Page 1

POWERFORCE
™
AUTOMATIC BATTERY CHARGER
OWNER’S MANUAL & WARRANTY INFORMATION
12 VOLT 2/10 AMPERE WITH 55 / AMPERE ENGINE START ASSIST
VEC074
• IMPOR
TANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
•
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
This manual contains important safety and operating instructions for battery charger Model VEC074
4140 SW 28TH WAY, FT. LAUDERDALE, FL 33312 • TEL: 945-584-4446 • FAX: 954-584-5556
GENERAL BATTERY SAFETY:
1. To reduce risk of battery explosion, follow these instructions and those published by the battery manufacturer and manufacturer of any equipment you intend to use in vicinity of battery. Review cautionary marking on these products and on engine.
2. Use charger for charging a LEAD-ACID battery only. It is not intended to supply power to a low voltage
electrical system other than in an automotive application. Do not use battery charger for charging drycell batteries that are commonly used with home and portable appliances. These batteries may burst and
cause injury to persons and damage to property.
3. Use of an attachment not recommended or sold by the battery charger manufacturer may result in a risk of fire,
electric shock, or injury to persons.
4. To reduce risk of damage to electric plug and cord, pull by plug rather than cord when disconnecting charger.
5. An extension cord should not be used unless absolutely necessary. Use of an improper extension cord could
result in a risk of fire and electric shock. If extension cord must be used, make sure:
a. That pins on plug of extension cord are the same number, size, and shape as those of plug on charger.
b. That extension cord is properly wired and in good electrical condition; and
c. That wire size is AWG #18 (18 gauge) to 100 feet and AWG #16 for distances over 100 feet.
6. Do not operate charger with damaged cord or plug - replace the cord or plug immediately.
7. Do not operate charger if it has received a sharp blow, been dropped, or otherwise damaged in any way; take
it to a qualified serviceman.
8. Do not disassemble charger; take it to a qualified serviceman when service or repair is required. Incorrect
reassembly may result in a risk of electric shock or fire.
9. To reduce risk of electric shock, unplug charger from outlet before attempting any maintenance or cleaning.
Tur ning off controls will not reduce this risk.
10. Do not expose charger to rain or snow.
11. Never charge a frozen battery
WORKING IN VICINITY OF A LEAD-ACID BATTERY IS DANGEROUS. BATTERIES GENERATE
EXPLOSIVE GASES DURING NORMAL BATTERY OPERATION. FOR THIS REASON, IT IS OF
UTMOST IMPORTANCE THAT EACH TIME BEFORE USING YOUR CHARGER, YOU READ THIS
MANUAL AND FOLLOW THE INSTRUCTIONS EXACTLY.
Page 2

PERSONAL PRECAUTIONS AND SAFETY
1. Someone should be within range of your voice or close enough to come to your aid when you work near a lead-acidbattery.
2. Have plenty of fresh water and soap nearby in case battery acid contacts skin, clothing, or eyes.
3. Wear complete eye protection and clothing protection. Avoid touching eyes while working with a battery. Acid, acid
particles or corrosion may get into eyes. Immediately flood eye with running cold water for at least 10 minutes and get
medical attention immediately.
4. If battery acid contacts skin or clothing, wash immediately with soap and water.
5. NEVER smoke or allow a spark or flame in vicinity of battery or engine.
6. Be extra cautious to reduce risk of dropping a metal tool onto battery. It might spark or short-circuit battery or other
electrical part that may cause explosion.
7. Remove personal metal items such as rings, bracelets, necklaces, and watches when working with a lead-acid battery.
A lead-acid battery can produce a short-circuit current high enough to weld a ring or the like to metal, causing a severe
burn.
PREPARING TO CHARGE
1. Determine voltage of battery by referring to car owner's manual and make sure that output voltage selector switch is set
at correct voltage.
2. If it is necessary to remove battery from vehicle to charge, or to clean terminals, always remove grounded terminal from
battery first. Make sure all accessories in the vehicle are off, so as not to cause an arc.
