Usp connectors EWP User Manual

EWP Product Guide 2005
P
www.
UUSSP
connectors.com
THF17925
Lumberton • Largo • North W
©
Copyright 2005 United Steel Products Company
LSSH23
ilkesboro • Montgomery • Houston • Rancho Cucamonga • Livermore • Long Beach • Thornhill, Ontario
THO171
18
USP952-051

2
USP Index
IInnddeexxees
s
BPHB
eam & Purlin Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . 22-23, 27-40, 55, 57
CBE Column Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48-49
CBS Column Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
CBSQ Column Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
EPCM End Post Caps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
EWP Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-13
HD Face Mount Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-15, 17-19, 55-56
H
LBHBeam Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26, 31-40, 55, 57-58
HTW Twist Straps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
HUS Face Mount Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-15, 17
KCB Column Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48-49
KCBQ Column Bases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
KCCC
olumn Caps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52-53
KCCQ Column Caps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
KECC End Column Caps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52-53
KECCQ End Column Caps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
KLCC Lally Column Caps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
KSTI Strap Ties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46-47
LBH Beam Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26, 31-40. 55, 57-58
LSSH Slope/Skew Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42, 56
LSTA Strap Ties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46-47
LSTI Strap Ties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46-47
MPH Masonry Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24-25, 27-40, 55, 57-58
MSH Strap Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
MSTA Strap Ties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46-47
MSTC Strap Ties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46-47
Reference Number Index
M
TW Twist Straps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
NA Nails . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-9
NFM Masonry Hangers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41, 55, 58-59
PAI Purlin Anchors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
PCM Post Caps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
PH Top Flange Hangers. . . . . . . . . . 24-25, 27-28, 33, 55, 57-58
PHI I-Joist Top Flange Hangers . . . . . . . 24-25, 27-35, 55, 57-58
PHMT
op Flange Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . 24-25, 27-40, 55, 57-58
PHX Top Flange Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . 24-25, 27-40, 55, 57-58
PHXU Top Flange Hangers . . . . . . . . . . 24-25, 27-40, 55, 57-58
RT Hurricane/Seismic Anchors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
SKH Skewed 45˚ Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20-21, 55
S
KHHSkewed 45˚ Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20-21, 55
Specialty Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55-58
Specification Tools. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
TFI Top Mount Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22-23, 29-31, 34-35
TFL Top Mount Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22-23, 29-30
THD Face Mount Hangers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-19, 55-56
THDH Face Mount Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-19, 55-56
THF Face Mount Hangers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-15, 17-19, 55-56
THO Top Mount Hangers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22-23, 27-40
TMP Rafter-to-Plate Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
TMPH Rafter-to-Plate Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
WS Wood Screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
WS Wood Screw Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-11
About the Reference Numbers
Reference numbers shown throughout the
charts in this catalog are part numbers which
may be more familiar to customers in various
regions of the United States. These are
included for the convenience of our new
customers who have recently switched from a
competitor’s product line to USP.
The reference numbers in this catalog are
for general application comparison only and
should not be used as a substitution tool.
The user is responsible to compare specific
load values, fastener schedules, material
specifications, and other factors to
determine suitability of use for any
particular product.
B Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27-34
CB Column Base . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
CBQ Column Base . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
CBS Column Base . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
CBSQ Column Base . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
CC Column Cap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
CCQ Column Cap
WARRANTY
United Steel Products Company warrants its products to be free from defects in material
and workmanship. Said products are further warranted as to adequacy of design, provided
products are used in strict accordance with United Steel Product Company’
design limits and are installed in a workmanlike manner
the event products are cut, notched, welded, drilled or in any way altered). No warranty
applies if deterioration occurs due to environmental conditions. United Steel Products
Company’s obligations under this warranty shall be limited to the replacement or repair of
those products demonstrated to be defective. Such remedy shall constitute Customer
sole and exclusive remedy and Customer hereby agrees that no other remedy (including,
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
ECC Column Cap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
ECCQ Column Cap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
EPC Post Cap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
GLTV Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31-40
H Hurricane Ties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
HB Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35-36
HGLTVHanger
HGUS Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18-19
HHUS Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18-19
HSUR/HSUL Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
HTS Twist Strap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
HU Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17-19
HUS Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
HW Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29-40
HWU Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31-40
ITT Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27-34
IUS Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
IUT Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17-18
LBV Hanger
LCB Column Base
LCC Lally Column Cap . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
LSSU Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
. (Said warranties do not apply in
s current published
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
but not limited to claims for INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR SPECIAL DAMAGES,
OR ANY CAUSE, LOSS, ACTION, CLAIM OR DAMAGE, INCLUDING LOSS OF TIME,
WHATSOEVER, OR INJURY TO PERSON OR PROPERTY OR ANY OTHER CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGE OR INCIDENTAL OR ECONOMIC LOSS) shall be available to Customer
said claims be asserted on the basis of warranty, negligence, strict liability or otherwise.
WARRANTY IS EXPRESSLY IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, ALL SUCH OTHER WARRANTIES BEING HEREBY
s
’
EXPRESSLY EXCLUDED.
31-40
32-37
49
LSTA Strap Tie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
LSTI Strap Tie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
MBHA Masonry Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . 41
MIT Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29-36
MIU Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17-19
MSTA Strap Tie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
MSTC Strap
Tie
MSTI Strap Tie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
MTS Twist Strap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Nails . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
PAI Purlin Anchor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
PC Post Cap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
SDS Screw . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-11
SUR/SUL Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
THA Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
THAC Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
THAI Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
W Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27-34
WM Hanger
WP Hanger
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
27-34
27-34
WPU Hanger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27-34
whether
THIS
Customer Service / Technical Assistance
Burnsville, MN Corporate Of
1-800-328-5934
fice

HHiissttoorryy && PPrroodduucctt IInnffoorrmmaattiioon
n
3
ompany History
C
USPS
Company) has been designing, manufacturing, and
marketing construction hardware for over 50 years.
T
engineering, and superior customer service has
allowed USP to be the leader in developing new
structural connectors for a changing construction
industry.
tructural Connectors
he company’s experience in marketing,
®
United Steel Products
(
Burnsville, MN Corporate Office
14305 Southcross Drive
Suite 200
Burnsville, MN 55306
Phone: 1-952-898-8772
Phone: 1-800-328-5934
Fax: 1-507-364-8762
Livermore, Western Region
2150 Kitty Hawk Road
Livermore, CA 94551-9522
Phone: 1-800-227-0470
Phone: 1-925-449-4100
Fax: 1-925-373-9213
Largo, Eastern Region
11910 62nd Street North
Largo, FL 33773-3705
Phone: 1-800-328-5934
Fax: 1-727-535-8199
roduct Questions & Answers
P
The Customer Service/ Technical Assistance staff is
ready to answer your questions and help solve your
connector related problems. Our staff can assist you
in developing economical solutions for your structural
connection problems.
When calling for Technical Assistance, please have
the following information ready:
• Which USP product are you using?
• What is the width and height of both the supported
and supporting members?
• What is the header material and application?
What is the load requirement?
•
Thornhill, Canadian Office
221 Racco Parkway
Thornhill, ON L4J 8X9
Phone: 1-800-387-3589
Fax: 1-905-669-1563
USP Operations Include:
• Nine strategically placed manufacturing and
warehousing locations.
• In-house quality control and testing with independent,
third-party plant inspection, and test witnessing.
• On staff licensed professional engineers.
• Our National Factory Technical Sales Force is
ready to help with application questions.
• Ongoing regional and national code evaluations as
products are developed.
ISO 9001:2000 Registered
UUSSPP SSttrruuccttuurraall CCoonnnneeccttoorrss®
in Montgomery, Livermore, Largo,
and North Wilkesboro achieved
registration of its quality
system in accordance with
the requirements of
ISO 9001:2000
®
USP952-051
4
Douglas Fir-Larch (DF-L) 0.50 1.00
Southern Pine (SP) 0.55 1.00
Spruce-Pine-Fir (S-P-F) 0.42 0.86
1) Allowable loads must be adjusted according to the
applicable wood species.
2) When using structural composite lumber, verify wood species
and use above listed adjustment factors.
Douglas Fir (S)
Hem Fir (N)
0.46
0.88
Allowable Load Adjustment Factor
Wood
Species
Specific
Gravity
Adjustment
Factor
PPrroodduucctt IInnffoorrmmaattiioon
n
Please Note
1) USP Structural Connectors®reserves the right to
change specifications, designs, and models without
otice and liability for such changes. This catalog may not
n
e reproduced in whole or in part without the prior written
b
approval of
2) This catalog reflects design changes and design
USP Structural Connectors®.
load
adjustments to some USP products. The information
presented in this publication supercedes all information
published in previous documents, and is valid until
December 31, 2005.
3) This Full Line Catalog was designed as a general
reference for the USP Product Line. Various
specialized publications have been developed for design
professionals, truss manufacturers, contractors, retail
dealers, and building material wholesalers. Product load
values may vary from one publication to
another due to recent product testing, changes in
regulatory criteria, or code evaluation updates. The most
current product information is available on USP’s website.
4) To achieve the allowable loads presented in this
catalog, all specified fasteners must be used and
proper installation procedures observed. Verify that the
dimensions of supporting members are sufficient to
receive specified fasteners. Any product modifications
void the warranty unless
prior written permission of
USP Structural Connectors®is obtained.
5) Some connector models are listed more than once to
indicate installation and/or fastener options.
6)
Nails specified as 8d, 10d and 16d are common
wire
nails.
7) Bolts specified conform to
ASTM A 307 or better.
8) Products are sized for standard lumber, glulam, or
engineered wood products. For applications involving
unusual supporting conditions, excessive shrinkage, or
hostile environments, contact USP Structural Connectors®.
NDS®
Standards
Unless otherwise noted, the load resistance values
presented in this catalog reflect the calculation criteria set
forth in the 1997 or 2001 National Design Specification for
ood Construction (NDS
W
®
) published by the
American
Forest and Paper Association. Load values presented in
this catalog may not match those presented in previous
publications. The values shown in this catalog supercede
those previously printed.
Testing
On all structurally-rated products, USP performs
full-scale testing in accordance with ICC-ES, AC13, or
ASTM D 1761, the standard recognized by all
omestic code agencies. All final testing is conducted by
d
a third-party testing laboratory.
Material
USP Structural Connectors®are manufactured
from prime quality steel which meets ASTM A 653
requirements for galvanized steel, and ASTM A 1011, or
ASTM A 36 for hot-rolled steel.
Finish
All galvanized products have a zinc coating as
specified in ASTM A 653. Hot-dip galvanized parts are
galvanized after fabrication per ASTM A 123.
Non-galvanized steel products are prime coated.
All standard galvanized products manufactured after
January 1, 2005 will be made from G90 material.
Product Design Loads
The design loads listed are the lowest results obtained by
one of the following methods:
1) The lowest ultimate tested load divided by three.
2) Lowest load producing
3) Calculations based on 1997 or 2001 NDS®and current codes.
1
˝ deflection.
/
8
Duration of load adjustments for mechanical fastenings
are as follows:
Floor / Design Load . . . . . 100% no increase.
Roof Snow . . . . . . . . . . . . 115% of design load for 2-month duration of load.
Roof Non-Snow
Uplift. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133% or 160% of design load for wind/seismic
. . . . . . . .
125% of design load for 7-day duration of load.
loading based on local code requirements.
Spruce-Pine-Fir or Hem Fir Equivalent Capacity
Unless otherwise noted, the published design loads in this
catalog apply to Douglas Fir-Larch or Southern
Pine lumber. When Spruce-Pine-Fir or Hem Fir lumber
is use with
face mount
hangers or
straps, the
nail shear
capacity
maybe
adjusted
according to
the chart to
the right.
Customer Service / Technical Assistance
Burnsville, MN Corporate Of
1-800-328-5934
fice
PPrroodduucctt IInnffoorrmmaattiioon
No
1
1605.3.1.1, 1605.3.2
1) Increase is permitted with multiple transient loads(North American Specification
for the Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members, 2001 Edition, NASPEC)
Steel Stress Increase Allowed
Basic Load
Combinations
Alternate Load
Combinations
n
Allowable Stress Increase Design Values
There have been recent changes in the model building
codes which affect the published design loads in this
catalog, as well as other USP catalogs. Historically,
ome design codes permitted the use of a one-third-
s
stress increase on steel allowable stress design values
hen resisting load combinations including wind and
w
seismic loads. Many states have recently adopted
model building codes which in some cases do not allow
you to take this stress increase. The table below shows
which building codes do and do not allow a
one-third-stress increase on steel.
Code Code Section
ASCE 7-98 No -- -- 2.4.3
ASCE 7-02 No -- -- 2.4.1
2000 IBC No Yes 1605.3.1, 1605.3.2
2003 IBC No
1997 UBC No Yes 1612.3.1, 1612.3.2
The code, however, does allow for a load duration
factor, which increases the allowable wood stress. This
is referenced in the National Design Specification
for Wood Construction which is referenced by
NDS®)
(
the model building codes. Load duration factors of
.15, 1.25, 1.33, and 1.6 are utilized for construction,
1
snow, wind, and seismic loads. For this reason the
tables in the catalog contain columns with allowable
loads listed for the different load duration factors. It is
important to note that the load duration factor is not
related to or affected by the recent changes in the steel
allowable stress increase.
As stated previously, removing the increases on
allowable steel stresses has affected the capacity of
some of our products. These products include many of
our strap ties and strap-type anchors. For these
products where a decrease in the allowable steel
stress controls the published value, the capacity of the
product, the published value reflects this. No
additional reduction is necessary. In addition, to match
the lower capacity of the connector, the minimum
number of nails required has been reduced in many
cases.
