Unimig KUMJR190, KUMJR175 User Manual

Lift Arc DC/TIG
Lift Arc DC/TIG
Lift Arc DC/TIG
3
TECHNOLOGY
YEARS Warranty
(Power Source)
240 Volt
Standard
MIG / MAG
TECHNOLOGY
MIG-TIG-STICK
OPERATING MANUAL
KUMJR175
KUMJR190
Please read and understand this instruction manual carefully
before the installation and operation of this equipment.
Welding Guns Of Australia PTY LTD 2012
©
1
WARRANTY
• 3 Years from date of purchase.
• Welding Guns Of Australia PTY LTD Ltd warranties all goods as specified by the manufacturer
of those goods.
• This Warranty does not cover freight or goods that have been interfered with.
• All goods in question must be repaired by an authorised repair agent as appointed by this
company.
• Warranty does not cover abuse, mis-use, accident, theft, general wear and tear.
• New product will not be supplied unless Welding Guns Of Australia PTY LTD has inspected
product returned for warranty and agree’s to replace product.
• Product will only be replaced if repair is not possible
• Please view full Warranty term and conditions supplied with machine or at www.unimig.com.au/
warranty.asp or at the back of this manual.
2

Thank you for your purchase of your UNI-MIG welding machine.
We are proud of our range of welding equipment that has a proven track record of innovation,
performance and reliability.
Our product range represents the latest developments in Inverter technology put together by our
professional team of highly skilled engineers. The expertise gained from our long involvement with
inverter technology has proven to be invaluable towards the evolution and future development of
our equipment range. This experience gives us the inside knowledge on what the arc
characteristics, performance and interface between man and machine should be.
Within our team are specialist welders that have a proven history of welding knowledge and
expertise, giving vital input towards ensuring that our machines deliver control and performance to
the utmost professional level.
We employ an expert team of professional sales, marketing and technical personnel that provide
us with market trends, market feedback and customer comments and requirements. Secondly they
provide a customer support service that is second to none, thus ensuring our customers have
condence that they will be well satised both now and in the future.
UNI-MIG welders are manufactured and compliant with - AS/NZ60974.1 2006 - AS60974-6:2006
guaranteeing you electrical safety and performance.
3

CONTENTS PAGE
Warranty 2
Technical Data, Product Information 5-6
Safety - Cautions 7-9
Machine Layout Pictogram 10
Installation Operation Cautions 11
Installation & Operation for MMA (stick) Welding 12
MMA (Stick) Welding Information 13-14
Installation & Operation for MIG Welding with Gas 15-16
Wire Feed Drive Roller Selection 17
Wire Installation Set up Guide 18
Installation & Operation for MIG Welding with No Gas 19-20
Installation Guide for Mig Torch Liner Installation 21
Mig Torch and Wire Feeder Set Up Guide for Aluminium Mig Wire 22-23
Installation & Operation for MIG Welding with Spool Gun 24-25
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Welding 26-27
Basic MIG Welding Guide 28-31
Installation & Operation for DC TIG Welding with Lift Arc 32-33
DC TIG Welding 34-35
Tungsten Electrodes 36-37
24 MIG Torch Parts Breakdown 38-39
SP135 Spool Gun Torch Parts Breakdown 40-41
17VTIG Torch Parts Breakdown 42-43
Mig Welding Shooting Guide 44-45
TIG Welding Shooting Guide 46-47
MMA Welding Trouble Shooting Guide 48
Machine Spare Parts Breakdown 49
Warranty Terms 50-51
4

KUMJR175
YEARS Warranty
2
(Power Source)
MIG/MMA/TIG - 175 Amp DC Welding Machine Lightweight & Portable
Welds: Steels, Stainless, Cast Iron, Bronze, Aluminium, Copper
Features
• Latest IGBT inverter technology
• Mig/Mag with Gas and Gasless wire function
• Stick Electrode (MMA) function
• DC Tig Welding with Lift Arc Function
• Semi industrial application
• Digital Amp - Volt Meters
• Internal wire feeder for up to 200mm Ø spool
• VRD (Voltage Reduction Device) greatly reduces the risk of
electric shock to the welding operator from potentially hazardous
secondary welding circuit voltage.