3. Clean battery terminals. Be careful to keep corrosion from coming in contact with eyes.
4. Add distilled water in each cell until battery acid reaches level specified by battery manufacturer. This helps purge
excessive gas from cells. Do not overfill. For a battery without cell caps, carefully follow manufacturer's recharging
instructions.
5. Study all battery manufacturers' specific precautions such as removing or not removing cell caps while charging and
recommended rates of charge.
6. Be sure area around battery is well ventilated while battery is being charged. Gas can be forcefully blown away by
using a piece of cardboard or other nonmetallic material as a fan.
7. Charge battery initially at the 2 Amp (lowest) rate.
CHARGER LOCATION
1. Locate charger as far away from battery as cables permit.
2. Never place charger directly above battery being charged; gases from battery will corrode and damage charger.
3. Never allow battery acid to drip on charger when reading gravity or filling battery.
4. Do not operate charger in a closed-in area or restrict ventilation in any way. Marine batteries must be removed and
charged on shore.
5. Do not set a battery on top of charger.
DC CONNECTION PRECAUTIONS
1. Connect and disconnect DC output clips only after removing AC cord from electric outlet.
2. Never allow clips to touch each other.
3. Attach clips to battery posts and twist or rock back and forth several times to make a good connection. This tends to
keep clips from slipping off terminals and helps to reduce risk of sparking.
FOLLOW THESE STEPS WHEN BATTERY IS INSTALLED IN VEHICLE. A SPARK NEAR BATTERY
MAY CAUSE BATTERY EXPLOSION. TO REDUCE RISK OF A SPARK NEAR BATTERY:
a. Position AC and DC cords to reduce risk of damage by hood, door, or moving engine part.
b. Stay clear of fan blades, belts, pulleys, and other parts that can cause injury to persons.
c. Check polarity of battery posts. POSITIVE (POS, P, +) battery post usually has larger diameter than NEGATIVE
(NEG, N,-) post.
d. Determine which post of battery is grounded (connected) to the chassis. If negative post is grounded to chassis (as
in most vehicles), see (e). If positive post is grounded to the chassis, see (f).
2
Page 3
DC CONNECTION PRECAUTIONS – CONTINUED
e. For negative-grounded vehicle, connect POSITIVE (RED) clip from battery charger to POSITIVE (POS, P, +)
ungrounded post of battery. Connect NEGATIVE (BLACK) clip to vehicle chassis or engine block away from battery. Do not connect clip to carburetor, fuel lines, or sheet-metal body parts. Connect to heavy gauge metal part of
the frame or engine block.
f. For positive-grounded vehicle, connect NEGATIVE (BLACK) clip from battery charger to NEGATIVE (NEG, N, -)
ungrounded post of battery. Connect POSITIVE (RED) clip to vehicle chassis or engine block away from battery. Do
not connect clip to carburetor, fuel lines, or sheet-metal body parts. Connect to a heavy gauge metal part of the
frame or engine block.
g. When disconnecting charger, turn switches to off, disconnect AC cord, remove clip from vehicle chassis, and then
remove clip from battery terminal.
h. See operating instructions for length of charge information.
