Page 1

908 Canada Court
City of Industry, CA 91748 U.S.A.
Phone: 626.964.7873 or 800.346.6668 Fax: 626.964.7880
www.unicomlink.com e-mail: info@unicomlink.com
©UNICOM 2003. UNICOM and “A Network Systems Solution” are trademarks of UNICOM Electric, Inc.
All rights reserved. Specifications subject to change without notice.
Rev: 07.01
Broadband Router / Ethernet Switch
Micro-Router/4 & 7
USER’S MANUAL
4 Port FEP-72104T
7 Port FEP-72107T
FEP-72107T Shown
Page 2

Page 3

Quick Find
➟
for the easiest setup, go to page 11
➟
for Advanced setup, go to page 16
➟
For NAT Server setup, go to page 25
➟
for Current System Settings, go to page 33
Table of Contents
Package Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
INTRODUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Hardware Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Software Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
HARDWARE DESCRIPTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Upper View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Rear Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Default Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
LED Indicators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Desktop Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Preparing your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Hardware Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
WEB MANAGEMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Login to Web Management Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Browser Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Logout the System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Online Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Wizard Setup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Changing the Password. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Default Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Advanced Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
General Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
DDNS Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Password Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
NAT (Network Address Translation)
An IETF standard that allows an organization to present itself to the Internet with
far fewer IP addresses than there are nodes on its internal network. The NAT
technology, which is typically implemented in a router, converts the private IP
addresses (such as in the 10.0.0.0 range) of the node on the internal private
network to one IP address or one of several IP addresses for the public Internet.
NAT not only conserves public IP addresses, but it also ser ves as a firewall by
keeping internal addresses hidden from the outside world. Implementations also
often include port address translation (PAT), which can alter the port numbers in
the header, adding another level of differentiation.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol Over Ethernet)
A standard for incorporating the popular PPP protocol, widely used for dial-up
Internet connections, into a cable modem connection that uses Ethernet as its
transport to the carrier's facilities. Used by a large number of cable modem
providers, PPPoE supports the protocol layers and authentication widely used in
PPP and enables a point-to-point connection to be established in the normally
multipoint architecture of Ethernet.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
A protocol from Microsoft that is used to create a vir tual private network (VPN) over
the Internet. It uses encryption based on RSA's RC4, known as Microsoft Point-toPoint Encryption (MPPE). Remote users can access their corporate networks via
any ISP that supports PPTP on its ser vers.
SUA Single User Account (SUA)
Allows multiple workstations on your LAN to access the Internet for the price of an
individual account. SUA accomplishes this through a mechanism called Network
Address Translation (NAT) that makes your whole LAN appear as a single host to
the Internet. You may hear other names such as “IP masquerading” or “IP
sharing”, but basically they mean the same thing.
If your ISP assigns you no address at all or only one IP address, then you have a
single user account, and so you must enable SUA.
You can designate one inside server machine on your LAN to be accessible to the
outside world under SUA. Please note that this one machine can host multiple
services, e.g., you can run a web server, an FTP server and a telnet ser ver all on one
machine. SUA offers the added benefit of firewalling if you do not define a ser ver.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol)
A version of the TCP/IP FTP protocol that has no directory or password capability.
UPnP (Universal Plug aNd Play)
A set of standards for interoperability of networking devices from Microsoft and the
UPnP Forum. UPnP extends the Plug and Play concept to network devices so that
they can be installed and set up without manual intervention. For example, the
UPnP Internet Gateway specification enables residential Internet gateways to be
automatically configured to handle multiple PCs in a home network.
1
40
Page 4