• IP21S rating for environmental/safety protection
• Tolerant to variable power supply
• Seamless voltage and wire feed control
• Excellent arc stability with all electrodes
• Spool Gun Connection
Technical Data
Power Supply / Phases (V-Ph) 240v - 1 +/- 15%
Duty Cycle @ 40°c as per AS/NZ60974 35% @ 175 Amps MIG
35% @ 155 Amps MMA
No Load Voltage (V) 53.0
Output Current Range MIG 30A/15.5V - 160/22.0V
Output Current Range MMA 10A/20.4V - 140A/25.6V
Rated Power MIG 4.9 KVA
Rated Power MMA 5.0 KVA
I Max MIG 20.3 Amps
MMA 20.7 Amps
I ieff MIG 12.0 Amps
MMA 12.2 Amps
Power factor 0.72
Protection Class P 21S
Insulation Class F
Wire Diameter Range (mm) 0.6, 0.8, 0.9
Dimensions Power Source (LxWxH) 480x230x360mm
Weight Power Source 17 Kg
Warranty 3 years on machine
MULTIFUNCTION INVERTER OPTIONS
SPOOL GUN
Part No: SPG135
MACHINE TROLLEY
Part No: UMJRTROLLEY2
17V TIG WELDING TORCH
Part No: 17V4MCP10/25
Overview
The Uni-Mig175 is an inverter-based portable Mig welding machine with added MMA and Tig function. The Mig function
allows you to weld with both Gas Shielded and Gasless wire. Easy step-less adjustment of voltage and wire feed make
for easy setting of welding parameters giving excellent, professional welding results. Wire inch gives easy feeding of
the wire during set up without gas wastage. Added MMA welding capability delivers easy electrode welding with high
quality results, including cast Iron, stainless and low hydrogen. Connection of the 17V tig torch provides quality Lift Arc
DC TIG welding of steel, stainless steel and copper. An additional feature is the Spoolgun ready function that allows
the simple connection of the SPG135 Spoolgun for the use of thin or softer wires that don’t have the column strength
to feed through standard mig torches, such as aluminium wire. A semi-industrial machine, it is lightweight and portable,
an optional trolley provides off the floor operation and better manoeuvrability around the workshop. Being 240v single phase gives great portability, it can be run from any 15 Amp power socket providing more flexible use for site and
home workshop locations. Ideal for general engineers, maintenance workshop, rural workshop, panel beaters, home
workshop. Designed and built to our specification. Certified to - AS/NZ60974.1 2006
MACHINE PACKAGE: KUMJR175
UNI-MIG 175 Multifunction Welding Inverter / SB24 4M UNI-MIG Sure Grip MIG torch with Euro connector
4M ARC lead set 10-25mm Dinse style connections / UNI-FLAME Twin Gauge Argon Regulator
2M Gas Hose Complete with fittings
5

KUMJR190
YEARS Warranty
2
(Power Source)
MIG/MMA/TIG - 190 Amp DC Welding Machine Lightweight & Portable
Welds: Steels, Stainless, Cast Iron, Bronze, Aluminium, Copper
Features
• Latest IGBT inverter technology
• Mig/Mag with Gas and Gasless wire function
• Stick Electrode (MMA) function
• DC Tig Welding with Lift Arc Function
• Semi industrial application
• Digital Amp - Volt Meters
• Internal wire feeder for up to 200mm Ø spool
• VRD (Voltage Reduction Device) greatly reduces the risk of
electric shock to the welding operator from potentially hazardous
secondary welding circuit voltage.
