Page 1

Manual
K2724 (-B), K2724S, K272U (-B), K2726 (-B)
Multi function Keyboard Magnetic Stripe Card Reader/
Bar Code Slot Reader & built-in Bar Code Decoder
for IBM or compatible computers
Date: March 2001
Version: 2.9 V2
Page 2

Preface
General Advice
Improper handling, storage, external influences and /or further processing
can lead to disturbances and defects during use.
This is also especially valid if trained personnel do not perform repairs
and maintenance work.
We reserve the right to make any technical alterations to in accordance
with technological advancements.
Information to the user
This device has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the device is operated in a commercial environment.
This device generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and,
if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in
which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
* All information is subject to change without prior notice.
* All brand names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
1. Overview Page 1
1.1. Ports and Input Device 2
1.2. Decoding Capability 2
1.2.1. Bar Code 2
1.2.2. Magnetic Stripe 3
1.3. Scanning Mode 3
1.4. Setup 4
2. Understanding the Operation Parameters 4
2.1. Intercharacter Delay 4
2.2. Function Code 5
2.3. Caps-Lock 5
2.4. Alt Key Mode 5
2.5. Code ID 5
2.6. Scanning Mode 6
2.7. Track 1 Output Sequence 7
2.8. Track 2 Output Sequence 8
2.9. Fix Length of 2 of 5 Codes 8
2.10. CLSI Format of Code bar 9
2.11. Zero Expansion of UPC-E 9
2.12. Bookland EAN 9
3. Setup 9
3.1. Setup from Keyboard (for DOS environment) 9
3.2. Setup the Keyboard from Bar Code Menu 10
3.2.1. General Settings 10
3.2.2. Bar Code Length Setting (example) 10
3.2.3. Code ID Setting (example) 11
3.2.4. Preamble, Postamble, and Output Sequence 11
3.3. Data Editing 12
3.4. Batch Setup 20
3.5. Scanner Configuration Manager Software 21
4. Using the Magnetic Stripe Card Reader 22
5. Pin assignment of the scanner port 22
6. Specification 23
Appendix A. – Function Codes
Appendix B. – Setup Menu
Appendix C. – Full ACPI Chart
Appendix D. – Bar Code Test Chart
Page 4

1. Overview
This is a family of multifunction keyboards with 104/105 keys (US/International version)
enhanced layout. The keyboards feature re-legendable keys, integrated Magnetic Stripe
Card Reader (or Bar Code Slot Reader), and built-in Bar Code scanning input port. The
keyboards also feature a minimal footprint and protection against damage from liquid
spillage.
Num
Caps
Scroll
Good
Lock
Lock
Lock
Read
Prt Sc
Delete
Num
Lock
7
Home
4
1
Page
Up
Page
End
Down
/
*
89
5
6
3
2
.
0
Del
Sys Rq
Scroll
Lock
Pause
Break
-
+
Enter
Esc
~
`
Tab
Caps Lock
Shift
Ctrl
F1
@
!
1
2
W
Q
ASD
ZX
Alt
F3 F4
F2
#
%
$
3
4
5
ERTY
FGHJK
C
F5
^
6
V
BNM
F6
F7 F8 F9 F10
&
*
890
7
IOP
U
()
L
<
,
Alt
English Language Keyboard
F11 F12 Insert Home
_
+
|
\
-
=
{
[}]
:
"
Enter
;
'
?/>
Shift
.
Ctrl
F1
Esc
_
a
_
o
Bloq
Mayus
Ctrl
\
!
|
1
Q
ASD
`
>
<
Alt
F2
.
"
@
#
3
2
ERTY
W
ZX
F3 F4
%
$
4
5
FGHJK
C
F5
&
6
V
BNM
/
L
7
F6
()
890
U
F7 F8 F9 F10
=
?
IOP
`
^
`
~
L
N
_
;
:
,
-
.
Alt Gr
Ctrl
?
!
[
:
{
`
Spanish Language Keyboard
Typical Applications
* Point-of-sale system
* Banking, financial, and insurance data input
* ID entry and security
* Industrial control and automated process applications
* Inventory control
* Shipping and receiving product identification
F11 F12 Insert Inicio
*
]
+
c
}
Supr
Bloq
Num
7
Inicio
4
1
Fin
Num
Lock
Fin
89
5
2
0
Ins
Caps
Scroll
Good
Lock
Lock
Read
Impr
Re
Pant
`
Pag
Pet Sis
Bloq
Av
`
Despl
Pag
Pausa
/
*
Inter
-
`
RePag
6
+
3
`
AvPag
Intro
.
Supr
Page 5

1.1 Ports and Input Device
The keyboard has two input ports to accept a variety of input devices:
A port with DB-9 squeeze release type connector at the upper-right hand side of the
keyboard supports barcode scanner input. Wand, CCD, or Laser scanners are supported.
An open slot at the upper-left corner of the keyboard can support a standard dual track
magnetic card reader. Alternatively, this open slot can be configured to support a single
track magnetic reader, triple track magnetic reader, or a bar code slot reader.
The following procedures should be followed when connecting an undecoded barcode
scanner to the scanner port:
•
Plug the connector of the scanner into the DB-9 connector located at the right hand
side of the keyboard.
• Switch the computer off.
Switch the computer back on.•
Card
Reader
Slot
Scanner
Port
1.2 Decoding Capability
1.2.1 Bar Code:
* Code 39 Standard and Full ASCII
* UPC\EAN with supplement codes
* Interleaved 2 of 5
* Standard 2 of 5
* MSI Code
* Plessey Code
K2724
(Beige)
K2724B
(Black)
Page 6

