Page 1
RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
12
4-
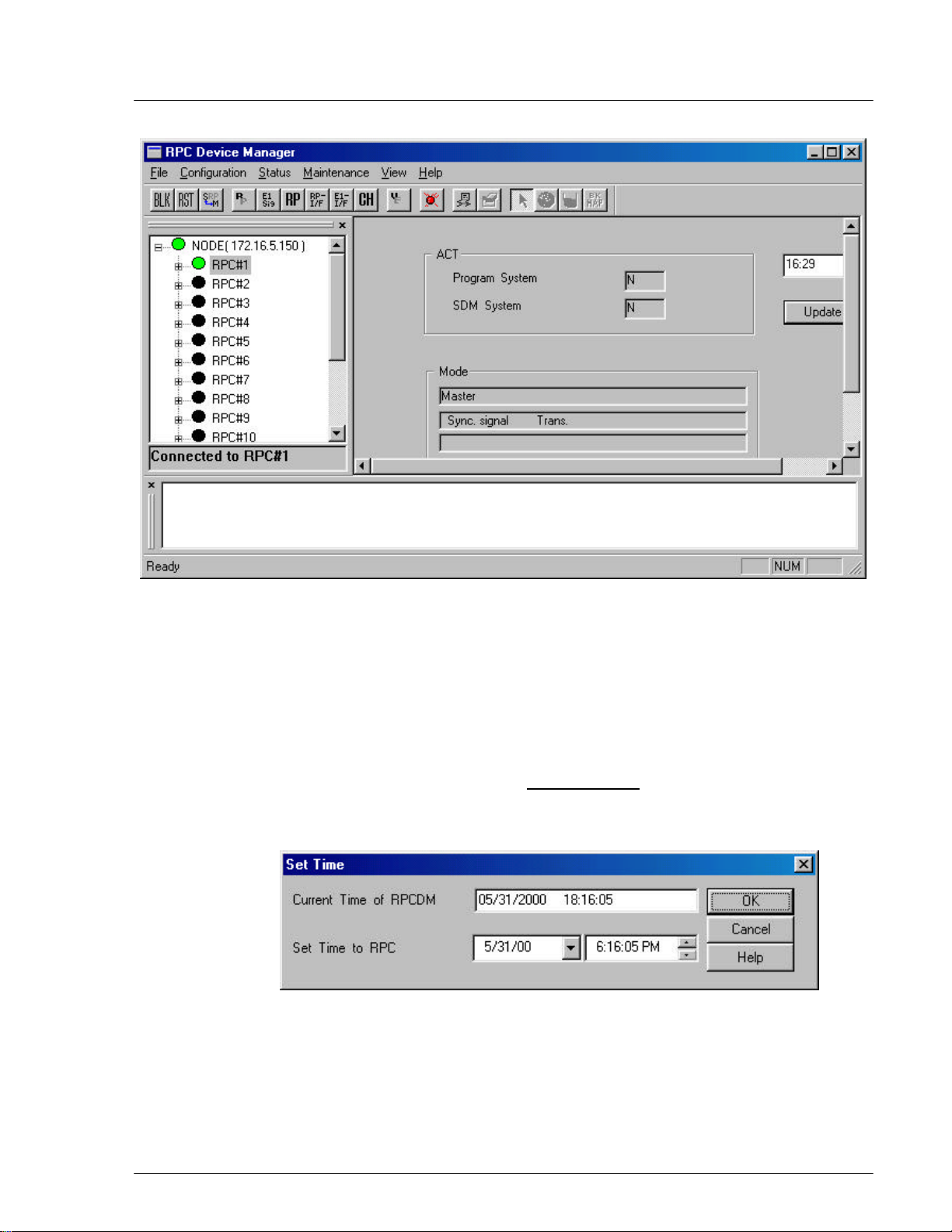
Figure 4-13: RPC Window
4.2.1 Set Time
To set the system time, follow the procedures below:
1. Click the Set Time option on the Configuration pull-down menu. The Set
Time window appears, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 4-14: Set Time Window
2. By default the RPC time is set to the current time of the PC. Set new date and
time to RPC if necessary. Make necessary adjustment using the Arrow
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 2
RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
13
buttons in the fields. Click OK to accept the setting or Cancel to stop the
transaction.
4.2.2 RPC Change
Sometimes the operation data for an RPC may not be compatible to the hosting
RPC. Use this function to make changes to the SDM (System Data Memory) so
that it can accommodate the hosting RPC. Before making any change, the RPC
device manager will disconnect from the RPC.
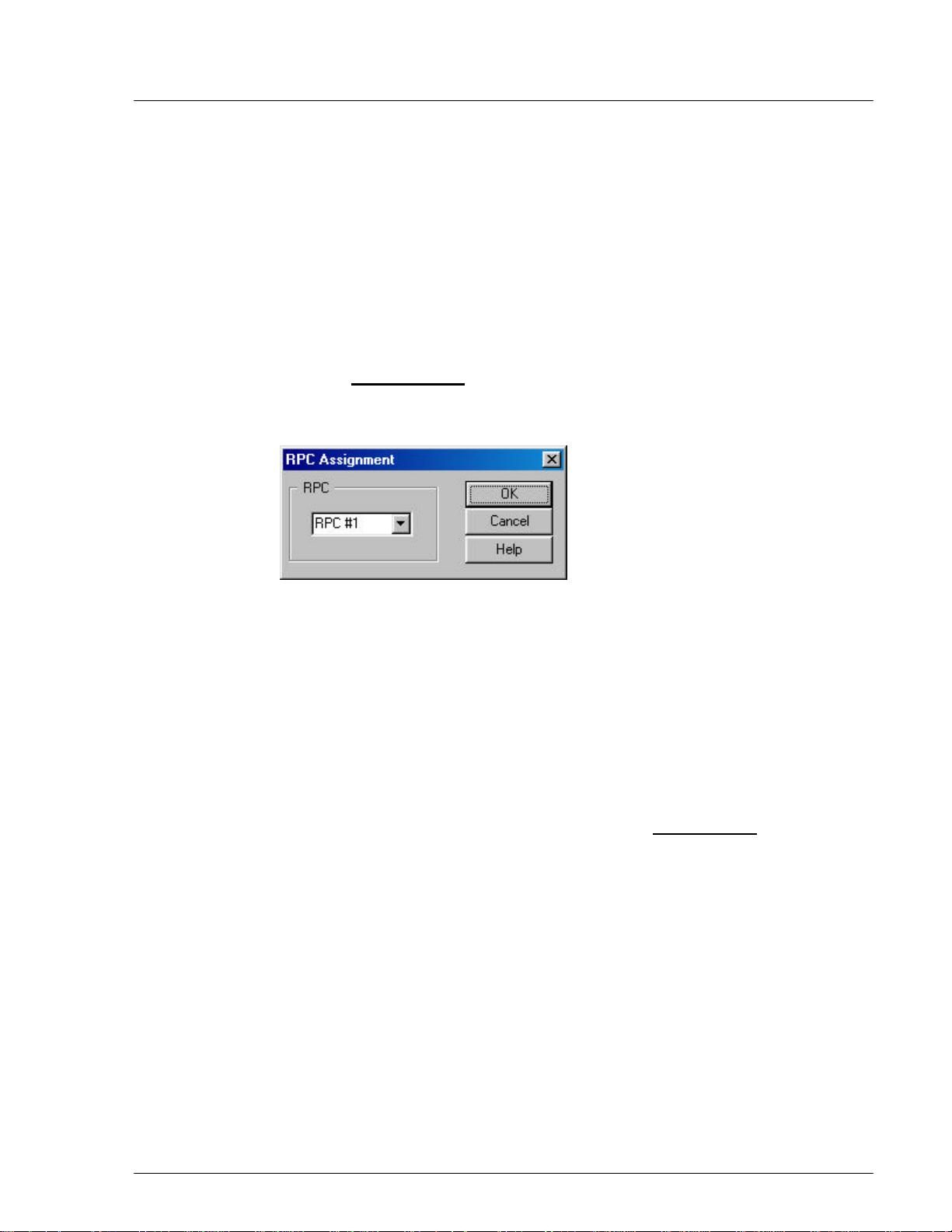
1. From the Configuration main menu, select RPC Change. This opens the
RPC Assignment window, as illustrated in the figure below.
4-
Figure 4-15: RPC Assignment Window
2. Select the target RPC and click OK. This will change the SDM to fit the
target RPC.
3. If this command doesn’t work, exit the current Netman session and restart.
4.2.3 Unit Control
The Unit Control option can be accessed through the Maintenance pull-down
menu. It has the following functions:
• Blockade: block or unblock RPIF, E1IF, RPCs, RPs
• TimeSlot Layout: configure the RP control channel time slot
• Maintenance: set or cancel system maintenance
• Master RP: change Master RP
• RPC Sync: RPC Synchronization
• Online Trace: retrieve the information of the active RP
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 3
RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
14
4-
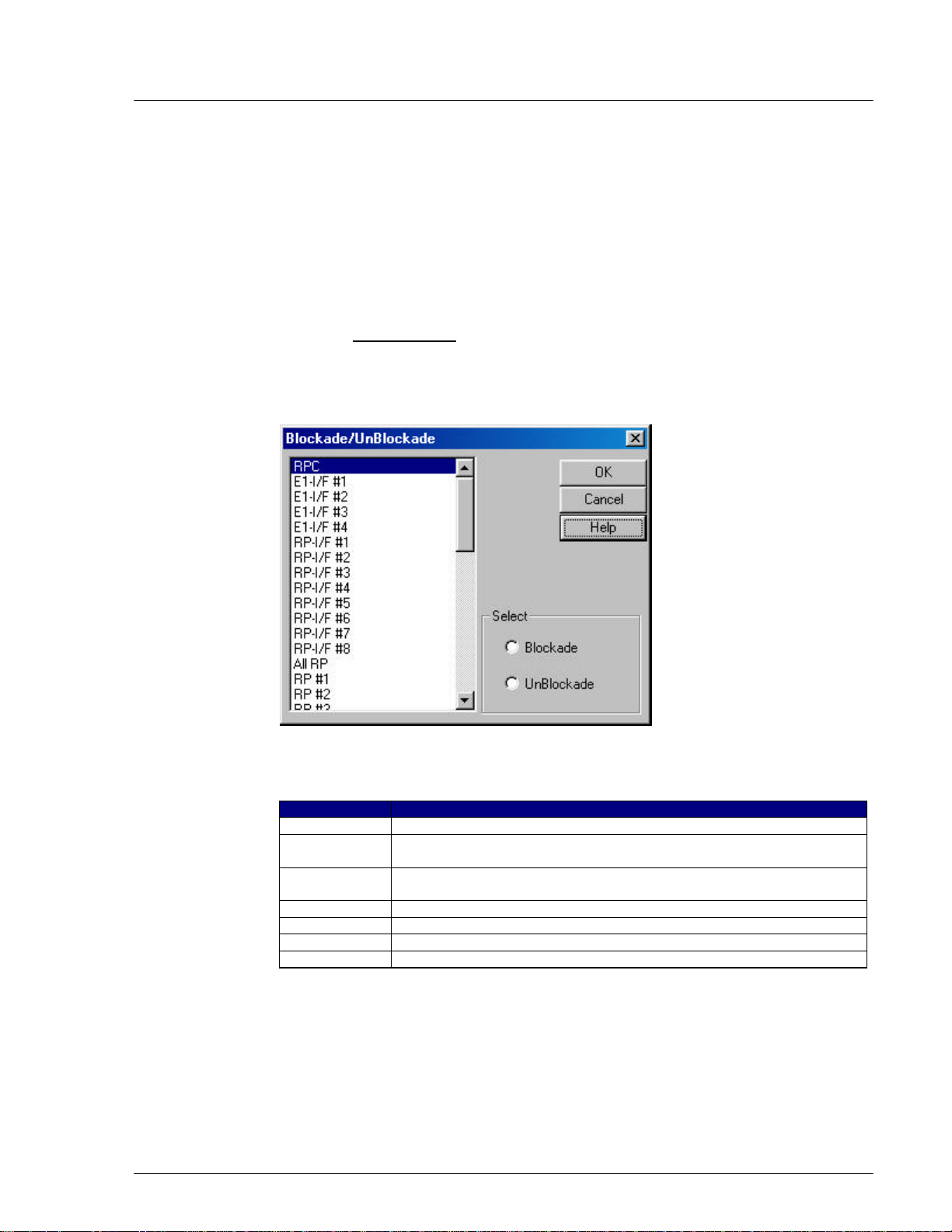
4.2.3.1 Blockade/Unblockade
The Blockade option is used to block or unblock RP interface, E1 interface, RPs,
or the entire RPC. Use this function to block traffic from a malfunctioning
device. It is also used when units are replaced. Netman 2000 must be connected
to the WLL/V5WLL in order to perform this function. Another important usage
of this option is to regain the synchronization of the slave RPCs upon the recovery
of the master RPC.
1. From the Maintenance main menu, select Unit Control and then Blockade.
This opens the Blockade/Unblockade window, as displayed in the figure
below.
Figure 4-16: Blockade/Unblockade Window
Field Name Description
RPC The entire RPC, including all the units under its control
E1-I/F #… E1 interface. Each RPC uses 4 E1 interfaces to communicate with
WLL/V5WLL.
RP-I/F #… RP interface. RPC uss 8 RP interfaces to control RPs. Each RP
interface is connected to 4 RPs.
All RP All the 32 RPs
RP #… Individual RP. There are altogether 32 RPs under each RPC.
Blockade If this radio button is selected, the selected unit is blocked.
UnBlockade If this radio button is selected, the selected unit is unblocked.
Table 4-1: Blockade/Unblockade Window Field Description
2. Select the target E1 interface, RP interface, RP, or RPC, and then select
Blockade or Unblockade. Click OK. Selecting RPC will block or unblock all
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 4
RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
15
the units controlled by the RPC. No new calls will be accepted and all the
calls in progress are allowed to complete and then dropped.
3. When the action is implemented, the system displays a message in the Self
Message window, and the Status View window will also show the Blockade
result, as illustrated in the figure below. Use the window to verify the result.
4-
Figure 4-17: Self Message and Status View window for Blockade
F NOTE: If an RPC or all RPs are blocked, calls cannot be made.
4. Zero “o” in the Blockade Maint column means the unit is blocked, and dash “” means the unit is unblocked. The Status and the Self Messages windows
both indicate that RP#1 and RP#2 are blocked.
5. There are two ways to access the Status View window. One is to click Status
and then the relevant options: RPC, RPs, RP-I/F Board, E1 Signal, Node-I/F
Board, Air Channel, or TimeSlot Status. The other is to click the target item
on the left frame of the RPC window. In either case the Status View window
opens on the right frame. Of course, one can always access the window by
clicking the relevant toolbar.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 5
RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
16
4-
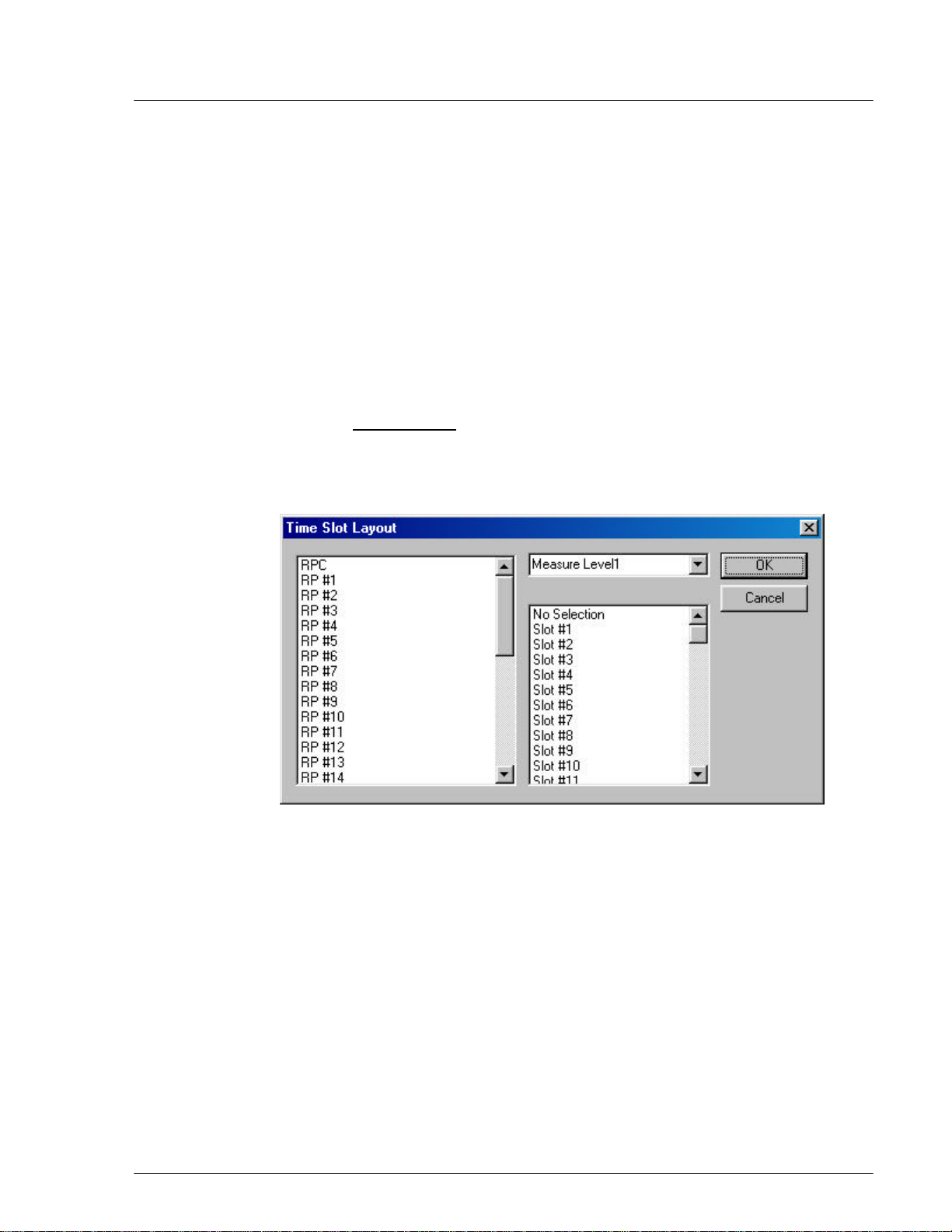
4.2.3.2 TimeSlot Layout
F WARNING: Users are NOT recommended to make changes to the settings of the
Time Slot. Use with caution!
When connected to an RPC, use this function to reconfigure the RP control
channel time slot. This function is used to complete the RP configuration and
make it usable. This function applies to both RPCs and RPs.
1. Before configuring the time slot, use the Blockade function to block the target
RPC or PC.
2. From the Maintenance main menu, select Unit Control and then TimeSlot
Layout. This opens the Time Slot Layout window, as shown in the figure
below.
Figure 4-18: Time Slot Layout Window
3. Select the target RPC or RP.
4. Select Measure Level1. If separation is not completed, try another one from
Measure Level2 through Measure Level4. Selecting No Selection may
accelerate separation.
5. Select No Selection. If selection must be made, select one from Slot #1
