Page 1

Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner
Device Driver User Guide
July 2007
VWorks3 and BenchWorks
Page 2

Copyright 2007 Velocity11
The information provided in this guide is intended to be accurate and reliable. However, Velocity11 does
not assume responsibility for its use or for any infringements upon the rights of third parties that may
result from its use.
The transfer of this guide, in any manner or form, to a representative of another company is strictly
forbidden.
BioCel, BenchCel, PlateLoc, Velocity11, VCode, and VPrep are registered trademarks of Velocity11.
BenchWorks, IWorks, and VWorks are trademarks of Velocity11.
Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation in the United States and
other countries.
All other trademarks are the sole property of their respective owners.
Velocity11
3565 Haven Avenue
Menlo Park, CA 94025
USA
Technical Support: 1.800.979.4811 or +1.650.846.6611
Customer Service: 1.866.428.9811 or +1.650.846.6601
Email: info@velocity11.com
Web: http://www.velocity11.com
Page 3

Table of Contents
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Who should read this guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
About Velocity11 user guides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
What this guide covers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
About devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
About device drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Installing device drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Adding devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
About diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Opening diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
About profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Setting the properties for a device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Adding and linking Sub Process tasks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Using JavaScript to set task parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
About reader output files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
About device initialization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
i
Chapter 2. Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Workflow for configuring the Microscan MS-3 Laser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Creating a Microscan MS-3 Laser profile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Setting Microscan MS-3 Laser task parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Operating the Microscan MS-3 Laser with diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Managing Microscan MS-3 Laser profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Page 4

Table of Contents
ii
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Page 5

Introduction
This chapter introduces Velocity11 device drivers and provides some
basic procedures that are needed to use them.
A Velocity11 device driver is software that plugs into VWorks or
BenchWorks software to allow them to control a specific device.
Before reading this guide, you should be familiar with the VWorks or
BenchWorks software user interface. Information about using VWorks or
BenchWorks software can be found in the VWorks Version 3 Automation
Control User Guide or BenchWorks Automation Control User Guide.
To set up and use Velocity11 device drivers, become familiar with the
content in this guide as well as the guides for the devices that use
VWorks or BenchWorks software.
This chapter contains the following topics:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
1
1
❑ “Who should read this guide” on page 2
❑ “About Velocity11 user guides” on page 3
❑ “What this guide covers” on page 5
❑ “About devices” on page 6
❑ “About device drivers” on page 7
❑ “Installing device drivers” on page 9
❑ “A dd i ng d ev i ce s ” o n pa g e 10
❑ “About diagnostics” on page 11
❑ “Opening diagnostics” on page 12
❑ “About profiles” on page 15
❑ “Setting the properties for a device” on page 16
❑ “Adding and linking Sub Process tasks” on page 19
❑ “Using JavaScript to set task parameters” on page 21
❑ “About reader output files” on page 22
❑ “About device initialization” on page 25
Page 6

2
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Who should read this guide
Job roles This user guide is for people with the following job roles:
Job role Responsibilities
Integrator Someone who writes software and
configures hardware controlled by
device drivers.
Related topics
Lab manager, administrator, or
technician
Someone who is responsible for:
❑ Installing device drivers
❑ Managing device drivers
❑ Developing the applications that
are run using device drivers
❑ Solving the more challenging
problems that might arise
❑ Developing training materials and
standard operating procedures for
operators
Operator Someone who performs the daily
production work using the device
driver and solves routine problems.
Your organization may choose to create
its own procedures for operators
including the procedures in this guide.
For information about... See...
Contacting Velocity11 http://www.velocity11.com/
contact.html
Accessing online help “About Velocity11 user guides” on
page 3
Device drivers “About device drivers” on page 7
Page 7

Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
About Velocity11 user guides
About this topic This topic describes the different formats of Velocity11 user information
and explains how to access the user information.
Formats available Velocity11 user information is provided to you as:
❑ Online help
❑ A PDF file
❑ A printed book
The information in each format is the same but each format has different
benefits.
3
Where to find user
information
Online help
The online help is added to your computer with the Velocity11 lab
automation system software installation.
PDF file
The PDF file of the user guide is on the software CD that is supplied with
the product.
Velocity11 website
You can search the online help or download the latest version of any
PDF file from the Velocity11 website at
Note: All Velocity11 user information can be searched from the website
at
www.velocity11.com.
www.velocity11.com.
Online help The online help is the best format to use when you are working at the
computer and when you want to perform fast or advanced searches for
information.
To open the online help:
1. In the Velocity11 lab automation software, press F1. The online help
window opens.
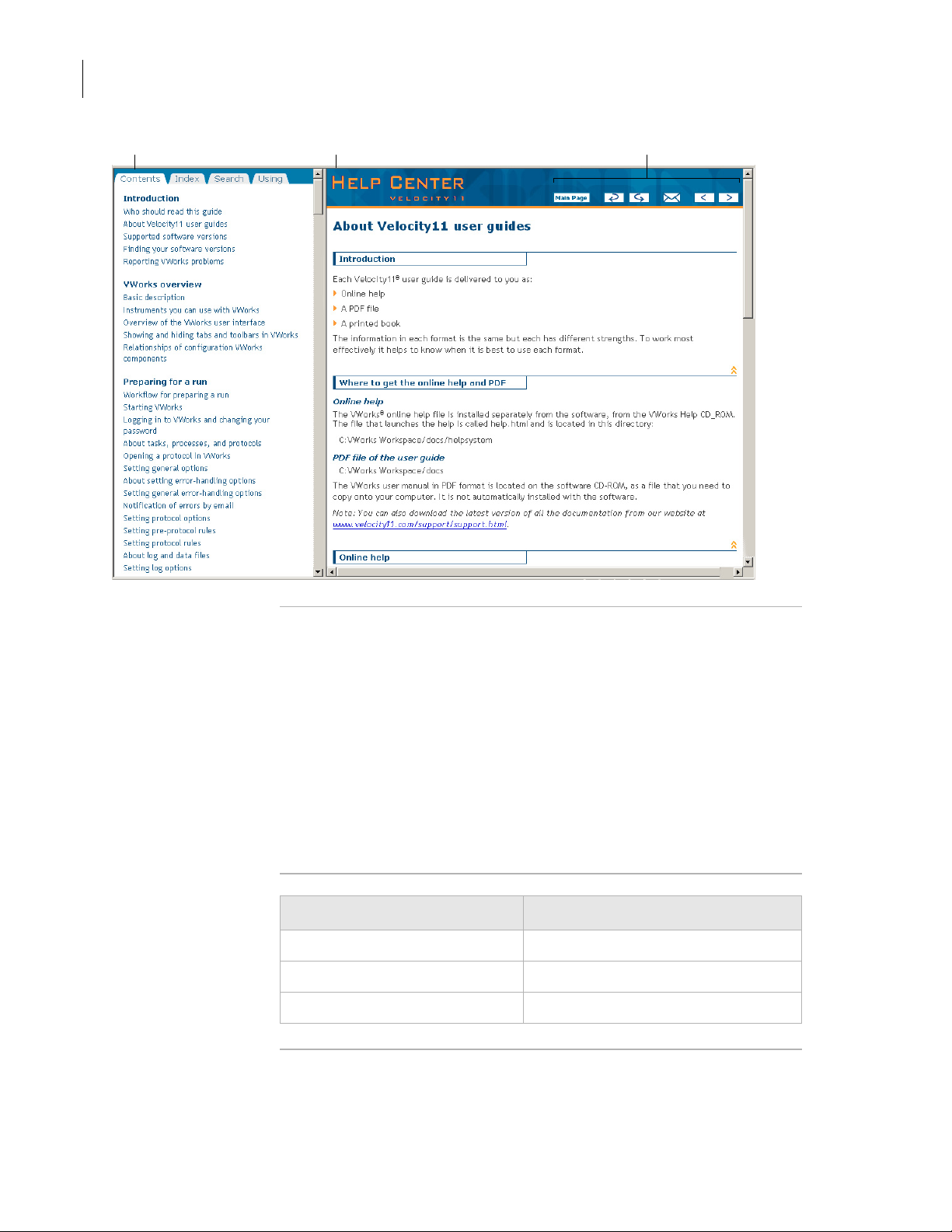
Main features
The online help window contains the following:
❑ Navigation pane. Consists of four tabs. The Contents, Index, and
Search tabs provide different ways to locate information. The Using
tab contains information about using the help system.
❑ Content pane. Displays the online help topics.
❑ Navigation buttons. Enables you to navigate through the pages.The
online help includes a navigation pane, content pane, and
navigation buttons.
Page 8
4
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Navigation pane Content pane Navigation buttons
PDF user guides Computer requirements
To open a user guide in PDF format, you need a PDF viewer. You can
download a free PDF viewer from the internet.
Printing and searching
The user guides in PDF format are mainly for printing additional copies.
You can perform simple searches in the PDF file, although these
searches are much slower than online help searches.
More information
For more information about using PDF documents, see the user
documentation for the PDF viewer.
Related topics
For information about... See...
Who this guide is for “Who should read this guide” on page 2
What’s in this guide “What this guide covers” on page 5
Device driver plug-ins “About device drivers” on page 7
Page 9

Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
What this guide covers
About this topic This topic presents an overview of what procedures and information are
provided in this user guide.
This guide explains how to:
❑ Install the driver for the device
❑ Configure the device in the device manager
❑ Set and use the tasks associated with the device
❑ Use Device Diagnostics
Also read Information about device drivers not covered in this guide and about
running VWorks or BenchWorks software can be found in the VWorks
Version 3 Automation Control User Guide or the BenchWorks Automation
Control User Guide.
Driver version To find version information for a driver in VWorks:
5
1. Start VWorks.
2. Click Help and select About VWorks.
The About VWorks dialog box lists the version numbers of all the
current software for all the devices and plug-ins.
To find version information for a driver in BenchWorks:
1. Start BenchWorks.
2. Click Help and select About BenchWorks.
The About BenchWorks dialog box lists the version numbers of all the
current software for all the devices and plug-ins.
Firmware version Some devices have firmware installed on them. Because each device is
different, the version number may not be the same for all devices.
To find version information for device firmware:
1. Open Device Diagnostics dialog box.
2. Click About.
The About Device Control message box appears displaying the
current version of firmware.
What this guide does
not cover
This guide does not cover the following:
❑ The operation of the device
❑ The operation of VWorks or BenchWorks software
❑ Velocity11 devices, such as the PlateLoc Sealer, VCode Microplate
Labeler, and VPrep Pipettor when used in stand-alone mode
Page 10