* China Postal Code (Toshiba Code).
* Codabar.
* UCC/EAN128
* Code 32 (Italian pharmacy).
* Code 93.
* Code 128.
* Label Code IV and V
* Delta Distance Code.
1.2.2. Magnetic Stripe:
* Track 1 – IATA.
* Track 2 – ABA.
* Track 3 – THRIFT.
1.3. Scanning Mode:
The keyboard provides seven scanning modes for CCD/Laser scanners:
* Trigger Mode:
Depressing the scanner’s trigger to activate the scanner and automatically turn
off the scanner after successful label read. Releasing the trigger will manually
de-activate the scanner.
* Flash Mode:
The Keyboard triggers the scanner to scan periodically - providing a trigger-less
scanning method. The scanner will strobe on and off until a label is detected.
Note – this feature may not work properly with older laser scanners.
* Multiscan:
The scanner’s trigger is held down during the reading of multiple labels - and the
scanner is turned off when trigger is released.
* One Press, One Scan:
The scanner’s trigger is pressed once and the scanner remains on until a
successful input.
* Test Mode:
The scanner’s trigger is pressed once and the scanner remains on to read
whatever label is presented and then sent to computer.
* Old Laser Flash Mode:
This feature is designed to work with older laser scanners. Some models may
not work properly with this feature.
* Continuous Mode:
The scanner’s trigger is pressed once and scanner remains on to read a label only
once. Subsequent presentations of the same label will be ignored.
Page 7

1.4. Setup
There are several ways to configure the Keyboard to fit the user’s
requirements:
* Keyboard: (Setup Magnetic Stripe Reader)
Setup via any text editor, such as Notepad or WordPad under Microsoft Windows
environment. Keyboard setup provides and interactive way to setup the
keyboard’s magnetic stripe reader through screen prompting.
* Bar code menu:
Besides the keyboard setup, the keyboard can be programmed by scanning a
sequence of bar code labels from the user’s manual. Refer to the Bar Code
Menu in Setup Menu of appendix B. Scan the following label to reset the
build-in wedge to the Factory Default setting.
Factory Default
* Batch Setup:
Produce custom setup labels and then scan these labels to duplicate the settings
on other keyboards
* Software Setup:
Scanner Configuration Manager is a utility program to configure scanner settings
on a computer using the Windows 95/98 operating system. Use Scanner
Configuration Manager to define the settings and then download the parameters
to the scanner.
The “GOOD READ” LED will blink when the Keyboard enters setup mode.
2. Understanding the Operating Parameters
This section describes the operating parameters of the Keyboard.
2.1. Intercharacter Delay
Intercharacter delay is the time period that the keyboard will wait before transmitting
the next character. For some applications, an intercharacter delay is necessary in
order for a system to keep pace with data transmitted from the Keyboard.
If incomplete data is sent from the Keyboard, increasing the value of this parameter
may correct the problem.
Page 8

2.2. Function Code
The keyboard can emulate special keys, such as function keys and cursor keys, by
scanning pre-defined bar code labels - which can be found in Appendix A. Print
these bar code labels by printing their corresponding Code 39 characters (in brackets).
2.3. Caps-Lock
This parameter will set the Caps-Lock state of the keyboard so that the character
transmitted by the keyboard is in the correct case.
* Auto Trace:
Normally the keyboard will trace the Caps-Lock state by itself, but some PC’s
scanning performance may be compromised because of Auto Tracing. If
scanning performance is poor (or not functioning at all) or if the keyboard cannot
output the upper/lower case characters correctly, select one of the next two
choices as an alternative to Auto Tracing.
* Lower Case:
When the Keyboard is in the unshifted state (CapsLock is not pressed), select
“Lower Case”.
* Upper Case:
When Keyboard has the CapsLock key on, select “Upper Case”.
2.4. Alt Key Mode
Alt Key Mode is an option found under Language Selection. Sending characters by
Alt key plus keys on the numeric keypad is a feature in MS-DOS. When “Alt Key
Mode” is selected, the keyboard outputs the native ASCII combination codes to
represent each character of the bar code scanned. If your system accepts Alt key
sending, you can enable this mode and ignore the “Upper/Lower Case” and
“Language” selections.
2.5. Code ID
The keyboard can add code IDs to data strings via the following pre-defined IDs for
bar code and magnetic stripe card readers. These IDs can be modified via bar code
setup.
Symbology Pre-Defined
UPC-A A
UPC-E E
EAN-13 F
EAN-8 FF
I 2 of 5 I
S 2 of 5 H
Page 9

Code 39 M
Codabar N
Code 93 L
Code 128 K
UCC/EAN128 ]C1
MSI O
Code 32 T
Delta Code D
Pressey Code P
Label Code IV, V B
China Postal Code C
Track I None
Track II None
Track III None
2.6. Scanning Mode
For CCD or Laser scanners, the keyboard provides the following seven scanning
modes:
* Trigger Mode:
When the trigger is pressed, the keyboard will power up the CCD or laser
scanner to read the bar code. If the bar code is decoded, the Keyboard will turn
off the scanner and upload the data. The Keyboard will turn off the scanner if
the label cannot be read within approximately 3 seconds.
To read the next label, release and press the trigger again.
* Flash Mode:
When Flash Mode is enabled, the keyboard causes the photo LEDs of the CCD
to strobe until it detects a label. When a bar code is detected and read, the
keyboard uploads the data and attempts to read the next bar code during the next
5 seconds. If no bar code is read during that period, the photo LEDs begin to
strobe again.
In Flash Mode, the keyboard is designed to not double-read the same barcode.
In order to deliberately re-read the same barcode, the barcode must be removed
from the scanner’s readable area for at least one second.
Pressing and releasing the trigger will stop the flashing and turn off the photo
LEDs. Pressing and releasing the trigger again will resume the flashing.
Note: The flash function is for CCD scanners only. It cannot support Wand or laser
scanners. Set the keyboard to Switch Mode in order to operate the scanner.
* Multiscan:
When Multiscan is enabled, pressing the trigger enables the scanner to read
Page 10

multiple labels, and the scanner will continue to read until the trigger is released.
This is useful to users that prefer multiple inputs during scanning.
* One Press, One Scan:
With this feature enabled, pressing the scanner’s trigger causes the scanner to
remain on until a successful input. This is useful because once the trigger is
pressed, the trigger can be released and the scanner will remain “On” until the
scanner performs a successful data input and then turns itself off.
* Test Mode:
The test mode tests the scanner or the system. The scanner will remain “On”
when the scanner’s trigger is pressed and will read whatever label is presented,
and then uploads the data to the computer.
* Old Laser Flash Mode:
This feature is designed to work with some older laser scanners. It will turn off
the laser scanner to avoid damaging the scan engine. Some very old models of
laser scanners may not work properly with this feature.
* Continuous Mode:
When Continuous Mode is enabled, user presses the scanner’s trigger once and
the scanner will remain “On” to read a label, but will not read the same label
twice. This is designed to avoid erroneous repeat data input.
2.7. Track 1 Output Sequence
Track 1 of magnetic cards contain account number, last name, first name, and
expiration date information. Programming the Output Sequence tells the keyboard
how to output those messages. The numbers corresponding to each message are as
follows:
Message Number
Account Number 1
Last Name 2
First Name 3
Expiration Year 4
Expiration Month 5
Discretionary Data 6
Use the assigned number and a separator character to produce your required output.
Example: To get the following output from track 1:
Account Number<Enter>
Last Name, First Name<Enter>
Expiration Month/Expiration Year<Enter>
Page 11

