Universal Air Tools UT5741A User Manual
Tel No
(01494) 883300
(01494) 883237
Includes - Foreseen Use, Work Stations, Putting Into Service, Operating,
Operator Instructions Important
Read these instructions carefully before installing, operating,
servicing or repairing this tool. Keep these instructions in a safe
Test Method
Tested in accordance with Pneurop
test code PN8NTC1 and ISO Standard 3744
Vibration Level
Test Method
Tested in accordance with ISO
Less than 2.5
Dismantling, Assembly and Safety Rules
Manufacturer/Supplier Product Type
Universal Air Tool Company Limited
Unit 8
Lane End Industrial Park
High Wycombe
Bucks
accessible place.
RPM
Straight Lever Type Drill
4,000
Cycles Per Min
N/A
Model No/Nos Serial No (if any)
UT5741A
HP14 3BY
Fax No
Product Nett Weight
2.0
0.91 3/8 10 30 10
Recommended Working
Recommended Minimum
Maximum
Use - Safety Glasses
Use - Safety Gloves
Use - Safety Boots
Use - Breathing Masks
Use - Ear Protectors
lbs
Kg
Air Pressure
Personal Safety Equipment
Recommended Use Of
Balancer Or Support
No
bar
6.3
n/a
7.0
bar
bar
90
n/a
100.0
Yes
Yes
Recommended Hose Bore
Noise Level
PSI
PSI
PSI
standard 8662/1
Size - Minimum
Ins M/M Ft M
Sound Pressure Level 89.1 dB(A)
Sound Power Level 100.0 dB(A)
Recommended Max.
Hose Length
Metres / Sec²
Foreseen Use Of Tool
This drill is designed for the purpose of drilling holes in all types of
materials, i.e. metals, wood, stone, plastics etc. using drilling bits
designed for this purpose. It may be used with other forms of cutting
tools, polishing devices or for sanding using coated abrasive products.
Before using any such products first check with the manufacturer
their suitability for use with this type of drill. Do not use bonded
abrasive products (i.e. grinding wheels) or saw blades or any device
which has a permitted safe working speed less than the free speed
of the drill.
Do not use this drill for any other purpose than that specified without
consulting the manufacturer or the manufacturer's authorised supplier.
Work Stations
The tool should only be
used as a handheld
hand operated tool. It is
always recommended
that the tool is used
when standing on the
solid floor. It can be
used in other positions
but before any such
use, the operator must
be in a secure position
having a firm grip and
footing and be aware
that the drill can develop
a torque reaction see
section "Operating".
Putting Into Service
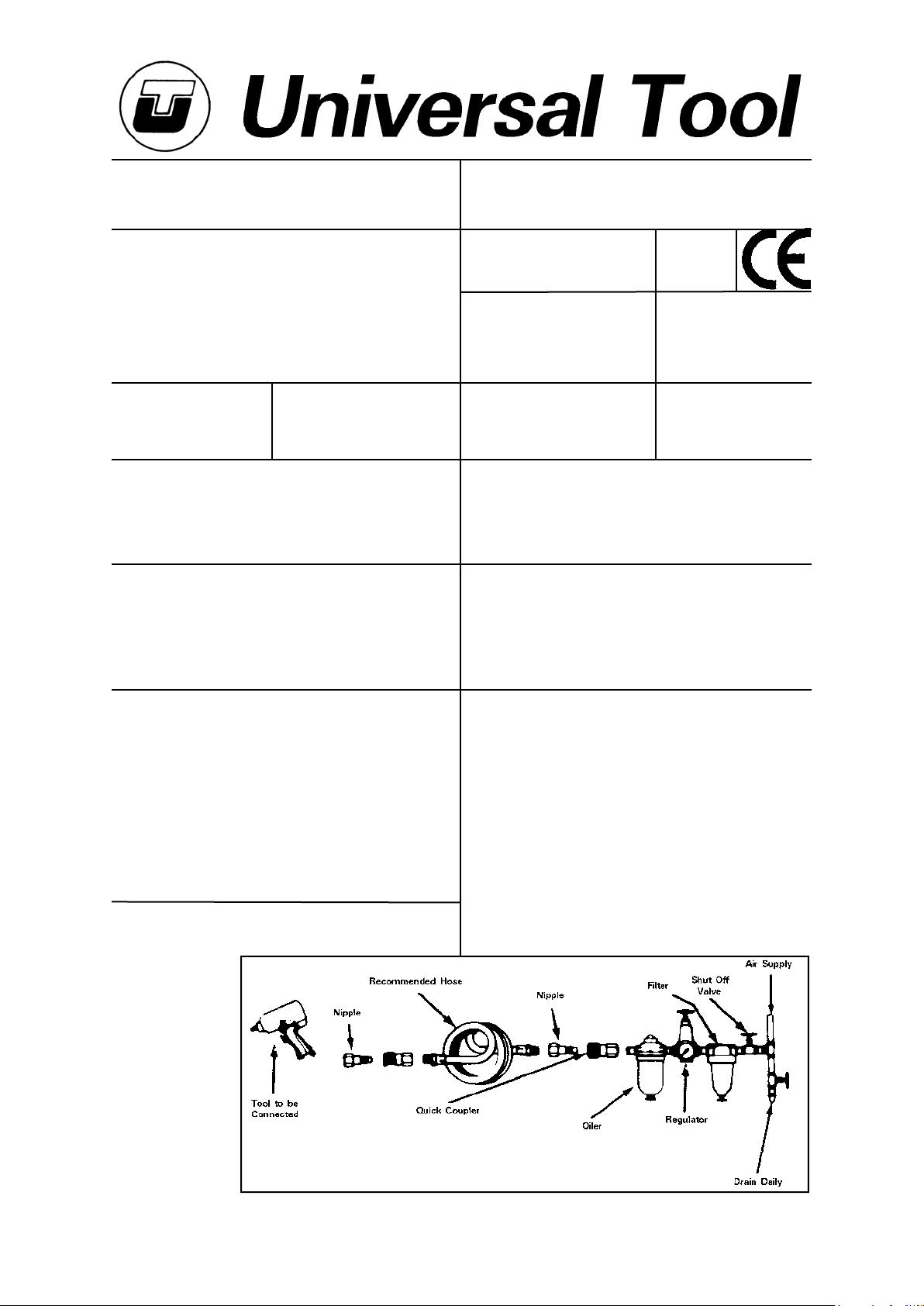
Air Supply
Use a clean lubricated air supply that will give a measured air pressure
at the tool of 90 p.s.i./6.3 bar when the tool is running with the trigger
fully depressed. Use recommended hose size and length. It is
recommended that the tool is connected to the air supply as shown
in figure 1. Do not connect the tool to the air line system without
incorporating an easy to reach and operate air shut off valve. The air
supply should be lubricated. It is strongly recommended that an air
filter, regulator, lubricator (FRL) is used as shown in Figure 1 as this
will supply clean, lubricated air at the correct pressure to the tool.
