Unique UGP-120WSPB Owner's Manual
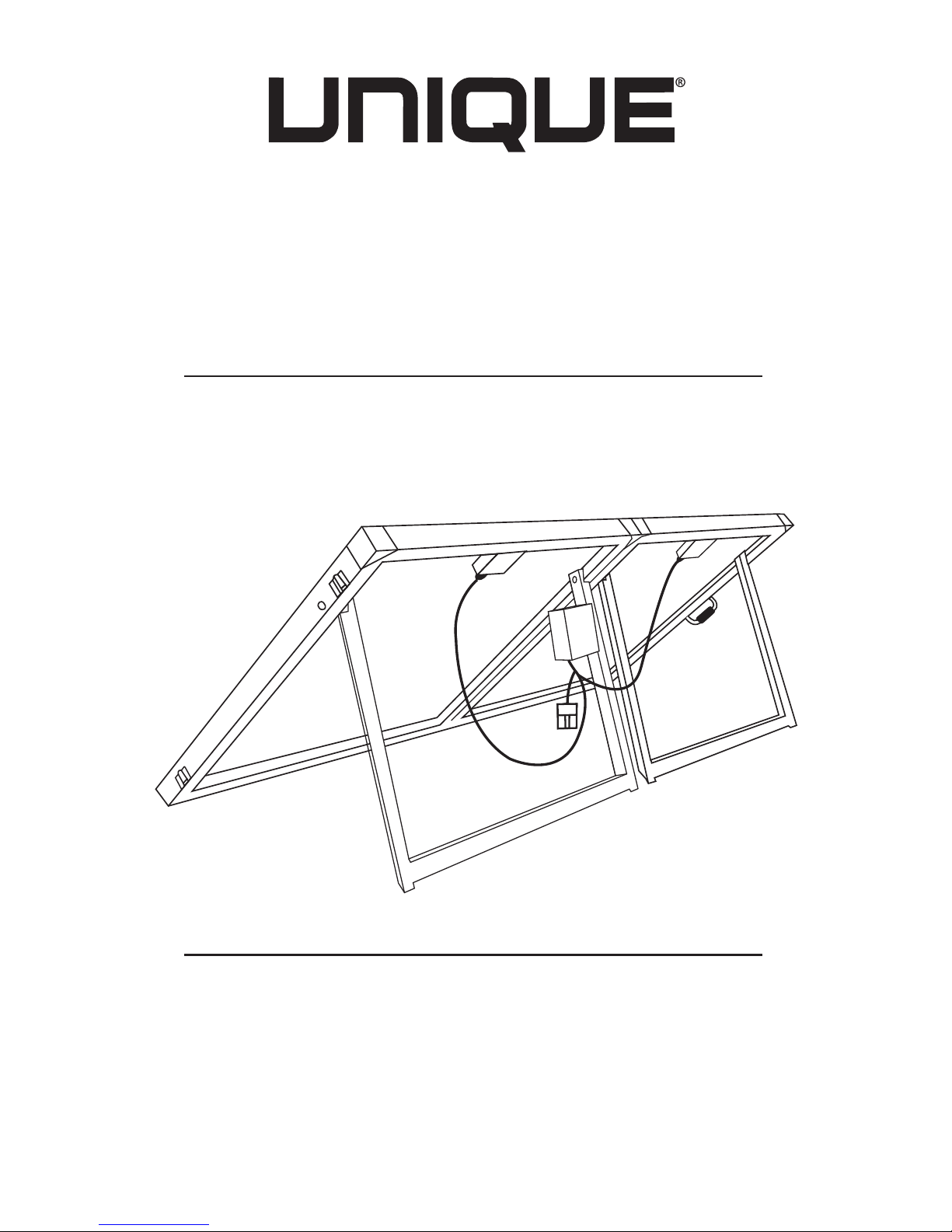
UGP-120WSPB
120 WATT PORTABLE
SOLAR PANEL SYSTEM
OWNER’S GUIDE
APR18V1
Congratulations on your purchase of a Unique 120 watt portable solar panel system! We
are very proud of our products and are completely committed to providing you with the best
service possible. Your satisfaction is our #1 priority. Please read this manual very
carefully, it contains valuable information on how to properly maintain your new solar panel system.
Thank You for choosing one of our Unique appliances - we hope you will consider
Unique for future purchases.
PLEASE READ AND SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
This manual provides specific operation instructions for your system. Use your solar panel
only as instructed in this manual. These instructions are not meant to cover every possible
condition and situation that may occur. Common sense and caution must be practiced
when installing, operating and maintaining the system.
Record in the space provided below the Serial No. and Purchase Date of this appliance.
Model No. UGP-120WSPB Type Number _______________________
Serial No. ________________________ Purchase Date________________________
Record these numbers for future use.
IMPORTANT: Keep a copy of your bill of sale. The date on the bill establishes the warranty
period should service be required. If service is performed, it is in your best interest to obtain and keep
all receipts. Please do this now.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
03 Features & accessories
04 Components & parts list
05 Function
05 Normal operating conditions
05 Energy output
06 Required battery capacity
07 Installation & connection
09 Typical battery connections
09 Typical series connections
10 Incorrect battery connections
11 Integrated waterproof smart solar controller
12 Integrated waterproof smart solar controller technical specifications
12 Integrated waterproof smart solar controller LED indicators
13 Integrated waterproof smart solar controller protection
14 Safety precautions
15 Regular maintenance
16 Troubleshooting
18 Technical specifications
19 Appliance information/notes
back Limited warranty & contact information