Program the Output Sequence as:
1<CR>2,3<CR>5/4<CR>
Here <CR> is hexadecimal 0D if the bar code menu is used for setup. Scan CR from
full ASCII chart to get this character. Or press Ctrl-M if you use keyboard setup.
The last <CR> will not be necessary if Terminator is set to Enter.
For a card with following messages:
%B012345678901234^ABEL/STEVE L MGR ^90010129999999?
You will get:
012345678901234
ABEL, STEVE
01/90
The maximum number of characters that can be input in Track 1 Output Sequence is
16. If nothing is defined, all messages will be output.
2.8 Track 2 Output Sequence
The same implementation as Track 1 Output Sequence, but with the following
message-number match:
Message Number
Account Number 1
Expiration Year 2
Expiration Month 3
Discretionary Data 4
The maximum number of characters that can be input in Track 2 Output Sequence is 8.
If nothing is defined, all messages will be output.
2.9. Fix Length of 2 of 5 Codes
For Interleaved 2 of 5 and Standard 2 of 5 codes, specifying the decoding length is
strongly recommended. By using a fixed length (default), the keyboard will accept
lengths of first three I 2 of 5 or S 2 of 5 after powering up as valid decoding lengths.
If a bar code has a different length than the first three lengths, the keyboard will not
accept that label.
2.10. CLSI Format of Codabar
If selected, 14 characters Codabar (Start/Stop not included) will be output to CLSI
format with spaces inserted.
For example
Page 12

Label content:
01234567890123
CLSI format:
0 1234 56789 0123
2.11. Zero Expansion of UPC-E
When selected, UPC-E will be converted to UPC-A format.
2.12. Bookland EAN (ISBN):
When enabled, the EAN-13 with “978” as first three digits will be converted to ISBN
format.
For example:
EAN-13 label: 9781234567897
ISBN format: 123456789X
3.Setup
The keyboard can be configured to fit the user’s specific applications. All
configuration parameters are stored in a non-volatile memory (256 bytes), which is
retained even if power is lost.
3.1 Setup MSR Port from Keyboard
The Magnetic Stripe Reader can be setup by using the keyboard itself. The setup
process can be done under any text editor software, such as Notepad or WordPad.
To activate keyboard setup, press Left Shift key and Right Shift key at the same time
immediately after system power-up. Setup messages will be displayed on the screen
when both Shift keys are released. Instructions on the screen make programming the
keyboard simple.
Hamster V2.6 Nov.18, 99
Use numeric keys on the top of alphabetic keys for digit input.
0-MCR 1-Others 2-Default 3-dump 4-Exit
Selectè _
Note: Keyboard setup must be activated within 10 keystrokes after system
Page 13

power-up. After 10 keys (other than Shift keys) are pressed, setup will not be
activated except by a system restart or by simply unplugging and re-plugging the
keyboard connector on your computer.
During setup, only Numeric keys (0 to 9) on the top row of keyboard are
accepted; Numeric keypad on the right of keyboard is not supported.
3.2. Setup the Keyboard from Bar Code Menu
The Menu setup lets the user configure the Reader by scanning labels into a setup
menu from Appendix B. The setup menu contains 8 groups as following:
Group 1: Beep and Delay
Group 2: Keyboard Interface
Group 3: Scanner Port
Group 4: Magnetic Reader
Group 5: Code 39, I 2 of 5, S 2 of 5, code 32, and EAN128
Group 6: Code 128, MSI, Code 93, Codabar, and Label Code
Group 7: UPC/EAN, and Delta Distance Code
Group 8: Data Editing
3.2.1. General Settings
For most parameters, follow the steps below:
1) Locate a group that contains the parameter to be changed.
2) Scan the “Enter Group” label to enter setup. The Keyboard will beep three times
to indicate that setup has begun.
3) Scan the label (on the right side) representing the parameter to be changed.
4) Scan the labels (number) representing the desired parameter value.
5) Repeat step 3 and 4, if necessary, to change the parameters in the same group.
6) Scan the “Exit” label to end the group setup. The Keyboard will beep twice and
return to normal.
3.2.2. Bar Code Length setting (example)
The following example illustrates how to set Code 39 with a minimum length of 5 and
a maximum length of 20:
* Scan Enter Group 5
* Scan F1 to select Code 39
* Scan MIN LENGTH to enter minimum length setting
* Scan 0 and 5 to select length 5
* Scan MIN LENGTH to end minimum length setting
* Scan MIN LENGTH to enter maximum length setting
* Scan 2 and 0 to select length 20
Page 14

* Scan Exit to end setup
3.2.3. Code ID Setting (example)
The following example shows how to set Code 93 with ID O and Code 128 without
ID
* Scan Enter Group 3
* Scan D2 to select Code ID
* Scan 1 for “Yes”
* Scan D3 to define IDs
* Scan 0 and 9 for selecting Code 93
* Scan O from Full ASCII Table (Appendix D) for new ID
* Scan 0 and “8” to select Code 128
* Scan NULL character from ASCII Table (Appendix D) for none ID
* Scan Exit to end setup
3.2.4. Preamble, Postamble, and Output Sequence
Setting of Output Sequence is the same procedure as setting preamble and postamble.
The Following is an example to set STX as preamble and ETX as postamble for the
scanner port:
* Scan Enter Group 3
* Scan PP to start preamble setting
* Scan STX character from Full ASCII Table
* Scan PP to end preamble setting
* Scan OO to start postamble setting
* Scan ETX from Full ASCII Table
* Scan OO to end postamble setting
* Scan Exit to end setup
The next example shows set track 1 output sequence as:
Account Number<Enter>
Expiration Month/Expiration Year<Enter>
* Scan Enter Group 4
* Scan E1 to select Terminator
* Scan 1 for None
* Scan “PP” to start track output sequence setting
* Scan 1 to select account number
* Scan CR from Full ASCII table
* Scan 5 for expiration month
* Scan / from Full ASCII table
Page 15

