Page 1

INSTALLATION GUIDE
Part 2: Configuration
DOMOTICS
Page 2

VelbusLink is regularly updated. The screenshots in this manual may differ from the most recent VelbusLink version.
© 2020 Velbus
Page 3

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 1 www.velbus.eu
Table of contents
1 VELBUSLINK .................................................................................................................................................................3
Downloading and installing .................................................................................................................................................................. 3
Connecting, scanning and synchronizing ....................................................................................................................................... 3
2 GETTING STARTED WITH A NEW PROJECT .....................................................................................................5
Creating a new VelbusLink project .................................................................................................................................................... 5
Changing electronic addresses ............................................................................................................................................................. 7
Operating channels from within VelbusLink ................................................................................................................................. 9
Renaming the modules and channels .............................................................................................................................................. 9
Optional: Layers ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 9
Using the detector tab .......................................................................................................................................................................... 10
Recap ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 11
3 ACTIONS ....................................................................................................................................................................... 12
How the system works .......................................................................................................................................................................... 12
Creating actions ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 12
Visualizing and modifying actions .................................................................................................................................................... 14
Explanation of the actions ................................................................................................................................................................... 16
Copying actions ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 16
The mAcro wizard .................................................................................................................................................................................... 16
4 CHANGING FEEDBACK CHARACTERISTICS OF INPUT MODULES ..................................................... 18
5 FORCING AND INHIBITING ................................................................................................................................. 20
Inhibiting .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 20
Forcing ........................................................................................................................................................................................................ 20
Priorities ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 20
6 CONFIGURING MODULES .................................................................................................................................... 21
7 DUAL MODE BUTTONS ........................................................................................................................................ 22
Step 1: Set up dual mode ..................................................................................................................................................................... 22
Step 2: Create the actions ................................................................................................................................................................... 23
Ready! .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
8 MULTI BUTTON MODE ......................................................................................................................................... 24
Step 1: Configuring multi mode ........................................................................................................................................................ 24
Step 2: Creating the actions................................................................................................................................................................ 25
Ready! .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 25
9 HEATING/COOLING CONTROL ......................................................................................................................... 26
1. Activate the temperature sensors ................................................................................................................................................ 26
2. Configure the thermostats ............................................................................................................................................................. 26
3. Showing the sensors on the OLED display ............................................................................................................................. 27
4. Create connections ...........................................................................................................................................................................28
5. Automatic heating and cooling .................................................................................................................................................... 29
6. Using input channels to set the heating/cooling mode (optional) ............................................................................... 30
10 CREATING AND MODIFYING PROGRAM STEPS......................................................................................... 32
a practical example ................................................................................................................................................................................ 32
Heating/cooling program steps ......................................................................................................................................................... 35
Page 4

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 2 www.velbus.eu
Programs versus program steps ....................................................................................................................................................... 35
Wake-up and bedtimes (optional) .................................................................................................................................................. 36
Actions related to program steps and programs ....................................................................................................................... 37
Modifying the sunset and sunrise times ........................................................................................................................................ 37
11 SPECIAL FUNCTIONS............................................................................................................................................. 39
Replacing a (faulty) module ............................................................................................................................................................... 39
Firmware updates ................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
Set the installation in a certain state during start-up .............................................................................................................. 40
12 TROUBLESHOOTING .............................................................................................................................................. 41
General step-by-step guide ................................................................................................................................................................ 41
My relay switches off ............................................................................................................................................................................. 42
A module is not reacting as desired ................................................................................................................................................ 42
My program steps are not executed or executed at the wrong moment ....................................................................... 42
VelbusLink shows the error message ‘communication error with your installation’, does not find all modules
when syncing, shows error messages when syncing… ....................................................................................................... 43
The scan worked perfectly but now I cannot find my installation any more ................................................................ 43
The scan is over but some modules are missing ....................................................................................................................... 43
The scan is over but some modules have a red X mark on the module name ......................................................... 43
My VMB8PBU modules give a different address than the one I set ................................................................................. 43
The addresses of my modules have suddenly changed ......................................................................................................... 43
Some input channels provide a wrong “pressed” status ....................................................................................................... 44
The LEDs on some modules blink or do not respond ............................................................................................................ 44
An input module stops responding ................................................................................................................................................ 44
Automatic detection selects the wrong module; the address of the module you are expecting is probably also
attributed to another module ..................................................................................................................................................... 44
Page 5

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 3 www.velbus.eu
1 VELBUSLINK
In this guide you will find instructions on how to configure the modules in a Velbus home automation
system. For more information on Velbus hardware (installing the modules and wiring), please refer to
“Velbus Installation Guide, Part 1: Hardware and Cabling”.
DOWNLOADING AND INSTALLING
VelbusLink is the free configuration software for Velbus. It can be downloaded from the www.velbus.eu website. To install
VelbusLink on your PC (Windows only), double click the setup file and follow the standard installation procedure.
A message will appear in the upper right corner in VelbusLink when a new version is available. You will need a working
internet connection.
CONNECTING, SCANNING AND SYNCHRONIZING
It is important to understand the following three basic concepts in VelbusLink: connecting, scanning and synchronizing.
Connecting
In VelbusLink Connecting means: making a connection between the VelbusLink software and the Velbus system (the
modules) through an USB or RS232 interface module1, through the VMBHIS Home Center server, through the Signum
server, the VMBUSBIP IP gateway, or through a TCP/IP server.
When choosing the Quick connecting option, a connection is automatically selected as follows:
• if connection data is saved in the project file, this data will be used
• if not, a USB connection is searched and automatically used if detected
• if no USB connection is detected, a window will pop up with a manual connection selection option
VelbusLink can also be used without being connected to the modules. In that case, changes made can be saved to the
VelbusLink project file (which is stored on your PC), and later written to the modules once a connection has been
established.
To work on a VelbusLink project without being connected to the installation, the modules need to have been scanned at
least once in advance (because VelbusLink identifies the modules by their serial numbers which are unique for every
module). Once the installation scanned and the project saved for the first time, the project can be completed offline and
later synced to the modules.
Scanning
When VelbusLink scans your physical installation, it creates on your PC a set of virtual copies of the modules.
You can then configure these virtual modules and create actions between them using VelbusLink’s graphical interface. For
instance, to make a certain push button switch a relay channel, you will create a “toggle” action in VelbusLink between the
button and the relay channel.
Synchronizing
By then writing your VelbusLink project (or certain parts of it) to the physical modules (synchronizing ) these actions and
other settings will then be written into the memory maps of the modules.
Synchronizing can be done in two directions: reading and writing (see below).
1
VMBRSUSB or VMB1USB
Page 6

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 4 www.velbus.eu
In VelbusLink reading means: copying the physical module’s contents to the PC. Writing means: copying the VelbusLink
project from your PC to the memory maps of the modules.
Always first connect – scan – synchronize
Whenever you start VelbusLink, it is good practice to always (in this order)
1. open the project file (or start a new project)
2. connect ,
3. scan and
4. synchronize (read if you have not made changes offline, write if you have made changes offline and want to
copy those to the modules)
before doing anything else. This way you are sure that what you see on your PC coincides perfectly with what’s written into
the modules.
Read
Write
Page 7

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 5 www.velbus.eu
2 GETTING STARTED WITH A NEW PROJECT
CREATING A NEW VELBUSLINK PROJECT
We will assume from this step on that VelbusLink is connected to a live Velbus installation with a USB cable. Make sure none
of your Velbus modules are in error mode (LEDs blinking several times, pause, then blinking again). In case of errors, please
refer to “Troubleshooting” on p.41 and solve the problems before continuing.
After having installed and started VelbusLink, click New or New project to start a wizard that will guide you through the
process of creating a new project.
Choose a file name and folder, and click Next.
Select Connect to my existing installation and press Next.
Page 8