through Slot #80.
6. Click OK to close the window.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 6
RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
17
7. Unblock the RPC or RP.
F NOTE: The Time Slot Layout window is for configuration purpose only. Actual
separation is done when the target RPC or RP is unblocked.
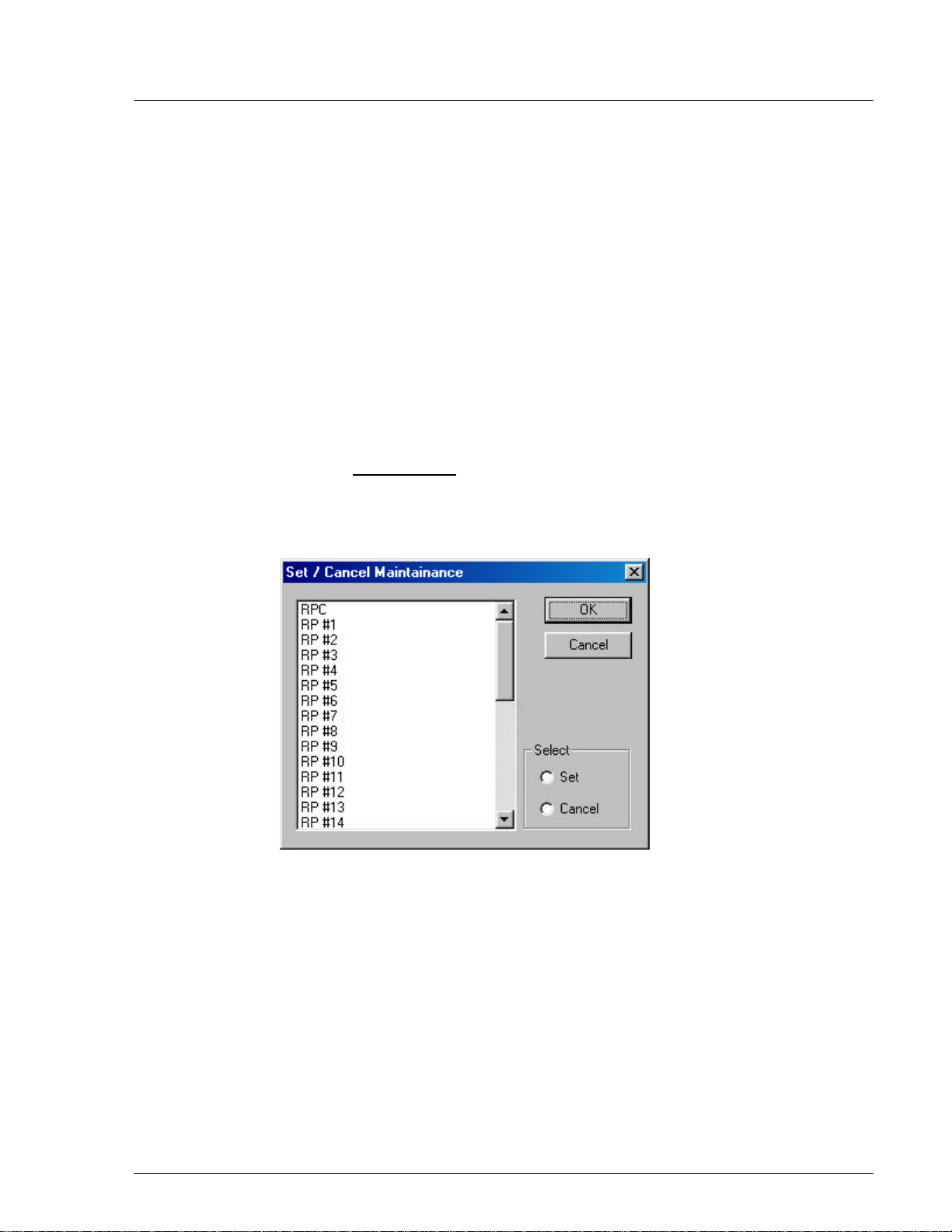
4.2.3.3 Maintenance
Use this function to set RPC maintenance status, test RPs, and do other
configuration. Eligible units are fully installed RPCs and installed RPs.
F NOTE: General PSs can not use RP when maintenance is under way.
1. From the Maintenance main menu, click Unit Control, and then
Maintenance. The Set/Cancel Maintenance window opens, as displayed in
the figure below.
4-
Figure 4-19: Set / Cancel Maintenance Window
2. Select the target RPC or RP, and click Set to set the maintenance status or
Cancel to remove the status.
3. Click OK to accept the selection and close the window.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 7
RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
18
4-
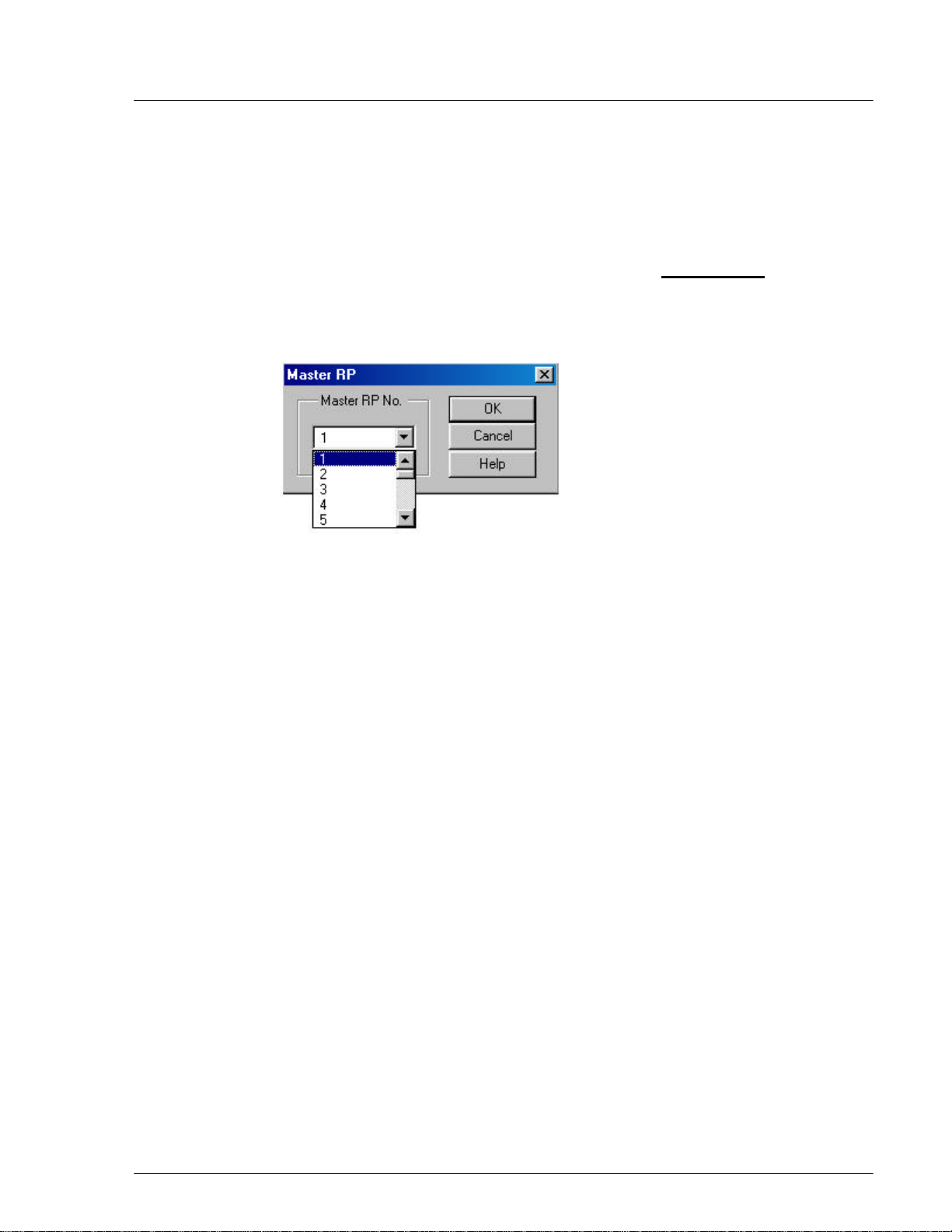
4.2.3.4 Change Master RP
For the operation in a group control mode, it sometimes becomes necessary to
switch a master RP to a slave RP, because the master RP is faulty or because the
NMS operation requires the switch. Use this feature to switch the function.
1. Select Unit Control, and then Master RP from the Maintenance pull-down
menu. The Master RP window appears as shown in the figure below.
Another way to access the window is to click the Change Master RP toolbar.
Figure 4-20: Master RP Window
2. Click the Arrow button in the Master RP No. field to get a list of all the 32
RP numbers. Select the RP to be the new master and click OK. That RP
becomes the new master RP. The Self Message window displays a message,
indicating the change has been made. The change can also be verified by
viewing the RP status.
F NOTE: Each group can have a maximum of 8 RPs.
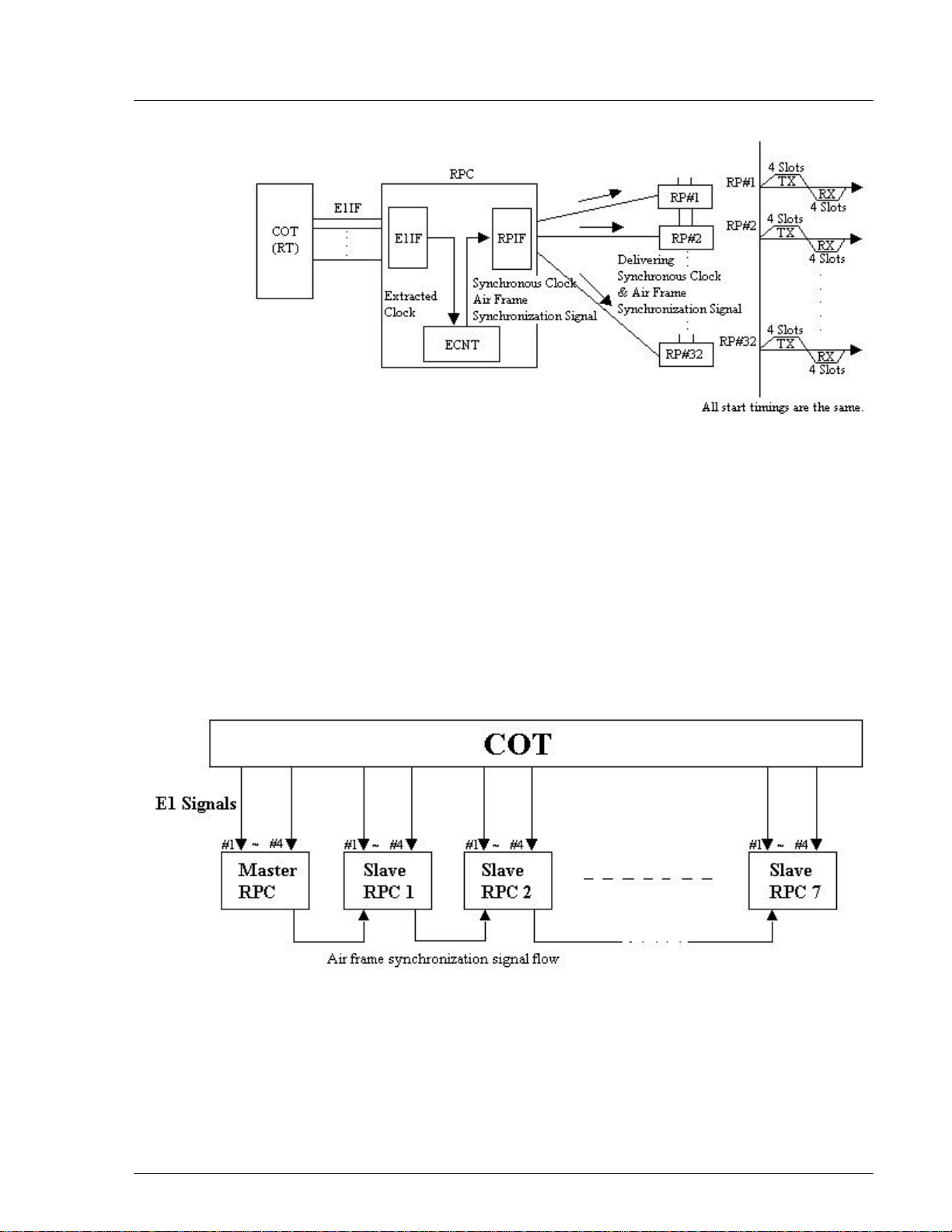
4.2.3.5 RPC Synchronization
The ECNT board on the RPC generates the synchronous clock and the air frame
synchronization signal by extracting clock from the E1 interface signal on the E1IF boards, and delivers them to RPs through the RP-IF boards. As a result, all the
RPs that are controlled by the same RPC are operating synchronously. The
following figure illustrates the process of clock synchronization and air frame
synchronization for one RPC.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 8
RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
19
Figure 4-21: Clock Synchronization and Frame Synchronization in One RPC
However, RPs that belong to different RPCs do not automatically operate with air
frame synchronization. This causes the inefficienct air channel usage. To redress
the problem, the synchronization group is created which includes as many as 8
RPCs. Those RPCs are connected by cables as open daisy chain, through which
the air frame synchronization signal is transmitted. The signal is shared by the
RPCs, so that the air frames of the RPs among the RPCs are synchronized. The
RPC which generates the air frame synchronization signal is named “Master”.
The RPCs which receive the signal are called “Slave”. The following figure
displays such a synchronization model.
4-
Figure 4-22: Wired Air Frame Synchronization Group Model
The master or slave mode is set using the rotary switches on the front of the
ECNT board. When the master RPC fails during the operation, the first slave
RPC in the synchronization signal flow becomes the provisional master RPC.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 9
RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
20
4-
Upon the restoration and restart of the failed master RPC, the first slave RPC
needs to be blocked and re-synchronized in order to regain synchronization. This
process is implemented through Netman.
1. From the Maintenance pull-down menu, select Unit Control, and then RPC
Sync. The RPC Synchronization window opens, as shown in the figure
below.
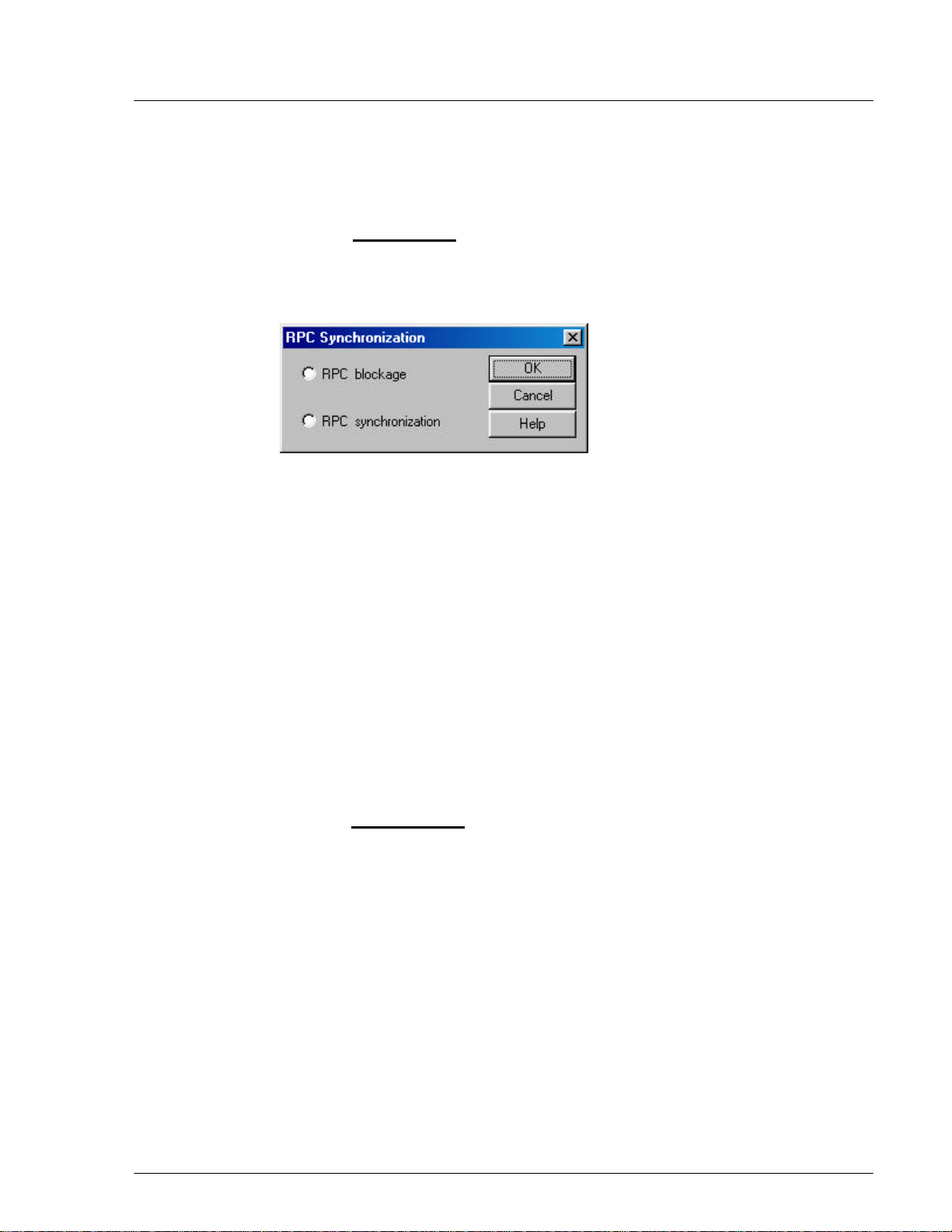
Figure 4-23: RPC Synchronization Window
2. Click the RPC blockage radio button to block the slave RPCs. Click OK to
execute the command. Verify the blockage by checking the RPC Status
window and the Self Message window.
3. Return to the RPC Synchronization window and click the RPC
synchronization radio button. Click OK to synchronize the slave RPCs.
After the command is implemented, the slave RPCs become synchronous in
operation to the upstream RPCs.
4.2.3.6 Online Trace
The Online Trace feature is used to check the time slot status of the RPs.
1. From the Configuration main menu, select Unit Control, and then Online
Trace. This opens the Select Online Trace window, as illustrated in the
figure below.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 10
RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
21
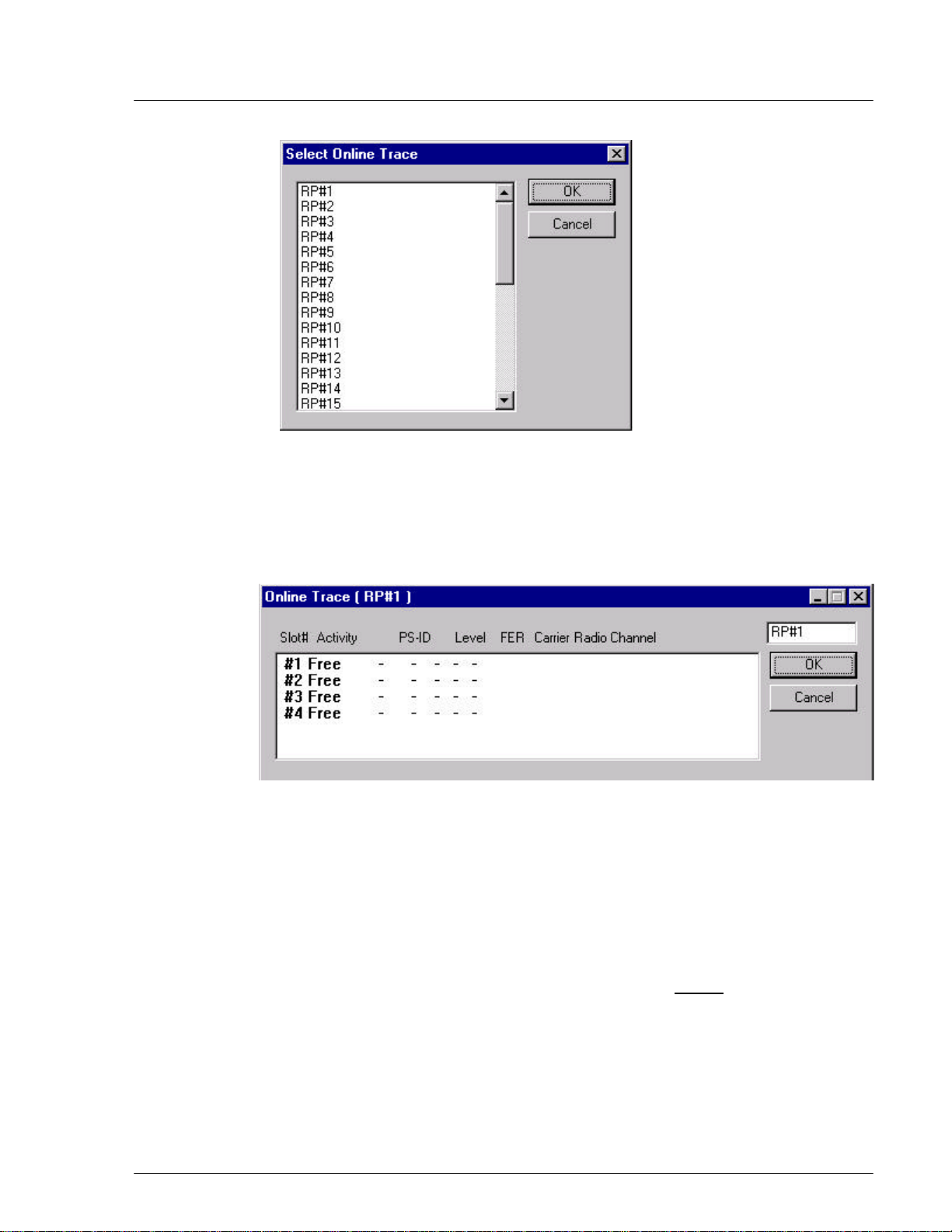
Figure 4-24: Select Online Trace Window
2. Click to highlight the target RP# and click OK. This opens the Online Trace
window, as shown below.
4-
Figure 4-25: Online Trace Window
3. This window displays the relevant Time Slot status information about the
target RP.
4.2.4 Function Status
The Status option windows can be accessed through the Status pull-down menu.
The following functions are available from the Status option:
• Collect and display the status for:
- RPC
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 11