* Scan 4 for expiration Year
* Scan CR from Full ASCII table for <Enter>
* Scan PP to end output sequence setting
* Scan “Exit: to end setup
3.3. Data Editing
The purpose of Data Edit is to enable you to define and modify a data record that
results from the decoding of a bar code. By using a combination of Formulas, you
can perform the following functions on the data received by the scanner:
A. Rearrange the output sequences.
B. Delete characters from the record.
C. Insert characters into the record, including function codes.
D. Duplicate characters in the record.
E. Insert a time delay into the record
Formula
Formula is a structure that tells the scanner what and how to process the original data
record to produce the desired output. The built-in wedge allows multiple Formulas,
but the number of the Formulas that can be defined depends upon the memory size
allocated for Data Editing.
Original Data Structure
The original data structure is the decoded data plus preamble and postamble. The
original data structure is as follows:
Decoded Data Postamble
Formula Structure:
A Formula consists of two parts: Qualifier and Modifier (See Figure 7.1).
Qualifier is used to verify if the data record meets the conditions specified, and
Modifier is processed only if all conditions in Qualifier are met.
Execution Sequence
If several Formulas are defined, data editing will perform sequentially from the first
Formula to the last Formula. If a Formula is qualified and executed, the subsequent
formulas will be ignored. If none of the Formulas are executed, the data record will
be discarded and there will be no output to the host.
Page 16
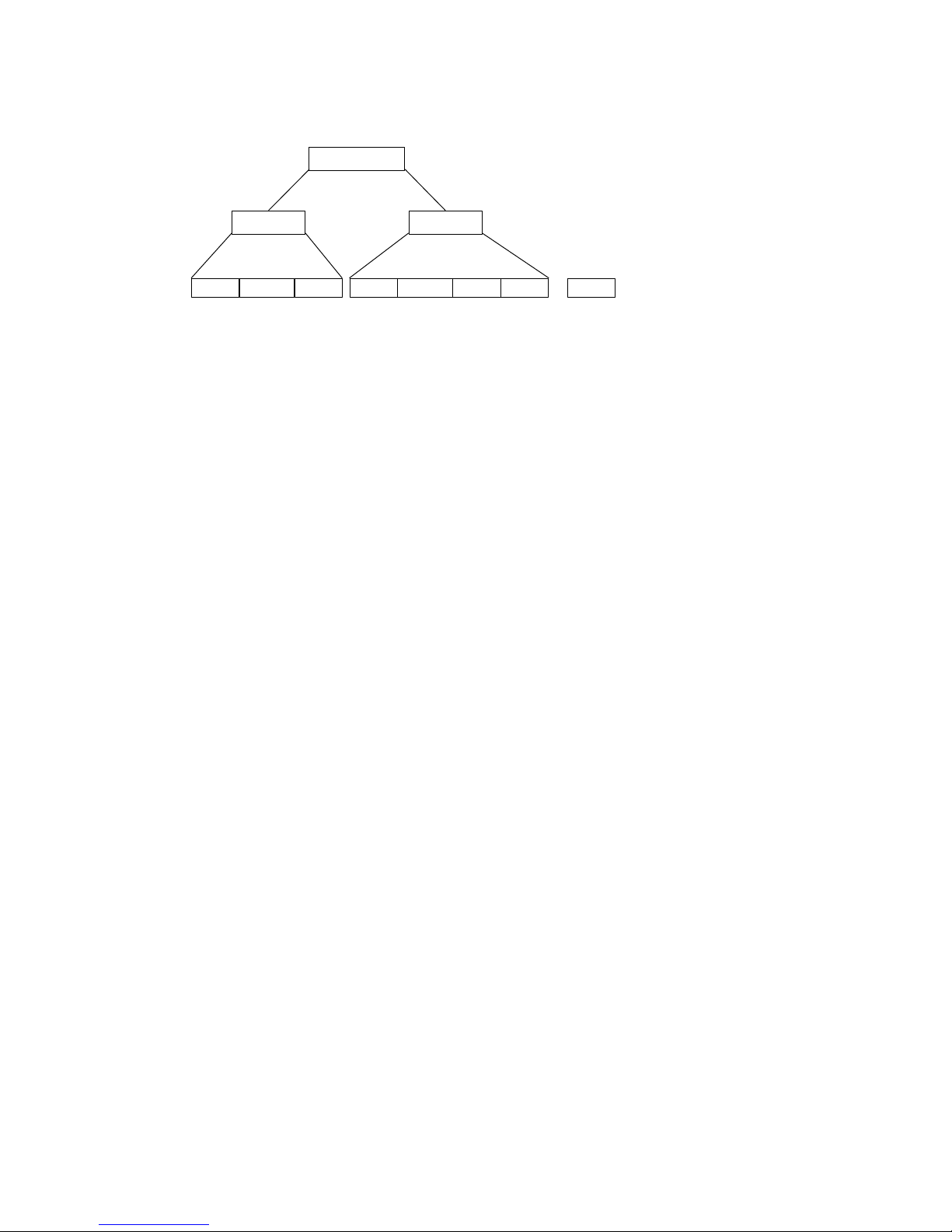
Formular
Qualifier Modifier
Input ID [Length] [Match] Input ID [Length] [Match] [Match] [Match]
A-String: String to be added.
O-String: Modified original data.
[] : Optional.
Figure 3.3 Formula Structure
...
Programming Sequence:
Each Formula is entered into the Reader in the following sequence:
Input_ID>>Length>>Match>>A-String>>O-String>>...>>O-String >>Enter
A Formula starts with Input_ID and ends with “Enter”(label included in the
programming sheet). If a field is optional and missing, the next one in the sequence
can be entered. “Enter” must be the last input of a formula.
Preparation
To begin the Data Editing, the following barcode sheets are required:
-- Programming Sheet. (Setup Sheet in Appendix B).
-- Full ASCII Sheet (Appendix C).
Before programming Data Editing, you should know the format of the original data
record that may be altered by the setup groups.
Programming Sheet
The bold and italicized characters in the following sections refer to barcode labels on
the Programming Sheet.
Enter Group
Scan this label to begin the formula input.
10
Group
Erase all formulas.
Default
Page 17