• IP21S rating for environmental/safety protection
• Tolerant to variable power supply
• Seamless voltage and wire feed control
• Excellent arc stability with all electrodes
• Spool Gun Connection
Technical Data
Power Supply / Phases (V-Ph) 240v - 1 +/- 15%
Duty Cycle @ 40°c as per AS/NZ60974 35% @ 190 Amps MIG
35% @ 160 Amps MMA
No Load Voltage (V) 53.0
Output Current Range MIG 30A/15.5V - 190/24.0V
Output Current Range MMA 10A/20.4V - 160A/26.4V
Rated Power MIG 5.8 KVA
Rated Power MMA 7.0 KVA
I Max MIG 24.0 Amps
MMA 29 0 Amps
I
i
eff MIG 14.2 Amps
MMA 17.0 Amps
Power factor 0.72
Protection Class P 21S
Insulation Class F
Wire Diameter Range (mm) 0.6, 0.8, 0.9
Dimensions Power Source (LxWxH) 528x250x425mm
Weight Power Source 19 Kg
Warranty 3 years on machine
MULTIFUNCTION INVERTER OPTIONS
SPOOL GUN
Part No: SPG135
MACHINE TROLLEY
Part No: UMJRTROLLEY2
17V TIG WELDING TORCH
Part No: 17V4MCP10/25
Overview
The Uni-Mig190 is an inverter-based portable Mig welding machine with added MMA and Tig function. The Mig function
allows you to weld with both Gas Shielded and Gasless wire. Easy step-less adjustment of voltage and wire feed make
for easy setting of welding parameters giving excellent, professional welding results. Wire inch gives easy feeding of
the wire during set up without gas wastage. Added MMA welding capability delivers easy electrode welding with high
quality results, including cast Iron, stainless and low hydrogen. Connection of the 17V tig torch provides quality Lift Arc
DC TIG welding of steel, stainless steel and copper. An additional feature is the Spoolgun ready function that allows
the simple connection of the SPG135 Spoolgun for the use of thin or softer wires that don’t have the column strength
to feed through standard mig torches, such as aluminium wire. A semi-industrial machine, it is lightweight and portable,
an optional trolley provides off the floor operation and better manoeuvrability around the workshop. Being 240v single phase gives great portability, it can be run from any 15 Amp power socket providing more flexible use for site and
home workshop locations. Ideal for general engineers, maintenance workshop, rural workshop, panel beaters, home
workshop. Designed and built to our specification. Certified to - AS/NZ60974.1 2006
MACHINE PACKAGE: KUMJR190
UNI-MIG 190 Multifunction Welding Inverter / SB24 4M UNI-MIG Sure Grip MIG torch with Euro connector
4M ARC lead set 10-25mm Dinse style connections / UNI-FLAME Twin Gauge Argon Regulator
2M Gas Hose Complete with fittings
6

SAFETY
Welding and cutting equipment can be dangerous to both the operator and people in or near the
surrounding working area, if the equipment is not correctly operated. Equipment must only be
used under the strict and comprehensive observance of all relevant safety regulations.
Read and understand this instruction manual carefully before the installation and operation of this
equipment.
Machine Operating Safety
• Do not switch the function modes while the machine is operating. Switching of the function modes during
welding can damage the machine. Damage caused in this manner will not be covered under warranty.
• Disconnect the electrode-holder cable from the machine before switching on the machine, to avoid arcing
should the electrode be in contact with the work piece.
• Operators should be trained and or qualied.
Electric shock: It can kill. Touching live electrical parts can cause fatal shocks or severe
burns. The electrode and work circuit is electrically live whenever the output is on. The input
power circuit and internal machine circuits are also live when power is on. In Mig/Mag welding,
the wire, drive rollers, wire feed housing, and all metal parts touching the welding wire are
electrically live. Incorrectly installed or improperly grounded equipment is dangerous.
• Connect the primary input cable according to Australian and New Zealand standards and regulations.
• Avoid all contact with live electrical parts of the welding circuit, electrodes and wires with bare hands.
The operator must wear dry welding gloves while he/she performs the welding task.
• The operator should keep the work piece insulated from himself/herself.
• Keep cords dry, free of oil and grease, and protected from hot metal and sparks.
• Frequently inspect input power cable for wear and tear, replace the cable immediately if damaged,
bare wiring is dangerous and can kill.
• Do not use damaged, under sized, or badly joined cables.
• Do not drape cables over your body.
• We recommend (RCD) safety switch is used with this equipment to detect any leakage of current to earth.
Fumes and gases are dangerous. Smoke and gas generated whilst welding or cutting can
be harmful to people’s health. Welding produces fumes and gases. Breathing these fumes and
gases can be hazardous to your health.
• Do not breathe the smoke and gas generated whilst welding or cutting, keep your head out of the fumes
• Keep the working area well ventilated, use fume extraction or ventilation to remove welding fumes and
gases.
• In conned or heavy fume environments always wear an approved air-supplied respirator.
Welding fumes and gases can displace air and lower the oxygen level causing injury or death. Be sure the
breathing air is safe.
• Do not weld in locations near de-greasing, cleaning, or spraying operations. The heat and rays of the arc
can react with vapours to form highly toxic and irritating gases.