5
Special Fastening Features
Seat Cleat™ Prongs – U.S. Patent #5,564,248
USP’s TFL, THO and THF I-Joist hangers feature the
patented Seat Cleat™ prong. The Seat Cleat™ allows
framers to “pop” I-Joists into hanger seats for a positive
bearing lock. This prevents spring back during nailing,
reduces post installation I-Joist movment, and eliminates
connector related floor system noise (if hangers are
installed according to
s specifications).
USP’
Simple, quick, and
Slant Nailing
via Dimple
Nail Holes
Seat
Cleat™
Prongs
easy-to-use, the Seat
Cleat™ eliminates the
need to bend tabs and
drive nails from an
awkward angle into the
Diamond
Holes
I-Joist bottom flange.
Slant Nailing via Dimple Nail Holes – U.S. Patent #5,217,317
USP’s Dimple Nail Holes are used to indicate the need
for slant nailing. Unlike tabs, the dimple retains its
shape better under misguided hammer strokes and cannot
be bent or broken. The Dimple Nail Hole also allows for
correct 45° angle placement in I-Joist hangers.
Diamond Holes
Diamond Holes are used to indicate either an optional
fastening pattern or for optional, temporary nailing to
aid installation.
Speed Prongs
Speed prongs help framers
by temporarily holding
connectors in place for
easier nail
Unless
stated otherwise,
fastening.
Speed
Prongs
speed prongs should not
be
considered an alternative
to nail fastening.
Slot Holes
Slot Holes are used to give
installers easier access to tight
fastening locations or to
provide floating action
Slot
Holes
between members. Fasteners
installed in slotted holes resist
shear only in one direction
while allowing limited drift in
the other direction.
www.USPconnectors.com
e-mail: info@USPconnectors.com
© Copyright 2005 United Steel Products Company
USP952-051

6
Product Information
Code Evaluations
ost USP structural products listed in this catalog
M
ave been evaluated or are in the submittal stage for
h
evaluation from one or more of the following code authorities.
With the consolidation of former services (ICBO ES, NES,
SBCCI PST & ESI, and BOCAI evaluation services) into ICC
valuation Service, Inc. (ICC ES), the following evaluation
E
reports now have the status of ICC-ES “Legacy Reports”.
The ICC-ES Web Site provides additional information, and
may be accessed at http://www.icc-es.org.
ICC-ES - ICC Evaluation Service, Inc. ESR-1178
NES - National Evaluation Service
NER-478, 505, 510, 530, 532, 564, 568, 608
ICBO - International Conference of Building Officials.
ICBO ES ER-2039, 2725, 3613, 4846, 5125, 5321,
5356, 5531, 5634, 5830
BOCA - Bldg. Officials and Code Admin. International, Inc.
SBCCI - Southern Bldg. Code Congress International, Inc.
State of Florida product Approvals - FL565, FL567,
METRO - Dade County, Florida
NER-478, 505, 510, 530, 532, 564, 568, 608
SBCCI PST & ESI 2031C, NER-478, 505, 510,
530, 532, 564, 568, 608
FL568, FL569, FL570, FL571, FL572, FL573, FL574,
FL575, FL576, FL577, FL578, FL815, FL816, FL817,
FL818, FL819, FL820, FL821, FL822, FL859, FL1247,
FL1777, FL2033, FL2620, FL2621, FL3017, FL3923
01-0327.04, 01-0417.11, 01-0724.06, 01-0912.05,
02-0102.04, 02-0102.05, 02-0102.06, 02-0128.05,
03-0206.03, 03-0219.02, 03-0508.04, 03-0508.05,
03-0611.05, 04-0427.02, 04-0427.03, 04-0427.04,
05-0204.01
DSA - Division of State Architect, California. DSA PA-076
LA CITY - City of Los Angeles, California
RR23888, 25104, 25029, 25113, 25283, 25303, 25325,
25327, 25332, 25337, 25357, 25433, 25434
ther code agencies may require specific reductions and
O
limitations and may have different load values than those
presented in this catalog. USP recommends consulting
specific code evaluation or product acceptance reports that
govern in the applicable area. Any questions about current
code listings should be directed to the Technical Assistance
staff. USP continuously updates code reports to reflect new
standards and requirements. Visit USP’s Web Site,
www.USPconnectors.com/codereports.htm, or specific
code agencies web sites for current listings. Code evaluation
reports referenced in this catalog may not apply to all stock
numbers or product series listed.
Code Watch
“Code Watch” items are included to highlight some sections
of the model building codes that discuss the use of products
contained in this catalog. The user is strongly encouraged to
consult with a qualified design professional to review the
exact requirements of the relevant code references. Please
note that not all code sections relating to the use of products
contained in this catalog are included. In addition, some
states and local municipalities have developed amendments
to the referenced code section. Shown references are for the
2003 International Residential Code (IRC), 2003 International
Building Code (IBC), and 1997 Uniform Building Code (UBC).
Corrosion Resistant Finishes
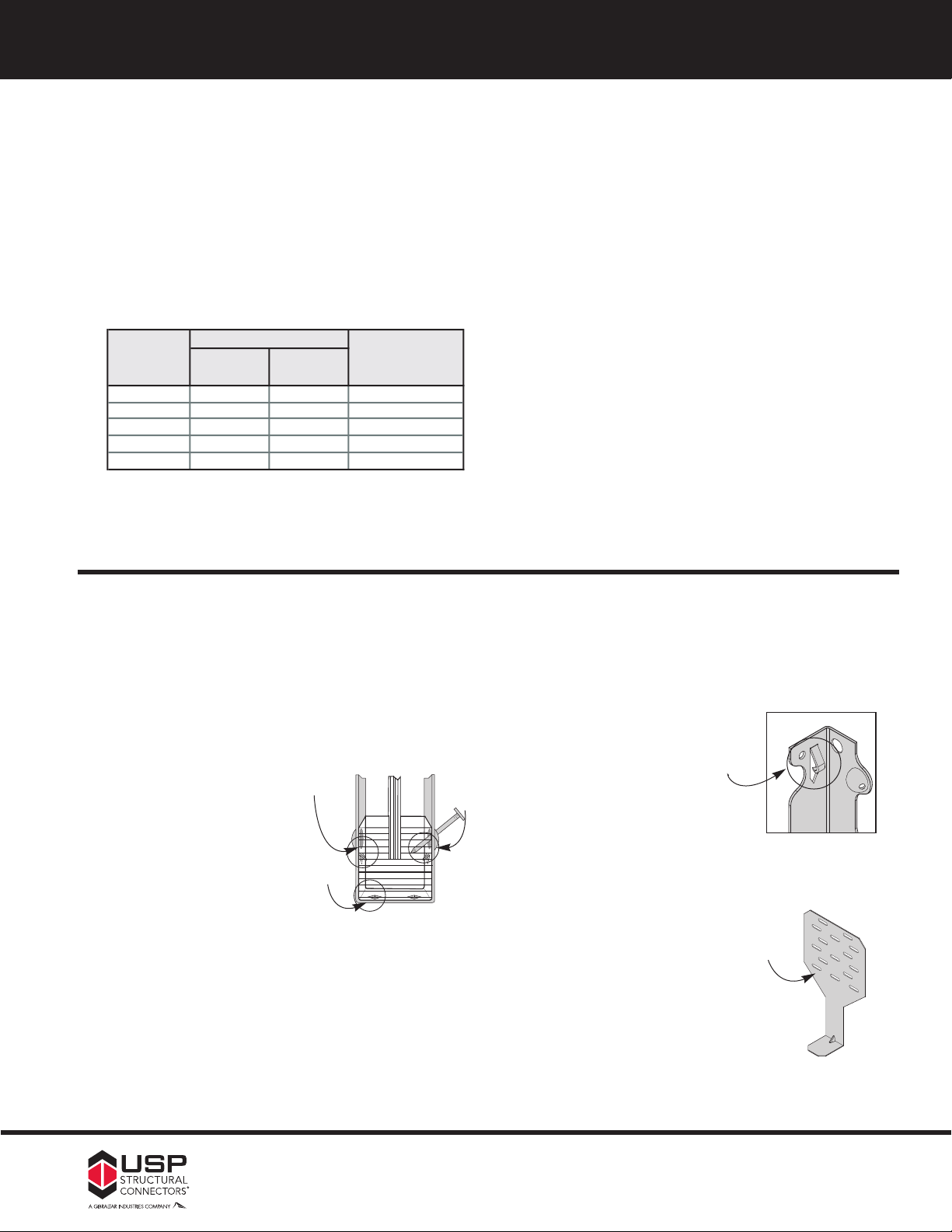
USP Structural Connectors™ offers three options for improved corrosion resistance:
Triple Zinc (TZ) – galvanizing provides a prefabrication coating of 1.85 (G-185) ounces of zinc per
square foot of surface area measured in accordance with ASTM A 653.
Required Fastener: Hot-dip galvanized fasteners
Hot-Dip Galvanized (HDG) – coating provides an after-fabrication hot-dipped zinc coating. The
coating thickness is dependent on the connector material, but generally ranges from 1.1 to 2.3
ounces of zinc per square foot of surface. Hot-dip products meet requirements set forth in
ASTM A 153.
Required Fastener: Hot-dip galvanized fasteners
Stainless Steel (SS) – is the best option for corrosion protection. Quality stainless steel (316SS
grade steel) is used to fabricate connectors. Although costs are higher, some applications
may need the virtual corrosion proof quality of stainless steel.
Required Fastener: Stainless Steel fasteners
Customer Service / Technical Assistance
Burnsville, MN Corporate Of
1-800-328-5934
fice
PPrroodduucctt IInnffoorrmmaattiioon
www.uspconnectors.com
PCS.
Para
Madera Tratada
n
Connector Use with Preservative Treated Wood
Recently the wood preservative manufacturers have
egun using Alkaline Copper Quat (ACQ) and Copper
b
Azole (CA-B) as replacement chemicals for CCA in
ome applications. The results of our corrosion testing
s
have shown that ACQ and CA-B preservative
reatments tend to corrode steel at a greater rate than
t
the CCA.
fasteners, installed in corrosive environments
to corrosive materials, or chemicals, can be
possibly resulting in the reduction of load values.
In general, connectors, including
anchors and
or exposed
damaged,
USP
recommends the use of stainless steel connectors for
maximum corrosion protection. However, as an
economical alternative, Triple Zinc G-185 connectors
may be used to provide a minimum level of corrosion
protection with the new wood preservatives. Standard
G90 connectors should not be installed in potentially
corrosive environments.
Corrosion is a multifaceted phenomenon dependent on
many variables. Most of these variables are
related to the environment the steel is placed in. These
variables include, but are not limited to,
exposure to ocean air or salt spray, chemicals used in
fire retardant and preservative treated wood, acid rain,
agricultural chemicals and fertilizers, animal wastes,
swimming pool chemicals, and even common outdoor
exposure with alternately wet and dry conditions. Of
course, there are many more possible corrosive
environments not mentioned here.
Galvanizing the steel, or coating it with a sacrificial
layer of zinc, is the most widely used protective system
in our lumber connector industry. Galvanized coatings
have a proven commercial history under a wide range
of environmental conditions.
• Ask for and follow recommendations of the
reservativewood treater for use of connectors and
p
fasteners in contact with their brand of treated wood
roduct.
p
• Connectors and their fasteners should always be of
ike materials.
l
• USP’s Zinc dichromate
WS Wood Screws are
not recommended for use with preservative or
fire-retardant treated wood.
• For any questions contact USP Technical Assistance
or visit our web site at
www.USPconnectors.com.
• USP clearly differentiates our Triple Zinc products
from standard G90 products. USP’s
TZ product
identification is embossed on all Triple Zinc products.
Following are examples of our Triple Zinc carton labels,
bin cards for retail displays, and individual product
labels.
Product Label
7
riple
T
Zinc G-185 contains roughly three times the
amount of zinc as G60 galvanizing. This provides
additional protection against corrosion attributed to the
new wood preservatives. Unfortunately, we are unable to
predict the service life of particular connectors in
selected environments. We can, however, provide
a relative level of protection information regarding
corrosion resistance. From this we can provide
guidance for the selection of corrosion protection based
on the anticipated environmental conditions.
Here are some Guidelines to follow:
• Potential for corrosion should be a part of the connector
selection criteria.
• USP
recommends the use of stainless steel
connectors for maximum corrosion protection.
