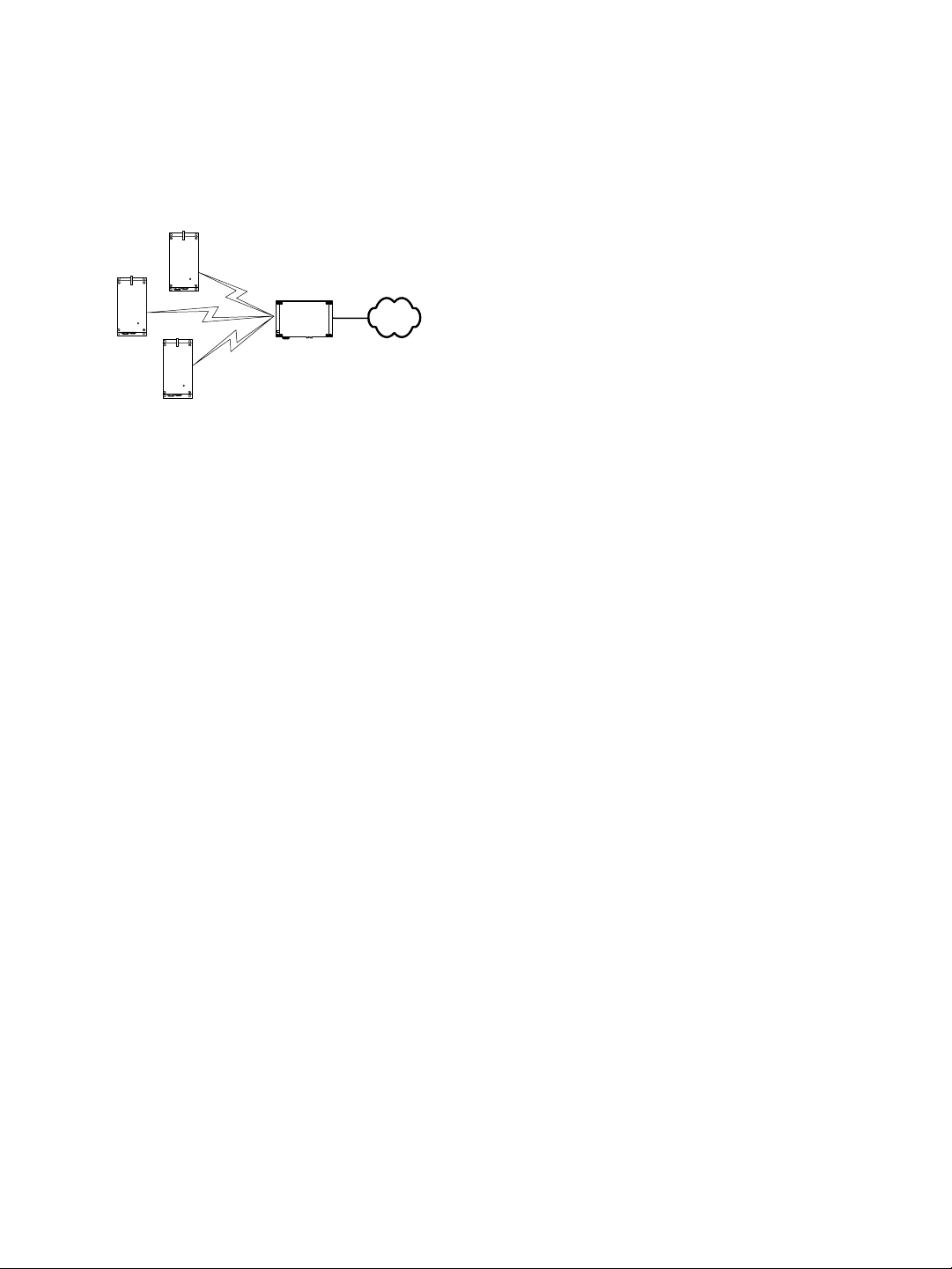
A wireless cell consists of a group of wireless devices that communicate together on the
same frequency channel and that share the same wireless passkey (described on page 42).
For example:
S3100
You can colocate many wireless cells if you respect certain conditions (see page 13).
802.11 Support
Starting at firmware version 4.0, you can use the S1100w devices with commercial
802.11-compliant access points. To support this new protocol, the 802.11 MAC (Media
Access Control) mode is introduced. This mode is available in all frequency bands (2.4 GHz,
4.9GHz, and 5GHz).
The S1100w in 802.11 mode supports the following security mechanisms:
No security—Not recommended
WEP—Not recommended
WPA and WPA2 (also known as 802.11i) in personal mode (PSK)
WPA and WPA2 in Enterprise mode, with an 802.1X authentication server
Note: WPA and WPA2 are not available with the proprietary SPCF MAC mode.
8 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

The supported authentication methods for WPA and WPA2 are:
Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Method Authentication
PSK—Pre-Shared Key
(personal)
EAP-TLS (Enterprise) login/password
EAP-TTLS (Enterprise) login/password
PEAP (Enterprise) login/password
means
passphrase Designed for home and small office networks. A
and certificate
and certificate
and certificate
Remarks
passphrase is required to connect to an access point
and therefore access the network.
Uses mutual authentication. The most secure option
available.
Creates a secure TLS tunnel. Supports MSCHAPv2 (the
Microsoft version of the Challenge Handshake
Authentication protocol) to validate logins and
passwords. A certificate is required on the server side.
Creates a secure TLS tunnel. Supports MSCHAPv2 (the
Microsoft version of the Challenge Handshake
Authentication protocol) to validate logins and
passwords. A certificate is required on the server side.
For more information about the TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol, refer to RFC 2246
at http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2246.txt
.
The supported encryption methods are:
WEP
AES-CCMP
TKIP
Auto-select—The device automatically chooses the best available encryption scheme.
The wireless parameters associated to 802.11 differ from those of the SPCF mode. For
more information about these parameters, see page 41 for the command line interface or
refer to the SConfigurator User Guide.
Be aware of the following limitations in using S1100w devices in a 802.11 environment:
The S1100w will not be able to connect itself to an S3100.
The inherent problems with 802.11 wireless network products, such as the “hidden
node” and quality of service issues, will be present. Furthermore, the ranges of the
equipment will be lower than with the SPCF protocol.
It is assumed that the network administrators wanting to add S1100w transmitters to their
802.11 wireless network are knowledgeable about this protocol. In the remaining of this
user guide, the access point will be a Nextiva S3100 using the SPCF protocol.
System Planning
When installing many wireless systems in the same area, you have to carefully plan their
positions in order to prevent radio interference and select the appropriate antennas.
The grouping of devices in each wireless cell is determined by their respective locations
with respect to one another and by the available outdoor wireless access points. As a rule of
thumb, there should be a clear RF line of sight between each S1100w device and the access
point in each cell. However, the S1100w devices can be completely hidden from one
another.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 9
2: System and RF Planning
Point-to-Multipoint Application
A point-to-multipoint application is a wireless cell made up of an S3100 access point (the
master) and several S1100w transmitters (the clients). Here is a typical point -to-multipoint
system:
S1100w
S3100
For example, to associate three S1100w devices to one access point, you need to:
1. Assign the same wireless passkey to the S1100w devices and the S3100 access point.
The wireless passkey must be different from that of other colocated cells, if any.
2. In a non-DFS context, assign a frequency channel to the S3100 device. In a DFS
context, the master device will automatically select a channel.
The associated S1100w devices will automatically use their master’s channel.
3. Install the S1100w devices such that each one has a clear RF line of sight with the
S3100 access point.
For the configuration and installation procedure, see page 23.
Compatibility Issues
When planning your wireless systems, you have to take into account the firmware versions
of the involved devices. It is recommended that the S1100w transmitters have the same
firmware versions as their associated master; however, from version 2.60 and up, the
devices are fully compatible (for example, an S1100w at version 4.0 with an S3100 at
version 3.62).
In a wireless cell, the order in which you configure the devices (either the first time or later
when they are installed in the field) or update their firmware is critical if you do not want to
lose access to them. You should then:
Update the devices starting with the farthest (in terms of number of RF hops) from the
computer running the upgrade procedure.
One step at a time, get closer to the computer.
10 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
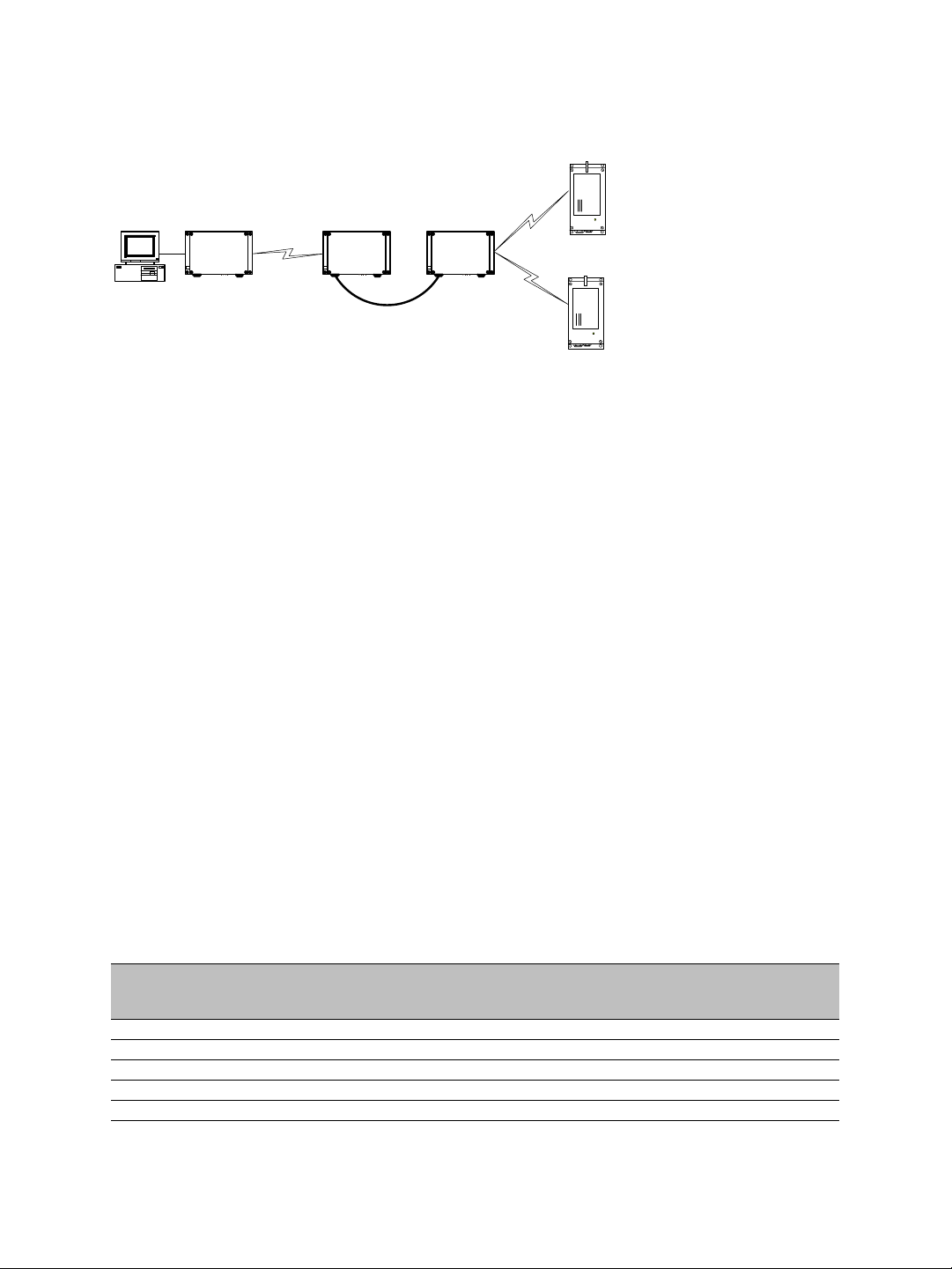
Nextiva S1100w User Guide
For example, consider the following setup:
S1100w 1
S3100 3 S3100 2
S3100 1
S1100w 2
You should update the devices in the following order:
1. S1100w 1—You then lose contact with S1100w 1.
2. S1100w 2—You then lose contact with S1100w 2.
3. S3100 1—You can then reach all devices.
4. S3100 2—You then lose contact will all devices except master S3100 3.
5. S3100 3—You can then reach all devices.
For the complete firmware update procedure, refer to the documentation of the Verint
software you are using.
Video Bit Rate and Data Throughput
You can theoretically connect up to 16 S1100w devices to a master access point in a
wireless cell. In practice however, video quality , fr ame rate, an d system layout can limit the
number of devices that a single master access point can support.
Each time multiple client devices are connected to a master S3100, the available bandwidth
is divided equally between the connections. For example, three S1100w clients connected
to a master on a 6 Mbps link each have 2 Mbps throughput.
Video quality and frame rate influence the required data throughput. Therefore, you need
to carefully plan the number of cameras that will work on a link.
The following figures were measured in typical setup situations. They may vary depending
on your configuration. The total data throughput in a unidirectional UDP link setup varies
depending on the frequency channel width: 20 MHz in all available bands, or 5 MHz and
10 MHz in the 4.9 GHz frequency band.
The throughput for a 20 MHz channel is:
Physical bit rate Throughput for a 3 mile
(5 km) distance
6 Mbps 3.5 Mbps 3.4 Mbps 3.3 Mbps
9 Mbps 4.7 Mbps 4.5 Mbps 4.4 Mbps
12 Mbps 5.6 Mbps 5.4 Mbps 5.2 Mbps
18 Mbps 7.0 Mbps 6.6 Mbps 6.3 Mbps
24 Mbps 8.1 Mbps 7.5 Mbps 7.1 Mbps
Throughput for a
9.3 mile (15 km)
distance
Throughput for a
15.5 mile (25 km)
distance
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 11

