Verint Nextiva S4200-BZ, Nextiva S4200-AS-2V-BZ, Nextiva S4200-2V-BZ, Nextiva S4200-AS-BZ User Manual

Nextiva S4200 Series User
Guide
Covering the S4200-BZ, S4200-2V-BZ,
S4200-AS-2V-BZ, S4200-AS-BZ
Firmware Release 5.30
April 2009

© 2009 Verint Systems Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide.
Unauthorized use, duplication, or modification of this document in whole or in part
without the written consent of Verint Systems Inc. is strictly prohibited. By providing
this document, Verint Systems Inc. is not making any representations regarding the
correctness or completeness of its contents and reserves the right to alter this document
at any time without notice. Features listed in this document are subject to change.
Verint Systems Inc. does not warrant, guarantee or make any representation regarding
the use or the results of the use of the information, links, tools, and materials in terms
of the accuracy, reliability, quality, validity, stability, completeness, currentness, or
otherwise of its content or products. The entire risk as to the use, results and
performance of information, links, tools and materials provided or referenced herein is
assumed by the user. Verint Systems Inc. shall not be liable for damages resulting from
the use, misuse or unlawful use of the information, links, tools, and materials contained
or referenced herein.
The Verint Systems Inc. products are protected by one or more of the following U.S.,
European or International Patents: USPN 5,659,768; USPN 5,689,442; USPN 5,790,798;
USPN 6,278,978; USPN 6,370,574; USPN 6,404,857; USPN 6,510,220; USPN
6,724,887; USPN 6,751,297; USPN 6,757,361; USPN 6,782,093; USPN 6,839,667;
USPN 6,952,732; USPN 6,959,078; USPN 6,959,405; USPN 7,047,296; USPN
7,149,788; USPN 7,155,399; USPN 7,203,285; USPN 7,216,162; USPN 7,219,138;
USPN 7,254,546; USPN 7,281,173; USPN 7,284,049; USPN 7,325,190; USPN
7,466,816; USPN 7,478,051; USPN RE40,634; and other provisional rights from one or
more of the following Published US Patent Applications: US 11/394,408; US 11/771,499;
US 11/396,514; US 11/772,440; US 11/565,943; US 11/565,946; US 11/565,948;
US 11/540,739; US 11/540,086; US 11/541,313; US 11/541,252; US 11/540,282;
US 11/529,947; US 11/540,785; US 11/540,736; US 11/540,904; US 11/540,353;
US 11/608,340; US 11/608,350; US 11/608,358; US 11/567,808; US 11/692,983;
US 11/693,933; US 11/693,923; US 11/693,828; US 11/567,852; US 11/608,440;
US 12/015,621; US 11/540,322; US 11/924,201; US 11/616,490; US 11/621,134;
US 11/752,458; US 11/712,933; US 11/824,980; US 11/729,185; US 11/804,748;
US 11/831,260; US 11/395,992; US 11/359,319; US 11/359,195; US 11/359,357;
US 10/832,509; US 11/742,733; US 11/831,257; US 11/831,250; US 11/691,530;
US 11/479,267; US 11/529,942; US 11/768,349; US 11/540,281; US 10/633,357;
US 11/693,899; US 11/479,056; US 11/529,132; US 11/540,320; US 11/037,604;
US 11/529,842; US 11/540,171; US 11/478,714; US 11/529,946; US 11/868,656;
US 11/776,659; US 11/090,638; US 11/410,004; US 10/771,315; US 10/771,409;
US 11/540,900; US 11/528,267; US 12/118,781; and other U.S. and International
Patents and Patents Pending.
VERINT, the VERINT logo, ACTIONABLE INTELLIGENCE, POWERING ACTIONABLE
INTELLIGENCE, WITNESS ACTIONABLE SOLUTIONS, STAR-GATE, RELIANT, VANTAGE,
X-TRACT, NEXTIVA, ULTRA, AUDIOLOG, WITNESS, the WITNESS logo, IMPACT 360, the
IMPACT 360 logo, IMPROVE EVERYTHING, EQUALITY, CONTACTSTORE, and
CLICK2STAFF are trademarks or registered trademarks of Verint Systems Inc. or its
subsidiaries. Other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
www.verint.com/videosolutions
Publication date: April 2, 2009
Publication revision: C

Contents
Preface ................................................................................................................ v
Chapter 1 Overview ..........................................................................................1
About the S4200 Series .....................................................................................2
Key Features ................................................................. ........................... ..2
Security .....................................................................................................3
Frame Rate and Performance ........................................................................3
Installation Kit ................... ............................ .. .. .. ........................... ... .. .. ..........6
Hardware Overview ..........................................................................................7
Hardware Dimensions and Mounting Angles .........................................................8
Chapter 2
Available Frequency Bands and Channels ...................................... .. .. .. ...............13
Wireless Cells ..................................... ............................ .. .. ...........................16
802.11 Support ..............................................................................................17
System Planning ............................................................................................18
Colocated Cells .............................................................................................. 25
RF Planning ...................................................................................................31
Chapter 3
Configuring the Wireless System ...................................................................... 35
Installing the Wireless System ......................................................................... 44
Chapter 4
Installing or Upgrading ActiveX Controls ............................................................ 56
System and RF Planning .................................................................12
2.4 GHz Band ........................................................................................... 13
4.9 GHz Band ........................................................................................... 13
5 GHz Band ..............................................................................................15
Point-to-Multipoint Application ............ ........................................................18
Using IP Cameras with the S4200 ............................................................ .. . 19
Compatibility Issues ..................................................................................21
Video Bit Rate and Data Throughput ............................................................ 22
TPC ......................................................................................................... 24
DFS ........................................................................................................ 24
Distance Limitations ......................... ............................ .. .. .. .......................25
4.9 GHz Band in the United States ..............................................................26
5 GHz Band in North America and 2.4 GHz ................................................... 27
5 GHz Band in Europe ................................................................................28
Location Evaluation ................................................................................... 31
Antenna Requirements ..............................................................................33
RF Exposure Considerations .......................................................................33
Configuring and Installing the Device .............................................34
Supplied Cables ........................................................................................35
Setting Parameters ...................................................................................36
Performing a Point-to-Point Connection ........................................................ 42
Installing the Transmitter ........................................................................... 44
Installing an External Antenna ....................................................................49
Connecting the RS-422/485 Serial Port .......................................... .............. 50
Configuring the I/Os ..................................................................................52
Using the Web Interface .................................................................55
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions iii

Contents
Viewing the Quick Status .................................................................................58
Configuring the Device ....................................................................................60
Configuring the Serial Port ..........................................................................60
Configuring Access Management .................................................................61
Viewing the System Status .........................................................................64
Configuring the Network .............................................................................65
Configuring Wireless Communication ...........................................................66
Configuring Video ......................................................................................76
Looking at Video Status ................................... .. .. ............................ .. .. .. ....82
Configuring VSIP .......................................................................................83
Configuring Audio ......................................................................................84
Configuring System Time ...........................................................................86
Configuring HTTP (Webserver) ....................................................................88
Viewing Live Video ..........................................................................................89
Configuring Live Video ...............................................................................89
Manipulating the PTZ Camera .....................................................................93
Maintaining the Device ....................................................................................94
Chapter 5
Maintaining and Troubleshooting the Device ...................................97
Updating the Firmware ....................................................................................98
Losing Connection to a Camera .........................................................................98
Finding a “Lost” S4200 ....................................................................................98
Performing a Reset .........................................................................................99
Recognizing the Status LEDs ............................................................................99
Using the Command Line Interface ............................ .. ............................ .. .. ....101
Accessing the CLI ....................................................................................102
Configuring Quality of Service ...................................................................103
Creating a Serial Connection in UDP ...........................................................103
Appendix A
Appendix B
Factory Default Configuration......................................................105
DHCP Support and APIPA ............................................................108
Appendix C Surge Protection..........................................................................110
12V/24V Power ............................................................................................111
External Antenna ..........................................................................................111
Video and Serial ...........................................................................................111
Ethernet Port .......................... .. .. .................................................................111
Appendix D
Reducing Wireless Interference ..................................................114
Interference from External Sources .................................................................115
Interference from Nextiva Devices ..................................................................115
Performing a Site Survey ..........................................................................116
Respecting Minimum Distances .................................................................120
Appendix E
Technical Specifications...............................................................123
Glossary ........................................................................................................... 126
Index ...............................................................................................................131
Compliance ......................................................................................................136
USA ............................................................................................................ 137
Canada .......................................................................................................139
Mexico ........................................................................................................141
Europe ........................................................................................................ 143
RoHS Declaration of Compliance .....................................................................145
iv Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Preface
The Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide presents the information and procedures for
installing, configuring, and using the Nextiva® S4200 series wireless video systems.
