
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 1
V962PBC Rev. B2
LOCAL BUS TO PCI BRIDGE
FOR DE-MULTIPLEXED A/D PROCESSORS
V3 Semiconductor reserves the right to change the specifications of this product without notice.
V962PBC and V96BMC are trademarks of V3 Semiconductor. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
• Glueless interface between Intel i960 Cx/Hx
processors and PCI bus
• Fully compliant with PCI 2.1 specification
• Configurable for primary master, bus master, or
target operation
• Up to 1Kbyte burst access support on both local
and PCI interface
• 576 bytes of programmable FIFO storage with
DYNAMIC BANDWIDTH ALLOCATION™
• Two channel DMA controller
• Enhanced support for 8/16-bit local bus devices
with programmable region size register
• 16 8-bit bi-directional mailbox registers with
doorbell interrupts
• Dual bi-directional address space remapping
• On-the-fly byte order (endian) conversion
• Optional power on serial EEPROM initialization
• I2O ATU and messaging unit including
hardware controlled circular queues
• Flexible PCI and local interrupt management
• Support for real-mode DOS "holes"
• Ability to generate both Type 0 and Type 1
configuration cycles
• 33MHz and 40MHz local bus versions available
with independent PCI operation up to 33MHz
• Low cost 160-pin EIAJ PQFP package
V962PBC provides the highest performance,
most flexible, and most economical method to
directly connect i960Cx/Hx processors to the PCI
bus. V292PBC is also a suitable candidate for
a variety of 32-bit de-multiplexed local bus
applications based on intel embedded
processors - where a minimal amount of glue
logic is required. V962PBC may also be used in
systems without a CPU for a generic PCI master/
target interface.
V962PBC Rev B2 is the first I2O ready PCI
bridge, fully backward compatible with V962PBC
Rev B1. The PCI bus can be run at the full
33MHz frequency, independent of local bus
clock rate. The overall throughput of the system
is dramatically improved by increasing the FIFO
depth and utilizing the unique DYNAMIC
BANDWIDTH ALLOCATION™ architecture.
Access to the PCI bus can be performed through
two programmable address apertures. Two more
apertures are provided for PCI-to-local bus
accesses. There are 32-bytes of read FIFO’s in
each direction, 16-byte dedicated for each
aperture. V962PBC also includes bi-directional
remapping capabilities, and on-the-fly byte order
conversion
Two DMA channels are provided for autonomous
PCI-to-Local/Local-to-PCI transfers. Mailbox
registers and flexible PCI interrupt controllers are
also included to provide a simple mechanism to
emulate PCI device control ports.
The part is available in 160-pin low cost EIAJ
Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP) package.
i960Cx/Hx
CPU
V96BMC
MEMORY
CONTROL
D
R
A
M
ROM
V962PBC
LOCAL TO
PCI BRIDGE
TYPICAL APPLICATION
PERIPHERAL
PCI
PCI SLOT or EDGE CONNECTOR

V962PBC
2 V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc.
This document contains the product codes, pinouts, package mechanical information, DC
characteristics, and AC characteristics for the V962PBC. Detailed functional information is contained
in the User’s Manual.
V3 Semiconductor retains the rights to change documentation, specifications, or device
functionality at any time without notice. Please verify that you have the latest copy of all
documents before finalizing a design.