• Materials such as galvanized, lead, or cadmium plated steel, containing elements that can give off toxic
fumes when welded. Do not weld these materials unless the area is very well ventilated, and or wearing
an air supplied respirator.
Arc rays: harmful to people’s eyes and skin. Arc rays from the welding process produce
intense visible and invisible ultraviolet and infrared rays that can burn eyes and skin.
• Always wear a welding helmet with correct shade of lter lens and suitable protective clothing including
welding gloves whilst the welding operation is performed.
• Measures should be taken to protect people in or near the surrounding working area. Use protective
screens or barriers to protect others from ash,glare and sparks; warn others not to watch the arc.
7

Fire hazard. Welding on closed containers, such as tanks,drums, or pipes, can cause them
to explode. Flying sparks from the welding arc, hot work piece, and hot equipment can cause
res and burns. Accidental contact of electrode to metal objects can cause sparks, explosion,
overheating, or re. Check and be sure the area is safe before doing any welding.
• The welding sparks & spatter may cause re, therefore remove any ammable materials well away from
the working area. Cover ammable materials and containers with approved covers if unable to be moved
from the welding area.
• Do not weld on closed containers such as tanks, drums, or pipes, unless they are properly prepared
according to the required Safety Standards to insure that ammable or toxic vapors and substances are
totally removed, these can cause an explosion even though the vessel has been “cleaned”.
Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or welding. They may explode.
• Do not weld where the atmosphere may contain ammable dust, gas, or liquid vapours (such as petrol)
• Have a re extinguisher nearby and know how to use it. Be alert that welding sparks and hot materials
from welding can easily go through small cracks and openings to adjacent areas. Be aware that welding
on a ceiling, oor, bulkhead, or partition can cause re on the hidden side.
Gas Cylinders. Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under high pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can explode. Because gas cylinders are normally part of the welding process, be sure to
treat them carefully. CYLINDERS can explode if damaged.
• Protect gas cylinders from excessive heat, mechanical shocks, physical damage, slag, open ames,
sparks, and arcs.
• Insure cylinders are held secure and upright to prevent tipping or falling over.
• Never allow the welding electrode or earth clamp to touch the gas cylinder, do not drape welding cables
over the cylinder.
• Never weld on a pressurised gas cylinder, it will explode and kill you.
• Open the cylinder valve slowly and turn your face away from the cylinder outlet valve and gas regulator.
Gas build up. The build up of gas can causes a toxic environment, deplete the oxygen content
in the air resulting in death or injury. Many gases use in welding are invisible and odourless.
• Shut off shielding gas supply when not in use.
• Always ventilate conned spaces or use approved air-supplied respirator.
Electronic magnetic elds. MAGNETIC FIELDS can affect Implanted Medical Devices.
• Wearers of Pacemakers and other Implanted Medical Devices should keep away.
• Implanted Medical Device wearers should consult their doctor and the device manufacturer before going
near any electric welding, cutting or heating operation.
Noise can damage hearing. Noise from some processes or equipment can damage hearing.
Wear approved ear protection if noise level is high.
Hot parts. Items being welded generate and hold high heat and can cause severe burns.
Do not touch hot parts with bare hands. Allow a cooling period before working on the welding
gun. Use insulated welding gloves and clothing to handle hot parts and prevent burns.
8

CAUTION
1. Working Environment.
1.1 The environment in which this welding equipment is installed must be free of grinding dust, corrosive
chemicals, ammable gas or materials etc, and at no more than maximum of 80% humidity.
1.2 When using the machine outdoors protect the machine from direct sun light, rain water and snow etc;
the temperature of working environment should be maintained within -10°C to +40°C.
1.3 Keep this equipment 30cm distant from the wall.
1.4 Ensure the working environment is well ventilated.
2. Safety Tips.
2.1 Ventilation
This equipment is small-sized, compact in structure, and of excellent performance in amperage output.
The fan is used to dissipate heat generated by this equipment during the welding operation.
Important: Maintain good ventilation of the louvers of this equipment. The minimum distance between
this equipment and any other objects in or near the working area should be 30 cm. Good ventilation is
of critical importance for the normal performance and service life of this equipment.
Thermal Overload protection.