Review
To view the formulas programmed in the
Wedge. By scanning this label during a
formula input (prior to scanning “Enter”
and thereby finishing), the current formula
will be displayed. Otherwise, all
programmed formulas will be displayed.
Backspace
,
"
*
Delete the last character.
Delimiter to separate parameters.
String specifier.
Wild character to specify any digit or any
position.
# Wild character to specify any letter (A--Z,
a--z) or last position
Enter
To end the current formula.
0 to 9 For digit input.
IN_ID
LEN
MATCH
O-STR
+
-
Exit
For ID field input.
For Length field input.
For Match field input.
For O-String input.
For O-String input.
For O-String input.
Save all formulas and exit setup.
Note: The '*', '#', '" ' and ',' on the Programming Sheet have special meanings as
mentioned above, and are different from those represented in the Full ASCII chart.
Always use characters in the Full ASCII chart for string parameters unless a special
function is required.
Parameter Entry
a) Digit Parameters and Numbers
Each digit parameter or number is represented by one to three digits with ‘,’
as the terminator. For example:
b) String Parameters
A string is a set of characters, wild characters, or sequence of adjacent
characters enclosed in double quotation marks, which are included in the
Programming Sheet. For example:
1,
023,
"A*B# "
Page 18

Here * and # are wild characters on the setup sheet.
Qualifier
There are three conditional fields in the Qualifier:
Input ID, Length and Match
Input ID
Format:
IN_ID,ID1, ... ,IDi,
Input ID is required and the original data record must correspond to Input ID of a
formula in order to be processed.
ID1 to IDi are represented by digits. The following Input IDs are available:
0 = Code 39 Full ASCII
1 = Code 39 Standard
2 = EAN 13
3 = EAN 8
4 = UPC A
5 = UPC E
6 = I 2 of 5
7 = Codabar
8 = Code 128
9 = Code 93
10 = S 2 of 5
11 = MSI
19 = UCC/EAN128
28 = All Inputs
There is no limitation on the number of IDs to be defined.
Example:
IN_ID,0,11,
means the original data can be Code 39 or MSI.
Length:
Format:
LEN,Min,Max,
Length field consists of two length parameters: minimum length (Min) and
Page 19

maximum length (Max). When defined, a formula will be performed if the length of
the original data falls between MIN and MAX.
When missing, the following fields of current Formula are always processed.
Example:
LEN,9,48,
means the length of original data must be within 9 and 48.
Match
Format:
MATCH, P0 ,"C0" ,P1, "C1" ,...,Pn, "Cn" ,
a pair of Pn and Cn forms a Match field (n indicates a sequential integer number).
To define a Match field, two parameters are required. The first is character position
(Pn) and the second is a string (Cn). Character position means the number of
characters, counting from the first character to the one to be positioned in the data
record.
For example, in the following data
BARCODE
'B' has position 1.
'A' has position 2.
...
'E' has position 7.
When Match field is defined, the original data string starts at the position specified by
the first parameter P and will be compared with string "C". If the match is identical,
processing of the current Formula continues.
The position parameter P could be a wild character * for any position or # for the
last position in the original data. If # is used,
#-N
is valid. Here N is a digit parameter.
The string parameter C can include * for any digit or # for any letter.
Examples:
MATCH,3,"AB",#,"?",
Checks if the original data has 'A' at position 3, 'B' at position '4' and last character is
'?'.
MATCH , 10 , " *A*",
Checks if the original data includes a string with a digit as first character and "A*"
Page 20

followed at position 10.
Modifier
Modifier has two types of fields: A-String and O-String to define the output
contents.
A-String
Format:
"abc..."
'a', 'b' and 'c' in the string can be any character.
A-String defines a string of characters to be added to the output. For example, if the
original data is:
BCD
and the output string is
BarCoDe
"ar", 'o' and 'e' in output string are added strings and can be defined by A-Strings.
Note: If '*' on Programming Sheet are included in A-String, one interblock delay
defined by Group 2 will be inserted.
O-String
Format:
O-STR , P, N,
O-String always applies to the original data. It contains two parameters: The first
is position parameter (P) that specifies the start output position in the original data.
Parameter N tells how many characters will be included beginning from P.
Example:
Original data is:
Barcode
Then
O-Str , 4, 4,
Gives output as
code
Note:
-- N can be '#' for all remaining characters from P.
-- If P greater than the length of original data, the O-String will be skipped.
-- If N is greater than the number of remaining characters counting from P, the
remaining characters are included as valid.
Page 21

Examples
Example 1
If the original data is Code 39 and content is "AA", output "ABC Company", and
otherwise output the original data as it is.
IN_ID,0,LEN,2,2,MATCH,1,"AA","ABC company",Enter
IN_ID,19,O-STR,1,#,Enter
Example 2
If the original data is Code 128 and is logically divided into:
-- First six characters are personal ID,
-- Other characters are person's name.
The output will be:
-- Personal ID first,
-- A 'CR' character,
-- Two interblock delay,
-- Name,
-- A 'CR' character.
The Formula will be:
IN_ID,8,O-STR,1,6,"<CR>**",O-STR,7,#,"<CR>", Enter
<CR> is a Carriage Return character scanned from the Full ASCII Chart.
Advanced Features
The O-String has the format:
O-STR,P,N,
Both parameters of the O-String mentioned above are numbers. But both
parameters can be specified as strings. If N is a string, it becomes a position and the
meaning of O-String will be "Output from position P to position N".
If P is defined as:
"ab...ik"
a, b, , i and k can be any character, the position will be evaluated as
-- Start from the first position of the original string and search character 'a'.
-- From the position next to 'a' in original data, search for 'b'.
-- ....
Page 22

