Page 1

Manual No: 577014-367 • Revision: D
Startup Guide
QuickServer Industrial Protocol Gateway
Page 2

Notice
Veeder-Root makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this publication, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose.
Veeder-Root shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in
connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this publication.
Veeder-Root reserves the right to change system options or features, or the information contained in this publication.
This publication contains proprietary information which is protected by copyright. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
photocopied, reproduced, or translated to another language without the prior written consent of Veeder-Root.
Contact TLS Systems Technical Support for additional troubleshooting information at 800-323-1799.
DAMAGE CLAIMS / LOST EQUIPMENT
Thoroughly examine all components and units as soon as they are received. If any cartons are damaged or missing, write a complete
and detailed description of the damage or shortage on the face of the freight bill. The carrier's agent must verify the inspection and sign
the description. Refuse only the damaged product, not the entire shipment.
Veeder-Root must be notified of any damages and/or shortages within 30 days of receipt of the shipment, as stated in our Terms and
Conditions.
VEEDER-ROOT’S PREFERRED CARRIER
1. Contact Veeder-Root Customer Service at 800-873-3313 with the specific part numbers and quantities that were missing or
received damaged.
2. Fax signed Bill of Lading (BOL) to Veeder-Root Customer Service at 800-234-5350.
3. Veeder-Root will file the claim with the carrier and replace the damaged/missing product at no charge to the customer. Customer
Service will work with production facility to have the replacement product shipped as soon as possible.
CUSTOMER’S PREFERRED CARRIER
1. It is the customer’s responsibility to file a claim with their carrier.
2. Customer may submit a replacement purchase order. Customer is responsible for all charges and freight associated with
replacement order. Customer Service will work with production facility to have the replacement product shipped as soon as
possible.
3. If “lost” equipment is delivered at a later date and is not needed, Veeder-Root will allow a Return to Stock without a restocking fee.
4. Veeder-Root will NOT be responsible for any compensation when a customer chooses their own carrier.
RETURN SHIPPING
For the parts return procedure, please follow the appropriate instructions in the "General Returned Goods Policy” pages in the
"Policies and Literature" section of the Veeder-Root North American Environmental Products price list. Veeder-Root will not accept
any return product without a Return Goods Authorization (RGA) number clearly printed on the outside of the package.
©Veeder-Root 2019. All rights reserved
.
ii
Page 3

Table of Contents
Introduction
Contractor Certification Requirements ..............................................................................1
Safety Precautions ............................................................................................................1
Safety Warnings ...............................................................................................................2
Related Documents ..........................................................................................................2
Precautions Against Static Electricity ................................................................................2
QuickServer Gateway. ......................................................................................................3
Quick Start Guide ..........................................................................................................4
Setup For QuickServer
Record Identification Data ................................................................................................5
Point Count Capacity And Registers Per Device ..............................................................5
Input COM Settings on the device connected to the QuickServer ....................................6
Selecting The Desired Protocol Configuration ..................................................................6
BMS Network Settings: MAC Address Node-ID And Baud Rate ......................................7
BACnet MS/TP: Setting The MAC Address For BMS Network ................................7
Modbus RTU And Modbus TCP/IP: Setting The Node-ID........................................7
BACnet MS/TP Or Modbus RTU: Setting The Baud Rate For BMS Network ..........8
Interfacing QuickServer To Devices
QuickServer ProtoNode Showing Connection Ports .........................................................9
Device Connections To QuickServer ................................................................................9
QuickServer 6-Pin Phoenix Connector.....................................................................9
Serial Network Wiring Field Port To RS-485 Network ............................................10
Power Up QuickServer ...................................................................................................11
Using QuickServer Web Configurator To Setup The Gateway
Connect The PC To QuickServer Via The Ethernet Port ................................................12
Connecting to QuickServer Web Configurator ................................................................13
Selecting Profiles for Devices Connected to QuickServer ..............................................13
Setting BACnet Parameters ............................................................................................15
Ethernet Network - Setting IP Address For Field Network ..............................................17
How To Start The Installation Over: Clearing Profiles
BACnet EXPLORER NG ................................................................................................19
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Lost Or Incorrect IP Address ........................................................................................ A-1
Viewing Diagnostic Information ....................................................................................A-2
Check Wiring And Settings ........................................................................................... A-2
LED Diagnostics For Communications Between QuickServer And Devices ................ A-3
Take Diagnostic Capture With The FieldServer Toolbox .............................................. A-4
Update Firmware .......................................................................................................... A-6
Unknown Alarm Category ............................................................................................. A-6
Securing QuickServer With Passwords ........................................................................ A-6
Appendix B: Vendor Information – Veeder-Root
Interface To BACnet & Modbus Tables ........................................................................ B-1
Appendix C: “A” Bank DIP Switch Settings
iii
Page 4

Figures
Table of Contents
Appendix D: Reference
Specifications ................................................................................................................D-1
Compliance With UL Regulations .................................................................................D-1
Certifications - BTL Mark - BACnet® Testing Laboratory ............................................. D-2
Figure 1. QuickServer ProtoNode Connectivity Diagram (TLS450PLUS Shown) .....3
Figure 2. QuickServer S Bank (Profile Selections) DIP Switches ..........................6
Figure 3. QuickServer A Bank DIP Switches .........................................................7
Figure 4. QuickServer B Bank DIP Switches .........................................................8
Figure 5. QuickServer ProtoNode Connections .....................................................9
Figure 6. QuickServer ATG RS-232 and Power Inputs .......................................10
Figure 7. QuickServer Connection To RS-485 Field Network .............................10
Figure 8. QuickServer RS-485 BMS Network EOL Switch Settings .................... 10
Figure 9. Assigning Static IP Address To The PC ...............................................12
Figure 10. Web Configurator Showing No Active Profiles .....................................14
Figure 11. Web Configurator Showing Available Profiles For Selection ................14
Figure 12. Web Configurator Showing Active Profile Additions .............................15
Figure 13. Web Configurator with Protocol Set to BACnet ....................................16
Figure 14. Web Configurator Screen With Active Profiles .....................................17
Figure 15. Changing IP Address Via FS-GUI ........................................................18
Figure 16. BACnet Explorer NG On A BACnet Network ........................................19
Figure A-1. Ethernet Port Location ........................................................................A-1
Figure A-2. Check IP Address ............................................................................... A-1
Figure A-3. Error Messages Screen ......................................................................A-2
Figure A-4. Ethernet Port Location ........................................................................A-3
Figure A-5. FS Toolbox Utility Screen ...................................................................A-4
Figure A-6. Selecting Full Diagnostic For Selected Device ................................... A-4
Figure A-7. Selecting Start Diagnostic For Selected Device ................................. A-5
Figure A-8. Launching Explorer To Located Device’s Diagnostic File ................... A-5
Figure A-9. FS-GUI Passwords Page ....................................................................A-7
Figure A-10. Password Recovery Page .................................................................. A-7
Tables
Table 1. QuickServer Part Number .........................................................................5
Table 2. Registers Per Device .................................................................................5
Table 3. COM Settings ............................................................................................6
Table 4. Profile Settings For QuickServer ...............................................................6
Table 5. BMS Baud Rate .........................................................................................8
Table 6. QuickServer Current Draw .....................................................................11
Table A-1. Diagnostic LED Descriptions ................................................................. A-3
Table B-1. System Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus ...................... B-1
Table B-2. Unknown_Type Veeder-Root Interface Mappings To BACnet
And Modbus .......................................................................................... B-1
Table B-3. Tank Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus .......................... B-2
Table B-4. Liquid Sensor Veeder-Root Interface Mappings To BACnet
And Modbus .......................................................................................... B-2
Table B-5. Input Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus .......................... B-3
Table B-6. Type A Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus .......... B-3
Table B-7. Type B Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus .......... B-3
Table B-8. Vapor Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus ............ B-3
iv
Page 5