However, as a minimum, Triple Zinc G-185 connectors
may be used as an economic alternative for corrosive
protection with the new wood preservatives.
www.USPconnectors.com
e-mail: info@USPconnectors.com
© Copyright 2005 United Steel Products Company
Bin Card
Carton Label
USP952-051

8
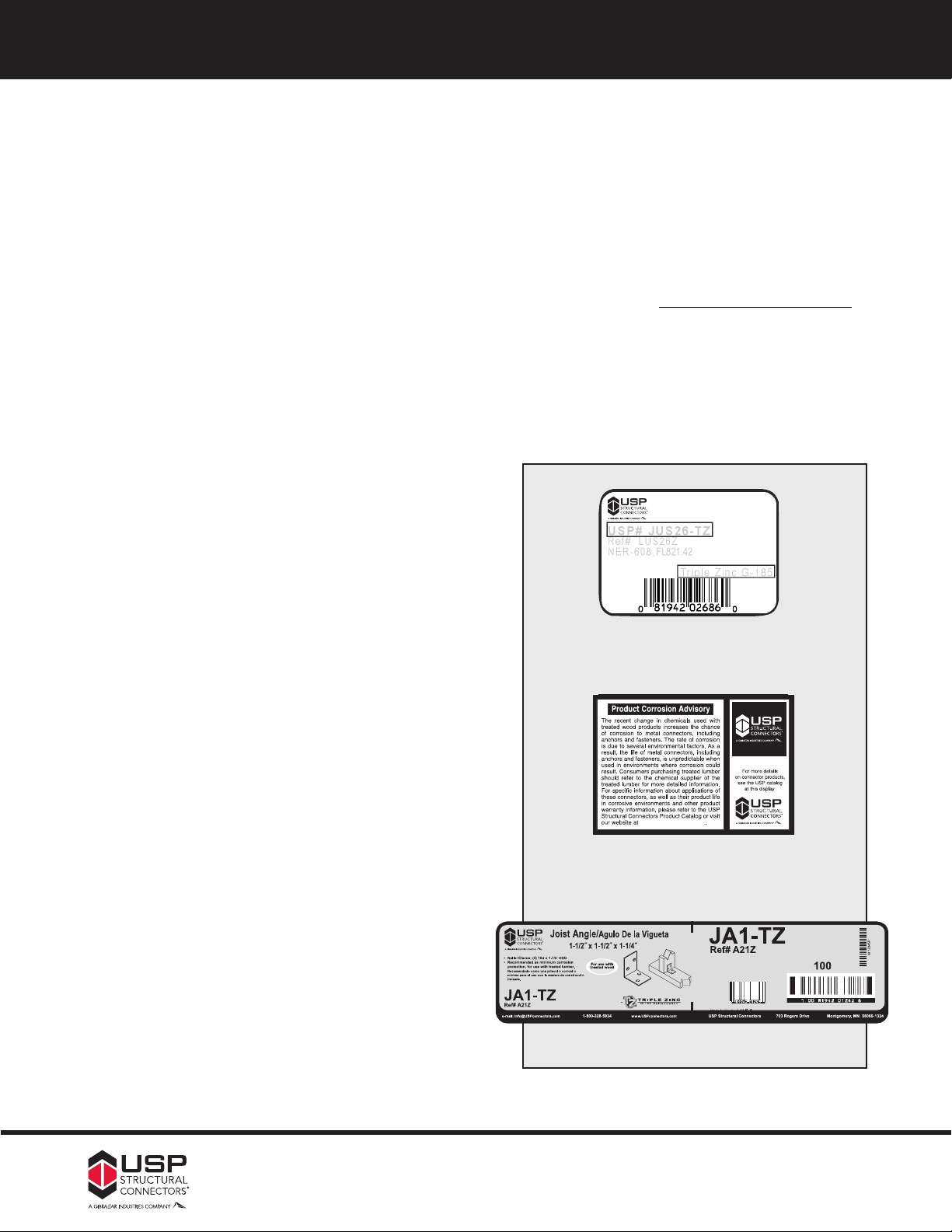
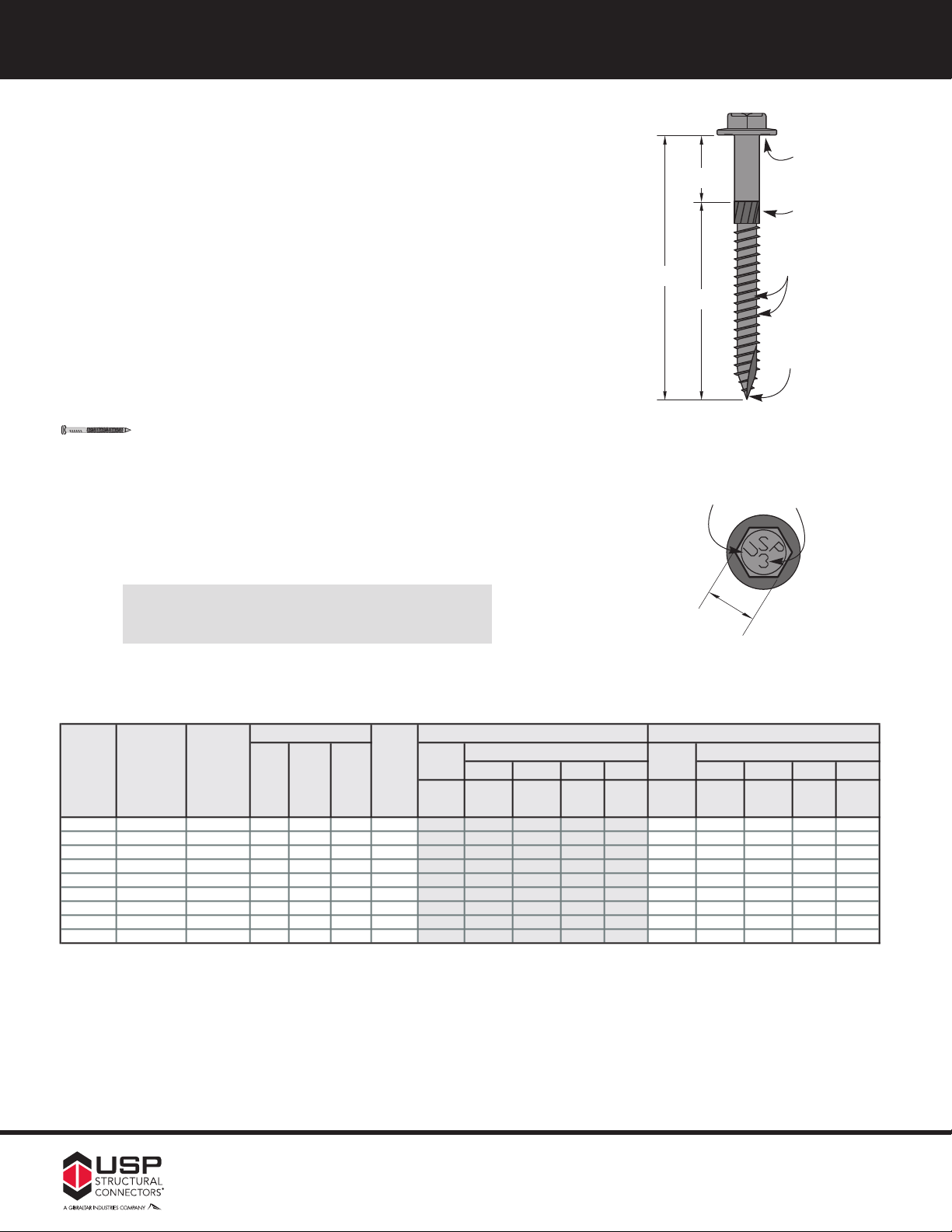
6d 11-1/2 ga. .113 1.13 0.68
8d 10-1/4 ga. .131 1.31 0.79
10d/16d Sinker 9 ga. .148 1.48 0.89
12d 9 ga. .148 1.48 0.89
16d 8 ga. .162 1.62 0.97
20d 6 ga. .192 1.92 1.15
1) Less than the specified nail penetration shall be
multiplied by the applicable adjustment factor.
2) For penetration less than this distance, the nail has no value.
Minimum
Penetration for
Reduced Load
2
(inches)
Minimum
Penetration
for Full Load
(inches)
Nail
Penny
Wire
Gauge
Shank
Diameter
(inches)
Ref. No. Description
Finish
4
Length 3 7 10 12 14 16 18 20 22
NA11 N8 8d x 1-1/2 HDG 0.131 1-1/2 48 152 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 96 95 94 94
NA11SS SSN8 8d x 1-1/2 SS 0.131 1-1/2 48 143 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 96 95 94 94
NA9D N10 10d x 1-1/2 HDG 0.148 1-1/2 54 100 -- -- -- -- 126 118 114 112 112 112 111
NA16D N16 16d x 2-1/2 HDG 0.162 2-1/2 99 66 192 177 158 147 140 138 136 136 -- --
NA16D-RS -- -- 16d Ring Shank Bright 0.148 3-1/2 140 47 181 164 147 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
8d Common -- -- 8d Common Bright 0.131 2-1/2 80 126 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 98 96 95 94 94
10d Common -- -- 10d Common Bright 0.148 3 108 70 -- -- 154 136 125 118 115 114 113 112
16d Sinker -- -- 16d Sinker Bright 0.148 3-1/4 117 60 160 154 136 125 118 115 114 113 -- --
16d Common -- -- 16d Common Bright 0.162 3-1/2 138 48 192 177 158 147 140 138 136 136 -- --
1) Loads are calculated according to specifications of Part II of the National Design Specifications for Wood Construction (NDS®), 2001 Edition.
2) Loads apply to Douglas Fir-Larch (G=0.50) and Southern Pine (G=0.55). For Spruce-Pine-Fir (G=0.42) multiply above values by 0.86, for other wood types
refer to NDS® or consult USP.
3) Value assumes full penetration of at least 10 nail diameters.
4) HDG = Hot-Dip Galvanized; SS = Stainless Steel; Bright = No Finish.
5) For steel with Fu=45,000 psi, and gage minimum bare metal thickness.
Allowable Shear per Nail (Lbs.)
1,2,3,5
Steel Gauge
Nails
Per Lb.
USP
Stock No.
Nail
Diameter
Withdrawal
Load
NNaaiillss –– NNAA sseerriiees
roper fasteners are a critical component in a sound wood frame structure. To ensure
P
s
successful installations of its connectors, USP offers a full range of structurally-rated nails. All
alvanized nails supplied by USP are Hot-dipped for greater corrosion resistance. Stainless
g
steel nails are available on a stock basis size of 8d x 1
1
˝ (see product chart). Any USP
/2
connector requiring a NA16D-RS, nail ships with the nails attached to the connector in
convenient poly bags.
inish:See chart
F
Installation:
• Allowable shear values assume nail embedment into the wood of the entire nail or 10 nail
diameters (whichever is less). Otherwise, the nail must be embedded at least 6 nail
diameters, with the load reduced using the equation below:
Reduced Load = Published Load x Actual Penetration
Nail Diameter x 10
• Load reductions may occur if nails are used other than those specified. See the chart Optional
Nails for Face Mount Hangers and Straight Straps on page 9 for load reduction factors
regarding nail substitutions.
Nail Specification Table
Minimum Fastener Penetration T
able
Reduced Fastener Penetration
Example:
HD210 – listed load is 1680 lbs. @
100% for 16d common nails.
Reduced HD210 capacity if using
2x DF-L or SP header:
1680 lbs. x 1.5 = 1555 lbs. @ 100%
1.62
Customer Service / Technical Assistance
Burnsville, MN Corporate Of
1-800-328-5934
fice
continued on next page
NNaaiillss –– NNAA sseerriieess
DF-L SP S-P-F LVL
16d common 8d common 0.70 0.75 0.60 0.70
16d common 10d Box 0.67 0.72 0.58 0.67
16d common 10d common 0.83 0.91 0.72 0.83
16d common 12d common 0.83 0.91 0.72 0.83
16d common 10d x 1-1/2 0.81 0.88 0.70 0.81
16d common 10d Sinker 0.59 0.64 0.51 0.59
16d common 16d Box 0.74 0.80 0.64 0.74
16d common 16d Sinker 0.83 0.91 0.72 0.83
16d common 16d x 2-1/2 1.00 1.00 0.86 1.00
16d common No. 8 x 1-1/2 Wood Screw 0.60 0.66 0.52 0.60
10d common 8d Box 0.63 0.68 0.54 0.63
10d common 10d Sinker 0.70 0.77 0.61 0.70
10d common 8d common 0.83 0.90 0.72 0.83
10d common 10d Box 0.80 0.87 0.70 0.80
10d common 8d x 1-1/4 0.64 0.69 0.55 0.64
10d common No. 8 x 1-1/2 Wood Screw 0.72 0.79 0.63 0.72
10d common 10d x 1-1/2 0.97 1.00 0.84 0.97
10d common 16d Sinker 1.00 1.00 0.86 1.00
10d common No. 8 x 1-1/2 Wood Screw 0.72 0.79 0.63 0.72
12d common 10d x 1-1/2 0.97 1.00 0.84 0.97
12d common 16d Sinker 1.00 1.00 0.86 1.00
12d common No. 8 x 1-1/2 Wood Screw 0.72 0.79 0.63 0.72
8d common 8d Box 0.75 0.81 0.65 0.75
8d common 8d x 1-1/4 0.76 0.83 0.66 0.76
8d common No. 8 x 1-1/2 Wood Screw 0.86 0.95 0.75 0.86
8d x 1-1/2 8d x 1-1/4 0.76 0.83 0.66 0.76
8d x 1-1/2 No. 8 x 1-1/2 Wood Screw 0.86 0.95 0.75 0.86
10d x 1-1/2 8d x 1-1/2 0.86 0.93 0.74 0.86
10d x 1-1/2 No. 8 x 1-1/2 Wood Screw 0.74 0.81 0.64 0.74
1) No. 8 x 1-1/2 Wood Screw has a shank diameter of 0.164˝ and shall conform to
ANSI/ASME Standard B18.6.1-1981.
Allowable Load
Adjustment Factor
Catalog
Nail
Replacement
Fastener1
N
NA16D-RS
.148 x 3 1/2˝ .162 x 2 1/2˝
A16D
NA9D
.148 x 1
continued
NA11
1
/2˝
.131 x 1
9
1
/2˝
Optional Nails for Face Mount Hangers and Straight Straps
e-mail: info@USPconnectors.com
load table
How to Use:
The base value is the catalog listed nail in Douglas
Fir-Larch and the adjustment factor is the multiplier for
the applicable replacement nail and wood combination.
• Adjustment factors may vary with some custom
hangers or steel thicker than 10 gauge. Contact USP for
exceptions.
• Roofing nails shall not be substituted for any nail size
or type.
Optional Nails Example:
JL210 – listed load is 1595 lbs.
@
If substituting:
8d common nails with DF-L, or
LVL:
1595 lbs. x .83 = 1325 lbs.
8d common nails with SP:
1595 lbs. x .90 = 1435 lbs.