1.0 Product Codes
2.0 Pin Description and Pinout
Table 2 below lists the pin types found on the V962PBC. Table 3 describes the function of each pin on
the V962PBC. Table 5 lists the pins by pin number. Figure 1 shows the pinout for the 160-pin EIAJ
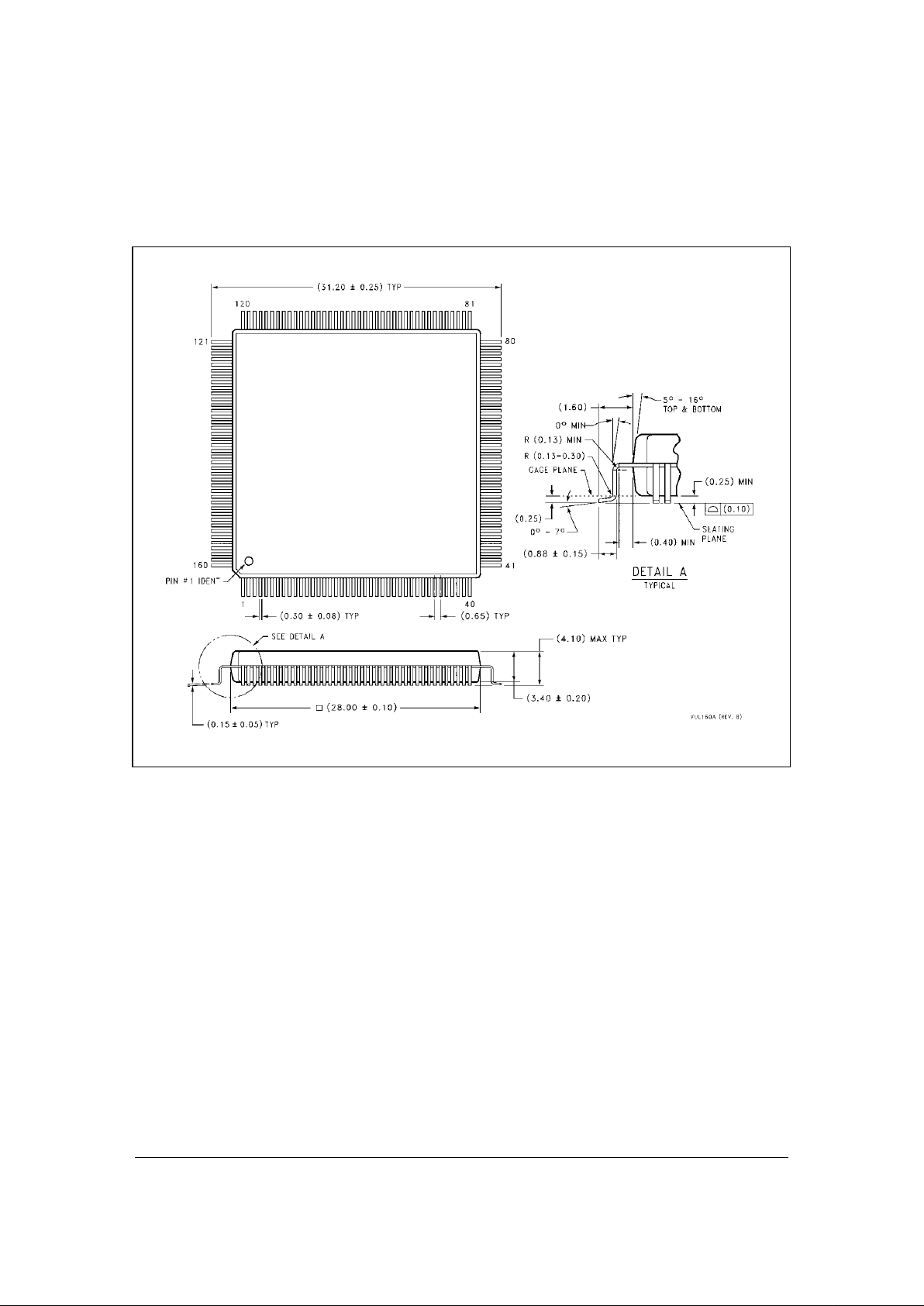
PQFP package and Figure 2 shows the mechanical dimensions of the package.
Table 1: Product Codes
Product Code Processor Bus Type Package Frequency
V962PBC-33 REV B2 i960Cx/Hx 32-bit de-multiplexed 160-pin EIAJ PQFP 33MHz
V962PBC-40 REV B2 i960Cx/Hx 32-bit de-multiplexed 160-pin EIAJ PQFP 40MHz
Table 2: Pin Types
Pin Type Description
PCI I PCI input only pin.
PCI O PCI output only pin.
PCI I/O PCI tri-state I/O pin.
PCI I/OD PCI input with open drain output.
I/O
4
TTL I/O pin with 4mA output drive.
I TTL input only pin.
O
4
TTL output pin with 4mA output drive.

V962PBC
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 3
Table 3: Signal Descriptions
PCI Bus Interface
Signal Type RaDescription
AD[31:0] PCI I/O Z Address and data, multiplexed on the same pins.
C/BE[3:0] PCI I/O Z Bus Command and Byte Enables, multiplexed on the same pins.
PAR PCI I/O Z Parity represents even parity across AD[31:0] and C/BE[3:0].
FRAME PCI I/O Z
Cycle Frame indicates the beginning and burst length of an
access.