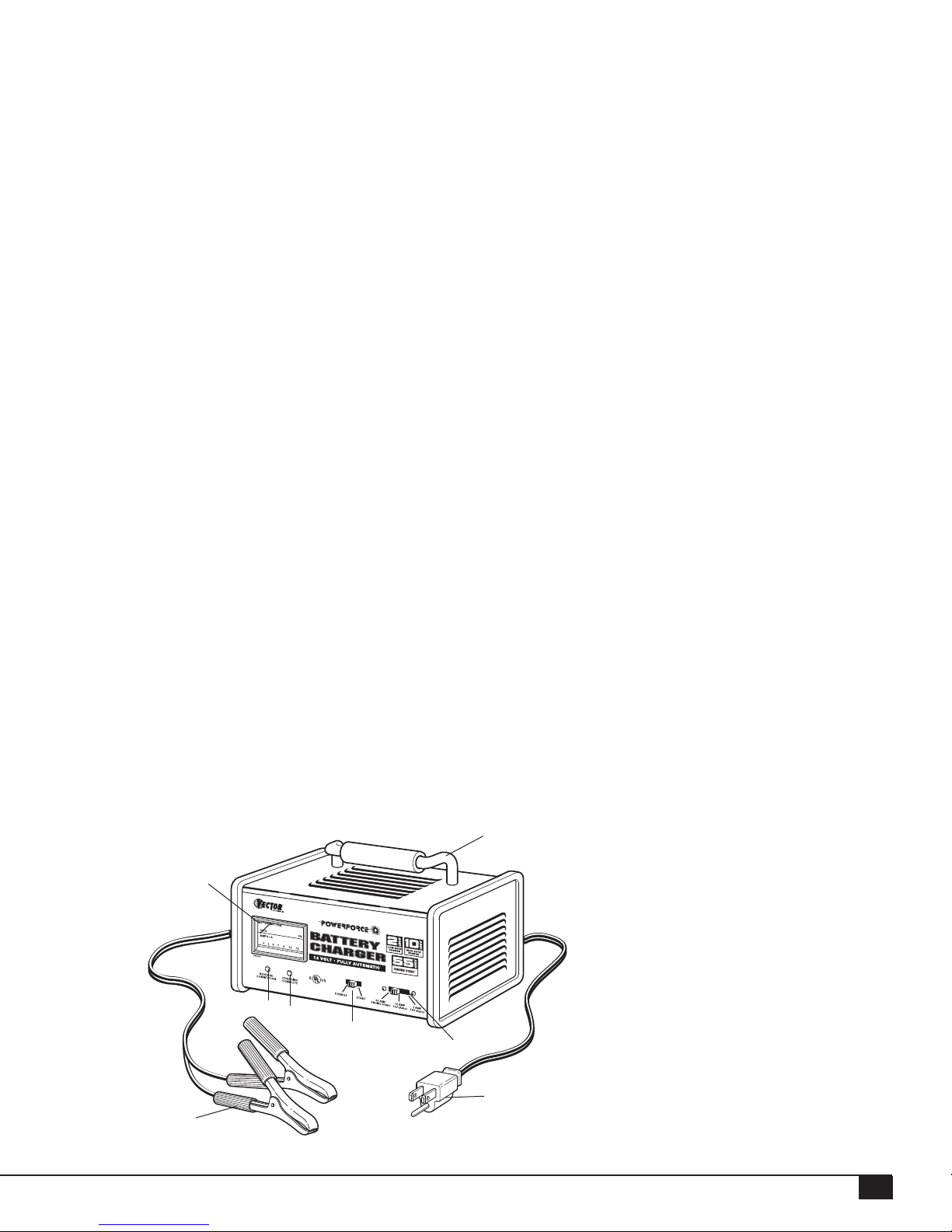
INTRODUCTION AND FEATURES
Thank you for selecting the Vector® Model VEC074 2/10/55 Battery Charger. With proper care and use, it will give you
years of dependable service. Please read all safety warnings and cautions, and this entire User's Manual, before using this
device. The manual should then be retained for easy reference whenever the unit is used.
This model battery charger has a high charge rate of up to 10 amps, and low charge rate of up to 2 amps. It is intended
for charging only 12 volt lead-acid batteries - maintenance-free, conventional automotive, marine deep cycle - that are usually used in cars, trucks, farm equipment, boats, RVs and SUVs, lawn mowers and garden tractors, motorcycles, personal
watercraft, snowmobiles, ATVs, and various light commercial applications. This charger can assist in engine starting by
delivering up to 55 amps for up to five minutes.
