V3 Semiconductor V960PBC-33REVB2 Datasheet
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V960PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 1
V960PBC Rev. B2
LOCAL BUS TO PCI BRIDGE
FOR i960Sx PROCESSORS
V3 Semiconductor reserves the right to change the specifications of this product without notice.
V960PBC and V96SSC are trademarks of V3 Semiconductor. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
• Glueless interface between Intel i960Sx,
processors and PCI bus
• Fully compliant with PCI 2.1 specification
• Configurable for primary master, bus master, or
target operation
• Up to 1Kbyte burst access support on both local
and PCI interface
• 576 bytes of programmable FIFO storage with
DYNAMIC BANDWIDTH ALLOCATION™
• Two channel DMA controller
• Enhanced support for 8/16-bit local bus devices
with programmable region size register
• 16 8-bit bi-directional mailbox registers with
doorbell interrupts
• Dual bi-directional address space remapping
• On-the-fly byte order (endian) conversion
• Optional power on serial EEPROM initialization
• I2O ATU and messaging unit including
hardware controlled circular queues
• Flexible PCI and local interrupt management
• Support for real-mode DOS "holes"
• Ability to generate both Type 0 and Type 1
configuration cycles
• 33MHz and 40MHz local bus versions available
with independent PCI operation up to 33MHz
• Low cost 160-pin EIAJ PQFP package
V960PBC provides the highest performance,
most flexible, and most economical method to
directly connect i960Sx processor to the PCI
bus. V961PBC may also be used in systems
without a CPU for a generic PCI master/target
interface.
V960PBC Rev B2 is the first I2O ready PCI
bridge, fully backward compatible with V960PBC
Rev B1. The PCI bus can be run at the full
33MHz frequency, independent of local bus
clock rate. The overall throughput of the system
is dramatically improved by increasing the FIFO
depth and utilizing the unique DYNAMIC
BANDWIDTH ALLOCATION™ architecture.
Access to the PCI bus can be performed through
two programmable address apertures. Two more
apertures are provided for PCI-to-local bus
accesses. There are 32-bytes of read FIFO’s in
each direction, 16-byte dedicated for each
aperture.
V960PBC also includes bi-directional remapping
capabilities, and on-the-fly byte order conversion
Two DMA channels are provided for autonomous