2: System and RF Planning
Physical bit rate Throughput for a 3 mile
(5 km) distance
36 Mbps 9.1 Mbps 8.6 Mbps 8.1 Mbps
48 Mbps 10.0 Mbps 9.3 Mbps 8.7 Mbps
54 Mbps 10.1 Mbps 9.5 Mbps 9.0 Mbps
Throughput for a
9.3 mile (15 km)
distance
Throughput for a
15.5 mile (25 km)
distance
The throughput for a 10 MHz channel is:
Physical bit rate Throughput for a 3 mile
(5 km) distance
3 Mbps 2.0 Mbps 1.9 Mbps 1.9 Mbps
4.5 Mbps 2.8 Mbps 2.7 Mbps 2.7 Mbps
6 Mbps 3.5 Mbps 3.4 Mbps 3.3 Mbps
9 Mbps 4.5 Mbps 4.4 Mbps 4.3 Mbps
12 Mbps 5.4 Mbps 5.1 Mbps 5.0 Mbps
18 Mbps 6.7 Mbps 6.3 Mbps 6.0 Mbps
24 Mbps 7.4 Mbps 7.1 Mbps 6.8 Mbps
27 Mbps 7.7 Mbps 7.4 Mbps 7.0 Mbps
Throughput for a
9.3 mile (15 km)
distance
Throughput for a
15.5 mile (25 km)
distance
The throughput for a 5 MHz channel is:
Physical bit rate Throughput for a 3 mile
(5 km) distance
1.5 Mbps 1.1 Mbps 1.1 Mbps 1.1 Mbps
2.25 Mbps 1.5 Mbps 1.5 Mbps 1.5 Mbps
3 Mbps 1.9 Mbps 1.9 Mbps 1.8 Mbps
4.5 Mbps 2.6 Mbps 2.6 Mbps 2.5 Mbps
6 Mbps 3.2 Mbps 3.2 Mbps 3.1 Mbps
9 Mbps 4.2 Mbps 4.1 Mbps 3.9 Mbps
12 Mbps 4.9 Mbps 4.7 Mbps 4.6 Mbps
13.5 Mbps 5.1 Mbps 5.0 Mbps 4.8 Mbps
Throughput for a
9.3 mile (15 km)
distance
Throughput for a
15.5 mile (25 km)
distance
The S1100w automatically adjusts the transmission speed with the current RF conditions.
For the bit rate requirements of the edge devices to which the cameras are connected,
consult the Bit Rate Settings for Video Servers document located on the Verint Video
Intelligence Solutions extranet (Technical Support, then Downloads, then Utilities and
Tools).
TPC
If the country of operation of the S1100w device requires conformity to the TPC (Transmit
Power Control) regulations, the transmission power of its radio is automatically reduced by
3 dB before leaving the Verint factory. However, in case of a weak wireless link (that is, a
link with an RF margin of less than 15 dB), you have the opportunity to use the maximum
transmission power (see page 46).
12 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
Nextiva S1100w User Guide
DFS
To follow the DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection) regulations specified by ETSI for the
selected country, it is the master S3100 device that performs the tasks relative to
frequency channel selection and radar detection. In other words, you cannot choose the
frequency channel on which the edge device will run.
The automatic selection of the frequency channel limits the number and the configuration of
the wireless cells. Furthermore, when colocating many cells, all masters must “see” each
other.
Note: DFS is required only in the 5 GHz band.
You should start the master first, then power the client when the other device is in normal
operation.
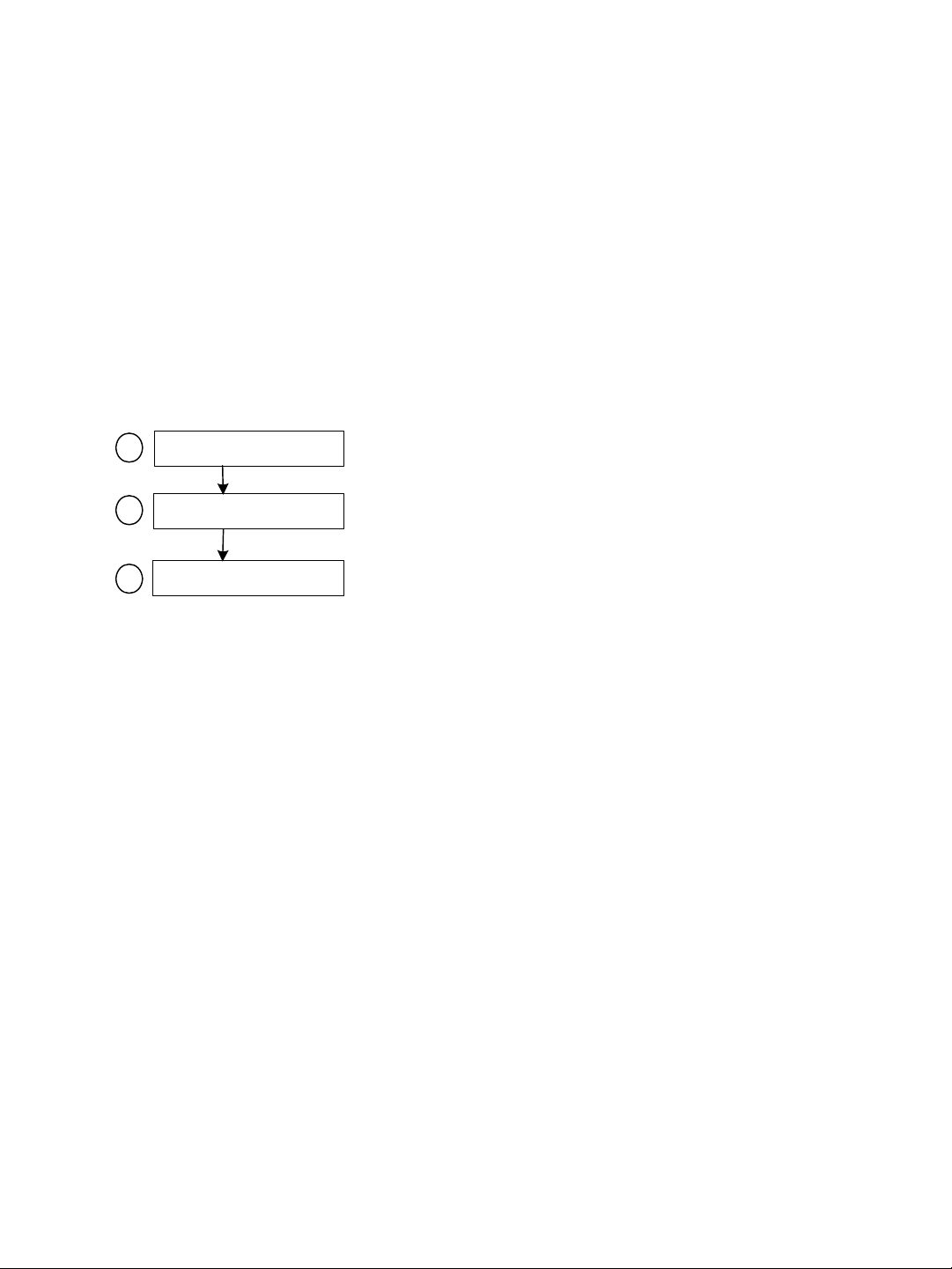
The boot sequence of client (transmitter) devices is:
Unit initialization (3 seconds)
1
Roaming (2-25 seconds)
2
Normal operation
3
1. The device goes through the standard startup procedure.
2. The device roams through the channels in the available frequency bands to locate its
master.
3. When the master is located, the client device runs normally on the selected frequency
channel.
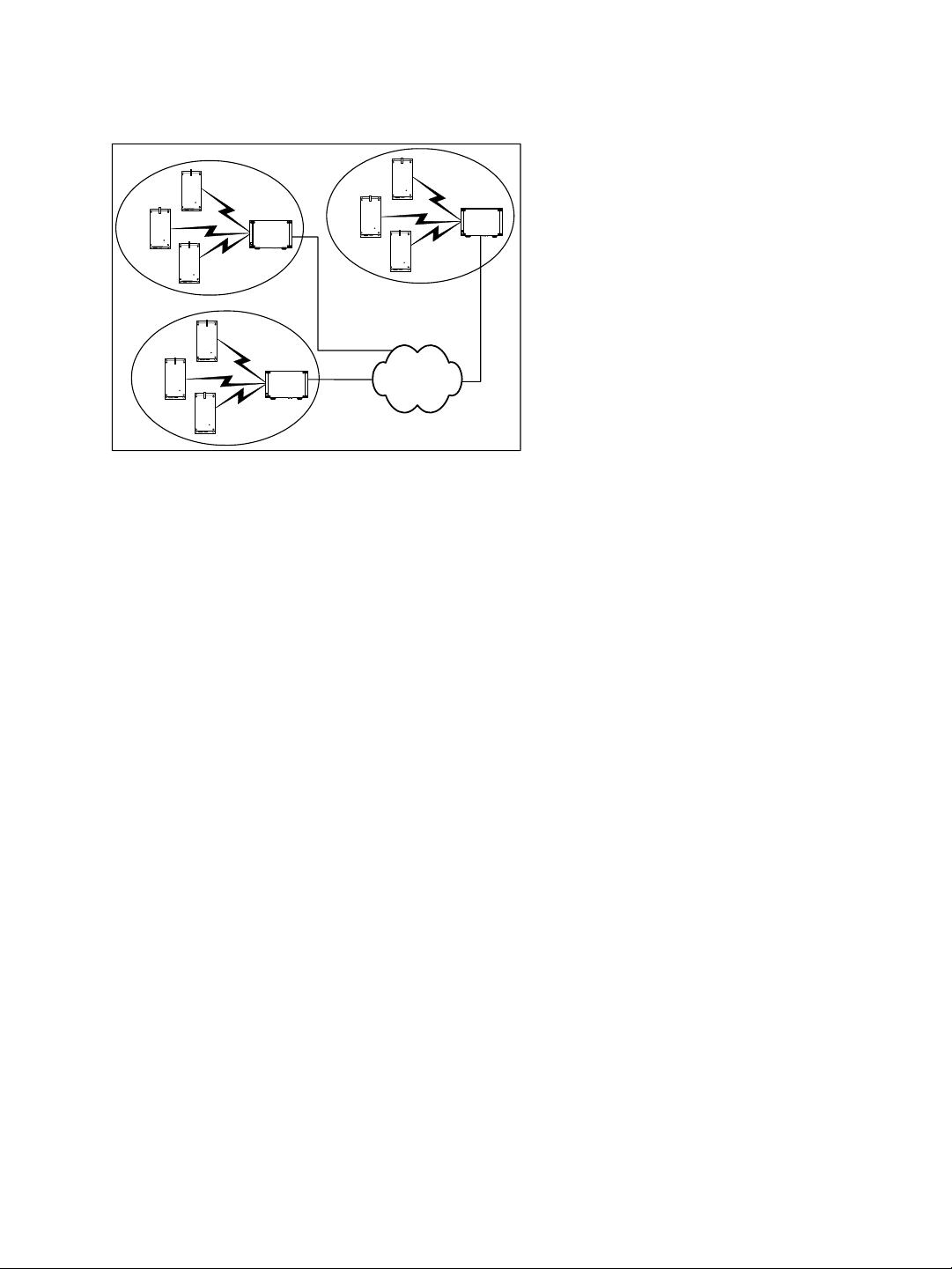
Colocated Cells
You can operate many wireless cells in the same location, provided you follow guidelines
relative to frequency channel, wireless passkey, and distance.
Regarding frequency channel, you cannot manually select one in the 5.40–5.725 GHz band
in Europe; for the detailed procedure, see page 16.
The wireless passkeys of colocated cells must be different from one another, regardless of
their frequency channels.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 13

