US Robotics SureConnect U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router, SureConnect Series User Manual
Page 1

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Contents:
US Robotics
SureConnect ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router
Configuration Utility
Summary
Web User Interface
Terminal User Interface
Command Line Interface
Configuration Examples
Installation
Uninstallation
Troubleshooting
Glossary
Regulatory Information
U.S. Robotics SureConnect™ ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Windows 95, 98, NT 4.0, Me, 2000, XP or later, Mac
and Linux
Installing the Router
Welcome to the Web page for your U.S. Robotics SureConnect™ ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router, Model 9003. This Web page details five aspects
of your router...
● Installation & Uninstallation: Complete instructions on how to
set up your router.
● Configuring the Modem: Command-level discussion of all three
user interfaces, with examples.
● Troubleshooting: Q&A format. Covers typical questions.
● Glossary: ADSL jargon, rendered into English.
● Regulatory Information:. Declaration of Conformity, FCC & CE
compliance statement, etc.
Technical Support
For current product support and contact information, go to the Support section of the U.S.
Robotics Web site:
http://www.usr.com/broadbandsupport
U.S. Robotics
part number
R46.0216.00
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003...de/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/index.htm (1 of 2) [11/6/2002 8:52:17 AM]
Page 2

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003...de/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/index.htm (2 of 2) [11/6/2002 8:52:17 AM]
Page 3

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Contents:
US Robotics
SureConnect ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router
Configuration Utility
Summary
Web User Interface
Quick Setup
Service Provider
Settings
Network
Firewall
Tools
Statistics
Terminal User Interface
Command Line
Interface
Configuration Examples
Installation
Uninstallation
Troubleshooting
Glossary
Regulatory Information
U.S. Robotics SureConnect™ ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Windows 95, 98, NT 4.0, Me, 2000, XP or later, Mac
and Linux
Web User Interface
Overview
The Web User Interface (WUI) is one of three router user interfaces. The other interfaces
are the Terminal User Interface (TUI) and Command Line Interface (CLI). Each interface
allows you to set up, modify, and view router configuration variables and operational data.
The Web User Interface is a system of graphical menus. Menu pages control router
parameters and provide information about them. The WUI organizes these router
parameters into six topics. Here are the six topics, in the order that the WUI displays them...
• Quick Setup • Firewall Settings
• Service Provider
Settings
• Tools
• Network Settings • Statistics
This part of the manual discusses all but the Quick Setup topic. You’ll find information on
using the Quick Setup feature in the Quick Installation Guide.
This manual begins topic discussions with a picture of the top-level menu screen. A
description of screen terms and procedures follows each screen shot. Either text or a table
defines screen variables. Afterward, summarized, step-by-step procedures often follow.
Selecting Topics. When you look at a menu page, notice the divider tabs at the very top of
the page. You can access any of the six router configuration and information topics by
clicking on its tab. The graphic below portrays the six divider tabs as they appear on a
menu.
Divider Tabs •
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (1 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 4

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Configuration Options. Most menus present configuration options and prompt you for a
response. For example, the screen may help you to set up service provider, network or
firewall parameters. Some menus offer additional or more specific options by presenting
lower-level (secondary) screens. The bottom of many screens includes a set of graphical
buttons. Clicking one of the buttons with your mouse determines the disposition of options
on the page. For example…
• Add • Delete
• Modify • Disable
• Configure XXX • Erase
Selecting or Enabling Features. You can select menu options by clicking radio buttons or
checking boxes on the screen. In either case, use your mouse to make selections. Radio
buttons allow you to select only one of several options. Checkboxes allow you to enable
none, one or many features. The graphic below includes examples of both radio buttons
and checkboxes.
Radio Buttons •
Checkboxes •
Accessing the Web User Interface
Your router includes the SureConnect ADSL Web Utility. This Web utility displays after you
complete installation.
To access the Web User Interface, follow these steps…
1. Install your router according to the Quick Installation Guide.
2. Connect the router to the Ethernet or USB port on your PC.
3. Open a Web browser and go to IP address http://192.168.1.1. (Otherwise, go to the
LAN IP designated for the router's management port.)
4. At the prompt, type in your user name and password. The default user name is "root."
The default password is "12345." (Don't type the quotation marks or period.)
Service Provider Setting Page
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (2 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 5

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
WAN Setup
Use this menu option to configure an ISP connection. ADSL employs Asynchronous
Transfer Mode (ATM) protocol to send data to the Internet Service Providers. An ATM
circuit uses Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC) as pathway to identify and route modem data.
The U.S. Robotics Ethernet/USB Router supports multiple PVC connections for multiple
ISPs.
To configure a PVC…
1. Delete any connection that you don’t need.
2. Select the PVC in the Current ATM PVC List.
3. Click Delete.
4. Click the connection type recommended by your ISP. Choose a mode: RFC1483
Bridged, RFC1483 Routed, PPPoE, PPPoA or MER.
• If you chose RFC1483 Bridged mode, follow these steps…
1. Enter VPI / VCI values.
2. Click the radio button for the desired encapsulation mode: LLC/SNAP or VC
Multiplexing.
3. Network Settings: Be sure that options Enable NAPT and Enable DHCP are not
selected.
4. Click Add.
• If you chose RFC1483 Routed mode, follow these steps…
1. Enter the WAN IP Address for your ISP.
2. Enter the WAN Subnet Mask for your ISP.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (3 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 6

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
3. Enter VPI / VCI values.
4. Click the radio button for the desired encapsulation mode: LLC/SNAP or VC
Multiplexing.
5. Network Settings: Be sure that options Enable NAPT and Enable DHCP remain
selected.
6. Click Add.
• If you chose PPPoE mode, follow these steps…
1. Enter Username and Password.
2. Select “Direct” Dialing mode. Only choose “Auto” if you prefer to start and stop
your connection while data is flowing.
3. Enter the IDLE Timeout: This function adjusts the number of minutes of no traffic
before the connection terminates. The idle timeout connection terminates when you
select “Auto” Dialing Mode.
4. Select the Authentication method: Chap or PAP or MS-CHAP.
5. Enter VPI / VCI values.
6. Click the radio button for the desired encapsulation mode: LLC/SNAP or VC
Multiplexing.
7. Network Settings: Be sure that options Enable NAPT and Enable DHCP remain
selected.
8. Click Add.
• If you chose PPPoA mode, follow these steps…
1. Enter Username and Password.
2. Select the Authentication method: Chap or PAP or MS-CHAP.
3. Enter VPI / VCI values.
4. Click the radio button for the desired encapsulation mode: LLC/SNAP or VC
Multiplexing.
5. Network Settings: Be sure that options Enable NAPT and Enable DHCP remain
selected.
6. Click Add.
• If you chose MER mode, follow these steps…
1. Enter the WAN IP Address for your ISP.
2. Enter WAN Subnet Mask for your ISP.
3. Enter VPI / VCI values.
4. Click the radio button for the desired encapsulation mode: LLC/SNAP or VC
Multiplexing.
5. Network Settings: Be sure that options Enable NAPT and Enable DHCP remain
selected.
6. Click Add.
Proceed to the Tools Menu to save your changes.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (4 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 7

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
ADSL Standard
The ADSL Standard menu configures the ADSL protocol. You’ll find four supported
protocols: Multi-mode, T1.413, G.dmt and G.lite. Your ISP determines the protocol to use.
In most cases, Multi-mode should allow a connection to the ISP.
PPPoE Relay
PPPoE Relay protocol supports multiple PPPoE sessions through the router, on a LAN
interface, over an RFC1483 Bridged PVC. The router supports multiple sessions by
maintaining a mapping table. In this table, each entry represents one session. The Client /
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (5 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 8

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Server side MAC address and the Session Id provide the basis for the mapping. Refer to
WAN setup instructions on configuring PPPoE. The PPPoE Relay option requires an ATM
PVC (server) and a LAN interface (client). The client initiates a PPPoE session with the
server via a third-party PPPoE client. Follow these steps…
1. Configure the client and server.
2. Click Enable to start the relay function.
NAPT Bridge
This screen provides the option of enabling or disabling MER PVC. From this screen, you
can also change this PVC’s ATM values. The MER Interface is an RFC1483 Bridged PVC,
terminated in the router with a static public address. The ISP provides the static public
address. This type PVC operates with Network Address Translation (NAT) and DHCP.
These protocols allow the router to serve LAN users with private addresses.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (6 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 9

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Bridging
You can group router LAN interfaces. Grouping allows forwarding of their Ethernet frames
to an ATM interface. The U.S. Robotics Ethernet/USB Router defaults to bridging on three
ports: ETH1, ETH2 and USB. The router bridges these ports to the atm0 interface or the
first PVC under WAN SETUP.
To change the grouping…
1. Click Erase All.
2. Click Interfaces.Choose the desired LAN Interfaces.
3. Click Apply.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (7 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 10

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
To bind the LAN Interfaces to an ATM interface, select “Add Bridge.”
1. Select the ATM Interface from the Interface Name drop-down list.
2. Enter the VPI / VCI to which this ATM circuit belongs. Refer to WAN Setup for
information on setting up a bridged PVC.
3. Click Apply.
4. At the List of Bridge Entries, click Enable. This action activates packet forwarding.
Advanced
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (8 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 11

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Use the Advanced Interface menu to configure LAN, PPP and ATM interfaces. Follow these
steps…
1. Select the Interface Name.
2. Set the IP and Subnet Mask by clicking Configure Interface. Some interfaces allow
the option of changing interface status.
Interfaces:
• Interface mer0 usage is reserved. Its status is always Down.
• Interface ADSL0 is the ADSL SNMP interface.
• Interface lo0 is the loopback interface. When you perform an
OAM loopback, the status field displays UP.
• Interfaces Atm0 to Atm 7 display the interfaces configured
for RFC1483 bridged mode or RFC 1483 routed mode.
• Interfaces pppo to ppp7 display the interfaces configured for
PPPoE or PPPoA.
Parameters:
• Dynamic IP address from DHCP: Selecting this option allows the DHCP Server to
assign the IP address.
• Static IP address: Selects the IP address to be statically assigned.
• Interface: The name of the selected interface.
• IP address: The IP address of the selected interface.
• Subnet Mask: The subnet mask of the selected interface.
• MTU: Sets the maximum transmission unit of the interface. The MTU limits the size of
packets that transmit on an interface. Not all interfaces support the MTU parameter. Some
interfaces, like Ethernet, have range restrictions (80 - 1500).
• Speed: Auto, 10 Mbps, or 100 Mbps.
• State: Enable and Disable. When you set an interface to Disable, the system won’t
attempt to transmit messages through that interface. When you set an interface to Enable,
you can transmit messages through the interface.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (9 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 12