Table of Contents
Table B-9. Groundwater Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet
And Modbus .......................................................................................... B-3
Table B-10. MAG Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus .............. B-4
Table B-11. Smart Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus ............ B-4
Table B-12. PLLD Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus ......................... B-4
Table C-1. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 26-50 ...............................C-1
Table C-2. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 51 - 75 .............................C-2
Table C-3. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 76 - 100 ...........................C-3
Table C-4. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 101-125 ........................... C-4
Table C-5. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 126 - 150 .........................C-5
Table C-6. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 151 - 175 .........................C-6
Table C-7. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 176 - 200 .........................C-7
Table C-8. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 201 - 225 .........................C-8
Table C-9. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 226-255 ........................... C-9
Table D-1. QuickServer ProtoNode Specifications .................................................D-1
v
Page 6

Introduction
OFF
The QuickServer is an external, high performance building automation multi-protocol gateway that is preconfigured
to automatically communicate between Veeder-Root’s products (hereafter called “device”) connected to the
QuickServer and automatically configures them for BACnet MS/TP, BACnet/IP, Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP/IP.
It is not necessary to download any configuration files to support the required applications. The QuickServer is
pre-loaded with tested profiles/configurations for the supported devices.
The QuickServer ProtoNode is compatible with:
TLS-3XX Consoles hardware/software requirements:
• RS-232/RS-485 Dual Interface Module
TLS-4XX Consoles hardware/software requirements:
• RS-232/RS-485 Dual Interface Module
Contractor Certification Requirements
Veeder-Root requires the following minimum training certifications for contractors who will install and setup the
equipment discussed in this manual:
Installer Certification (Level 1): Contractors holding valid Installer Certification are approved to perform wiring
and conduit routing; equipment mounting; probe, sensor and carbon canister vapor polisher installation; wireless
equipment installation; tank and line preparation; and line leak detector installation.
Technician Certification (Level 2/3): Contractors holding valid Technician Certifications are approved to
perform installation checkout, startup, programming and operations training, system tests, troubleshooting and
servicing for all Veeder-Root Series Tank Monitoring Systems, including Line Leak Detection. In addition,
Contractors with the following sub-certification designations are approved to perform installation checkout, startup,
programming, system tests, troubleshooting, service techniques and operations training on the designated system.
•Wireless 2
• Tall Tank
Warranty Registrations may only be submitted by selected Distributors.
Safety Precautions
The following safety symbols may be used throughout this manual to alert you to important safety hazards and
precautions
EXPLOSIVE
Fuels and their vapors are extremely explosive if ignited.
ELECTRICITY
High voltage exists in, and is supplied to, the device. A
potential shock hazard exists.
FLAMMABLE
Fuels and their vapors are extremely flammable.
TURN POWER OFF
Live power to a device creates a potential shock hazard.
Turn Off power to the device and associated accessories
when servicing the unit.
1
Page 7

Introduction Safety Warnings
OFF
WARNING
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury.
Safety Warnings
READ ALL RELATED MANUALS
Knowledge of all related procedures before you begin
work is important. Read and understand all manuals thoroughly. If you do not understand a procedure, ask someone who does.
WARNING
This console contains high voltages which can be lethal. It is also connected to low
power devices that must be kept intrinsically safe.
FAILURE TO COMPLY WITH THE FOLLOWING WARNINGS AND SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS COULD CAUSE DAMAGE TO PROPERTY, ENVIRONMENT,
RESULTING IN SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH.
1. Turn off and tag power at the circuit breaker. Do not connect the console AC
power supply wires at the breaker until all devices are connected.
2. Attach conduit from the power panel to the console's Power Area knockouts
only.
3. Comply with all applicable codes including: the National Electrical Code;
federal, state, and local codes; and other applicable safety codes.
Connecting power wires to a live circuit can cause electrical shock that may result in
serious injury or death.
Routing conduit for power wires into the intrinsically safe compartment can result in
fire or explosion resulting in serious injury or death.
Related Documents
576013-879 TLS-3XX Console Site Prep And Installation Manual
577014-073 TLS-450PLUS Console Site Prep And Installation Manual
577013-879 TLS-450 Console Site Prep And Installation Manual
577014-110 TLS-450PLUS/TLS4 Operator’s Manual
Precautions Against Static Electricity
If necessary to install electronic components in the ATG to implement this feature, read the following static
electricity precautions:
1. Before handling any components, discharge your body's static electric charge by touching a grounded surface.
2. Do not remove parts from their anti-static bags until you are ready to install them.
3. Do not lay parts on the anti-static bags! Only the insides are anti-static.
4. When handling parts, hold them by their edges and their metal mounting brackets.
5. Avoid touching comm board components or edge connectors that plug into slots when handling.
6. Never slide parts over any surface.
7. Avoid plastic, vinyl, and Styrofoam in your work area.
2
Page 8

Introduction QuickServer Gateway.
QuickServer Gateway.
Figure 1. QuickServer ProtoNode Connectivity Diagram (TLS450PLUS Shown)
3
Page 9

Quick Start Guide
1
2
5
7
8
10
11
12
1. Record the information about the unit. ( page 5)
2. Set the device’s COM settings for each of the devices that are to connect to the QuickServer. ( page 6)
3. Select the protocol configuration on the S Bank DIP switches. ( page 6)
4. BACnet MS/TP: Set the MAC Address on the A Bank DIP switches. ( page 7)
5. Modbus RTU or Modbus TCP/IP: Set the Node-ID. ( page 7)
6. BACnet MS/TP or Modbus RTU: Set the baud rate of the field protocol on the B Bank DIP switches. (
page 8)
7. Connect the QuickServer 6-pin RS-232 connector to the Veeder-Root ATG. ( page 9)
8. Connect the QuickServer ProtoNode 3 pin RS-485 port to the field protocol cabling. ( page 10)
9. Connect power to the QuickServer 6-pin connector. ( page 11)
10.Use a web browser to access the QuickServer Web Configurator page to select the profiles of the devices
attached to the QuickServer and input the Node-ID from each device. Once the devices are selected, the
QuickServer automatically builds and loads the appropriate configuration. ( page 12)
11.BACnet MS/TP or BACnet/IP: Set the BACnet Device Instance. ( page 15)
12.Ethernet Network: Use a web browser to access the QuickServer Web Configurator page to change the IP
Address. No changes to the configuration are necessary. ( page 17)
9
3
4
6
4
Page 10

Setup For QuickServer
1
Record Identification Data
The QuickServer has a unique part number located on the side or the back of the unit. This number should be
recorded, as it may be required for technical support. The numbers are as follows:
Table 1. QuickServer Part Number
Model Part Number
QuickServer ProtoNode 330020-840 /
QuickServer ProtoNode units have the following 3 ports: RS-232 , Ethernet and RS-485.
330020-841
Point Count Capacity And Registers Per Device
The total number of points presented by the device attached to the QuickServer ProtoNode-1504 cannot exceed
5000.
The total number of points per QuickServer profile is shown in Table 2:
Table 2. Registers Per Device
Profile Points Per Device
System 29
Unknown Type 3
Tank 56
Liquid Sensor 9
Input 6
Type A Sensor 5
Type B Sensor 6
Vapor Sensor 9
Groundwater Sensor 9
MAG Sensor 14
Smart Sensor 17
PLLD 19
5
Page 11

Setup For QuickServer Input COM Settings on the device connected to the QuickServer
2
S0 - S3 DIP Switches Bank DIP Switch Location
When setting DIP switches,
ensure that power to the
board is OFF.
NOTICE
Input COM Settings on the device connected to the QuickServer
• The connected serial device MUST have the same baud rate, data bits, stop bits, and parity settings as the
QuickServer.
• To set the QuickServer’s COM settings, See “Connecting to QuickServer Web Configurator” on page 13.
• Table 3 specifies the device serial port settings required to communicate with the QuickServer.
Table 3. COM Settings
Port Setting TLS-3XX/TLS4XX
Protocol V-R Interface
Baud Rate 9600
Parity Odd
Data Bits 7
Stop Bits 1
Selecting The Desired Protocol Configuration
3
QuickServer ProtoNode units use the ‘S’ bank of DIP switches (S0 - S3) to select the protocol configuration (see
Figure 2).
Off On
S3
S2
S1
S0
Figure 2. QuickServer S Bank (Profile Selections) DIP Switches
See Table 4 for the S Bank DIP switch settings.
Table 4. Profile Settings For QuickServer
QuickServer ProtoNode S Bank DIP Switches
Profile S0 S1 S2 S3
BACnet/IP Off Off Off Off
BACnet MS/TP On Off Off Off
6
Page 12