2.2
Should the machine be used to an excessive level, or in high temperature environment, poorly
ventilated area or if the fan malfunctions the Thermal Overload Switch will be activated and the
machine will cease to operate. Under this circumstance, leave the machine switched on to keep the
built-in fan working to bring down the temperature inside the equipment. The machine will be ready for
use again when the internal temperature reaches safe level.
Over-Voltage Supply
2.3
Regarding the power supply voltage range of the machine, please refer to “Main parameter” table.
This equipment is of automatic voltage compensation, which enables the maintaining of the voltage
range within the given range. In case that the voltage of input power supply amperage exceeds the
stipulated value, it is possible to cause damage to the components of this equipment. Please ensure
your primary power supply is correct.
2.4 Do not come into contact with the output terminals while the machine is in operation. An electric shock
may possibly occur.
MAINTENANCE
Exposure to extremely dusty, damp, or corrosive air is damaging to the welding machine. In order to prevent any possible failure or fault of this welding equipment, clean the dust at regular intervals with clean and
dry compressed air of required pressure.
Please note that: lack of maintenance can result in the cancellation of the guarantee; the guarantee of
this welding equipment will be void if the machine has been modied, attempt to take apart the machine or
open the factory-made sealing of the machine without the consent of an authorized representative of the
manufacturer.
TROUBLE SHOOTING
Caution: Only qualied technicians are authorized to undertake the repair of this welding equipment.
For your safety and to avoid Electrical Shock, please observe all safety notes and precautions
detailed in this manual.
Note:
Minimum Motor Generator Power Suggested:- 5.5KVA for Mig175 - 7KVA for MIG190
9

FRONT PANEL LAYOUT
1. Amperage Meter
2. Voltage Meter
3. VRD LED
4. Wire Inch Button
5. Mig/MMA/Tig Mode Selector Switch
6. Wire Feed Adjustment Knob (MIG/MAG)
7. Standard Mig / Spoolgun Selector Switch
8. “-” Output terminal
9. SpoolGun Power Supply Connection
10. “+” Output terminal
11. Euro Mig Torch Connector (MIG/MAG)
12. Voltage Adjustment Knob (MIG/MAG)
13. Amperage Adjustment Knob (MMA/TIG)
14. Thermal Overload LED
15. Mains Power LED
1 2 3 4 5
15
14
13
12
20
6
7
8
9
10
11
BACK PANEL LAYOUT
16. Input power cable
17. Power switch
18. Fan
19. Gas Inlet
20. Data Plate
20
21
16
17
18
19
22
INTERNAL PANEL LAYOUT
20. DC Positive output terminal
21. DC Negative output terminal
22. Burn back control
23. Spool holder assembly
24. Wire feeder mechanism
10
2324

INSTALLATION & OPERATION
Please install the machine strictly according to the following steps.
The protection class of this machine is IP21S, so avoid using it in rain.
Connection of Input Cables
Primary input cable is supplied with this welding equipment. Connect the primary input cable with power
supply of required input voltage. Refer to data plate on machine for Input voltage, IMAX and IEFF.
WARNING!
Before MMA (Stick)Welding:
Disconnect the cable with twist lock connector
that is attached to the wire feeder from the output
socket’s “GAS” “NO-GAS” on the backboard.
If cable is not disconnected welding voltage is pre-
sent and can cause arcing or ash.
11

Installation set up for MMA (Stick) Welding with UNI-MIG MIG175/190 MTS
(1) Turn the power source on and select the MMA function with the Tig/MMA/Mig selector switch.
(2) Connection of Output Cables
Two sockets are available on this welding machine. For MMA welding the electrode holder is shown
be connected to the positive socket, while the earth lead (work piece) is connected to the negative
socket, this is known as DC+ polarity. However various electrodes require a different polarity for
optimum results and careful attention should be paid to the polarity, refer to the electrode
manufacturers information for the correct polarity.
DC+ Electrode connected to output socket.
DC- Electrode connected to output socket.
(3) Set the welding current relevant to the electrode type and size being used as recommended by the
electrode manufacturer.
(1) Set Tig/MMA/Mig selector
switch to MMA
(2) Connect earth
lead to
(3) Set the welding current using the amperage
control dial.
(4) Place the electrode into the electrode holder
and clamp tight.
(2) Connect the electrode
lead to
(5) Strike the electrode against the workpiece to
create an arc and hold the electrode steady to
maintain the arc.
