UniCarriers FG20 Series, FD20T4C, FD20T3CZ, FG25T3C, FG30 Series Operation & Maintenance Manual
...
OPER. & MAINT. MANUAL No. OMFBE-CK9140
FG20 - FD30
No. OMFBE-CK9140
OPERATION &
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
FORKLIFT TRUCK
FG20 - FG30
FD20 - FD30
It is the responsibility of the operator and supervisor to read and understand this
manual.
Protect the earth and be kind to your lift truck.

Thank you very much for your purchase of UniCarriers’ product.
This original Operation & Maintenance Manual was written to provide the owner/
operator with information about the safe operation and maintenance of the
UniCarriers forklift truck. Read this original manual thoroughly and become
completely familiar with the lift truck before using it. If you have any questions,
see your dealer.
Due to improvements in design, it is possible that the description contained
herein may not completely apply to the truck delivered to you.
CAUTION
If the truck is to be leased, loaned or sold to anyone, this manual must
be with the truck.
Rated load Truck model Engine model
2 tons FG20T3C K21
FD20T4C V2403
FD20T3CZ C240
2.5 tons
FG25T3C K21
FD25T4C V2403
FD25T3CZ C240
3 tons
FG30T3C K21
FD30T4C V2403
FD30T3CZ C240

CONTENTS
1. SAFETY
FOR SUPERVISORS ..........................................1-2
QUALIFIED OPERATORS ..............................1-3
PLANNING AND WORKING AREA .................1-4
PROPER AND IMPROPER USES ..................1-7
TYPES OF VEHICLES AND LOADS ..............1-8
INSPECTION .................................................1-11
TRANSPORTING THE LIFT TRUCK ............1-12
TRAVELING ON PUBLIC ROADS ................1-13
MODIFICATIONS ..........................................1-14
HOW THE LIFT TRUCK WORKS? ...................1-15
TRAVELING ......................................................1-18
LOAD HANDLING .............................................1-24
PARKING ...........................................................1-28
INSPECTION AND SERVICE ...........................1-30
PREVENTING VEHICLE FIRES .......................1-39
CAUTION PLATES ............................................1-41
2. OPERATING CONTROLS
PICTORIAL NOMENCLATURE ...........................2-2
INSTRUMENTS AND CONTROLS .....................2-3
SWITCHES ......................................................2-5
METERS AND WARNING LIGHTS .................2-7
LEVERS AND PEDALS .................................2-10
TRUCK BODY ..............................................2-14
OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT ..............................2-25
3. OPERATION
PROPER OPERATION .......................................3-2
DURING BREAK-IN ........................................3-2
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LOAD AND
STABILITY OF TRUCK ....................................3-2
BASIC LOAD CENTER AND RATED
LOAD ...............................................................3-3
STABILITY OF LIFT TRUCK ...........................3-3
USING INCHING PEDAL ................................3-3
TRAVELING AND STARTING ON
A SLOPE .........................................................3-4
TRANSPORTING LIFT TRUCK ......................3-4
MOVING LIFT TRUCK
(IN AN EMERGENCY) .....................................3-5
OPERATING LIFT TRUCK ..............................3-6
MEASURES AGAINST COLD OR
HOT WEATHER ................................................3-10
IN COLD WEATHER .....................................3-10
IN HOT WEATHER ........................................ 3-11