Setup For QuickServer BMS Network Settings: MAC Address Node-ID And Baud Rate
NOTICE
A0 - A7 DIP Switches Bank DIP Switch Location
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
Off On
When setting DIP switches,
ensure that power to the
board is OFF.
NOTICE
Table 4. Profile Settings For QuickServer (Continued)
QuickServer ProtoNode S Bank DIP Switches
Profile S0 S1 S2 S3
Modbus TCP/IP and Modbus RTU
Off On Off Off
BMS Network Settings: MAC Address Node-ID And Baud Rate
BACNET MS/TP: SETTING THE MAC ADDRESS FOR BMS NETWORK
4
Only 1 MAC Address is set for QuickServer regardless of how many devices are connected to QuickServer.
•
• Set the BACnet MS/TP MAC Address of the QuickServer to a value between 1 to 127 (Master MAC Address);
this is so that the BMS front end can find QuickServer via BACnet Auto-Discovery.
Never set a BACnet MS/TP MAC Address of the QuickServer to a value from 128 to 255.
Addresses from 128 to 255 are Slave Addresses and can not be discovered by BMS front
ends that support Auto-Discovery of BACnet MS/TP devices.
• Set “A” bank DIP switches A0 – A7 to assign a MAC Address to the QuickServer for BACnet MS/TP (see
Figure 3).
• Refer to Appendix C for the complete range of MAC Addresses and DIP switch settings.
MODBUS RTU AND MODBUS TCP/IP: SETTING THE NODE-ID
5
The Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP/IP Node-IDs are assigned by setting the A-bank dip switches. (see
•
Figure 3).
• Node-ID’s range from 1-255. Refer to Appendix C for the full range of addresses for setting Node-ID.
Figure 3. QuickServer A Bank DIP Switches
7
Page 13

Setup For QuickServer BMS Network Settings: MAC Address Node-ID And Baud Rate
BACNET MS/TP OR MODBUS RTU: SETTING THE BAUD RATE FOR BMS NETWORK
6
DIP switches B0 – B3 can be used to set the field baud rate of the QuickServer to match the baud rate required
by the BMS for BACnet MS/TP (see Figure 4).
Off
B0
B1
B2
B3
On
B0 - B3 DIP Switches Bank DIP Switch Location
Figure 4. QuickServer B Bank DIP Switches
BMS baud rate dip switch selections are shown in Table 5.
.
Table 5. BMS Baud Rate
Baud Rate B0 B1 B2 B3
9600 On On On Off
19200 Off Off Off On
NOTICE
When setting DIP switches,
ensure that power to the
board is OFF.
38400* On On Off On
57600 Off Off On On
76800 On Off On On
*Factory default setting.
8
Page 14

Interfacing QuickServer To Devices
Phoenix
Connector
NOTICE
QuickServer ProtoNode Showing Connection Ports
Figure 5. QuickServer ProtoNode Connections
Device Connections To QuickServer
QUICKSERVER 6-PIN PHOENIX CONNECTOR
7
Pins 1 - 3 are for Veeder-Root ATG input (see Figure 6).
•
• Pins 4 - 6 are for QuickServer power. QuickServer accepts either 9-30V DC or 12-24V AC on pins 4 and 5.
Do not power up QuickServer at this time.
9
Page 15

Interfacing QuickServer To Devices Device Connections To QuickServer
Pin 3 Rx/Pin 2 Tx/+
Pin 5 GND
Pin 3 Rx/-
Pin 2 Tx/+
Pin 7 GND
Power In (+)
Power In (-)
Frame Ground (must be connected)
Pin 1 Pin 6
(If 25 Pin) (If 9 Pin)
Power
Input
Use standard grounding
principles for RS-232 GND.
NOTICE
Console RS-232 Connector
RS-485 (+)
RS-485 (-)
RS-485 GND
BMS
Input
Pin 1
Pin 3
Off (Default)
On
EOL Switch
Figure 6. QuickServer ATG RS-232 and Power Inputs
SERIAL NETWORK WIRING FIELD PORT TO RS-485 NETWORK
8
•
Connect the RS-485 network wires to the 3-pin RS-485 connector on QuickServer ProtoNode as shown in
Figure 7.
• See “Ethernet Network - Setting IP Address For Field Network” on page 17. for information on connecting to
BACnet/IP network.
• If the QuickServer is the last device on the trunk, then the End-Of-Line Termination Switch needs to be set to
the On position (the EOL Termination default setting is Off). If necessary, set the switch to the On position
(see Figure 8).
Figure 7. QuickServer Connection To RS-485 Field Network
Figure 8. QuickServer RS-485 BMS Network EOL Switch Settings
10
Page 16

Interfacing QuickServer To Devices Power Up QuickServer
Power Up QuickServer
9
Verify QuickServer nominal power requirements in Table 6.
Table 6. QuickServer Current Draw
Current Draw
NOTICE
QuickServer ProtoNode
Typical 170 mA 100 mA‘ 80 mA
Maximum 240 mA 140 mA 100 mA
These values are ‘nominal’ and a safety margin should be added to the power supply of the
12V DC/AC 24V DC/AC 30V DC
host system. A safety margin of 25% is recommended.
After verifying power source and with frame ground connected as shown in Figure 6. apply power to QuickServer.
11
Page 17

Using QuickServer Web Configurator To Setup The Gateway
Connect The PC To QuickServer Via The Ethernet Port
10
• Connect a CAT5 Ethernet cable (Straight through or Cross-Over) between the local PC and QuickServer.
• The Default IP Address of QuickServer is 192.168.1.24, subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. If the PC and
QuickServer are on different IP Networks, assign a static IP Address to the PC on the 192.168.1.xxx network:
For Windows 10, Right click on .
click on Local Area Connections. When the Local Area Connections Status box appears click Properties. Click
on Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) then click Properties. When the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/
IPv4) Properties dialog box appears, click, ‘Use the following IP address’ radio button and enter the ‘IP address’
and ‘Subnet mask’ entries shown in Figure 9, the click the OK button , then the Close buttons to exit.
Then click on Network Connections>Change Adapter Options. Double
Figure 9. Assigning Static IP Address To The PC
12
Page 18

Using QuickServer Web Configurator To Setup The Gateway Connecting to QuickServer Web Configurator
NOTICE
NOTICE
NOTICE
After disconnecting from the QuickServer return to the PC’s Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
dialog box and click the Obtain an IP Address Automatically’ radio button to return the PC to its original Local Area
Connection settings.
Connecting to QuickServer Web Configurator
After setting a local PC on the same subnet as the QuickServer (refer to above paragraph), open a web browser
on the PC and enter the IP Address of the QuickServer (the default address is 192.168.1.24).
If the IP Address of the QuickServer was changed, the assigned IP Address can be
discovered using the FS Toolbox utility. See ‘Lost Or Incorrect IP Address’ (Appendix A, page
A-1) for instructions.
Selecting Profiles for Devices Connected to QuickServer
• In the Web Configurator, the Active Profiles are shown below the Configuration Parameters.
• Fill in the parameter values as needed.
- Enter the Veeder-Root PLC Type and COM settings.
See “Input COM Settings on the device connected to the QuickServer” on page 6 for
correct COM settings per PLC Type.
- Once a parameter value is changed as desired click Submit to save it.
• The Active profiles section lists the currently active device profiles, including previous Web Configurator
additions. This list is empty for new installations, or after clearing all configurations (see Figure 10).
• To add an active profile to support a device, click the Add button under the Active Profiles heading. This will
present a drop-down box underneath the Current profile column that lists all the available profiles (see
Figure 11).
• Once the profile for the device has been selected from the drop-down list, enter the value of the Node-ID.
The first entered Node-ID must be set to “1” and be followed by sequential values.
• Then enter the Address Parameter. The Address is used to specify the tank, sensor or input number. This
information can be found in the Veeder-Root ATG Report.
- Tanks are addressed from 1-12.
- Sensors are addressed from 1-64.
- Inputs are addressed from 1-64.
• Then press the “Submit” button to add the Profile to the list of devices to be configured.
• Repeat this process until all the devices have been added.
13
Page 19