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 6 www.velbus.eu
In the following window, select Direct cable connection (RS232, USB) and press Next.
The software will automatically choose the port on which the Velbus USB module is connected. (If the USB connection is
not found, try to connect the USB cable in another USB port of your PC.) The PC will now connect to the modules.
In the next window, click Next. This will make VelbusLink scan for modules and the addresses will be automatically attributed
to the modules.
Page 9

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 7 www.velbus.eu
Once the scan has completed, VelbusLink will ask if you want to retrieve the module memories, or start with empty
modules. We recommend (Read settings from my existing installation), as this is the only way to be sure that your project
configuration in VelbusLink matches the actual configuration in the physical modules.
A window may pop up showing the progress of the memory read, after which you will be notified that your new project has
been created. Press Finish to start configuring your Velbus installation.
CHANGING ELECTRONIC ADDRESSES
About hexadecimal and decimal notation
In VelbusLink addresses can be represented hexadecimally (00-FF) or decimally (0-255). In this manual
we will use hexadecimal representation.
The hexadecimal address FF is the same as the decimal address 255, they are only represented in a
different way. The same goes for hexadecimal 1A and decimal 11, and so on. VelbusLink can be
configured to display addresses decimally or hexadecimally, according to the user’s preference (icon
- ).
All Velbus modules need to have a unique address between 01 and FE (hexadecimally) or 1 and 254 (decimally). Addresses
00 and FF (hexadecimally), or 0 and 255 (decimally) are reserved by the system. They are not to be used as addresses for
active Velbus modules.
Page 10

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 8 www.velbus.eu
Auto-assigning addresses
The wizard “New project” will automatically address the modules. If you checked this option, you will not have to do
anything concerning addressing. Continue with “Operating channels from within VelbusLink” on p.9.
Manually assigning addresses
If you chose to uncheck the option “Auto-assign” in the “New project” wizard, you will have to address the modules now. You
can do this by selecting a random module and by pressing the Address Management icon .
In the address management window, the “automatic addressing” can also be applied. This is the easiest option as VelbusLink
will attribute a free address to every module. To do so, press Auto-assign.
If you want to auto-assign your modules individually, use button Auto next to the “address” field. A free address will be
entered in the field. Accept by pressing Change.
To select the addresses yourself, enter them directly in the “address” field, and press Change.
New addresses are immediately written into the module, even without synchronizing. The addresses can be modified
afterwards without affecting the system.
This way, attribute valid, unique address (01-FE hexadecimal or 01-254 decimal) to every module in the installation.
Click “Auto-assign” to assign a free
address to all unaddressed
modules in the installation
Enter a free address for the
selected module with the “Auto”
button
Press “Change” to make the
change
Enter an address here if
so desired
Page 11

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 9 www.velbus.eu
OPERATING CHANNELS FROM WITHIN VELBUSLINK
You can operate a channel from within VelbusLink by right-clicking on the channel (for instance a relay channel) and
choosing operate from the dropdown list. A window will pop up allowing you to operate the channel, e.g. switch a relay
channel on or off.
In the example above we operate a relay channel. Not only relay channels can be operated, but also push buttons, input
channels, dimmer channels, blind channels, and so on.
RENAMING THE MODULES AND CHANNELS
In a new VelbusLink project the module names are identical to the type-code (e.g. VMBGPOD or VMB4RYNO). Modules can
be renamed (e.g. “VMBGPOD kitchen”). Names can be 64 characters long and may contain any alphanumerical character.
Most module names are stored only in VelbusLink and not in the modules. Newer modules now store their name too (after
synchronizing).
You can rename a module in different ways:
• by double-clicking on the name
• by selecting the module and pressing the F2-key on your keyboard
• by selecting the module and clicking on the rename icon above
• by right-clicking on it and selecting Rename
Channels can be renamed in the same way. Channels names can be 16 or 64 characters long (depending of the module type
and firmware version) and are always stored in the modules.
We advise to give modules and output channels meaningful names (based on their location and/or function for instance).
This will make it easy to find the right modules and channels in VelbusLink when creating actions. It will also facilitate
understanding the VelbusLink project if modifications need to be made later.
OPTIONAL: LAYERS
If you have many modules, you may want to organise them in layers, which you can hide or show in VelbusLink. You can for
instance put all input modules on the ground floor in one layer, and all input modules on the first floor in another layer. You
can then make these layers visible or invisible in the navigator window.
To create, manage and toggle the visibility of layers, click Layer Manager icon . This will open the Layer Manager
window.
Page 12
Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 10 www.velbus.eu
Adding a layer is done by clicking on the building block with the green “+” symbol . To delete a layer, highlight the
unwanted layer and click on the building block with the red “-“ symbol . Likewise, layers can be renamed by clicking on the
building block with the pencil .
Once the layers have been created, go back to the navigator window. Modules can now be assigned (select multiple modules
by holding Ctrl or Shift pressed when clicking) to a layer by selecting the module and clicking on the Assign to a layer icon
.
Once the modules have been assigned to layers, their visibility in VelbusLink can be toggled unchecking the checkboxes
below the eye symbol.
Adding, naming or deleting a layer has no effect on the project, apart from making certain modules temporarily visible or
invisible in the navigator window.
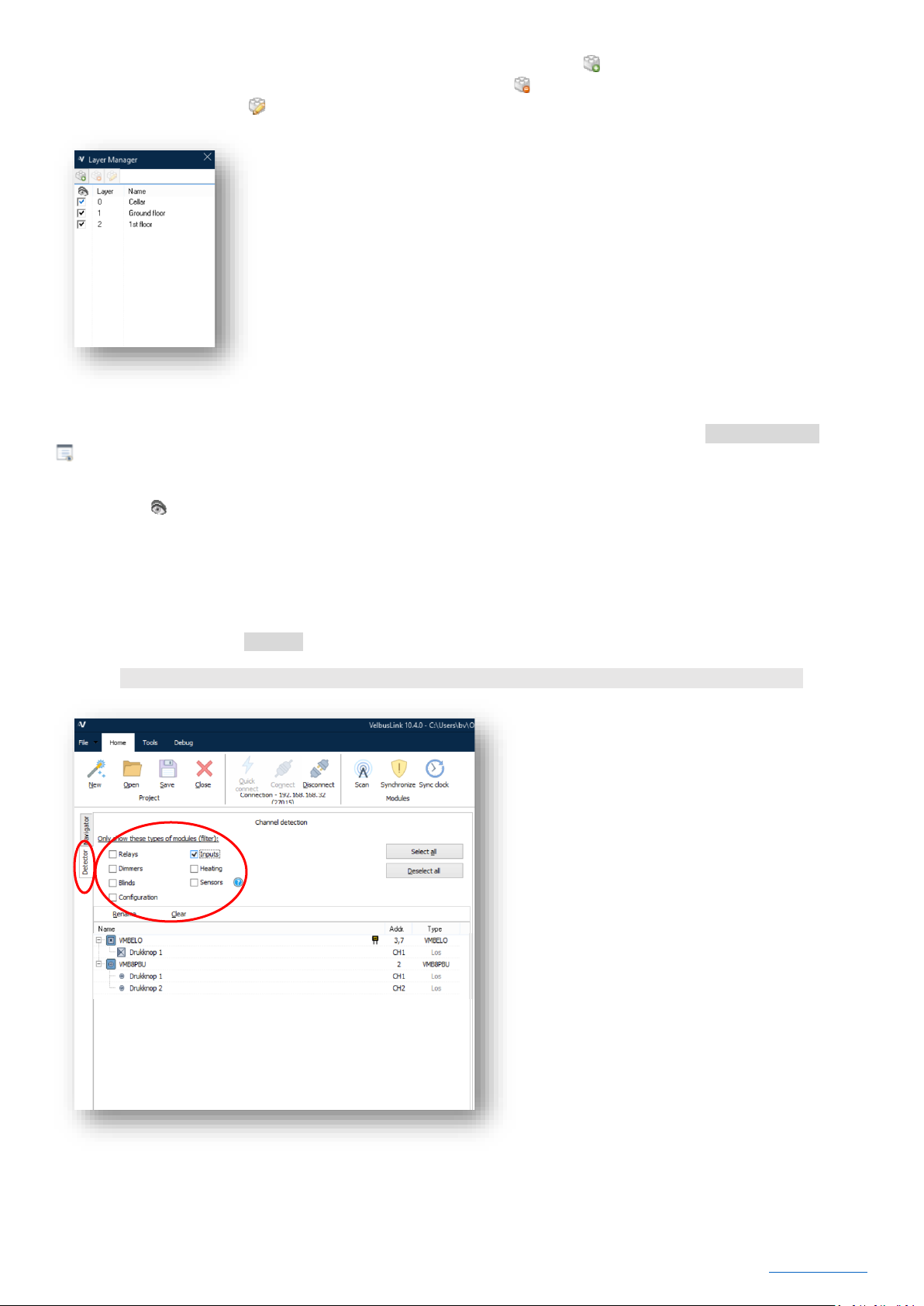
USING THE DETECTOR TAB
After scanning the installation, the modules will appear with their typecode in VelbusLink. A useful feature for finding
modules and channels is the Detector. You can also use it for renaming channels.
Only to be used once all modules have received a valid, unique address.
Page 13