GLOSSARY
DNS (Domain Name System)
Name resolution software that lets users locate computers on a UNIX network or
the Internet (TCP/IP network) by domain name. The DNS server maintains a
database of domain names (host names) and their corresponding IP addresses. In
this hypothetical example, if www.mycompany.com were presented to a DNS
server, the IP address 204.0.8.51 would be returned.
DDNS (Dynamic DNS)
The ability to automatically update a DNS server when an IP address is
automatically assigned (typically from DHCP) to a network device.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
Software that automatically assigns IP addresses to client stations logging onto a
TCP/IP network. It eliminates having to manually assign permanent IP addresses.
DHCP software typically runs in ser vers and is also found in network devices such
as ISDN routers and modem routers that allow multiple users access to the
Internet. Newer DHCP servers dynamically update the DNS servers after making
assignments.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol)
The protocol that governs the management of multicast groups in a TCP/IP
network. To sign up for a multicast group, a Host Membership Report is sent by a
user's machine to its nearest routers, which forward that data to routers outside
the local network. The routers are kept current by polling the users' machines with
Host Membership Query messages.
ISP (Internet service provider)
An organization that provides access to the Internet. Small Internet service
providers (ISPs) provide service via modem and ISDN while the larger ones also
offer private line hookups (T1, fractional T1, etc.). Customers are generally billed
a fixed rate per month, but other charges may apply. For a fee, a Web site can be
created and maintained on the ISP's server, allowing the smaller organization to
have a presence on the Web with its own domain name. America Online (AOL),
Earthlink, and Microsoft Network (MSN), are all ISPs.
Multicast
In communications networks, to transmit a message to multiple recipients at the
same time. Multicast is a one-to-many transmission similar to broadcasting,
except that multicasting means sending to specific groups, whereas broadcasting
implies sending to everybody. When sending large volumes of data, multicast
saves considerable bandwidth, because the bulk of the data is transmitted once
from its source through major backbones and are multiplied, or distributed out, at
switching points closer to the end users.
2
Time Zone Setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
LAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Setup DHCP server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
LAN Setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
WAN Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
ISP Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
WAN Interface Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
MAC Address Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
NAT Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Configure Static Route. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Filter Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Generic Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
TCP/IP Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
UPnP Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Install UPnP on Windows XP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Checking the UPnP installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Configure UPnP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
System Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
DHCP Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
F/W Upload. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Reset to Default . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Backup Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Restore Previous Configuration . . . . . . . . . . 35
TROUBLESHOOTING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
GLOSSARY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
For full coverage of your warranty, be sure
to register your product using the enclosed
registration card.
39
Page 5
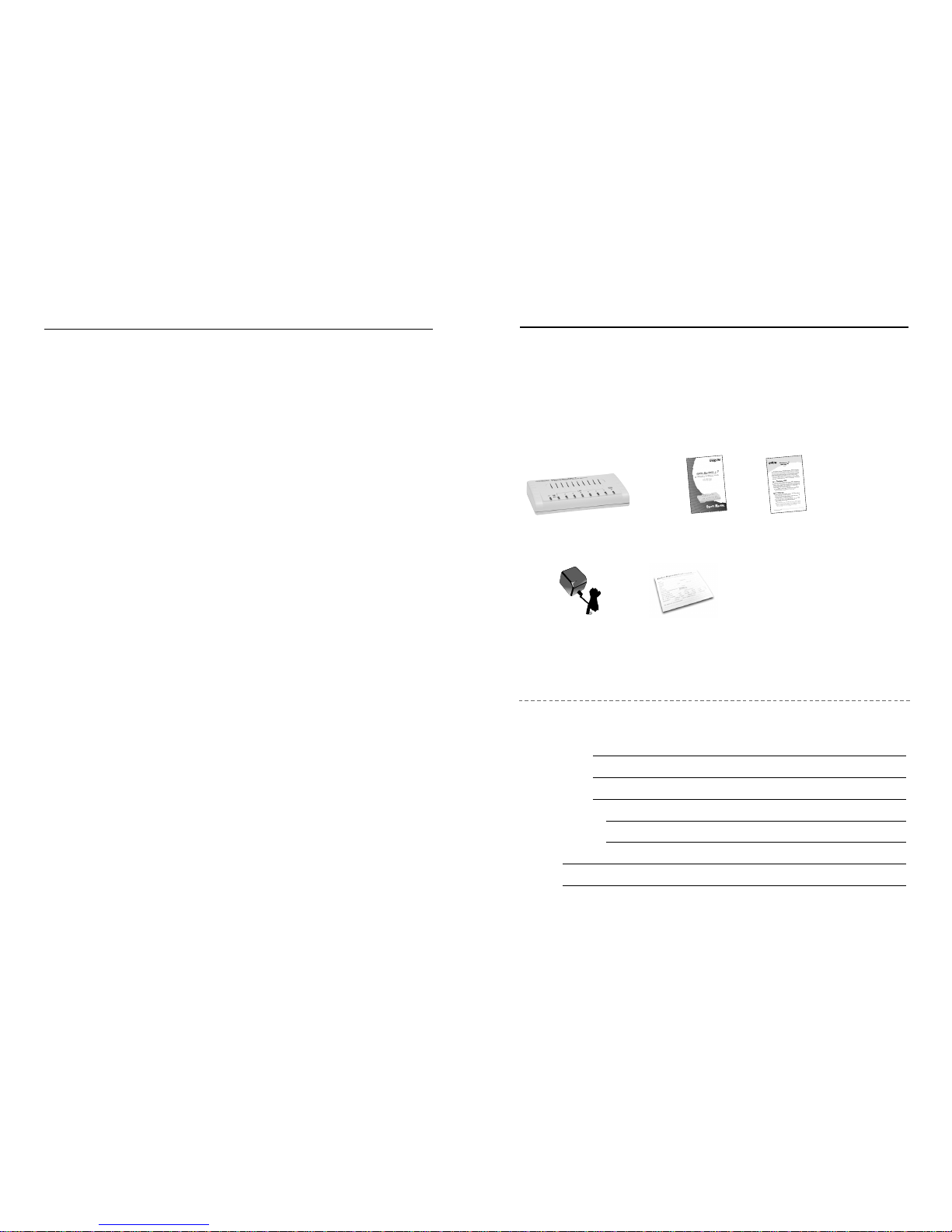
Package Contents
Package contents include the following:
338
Physical Specifications
Standards: IEEE802.3 10Base-T
IEEE802.3u 100Base-TX with Auto Negotiation
IEEE802.3x Flow Control for full duplex and back
pressure for half duplex
Connectors: LAN: (4) or (7) RJ-45 Ports with N-way auto negotiation
and Auto MDIX
WAN: (1) RJ-45 Por with N-way auto negotiation
and Auto MDI-X
CPU: 32 Bits RISC CPU
ROM: 2 Mb
RAM: 8 Mb
Default
Button: One-push button for factory default setting
LEDs: LAN: Link/Activity
WAN: Link/Activity,
System: Power
Power: External power adapter,
DC: 9V / 700mA
Dimension: 145mm x 26mm x 85mm
Enclosure: Plastic
EMI & Safety: FCC Class B, CE
■ Micro-Router (Either 4 Por t of 7 Por t)
■ Quick Star t Guide
■ Full User’s Guide
■ DC Power Adapter
■ Warranty card
For Your Records
Product Name:
Serial Number:
Date of Purchase:
Purchased from:
Notes:
Micro-Router/4 & 7 Full User’s Quick Guide
Guide
DC Power Warranty Card
Adapter
IMPORTANT: If any piece is missing or damaged, please contact your
local dealer or reseller for service.
Page 6
Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of UNICOM’s Micro-Router/4 or 7.
These Broadband Routers/Fast Ethernet Switches are the per fect option
to connect a group of PCs to one Internet connection in a home or small
office environment. The Micro-Router Series is designed to be powerful
yet easy to use.
They include either four or seven 10/100Mbps auto sensing ports with
Auto MDIX which lets you connect multiple computers directly to the
Router. The Web Management feature provides quick, feature-filled
access to the Router via most web browsers and the inclusion of the
NAT (Network Address Translation) feature allows multiple users to
access the Web for the cost of only one Internet account.
Features
■
Conforms to IEEE 802.3, IEEE802.3u, and IEEE802.3x standards
■
Four or Seven 10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet LAN ports
■
One 10/100Mbps WAN port
■
Auto MDIX and N-way Auto Negotiation
■
Dynamic and Static DNS Routing
■
Advanced NAT features
■
Virtual Server
■
Supports IGMP v1/ v2
■
DHCP Client/Server
■
Upgradeable TFTP Firmware
■
One-Touch™default setting
■
Web-based Management.
■
LED Indicators: LAN: Link/Activity
WAN: Link/Activity,
System: Power
1) Ensure all connections are snug.
2) Ensure your Ethernet cables are working
properly.
3) Click Advanced, ➞ WAN, ➞ verify your settings
(Service type, User name, and Password)
4) Reboot computer and router
5) If error persists, please contact Unicom Tech
Support
374
Unable to access the
internet
Page 7
Software Features
Management Web based management.
Configuration file backup and restore.
Firmware upload.
Back to factory default
NAT Technology Support 256 connection
Multimedia applications support.
SUA Server
Address Mapping
Trigger Port
Internet Multimedia Netmeeting, CuSeeMe, IP TV, Quick Time, Real
Application Support Player, ICQ, and also Internet games, e.g. Quake,
Quake II, Quake III, DOOM, Star Craft, etc.
IP Management DHCP Server
Internet setup DHCP Client
PPPoE, PPTP
MAC Clone
RoadRunner login
Application DNS Proxy
Dynamic DNS support
Internet time calibration
Routing IP Routing support: UPD, TCP, ICMP, ARP, RIPv1 &
RIPv2
Programmable Static Routes, up to 8 route rules.
IP Multicast, supports IGMP v1 and v2
Security IP Protocol Filter
RAW Ethernet Packet Filter
Power on FLASH
Self Test SDRAM
LAN and WAN
UPnP Windows XP Compatible
536
Corrective Action
1) Make sure that you have the correct 9V DC
power adapter connected to the Router and
that it is plugged into an appropriate power
source.
2) If the error persists, you may have a hardware
problem. Please contact your local dealer or
reseller.
1) Verify that the browser and the browser’s URL
are correct (192.168.1.1)
2) Verify that your TCP/IP is set to "DHCP
Server".
3) Check your Ethernet cable type and
connections. Ensure your NIC is functioning
properly.
1) The WAN IP is provided after the ISP verifies
the MAC address, host name and user ID.
2) Find out the verification method used by your
ISP and configure the corresponding fields.
3) If the ISP authenticates the WAN MAC
address, click MAINTENANCE ➞ DHCP table
to display the router’s WAN MAC address.
Send it to ISP.
4) If the ISP does not allow you to use a new
MAC address, then you may need to spoof (or
clone) the MAC address from your PC. Click
ADVANCED ➞ WAN ➞ MAC table. Spoof the
MAC from the LAN as the WAN. We
recommend that you configure this menu even
if your ISP does not currently require MAC
address authentication.
5) If the ISP checks the host name, enter your
computer’s name in the System Name field in
the Wizard Setup
Troubleshooting
This section is intended to help you solve the most common problems
encountered with the Micro-Router Series Router/Switches.
Problem
No LEDs light when
router is powered on
Cannot access the
Router from the LAN
Cannot get a WAN IP
address from the ISP
Page 8