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Use the Advance–VCC menu to add and delete ISP connections. This menu also includes
options to enter ATM Quality of Service (Qos) parameters. The Advance–VCC menu
operates similarly to the WAN Setup menu.
The menu only supports Data type ATM circuits.
To list the Quality of Service setting per PVC, click the Show QOS Settings button.
Advance–VCC Menu Add Parameters
Parameter Definition
VPI
Virtual Path Identifier (VPI) that identifies
the ATM connection. The vpi is an integer
that ranges from 0 to 4,095.
VCI
Virtual Channel Identifier (VCI) that
identifies the ATM connection. The VCI is
an integer that ranges from 0 to 65,535.
Peak Cell Rate (Cells/sec) Maximum rate for sending cells to the
network.
Average Cell Rate
(Cells/sec)
Maximum sustainable or average rate for
sending cells to the network. Average Cell
Rate specifies bandwidth utilization. This
value must always be less than or equal to
Peak Cell Rate.
Burst Size (cells)
Maximum number of cells that the user can
send at peak rate in a burst. We measure
burst size from within a sustainable rate.
CDVT (cells)
Constrains the number of cells the user can
send to the network at the maximum line
rate.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (10 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 13

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Type
Only data support – NO voice.
Service Type
cbr Constant Bit Rate
Supports real-time applications that require
a fixed amount of bandwidth. These
applications, such as a video stream,
produce data at regular intervals. The user
can specify how much bandwidth that he
wishes to reserve.
rtvbr Real Time
Variable Bit Rate
Supports time-sensitive applications such
as voice. Varies the rate at which cells
arrive.
Nrtvbr Non Real Time
Variable Bit Rate:
Supports applications that have no
constraints on delay and delay variation, but
still have variable-rate and bursty traffic
characteristics.
Ubr Unspecified Bit
Rate
Best effort service that does not require
tightly constrained delay and delay
variation. UBR provides no specific quality
of service or guaranteed throughput.
Advance–PPPOE. Use Advance–PPPoE to connect to, or disconnect from a PPPoE
server. Click Start to use the connection. Click Stop to disconnect. The menu also includes
two other button options. Click Default to make the ISP connection your default connection.
Click Delete to delete the connection.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (11 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 14

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Advance–PPPOA. Use Advance–PPPoA to connect to, or disconnect from a PPPoA
server. Click Start to use the connection. Click Stop to disconnect. The menu also includes
two other button options. Click Default to make the ISP connection your default connection.
Click Delete to delete the connection.
Network Setting Page
LAN Setup
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (12 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 15

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Use LAN Setup to set the router’s IP Address and Subnet Mask. The LAN IP address
allows you to connect the router to your LAN. This address also allows you to manage the
router from your LAN. A LAN (Local Area Network) connects computers in the same
building or area.
Subnet masks split one network into a set of mini networks or subnets. Subnetting helps to
reduce traffic on each subnet. Subnetting also makes the network more manageable. Each
subnet functions as if it were an independent network.
To set up the LAN…
1. Enter the LAN IP Address for the router to use on the network.
2. Enter the Subnet Mask for the network that the router connects to.
3. Click Apply.
NOTICE. The LAN setup process changes the IP address of the Web User Interface. The
apply action causes the router to save your current configuration and then restart. After the
router restarts, you'll have to reapply to the Web User Interface using a new IP address.
DHCP
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. This protocol dynamically assigns
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (13 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 16

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
IP addresses and related information to Local Area Network (LAN) nodes. For temporarily
connected network users, DHCP provides safe, reliable, and simple TCP/IP network
configuration.
The top DHCP menu screen lists DHCP server entries. To remove the entry…
1. Click the radio button beside the entry.
2. Click Delete.
You can also start or stop the DHCP server by clicking Start/Stop.
To create a new DHCP server entry, click Add.
Note: Before adding a new DHCP server entry, you must first stop the DHCP server.
The following screen appears:
Configure the following parameters:
•Interface. LAN port that the DHCP server will support.
•Starting IP Address. First IP address in a block of addresses. The DHCP server uses this
address in responding to a LAN port node’s DHCP request.
•End IP Address. Last IP address in a block of addresses. The DHCP server uses this
address in responding to a LAN port node’s DHCP request.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (14 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 17
U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
•Gateway. IP address of the Default Gateway or Router that the node will use.
•Netmask. Subnet Mask for the LAN that the node will be on.
•DNS. Domain Name Server. The DNS that the node will use. DNS is a server with a
database. The database translates a domain name into a corresponding IP address. For
example, “USR.com” resolves into IP address 231.222.320.4. Communications over the
LAN between the node and USR.com web site use this address.
•Lease Time. Number of days that the node can use a DHCP lease. Subsequently, you
must renew the lease with the DHCP server.
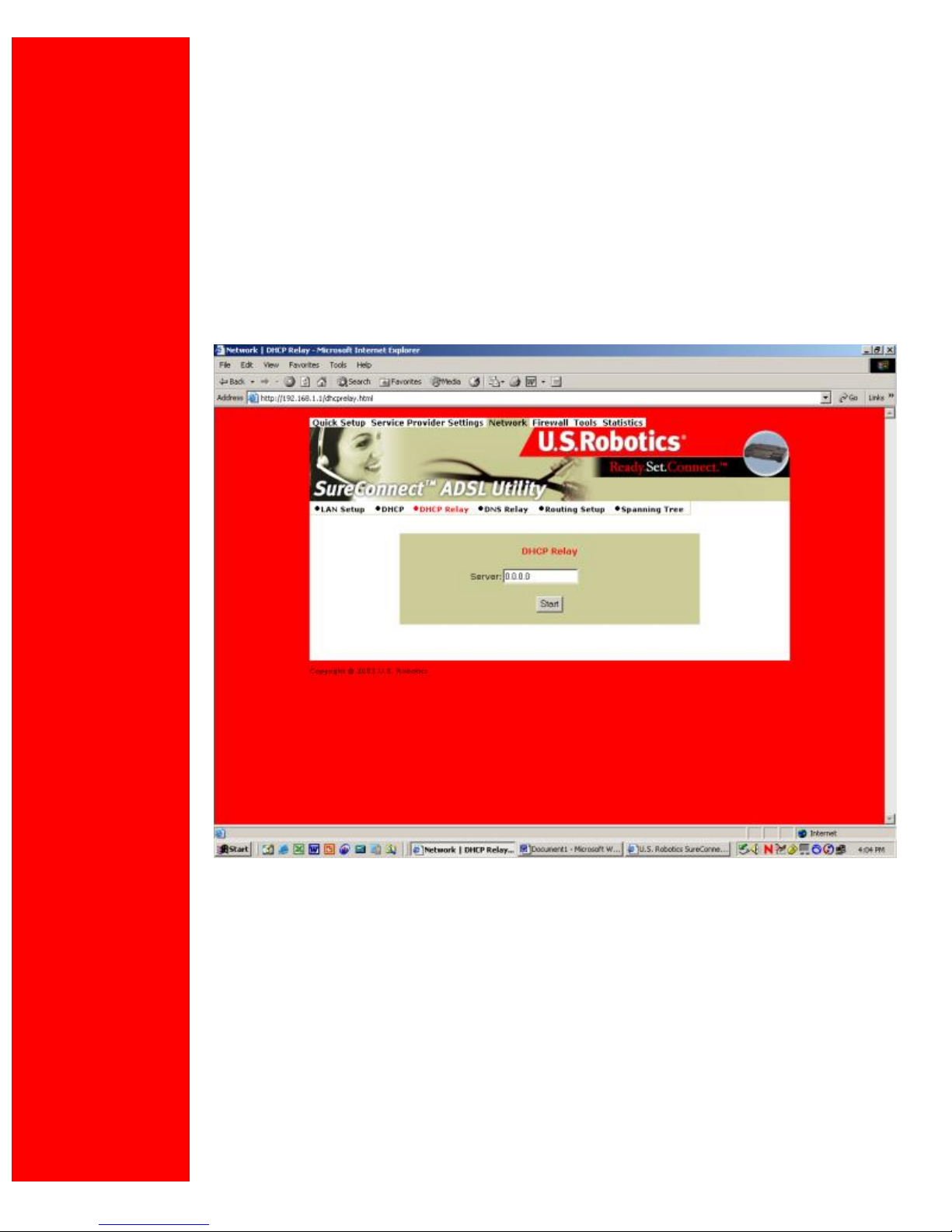
DHCP Relay
Suppose that a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server resides on a different
LAN than the node broadcasting for DHCP service. Then the DHCP broadcast request must
be forwarded across the router/WAN to a subnet where a DHCP server resides. The router
must relay the DHCP request. DHCP relay assures that the requesting node receives an IP
address that corresponds to the node’s subnet. The router must have a record of the DHCP
server’s IP address. With this address, the router can correctly direct the request to the
appropriate DHCP server.
After you input the IP address into the menu, start the relay agent by clicking Start.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (15 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 18
U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
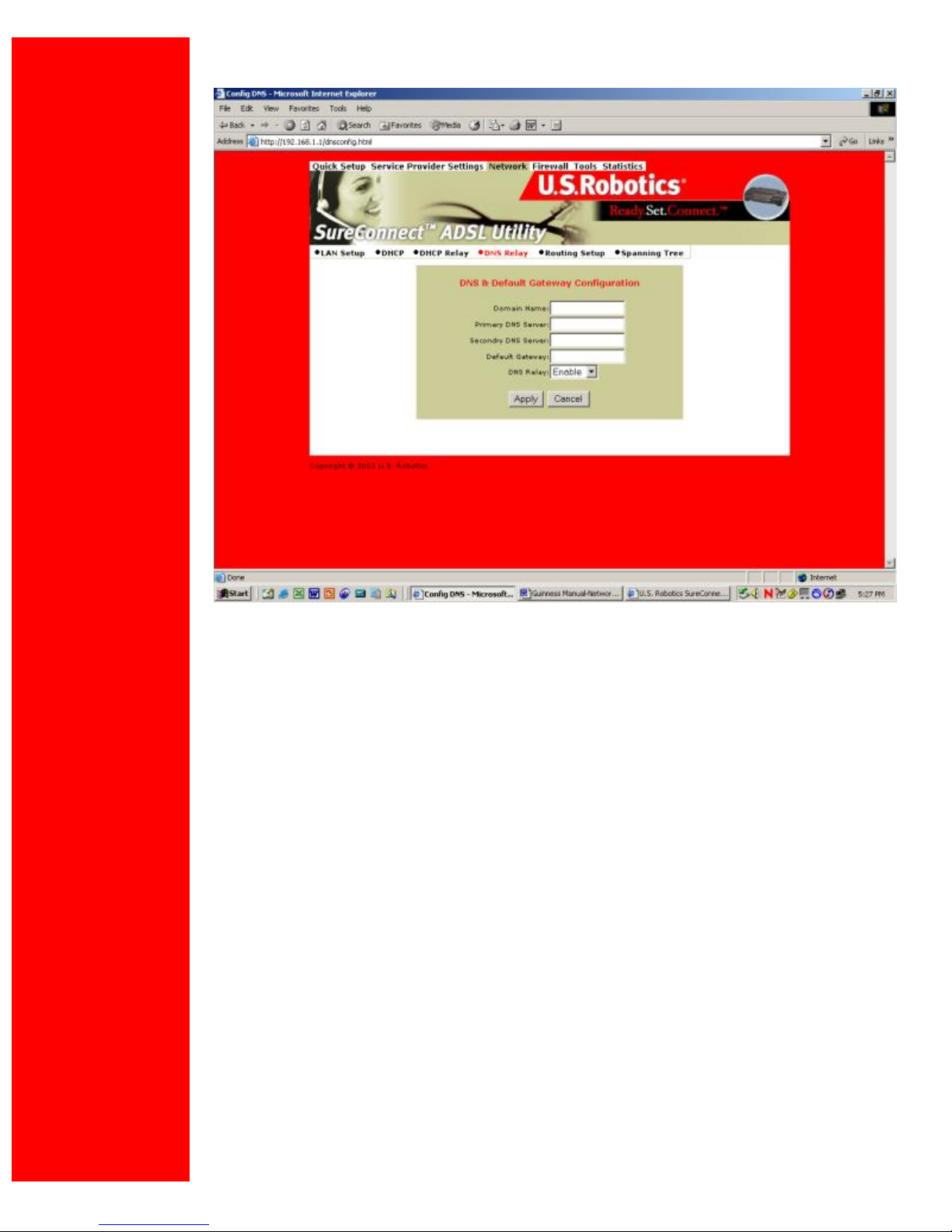
DNS Relay
The DNS Relay function supports forwarding of DNS requests from a LAN node to a known
DNS server.
•Domain Name. Internet site address that the router is a group of (i.e. usr.com).
•Primary DNS Server. IP address of the Primary DNS that the router will use. Domain
Name Server (DNS) is a server with a database. This server translates a domain name into
the corresponding IP address. For example, USR.com resolves into IP address
231.222.320.4. Communications over the LAN between the node and web site USR.com
use this address.
•Secondary DNS Server. IP address of the Secondary DNS that the router will use.
•Gateway. IP address of the Default Gateway the Router is to use.
•DNS Relay. Enabling or Disabling router ability to convey a DNS request from a LAN node.
To save and install DNS relay data…
1. Input the data.
2. Click Apply.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (16 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 19