-- From the position next to 'i', search for k.
-- If above searches are all found, the result of the parameter will be the position
where 'k' is located.
If N is a string, the position evaluation of N is the same as P except that the searching
position starts from P+1.
For both P and N, if string is defined, a value can be added to or subtracted from the
position. That following O-Strings:
"ab...ik"+M,
And
"ab...ik"-M,
Are meaningful. M is an integer number.
Example:
Suppose the following is a message to be modified:
%B012345678901234^ABEL/STEVE L MGR ^90010129999999?
in this message:
"%" is start sentinel.
"012345678901234" is account number.
"^" is a separator
6. "ABEL" is surname.
"/" is a separator.
"STEVE" is first name.
"L" is initial.
"MGR" is title
"^" is a separator.
"9001" is expiration date.
"?" is end sentinel.
The output sequence desired is:
Surname, First Name [CR] Account Number [CR] Expiration Date [CR]
The formula input will be:
IN_ID,0,O-STR,"^"+1,"/"-1,",",O-STR,"/"+1,"<SP>"-1,"<CR>", O-STR,3,"^"-1,
"<CR>",O-STR,"^^"+1,4,"<CR>",Enter
Here <SP> is a Space character and <CR> is a Carriage Return character.
Page 23

The output of above input will be
ABEL,STEVE[CR]
012345678901234[CR]
9001[CR]
3.4. Batch Setup
Having configured a keyboard, you may duplicate the settings of the keyboard
(master) to the others. You can do this by producing a set of custom setup labels
derived from the master keyboard and scanning these labels from other keyboards.
Contents of custom setup labels are represented by a set of ASCII strings produced by
the master keyboard. There are two ways to get the strings:
l By scanning the following bar code label the settings of the keyboard will dump to
the screen as one or several ASCII strings.
l From keyboard setup, select choice 7 to produce the strings
Print the strings into bar code label in Code 39, you get the batch setup labels to
duplicate other keyboards.
The Following issues should be observed:
l The sequence of the strings dumped by the keyboard is important. Print the bar
code labels and scan them in the same sequence as the one that the master
keyboard dumped.
l Only those settings that are different from the default values will be dumped.
The number of labels produced depends on how many settings are being changed.
l Adjust the length of the dumped strings by combining multiple strings into one
string or breaking up one string into multiple strings. You cannot delete any
character from or add any character into multiple strings. You cannot delete any
character from or add any character into the strings, and … must be the first three
characters in the first string.
l All characters in dumped strings are upper case. If lower case characters are
present in dumped strings, change them to upper case.
l When scanning the batch setup labels to configure a keyboard, the previous
settings on that keyboard are reset to default and then replaced by the settings
contained in the batch labels.
The following is an example of the dumped strings:
…I800C06D51DJ8080
80A0O7C005354415254.
Page 24

3.5. Scanner Configuration Manager Software
Scanner Configuration Manager is a utility program to configure scanner settings on a
computer using the Windows 95/98 operating system. Use the program to define the
settings and then download the parameters to the scanner. Download the program
from our web site at www.unitech-adc.com.
4. Using the Magnetic Stripe Card Reader
* Hold the card with the side of magnetic stripe downwards toward you. (As shown in
the diagram below.)
* Slide the magnetic stripe card through the reader from right to left at a constant,
moderate speed. Note that extreme acceleration, deceleration and interruption on the
slide speed may cause reading error.
* An audible signal will be emitted and the “Good Read” LED will blink when the
card has been correctly slid.
5. Pin Assignment of the Scanner Port
The scanner port, which is a DB-9 squeeze-release type connector, accepts an
undecoded bar code scanner and an RS232 input.
5.1. Wand
Pin Number Signal
2 Data
7 GND
9 VCC
Page 25

Pin Number Signal
1 Start Of Scan
2 Data
3 Good Read
4 N/C
5 Switch Detect
6 Power Control
7 GND
8 VCC
6. Specification
Keyboard
Interface Enhanced AT, PS/2 keyboard
5-pin DIN / 6-pin mini DIN male coiled cable
Power Voltage: 5 VDC +/- 5%
Current: 250mA (including magnetic stripe reader)
Dimension (LxWxH) 400x210x43 mm (15.74x8.26x1.69 inches)
Net Weight 1.30 kg (2.86 lbs)
Operating Temperature: 0oC to 55oC
Humidity: 10% to 90% RH
Storage Temperature: -20oC to 55oC
Humidity: 10% to 95% RH
Magnetic Stripe Card Reader
Card Standard ISO 7811/2 through 5
Track Configuration Read ISO single track, dual track, Triple Track
Card Feed Bi-direction for ISO card
Card Swipe Speed 5 to 60 IPS (inch per second)
Page 26

Bit Density Reads 75 to 210 BPI
Reliability 300000 passes in a clean environment (minimum)
Bar Code Decoder Unit
Connector DB-9 male type
Interface TTL
Symbologies Code 39 Standard and Full ASCII, UPC\EAN,
Codabar, Interleaved 2 of 5, Standard 2 of 5,
MSI, Code 128, Code 93, MSI code, Code 32,
Delta Distance Code, Label IV & V,
Toshiba Code, UCC/EAN128.
Page 27