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
22
4-
- RPs
- RP-I/F Board
- E1 Signal
- Node-I/F Board
- Air Channel
- TimeSlot Status
• Collect hourly traffic data for RPCs and RPs
• View configuration data for each RP control channel
• Verify configuration results
4.2.4.1 RPC Status
1. To view the status of the current RPC, click RPC from the Status option.
Another way to open the RPC Status window is to click the RPC Status
button. The RPC status is displayed on the Status View window, as shown in
the figure below.
F NOTE: The following figure is cut out from the RPC window. The other Status
View windows in Section 4.2.4 are also cropped from the overall RPC window.
Figure 4-26: RPC Status Window
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 12

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
23
Field Name Description
ACT The active SDM or PDM system for RPC running
Program System PDM system. There are two plane memory areas for the
program data: N and E. Any one can be active or standby.
SDM System SDM system. There are two plane memory areas for the
operation data: N and E. Any one can be active or standby.
Update Retrieve the latest mode information and display the time
when the mode information is updated.
Mode Display mode information for the current RPC, such as,
master/slave status, synchronization status, transmission
status, etc. The following rows describe various mode
displays.
Mode Display Description
Master Master RPC - the RPC that generates the air frame
synchronization signal.
Slave Slave RPC - the RPC that receives the air frame
synchronization signal.
Sync. signal Trans. The RPC transmits the synchronization signal to the slave
RPC or the next slave RPC.
Sync. signal Stop The RPC doesn’t transmit the synchronization signal to the
slave RPC or the next slave RPC.
Sync. between RPC Sync. The slave RPC synchronizes to the upstream RPC.
Sync. between RPC Async. The slave RPC doesn’t synchronize to the upstream RPC.
4-
Table 4-2: RPC Status Window Field Description
2. This window is for view only. In this instance, there is no special meaning for
N or E. It simply displays which system is active. Refer to Section 4.3 for the
description of the N and E systems.
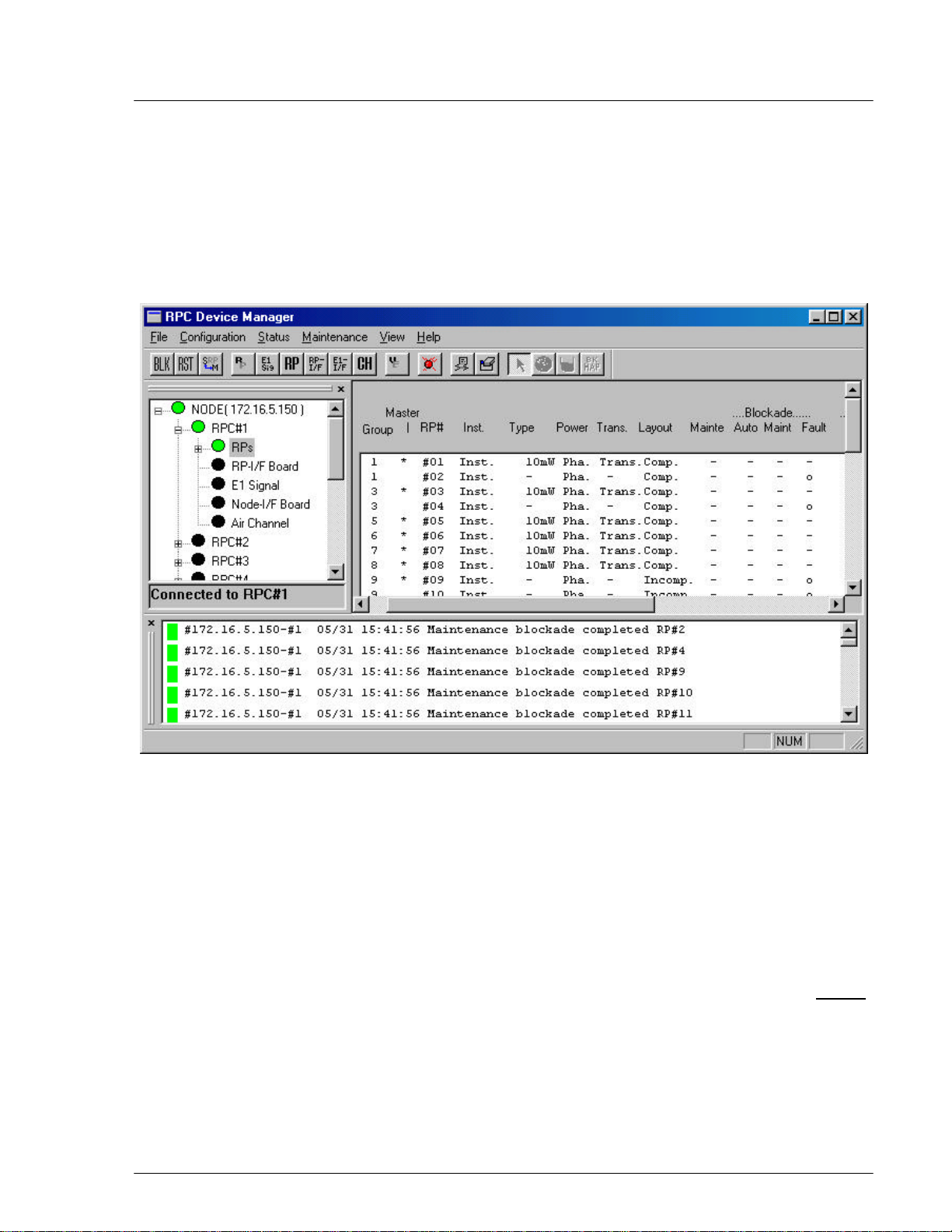
4.2.4.2 RP Status
Use the RP Status option to monitor the operation status of individual RPs and to
verify any change made to the RP configuration and setting.
1. To access the RP Status window, click Status, then Status, and then RPs.
Another way to display the window is to click the RP Status button. The RP
status is displayed on the Status View window, as shown in the figure below.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 13
RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
24
4-
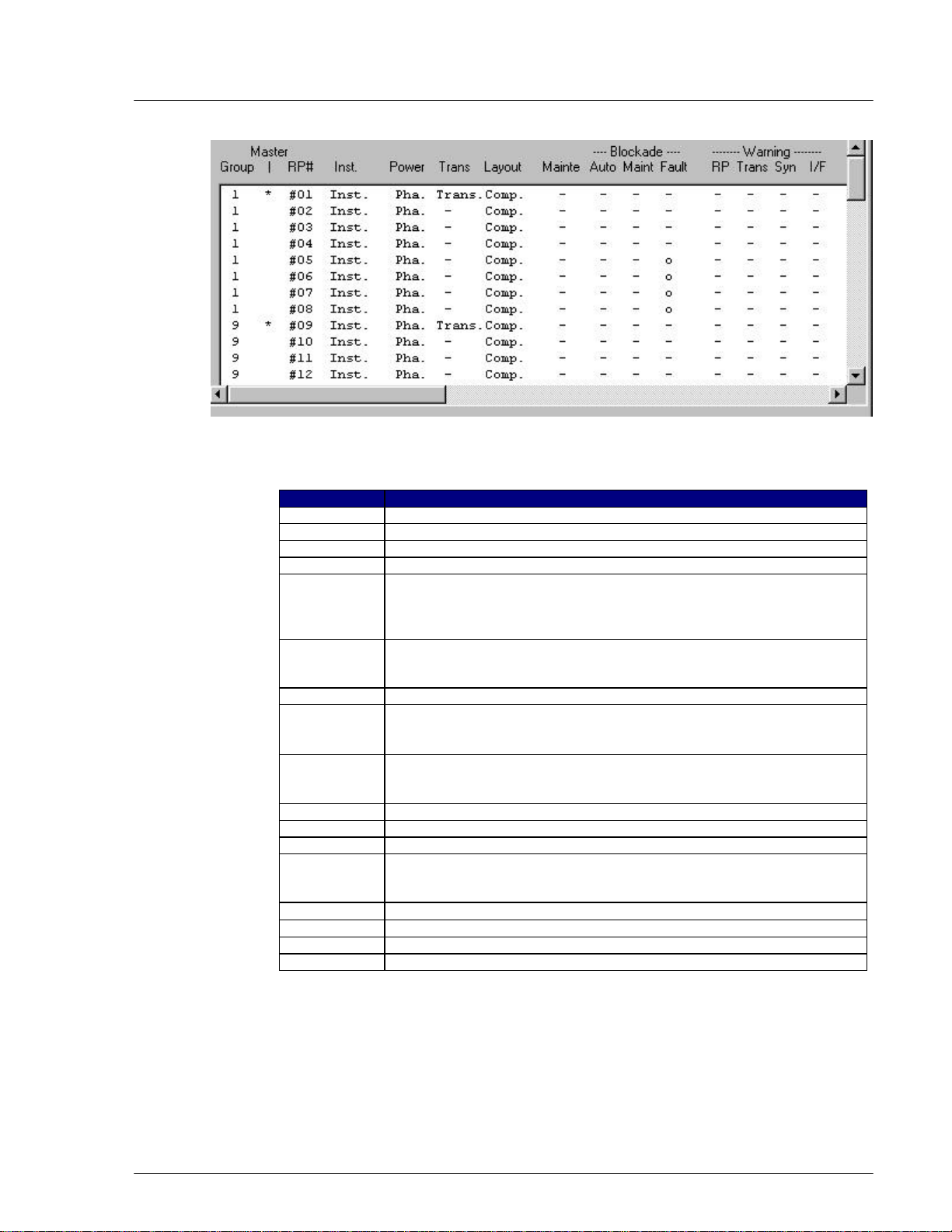
Figure 4-27: RPs Operation Status View window
Field Name Description
Group The ID number of the group to which the RP belongs
Master The sign * indicates the master RP.
RP# Radio port ID number
Inst. Installation status. “Inst.” Indicates that the RP has been installed.
Power The voltage of power. Usually it is 10mW. There are two power supply
state:
Pha. - supplied from RPC (Phantom)
Loc. - supplied from RP power unit (Local)
Trans. Transmission state for control channel. Group control maximizes the
number of channels available for traffic by allowing one control channel to
control up to 8 RPs.
Layout Configuration of the control channel: completed/incompleted.
Mainte Maintenance state:
o indicates the maintenance is configurated.
- indicates the maintenance is not configured.
Blockade Blockage state:
Auto Automatically blocked by automatic reconfiguration processing
Maint Blocked manually by HOST or Netman
Fault Cut off from operation system due to unit trouble
Warning Warning state:
RP RP interface detects RP suspension.
Trans. RP transmission power is incorrect.
Syn RP synchronization is lost.
I/F RP interface detects cut-off from RP.
o indicates the unit is blocked.
- indicates the unit is not blocked.
o indicates the existence of a warning.
- indicates no warning exits.
Table 4-3: RP Status Window Field Description
2. This window displays the operational status for all the RPs controlled by the
target RPC. Click the Update button to retrieve the current RP status. The
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 14