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Routing Setup
A router forwards data packets between local area networks (LANs) or wide area networks
(WANs). Based on routing tables and routing protocols, routers read the network address in
each transmitted packet. Routers then decide where to send the packet. A router bases this
decision on the best route. The Routing Setup menu allows the user to configure how the
router forwards received IP packets.
RIP Information
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a routing protocol and is part of the TCP/IP suite. RIP
determines a route based on the smallest hop count between source and destination. RIP
determines the smallest hop count by communicating with other routers within the network.
Only use RIP if the target router also utilizes RIP.
•RIP Status=On/Off selection.
•Version= Version 1 (RIP1) or Version 2 (RIP2). Should match RIP versions used by other
routers in the network.
To save and install RIP data…
1. Input the data.
2. Click Apply.
Route Configuration
Use the Routing Setup area to add, delete or modify static routes. Static routes are
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (17 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 20

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
permanent routes that the router stores. The router uses these routes when determining
where to forward IP packets that it receives.
•Destination Network ID. IP address of the network that you’re defining in the table.
•Destination Subnet Mask. Network Subnet Mask of the defined entry in the table.
•Next Hop IP. IP address of the next router that will forward packets to the destination
network.
•Add. Add information to the routing table.
•Modify. Modifies an entry. To modify an entry…
1. From the List of Static Routes, select the route to modify. To do that, click Select next
to the route you’re modifying.
2. Then click Modify.
•Delete. Used to delete an existing entry. To delete…
1. Select the route to modify from the List of Static Routes. Do that by clicking Select
next to the route you’re deleting.
2. Click Delete.
•Erase All. Erases all routes in the List of Static Routes. This feature won’t erase networks
defined on interfaces of the router.
List of Static Routes
The list of networks known by the router. The list also includes the Next Hop to get to these
networks. Static routes may be networks added statically or learned from other networks.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (18 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 21

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Spanning Tree-Bridging
Transparent bridges use the spanning tree algorithm to dynamically determine the best
source-to- destination path. This algorithm avoids bridge loops (multiple paths linking one
segment to another) within a network. The algorithm determines all redundant paths and
makes only one of them active. The spanning tree protocol (STP) is part of the IEEE 802.1d
standard.
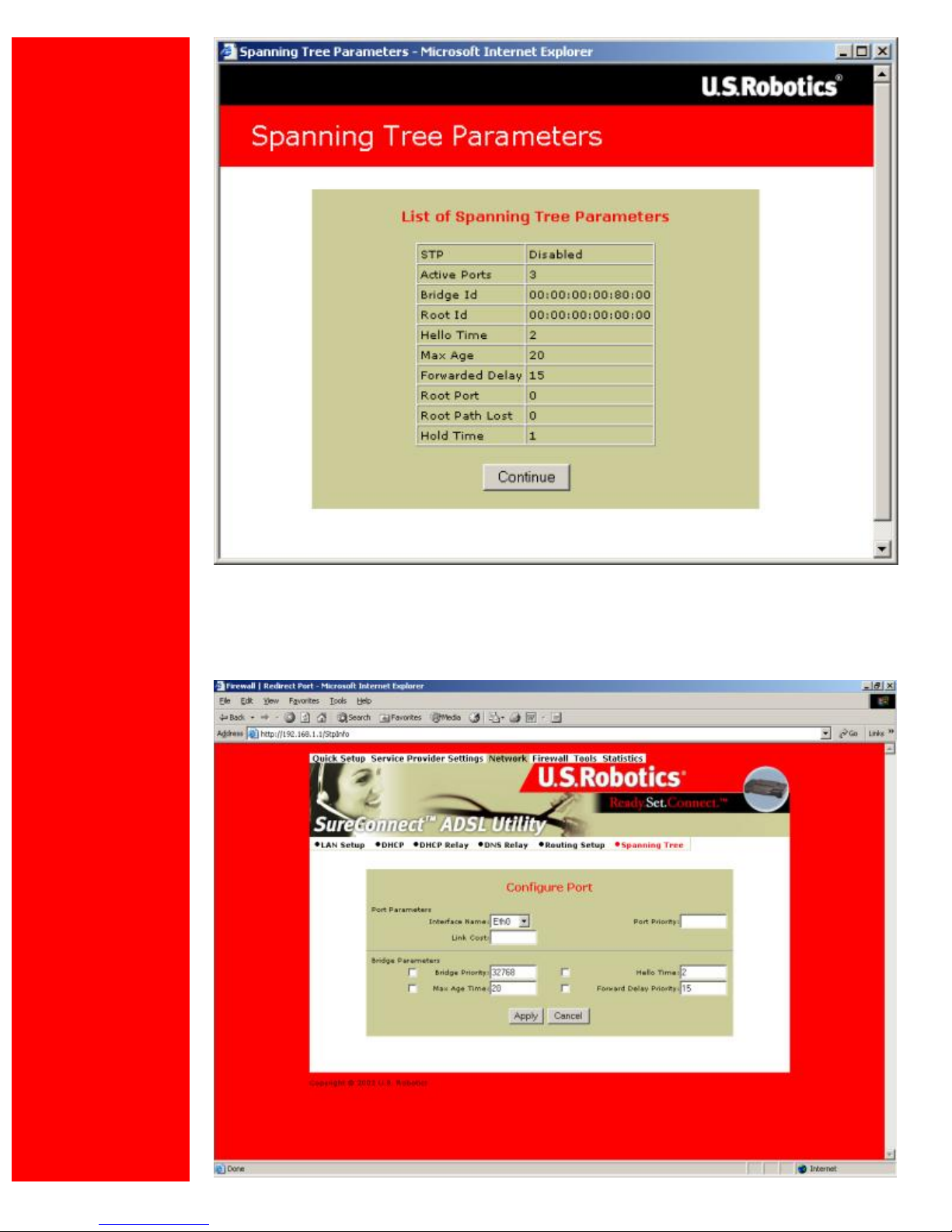
List of Spanning Tree Entries
List all known router bridging ports and their current state.
To view the current state of the spanning tree bridge click Parameters. The following
screen appears…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (19 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 22
U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
To close the screen, click Continue.
To configure a port, click Config Port. The following screen appears…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (20 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 23