2: System and RF Planning
Distance Limitations
The distance limitations between devices are:
The minimum distance between two devices is 3 feet (1 meter), regardless of the band
or channel used.
To avoid material damages, you must never power any two devices while their
antennas are facing one another with a distance of less than 10 feet (3 meters).
If using adjacent channels, see page 65 for the recommendations on the minimum
distances to respect.
To reduce radio interference possibilities between two adjacent frequency channels,
ensure that the maximum margin between the emission of the two wireless cells is
25 dB; for more information, see Appendix F on page 65.
4.9 GHz Band in North America
Depending on the channel width (20, 10, or 5 MHz), you can colocate 2, 4, or 10 wireless
cells respectively. For the available channels in each of the three scenarios, see page 7.
The following example presents three wireless cells with 10-MHz channels. To install such a
system, you have to:
1. In each cell, assign the same wireless passkey to the S1100w devices and the S3100
access point. The wireless passkey must be different from that of the other cells.
2. Assign a different frequency channel to each S3100 device; the associated S1100w
devices will automatically use their master’s channel:
Device Cell Channel Wireless Passkey
S3100_A A 7 ertynmbvcxzapoiu
S1100w_A1 A 7 ertynmbvcxzapoiu
S1100w_A2 A 7 ertynmbvcxzapoiu
S1100w_A3 A 7 ertynmbvcxzapoiu
S3100_B B 13 PUK98rewq4123qzx
S1100w_B1 B 13 PUK98rewq4123qzx
S1100w_B2 B 13 PUK98rewq4123qzx
S1100w_B3 B 13 PUK98rewq4123qzx
S3100_C C 11 987123jkl456wert
S1100w_C1 C 11 987123jkl456wert
S1100w_C2 C 11 987123jkl456wert
S1100w_C3 C 11 987123jkl456wert
3. In each cell, install the S1100w devices such that each one has a clear RF line of sight
with its associated S3100 access point.
14 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
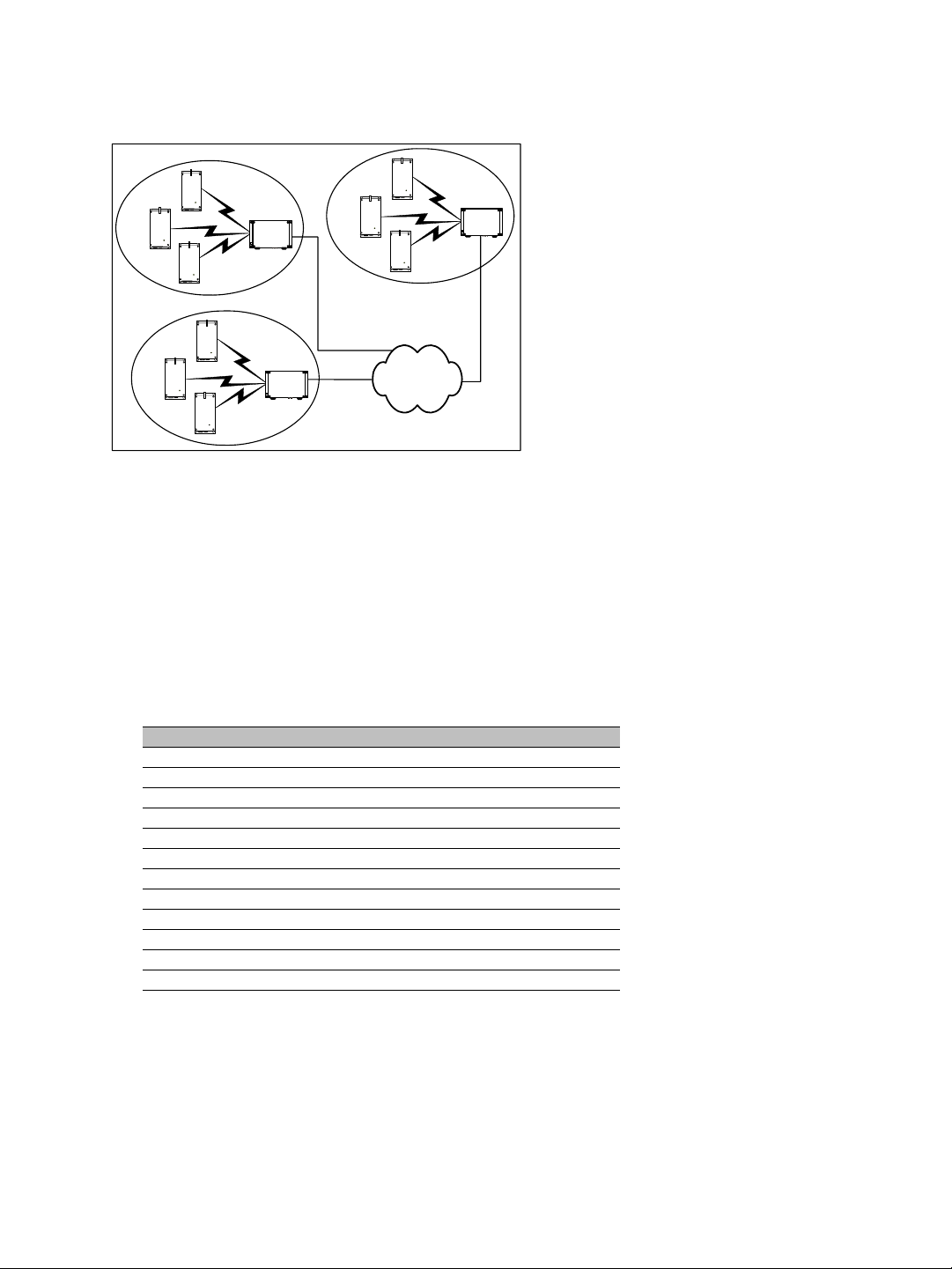
Nextiva S1100w User Guide
This application can be illustrated this way, where the three cells are in the same location:
B
C
A
5 GHz Band in North America and 2.4 GHz
In the 2.4 GHz band in North America and Europe, you can use the three independent
channels (channels 1, 6, and 11) to colocate wireless cells. In the 5 GHz band, all channels
are independent.
A typical colocation example is three wireless cells. To install such a system, you have to:
1. In each cell, assign the same wireless passkey to the S1100w devices and the S3100
access point. The wireless passkey must be different from that of the other cells.
2. Assign a different frequency channel to each S3100 device; the associated S1100w
devices will automatically use their master’s channel. For example, in the 5 GHz band:
Device Cell Channel Wireless Passkey
S3100_A A 149 ertynmbvcxzapoiu
S1100w_A1 A 149 ertynmbvcxzapoiu
S1100w_A2 A 149 ertynmbvcxzapoiu
S1100w_A3 A 149 ertynmbvcxzapoiu
S3100_B B 165 PUK98rewq4123qzx
S1100w_B1 B 165 PUK98rewq4123qzx
S1100w_B2 B 165 PUK98rewq4123qzx
S1100w_B3 B 165 PUK98rewq4123qzx
S3100_C C 157 987123jkl456wert
S1100w_C1 C 157 987123jkl456wert
S1100w_C2 C 157 987123jkl456wert
S1100w_C3 C 157 987123jkl456wert
3. In each cell, install the S1100w devices such that each one has a clear RF line of sight
with its associated S3100 access point.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 15
2: System and RF Planning
This application can be illustrated this way, where the three cells are in the same location:
B
C
A
5 GHz Band in Europe
The maximum number of colocated cells corresponds to the number of channels in the
available frequency bands that can be used outdoors. For instance, in most countries of
Western Europe, you can have up to 11 colocated cells in the 5.40–5.725 GHz band.
However, because the master devices must see each other in a DFS context, the variety of
supported setups is limited.
In this context, you can easily install up to five cells. By respecting the following steps, you
can assume that the cells will not share the same frequency channel, making the complete
bandwidth available for each one. You have to:
1. Assign a different wireless passkey to each cell.
2. Ensure that all masters “see” one another. For more information, refer to the “RF
Contact between Masters” appendix in the Nextiva S3100 Series User Guide.
3. Position the devices so that there is at least 3 feet (1 meter) between each antenna.
4. In each master device, set a different starting order: 1 for the first device, 2 for the
device next to it, 3 for the third one, and so on.
Installing more than five cells in the 5.40–5.725 GHz band requires the use of adjacent
channels. This situation demands greater distances between the antennas to reduce
potential radio interference. Therefore, you should contact the Verint Video Intelligence
Solutions project engineering group for assistance.
16 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Supported Setups
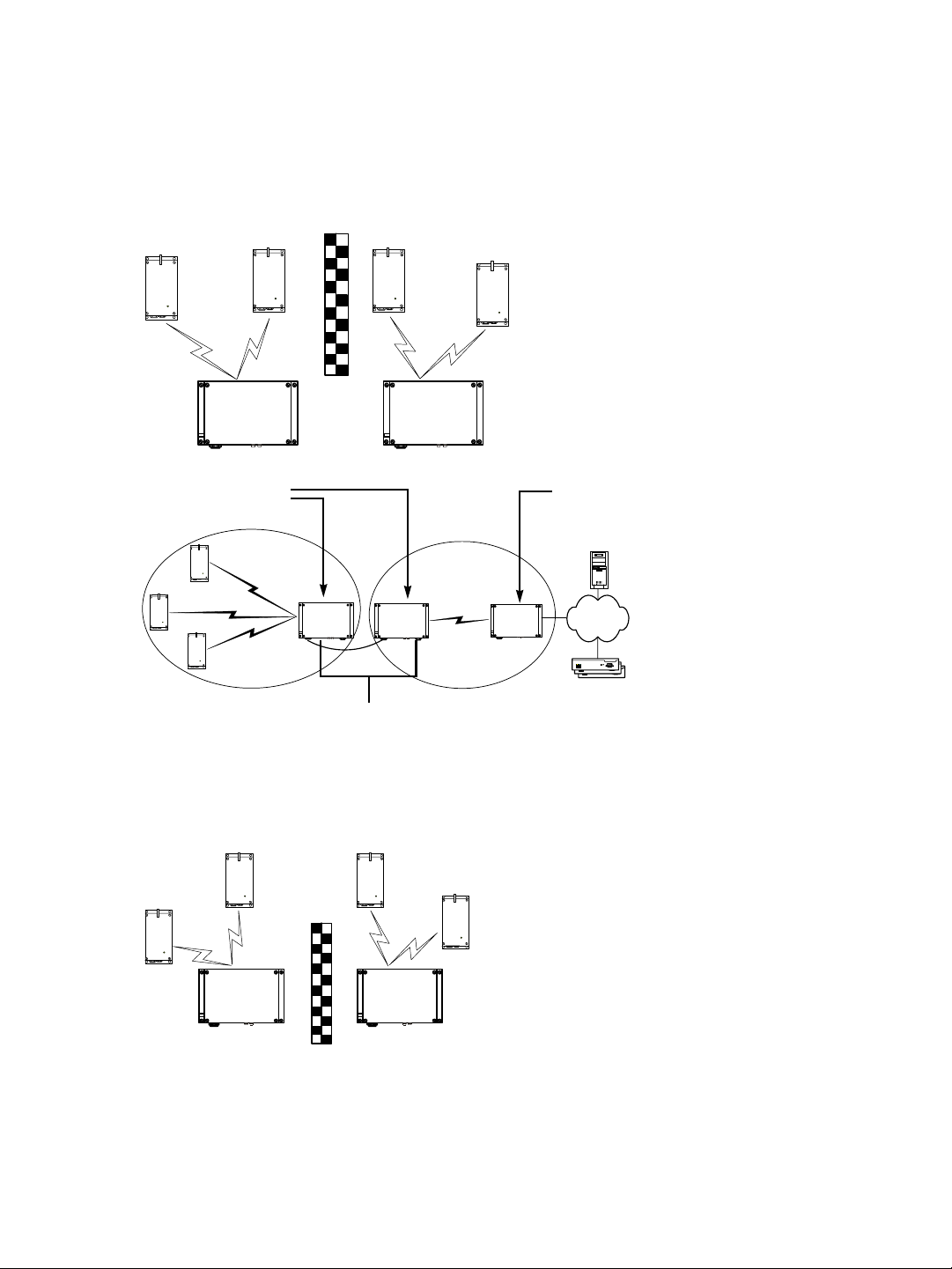
The following colocated systems are supported in the 5.40–5.725 GHz band:
T wo access point applications, in which the transmitters from one system do not see the
transmitters from the other cell. Both master devices see each other.
S3100 S3100
A point-to-multipoint repeater. Both master devices see each other.
Master
Slave
Video
management
software
S3100 S3100S3100
Receivers
Repeater
Unsupported Setup
You cannot install the following colocated system in the 5 GHz band in Europe:
Access point applications with hidden masters. In this context, the two S3100 masters
do not see each other, while transmitters 2 and 3 do.
2
1
S3100 S3100
3
4
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 17
2: System and RF Planning
RF Planning
Successful operation of a wireless link depends on proper RF path planning and antenna
installation. You have to install the devices in such a way that there is a clear RF line of
sight between the two antennas.
Location Evaluation
The path between the two antennas must be free of obstacles that could disturb
propagation. For very short link distances—less than 500 feet (152 meters)—you may be
able to establish a working link despite partial path obstruction. However, radio waves will
be in part absorbed and in part diffracted by the obstacles, therefore affecting link
reliability. Because the reliability of such an installation is highly unpredictable, Verint does
not recommend it. A path free of any obstacle is called an RF line-of-sight path.
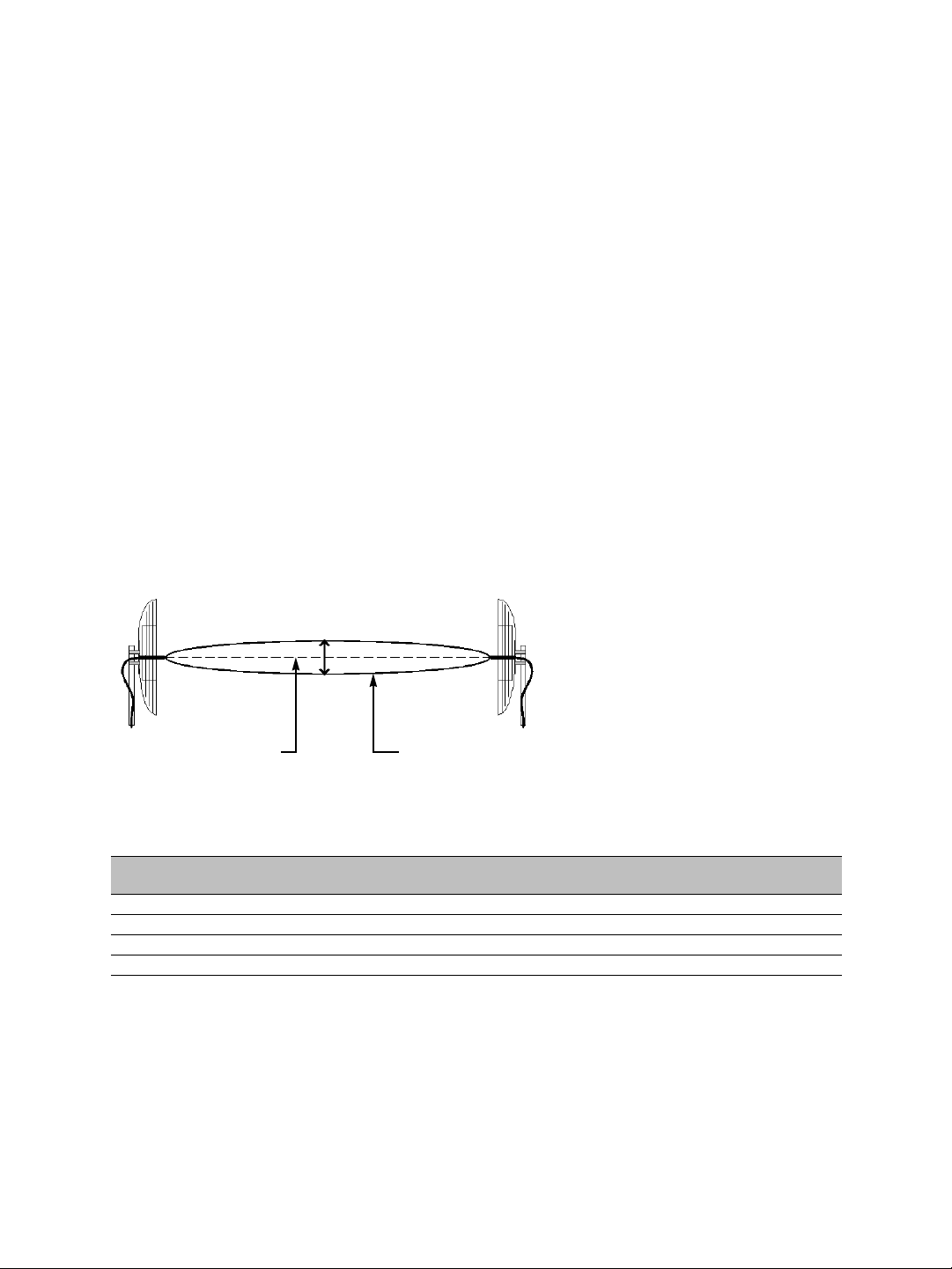
To establis h an RF line-of-sight path, you must take into account the beam width of the
radio signal transmitted between the two antennas. This beam width is an elliptical area
immediately surrounding the visual line of sight. It varies in thickness depending on the
length of the line of sight; the longer the length, the thicker the beam width becomes.
The region outlined by the signal beam width is known as the first Fresnel zone. The
Fresnel zone is always thicker at the mid-point between the two antennas. Therefore what
appears to be a perfect line-of-sight path between the base and a remote station may not
be adequate for a radio signal; this is the difference between “visual” and “RF” line of sight.
Visual line of sight First Fresnel zone (F1)
In practice, it has been determined that a radio path can be considered an RF line-of-sight
path if it has a clear opening through 60% of the first Fresnel zone (or 0.6 F1). Here are
values for 0.6 F1 for various signal path distances and frequency bands:
Distance
(mi./km)
1 / 1.6 14 / 4.2 9.8 / 3.0 9.5 / 2.9 8.9 / 2.7 0
4 / 6.5 27 / 8.4 19.5 / 5.9 18.7 / 5.7 18 / 5.5 2 / 0.6
7 / 11.3 37 / 11 25.8 / 7.9 25 / 7.6 23.6 / 7.2 6 / 1.8
15 / 24 53 / 16 37.8 / 11.5 36.4 / 11.1 35 / 10.6 29 / 8.8
2.45 GHz
(feet/m)
4.9 GHz
(feet/m)
5.3 GHz
(feet/m)
5.8 GHz
(feet/m)
Earth curvature effect
(feet/m)
For distances under seven miles, the earth curvature effect is negligible. However, for
greater distances, you need to consider it in your calculations; for instance, for a 15-mile
link in the 2.4 GHz band, the two antennas must be located 82 feet higher than the highest
obstacle in the RF line of sight between them (that is, 53 feet for the Fresnel zone plus
29 feet for the earth curvature effect). For help, consult the Verint Video Intelligence
Solutions Support group.
18 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
A common problem encountered in the field and related to the 0.6 F1 clearance rule is
building obstruction. The proposed visual path may just barely clear a building but the RF
line of sight will not. In such a case, the signal will be partially absorbed and diffracted.
Increasing the height of the two antennas or the gain of the antennas are the only
alternatives to improve the link quality.
Note: At 2.4, 4.9, and 5 GHz, radio waves are highly attenuated by dense foliage. A link
established in the fall or winter season may be adversely affected in the spring and
summertime, if it is established below tree level.
Antenna Requirements
Verint offers many antennas to meet various distance requirements. You need to consider
many factors when choosing an antenna, including the distance to cover, the RF bit rate,
the radiated power (EIRP), and the frequency band. For systems located in North America
on the 5 GHz band, you can use the Wireless System Margin Calculator located on the
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions extranet (Technical Support, then Downloads, then
Utilities and Tools).
The combined transmission power of the device and antenna must not exceed the
maximum value established by your country’s regulations. To ensure that this maximum is
not exceeded, enter the gain of the chosen antenna in the CLI (Wireless Communication
menu) or SConfigurator (Wireless pane). The device will automatically take it into account
and adjust its own transmission power accordingly at startup.
Note: Connecting an antenna with a gain higher than the calculated value contravenes your
country’s regulations. It is your responsibility to ensure that you respect the
regulations in place. You can only use antennas certified by Verint.
The maximum antenna gain supported to meet local regulations are:
Location Band Antenna gain Comment
Europe 2.4 GHz 8.5 dBi
5 GHz 13 dBi
North America 2.4 GHz 16 dBi
4.9 GHz 13 dBi To be used only with the S1100w-49
5 GHz 1
9 dBi
The antennas certified by Verint are:
ANT- WP8-24/S: 8.5 dBi gain, 2.4 GHz band, 65° beamwidth, patch antenna with 3-foot
(1-meter) SMA-SMA cable
ANT-WP13-5x/S: 13 dBi gain, 5.25-5.85 GHz band, 40° beamwidth, patch antenna
SMA/F connector
ANT-WP13-49-5x/S: 13 dBi gain, 4.9-5.85 GHz band, 40° beamwidth, patch antenna
SMA/F connector
ANT- WP16-24/S: 16dBi gain, 2.4 GHz band, 27° beamwidth, patch antenna with 3-foot
(1-meter) SMA-N cable
ANT- WP19-5x/S: 19 dBi gain, 5.25-5.85 GHz band, 18° beamwidth, patch antenna with
3-foot (1-meter) SMA-N cable
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 19