Audience
This guide has been prepared for the following audience:
Managers
IT system administrators
Engineers
Technicians
This guide assumes that you are familiar with:
Installation and manipulation of electronic equipment
General use of computers
Local area networks (LANs) and basic IP data communication concepts and practices
Radio frequency (RF) platforms
801.11 networks if the 802.11 MAC mode is used
Web browsers
Microsoft Windows operating systems
Reference
In addition to this guide, the following documentation is also available:
Nextiva S4200 Series Installation Guide
Verint SConfigurator User Guide
Nextiva S4X00 Release Notes
A paper copy of the installation guide is included with your order.
How to Contact Us
The following Web sites and e-mail addresses provide information and support for Verint
Video Solutions and the Nextiva Intelligent Edge Device product line.
Find general information on Verint Video Solutions, including marketing material and
product information at www.verint.com/videosolutions
Download the documentation of the Intelligent Edge Devices at www.verint.com/manuals
Download firmware from the Verint Video Solutions partner extranet at
http://vvs.verint.com
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions v
.
.
.

Preface
Send your questions or comments on the current document, or any other Nextiva user
documentation, to our documentation feedback team at
documentationfeedback@verint.com.
Find contact information for the Verint Customer Service team, by phone or e-mail, or fill
out a Web request for support with a specific issues at www.verint.com/videoservice
. For
immediate assistance, contact the Customer Service team:
Location Telephone E-mail
USA and Canada 1-888-747-6246 vissupport@verint.com
Central and Latin
America
Europe, Middle East,
and Africa
Asia/Pacific
Hong Kong
Singapore
+1-631-962-9202 vissupport@verint.com
+44 (0) 845-843-7333 customersupport.emea@verint.com
+49 (0) 4321-269 81 36 mobilesupport@verint.com
(Transit applications only)
APAC_VIS_Services@verint.comp
+852 2797 5678
+65-68266099
vi Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Overview
The S4200 series allows digital video transmission over license-free and licensed bands. It
delivers dual-stream video over local and wide area networks (LANs and WANs). Many
compression modes (also called codecs—coder/decoder) are available: a proprietary
MPEG-4-based mode called SM4, the MPEG-4 ISO 14496-2 comp liant mode, and MJPEG
(Motion JPEG). This wireless edge device is built on open standards to provide long-term
investment protection.
Combined with a Nextiva S4300 multipurpose outdoor wireless device or a commercial
802.11 access point, the S4200 series enables analog CCTV extension over the enterprise’s
network at a cost lower than that of laying new cables. The S4200 series also allows the
migration of analog CCTV cameras to an IP network.
Note: The S4200 series edge devices require professional installation.
The overview covers the following:
About the S4200 Series
Installation Kit
Hardware Overview
Hardware Dimensions and Mounting Angles
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 1
1: Overview
About the S4200 Series
The S4200 series devices are outdoor multiband encoders/transmitters covering the
2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands in the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands in America
(United States, Canada, and Mexico) and Europe, and the 4.9 GHz public safety band in
America.
Key Features
The S4200 series offers many models to cover your system needs:
Device Number of
Video Inputs
S4200 1 2
S4200-2V 2 1
S4200-AS 1
S4200-AS-2V 2
1
The analytics license is not included. The analytics capabilities can be used with a Nextiva
IntelliView solution, version 5.1 or higher . Camer a tampering detection and analytics run on
the first video input of the devices. For details, refer to your Verint representative.
2
The second encoder of each input can be used for analytics or to encode video. The
second encoder gives better video encoding performances than the first one.
You can also purchase each device for the 4.9 GHz public safety band (the suffix -49 is
added to the product name, for example S4200-2V-49).
Unless otherwise specified, the word S4200 refers to any of these devices.
The S4200 offers the following additional key features:
Integration of a multiband radio, video encoder, and antenna into small outdoor rated
enclosures, for convenient, discreet, secure, and reliable installation in real-world video
security applications
Integrated antenna covering the 2.4 GHz (8.5 dBi gain), 4.9 GHz (12 dBi gain), and
5GHz (12dBi gain) bands
Video analytics capabilities on the S4200-AS and S4200-AS-2V models. In the Nextiva
IntelliView Analytics Rule Builder, the -AS models support a maximum of five active
rules and six views. For more information, refer to the documentation set of the Nextiv a
enterprise video management platform.
Camera tampering detection on the S4200-AS and S4200-AS-2V models, to
automatically monitor video images captured by a camera and provide alerts whenev er
specific characteristic of these images have changed
Number of
Video Encoders
per Input
2
2
2
2
Alarm and Audio
(with Optional
Cable)
3
33
Analytics and
Camera
Tampering
Detection
3
1
2 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
Specific design for wireless video security applications (integrated video, bidirectional
audio, data, and I/Os)
Codec optimization for typical outdoor video surveillance scenes, to reduce the required
bit rate without impacting video quality
Wireless MAC/protocol enhancements specific to wireless video security applications
Resolution of limitations of standard WiFi technology for wireless video security
applications (hidden nodes, latency, range, and QoS)
Low-latency communication to avoid problems such as PTZ over control
12V DC or 24V AC input power
MPEG-4 ISO 14496-2 compliant and MJPEG support
RTC (Real-Time Clock) and NTP (Network Time Protocol) support
Dual encoding on the S4200, S4200-AS, and S4200-AS-2V models
Ethernet port for configuring the device or connecting an IP camera
Web interface for easy configuration and live viewing
Default serial port settings compatible with the most popular camera data port
configuration (4800 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit)
Security
Every S4200 device comes with the following security features:
SSL —Every edge device comes with a unique SSL (Secure Sockets La yer) certificate for
securing its IP link. SSL is a commonly used protocol for managing the security of IP
message transmission. If enabled, the SSL protocol secures the VSIP communication
data. It does not apply to audio and video transmission.
SPCF (SmartSight Point Coordination Function)—This proprietary MAC (Media Access
Control) protocol using AES encryption (with key rotation) over the wireless link to
secure communication between the devices and resolve “hidden node,” quality of
service, range, and problems inherent to 802.11 wireless networking products. SPCF
secures VSIP communication as well as audio, video, and serial data.
Frame Rate and Performance
The available video frame rates of each encoder of the transmitter are:
NTSC—1 to 7, 10, 15, or 30 frames per second (fps)
PAL—1 to 6, 8, 12, or 25 fps
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 3

1: Overview
On the S4200, S4200-AS, and S4200-AS-2V devices, the composite signal of a video input
is sent to two separate encoders. You can customize each encoder to meet your system
needs, for instance in terms of frame rate and resolution. Here are typical scenarios
regarding encoder use:
Scenario Encoder 1 Encoder 2
point-to-point point-to-point unused
unused point-to-point
point-to-point and web interface web viewing at rate A point-to-point at rate B
web viewing and
unused
point-to-point at rate C
video management software view at rate D record at rate E
Note: You should not use the web interface and a video management software at the
same time to avoid configuration conflicts.
The video resolutions supported by the S4200 device are:
Resolution Number of Columns Number of Lines
NTSC/PAL NTSC PAL
QCIF 176 128 144
CIF 352 240 288
2CIF 704 240 288
4CIF 704 480 576
All lines 352 480 576
2/3 D1 480 480 576
VGA 640 480 480
The following performances can be achieved using single-stream encoding. For dual
encoding values, refer to the Nextiva Intelligent Edge Devices Single-Dual Stream
Performance document, available on the extranet (Community Links > Technical Briefs >
Nextiva Intelligent Edge Devices).