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Port Parameters
•Interface Name. Router interface to be configured for spanning tree.
•Link Cost. Cost associated with that interface. Based on this cost, the bridge decides
which link to forward data over. The options range from 0 to 65,535.
•Port Priority. Determines which port becomes the root port. Options range from 0 to 255.
Bridge Parameters
•Bridge Priority. Determines which bridge becomes the root bridge. Options range from 0
to 65,000.
•Max Age Time. All bridges in the bridged LAN use this timeout value. The root sets Max
Age value. Options range from 1 to 60 seconds.
•Hello Time. Time interval between generations of configuration BPDUs (Bridge Protocol
Data Units). The root generates configuration BPDUs. Options range from 1 to 10 seconds.
•Forward Delay Time. All bridges in the bridged LAN use this timeout value. The root sets
the forward delay value. Options range from 1 to 200 seconds.
To configure port information…
1. Input the information.
2. Click Apply.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (21 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 24

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Spanning Tree - MAC Filters
The MAC address is a unique serial number burned into Ethernet adapters. This address
distinguishes the network card from others. MAC Filters allow or reject WAN access for
specific machines.
•List of MAC Address Filters. Known MAC addresses and the ports on which the router
learned the addresses.
To view current filter states, click Parameters. The following screen appears…
To close the screen, click OK.
To add a static MAC address to the table, click Add. The following screen appears…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (22 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 25

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
•MAC Address. Static MAC address to add to the table.
•Frame. What the router should do with a data frame from this MAC address. The options
are Forward or Drop.
To set the Add/Modify Filter information…
1. Input the information.
2. Click Apply.
To delete an entry from the List of MAC Address Filters…
1. Check the radio button to the left of the entry.
2. Click Delete.
To modify a MAC address in the List of MAC Address Filters, or to make the address
static…
1. Check the radio button beside the entry.
2. Click Modify.
3. Proceed by following the same steps as in Add.
To erase all non-static MAC addresses, click Erase All.
Firewall Settings Page
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (23 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 26

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
IP Filtering
Click the IP Filtering header and view the List of Firewall Policies. The firewall’s factorydefault setting is “Deny All.” The router includes factory-configured policies that allow
access from LAN to WAN.
List of Firewall Policies
This screen displays the current list of firewall policies as defined in the router. The list
appears in table form.
To remove an entry…
1. Click the radio button beside the entry.
2. Click Delete.
To add new policies, click Add. The following screen appears:
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (24 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 27

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Policy Parameters
On the Firewall Configuration page, notice the header “Policy Parameters.” The Policy
Parameters menu presents you with the following onscreen options …
• Precedence. Priority of the policy that you’re creating. Options range from 0 to
65,535. The lower precedence number takes priority.
• Src IP Address. Data source. Enter either a specific IP address or network
address.
• Src Net Mask. Subnet Mask for the data’s network source. Options range from
/12 (255.240.0.0) to /32 (255.255.255.255).
• Dest IP Address. Data destination. Enter either a specific IP address or network
address.
• Dest Net Mask. Subnet Mask for the data’s network destination. Options range
from /12 (255.240.0.0) to /32 (255.255.255.255).
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (25 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:37 AM]
Page 28

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
• Source Port. Transport layer source port. Options range from 0 to 65,535.
• Destination Port. Transport layer destination port. Options range from 0 to
65,535.
• Protocol. IP protocols to be filtered. Options are: Any (all), TCP, UDP, ICMP, AH,
ESP.
• TCP Flags. Filtering of the TCP Flags that control session setup and termination.
Options are: None, urg (Urgent), ack (acknowledgement), psh (push), rst (reset), syn
(synchronize), fin (finished).
Firewall Parameters
To edit a firewall parameter…
1. Click the radio button beside “Existing ActionID.”
2. Enter the “FW Action ID” to modify.
To create a new firewall parameter, Click the radio button beside “New Action.” The screen
presents you with a number of options and sub-options…
● Interface Name. Name of the Interface to apply the parameter to.
● FW Action. How the system handles packets. Your sub-options include…
§ Allow. Permits packets to enter or leave the system.
§ Reset. Forces the TCP connection to reset.
§ Reject. Drops the packet and issues an “unreach host” ICMP error.
§ Deny. Drops the packet.
● Direction. Specifies whether the action applies to incoming, outgoing, or both
incoming and outgoing traffic. Options are: Any, In, Out.
● Time. The parameter applies during the time period that you specify. Click the start
(From) day, time and stop (To) day and time.
To save and install firewall configuration data…
1. Input the data.
2. Click Apply.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (26 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 29
U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
• NOTICE. Check your firewall configuration data. See View Actions at the top menu.
There, you’ll find a selection List of Firewall Policies. This selection summarizes the
action that you entered for each parameter. When you click View Actions, the following
screen appears.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (27 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 30

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
IGMP Proxy
Click the IGMP Proxy radio button and view the List of IGMP Proxy Entries.
List of IGMP Proxy Entries
This screen displays a list of IGMP Proxy entries.
IGMP (Internet Group Membership Protocol) is a protocol. IP hosts use IGMP to report their
multicast group memberships to immediately nearest routers.
To remove an entry…
1. Click the radio button beside the entry.
2. Click Delete.
To create a new IGMP Proxy entry, click Add. The IGMP Proxy Configuration screen
appears…
IGMP Proxy Configuration
On the IGMP Proxy configuration Screen, follow these steps to set up your IGMP proxy…
1. Select Proxy interface, router interface, or both: Check the box next to the interface.
2. Use the pull-down menu to the right to select the eth, usb, atm, or ppp Interface.
To save and install IGMP Proxy Configuration data…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (28 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 31

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
1. Input the data.
2. Click Apply.
NAT=>List of Static WAN Addresses
From the List of Static Wan Addresses menu, you can remove or add entries. To remove an
entry…
1. Click the radio button beside the entry.
2. Click Delete.
To create a new Static WAN Address entry, click Add. The Static WAN Address
Configuration screen appears…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (29 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 32

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
NAT=>Static WAN Address Configuration
Public IP Address. Public IP address that the router uses when translating network
addresses.
To save and install Static WAN Address Configuration data…
1. Input the data.
2. Click Apply.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (30 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 33

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
NAT=>Port Range Mapping
Click the NAT header and view the List of Port Range Entries. NAT port range mapping
allows the router to map public addresses and ports to private addresses and ports.
List of Port Range Entries
NAT stands for Network Address Translation. NAT enhances the power of Port Range
Mapping. Together, they can map a local IP address and port to a public IP address and
port.
To remove an entry…
1. Click the radio button beside the entry.
2. Click Delete.
To create a new Port Range entry: Click Add on the top screen. The Port Range
Configuration screen appears…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (31 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 34

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
NAT=>Port Range Configuration
To add a Static NAT entry, set the following parameters…
● Public Address. Set the public, destination IP address inside a packet header. The
router will map or redirect packets with the address that you specify.
● Public Port From. Set the first (From) port of the public address that the router maps
or redirects. Options range from 1 to 65,535.
● Public Port To. Set the last (To) port of the public address that the router maps or
redirects. Options range from 1 to 65,535.
● Local Address. Set the IP address of a machine on the local LAN. The router directs
packets to this address.
● Local Port From. Set the first (From) port of the local address that the router uses.
Options range from 1 to 65,535.
● Local Port To. Set the last (To) port of the local address that the router uses. Options
range from 1 to 65,535.
● Protocol. Set protocol. Your protocol setting applies to the other parameters on this
page. Your options are TCP or UDP port numbers.
To save and install Port Range Configuration data…
1. Input the data.
2. Click Apply.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (32 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 35

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
NAT=>Static NAT Mapping
Static Network Address Translation (NAT) maps multiple local IP addresses to a public IP
address.
List of Static NAT Configuration
From the List of Static NAT Configuration menu, you can remove or add static NAT entries.
To remove a entry…
1. Click the radio button beside the entry.
2. Click Delete.
To create a new Static NAT Configuration entry, click Add. The Static NAT Configuration
screen appears…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (33 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 36

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
NAT=>Static NAT Configuration
To add a Static NAT entry, set the following parameters…
● Local Address From. First address in a range of local IP addresses. The router
maps these addresses to the public IP address.
● Local Address To. Last address in a range of local IP addresses. The router maps
these addresses to the public IP address.
● NAT Public Address. Public address. The router maps local addresses to this public
address.
To save and install Static NAT Configuration data…
1. Input the data.
2. Click Apply.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (34 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 37

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Proxy Configuration
Proxy Services are specialized application programs. These programs accept users’
requests from LAN clients for Internet services like HTTP. On behalf of LAN clients, proxy
services also set up connections to WAN servers. A proxy server authenticates against the
user database (Access Control). The proxy server filters a request against the Access
Control List (ACL). Then the server forwards the request to actual services. Proxy Servers
are application specific. Each application needs its own proxy server.
To save and install proxy configuration data…
1. Click the radio button beside the HTTP proxy that you want to enable. (The illustration
above doesn’t show proxy radio buttons.)
2. Click Enable beside HTTP Proxy.
3. Click Authentication. Clicking this box authenticates the user during the HTTP
Proxy.
4. Click Apply.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (35 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 38

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
ACL (Access Control List)
The ACL List screen displays currently configured Access Control Lists (ACL).
To remove an ACL List entry…
1. Click the radio button beside the entry.
2. Click Delete.
To create a new ACL entry, click Add from the top screen. The following screen appears…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (36 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 39

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Proxy Parameters
Term Definition
Port Proxy port.
Priority Priority of the policy you’re creating. Options range from 0
to 65,535.
User Name A configured user in the router’s internal database. You
must configure users through the Access Control Menu.
Application Type HTTP application file type (MIME) to filter or proxy.
Options are… •application (all), •image (all), •video (all),
•audio (all), •application/octet-stream, •audio/x-wav,
•audio/x-mpeg, •image/jpeg, •video/mpeg.
Destination Address Destination IP address of the FTP or HTTP server on the
WAN.
Source Range Local IP address range that the rule applies to. “From” is
the first IP address in the range. “To” is the last IP
address in the range.
Domain Name Address of an Internet site to filter.
Day From/To Set the effective start (From) day and time for the policy.
Set the effective stop (To) day and time for the policy.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (37 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 40