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 11 www.velbus.eu
First, check the modules you want to detect under Filter on type. Here you can filter out modules by unchecking the groups
they belong to. This can be useful to ignore modules that periodically put data on the bus (like temperature or movement
sensors) and that would otherwise appear without being activated by you.
When you press on a button (a button on the input module, or a local button on the relay module), the module will appear in
the detector window. Both the module and the channel are detected. In the example above, button 1 on the command
module with glass panel Edge Lit (VMBELO) is pressed, and then 2 buttons connected to the VMB8PBU interface .
Changing names of modules and channels here is similar as explained above under “Renaming the modules and channels”
on p.9.
The Detector tab is a great feature to use if you have an assistant to press buttons in the installation. If you are alone, you can
walk around the house yourself and operate modules/channels in a certain order. When you return to VelbusLink, the
channels will have appeared in the order you activated them and you can rename them accordingly.
RECAP
In short, to get started with a new Velbus project, follow the next steps:
1. connect your Velbus installation to your PC (for instance with a USB cable to a VMBRSUSB configuration module)
2. start VelbusLink
3. click on New project and follow the wizard
4. give all modules a unique, valid address
Don’t forget to save your VelbusLink project file from time to time.
If you lose your VelbusLink project file, there’s nothing to be worried about. All actions, configurations and even channel
names will appear in your VelbusLink project, since they were saved in the modules themselves. You can simply start a new
project in VelbusLink and to Synchronize > Read to recall all data. Only the module names will be lost (for all but the most
recent modules).
Page 14

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 12 www.velbus.eu
3 ACTIONS
HOW THE SYSTEM WORKS
In VelbusLink, all connections between various channels are created following the same basic pattern:
initiator – action – subject.
For instance, to make a push button switch a light relay on and off (connected to a relay channel), you would create the
following connection:
In the above example, the push button is the initiator and the relay channel is the subject. But any kind of channel can be an
initiator or a subject. For instance, to make a relay channel lock a push button, we will create the following action between
the relay channel (this time acting as initiator) and the push button (this time acting as subject):
One initiator can have more subjects, and one subject can have more initiators.
One channel can simultaneously be the initiator of an action, and subject of another action.
CREATING ACTIONS
There are many ways of creating an action. Whichever way you choose to create actions within VelbusLink, the results that
will be written to the modules are the same.
As an example, we will demonstrate the connection of an input channel (a push button) to an output channel (a relay)
through an action “on/off”.
(Note that each relay channel can have a maximum of 36 actions assigned to it.)
1. Drag and drop
For a smaller installation, a simple way to create an action is to “Drag and Drop”. In the example below, push button 1 is
“clicked” (click on the channel Push button 1 and keep the mouse button pressed), dragged on top of the relay channel
Hallway light, and dropped.
Doing this will cause the Action properties window to appear, and be pre-populated with the combination selected by this
“drag and drop” process.
Initiator
Subject
Action
Push button
Relay channel
On/off
Relay channel
Push button
Lock
Push button
Relay channel
On
Relay channel
Relay channel
Push button
Relay channel
Push button
Push button
On
Push button
Relay channel
On
Relay channel
Momentary
Page 15

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 13 www.velbus.eu
All that remains to do is to define the type of action (e.g. On/off) and to click OK. If necessary, the action parameters (e.g. the
timer delay) on the right in the Action properties window can be modified.
2. Double-click and select
As with most software, there are various ways to achieve the same goal. Here we show you another example of this process.
Start by double clicking on either the input button or the output channel that you want to feature in the next action. The
screenshot below appears after double-clicking Push button 1 of the “VMBGPOD living” module.
The Add action window will appear, and the input selection will be pre-populated with the button selected here. (Note the
double arrow to the left of Initiator and Subject: clicking on the arrow will switch the selected channels around.)
Clicking on Click to select a subject or the Select button on the right. A new window will appear, from where you can locate
the channel which will act as subject. In the example below, we have selected the channel “Hallway light” of the
“VMB4RYNO” module to act as subject.
Page 16

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 14 www.velbus.eu
Each module’s channels are only shown after the module has been expanded (by clicking on the + sign to the left of it). If
you can’t find the module you’re looking for, make sure its type is checked in the filter at the bottom of the Select a channel
dialogue.
With the desired output channel highlighted, click on OK. The selection window will close and take you back to the Add
action window, so that you can now choose the type of action you want to happen (see “1. Drag and drop” above).
3. Detection
Instead of looking up the channel as described above, a channel can also be selected by detecting it.
Double-click on a channel, e.g. a relay channel. In the Add action window, click on Detect (instead of Select).
An Attempting to detect… window will pop up. Press the physical button you want to use, and its corresponding channel will
appear in the Attempting to detect window. (If the detection does not seem to work, make sure the appropriate filters are
checked at the bottom of the Attempting to detect…)
Here we have pressed the first push button of the VMBGPOD module.
Press Accept to fill in this channel as subject in the Add action window. You can then select the type of action you want to
happen.
VISUALIZING AND MODIFYING ACTIONS
By selecting any element of your installation (one or more modules or channels) in the navigator (left hand pane of
VelbusLink), the actions associated with it will be shown in the right hand pane Actions. To edit an action, double-click on the
Page 17

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 15 www.velbus.eu
name of the action and the Edit action window will pop up. All properties of the action (initiator, subject, action type and
parameters) can be changed. Changes will only be written to the modules after synchronisation of course.
In the navigator window, you can also see that next to every channel associated with an action, a “chain link” icon appears.
According to what has been configured into them, other icons may appear next to modules or channels. The icon key can be
shown by pressing the Legend button at the bottom of the main window.
NAVIGATION
PANE
ACTION
PANE
Double click on an action to edit it
Page 18

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 16 www.velbus.eu
EXPLANATION OF THE ACTIONS
From within VelbusLink a detailed overview of the actions can be opened, which contains a complete explanation per action:
name, description, parameters and where necessary a graphical representation.
To access this overview, right-click an action in the Action properties or Create action window, and select Info.
COPYING ACTIONS
Actions can be copied from one channel (initiator or subject) to another of the same type. The copied actions are added to
the present actions.
This can be done in the following two ways:
1. by dragging the first channel to the second while holding the Ctrl-key pressed. Release the mouse button first, and
then the Ctrl-key.
2. by right-clicking on the first channel and selecting Actions > Copy. A dialogue will open where the destination
channel can be selected.
THE MACRO WIZARD
Instead of copying the same action several times, the Macro wizard can be used. The Macro wizard allows you to create the
same action between multiple initiators and subjects.
Page 19