PCI-to-Local/Local-to-PCI transfers. Mailbox
registers and flexible PCI interrupt controllers are
also included to provide a simple mechanism to
emulate PCI device control ports.
The part is available in 160-pin low cost EIAJ
Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP) package.
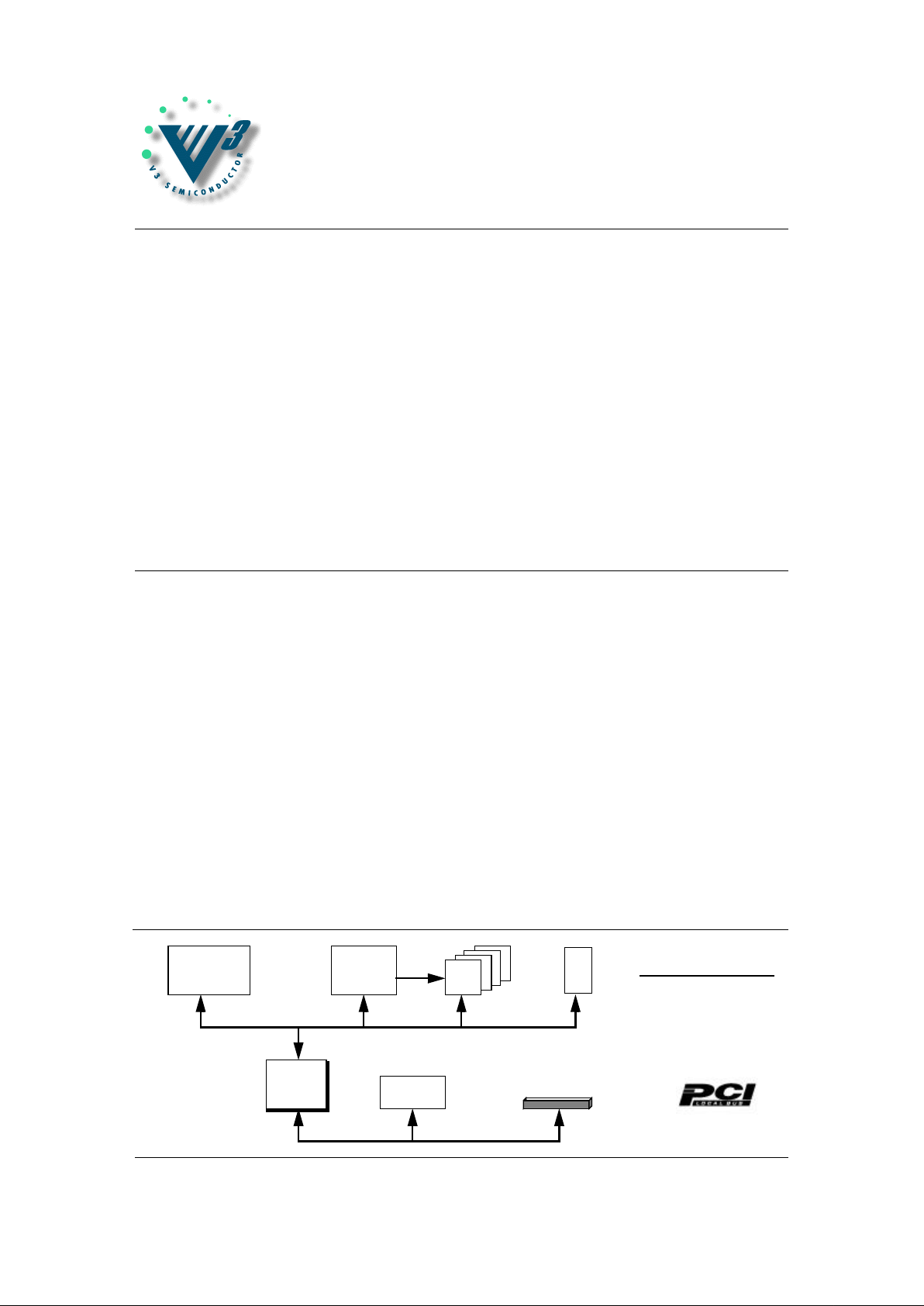
i960Sx
CPU
V96SSC
MEMORY
CONTROL
D
R
A
M
ROM
V960PBC
LOCAL TO
PCI BRIDGE
TYPICAL APPLICATION
PERIPHERAL
PCI
PCI SLOT or EDGE CONNECTOR
V960PBC
2 V960PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc.
This document contains the product codes, pinouts, package mechanical information, DC
characteristics, and AC characteristics for the V960PBC. Detailed functional information is contained
in the User’s Manual.
V3 Semiconductor retains the rights to change documentation, specifications, or device
functionality at any time without notice. Please verify that you have the latest copy of all
documents before finalizing a design.
1.0 Product Codes
2.0 Pin Description and Pinout
Table 2 below lists the pin types found on the V960PBC. Table 3 describes the function of each pin on
the V960PBC. Table 5 lists the pins by pin number. Figure 1 shows the pinout for the 160-pin EIAJ
PQFP package and Figure 2 shows the mechanical dimensions of the package.
Table 1: Product Codes
Product Code Processor Bus Type Package Frequency
V960PBC-33 REV B2 i960SA/SB 16-bit multiplexed 160-pin EIAJ PQFP 33MHz
Table 2: Pin Types
Pin Type Description
PCI I PCI input only pin.
PCI O PCI output only pin.
PCI I/O PCI tri-state I/O pin.
PCI I/OD PCI input with open drain output.
I/O
4
TTL I/O pin with 4mA output drive.
I TTL input only pin.
O
4
TTL output pin with 4mA output drive.

V960PBC
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V960PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 3
Table 3: Signal Descriptions
PCI Bus Interface
Signal Type R
a
Description
AD[31:0] PCI I/O Z Address and data, multiplexed on the same pins.
C/BE[3:0] PCI I/O Z Bus Command and Byte Enables, multiplexed on the same pins.
PAR PCI I/O Z Parity represents even parity across AD[31:0] and C/BE[3:0].
FRAME PCI I/O Z
Cycle Frame indicates the beginning and burst length of an
access.
IRDY PCI I/O Z
Initiator Ready indicates the initiating agent’s (bus master’s) ability
to complete the current data phase of the transaction.