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Action Specifies how the ACL deals with requests to the policy.
Options are Allow or Deny.
To save and install Access List configuration data…
1. Input the data.
2. Click desired radio button options. The router only applies options that you select.
3. Click Apply.
Access Control
List of Users. The List of Users allows you to delete or authorize user access privileges. To
set up a new user account, you assign a username and password. With the username and
password, you can open a new account with either administrative or ordinary privileges.
To delete a user account…
1. Click the radio button beside the user entry.
2. Click Delete.
To create a new user entry…
1. Click Add on the top-level, List of Users screen. The following screen appears…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (38 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 41

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
User Configuration
User Configuration Parameters
User Account Data Term Definition
Username Configurable username with up to 19 characters.
Password Configurable user password with up to 19
characters.
Services Services available to the user. Options are CLI,
HTTP, and FTP. To select all, perform a <SHIFT>
right click. To make multiple selections, <CTRL>
click on each selection.
Permissions Administration access or Ordinary access.
To save and install User Configuration data…
1. See the table above. Input the user account data.
2. Click Apply.
To modify a User entry…
1. Click the radio button next to the user to be modified.
2. Click Modify from the top-level, List of Users screen. The following screen appears...
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (39 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 42

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
User Modification
User Account Modification Parameters
User Account Data Term Definition
User Name &
Authorization Old
User account that you’re modifying. You can’t
change these settings.
Authorization Select the new authorization level for this user.
Your options are CLI, HTTP, and FTP. To select
all, perform a <SHIFT> right click. To make
multiple selections, <CTRL> click on each
selection.
Permission Select the new Permission level for this user.
Choose Administration access or Ordinary
access.
To save and install user account modification data…
1. Input user account modification data.
2. Click Apply.
To change a user’s password,,,
1. Click the radio button next to the appropriate user account.
2. Click Change Password from the top-level, List of Users screen. The following
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (40 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 43

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
screen appears…
Change Password
User Password Change Parameters
Password Data Term Definition
Old Password Enter the user’s old password.
New Password Enter the user’s new password.
Confirm New Password Confirm a correct entry by reentering the user’s
new password.
To save and install User Modification Configuration data…
1. Input the data.
2. Click Apply.
Tools Page
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (41 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 44

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a software component that resides in a
network device. SNMP responds to requests for information and action from a network
management station. Within the network device, an object-like format called a Management
Information Base (MIB) stores the information exchanged during SNMP.
SNMP=>System
The System function displays the SNMP parameter as assigned by the SNMP
Administrator. Modify the default settings by following these steps...
1. Click Modify.
2. Enter your changes.
3. Click Apply.
•NOTICE. To stop the SNMP agent, click Stop. The Stop button toggles to become the
Start button. After the process ends, you can start the agent by clicking Start.
Configure the SNMP listening port by following these steps...
1. Click Stop to stop the agent.
2. Click Configure SMNP Agent.
3. Enter your changes.
4. Click Apply.
5. Restart the agent.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (42 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 45

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
SNMP=>Trap
Set the agent to report up or down status by following these steps...
1. Select the version of SNMP manager that the community is running.
2. Click Modify.
3. Enter the SNMP manager's IP address into its community name.
4. Select Enable for that status option.
5. Click Apply.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (43 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 46

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
SNMP=>Community
Set the SNMP manager's IP address and community name for SNMP message exchange
by following these steps...
1. Click Configure Community.
2. Enter your changes.
3. Click Apply.
Diagnostic
The Diagnostic feature can generate ATM or IP traffic for troubleshooting or testing your
router’s configuration. Sometimes the request for a response fails. The failure may be due
to your ISP’s disabling its equipment from responding to these requests. The ISP may
disable responses for many reasons, including your security.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (44 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 47

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Diagnostic=>OAM Loopback
OAM Loopback generates two forms of ATM frames for testing the integrity of your ATM
circuit. F5 Segment (F5 SEG) frames transmit, but the ISP’s ATM switch doesn’t loop them
back. F5 End-to-End (F5 ETE) frames transmit and the ISP’s ATM switch replies.
To Start the OAM Loopback Test…
1. Select the frame type.
2. Enter an existing PVC (VPI/VCI) for the F5 ETE frames.
3. Enter the ATM switch loopback ID for the F5 ETE frames.
4. Click the Start Loopback to begin the test.
5. After the test completes, a screen reports results. Click Back to return to the
Diagnostic screen.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (45 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 48

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
IP Address Ping Test
To Start the Address Ping Test…
1. Enter the IP of the network device that accepts ICMP packets.
2. Click Ping. If someone disabled ICMP packet forwarding on the device, the
Ping will fail.
Save and Restart
Whenever you make changes to the router’s configuration, the router saves the changes
in temporary memory storage. A power loss or power switch disconnection can cause the
router to lose changes. To make permanent changes, save changes and restart the
router.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (46 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 49

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
After you click Save, the router returns to the Save and Restart screen. You may reboot
your router by clicking Restart. Another way to reboot is to turn the router off and on from
the router’s power switch.
• CAUTION. The Restart button doesn’t return you to the Save and Restart menu. You
can return by either of two methods: Click the browser’s Back Arrow key. Or reenter the
router management IP address on your browser’s address line.
Restore and Restart
The Restore and Restart option returns the router’s configuration to factory default
settings.
• CAUTION. During restoration to default settings, the router loses all your changes. After
the restoration process completes, you must reenter changes.
To erase the current router configuration…
1. Click Restore.
2. Click Restart.
3. Allow the router a few minutes to restore to factory settings.
4. Enter the router management IP address in the address line of your browser. The
router main menu appears.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (47 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 50

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Date and Time
To set the router's date and time input...
1. Key in your entry for the "Date" field. Use the format MM:DD:YYYY.
2. Key in your entry for the "Time" screen. Use the format HH:MM:SS.
3. Click Apply.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (48 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 51

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Version
Click the Version option to see the router firmware version.
Statistics Page
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (49 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 52

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
ADSL Link Status
Displays ADSL line settings and connection status
Status Term Meaning
ADSL Line Status Displays the current ADSL line status
ADSL Standard Displays the ADSL standard within the
current configuration. The standards are:
MULTI, T1.413, G.dmt, and G.Lite.
UpStream
Displays the upstream data rate, as
negotiated by DSL link (Kb/s)
DownStream Displays the downstream data rate, as
negotiated by DSL link (Kb/s)
Attenuation Displays the current attenuation in
decibels
SNR Margin Displays the current SNR margin in
decibels
HEC Count
Displays the number of ATM cells
received with errors since start of link.
Firmware
Displays the version number of the
firmware
15 min ES Counter
Displays the number of errors per second
for the current 15-minute period
CRC Errors Displays the number of cyclical
redundancy check errors per second
since training
1 day ES Counter
Displays the number of errors per second
for the current day
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (50 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 53

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
System Statistics
Interface Statistics
Interface Statistics displays the statistics for all interfaces.
Screen Term Meaning
Interface Name Name of the interface
Admin Status Indicates whether the interface is up or
down
Octets In Number of received octets (in bytes)
Unicast PktsIn Number of received unicast packets
Broadcast PktsIn Number of received broadcast packets
Discards In Number of received and discarded packets
Errors In Number of received errors
Octets Out Number of transmitted octets (in bytes)
Unicast PktsOut Number of transmitted unicast packets
Broadcast PktsOut Number of transmitted broadcast packets
Discards Out Number of transmitted and discarded
packets
Errors Out Number of transmitted errors
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (51 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 54

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
TCP-IP
The TCP-IP screen displays IP, UDP, TCP and ICMP statistics.
DHCP Lease
The DHCP-Lease displays names of devices on the network. These devices received an IP
address from the router’s DHCP server address pools. The screen also displays how long
you can use this IP.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (52 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 55

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
ATM Statistics
The ATM Statistics Screen displays traffic statistics for Adaptation Layer 5 of the ATM
protocol and encapsulation.
AAL5 Statistics
The AAL5 Screen totals transmitted and received cells. The screen also reports total CRC
(Cyclical Redundancy Check) errors.
Subnetwork Dependent Convergence Protocol (SNDCP)
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (53 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 56

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
For the permanent virtual circuit (PVC), the SNDCP Screen organizes packet information by
Encapsulation Method.
Firewall Statistics
The Firewall Statistics Screen maintains flow-based statistics for incoming, outgoing and
dropped packets. Flow statistics describe the source address, source port, destination
address, destination port and protocol.
Traffic Statistics
The Traffic Statistics Screen displays data about inbound, outbound and dropped packets.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (54 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 57

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
HTTP Proxy Statistics
The HTTP Proxy Statistics screen maintains data on the user. Software collects statistics
for incoming packets, outgoing packets, incoming bytes and outgoing bytes. If you disable
authentication, this screen displays statistics on the general user.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...ide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/wui.htm (55 of 55) [11/6/2002 8:53:38 AM]
Page 58

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Contents:
US Robotics
SureConnect ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router
Configuration Utility
Summary
Web User Interface
Terminal User Interface
Command Line
Interface
Configuration Examples
Installation
Uninstallation
Troubleshooting
Glossary
Regulatory Information
U.S. Robotics SureConnect™ ADSL Ethernet/USB
Router User Guide
Windows 95, 98, NT 4.0, Me, 2000, XP or later, Mac and Linux
Installing the Router
For current product support and contact information, go to the following Web site:
http://www.usr.com/broadbandsupport
Thanks for purchasing the U.S. Robotics SureConnect™ ADSL Ethernet/USB Router, Model
9003. The following instructions walk you through installation of the router and the U.S.
Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router.
Please write down your serial number for future reference. If you need to call our Technical
Support department, you must have this number to receive assistance. You'll find your serial
number on a bar code sticker on the bottom of the router and also on the box. This number
has 12 characters. You will also need your model number, which is USR9003.
Installation Overview & System Requirements
What You Need Before You Begin
● Active ADSL and Internet service from your local telephone company or Internet Service
Provider (ISP).
● A microfilter may be required for each telephone device (telephones, answering
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (1 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 59