2: System and RF Planning
Interference
In most countries, the 2.4 GHz band is not regulated by a government agency; this absence
of frequency coordination can result in interference between various systems. For instance,
if a link with an RF line of sight is subject to excessive video delay and very low frame rate
(or possibly breakdown of video images), it could be due to interference. Fortunately, you
have ways of adapting your setup to avoid interference:
RF channel selection—The S1100w has 11 or 13 channels to choose from. In case of
interference, it is recommended to change channel until you find a clean one.
Antenna selection—Replacement of the integrated antenna by a higher gain one can
significantly lower the interference from other radio systems. Replace the antenna if
switching channels does not correct the problem or if all channels must be used to
colocate several systems.
There should not be any interference in the 4.9 GHz band, since it is a licensed band with
limited usage to public safety.
The 5 GHz band is less cluttered than the 2.4 GHz band, resulting in less potential
interference from other wireless systems.
RF Exposure Considerations
In order to comply with the RF exposure requirements of CFR 47 part 15 in North America,
the devices must be installed in such a way as to allow a minimum separation distance of
12 inches (30 cm) between antennas and persons nearby.
20 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Configuring and
Installing the Device
The steps required to prepare your S1100w device for operation are:
Basic configuration
Physical installation in its final location
Alarm and audio configuration
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 21

3: Configuring and Installing the Device
Cable for Power, Video, and Serial Data
The supplied CAB9P cable assembly is used for video, power, and serial port connection.
Mating connector
Terminal block Power wires BNC video connector
For the detailed pinout, see page 54.
Serial Port
The S1100w integrates one multipurpose serial port. This port is used for system
configuration and data communication: pan-tilt-z oom (PTZ), access control, or other. By
default, the port automatically detects if it is connected to an RS-232 or RS-422/485 serial
device.
DB-9 connector
The CAB9P cable is supplied with a female DB-9 plug enabling RS-232 connections.
However, most PTZ cameras, keyboards, and similar devices use RS-422/485 connections.
Therefore, you will have to adapt the CAB9P cable for its different uses:
During the configuration process of the S1100w, you need to access a computer, so the
DB-9 connector is required for RS-232 communication.
Later, when installing the device in its final location, you will likely want to connect it to
RS-422/485 equipment, therefore requiring changes on the cable. You should k eep the
DB-9 connector on the cable for later use.
Warning: At any time there must be only one serial device connected to the S1100w
device. For instance, when configuring the device, you must unplug any
RS-422/485 device.
Power
Use the red and black wire pair of the CAB9P cable to connect the S1100w device to an
external power supply.
22 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
To power an S1100w device:
1. In 12V DC, the red wire is for input and the black wire is for power ground.
a. Twist together the black power wire of the cable and the wire with the dashed white
lines of the supplied power supply.
b. Twist together the red power wire of the cable and the other power supply wire.
2. In 24V AC, both wires are used for power. Connect the two power wires of the cable to
the screws labelled 1 and 3 on the power supply; it does not matter which wire goes on
which screw.
Configuring the Wireless System
The configuration steps to execute are:
Set a series of parameters
If required, establish a point-to-point connection between the transmitter and a
receiver
To configure the device, you need the proprietary SConfigurator tool. It is included on the
Utilities CD shipped with your device; you can also find its latest version on the Verint
Video Intelligence Solutions extranet (T echnical Support, then Downloads, then Utilities and
Tools). You have to copy its executable file to the hard disk of your computer.
Computer Requirements
The minimum hardware and software requirements for the host computer needed to
configure the edge device are:
An Ethernet network card
A serial port (not through a USB converter)
Windows 2000 Service Pack 2 or higher, or Windows XP Service Pack 2
Setting Parameters
Before installing a wireless system, you need to set parameters relative to wireless
communication, IP networking, and serial port. You also need to establish proper
communication with the corresponding S3100 outdoor wireless access point.
c
The first step in installing an S1100w device is to change its IP address to ensure
compatibility with an existing network. The default IP addresses of all devices are based on
the APIPA addressing scheme and will be in the range 169.254.X.Y, where X and Y are
relative to the MAC address of the individual device; for more information about APIPA, see
page 57.
To work properly , devices on the same network must have unique IP addresses. The device
will not prevent you from entering a duplicate address. However, its system status LED will
turn to flashing red; then the device will use an APIPA address.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 23

3: Configuring and Installing the Device
To configure a wireless system:
1. In a lab, unpack the transmitter and the access point and place them on a table.
2. Connect the external antenna on the S3100 and optionally on the S1100w.
Warning: To avoid material damages, you must never power any two devices while
their antennas are facing one another with a distance of less than 10 feet
(3 meters).
3. Unpack the cable assembly (CAB9P) and plug its mating connector on the main
connector of the S1100w transmitter.
4. Connect the DB-9 plug of the cable to a COM port on your computer.
5. Power the device using the red and black wires of the CAB9P cable (see page 22).
The status LED turns steady red and then flashes green, indicating normal operation.
6. Configure the S1100w parameters with the command line interface (CLI):
a. Country of operation
b. Frequency band
c. Passkey
d. IP address
e. Serial port parameters
For the description of the procedure, see Chapter 4 on page 35.
7. Configure the wireless access point for a point-to-multipoint application.
For the detailed procedure, refer to the Nextiva S3100 Series User Guide.
8. Using SConfigurator, ensure that the S3100 and the S1100w transmitters communicate
well together:
In the Units tab, the S1100w should be hierarchically positioned under the S3100.
In the Link Status pane of the S3100, the S1100w should be in the Clients/Slaves
list.
Ensure that there is end-to-end video transmission in the lab before installing the
devices in their final location.
The initial configuration is now complete for the two devices.
Point-to-Point Connection
c
To allow video display on a monitor in a point-to-point context, you have to create a fixed
connection between the S1100w transmitter and an S1970e-R receiver. You can connect to
up to four transmitters to this receiver, to create four different point-to-point connections.
Typically , both devices sit on the same IP subnet as SConfigur ator and hav e the same VSIP
port; to access other devices, refer to the device discovery section in the SConfigurator
User Guide.
For more information about the connection procedure, re fer to the “Managin g Connecti ons”
chapter, in the SConfigurator User Guide.
24 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
To perform a point-to-point connection:
1. Start SConfigurator.
2. In the Units tab, discover the desired devices.
The discovered devices appear in the Units box.
3. Select the Connections tab, then click Add.
The Connection Creator window appears.
4. Select a transmitter in the left column and a receiver in the right one.
In the Transmitters column, you have access to the two encoders of each input; the
video stream is the same for both.
5. In the Video list, select the desired video mode.
6. To disable I/O data transmission (for example, alarms) between the two selected
devices, clear Forward I/O.
7. To disable serial port data transmission (like PTZ commands), clear Forward Serial
Port Data.
8. To enable audio between the devices, ensure that Enable Audio is checked, then select
the audio mode.
Note: On the S1970e-R, you can activate audio on a single connection only. The active
audio connection is the last that was performed. Furthermore, the audio
connection will remain the same even if the S1970e-R is in guard tour mode, that
is, the receiver will not switch between the audio streams of its four connected
transmitters. For more information, refer to the Nextiva S1900e Series User
Guide.
9. Click Connect.
10. In the SConfigurator confirmation window, click OK.
You should now have video on the monitor connected to the receiver.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 25

3: Configuring and Installing the Device
Installing the Wireless System
After configuring successfully your wireless system, you are ready to install it. To optimize
your system radio performance, carefully review the site planning information presented in
Chapter 2 on page 5. For more information about the installation procedure of your outdoor
wireless access point, refer to the Nextiva S3100 Series User Guide.
Installing the Transmitter
Warning: When installing colocated wireless systems, you have to take into account the
distance limitations listed on page 14.
Warning: Always mount the device with the mating connectors pointing downwards.
Otherwise moisture may penetrate the device; the associated repair costs would
not be covered by the warranty.
To install a transmitter:
1. To install the S1100w on a light pole or mast, use the supplied pole mount brackets and
stainless steel clamps. For wall mounting, use the side brackets already installed on the
device.
2. If you are in stalling the S1100w equipm ent in a lightning prone environment or in a site
where large AC mains power fluctuations are a common occurrence, add additional
external surge protection to all vulnerable connections.
Vulnerable connections are those that run for a long distance between the S1100w
device and the connected equipment. For more information about surge protection, see
Appendix E on page 63.
3. If the S1100w device will be directly exposed to the sun in an environment likely to
reach 122°F (50°C), install a sun shield.
A derate of 13°F (7°C) is required to protect the equipment.
4. If required, install an external antenna (see page 27).
5. Apply silicone grease on the mating connector of the CAB9P cable and on the main
connector of the device.
For the detailed procedure, refer to the leaflet shipped with the cable.
Warning: Failure to apply the grease will void the warranty.
6. Connect the CAB9P cable to the S1100w device.
To properly install the cable connector on the device , you have to turn until you feel a
positive click.
7. Plug the BNC video connector of the CAB9P cable on the camera.
8. Perform the serial connection to the camera, if required (see page 27).
9. If you are using a junction box, route all wires to it first; then route the wires from the
box to the target device.
10. Power up the transmitter.
26 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Installing an Antenna
If you bought a high gain antenna, install it after the S1100w is in place. The antennas
provided by Verint Video Intelligence Solutions are designed to be mounted on a mast or
pole of 2–3 inch (5–7.5 centimeter) diameter.
To install an external antenna:
1. Install the antenna above the S1100w device. If you bought your antenna from Verint
Video Intelligence Solutions, use the supplied pole mount bracket.
2. Screw the SMA connector of the antenna cable to the S1100w antenna port and tighten
it with a 0.25-inch (0.6 centimeter) wrench.
Warning: Do not over-tighten to avoid damaging the connector. The recommended
torque is 8 lb.-in. (100 N-cm). You could use a calibrated SMA torque wrench
(for instance, from the Pasternack company, available at
www.pasternack.com).
3. Apply two or three layers of electrical tape around all RF connections.
The antenna cable and connectors are weather-tight; however, vibration caused by the
wind will over time loosen the connectors and reduce the efficiency of the gaskets. The
electrical tape will prevent this situation.
4. Carefully align the antennas of the S1100w and access point so that they have a clear
RF line of sight.
5. To improve the signal level between both devices, use the antenna alignment utility
from SConfigurator.
Performing the RS-422/485 Serial Connection
The Nextiva edge devices support only the RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 asynchronous
protocols. For any other protocol, you may need a converter.
Warning: At any time there must be only one serial peripheral connected to the edge
device. For instance, when configuring the device through a COM port of the
computer, you must unplug any RS-422/485 peripheral.
RS-422/485
You use the CAB9P cable to properly connect the device to an RS-422 or RS-485 peripheral.
Here is the wiring scheme for the four-wire RS-422 or RS-485 protocol:
Cable Peripheral
Signal name Wire pair Wire color Signal name
Rx+ green/black green Rx+
Rx- black RxTx+ yellow/black yellow Tx+
Tx- black TxSignal ground brown/black brown Signal ground
Signal ground black Signal ground
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 27

3: Configuring and Installing the Device
For example, here is an S1100w transmitter connected to a PTZ camera in an RS-422
2-wire context:
BNC barrel
connector
Rx+ / Rx-
Signal ground
Coax cable
Target device (PTZ)
Power (red and black)
Tx+ / Tx(yellow and black)
Status
Rx+ / Rx(green and black)
Signal ground
(brown and black)
For a two-wire, half-duplex RS-485 connection:
1. Use the following wiring scheme:
Cable Peripheral
Signal name Wire pair Wire color Signal name
Data+ green/black green Data+
Data- black DataSignal ground brown/black brown Signal ground
Signal ground black Signal ground
2. Set the line driver to the 485h-f value (see page 38).
RS-232
For an RS-232 connection, use the following wiring scheme to plug the device to the
peripheral, using the DB-9 connector on the CAB9P cable:
DB-9 pin number Cable signal name
2RxD
3TxD
5 Signal ground
7RTS
8CTS
28 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
The numbering of the pins on the DB-9 connector is:
Configuring the I/Os
To program alarms (or events) or use the audio features of the S1100w device, you need
the CAB8P cable assembly. For detailed pinout information, see page 55.
The S1100w supports two inputs and one output. Each signal has a dedicated purpose:
Input 1—Either a transparent alarm link in a point-to-point configuration or with a video
management software, or PTL (push-to-listen) audio transmission mode.
Input 2—Push-to-talk (PTT) audio transmission mode.
Output—Relay for the input 1 signal in point-to-point alarm mode.
You cannot program PTT/PTL audio and alarms at the same time, since input 1 is used in
both contexts.
Since the S1100w transmitters are mostly used with a video management software, you
will perform most configuration and activation steps in it. Otherwise, in a point-to-point
connection, you use SConfigurator for setup.
Audio
Tw o transmission modes for audio data are available, provided audio is supported
everywhere in your system:
Full duplex—Data is transferred in both directions simultaneously. The I/Os are
available for alarms.
PTT—The push-to-talk mode allows you to control audio communication between two
devices.
When creating a point-to-point connection between an S1100w transmitter and an S1970e
receiver in SConfigurator, you set the transmission mode in the Connection Creator window.
To activate the audio transmission channel, you must trigger an activation switch (for
example, a button) that is based on the short ing of the al arm input 2 and alarm ground
signals. If the PTT switches of both the transmitter and receiver are activated at the same
time, the receiver will have precedence: Audio will be transferred from the S1970e receiver
to the S1100w transmitter.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 29