(6) Hold the electrode slightly above the work
maintaining the arc while travelling at an even
speed.
12
(7) To nish the weld, break the arc by quickly
snapping the electrode away from the work
piece.
(8) Wait for the weld to cool and carefully chip
away the slag to reveal the weld metal below.
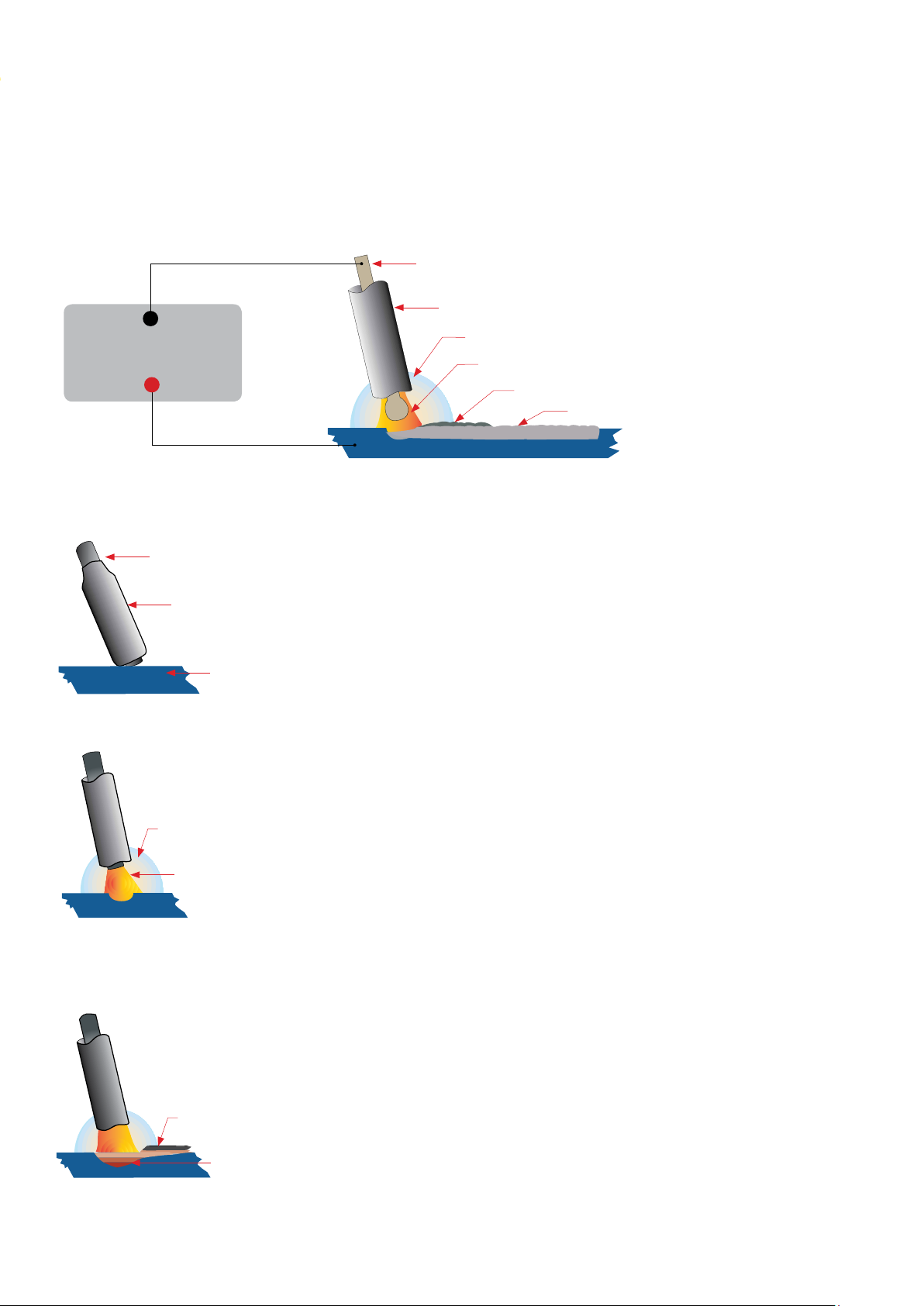
MMA (Manual Metal Arc) Welding
One of the most common types of arc welding is manual metal arc welding (MMA) or stick welding. An electric current is used to strike an arc between the base material and a consumable electrode rod or ‘stick’. The electrode rod
is made of a material that is compatible with the base material being welded and is covered with a ux that gives off
gaseous vapours that serve as a shielding gas and providing a layer of slag, both of which protect the weld area from
atmospheric contamination. The electrode core itself acts as ller material the residue from the ux that forms a slag
covering over the weld metal must be chipped away after welding.