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
machines, and fax machines) that shares the same phone line as the ADSL signal.
Make sure that no filter connects between the ADSL router and telephone wall jack.
(Some installations require a special type splitter between the router and wall jack. In
these installations, the splitter must include both telephone and router jacks. If the
splitter doesn't, don't install it between the phone jack and router.)
Your ISP should be able to provide the following:
● Your user name and password if they were assigned.
● ADSL Standard (Modulation)
❍ G.dmt
❍ G.lite
❍ Multi-Mode
❍ T1.413, Issue 2
● VPI/VCI Settings
● Encapsulation Mode
❍ RFC1483 Bridged
❍ RFC1483 Routed
❍ PPPoE
❍ PPPoA
❍ MER
Computer Requirements
Minimum System Requirements – Ethernet Port
● Any computer with an Ethernet 10/100 Ethernet adapter (NIC)
● 32 MB RAM
● 10 MB hard disk space
● Any operating system that supports an Ethernet connection with an IP stack
● Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator 4.0 or later Web browser
● SureConnect Installation CD-ROM requires Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows Me,
Windows NT4.0, Windows 2000, or Windows XP
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (2 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 60

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Minimum System Requirements –USB Port
● Pentium 200 MHz or faster compatible CPU
● Host PC with Universal Serial Bus (USB)support
● 32 MB RAM
● 10 MB hard disk space
● Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator 4.0 or later Web browser
NOTICE
Make sure that your computer is on. You should have your operating system CD-ROM
readily available. The installation program requires use of the Windows Setup CD.
● SureConnect Installation CD-ROM requires Windows 98, Windows Me, Windows 2000
or Windows XP
ADSL Network Requirements
ADSL and Internet service from your local telephone company or Internet Service Provider
(ISP).
Power Requirements
The U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router obtains power from the included
power supply. Be sure to only use the included power supply when operating this device.
This U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router package includes the following
items:
U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router
Model 9003
Standard 7 ft RJ-11 telephone cable
(4 wire)
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (3 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 61

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Power Adapter
USB Cable
(3 ft/1 m)
Ethernet Straight Through Cable
(6 ft/1.8 m)
Quick Installation Guide
U.S. Robotics SureConnect Installation CD-ROM
with User Guide
Optional Components
Some models may include a microfilter in the box, or your ISP
may supply a microfilter. Check with your ISP to see if you
need a microfilter. The next section discusses microfilter
installation.
If you discover incorrect, missing, or damaged parts, inform your dealer.
Should You Connect via Ethernet or USB?
The U.S. Robotics ADSL Ethernet/USB Router gives you the option to connect through a
USB or an Ethernet port. Selecting how to connect your router is a matter of preference.
Connection also depends on your available computer ports and the operating system that you
use. For example, you must use an Ethernet connection with these operating systems:
Windows 95, Windows NT 4.0, Macintosh and Linux.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (4 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 62

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Step 1. Connect Microfilters (If Necessary)
● If your package didn't include microfilters, and your ISP didn't provide any: Skip to Step
2 of these instructions.
● If your installation requires microfilters: Install one on each telephone device that shares
the same phone line as the ADSL signal. (Telephone devices include telephones,
answering machines, and fax machines.)
A microfilter is a small device that reduces interference between ADSL signals and telephone
signals. You only need a microfilter if the ADSL router and a telephone device share the
same phone line. If you don't use a microfilter, you may experience background noise on your
telephone during data transmission. Also, telephone calls may interrupt data transmissions.
Connect Microfilters to Telephone Devices
To install the microfilter, plug the phone into the microfilter, and then plug the microfilter into
the telephone wall jack. Do not install a microfilter on the cable that connects your router to
the telephone jack unless your microfilter has a connection for both the telephone and the
DSL device.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (5 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 63

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Step 2. Install the ADSL Ethernet/USB Router
Windows 95 & NT 4.0, Macintosh and Linux Users
If you’re installing the U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router on a
system running Windows 95, NT 4.0, Macintosh or Linux, you must install the router
using the Ethernet option.
To install the U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router, insert the Installation
CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive of your computer. If the installation does not start
automatically, go to your desktop and double-click My Computer, double-click the drive letter
associated with your CD-ROM drive, and then double-click Setup.
The U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router Installer Welcome window will
display. Click Next to continue installing the U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB
Router.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (6 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 64

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
● Select the connection type that you will use to connect the router to your computer. Click
Next.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (7 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 65

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
●
A qualification test will run to verify that your system meets the minimum installation
requirements. The Results screen will display those items in your configuration that
passed with a green flag and the ones that failed with a red flag. If your system passed
the qualification, click Next.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (8 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 66

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
If the software notifies you that your system failed the test, click View Report. The report
identifies which component failed.
Step 3. Connect the Cables
The table below summarizes data for connections and ports on the back of the router.
Item Description
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (9 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 67

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
O/I Pushbutton switch that turns the U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router on and off.
Power Input jack that accepts cable from wall power supply.
Console Connects an RS-232 cable (not included) to the router. You can use the cable
to communicate to the router through the Terminal User Interface. The Terminal
User Interface (TUI) is another way to configure the router or get diagnostic
information. The TUI substitutes for the Web User Interface.
USB Universal serial bus port on the back of the router.
ENET1 Ethernet Port 1 on the back of the router.
ENET2 Ethernet Port 2 on the back of the router.
ADSL Digital subscriber line RJ-11 service jack on the back of the router.
Connect the Power Adapter
Be sure to only use the included power supply. Connect the power adapter cord to the
“Power” jack at the rear of the router. Connect the power adapter to a standard wall outlet.
Turn on the router by pressing the power button labeled “O / I.” The “PWR” LED on the front
panel of the U.S. Robotics ADSL Ethernet/USB Router will be illuminated if power is being
supplied to the router. The router will initialize after the power is plugged in. This process
takes about a minute. Click Next to initialize the router.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (10 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 68

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Connect the Telephone Cable
Connect one end of the included telephone cable to the “ADSL”telephone port on the back of
your router. Connect the other end of the cable into the telephone wall jack. Click Next.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (11 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 69

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Connect the Ethernet or USB Cable
Ethernet
If you are connecting up to two devices, you can plug them directly into the back of the router.
Doing so eliminates the need for a separate hub. Insert one end of the Ethernet cable into
either the “ENET1” or “ENET2” port on the back of the U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router. Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on
your computer’s 10/100 Network Interface Card (NIC).
● Click Finish.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (12 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 70

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
USB
● If you have chosen to connect via the USB port, insert the rectangular end of the
included USB cable into the USB port of the computer. Insert the square end of the
cable into the port labeled “USB” on the U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router.
● After you plug in the USB cable, the router detects your PC. Then the router
automatically installs its software on your PC. (Your system may require a system
reboot.)
● The Found New Hardware Wizard notifies you that the PC detects the router. Click
Finish.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (13 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 71

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Congratulations! Installation Complete!
You've completed installation of the U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router.
Click Finish. The installer will automatically launch the Internet browser. The Internet browser
will point to IP address 192.168.1.1.
At this point, the software prompts you for a username and password. The default username
is "root." The default password is "12345." Enter these values (without periods or quotation
marks).
If your browser doesn't auto-launch...
Begin the Quick Setup by launching your Internet browser and entering http://192.168.1.1.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (14 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 72

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
The SureConnect ADSL Utility Quick Setup screen will display.
Step 4. Using the Quick Setup Menu
The U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router comes equipped with the
SureConnect ADSL Web Utility. This utility helps you to get the router set up in three easy
steps.
1. Select ADSL Standard.
2. Configure service provider settings.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (15 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 73

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
3. Save and restart.
CAUTION!
Do not turn the power off or disturb the router before the save operation completes.
Interrupting this process will cause the router to lose setup data.
Select ADSL Standard
1. Click ADSL Standard. The ADSL Standard window opens. This window helps you to
select the ADSL standard that you'll use.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (16 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 74

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
2. From the ADSL Standard drop-down list, select G.dmt, G.lite, T1.413, or Multi-Mode. In
most cases, the default setting of Multi-Mode is sufficient. Check with your ISP to
confirm the correct settings. Once you have made your selection, click Apply.
3. Click Next in the lower right corner of the screen to continue to the WAN Setup page.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (17 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 75

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Configure Service Provider Settings
In the Service Provider Settings/WAN Setup screen, enter in the values obtained from your
ISP. See the ISP Settings Table at the end of this Web page for popular ISP settings.
(Settings may vary from the table listing. Check with your ISP.) If you don't find your ISP on
the table, call your ISP to obtain the correct settings.
1. See the Current ATM PVC List at the bottom of the screen. On this list, delete any
connection type that you don't need.
2. Select the connection type recommended by your ISP. Choose either RFC1483 bridged
mode, RFC 1483 routed mode, PPPoE mode, PPPoA mode, or MER mode. Some
connection types may require additional information, such as IP address or username
and password.
3. At the top of the WAN Screen, fill in the VPI and VCI values.
4. Select Encapsulation. Click either LLC/SNAP or VC Multiplexing.
5. If appropriate, select Enable NAPT.
6. If appropriate, select Enable DHCP.
7. Click Add.
8. To continue, click Next in the lower right corner of the screen.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (18 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 76

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Save and Restart
Once you've selected the ADSL Standard and WAN Setup screens, save your settings and
restart your router.
1. On the Save & Restart screen, click Save.
2. Once the save is complete, click Restart.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (19 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 77

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
NOTICE
If your ISP gave you software to install, install the software now. Be sure to read and
follow the installation instructions.
3. You can test your connection by registering your router at...
http://www.usr.com/productreg
Service Provider Settings
!++++++++++++++++++++Start of header row+++++++++++++++++>
Service Provider Region WAN Service VPI VCI
Encapsulation -LLC or
VCMUX
Australia
All ISP
Australia
PPPoE
RfC2516
Embedded
8 35 LLC
Belgacom ADSL Belgium PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 LLC
Telus Canada RFC 1483 Bridged 0 35 LLC
Tiscali (World Online) Denmark PPPoA - RFC2364 0 35 VCMUX
Cybercity Denmark PPPoA - RFC2364 0 35 VCMUX
AOL France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Generic Netissimo France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 LLC
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (20 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 78

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
9Online France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Claranet France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Club-Internet France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
EasyConnect France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 LLC
Freesurf France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
HRNet France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Nerim France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Service Provider Region WAN Service VPI VCI
Encapsulation -LLC or
VCMUX
Nordnet France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Tiscaly Liberty Surf France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 LLC
Wanadoo France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 LLC
Worldnet France PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
T-Online (Dun) Germany
PPPoE RFC2516
Embedded
1 32 LLC
T-Online (Soft) Germany RFC 1483 Bridged 1 32 LLC
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (21 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 79