Hardware Description
This Section describes the Router hardware and provides a physical and
functional overview.
The physical dimensions of both routers are:
145mm x 26mm x 85mm (L x W x H)
Top View
The upper view of the Micro-Routers consists of one 10/100Mbps WAN
port, four or seven 10/100Base-TX RJ-45 (Auto MDI/MDIX) Ethernet
ports, and a Power LED indicator.
Rear Panel
Connect the female end of the power adapter to the port labeled 9VDC
on the rear panel of your Micro-Router.
Note:
Use only the included power adapter. Using the wrong adapter
may cause damage or injury.
Default Button
If you forget your password or cannot access the Micro-Router, press the
Default button on the rear panel of the Router. This button re-installs the
factory configuration file, replacing the current configuration with the
Router’s default settings. WARNING:
All user settings will be deleted.
Configuration
In the Configuration window, users can reset the Router to its default
setting, backup the Router configuration, and restore the previously
saved configuration.
Reset to Default
1. Click button.
2. The Router will reboot.
Backup Configuration
1. Click button.
2. Save the backup file onto your computer hard disk or other
storage device.
Restore Previous Configuration
1. Click button to find the previously saved configuration file.
2. Click button.
356
Micro-Router/4 Micro-Router/7
Micro-Router/4 Micro-Router/7
Reset
Backup
Upload
Browse
Page 9