Core wire
+
Flux coating
Power Source
▬
Core wire
Flux coating
Gas shield from ux melt
Arc with core wire melt
Flux residue forms slag cover
Weld metal
• The arc is initiated by momentarily touching the electrode to the base metal.
• The heat of the arc melts the surface of the base metal to form a molten pool
at the end of the electrode.
• The melted electrode metal is transferred across the arc into the molten pool
and becomes the deposited weld metal.
Base metal
• The deposit is covered and protected by a slag which comes from the
electrode coating.
• The arc and the immediate area are enveloped by an atmosphere of
protective gas
Protective gas
Arc
Slag
Weld pool
Manual metal arc ( stick) electrodes have a solid metal wire core and a ux
coating. These electrodes are identied by the wire diameter and by
a series of letters and numbers. The letters and numbers identify the metal
alloy and the intended use of the electrode.
The Metal Wire Core works as conductor of the current that maintains the arc.
The core wire melts and is deposited into the welding pool.
The covering on a shielded metal arc welding electrode is called Flux.
The ux on the electrode performs many different functions.
These include:
● producing a protective gas around the weld area
● providing uxing elements and deoxidizers
● creating a protective slag coating over the weld as it cools
● establishing arc characteristics
● adding alloying elements.
Covered electrodes serve many purposes in addition to adding ller metal to
the molten pool. These additional functions are provided mainly by the covering on the electrode.
13

MMA (Stick) Welding Fundamentals
Electrode Selection
As a general rule, the selection of an electrode is straight forward,in that it is only a matter of selecting an
electrode of similar composition to the parent metal. However, for some metals there is a choice of several
electrodes, each of which has particular properties to suit specic classes of work. It is recommend to consult your welding supplier for the correct selection of electrode.
Electrode Size
Average Thickness Maximum Recommended
of Material Electrode Diameter
1.0 - 2.0mm 2.5mm
2.0 - 5.0mm 3.2mm
5.0 - 8.0mm 4.0mm
8.0 - > mm 5.0mm
Welding Current (Amperage)
Electrode Size Current Range
ø mm (Amps)
2.5mm 60 - 100
3.2mm 100 - 130
4.0mm 130 - 165
5.0mm 165 - 260
excessive spatter. Normal current for a particular job may be considered as the maximum, which can be
used without burning through the work, over-heating the electrode or producing a rough spattered surface.
The table shows current ranges generally recommended for a general purpose type 6013 electrode.
Arc Length
To strike the arc, the electrode should be gently scraped on the work until the arc is established. There is a
simple rule for the proper arc length; it should be the shortest arc that gives a good surface to the weld. An
arc too long reduces penetration, produces spatter and gives a rough surface nish to the weld. An excessively short arc will cause sticking of the electrode and result in poor quality welds. General rule of thumb
for down hand welding is to have an arc length no greater than the diameter of the core wire.
The size of the electrode generally depends on the
thickness of the section being welded, and the thicker
the section the larger the electrode required. The table
gives the maximum size of electrodes that maybe used
for various thicknesses of section base on using a general purpose type 6013 electrode.
Correct current selection for a particular job is an important factor in arc welding. With the current set too
low, difculty is experienced in striking and maintaining
a stable arc. The electrode tends to stick to the work,
penetration is poor and beads with a distinct rounded
prole will be deposited. Too high current is accompanied by overheating of the electrode resulting undercut
and burning through of the base metal and producing
Electrode Angle
The angle that the electrode makes with the work is important to ensure a smooth, even transfer of metal.
When welding in down hand, llet, horizontal or overhead the angle of the electrode is generally between 5
and 15 degrees towards the direction of travel. When vertical up welding the angle of the electrode should
be between 80 and 90 degrees to the work piece.