3: Configuring and Installing the Device
Here is a typical PTT application in a point-to-point context:
S1100w
S3100
S1970e-R
In 2 and Gnd
signals
PTT
Audio Out
signal
Audio In
signal
In 2 and Gnd
terminals
PTT
Audio Out
connector
Audio In
connector
The S1100w device supports the line-in input type. With SConfigurator, ensure that the
input type in the Audio tab reflects this value.
Regardless of the transmission mode, the connections for the audio equipment are:
You plug the audio input signal of the device to the Line-out connector on a
pre-amplifier. Then you plug a microphone on the pre-amplifier.
You plug the audio output signal of the device to the Line-in connector on an amplifier.
Then you plug a speaker on the amplifier.
The audio input/output specifications are:
Mode Gain Impedance Frequency range
Input -20 to -3 dBV 30 kohm
Output -45 to -3 dBV 8 ohms min.
300–3600 Hz
Alarms
The S1100w device can generate and receive alarms. To generate an alarm, you have to
short the alarm input 1 and alarm ground signals on the S1100w device.
When receiving an alarm in a point-to-point configuration, the relay output is configured to
close the contact between the two alarm output pins (up to 48V at 100 mA). For example,
with an S1970e receiver:
S1100w
S3100
Alarm
Alarm
Ground
Alarm Out+ Alarm Out-
Input 1
Event sensor Event sensor
S1970e-R
Input 1 Ground Relay Relay
With SConfigurator, you activate the alarm process by checking the Forward I/O box in the
Connection Creator window.
30 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Updating the Firmware
You can update the firmware of the S1100w devices with the SConfigurator utility or a video
management software; for the detailed procedure, refer to the documentation of the
software. The latest firmware files are available on the Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
extranet (Technical Support, then Downloads, then Firmware Upgrades).
Warning: Firmware downgrade is not supported on any device. If you perform a
downgrade, any problem encountered will not be covered by your product
warranty.
The preferred method to update the firmware is through an IP network connection. If this
update procedure fails:
1. Do not reboot the device, and restart the same procedure immediately.
If you reboot the device before proceeding with the update procedure, it will stop
responding.
2. If the problem persists, perform a firmware update through the RS-232 serial port.
You should take into consideration the following facts regarding firmware update using the
IP network:
It can be deactivated in the command line interface (CLI).
Ensure that the IP link is stable before starting the procedure; therefore it is not
recommended to perform it over the Internet.
Performing a Hardware Reset
You can perform a hardware reset on the transmitter. This operation will assign the factory
default settings to the S1100w (listed in Appendix A on page 51). All user-defined values
will be lost. To reset the device parameters to their factory defaults without performing a
hardware operation, see page 49.
Following a reset, you will need to reprogram the S1100w device (for instance, its IP
address, VSIP port, and wireless passkey) for proper operation within its network or with its
wireless access point.
To perform a hardware reset:
1. Power down the device.
2. Short the TxD and CTS wires together (to locate them, see page 54).
3. Power up the device and wait until the normal boot-up sequence is completed.
4. Remove the short on the TxD and CTS pins.
The device is ready for use with the factory default settings.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 31

3: Configuring and Installing the Device
Red/Blue Display
If an S1100w transmitter currently streaming video to a management software loses its
connection to a camera, the corresponding display tile in the software will present an error
sequence, typically a half red, half blue pattern.
Quality of Service
Quality of Service (QoS) is a set of low-level networking protocols giving higher priority to
more important data flows while ensuring that the less important ones do not fail. QoS is an
essential technology for organizations rolling out a new generation of network applications
such as real-time voice communications and high-quality video delivery.
In the Nextiva edge devices, the two available QoS flavors are Type of Service (ToS) and
Differentiated Service Code Points (DSCP).
For QoS to be taken into account, the network infrastructure equipment (switches and
routers) must support one of these protocols. If any of these devices does not support QoS,
the QoS data will simply be processed as traditional non-QoS data. Furthermore, all Nextiva
edge devices on a network must support the same QoS protocol (or no protocols at all).
You can set a priority flag to three data types coming out of an edge device: video, audio,
and control. A QoS-enabled switch (or router) uses this flag to determine how the current
data compares to what is currently going through it.
To set the QoS values, you need to go in the command line interface (CLI) of the device,
access the Advanced > Quality of Service menu. For the procedure to access the CLI, see
page 35.
Status LED
The system status LED is a bicolor (green-red) LED providing detailed information on the
current state of the device.
Condition Indication
Steady red for 5 sec. The device is powering up.
Flashing red (1 sec. intervals) The IP address of the device is already assigned to another device
Flashing green (3 sec. intervals) The firmware has started, but RF communication is not
Flashing green (1 sec. intervals) The firmware has started, RF communication is established, but no
Flashing green (0.2 sec. intervals) The firmware has started, RF communication is established, and
Three consecutive red blinks
every 2 sec.
Flashing green-red (1 sec.
intervals)
Flashing red (0.1 sec. intervals) The device is being identified.
* At least one of them must be transferred to obtain the LED condition.
32 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
in the network.
established.
video/serial* data is transmitted.
video/serial* data is transmitted.
No video source is detected and no video is transmitted.
The device is undergoing a firmware update or is in backup mode.

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
The following power-up conditions on the system status LED are abnormal:
LED not lit—Check the power supply and cabling. If power is available and the LED
stays off, call Verint Video Intelligence Solutions customer service for assistance.
Steady red LED persisting more than 10 seconds—There is an internal error that
prevents the device from starting normally. Power down the device, wait 30 seconds,
then power it up. If the condition persists, call Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
customer service.
Flashing green-red LED not during a firmware update—The device requires a new
firmware with a serial connection.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 33

34 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Setting Parameters with
the CLI
The S1100w devices come with a simple command line interface (CLI) for configuration
purposes. The CLI is hierarchically organized, with menus, sub-menus, and individual
options representing configuration parameters. Only the par ameters that you are likely to
change are described.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 35

4: Setting Parameters with the CLI
Getting Started
You can access the CLI with:
A serial connection and the SConfigurator console
A network connection and the Telnet utility
To access the CLI with the SConfigurator console:
1. Connect the S1100w device to a COM port of the computer using the DB-9 connector of
the CAB9P cable.
2. Start SConfigurator.
The SConfigurator window appears.
3. From the General tab, click Console.
The Verint Console window appears.
4. In the Connect using list, select the COM port used to communicate with the device.
5. Click Connect.
The CLI main menu appears.
The CLI has a timeout that is triggered after three minutes of inactivity. When the
timeout occurs:
You lose access to the command line.
The “Thank you for using the Verint CLI” message appears at the command line.
The Verint Console window becomes disabled.
The Disconnect button switches to Connect.
6. To reactivate the CLI after a timeout, click Connect.
36 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
7. To work through the CLI menu structure, follow these guidelines:
To ex ecute a command or open a menu, type in the corresponding letter or number,
then press Enter.
To return to the previous menu, enter p.
8. To end the CLI work session:
a. Save the settings by entering s at the main menu, then pressing Enter.
b. Exit the CLI by entering q at the main menu, then pressing Enter.
Depending on the changed settings, the device may perform a soft boot.
c. Close the Verint Console window.
Warning: Do not use the Disconnect button to exit the CLI. Clicking it does not free
the RS-232 connection and does not save your settings.
To enter the CLI with Telnet:
Note: Ensure that your computer and the S1100w device are in the same IP subnet.
1. Open SConfigurator.
2. In the Units tab, discover the devices.
3. Select the desired device, then click Telnet.
The CLI main menu appears in the Verint Console window.
Serial Port
The Serial Port menu enables you to establish the proper settings ensuring compatibility
between the S1100w and the serial equipment with which it is connected (for example, PTZ
camera). For more information about the serial port settings of this hardware product, refer
to its user guide or contact your manufacturer.
The S1100w transmitters have one configurable serial port for communicating with an
external device.
The parameters for the serial port are:
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 37

4: Setting Parameters with the CLI
Bit Rate
The bit rate represents the data rate at which the target product operates. Possible values
range from 1200 bps to 230,400 bps.
Parity
The serial equipment may have a parity of odd or even. It may also not have parity check;
most communication devices do not use parity.
Line Driver
By default, your device automatically detects the electrical line interface of the serial port
(RS-232 or RS-422/485). However, if your device cannot properly detect the electrical level
(for instance when there is too much noise on the line or too much signal attenuation due
to excessive cable length), you can use the line driver setting to force its electrical line
interface.
Here are the possible line driver settings, where -d indicates that the auto-detection mode
is activated, and -f, that the line driver is forced:
Setting Description
232f-d RS-232 auto-detected, full-duplex operation
232f-f RS-232 forced, full-duplex operation
485f-d RS-422/485 auto-detected, 4-wire full-duplex, RS-485 operation
485h-d RS-422/485 auto-detected, 2-wire half-duplex, RS-485 operation
485h-f RS-422/485 forced, 2-wire half-duplex, RS-485 operation
485f-f RS-422/485 forced, 4-wire full-duplex, RS-485 operation
422f-d RS-422/485 auto-detected, 4-wire full-duplex, RS-422 operation
422f-f RS-422/485 forced, 4-wire full-duplex, RS-422 operation
Warning: If the line driver is forced to an RS-422/485 setting, you will not have access to
the CLI unless you use an RS-485 to RS-232 converter or perform a hardware
reset (described on page 31).
RS-422/485 Operating Mode
The operating mode setting enables you to establish the way your RS-422/485 serial
equipment will interface with the S1100w device. The supported modes are:
RS-422 4 Wires
RS-485 4 Wires
RS-485 2 Wires
38 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Access Management
The Access Management menu takes care of user accounts (user names and passwords)
and device security.
User Accounts
The User Accounts menu enables you to protect the configuration of the device by
restricting its access with a user name and a password. Once the user account mode is
activated, you need the user name/password combination to access the CLI through a
serial connection or a Telnet session.
Security
The Security menu holds commands relative to the protection of the device.
It allows you to control:
Firmware updates through the IP network
Access to Telnet
SSL
IP Firmware Update
You can prev ent firm w are updates to be perfor med on you r device through the IP network.
By default, this type of update is allowed.
For more information about firmware updates, refer to the SConfigurator User Guide.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 39

4: Setting Parameters with the CLI
Telnet Session
By default, you can use Telnet to access the CLI of your device. To improve the security of
your system, you may prohibit such an access. In this case, the CLI will only be accessible
through a serial connection (with the SConfigurator console).
Global Security Profile
If you activate the global security profile, the device will only accept secure SSL
connections. It also means that you cannot access the device anymore with Telnet and you
cannot perform firmware updates through the IP network on it.
SSL Passkey
T o secure a device with SSL, y ou need to provide a passkey. This passkey must be the same
for all devices and the software tools to allow proper secure communication between them.
It is recommended to perform this operation in SConfigurator (version 2.55 or higher for
the tool and the device) or nDVR (in the Resource Administration Tool). Otherwise, to build
a truly secure system, you should access the CLI through a physical serial connection, not
through Telnet, therefore avoiding eavesdropping on the network.
Network
The Network menu allows you to configure several parameters to ensure the compatibility
between the S1100w and its IP network.
For more information about these settings, contact your network administrator.
DHCP Configuration
DHCP (dynamic host configuration protocol) allows devices and computers connected to a
network to automatically get a valid network configuration from a server. For more
information about DHCP, see Appendix C on page 57.
You can set this option only if the S1100w is connected to a network that uses a DHCP
server.
Local IP Address
The IP address is the identifier of the S1100w on the network. Its format is a 32-bit
numeric address written as four numbers separated by periods. Each number is in the
0–255 range. Each device on a network must have a unique IP address.
40 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Subnet Mask
The subnet mask is the binary configuration specifying in which subnet the IP address of
the device belongs. A subnet is a portion of a network that shares a common address
component. On TCP/IP networks, a subnet is defined as a group of devices whose IP
addresses have the same prefix. Unless otherwise specified by your network administrator,
it is recommended to use a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.
Gateway
The gateway represents a network point that acts as an entrance to another network.
Warning: Never use the IP address of the device as the gateway value.
Ping Request
Ping is a basic Internet program that allows you to check that a particular IP address exists
and can accept requests.
To ping a specific device:
1. In the Ping Request Send Buffer Size parameter, enter the buffer size (in bytes).
2. In the Ping Request Target parameter, enter the IP address of the device.
3. Execute the Ping Remote Address command.
Wireless Communication
The Wireless Communication menu contains a set of parameters relative to r adio frequency
(RF) and wireless security. The parameter set varies depending on the MAC mode (SPCF or
802.11).
The parameters for SPCF are:
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 41

4: Setting Parameters with the CLI
The parameters for the 802.11 protocol are:
Basic Parameters
Passkey (SPCF only)
The wireless passkey is a unique case-sensitive identifier enabling secure and encrypted RF
communication between the S1100w device and its access point. The passkey size varies
depending on the key entry format (presented on page 46):
32 digits if hexadecimal
16 string characters if string (default)
For the wireless connection to be secure, do no enter a known name (like a street name),
but instead use a mix of digits and letters. Furthermore, do not disclose the passkey. The
connection security is based on the secrecy and uniqueness of the passkey.
It is a good practice to change the default passkey during the configuration process.
MAC Mode
The available MAC (Media Access Control) protocols are:
SPCF—The proprietary protocol that uses AES encryption (with key rotation) over the
wireless link to secure communication between the devices and resolve “hidden node,”
quality of service, range, and problems inherent to 802.11 wireless networking
products. The access point for an S1100w in SPCF is the Nextiva S3100.
IEEE 802.11—The standard protocol for using commercial 802.11-compliant access
points.
SSID (Service Set ID) (802.11 only)
The service set ID is the name of the wireless network; it is a 0–32 character string.
The service set ID must be the same in the S1100w and in the access point.
42 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
WPA Authentication Method (802.11 only)
The S1100w in 802.11 mode supports the following authentication mechanisms:
WPA-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access version 1 in Pre-Shared Key mode, also known as
personal mode)
WPA2-PSK (WPA version 2, also known as 802.11i, in personal mode)
WPA-EAP-TLS (WPA in Enterprise mode with Extensible Authentication Protocol and
Transport Layer Security)
WPA2-EAP-TLS
WPA-EAP-TTLS (MSCHAPv2) (WPA in Enterprise mode with Extensible Authentication
Protocol, Tunneled Transport Layer Security, and the Microsoft version of the Challenge
Handshake Authentication protocol)
WPA2-EAP-TTLS (MSCHAPv2)
WPA-PEAP-TLS (MSCHAPv2) (WPA in Enterprise mode with Protected Extensible
Authentication Protocol, Transport Layer Security, and the Microsoft version of the
Challenge Handshake Authentication protocol)
WPA2-PEAP-TLS (MSCHAPv2)
You can also choose to not use an authentication method.
The authentication method must be the same in the S1100w and in the access point.
Encryption Algorithm (802.11 only)
The encryption algorithm indicates how wireless data is encrypted. The following algorithms
are available:
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)—This encryption type is available only when the
authentication method is NONE.
AES-CCMP (Advanced Encryption Standard-Counter Mode CBC-MAC Protocol)
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol)
WPA-AUTO-SELECT—The encryption type is automatically chosen.
You can also choose to not use an encryption algorithm.
The encryption algorithm must be the same in the S1100w and in the access point.
WPA Encryption Passphrase (802.11 only)
The encryption passphrase is an identifier (from 8 to 63 characters) used to secure the RF
communication between the S1100w device and its access point when the authentication
method is any WPA or WPA2 flavor.
For the wireless connection to be secure, do no enter a known name (like a street name),
but instead use a mix of digits and letters. Furthermore, do not disclose the passphrase.
The connection security is based on the secrecy and uniqueness of the passphrase.
It is a good practice to change the default passphrase during the configuration process.
The passphrase must be the same in the S1100w and in the access point.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 43