LED Indicators
The LED Indicators give real-time information of systematic operation
status. The following table provides descriptions of LED status and
meaning.
Desktop Installation
Place the switch on a sufficiently large flat space with a power outlet
nearby. The surface should be clean, smooth, level and sturdy. Make sure
there is enough clearance around the switch, cables, and power cord to
allow adequate air circulation.
Power On
Connect the power cord to the power socket on the rear panel of the
Router. The other side of power cord connects to the power outlet. The
external power supply of the Router works in an AC range of 120VAC and
a frequency of 60Hz.
Check the power indicator on the upper panel to see if power is properly
supplied.
Preparing Your Network
The Micro-Router interfaces with the Internet through TCP/IP, a standard
network protocol. In order to use the router, your computer must have
TCP/IP software. Virtually all computers using a Windows, Macintosh,
Linux, or Unix operating system have the necessary software. Check to
make sure it is installed. Refer to your computer’s User’s Guide for
information about TCP/IP.
734
LEDs Status Color Description
Power On Green The router is supplied with
suitable power.
On Green The port is connecting with
device.
Blinks Green The port is receiving or
transmitting data.
Off The port is not linked
successfully with the device.
LK/ACT
LAN
and
WAN
DHCP Table
This window displays DHCP table information. Click button to get
newest DHCP table information.
F/W Upload
This window allows users to upgrade the router’s firmware via an upload.
1. Download the most current firmware upgrade from Unicom’s
website. Go to www.unicomlink.com/download.asp.
2. Click button to locate the firmware on the Hard drive and
then click button to upgrade the Router.
Refresh
Upload
Browse
Statistic display Window
Page 10

turn, a device can leave a network smoothly and automatically when it is
no longer in use.
UPnP configuration interface
1. Enable the Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) feature: Activates UPnP.
2. Allow users to make configuration changes through UPnP: Allows
users to configure UPnP-enabled applications.
3. Click button.
System Maintenance
In Maintenance, there are four functions – Status, DHCP Table, F/W
Upload, and Configuration. Each function is described below.
Status
You can view the Router’s current system parameter – System name,
Firmware version, Routing protocol, WAN interface configuration and LAN
interface configuration.
You can also view WAN and LAN interface statistics by clicking the
button. In the Statistic display window, you can set the polling
interval time. The default value is 5 seconds. To stop polling, click on
button. To start polling, set the Interval Time and click button.
1. Once you confirm the proper software is installed, set the TCP/IP
setting to "Using DHCP Server" or something similar. Proceed to
Hardware Setup.
Hardware Setup
1. Plug the Micro-Router into a standard 110V wall outlet. The Power
LED will turn on. Allow Router 10 seconds to start up.
2. Connect the Router to your primar y computer via one of the
router’s LAN ports with a Category 5 or higher Ethernet patch cord.
3. Next connect the Router to your Broadband Modem via the router’s
WAN port with another Categor y 5 or higher Ethernet patch cord.
Note: It is important to configure your Micro-Router with the computer
originally attached to your Broadband device. Trying to configure the router
from a different computer on a network is not recommended. If your
Broadband system is new, configure your Broadband device before
configuring your Micro-Router.
338
Apply
Stop
Show Statistics
Set Interval
Page 11