Using QuickServer Web Configurator To Setup The Gateway Selecting Profiles for Devices Connected to QuickServer
Figure 10. Web Configurator Showing No Active Profiles
Figure 11. Web Configurator Showing Available Profiles For Selection
14
Page 20

Using QuickServer Web Configurator To Setup The Gateway Setting BACnet Parameters
NOTICE
NOTICE
• Completed additions are listed under “Active Profiles” as shown the Figure 12 example.
Figure 12. Web Configurator Showing Active Profile Additions
Figure 12 shows a console with 3 tanks and 4 liquid sensors. The node IDs are sequential, starting with 1; the
addresses match the console numbering of the tanks (i.e., there is no tank 3 set up in the console). The Node
ID is used for the BACnet Object or Modbus Register (see Appendix B) and its address must match the device
number programmed in the console.
System and Unknown Type points are automatically configured therefore no profile is
required. Refer to Table B-1 and Table B-2 in Appendix B for a list of available points.
Setting BACnet Parameters
11
• Open the Web Configurator with the protocol set to BACnet in “Selecting The Desired Protocol Configuration”
on page 6.
• Fill in the parameter values as needed (see Figure 13).
- Enter the Veeder-Root PLC Type, COM settings and BACnet settings (Bac_device_id)
See See “Input COM Settings on the device connected to the QuickServer” on page 6.
for correct COM settings per PLC Type.
The Bac_device_id field will display the current value (default = 50,000). The BACnet
Device Instance can range from 1 to 4,194,303.
- Once a parameter value is changed as desired click Submit to save it.
15
Page 21

Using QuickServer Web Configurator To Setup The Gateway Setting BACnet Parameters
Figure 13. Web Configurator with Protocol Set to BACnet
16
Page 22

Using QuickServer Web Configurator To Setup The Gateway Ethernet Network - Setting IP Address For Field Network
Ethernet Network - Setting IP Address For Field Network
12
• After setting a local PC to the same subnet as the QuickServer (See “Connect The PC To QuickServer Via The
Ethernet Port” on page 12., open a web browser on the PC and enter the IP Address of the QuickServer; the
default address is 192.168.1.24.
• The Web Configurator is displayed as the landing page (see Figure 14).
• To access the FS-GUI, click on the “Diagnostics & Debugging” button in the bottom right corner of the page.
Figure 14. Web Configurator Screen With Active Profiles
• From the FS-GUI landing page, click on “Setup” to expand the navigation tree and then select “Network
Settings” to access the IP Settings menu (see Figure 15).
17
Page 23

Using QuickServer Web Configurator To Setup The Gateway Ethernet Network - Setting IP Address For Field Network
NOTICE
NOTICE
Figure 15. Changing IP Address Via FS-GUI
• Modify the IP Address (N1 IP Address field) of the QuickServer Ethernet port.
• If necessary, change the Netmask (N1 Netmask field).
• If necessary, change the IP Gateway (Default Gateway field).
If the QuickServer is connected to a managed switch/router, the IP Gateway of the
QuickServer should be set to the IP Address of that managed switch/router.
•Click the “System Restart” button at the bottom of the page to apply changes and restart the QuickServer.
•Unplug Ethernet cable from PC and connect it to the network switch or router.
•Record the IP Address assigned to the QuickServer for future reference.
The FieldPoP™ button (see Figure 15) allows users to connect to FieldPoP, Sierra
Monitor’s device cloud solution for the IIoT. FieldPoP enables secure remote connection to
field devices through a FieldServer and its local applications for configuration, management,
maintenance. For more information about FieldPoP, refer to the FieldPoP™ Device Cloud
Start-up Guide.
18
Page 24

How To Start The Installation Over: Clearing Profiles
1. After setting a local PC to the same subnet as the QuickServer (“Connect The PC To QuickServer Via The
Ethernet Port” on page 12), open a web browser on the PC and enter the IP Address of the QuickServer.
2. If the IP Address of the QuickServer has been changed by previous configuration, the assigned IP Address
must be gathered from the network administrator.
3. The Web Configurator is displayed as the landing page.
4. At the bottom-left of the page, click the “Clear Profiles and Restart” button.
5. Once restart is complete, all past profiles discovered and/or added via Web configurator are deleted. The unit
can now be reinstalled.
BACnet EXPLORER NG
A typical working example of a BACnet Explorer NG on a BACnet Network (see Figure 16).
BACnet Explorer NG
BACnet MS/TP
PC Connected to
BACnet
Explorer’s Web
Browser
Up to 32 BACnet
MS/TP devices
BACnet Router
Multi-Port Swtich
Modbus RTU
BACnet MS/TP
BACnet MS/TP
Modbus RTU
Up to 32 BACnet
MS/TP devices
Figure 16. BACnet Explorer NG On A BACnet Network
• For additional details related to the BACnet Explorer NG, go to the Sierra Monitor website’s Resource Center
and download the BACnet Explorer NG Start-Up Guide
.
• For purchasing information, look up the BACnet Explorer NG page on the Sierra Monitor website and click on
the “BUY NOW” tab.
19
Page 25

Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Lost Or Incorrect IP Address
1. Ensure that FieldServer Toolbox is loaded onto the local PC. Otherwise, download the FieldServer Toolbox.zip
via the Sierra Monitor Resource Center at https://www.sierramonitor.com/content/fieldserver-toolbox-0
2. Extract the executable file and complete the installation.
Ethernet port
Figure A-1. Ethernet Port Location
3. Connect a standard CAT5 Ethernet cable between the user’s PC and QuickServer.
4. Double click on the FS Toolbox Utility and click Discover Now on the splash page.
5. Check for the IP Address of the desired gateway.
Figure A-2. Check IP Address
A-1
Page 26

Appendix A Viewing Diagnostic Information
6. If correcting the IP Address of the gateway: click the settings icon on the same row as the gateway (see
Figure A-2), then click Network Settings, change the IP Address and click Update IP Settings to save.
Viewing Diagnostic Information
1. Type the IP Address of the QuickServer into the web browser or use the FieldServer Toolbox to connect to the
QuickServer.
2. Click on Diagnostics and Debugging Button, then click on view, and then on connections.
3. If there are any errors showing on the Connection page, refer to “Check Wiring And Settings” below for the
relevant wiring and settings.
Figure A-3. Error Messages Screen
Check Wiring And Settings
• No COMS on Veeder-Root Interface side. If the Tx/Rx LEDs are not flashing rapidly then there is a COM issue.
To fix this, check the following:
- Visual observations of LEDs on QuickServer (See “LED Diagnostics For Communications Between
QuickServer And Devices” on page A-3.)
A-2
Page 27