Details of such equipment can be obtained from your supplier. If such
equipment is not used then the tool should be lubricated by shutting
off the air supply to the tool, depressurising the line by pressing the
trigger on the tool. Disconnect the air line and pour into the intake
Page No 1

bushing a teaspoonful (5ml) of a suitable pneumatic motor lubricating
oil preferably incorporating a rust inhibitor. Reconnect tool to air
supply and run tool slowly for a few seconds to allow air to circulate
the oil. If tool is used frequently lubricate on daily basis and if tool
starts to slow or lose power.
It is recommended that the air pressure at the tool whilst the tool is
running is 90 p.s.i./6.3 bar. The tool can run at lower and higher
pressures with the maximum permitted working air pressure of 100
p.s.i./7.0 bar.
Operating
Select suitable drill bit, insert the shank into the drill chuck as far as
possible and tighten chuck with key supplied making sure that the
shank of the device is securely clamped centrally between the three
chuck jaws. Remove chuck key.
When drilling holes of all sizes it is advised to use a pointed punch to
mark the centre at which the hole is to be drilled as this will provide
a starting point for the drill tip. This procedure will prevent the drill bit
from skidding, ensure that the hole is drilled where intended and help
to prevent drill breakage when using small drills. When drilling,
particularly with small diameter drills, always try to ensure that load
applied to the drill is such that the drill bit is always at right angles to
the hole being drilled. Do not force the drill but allow it to cut.
When drilling always adopt a firm posture to be able to counteract
any sudden movement of the drill due to torque reaction. Such torque
reaction can occur when the drill stalls due to a too heavy load being
applied or the material being too hard or tough. The torque reaction
can occur when the drill breaks through the material being drilled,
particularly on sheet metal. Always use eye protection and hand
protection is advised, particularly when drilling holes in metals where
the material being removed from the hole is in the form of long sharp
strips. Do not tie the drill chuck key to the drill as the attaching device
i.e. string or chain could become entangled with the rotating chuck
and bit etc.
If using an abrasive device, drilling stone or performing any operation
where dust is created, it is recommended to use a breathing mask.
Always ensure that the material to be drilled is firmly fixed to prevent
its movement.
It is also recommended that when drilling holes of large diameter to
first pre drill a hole of smaller diameter as this will reduce effort
required to drill the hole and minimise torque reaction.
Dismantling & Assembly Instruction
Disconnect tool from air supply.
Insert the drill chuck key securely into the chuck (33) and strike the
chuck key a sharp blow with a hammer in a direction to loosen a
right hand treaded joint to remove the chuck and chuck spacer (28).