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
25
time will be displayed in the box above the button, indicating the time when
the data are updated.
3. With this window you can verify RP installation status, monitor alarms, power
supply status, and transmission information, and identify areas of trouble.
4. If you want to view the status for an individual RP, you may access such a
window by clicking the “+” sign to the left of RPs on the Unit View window.
This displays all the RPs under the RPC. Click the target RP and the Status
View window opens for that RP, as illustrated in Figure 4-28. With this
window you may view or enter the following information about that RP:
• Node Address
• RP Number
• RPC Number
• RP Location
• RP Information
• RP-RPC Line Information
• RP Antenna Parameters
4-
F NOTE: This is an optional information window. The information is stored on
Netman 2000 and will be used in network management, network optimization, and
value-added services, such as location services. The information entered does not
affect the operation of the RP.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 15
RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
26
4-
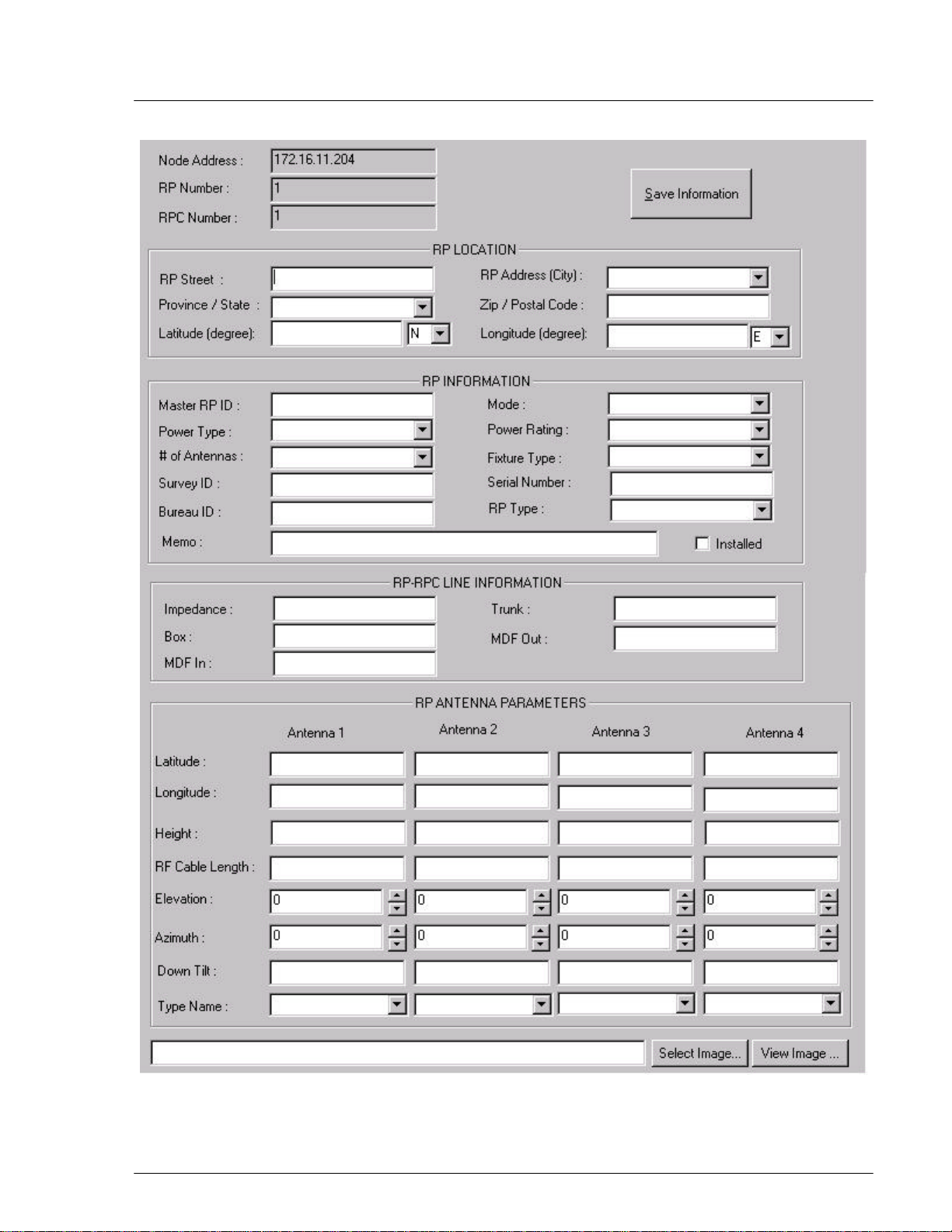
Figure 4-28: Status View window for One Individual RP
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 16

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
27
Field Name Description
Node Address The IP address of the node to which the RP is associated
RP Number The ID number of the RP
RPC Number The ID number of the RPC which controls the RP
RP Location The physical location of the RP
RP Street The street name of the location
Province/State The province/state name of the location. Select from the drop-down list.
RP Address (City) The city name of the location. Select from the drop-down list.
Zip/Postal Code Zip/Postal Code of the location
Latitude (degree) Latitude degree of the RP location.
Longitude (degree) Longitude degree of the RP location
RP information Information about the RP operation status
Master RP ID The ID number of the Master RP
Power Type There are two power supply patterns:
Local - the power is supplied from the RP power unit.
Remo - the power is supplied from the RPC.
Select from the drop-down list.
# of Antennas The number of the antennas the RP has. The indoor or outdoor 10mW RP
has 2 antennas, and the outdoor 200mW RP has 4 antennas. Select from
the drop-down list.
Survey ID The ID number of the survey
Bureau ID The ID number of the bureau
Memo Short note
Mode Master RP or slave RP. Select from the drop-down list.
Power Rating Power: 10mW or 200mW. Select from the drop-down list.
Fixture Type The way the RP is mounted. Select from the drop-down list.
Serial Number The serial number of the RP
RP Type Indoor or outdoor type. Select from the drop-down list.
Installed If the RP is installed, check the box.
RP-RPC Line Information Information about the communication cable connecting the RP and the
controlling RPC
Impedance The resistance of the communication cable
Box The specification of the switch box. For instance, a 200mW RP can have
the following specification:
Power Voltage – 220V AC
Dimension – 217mm x 258.5mm x 98mm
Weight – about 4.1 kg
MDF In Main Distribution Frame. The wiring arrangement which connects the
cable coming in from outside
MDF Out Main Distribution Frame. The wiring arrangement which connects the
cable going out from inside
Trunk The communication line between the RP and the RPC
RP Antenna Parameters The specification of the RP antennas
Latitude Latitude of the antenna location (string) (WGS94)
Longitude Longitude of the antenna location
Height Height of the antenna
RF Cable Length Radio Frequency cable length
Elevation Height above the ground
Azimuth The horizontal angle which the radiating lobe of an antenna makes in
angular degrees, in a clockwise direction, from a north-south line in the
northern hemisphere. In the southern hemisphere, the reference is the
south-north line.
Down Tilt The extent with which the antenna mechanically slopes downward
Type Name Name of the antenna type, for instance, OMNI antenna (Co-Liner antenna)
Select Image Selet an image file in .bmp format which presents the mounted RP.
View Image Use the Image Viewer to view the selected image file.
4-
Table 4-4: RP Status Window Field Description
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 17

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
28
4-
5. The window in the above window may not display all the information in one
screen. Use the horizontal and vertical scroll bars to see all the information.
4.2.4.3 RP-I/F Board Status
With the RP-I/F Board Status View window you can view or verify such RP
interface operational statuses as RP-IF#, installation, or warning.
1. To access the RP-I/F Status View window, click Status, then the Status
option, and then the RP-I/F Board option. This opens the RP-IF Status
View window on the RPC window, as illustrated in the figure below.
Figure 4-29: RP-IF Status View window
Field Name Description
RP-IF# The ID number of the RF-IF#. Each RPC can have 8 RP interface modules,
each of which can be connected to 4 RPs.
Inst
Warn The warning status of the RP interface.
Update Retrieve the latest status information.
Table 4-5: RP-IF Status View window Field Description
The installation status of the RP interface. Inst in the column Indicates that
the RP-IF is installed.
o indicates the existence of a warning.
- indicates no warning exits.
2. Click Update to display the current status.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 18

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
29
4.2.4.4 E1 Signal Status
Each RPC can have 4 E1 lines to communicate with the WLL/V5WLL.
However, the D-channel can be established on only one E1 line. The E1 line on
which the D-channel is established is named the master E1 and the other three E1
lines are named slave E1s. If the master E1 line is down, a slave E1 line will be
promoted by the system to become the master E1. The D-channel can be
established on this slave E1 line. The selection of the master E1 follows the
round-robin order.
Use the E1 Signal option to monitor and verify the operational status of the E1
signal, including four E1 interfaces, E1 warning, Layers 1 through 3, and other
status information.
1. From the Status main menu, select Status, and then E1 Signal. The E1
Signal Status window appears on the right frame of the RPC window, as
shown in the figure below. Another way to open the window is to click the
E1 Status button.
4-
Figure 4-30: E1 Signal Status Window
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 19