TRDY PCI I/O Z
Target Ready indicates the target agent’s (selected device’s) ability to complete the current data phase of the transaction.
STOP PCI I/O Z
Stop indicates the current target is requesting the master to stop
the current transaction (retry or disconnect).
DEVSEL PCI I/O Z
Device Select, when actively driven by a target, indicates the driving device has decoded its address as the target of the current
access. As an input to the initiator, DEVSEL indicates whether
any device on the bus has been selected.
IDSEL PCI I
Initialization Device Select is used as a chip select during configuration read and write transactions. It must be driven high in order
to access the chip’s internal configuration space.
REQ PCI O H
Request indicates to the arbiter that this agent requests use of the
bus.
GNT PCI I
Grant indicates to the agent that access to the bus has been
granted.
PCLK PCI I PCLK provides timing for all transactions on the PCI bus.
PRST PCI I/O Z/L
Acts as an input when RDIR is high, an output when RDIR is low.
As an input it is asserted low to bring all internal PBC operation to
a reset state.
PERR PCI I/O Z
Parity Error is used to report data parity errors during all PCI
transactions except a Special Cycle.
SERR PCI I/OD Z
System Error is used to report address parity errors, data parity
errors on the Special Cycle command, or any other system error
where the result will be catastrophic.
INT[A:D] PCI I/OD Z Level-sensitive interrupt requests may be received or generated.
V960PBC
4 V960PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc.
Local Bus Interface
Signal Type R Description
LA[31:16] I/O4 Z Local address bus.
LAD[15:0] I/O4 Z Local multiplexed address and data bus.
LA[5:2] I/O4 Z Local address bus.
BE[1:0] I/O4 Z Local bus byte enables.
W/R I/O4 Z Write/Read.
ALE I/O4 Z
Address Latch Enable: used to latch the address during the
address phase.
AS I/O4 Z Asserted low to indicate the beginning of a bus cycle.
READY I/O4 Z Local Bus data ready.
HOLD O4 L
Local bus hold request: asserted by the chip to initiate a local bus
master cycle.
HLDA I Local bus hold acknowledge.
LPAR[1:0] I/O4 Z Local bus parity.
BLAST I/O4 Z Burst last.
LINT O4 H Local interrupt request.
LRST I/O4 L/Z Local bus RESET signal.
LCLK I Local bus clock.
Serial EEPROM Interface
Signal Type R Description
SCL/LPERR O4 X EEPROM clock. Local parity error.
SDA I/O4 X EEPROM data.
Configuration
Signal Type R Description
RDIR I
Reset direction. Tie low to drive PRST out and LRST in, high to
drive LRST out and PRST in.
Table 3: Signal Descriptions (cont’d)
V960PBC
Copyright © 1998, V3 Semiconductor Inc. V960PBC Data Sheet Rev 2.4 5
2.1 Test Mode Pins
Several device pins are used during manufacturing test to put the V960PBC device into various test
modes. These pins must be maintained at proper levels during reset to insure proper operation.
This is typically handled through pull-up or pull-down resistors (typically 1K to 10K) on the signal pins if
they are not guaranteed to be at the proper level during reset. Table 4 below shows the reset states for
test mode pins:
Power and Ground Signals
Signal Type R Description
V
CC
-
POWER leads intended for external connection to a VCC board
plane.
GND -
GROUND leads intended for external connection to a GND board
plane.
a. R indicates state during reset.
Table 4: RESET State for Test Mode Pins
PIN# 134 135 153
Connection Pull-Down Pull-Down Pull-Down
Table 5: Pin Assignments
PIN # Signal PIN # Signal PIN # Signal PIN # Signal
1 V
CC
41 V
CC
81 V
CC
121 V
CC
2 INTD 42 AD14 82 NC 122 NC
3 PRST 43 AD13 83 LAD8 123 LA25
4 PCLK 44 AD12 84 NC 124 LA5
5 GNT 45 AD11 85 LAD9 125 LA26
6 REQ 46 AD10 86 NC 126 LA4
7 AD31 47 AD9 87 LAD10 127 LA27
8 AD30 48 AD8 88 NC 128 LA3
Table 3: Signal Descriptions (cont’d)
 Loading...
Loading...