Appendix A. Function Codes
Function Codes for PC
F1 (%VA)
F3 (%VC)
F5 (%VE)
F7 (%VG)
F9 (%VI)
F11 (%VK)
Cursor Right (/FC)
Cursor Up (/FE)
PgUp (/FG)
TAB (/FI)
F2 (%VB)
F4 (%VD)
F6 (%VF)
F8 (%VH)
F10 (%VJ)
F12 (%VL)
Cursor Left (/FD)
Cursor Down (/FF)
PgDn (/FH)
Back Tab (/FJ)
Esc (/FK)
Right Ctrl (/FO)
Shift Make (/FP)
Ctrl Make (/FQ)
Alt Make (/FR)
Del (/FX)
Left Enter (/FL)
Right Enter (/FM)
Ins (/FW)
Shift Break (/FS)
Ctrl Break (/FT)
Alt Break (/FU)
Page A.1
Page 28
Page B.1
Appendix B. Setup Menu
B.1 Beeps and Delays
Enter Group 1 Group Default
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Beep Tone:
0 -- None
1 -- Low
2 -- Medium
3 -- High
4 -- Low to High
5 -- High to Low
Interblock Delay:
0 -- 0 ms
1 -- 10 ms
2 -- 50 ms
3 -- 100 ms
4 -- 500 ms
5 -- 1 seconds
6 -- 3 seconds
7 -- 5 seconds
Intercharacter Delay:
0 -- 0 ms
1 -- 1 ms
2 -- 2 ms
3 -- 5 ms
4 -- 10 ms
5 -- 30 ms
6 -- 50 ms
7 -- 100 ms
A 1
A 2
A 3
Exit
Page 29

Page B.2
B.2 Keyboard Interface:
Enter Group 2 Group Default
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Function Code:
0 -- Off
1 -- ON
Caps-Lock:
0 – Auto Trace(PC/XT,AT)
1 – Lower Case
2 – Upper Case
Language (For PC/XT/AT):
0-U.S.
5-Norwegian :-Danish
1-U.K. 6-Italian
2-Swiss 7-German
3-Swedish 8-French
4-Spanish 9-Alt Key Mode
Reserve:
Reserve:
Reserve:
Pre-define Label:
0—Label 0 1—Label 1 2—Label 2
(See “Pre-defined label” section for detail)
Use number keypad digits:
0—Disable 1—Enable
B 1
B 2
B 3
B 4
B 5
B 6
B
7
B 8
Exit
Page 30

Page B.3
B.3 Scanner Port:
Enter Group 3 Group Default
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Terminator:
0—Enter 1—Return (on digits keypad)
2 —Field Exit or Right Ctrl 3—None
D 1
Code ID: 0 – disable 1 – Enable
Note: This setting doesn’t affect EAN128 Code ID.
EAN128 has its own Code ID setting on page D.7.
D 2
Define Code ID:
00–Code 39 Full ASCII
01–Code 39 Standard
02–EAN-13
03–UPC-A
04–EAN-8
05–UPC-E
06–Interleaved 2 of 5
07–Codabar
08–Code 128
09–Code 93
10–Standard 2 of 5
11–MSI Code
12– EAN128
13–Code32 (Italian
harmacy)
14–Delta Code
15–Label Code
16–Plessey Code
17– Code 11(Special)
18–China Postal code
(Toshiba Code)
D 3
Scan two digits to
choose a code, then
scan a char. From full
ASCII table to define
ID.
Double Verification:
0 – Off
1~7 – On(Verify 1~7 times)
D 4
Scanning Mode:
0 –Trigger 1– Flashing 2 –Multiscan
3–One Press One Scan 4 –Test Mode
5–Old Laser flash Mode 6 –Continuous
D 5
Label Type:
0 – Positive
1 – Positive and Negative
D 6
Aim function for long range laser engine:
0—Disable
1—Enable
D 7
Data Length (Two Digits) Send:
0—Disable
1—Enable
D
8
Preamble Postamble
PP
OO
Scan ‘PP\OO’ for Pre\Postamble. Scan characters
from Full ASCII char or Function
Exit
Page 31

Page B.4
B.4 Magnetic Reader
Enter Group 4 Group Default
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Terminator
0—Enter 1—Return (on digits keypad)
2 —Field Exit or Right Ctrl 3—None
E
1
Start/Stop Sentinel
0—No Send
1—Send
E
2
Track Selection
0—All Tracks 1—Track1 & track2
2—Track1 & track3 3—Track2 & track3
4—Track 1 5—Track 2
6—Track 3
E
3
Track 2 Account Number Only
0—No
1—Yes
E
4
Separator Character
Scan a character from Full ASCII table.
Default: None
E
5
Output Data even other selected tracks
may have some errors.
0—No
1—Yes
E
6
Track I Output Sequence:
Scan characters from full ASCII Table.
Maximum is 16 character. Scan right to
end. Default: None.
P
P
Track II Output Sequence:
Scan characters from full ASCII Table.
Maximum is 8 character. Scan right to
end. Default: None.
O
O
Exit
Page 32

Page B.5
B.5 Code 39 / I 2 of 5 / S 2 of 5 / Code 32 / EAN128
Enter Group 5 Group Default
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Code 39: 0/1--Disable/Enable.
2/3--Full ASCII/ Standard.
4--Check Digit (CD) Calculate & Send.
5--CD Calculate, not send. 6 --CD not Calculate.
7/8 -- Send/No Send Start/Stop
9/: -- Double labels decoding Off/On
0 - 48 -- Min length 0 / Max length 48
F 1
I 2 of 5 (ITF): 0/1--Disable/Enable
2/3--Fix Length On/Off ( by first three reads)
4--Check Digit (CD) Calculate & Send
5--CD Calculate, not send. 6--CD not Calculate
7--First Digit Suppressed. 8--Last Digit Suppressed
9 -- Not Suppressed
2 - 64 -- Min length 10 / Max length 64
F 2
S 2 of 5 / China Postal Code(Toshiba Code):
0/1--Disable/Enable
2/3 -- Fix Length On/Off ( by first three reads)
4--Check Digit (CD) Calculate & Send
5--CD Calculate, not send. 6--CD not Calculate
1 - 48 -- Min length 4 / Max length 48
F 3
Code 32(Italian pharmacy):
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
2/3 -- Leading Character Send / No Send
4/5 -- Tailing Character Send / No Send
F 4
Telepen:
0/1 – Disable/Enable 2/3 – Standard/Numeric Set
F 5
UCC/EAN 128: 0/1—disable/Enable
2/3—Code ID disable/Enable
Note: If EAN128 be disabled, the EAN128 labels will
be decoded as Code 128
F 6
Define the EAN128 Fields separator:
Scan a ASCII code in full ASCII code chart to select
a new Fields Separator
F 7
Define a separator for double labels:
Scan a ASCII code in full ASCII code chart to select a
new definition of Func1
F8
Min Length Max Length
MM
N N
Exit
Page 33