Appendix A LED Diagnostics For Communications Between QuickServer And Devices
NOTICE
SPL
RUN
ERR
RX
TX
PWR
- Check baud rate, parity, data bits, stop bits
- Check device address
- Verify wiring
- Verify device is connected to the same subnet as the QuickServer
- Verify the Modbus device was discovered in Web Configurator (See “Connecting to QuickServer Web
Configurator” on page
• Field COM problems:
13.).
- If Ethernet protocols are used, observe Ethernet LEDs on the QuickServer (See “LED Diagnostics For
Commun
ications Between QuickServer And Devices” below).
- Check DIP switch settings (using correct baud rate and device instance)
- Verify IP Address setting
- Verify wiring
If the problem persists, a Diagnostic Capture needs to be taken and sent to support. (See “Take Diagnostic Capture With The FieldServer Toolbox” on page A-4.).
LED Diagnostics For Communications Between QuickServer And Devices
Reference Figure A-4 and Table A-1 for understanding QuickServer ProtoNode diagnostic LEDs.
Figure A-4. Ethernet Port Location
Table A-1. Diagnostic LED Descriptions
LED Description
SPL The SPL LED will light if the unit is not getting a response from one or more of the configured devices.
RUN The RUN LED will start flashing 20 seconds after power indicating normal operation.
ERR
RX
The SYS ERR LED will go on solid 15 seconds after power up. It will turn off after 5 seconds. A steady red
light will indicate there is a system error on the unit. If this occurs, immediately report the related “system
error” shown in the error screen of the GUI interface to support for evaluation.
The RX LED will flash when a message is received on the serial port on the 6-pin connector. If the serial
port is not used, this LED is non-operational.
TX
PWR This is the power light and should show steady green at all times when unit is powered.
The TX LED will flash when a message is sent on the serial port on the 6-pin connector. If the serial port is
not used, this LED is non-operational.
A-3
Page 28

Appendix A Take Diagnostic Capture With The FieldServer Toolbox
NOTICE
NOTICE
Take Diagnostic Capture With The FieldServer Toolbox
Once the Diagnostic Capture is complete, email it to technical support. The Diagnostic Capture will accelerate diagnosis of the problem.
• Ensure that FieldServer Toolbox is loaded onto the local PC. Otherwise, download the FieldServer Toolbox.zip
via the Sierra Monitor Resource Center Software Downloads. Reference Figure A-1.
• Extract the executable file and complete the installation.
• Connect a standard CAT5 Ethernet cable between the PC and QuickServer.
• Double click on the FS Toolbox Utility.
1. Take a log
a.Click on the diagnose icon of the desired device.
Figure A-5. FS Toolbox Utility Screen
b.Ensure “Full Diagnostic" is selected (this is the default).
Figure A-6. Selecting Full Diagnostic For Selected Device
If desired, the default capture period can be changed.
A-4
Page 29

Appendix A Take Diagnostic Capture With The FieldServer Toolbox
c.Click on ‘Start Diagnostic’.
Figure A-7. Selecting Start Diagnostic For Selected Device
d.When the capture period is finished, the “Diagnostic Test Complete” window will appear
2. Send Log
a.Once the diagnostic test is complete, a zip file is saved on the PC.
Figure A-8. Launching Explorer To Located Device’s Diagnostic File
b.Choose ‘Open’ to launch explorer and have it point directly at the correct folder.
A-5
Page 30

Appendix A Update Firmware
c.Send the Diagnostic zip file to technical support (technicalsupport@veeder.com).
Update Firmware
To load a new version of the firmware, follow these instructions:
1. Extract and save the new file onto the local PC.
2. Open a web browser and type the IP Address of the FieldServer in the address bar.
- Default IP Address is 192.168.1.24
- Use the FS Toolbox utility if the IP Address is unknown (See “Lost Or Incorrect IP Address” on page A-1.).
3. Click on the “Diagnostics & Debugging” button.
4. In the Navigation Tree on the left hand side, do the following:
a.Click on “Setup”
b.Click on “File Transfer”
c.Click on the “General” tab
5. In the General tab, click on “Choose Files” and select the web.img file extracted in Step 1.
6. Click on the orange “Submit” button.
Unknown Alarm Category
If the ProtoNode receives an alarm and or device ID that it does not recognize, it will be stored in the DA_UNKCAT
data array. Only the last device ID, Alarm ID, and address will be stored.
Securing QuickServer With Passwords
Access to the QuickServer can be restricted by enabling a password on the FS-GUI Passwords page – click
Setup and then Passwords in the navigation panel. There are 2 access levels defined by 2 account names: Admin
and User.
• The Admin account has unrestricted access to the QuickServer.
• The User account can view any QuickServer information, but cannot make any changes or restart the
QuickServer.
The password needs to be a minimum of eight characters and is case sensitive.
If the password is lost, click cancel on the password authentication popup window (see Figure A-9), and email the
password recovery token (see Figure A-10) to technical support to receive a temporary password from the support
team. Access the QuickServer to set a new password.
A-6
Page 31

Appendix A Securing QuickServer With Passwords
Figure A-9. FS-GUI Passwords Page
Figure A-10. Password Recovery Page
A-7
Page 32

Appendix B: Vendor Information – Veeder-Root
NOTICE
The ProtoNode provides capability to support any Veeder-Root serial command by defining customized map
descriptors for any command or data type. Refer to Appendix A of the 577014-368 QuickServer Industrial Protocol
Gateway Installation And Setup manual. Appendix A (Security Code) of the same manual also contains instructions
on using a Security Code for the TLS communications port.
Interface To BACnet & Modbus Tables
An X in the BACnet Object ID or Modbus Register represents a one- or two-digit number that equals
the Node ID. In the Liquid Sensor X Fuel Alarm examples below, with a Node ID of 3, the X will be 3;
for a Node ID of 11, the X will be 11.
Point Name Node ID BACnet Object ID (X002) Modbus Register (10X02)
Sensor X Fuel Alarm 3
Sensor X Fuel Alarm 11
Table B-1. System Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
Printer out of Paper BI 1 10001
Printer Error BI 2 10002
EEPROM Configuration Error BI 3 10003
Battery Off BI 4 10004
Too Many Tanks BI 5 10005
System Security Warning BI 6 10006
ROM Revision Warning BI 7 10007
Remote Display Communications Error BI 8 10008
Autodial Error BI 9 10009
Software Module Warning BI 10 10010
Tank Test Shutdown Warning BI 11 10011
Protective Cover Alarm BI 12 10012
BIR Shift Close Pending BI 13 10013
BIR Daily Close Pending BI 14 10014
PC(H8) Revision Warning BI 15 10015
System Self Test Error BI 16 10016
System Clock Incorrect Warning BI 17 10017
System Device Poll Timeout BI 18 10018
Maintenance Tracker NVMem BI 19 10019
Maintenance Tracker Communication Module BI 20 10020
Database Error BI 21 10021
File System Error BI 22 10022
BIR Status Warning BI 23 10023
VR Bus Power Outage Warning BI 24 10024
Software Upgrade Failure Alarm BI 25 10025
iButton Fault Warning BI 26 10026
iButton Fault Alarm BI 27 10027
Version Upgrade Available BI 28 10028
Expansion Box Unsupported BI 29 10029
3002 10302
11002 101102
Table B-2. Unknown_Type Veeder-Root Interface Mappings To BACnet And Modbus
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
Unknown Device Address AI 1 30001
Unknown Alarm Category AI 2 30002
Unknown Alarm Type AI 3 30003
B-1
Page 33