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
30
4-
Field Name Definition
E1#1 Corresponding to E1-I/F#1, Bch#1 - 30
E1#2 Corresponding to E1-I/F#2, Bch#31 - 60
E1#3 Corresponding to E1-I/F#3, Bch#61 - 90
E1#4 Corresponding to E1-I/F#4, Bch#91 - 120
Layer 1 Physical layer with SAPI=0,16
Layer 2 (SAPI=0) Data Link layer for call processing
Layer 2 (SAPI=16) Data Link layer for HOST interface
Layer 3 (SAPI=16) Network layer for HOST interface
Master Master E1 on which D-channel is established.
Slave Slave E1
Warning There is a warning for the E1.
No warn There is no warning for the E1.
Table 4-6: Signal Status Field Name Definition
2. Click Update to display the current status.
4.2.4.5 E1 Interface Status
Each RPC has four E1 interface boards to communicate with the WLL/V5WLL.
Use the E1 Interface option to verify E1 Interface status, monitor alarms, and
identify areas of trouble.
1. From the Status pull-down menu, click Status, and then Node-I/F Board.
This displays the E1 Interface status on the Status View window, as shown in
the figure below. Another way to open this window is to click the E1-
Interface Status button.
Figure 4-31: E1 Interface Status Window
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 20
RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
31
Field Name Description
E1-IF# E1 interface ID number
Inst Installation state configured by the system operation
data. There are two states: Inst/Uninst.
Maint Blocked manually by HOST or RMT
o indicates blockage.
- indicates no blockage.
Fault Cut off from the operation system due to the unit trouble.
o indicates the existence of error.
- indicates no error exists.
Warn Warning status:
o indicates the existence of warning
- indicates no warning exists.
Table 4-7Table 5-23: E1 Interface Status Window Field Description
3. Click Update to display the current status.
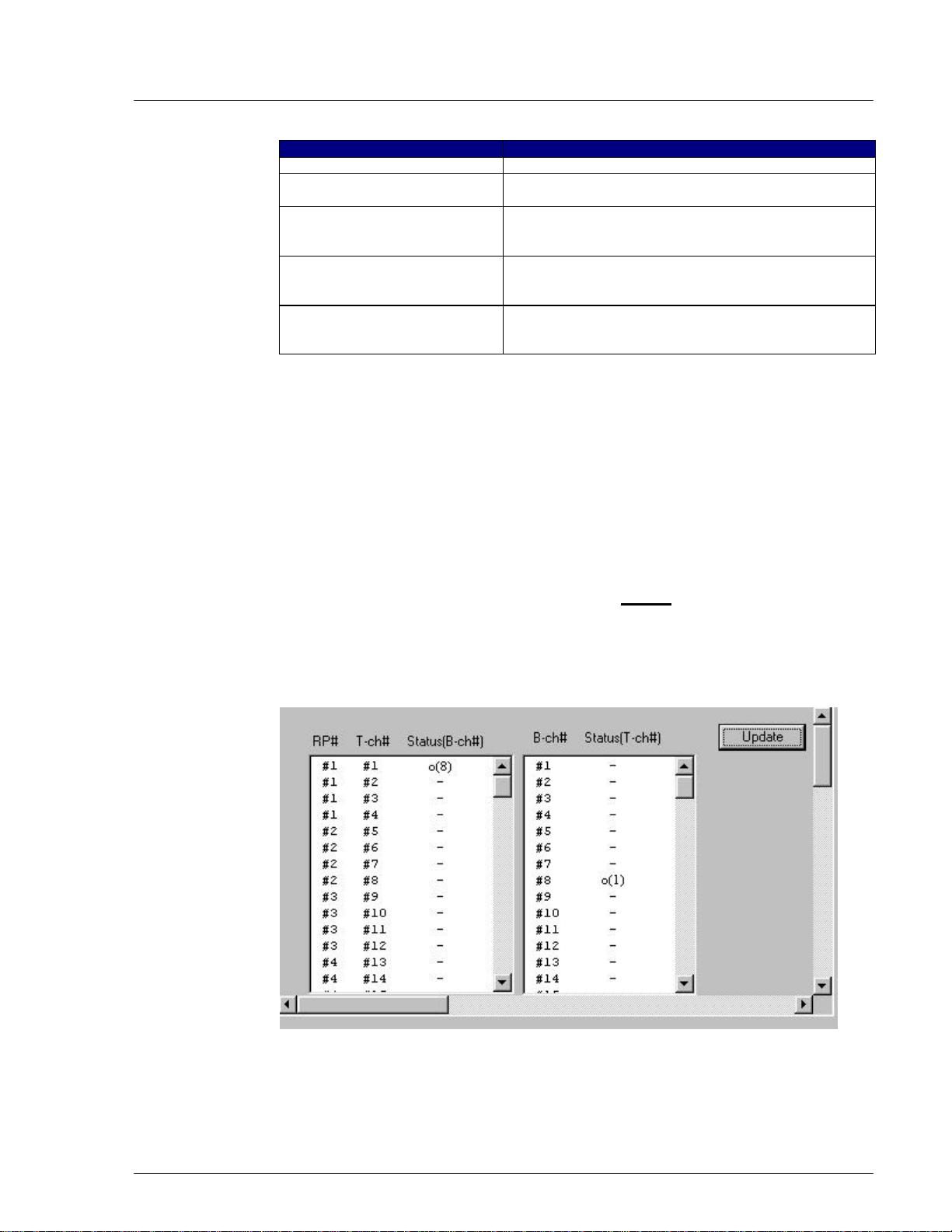
4.2.4.6 Air Channel Status
This function displays the state of wired/wireless channels in use. Use the
Channel Status View window to determine the availability of the channels.
4-
1. To access the Status View window, click the Status pull-down menu, then
Status, and then Air Channel. The channel status is displayed on the Status
View window, as shown in the figure below. The table following the figure
provides the description for each field on the Channel Status View window.
Figure 4-32: Channel Status View window
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 21
RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
32
4-
Field Name Definition
RP# RP ID number
T-ch# Traffic Channel ID number
B-ch# Bearer Channel ID number
Status(B-ch#) An o indicates the B channel enclosed in the parentheses is in use by
the T channel number. In the example above, B channel 8 is in use by
T channel 1.
Status(T-ch#) An o indicates the T channel enclosed in the parentheses is in use by
the B channel number. In the example above, T channel 1 is in use by
B channel 8.
Table 4-8: Channel Status Field Definitions
2. Click the Update button to display the current status.
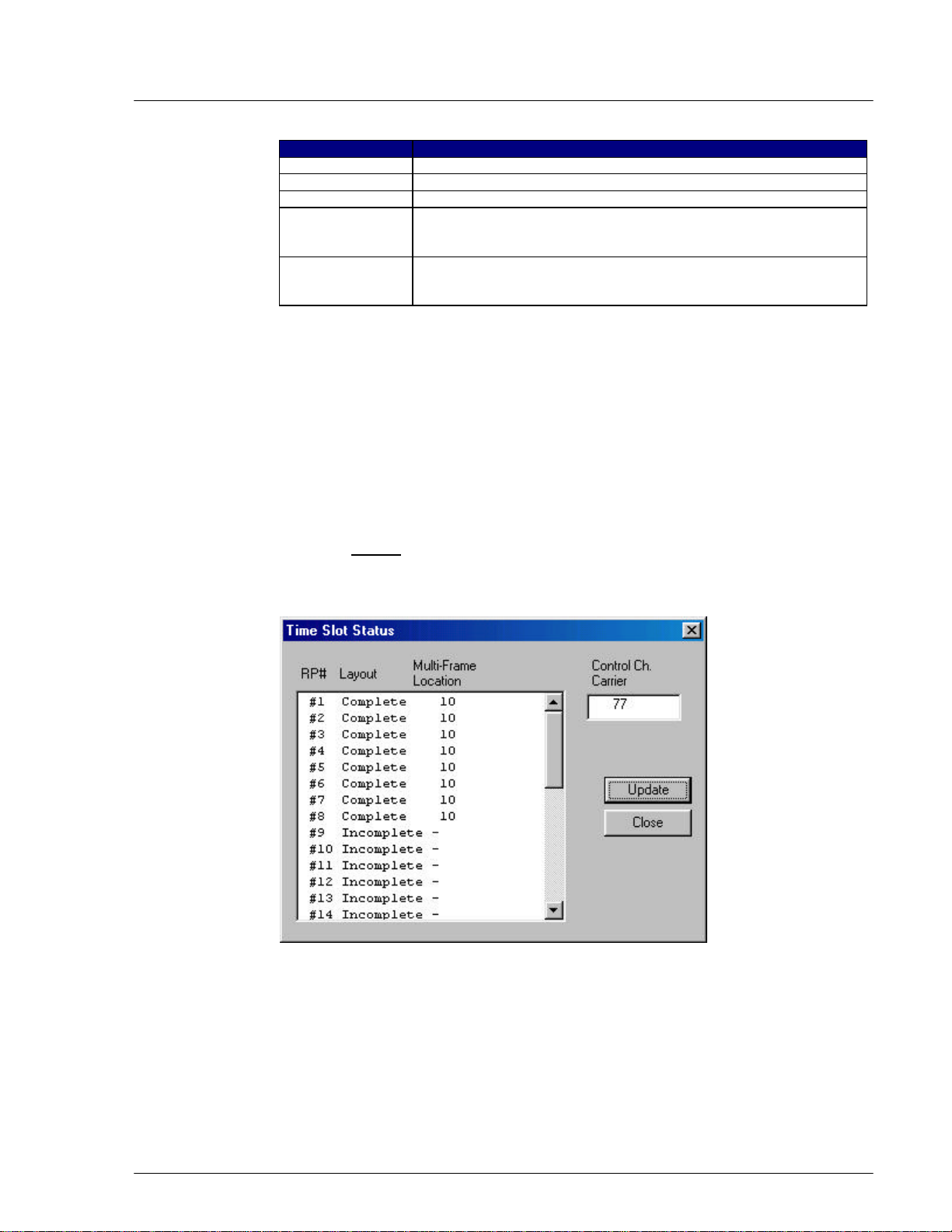
4.2.4.7 Time Slot Status
This function is used to display the configuration state of each RP’s control
channel.
1. From the Status main menu, click Status, and then TimeSlot Status. This
opens the Time Slot Status window, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 4-33: Time Slot Status Window
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 22

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
33
Field Name Description
RP# The ID number of the RP which transmits control channel LCCH
Layout Complete/Incomplete configuration.
Complete: RP has found the control channel.
Incomplete: RP has not been able to find the control channel (e.g.
due to interference).
Multi-Frame Location Position to which the RP transmits control channel LCCH
Control Ch. Carrier Channels over which the RP transmits control channel LCCH
Update Retrieve the latest status information.
Table 4-9: Time Slot Status Window Field Description
2. Click the Update button to get the latest status information. Click Close to
close the window.
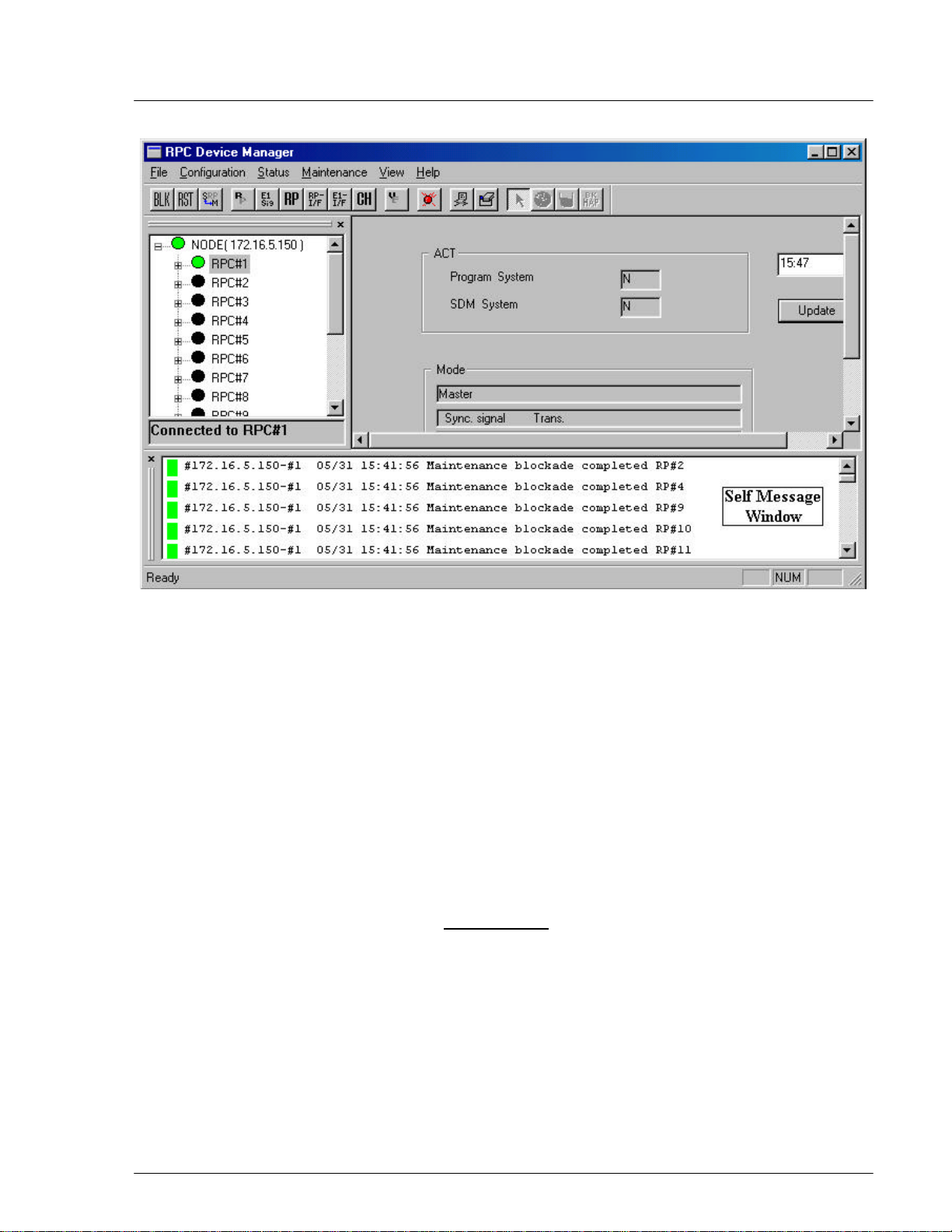
4.2.5 Self Messages
Whenever there is a change in configuration or a new warning is received, a
message will be displayed in the Self Message window, notifying of the situation.
The Self Message View window is located at the bottom of the RPC window.
Figure 4-34 illustrates the Self Message window with event messages.
4-
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 23
RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
34
4-
Figure 4-34: Self Message Window
This Self Message window displays only the event messages received from the
RPCs that are connected to the host RT. In the above example the host RT has
the IP address of 172.16.5 150. This RT controls 15 RPCs. The Self Message
window is updated without the need for special operation action.
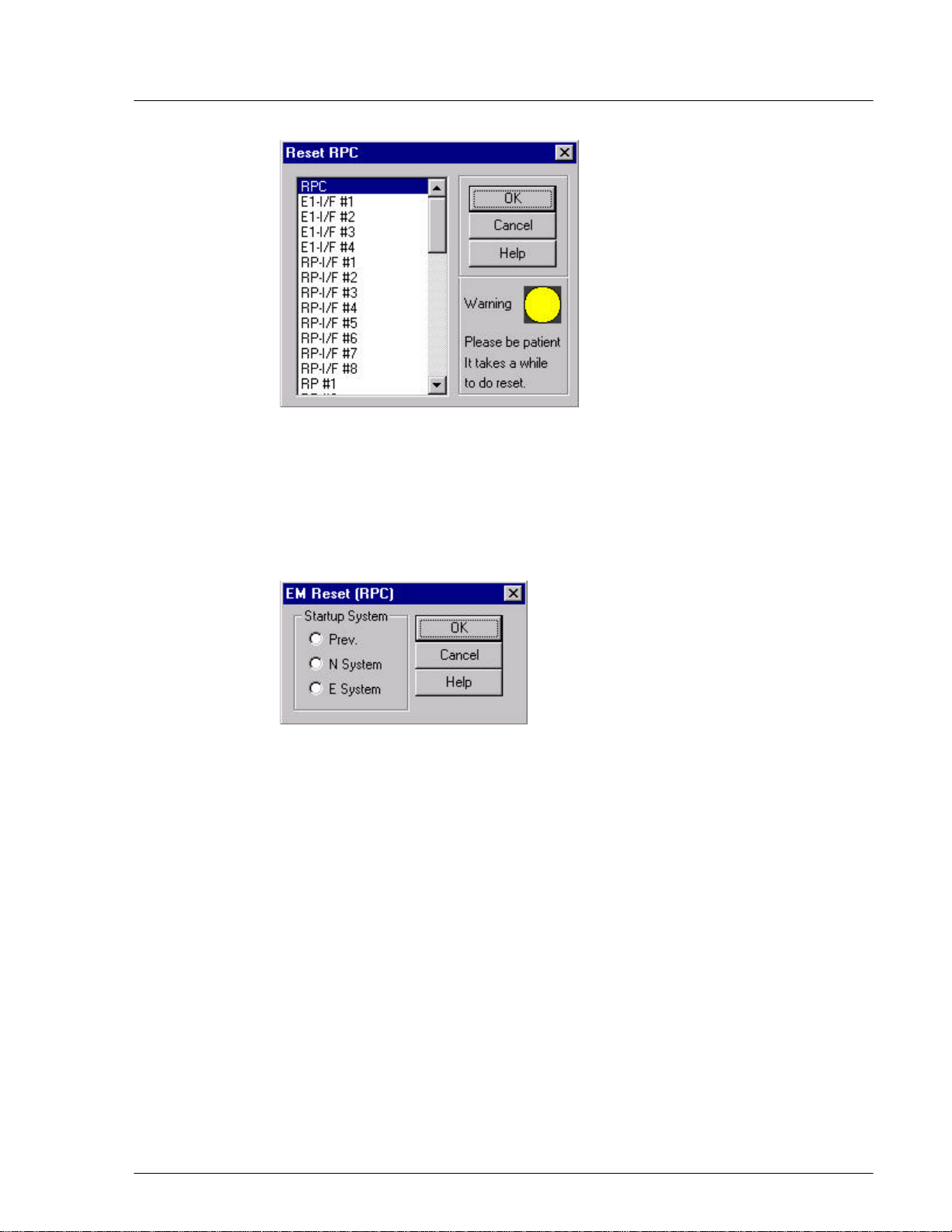
4.2.6 Reset RPC
When a system component experiences trouble and the problem cannot be solved,
it may be necessary to reset that component. RPC resetting may also be needed
after certain provisioning operation.
1. Select Reset from the Maintenance main menu. The Reset RPC window
appears as shown in Figure 4-35.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 24
RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
35
Figure 4-35: Reset RPC Window
2. Before resetting any component, verify that there are no calls active by
checking the air channel status. Select the target component and click on OK.
If an RPC is selected to be reset the following window opens.
4-
Figure 4-36: EM Reset Window
There are three options for Startup System.
- Prev
- N system
- E system
3. Select the system to be reset and click OK.
4. After EM reset is complete, the RPC is disconnected. To resume normal
operation, reconnect to the RPC.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 25