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 17 www.velbus.eu
Preset wizards
VelbusLink has predefined macro wizards installed, like All on, All off, All off with status monitoring (so the feedback led will
be lit if a linked subject is on), All blinds up, All blinds down and Status monitoring. To use these, select the initiator channel
(e.g. a push-button) and click on the wizard symbol . Select the desired wizard in the drop-down menu. The wizard
starts with the initiator already selected, and all the subjects corresponding to the action also preselected. Make the
necessary modifications (e.g. deselecting certain subjects) and click Done. The action will be added to all the selected
subjects.
Universal wizard
The macro wizard can not only be used with preconfigured actions (e.g. All on, All off), but also with any other action. Any
action can be created between multiple initiators and/or subjects. To make a custom macro wizard, click the wizard symbol
and select Macro wizard. Follow the instructions from the wizard.
Page 20

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 18 www.velbus.eu
4 CHANGING FEEDBACK CHARACTERISTICS OF INPUT MODULES
By default any feedback provided by an input module (e.g. a push button module or a touch button glass panel) will
represent the state of the output connected to it. For instance, if a relay channel is connected to a button, the default
behaviour of the button LED will be: feedback LED on when relay is closed, feedback LED off (or dimmed) when relay is off.
Feedback LEDs can also blink, for instance when a dimmer is dimming, a timer is running, a blind is going up or down, et
cetera.
In some situations, you may want to change this default feedback behaviour, for instance to link the feedback LED of a
button to a different output than the default one it has been associated with. This can easily be accomplished in VelbusLink.
For example, you may have a button in your living room commanding the ceiling light. Since the button is close to the light,
you don’t need the feedback LED to show the state of the light. You can use this feedback LED to show the state of the light
in the children’s room, for instance.
To do so, two steps need to be taken.
Step 1 is to configure the button channel to change its default feedback behaviour to Monitoring:
1. select the input module in VelbusLink (e.g. the push button)
2. click on the Configure icon
3. in the Configuration settings window that appearsn click on the tab LED feedback. (If this tab is not visible, check
Show advanced features at the bottom of the window.)
4. double-click on Feedback next to the channel's name.
5. in the LED Feedback window that pops up, select Monitoring
Click OK, then on Done.
Step 2 is defining which output channel has to be monitored. Create the following action (see also “Creating actions” p.12):
• initiator: output channel (e.g. relay)
• subject: input channel (e.g. push button)
• action: 0135. Monitor status of initiator
1
2 3 4
5
Page 21

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 19 www.velbus.eu
As always, don’t forget to synchronize (write).
The feedback LED of the push button in the living room will now reflect the state of the light in the children’s room.
Other examples of possible LED feedback configurations are: showing the status of a doorbell, a light in an out building, or
even the status of a connected burglar alarm (depending on hardware capability). These are all configured following the
same steps as described above.
Page 22

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 20 www.velbus.eu
5 FORCING AND INHIBITING
For many modules forcing and inhibiting actions are available. These can be used to realise more advanced configurations.
INHIBITING
While inhibited, a channel will be turned off (released). During inhibition mode, it will no longer respond to signals coming
from the bus. It will however still pick up these signals, and when coming out of inhibition mode, it will execute the last
command received, even if this was sent during inhibition mode.
For instance: a push button is connected to a relay channel by means of the action “On”. While the relay is inhibited, the push
button is pressed. As long as the inhibit mode is active, the relay will stay off (but the button push is registered). As soon as the inhibit
mode ends, the “on” will be executed.
FORCING
A forced channel can be “forced on” or “forced off”. While forced, it will no longer respond to signals coming from the bus.
Furthermore, it will be completely “deaf” to all commands. When coming out of forced mode, it will not execute commands
put on the bus during forced mode.
For instance: a push button is connected to a relay channel by means of the action “On”. While the relay is “forced off”, the push
button is pressed. As long as the forced mode is active, the relay will stay off and ignore the button push. After the forced mode ends,
the relay will stay off.
PRIORITIES
Using a combination of regular, inhibiting and forcing actions one can set different levels of priorities. “Forced off” has
priority over “forced on”, which has priority over inhibiting actions, which in turn have priority over regular actions.
Example: a sunscreen has to be lowered when the indoor temperature exceeds 25°C. But when the wind sensor closes (too much
wind), the screen has to go up regardless of all other commands. This can be achieved by using an inhibiting action for the indoor
temperature alarm (e.g. “inhibit but preset down at closed switch”), and a forced action for the wind alarm (e.g. “forced up at closed
switch”). The inhibit action will overrule normal button control. The force action will overrule all other actions, including the inhibit
actions.
Relay
Push button
relay is
on
begin of
inhibition
end of inhibition
relay is
off
relay is
inhibited
On
Aan
Relay
Push button
begin
of forced mode
end of forced
mode
relay is
off
relay is forced
off
On
Aan
relay
remains
off!
is ignored
Page 23

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 21 www.velbus.eu
6 CONFIGURING MODULES
All electronically addressable Velbus modules have settings that can be configured. These vary depending on the type of
module. For relay modules the channels for instance can be set to “normally closed” or “normally open”. For input modules
(e.g. pushbuttons) the array of possible settings is much wider: the response time can be set, single/dual/multi mode can be
chosen, LED indication and backlights can be configured, program steps can be added, and so on. In glass panels,
additionally the thermometer and thermostat functions can be configured, display settings can be edited, and so on. For
dimmers the operation mode may be configurable, multi step presets can be set, and so on.
To access the Configuration dialogue of the module, select the module in the navigator and click on the gear icon . In the
example below, we opened the configuration dialogue of a VMBGPOD module.
(For detailed explanations per module, please visit the Velbus products pages on www.velbus.eu > Products.)
Page 24

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 22 www.velbus.eu
7 DUAL MODE BUTTONS
Velbus allows for dual mode functioning of push and touch buttons. In dual mode the same button has two different
functions: one when short pressed (e.g. all off), and another one when long pressed (e.g. all on). The long press time can be
set to 1, 2 or 3 seconds.
In the explanation below we will use a VMBGP2 two touch button glass input module, but other input modules (push button
as well as touch button) also allow for dual mode functioning 2.
As an example we will configure push button no. 1 to act as “on-off” for the corridor when short pressed and as “all off” when
long pressed.
Practically, when long pressing the module will simulate a different channel. Example: Long-press button no. 2 to make the
module activate press button 8. The most logical way to proceed, is to use a virtual channel for the second channel.
A virtual channel is a channel to which no physical hardware is being connected, e.g. a non-connected push button on a
universal 8-channel push button module, or push button channels 3 to 8 on a 2-button glass command module. (Relay
channels also have virtual channels, but they are not applicable.)
STEP 1: SET UP DUAL MODE
Select the push button module in the navigation pane and click on the gear icon . In the configuration window, select the
Button mode tab.
Double click the button that needs to be set to dual mode (in our example Push button 1 (CH1)). The Mode push button
dialogue pops up. Select Dual in the upper left corner. Then select next to Long press button which (virtual) button needs to
be activated on long press. In our example, we select “Virtual button 6” (channel 8).
2
Except the VMBGPOD glass command module with touchscreen and OLED display. Only the first page can accept dual mode.
Page 25