Appendix B Interface To BACnet & Modbus Tables
Table B-3. Tank Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus
Tank X Inventory Volume AI X001 30X01
Tank X Inventory TC Volume AI X002 30X02
Tank X Inventory Ullage AI X003 30X03
Tank X Inventory Height AI X004 30X04
Tank X Inventory Water AI X005 30X05
Tank X Inventory Temperature AI X006 30X06
Tank X Inventory Water Volume AI X007 30X07
Tank X Delivery Product Code AI X008 30X08
Tank X Delivery Number of Deliveries AI X009 30X09
Tank X Delivery Start Time from 01/01/1970 AI X010 30X10
Tank X Delivery Stop Time from 01/01/1970 AI X011 30X11
Tank X Delivery Starting Volume AI X012 30X12
Tank X Delivery Starting TC Volume AI X013 30X13
Tank X Delivery Starting Water AI X014 30X14
Tank X Delivery Starting Temp AI X015 30X15
Tank X Delivery Ending Volume AI X016 30X16
Tank X Delivery Ending TC Volume AI X017 30X17
Tank X Delivery Ending Water AI X018 30X18
Tank X Delivery Ending Temp AI X019 30X19
Tank X Delivery Starting Height AI X020 30X20
Tank X Delivery Ending Height AI X021 30X21
Tank X Tank Setup Warning BI X001 10X01
Tank X Tank Leak Alarm BI X002 10X02
Tank X High Water Alarm BI X003 10X03
Tank X Overfill Alarm BI X004 10X04
Tank X Low Limit Alarm BI X005 10X05
Tank X Theft Alarm BI X006 10X06
Tank X High Limit Alarm BI X007 10X07
Tank X Invalid Height Alarm BI X008 10X08
Tank X Probe Out Alarm BI X009 10X09
Tank X High Water Alarm BI X010 10X10
Tank X Delivery Needed BI X011 10X11
Tank X Maximum Level Alarm BI X012 10X12
Tank X Gross Leak Test Alarm BI X013 10X13
Tank X Monthly Leak Test Alarm BI X014 10X14
Tank X Annual Leak Test Alarm BI X015 10X15
Tank X Monthly Test Warning BI X016 10X16
Tank X Annual Test Warning BI X017 10X17
Tank X Monthly Test Alarm BI X018 10X18
Tank X Annual Test Alarm BI X019 10X19
Tank X Leak Test Active BI X020 10X20
Tank X No CSLD Idle Time Warning BI X021 10X21
Tank X Siphon Break Active Warning BI X022 10X22
Tank X CSLD Rate Increase Warning BI X023 10X23
Tank X AccuChart Calibration Warning BI X024 10X24
Tank X HRM Reconciliation Warning BI X025 10X25
Tank X HRM Reconciliation Alarm BI X026 10X26
Tank X Cold Temperature Warning BI X027 10X27
Tank X Missing Delivery Ticket Warning BI X028 10X28
Tank X Gross Leak Alarm BI X029 10X29
Tank X Delivery Density Warning BI X030 10X30
Tank X Density warning BI X031 10X31
Tank X Fuel Quality Alarm BI X032 10X32
Tank X Tank High Temperature Warning BI x033 10X33
Tank X Tank Low Temperature Warning BI x034 10X34
Tank X Density Offset Warning BI x035 10X35
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
Table B-4. Liquid Sensor Veeder-Root Interface Mappings To BACnet And Modbus
Sensor X Setup Data Warning BI X001 10X01
Sensor X Fuel Alarm BI X002 10X02
Sensor X Out Alarm BI X003 10X03
Sensor X Short Alarm BI X004 10X04
Sensor X Water Alarm BI X005 10X05
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
B-2
Page 34

Appendix B Interface To BACnet & Modbus Tables
Sensor X Water Out Alarm BI X006 10X06
Sensor X High Liquid Alarm BI X007 10X07
Sensor X Low Liquid Alarm BI X008 10X08
Sensor X Liquid Warning BI X009 10X09
Table B-5. Input Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus
Input X Input Setup Data Warning BI X001 10X01
Input X Input Normal BI X002 10X02
Input X Input Alarm BI X003 10X03
Input X Generator Off BI X004 10X04
Input X Generator On BI X005 10X05
Input X Input Out Alarm BI X006 10X06
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
Table B-6. Type A Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus
Type-A Sensor X Setup Data Warning BI X001 10X01
Type-A Sensor X Fuel Alarm BI X002 10X02
Type-A Sensor X Out Alarm BI X003 10X03
Type-A Sensor X Short Alarm BI X004 10X04
Type-A Sensor X Water Alarm BI X005 10X05
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
Table B-7. Type B Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus
Type-B Sensor X Setup Data Warning BI X001 10X01
Type-B Sensor X Fuel Alarm BI X002 10X02
Type-B Sensor X Out Alarm BI X003 10X03
Type-B Sensor X Short Alarm BI X004 10X04
Type-B Sensor X High Liquid Alarm BI X005 10X05
Type-B Sensor X Liquid Warning BI X006 10X06
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
Table B-8. Vapor Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus
Vapor Sensor X Setup Data Warninq BI X001 10X01
Vapor Sensor X Fuel Alarm BI X002 10X02
Vapor Sensor X Out Alarm BI X003 10X03
Vapor Sensor X Short Alarm BI X004 10X04
Vapor Sensor X Water Alarm BI X005 10X05
Vapor Sensor X Water Out Alarm BI X006 10X06
Vapor Sensor X High Liquid Alarm BI X007 10X07
Vapor Sensor X Low Liquid Alarm BI X008 10X08
Vapor Sensor X Liquid Warning BI X009 10X09
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
Table B-9. Groundwater Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus
Groundwater Sensor X Setup Data Warninq BI X001 10X01
Groundwater Sensor X Fuel Alarm BI X002 10X02
Groundwater Sensor X Out Alarm BI X003 10X03
Groundwater Sensor X Short Alarm BI X004 10X04
Groundwater Sensor X Water Alarm BI X005 10X05
Groundwater Sensor X Water Out Alarm BI X006 10X06
Groundwater Sensor X High Liquid Alarm BI X007 10X07
Groundwater Sensor X Low Liquid Alarm BI X008 10X08
Groundwater Sensor X Liquid Warning BI X009 10X09
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
B-3
Page 35

Appendix B Interface To BACnet & Modbus Tables
Table B-10. MAG Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus
MAG Sensor X Setup Data Warninq BI X001 10X01
MAG Sensor X Communication Alarm BI X002 10X02
MAG Sensor X Fault Alarm BI X003 10X03
MAG Sensor X Fuel Warning BI X004 10X04
MAG Sensor X Fuel Alarm BI X005 10X05
MAG Sensor X Water Warning BI X006 10X06
MAG Sensor X Water Alarm BI X007 10X07
MAG Sensor X High Liquid Warning BI X008 10X08
MAG Sensor X High Liquid Alarm BI X009 10X09
MAG Sensor X Low Liquid Warning BI X010 10X10
MAG Sensor X Low Liquid Alarm BI X011 10X11
MAG Sensor X Temperature Warning BI X012 10X12
MAG Sensor X Relay Active BI X013 10X13
MAG Sensor X Install Alarm BI X014 10X14
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
Table B-11. Smart Sensor Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus
Smart Sensor X Setup Data Warninq BI X001 10X01
Smart Sensor X Communication Alarm BI X002 10X02
Smart Sensor X Fault Alarm BI X003 10X03
Smart Sensor X Fuel Warning BI X004 10X04
Smart Sensor X Fuel Alarm BI X005 10X05
Smart Sensor X Water Warning BI X006 10X06
Smart Sensor X Water Alarm BI X007 10X07
Smart Sensor X High Liquid Warning BI X008 10X08
Smart Sensor X High Liquid Alarm BI X009 10X09
Smart Sensor X Low Liquid Warning BI X010 10X10
Smart Sensor X Low Liquid Alarm BI X011 10X11
Smart Sensor X Temperature Warning BI X012 10X12
Smart Sensor X Relay Active X013 10X13
Smart Sensor X Install Alarm X014 10X14
Smart Sensor X Fault Warning X015 10X15
Smart Sensor X Vacuum Warning X016 10X16
Smart Sensor X No Vacuum Warning X017 10X17
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
Table B-12. PLLD Veeder-Root Interface To BACnet And Modbus
PLLD X Setup Data Warninq BI X001 10X01
PLLD X Gross Test Fail Alarm BI X002 10X02
PLLD X Annual Test Fail Alarm BI X003 10X03
PLLD X Periodic Test Needed Warning BI X004 10X04
PLLD X Periodic Test Needed Alarm BI X005 10X05
PLLD X Sensor Open Alarm BI X006 10X06
PLLD X High Pressure Alarm BI X007 10X07
PLLD X Shutdown Alarm BI X008 10X08
PLLD X High Pressure Warning BI X009 10X09
PLLD X Continuous Handle On Warning BI X010 10X10
PLLD X Periodic Test Fail Alarm BI X011 10X11
PLLD X Annual Test Needed Warning BI X012 10X12
PLLD X Annual Test Needed Alarm BI X013 10X13
PLLD X Low Pressure Alarm BI X014 10X14
PLLD X Sensor Short Alarm BI X015 10X15
PLLD X Continuous Handle On Alarm BI X016 10X16
PLLD X Fuel Out Alarm BI X017 10X17
PLLD X Line Equipment Alarm BI X018 10X18
PLLD X Gross Test Needed Alarm BI X019 10X19
Point Name BACnet Object Type BACnet Object ID Modbus Register
B-4
Page 36