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
36
4-
4.2.7 Antenna Information
1. Select Antenna Information from the Maintenance main menu, and the
Antenna Information window opens as shown in Figure 4-37.
Figure 4-37: Antenna Information Window
2. Antenna name and type are read from the database. If new information is
added, click the Add New button and the new information is saved into the
database.
3. If users want to add more pattern resolution, click Add and the Add a Point
window opens as shown in Figure 4-38. Users enter the values and click OK.
The values are added into the list box of the Antenna Information window.
Figure 4-38: Add a Point Window
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 26

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
37
4.2.8 RPC Connection
To change the number of RPCs to be connected, select RPC Connection from the
Configuration main menu, the Connect RPCs window displays as shown in
Figure 4-39. Click the check button of the target RPCs to be connected and click
OK to connect to the selected RPCs.
4-
Figure 4-39: Connect RPCs Window
4.2.9 Version Window
1. From the Configuration pull-down menu, click the Version option. This
opens the Version window, as illustrated in the figure below.
Figure 4-40: Version Window
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 27

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
38
4-
2. There are two columns in this window. The left column lists the item names.
The right column shows the corresponding version. This window displays the
version of each item in operation.
4.3 Manage RPC Data
RPC data include program data and operation data. RPCs have two plane
memory areas for the program data and two plane memory areas for the operation
data. As a result, the RPC data can be categorized into the following types:
1. For the program data
• PDM (Program Data Memory)-#N
• PDM (Program Data Memory)-#E
2. For the operation data
• SDM (System Data Memory)-#N
• SDM (System Data Memory)-#E
In effect, the RPC continues to run based on 1 SDM and 1 PDM. Therefore,
SDM and PDM have two types of operation status:
1. Active (ACT): the SDM and PDM which are used for RPC running.
2. Standby (STY): the SDM and PDM which are not used for RPC running.
Suppose that an RPC ran based on SDM-#N and PDM-#E, the operation status for
the RPC data systems would be:
• SDM-#N: ACT
• SDM-#E: SBY
• PDM-#N: SBY
• PDM-#E: ACT
These data systems can be manipulated through the options under the
Configuration and Maintenance main menus. Use the procedure in this section
to manage the RPC data.
4.3.1 Program Load
The Program Download option of the Maintenance pull-down menu offers the
function of downloading the program data from Netman 2000 to the SBY PDM of
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 28

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
39
the target RPC and putting it into operation by switching to the new program data
at the specified time.
F NOTE: It is recommended that program download be done using RMT via
WLL/V5WLL.
During the operation the system prompts you to disconnect the target RPC. Click
OK to disconnect it. After the operation reconnect the RPC.
1. Click the Maintenance main menu, select the Program Download option,
and then the Program Load option. This opens the File for Program
Download window, as shown in the figure below.
4-
Figure 4-41: File for Program Download Window
F NOTE: The program file must be in the Netman directory. The proper path
should be: C:\program files\UTStarcom\Netman\data. This rule applies to other
data files and data operation.
2. Select the program data file to be downloaded. The program data file must be
of the .prg or .PRG type. When the Open button is clicked, a confirmation
dialog box opens, as displayed below.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 29

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
40
4-
Figure 4-42: Download Confirmation Dialog Box
3. Click OK, and the Program Download window opens, as shown in the figure
below.
Figure 4-43: Program Download Window
Field Name Description
RPC The ID number of the RPC to which the program data are to be
Immediate switch after
loading
Specified switch date If selected, the RPC will switch to the new program data at the
Table 4-10: Program Download Window Field Description
4. Select the RPC to which the program data are to be downloaded, and make a
selection in the Operation Switch Timing block. Click OK. The program
data are downloaded to the SBY PDM.
5. After the data have been downloaded, click OK.
4.3.2 Program Switch
downloaded. Click the Arrow button to make a selection.
If selected, the RPC will switch to the new program data
immediately after downloading.
date and time specified in the two fields provided.
Use the Program Switch option to switch the operation status of the SBY PDM
and the ACT PDM.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 30

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
41
1. From the Maintenance pull-down menu, select Program Download, and then
Program Switch. The Program Switch window appears, as shown in the
figure below.
Figure 4-44: Program Switch Window
2. This window is exactly the same as the previous one. Make a selection in the
Operation Switch Timing block. If you click the Specified switch date
radio button, specify the date and time for the new program to go into
operation. Click OK to accept the setting or Cancel to stop the transaction.
After switching at the specified time, RPC runs based on the SBY PDM and
each PDM status is switched.
4-
4.3.3 Data Load
Operation data can be loaded and put into operation by selecting the Service Data
options. Use the procedure in this section to load the operation data to the SBY
SDM and to specify the time to switch to the new data.
1. From the Configuration pull-down menu, select Service Data, then Data
Download, and then Data load. This opens the File for Data Download
window, as illustrated in the figure below.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 31

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
42
4-
Figure 4-45: File for Data Download Window
2. Select the data file to be downloaded. The data file must be of the .DAT or
.EEP type. When the Open button is clicked, a confirmation window opens.
Click OK. This opens the Service Data Download window, as shown in the
figure below.
Figure 4-46: Service Data Download Window
3. Select the target RPC to which to download the data. Make a selection in the
Operation Switch Timing block. If the Specified switch date radio button is
selected, specify the date and time for the switch operation to be executed.
Click OK. The operation data is downloaded to the SBY SDM.
4.3.4 Data Switch
Use the Data Switch option to specify the date and time to switch to the SBY
SDM.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 32

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
43
1. From the Configuration pull-down menu, select Service Data, then Data
Download, and then Data Switch. The Service Data Switch window
appears, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 4-47: Service Data Switch Window
2. Select the target RPC. Make a selection in the Operation Switch Timing
block. If you click the Specified switch date radio button, specify the date
and time for the switch operation to be executed. Click OK to accept the
setting. After switching at the specified time, RPC runs based on the SBY
SDM and each SDM status is switched.
4-
4.3.5 Read Data
Use this function to read the operation data from the current RPC to Netman 2000
while the RPC is operating.
1. From the Configuration main menu, select Service Data, and then Read
Data. This opens the Read System Service Data window, as displayed in the
figure below.
Figure 4-48: Read System Service Data Window
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 33

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
44
4-
Field Name Description
SDM Selection Select one of the two operation data systems: SDM-
#N or SDM-#E. Any one can be ACT or SBY.
N System One of the two operation data systems
E System One of the two operation data systems
Table 4-11: Read System Service Data Window Field Description
2. Make a selection in the SDM Selection block and click OK.
3. The following window appears, prompting for the folder and file name in
which to save the service data after reading out.
Figure 4-49: Save File after Reading Service Data Window
4. Select a folder and enter a file name. The file name must have the extension
of .dat or .eep. In addition, the file name must start with W and have 8
letters. Then click Save.
5. A confirmation box appears. Click Yes to start the reading of the data.
4.3.6 Write Data
Use the procedure in this section to load the operation data to both the SDMs
while the RPC is operating. As for this command, automatic switching is not
supported. After the implementation of the command, the RPC still runs based on
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 34

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
45
the old loaded operation data. For the RPC to run based on the newly loaded
operation data, the RPC needs to be reset.
1. From the Configuration main menu, click Service Data, and then Write
Data. This opens the Write System Service Data window, as shown in the
figure below.
Figure 4-50: Write System Service Data Window
4-
2. Click the Write radio button and then click OK. The Select File for Writing
Service Data window appears, as illustrated in the figure below.
Figure 4-51: Select File for Writing Service Data Window
3. Select the target file with either a .dat or a .eep extension and click Open.
The system overwrites the service data on both the SDMs of the RPC.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 35

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
46
4-
4.3.7 Copy Data
This function is used to copy the operating data from the ACT SDM to the SBY
SDM. The automatic SDM switching is not supported for this function.
1. From the Configure main menu, click Service Data, and then Write Data.
This opens the Write System Service Data window, as shown in the figure
below.
Figure 4-52: Write System Service Data Window
2. Click the Copy radio button and then click OK. A confirmation dialog box
appears, as illustrated in the figure below. Click OK to confirm the copying
command.
Figure 4-53: Confirmation Dialog Box
4.3.8 Edit Data
RPC operation data contain three categories:
1. Service data 1: RP installation
2. Service data 2: Group control configuration
3. Service data 3: System parameters
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 36

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
47
Use this function to edit an existing operation data file while the RPC is
operating.
F NOTE: Operation data must be edited locally in a file, and then downloaded to
the system.
4.3.8.1 Service Data 1: RP Installation
1. From the Configuration main menu, click the Service Data option, and then
the Edit Data option. This brings up the Specify File for Edit window, as
shown in the figure below.
4-
Figure 4-54: Specify file for Edit Window
2. Select the target .dat or .eep file and click Open. The system edits all the files
with any one of the two suffixes. The Edit of Service Data 1 window opens,
as shown in the figure below.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 37

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
48
4-
Figure 4-55: Edit of Service Data 1 Window
Field Name Description
RP# RP ID number
Inst. Set “installed” or “not installed” for RPs according to
RP installation plan.
Phantom The power is supplied by the RPC.
Local The power is supplied by the RP power unit.
Save Save the setting to a local file.
Next Switch to the next Service Data window.
Cancel Cancel the editing.
Switch 1,2,3 Switch to one of the three Service Data windows.
Table 4-12: Edit of Service Data 1 Window Field Description
3. For each installed RP, enter a √ in the Inst. row. For each installed RP,
specify the power source by clicking on either the Phantom button or the
Local button. For WLL, the power source is Phantom. Local is for future
use when the power is 20 milliwatts or higher.
4.3.8.2 Service Data 2: Group Control Configuration
1. To get to the Edit of Service Data 2 window, click Next or Switch 2. The
Edit of Service Data 2 window opens, as shown in the figure below.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 38

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
49
Figure 4-56: Edit of Service Data 2 Window
4-
Field Name Description
RP-I/F RP interface ID number
Group # Group ID number
RP# RP ID number
Master Master/Slave status of the RPs
Save Save the Service Data toa a file.
Next Switch to the next window
Table 4-13: Edit of Service Data 2 Window Field Description
F NOTE: RP ID numbers are defined according to the connected physical port
numbers on the RP interface boards, as listed below:
RP-IF#1 port 1 ----- RP#1
RP-IF#1 port 2 ----- RP#2
RP-IF#1 port 3 ----- RP#3
RP-IF#1 port 4 ----- RP#4
RP-IF#2 port 1 ----- RP#5
…..
RP-IF#3 port 1 ----- RP#9
…..
RP-IF#8 port 1 ----- RP#29
RP-IF#8 port 2 ----- RP#30
RP-IF#8 port 3 ----- RP#31
RP-IF#8 port 4 ----- RP#32
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 39

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
50
4-
2. This window is for the configuration of Group Control. Group Control
maximizes the number of channels available for traffic by allowing one
control channel to control up to 8 RPs (up to 31 traffic channels). A group
can be set up only within two adjacent RP interface boards. Group members
must be within the two RP Interface boards. For each RP, enter the group
number and designate the master. In the above window, 7 RPs on RP
Interface card 5 and 6 are in group 17 with the master RP designated as RP
number 17. The master RP must be the RP with the lowest RP number in the
group. The RPs that are not in group control must be designated as their own
masters and have their own group numbers, as is the case for RP# 21 in the
above figure.
4.3.8.3 Service Data 3: System Parameters
The third Edit of Service Data window contains system parameters. It is not
necessary to administer the parameters, as they are set at the factory. Users can
only change the relevant values for the parameters. Click on Next or Switch 3 to
open the Edit of Service Data 3 window, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 4-57: Edit of Service Data 3 Window
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 40

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
51
Field Name Definition
No. Item sequence numbers, starting from 1
Value Specified value for the item. The value can be selected from the arrow
drop-down list.
Item Item name and value description
Basic Basic value
Unit Item value unit
Min The minimum value which can be specified for the item
Max The maximum value which can be specified for the item
HEX val. Switch between the hexadecimal and the decimal value
Button Name Description
Target Select the target PRC ID number to display its system parameters.
Item Only item names are displayed on the right column.
Basic Basic value, unit value, and item names are displayed on the right
column.
Range Maximum value, minimum value, unit value, and item names are
displayed on the right column.
< Scroll the window downward one line at a time.
> Scroll the window upward one line at a time.
<< Scroll the window downward one page at a time.
>> Scroll the window upward one page at a time.
Save Save the value setting.
Top Go to Service Data 1 window.
4-
Table 4-14: Edit of Service Data 3 Window Field Definition
There are three different windows for this function: Item, Basic, and Range. Use
the View Block to switch to different windows. Edit the data as necessary and
click Save. A confirmation box appears, prompting: “Current file will be replaced
by this contents. OK?” Click Yes to confirm or No to stop the transaction.
The operation data in the Item block contain many system parameters. They are
for view only. Users should use the Arrow drop-down list in the Value field to
make any necessary change to the setting. Each of the system parameters in the
Item block is described as follows:
Call discrimination code
The length of the Call Discrimination Code data field is 48 bits, but the
last 6 bits are not used. So the remaining 42 bits are used for call
discrimination code. The value determines the RP-ID (CS-ID). And it
needs to be unique among all RPCs. The following diagram describes
how the 42 bits are split into several divisions.
Call Discrimination Code
-----------------------------------------------------42 bits-----------------------------------------------------Operation ID Code
----------9 bits---------
---------------------------------------33 bits-------------------------------------Paging Area Number
-------------------------22 bits-------------------
Public System Additional ID
Additional ID
--------11 bits--------
-----
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 41

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
52
4-
Operator ID Code: MSB is always set to "1". The remaining 8 bits are
used for Operator ID. The Operator ID’s of all RPs that connect to the
same RPC take the same value, and the value is equal to the setting value
of this data field.
Paging Area Number refers to the area where the call is broadcast for the
FSU or PS that has location registration for that area. In effect, PS doesn't
need to request location registration while it stays inside the area, even if it
switches RPs. The Paging Area Number of all RPs that connect to the
same RPC takes the same value, and the value is equal to the setting value
of this data field.
Additional ID (11bits) of this data field is set from "00000000000" to
"11111100000". The upper 6 bits of the Additional ID of the RPs that
connect to the same RPC take the same value, and the value is equal to the
setting value of this data field.
The first 37 bits of this Call Discrimination Code correspond to the RP-ID
(CS-ID) of each RP that connects to the same RPC, and the value of the 37
bits is the same for all the RPs which connect to the same RPC. The last 5
bits are unique for each RP under the same RPC, as illustrated below:
RP #
Last 5 bits
RP #1 RP #2 RP #3 RP #4 …… RP #32
00000 00001 00010 00011 …… 11111
For instance, when the field data (48bits) of the Call Discrimination Code
are 9E 00 00 00 03 80 (HEX), the RP-ID (42 bits) of RP#4 is as follows:
1001 1110 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0011 11 (Binary)
Operator ID: 1001 1110 0 (Binary)
Paging area: 000 0000 0000 0000 0000 000 (Binary)
Additional ID: 0 0000 0011 11 (Binary)
F NOTE: The RP-ID that is described in this section is used between RP/RPC and
FSU/PS. The RP-ID is also defined between WLL/V5WLL and RPC but the
length is 48 bits. This RP-ID is generated by the RP-ID of the air interface but is
not the same as the RP-ID of the air interface. RPC can translate between the
RP-ID of the WLL/V5WLL/RPC and the RP-ID of the air interface..
E1 interface install setting
This item is used to configure E1 interface install setting (1), as described
below:
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 42