3
FEATURES & ACCESSORIES
Convenient carry bag
Made of durable polyester, this water-resistant padded
bag has reinforced corners and protectors to ensure safe
transportation and storage.
Easy carry handle and safety fasteners
Two heavy-duty safety fasteners lock the panels in the folded position for transportation and storage,
while the durable, ergonomic handle allows for easy carrying.
Integrated waterproof smart solar controller with LED indicators - SDN-P Series
The smart controller ensures easy and safe operation of the solar panels, and will turn off when the
batteries are fully charged, during solar panel use and in situations where reverse polarity may occur.
The controller features a switch allowing for use with lead-acid and gel type batteries.
Continual green lit LEDs indicate that the batteries are fully charged. See complete product specifications on page 11.
Folding support legs
Easy to open and close, the sturdy folding legs allow the panels to be positioned for maximum sun
exposure and maximum power output.
Connecting cables
The system includes 10m cables extending from the controller

4
PARTS LIST
1. 2 folding mono-crystalline silicon solar panels with heavy-duty anodized aluminium frame
2. Heavy-duty carrying handle
3. Heavy-duty steel safety fasteners
4. Heavy-duty aluminium folding support legs
5. Automatic SMART solar controller with LED indicators
6. 10m connection cables extending from the controller
7. Battery clamp
8. Hinges
9. Solar panel junction box
10. Connected cable between the left solar panel and the controller
11. Connected cable between the right solar panel and the controller
COMPONENTS
1
8
3
4
5
9
10
11
6
2
7
5
FUNCTION
The solar panel converts sunlight energy into DC electrical power and can be used to charge a
rechargeable battery. This product is designed to charge 12V deep cell batteries, which are commonly
used in cars, RVs, ATVs, boats and other motor vehicles.
NORMAL OPERATING CONDITIONS
Operation temperature: 5˚C – 60˚C
Operation Humidity: 20%RH~80%RH
Air Pressure: 86kPa~105kPa
ENERGY OUTPUT
As a general rule, the user should establish the amps required to run the appliances and multiply
them by the expected module voltage.
Power calculations
Amp hours (Ah) = Current (Amps) x Working Time (Hours)
Module power (W) = Current (Amps) x Expected module voltage (V)
After completing these calculations the capacity of the solar panels can be established.
Example: The following table represents a typical portable appliance configuration:
APPLIANCE WATTS VOLTAGE AMPS HOURS AMP HOURS
12V fluorescent light 8 12V 0.65 4 2.6
12V bandW television 20 12V 1.67 1 1.67
12V radio 5 12V 0.42 1 0.45
12V fan 4 12V 0.33 5 1.65
12V travel iron 120 12V 10 1/6 1.67
12V fridge 45 12V 3.75 6 22.5
ESTIMATED CONSUMPTION 30.51
Amp hours: 30.51 Amp hours per day
Assumption: the solar panel is exposed to 6 hours of suitable sunlight each day.
The required current from the system would be 30.51 amp hours/6 hours = 5.09 A
The required watts of the stem would be: 5.09 A x 12.2 V / 0.8 = 110W
(17.2 - Module vmp, 0.8 - Power consumption factor)
In this example, a 110w panel is required to run the appliances for the desired time.

6
REQUIRED BATTERY CAPACITY
Solar panel systems are general sized to give plenty of reserve (autonomy) in the batteries.
Battery capacity calculation:
current (amps) x hours = amp hour (Ah)
In the preceding example, we have determined that it is required to have 30.51 Ah current per day.
It is not good to run a battery to zero during each charge cycle. For the example above, at least 30%
charge is needed to be left in the battery.
We need at least 30.51 Ah/0.7 - 43.6 Ah battery for each day use.
If the battery is going to be used for 3 days without charging, then the minimum battery capacity
recommended would be 43.6*3 = 131 Ah at related discharge rate.
Please note:
• Solar panels and their controller are maintenance-free.
• There are no user-serviceable parts in this unit.
• If you have any problems, please contact Unique or the point of purchase immediately.
 Loading...
Loading...