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 23 www.velbus.eu
The long pressed time can be set to 1, 2 or 3 seconds.
Select OK. In the tab Push button mode tab of the configuration window we can now see that dual mode has been
configured for button 1. We can verify that a short press (S) activates channel 1, and a long press (2s) channel 8.
Close the configuration window. An icon will appear next to the channel with dual mode. Change the name of the button to
“Corridor on/off”
The virtual channel we chose for the long press action is also visible now in the navigation pane. Change its name to “All off”.
STEP 2: CREATE THE ACTIONS
Now create the two actions (see “Actions” p.12.).
• For push button “Corridor on/off”, create a “Toggle” action for the light relay
• For the virtual button “All off”, use the wizard (see “The macro wizard” p.16) for the “all off” action.
READY!
If we now briefly press the left button on the glass control module, we operate the light in the hallway (on / off). If we press
for a long time, all the lights go out.
Page 26

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 24 www.velbus.eu
8 MULTI BUTTON MODE
Apart from dual button mode (p. 22), a button can also be configured to work in multi mode. In that case, one input channel
will loop through a series of other input channels at each press of the button.
E.g.: to control ventilation speeds multi mode can be used. At the first press low speed is activated, a second press activates medium
speed, a third press high speed and a fourth press will turn it off. Pressing again restarts the loop from the beginning.
What actually happens is that the input module will consecutively activate different push button channels. These channels
can be freely chosen, but must form one continuous series.
E.g.: Push button 1 is configured to function in multi mode for channels 3 to 6. Pushing button 1 will activate channels 3, t hen
4, then 5, then 6, then 3 again, and so on.
In the example below we use a VMBGP2 glass control module with 2 tactile buttons, but also other input modules (both
glass control modules as push buttons) allow for multi mode function3.
STEP 1: CONFIGURING MULTI MODE
Select the module in the navigation pane and click on the gear icon . In the configuration window, select the tab General >
Push button mode.
Double-click the button that needs to function in dual mode (in our example Push button 1 (CH1)). the dialogue Mode
push button appears (see screenshot below). Select Multi mode Dual on the top left. Then select to the right the first
channel of the series (in our example Virtual 1 (CH3)) and the last (in our example Virtual 4 (CH6)). This way, at each button
press, virtual button 1 (CH3), then 2 (CH4), then 3 (CH5) and 4 (CH6) will be activated.
3
Except the VMBGPOD glass control module with OLED display.
Page 27

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 25 www.velbus.eu
If the option Restart at the beginning if idle for more than 5 seconds is selected, after 5 seconds of inactivity, pressing the
button will activate the first button in the series. If not, the module will remember the last channel that has been activated
and continue from there.
Press OK. The tab Push button mode of the configuration dialogue now shows that multi mode is enabled for the first
button, and that when pressed, channels 3 to 6 will be activated.
Close the configuration window. An “M” icon will appear next to the channel with multi mode.
STEP 2: CREATING THE ACTIONS
Create on the virtual buttons the actions that will have to be executed.
In our example:
• for virtual button 1 (CH3) the action is made that corresponds to the first button press
• for virtual button 2 (CH4) the action is made that corresponds to the second button press
• and so on until virtual button 4 (CH6)
READY!
Each time we press button 1, the module will cycle through the actions attributed to the virtual buttons.
Page 28

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 26 www.velbus.eu
9 HEATING/COOLING CONTROL
Velbus can easily be configured to command a heating and/or cooling system (see “Installation Guide, Part 1: Hardware and
Cabling” for a quick overview of relevant modules).
We will explain here the principle of heating control using a VMBGPOD glass panel with OLED display as master panel in the
living room, and a VMBGP2 two-button glass panel in the bathroom.
1. ACTIVATE THE TEMPERATURE SENSORS
First of all, the thermostat functions of both panels have to be activated by assigning them an address (different from FF).
Access the Address management dialogue by clicking the icon . Below, as an example, we have selected the VMBGPOD.
Check the Thermostat checkbox. A free address is automatically attributed to the thermostat. Click on Change. Do the same
for other modules as necessary. Then press Close.
2. CONFIGURE THE THERMOSTATS
Now, in the navigator window, select the VMBGP2 panel and access its configuration dialogue by clicking on .
Edit the settings in the tab Temperature sensor > General. Change the sensor name (we chose “Bathroom”). The sensor
name chosen here will also appear on the VMBGPOD display when we configure this later on.
Set in the tab Temperature sensor > Presets the desired temperatures for every heating mode.
Page 29

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 27 www.velbus.eu
Click on Close.
Next, configure the VMBGPOD master panel in the living room.
3. SHOWING THE SENSORS ON THE OLED DISPLAY
We will show both thermostats on the OLED display of the VMBGPOD module, so we can access both from the command
module.
In the VMBGPOD configuration settings, go to the tab Temperature > Sensors.
Select the “Local” sensor, click on the Edit name button, and change its name to “Living”.
Then click on Show. This makes this thermostat visible on the screen of the VMBGPOD.
Page 30

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 28 www.velbus.eu
Next, select the “Bathroom” sensor and click on Show. Check the box “Access” to access the bathroom thermostat from the
living.
Press Done to exit the dialogue.
After synchronisation (write) you will now be able to access from the VMBGPOD glass panel’s display both the “Living” and
the “Bathroom” thermostat functions. These include setting the mode (anti-freeze, night, day, or comfort) and changing the
current target temperature. This change can be timed (e.g. 2° warmer for one hour) or it can remain active until the next
program step or the next manual intervention. (Please refer to the VMBGPOD product pages and the FAQ on www.velbus.eu
for more details).
4. CREATE CONNECTIONS
Finally, we need to create the right connections (actions) between the thermostat channels on the glass panels and the relay
channels controlling the heating system.
How the Velbus relays need to be physically connected to the heating system depends on the specific system. A standard
setup could be, for instance, one relay commanding the central pump of the heating system, and for each heating circuit a
separate relay channel that controls the flow valve.
The glass panels have 8 special channels for heating and cooling (see screenshot below). In our example the “Pump” and
“Heater” channels interest us most. Whenever the measured temperature drops below the target temperature, these
channels will be closed (“Pressed”). Once the temperature is again equal to or higher than the target temperature, the
channels open again (“Released”).
In the example below, the measured temperature is 22.5°C. The target temperature has not been reached, thus the “heater”
and “pump” channels are closed (“Pressed”).
1
2
Page 31

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 29 www.velbus.eu
Schematically represented, the actions to be created are the following:
Note: The “momentary” action means that the subject will follow the state of the initiator. As long as the initiator is pressed (closed),
the subject will be pressed (closed) also. As long as the initiator is released (open), the subject will be released (open) also. The
“Momentary” action, when used with multiple initiators on the same subject, will function as a logical “OR”: as long as at least one of
the initiators remains closed (“Pressed”), the subject will remain closed (“Pressed”) also. Only when all initiators are open (“Released”)
will the subject be open (“Released”).
Thanks to the “momentary” actions, whenever the “pump” and “heater” channels are being pressed, the connected relays
also close and thus activate the heating system. Once the “pump” and “heater” channels open again, the relevant parts of
the heating system will be deactivated too. Note that as long as at least one connected “pump” channel is closed, the pump
relay will also remain closed. Thus the pump will continue working as long as at least one glass panel demands heating.
More configuration options, e.g. hysteresis, sensor calibration, delays etc. are accessible under the Temperature tab. For
details, please refer to www.velbus.eu (product pages and FAQ).
5. AUTOMATIC HEATING AND COOLING
To automatically set the heating to day mode in the morning, night mode in the evening etc., program steps are used for the
temperature sensor. These can be created in the module’s configuration dialog, tab Programs > Program steps >
Thermostat. (Further explanations concerning program steps can be found under “Creating and modifying program steps”
on p. 32).
In the example below two program steps are created, one to set the heating to day mode and a second one to set it to night
mode.
Relay Pump
Relay valve
living room
Relay valve
bathroom
VMBGPOD living
Channel
“Pump”
Channel
“Heater”
VMBGP2 bathroom
Channel
“Pump”
Channel
“Heater”
104.Momentary
(follow)
104.Momentary
(follow)
104.Momentary
(follow)
104.Momentary
(follow)
Page 32