6
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
VWorks or
BenchWorks
compatibility
BenchWorks
versions
If you have purchased a device driver plug-in and are installing it
yourself, check with the Velocity11 Technical Support to be sure your
version of VWorks or BenchWorks software and the device driver plug-in
are using the same version of IWorks software.
Device driver plug-ins used with BenchWorks software may not include
some newer features that were specifically added for use with VWorks
software and that are described in this manual.
Related topics
For information about... See...
Who this guide is for “Who should read this guide” on page 2
User documentation “About Velocity11 user guides” on
Device driver plug-ins “About device drivers” on page 7
About devices
page 3
About this topic This topic presents a definition of a Velocity11 device and the device
file.
Read this topic if you are unfamiliar with Velocity11 devices and VWorks
or BenchWorks software.
Device defined A device is an item on your lab automation system that has an entry in
the device manager. A device can be a robot, an instrument, or a
location on the lab automation system that can hold a piece of labware.
Examples of devices:
❑ Ve l o c i t y 1 1 r o b o t
❑ Human robot
❑ PlateLoc Thermal Plate Sealer
❑ Labcyte Echo550
❑ Platepad
❑ VPrep shelf
❑ Wa st e
Device file defined The data entered into the device manager and saved as a device file
contains the configuration information for your devices.
Page 11

Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
Device file location Device files have the file name format file name.dev and are stored in
the folder location that you specify when saving the file.
Related topics
For information about... See...
Device diagnostics “About diagnostics” on page 11
Device profiles “About profiles” on page 15
7
Adding a device to the device
manager
“Adding devices” on page 10
About device drivers
About this topic This topic describes what device drivers are and what they do.
Velocity11 device drivers enable mechanical devices or software
programs to work with VWorks or BenchWorks software.
Read this topic if you are:
❑ An administrator in charge of installing device drivers and managing
Ve l o c i t y 1 1 d ev i c es
❑ A lab automation system integrator who writes software and
configures hardware controlled by VWorks or BenchWorks software
Device driver
defined
A Velocity11 device driver enables VWorks or BenchWorks software to
control and communicate with the specific type of device. Each type of
device that you operate with VWorks or BenchWorks software requires a
device driver.
For example, VWorks software uses the:
❑ VPrep Pipettor device driver to communicate with the Velocity11
VPrep Pipettor device
❑ Softmax Reader device driver to communicate with Molecular
Devices readers
Plug-in defined A plug-in is a software program that when added to another program
extends it.
Plug-in device
drivers
Some device drivers are incorporated directly into the VWorks or
BenchWorks software application. Other device drivers are distributed
as plug-ins. All the device drivers covered in this guide are the plug-in
type.
Page 12

8
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Advantages of distributing device drivers as plug-ins are:
❑ You only need to install the plug-ins for the devices you use
❑ When new plug-ins become available, they can be easily added.
There is no need to re-install the VWorks or BenchWorks software
application
IWorks interface The device driver plug-ins and VWorks or BenchWorks software use
IWorks software as a common interface to communicate with each
other. Using a common interface allows the creation of a device driver
plug-in without the necessity of changing the software.
!! IMPORTANT !! Both VWorks or BenchWorks software and the
device driver must be using the same version of IWorks to work
properly.
Writing your own
device driver
What functions do
the device drivers
provide?
Related topics
If you are a lab automation system integrator who writes software and
configures hardware controlled by VWorks or BenchWorks software, you
can write your own driver plug-in for a new device. Contact the
Velocity11 Technical Support for information about how to do this.
Once installed, the following items are enabled:
❑ Tasks associated with the device.
Device-specific tasks appear in the Protocol Tasks list and are
available for use in protocol editor processes.
❑ Task parameters associated with the device.
Device-specific task parameters appear in the Protocol Task
Parameters toolbar. These determine the conditions with which to
execute the tasks of the device.
❑ Diagnostic commands specific to the device.
Device-specific diagnostic commands and options appear in the
Device Diagnostics dialog box. These commands enable direct
control of the device.
For information about... See...
Adding a device to the device
manager
Opening diagnostics “Opening diagnostics” on page 12
Installing a device driver “Installing device drivers” on page 9
Devices “About devices” on page 6
“Adding devices” on page 10
Page 13

Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
Installing device drivers
About this topic Devices are integrated into VWorks or BenchWorks software using
device driver plug-ins. Plug-ins need to be installed before the device
can be configured and used.
This topic describes how to install device drivers if they are not already
installed on your system. Read this topic if you are an administrator in
charge of managing Velocity11 devices.
Procedure To install device drivers:
1. Insert the device driver installation disc into the CD-ROM of the
computer running VWorks or BenchWorks software.
2. Follow the on-screen instructions for installation, selecting the
default values when available.
3. When finished, exit VWorks or BenchWorks software.
4. Log off Windows and restart your computer.
5. Start VWorks or BenchWorks software.
9
Related topics
For this
application...
VWorks software C:\VWorks Workspace\bin\plugins
BenchWorks
software
For information about... See...
Device drivers “About device drivers” on page 7
Opening diagnostics “Opening diagnostics” on page 12
The default location for the device driver is...
C:\Program Files\Velocity11\BenchWorks\plugins
Page 14

10
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Adding devices
About this topic To configure your lab automation system to use a device, you need to
add it to a device file in VWorks or BenchWorks software. The VWorks or
BenchWorks software device manager uses the information in the
device file to communicate and operate the device within the
automation system.
This topic describes how to:
❑ Create a new device file (if one does not already exist)
❑ Add devices
❑ Save the device file
Read this topic if you are an administrator in charge of managing
Ve l o c i t y 1 1 d ev i c es .
Procedure To add devices to a device file:
1. Make sure that the devices are physically networked to the VWorks
or BenchWorks software computer and turned on.
2. Start VWorks or BenchWorks software and login as an Administrator.
3. Do one of the following:
If you have an existing device file that you want to add to, select
File > Device File, click Open, and select your device file.
If you are creating a new device file, select File > Device File and
click New.
4. Click the Device Manager tab.
5. Click New device in the Device List toolbar and enter a name for the
device you are adding.
6. In the device manager, set the Device type.
The default type is Plate Pad, Standard.
7. Repeat step 5 and step 6 for each device.
Page 15

Related topics
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
8. Select File > Device File > Save.
If you are creating a new device file, you are prompted to enter a
name for your device file.
Alternatively, you can select File > Save All. This saves the device file
and the current protocol file at the same time.
For information about... See...
Device drivers “About device drivers” on page 7
Setting generic device properties “Setting the properties for a device” on
page 16
Adding a sub-process to a protocol “Adding and linking Sub Process tasks”
on page 19
Opening diagnostics “Opening diagnostics” on page 12
11
About diagnostics
About this topic This topic presents an overview of diagnostics software.
Read this topic if you need to set up or troubleshoot a device running
VWorks or BenchWorks software.
Background Devices can be controlled in real time directly through the VWorks or
BenchWorks software Diagnostics using simple commands.
Diagnostics software is used for:
❑ Troubleshooting
❑ Setting teachpoints
❑ Performing manual operations outside a protocol
❑ Creating and editing profiles
For example, if an error occurs during a run that leaves a plate and the
robot where they should not be, you can use robot diagnostics to move
the plate and return the robot to its home position.
Types of diagnostics
software
Devices and robots manufactured by Velocity11 include their own
diagnostics software. You can find instructions for using this software in
the relevant user guide.
Page 16

12
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Related topics
For information about... See...
Opening diagnostics “Opening diagnostics” on page 12
Adding a device to the device
manager
Device drivers “About device drivers” on page 7
The definition of devices “About devices” on page 6
“Adding devices” on page 10
Opening diagnostics
About this topic Every device has diagnostics software to assist you with troubleshooting
and setting up the device. This topic describes how to open a device’s
diagnostics in VWorks or BenchWorks software.
Read this topic if you need to access a device’s diagnostics to perform a
device setup task or manually operate a device.
Procedure 1 If you are using VWorks4 software
To open Diagnostics:
1. Click Diagnostics on the Control toolbar.
2. In the device file’s window, select the device. Expand the general
name of the device, if necessary.
3. Click Device diagnostics located at the bottom of the window. The
device’s diagnostics dialog box opens.
If you are using VWorks3 or BenchWorks software
To open Diagnostics:
1. Click Diagnostics on the Control toolbar.
Page 17

Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
2. In the Diagnostics window, select thedevice. Expand the general
name of the device, if necessary.
3. Click Device diagnostics. The device’s diagnostics dialog box opens.
Procedure 2 If you are using VWorks4 software
To open Diagnostics:
Chapter 1: Introduction
13
1. Click the Device File tab.
2. Select the device from the Devices toolbar.
Expand the general name of the device, if necessary.
3. Click Device diagnostics located at the bottom of the Devices
toolbar.
The device’s diagnostics dialog box opens.
If you are using VWork3 or BenchWorks software
To open Diagnostics:
1. Click the Device Manager tab.
2. Select the device from the Device List toolbar. Expand the general
name of the device, if necessary.
Page 18

14
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
3. Click Device diagnostics located at the bottom of the Device List
toolbar.
The device’s diagnostics dialog box opens.
Related topics
For information about... See...
Diagnostics “About diagnostics” on page 11
About device drivers “About device drivers” on page 7
Adding a device to the device
manager
Setting generic device properties “Setting the properties for a device” on
“Adding devices” on page 10
page 16
Page 19

Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
About profiles
About this topic This topic describes what profiles are and what they do.
Read this topic if you are an administrator in charge of managing
Ve l o c i t y 1 1 d ev i c es .
Profiles defined A profile contains the initialization settings needed for communication
between a device and device driver. The data in a profile is used by
VWorks or BenchWorks software to identify each device on the network.
A profile can also contain other basic settings that you are unlikely to
change once set up.
Because profiles identify device driver devices on the network, each
device driver device must have its own profile.
You can create, modify, and delete profiles as needed.
Stored settings Profiles are stored in the Windows registry.
The settings stored in a device driver profile include:
15
Related topics
❑ Whether the device is connected using serial or Ethernet
❑ If the device is connected using Ethernet, the Device ID of the
device on the network
❑ If the device is connected using serial, the COM port that the
controlling computer uses for communication
❑ Configuration of accessories
For information about... See...
Device drivers “About device drivers” on page 7
Adding a device to the device
manager
Opening device diagnostics “Opening diagnostics” on page 12
“Adding devices” on page 10
Page 20

16
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Setting the properties for a device
About this topic The device properties provide VWorks or BenchWorks software with
additional information about the device’s current configuration, such as
which profile to use, and stores the information in the device file. The
device file is automatically loaded when you open a protocol.
The device properties need to be set when configuring the device.
Typically, these properties only need to be set once. This topic describes
how to set the following device properties:
❑ General
❑ Te a c h p o i n t
❑ Barcode
❑ Location (for devices with multiple teachpoints)
❑ Device Properties
Read this topic if you are an administrator in charge of managing
Ve l o c i t y 1 1 d ev i c es .
Before you start Make sure that you have installed the device driver plug-in and have
added the device to the device manager.
See “Related information” for procedures on how to do these tasks.
Setting general
properties
To set the general properties for a device:
1. Click the Device Manager tab.
2. Select the device from the Device List toolbar. (Expand the device
name, if necessary.)
Note: For devic es with Locations, see “Setting location properties”
on page 17. If no Locations, continue with step 3.
3. In the General group, set the following:
a. Approach height. This is the height to raise the robot gripper
above the teachpoint when the robot moves the plate
horizontally towards or away from it.
b. Allowed/prohibited labware. Click the adjacent field to open the
dialog box. Move the labware classes by selecting them and
clicking one of the arrow buttons.
4. In the Device Properties, select the desired profile if it is not already
selected.
5. Select File > Device File > Save to save the changes to the device file.
Page 21

Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
Setting teachpoints Teachpoints are the coordinates in space that a robot travels to in order
to interact with a device. Only the devices that are accessible by robots
are able to have teachpoints.
To set the teachpoint properties:
1. Open the Device Properties page.
2. In the Teachpoints property group, set the following:
a. Device is accessible from robot robot’s name. Choose Yes or
No.
b. Teachpoint for robot robot’s name. Choose a file.
17
Setting barcode
location
Setting location
properties
If your device has a barcode reader, indicate where the reader is
located.
To set the barcode readers property:
1. In the Barcode Readers property group, set the side that has the
barcode to Yes.
2. Enter the number of the COM port to which the device is connected.
Note: The options available under Location groups might differ for
software and hardware device drivers. Software devices do not have
robot-accessible labware positions.
For hardware devices that have more than one robot-accessible labware
position, the approach height, allowable/prohibited labware,
teachpoint, and barcode properties are located under Location groups.
To set the Location properties:
1. Hardware device drivers only. Set the Use linked location. Follow the
procedure in
“Setting the Use linked location” on page 18.
2. Hardware device drivers only Set the Teachpoints. Follow the
procedure in
“Setting teachpoints” on page 17.
Page 22

18
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
3. Some software device drivers only. Set the Approach height and
Allowed/prohibited labware. Follow the procedure in
general properties” on page 16.
4. Set the Barcode Readers location. Follow the procedure in “Setting
barcode location” on page 17.
5. Assign the Labware used by the location by selecting the correct
labware type from the list.
6. In the Device Properties, select the desired profile if it is not already
selected.
7. Select File > Device File > Save to save the changes to the device file.
“Setting
Setting the Use
linked location
Related topics
Currently, this feature is enabled for the special situations in which there
is a storage device such as a PlateHub Carousel, StoreX, or Cytomat and
a robot, such as the Velocity11 Translator robot that is shuttling plates
between systems.
To use this feature, select yes and then select the device location to
which you want to link. This tells the software that the current device
location is the same physical location as the device selected from the
Device to use list.
Note: Selecting this option when it is not enabled will have no effect on
the system.
For information about... See...
Device drivers “About device drivers” on page 7
Installing a device driver plug-in “Installing device drivers” on page 9
Profiles “About profiles” on page 15
Adding a device to the device
manager
Opening diagnostics “Opening diagnostics” on page 12
“Adding devices” on page 10
Page 23

Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
Adding and linking Sub Process tasks
About this topic This topic describes how to add a sub-process to a protocol and
configure it. Read this topic if you are an administrator or technician
and are responsible for creating protocols in VWorks or BenchWorks
software.
Before you read this Before you read this topic, become familiar with the topics in the
VWorks Version 3 Automation Control User Guide or BenchWorks
Automation Control User Guide describing what a protocol is and how it
is created.
19
Sub Process task
defined
Adding a Sub
Process task
Setting Sub Process
task parameters
Sub Process tasks indicate the existence of a subroutine within a
protocol. Sub-processes typically contain a series of liquid handling
tasks used by devices such as the VPrep Pipettor or Multimek dispenser.
The first step in creating a pipette process is to add a Sub Process task to
the protocol editor. Drag the Sub Process icon into the process.
When you add the Sub Process task, a new sub-process is started in the
pipette process editor. This process is identified by its sub-process link
icon.
Because you can have more than one sub-process in a protocol, you
must link the Sub Process task to the correct sub-process.
To link the Sub Process task to the correct sub-process:
1. In the Protocol Editor, add a Sub Process task to the protocol and
then select it in the protocol sequence.
2. In the Protocol Task Parameters toolbar, select the sub-process that
you want to use for this pipetting task from the
Use Sub Process list.
Page 24

20
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
3. If there is only one sub-process and you need to create a second
one, click
Add New.
Associating the subprocess to a device
Because you can have more than one device that uses sub-processes on
a lab automation system, you must link each sub-process link icon with
one or more devices that you want the sub-process to be able to use. You
do this by setting the parameter for the sub-process link icon.
To link a Sub Process task to a device:
1. In the Pipette Process Editor, select the Sub Process link icon.
2. In the Available devices list of the Pipette Task Parameters toolbar,
select one or more pipettors to link to and click
Add.
The selected pipettors move to the lower box and become available
for use.
Page 25

Related topics
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
For information about... See...
Device drivers “About device drivers” on page 7
Setting common device properties “Setting the properties for a device” on
page 16
21
Adding a device to the device
manager
Creating protocols
“Adding devices” on page 10
❑ VWorks Version 3 Automation
Control User Guide
❑ BenchWorks Automation Control
User Guide
Using JavaScript to set task parameters
About this topic JavaScript programs (scripts) can be used to change the parameters of a
protocol task immediately before it is scheduled. This extends the
capability of VWorks or BenchWorks software because the parameters
can be changed dynamically during a run, based on the following:
❑ Information passed from an external source, such as a database
❑ The number of times the protocol has cycled
❑ Feedback on changing conditions during the run
This topic describes the use of JavaScript to set task parameters in a
protocol.
Read this topic if you are an administrator or technician responsible for
creating VWorks or BenchWorks software protocols and want to add
functionality to a task using JavaScript.
Where scripts are
written
Scripts can be written in two ways:
❑ Directly into the box in the Advanced Settings tab of the Task
Parameters toolbar
❑ As an external file that is located by clicking Browse in the
Advanced Settings tab and navigating to its location on the hard
drive
Note: You can also call an external file by embedding the “open( )”
function in the box.
The following screenshot displays a short script that prints the
parameters of a task to the log toolbar, just before the task runs. In this
case, the script is written directly in the Advanced Settings box.
Page 26

22
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
For more information about using JavaScript, refer to the VWorks Version
3 Automation Control User Guide or the BenchWorks Automation Control
User Guide.
Related topics
For information about... See...
Using JavaScript in protocols
❑ VWorks Version 3 Automation
Control User Guide
❑ BenchWorks Automation Control
User Guide
Adding tasks to protocols
❑ VWorks Version 3 Automation
Control User Guide
❑ BenchWorks Automation Control
User Guide
About reader output files
About this topic Plug-in device drivers that are written for plate readers have a common
way of naming their output files. This topic explains the concepts related
to output file naming. By reading this topic, you will learn how to
prevent data in the reader output files from being overwritten by newer
data.
Read this topic if you are an operator who wants to make changes to the
task parameters for one of these readers:
Plug-in default
output file
❑ VR4000
❑ Analyst GT
❑ Fusion
❑ Viewlux
❑ Te c a n r e a d e r s
When you first install a reader device driver plug-in, all data recorded
during a protocol or by a manual read using diagnostics software is
written to a single file stored in the C: drive.
Page 27

Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
The exact name of the file is specific to the device. For example, the
RVSI VR4000 device driver creates a file with the name
vialreaderresults.txt.
This file can only store data for one read, which means that the set of
data for each read overwrites the last set in the file. To avoid this
problem you must set up an output file naming convention.
23
Profile default
output file name
Some device drivers allow more than one device of that type to be used
in the lab automation system. In this case, each device must have its
own profile. Even if you have only one device, you can still set up
multiple profiles for it, with each storing different settings.
In these cases, you probably want each profile to have a separate default
output filename to prevent the data from runs using one profile
overwriting those of another.
Filename suffixes To prevent the data from one read overwriting the data from another,
you need to append a variable suffix to the file name. You can append a
date/time stamp and one or more bar codes on the rack or plate.
Example The example output file folder below shows that a profile default file
name of output.txt was created at one time. At another time, a suffix was
appended in the profile for the device driver, which added a barcode
identifier to the file name (for example output_C100040329.txt).
Page 28