IRDY PCI I/O Z
Initiator Ready indicates the initiating agent’s (bus master’s) ability
to complete the current data phase of the transaction.
TRDY PCI I/O Z
Target Ready indicates the target agent’s (selected device’s) ability to complete the current data phase of the transaction.
STOP PCI I/O Z
Stop indicates the current target is requesting the master to stop
the current transaction (retry or disconnect).
DEVSEL PCI I/O Z
Device Select, when actively driven by a target, indicates the driving device has decoded its address as the target of the current
access. As an input to the initiator, DEVSEL indicates whether
any device on the bus has been selected.
IDSEL PCI I
Initialization Device Select is used as a chip select during configuration read and write transactions. It must be driven high in order
to access the chip’s internal configuration space.
REQ PCI O H
Request indicates to the arbiter that this agent requests use of the
bus.
GNT PCI I
Grant indicates to the agent that access to the bus has been
granted.
PCLK PCI I PCLK provides timing for all transactions on the PCI bus.
PRST PCI I/O Z/L
Acts as an input when RDIR is high, an output when RDIR is low.
As an input it is asserted low to bring all internal PBC operation to
a reset state.
PERR PCI I/O Z
Parity Error is used to report data parity errors during all PCI
transactions except a Special Cycle.
SERR PCI I/OD Z
System Error is used to report address parity errors, data parity
errors on the Special Cycle command, or any other system error
where the result will be catastrophic.
INT[A:D] PCI I/OD Z Level-sensitive interrupt requests may be received or generated.

V962PBC
4 V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc.
Local Bus Interface
Signal Type R Description
LD[31:0] I/O4 Z Local multiplexed address and data bus.
LA[31:2] I/O4 Z Local address bus.
BE[3:0] I/O4 Z Local bus byte enables.
W/R I/O4 Z Write/Read.
ADS I/O4 Z Asserted low to indicate the beginning of a bus cycle.
READY I/O4 Z Local Bus data ready
HOLD O4 L
Local bus hold request: asserted by the chip to initiate a local bus
master cycle.
HOLDA I Local bus hold acknowledge.
LPAR[3:0] I/O4 Z Local bus parity.
BLAST I/O4 Z Burst request. Burst last.
BTERM I/O4 Z Bus Time-out. Burst terminate.
LINT O4 H Local interrupt request.
LRST I/O4 L/Z Local bus RESET signal.
LCLK I Local bus clock.
Serial EEPROM Interface
Signal Type R Description
SCL/LPERR O4 X EEPROM clock. Local parity error.
SDA I/O4 X EEPROM data.
Configuration
Signal Type R Description
RDIR I
Reset direction. Tie low to drive PRST out and LRST in, high to
drive LRST out and PRST in.
Table 3: Signal Descriptions (cont’d)

V962PBC
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 5
2.1 Test Mode Pins
Several device pins are used during manufacturing test to put the V962PBC device into various test
modes. These pins must be maintained at proper levels during reset to insure proper operation.
This is typically handled through pull-up or pull-down resistors (typically 1K to 10K) on the signal pins if
they are not guaranteed to be at the proper level during reset. Table 4 below shows the reset states for
test mode pins:
Power and Ground Signals
Signal Type R Description
V
CC
-
POWER leads intended for external connection to a VCC board
plane.
GND -
GROUND leads intended for external connection to a GND board
plane.
a. R indicates state during reset.
Table 4: RESET State for Test Mode Pins
PIN# 134 135 153
Connection Pull-Up Pull-Up Pull-Up
Table 5: Pin Assignments
PIN # Signal PIN # Signal PIN # Signal PIN # Signal
1 V
CC
41 V
CC
81 V
CC
121 V
CC
2 INTD 42 AD14 82 LA23 122 LA6
3 PRST 43 AD13 83 LD8 123 LD25
4 PCLK 44 AD12 84 LA22 124 LA5
5 GNT 45 AD11 85 LD9 125 LD26
6 REQ 46 AD10 86 LA21 126 LA4
7 AD31 47 AD9 87 LD10 127 LD27
8 AD30 48 AD8 88 LA20 128 LA3
Table 3: Signal Descriptions (cont’d)