Web Management
Login to the Web Management Interface
The Micro-Router/4 and 7 both feature GUI Web Management programs.
You can use a browser to connect to your Router for management and
configuration. The following steps show the login to the Router.
Using a Web Browser to configure your Router
Unicom recommends the following browsers for best results.
Windows (Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher)
(Netscape 6.0 or higher)
Macintosh OS 9 and OS X (Netscape 7.0 or higher)
Linux & Unix (Assorted browsers)
1. Launch your web browser and enter the Router’s Default IP
(192.168.1.1) address in the URL field.
2. You will see the Router’s Login Screen. (see below)
3. Type "root" into the Password field and click the button.
4. This will bring you to the Router’s MAIN MENU screen. (see below)
932
* Forward - Forwards the packets.
* Drop - Drops the packets.
24. Click button.
UPnP Configuration (for Windows XP only)
Before you attempt to configure UPnP (Universal Plug and Play), please
ensure your computer supports it.
Install UPnP on your computer
1. Go to Start ➞ Control Panel ➞ Add/Remove Programs.
2. Click Network Connections.
3. Click Advanced in menu bar.
4. Select Optional Networking Components.
5. Click Details.
6. Select Universal Plug and Play.
7. Click "OK" and then "Next".
8. Restart the computer after installation.
Checking the UPnP was installed
1. Go to Control Panel ➞ Network Connection.
2. You will see the Internet Connection icon under the Internet
Gateway section.
Configure UPnP
A UPnP device can dynamically join a network, obtain an IP address,
convey its capabilities, and learn about other devices on the network. In
Login
Apply
Page 12

You are now in the WEB CONFIGURATION software. Follow the instructions
in the MAIN MENU to navigate screens or use the Help icon in the
upper right hand corner of the screen.
Click WIZARD SETUP for initial configuration.
Click LOGOUT at any time to exit the WEB CONFIGURATION.
3110
18. Active: Enables this Filter Rule.
19. IP Protocol: Refers to the upper layer protocol, ex: TCP is 6, UDP
is 7.
20. IP Source Route: Enables or disables the rule to follow the IP
source route. “Yes” means enable. “No” means disable.
21. Destination:
• IP Addr: The destination IP Address of the packet you wish to
filter. This field will be disregarded if it is 0.0.0.0
•IP Mask: The destination IP address mask.
• Port #: The destination por t of the packets you wish to filter. The
range is 0 to 65535. This field will be disregarded if is 0.
• Port # Comp: Select the destination por t of the packet that you
wish to compare against the value given in the Port # field.
“None” means don’
t compare.
22. Source:
• IP Addr: The source IP address of the packet you wish to filter.
This field will be disregarded if it is 0.0.0.0
• IP Mask: The source IP address mask
• Port #: The source por t of the packets that you wish to filter. The
range is 0 to 65535. This field will be disregarded if it is 0.
• Port # Comp: Select the destination por t of the packet that you
wish to compare against the value given in the Port # field.
“None” means don’
t compare.
23. More: “Yes” means that a matching packet is passed to the next
Filter Rule before an action is taken. “No” specifies that the packet
is disposed of according to the action fields. If "Yes" is selected,
then Action Matched and Action Not Matched will default to "Check
Next Rule".
• When the More field is marked "No" the Action Matched
field
offers three selections
* Check Next Rule - Checks next available Filter Rule.
* Forward - Forwards the packets.
* Drop - Drops the packets.
• When the More field is marked "No" the Action Not Matched
field
offers three selections
* Check Next Rule - Checks next available Filter Rule.
Now you will see the Change the Password screen. At this time Unicom
recommends you change the password. The password can be numbers or
letters in any combination. If you choose to change the password, type in
the new password in both boxes and click . Choose if you wish
to bypass this operation. The password can be changed at anytime.
Apply
Ignore
Page 13

Wizard Setup
The Wizard Setup provides the fastest way to configure the Micro-Router.
The Wizard will take you through the configuration process step by step.
When you have finished the Wizard setup, you can go to Advanced
Configuration for more detailed configuration. (see next page)
1. System Name: give a name to your Router
2. Domain Name: type in your domain name (e.g. www.myisp.com)
Click button to go to next step.
Encapsulation: Select the proper encapsulation type. The three
choices are Ethernet, PPP over Ethernet, and PPTP. Following are
the terms and descriptions.
1130
12. Click button.
TCP/IP Filter
The TCP/IP filter allows you to base the rule on the fields in the IP and
the upper layer protocol. TCP/IP filter has a default filter rule.
13. Click on radio button of the number
14. Click button to enter File rule selection interface. Each Filter
can configure up to six filter rules.
15. Filter Set Comments: Give a name to this Filter Rule. If the File
Set Comments column is left blank, the Filter Rule will be deleted.
16. Select the Filter Rule number by clicking on radio button.
17. Click button for detail Filter Rule configuration.
Next
Edit
Edit
Edit
Apply
Page 14