Page B.6
B.6 Code 128 / MSI Code / Code 93 / Codabar/ Label Code:
Enter Group 6 Group Default
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Code 128:
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
1-64 -- Min Length 1 / Max Length 64
MSI /Pleasey Code:
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
2/3 -- Check Digit Send / No Send
4 -- Check Digit Double Module 10
5 -- Check Digit Module 11 plus 10
6 -- Check Digit Single Module 10
1-16 -- Min Length 1 / Max Length 16
Code 93:
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
1-48 -- Min Length 1 / Max Length 48
Code 11: (Special)
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
2/3 -- One / Two Check Digit
4/5 -- Check Send / No Send
1-48 -- Min Length 1 / Max Length 48
Codabar:
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
2/3 -- Start & Stop Send / No Send
4 -- Check Digit Calculate & Send
5 -- Check Digit Calculate but not Send
6 -- Check Digit not Calculate
7/8 -- CLSI Format On / Off
3-48 -- Min Length 3 / Max Length 48
Label Code IV and V:
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
2/3 – Checksum send/ No send
Min Length
MM
G1
G2
G3
G4
G5
G6
Max Length
NN
Exit
Page 34

Page B.7
B.7 UPC / EAN / Delta Code
Enter Group 7 Group Default
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
UPC-A:
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
2/3 -- Leading Digit Send / No Send
4/5 -- Check Digit Send / No Send
UPC-E:
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
2/3 -- Leading Digit Send / No Send
4/5 -- Check Digit Send / No Send
6/7 -- Zero Expansion On / Off
8/9 – Disable/Enable NSC=1
EAN-13:
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
2/3 -- Leading Digit Send / No Send
4/5 -- Check Digit Send / No Send
6/7 -- Bookland EAN Enable / Disable
EAN-8:
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
2/3 -- Leading Digit Send / No Send
4/5 -- Check Digit Send / No Send
Supplement Code:
0/1 -- Two Supplement Code Off / On
2/3 -- Five Supplement Code Off / On
4 -- Transmitted if Present
5 -- Must Present.
6/7 -- Srace Separator Inserted / Not Inserted
Delta Distance Code:
0/1 -- Disable/Enable
2/3 -- Check Digit Claculated / Not Calculated
4/5 -- Check Digit Send / No Send
Reserved:
H1
H2
H3
H4
H5
H6
H7
Exit
Page 35

Page B.8
B.8 Data Editing:
Enter Group 8 Group Default
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
+ -
Review
IN_ID
LEN
MATCH
O-STR
“
*
#
Enter
Backspace
,
Exit
Code Type:
0 -- Code 39 Full 12 -- EAN 128
1 -- Code 39 Std. 13 -- Code 32
2 -- EAN-13 14 -- Delta Code
3 -- UPC-A 15 – Label Code
4 -- EAN-8 16 – Plessey Code
5 -- UPC-E 17 -- Code 11(Special)
6 -- I 2 of 5 18 – China Postal Code
7 -- Codabar 19 – All Inputs
8 -- Code 128
9 -- Code 93
10 -- S 2 of 5
11 -- MSI Code
Formula Format:
Input ID: IN_ID, ID1, ..., IDi,
Length: LEN, MIN, MAX,
Match: MATCH, P1,S1, ..., Pi, Si,
A-String: “abc...”,
O-String: O-STR, P, N,
IDi -- number for Code ID.
Pi -- position.
Si -- string, “abc...”.
P -- number or string for start position.
N -- number of char. or string to end position.
Special Characters on this sheet:
, -- delimiter to separate parameters.
“ -- string specifier.
* -- specify any digit or any position.
# -- specify any letter or last position.
Page 36

Page C.1
Appendix C. Full ASCII Chart
(Characters in parentheses represent Code 39 bar code printing)
NUL (%U)
SOH ($A)
STX ($B)
ETX ($C)
EOT ($D)
ENQ ($E)
ACK ($F)
BEL ($G)
BS ($H)
HT ($I)
LF ($J)
VT ($K)
FF ($L)
CR ($M)
SO ($N)
SI ($O)
DLE ($P)
DC1 ($Q)
DC2 ($R)
DC3 ($S)
DC4 ($T)
NAK ($U)
SYN ($V)
ETB ($W)
CAN ($X)
EM ($Y)
SUB ($Z)
ESC (%A)
FS (%B)
GS (%C)
Page 37

Page C.2
RS (%D)
US (%E)
SP
! (/A)
” (/B)
# (/C)
$
%
& (/F)
’ (/G)
( (/H)
) (/I)
* (/J)
+
, (/L)
-
.
/
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
: (/Z)
; (%F)
< (%G)
= (%H)
> (%I)
Page 38

Page C.3
? (%J)
@ (%V)
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
[ (%K)
\ (%L)
] (%M)
^ (%N)
_ (%O)
Page 39

Page C.4
` (%W)
a (+A)
b (+B)
c (+C)
d (+D)
e (+E)
f (+F)
g (+G)
h (+H)
i (+I)
j (+J)
k (+K)
l (+L)
m (+M)
n (+N)
o (+O)
p (+P)
q (+Q)
r (+R)
s (+S)
t (+T)
u (+U)
v (+V)
w (+W)
x (+X)
y (+Y)
z (+Z)
{ (%P)
| (%Q)
} (%R)
~ (%S)
DEL (%T)
Page 40

Page D.1
Appendix D. Bar Code Test Chart
EAN-13
3 04 5 2 1 4 8 3 4 1 2 3
EAN-8
8 0 1 2 3 4 5 3
UPC-A
UPC-E
0 21 2 3 4 5 7
99
ISBN 957-630-239-0
9 7 8 9 5 7 6 3 0 23 9 8
07200
Interleaved 2 of 5
0987654321
Code 39
W+ E + D + G + E
Code 39 with C/D
UNI T E CH- E
EAN 128
(01)054123456789(01)659344
Code 128
Unitech 128
Codabar
A2 2 3 5 7 0 0 0 5 9 9 8 7 6 B
MSI Code
0 6
4 7 6 6 9 1 3 7 1 6
1234558
 Loading...
Loading...