4: Setting Parameters with the CLI
WPA Private Key Passphrase (802.11 only)
The private key passphrase is a case-sensitive identifier (from 0 to 63 characters) used to
secure the access to an 802.11 certificate.
WPA Negotiation Timeout (802.11 only)
The negotiation timeout is the maximum time (in seconds) given for the device to be
authenticated.
WPA Reauthentication Period (802.11 only)
The reauthentication period is the frequency (in days) at which the authentication process
will be re-activated with new keys, if a WP A2 authentication method was selected.
WPA EAP Login (802.11 only)
The EAP login is a case-sensitive identifier (from 0 to 63 characters) used to recognize the
device when a TTLS or PEAP authentication method was selected.
WPA EAP Password (802.11 only)
The EAP password is a case-sensitive password (from 0 to 63 characters) used to secure
the authentication process when a TTLS or PEAP method was selected.
WEP Key (802.11 only)
The WEP key is a case-sensitive identifier used to secure the RF connection when the
authentication method is NONE; this parameter is not displayed in the other contexts.
The size of the key varies depending on the WEP scheme:
5 string or 10 hexadecimal characters in 64-bit WEP
13 string or 26 hexadecimal characters in 128-bit WEP
16 string or 32 hexadecimal characters in 152-bit WEP
The WEP key must be the same in the S1100w and in the access point.
RF Band
The following frequency bands are available:
802.11a (5 GHz OFDM)
802.11g (2.4 GHz OFDM)
public safety (4.9 GHz OFDM)
Channel
The RF channel used by the S1100w device is determined by its wireless access point.
However, in a non-DFS context, you can specify an initial value for the roaming process by
which the S1100w will find its access point; be aware that this initial channel may not be
the one used by the access point.
44 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
In a 4.9 GHz band context, the list of channels varies depending on the chosen bandwidth.
For the list of channels, see page 7; for the channel bandwidth parameter, see next.
Channel Bandwidth
In the 4.9 GHz band, the bandwidth can be fragmented to allow 5- and 10-MHz channels;
the default channel width is 20 MHz. This parameter only appears if the RF band is 4.9 GHz.
The list of available channels varies depending on the chosen bandwidth.
Tx Bit Rate
The transmission bit rate is the data rate at which the device operates. A high bit rate
reduces the effective distance between two functional devices.
When an S1100w connects to its master for the first time, it automatically receives the best
possible value (the Auto value), with a default RF margin set to 15 dB (to change the
margin, see page 47).
Once the device is operating properly, Verint strongly recommends to change the
configured bit rate from Auto to the actual bit rate of the connection. This way, the wireless
communication will be more stable in the presence of changing atmospheric conditions or
other RF interferers. To know the actual bit rate of the connection, look in the Advanced >
Communication Status and Statistics > Wireless Status menu. If the quality of the RF link
degrades severely, the actual bit rate could be lower that the manually configured one.
The available bit rates for the S1100w device are:
Band Channel width Bit rates (Mbps)
2.4 GHz N/A 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54
4.9 GHz 5 MHz 1.5, 2.25, 3, 4.5, 6, 9, 12, and 13.5
10 MHz 3, 4.5, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, and 27
20 MHz 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54
5 GHz N/A 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54
Antenna Gain
If you enter the gain of the antenna you connect to the device, the S1100w will be able to
automatically change its transmission power so that the total power (device and antenna)
does not exceed the maximum value established by your country’s regulations. For more
information about the maximum antenna gain you can use, see page 19.
ISO Country Code
You must assign the proper country of operation to the device, so that it will:
Comply to the DFS/TPC regulations, if applicable
Respect the EIRP rules
Use the proper set of frequency channels
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 45

4: Setting Parameters with the CLI
Advanced Parameters
The Advanced Wireless Setup menu contains specialized RF features. The parameter set
varies depending on the MAC mode (SPCF or 802.11).
The parameters for SPCF are:
The parameter for the 802.11 protocol are:
Passkey Entry Format
The wireless and WEP passkeys can have two formats: String (default) or Hexadecimal.
Tx Power Scale
The transmission power scale indicates the level of emitting power of the device radio. The
available values are:
Maximum—The maximum allowed.
50%—The power is reduced by 3 dB.
25%—The power is reduced by 6 dB.
12.5%—The power is reduced by 9 dB.
Minimum—The power is set at 3 dBm.
Sensitivity Threshold (SPCF only)
The sensitivity threshold is the minimum signal level perceived by the radio of the device.
Reducing the sensitivity of the radio enables unw anted “noise” to be filtered out. A safe
value is 10 dB below the current received signal level (displayed in the Advanced >
Communication Status and Statistics > Wireless Status menu).
The default value, Normal, represents the most sensitive context. You must be careful not
to reduce the sensitivity to a level where the device would not “hear” its legitimate
correspondent.
46 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Minimum Margin (SPCF only)
The minimum margin is used when the transmission bit rate is set to Auto (see page 45). It
represents the difference in dB between the actual signal received by the device and the
minimum signal required by a given bit rate to correctly receive data on the RF link. The
default minimum margin is 15 dB.
Indoor/Outdoor RF Regulation
Depending on the country of operation and the chosen frequency band, the device is
allowed to operate indoors only , outdoors only, or either indoors or outdoors. The frequency
channels available in the indoor-only regulation are different from those assigned to
indoors/outdoors; the same goes for the outdoor-only channels.
Note: Under the RF regulation, a device programmed to be used only indoors must not be
installed outdoors, and vice versa.
To know which frequency channels are available in your country of operation in each of the
three operation modes, refer to the Wireless Frequency Plan document located on the
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions extranet (Technical Support, then Downloads, then
Utilities and Tools).
The default factory value for most countries is indoor/outdoor.
System Status
The system status information indicates the current values of internal S1100w parameters,
including the firmware version.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 47

4: Setting Parameters with the CLI
Advanced
The Advanced menu holds a series of advanced setups mainly used by Verint Video
Intelligence Solutions technical support. Some of these parameters are available through
SConfigurator or a video management software.
Identifying a Device
To recognize an S1100w among a large set of devices, you can make its LED flash red
rapidly.
To identify an S1100w device:
1. From the main menu, choose Advanced, then press Enter.
2. Enter i to make the LED flash red. Re-enter i to set the LED to its previous state.
3. Enter p until you are in the main menu.
4. Enter q to exit.
Setting the VSIP Port
The VSIP port (accessible through the VSIP menu) is a communication port used for
protocol messaging between your computer and Nextiva devices. The default VSIP port of
all devices is 5510.
Note: VSIP ports 9541, 65500, and those under 1024 are reserved and should not be used,
not even for serial port, video, or audio communication. The maximum value is
65535.
48 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Conducting Site Surveys
The S1100w device allows you to perform site surveys on your RF network. A site survey
scans all frequency channels, evaluate the interference level in each channel, and allows
you to choose the channel with the less interference.
You can perform the following operations relative to RF site surveys:
Specify the number of consecutive surveys to perform
Start and stop a site survey
Look at the last survey report
Reset the survey database
To conduct site surveys:
1. From the main menu, choose Advanced > Communication Status an d Statistics >
Wireless Status, then press Enter.
2. Perform the required operations.
Note: During the site survey execution, the RF link will be momentarily broken
(duration varies depending on the number of iterations). The link is automatically
restored when the survey is finished.
3. Enter p until you are in the main menu.
4. Enter q to exit.
Load Default Configuration
The Load Default Configuration command, located in the main menu, resets all device
parameters to their factory settings (described in Appendix A on page 51). All user-defined
values will be lost. To reset the parameters to their factory defaults with a hardware
operation instead, see page 31.
Following a reset, you will need to reprogram the S1100w device (for instance, its IP
address and VSIP port) for proper operation within its network.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 49

4: Setting Parameters with the CLI
Reboot System
The Reboot System command, located in the main menu, performs a soft boot on the
S1100w. A system reboot clears all unsaved changes in the CLI and returns to your preset
configuration.
50 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Factory Default
Configuration
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 51

A: Factory Default Configuration
The S1100w is programmed at the factory with the following configuration:
Type Configuration
Serial port
Access management
Network
Video settings (North America)
Video settings (Europe)
Wireless Communication (North America)
Wireless Communication (Europe)
VSIP
Bit rate: 4800 bauds
Data bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop bit: 1
Line driver: auto-detected
RS-422/485 operating mode: RS422 4 Wires
User name: USERNAME
Password: PASSWORD
User accounts: Disabled
Telnet sessions: Enabled
IP firmware update: Enabled
Global security profile: Disabled
SSL passkey: <empty>
DHCP configuration: Disabled
IP address: 169.254.*.* (MAC address of the device)
Subnet mask: 255.255.0.0
Gateway: 0.0.0.0
Target frame rate: 30 fps
Target bit rate: 800 kbps
Maximum quantizer: 24
Resolution: CIF (352 x 240)
Video standard: NTSC
Target frame rate: 30 fps
Target bit rate: 800 kbps
Maximum quantizer: 24
Resolution: CIF (352 x 240)
Video standard: PAL
Wireless passkey: ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP
Frequency band: 802.11a (5 GHz OFDM)
Channel: Auto
Tx bit rate: Auto
Antenna gain: 13 dBi
Country: USA
Tx power scale: Maximum
Wireless passkey: ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP
Frequency band: 802.11a (5 GHz OFDM)
Channel: Auto
Tx bit rate: Auto
Antenna gain: 13 dBi
Country: United Kingdom
Tx power scale: 50% (-3 dB)
VSIP Port: 5510
VSIP Multicast IP Address: 224.16.32.1
VSIP Discovery IP Address: 255.255.255.255
52 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Cable Connections
The wireless devices use the following two cables:
CAB9P—Power, video, and serial data communication
CAB8P—Audio and alarms
Note: To determine the Rx and Tx pins of your equipment, see Appendix D on page 59.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 53

B: Cable Connections
CAB9P
The CAB9P cable supplied with the wireless devices is used for power, video, and serial
communication (that is, PTZ data with the RS-422/485 protocol, or RS-232 communication
with the DB-9 connector).
The mating side view of the cable is, using the RS-232 signal terminology:
VG
CAM4/
MON
7
6
TxD
(Tx+)
5
VIN RT
1
SG
RxD
(Rx-)
9
VIN
8
2
CTS
(Rx+)
3
RTS
(Tx-)
Here is the pinout of the CAB9P cable:
4
where:
The RS-422/485 signal terminology is enclosed in parentheses.
The other wire of each twisted pair is enclosed in square brackets.
N.C. means not connected.
54 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Based on the pinout, the wiring scheme for an RS-232 connection to a computer is:
Cable Computer
Signal name Wire pair Wire color Signal name
CTS green/black green not connected
RxD black RxD
TxD yellow/black yellow TxD
RTS black not connected
SG brown/black brown SG
SG black
SG
CAB8P
The CAB8P cable is used for audio and alarms. The mating side view of the cable is:
Alarm
In 1
Audio
Out
5
Audio
Ground
4
Alarm
Out B
6
7
Alarm
Ground
8
Alarm
Out A
1
Alarm
In 2
2
Audio
In
3
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 55

B: Cable Connections
Here is its pinout:
where:
The other wire of the twisted pair is enclosed in square brackets.
56 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

DHCP Support and
APIPA
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) allows devices and computers connected to a
network to automatically get a valid IP configuration from a dedicated server.
The APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing) scheme, available on the Windows operating
systems, enables a device to assign itself a temporary IP address.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 57

C: DHCP Support and APIPA
At startup, an edge device searches for a valid IP network configuration. The device
requires this configuration prior to starting its functions. The network configuration for
Nextiva devices consists of:
An IP address
A subnet mask
A gateway
The device first looks in its local memory. If no configuration is found, it tries to contact a
DHCP server. If DHCP configuration fails—if the device does not find a server or if it cannot
get a configuration from it within one minute—the device assigns itself temporary network
settings based on the APIPA addressing scheme. This scheme allows a device to find a
unique IP address until it receives a complete network configuration, either manually or
from a DHCP server.
A device in APIPA mode does not reside on the same subnet as the other devices on the IP
network; therefore, it may not be able to see them or be visible to them. Devices use the
following temporary APIPA configuration:
IP address: 169.254. *. *
Subnet mask: 255.255.0.0
Gateway: 169.254. *. *
The *. * portion is based on the MAC address of the device.
A device is in APIPA mode:
The first time it boots up
After receiving a duplicate IP address
After a hardware reset
When the DHCP server does not have any available IP addresses
After loading the default settings
DHCP configuration is automatically disabled:
After a firmware upgrade
After a factory reset
58 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

DTE and DCE
Connections
Before connecting a Nextiva edge device to other RS-232 serial equipment, you need to
determine if they are DTE (data terminal equipment) or DCE (data communication
equipment).
Here are examples of both equipment types:
DCE—Nextiva edge devices, modems
DTE—Computers, switches, multiplexers, cameras, keyboards
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 59

D: DTE and DCE Connections
In the following descriptions:
Voltage is measured when no data is transferred on the Rx and Tx pins.
-X volts represents a negative voltage value.
Data Terminal Equipment
DTE modules have the following electrical-level setup:
Pin number on the DB9 connector Signal Measured voltage
3Tx-X volts
2Rx0 volt
Tx
Rx
Ground
-X volts measured for the Tx pin
0 volt measured for the Rx pin
Data Communication Equipment
DCE modules have the following electrical-level setup:
Pin number on the DB9 connector Signal Measured voltage
3Tx0 volt
2Rx-X volts
Tx
Rx
Ground
-X volts measured for the Rx pin
-0 volt measured for the Tx pin
60 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Connecting DTE and DCE
When connecting two modules of the same type, you have to cross the data wires to create
proper communication. On the other hand, when connecting a DTE with a DCE, a straight
cable is required.
Rx
Rx
DCE DCE
Tx
Tx
Rx
Rx
DTE DTE
Tx
Rx
Tx
Rx
DTE DCE
Tx
Tx
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 61

62 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Surge Protection
Voltage and current surges can be induced by lightning strikes or power line transients. In
the real world, under the right circumstances, these surges can reach sufficiently high
levels to damage almost any electronic equipment. Therefore you need to add protection to
your devices.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 63

E: Surge Protection
The S1100w provides basic surge protection on all electrical lines. If you are installing the
equipment in a lightning prone or heavy lightning environment, or in a site where large AC
mains power fluctuations are a common occurrence, Verint strongly recommends that you
add additional external surge protection to all vulnerable connections. Vulnerable
connections are those that run for a long distance between the S1100w device and the
connected equipment.
The video camera is usually within a short distance of the S1100w transmitter; the S1100w
interface cable can be routed directly into the camera housing. Therefore, the video line
(and the serial port if using a PTZ camera) will seldom need additional protection. The
power feed usually runs down the mounting mast or wall for more than 20 feet
(7.6 meters); it is a good candidate for additional protection in a surge prone environment.
This protection will benefit both the camera and the device.
Excellent international sources for external surge protection equipment and general surge
and lightning protection information are:
Polyphaser Corporation—www.polyphaser. com
Citel inc.—www.citelprotection.com
Transtector—www.transtector.com
For the curious mind, a surge protector helps to clamp the surge to safe levels and divert its
energy to the earthing point, preventing device damage. Experienced installers know that
an effective surge protection must be installed with proper earthing and grounding.
64 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Separation Between
Devices Using Adjacent
Channels
Wireless interference can occur between wireless cells using adjacent frequency channels
(for example, channels 149 and 153 in the 5 GHz band). Therefore, it is preferable to avoid
using adjacent channels. However, if your setup requires you to, you must follow specific
guidelines regarding minimum distances between antennas and signal level margin.
Note: In the 2.4 GHz band, the adjacent channel term applies only to the three
independent channels (1, 6, and 11).
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 65