Ethernet - encapsulation choice 1
• Ethernet: Also called Dynamic TCP/IP. If you are connected to an ISP
that automatically assigns a DNS address, use this choice. Most
newer ISPs use this type of system.
• Service Type: Select the service type.
2912
4. Select the Filter Rule number by clicking on radio button.
5. Click button for detail Filter Rule configuration.
6. Active: Enables this filter rule.
7. Offset: The starting byte of the data por tion in the packet that
you wish to compare.
8. Length: The byte count of the data portion in the packet that you
wish to compare. The range is 0 to 8.
9. Mask: The Mask (in Hexadecimal) to apply to the data portion
before comparison.
10. Value: The value (in Hexadecimal) to compare with the data
portion.
11. More: “Yes” means that a matching packet is passed to the next
Filter Rule before an action is taken. “No” specifies that the
packet is disposed of according to the action fields. If "Yes" is
selected, then Action Matched and Action Not Matched will default
to "Check Next Rule".
• When the More field is marked "No" the Action Matched
field
offers three selections
* Check Next Rule - Checks next available Filter Rule.
* Forward - For wards the packets.
* Drop - Drops the packets.
• When the More field is marked "No" the Action Not Matched
field
offers three selections
* Check Next Rule - Checks next available Filter Rule.
* Forward - For wards the packets.
* Drop - Drops the packets.
Apply
Page 15

Filter Configuration
This configuration allows users to filter the incoming data packets. There
are two types of filters – a Generic filter and a TCP/IP filter. You can
configure up to eight different filter sets ( four Generic and four TCP/IP)
with up to six filter rules in each set.
Generic Filter
The Generic filter allows you to filter non-IP packets.
1. Click on radio button of the number
2. Click button to enter Filter Rule selection inter face. Each Filter
can configure up to six filter rules.
3. Filter Set Comments: Give a name to this Filter Rule. If the File
Set Comments column is left blank, the Filter Rule will be deleted.
28 13
PPP over Ethernet - encapsulation choice 2
• PPP over Ethernet: A connection using PPPoE. Many ISPs utilizing
dial-up modems use this type of connection.
• Service Name (optional): Fill in the PPPoE service name that your
PPPoE service provider has given to you. PPPoE uses a service
name to identify and reach the PPPoE server. If your PPPoE service
provider doesn’t supply a service name, then you don’t need to fill
this space.
• Username: User ID for login to the PPPoE server.
• Password: Password for login to the PPPoE server.
• Dial-Up Connection: Keeps the connection with the PPPoE server
from disconnecting.
• Idle Timeout: The time before disconnect. The default value is 300
seconds (5 min).
Edit
Page 16

3. Route Name: Assign a name to this routing path that describes or
identifies the route. If the route name is left blank, the route will
be deleted.
4. Active: Enables the routing. You can unmark the active checkbox
to disable the routing but the routing rule will still remain in the
system route table.
5. Destination IP Address: Assign the routing destination IP address.
6. IP Subnet Mask: Assign destination IP subnet mask.
7. Gateway IP Address: Assign gateway IP address.
8. Metric: Maximum route hop number
9. Private: When this option is selected; the route is kept private
and not included in the RIP broadcast. If it is not selected, the
route to this remote node will be propagated to other hosts
through RIP broadcasts.
10. Click button.
11. You will now see the routing rule in the Static route summary table.
12. Repeat the previous steps to add more routes.
14
27
PPTP - encapsulation choice 3
• PPTP: A network protocol that enables secure transfer of data
from a remote client to a private server, creating a Virtual Private
Network (VPN) using TCP/IP-based networks
• Username: Username for login PPTP server
• Password: Password for login PPTP server
• Dial-Up Connection: Keeps the connection with PPPoE server from
disconnecting.
• Idle Timeout: The time before disconnect. The default value is 300
seconds (5 min).
• My IP Address: IP address assigned by your ISP. It usually will be
a WAN interface IP address.
• My IP Subnet Mask: IP subnet mask.
• Server IP Address: IP address of the PPTP server.
• Connection ID/Name: Your identification name for the PPTP
server.
• Click button to go next step.
Next
Apply
Page 17

2. Active: Enable this mapping rule by marking the check box.
3. Name: Give a name to this mapping.
4. Start Port: The star t of mapping port, ex: 20.
5. End Port: The end of mapping port, ex: 25. End por t can be same
as start port.
6. Server IP Address: The server IP address.
7. Click button.
8. You will see the complete setup information at bottom of screen.
9. Repeat the previous steps to setup another NAT mapping rule.
Configure Static Route
Users must configure routing for network PCs to access the Internet.
1. Click on radio button of index number.
2. Click button to enter Route Entr y configuration inter face.
26 15
WAN IP Assignment: configure WAN interface.
• Get automatically from ISP (Default): Select this option if you do
not need to assign a specific IP for this router. The Router will
automatically get the IP from your ISP. This is common with ADSL.
• Use fixed IP address: User can assign a specific IP address to the
Router WAN interface. Fill in the IP, Subnet Mask, and Gateway IP.
This is common when a Static IP is used.
WAN MAC Address: configure WAN MAC address.
• Factory default: use the factory default.
• Spoof this computer’s MAC address-IP address: Detects this
router’s WAN MAC address.
8. Click button to complete the setup.
Your Router is now configured for Internet use. If you have problems
accessing the internet, please consult the Troubleshooting Section.
Finish
Edit
Edit
Page 18