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 30 www.velbus.eu
Don’t forget to check that the right program is active. This can only be done when VelbusLink is connected to the installation.
6. USING INPUT CHANNELS TO SET THE HEATING/COOLING MODE (OPTIONAL)
Input channels (e.g. push buttons) can be configured to change the active heating/cooling mode. To do so, create an action
with the input channel as initiator and a temperature sensor channel as subject.
In the example below, we selected as subject the temperature sensor channel of a VMBGPOD glass panel.
Page 33

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 31 www.velbus.eu
Available actions are switching to day/night/safe/comfort mode, to heating or cooling mode, and so on.
Page 34

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 32 www.velbus.eu
10 CREATING AND MODIFYING PROGRAM STEPS
All Velbus input modules (push buttons, sensors...) can be configured to activate, deactivate, lock, unlock, press, long press or
release their own channels at certain times. Time settings can be fixed times, sunrise/sunset with or without offset, and
more. Every input module has a built-in astronomical clock with sunset and sunrise hours predefined.
A program step can be considered as a input module commanding, locking and unlocking its own channel on a given time. A
push button can automatically activate at 22:00, and so activate the action related to this push button (e.g. activating a
relay). A twilight sensor (or a push button) can lock itself at sunset, and unlock at sunset.
A PRACTICAL EXAMPLE
You want the light on the wall to switch on automatically at 22:00, and switch off at 03:00.
For this purpose, we need two push buttons (the first one with the action “on” to the light relay, and the second one with the
action “off” to that same relay). We leave the push button with the “on”-action to short-press at 22:00. The action is
executed, as of the push button is physically pressed, and the light switch on. We leave the push button “off” to short-press
at 03:00 to execute the coupled action “off” so the light switches off.
We note two important remarks:
1. Do not use “on/off” actions for program steps, but do so for individual “on” and “off” actions. For instance, if
someone has switched on the light at 21:00, and the program step “on/off” is set at 22:00, the light will switch off
instead of switch on. To make sure the light switches off, regardless of what happened before, we need to use the
“on” action. (And the same for “off”).
2. For program steps on push buttons we will generally use virtual channels instead of regular channels. That way, we
will be able to use the regular channels for manually controlled functions (e.g. “on/off” actions), without having to
sacrifice them for program step actions.
For automatic façade lighting, please follow the steps below:
Step 1: Activating virtual channels on an input module
Open the configuration settings of the desired push button module (below is a VMBEL4 4-button Edge Lit module). Change
the reaction delay of the two virtual channels to “Direct” and change the names to “Façade on” and “Façade off”.
These channels will appear in the navigation pane:
Page 35

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 33 www.velbus.eu
Step 2: Creating actions on virtual channels
Create an action “101. On” with the virtual push button “Façade on” as initiator and the light relay as subject. Create a second
action “102. Off” with the virtual push button “Façade off” as initiator.
Step 3: Creating program steps for the virtual push buttons
Open the configuration settings of the input module and go to the tab “Programs”. Create the two following program steps:
Page 36

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 34 www.velbus.eu
Step 4: Checking if the program is active
To make a module execute a program step, we need the corresponding program to be active (see screenshot below). This
configuration is only available when VelbusLink is connected, since the active program is set directly on the module, even
without synchronisation.
Generally, program 1 is always active, but it is recommended to check to make sure.
Page 37

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 35 www.velbus.eu
HEATING/COOLING PROGRAM STEPS
Those modules that have thermostat functions (e.g. the glass control module series) also have a configuration tab for
program steps related to heating and cooling. For more information, see “5. Automatic heating and cooling” on p. 29). These
are configured in the same way as other program steps (see above).
PROGRAMS VERSUS PROGRAM STEPS
Every input module has three possible programs: Program 1, 2 and 3. Programs are not the same as program steps.
A program step can be for instance: “activate input channel 3 during 1 minute every day at 07:00”. A program is a set or group
of such program steps. Only one program at a time can be active for a given module, containing multiple program steps.
In most cases only one program will be used, containing all the needed program steps.
For the program steps to be executed on a module, the program they belong to needs to be active (see screenshot below).
This setting is only accessible when VelbusLink is connected, as the active program is immediately set on the module, even
without syncing.
Program 1
Program step
Program step
Program step
Program step
Program step
…
Program 2
Program 3
Program step
Program step
Program step
Program step
Program step
…
Program step
Program step
Program step
Program step
Program step
…
Page 38

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 36 www.velbus.eu
WAKE-UP AND BEDTIMES (OPTIONAL)
Program steps are normally used with fixed times, or with sunset/sunrise times. If so desired, optionally one can use wakeupand bedtimes. This is an advanced option that can be useful in some cases, but it is not at all required.
Wakeup- and bedtimes can be seen as variables, whose value can be set in the tab “Clock alarms” of VelbusLink, or on the
OLED screen of a VMBGPOD glass control module. The scope of this variable is initially limited to the module. But wakeup and bedtimes can be made member of alarm groups. In that case, when the value is changed for one member of the group,
all other members of the group will copy this value.
In the example below module 1 is not a member of any alarm group. Changes to wakeup- and bedtimes will only have a local
effect (in the module itself). Modules 2 and 3 are members of the same alarm group. Changes to wakeup- or bedtime in
module 2 will be automatically copied by module 3 and vice versa.
Module 1
Alarm 1
Wake-up 07:00
Bedtime 22:00
Member of group 1
Module 2
Alarm 1
Wake-up 08:30
Bedtime 23:30
Member of group 1
X
X
Changes to wake-up and
bedtime only affect module 1
(not a member of any alarm
group)
Module 3
Alarm 1
Wake-up 08:30
Bedtime 23:30
Member of group 1
X
Changes to wake-up and bedtime affect both modules 2 and 3
(because both are members of the same alarm group)
Program step: “Set to day
mode at wake-up time” is
activated at 07:00
Program step: “Set to day
mode at wake-up time” is
activated at 08:30
Program step: “Set to day
mode at wake-up time” is
activated at 08:30
Page 39

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 37 www.velbus.eu
E.g.: the temperature sensor of multiple modules needs to be set to day mode in the morning. In each of the modules a program step
“set to day mode at wakeup time” is created. All modules are made members of the same alarm group. If the wakeup time needs to
be adjusted later on, it suffices to change it in one module. The other modules will automatically copy it.
Note: activating and deactivating these alarm scan only be done through push buttons. To do so, create
an action with as initiator a push button, as subject “Module actions” of the module containing the
alarms, and use one of the actions concerning alarms (numbers 1001 through 1014).
ACTIONS RELATED TO PROGRAM STEPS AND PROGRAMS
Manipulating program steps
Program steps can be activated and deactivated by other Velbus channels. To do so, create an action and as subject choose
the input channel for which the program steps have been configured.
Possible actions are activating and deactivating (temporary or permanent) the program steps on that channel.
Manipulating programs
The active program of an input module can also be configured by another channel. To do so, create an action and as subject
choose the input module, channel “Module actions” (see screenshot below).
Available actions are: setting the active program on the module, deactivating all programs, and so on.
MODIFYING THE SUNSET AND SUNRISE TIMES
Every input module contains a table with sunrise and sunset times. These can be used for program steps.
To manually modify the table with sunrise and sunset times, go to the tab Programs > Advanced > Sunrise/Sunset.
Page 40

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 38 www.velbus.eu
Select a row and press the button Edit to change the value. Each module has its own table with sunrise and sunset times, so
changes to the table only have an effect in the module you are editing.
Caution: the difference between two consecutive sunrise times in the table, or two consecutive sunset
times, must not be greater than 128 minutes (two hours and 8 minutes).
To reset all values to factory defaults, press the button Reset all.
Page 41