LOAD HANDLING ...........................................3-12
PICK-UP ........................................................3-12
STACKING.....................................................3-12
UNSTACKING ...............................................3-12
STORING ..........................................................3-13
BEFORE STORING; DAILY STORAGE ........3-13
LONG-TERM STORAGE;
OPERATING AFTER
LONG-TERM STORAGE...............................3-13
4. MAINTENANCE
PREOPERATIONAL CHECKS ............................4-2
GENERAL RULES ON INSPECTION .............4-2
ITEMS TO BE CHECKED ...............................4-3
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE .........................4-18
ENGINE ROOM .............................................4-18
REPLACING TIRES AND REPAIRING
FLAT TIRE .....................................................4-26
REPLACING LAMP BULBS .........................4-28
STARTING THE ENGINE WITH
AUXILIARY BATTERY ...................................4-28
ADJUSTING OPERATING FORCE OF
PARKING BRAKE LEVER .............................4-29
PERIODIC INSPECTION ..................................4-30
PERIODICAL REPLACEMENT OF
SAFETY PARTS ............................................4-30
MONTHLY (200 HOURS) CHECKS ..............4-31
3 MONTHS (600 HOURS) CHECKS .............4-37
6 MONTHS (1200 HOURS) CHECKS ...........4-39
ANNUAL (2400 HOURS) CHECKS ...............4-40
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULE ..................................................4-41

CONTENTS
5. SPECIFICATIONS & SERVICE DATA
SPECIFICATIONS ...............................................5-2
EQUIPMENT .......................................................5-6
LOAD CHART .....................................................5-7
SERVICE DATA ...................................................5-8
SERVICE DATA ...............................................5-8
BOLT AND NUT TORQUE ...............................5-9
AFTER-THE-SALE SERVICE ...........................5-13
TRUCK SERIAL NUMBER ............................5-13
SERIAL NUMBERS OF MAJOR
COMPONENTS .............................................5-13
NAME PLATE ................................................5-13
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBER ...........................5-14
GENUINE UniCarriers PARTS ......................5-15
GENUINE UniCarriers LUBRICANTS ...........5-15
TRUCK DATA ................................................5-16
6. INDEX
1. SAFETY
CONTENTS
FOR SUPERVISORS .......................................... 1-2
QUALIFIED OPERATORS ............................. 1-3
PLANNING AND WORKING AREA ................ 1-4
PROPER AND IMPROPER USES ................. 1-7
TYPES OF VEHICLES AND LOADS ............. 1-8
INSPECTION .................................................1-11
TRANSPORTING THE LIFT TRUCK ........... 1-12
TRAVELING ON PUBLIC ROADS ............... 1-13
MODIFICATIONS ......................................... 1-14
HOW THE LIFT TRUCK WORKS? ................... 1-15
TRAVELING ...................................................... 1-18
LOAD HANDLING ............................................. 1-24
PARKING ........................................................... 1-28
INSPECTION AND SERVICE ........................... 1-30
PREVENTING VEHICLE FIRES ....................... 1-39
CAUTION PLATES ............................................ 1-41
This is the safety alert symbol. It is used to warn the
reader about a potential source of human injury. To
prevent injury or death, make sure you understand