Configure system MAC address.
1. WAN MAC Address: configure WAN MAC address.
• Factory default: Use the factor y default.
• Spoof this computer’s MAC address-IP address: Automatically
detects the router’s WAN MAC address.
2. Click button.
NAT Configuration
Configure the internal mapping port for external accessing.
1. Default Server: A default ser ver receives packets from ports that
are not specified in the mapping rule list. If you do not assign a
default server, then all packets received for ports not specified in
mapping rule table will be dropped.
16 25
Default Settings
The default Router configuration is as follows:
• IP address: 192.168.1.1
• Password: root
• Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
• DHCP Server (LAN): Enable
• DHCP Client (WAN): Enable
• Filter (WAN): Web service
If you want to reset to the default configuration, press the "Default
Button" on the rear panel of the Router. Follow the steps below to reset
the Router to default configuration.
1. Use a pointed object to depress the Default Button until the LAN
LEDs turn off and then release it.
2. Wait about 10 seconds for the router to finish restarting.
3. When the Router restar ts, proceed to step 6. If the router does not
restart, go to step 4.
4. Cycle power off and on.
5. Repeat steps 1 and 2.
6. Login to Web Management to ensure the router is working properly.
Advanced Configuration
Advanced configuration provides a more detailed configuration of the
Router. User can configure the functions to specific needs.
Apply
Page 19

WAN Interface Configuration
User must configure WAN interface for accessing Internet connection.
1. WAN IP Address Assignment:
• Get automatically from ISP (Default): When you select this
option you don’t need to assign an IP for this router. The Router
will automatically get the IP from the service provider
• Use fixed IP address: Users can assign a specific IP address to
the WAN interface. Fill in the IP, Subnet Mask, and Gateway IP.
2. Network Address Translation (NAT): Enables NAT function. When
an internal network uses a private IP to access the Internet, the
NAT will automatically translate the private IP to a public IP.
3. RIP Direction: controls the sending and receiving of RIP packets.
• None: The router will not send any RIP packets and will ignore
any RIP packets received.
• Both: The router will broadcast its routing table periodically and
incorporate the RIP information that it receives.
• InOnly: The router will incorporate the RIP information that it
receives and drop or ignore the rest of RIP packets.
• OutOnly: The router will broadcast its routing table periodically
and drop or ignore the rest of RIP packets.
4. RIP Version: select the RIP version – RIPv-1, RIP-2B, and RIP –2M.
5. Multicast: select the multicast type – IGMP-v1 and IGMP-v2. The
default value is no multicast.
6. Click button.
24 17
System Configuration
In the System configuration, users can configure general system
information, DDNS, change the password, and configure system date
and time.
General Settings
In the General settings, users can configure System Name and Domain
Name. Click the button to clear the fields.
1. System Name: give a name to this Router.
2. Domain Name: key in your domain name.
3. Click button to go next step.
DDNS Configuration
The DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) allows you to use Static
Host Name mapping with a dynamic IP address. When you change the
domain name, the Router will automatically update your new domain
name to your ISP DNS.
1. Active: Click the checkbox to activate the DDNS function.
2. Service Provider: Select your ISP.
3. DDNS Type: Select the DDNS type. Dynamic DNS: use dynamic
DNS. Static DNS: DNS is static. Custom DNS: a special DNS that
provided by ISP.
4. Host name: You can type in the host name that will match your
web server IP address. You can fill in up to three different host
names for mapping.
Apply
Reset
Reset
Page 20