V962PBC
6 V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc.
9 AD29 49 C/BE0 89 LD11 129 LD28
10 AD28 50 V
CC
90 LA19 130 LA2
11 GND 51 GND 91 LD12 131 LD29
12 AD27 52 AD7 92 LA18 132 LD30
13 AD26 53 AD6 93 LD13 133 LD31
14 AD25 54 AD5 94 LA17 134 '1'
15 AD24 55 AD4 95 LD14 135 BTERM
16 C/BE3 56 AD3 96 LA16 136 READY
17 IDSEL 57 AD2 97 LD15 137 HOLD
18 AD23 58 AD1 98 LA15 138 HOLDA
19 AD22 59 AD0 99 LD16 139 ADS
20 V
CC
60 V
CC
100 V
CC
140 V
CC
21 GND 61 GND 101 GND 141 GND
22 AD21 62 LD0 102 LA14 142 LCLK
23 AD20 63 LA31 103 LD17 143 GND
24 AD19 64 LD1 104 LA13 144 V
CC
25 AD18 65 LA30 105 LD18 145 BE3
26 AD17 66 LD2 106 LA12 146 BE2
27 AD16 67 LA29 107 LD19 147 BE1
28 C/BE2 68 LD3 108 LA11 148 BE0
29 FRAME 69 LA28 109 LD20 149 BLAST
30 GND 70 LD4 110 LA10 150 W/R
31 IRDY 71 LA27 111 LD21 151 RDIR
32 TRDY 72 LD5 112 LA9 152 LRST
33 DEVSEL 73 LA26 113 LD22 153 ’1’
34 STOP 74 LD6 114 LA8 154 LINT
35 PERR 75 LA25 115 LD23 155 SDA
Table 5: Pin Assignments (cont’d)
PIN # Signal PIN # Signal PIN # Signal PIN # Signal

V962PBC
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 7
Figure 1: Pinout for 160-pin EIAJ PQFP (top view)
36 SERR 76 LD7 116 LA7 156
SCL/
LPERR
37 PAR 77 LA24 117 LPAR2 157 INTA
38 C/BE1 78 LPAR0 118 LPAR3 158 INTB
39 AD15 79 LPAR1 119 LD24 159 INTC
40 GND 80 GND 120 GND 160 GND
Table 5: Pin Assignments (cont’d)
PIN # Signal PIN # Signal PIN # Signal PIN # Signal
V962PBC
8 V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc.
Figure 2: 160-pin EIAJ PQFP mechanical details
Unit of Measurement = millimeters

V962PBC
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 9
3.0 DC Specifications
The DC specifications for the PCI bus signals match exactly those given in the PCI Specification, Rev.
2.1, Section 4.2.1.1. For more information on the PCI DC specifications, see the PCI Specification.
3.1 PCI Bus DC Specifications
Table 6: Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Units
V
CC
Supply voltage -0.3 to +7 V
V
IN
DC input voltage -0.3 to VCC+0.3 V
I
IN
DC input current ± 10 mA
T
STG
Storage temperature range -40 to +125 °C
Table 7: Guaranteed Operating Conditions
Symbol Parameter Value Units
V
CC
Supply voltage 4.75 to 5.25 V
T
A
Ambient temperature range 0 to 70 °C
Table 8: PCI Bus Signals DC Operating Specifications
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Max Units Notes
V
IH
Input high voltage 2.0 VCC+0.5 V
V
IL
Input low voltage -0.5 0.8 V
I
IH
Input high leakage current VIN = 2.7V 70 µA 1
I
IL
Input low leakage current VIN = 0.5V -70 µA 1
V
OH
Output high voltage I
OUT
= -2mA 2.4 V
V
OL
Output low voltage I
OUT
= 3mA, 6mA 0.55 V 2
C
IN
Input pin capacitance 10 pF 3
C
CLK
PCLK pin capacitance 5 12 pF
C
IDSEL
IDSEL pin capacitance 8 pF 4
L
PIN
Pin inductance 20 nH
V962PBC
10 V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc.
Notes:
1. Input leakage currents include high impedance output leakage for all bi-directional buffers with tri-state outputs.
2. Signals without pull-up resistors have greater than 3mA low output current. Signals requiring pull resistors
have greater than 6mA output current. The latter include FRAME, TRDY, IRDY, STOP, SERR, PERR.