Charges 12 Volt automotive batteries in only 4-6 hours. Three settings,with sliding power selector:
a) 2 amps: 12-volt motorcycle, lawn mower, and Jet Ski type batteries.
b) 10 amps: 12-volt automotive, truck and marine deep-cycle batteries.
c) 55 Amps for up to five minutes for Engine Start Assist.
Built-in meter displays charge rate and battery charge level on color-coded, easy-to-read display.
• Automatically taper charges and stops charging when battery is fully charged
• Heavy-duty transformer and rectifier for dependability
• Built-in circuit protection guards against overcharging or short circuit
• Automatically checks for correct polarity (requires a minimum of 4.0 volts at the battery terminals)
• Heavy-duty cables and copper clamps are corrosion-resistant for better connections
• Connect to side- or top-mount battery terminals
• Rugged steel case with baked-on finish, plus sturdy handle
• Ideal for charging or boosting during winter season when the starting performance of vehicle batteries is lowered by
cold or extreme weather conditions. See Figure 1.
1. AMMETER
2. HANDLE
3. CHARGE RATE SWITCH
4. GROUNDED PLUG
5. CHARGE/ASSIST SWITCH
6. CHARGING COMPLETE LED
7. REVERSE CONNECTION LED
8. BATTERY CLAMPS
1
2
3
4
8
5
6
7
FIGURE 1
3
Page 4

CHARGER CONTROLS
Charger controls are located on the front panel. Understand control use before operating charger.
CHARGE/ASSIST SWITCH
The Charge/Assist switch protects the Ammeter during Start conditions and enables the Charge Rate Selector Switch to turn
on the Engine Start Assist function. During charge operations, the Charge/Assist switch must be in the Charge (LEFT) position. For Engine Start Assist functions, the switch must be in the Assist (RIGHT) position. See Figure 2.
CHARGE RATE SELECTOR SWITCH
• The sliding selector switch on the front panel of the charger offers two Charge Rates for charging various types of batteries and a Start position to assist starting engines.
• Select the correct switch position BEFORE connecting the charger to a battery or AC power source.
• Selections are made by sliding the switch into the correct position, corresponding with the type of battery being charged,
as follows:
• Small 12 volt DC batteries such as those used in motorcycles, garden tractors, ATVs, jet skis, and snowmobiles can be
damaged by high rates of charge. ALWAYS select the 2 Amp/12 Volt setting (RIGHT switch position) to charge this type
of battery. For a slower charging time on larger batteries select the 2 Amp/12 Volt setting.
SELECTOR SWITCH POSITION CHARGING RATE
LEFT 55 AMP ENGINE START ASSIST
CENTER 10 A
MP/12 VOLT DC CHARGE (LARGER BATTERIES)
RIGHT 2 A
MP/12 VOLT DC CHARGE (SMALLER BATTERIES)
WARNING: IF IN DOUBT ABOUT SELECTING A CHARGE RATE, SELECT THE LOWER RATE. BATTERIES GET
WARM DURING CHARGING - IF BATTERIES ARE GETTING HOT, DISCONTINUE CHARGING AND INVESTIGATE FOR DAMAGED BATTERY.
AMMETER AND INDICATORS
The ammeter is the colored (red, green and blue) chart on the front of the unit. It displays the current flowing from the charger to the battery, in amperes.
The current when starting to charge a battery will depend on the battery's percent of charge. The actual current will usually be lower than the current selected on the charger's switch, unless the battery is severely discharged. As the battery charge
level increases, the current reduces.
The ammeter is intended to show how the charging process is proceeding, it should not be used to determine the level of
battery charge - this should be done using a hydrometer or a voltmeter.
Typically 12.6 VDC is considered full charge on a 12 volt battery if the voltage is measured one hour after the charger is
disconnected. During charging, a nominal 12 volt battery can be 13.6 volts or somewhat higher, so it needs to rest after
charging to measure actual state of charge.