8d common nails with S-P-F:
1595 lbs. x .72 = 1150 lbs.
www.USPconnectors.com
© Copyright 2005 United Steel Products Company
100% for 10d common nails.
No further reductions
are required.
USP952-051
10
12 Gauge 10 Gauge 7 Gauge 3 Gauge 12 Gauge 10 Gauge 7 Gauge 3 Gauge
Ref. No. Description L SH T
Finish
1,5
WS15 SDS1/4x1 1/2 1/4˝ x 1-1/2˝ 1-1/2˝ 1/4˝ 1-1/4˝ Zinc -- -- 251 248 244 243 -- -- 217 214 211 211
WS17 SDS1/4x1 3/4 1/4˝ x 1-3/4˝ 1-3/4˝ 3/8˝ 1-3/8˝ Zinc -- -- 296 293 290 292 -- -- 255 253 251 253
WS2 SDS1/4x2 1/4˝ x 2˝ 2˝ 1/4˝ 1-3/4˝ Zinc -- -- 304 306 313 327 -- -- 262 264 271 284
WS25 SDS1/4x2 1/2 1/4˝ x 2-1/2˝ 2-1/2˝ 1/4˝ 2-1/4˝ Zinc 177 304 306 313 327 137 262 264 271 284
WS3 SDS1/4x3 1/4˝ x 3˝ 3˝ 3/4˝ 2-1/4˝ Zinc 229 304 306 313 327 177 262 264 271 284
WS35 SDS1/4x3 1/2 1/4˝ x 3-1/2˝ 3-1/2˝ 3/4˝ 2-3/4˝ Zinc 229 304 306 313 327 177 262 264 271 284
WS4 -- -- 1/4˝ x 4˝ 4˝ 1˝ 3˝ Zinc 229 304 306 313 327 177 262 264 271 284
WS45 SDS1/4x4 1/2 1/4˝ x 4-1/2˝ 4-1/2˝ 1-1/4˝ 3-1/4˝ Zinc 272 304 306 313 327 216 262 264 271 284
WS6 SDS1/4x6 1/4˝ x 6˝ 6˝ 1-3/4˝ 4-1/4˝ Zinc 272 304 306 313 327 216 262 264 271 284
1) Zinc = Yellow zinc dichromate.
2) Allowable loads are based on the 1997 NDS®. Light Gauge or 3 Gauge loads given assume use with metal side plates, Fes = 45 ksi.
3) Wood-to-wood loads are based on 1-1/2˝ thick wood side members.
4) Loads are for 100% duration of load factors, and may be increased for other duration factors in accordance with the NDS.
DF-L / SP
2,4
Steel to Wood
Steel to Wood
Shear
(100)
Shear
(100)
Wood
to Wood
Shear
(100)
Shear
(100)
Dimensions
USP
Stock No.
Shear
(100)
Shear
(100)
Shear
(100)
Wood
to Wood
(DF-L
to DF-L)
(S-P-F
to S-P-F)
Shear
(100)
S-P-F
2,4
WWoooodd SSccrreewwss –– WWSS sseerriiees
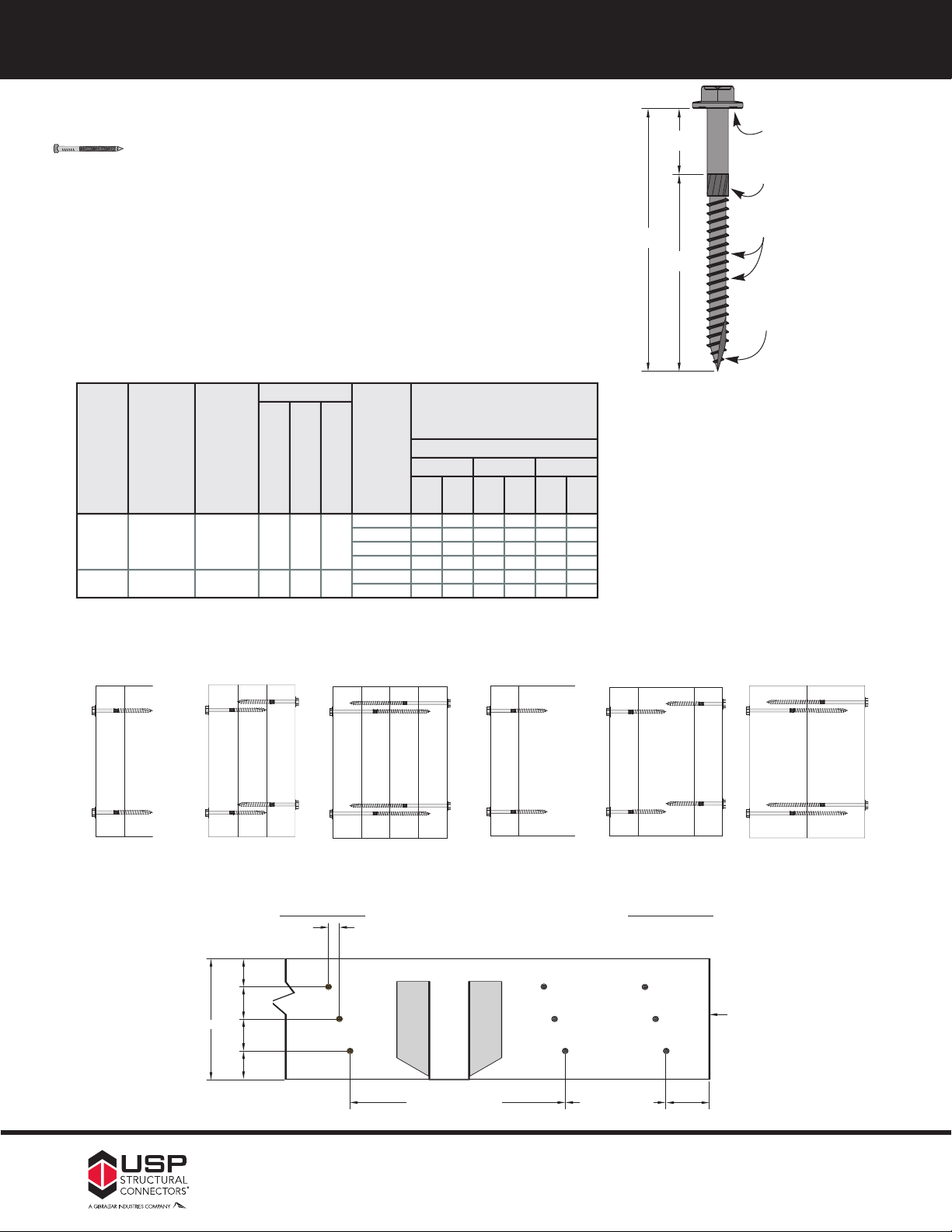
s
The WS Wood Screw is a self-drilling screw used for numerous framing
pplications. This screw features a reverse locking serration on the
a
ottom of the screw head to prevent over tightening against a steel
b
plate which could cause the screw head to shear off. The USP head
stamp identifies screws for easy inspection.
Screw shear capacities are based on a diameter of 0.242˝ when the
shear plane is on the screw shank (SH) and 0.185˝ when the shear
plane is on the knurl or threads (T). USP
WS Wood Screws have a
bending yield strength of 217,000 psi. For conditions not charted here,
screw loads may be calculated as shown in the current NDS® and
increased for duration of load.
Serrations
SH
Beveled reamer on
2-1/2˝ or longer
Wood Screws
L
T
Cut threads
Materials: 1/4˝ diameter Grade 5 steel
Finish: Yellow zinc dichromate
Codes: ICBO 5634, L.A.City RR 25433
Installation:
• Screws are self-drilling.
3
• Install using a low speed clutch drill with
˝ hex head driver. The
8
/
washer head should be flat to the surface and the serrations will
oppose turning and release the clutch. Do not over-tighten the screws.
For Attaching Multi-Ply LVL or PSL members,
see page
11
Self-drilling point
USP name Screw length
3/8˝
Customer Service / Technical Assistance
Burnsville, MN Corporate Of
1-800-328-5934
fice
WWoooodd SSccrreeww AApppplliiccaattiioonnss –– WWSS sseerriiees
1) Allowable Uniform Loads are based on the 1997 NDS®.
2) Based on Zscrew = 250 lbs. in Douglas Fir-Larch (G=0.50)
with a side member thickness of not less than 1-3/4˝.
3) Load values depicted assume all uniform load is applied
to the most narrow outside ply only.
4) Load values neglect any contribution of screws installed
Ref. No. Description L SH T to opposite side, even if they extend significantly into the
1 1
00015006651000500750 loaded ply.
2 750 1125 500 750 375 565 5) Loads are for normal (100%) duration of load, and may
4 750 1125 500 750 375 565 be increased in accordance with the code.
5 665 1000 445 665 335 500 6) Uniform loads in table represent the capacity of the
3 665 1000 445 665 335 500 fasteners. The capacity of the LVL or PSL beam may be
6 1000 1500 665 1000 500 750 less and should be checked by a qualified designer or
7) A qualified designer shall ensure the adequacy of a 7˝
wide beam to resist the applied load on one edge;
otherwise, the loads shall be uniformly distributed across
the width or applied equally on both sides.
1-3/4˝
4-1/4˝
WS35
WS6
SDS1/4x6
1/4˝ x 6˝
6˝
SDS1/4x3 1/2
1/4˝ x 3-1/2˝
2-1/2˝
24˝ O.C.
Maximum Allowable Uniform Loads
t
hat can be applied to either outside
m
ember (Lbs. Per Lineal Ft.)
1,2,4,5,6,7
3-1/2˝
1˝
D
imensions
3
Rows
USP
Stock No.
2
Rows3Rows2Rows
M
ultiple
M
embers
Installation
F
igure
3
12˝ O.C.
18˝ O.C.
Wood Screw Spacing
2
Rows3Rows
1) Allowable Uniform Loads are based on the 1997 NDS®.
2) Based on Zscrew = 250 lbs. in Douglas Fir-Larch (G=0.50)
with a side member thickness of not less than 1-3/4˝.
3) Load values depicted assume all uniform load is applied
to the most narrow outside ply only.
4) Load values neglect any contribution of screws installed
to opposite side, even if they extend significantly into the
loaded ply.
5) Loads are for normal (100%) duration of load, and may
be increased in accordance with the code.
6) Uniform loads in table represent the capacity of the
fasteners. The capacity of the LVL or PSL beam may be
less and should be checked by a qualified designer or
with the manufacturer's literature.
7) A qualified designer shall ensure the adequacy of a 7˝
wide beam to resist the applied load on one edge;
otherwise, the loads shall be uniformly distributed across
the width or applied equally on both sides.
Joining 2, 3, or 4 Ply LVL or PSL Member
nstallation Notes:
I
• For 2 ply members, wood screws shall be installed with the screw heads in the
loaded ply.
• For 3 or 4 ply members, wood screws shall be installed in both outer plys.
Designer shall specify all wood screws locations.
•
• Increase edge and end distances if wood splitting occurs.
• Stagger all screws installed into the opposite face.
• A minimum of 2 rows of screws shall be used for all members with H = 5
and larger.
1
/
s
SH
Serrations
11
Beveled reamer
L
Cut threads
T
˝
2
Self-drilling point
Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3
WS35 installed
3
in (2) 1
/4˝ Ply
WS35 installed
3
in (3) 1
/4˝ Ply
WS6 installed
in (4) 1
3
/4˝ Ply
Figure 4
WS35 installed
3
in (1) 1
(1) 3
/4˝,
1
/2˝ Ply
Figure 5
WS35 installed
3
in (2) 1
(1) 3
1
/2˝ Ply
/4˝,
Recommended Row Guidelines
1˝ min. Recommended (T
Other Stagger patterns as appr
1
1
/
2˝
min.
1
2
/
2˝
min.
H
1
2
/
2˝
min.
1
1
/
2˝
min.
yp)
Spacing
4˝ min. – 24˝ max.
ed by Engineer ar
ov
e acceptable
Spacing
4˝ min. – 24˝ max.
End of member
4˝ min.