3. Absolute maximum pin capacitance for a PCI unit is 10pF (except for CLK).
4. Lower capacitance on this input-only pin allows for non-resistive coupling to AD[xx].
3.2 Local Bus DC Specifications
Table 9: Local Bus Signals DC Operating Specifications
Symbol Description Conditions Min Max Units
V
IL
Low level input voltage VCC = 4.75V 0.8 V
V
IH
High level input voltage VCC = 5.25V 2.0 V
I
IL
Low level input current VIN=GND, VCC=5.25V -10 µA
I
IH
High level input current V
IN
= V
CC
= 5.25V 10 µA
V
OL4
Low level output voltage for 4 mA
outputs and I/O pins
I
OL
= -4 mA 0.4 V
V
OH4
High level output voltage for 4 mA
outputs and I/O pins
I
OH
= 4 mA 2.4 V
I
OZL
Low level float input leakage V
IN
= GND -10 µA
I
OZH
High level float input leakage V
IN
= V
CC
10 µA
ICC (max) Maximum supply current
V
CC
= 5.25V
PCLK = LCLK = 33MHz
150 mA
I
CC
(typ) Typical supply current
V
CC
= 5.0V
PCLK = LCLK = 33MHz
120 mA
C
IO
Input and output capacitance 10 pF
V962PBC
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 11
4.0 AC Specifications
The AC specifications for the PCI bus signals match exactly those given in the PCI Specification, Rev.
2.1, Section 4.2.1.2. For more information on the PCI AC specifications, including the V/I curves for 5V
signalling, see section 4.2.1.2 of Rev 2.1 PCI Specification.
4.1 PCI Bus Timings
Notes:
1. Refer to the V/I curves in Section 4.2.1 of the PCI Specification. This specification does not apply to CLK and
RST which are system outputs. “Switching Current High” specifications are not relevant to open drain outputs
such as SERR and INTA-INTD.
2. Note that this segment of the minimum current curve is drawn from the AC drive point directly to the DC drive
point rather than toward the voltage rail (as it does in the pull-down curve). This difference is intended to allow
for an optional N-channel pull-up.
3. Maximum current requirements are met as drivers pull beyond the first step voltage (AC drive point). Equations
defining these maximums (A and B) are provided with the respective V/I curves given in the PCI Spec. The equation defined maxima is met by design.
4. The minimum slew rate (slowest signal edge) is met by the PCI drivers. The maximum slew rate (fastest signal
edge) is a guideline. Motherboard designers must bear in mind that rise and fall times faster than this maximum
guideline could occur, and should ensure that signal integrity modeling accounts for this.
Table 10: PCI Bus Signals AC Operating Specifications
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Max Units Notes
I
OH(AC)
Switching
current high
0V<V
OUT
≤1.4V -44 mA 1
1.4V<V
OUT
<2.4V -44+(V
OUT
-1.4)/0.024 Equation A mA 1, 2, 3
(Test point) V
OUT
=3.1V -142 mA 3
I
OL(AC)
Switching
current low
V
OUT
≥2.2V 95 mA 1
2.2V>V
OUT
>0.55 V
OUT
/0.023 Equation B mA 1, 3
(Test point) V
OUT
=0.71 206 mA 3
I
CL
Low clamp
current
-5<VIN≤-1 -25+(VIN+1)/0.015 mA
t
R
Unloaded
output rise
time
0.4V to 2.4V 1 5 V/ns 4
t
F
Unloaded
output fall
time
2.4V to 0.4V 1 5 V/ns 4
Equation A: IOH = 11.9·(V
OUT
- 5.25V)·(V
OUT
+ 2.45V) for VCC > V
OUT
> 3.1V
Equation B: IOL = 78.5·V
OUT
(4.4V - V
OUT
) for 0V < V
OUT
< 0.71V