The charger's built-in battery full circuitry automatically taper charges the battery as it approaches full charge and discontinues charging when the battery reaches full charge. When the battery is fully charged the Charging Complete indicator
lights. See Figure 4B Charging Complete indicator and Polarity indicator.
FIGURE 2
FIGURE 3
4
Page 5

To the left of the Charging Complete indicator is an indicator that lights when incorrect polarity is sensed. It indicates that
the charger to battery connection is reversed and it must be corrected before charging can begin. This feature only operates
when at least 4 volts or higher voltage remains in the battery to be charged.
CIRCUIT BREAKER
This battery charger has an internal self-resetting circuit breaker that protects the charger from temporary overloads. When
it operates it makes a clicking sound. You will see the ammeter reduce to zero when the breaker is open. After a cool-down
period, the breaker will automatically close and the ammeter will show a high rate of charge. If the breaker continues to
cycle every few minutes, reduce charge rate or discontinue charging.
PRE-CHARGE ACTIVATION
CAUTION: Be aware that a fully charged battery will also cause a low Ammeter reading. Attempting pre-charge activa-
tion of a fully charged battery may cause explosion - make sure that battery really is discharged, before using this procedure.
Pre-charge activation is the term for the time it takes before a battery begins to accept a measurable rate of charge - it can
be as long as 4-8 hours from the time the charging process begins.
Pre-charge activation is indicated if the ammeter reading is zero and a hydrometer or voltmeter reading shows that the battery is fully discharged.
NOTE: The newer, high-calcium-type 12 Volt DC batteries may need pre-charge activation if their charge has been allowed
to drop to a very low level. When deeply discharged, this type of battery will provide only a very low voltage output and
will draw less than 1 amp during the recharging process, until activated.
CHARGING IF BATTERY IS INSTALLED IN A VEHICLE
a) Set charger's Charge Rate Selector switch to appropriate setting according to battery size. Make sure the
Charge/Start switch is in the Charge position.
b) Check polarity of battery posts - For top-mounted battery connectors, the Positive post (marked POS, P, +) usually
has a larger diameter than the Negative battery post (marked NEG, N, -). For side-mounted battery connectors, the
terminals are marked Positive -red and Negative -black.
c)
Attach charger clamps to battery connections, as follows, ensuring a good connection (if there is a mistake, the Reverse
Polarity Indicator will light): NEGATIVE-GROUNDED VEHICLE: Connect the POSITIVE (RED) charger clamp to the POSITIVE (POS, P, +) ungrounded battery terminal. Then, connect the NEGATIVE (BLACK) charger clamp to the vehicle chassis, or the engine block (away from the battery). Do not connect the clamp to the carburetor, fuel lines, or sheet-metal body
parts: connect only to a heavy gauge metal part of the frame or engine block.
NOTE: NEGATIVE-GROUNDED TYPE SYSTEMS ARE THE MOST COMMON IN TODAY'S VEHICLES.
POSITIVE-GROUNDED VEHICLE: Connect the NEGATIVE (BLACK) charger clamp to the NEGATIVE (NEG,
N, -) ungrounded battery post. Then, connect the POSITIVE (RED) battery clamp to the vehicle chassis or engine part (away
from the battery). Do not connect the clamp to the carburetor, fuel lines, or sheet-metal body parts: connect only to a heavy
gauge, stable metal part of the frame or engine block. NOTE: If there is any problem connecting the charger clamps to the
battery terminals, contact the Vector Technical Support Department at (954 - 584-4446) for assistance.
d) Plug battery charger power cord into grounded AC power outlet and refer to Appendix A at the end of this doc-
ument for approximate charging times.
e) When charging is completed, disconnect cables and clamps in reverse order from which they were connected.
NOTE: Use of Extension Cords
If it is necessary to use an extension cord, as is often the case, observe the following important safety information:
• Before using any extension cord, ensure that the wire size is at least 16 AWG or larger and 14 AWG for longer than
100 feet.