Figure 6
WS6 installed
3
in (2) 1
/4˝ Ply
www.USPconnectors.com
e-mail: info@USPconnectors.com
© Copyright 2005 United Steel Products Company
USP952-051
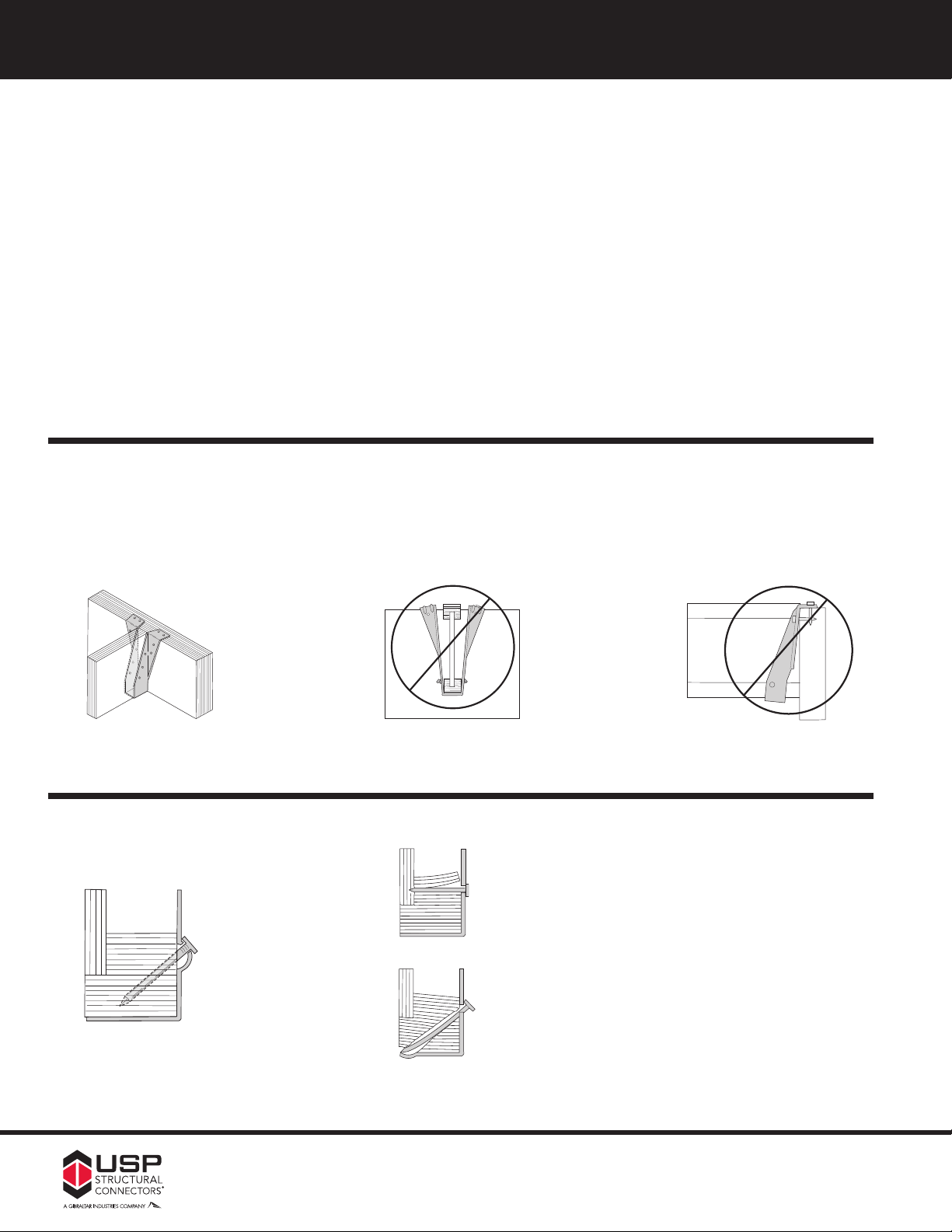
WWoooodd II--JJooiisstt IInnssttaallllaattiioonn ttoo WWooood
12
d
Sloped I-Joists
Use sloped seat hangers and beveled web stiffeners
whenever the slope exceeds the following:
earing lengths of 2
b
of 3
1
2
˝
a
/
2
1
˝.
/
2
etween
b
excess
nd 3
1
or less;
˝
/
2
1
˝
/
2
;
and
3
12 for bearing lengths
:
/
8
1
12 for bearing lengths in
:
/
4
1
:12 for seat
/
2
Multiple I-Joist Plys
Fasten together multiple plys of wood I-Joists, in
accordance with the manufacturer’s installation guidelines,
such that the joists act as a single unit.
I-Joist Rotation
It may be necessary to install straps, blocking, or
sheathing to restrain torsional rotation of a supporting
wood I-Joist when using top mount I-Joist hangers.
Fasteners
I-Joists may split if larger diameter nails or longer nails
installed. Do not install nails larger than 16d common
ails (0.162˝ diameter) into the web stiffeners in the wood
n
-Joist.
I
acker Blocks
B
Pattern the nails used to install backer blocks or web
stiffeners in wood I-Joists to avoid splitting the block. The
nail pattern should be sufficiently spaced to avoid the
same grain line, particularly with solid sawn backer blocks.
Backer blocks must be installed on wood I-Joist acting as
the header, or supporting member. Install in accordance
with the I-Joist manufacturer’s installation guidelines. The
nails used to install hangers mounted to an I-Joist header
must penetrate through the web and into the backer block
on the opposite side.
Install only the specified nails. The flanges of wood
Top Flange Hangers
The thickness of the hanger metal and nail heads on top mount hangers must be evaluated for the effect on
subsequent sheathing. Ensure that the top mount hanger is installed so the flanges of the hanger are not
over-spread which tends to elevate the supported I-Joist causing uneven floor surfaces and squeaking. Similarly, ensure
that the hanger is installed plumb such that the face flanges of the hanger are mounted firmly against the
wide-face surface of the header.
are
wire
Flush framing
Correct Slant Nail Installation
Always secure
wood I-Joist using
10d x 1
nail driven at a
45° angle
and firmly seated
Hanger over-spread
Hanger not plumb
Common Nailing Errors
Wrong Angle
When a nail is driven into the bottom flange of the
wood I-Joist parallel to the glue lines, separation of
1
˝
⁄ 2
veneers can occur which substantially reduces the
design loads of the connection.
Nail Too Long
When using nails longer than USP’s recommended
nails, bottom flange splitting may occur. Also, this can
raise the wood I-Joist off the seat, resulting in uneven
surfaces and squeaky floors along with reduced
allowable loads.
Customer Service / Technical Assistance
Burnsville, MN Corporate Of
1-800-328-5934
fice
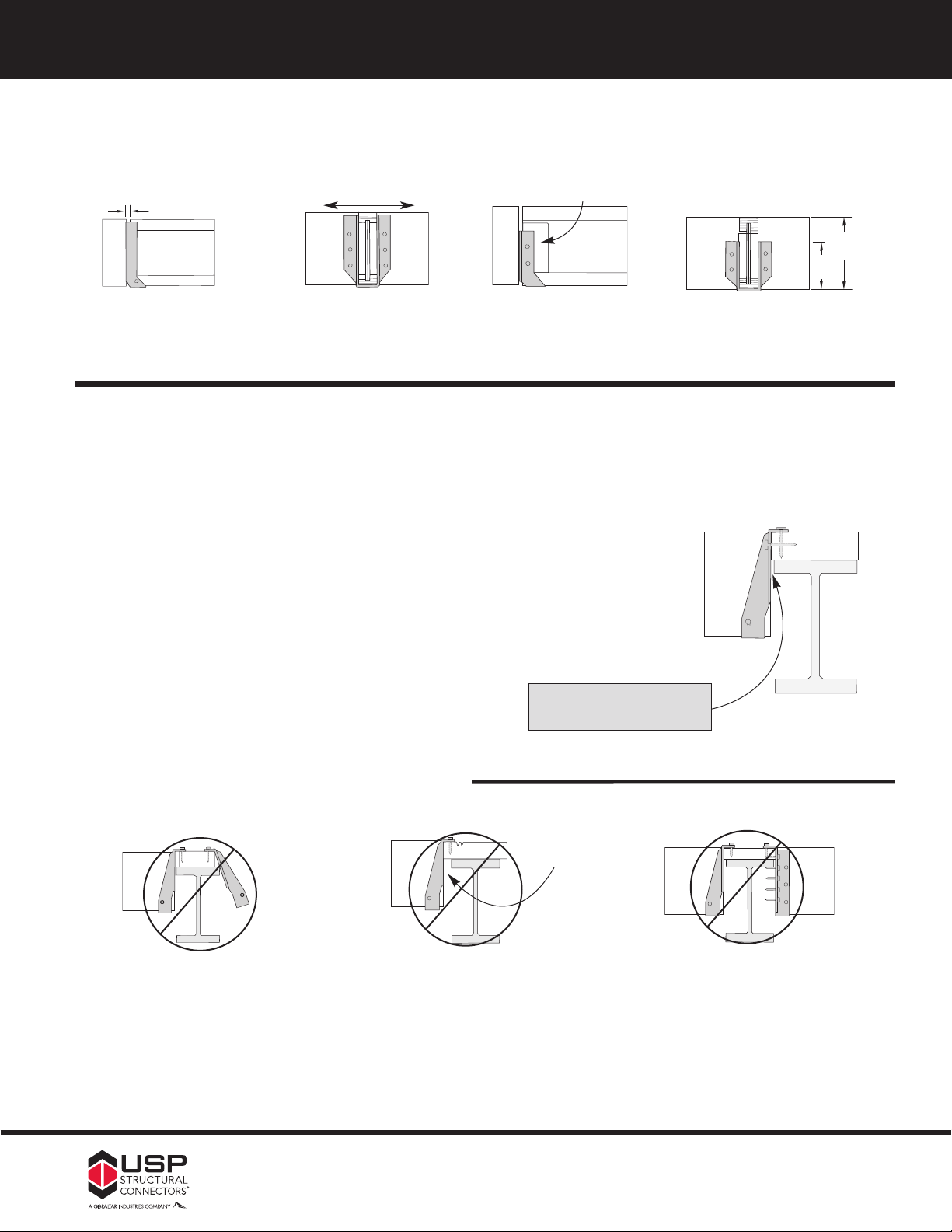
SSuuppppoorrtt HHeeiigghhtt && LLaatteerraall SSttaabbiilliitty
y
13
Hangers for joists without web stiffeners must
support the I-Joist’s top flange and provide lateral
resistance with no more than
1/8˝ maximum gap
1
˝ horizontal deflection.
⁄
8
Resist lateral movement
Hangers for joists with web stiffeners must support a
minimum of 60% of joist depth.
Web stiffener
(Top flange support requirements can be verified in this sections charts under the Web Stiffener Reqd. column.)
Nailer Installations
Correct Hanger Attachment to Nailer
A nailer or sill plate is considered to be any wood member attached to a steel
beam, concrete block wall, concrete stem wall, or other structure unsuitable for
nailing, which is used as a nailing surface for top mount hangers to hold beams
or joists.
Nailer Sized Correctly
Top flange of hanger is fully supported and recommended nails have full
1
/
penetration into nailer, resulting in a carried member hanging safely at the
proper height.
Max.
4˝
60%
M
oist
J
depth
in.
The nailer must be sized to fit the support width as shown and be of sufficient
thickness to satisfy recommended top flange nailing requirements. A design
professional must specify nailer attachment to steel beams.
Avoid direct contact between
hangers and steel beams, which
may cause squeaks.
Wrong Nailer Size Causes Component Failure
1
⁄4˝ Max.
ide
oo W
Too Narrow
op flange not fully supported
T
can cause nail breakout. Or, by
fully supporting top flange,
hanger is tilted back, causing
lifting of carried member which
results in uneven surfaces and
squeaky floors.
Loading can cause cross
grain breaking of nailer.
The recommended nailer
overhang is
per side.
T
1
˝ maximum
⁄
4
Too Thin
op flange nailing cannot fully
T
penetrate nailer, causing reduced
allowable loads. Never use
hangers which require multiple
face nails since the allowable
loads are dependent on all nail
holes being used.
www.USPconnectors.com
e-mail: info@USPconnectors.com
© Copyright 2005 United Steel Products Company
USP952-051
14
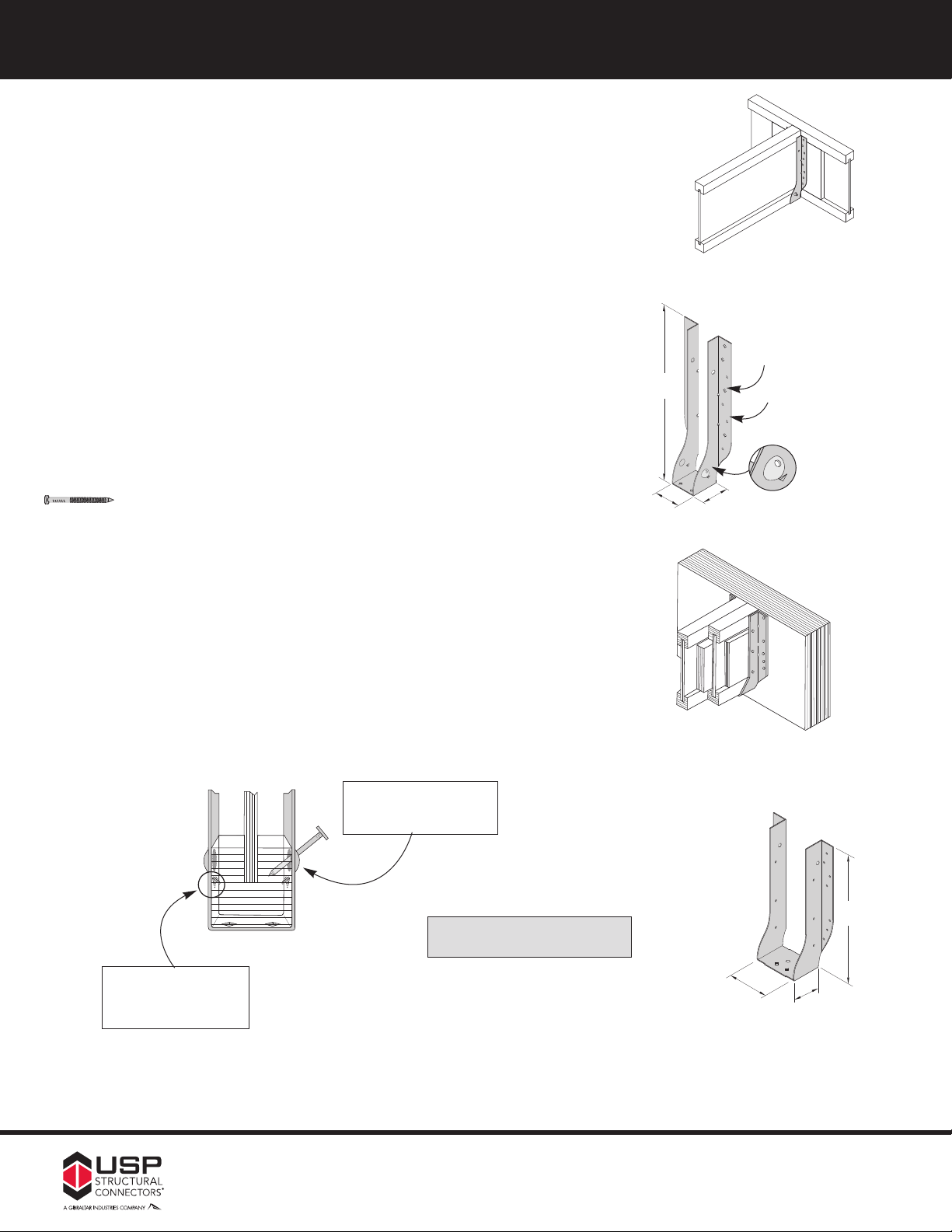
FFaaccee MMoouunntt HHaannggeerrss –– HHDD,, HHUUSS,, && TTHHFF sseerriiees
THF – Designed to provide lateral support for the top chords of I-Joists in
depths up to 16˝. Eliminates the need for web stiffeners in most applications
(see Web Stiffener Reqd. column in EWP Face Mount Hanger chart for
specific applications). Raised Dimple nailing guides help assure correct 45°
nailing into the I-Joist bottom flange.