V962PBC
12 V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc.
4.2 Local Bus Timings
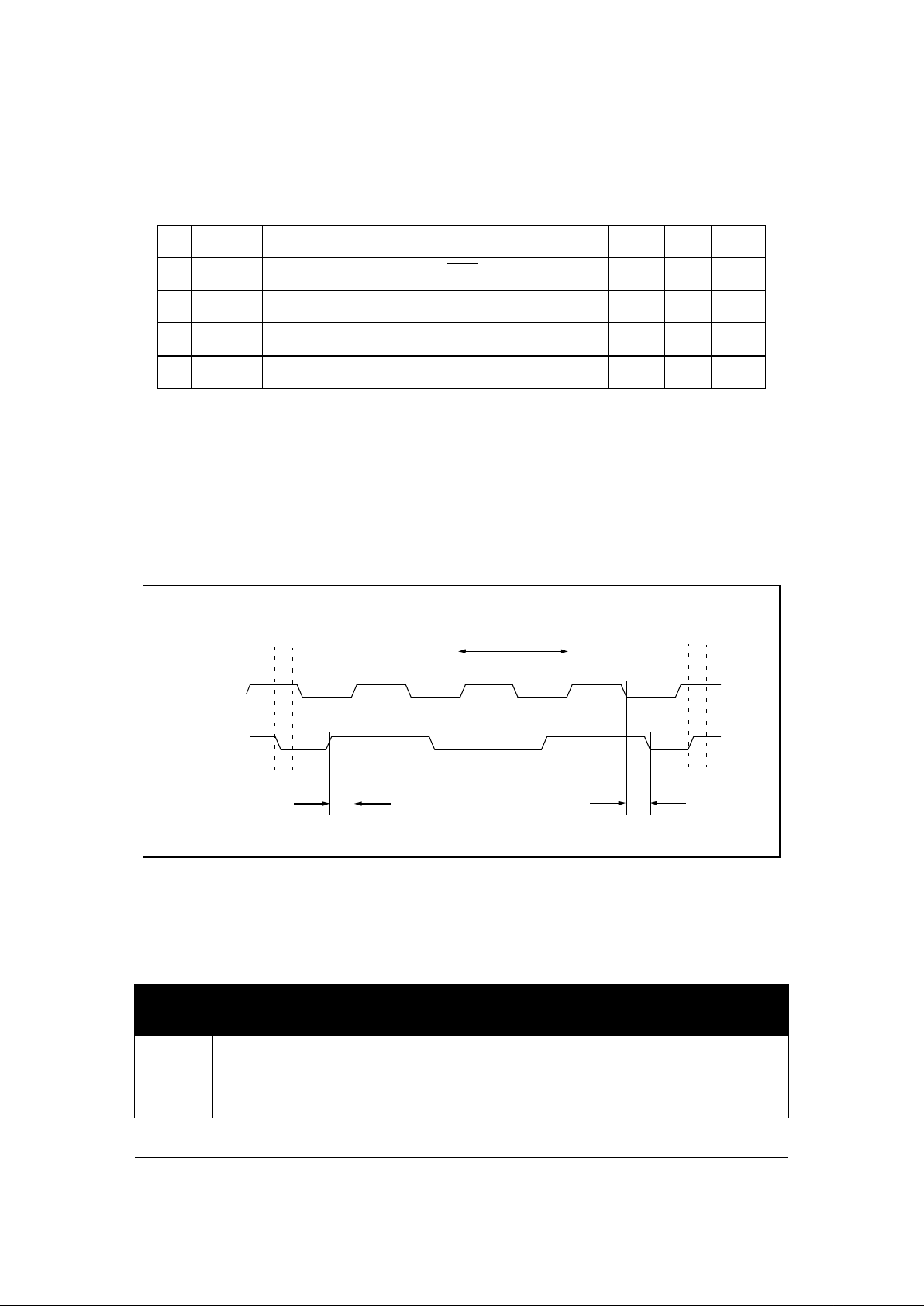
Figure 3: Clock and Synchronous Signals
Table 11: i960Cx/Hx Local Bus AC Test Conditions
Symbol Parameter Limits Units
V
CC
Supply voltage 4.75 to 5.25 V
V
IN
Input low and high voltages 0.4 and 2.0 V
C
OUT
Capacitive load on output and I/O pins 50 pF
Table 12: Capacitive Derating for Output and I/O Pins
Output Drive Limit Derating
4mA 0.058 ns/pF for loads > 50pF

V962PBC
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 13
Notes:
1. Measured at 1.5V.
2. All local bus signals except those in 4a, 4b, 4c, 4d and 4e.
3. All local bus signals except those in 6a.
4. READY, BLAST, ADS are driven to high impedance at the falling edge of LCLK.
Table 13: Local Bus Timing Parameters for Vcc = 5 Volts +/- 5%
33MHz 40MHz
# Symbol Description Notes Min Max Min Max Units
1 T
C
LCLK period 30 25 ns
2 T
CH
LCLK high time 1 12 11 ns
3 T
CL
LCLK low time 1 12 11 ns
4 T
SU
Synchronous input setup 2 7 6 ns
4a T
SU
Synchronous input setup (BLAST) 8 7 ns
4b T
SU
Synchronous input setup (W/R, BTERM) 4 4 ns
4c T
SU
Synchronous input setup (ADS) 6 5 ns
4d T
SU
Synchronous input setup (address, data,
byte enables)
9 8 ns
4e T
SU
Synchronous input setup for read data
when in local bus master mode
5 5 ns
5 T
H
Synchronous input hold 2 2 ns
6 T
COV
LCLK to output valid delay 3 3 14 3 12 ns
6a T
COV
LCLK to output valid delay (address, data,
byte enable, parity)
3 15 3 14 ns
7 T
CZO
LCLK to output driving delay 3 15 3 14 ns
8 T
COZ
LCLK to high impedance delay 4 3 15 3 14 ns
9 T
RST
Reset period when LRST used as input 16·T
C
16·T
C
ns
Table 14: PCI Bus Timing Parameters for Vcc = 5 Volts +/- 5%
# Symbol Description Notes Min Max Units
1 T
C
PCLK period 30 ns
2 T
SU
Synchronous input setup to PCLK 1 7 ns
2a T
SU
Synchronous input setup to PCLK (GNT) 10 ns
3 T
H
Synchronous input hold from PCLK 0 ns
V962PBC
14 V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc.
Notes:
1. All PCI bus signals except those in 2a.
2. All PCI bus signals except those in 4a.
4.3 Serial EEPROM Port TImings
The clock for the serial EEPROM interface is derived by dividing the PCI bus clock. The waveforms
generated are shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Serial EEPROM Waveforms and Timings
5.0 Revision History
4 T
COV
PCLK to output valid delay 2 3 11 ns
4a T
COV
PCLK to output valid delay (REQ) 4 12 ns
5 T
CZO
PCLK to output driving delay 4 11 ns
6 T
COZ
PCLK to high impedance delay 5 18 ns
7 T
RST
Reset period when PRST used as input 16·T
C
Table 15: Revision History
Revision
Number
Date Comments and Changes
2.4 5/98 Data sheet up date to B2-step values
2.3 10/96
Data Book revision.
1. In Table 3, changed “LPAR[3:0]” to “LPAR[3:0]”.
Table 14: PCI Bus Timing Parameters for Vcc = 5 Volts +/- 5%
SCL
SDA
START CONDITION
STOP CONDITION
512 PCI BUS
CLOCKS
256 PCI BUS
CLOCKS
256 PCI BUS
CLOCKS

V962PBC
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 15
2.2 06/96
1. In Table 3, changed “PERR I/OD” to “PERR I/O”.
2. In Table 3, added “VCC“ and “GND” description.
3. In Table 13 and 14 , added min T
COV
and min T
CZO
timing.
2.1 03/96
1. Updated timings to final B1-step values.
2. Simplified data sheet format.
2.0 11/95
Removed operational description (found in User’s Manual). Device related
changes:
1. LA5, LA4, LA3, LA2 pins added to pinout for V960PBC and V961PBC.
2. Changed references to PCI 2.0 to PCI 2.1 spec level compliance.
3. Updated timings to final B0-step values.
4. Added new T
CZO
timing.
5. Added test mode pin description.
1.3 4/95
1. In Table 1, changed Draining Strategy to “3 or more words” from “4 or more
writes”.
2. In Table 3, changed Base Address 3 to Unimplemented.
3. In Table 5, changed “PAR” to “PAR”.
4. In Table 6, changed “SCL” to “SCL/PERR”.
5. In Table 6, changed SDA to “I/O4 from “O4”.
6. In Table 6, changed ROMCSx,LREQ, and ADS to “I/O4” from”O4” (device
dependent).
7. In Table 6, changed GREQ,LBREQ, and HOLD to “O4” from “I/O4” (device
dependent).
8. In Table 6, changed BURST and BLAST to “I/O4” from “O4” (device dependent).
9. In Table 6, changed ERR and BTERM to “I/O4” from “O4” (device dependent).
10. In Table 14, added timings for 16MHz and 40MHz (device dependent).
1.2 3/95
First released version of the data sheet. Some changes to AC and DC specifications and to waveforms. All future changes to the data sheet will be documented
in detail in this section.
1.1 2/95
Clean pinouts. Some DC and AC specs. Sent only to a limited number of customers.
1.0 1/95
First pre-silicon revision of preliminary data sheet. DC and AC specs TBD. Sent
only to a limited number of customers.
Table 15: Revision History (cont’d)
Revision
Number
Date Comments and Changes

V962PBC
16 V962PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...