• Use only a good quality, good condition, UL-approved extension cord, and ALWAYS connect charger to the extension
FIGURE 4A FIGURE 4B
5
Page 6

cord before plugging the extension cord into a 110/120-volt AC power outlet. The use of a poor quality extension cord
or one that is not in good repair could cause fire and/or electric shock.
• Use a three-wire extension cord with a 3-prong plug and 3-conductor socket.
CHARGING IF BATTERY IS OUTSIDE OF VEHICLE
Set charger's Charge Rate Selector switch to appropriate setting according to battery size. Make sure the Charge/Start
switch is in the Charge position.
a) Check polarity of battery posts- For top-mounted battery connectors, the positive post (marked POS, P, +) usually
has a larger diameter than the Negative battery post (marked NEG, N, -). For side-mounted battery connections
the Positive terminal is red, the Negative terminal is black.
b) Attach a 24-inch (minimum length) 6 AWG insulated battery cable to the Negative battery post
(marked NEG, N, -).
c) Connect the Positive (RED) battery clamp to the Positive battery connector (marked POS, P, + or red).
d) Stand as far back from battery as possible, and do not face battery when making final connection.
e) Carefully connect the Negative (BLACK) charger clamp to the free end of the battery cable connected to the nega-
tive terminal. Connect the charger's power cord to a grounded 110/120-volt AC power outlet, and refer to section
8 for approximate charging times.
f)
When charging is completed, disconnect cables and clamps in reverse order from which they were connected.
NOTE: A marine abattery must be removed and charged on shore. To charge it on board requires equipment specially
designed for marine use.
CHARGING TIMES
The VEC074 is a fully automatic battery charger. It automatically adjusts the charge rate as the battery becomes charged
and stops charging when the battery is fully charged. If you require some estimate of the time it takes to charge a battery
refer to Appendix A for these details.
ENGINE START ASSIST
The Engine Start Assist function can supply up to 55 amps of current during engine starting. This function is protected by a
thermal circuit breaker and there is a five-minute limit at this output level. Follow all precautions as if charging a battery in
a vehicle, except that the Charge/Assist Switch is placed in the Assist position and the Charge Rate Switch is placed in the
Engine Start Assist position. DO NOT MAKE BATTERY AND CHASSIS CONNECTIONS WITH CHARGER PLUGGED INTO
AC. Make the final connection to battery and chassis and plug in the charger. Immediately crank the engine in three-second bursts until it starts. Disconnect the charger's AC connection first and then the chassis and battery connections. If the
engine fails to start, you may change switch positions and charge the battery without disconnecting the charger from AC.
After charging, if the charger is already powered and connected to the battery, you may safely move the charger's switches to the Start and Engine Start Assist positions without disconnecting the charger from AC. After the engine starts, disconnect AC, then the chassis and battery connections.
CARE AND MAINTENANCE
With only minimal maintenance, the Vector 2/10/55 Battery Charger will deliver years of dependable service. Follow these
simple steps to maintain the charger in optimum condition:
• After each use, clean the battery charger clamps - be sure to remove any battery fluid that will cause corrosion of the
copper clamps.
• Clean the outside case of the charger with a soft cloth and, if necessary, mild soap solution.
• Keep the charger cords loosely coiled during storage to prevent damage to the cords. Do not use the charger if cords or
clamps have been damaged in any way - call Vector Technical Support Department at (954) 584-4446 for details on
replacing cords and clamps.
TROUBLESHOOTING
VERY COLD BATTERY
If the battery to be charged is extremely cold (in temperatures less than freezing - 0ºC/32ºF) it cannot accept a high rate
of charge so the initial charge rate will be slow. The rate of charge will increase as the battery warms. WARNING: DO
NOT attempt to charge a frozen battery.
SULFATED BATTERY
When batteries are left in a discharged state for a long period of time, they become "sulfated". Sulfated batteries cannot accept
a high rate of charge since the internal plates are coated with lead sulphate. To see if a battery in this condition can be "saved",
take it to a service station or battery distributor for professional evaluation and/or service
.