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
AOL Deutschland
(Soft)
Germany RFC 1483 Bridged 1 32 LLC
QSC Germany PPPoE RFC2516 1 32 LLC
Arcor Germany PPPoE RFC2516 1 32 LLC
1&1 (Dun) Germany
PPPoE RFC2516
Embedded
1 32 LLC
Anderer Provider für TDSL (Dun)
Germany
PPPoE RFC2516
Embedded
1 32 LLC
Anderer Provider für TDSL (Soft)
Germany RFC 1483 Bridged 1 32 LLC
Tiscali Germany PPPoE - RFC2516 1 32 LLC
Service Provider Region WAN Service VPI VCI
Encapsulation -LLC or
VCMUX
Islandssimi Iceland PPPoA - RFC2364 0 35 VCMUX
Landssimi Iceland PPPoA - RFC2364 8 48 VCMUX
Nextra Italy PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Tiscali Italy PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Aruba Italy PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (22 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 80

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
MC-link Italy PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Wind Italy PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 LLC-VCMUX
Telvia Italy PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Albacom Italy PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Telecom Italia Italy PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 LLC
KPN MXSTREAM Netherlands PPPoA - RFC2364 8 48 VCMUX
New Zealand Telecom New Zealand PPPoA - RFC2364 0 100 VCMUX
Portugal Telecom Portugal RFC 1483 Routed 8 35 LLC
SingNet Broadband Singapore PPPoA - RFC2364 0 100 VCMUX
Service Provider Region WAN Service VPI VCI
Encapsulation -LLC or
VCMUX
Wanadoo Spain Spain RFC1483 Routed 8 32 LLC
Ya.com Spain RFC 1483 Routed 8 32 LLC
Uni2 Spain PPPoA - RFC2364 1 33 LLC
Telefonica Spain RFC 1483 Routed 8 32 LLC - VCMUX
ERES MAS Spain PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 LLC
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (23 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 81

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Jazztel Spain PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 LLC
Terra Spain RFC 1483 Routed 8 32 LLC
Retevision Spain PPPoA - RFC2364 8 35 VCMUX
Tiscali Spain PPPoA - RFC2364 1 32 VCMUX
Telepac Spain
PPPoE RFC2516
Embedded
0 35 LLC
Skanova Sweden RFC 1483 Bridged 8 35 LLC
Etisalat Classical IP
Single User
UAE
RFC 1577 (1483)
Routed
0 100 LLC
Etisalat Classical IP for
Business
UAE PPPoA - RFC2364 0 50 VcMux
UAE-Other UAE
PPPoE RFC2516
Embedded
0 50 LLC
UAE-Other UAE RFC1483 Routed 0 100 LLC
Service Provider Region WAN Service VPI VCI
Encapsulation -LLC or
VCMUX
UK All ISP UK PPPoA - RFC2364 0 38 VCMUX
AOL US RFC 1483 Bridged 0 35 LLC
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (24 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 82

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
SBC US RFC 1483 Bridged 0 35 LLC
Sprint US RFC 1483 Bridged 0 35 LLC
BellSouth US RFC 1483 Bridged 8 35 LLC
Qwest US RFC 1483 Bridged 0 32 LLC
Verizon US RFC 1483 Bridged 0 35 LLC
Covad US RFC 1483 Bridged 0 35 LLC
EarthLink US RFC 1483 Bridged 0 35 LLC
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003%20(Guinness)/User%20Guide/9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/installa.htm (25 of 25) [11/6/2002 8:55:05 AM]
Page 83

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Contents:
US Robotics
SureConnect ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router
Configuration Utility
Summary
Web User Interface
Terminal User Interface
Command Line
Interface
Configuration Examples
Installation
Uninstallation
Troubleshooting
Glossary
Regulatory Information
U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL
Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Windows 95, 98, NT 4.0, Me, 2000, XP or later,
Mac and Linux
Terminal User Interface
Overview
The Terminal User Interface (TUI) is one of three router user interfaces. The other interfaces are
the Web User Interface (WUI) and Command Line Interface (CLI). Each interface allows you to
set up, modify, and view router configuration variables and operational data.
The Terminal User Interface is a system of hierarchical, character-based menus. See the
nearby overview for a graphic map of the interface.
Each menu presents options and prompts you for a response. Options occupy most of a menu
screen. The bottom of the screen provides information about expected responses…
● Mandatory vs. optional
● Allowable formats
● Operation success or failure
● Error messages
● Directions on what to do next
This document often refers to menu screens with path notation. For example, consider the
example in the following table…
The Desired Action The Process The Path Notation
Access PPPoA configuration
menu from Main Menu
screen.
Choose 2 for ‘ADVANCED’, 7
for ‘SNDCP’, 3 for ‘PPPoA’,
and 2 for ‘CONFIGURE
PPPoA’.
Main Menu=>Advanced=>
SNDCP=>PPPoA=>
Configure PPPoA
Screen shots best describe some menu options. In this manual, a description precedes each
screen shot. Afterward, the manual provides definitions of screen variables. Pages without
screen shots include a menu path, followed by a description and necessary definitions.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003.../9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (1 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 84

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Accessing the Terminal User Interface
To access the Terminal User Interface, follow these steps…
1. Connect a console cable between a computer and the router.
2. Launch a terminal emulation program.
3. Configure the terminal emulation program as follows…
• Terminal Type: VT-100 • Parity: None
• Bits Per Second: 9600 • Stop Bits: 1
• Data Bits: 8 • Flow Control: None
4. Turn on the router. Configuration messages appear as the router boots up.
5. Allow the default configuration to load.
6. When prompted, type in the User Name and Password. The default user name is Root. The
default password is 12345.
Terminal User Interface Map
Click for PDF
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003.../9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (2 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 85

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
version of TUI map:
Main Menu
The Main Menu is the first or top-level menu in the Terminal User Interface. The Main Menu
presents you with three options…
● Enter 1 to open the to the Basic Menu.
● Enter 2 to open the Advanced Menu.
● Enter 0 to exit the Terminal User Interface.
Main Menu=>
Basic
Enter 1 at the Main Menu. The Basic Menu appears. This menu includes the following options…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003.../9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (3 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 86

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Main Menu=>Basic=>
Access Control
Enter 1 at the Basic Menu. The Access Control Menu appears. This menu provides the following
options…
• List Users. Lists currently defined users by type, and provides associated services. The
user “root” is the default administrative login for the router.
• Configure User. Opens the Configure User Menu, which allows you to add or delete users.
Add users to enforce ACL (Access Control List) and proxy services. Options include…
§ User Name § Password
§ Permissions (admin /
ordinary)
• Delete User. Allows you to delete users by user name.
• Change Password. Allows you to change a user’s password. Options include…
§ User Name § Old Password
§ New Password § Confirm Password
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003.../9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (4 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 87

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Main Menu=>Basic=>
Link Status
Enter 2 at the Basic Menu. The Link Status Menu appears. This menu displays current link
status. Link status parameters include…
Link Status Parameters
Status Term Meaning
ADSL Line Status Displays the current ADSL line status
ADSL Standard Displays the ADSL standard within the
current configuration. The standards are:
MULTI, T1.413, G.dmt, and G.Lite.
UpStream Displays the upstream data rate, as
negotiated by DSL link (KB/s)
DownStream Displays the downstream data rate, as
negotiated by DSL link (KB/s)
Attenuation Displays the current attenuation in decibels
SNR Margin Displays the current SNR margin in decibels
HEC Count Displays the number of ATM cells received
with errors since start of link.
Firmware Displays the version number of the firmware
15 min ES Counter Displays the number of errors per second
for the current 15-minute period
CRC Errors Displays the number of cyclical redundancy
check errors per second since training
1 day ES Counter Displays the number of errors per second
for the current day
Main Menu=>Basic=>
WAN Setup
Enter 3 at the Basic Menu. The WAN Setup Menu appears. This menu allows you list, configure,
or delete ATM PVCs. Each option takes you to another screen.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003.../9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (5 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 88

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
• ATM PVC List. Enter 1 at the WAN Setup Menu. The ATM PVC List Menu appears. This
menu displays a list of currently defined PVCs.
• ATM PVC Configuration. Enter 2 at the WAN Setup Menu. The ATM PVC Configuration
Menu appears. To configure an ATM PVC…
1. Enter a 2 on the WAN Setup Menu. The ATM PVC Configuration Menu appears.
2. Enter VPI and VCI data…
§ VPI [0-255]
§ VCI [0-65,535]
§ SNDCP Component ( )
§ [Bridge / Routed / PPPoE /
PPPoA / MER]
§ Encap [vc / 11c]
§ Nat [Enable / Disable]
§ WAN IP Address ( )
§ Subnet Mask ( )
§ User Name
§ Password
§ Mode [Auto / Direct]
§ Idle Timeout [min]
§ Authentication ( )
§ [pap / chap / mschapv1 /
mschapv2]
§ DHCP Server ( )
3. Five Subnetwork Dependent Convergence Protocol (SNDCP) options appear. (Bridge /
Routed / PPPoE / PPPoA / MER)
4. Choose the SNDCP option provided by your DSL service provider. Next, SNDCP
options for the SNDCP that you selected appear. Subsequent screens present several
options for each SNDCP.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003.../9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (6 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 89

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
5. Enter the required information…
Main Menu=>Basic=>
WAN Setup (continued)
§ Bridge
A. For a bridge PVC, enter a 1 at SNDCP Component.
B. Enter the encapsulation type (vc or 11c).
§ Routed
A. Enter SNDCP option 2 for routed.
B. Choose the encapsulation method.
C. Choose to enable or disable the NAT.
D. Configure the WAN IP Address.
E. Configure the subnet mask.
§ PPPoE
A. Enter SNDCP option 3 for PPPoE.
B. Enter remaining information as provided by your DSL service provider.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003.../9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (7 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 90