• Idle Timeout: The time before disconnect. The default value is 300
seconds (5 min).
PPTP - encapsulation choice 3
• PPTP: A network protocol that enables secure transfer of data from
a remote client to a private server, creating a Virtual Private Network
(VPN) using TCP/IP-based networks
• Username: Username for login PPTP server
• Password: Password for login PPTP server
• Dial-Up Connection: Keeps the connection with PPPoE ser ver from
disconnecting.
• Idle Timeout: The time before disconnect. The default value is 300
seconds (5 min).
• My IP Address: IP address assigned by your ISP. It usually will be a
WAN interface IP address.
• My IP Subnet Mask: IP subnet mask.
• Server IP Address: IP address of the PPTP server.
• Connection ID/Name: Your identification name for the PPTP server.
• Click button to go next step.
18 23
5. User: When updating the information to an ISP DNS, the ISP
needs a User ID to verify the account.
6. Password: When updating the information to an ISP DNS, the ISP
needs a password to verify the account.
7. Enable Wildcard: This option provides domain name mapping to
reach your web domain without keying in a specific domain
address. For example: the domain name is www.bbb.com. User can
browse aaa.www.bbb.com which will automatically redirect to
www.bbb.com instead of displaying an error message.
8. Off line: This option is only available when Custom DNS is
selected in the DDNS Type field. Contact your Dynamic DNS
service provider to have traffic redirected to an URL (that you
specify) while you are off line.
9. Click button.
Password Setting
User can change the default password. We strongly suggest changing
the password to enhance network security.
1. Old Password: Type in the default password or the password you
would like to change.
2. New Password: Type in the new password. Password can be
numbers and/or characters in any combination.
3. Retype to Confirm: Re-enter the new password.
4. Click button.
Apply
Apply
Apply
Page 21

Time Zone Setting
Users can configure the system time and date in this section.
1. Use Time Server at Bootup: Select this option to retrieve the
current time from a time ser ver. There are four time server
selections: None, Daytime (RFC-867), Time (RFC-868), and NTP
(RFC-1035). If you have no time server, select “None”.
2. Time Server IP Address: If you select "None" for time server, then
you don’t have to fill in the time server IP. When you select one of
the other options from the menu, you can fill in alternative IP
addresses of time servers other than the default.
3. Current Time (hh-mm-ss): The system’s current time
4. New Time (hh-mm-ss): Enter the correct time for system
5. Current Date (yyyy-mm-dd): the system’s current date
6. New Date (yyyy-mm-dd): Enter correct date for system
7. Time Zone: Select the country time zone where Router is located.
8. Daylight Saving: Enable daylight saving.
• Start Date: Enter the daylight saving start date.
• End Date: Enter the daylight saving end date.
9. Click button to complete the time setting.
Ethernet - encapsulation choice 1
• Ethernet: Also called Dynamic TCP/IP. If you are connected to an ISP
that automatically assigns a DNS address, use this choice. Most
newer ISPs use this type of system.
• Service Type: Select the service type.
PPP over Ethernet - encapsulation choice 2
• PPP over Ethernet: A connection using PPPoE. Many ISPs utilizing
dial-up modems use this type of connection.
• Service Name (optional): Fill in the PPPoE service name that your
PPPoE service provider has given to you. PPPoE uses a service name
to identify and reach the PPPoE server. If your PPPoE service provider
doesn’t supply a service name, then you don’t need to fill this space.
• Username: User ID for login to the PPPoE server.
• Password: Password for login to the PPPoE server.
• Dial-Up Connection: Keeps the connection with the PPPoE server
from disconnecting.
22 19
Apply
Page 22

LAN Setting
Users must configure the LAN interface for a network connection. The
LAN interface has a default value but can be reconfigured if necessary.
1. IP Address: Assign the LAN inter face IP address. The default IP
address is 192.168.1.1.
2. IP Subnet Mask: Assign the LAN IP subnet mask. The default
subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
3. Multicast: Select the multicast type – IGMP-v1 and IGMP-v2. The
default value is no multicast.
4. RIP Direction: Controls the sending and receiving of RIP packets.
• None: The router will not send any RIP packets and will ignore any
RIP packets received.
•Both: The router will broadcast its routing table periodically and
incorporate the RIP information that it receives.
• InOnly: The router will incorporate the RIP information that it
receives and drop or ignore the rest of RIP packets.
• OutOnly: The router will broadcast its routing table periodically and
drop or ignore the rest of RIP packets.
5. RIP Version: Select the RIP version, RIPv–1, RIP–2B, or RIP–2M.
6. Click button.
WAN Configuration
In WAN configuration, users can configure ISP information, the WAN
interface, and the MAC address.
Configure ISP Information
Encapsulation: Select the proper encapsulation type. The three choices
are Ethernet, PPP over Ethernet, and PPTP. Following are the terms
and descriptions.
LAN Configuration
Users can configure the DHCP server and the LAN interface in this
section. LAN interface must be configured for network access.
Setup DHCP server
1. DHCP Server: Click the checkbox to enable the DHCP ser ver
feature.
2. IP Pool Starting Address: Assigns the IP pool starting address.
For example: starting from 192.168.1.33, the pool could extend
from 192.168.1.33 to 192.168.1.254.
3. Pool size: The pool size or range depends on where the IP pool
address starts and ends. For example: if the IP goes from
192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.254, then the pool size is 253 (254 -
1). Remember that the starting number is ALWAYS included in the
pool size total.
4. Primary DNS Server: Fill in the primary DNS server.
5. Secondary DNS Server: Fill in a secondary DNS server as a
backup when the primary DNS server is out of service or offline.
6. Click button to apply the setting.
20 21
Apply
Apply
 Loading...
Loading...