F: Separation Between Devices Using Adjacent Channels
If using adjacent frequency channels in a non-DFS environment, you should respect
guidelines relative to the minimum separation between device antennas, to avoid
interference.
T o reduce radio interference possibilities between two adjacent channels, you should ensure
that the maximum margin between the emission of the two wireless cells is 25 dB. To meet
this objective, perform a site survey and apply minimum distance guidelines.
Performing a Site Survey
The difference in signal level between two adjacent cells must be less than or equal to
25 dB. If this margin is higher than 25 dB, there will be too much interference in the two
adjacent wireless cells. To calculate this margin, you need to perform a site survey; for
more information, see page 49. Here is an example of a 25 dB margin between channels 8
and 9 in the 4.9 GHz band:
Interference between the two channels
Consider the following setup in the 4.9 GHz band with 5-MHz bandwidth, where Cell B uses
channel 6 and you are trying to add Cell A on channel 3 (adjacent to channel 6):
B3B2
A2
A3
A1B1
Cell B Cell A
To determine if this setup is feasible, you need to conduct a site survey on device A1 (the
master device in Cell A), then calculate the margin between the two cells. During the site
survey, device A1 will find the other five devices. With the provided signal levels, you need
to check if S2 - S1 <= 25 dB, where:
S1 is the lowest signal level in the wireless cell of the device performing the site survey
(A1 in the example).
S2 is the highest signal level in the adjacent cell (Cell B in the example).
66 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
To calculate the emission margin between two adjacent wireless cells:
1. Open SConfigurator, then go to the Units tab.
2. Select the master device in the wireless cell you are adding, then click Telnet.
3. From the main menu of the command line interface (CLI), choose Advanced >
Communication Status and Statistics > Wireless Status, then press Enter.
4. For a thorough scan, specify 60 site survey iterations.
5. Start the site survey operation.
Note: During the execution, the RF link will be momentarily broken (duration varies
depending on the number of iterations). The link is automatically restored when
the survey is finished.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 67

F: Separation Between Devices Using Adjacent Channels
6. When the survey is complete, visualize the report. For example:
Devices found on channel 3
Devices found on channel 6
Device name
Signal level
This report provides the signal levels between device A1 and the other five devices in
the network.
B3B2
A2
-75
A3
-60
-70
A1
B1
-75
-45
Cell B Cell A
The lowest signal in Cell A is -75 (S1) and the highest signal in Cell B is -45 (S2). The
result of S2 - S1 (-45 - -75) is 30. Since the margin is higher than 25 dB, there will be
interference issues.
68 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Minimum Distances
To respect the 25 dB margin between two adjacent channels, in addition to performing a
site survey, you can use guidelines relative to minimum distances between the wireless
devices. By respecting them, you can assume that there will not be radio interference
between the devices.
Three physical setups are covered:
Side by side: On top:
Back to back:
The minimum separation between devices using adjacent channels is:
Setup 5 GHz (13-dBi antenna
with 40º beam width)
Side by side 43 feet (13m) 36.1 feet (11m) 55.8 feet (17m)
On top 13 feet (4m) 6.6 feet (2m) 6.2 feet (1.9m)
Back to back 7.8 feet (2.4m) 13.1 feet (4m) 15.7 feet (4.8m)
4.9 GHz (13-dBi antenna
with 40º beam width)
2.4 GHz (8.5-dBi antenna
with 60º beam width)
If you are using other antennas with narrower beam widths, the distances may be reduced.
For assistance, contact the Verint Video Intelligence Solutions Support group.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 69

F: Separation Between Devices Using Adjacent Channels
The following deployment scenarios respect these limitations:
Using only 5 GHz channels, all on the same side of a building:
5.8 GHz
165
5.3 GHz565.8 GHz
157
5.3 GHz645.8 GHz
149
5.3 GHz
52
5.8 GHz
161
5.3 GHz605.8 GHz
153
43 feet (13m)3 feet (1m) each
Notice that the devices using the adjacent channels 52 and 56 are separated by the
prescribed 43 feet (13m). However, you can intersperse other devices in-between, as
long as they do not use adjacent channels. This way, you can increase the device
density without encountering interference problems.
In the 4.9 GHz band, using only 5 MHz channels, all on the same side of a building:
4.9 GHz
3
4.9 GHz
7
4.9 GHz
9
4.9 GHz
11
4.9 GHz
4.9 GHz
13
4.9 GHz
6
4.9 GHz
8
4.9 GHz
10
12
36 feet (11m)3 feet (1m) each
Notice that the devices using the adjacent channels 7 and 6 are separated by the
prescribed 36 feet (11m). However, you can intersperse other devices in-between, as
long as they do not use adjacent channels. This way, you can increase the device
density without encountering interference problems.
In the 4.9 GHz band, using only 10 MHz channels, all on the same side of a building:
4.9 GHz
7
4.9 GHz
11
4.9 GHz
4.9 GHz
9
13
36 feet (11m)
3 feet (1m) each
Since only four channels are available, it is unavoidable th at two adjacent chan nels are
positioned next to each other.
70 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Using 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz channels, all on the same side of a building:
2.4 GHz
6
5.8 GHz
165
5.3 GHz
56
5.8 GHz
157
5.3 GHz
64
5.8 GHz
149
2.4 GHz
11
5.3 GHz
52
5.8 GHz
161
5.3 GHz
60
5.8 GHz
153
2.4 GHz
1
3 feet (1m) each 43 feet (13m)
56 feet (17m)
The devices using the adjacent channels 6 and 11 in the 2.4 GHz are separated by the
prescribed 56 feet (17m).
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 71

72 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

DFS and False Radar
Detection
Nextiva wireless devices operating in the European Union must adhere to the Dynamic
Frequency Selection (DFS) standard; this standard forces any RF transmitter to change
frequency channels if radar activity is detected on the current operating channel. If two
colocated wireless cells are communicating on adjacent channels, it is possible that the
interference between the two systems causes false radar detections. This side-effect is a
well-known industry-wide problem. New features in the wireless devices help minimize the
occurrence of false detection events.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 73

G: DFS and False Radar Detection
To avoid false radar detection caused by an adjacent channel, the signal level of an
potential interfering device on the first adjacent channel must not exceed -50 dB, -36 dB on
the second channel, and -32 dB on the third channel; for example, if you use channel 100,
104 is the first adjacent channel, 108 the second channel, and 112 is the third channel.
The design of wireless systems in a DFS context becomes difficult because not only can the
master devices cause an interference, but the clients and slaves on an adjacent channel can
also generate interferences that can cause false radar detection. There should be a reduced
number of cells available to limit the amount of possible false radar detections; it is strongly
suggested to limit the number of colocated cells to six.
The new features that help reduce the possibility of false detection events are:
Half Channel Selection
This new parameter of the command line interface (CLI) eliminates the possibility of
using adjacent channels. Enable this feature on all masters (S3100, S1100-R) in a new
installation to avoid the potential conflict of having two masters on adjacent channels.
By default this feature is disabled.
If this option is enabled, the channel list becomes:
100(DFS), 108(DFS), 116(DFS), 124(DFS), 132(DFS), 140(DFS), 254(Auto DFS/TPC)
The full channel list is:
100(DFS), 104(DFS), 108(DFS), 112(DFS), 116(DFS), 120(DFS), 124(DFS), 128(DFS),
132(DFS), 136(DFS), 140(DFS), 254(Auto DFS/TPC)
In the CLI: Wireless Communication > Advanced Wireless Setup > DFS/TPC Adjacent
Channel Removal
Slave Radar Detection Management
A new CLI parameter allows you to disable radar detection on slave or client devices,
therefore reducing the number of nodes that can detect radars. In a typical DFS
environment, the slave or client can detect a radar and alert its master to change the
frequency channel. This situation can cause a major problem because it increases the
number of nodes that can detect radars.
The default value is Disabled, meaning that the slave/client does not detect radars; in
this case, the slave/client EIRP is reduced from 30 to 23 dBm.
In the CLI: Wireless Communication > Advanced Wireless Setup > Enable Radar
Detection on Slave
Manual Channel Selection
You can now select the initial frequency channel that will be used by the master, with
SConfigurator or the CLI. This new feature does not disable radar detection on master
devices. This process will still take place and if a radar is detected, the device will go
through the regular DFS process (stop transmission on the channel, block this channel
for 30 minutes, and select a new channel in the available channel list).
74 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

S1100w Technical
Specifications
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 75

S1100w Technical Specifications
Here are the S1100w technical specifications:
Network RF interface Proprietary SPCF, 802.11
Modulation OFDM
Encryption 128-bit AES
Data rate
(max. burst rate)
Protocols Transport: RTP/IP, UDP/IP, TCP/IP, multicast IP
Video Compression MPEG-4-based
Frame rate NTSC: 1–30 fps programmable, 60 fields per second
Input 1 composite, 1 Vpp into 75 ohms (NTSC/PAL)
Serial Port Operating mode Transparent: supports any asynchronous PTZ serial
Electrical level Autolevel sensing RS-232 or RS-422/485
Alarm and Audio Alarm input 2 dry contact inputs (1 mA max.)
Alarm output 1 relay contact output (up to 48V at 100 mA)
Bidirectional audio Input: -20 to -3 dBV into 30 kohm
Power Input voltage 24V AC +/- 10%
Consumption 28 VA at 24V AC
Physical Enclosure NEMA 4X/IP 66 powder coat painted die-cas t alum inum
Size 9.0L x 3.9W x 3.8H inches (230L x 100W x 96H mm)
Weight 3.6 lb (1.65 kg)
Environment -22ºF to 122ºF (-30ºC to 50ºC)
Humidity 100% at 122°F (50°C)
Certification/
Regulation
USA FCC part 15 (subparts B and E)
Canada Industry Canada RSS-210, RSS-139, and ICES-003
Europe CE marked
6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, and 54 Mbps
Others: DNS and DHCP client, HTTP 1.1 (web server)
PAL: 1–25 fps programmable, 50 fields per second
protocol
Output: -45 to -3 dBV into 8 ohms min.
12V DC +/- 10% (optional)
12W (970 mA at 12V DC)
with wall mounting brackets
EN 300 328-2 V1.2.1 (2001-12)
EN 301 893 V1.2.3 (2003-08)
EN 301 489-01 V1.4.1 (2002-08)
EN 301 489-17 V1.2.1 (2002-08)
EN 60950:2000
Directive 2002/95/EC of the European Parliament and of
the Council of 27 January 2003 (RoHS)
76 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Glossary
This glossary is common to the Nextiva line of edge device products.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 77

Glossary
Access Point A communication hub for connecting wireless edge devices (S1100w) to a
wired LAN. The Nextiva access point is the S3100 product.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) An encryption standard used in the WPA2
authentication method.
APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing) A feature of Windows-based operating systems
that enables a device to automatically assign itself an IP address when there is no Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server available to perform that function. Also known as
AutoIP.
Bridge See Wireless Bridge.
Camera, IP See S2500e, S2600e Series, or S2700e Series.
CCTV (cLosed Circuit Television) A television system in which signals are not publicly
distributed; cameras are connected to television monitors in a limited area such as a store,
an office building, or on a college campus. CCTV is commonly used in surveillance systems.
CIF (Common Intermediate Format) A video format that easily supports both NTSC and PAL
signals. Many CIF flavors are available, including CIF, QCIF, 2CIF, and 4CIF. Each flavor
corresponds to a specific number of lines and columns per video frame.
CLI (command line interface) A textual user interface in which the user responds to a
prompt by typing a command.
Codec (Coder/Decoder) A device that encodes or decodes a signal.
Configuration Assistant A proprietary graphical program used to configure and update
the firmware of the S1100 edge devices.
DCE (Data Communication Equipment) In an RS-232 communication channel, a device that
connects to the RS-232 interface. Nextiva edge devices and modems are DCE.
Decoder See Receiver.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) A communication protocol that lets network
administrators manage centrally and automate the assignment of Internet Protocol (IP)
addresses in a network.
DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) In an RS-232 communication channel, the device to which
the RS-232 interface connects. Computers, switches, multiplexers, cameras, and keyboards
are DTE.
DVR (Digital Video Recorder) A device (usually a computer) that acts like a VCR in that it
has the ability to record and play back video images. The DVR takes the feed from a camera
and records it into a digital format on a storage device which is most commonly the hard
drive.
Edge Device A Nextiva device transmitting or receiving video signals through an IP
network. The devices can be wireless or wired; some transmitters are IP cameras.
Encoder See Transmitter.
Ethernet A local area network (LAN) architecture using a bus or star topology and
supporting data transfer rates of 10, 100, and 1000 Mbps. It is one of the most widely
implemented LAN standards. The 802.11 protocols are often referred to as “wireless
Ethernet.”
8 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
7

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
Firmware Software stored in read-only memory (ROM) or programmable ROM (PROM),
therefore becoming a permanent part of a computing device.
IP (Internet Protocol) The network layer for the TCP/IP protocol suite widely used on
Ethernet networks.
IP Camera See S2500e, S2600e Series, or S2700e Series.
LAN (Local Area Network) A computer network that spans a relatively small area. A LAN
can connect workstations, personal computers, and surveillance equipment (like edge
devices). See also WAN.
MPEG-4 A graphics and video lossy compression algorithm standard that is derived from
MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and H.263. MPEG-4 extends these earlier algorithms with synthesis of
speech and video, fractal compression, computer visualization, and artificial
intelligence-based image processing techniques.
Multicast Communication between a sender and multiple receivers on a network; the
devices can be located across multiple subnets, but not through the Internet. Multicast is a
set of protocols using UDP/IP for transport.
Multiport S17XXe Series The series of wired video transmitters designed for a variety of
video monitoring and surveillance applications in which a high concentration of cameras
terminates within the same area. The transmitters in the series offer 4, 8, 12, or 24 video
inputs. Some models offer onboard video analytics capabilities.
nDVR A video management and storage software sold by Verint. This graphical product is
used in conjunction with wired and wireless edge devices.
Nextiva The powerful, enterprise-class video management platform and suite of
applications from Verint that helps enhance security and improve performance. Nextiva
simplifies the management of large scale, distributed video operations and promotes
efficient use of network resources.
NTSC (National Television Standards Committee) The North American standard (525-line
interlaced raster-scanned video) for the generation, transmission, and reception of television
signals. In addition to North America, the NTSC standard is used in Central America, a
number of South American countries, and some Asian countries, including Japan. Compare
with PAL.
NTP (Network Time Protocol) A protocol designed to synchronize the clocks of devices over
a network.
OSD (On-screen Display) Status information displayed on the video monitor connected to
a receiver edge device.
PAL (Phase Alternation by Line) A television signal standard (625 lines) used in the United
Kingdom, much of western Europe, several South American countries, some Middle East and
Asian countries, several African countries, Australia, New Zealand, and other Pacific island
countries. Compare with NTSC.
PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol)—A method to securely transmit
authentication information, including passwords, over a wireless network.
PSK (Pre-Shared Key) A mode of the WPA and WPA2 security protocols, designed for home
and small office networks that cannot afford the cost and complexity of an authentication
server. It is also known as personal mode.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 79