Travel Speed
The electrode should be moved along in the direction of the joint being welded at a speed that will give the
size of run required. At the same time, the electrode is fed downwards to keep the correct arc length at all
times. Excessive travel speeds lead to poor fusion, lack of penetration etc, while too slow a rate of travel
will frequently lead to arc instability,slag inclusions and poor mechanical properties.
Material and Joint Preparation
The material to be welded should be clean and free of any moisture, paint, oil, grease, mill scale, rust or
any other material that will hinder the arc and contaminate the weld material. Joint preparation will depend
on the method used include sawing, punching, shearing, machining, ame cutting and others. In all cases
edges should be clean and free of any contaminates. The type of joint will be determined by the chosen
application.
14

Installation set up for MIG with Gas for UNI-MIG MIG175/190 MTS
(1) Select the MIG function with the Tig/MMA/Mig selector switch.
(2) Select Standard using the Standard/Spool Gun selector switch.
(3) Plug the welding torch into the Euro Mig torch connection socket on the front panel, and tighten it.
IMPORTANT : When connecting the torch be sure to tighten the connection. A loose connection can
result in the connector arcing and damaging the machine and gun connector.
This damage is not covered under warranty.
(4) Insert the earth cable plug into the negative socket on the front of the machine and tighten it.
(5) Connect Gas Line to Gas Regulator and connect the gas regulator to the Gas Cylinder.
(6) Connect the weld power cable plug inside the wire feeder to the output socket GAS, and tighten it.
(7) Place the Wire Spool onto the Spool Holder - Note: the spool retaining nut is Left Hand thread.
Snip the wire from the spool being sure to hold the wire to prevent rapid uncoiling. Feed the wire into
the wire feeder inlet guide tube through to the drive roller.
(8) Carefully feed the wire over the drive roller into the outlet guide tube, feed through about 150mm into
the torch receptacle. Check that the drive roller being used complies with the wire diameter, replace the
roller if necessary.
(5) Connect the gas line to the regulator
and connect to the gas cylinder
(4) Connect earth lead to
(1) Set Tig/MMA/Mig selector
switch to Mig
(2) Set Standard/Spoolgun
selector switch to Standard
(3) Connect Mig torch
IMPORTANT : When connecting the torch
be sure to tighten the connection.
(6) Connect weld power lead to GAS
(7) Place wire onto spool holder - (spool
retaining nut is left hand thread ) Feed the wire
through the inlet guide tube on to the drive
roller.
(8) Feed wire over the drive roller into the outlet
guide tube, Push the wire through approx
150mm.
Caution:
Disconnect the Electrode Holder cable from the machine before using MIG function. If cable is not disconnected welding
voltage is present and can cause arcing or ash.
15

Continued set up for MIG with Gas for UNI-MIG MIG175/190 MTS
(9) Align the wire into the groove of the drive roller and close down the top roller making sure the wire is in
the groove of the bottom drive roller, lock the pressure arm into place.
(10) Apply a medium amount of pressure to the drive roller.
(11) Remove the gas nozzle and contact tip from the torch neck,
(12) Press and hold the inch button to feed the wire through to the torch neck, release the inch button when
the wire exits the torch neck.
(13) Fit the correct sized contact tip and feed the wire through it, screw the contact tip into the tip holder of
the torch head and nip it up tightly.
(14) Fit the gas nozzle to the torch head.
(15) Carefully open the gas cylinder valve and set the ow rate to between 5-10 l/min.
(16) Set the welding parameters using the wire feed and voltage control knobs.
(17) Using the Burn Back control set the amount of wire to ‘burn back’ after you release the torch
trigger. This prevents the wire becoming stuck in the weld pool when nishing the weld.
(9) Close down the top roller bracket and clip
the pressure arm into place.
(12) Press and hold the inch wire button to
feed the wire down the torch cable through
to the torch head.
(10) Apply a medium amount of
pressure to the drive roller
(13) Fit the correct size contact tip over
the wire and fasten tightly into the tip
holder.
(11) Remove the gas nozzle and contact tip
from the front end of the mig torch.
(14) Fit the gas nozzle to the torch head.
(15) Carefully open the valve of the gas
cylinder, set the ow to 10 l/min
16
(16) Set welding parameters using the
voltage and wire feed controls.
(17) Adjust the burn back control to prevent
the wire sticking in the weld pool.
 Loading...
Loading...