Each performance value includes:
A video resolution
A frame rate expressed in frames per second (fps) using the NTSC/PAL format
4 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
A bit rate expressed in kilobits per second (kbps)
The recommended performances for each video encoder of an S4200 and S4200-2V are:
Codec S4200 S4200-2V
Input 1 Input 2
SM4 4CIF, 30/25 fps,
3000 kbps (low to
2CIF, 30/25 fps,
2000 kbps
CIF, 30/25 fps,
800 kbps
medium motion scene)
MPEG-4 ISO 4CIF, 15/12 fps,
2000 kbps
MJPEG 4CIF, 15/12 fps,
20 kBytes
2CIF, 15/12 fps,
1500 kbps
4CIF, 15/12 fps,
20 kBytes
CIF, 30/25 fps,
800 kbps
CIF, 30/25 fps,
10 kBytes
The recommended performances for each video encoder of an S4200-AS and S4200-AS-2V
are:
Codec S4200-AS S4200-AS-2V
Input 1 Input 2
SM4 4CIF, 30/25 fps,
With analytics functionality:
4000 kbps
4CIF, 10/8 fps,
2000 kbps
CIF, 30/25 fps,
800 kbps
Without analytics functionality:
4CIF, 30/25 fps,
4000 kbps
2CIF, 30/25 fps,
2000 kbps
MPEG-4 ISO 4CIF, 30/25 fps,
With analytics functionality:
3000 kbps
2CIF, 30/25 fps,
2000 kbps
CIF, 30/25 fps,
800 kbps
Without analytics functionality:
4CIF, 30/25 fps,
4000 kbps
MJPEG 4CIF, 15/12 fps,
20 kBytes
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 5
4CIF, 15/12 fps,
20 kBytes
2CIF, 30/25 fps,
2000 kbps
CIF, 30/25 fps,
10 kBytes

1: Overview
Installation Kit
The package contents are:
Item Description
Transmitter S4200, S4200-AS, S4200-2V, or S4200-AS-2V; includes
an integrated antenna
Mounting assembly set One set for installation on a wall or pole
Cable for video, serial port,
and power
Printed material The Nextiva S4200 Series Installation Guide
Options
High-gain antenna One external antenna; the available antennas vary