SHORT-CIRCUITED BATTERY
• If the battery being charged has been short-circuited, the ammeter will show that the battery has zero charge level, and
6
Page 7

that the charger is operating at peak amperage. If, after 5 minutes charging time, the ammeter reading has not
decreased, unplug the charger and discontinue the charging process.
• Using a voltmeter, determine the voltage of the battery and if it is under 12 volts, the battery is probably beyond
repair or recharging, and will need to be replaced.
• If the voltage is over 12 volts, reconnect the charger and resume the charging process for another 15-20 minutes. If, after
that time, the ammeter still has not moved towards a lower reading, repeat the voltmeter test. If the reading is still over 12
volts, there is a problem with the battery that requires professional service or replacement.
NO AMMETER READING
• Make sure that the charger is powered by a "live" 110/120-volt AC outlet.
• Unplug charger and check battery connections - ensure that there is a good connection with the battery terminal and/or
vehicle chassis.
• Check to be sure that the battery is not sulfated.
• Check that the correct charge rate has been selected for the battery being charged.
•
Ensure that enough charging time has been allowed for - check table in Appendix for approximate charging times.
• See Pre-charge Battery Activation
AMMETER DISPLAYS A READING, BUT BATTERY IS NOT ACCEPTING CHARGE
• First, make sure that battery is capable of being charged - ensure that it is not sulfated or damaged.
• Refer to Charging Time Table in Appendix to ensure that enough time is being allowed to charge the battery.
APPENDIX A – CHARGING TIMES
To calculate the approximate charging time required to fully charge a battery, it is necessary to determine the specific gravity (or, percent of battery charge) using a hydrometer. Use this technique, if battery vent caps can be removed. Check each
cell. If there is one cell with a very low specific gravity compared to the other cells, there is probably a shorted cell in the
battery. Replace the battery.
The following chart converts hydrometer readings into percent of charge values.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY PERCENT OF CHARGE PERCENT OF CHARGE NEEDED
(HYDROMETER READING) IN BATTERY BY BATTERY
1.265 ....................100% ..........................0%
1.225 ......................75% ..........................25%
1.190 ......................50% ..........................50%
1.155 ......................25% ..........................75%
1.120 ......................0% ..........................100%
Refer to the chart below for approximate charging times.
PERCENT OF CHARGE 75% 50% 25% 0%
2 AMPS/12 VOLTS 6.5 HRS 12 HRS 18 HRS 23 HRS
10 AMPS/12 VOLTS 1.8 HRS 3.0 HRS 4.5 HRS 6 HRS
The times shown in the chart above are approximate and refer to an average automotive battery. For smaller batteries, the
charge time should be adjusted using the formula shown below and adding 1 hour to the time calculated.
To estimate charging time for a discharged battery, divide the AH rating of the battery by the charge rate selected. This is
the number of hours required to recharge the battery. For example, a 50 AH (12 volt) battery is discharged (10 volts). How
long should it be charged at the 10 Amp rate? Divide the 50 AH by 10 AH. The answer is approximately 5 hours. Always
round up the charge time by 25% to ensure full charge. In most cases, battery recharge times will vary depending on the
age and condition of the battery. Smaller batteries should be charged at the lower rate (2 Amps) and add an extra hour to
charge time.
APPENDIX B – SPECIFICATIONS
Height ..........................................................................................................5.5" (14.0 cm)
Width ............................................................................................................9.5" (24.1 cm)
Depth ............................................................................................................6.5" (16.5 cm)
Weight ..........................................................................................................7 lbs
Internal protection ..........................................................................................self-resetting breaker
Input voltage ..................................................................................................120 VAC 60 Hz, 1.3 amperes.
Reverse polarity ..............................................................................................indicator LED
Charging complete ..........................................................................................auto shut-off LED
Convenience features ......................................................................................Handle
7
 Loading...
Loading...