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 39 www.velbus.eu
11 SPECIAL FUNCTIONS
REPLACING A (FAULTY) MODULE
A faulty module in the installation can easily be replaced with a new one. VelbusLink contains a wizard which will write all
settings from the old module to the new module. The old module will be deleted automatically from the project. If the faulty
module still reacts on the bus, the module memory can be read. If it does not react, the VelbusLink project map must be
available to copy the settings to the new module.
To start the wizard Replace a module, click the corresponding button in the Tools menu. Next, follow the instructions of the
wizard.
FIRMWARE UPDATES
All modules connected to the bus contain firmware. This firmware can be updated free of charge to the latest version from
VelbusLink. An Internet connection is not necessary, since firmware files are registered in VelbusLink.
A firmware update may be desirable or necessary to activate new features, or to detect or fix a bug. When important
firmware updates are available, an icon will appear on top of the navigation pane.
Firmware updates can be executed by pressing the button Firmware updates in the Tools menu, and to follow the
instructions. This will allow to do all firmware updates one after another without any intervention.
Calculate the power consumption
In the Tools menu, a calculator allows you to calculate the maximum energy consumption of the installation based on the
used modules.
To do this, press the calculator icon .
A window appears displaying the total power consumption at 15V, allowing you to check the detailed calculation.
Page 42

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 40 www.velbus.eu
If several power supplies are connected, interconnect all the negative poles and distribute the positive poles over the
modules.
SET THE INSTALLATION IN A CERTAIN STATE DURING START-UP
In some installations, it is desirable or important that certain channels return to a certain state when power returns after a
power cut. To do this, you can use a (virtual) push button which is set on “N.C.”. When the power supply returns, the input
channel will immediately close, and the corresponding actions will execute immediately.
• Set a (virtual) button of a VMB8PBU, VMB6PBN, VMB7IN or VMB2PB(A)N-R input module
4
on “N.C.” (“Normally
Closed”). Select the module, click on the configuration symbol , go to the tab NO/NC and set the corresponding
button on NC. At start-up, this button will close immediately.
• Make an action 412 “restartable timer” (1s) with the N.C. push button as initiator and an unused (virtual) relay at
random as subject (the “start-up relay”). This start-up relay will be used as initiator to set all channels in the correct
state at start-up. For instance, if a relay must be suppressed when the power returns, configure an action “suppress”
between the virtual start-up relay (as initiator) and the relay channel (as subject).
• Now, create all actions to set the desired channels in the correct state at start-up. Use the start-up relay as initiator.
4
The push button channels of the command modules cannot be set on N.C..
Page 43

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 41 www.velbus.eu
12 TROUBLESHOOTING
GENERAL STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
Velbus is a very reliable system. In the unlikely event that a problem occurs, it will most certainly be due to one of following
causes:
• wiring problem (faulty contact, H and L inverted, short-circuit…) -> check the wiring
• terminators have not been set correctly (each installation should have 2 or 3 closed terminators) -> check the
terminators
• the power supply does not deliver enough power for the number of modules -> close all relays and measure on the
furthest modules in the chain if they are receiving at least 12 V
• an older version of VelbusLink -> go to www.velbus.eu and download the latest version of VelbusLink
• remaining configuration or statuses in the modules' memory -> switch the installation off and on again
If the problem has not been solved with the above measures, please follow the step-by-step guide below (the above
measures are included for the sake of completeness):
1. Install the latest version of VelbusLink: free download at www.velbus.eu
2. PS LEDs: Check if the PS (Power Supply) LED burns continuously on all modules. If the PS LED does not burn, the
module is not receiving (enough) power.
3. Provide enough power: Use the consumption calculator in VelbusLink (in the Tools menu) to calculate the
necessary amount of power to feed all the modules in every circumstance. Check if you have provided enough
power. If several modules are used on the same bus, interconnect all the negative poles and distribute the positive
poles over the modules (these must not be interconnected).
4. Measuring voltage on the modules: If you have provided enough power according to the consumption calculator,
close as much relays as possible and measure the voltage on the modules at the outer ends of the power supply.
The supply voltage must be at least 12 V. Due to voltage drops over the wiring, or not enough power supplies for the
number of modules, the voltage on some modules can be too low. In case the supply voltage on a module is too
low, the channel LEDs will blink 3 times. In case it's too high, they will blink 4 times. To be sure, measure the supply
voltage on the modules.
5. Terminators (terminal resistances): Check if the terminators have been set correctly. A standard Velbus installation
should have two or three terminators set, ideally at the outer ends of the installation (with the longest distance of
cable between them). See also “Velbus Installation Guide, Part 1: Hardware and Cabling”.
6. Status LEDs and error messages: For those modules featuring status LEDs (e.g. the majority of the DIN-rail
modules): check if they do not give an error message (blinking).
o continuous blinking means there is a timer running
o blinking a couple of times, pause, blinking a couple of times, etc. means there is an error:
▪ blinking 2 x, pause, blinking 2 x, etc.: communication error. The installation may have a wiring
problem (e.g. H and L are inverted in the installation, bad contact, short-circuit), and, in some
cases, a faulty module.
▪ blinking 3 x, pause, blinking 3 x, etc.:
• for most modules: power supply voltage too low
• for VMBDMI(-R) dimmers: non-dimmable load
▪ blinking 4 x, pause, blinking 4 x, etc.:
• for most modules: power supply voltage too high
• for VMBDMI(-R) dimmers: temperature alarm (but still working)
▪ blinking 5 x, pause, blinking 5 x, etc.: switched off due to temperature protection (only for some
modules, e.g. dimmers)
7. Rx and Tx LEDs: Those indicate reception and transmission respectively on the bus. In normal operation they
occasionally blink shortly (when the module sends or receives). While syncing (reading or writing) these blink for a
longer time, however outside syncing it is not normal if they continue to blink. This usually indicates a
communication error. The installation may have a wiring problem (e.g. H and L are inverted in the installation, bad
contact, short-circuit), and, in some cases, a faulty module.
8. Restart the system: If the above points are met, briefly disconnect the power supply and reconnect after 10s.
Exceptionally, the modules contain residual configuration and must be restarted after the configuration
modification.
9. Systematic debugging: If faults persist, try to isolate the problem systematically.
Page 44