CABAA cable One cable for alarm or audio
CABET-25 cable An 82-foot (25-meter) outdoor Ethernet cable with a
CABET-50 cable A 164-foot (50-meter) outdoor Ethernet cable with a
CABPV cable A cable for video, serial port, and power
PS2440 power supply An indoor-only 24V AC power supply
Note: You must use on ly antennas certified by Verint. Doing so ensures that the combined
transmission power of the device and antenna does not exceed the maximum value
established by your country’s regulations. For more information, see page 28 and
page 136.
One cable for the S4200 and S4200-AS, two cables for the
S4200-2V and S4200-AS-2V
depending on the frequency band and the country.
weatherproof connector
weatherproof connector
6 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
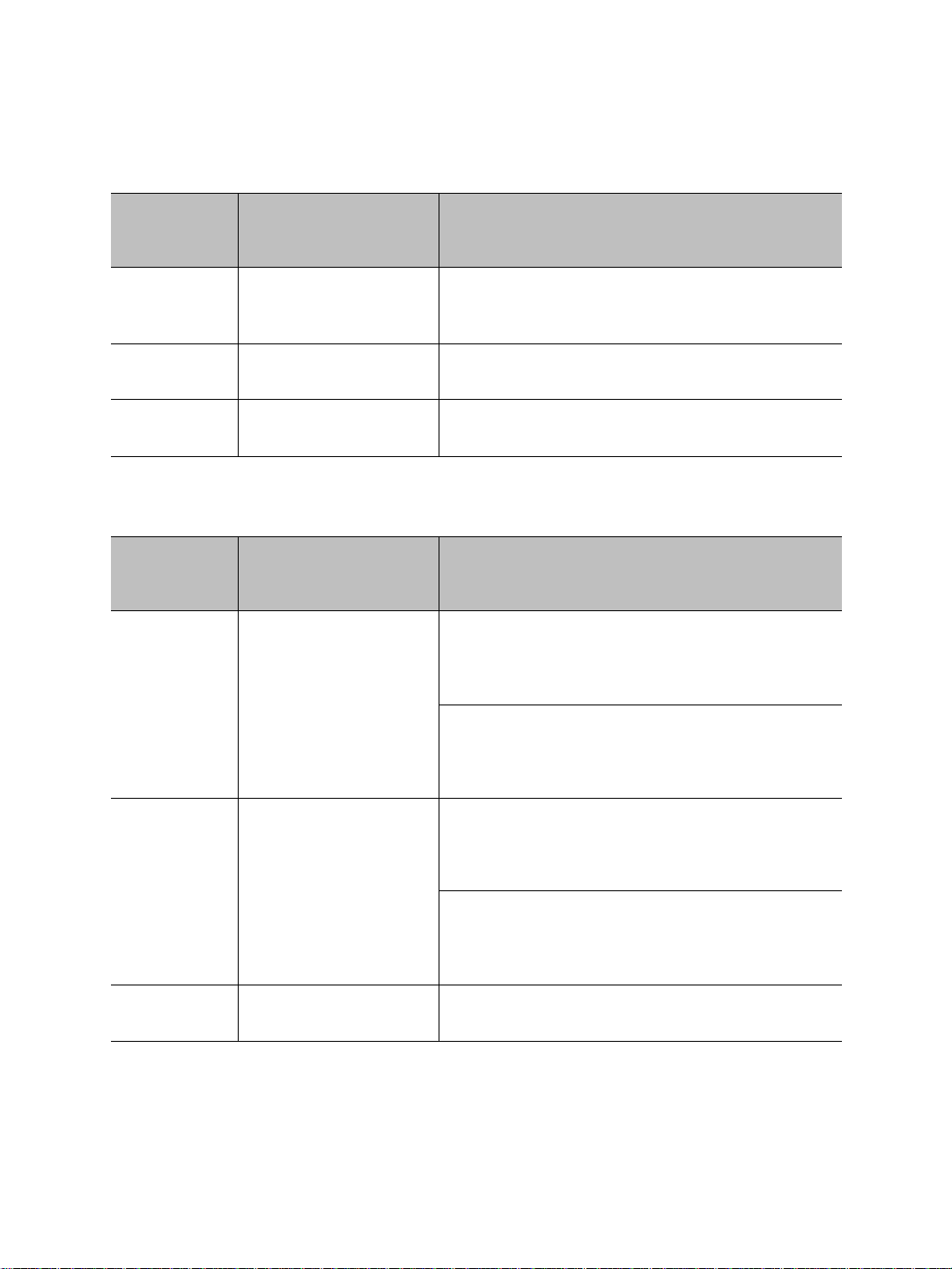
Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
Integrated antenna
Auxiliary connector: either video 2 and serial port or
alarm and audio
Main connector for video 1, serial port, and power
Network (RJ-45) connector
LEDs
External SMA antenna connector
Hardware Overview
The S4200 electronics are enclosed in a weather-tight cast aluminum module with an
integrated wide-band antenna located in the top of the casing. All cable entries are
mounted on the underside of the module to maintain its weatherproof properties.
The underside consists of:
A network (RJ-45) connector
A main connector for video 1, serial port, and power
An auxiliary connector for video 2 and serial port (on -2V devices) or alarm and audio
(on S4200 and S4200-AS devices)
An external SMA antenna connector
Three LEDs
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 7
1: Overview