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
53
MSB LSB
Bit 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0 0 0 0 X X X X
Bit 1 corresponds to the installation status of E1-IF#1
Bit 2 corresponds to the installation status of E1-IF#2
Bit 3 corresponds to the installation status of E1-IF#3
Bit 4 corresponds to the installation status of E1-IF#4
Installation status: Installed à 1
Not installed à 0
Set "installed" or "not installed" for each E1-IF according to the E1-IF
installation plan. Set "installed" for all E1-IF’s for future expansion.
E1 interface install setting (2) is reserved for system expansion.
LCCH frequency (Control carrier frequency)
4-
This item is used to set LCCH frequency of the system. The system can
use one carrier from No. 1 to No. 77. This value is assigned by the
operator or Government. For instance, if LCCH frequency is No.71, the
setting value is 71 (HEX: 4D). In one-service area LCCH frequency and
Operator ID must be the same for all RPs and RPCs.
Channel frequency use control (1-8), (9-16) ….. (73-77)
The item is used to set the availability of Traffic channels. Every channel
frequency (carrier number 1 through 77) can be set "available" or
"unavailable". For Channel frequency use control (1-8) the values are set
as follows:
MSB LSB
Bit 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
X X X X X X X X
Bit 1 corresponds to Channel frequency No.1 (carrier No.1)
Bit 2 corresponds to Channel frequency No.2 (carrier No.2)
................
Bit 7 corresponds to Channel frequency No. 7 (carrier No.7)
Bit 8 corresponds to Channel frequency No. 8 (carrier No.8)
Setting value: Available à 1
Unavailable à 0
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 43

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
54
4-
For instance, if Channel frequency No. 1, 3, 5 are available and Channel
frequency No. 2, 4, 6, 7, 8 are unavailable, the values are set as follows:
Channel frequency use control (1-8): 0001 0101(Binary) (HEX: 15)
Channel frequency use control (9-16) ….. (73-77) are set in the same way.
The previous and the next Channel frequency of LCCH frequency must be
set "Unavailable" for traffic channel to avoid the interference.
Loudness control value (input loudness value)
This item is used to set the RPC input loudness control value, as described
below:
MSB LSB
Bit 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0 0 0 y x x x x
Bit 1-4 (xxxx) are the value of loudness, as listed below:
Real level Bit 4 3 2 1
0 dB à 0 0 0 0
2 dB à 0 0 0 1
4 dB à 0 0 1 0
6 dB à 0 0 1 1
...............
Bit 5 is the value of sign.
Sign Bit 5
à 1
à 0
...................
For instance, if the input loudness of RPC needs to be set to + 8 dB, the
setting value is as follows:
0001 0100 (Binary)
This value is determined in accordance with the system level plan.
Loudness control value (output loudness value)
This item is used to set the RPC output loudness control value, as
described below:
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 44

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
55
MSB LSB
Bit 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0 0 0 y x x x x
Bit 1-4 (xxxx) are the value of loudness, as listed below:
Real level Bit 4 3 2 1
0 dB à 0 0 0 0
2 dB à 0 0 0 1
4 dB à 0 0 1 0
6 dB à 0 0 1 1
...............
Bit 5 is the value of sign.
Sign Bit 5
à 1
à 0
...................
For instance, if the output loudness of RPC needs to be set to + 8 dB, the
setting value is as follows:
4-
0001 0100 (Binary)
This value is determined in accordance with the system level plan.
Loudness control value (DTMF signal loudness value)
In the case of PS origination, dialing information is transferred as a
message from the PS to the RPC. The RPC generates the DTMF signal
tone according to the received message. This item used for the setting of
output DTMF signal loudness, as described below:
MSB LSB
Bit 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0 0 0 y x x x x
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 45

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
56
4-
Bit 1-4 (xxxx) are the value of loudness, as listed below:
Real level Bit 4 3 2 1
0 dB à 0 0 0 0
2 dB à 0 0 0 1
4 dB à 0 0 1 0
6 dB à 0 0 1 1
...............
Bit 5 is the value of sign.
Sign Bit 5
à 1
à 0
...................
For instance, if the output loudness of RPC needs to be set to + 8 dB, the
setting value is as follows:
0001 0100 (Binary)
This value is determined in accordance with the system level plan.
DTMF sound sending interval value
In the case of PS origination, dialing information is transferred as a
message from the PS to the RPC. The RPC generates the DTMF signal
tone according to the received message. This item is used for the setting
of DTMF minimum pause of the DTMF signal. The value (unit: msec) is
directly set in the value field.
For instance, if the sending interval time needs to be set to 80 msec, the
setting value is "50" (HEX).
DTMF sound sending time value
In the case of PS origination, dialing information is transferred as a
message from the PS to the RPC. The RPC generates the DTMF signal
tone according to the received message. This item is used for the setting
of DTMF sending time of the DTMF signal. The value (unit: msec) is
directly set in the value field.
For instance, if the sending time needs to be set to 80 msec, the setting
value is "50" (HEX).
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 46

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
57
Country number 1, 2
This item is used for the setting of Country Code. The Country code is
used to represent the country which assigns the RP identification code.
System type
This item is used for the setting of system type. This system is applicable
for the system. The system type is 3. The coding is "0000 0100" (Binary).
Standby zone selection level
This item is used for the setting of air-interface.
Standby zone hold level
This item is used for the setting of air-interface.
Recalling-type handover process level
4-
This item is used for the setting of air-interface.
Recalling-type handover destination zone selection level
This item is used for the setting of air-interface.
Channel switching FER threshold value
This item is used for the setting of air-interface.
Reservation/Area information report status number
This item is used for the setting of air-interface.
TCH switching-type handover process level
This item is used for the setting of air-interface.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 47

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
58
4-
FSU mobility limitation
This item is used for the control of FSU mobility limitation. Depending
on the setting value, one mode might be that RPC reports RP-ID to
WLL/V5WLL for mobility, the other mode might be that RPC doesn't
report RP-ID to WLL/V5WLL for mobility. In the case that RPC reports
RP-ID to WLL/V5WLL, WLL/V5WLL controls FSU mobility in
accordance with the subscriber setting. In the case that RPC doesn't report
RP-ID, FSU mobility isn't limited regardless of the subscriber setting. The
way of setting is as follows,
Bit 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 à The mode that RPC doesn’t report RP-ID
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 à The mode that RPC reports RP-ID
4.3.9 Change Data (RP Installation)
Use the procedure in this section to change the operation data for the selected
RPC. The diagrams displayed in this section are very similar to those in the
previous section. The only difference is that there are two configuration windows
instead of three.
1. To change the operation data for an RPC, click the Configuration main menu
and select the Service Data option, then the Change Data option, and then the
RP Installation option. This opens the RP Installation (Group
Composition 1) window, as displayed in the figure below.
F NOTE: Before making any changes to the operation data, be sure to block the
E1/IF and RP/IF. After the setting is modified, the RP/IF will restart itself.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 48

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
59
Figure 4-58: RP Installation (Group Composition 1) Window
4-
2. This window is used to configure RP connection. For each installed RP, enter
a √ in the Inst. row. For each installed RP, specify the power source by
clicking on either the Phantom button or the Local button. Phantom means
the power is supplied by the RPC. For WLL, the power source is Phantom.
3. To get to the RP Installation (Group Composition 2) window, click Next or
Switch 2. The RP Installation (Group Composition 2) window is shown in
the figure below.
Figure 4-59: RP Installation (Group Composition 2) Window
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 49

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
60
4-
4. This window is for the configuration of Group Control. Group Control
maximizes the number of channels available for traffic by allowing one
control channel to control up to 8 RPs (up to 31 traffic channels). Each group
contains two RP Interface boards. Group members must be within the two RP
Interface boards. For each RP, enter the group number and designate the
master. In the above window, 7 RPs on RP Interface boards 5 and 6 are in
group 17 with the master RP designated as RP number 17. The master RP
must be the RP with the lowest RP number in the group. The RPs that are not
in group control must be designated as their own masters and have their own
group numbers, as is the case for RP# 21 in the above figure.
5. After editing the operation data click OK. A dialog box opens for
confirmation, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 4-60: Confirmation Dialog Box
6. Click Yes to confirm, or No to stop the transaction. If the Version
Confirmation window opens when Yes button is clicked, verify that the
version is correct and then click OK.
4.3.10 Change Data (E1-IF Board Installation)
Each RPC can have 4 E1 interface boards to communicate with WLL/V5WLL.
Use the steps in this section to select the target E1 interfaces to be installed or
uninstalled.
1. First use the Blockade option under Unit Control to block the target E1
interfaces.
2. From the Configuration pull-down menu, select Service Data, then Change
Data, and then E1-I/F Board Installation. This opens the E1-I/F Board
Installation window, as shown in the figure below.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 50

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
61
Figure 4-61: E1-IF Board Installation
3. Check or uncheck the boxes in front of the target E1 interfaces to be installed
or uninstalled, and click OK.
4.3.11 Change Data (Data Value)
Use this function to change the operation data value.
4-
F NOTE: This feature is not recommended. Use with care.
1. From the Configuration main menu, click Service Data, then Change Data,
and then Data Value. The Data Value Change window opens, as illustrated
in the figure below.
Figure 4-62: Data Value Change Window
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 51

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
62
4-
Field Name Definition
No. Item sequence numbers, starting from 1
Value
Item Item name and value description
Basic Basic value
Unit Item value unit
Min The minimum value which can be specified for the item
Max The maximum value which can be specified for the item
HEX addr. Switch between hexadecimal and decimal value
Button Name Description
Item Only item names are displayed on the right column.
Basic Basic value, unit value, and item names are displayed on the right
Range Maximum value, minimum value, unit value, and item names are
< Scroll the window downward one line at a time.
> Scroll the window upward one line at a time.
<< Scroll the window downward one page at a time.
>> Scroll the window upward one page at a time.
OK Implement the command.
Table 4-15: Data Value Change Window Field Description
Specified value for the item. The valid values are displayed in the Item
block and can be selected from the arrow drop-down list.
column.
displayed on the right column.
2. There are three different windows for this function: Item, Basic, and Range.
Use the View block to switch between different windows. Refer to Section
4.3.8.3 for the detailed description for the Value field and the Item block.
3. Make necessary changes and click OK to close the window.
4.4 Manage RPC Alarms
This section discusses several aspects concerning the RPC warning and alarm
history. Through the RPC device manager, we can update and clear the alarm, or
save the alarm history to files for further analysis.
The warning messages are also displayed in the Status View windows for RPCs,
RPs, and interfaces, as described in Section 4.2.4.
4.4.1 Warning Status
The RPC device manager can display currently occurring warnings about the
RPC, RP, E1 interface, and RP interface.
1. On the Main View window, click the RPC R2.4 node. Get connected to the
target RPC.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 52

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
63
2. To view the RPC warnings, click the Status main menu, and select the
Warning option. The Warning window appears, as displayed in the figure
below. Another way to open the window is to click the Warning button.
4-
Figure 4-63: Warning Window
3. Click the Update button to retrieve the latest information. The color of the
small rectangle in front of each warning message indicates the alarm’s
severity.
4. After viewing the warning, click Close to close the window.
4.4.2 Alarm History
The Alarm History option provides access to a chronological log of all the RPC,
RP, interfaces, and synchronization warnings. This log may contain information
useful in diagnosing equipment malfunctions.
• Red - Major Alarm
• Yellow - Minor Alarm
• Green - No Alarm
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 53

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
64
4-
1. To view the log of the Alarm History, select the Alarm History option from
the Status main menu. The Alarm History window appears as shown in the
figure below. Another way to open the window is to click the Fault History
button.
Figure 4-64: Alarm History Window
F NOTE: This log has a capacity of storing 127 messages. When this limit is
reached, the oldest message is deleted when the newest one is added.
2. Click Update to display the historical information. To clear the present alarm
history, click Clear. The contents of this window can be saved to a file for
further analysis. Click the Save button and specify a file name.
3. Click Close to close this window.
4.5 Reset RPC
When an RPC or its other components experience trouble and the problem cannot
be solved, it may be necessary to reset the component. Use the following
procedures to reset an E1 interface, an RP interface, an RP, or an RPC.
F WARNING: Do not directly reset a unit in operation since this will cause active
subscriber calls to be dropped. Before resetting a unit, block the unit temporarily
by resorting to the Configuration à Unit Control à Blockade option. Check
the Channel Status to verify that there are no active calls. Click the Channel
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 54

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
65
button or click Air Channel on the Unit View window of the RPC window to
open the Channel Status View window. After resetting, unblock the unit.
1. On the Main View window, click the target RPC-DM node and connect to the
RPC. This opens the RPC window.
2. Select the Reset option from the Maintenance pull-down menu or click the
Reset button. The Reset window appears, as shown in the figure below.
4-
Figure 4-65: Reset RPC Window
3. Select either an RP, an E1 interface, an RP interface, or the entire RPC. Click
OK. The system resets the unit, returns it to operation, and sends a message to
the Self Messages window. Suppose that the RP#1 of the RPC#2 were reset,
the window would be like the figure below.
Figure 4-66: Self Messages Window for Reset
4. If an RPC needs to be reset, select the RPC and click OK. This brings up the
EM Reset (RPC) window as shown in the figure below.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 55

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
66
4-
Figure 4-67: EM Reset (RPC) Window
Field Name Description
Startup System Determine which SDM to use for operating RPC after resetting.
Prev. Previous ACT SDM. After resetting, RPC starts up and runs based on
the previous ACT SDM.
N System SDM-#N. After resetting, RPC starts up and runs based on SDM-#N.
E System SDM-#E. After resetting, RPC starts up and runs based on SDM-#E.
Table 4-16: EM Reset (RPC) Window Field Description
F NOTE: Refer to Section 4.3 for detailed description of the N and E systems.
5. There are three options in the Startup System block. Select the system to
start with and click OK.
6. A confirmation window appears, as displayed in the figure below. Click OK
to reset the RPC or Cancel to stop the transaction.
Figure 4-68: Reset Confirmation Window
7. After EM reset is complete, the PC will disconnect from the RPC. To resume
normal operations, reconnect to the RPC.
8. Click the RPC Status button to open the RPC Status View window to verify
that the component is in operation.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 56

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
67
4.6 RPC Statistics
The function of RPC statistics can generate an RPC traffic report that displays the
traffic status for either the entire period and all the RPCs and RPs, or the specific
period and an individual RPC or RP. This is a useful feature for analyzing the
RPC traffic. In addition, the RPC statistics can also create the RP status report.
4.6.1 RPC Traffic Report
1. To generate the RPC/RP traffic report, click the Statistics main menu on the
Client View window and select RPC Statistics Report. The criteria setting
window opens, as shown in the figure below.
4-
Figure 4-69: Criteria Setting Window
2. Select the criteria for the RPC traffic data to be retrieved and click the Refresh
button. After a few seconds the RPC/RP Traffic Report appears on the
screen, as illustrated in the figure below.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 57