Glossary
PTL (Push-To-Listen) In a two-way system, the communication mode in which the listener
must push a button while listening.
PTT (push-To-Talk) In a two-way system, the communication mode in which the talker
must push a button while talking.
PTZ Camera (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) An electronic camera that can be rotated left, right, up, or
down as well as zoomed in to get a magnified view of an object or area. A PTZ camera
monitors a larger area than a fixed camera.
QoS (Quality of Service) A set of low-level networking protocols giving higher priority to
more important data flows while ensuring that the less important ones do not fail.
Receiver A device converting a digital video signal into an analog form. Also called
decoder.
Repeater A range extender for wireless links. The Nextiva repeater is the S3100-RP
product, made up of two devices.
RF (Radio Frequency) Any frequency within the electromagnetic spectrum associated with
radio wave propagation. When a modulated signal is supplied to an antenna, an
electromagnetic field is created that is able to propagate through space. Many wireless
technologies are based on RF field propagation.
RS-232 A standard interface approved by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) for
connecting serial devices.
RS-422 A standard interface approved by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) for
connecting serial devices, designed to replace the older RS-232 standard because it supports
higher data rates and greater immunity to electrical interference.
RS-485 An Electronics Industry Alliance (EIA) standard for multipoint communications.
S1100 The series of secure outdoor wireless video systems (one receiver and one
transmitter per system) covering the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands in North America and Europe, and
the public safety 4.9 GHz band in North America.
S1100w The outdoor wireless video transmitter covering the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands in North
America and Europe, and the public safety 4.9 GHz band in North America.
S1500e Series The series of wired edge devices (receivers and transmitters) designed for
video monitoring and surveillance over IP networks. The transmitters in the series offer from
one to eight video inputs; the series proposes two receivers with one and four video outputs.
S1700e Series The series of wired video transmitters designed for video monitoring and
surveillance over IP networks, offering DVD-quality video and power over Ethernet. The
transmitter in the series offers one video input and web access.
S17XXe Series (Multiport) The series of wired video transmitters designed for a variety
of video monitoring and surveillance applications in which a high concentration of cameras
terminates within the same area. The transmitters in the series offer 4, 8, 12, or 24 video
inputs. Some models offer onboard video analytics capabilities.
S1900e Series The highly compact, single-input video transmitter designed for video
monitoring and surveillance over IP networks, offering various video qualities and
functionality sets, as well as web access for configuration and live viewing. The series
includes one receiver, the S1970e-R (displaying up to four video streams), and three
transmitters, the S1900e-AS (with onboard analytics capabilities), the S1950e (a cost
optimized solution), and the S1970e (for better video performance).
80 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
S1900e-Vicon The board holding the S1900e compact IP technology, to be included into
Vicon SurveyorVFT dome cameras.
S2500e The MPEG-4-compliant professional IP camera integrating a video sensor and an
Ethernet encoder in the same compact enclosure.
S2600e Series The set of professional IP cameras with a super wide range for excellent
quality in high-contrast environments. These MPEG-4-compliant cameras integrate a video
sensor and an Ethernet encoder in the same compact enclosure. The series includes color,
day/night, and analytics-ready cameras. All models provide web access for configuration and
live viewing.
S2700e Series The set of high-resolution, IP mini-dome cameras with triple axis lens
rotation for flexible installation, and low lux sensitivity for crisp clear images in a variety of
lighting conditions. The S2700e cameras offer DVD-quality video and web access for
configuration and live viewing. The models are separate for NTSC and PAL; for each video
standard, there are two models: indoor and vandal-resistant.
S3100 Series The set of multipurpose outdoor, wireless, digital video products. The series
includes the S3100 (for access point systems), S3100-BR (for wireless bridge applications),
and S3100-RP (for point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and wireless bridge repeaters). The
S3100 series covers the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands in North America and Europe, and the public
safety 4.9 GHz band in North America
SConfigurator A proprietary graphical program used to configure and update the firmware
of edge devices.
Serial Port An interface that can be used for serial communication, in which only one bit is
transmitted at a time. A serial port is a general-purpose interface that can be used for almost
any type of device.
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) A commonly used protocol for transmitting private documents
via the Internet. SSL works by using a public key to encrypt data that is transferred over the
SSL connection. The SSL protocol secures the following data: I/O, serial port, and VSIP
communication; it does not apply to audio and video transmission.
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol)—A security protocol used in the WPA authentication
method.
TLS (Transport Layer Security)—A cryptographic protocol that provide secure
communications on a wireless network.
Transceiver (Transmitter/Receiver) A device that both transmits and receives analog or
digital signals.
Transmitter A device sending video signals captured with a connected camera to a
receiver. The transmitter converts the analog signal into a digital form before transmitting
it. Also called encoder.
TTLS (T unneled Transport Layer Security)—A cryptographic protocol that creates a secure
TLS tunnel.
VSIP (Video Services over IP) A proprietary communication protocol for sending messages
between a computer and a Nextiva edge device, or between two devices.
WAN (Wide Area Network) A computer network that spans a relatively large geographical
area. Typically, a WAN consists of two or more local area networks (LANs).
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 81

Glossary
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) A security protocol for wireless local area networks
(WLANs) defined in the 802.11b standard. It is designed to afford wireless networks the
same level of protection as a comparable wired network.
Wireless Bridge A link between two networks, wired or wireless. The Nextiva wireless
bridge is the S3100-BR product, made up of two devices.
Wireless Cell A group of wireless devices that communicate together on the same radio
frequency channel and share the same wireless passkey.
Wireless Transmission A technology in which electronic devices send information to
receivers using radio waves rather than wiring.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access version 1) An authentication method to secure wireless
systems. It is the successor of WEP. WPA implements the majority of the IEEE 802.11i
standard.
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access version 2) An authentication method that implements the
full 802.11i standard, but will not work with some older network cards. It is also known as
802.11i.
2 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
8

Index
Numerics
0.6 F1 18
2.4 GHz frequency band. See frequency band.
24V AC power connection warning iii
4.9 GHz frequency band. See frequency band.
5 GHz frequency band. See frequency band.
802.11 8
802.11a. See frequency band.
802.11g. See frequency band.
802.11i 43
, 42–47
A
abnormal power-up conditions 33
Access Management menu 39
access point. See S3100.
account, user 39
address, IP. See IP address.
adjacent channel 16
administrator account 39
Advanced menu 48
AES-CCMP 9
alarm
cable pinout 55
configuring 29
allocation of frequency bands 7
antenna
choosing 19
gain 19
installation 27
integrated 3
location, for Fresnel zone 18
requirements 19
separation, in colocated systems 14
APIPA addressing scheme 23
audio
cable pinout 55
configuring 29
authentication 9
, 43
, 45
, 65–71
, 30
, 65–71
, 57
–30
, 43
B
band, frequency. See frequency band.
bandwidth, channel 6
bidirectional audio 29
bit rate
dynamic 12
RF 45
serial port 38
video 11
BNC video connector 22
boot sequence 13
boot, soft 50
, 45
C
CAB8P
mating view 55
pinout 56
usage 29
CAB9P
mating view 54
pinout 54
usage 22
wiring for serial connection 27
CAB9P cable 53
cable
alarm. See CAB8P.
audio. See CAB8P.
CAB8P. See CAB8P.
CAB9P. See CAB9P.
description 53
power 22
serial port. See CAB9P.
camera
data port configuration 2
losing a connection 32
PTZ connection 27
casing of the device 4
CD, Utilities viii
cell, wireless. See wireless cell.
certificate, SSL 2
channel, RF
automatic selection with DFS 13
available 6
fragmenting 6
selecting the location 47
selecting, in the CLI 44
characteristics of the device 2
CLI (command line interface)
accessing 36
main menu 36
menus 37
timeout 36
client
boot sequence with DFS 13
communication with master 24
maximum number in a cell 11
colocated cell 13
COM port 36
command line interface. See CLI (command line
interface).
communication between S3100 and S1100w 24
compatibility of firmware versions 10
compliance 87
computer requirements 23
–56
, 40
, 45
–50
–17
–29, 54–55
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 83

Index
configuration
alarm 29
audio 29
camera data port 2
default 31
device 23
I/O 29
order, in the wireless cell 10
connection
to a camera, losing 32
DCE/DTE 59
point-to-point 24
power iii
RS-232 28
serial 22
connectors on the CAB9P cable 22
console, SConfigurator 36
constraints in Europe 12
contact between two masters 16
country
available frequency bands 7
selecting, in the CLI 45
customer service ix
, 30
–30
, 49, 51
–24
–30
, 22
, 27–29
–13, 16–17
D
data throughput 11
DB-9 connector 22
DCE (data communication equipment) 59
default configuration 31
DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection)
boot sequence 13
defined 7
setups in Europe 16
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) 40
57
distance
between antennas 13
between antennas and persons 20
between colocated devices 13
downgrade of firmware 31
DSCP (Differentiated Service Code Points) 32
DTE (data terminal equipment) 59
duplex audio 29
duplicate IP address 23
dynamic bit rate control 12
Dynamic Frequency Sel ection. See DFS (Dynamic
Frequency Selection).
, 28
, 49, 51
–17
, 69–71
, 69–71
E
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) 9, 43
EIRP 19
electrical line interface 38
emitting power. See transmission power.
enclosure of the device 4
encryption 9
Enterprise mode, WPA or WPA2 8
, 43
, 43
equipment list 3
ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards
Institute) 7
Europe
colocation in the 5 GHz band 16
DFS context 7
TPC context 7
evaluating the location 18
exposure, RF 20
external antenna. See antenna .
extranet, Verint Video Intelligence Solutions ix
, 13
, 12
–17
F
factory default configuration 31, 49, 51
features of the device 2
firmware update
downgrading 31
performing 31
preventing 39
without losing devices 10
firmware version
compatibility between devices 10
displayed 47
first Fresnel zone 18
forcing the electrical line interface 38
frame rate 2
frequency band
available 6
distance limitations 65
licensed 6
public safety 6
selecting, in the CLI 44
frequency channel
,
automatic selection with DFS 13
available 6
fragmenting 6
selecting the location 47
selecting, in the CLI 44
Fresnel zone 18
full duplex audio 2 9
, 45
–71
G
gain of an antenna 19, 45
gateway 41
global security profile 40
H
hardware reset 31, 51
I
I/O, alarm or audio 29–30
identifying a device 48
indoor/outdoor RF regulation 47
installation 26
integrated antenna 3
4 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
8

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
interference, RF 20
IP address
APIPA 57
duplicate 23
setting 23
temporary 57
, 65
, 40
K
key. See passkey.
L
LED, status 32
licensed band. See frequency band.
limitations
distance 13
Europe 12
line interface, electrical 38
line-of-sight path 18
loading default configuration 49
location evaluation 18
login name. See user name.
losing a connection to a camera 32
, 69–71
–13, 16–17
, 51
M
MAC mode 42
main menu of the CLI 36
margin between adjacent channels 66
margin, minimum RF 47
mask, subnet 41
master
constraint in DFS 13
defined 10
ensuring RF contact 16
See also S3100.
maximum gain of an antenna 19
maximum number of devices in a cell 11
maximum transmission power. See transmission
power.
menus in the CLI 37
minimum RF margin 47
–50
P
pan-tilt-zoom 27
parity 38
passkey
private key, for WPA 44
for serial connection 39
SSL 40
for Telnet connection 39
WEP 44
wireless 13
WPA EAP 44
passphrase. See passkey.
password. See passkey.
PEAP (Protected Extensible Authenticati o n
Protocol) 9
personal mode, WPA or WPA2 8
ping request 41
pinout of the cables 54
planning
RF 18
system 9
plug. See connectors on the CAB9P cable.
point-to-multipoint system 13
point-to-point connection 24
port, VSIP. See VSIP port.
power connection
performing 22
warning on 24V AC iii
power requirement 3
power, transmission. See transmission power.
power-up conditions 33
preventing firmware update 39
protection
device configuration 39
surge 26
protocol, SPCF 2
protocols supported, serial 27
PSK (Pre-Shared Key) 8
PTT (push-to-talk) 29
PTZ camera connection 27
public safety band. See frequency band.
, 42
, 43
, 43
–56
–20
–16
, 63
, 43
N
network
menu in the CLI 40
planning 5
–16
O
operating mode, RS-422/485 38
options, when ordering a device 3
order in the configuration and update process 10
output, alarm or audio 29
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 8
–30
Q
Quality of Service (QoS) 32
R
radio frequency. See RF (radio frequency).
radio transmission power. See transmission
power.
reboot, soft 50
receiver device 24
recognizing a device 48
red/blue display 32
5

Index
requirements
antenna 19
computer 23
power 3
video bit rate 12
reserved VSIP ports 48
reset to factory default 31
resolution, video 3
RF (radio frequency)
channel. See frequency channel.
contact between two masters 16
exposure considerations 20
global spectrum allocation 7
line of sight 18
menu in the CLI 41
planning 18
See also the "wireless" entries.
RoHS 91
RS-232
cable pinout 54
connection 28
menu in the CLI 37
usage 22
RS-422/485
cable pinout 54
connection 27
menu in the CLI 37
–20
–28
, 49, 51
S
S3100
communication with S1100w 24
compatibility with S1100w 10
context of use 8
See also master.
SConfigurator
checking communication between devices 24
console 36
creating a connection 25
security
for the device 39
for wireless data 2
sensitivity threshold 46
separation between antennas 69
sequence of boot 13
serial connection 27
serial port
cable pinout 54
cabling 27
hardware setup 27
menu in the CLI 37
serial protocols supported 27
setups in Europe 17
shipment list 3
site survey
adjacent channels 66
CLI commands 49
soft reboot 50
–29
, 41–44
–71
–29
software reset 49
, 42
SPCF 2
spectrum allocation 7
SSID 42
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) 2
status LED 32
status, system 47
subnet mask 41
support, technical ix
surge protection 26
survey, site
adjacent channels 66
CLI commands 49
system reboot 50
system status 47
, 40
T
target device, connecting 27–29
technical support ix
Telnet
preventing access 40
temporary IP address 57
terminal block on the CAB9P cable 22
threshold, sensitivity 46
throughput, data 11
timeout, CLI 36
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) 9
TLS (Transport Layer Security) 9
ToS (Type of Service) 32
TPC (Transmit Power Control) 7
transmission power
when choosing an antenna 19
in the CLI 46
reducing, for TPC 12
TTLS (Tunneled Transport Layer Security) 9
, 54
, 43
, 43
, 12
U
user account 39
user name 39
Utilities CD viii
V
Verint web site ix
version of firmware
compatibility 10
displayed 47
video connector 22
video settings 2
VSIP port 48
W
warranty x
web site, Verint ix
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) 8
width, channel 6
, 45
, 44
, 43
6 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
8

Nextiva S1100w User Guide
wireless cell 8
wireless communication parameters 41
wireless frequency plan 7
wiring scheme
alarm 55
audio 55
RS-232 54
RS-422/485 27
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) 8
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access version 2) 8
–16
–47
–55
–28
, 43
, 43
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 8
7

88 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
 Loading...
Loading...