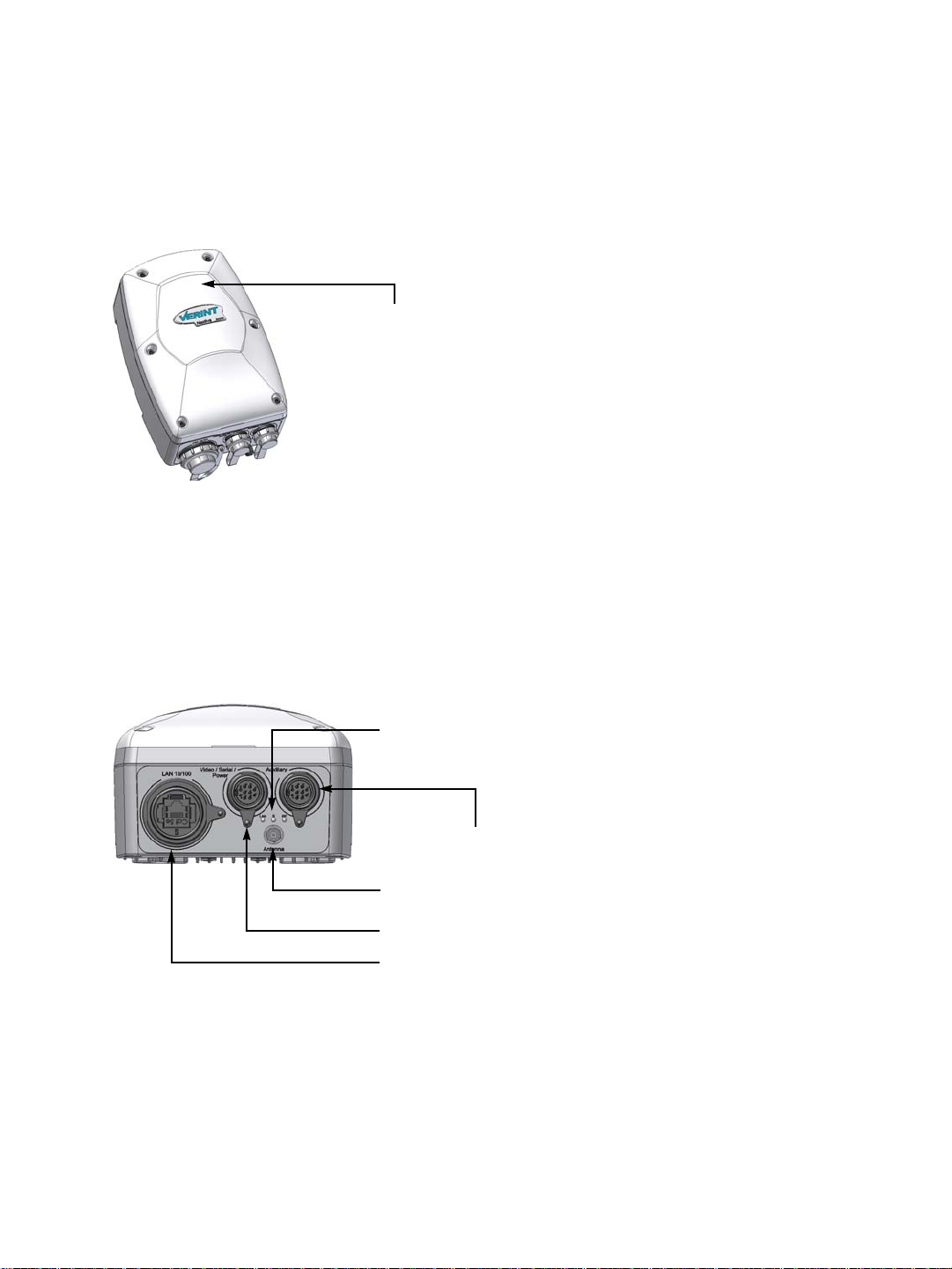
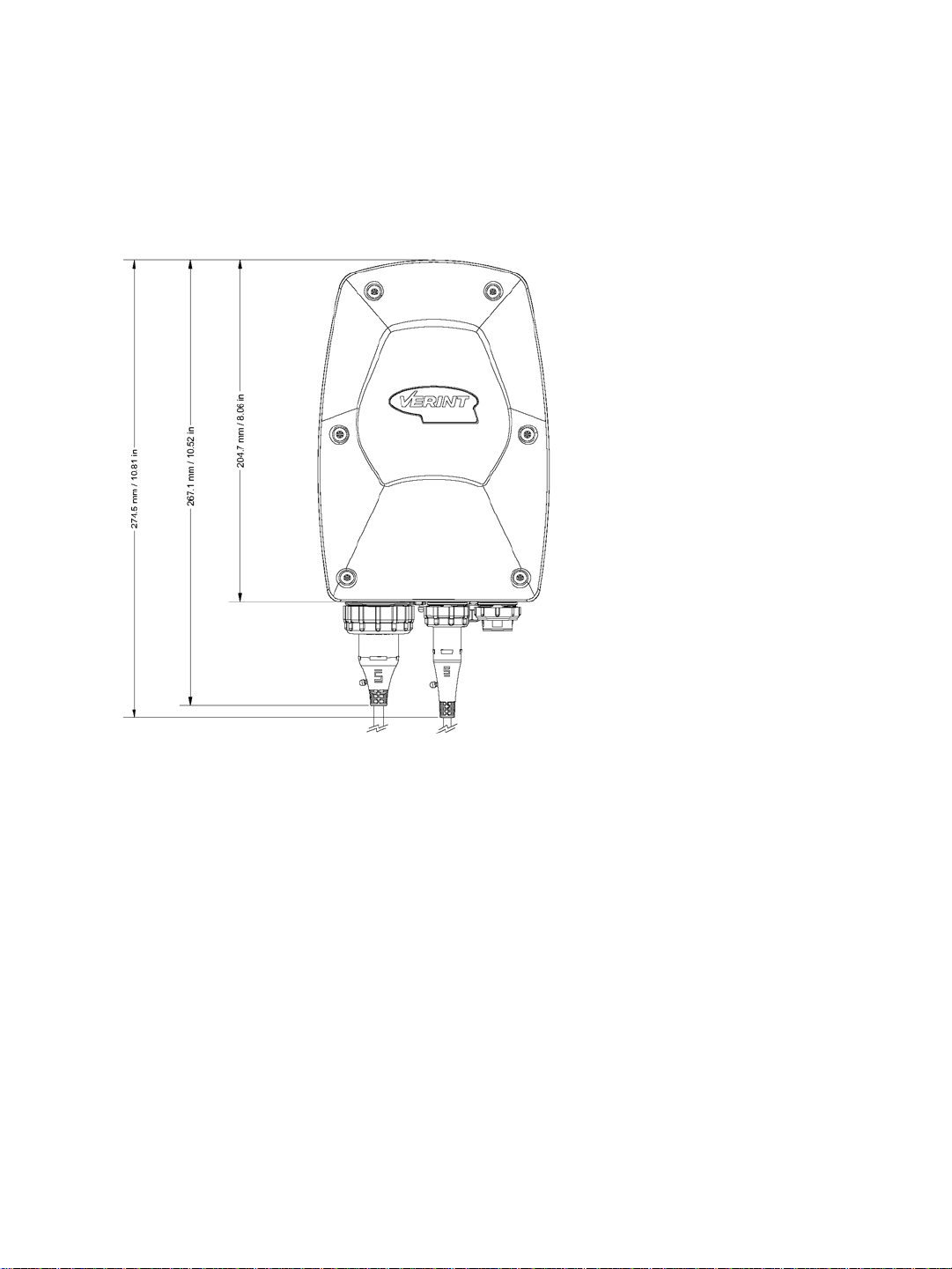
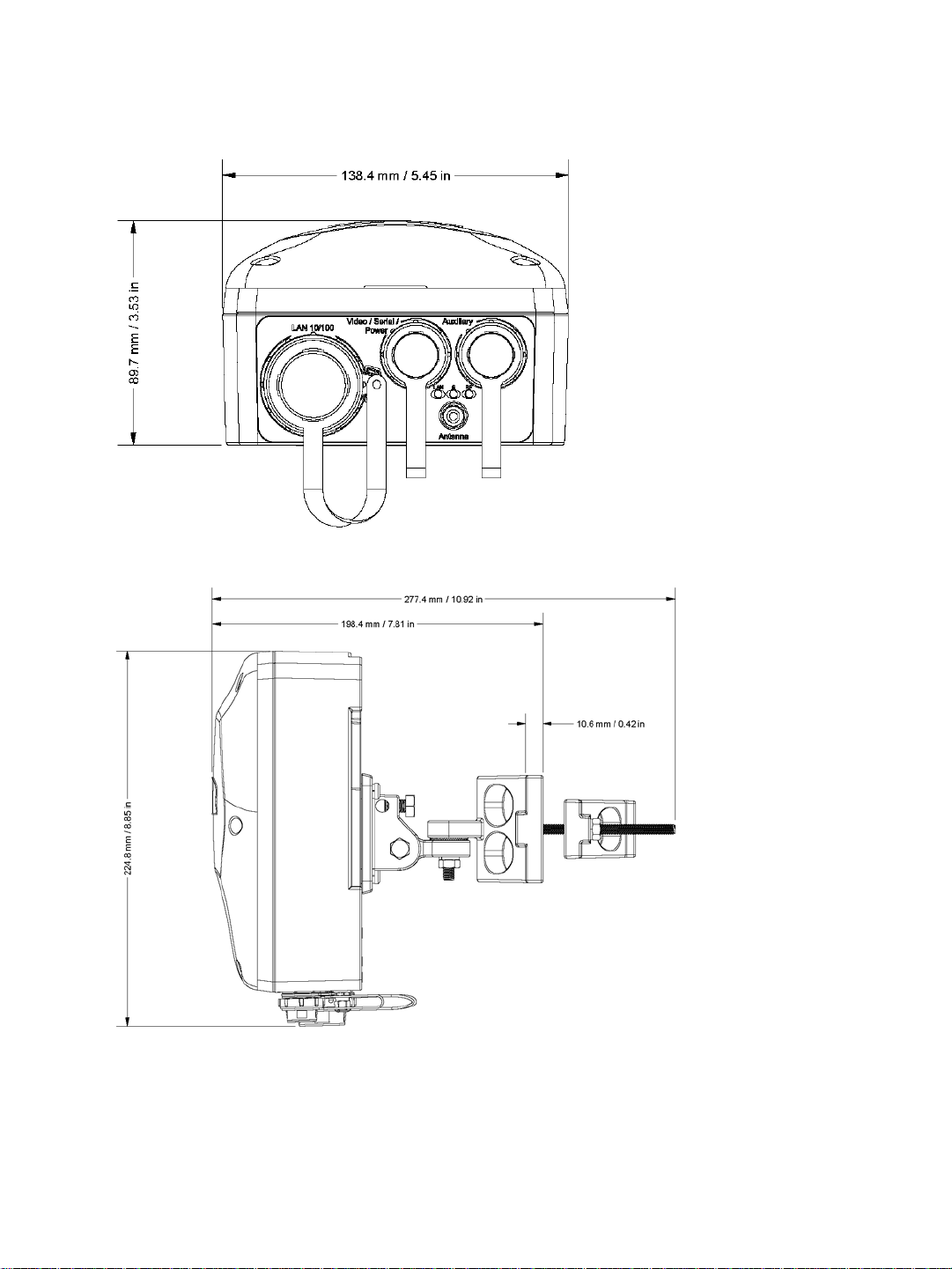
Hardware Dimensions and Mounting Angles
The top view dimensions of the S4200 are:
8 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
The back view dimensions are:
The side view dimensions with the mounting assembly installed are:
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 9
1: Overview
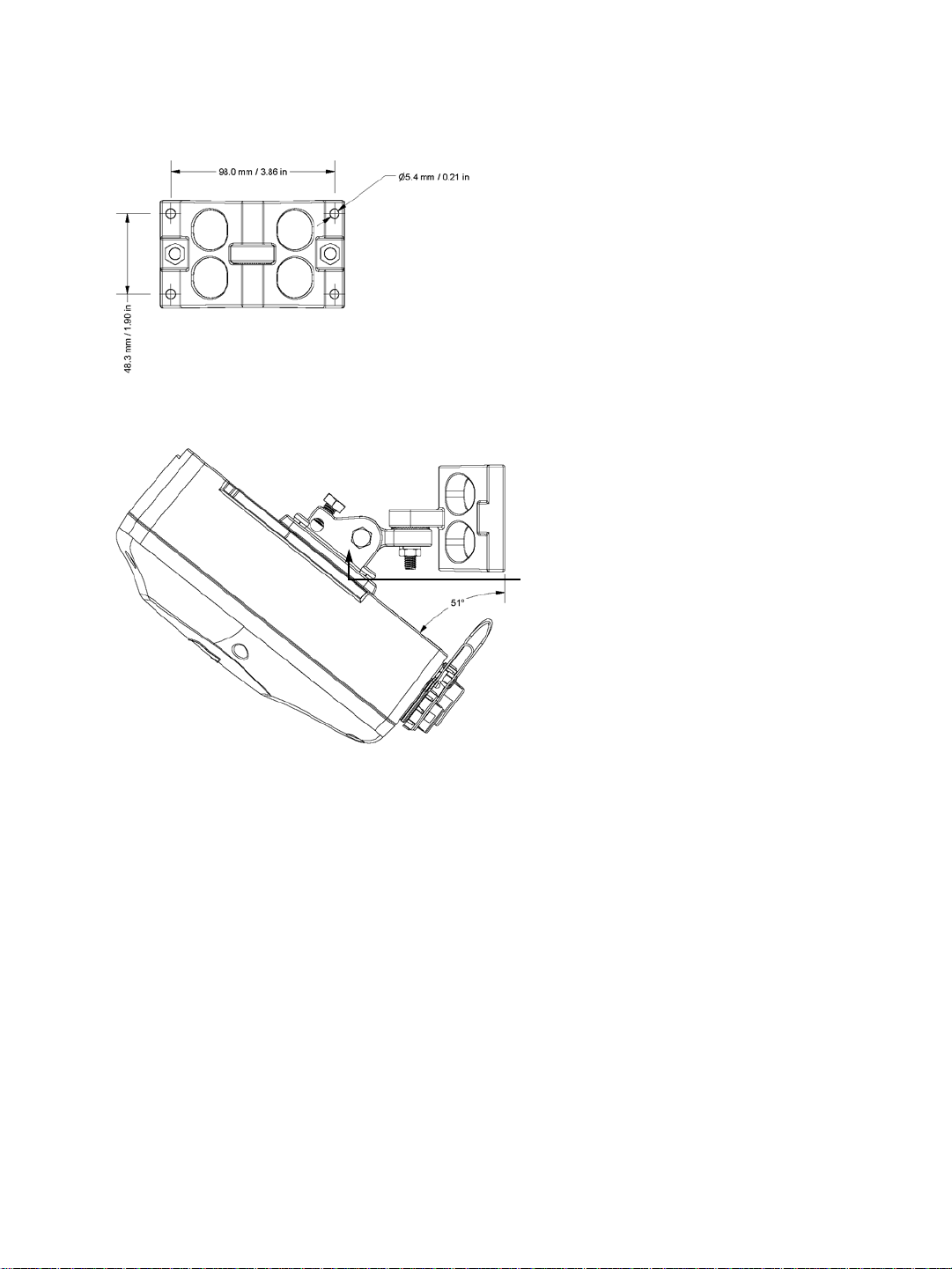
Mounting bracket
The dimensions of the wall pivot mount are:
The maximum angular positions allowed by the mounting bracket vary depending on the
cables and the mounting structure (pipe, wall, and so on). Here is a downward tilt:
To cover more installation possibilities, you can install the mounting bracket upside down in
order to flip all the angles; for instance, to provide a downward tilt the same maximum
angle as an upward tilt. For more information about the mounting procedure, see
“Installing the Wireless System” on page 44.
10 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
An upward tilt is:
Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
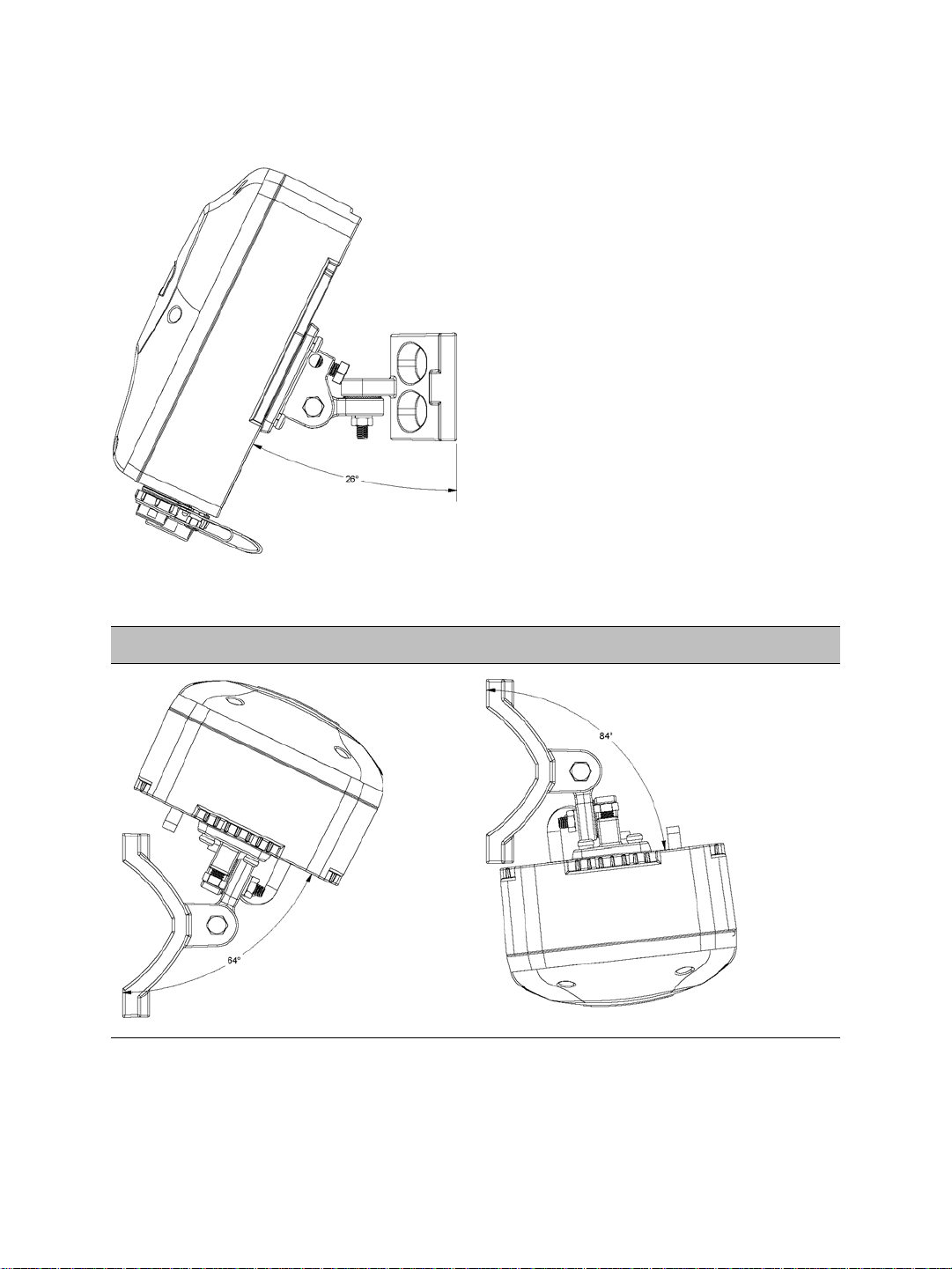
Finally, here are rotation examples:
Left Rotation Right Rotation
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 11

System and RF Planning
To allow optimal configuration, you must properly plan your network, especially
configuration layout and RF (radio frequency). Planni ng is especially required i f you want
to install many systems in the same area, in order to prevent radio interference
between the colocated devices and to select the appropriate antennas. In all cases, follow
the recognized RF installation practices.