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
68
4-
Figure 4-70: RPC/RP Traffic Report Window
F NOTE: Sometimes nothing happens after the Refresh button is clicked. The
reason is that the RPC board may have been reset by RTs and there is no
synchronization between the RPC device manager and the RPC board. In that
case go to the RPC System View window, click open the Configure main menu,
and select Set Time. The Set Time window opens. Click OK to synchronize the
RPC device manager with the RPC board. After the traffic data pile up in the
board the RPC device manager can retrieve the traffic report. This rule also
applies to the RP Status Report operation, as described in Section 4.6.3.
3. Figure 4-70 presents the traffic report for each of the 32 associated RPs. The
report is organized in such a way that each block displays all the 29 traffic
statistics elements for an RP for the period of one hour. Refer to the following
figure for the description of each of the 29 statistics elements.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 58

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
69
4-
Figure 4-71: Description of RPC Traffic Status
4.6.2 RPC Outstanding Alarms
RPC Outstanding Alarms list all the alarms for each RPC which haven’t been
fixed.
1. To display the RPC outstanding alarms, click the Statistics main menu on the
Client View window and select the RPC Outstanding Alarms option. This
brings up the RPC Outstanding Alarm window, as shown in Figure 4-72.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 59

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
70
4-
Figure 4-72: RPC Outstanding Alarm Window
2. Click the Refresh button to retrieve the current outstanding alarms.
4.6.3 RP Status Report
This feature displays the blockade and warning statuses for all the 32 RPs of the
selected RPC.
1. To view the report, click the Statistics main menu and select the RP Status
Report option on the Client View window. The RP Status Report page opens
on the Main View window, as shown below.
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 60

RPC/RP Manual RPC/RP Configuration
71
4-
Figure 4-73: RP Status Report Page
2. Select the target RPC on the left frame to bring up the status report for the
associated RPs.
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 61

RPC/RP Configuration RPC/RP Manual
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
72
4-
Page 62

A
Specifications
A Specifications
A.1 RPC Specifications
Item Specifications
Functions
Capacity
Max. number of controlled subscribers 960
Max. number of controlled RPs 32
Max. number of COT interfaces 4
Max. speech paths 120
COT Interface
Physical Interface E1 interface (30B+D)
Speech coding rule A-law
Logical Interface Non-facility associated signaling
RP Interface
Physical Interface Proprietary (4B+D+K)
Speech coding rule ADPCM
Line power feeding voltage 112-116 V DC
Logical Interface Layer 2: TTC Rec. JT-Q921-b
Power Condition
Input voltage 42-58 V DC
Max. input current Approx. 7.5 A
Operational Environment
Temperature -10° - +50° C
Humidity Less than 95% (non-condensing)
Dimensions
Control and power feeding to RPs
Concentration of speech path
Conversion of protocol
2.048 Mbit/s (B: 64 kbit/s D: 64 kbit/s)
TE mode
ITU-T Rec. G.703, G.704
Q.931
192 kbit/s
(B: 32 kbit/s D: 16 kbit/s K: 8 kbit/s)
Layer 3: Proprietary
640mm (H) x 494mm (W) x 210mm (D)
Table A-1: RPC Specifications
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 63

Specifications RPC/RP Manual
A-2
A.1.1 Champ Connector Pin Assignments
Assignment Pin # Pin # Assignment Remarks
RP # 1 (L1) 1 26 RP # 1 (L2)
RP # 2 (L1) 2 27 RP # 2 (L2)
RP # 3 (L1) 3 28 RP # 3 (L2)
RP # 4 (L1) 4 29 RP # 4 (L2)
RP # 5 (L1) 5 30 RP # 5 (L2)
RP # 6 (L1) 6 31 RP # 6 (L2)
RP # 7 (L1) 7 32 RP # 7 (L2)
RP # 8 (L1) 8 33 RP # 8 (L2)
RP # 9 (L1) 9 34 RP # 9 (L2)
RP# 10 (L1) 10 35 RP # 10 (L2)
RP# 11 (L1) 11 36 RP # 11 (L2)
RP# 12 (L1) 12 37 RP # 12 (L2)
RP# 13 (L1) 13 38 RP # 13 (L2)
RP# 14 (L1) 14 39 RP # 14 (L2)
RP# 15 (L1) 15 40 RP # 15 (L2)
RP# 16 (L1) 16 41 RP # 16 (L2)
Not in use 17 42 Not in use
Not in use 18 43 Not in use
Not in use 19 44 Not in use
Not in use 20 45 Not in use
Not in use 21 46 Not in use
Not in use 22 47 Not in use
Not in use 23 48 Not in use
Not in use 24 49 Not in use
Not in use 25 50 Not in use
RPIF Card #1
RPIF Card #2
RPIF Card #3
RPIF Card #4
No need to attach
Table A-2: Champ Connector 1-Pin Assignments
The Pin numbers are marked on the Champ connector. This chart applies to J16
on the motherboard in the RPC. RP has no polarity.
Figure A-1: Champ Connector Contact Face View
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 64

RPC/RP Manual Specifications
Assignment Pin # Pin # Assignment Remarks
RP # 17 (L1) 1 26 RP # 17 (L2)
RP # 18 (L1) 2 27 RP # 18 (L2)
RP # 19(L1) 3 28 RP # 19 (L2)
RP # 20(L1) 4 29 RP # 20 (L2)
RP # 21(L1) 5 30 RP # 21 (L2)
RP # 22(L1) 6 31 RP # 22 (L2)
RP # 23(L1) 7 32 RP # 23 (L2)
RP # 24(L1) 8 33 RP # 24 (L2)
RP # 25(L1) 9 34 RP # 25 (L2)
RP# 26 (L1) 10 35 RP # 26 (L2)
RP# 27(L1) 11 36 RP # 27 (L2)
RP# 28(L1) 12 37 RP # 28 (L2)
RP# 29(L1) 13 38 RP # 29 (L2)
RP# 30(L1) 14 39 RP # 30 (L2)
RP# 31(L1) 15 40 RP # 31 (L2)
RP# 32(L1) 16 41 RP # 32 (L2)
Not in use 17 42 Not in use
Not in use 18 43 Not in use
Not in use 19 44 Not in use
Not in use 20 45 Not in use
Not in use 21 46 Not in use
Not in use 22 47 Not in use
Not in use 23 48 Not in use
Not in use 24 49 Not in use
Not in use 25 50 Not in use
RPIF Card #5
RPIF Card #6
RPIF Card #7
RPIF Card #8
No need to attach
A-3
Table A-3: Champ Connector 2 - Pin Assignment
Pin numbers are marked on the Champ connector. This chart applies to J17 on
the motherboard in the RPC. RP has no polarity.
Figure A-2: Champ Connector Contact Face View
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 65

Specifications RPC/RP Manual
A-4
A.2 RP Specifications
A.2.1 Radio Features
Item Contents
Radio frequency For private use: 1,895-1,906.1 MHz
For public use: 1,895-1,910 MHz
Carrier spacing 300 KHz
Output power 10 mW
Radio access TDMA-TDD
Number of TDMA slots 4 (for full rate CODEC)
Modulation π/4 shift QPSK (roll-off factor = 0.5)
Transmission bit rate 384 kbps
Speech coding 32 kbps ADPCM
Table A-4: Radio Features
A.2.2 Outdoor Type RP
Item Specifications
RF output power average
(Peak)
Sensitivity (Static BER = 1%) 14 dB µV
Antenna (Diversity) 2 external antennae (2 branch)
Diversity
RX (uplink) Antenna selection diversity (frame by frame)
TX (downlink) Transmitter antenna selection diversity (2 branch)
Air interface Based on RCR STD-28 ver.2
RPC interface Proprietary
Speech coding rate 32 kbps (ADPCM) x 3 or 4
Maximum wire line length (⇔
RPC)
Maximum power consumption Approx. 3 W
Power source Line power feeding (phantom) from RPC
Operational Environment
Temperature -10° to + 50°C
Humidity Less than 95 % (non-condensing)
Size 260 x 215 x 100 mm
Weight Approx. 2 kg
Line connection Screw less terminal
Antenna connection TNC connector
Battery backup None
10 mW
(80 mW)
BRI equivalent
(4B+D+K) x 1
3.5 km (φ 0.4)
5.0 km (φ 0.5)
56 - 116 V DC
Table A-5: Outdoor RP Specifications
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 66

RPC/RP Manual Specifications
A.2.2.1 Antenna
The recommended antenna specifications for the outdoor type RP are shown in
Table A-6.
Items: Recommended Specifications
Type Co-Liner antenna (Omni-directional) 2 branch
Gain 7dBi
Impedance 50Ω
VSWR less than 1.5
Cable Length: within 1m
Attenuation: 0.5dB/m
Table A-6: Antenna Specifications - Outdoor Type RP
A.2.3 Indoor Type RP
Item Specifications
RF output power average
(Peak)
Sensitivity (Static BER = 1%) 14 dB µV
Antenna (Diversity) Built-in antenna (2 branch 2.4 dBi)
Diversity
RX (uplink) Antenna selection diversity (frame by frame)
TX (downlink) Transmitter antenna selection diversity (2 branch)
Air interface Based on RCR STD-28 ver.2
RPC interface Proprietary
Speech cording rate 32 kbps (ADPCM) x 3 or 4
Maximum wire line length (⇔
RPC)
Maximum power consumption Approx. 3 W
Power source Line power feeding (phantom) from RPC
Operational Environment
Temperature 0° C to +50° C
Humidity Less than 95 % (non-condensing)
Size 154(H) x 142(W) x 47(D) mm
Weight Approx. 0.6 kg
Line connection Modular connector
Battery backup None
10 mW
(80 mW)
BRI equivalent
(4B+D+K) x 1
km (φ 0.4)
5.0 km (φ 0.5)
56 - 116 V DC
A-5
Table A-7: Indoor RP Specifications
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 67

Specifications RPC/RP Manual
A-6
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 68

Glossary
B Glossary
ADPCM Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation
BRI Basic Rate Interface
CNT Control Module
COT Central Office Terminal
B
CPU Central Processing Unit
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
E1IF E1 Interface
ECNT Enhanced Control Module
FIFO First In - First Out
HDLC High speed Digital Loop Carrier
HDSL High speed Digital Subscriber Loop
ISDN Integrated Services Digital Network
ITU International Telecommunications Union
LE Local Exchange
LED Light Emitting Diode
LIF Line Interface
OA&M Operations, Administration and Maintenance
PC Personal Computer
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 69

Glossary RPC/RP Manual
2
B-
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
PHS Personal Handyphone System
RAM Random Access Memory
ROM Read Only Memory
RP Radio Port
RPC Radio Port Controller
RPIF Radio Port Interface
TIF Trunk Interface
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 70

RPC/RP Manual Glossary
3
B-
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 71

Editor’s Note
C Editor’s Note
C.1 Notice to Customers
UTStarcom reserves the right to change the specifications and materials contained
herein without notice, and shall not be responsible for any damages caused by
reliance on the material as presented, including, but not limited to, typographical,
arithmetic, and listing errors.
Trademarks
C
All trademarks and service marks used in this document belong to their respective
owners.
Warranty and Return Policy
Refer to the terms and conditions of the contract for warranty and return policy
details.
Customer Service
Refer to the terms and conditions of the contract for customer service policy
details, or call the local UTStarcom Facility. Contact UTStarcom’s US
headquarters if you can’t find your local UTStarcom facility in the list below.
UTStarcom, Inc.
1275 Harbor Bay Parkway, Suite 100
Alameda, CA 94502, USA
Tel. 1-510-864-8800
Fax 1-510-864-8802
U.S. Facilities and Operations
UTStarcom New Jersey R&D Center
33 Wood Avenue South 8th floor
Iselin, NJ 08830, USA
Tel. 1-732-767-5200
Fax 1-732-548-1099
China Facilities and Operations
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 72

Editor’s Note RPC/RP Manual
2
C-
UTStarcom (China) Ltd.
CNT Manhattan Building, 11th Floor
6 Chao Yang Men Bei Da Jie
Dong Cheng District, Beijing, 100027
P.R. China
Tel. 86-10-6554-2030
Fax 86-10- 6554-2058
UTStarcom, Shanghai Office
Rm 1901-1902
227 Huang Pi North Road
Shanghai, 200237, P.R. China
Tel. 86-21-637-58766
Fax 86-21-637-58755
UTS Guangzhou Subsidiary
10F GuangZhou Gold Lion Tower
138 Tiyu Road East
Guangzhou, 510620, P.R. China
Tel. 86-20-3878-0263
Fax 86-20-3880-7411
International Facilities and Operations
UTStarcom, Singapore Office
ACTEL Communications
141 Middle Road #06-02
GSM Building, Singapore 188976
Tel. 65-334-6602
Fax 65-334-6606
UTStarcom, Thailand Office
For Your Infosys Co., Ltd
47/15 Soi Lardprao 122
Bangkapi Bangkok 10310, Thailand
Tel. 66-2-539-7140
or 66-2-934-0179 ext 80
Fax 66-2-539-7431
Zhejiang Unitel Telecommunications
Equipment Ltd
3 Yile Industrial Park 3/4F Building
129 Wen Yi Rd.
Hangzhou, 310012, P.R. China
Tel. 86-571-886-2341
Fax 86-571-886-2349
Guangdong UTStarcom Co. Ltd.
4 Yunshan Road East, North River
Huizhou, Guangdong 516001, P.R. China
Tel. 86-752-280-8868
or 86-752-280-8818
Fax 86-20-280-8838
UTStarcom (Hangzhou) Ltd.
3 Yile Industrial Park 3/4F Building
129 Wenyi Rd.
Hangzhou, 310012, P.R. China
Tel. 86-571-886-2341
Fax 86-571-886-2349
UTStarcom, India Office
W.S. Telesystems Limited
Dr. Brownamma Towers
11 Floor, 70/1, Mission Road
Bangalore - 560 027, India
Tel. 91-80-227-4444
Fax 91-80-222-5268
UTStarcom, Philippines Office
Rocis, Inc.
GF-A Cordova Condominium Building
Valero cor. Sedeño Sts.
Salcedo Village, Makati, Metro Manila,
Philippines 1227
Tel. 63-2-818-9783
Fax 63-2-815-2727
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 73

RPC/RP Manual Editor’s Note
3
C.2 How to Comment on This Document
UTStarcom strives to continuously improve its products and services to better
help our customers succeed. As our valued customer, you can help us by giving
us your comments on this manual. A feedback form is located on the next page.
Please take a few minutes to complete the form and send it to the following
address by mail or fax. If you have any comments and suggestions, please send
them to this address, too. Your valuable feedback is highly appreciated.
Wireless Product Manager
UTStarcom Inc.
33 Wood Avenue South, 8th floor
Iselin, New Jersey 08830
USA
Fax: 732-548-1099 Web Site: http://www.utstar.com
Email: wireless_prod_mgr@utstar.com
C-
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 74

Editor’s Note RPC/RP Manual
4
C-
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 75

RPC/RP Manual Editor’s Note
5
C.3 Feedback Form
Organization of this manual:
r extremely poor r poor r moderate r good r excellent
Clarity of this manual:
r extremely poor r poor r moderate r good r excellent
Level of detail of this manual:
r not enough r just right r too much
Level of technical description:
r too superficial r just right r hard to understand
Suggested improvements and topics you want to see covered in future releases:
Errors found (attach additional sheets if necessary):
Page # Description
C-
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
Page 76

Editor’s Note RPC/RP Manual
6
C-
Please tell us about yourself:
Company
Title / Job Responsibility
Years of Experience
In case we contact you, please provide the following (optional):
Your Name
Phone Number
E-mail Address
------------------- fold along line ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------tape here
------------------- fold along line -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Wireless Product Manager
Post Office
will not
deliver
without
stamp
UTStarcom
33 Wood Avenue South, 8th floor
ISELIN, NJ 08830
USA
WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0 19June2000
Page 77

RPC/RP Manual Editor’s Note
7
C-
19June2000 WLL-RPC/RP-IN/UM-1.0
 Loading...
Loading...