Appendix C: “A” Bank DIP Switch Settings
Table C-1. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 26-50
Address A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
26 Off On Off On On Off Off
27 On On Off On On Off Off
28 Off Off On On On Off Off
29 OnOffOnOnOnOffOff
30 OffOnOnOnOnOffOff
31 On On On On On Off Off
32 Off Off Off Off Off On Off
33 On Off Off Off Off On Off
34 Off On Off Off Off On Off
35 On On Off Off Off On Off
36 Off Off On Off Off On Off
37 On Off On Off Off On Off
38 OffOnOnOffOffOnOff
39 On On On Off Off On Off
40 Off Off Off On Off On Off
41 On Off Off On Off On Off
42 Off On Off On Off On Off
43 On On Off On Off On Off
44 Off Off On On Off On Off
45 On Off On On Off On Off
46 OffOnOnOnOffOnOff
47 On On On On Off On Off
48 Off Off Off Off On On Off
49 On Off Off Off On On Off
50 OffOnOffOffOnOnOff
C-1
Page 37

Appendix C
Table C-2. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 51 - 75
Address A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
51 On On Off Off On On Off
52 Off Off On Off On On Off
53 On Off On Off On On Off
54 Off On On Off On On Off
55 On On On Off On On Off
56 OffOffOffOnOnOnOff
57 On Off Off On On On Off
58 Off On Off On On On Off
59 On On Off On On On Off
60 Off Off On On On On Off
61 OnOffOnOnOnOnOff
62 OffOnOnOnOnOnOff
63 On On On On On On Off
64 Off Off Off Off Off Off On
65 On Off Off Off Off Off On
66 Off On Off Off Off Off On
67 On On Off Off Off Off On
68 Off Off On Off Off Off On
69 On Off On Off Off Off On
70 Off On On Off Off Off On
71 On On On Off Off Off On
72 Off Off Off On Off Off On
73 On Off Off On Off Off On
74 Off On Off On Off Off On
75 On On Off On Off Off On
C-2
Page 38
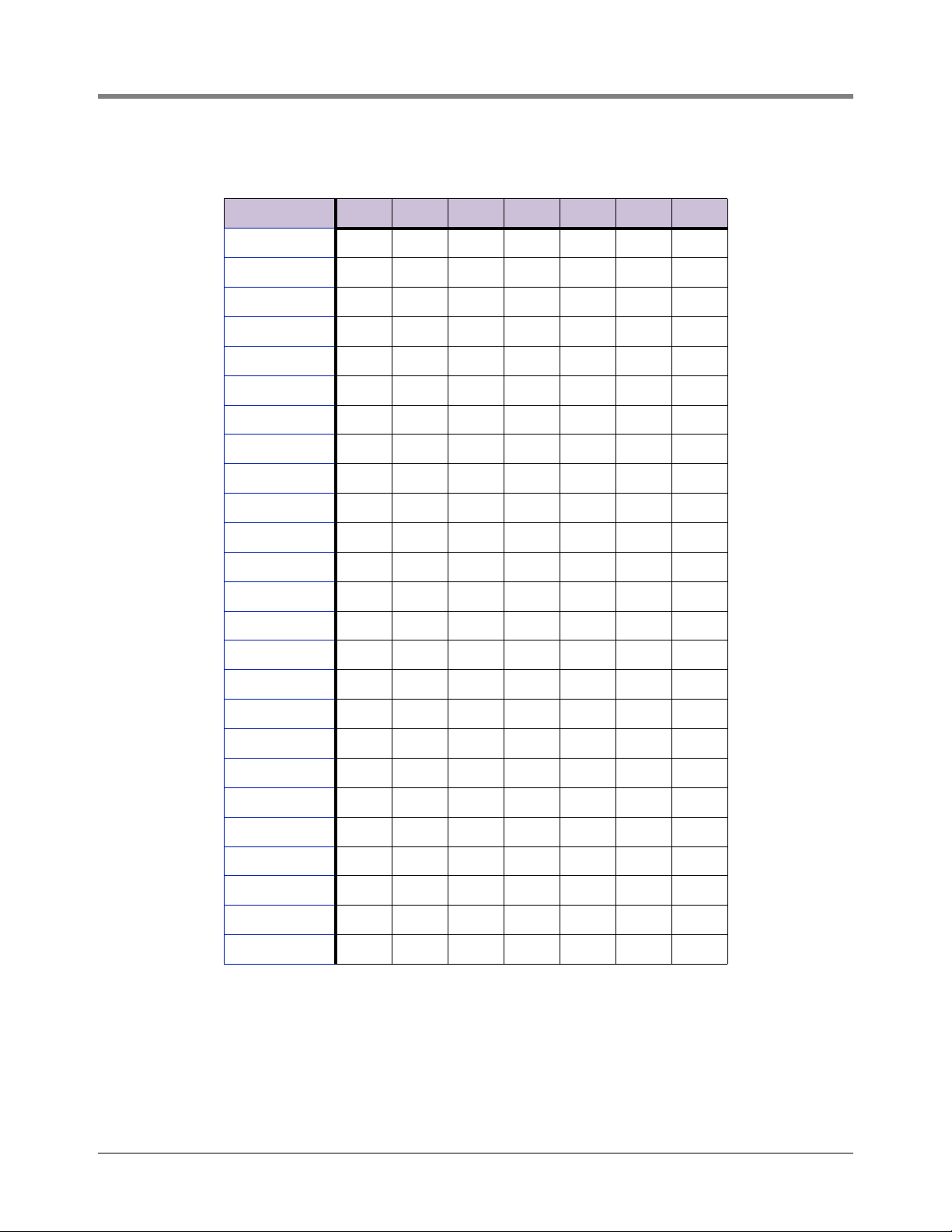
Appendix C
Table C-3. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 76 - 100
Address A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
76 Off Off On On Off Off On
77 On Off On On Off Off On
78 OffOnOnOnOffOffOn
79 On On On On Off Off On
80 Off Off Off Off On Off On
81 On Off Off Off On Off On
82 Off On Off Off On Off On
83 On On Off Off On Off On
84 Off Off On Off On Off On
85 On Off On Off On Off On
86 Off On On Off On Off On
87 On On On Off On Off On
88 Off Off Off On On Off On
89 On Off Off On On Off On
90 Off On Off On On Off On
91 On On Off On On Off On
92 Off Off On On On Off On
93 OnOffOnOnOnOffOn
94 OffOnOnOnOnOffOn
95 On On On On On Off On
96 Off Off Off Off Off On On
97 On Off Off Off Off On On
98 Off On Off Off Off On On
99 On On Off Off Off On On
100 Off Off On Off Off On On
C-3
Page 39

Appendix C
Table C-4. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 101-125
Address A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
101 On Off On Off Off On On
102 OffOnOnOffOffOnOn
103 On On On Off Off On On
104 Off Off Off On Off On On
105 On Off Off On Off On On
106 Off On Off On Off On On
107 On On Off On Off On On
108 Off Off On On Off On On
109 On Off On On Off On On
110 OffOnOnOnOffOnOn
111 On On On On Off On On
112 Off Off Off Off On On On
113 On Off Off Off On On On
114 OffOnOffOffOnOnOn
115 On On Off Off On On On
116 Off Off On Off On On On
117 On Off On Off On On On
118 Off On On Off On On On
119 On On On Off On On On
120 OffOffOffOnOnOnOn
121 On Off Off On On On On
122 Off On Off On On On On
123 On On Off On On On On
124 Off Off On On On On On
125 OnOffOnOnOnOnOn
C-4
Page 40