24
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Overriding output
file names with
tasks
Related topics
You can override the default output file name that is set in the profile
using the Output filename property of the Read task parameters.
This allows you to use different output file names for every task.
The suffix used for the file name that you set in the task parameters is
taken from the suffix specified in the device diagnostics profile. So if you
select date/time stamp in the profile, the date/time stamp will also be
appended during a run in which you have specified a different file
name.
For more information about... See...
Opening diagnostics “Opening diagnostics” on page 12
Profiles “About profiles” on page 15
Page 29

Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
About device initialization
About this topic When working in device diagnostics software, you are often required to
initialize the device. This topic explains why device initialization is
necessary.
25
Opening
communications
Initializing a device opens communications with it. For example, if the
device is connected with a serial cable, the COM port is opened, and if
the device is connected with an Ethernet cable, the TCP/IP socket is
connected.
Homing motors Initializing a device homes motors that do not track their position along
their line of travel. Homing a motor moves it until it triggers an event,
called a home flag. This tells the motor its location.
The motors on some devices automatically move to their home
positions when the device is turned on. The motors on other devices
must be initialized to be homed.
Setting profile
parameters
Setting state and
memory variables
Initializing a device applies relevant parameters set in the device’s
profile.
Most devices store variables in software or firmware. Initializing a device
sets these variables to their initial values.
Related topics
For information about... See...
Using Diagnostics
❑ “About diagnostics” on page 11
❑ “Opening diagnostics” on page 12
Workflow for configuring devices “Adding devices” on page 10
Page 30

26
Chapter 1: Introduction
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Page 31

Chapter 2: Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner
The Microscan MS-3 Laser is a barcode scanner that can be configured
to work in lab automation systems running VWorks or BenchWorks
software.
This chapter contains the following topics:
❑ “Workflow for configuring the Microscan MS-3 Laser” on page 28
❑ “Creating a Microscan MS-3 Laser profile” on page 29
❑ “Setting Microscan MS-3 Laser task parameters” on page 30
❑ “Operating the Microscan MS-3 Laser with diagnostics” on page 32
27
2
❑ “Managing Microscan MS-3 Laser profiles” on page 33
Page 32

28
Chapter 2: Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Workflow for configuring the Microscan MS-3 Laser
About this topic This topic presents the workflow for configuring the Microscan MS-3
Laser device driver.
Read this topic if you are an administrator responsible for setting up
devices in VWorks or BenchWorks software.
Before you start Before you can configure the Microscan MS-3 Laser device driver, you
must have installed it. For installation instructions, see “Installing device
drivers” on page 9.
Workflow
Step Topic
1 “Setting the properties for a device” on page 16
2 “Creating a Microscan MS-3 Laser profile” on page 29
Related topics
3 “Setting the properties for a device” on page 16
For information about... See...
Device drivers “Setting the properties for a device” on
page 16
Setting Microscan MS-3 Laser task
parameters
Managing Microscan MS-3 Laser
profiles
Using Microscan MS-3 Laser
Diagnostics
“Setting Microscan MS-3 Laser task
parameters” on page 30
“Managing Microscan MS-3 Laser
profiles” on page 33
“Operating the Microscan MS-3 Laser
with diagnostics” on page 32
Page 33

Chapter 2: Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
Creating a Microscan MS-3 Laser profile
About this topic This topic describes how to create a profile for the Microscan MS-3
Laser.
Read this topic if you are an administrator responsible for setting up
devices in VWorks or BenchWorks software.
Before you start Before you create a profile, you need to have installed the device driver
and added the Microscan MS-3 Laser to the device manager.
Procedure To create an Microscan MS-3 Laser profile:
29
1. Open the
2. Click the
3. Click
Create a new profile, enter a name, and click OK.
Microscan Bar Code Reader Diagnostics.
Profiles tab.
4. In the Profile Settings area, set the following:
Setting Comments
Serial port The number of the COM port that is
connected to the Microscan MS-3
Laser.
Beep on decode Select to have the Microscan MS-3
Laser beep when a scanned barcode
is decoded.
5. Click Update this profile.
Page 34