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
§ PPPoA
A. Enter SNDCP option 4 for PPPoA.
B. Enter remaining information as provided by your DSL service provider.
§ MER
A. Enter SNDCP option 5 for MER.
B. Enter remaining information as provided by your DSL service provider.
6. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save
& Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
Main Menu=>Basic=>
WAN Setup (continued)
• ATM PVC Deletion. Enter 3 at the WAN Setup Menu. The ATM PVC Deletion Menu
appears. To delete an ATM PVC…
1. Enter valid VPI and VCI values.
2. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save
& Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
Main Menu=>Basic=>
LAN Setup
Enter 4 at the Basic Menu. The IP LAN Menu appears. To configure a LAN IP address…
1. Accept default values or enter new IP address and subnet mask values.
2. Use LAN Setup to set the router’s IP Address and Subnet Mask.
3. Setup the LAN IP address to connect the router to.
4. Manage the router from your Local Area Network (LAN). A LAN connects computers in
the same building or area.
5. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save
& Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003.../9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (8 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 91

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
IP addresses deliver packets of data across a network. These addresses differentiate the
source and destination IP address and keep them constant. When a router port detects a
packet, the router checks the routing table. The port attempts to match the network number of
the destination IP address with its routing table entry. If the port finds a match, it forwards the
packet to the destination network. With no match, the port forwards the packet to a router
defined as the default gateway.
Subnet masks split one network into a set of mini networks or subnets. Subnetting helps to
reduce traffic on each subnet. Subnetting also makes the network more manageable. Each
subnet functions as if it were an independent network.
Main Menu=>Basic=>
USB Configuration
Enter 5 at the Basic Menu. The Configure USB Interface Menu appears. To configure the USB
interface…
1. Enter a valid IP Address.
2. Enter a valid subnet mask.
3. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save
& Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/9003.../9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (9 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 92

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Main Menu=>Basic=>
MER Configuration
Enter 6 at the Basic Menu. The Configure MER Menu appears. To configure the MER
interface…
1. Enter a valid subnet mask.
2. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save
& Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (10 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 93

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Main Menu=>Basic=>
Routing Setup
Enter 7 at the Basic Menu. The Routing Setup Menu appears. The Routing Setup menu
provides seven menu options. These options allow you to configure a route.
● List Of Static Routes. Enter 1 at the Routing Setup Menu. The List of Static Routes
Menu appears. This menu lists defined static routes by Network ID address, subnet mask,
and next hop address.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (11 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 94

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
● Configure Route. Enter 2 at the Routing Setup Menu. The Configure Route Menu
appears. From this menu, you can add new static routes. A router forwards data packets
between local area networks (LANs) or wide area networks (WANs). Based on routing
tables and routing protocols, routers read the network address in each transmitted frame.
Routers then decide how to send the frame. A router bases this decision on the best
route. The Configure Route Menu allows you to adjust how the router forwards received
IP packets.
To configure a route…
1. Enter a valid destination network ID. This is the network IP designation of the network
defined in the table.
2. Enter a valid destination subnet mask. This is the network subnet mask of the entry
defined in the table.
3. Enter a valid next hop ID. This is the IP address or gateway that the router uses to arrive
at the destination address.
4. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save
& Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
Main Menu=>Basic=>
Routing Setup (continued)
• Delete Route. Enter 3 at the Routing Setup Menu. The Delete Route Menu appears. From
this menu, you can delete a route. To delete a route…
1. Enter the appropriate network ID.
2. Enter subnet mask data.
3. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save
& Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
• Flush Routing Table. Enter 4 at the Routing Setup Menu. The Flush Routing Table Menu
appears. To flush a routing table…
1. Type Y.
2. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save &
Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
• RIP Information. Enter 5 at the Routing Setup Menu. The RIP Information Menu appears.
This menu lists currently configured RIP information.
• Configure RIP. Enter 6 at the Routing Setup Menu. The Configure RIP Menu appears. Use
this menu to turn RIP on or off. Also use the menu to define which RIP version to use. Routing
Information Protocol (RIP) is a routing protocol and is part of the TCP/IP suite. RIP plots a route
based on the smallest hop count between source and destination. RIP determines the smallest
hop count by communicating with other routers in the network. Only use RIP if the target router
also utilizes RIP.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (12 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 95

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
To set up a route…
1. Enter the RIP status. Set RIP Status to either “on” or “off.”
2. Enter a number for the version. Either set RIP Version to 1 (for RIP1) or 2 (for RIP2). The
version number must match the RIP version that other routers in the network use.
3. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save
& Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
• RIP List. Enter 7 at the Routing Setup Menu. The RIP List Menu appears. This menu
displays routes that the RIP has learned. You’ll see an empty list if RIP is off or if the router
hasn’t learned any routes.
Main Menu=>Basic=>
Save & Reboot
Enter 8 at the Basic Menu. The Save & Reboot Menu appears. This menu allows you to save
the current configuration and reboot the router.
Main Menu=>Basic=>
Erase & Reboot
Enter 9 at the Basic Menu. The Erase & Reboot Menu appears. This menu allows you to erase
the saved configuration and reboot the router.
Main Menu=>
Advanced
Enter 2 at the Main Menu. The Advanced Menu appears. This menu provides the following
options…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (13 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 96

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Main Menu=>Advanced=>
ADSL Mode
Enter 1 at the Advanced Menu. The ADSL Mode Menu appears. This menu allows you to read
or write configuration and management variables, or configure the ADSL mode. The router uses
configuration and management variables (CMV) to tweak performance and provide
management functions. Router firmware defines these values.
!
CAUTION
Don’t write configuration and management variables unless you
receive explicit instructions to do so. Alteration of CMV values can
adversely affect router performance.
• Configure ADSL Mode. Enter 3 at the ADSL Mode Menu. The Configure ADSL Mode
Menu appears. This menu allows you to switch the ADSL mode to ANSI (T1.413), G.dmt, G.lite
or Multimode. Your ADSL service provider determines these values.
!
CAUTION
Leave ADSL mode values alone unless you receive specific
instructions on what to do. Alteration of the ADSL mode can
adversely affect router performance.
Main Menu=>Advanced=>
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (14 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 97

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
DHCP Server
Enter 2 at the Advanced Menu. The DHCP Server Menu appears. DHCP stands for Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol. This protocol dynamically assigns IP addresses and related
information to Local Area Network (LAN) nodes. For temporarily connected network users,
DHCP provides safe, reliable, and simple TCP/IP network configuration. DHCP confers these
benefits by preventing address conflicts and conserving IP address use. To conserve address
use, DHCP centralizes address allocation.
The DHCP Server menu provides the following options…
● List DHCP Server. Enter 1 at the DHCP Server Menu. The List DHCP Server Menu
appears. This menu provides a list of currently configured DHCP servers and associated
variables.
● Configure DHCP Server. Enter 2 at the DHCP Server Menu. The Configure DHCP
Server Menu appears. To configure a DHCP server…
1. Choose an Ethernet interface. The remaining DHCP options appear on the screen.
2. Create a new DHCP server for the selected interface by entering legal values for each
variable. See DHCP variables below.
3. Set the following parameters…
DHCP Parameters
DHCP Term Definition
Interface LAN port that the DHCP server will support.
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (15 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 98

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
Starting IP Address First IP address provided on a LAN port node’s DHCP
request.
End IP Address Last IP address in the pool provided on a LAN port
node’s DHCP request.
Gateway IP address of the Default Gateway or Router that the
node will use.
Netmask Subnet Mask for the LAN that the node will be on.
DNS Domain Name Server. Actually, here we aren’t referring
to the DNS itself. Instead, we refer to the IP address of
the DNS that the node will use. DNS is a server with a
database. The database translates a domain name into a
corresponding IP address. For example, “USR.com”
resolves into IP address 231.222.320.04. Use this
address to communicate over the LAN between the node
and USR.com web site.
Lease Time Number of days that the node can use a DHCP lease.
Subsequently, you must renew the lease with the DHCP
server.
4. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save
& Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
Main Menu=>Advanced=>
DHCP Server (continued)
● DHCP Server Status. Enter 3 at the DHCP Server Menu. The DHCP Server Status Menu
appears. This menu displays current DHCP server status. The menu also allows you to
enable, disable, or delete DHCP servers.
● List DHCP Relay. Enter 4 at the DHCP Server Menu. The List DHCP Relay Menu
appears. This menu displays DHCP Relay information.
● Configure DHCP Relay. Enter 5 at the DHCP Server Menu. The DHCP Server Status
Menu appears. This menu allows you to configure DHCP relay functions. Suppose that a
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server resides on a different LAN than the
node broadcasting for DHCP service. Then the DHCP broadcast request must be
forwarded across the router/WAN to a subnet where a DHCP server resides. To assure
receipt of an IP address that corresponds to this subnet, the router relays DHCP. The
router must have a record of the DHCP server’s IP address. With this address, the router
can direct the request to the DHCP server’s appropriate input IP address.
To configure a DHCP relay, follow these steps…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (16 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 99

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
1. On the Configure DHCP Relay Menu, input the IP address of DHCP server.
2. Enable the relay agent.
3. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The Save &
Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the router.
Main Menu=>Advanced=>
SNMP
Enter 3 at the Advanced Menu. The SNMP Menu appears. This menu provides the following
options…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (17 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
Page 100

U.S. Robotics SureConnect ADSL Ethernet/USB Router User Guide
● List of SNMP Entries. Enter 1 at the SNMP Menu. The SNMP Entries Menu appears.
This menu lists your SNMP variable settings.
● Configure SNMP. Enter 2 at the SNMP Menu. The Configure SNMP Menu appears. This
menu allows you to configure SNMP variables.
1. Enter VPI and VCI data…
§ System Version description ( )
§ System Contact ( )
§ System Location ( )
2. After you complete your configuration, proceed to the Basic Menu and enter 8. The
Save & Reboot Menu appears. From this menu, save your changes and reboot the
router.
● Shutdown SNMP Agent. Enter 3 at the SNMP Menu. The Shutdown SNMP Agent Menu
appears. This menu allows you to shut down the SNMP agent.
Main Menu=>Advanced=>
Firewall
Enter 4 at the Advanced Menu. The Firewall Menu appears. This menu provides the following
options…
file:///P|/T_WRITER/Documentation/Released/900...9003%20(Guiness)%20prac%20template/tquicks.htm (18 of 42) [11/6/2002 8:58:14 AM]
 Loading...
Loading...