Appendix C
Table C-5. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 126 - 150
Address A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
126 OffOnOnOnOnOnOn
127 On On On On On On On
128 Off Off Off Off Off Off Off
129 On Off Off Off Off Off Off
130 Off On Off Off Off Off Off
131 On On Off Off Off Off Off
132 Off Off On Off Off Off Off
133 On Off On Off Off Off Off
134 Off On On Off Off Off Off
135 On On On Off Off Off Off
136 Off Off Off On Off Off Off
137 On Off Off On Off Off Off
138 Off On Off On Off Off Off
139 On On Off On Off Off Off
140 Off Off On On Off Off Off
141 On Off On On Off Off Off
142 OffOnOnOnOffOffOff
143 On On On On Off Off Off
144 Off Off Off Off On Off Off
145 On Off Off Off On Off Off
146 Off On Off Off On Off Off
147 On On Off Off On Off Off
148 Off Off On Off On Off Off
149 On Off On Off On Off Off
150 Off On On Off On Off Off
C-5
Page 41

Appendix C
Table C-6. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 151 - 175
Address A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
151 On On On Off On Off Off
152 Off Off Off On On Off Off
153 On Off Off On On Off Off
154 Off On Off On On Off Off
155 On On Off On On Off Off
156 Off Off On On On Off Off
157 OnOffOnOnOnOffOff
158 OffOnOnOnOnOffOff
159 On On On On On Off Off
160 Off Off Off Off Off On Off
161 On Off Off Off Off On Off
162 Off On Off Off Off On Off
163 On On Off Off Off On Off
164 Off Off On Off Off On Off
165 On Off On Off Off On Off
166 OffOnOnOffOffOnOff
167 On On On Off Off On Off
168 Off Off Off On Off On Off
169 On Off Off On Off On Off
170 Off On Off On Off On Off
171 On On Off On Off On Off
172 Off Off On On Off On Off
173 On Off On On Off On Off
174 OffOnOnOnOffOnOff
175 On On On On Off On Off
C-6
Page 42

Appendix C
Table C-7. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 176 - 200
Address A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
176 Off Off Off Off On On Off
177 On Off Off Off On On Off
178 OffOnOffOffOnOnOff
179 On On Off Off On On Off
180 Off Off On Off On On Off
181 On Off On Off On On Off
182 Off On On Off On On Off
183 On On On Off On On Off
184 OffOffOffOnOnOnOff
185 On Off Off On On On Off
186 Off On Off On On On Off
187 On On Off On On On Off
188 Off Off On On On On Off
189 OnOffOnOnOnOnOff
190 OffOnOnOnOnOnOff
191 On On On On On On Off
192 Off Off Off Off Off Off On
193 On Off Off Off Off Off On
194 Off On Off Off Off Off On
195 On On Off Off Off Off On
196 Off Off On Off Off Off On
197 On Off On Off Off Off On
198 Off On On Off Off Off On
199 On On On Off Off Off On
200 Off Off Off On Off Off On
C-7
Page 43

Appendix C
Table C-8. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 201 - 225
Address A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
201 On Off Off On Off Off On
202 Off On Off On Off Off On
203 On On Off On Off Off On
204 Off Off On On Off Off On
205 On Off On On Off Off On
206 OffOnOnOnOffOffOn
207 On On On On Off Off On
208 Off Off Off Off On Off On
209 On Off Off Off On Off On
210 Off On Off Off On Off On
211 On On Off Off On Off On
212 Off Off On Off On Off On
213 On Off On Off On Off On
214 Off On On Off On Off On
215 On On On Off On Off On
216 Off Off Off On On Off On
217 On Off Off On On Off On
218 Off On Off On On Off On
219 On On Off On On Off On
220 Off Off On On On Off On
221 OnOffOnOnOnOffOn
222 OffOnOnOnOnOffOn
223 On On On On On Off On
224 Off Off Off Off Off On On
225 On Off Off Off Off On On
C-8
Page 44

Appendix C
Table C-9. A Bank DIP Switch Settings For Addresses 226-255
Address A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
226 Off On Off Off Off On On
227 On On Off Off Off On On
228 Off Off On Off Off On On
229 On Off On Off Off On On
230 OffOnOnOffOffOnOn
231 On On On Off Off On On
232 Off Off Off On Off On On
233 On Off Off On Off On On
234 Off On Off On Off On On
235 On On Off On Off On On
236 Off Off On On Off On On
237 On Off On On Off On On
238 OffOnOnOnOffOnOn
239 On On On On Off On On
240 Off Off Off Off On On On
241 On Off Off Off On On On
242 OffOnOffOffOnOnOn
243 On On Off Off On On On
244 Off Off On Off On On On
245 On Off On Off On On On
246 Off On On Off On On On
247 On On On Off On On On
248 OffOffOffOnOnOnOn
249 On Off Off On On On On
250 Off On Off On On On On
251 On On Off On On On On
252 Off Off On On On On On
253 OnOffOnOnOnOnOn
254 OffOnOnOnOnOnOn
255 On On On On On On On
C-9
Page 45

Appendix D: Reference
NOTICE
Specifications
Specifications subject to change without notice.
Table D-1. QuickServer ProtoNode Specifications
Item Description
Electrical Connections
One 6-pin Phoenix connector with RS-232 port (+/-/gnd) and
Power port (+/-/Frame-gnd)
One 3-pin Phoenix connector with RS-485 port (+/-/gnd)
One Ethernet 10/100 BaseT port
CE Certified; TUV approved to UL 916, EN 60950-1, EN
50491-3 and CSA C22-2 standards; FCC Class A Part 15;
Approvals
Power Requirements Multi-mode power adapter 9-30V DC or 12 - 24V AC
Physical Dimensions 11.5 cm L x 8.3 cm W x 4.1 cm H (4.5 x 3.2 x 1.6 in)
Weight 0.2 kg (0.4 lbs)
Operating Temperature -40°C o 75°C (-40°F to 167°F)
Surge Suppression EN61000-4-2 ESD EN61000-4-3 EMC EN61000-4-4 EFT
Humidity 5 - 90% RH (non-condensing)
DNP 3.0 Conformance Tested; RoHS Compliant; CSA 205
Approved
BTL Marked
Compliance With UL Regulations
For UL compliance, the following instructions must be met when operating QuickServer.
• The units shall be powered by listed LPS or Class 2 power supply suited to the expected operating temperature
range.
• The interconnecting power connector and power cable shall:
- Comply with local electrical code
D-1
Page 46

Appendix D Certifications - BTL Mark - BACnet® Testing Laboratory
NOTICE
- Be suited to the expected operating temperature range
- Meet the current and voltage rating for QuickServer
• Furthermore, the interconnecting power cable shall:
- Be of length not exceeding 3.05m (118.3”)
- Be constructed of materials rated VW-1, FT-1 or better
• If the unit is to be installed in an operating environment with a temperature above 65 °C, it should be installed in
a Restricted Access Area requiring a key or a special tool to gain access.
• This device must not be connected to a LAN segment with outdoor wiring.
Certifications - BTL Mark - BACnet® Testing Laboratory
The BTL Mark on QuickServer is a symbol that indicates that a
product has passed a series of rigorous tests conducted by an
independent laboratory which verifies that the product correctly
implements the BACnet features claimed in the listing. The mark
is a symbol of a high-quality BACnet product.
Go to www.BACnetInternational.net for more information about
the BACnet Testing Laboratory. Click here
Statement.
for the BACnet PIC
BACnet is a registered trademark of ASHRAE
D-2
Page 47

For technical support, sales or
other assistance, please visit:
www.veeder.com
 Loading...
Loading...