HD – Designed to support LVL, LSL, and PSL beams and headers in
medium load conditions.
HUS – Designed for medium load conditions. Extended 3˝ deep seat
provides extra truss bearing.
Materials: See EWP Face Mount Hangers charts, pages 17-19.
Finish: G90 galvanizing
Options: See Specialty Options chart on page 15.
Codes: SBCCI, BOCA – NER 478, NER 608, & NER 510,
ICBO 2039, L.A. City RR 25283 &
RR 23888, FL815, FL818, FL821,
DSA PA-076
Patents: #5,217,317 – THF & HUS
#5,564,248 – THF (all models except doubles)
s
Typical THF I-Joist to
I-Joist installation
Additional diamond
nail holes for
H
maximum nailing
Standar
nail holes for
minimum nailing
d round
Installation:
• Use all specified fasteners.
• THF – Install 10d x 1
1
˝ nails into joist through raised dimple at 45° angle.
2
/
• THF Min – Fill all round nail holes.
• THF Max – Fill all round and diamond holes.
• HD – Drive bend line nails into header at 45° to achieve listed loads.
• HUS – Joist nails must be driven at a 30° to 45° angle through the joist into
the header to achieve listed loads.
atented Raised Dimple nail
P
holes allow 45
oist bottom flange
I-J
nailing into
°
.
Some model designs may
vary from illustration shown
W
2˝
THF single
Typical
THF double I-Joist
to LVL installation
Patented dimple
allows 45° nailing
H
atented Seat Cleat™
P
helps lock I-J
for positiv
oist into place
e seating and
nailing ease
W
.
D
THF double
continued on next page
Customer Service / Technical Assistance
Burnsville, MN Corporate Of
1-800-328-5934
fice
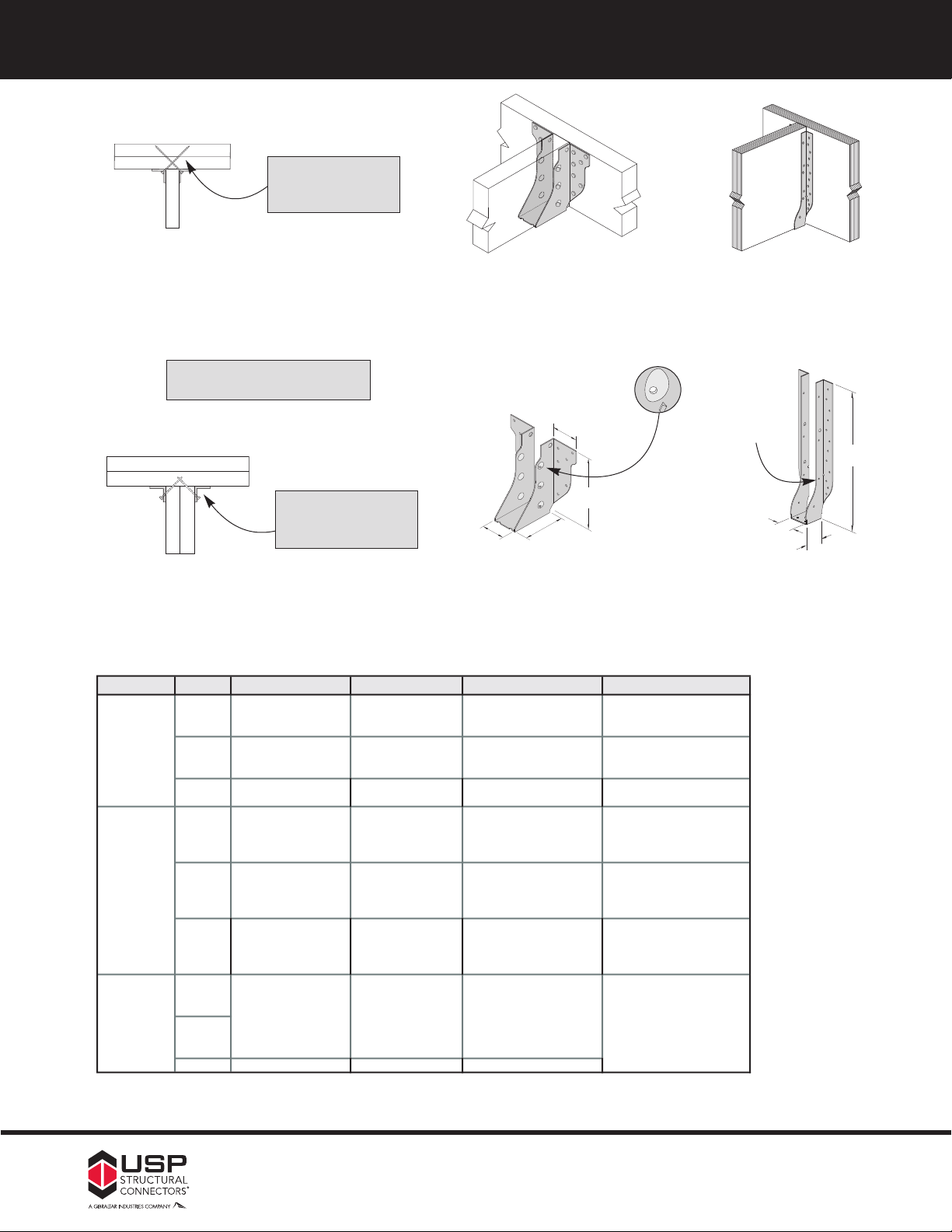
FFaaccee MMoouunntt HHaannggeerrss ––
Option USP Series
Skewed
1,3
Sloped Seat
2,3
Sloped / Skewed
1,2,3
Inverted Flange
HUS -- -- -- -- -- --
1) Skewed hangers with skews greater than 15° may have all joist nailing on outside flange.
2) Sloped or sloped / skewed hangers with slopes greater than 15° may have additional joist nails.
3) All sloped, skewed, or combinations require bevel cut on joist in all applications.
4) Modifications to THF hangers do not feature seat cleats.
Not available in
widths less than 2-1/4˝
100% of table load.
65% of table load when
nailing into the support
members end grain.
See Sloped Seat and Skewed
THF
Not available in
widths less than 2-1/4˝
HD
1˚ to 45˚
100% of table load.
65% of table load when
nailing into the support
members end grain.
Allowable
Loads
100% of table load.
75% of uplift load on
skews greater than 15˚.
THF
100% of table load.
75% of uplift load on
skews greater than 15˚.
100% of table load
80% of table load.
75% of uplift load on
skews greater than 15˚.
See Sloped Seat and Skewed
See Sloped Seat and Skewed
Example:
HD410-SK45RSL30D
100% of table load
100% of table load.
65% of table load when
nailing into the support
members end grain.
Add IF,
to product number.
Example: HD410IF
80% of table load.
75% of uplift load on
skews greater than 15˚.
-- --
Range
HUS
Not available in
widths less than 2-1/4˝
-- --
-- --
-- --
1˚ to 45˚
1˚ to 67-1/2˚
when width is 1-3/4˝ or less.
1˚ to 50˚ on all others.
1˚ to 67-1/2˚
when width is 1-3/4˝ or less.
1˚ to 50˚ on all others.
HD
Ordering
HUS
-- --
-- --
Add SK,
angle required,
and right (R) or left (L),
to product number.
Example:
HD410-SK45R
Add SL,
slope required,
and up (U) or down (D),
to product number.
Example:
HD410-SL30D
HD
THF
Drive bend line nails
into header at 45° to
achieve listed loads.
HHDD,, HHUUSS,, && TTHHFF sseerriiees
s
c
ontinued
15
Typical HD
bend line nail installation
Typical HUS
installation
Some model designs may
vary from illustration shown
Drive joist nails into
header at 30° to 45° to
achieve listed loads.
Typical HUS
Patented dimple allows
30° to 45° nailing
2˝
W
D
HUS
H
double shear installation
Specialty Options Chart – refer to Specialty Options pages 55 to 58 for additional details.
Typical HD
installation
Bend line
nailing
H
W
D
HD
e-mail: info@USPconnectors.com
www.USPconnectors.com
© Copyright 2005 United Steel Products Company
USP952-051
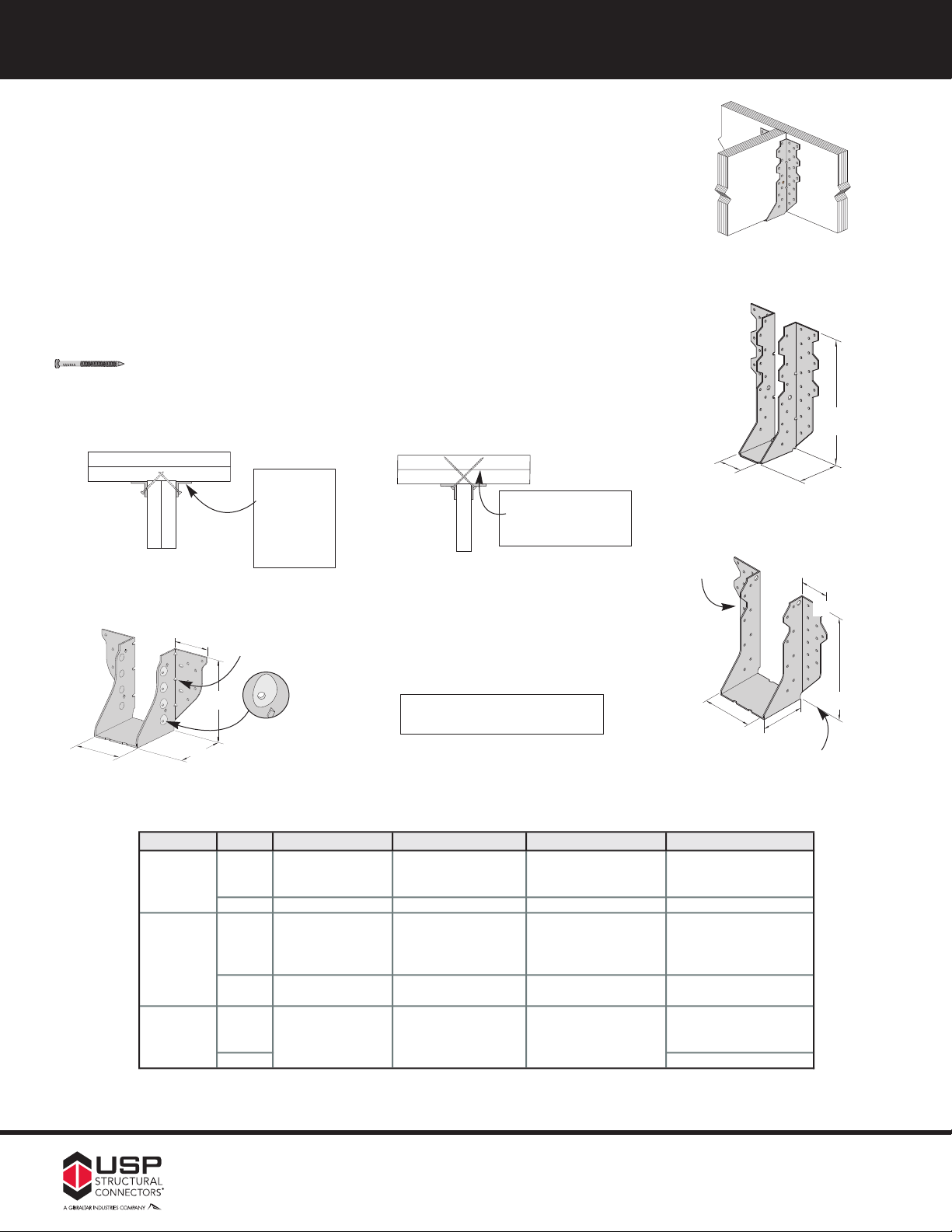
16
Skewed
1,3
Sloped Seat
2,3
Sloped / Skewed
1,2,3
Inverted Flange
1) Skewed hangers with skews greater than 15° may have all joist nailing on outside flange. All skewed THDH hangers have nails on one side only.
2) Sloped or sloped / skewed hangers with slopes greater than 15° may have additional joist nails.
3) All sloped, skewed, or combinations require bevel cut on joist in all applications.
THD
Add SK, angle required,
and right (R) or left (L),
to product number.
Example: THDH410-SK45R
Add SL, slope required,
and up (U) or down (D),
to product number.
Example: THDH410-SL30D
1˚ to 45˚
65% of table load
THD
THD
THDH
Not available in widths
less than 3˝. Widths greater
can have one flange inverted.
See Sloped Seat and Skewed
See Sloped Seat and Skewed
Example:
THDH410-SK45RSL30D
Range
Allowable
Loads
85% of table load.
50% of table uplift load.