To help you with your planning, you may consult the Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
extranet:
The Wireless System Margin Calculator is a tool based on an Excel spreadsheet
designed to simplify the creation of RF systems. It is located under Tools.
The Nextiva Wireless Devices Primer provides standardized information about the
design, features, and benefits of the Nextiva wireless devices. It is located under
Community Links > Technical Briefs > Nextiva Intelligent Edge Devices.
The system and RF planning tasks cover the following topics:
Available frequency bands and channels
Wireless cells
802.11 support
System planning
Colocated cells
RF planning
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 12
Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
Available Frequency Bands and Channels
The S4200 supports communications in the following frequency bands in America and
Europe:
2.4 GHz OFDM, also known as 802.11g
4.9 GHz OFDM, a public safety band available in the United States and Canada only
5 GHz OFDM, also known as 802.11a
To meet local regulations, you must use only antennas that conform to the requirements
specified in the “Compliance” appendix on page 136.
2.4 GHz Band
The 2.4 GHz band provides 11 channels in the United States, Canada, and Mexico, and 13
in Europe. In these two regions, only channels 1, 6, and 11 are independent (that is,
non-overlapping); in most countries, they can be used indoors or outdoors. For more
information on the availability of these channels depending on the countries, see the
“Compliance” appendix on page 136. The center frequencies of the channels are:
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Frequency (GHz)
1 2.412 8 2.447
2 2.417 9 2.452
3 2.422 10 2.457
4 2.427 11 2.462
5 2.432 12 2.467 (Europe only)
6 2.437 13 2.472 (Europe only)
72.442
4.9 GHz Band
The 4.9 GHz band is a licensed band for entities providing public safety services focused on
the protection of life, health, or property in the United States, Canada, and Mexico. This
band provides license holders with an interference-free, secure channel for robust and
secure broadband technologies, including wireless video surveillance systems.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 13

2: System and RF Planning
For more detailed information concerning the regulations governing licensing and use of
frequencies in the 4.9 GHz band:
United States—See Subpart Y of the FCC document, Memorandum Opinion and Order
and Third Report and Order at:
http://hraunfoss.fcc.gov/edocs_public/attachmatch/FCC-03-99A1.pdf
Canada—See the document SP-4940 (Spectrum Utilization Policy, Technical and
Licensing Requirements for Broadband safety in the band 4940-4990) at:
http://strategis.ic.gc.ca/epic/site/smt-gst.nsf/en/sf08667e.html
Mexico—The use of the 4.9 GHz in Mexico is subject to a special approval from
COFETEL.
The 4.9 GHz band has a width of 50 MHz (4940 to 4990 MHz). Since the standard channel
width is 20 MHz, only two independent channels can co-exist in the band. However, the
S4200 supports channel fragmentation, allowing narrower channels of 5 MHz and 10 MHz.
You can have up to four independent channels with a 10 MHz width, and up to 10 with a
5 MHz width. All these channels are for indoor or outdoor use.
The available channels are:
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Width
3 4.9425 5 MHz
6 4.9475 5 MHz
7 4.9525 5 MHz or 10 MHz
7 4.950 20 MHz
8 4.9575 5 MHz
9 4.9625 5 MHz or 10 MHz
10 4.9675 5 MHz
11 4.9725 5 MHz or 10 MHz
11 4.970 20 MHz
12 4.9775 5 MHz
13 4.9825 5 MHz or 10 MHz
16 4.9875 5 MHz
14 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
5 GHz Band
In the 5 GHz band, the number of available channels and sub-bands vary depending on the
country of operation.
Most European countries adhere to the DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection) and TPC
(Transmit Power Control) regulations established by the European Telecommunications
Standards Institute (ETSI); these regulations apply to the 5 GHz frequency band only. To
know which bands are available in your country of operation and whether your country
adheres to DFS and TPC, see the “Compliance” appendix on page 136.
In the United States and Canada, five channels are available in the 5 GHz band, all
independent and for indoor or outdoor use. The center frequencies of these channels are:
Channel Frequency (GHz)
149 5.745
153 5.765
157 5.785
161 5.805
165 5.825
In Mexico, the following channels are available, all independent and for indoor or outdoor
use:
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Frequency (GHz)
36 5.18 64 5.32
40 5.2 149 5.745
44 5.22 153 5.765
48 5.24 157 5.785
52 5.26 161 5.805
56 5.28 165 5.825
60 5.30
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 15
2: System and RF Planning
S4300
S4200
In Europe, the 11 independent channels, for indoor or outdoor use, are:
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Frequency (GHz)
100 5.50 124 5.62
104 5.52 128 5.64
108 5.54 132 5.66
112 5.56 136 5.68
116 5.58 140 5.70
120 5.60
Wireless Cells
A wireless network is designed such that information can travel back and forth between two
points without the need for wires. For the S4200, this information consists of digitized
video, audio, and PTZ data sent to and from the wired network via an outdoor wireless
access point—either the Nextiva S4300 device or a commercial 802.11 access point.
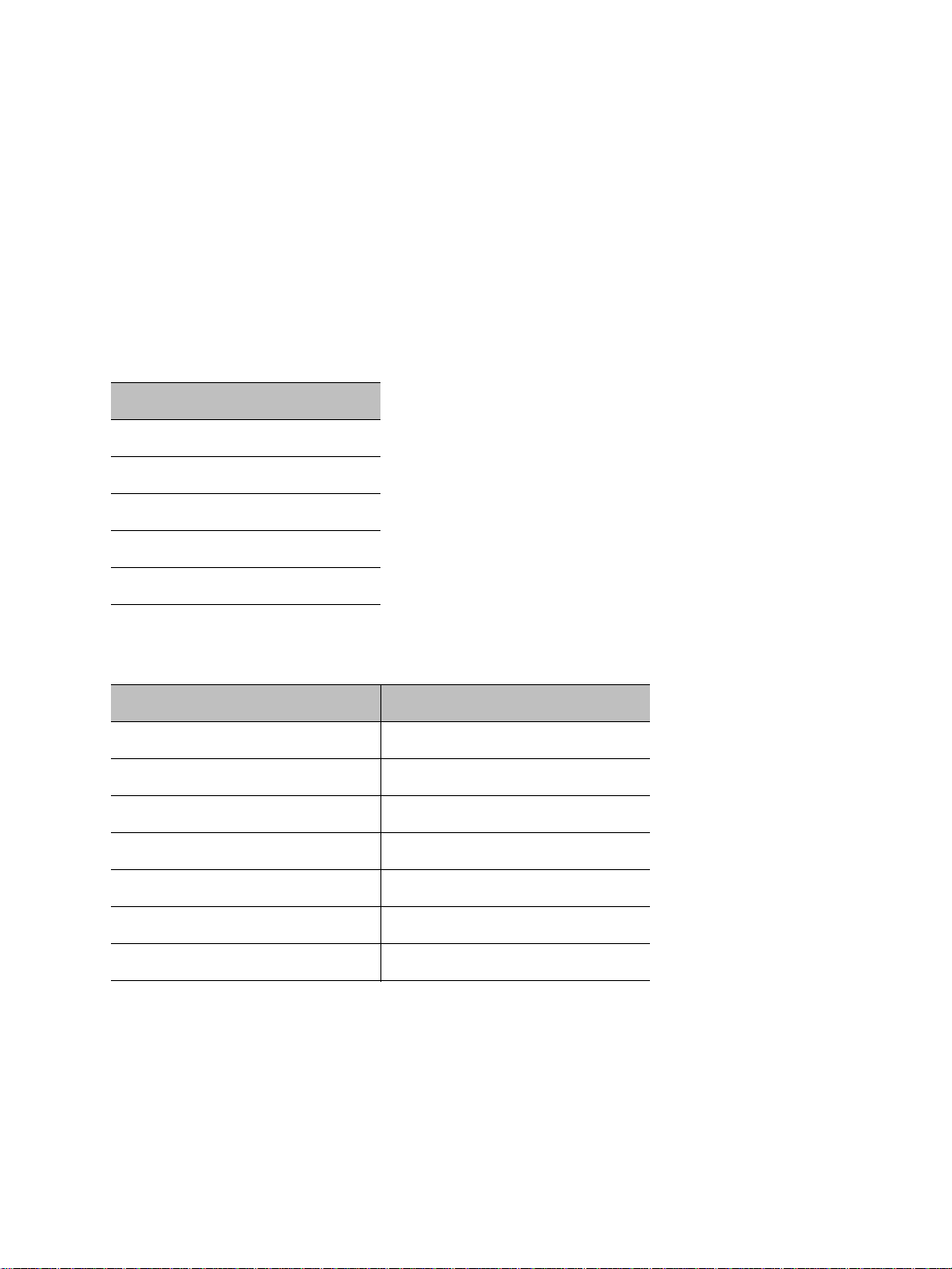
A wireless cell consists of a group of wireless devices that communicate together on the
same frequency channel and that share the same wireless passkey. For example:
You can colocate many wireless cells if you respect certain conditions (see page 31).