30
Chapter 2: Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Related topics
For information about... See...
Opening diagnostics “Setting the properties for a device” on
page 16
Adding the Microscan MS-3 Laser
to the device manager
The next step “Setting the properties for a device” on
The workflow this procedure
belongs to
Managing Microscan MS-3 Laser
profiles
Using Microscan MS-3 Laser
Diagnostics
Using Microscan MS-3 Laser tasks “Setting Microscan MS-3 Laser task
Profiles “About profiles” on page 15
“Setting the properties for a device” on
page 16
page 16
“Workflow for configuring the
Microscan MS-3 Laser” on page 28
“Managing Microscan MS-3 Laser
profiles” on page 33
“Operating the Microscan MS-3 Laser
with diagnostics” on page 32
parameters” on page 30
Setting Microscan MS-3 Laser task parameters
About this topic When the Microscan MS-3 Laser is added to the device manager, the task
associated with the device becomes available in the protocol editor.
When a task is added to a protocol, you need to set the parameters for it.
This includes choosing the Microscan MS-3 Laser to use and the side of
the labware on which the barcode is located.
About Microscan
MS-3 Laser tasks
This topic describes the task and its parameters.
Read this topic if you are:
❑ An administrator or technician responsible for creating protocols
❑ An operator who wants to make changes to the Microscan MS-3
Laser task parameters in a protocol
Note: Operators cannot save changes to protocols.
The Microscan MS-3 Laser device driver adds one task to VWorks or
BenchWorks software. This task instructs the Microscan MS-3 Laser to
scan a barcode.
The Microscan MS-3 Laser task is represented by this icon in the Protocol
Tasks toolbar:
Page 35

Chapter 2: Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
This task is available in the protocol editor.
31
Setting the
Microscan MS-3
Laser task
parameters
Related topics
To set the Scan bar code task parameters:
1. Add the Scan bar code
task to the protocol process.
2. In the Protocol Task Parameters toolbar, click the Task Settings tab.
3. Select the Microscan MS-3 Laser you want to use from the left side
and click
Add.
The device name moves to the right.
4. In the “Scan bar code” properties area, set the location of the
barcode to be scanned by selecting North, South, East, or West from
the Side to scan list.
For more information about... See...
The workflow for configuring the
Microscan MS-3 Laser
Creating protocols, pre-protocols,
post-protocols, and pipette
processes
Opening Microscan MS-3 Laser
device properties page
Creating a Microscan MS-3 Laser
profile
Managing Microscan MS-3 Laser
profiles
Using Microscan MS-3 Laser
Diagnostics
“Workflow for configuring the
Microscan MS-3 Laser” on page 28
❑ VWorks Version 3 Automation
Control User Guide
❑ BenchWorks Automation Control
User Guide
“Setting the properties for a device” on
page 16
“Creating a Microscan MS-3 Laser
profile” on page 29
“Managing Microscan MS-3 Laser
profiles” on page 33
“Operating the Microscan MS-3 Laser
with diagnostics” on page 32
Page 36

32
Chapter 2: Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Operating the Microscan MS-3 Laser with diagnostics
About this topic This topic describes how to:
❑ Initialize the Microscan MS-3 Laser
❑ Scan a barcode
Read this topic if you are an operator who wants to troubleshoot or
operate the Microscan MS-3 Laser using direct commands.
Before you start Before you can send commands to the Microscan MS-3 Laser, or receive
status information from the Microscan MS-3 Laser, you need to initialize
it.
To initialize the Microscan MS-3 Laser:
1. Open
2. Click the
3. Select a profile from the Profile name list.
4. Click Initialize this profile.
Microscan Bar Code Reader Diagnostics.
Profiles tab.
Scanning a barcode To sca n a barcode:
1. Open
Microscan Bar Code Reader Diagnostics.
Click the
Controls tab.
2. Place the labware on the device that has the Microscan MS-3 Laser.
Page 37

Related topics
Chapter 2: Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner
Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner Device Dr iver User Guide
3. Click Scan. The decoded barcode appears in the Result box and
results are saved in the protocol log.
4. Click Calibrate to optimize the Microscan MS-3 Laser scanner
settings.
Note: During the calibration process, the scanner attempts
various settings to determine the optimum decode rate for the
given conditions.
For more information about... See...
33
Opening Microscan Bar Code
Reader Diagnostics
The workflow for configuring the
Microscan MS-3 Laser
Creating a Microscan MS-3 Laser
profile
Operating the Microscan MS-3
Laser
Initializing a device “About device initialization” on page 25
“Setting the properties for a device” on
page 16
“Workflow for configuring the
Microscan MS-3 Laser” on page 28
“Creating a Microscan MS-3 Laser
profile” on page 29
“Operating the Microscan MS-3 Laser
with diagnostics” on page 32
Managing Microscan MS-3 Laser profiles
About this topic This topic describes how administrators and technicians can manage
Microscan MS-3 Laser profiles.
Managing profiles To manage Microscan MS-3 Laser profiles:
1. Open the
Microscan Bar Code Reader Diagnostics.
2. Click the
Profiles tab.
Page 38

34
Chapter 2: Microscan MS-3 Laser Scanner
Microscan M S-3 Laser Scanner Device Driver User Guide
Related topics
3. Select a profile from the Profile name list.
4. Perform the management task.
Management tasks include the following:
Updating the profile
Copying a profile
Renaming a profile
Deleting a profile
Saving changes to a profile
Note: Click Update this profile to save edits.
For more information about... See...
Opening Microscan MS-3 Laser
Diagnostics
The workflow for configuring the
Microscan MS-3 Laser
Creating a Microscan MS-3 Laser
profile
“Setting the properties for a device” on
page 16
“Workflow for configuring the
Microscan MS-3 Laser” on page 28
“Creating a Microscan MS-3 Laser
profile” on page 29
 Loading...
Loading...