1˚ to 45˚
Ordering
100% of table load.
65% of table load when
nailing into the support
members end grain.
85% of table load
Add 1IF, one flange,
right (R) and left (L),
Example: THD4101IFR
65% of table load
N/A
52% of table load
52% of table load.
50% of table uplift load.
FFaaccee MMoouunntt HHaannggeerrss ––
TTHHDD && TTHHDDHH sseerriieess
THD – Medium-duty hanger for LVL, LSL, and PSL beams.
THDH – Heavy-duty hanger for LVL, LSL, and PSL beams.
Materials: See EWP Face Mount Hangers charts, pages 17-19.
Finish: G90 galvanizing
Options: Rough/ Full sizes available for THD series. THD hangers
with widths greater than 3˝ can have one flange inverted
with no load reduction. Specify left (L) or right (R) flange.
See Specialty Options chart.
Codes: SBCCI, BOCA – NER 478 & NER 608,
ICBO 2039, L.A. City RR 25283,
DSA PA-076, FL815, FL821
Patents: #5,217,317 – THDH
Installation:
• Use all specified fasteners.
• THDH – Drive joist nails into header at 30° to 45° to achieve listed loads.
Typical THD179
installation
H
Typical THDH
double shear installation
21/2˝
H
W
D
THDH26-2
Specialty Options Chart – refer to Specialty Options pages 55 to 58 for additional details.
Option USP Series
THDH 1˚ to 45˚ 1˚ to 45˚ See Sloped Seat and Skewed N/A
Drive joist
nails into
header at
30° to 45°
to achieve
listed loads.
Bend line nailing
Patented dimple
allows 30° to 45°
nailing
Drive bend line nails
into header at 45° to
achieve listed loads.
Typical THDH
bend line nail installation
Some model designs may
vary from illustration shown
Left flange
W
THD single
THD single
W
D
D
3˝
H
Right flange
THD double or larger
THDH N/A
Customer Service / Technical Assistance
Burnsville, MN Corporate Of
1-800-328-5934
fice
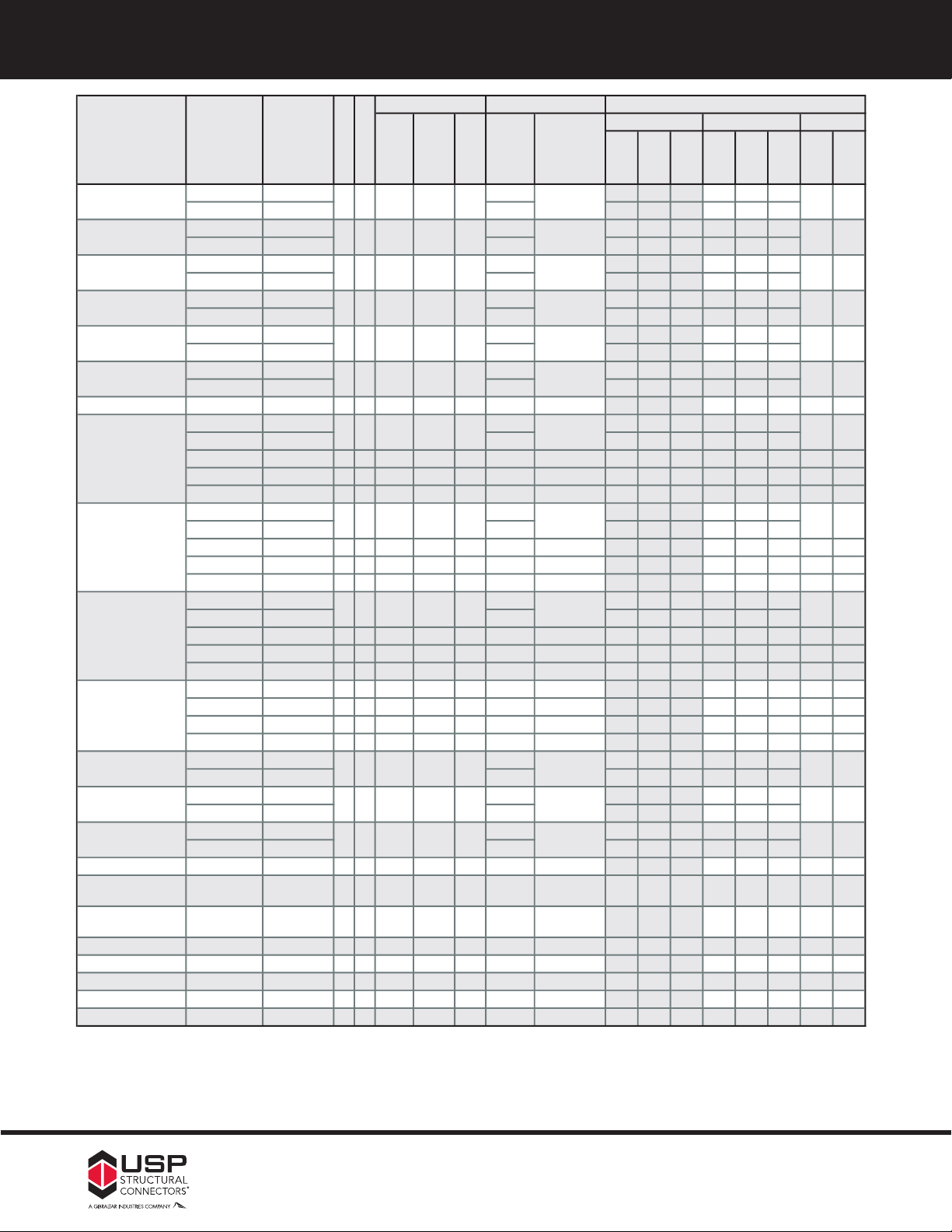
EEWWPP FFaaccee MMoouunntt HHaannggeerrss CChhaarrttss
D
imensions
D
F-L / SP Header
S
-P-F Header
Joist Size Ref. No. W H D
Header
3
Joist
1
100% 115% 125% 100% 115% 125% 133% 160%
THF15925 Min IUS1.56/9.5 (8) 10d 910 1050 1140 785 900 980
THF15925 Max IUT29
(
12) 10d
1
37015751710117513501470
THF15112 Min IUS1.56/11.88
(
8) 10d
9101
0501140785900980
THF15112 Max IUT211
(
16) 10d
1
82521002155157018051960
THF15140 Min
-
- --
(
12) 10d
1
37015751710117513501470
THF15140 Max IUT214 (20) 10d 2100 2135 2155 1960 2135 2155
THF16925 Min -- -- (8) 10d 910 1050 1140 785 900 980
THF16925 Max IUT1.68/9 (12) 10d 1370 1575 1710 1175 1350 1470
THF16112 Min -- -- (8) 10d 910 1050 1140 785 900 980
THF16112 Max IUT1.68/11
(
16) 10d
1
82521002280157018051960
THF16140 Min
-
- --
(
12) 10d
1
37015751710117513501470
THF16140 Max IUT1.68/14
(
20) 10d
2
25522902310196022552310
1-3/4 x 7-1/4 HD1770 HU7 x 14 1-13/16 7-1/8 2 (14) 16d (4) 10d x 1-1/2 1960 2255 2335 1695 1950 2120 610 730
THF17925 Min IUS1.81/9.5 (8) 10d 910 1050 1140 785 900 980
THF17925 Max IUT9 (12) 10d 1370 1575 1710 1175 1350 1470
HD17925 HU9 x 14
1-13/16 9-1/8
2 (18) 16d (6) 10d x 1-1/2 2520 2775 2775 2180 2505 2725 910 1065
THD179 -- -- x 14 1-7/8 8-7/8 3 (38) 16d (20) 10d x 1-1/2 5320 5800 5800 4210 4510 4705 3040 3095
HUS179 HUS1.81/10 x 16 1-13/16 9-1/8 3 (30) 16d (10) 16d 4925 5130 5270 4570 4910 5030 3205 3205
THF17112 Min IUS1.81/11.88 (8) 10d 910 1050 1140 785 900 980
THF17112 Max IUT11 (16) 10d 1825 2100 2280 1570 1805 1960
HD17112
HU11
x 1
4
1-13/16 11-3/8
2 (
22) 16d(6) 10d x 1-1/22870297530452660297530459101065
THD179
-- --
x 141
-7/88-7/8
3 (
38) 16d(20) 10d x 1-1/253205800580042104510470530403095
HUS179 HUS1.81/10 x 16 1-13/16 9-1/8 3 (30) 16d (10) 16d 4925 5130 5270 4570 4910 5030 3205 3205
THF17140 Min IUS1.81/14 (12) 10d 1370 1575 1710 1175 1350 1470
THF17140 Max IUT14 (20) 10d 2280 2445 2470 1960 2255 2450
HD1714 HU14 x 14
1-13/16 13-5/16
2 (26) 16d (8) 10d x 1-1/2 3100 3235 3330 3100 3235 3330 1065 1065
THD179 -- -- x 14 1-7/8 8-7/8 3 (38) 16d (20) 10d x 1-1/2 5320 5800 5800 4210 4510 4705 3040 3095
HUS179 HUS1.81/10 x 16 1-13/16 9-1/8 3 (30) 16d (10) 16d 4925 5130 5270 4570 4910 5030 3205 3205
THF17157 MIU1.81/16 -- 18 1-13/16 15-3/4 3-1/2 (24) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 2735 3145 3310 2350 2705 2940 280 280
HD1714 HU14 x 14
1-13/16 13-5/16
2 (26) 16d (8) 10d x 1-1/2 3100 3235 3330 3100 3235 3330 1065 1065
THD179 -- -- x 14 1-7/8 8-7/8 3 (38) 16d (20) 10d x 1-1/2 5320 5800 5800 4210 4510 4705 3040 3095
HUS179 HUS1.81/10 x 16 1-13/16 9-1/8 3 (30) 16d (10) 16d 4925 5130 5270 4570 4910 5030 3205 3205
THF20925 Min IUS2.06/9.5 (8) 10d 910 1050 1140 785 900 980
THF20925 Max IUT2.06/9 (12) 10d 1370 1575 1710 1175 1350 1470
THF20112 Min IUS2.06/11.88 (8) 10d 910 1050 1140 785 900 980
THF20112 Max IUT2.06/11 (16) 10d 1825 2100 2280 1570 1805 1960
THF20140 Min IUS2.06/14 (12) 10d 1370 1575 1710 1175 1350 1470
THF20140 Max IUT2.06/14 (20) 10d 2280 2470 2470 1960 2255 2450
2 - 2-1/8 x 16 THF20157 IUT2.06/16 -- 18 2-1/8 15-3/4 3-3/8 (24) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 2735 3145 3310 2350 2705 2940 280 280
2-1/4 - 2-5/16
x 9-1/4 - 9-1/2
THF23925 IUT3510 -- 18 2-5/16 9-3/16 2-1/2 (12) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 1370 1575 1710 1175 1350 1470 175 175
2-1/4 - 2-5/16
x 11-1/4 - 11-7/8
THF23118 IUT3512 -- 18 2-5/16 11-3/16 2-1/2 (14) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 1595 1835 1995 1370 1580 1715 300 360
2-1/4 - 2-5/16 x 14 THF23140 IUT3514 -- 16 2-5/16 13-1/2 2-1/2 (18) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 2090 2400 2610 1800 2070 2250 300 360
2-1/4 - 2-5/16 x 16 THF23160 MIU2.37/16 -- 16 2-5/16 15-9/16 2-1/2 (22) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 2550 2935 3035 2200 2530 2750 300 360
2-1/4 - 2-5/16 x 18 - 28 THF23180 MIU2.37/18 x 16 2-5/16 17-1/8 2-1/2 (24) 10d (8) 10d x 1-1/2 2785 3200 3480 2400 2760 3000 1205 1295
2-1/2 x 9-1/4 - 9-1/2 THF25925 IUT310 -- 18 2-1/2 9-1/8 2-1/2 (12) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 1370 1575 1710 1175 1350 1470 175 175
2-1/2 x 11-1/4 - 11-7/8 THF25112 IUT312 -- 18 2-1/2 11-1/8 2-1/2 (14) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 1595 1835 1995 1370 1580 1715 300 360
1) 10d x 1-1/2 nails are 9 gauge (0.148˝ diameter) by 1-1/2˝ long.
2) Uplift loads have been increased 33-1/3% or 60% for wind or seismic loads; no further increase shall be permitted.
3) Minimum nail penetration shall be 1-1/2˝ for 10d nails and 1-5/8˝ for 16d nails.
Load tables address hanger/header/fastener limitations only. Joist limitations must be determined for each installation.
(2) 10d x 1-1/2
280
280
280
280
(2) 10d x 1-1/2
280
280
(2) 10d x 1-1/2
(
2) 10d x 1-1/2
280280280
280
(2) 10d x 1-1/2
280
280
(
2) 10d x 1-1/2
(2) 10d x 1-1/2
2802
80
2802
80
280
280
280
280
280
2802
80
--182-1/8
13-1/4
18
2-1/8
10-7/8
A
llowable Loads (Lbs.)
2
(2) 10d x 1-1/2
(2) 10d x 1-1/2
(
2) 10d x 1-1/2
(
2) 10d x 1-1/2
(2) 10d x 1-1/2
--182-1/8
8-7/8
--1
8
1-3/4
10-15/16
--181-3/4
13-3/8
8-15/16
2
U
plift
2
13-1/2
2
1
1
2
1
3-7/16
2
280
--1
8
1-3/4
--
18
1
-5/8 1-5/8 x 14
--
18
1
-5/8 1-5/8 x 11-1/4 - 12
1-5/8 x 9-1/4 - 9-1/2
--1
8
1-1/2 x 9 -1/4 - 9-1/2
1-5/8
1-1/2 x 14
--1
8
1-1/2
1-1/2 x 11-1/4 - 11-7/8
--
18
1
-1/2
1-3/4 x 11-1/4 - 11-7/8
1-3/4 x 14
2 - 2-1/8
x 9-1/4 - 9-1/2
1-3/4 x 9-1/4 - 9-1/2
1-3/4 x 16
2 - 2-1/8
x 11-1/4 - 11-7/8
2 - 2-1/8 x 14
--
2
USP
Stock No.