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 42 www.velbus.eu
o Disconnect as many parts as possible off the bus. Set new terminators so that the connected part contains
2 or 3 closed terminators, as far as possible from each other.
o Scan this part of the installation.
o If VelbusLink can scan this part correctly, connect an additional part of the installation (and modify the
position of the terminators so that the entire connected system contains 2 or 3 closed terminators, as far as
possible from each other).
o Continue gradually until the problem happens. This may give an indication of where the problem is situated
(i.e. in the last connected part).
Most recurring faults are the inversion of the H and L conductors (or other connection faults) on 1 or more
modules, and faulty contacts. Delicately pull the conductors on each module to see if these are not loose.
Tighten the screws at the interconnection rails (VMBRAIL) and at the connected modules. Also check for
possible cable breaks.
10. Measuring the bus resistance: Measure the bus resistance. Disconnect the entire installation from the power supply
and measure the resistance at different places between conductors H and L with a multimeter. The resistance must
be between 40 and 120 ohms. If the resistance is too low, then there are too many terminators (or there is a fault,
e.g. a short-circuit or faulty module). If the resistance is too high, then there are not enough terminators (or there is a
fault, e.g. a faulty module).
MY RELAY SWITCHES OFF
The main reason for a relay to switch off is an insufficient power supply voltage for the system. Use the consumption
calculator in VelbusLink (in the Tools menu) and calculate how much power is needed to power all modules in every
circumstance. Check if you have provided sufficient power supply voltage. If several modules are used on the same bus,
interconnect all the negative poles and distribute the positive poles over the modules (these must not be interconnected).
A MODULE IS NOT REACTING AS DESIRED
• Check the icons next to the modules in VelbusLink. Discover what they mean in the Legend (button below in
VelbusLink).
• Make sure all modifications are being written onto the modules. The Sync shield must be green.
• Uncheck the box “modifications only” in the Sync window, and write to the modules. If necessary, write to the entire
system (caution, this can take several minutes according to the size of the installation).
• Take into consideration that most actions are being saved in the output modules. Example: When creating an action
from a push-button to a relay, and you synchronize (write) to the push-button only, the action will not be
memorized in the system. In this case, you must (also) write to the relay module. (VelbusLink takes this into account,
generally it is enough to only execute the proposed synchronizations, if necessary with the “modifications only” box
unchecked.)
• Restart the module. Click with the right mouse button on the module and select Restart module. Sometimes there
is some residual configuration or statuses in the modules, which will be deleted by restarting the modules. If
necessary, disconnect the power supply of the entire system, and reconnect.
• Check what happens in VelbusLink when executing actions. The channel status (“Pressed”, “Unpressed”,
“Suppressed”…) shows you what happens. Is the push-button being pressed? Does the relay switch? … You can
follow live in VelbusLink.
• Mind the icons next to the modules and channels, and consult the Legend (button below) to see what they mean.
Are some channels locked, are program steps deactivated...?
• Read the modules' memory and check which actions and configurations are memorized.
• It is possible a firmware bug, and new firmware is available. Click Firmware updates in the Tools main menu and
follow the instructions.
MY PROGRAM STEPS ARE NOT EXECUTED OR EXECUTED AT THE WRONG MOMENT
If program steps are not at all executed, the active program of the module might not or erroneously be configured. See
“Step 4: Checking if the program is active” on p.34Error! Bookmark not defined. for more info.
If program steps are executed at the wrong moment, the clock of the module is possibly set incorrectly. To verify this, click
with the right mouse button on the module, and select “Request time”. If the time is set incorrectly, set the correct time by
clicking “Sync clock” at the top in VelbusLink. If the time was set correctly, the problem has a different cause. Check the
configuration carefully.
Page 45

Velbus Installation Guide
© 2020 Velbus – v07 43 www.velbus.eu
VELBUSLINK SHOWS THE ERROR MESSAGE ‘COMMUNICATION ERROR WITH YOUR INSTALLATION’,
DOES NOT FIND ALL MODULES WHEN SYNCING, SHOWS ERROR MESSAGES WHEN SYNCING…
• Follow the step “General step-by-step guide” above
• using USB cables which are (too) long may cause wiring problems (dependent from PC to PC). Try another, shorter
cable (1 m or shorter).
• the PC interface module (VMBRSUSB, VMB1USB or other) is defective or in error mode. Power down your
installation (or the PC interface module ONLY), wait 5 seconds and power up again. Unplug the USB cable and plug
it in again (preferably using another PC-port), reconnect VelbusLink and perform a new scan. If this does not solve
the problem, the PC interface module might be defective. In most cases however the problem lies with faulty wiring
or a terminator problem
• Does your configuration module (VMBRSUSB, VMB1USB or other) have contact with the bus? This module is
sometimes connected with a loose piece of cable in which a bus wire can easily break.
THE SCAN WORKED PERFECTLY BUT NOW I CANNOT FIND MY INSTALLATION ANY MORE
The USB port of the PC can lose communication with the Velbus installation, e.g. after the PC enters sleep mode. The
simplest solution is to unplug the USB cable and to plug it into another port.
THE SCAN IS OVER BUT SOME MODULES ARE MISSING
• See the above advice concerning wiring problems “VelbusLink shows the error message ‘communication error with
your installation’, does not find all modules when syncing, shows error messages when syncing…”
• carefully check the addresses again of the “missing” modules. There is a chance that addresses have been
duplicated.
• do not forget that addresses of some older modules (e.g. VMB4PD and VMB1TC) can be manually set via the
module.
• are you using the latest version of VelbusLink? (Free download on www.velbus.eu > Support > Downloads.) Modules
that are more recent than your VelbusLink version cannot be scanned.
THE SCAN IS OVER BUT SOME MODULES HAVE A RED X MARK ON THE MODULE NAME
Modules are shown with a red ‘X’ mark over the module name when they have not been found during a scan. This typically
happens when a module has been removed from the installation.
If you did not remove modules but still have a red cross in VelbusLink, check the following:
• have you replaced the module? VelbusLink takes into account the serial number of the modules. If you replace a
module by a new one, VelbusLink will consider this new module as being different from the original one (even if you
gave both the same address). Both modules will appear in VelbusLink after a scan, one with a red ‘X’ mark (namely
the original, removed one), one without the red ‘X’ (the new one). Select the crossed out module in VelbusLink and
delete it by pressing on the icon on top of the navigation pane. After a new scan, only the new module will appear.
• in case the Velbus installation has not been changed and red crosses appear after a new scan, there is probably a
wiring or terminator problem. See “General step-by-step guide” above.
• Check that you have not accidentally changed the address of the module? You can find the module by opening the
detection window in VelbusLink and physically operate the module. You will see the module appear in VelbusLink
along with its correct address.
MY VMB8PBU MODULES GIVE A DIFFERENT ADDRESS THAN THE ONE I SET
Care to the wiring of the push-buttons is needed when installing VMB8PBU modules. The left two wires are common
(marked "COM"). If, instead of these, you use other wires (of the channels) as common wires, you will get such strange
effects. Do not blindly follow the colours of any wires and mind the connections carefully.
THE ADDRESSES OF MY MODULES HAVE SUDDENLY CHANGED
Sometimes addresses appear to have been changed in VelbusLink simply because the view has been switched from
hexadecimal to decimal or vice versa. This setting can be changed in the View menu, or with the or button (see
also “Changing electronic addresses” p.7).
Modifying the view (HEX <-> DEC) does not affect the installation or the modules, only the view in VelbusLink.
Page 46

Part 2: configuration
© 2020 Velbus – v07 44 www.velbus.eu
SOME INPUT CHANNELS PROVIDE A WRONG “PRESSED” STATUS
If you connect feedback LEDs, you must respect the polarity of these LEDs. If you mount them backwards you get the effect
of an activated push-button. Some LEDs are available in “Dual Polarity”, which can adversely affect the push-button
interface. A simple diode in line will correct this.
THE LEDS ON SOME MODULES BLINK OR DO NOT RESPOND
The most common cause for this problem is a wiring or terminator fault. See “General step-by-step guide” above for more
info.
AN INPUT MODULE STOPS RESPONDING
Check if you haven’t configured a delay in the button or input channel. Push the button for at least three seconds and check
if the action is executed. Delays on push-buttons appear with an icon in VelbusLink.
The channel may also be locked. To unlock, right-click on the channel and select Operate. You can unlock the channel in the
Operate dialogue. If this fails to unlock the channel, temporarily configure a push-button to unlock the channel (by creating
an “unlock” action between the two). By pressing this push-button, the locked channel will be unlocked. Once the channel
unlocked, you can remove the “unlock” action.
The problem can also be caused by a static electrical discharge. Power down the system, wait 5 seconds and power up again.
AUTOMATIC DETECTION SELECTS THE WRONG MODULE; THE ADDRESS OF THE MODULE YOU ARE
EXPECTING IS PROBABLY ALSO ATTRIBUTED TO ANOTHER MODULE
The module's address has probably been assigned to another module. Rare is the case that both modules have the identical
serial number. To resolve this, delete 1 module from the bus (disconnect H and L), scan, activate the Advanced mode in
VelbusLink (via the Tools menu), right-click on the module which is scanned and change the address (via Change address)
and serial number (via Advanced > Change serial number).
Next, disconnect this module, reconnect the other module, and change the address and serial number from the latter (use a
different address and serial number than the first module). You should not encounter any problems once both modules are
connected.
See also
Installation Guide, Part 1: Hardware and Cabling
www.velbus.eu > Support
 Loading...
Loading...