Grip motor housing (4) with housing sleeve (4A) in a vise fitted with
soft jaws and unscrew inlet bushing (1) together with exhaust washer
and deflector (2 & 3). Drive out pin (6) and remove throttle lever
assembly (5). Unscrew valve screw (14) with o-rings (12 & 13) and
from the lever side push out air regulator (11), spring (10), o-ring (9),
and throttle valve (8). Unscrew gear cap (26) complete with the
internal gear drive assembly. From the front end push out the internal
gear assembly complete with gear ring (25). Pull off bearings (24),
idler gear plate (25), needle bearing (22P) and idler gear (22). Pull
out the motor assembly from the motor housing (4). Grip front plate
(21) by hand and tap the spindle end of rotor (18) with a non metallic
(lead or aluminum) hammer so as to drive the rotor through the front
end plate and bearing assembly. Pull off bearing (21Q) from the front
plate (21). Do not remove pins (17 and 21P) from the end plates (21
& 16) unless replacements are required. Take off cylinder (20) noting
its orientation with the rear plate (16) for reassembly and take out 4
off rotor blades from rotor (19). Support the rear plate (16) in a piece
of tube with a bore diameter as close as possible to the maximum
diameter of the rotor (18) and tap the non-splined end of the rotor
to drive it through the rear plate and bearing assembly. With a suitable
punch tap out bearing (15) from rear plate (16). Remove the housing
cover (4A) from motor housing (4) when needed.
Reassembly
Clean all component parts and examine to wear before reassembling.
Use only manufacturer or distributor supplied spare parts. Check in
particular for wear and cuts on o-rings and wear on rotor blades.
Lightly coat all parts with suitable pneumatic tool lubricating oil
preferably one incorporating a rust inhibitor. Pack all bearings and
gearbox with a lithium or molybdenum based general purpose
reassemble in the reverse order (see note below). For the motor
assembly ensure that front and rear plates that abut the cylinder are
clean and free from burrs and surface marking. If necessary, lap faces
that abut the cylinder on a flat fine grade of abrasive paper. Press
bearings into front and rear plates, support the bearing in the rear
plate on its inner ring and tap the rotor its splined end with a soft
metallic hammer into the bearing until rotor locates against the rear
plate. Support the inner face of the end plate as close as possible to
the largest diameter of the rotor and tap the non-splined end of the
rotor until a clearance of 0.0015” (0.04mm) to 0.0025” (0.065mm)
is obtained between the inner face of the rear plate and rotor. This
clearance has to be checked when pulling the rotor away from the
rear plate and bearing assembly. Spin rotor to ensure that it will rotate
freely in the rear plate bearing. Locate the cylinder by the locating pin
to the rear plate checking that the ports in the end plate match with
those in the cylinder. Insert the four motor blades into the rotor and
locate correctly the front plate to the cylinder using the locating pin.
Ensure that the rotor will spin freely in the assembly. This is
the best checked by placing the motor assembly in a vee
block and squeezing the front and rear plates against the
cylinder. When refitting motor assembly to motor housing (4)
ensure that pin (21P) in the side of front plate (21) locates in
the slot in the front of the main bore of motor housing (4).
Safety Rules When Using A Drill
1) Read all the instructions before using this tool. All operators must
be fully trained in its use and aware of these safety rules. All service
and repair must be carried out by trained personnel.
2) Always select a suitable cutting, abrasive device suitable for use
with this drill.
3) Always shut off the air supply to the drill and depress the trigger
to exhaust air from the feed hose before fitting, adjusting or removing
the device. Remove drill chuck.
4) Always adopt a firm footing and/or position and be aware of
torque reaction developed by the drill.
5) Use only correct spare parts.
6) Check hose and fittings regularly for wear. Do not carry the tool
by its hose and ensure that the hand is remote from the on/off valve
(trigger) when carrying the tool with air supply connected.
7) Do not exceed maximum recommended air pressure. Avoid low
air pressures as this will allow the drill to stall more easily and develop
torque reaction.
8) Use safety equipment as recommended.
9) The tool is not electrically insulated. Do not use where there is a
possibility of coming into contact with live electricity, gas pipes, water
pipes, etc. Check the area of operation before performing the
operation.
10) Take care against entanglement of moving parts of the tool with
clothing, ties, hair, cleaning rags, etc. This will cause the body to be
moved towards the work process and can be very dangerous.
11) Do not attempt to hold or guide the drill chuck when the tool is
running. Keep hands clear of the drilling process.
12) Use only compressed air at recommended conditions.
13) Do not attempt to fit attachments, i.e. for sawing, hedge cutting,
grinding, chain sawing, etc.
14) If the tool appears to malfunction remove from use immediately
and arrange for service and repair.
15) If an additional side handle is fitted to the tool ensure that it is
correctly positioned and fixed securely.
16) If the drill is used with a balancer or other suspension device
ensure that it is fixed securely.
Page No 2
 Loading...
Loading...