9
9
-1/1611-1/16
18
1
-1/2
--
F
astener Schedule
22222
2
Steel Gauge
Web Stiffener Reqd.
17
www.USPconnectors.com
e-mail: info@USPconnectors.com
© Copyright 2005 United Steel Products Company
continued on next page
USP952-051
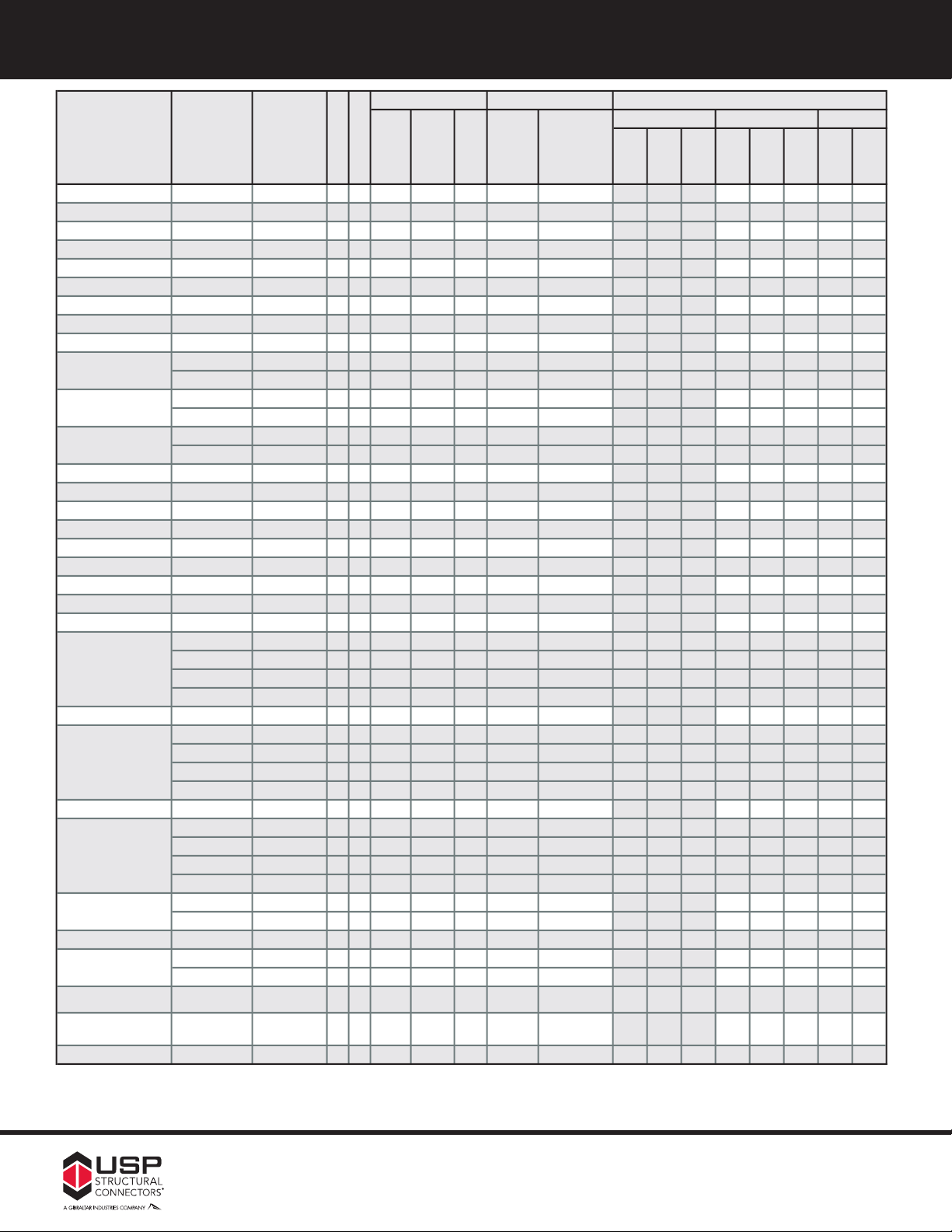
18
Dimensions
DF-L / SP Header S-P-F Header
J
oist Size
R
ef. No.
W
H
D
H
eader
3
J
oist
1
1
00%115%125%100%115%125%133%160%
2-1/2 x 13
THF25130
-- --
--162
-1/212-1/42-1/2(18) 10d(2) 10d x 1-1/2209022802280180020702250300360
2-1/2 x 14
THF25140
IUT314
--162
-1/213-7/162-1/2(18) 10d(2) 10d x 1-1/2209024002610180020702250300360
2-1/2 x 16 THF25160 MIU316 -- 16 2-1/2 15-1/2 2-1/2 (22) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 2550 2935 3035 2200 2530 2750 300 360
2-1/2 x 18 - 24 THF25160 MIU316 x 16 2-1/2 15-1/2 2-1/2 (22) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 2550 2935 3035 2200 2530 2750 300 360
2-5/8 x 9-1/4 - 9-1/2 THF26925 IUT2.68/10 -- 18 2-5/8 9-1/16 2-1/2 (12) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 1370 1575 1710 1175 1350 1470 175 175
2-5/8 x 11-1/4 - 11-7/8 THF26112 IUT2.68/12 -- 18 2-5/8 11-1/16 2-1/2 (14) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 1595 1835 1995 1370 1580 1715 300 360
2-5/8 x 14
THF26140
IUT2.68/14
--162
-5/813-3/82-1/2(18) 10d(2) 10d x 1-1/2209024002610180020702250300360
2-5/8 x 16
THF26160
MIU2.68/16--162-5/815-7/162-1/2(22) 10d(2) 10d x 1-1/2255029353035220025302750300360
2-5/8 x 18 - 24
THF26160
MIU2.68/16
x 162
-5/815-7/162-1/2(22) 10d(2) 10d x 1-1/2255029353035220025302750300360
HD27925
HU2.75/10
x 142
-3/48-5/8
2 (
18) 16d(6) 10d x 1-1/22520277527752180250527259101065
THDH27925 HGUS2.75/10 x 12 2-3/4 9-1/8 4 (46) 16d (12) 16d 8170 8260 8260 7250 8260 8260 3490 3490
HD27112 HU2.75/12 x 14 2-3/4 10-7/8 2 (22) 16d (6) 10d x 1-1/2 3080 3540 3610 2660 3060 3330 910 1065
THDH27112 HGUS2.75/12 x 12 2-3/4 10-7/8 4 (56) 16d (14) 16d 8785 9090 9300 8505 8770 8950 4935 5925
HD2714
HU2.75/14
x 142
-3/412-7/8
2 (
26) 16d(8) 10d x 1-1/236103610361031453610361010651065
THDH2714
HGUS2.75/14
x 122
-3/412-1/4
4 (
66) 16d
(
16) 16d
9
0759430966587559060926556456770
3 x 9-1/4 - 14
THF15925-2 MIU29-2
x 163
-1/89-3/162-1/2(12) 10d
(
6) 10d
1
390160017401200138015009301115
3 x 11-1/4 - 14
THF15112-2 MIU211-2
x 163
-1/810-13/162-1/2(14) 10d
(
6) 10d
1
625187020301400161017509301115
3 x 14 THF15140-2 -- -- x 12 3-1/8 12-3/4 2-1/2 (18) 10d (6) 10d 2250 2590 2815 1960 2255 2455 1000 1200
3-1/8 x 9-1/4 - 14 THDH3210 HGUS3.25/10 x 12 3-1/4 9-3/8 4 (46) 16d (12) 16d 8170 8260 8260 7250 8260 8260 3490 3490
3-1/8 x 11-1/4 - 14 THDH3212 HGUS3.25/12 x 12 3-1/4 10-5/8 4 (56) 16d (14) 16d 9870 10180 10385 8755 9855 10035 4935 5925
3-1/4 x 9-1/4 - 14 THF16925-2 HU3.31/9 x 16 3-3/8 9-1/16 2-1/2 (12) 10d (6) 10d 1390 1600 1740 1200 1380 1500 930 1115
3-1/4 x 11-1/4 - 14 THF16112-2 HU3.31/11 x 16 3-3/8 10-3/4 2-1/2 (14) 10d (6) 10d 1625 1870 2030 1400 1610 1750 930 1115
3-1/4 x 14 THF16140-2 HU3.31/14 x 12 3-3/8 12-5/8 2-1/2 (18) 10d (6) 10d 2250 2590 2815 1960 2255 2455 1000 1200
3-1/2 x 9-1/4 - 9-1/2 THF35925 IUT410 -- 18 3-1/2 8-5/8 2-1/2 (12) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 1370 1575 1710 1175 1350 1470 245 245
THF17925-2 -- -- x 16 3-9/16 8-15/16 2-1/2 (12) 10d (6) 10d 1390 1600 1740 1200 1380 1500 930 1115
HD410 HU410 x 14 3-9/16 8-13/16 2-1/2 (18) 16d (10) 10d 2520 2900 3150 2180 2505 2725 1575 1890
THD410 HHUS410 x 14 3-5/8 9 3 (38) 16d (20) 10d 5320 6120 6650 4600 5290 5750 3145 3775
THDH410 HGUS410 x 12 3-5/8 9-1/16 4 (46) 16d (12) 16d 8170 9010 9010 7040 7705 7855 3970 3970
3-1/2 x 11-1/4 - 12 THF35112 IUT412 -- 18 3-1/2 10-5/8 2-1/2 (16) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 1825 2100 2280 1570 1805 1960 245 245
THF17112-2 -- -- x 16 3-5/8 10-9/16 2-1/2 (14) 10d (6) 10d 1625 1870 2030 1400 1610 1750 930 1115
HD412 HU412 x 14 3-9/16 10-13/16 2-1/2 (22) 16d (10) 10d 3080 3540 3850 2660 3060 3330 1575 1890
THD412 -- -- x 14 3-5/8 11 3 (48) 16d (20) 10d 6650 6650 6650 5810 6435 6640 3145 3775
THDH412 HGUS412 x 12 3-5/8 11-1/16 4 (56) 16d (14) 16d 9845 9845 9845 7730 7995 8175 4935 5225
3-1/2 x 14 THF35140 IUT414 -- 16 3-1/2 12-15/16 2-1/2 (20) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 2320 2670 2900 2000 2300 2500 245 245
THF17140-2 -- -- x 12 3-5/8 12-1/2 2-1/2 (20) 10d (6) 10d 2500 2875 3125 2180 2505 2725 1000 1200
HD414 HU414 x 14 3-9/16 12-13/16 2-1/2 (24) 16d (10) 10d 3360 3865 4200 2905 3340 3630 1575 1890
THD414 -- -- x 14 3-5/8 12-7/8 3 (58) 16d (20) 10d 7335 7335 7335 7335 7335 7335 3335 4000
THDH414 HGUS414 x 12 3-5/8 13-1/16 4 (66) 16d (16) 16d 9845 9845 9845 7980 8285 8490 5645 6115
THF17157-2 -- -- x 12 3-5/8 15-3/4 2-1/2 (22) 10d (6) 10d 2750 3165 3440 2400 2760 3000 1000 1200
HD416 HU416 x 14 3-9/16 14-13/16 2-1/2 (26) 16d (12) 10d 3640 4185 4550 3145 3620 3935 1890 2265
3-1/2 x 16 THF35157 IUT416 -- 16 3-1/2 15 2-1/2 (22) 10d (2) 10d x 1-1/2 2550 2935 3190 2200 2530 2750 245 245
THF35165 IUT418 x 16 3-1/2 16-9/16 2-1/2 (24) 10d (8) 10d x 1-1/2 2785 3200 3480 2400 2760 3000 1235 1295
HD418 -- -- x 14 3-9/16 16-1/2 2-1/2 (28) 16d (8) 10d 3920 4510 4570 3390 3895 4255 1260 1425
4 - 4-3/16 x 9-1/4 - 9-1/2 THF20925-2
HU4.12/9,
HU4.28/9
-- 16 4-3/16 8-11/16 2-1/2 (12) 10d (6) 10d 1390 1600 1740 1200 1380 1500 930 1115
4 - 4-3/16
x 11-1/4 - 11-7/8
THF20112-2
HU4.12/11,
HU4.28/11
-- 16 4-3/16 11 2-1/2 (16) 10d (6) 10d 1855 2135 2320 1600 1840 2000 930 1115
4 - 4-3/16 x 14 THF20140-2 -- -- -- 16 4-3/16 13-5/8 2-1/2 (20) 10d (6) 10d 2320 2670 2900 2000 2300 2500 930 1115
2-11/16 x 9-1/4 - 14
3-1/2 x 14 - 20
3-1/2 x 11-1/4 - 16
2-11/16 x 14 - 16
3-1/2 x 9-1/4 - 14
Allowable Loads (Lbs.)
Uplift
2
2-11/16 x 11-1/4 - 16
U
SP
S
tock No.
3-1/2 x 18 - 26
3-1/2 x 16 - 22
Fastener Schedule
EEWWPP FFaaccee MMoouunntt HHaannggeerrss CChhaarrttss
Web Stiffener Reqd.
Steel Gauge
continued
continued on next page
Customer Service / Technical Assistance
Burnsville, MN Corporate Of
1-800-328-5934
fice
 Loading...
Loading...