Devices in a wireless cell can have two MAC (Media Access Control) roles, master or slave:
A master device controls the access over the wireless medium. It takes care of channel
selection and slave authentication to provide access to the wireless network. Finally , the
master allocates bandwidth among all connected slaves.
Slave devices need a master to access the wireless medium to transfer data, through a
polling mechanism. The S4200 devices are always slaves.
16 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
802.11 Support
The S4200 devices can use commercial 802.11-compliant access points in all frequency
bands (2.4 GHz, 4.9 GHz, and 5 GHz).
It is assumed that the network administrators wanting to add S4200 transmitters to their
802.11 wireless network are knowledgeable about this protocol. In the remaining of this
user guide, the access point will be a Nextiva S4300.
The S4200 in the 802.11 mode supports the following security mechanisms:
No security—Not recommended
WEP—Not recommended
WPA and WPA2 (also known as 802.11i) in personal mode (PSK)
WPA and WPA2 in Enterprise mode, with an 802.1X authentication server
Note: WPA and WPA2 are not available with the proprietary SPCF MAC mode.
The supported authentication methods for WPA and WPA2 are:
Method Authentication
Means
PSK—Pre-Shared Key
(personal)
EAP-TLS (Enterprise) certificate Uses mutual authentication. The most secure
EAP-TTLS (Enterprise) login/password
PEAP (Enterprise) login/password
For more information about the TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol, refer to RFC 2246
at http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2246.txt
The supported encryption methods are:
WEP
passphrase A passphrase is required to connect to an
and certificate
and certificate
Remarks
access point and therefore access the
network.
option available.
Creates a secure TLS tunnel. Supports
MSCHAPv2 (the Microsoft version of the
Challenge Handshake Authentication protocol)
to validate logins and passwords. A certificate
is required on the server side.
Creates a secure TLS tunnel. Supports
MSCHAPv2 (the Microsoft version of the
Challenge Handshake Authentication protocol)
to validate logins and passwords. A certificate
is required on the server side.
.
AES-CCMP
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 17

2: System and RF Planning
S4300
S4200
TKIP
Auto-select—The device automatically chooses the best available encryption scheme.
The wireless parameters associated to 802.11 differ from those of the SPCF mode. For
more information about these parameters, refer to the Verint SConfigurator User Guide.
Be aware of the following limitations in using S4200 devices in a 802.11 environment:
The S4200 will not be able to connect to an S4300.
The inherent problems with 802.11 wireless network products, such as the “hidden
node” and quality of service issues, will be present. Furthermore, the ranges of the
equipment will be lower than with the SPCF protocol.
System Planning
When installing many wireless systems in the same area, you have to carefully plan their
positions in order to prevent radio interference and select the appropriate antennas.
The grouping of devices in each wireless cell is determined by their respective locations
with respect to one another and by the available outdoor wireless access points. As a rule of
thumb, there should be a clear RF line of sight between each S4200 device and the access
point in each cell. However, the S4200 devices can be completely hidden from one another.
Point-to-Multipoint Application
A point-to-multipoint application is a wireless cell made up of an S4300 access point (the
master) and several S4200 transmitters (the slaves). Here is a typical point-to-multipoint
system:
For example, to associate three S4200 devices to one access point, you need to:
1. Assign the same wireless passkey to the S4200 devices and the S4300 access point.
The wireless passkey must be different from that of other colocated cells, if any.
2. Assign a frequency channel to the S4300 device. The associated S4200 devices will
automatically use their master’s channel.
3. Install the S4200 devices such that each one has a clear RF line of sight with the S4300
access point.
For the configuration and installation procedure, see page 34.
18 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
Using IP Cameras with the S4200
The Ethernet port on the S4200 and the optional two-camera models provide new
configuration possibilities. Although video data from more than a single camera can be
transmitted from one S4200 transmitter, you must take several factors into account: the
total throughput available from the S4200, the available bandwidth for the wireless cell,
and the total amount of bandwidth used by each link in the cell.
If using a single S4200 for multiple camera transmission, it is important to remember that
the onboard processor has a finite amount of processing power available. F or instance, you
can achieve 4CIF resolution at 30 fps with a single analog camera connected to an S4200
transmitter; however, if an IP camera is connected to the Ethernet port of the S4200, some
processing power is required to transport the data stream of the IP camera from the
Ethernet port out to the radio for transmission to the S4300 access point.
The S4200 processor has the ability to forward an Ethernet stream equal to the maximum
available bandwidth on the wireless link. Obviously, using the maximum available
bandwidth only for the Ethernet port leaves no bandwidth for the video streams from the
encoders. Also, to attain good encoding performance for the analog cameras connected to
the S4200, the maximum amount of Ethernet traffic from the Ethernet port should not
exceed 2 Mbps; exceeding this value will seriously affect the performance of the encoders.
If maximum encoder performance is required (4CIF 30 fps), the total amount of Ethernet
traffic being sent from the S4200 should not exceed 4 Mbps.
For example, consider a wireless cell with four cameras using two S4200 transmitters. If
this system is designed such that the distances dictate a channel data rate of 12 Mbps, the
total amount of video bandwidth for the entire wireless cell will be 9.5 Mbps at distances of
less than 3.1 miles (5 km).
The SPCF MAC protocol divides this video bandwidth equally between the two transmitters,
therefore providing 4.75 Mbps for each pair of cameras in the wireless cell. This equates to
a total of 2.4 Mbps per camera, which can accommodate the following resolution and frame
rate (NTSC/PAL) combinations, with either two analog cameras or a combination of one
analog and one IP camera using MPEG-4 encoding:
4CIF at 15/12 fps
2CIF at 30/25 fps
CIF at 30/25 fps
As the number of multicamera links increases, the video bandwidth available for each
camera reduces. With the previous example and four transmitters instead of two, the
bandwidth available for each camera is 1.2 Mbps (9.5 Mbps divided by four transmitters
divided by two cameras per transmitter).
If an IP camera is used with MJPEG compression, you must be careful in ensuring that the
combination of frame rates and resolutions from both the IP and analog cameras do not
exceed the maximum video bandwidth available.
As link distances increase, the total available video bandwidth will decrease due to free
space loss and other attenuating factors. If this is not taken into account in the design
phase, problems will surface which will have a detrimental effect on the total system
performance.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 19
2: System and RF Planning
To help you plan your system, here are typical scenarios, where:
The maximum number of analog cameras is connected on the device (one for the
S4200 and two for the S4200-2V).
The compression mode is MPEG-4 or SM4.
There is a single stream per camera.
There is clear RF line of sight, with an RF margin of 15 dB or better to maintain the data
rate specified.
The video performances supplied include a video resolution, a frame rate expressed in
frames per second (fps), and bit rate expressed in kilobits per second (kbps).
The first scenario proposes a channel data rate of 6 Mbps and a maximum available video
bandwidth of 5.1 Mbps:
Analog Cameras IP Camera on S4200 IP Camera on S4200-2V
1 camera at 4CIF, 30/25 fps,
3Mbps
2 cameras at 4CIF,
1 IP camera at CIF,
30/25 fps, 1 Mbps
N/A Available bandwidth is
30/25 fps, 6 Mbps
1 camera at 4CIF, 15/12 fps,
2Mbps
2 cameras at 4CIF,
1 IP camera at CIF,
30/25 fps, 1 Mbps
N/A 1 IP camera at CIF,
15/12 fps, 4 Mbps
1 camera at 2CIF, 30/25 fps,
2Mbps
2 cameras at 2CIF,
1 IP camera at 2CIF,
30/25 fps, 2 Mbps
N/A 1 IP camera at CIF,
30/25 fps, 4 Mbps
1 camera at CIF, 30/25 fps,
1Mbps
2 cameras at CIF, 30/25 fps,
1 IP camera at 4CIF,
15/12 fps, 2 Mbps
N/A 1 IP camera at 2CIF,
2Mpbs
0 camera 1 IP camera at 4CIF,
30/25 fps, 4 Mbps
N/A
exceeded
N/A
30/25 fps, 1 Mbps
N/A
30/25 fps, 1 Mbps
N/A
30/25 fps, 2 Mbps
N/A
20 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
The second scenario proposes a channel data rate of 54 Mbps and a maximum available
video bandwidth of 28.1 Mbps. Th ere are two transmitters in the wireless cell with exactly
the same combination of analog and IP cameras:
Analog Cameras IP Camera on S4200 IP Camera on S4200-2V
1 camera at 4CIF, 30/25 fps,
3Mbps
2 cameras at 4CIF,
30/25 fps, 6 Mbps
1 camera at 4CIF, 15/12 fps,
2Mbps
2 cameras at 4CIF,
15/12 fps, 4 Mbps
1 camera at 2CIF, 30/25 fps,
2Mbps
1 camera at CIF, 30/25 fps,
1Mbps
2 cameras at CIF, 30/25 fps,
2Mpbs
0 camera 7 IP cameras at 4CIF,
The creation and transmission of analytics metadata on the S4200-AS and S4200-AS-2V, in
conjunction with the use of an IP camera or a high bit rate Ethernet stream on the Ethernet
port, will reduce the capabilities of the video encoders. Since applications vary, you must
perform tests to determine the maximum performance of these devices when using IP
devices generating data streams in excess of 2 Mbps.
1 IP camera at CIF,
30/25 fps, 1 Mbps
N/A Not enough processing
1 IP camera at 4CIF,
15/12 fps, 2 Mbps
N/A 1 IP camera at CIF,
1 IP camera at 4CIF,
15/12 fps, 2 Mbps
1 IP camera at 4CIF,
30/25 fps, 4 Mbps
N/A 1 IP camera at 4CIF,
30/25 fps, 4 Mbps
N/A
power
N/A
30/25 fps, 1 Mbps
N/A
N/A
15/12 fps, 2 Mbps
N/A
Compatibility Issues
When planning your wireless systems, you have to take into account the firmware versions
of the involved devices. It is recommended that the S4200 transmitters have the same
firmware versions as their associated S4300 master. Furthermore, you can use the S4200
with an S3100 access point at firmware version 4.12 or higher.
In a wireless cell, the order in which you configure the devices (either the first time or later
when they are installed in the field) or update their firmware is critical if you do not want to
lose access to them. You should then:
Update the devices starting with the farthest (in terms of number of RF hops) from the
computer running the procedure.
One step at a time, get closer to the computer.
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 21

2: System and RF Planning
S4300 3
S4300 2
S4200 2
S4200 1
S4300 1
For example, consider the following setup:
You should update the devices in the following order:
1. S4200 1—You then lose contact with S4200 1.
2. S4200 2—You then lose contact with S4200 2.
3. S4300 1—You can then reach all devices.
4. S4300 2—You then lose contact will all devices except master S4300 3.
5. S4300 3—You can then reach all devices.
For the complete firmware update procedure, refer to the documentation of the Verint
software you are using.
Video Bit Rate and Data Throughput
You can theoretically connect up to 24 S4200 devices to a master access point in a wireless
cell. In practice however, video quality , frame r ate, and system lay out can limit the number
of devices that a single master access point can support.
Available video data throughput can be evaluated using the Wireless System Margin
Calculator that you can find on the Verint extranet. Available video data throughput
depends on the transmission (tx) bit rate used by each slave on the wireless network.
Video quality and frame rate influence the required data throughput. Therefore, you need
to carefully plan the number of cameras that will work on a link.
The following figures were measured in typical setup situations. They may vary depending
on your configuration. The total data throughput in a unidirectional UDP link setup varies
depending on the frequency channel width: 20 MHz in all available bands, or 5 MHz and
10 MHz in the 4.9 GHz frequency band.
The throughput for a 20 MHz channel is:
Physical Bit
Rate
6 Mbps 5.1 Mbps 5.1 Mbps 5.0 Mbps
9 Mbps 7.3 Mbps 7.3 Mbps 7.2 Mbps
Throughput for a
3-Mile (5 km)
Distance
Throughput for a
9.3-Mile (15 km)
Distance
Throughput for a
15.5-Mile (25 km)
Distance
22 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions

Nextiva S4200 Series User Guide
Physical Bit
Rate
Throughput for a
3-Mile (5 km)
Distance
Throughput for a
9.3-Mile (15 km)
Distance
Throughput for a
15.5-Mile (25 km)
Distance
12 Mbps 9.5 Mbps 9.5 Mbps 9.4 Mbps
18 Mbps 13.4 Mbps 13.3 Mbps 13.1 Mbps
24 Mbps 16.8 Mbps 16.7 Mbps 16.4 Mbps
36 Mbps 22.0 Mbps 22.0 Mbps 21.9 Mbps
48 Mbps 26.3 Mbps 25.5 Mbps 25.0 Mbps
54 Mbps 28.1 Mbps 27.1 Mbps 26.0 Mbps
The throughput for a 10 MHz channel is:
Physical Bit
Rate
Throughput for a
3-Mile (5 km)
Distance
Throughput for a
9.3-Mile (15 km)
Distance
Throughput for a
15.5-Mile (25 km)
Distance
3 Mbps 2.3 Mbps 2.3 Mbps 2.3 Mbps
4.5 Mbps 3.8 Mbps 3.7 Mbps 3.7 Mbps
6 Mbps 5.0 Mbps 4.9 Mbps 4.9 Mbps
9 Mbps 7.2 Mbps 7.1 Mbps 7.1 Mbps
12 Mbps 9.3 Mbps 9.3 Mbps 9.2 Mbps
18 Mbps 12.9 Mbps 12.8 Mbps 12.6 Mbps
24 Mbps 16.0 Mbps 15.8 Mbps 15.5 Mbps
27 Mbps 17.2 Mbps 16.9 Mbps 16.7 Mbps
The throughput for a 5 MHz channel is:
Physical Bit
Rate
Throughput for a
3-Mile (5 km)
Distance
Throughput for a
9.3-Mile (15 km)
Distance
Throughput for a
15.5-Mile (25 km)
Distance
1.5 Mbps 1.3 Mbps 1.3 Mbps 1.3 Mbps
2.25 Mbps 2.0 Mbps 2.0 Mbps 2.0 Mbps
3 Mbps 2.5 Mbps 2.5 Mbps 2.5 Mbps
4.5 Mbps 3.7 Mbps 3.6 Mbps 3.6 Mbps
Verint Video Intelligence Solutions 23

2: System and RF Planning
Physical Bit
Rate
6 Mbps 4.7 Mbps 4.6 Mbps 4.6 Mbps
9 Mbps 6.8 Mbps 6.7 Mbps 6.7 Mbps
12 Mbps 8.5 Mbps 8.5 Mbps 8.4 Mbps
13.5 Mbps 9.5 Mbps 9.4 Mbps 9.3 Mbps
The S4200 automatically adjusts the transmission speed with the current RF conditions.
Throughput for a
3-Mile (5 km)
Distance
Throughput for a
9.3-Mile (15 km)
Distance
Throughput for a
15.5-Mile (25 km)
Distance
TPC
If the country of operation of the S4200 device requires conformity to the TPC (Transmit
Power Control) rules, the maximum EIRP (effective isotropic radiated power) is reduced by
3 dBm from the allowed maximum value; for example, if the maximum EIRP is 30 dBm in
the band and region of operation, the maximum EIRP in the device will be set to 27 dBm.
The combined transmission power of the device and its antenna must not exceed this
maximum value. For that reason, you must specify the antenna gain during configuration;
the device will automatically take it into account and adjust its own transmission power
accordingly at startup. This adjustment is done in all wireless devices (masters and slaves).
To meet local regulations, you must use only antennas that conform to the requirements
specified in the “Compliance” appendix on page 136.
DFS
In countries following the DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection) regulations, frequency
channel selection is performed by the master S4300 device. Frequency channel selection
can be automatic (default) or manual; manual selection allows a better RF planning.
Note: DFS is required only in the 5 GHz band.
The radar detection mechanism (including channel availability check and non-occupancy
period) can be performed on all wireless devices (master and slave); it also allows for
RF planning and optimal wireless network performance.
regardless of the type of frequency channel selection.
Note: To minimize the false radar detection problem in colocated systems using adjacent
frequency channels, see page 29.
You should start the master first, then power the slave when the other device is in normal
operation.
24 Verint Video Intelligence Solutions
The procedure is the same
better
 Loading...
Loading...