and follow all the safety messages following this safety
alert symbol.
Signal word
(designates the
degree of hazard)
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
CAUTION
NOTE
Denition
Indica te s a n imm in en tly h az ardous
situation which, if not avoided, wi ll
result in death or serious injury.
Ind i c ates a poten t i ally h azar d o us
situation which, if not avoided, could
result in death or serious injury.
Ind i c ates a poten t i ally h azar d o us
situation which , if not avoided, may
result in minor or moderate injury.
Indicates a hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, may result in damage to
the truck or other property.
Indicates information which will help
extend the service life of the truck.
1-1
1-2
FOR SUPERVISORS
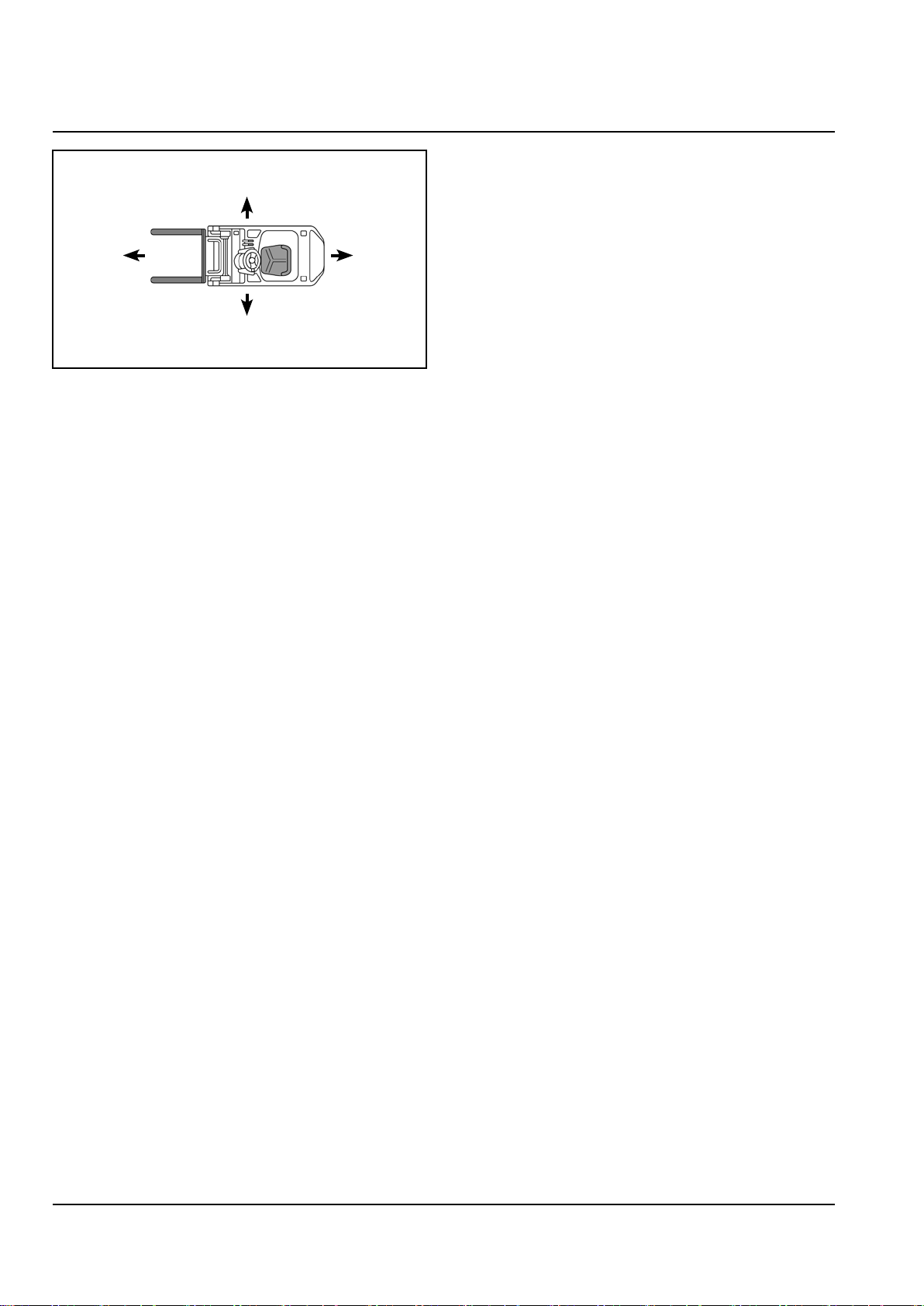
Right
Forward
Left
The diagram above indicates the meanings of the
terms “forward”, “backward”, “right” and “left” used
in this manual.
Backward
FOR SUPERVISORS
Lift truck accidents cause dozens or hundreds of
deaths every year, and even greater numbers of
personal injuries.
UniCarriers has steadily improved the design and
fabrication of our lift trucks so they may be used
more safely and efciently, but many accidents still
occur due to improper use. Accidents are often
the result of more than just “bad driving”. The use
of inappropriate types of equipment, the selection
of inap p ropriat e attachm ents or acces sories,
inappropriate operating environments, careless
designation of operators, and failure to properly
train the operator are other common causes of
accidents.
It i s no t pos s i b le t o de s c ribe a ll p o t e ntiall y
hazar d o u s s i tuations which may occur while
operating, inspecting or servicing a forklift truck.
The warnings and cautions in this manual, including
the decals attached to the forklift, are not intended
to cover all possible working hazards.
If you operate, inspect or service the forklift in a
manner not described in this manual, please be
careful because you do so at your own risk.
Thi s chapt er cover s the meth ods of acci dent
prevention which are primarily the responsibility of
supervisory personnel.
Pages 1-3 through 1-14 contain instructions
•
which should be enforced by the personnel
supervising the operation of the lift truck. Please
make sure the operators also read these pages.
Pa ge 1-15 and the f ollowing pages cont ain
•
spe c i fic precaut i o ns directly relate d t o t he
operation of the lift truck.
1-3
FOR SUPERVISORS
QUALIFIED OPERATORS
TRAIN OPERATOR TO STACK SAFELY
■
Unstacking
Stacking
“Stacking” means piling up a palleted load or
material directly on top of each other, without using
racks or shelves to separate them. If stacking work
is not done properly, the loads may slip or fall,
endangering the operator as well as fellow workers
in the area.
Safety classes should be held to train all operators
in the proper method of stacking and unstacking
loads.
(Your UniCarriers dealer can provide information
about safety stacking training.)
TIRED OR UNWELL? SEND THEM
■
HOME!
WEAR PROTECTIVE GEAR
■
Hard Hat
Goggles
Work
Clothes
Gloves
Always wear proper work clothes for driving.
•
Safety
Shoes
Work clothes should be designed to prevent any
part from accidentally catching on knobs or other
parts of the truck or equipment. For example,
shirts and trousers should have tight cuffs.
Always wear a hard hat and safety shoes.
•
Wear other protective gear as appropriate to
•
the conditions of the work site, i.e., goggles or
gloves.
PROVIDE AND MAINTAIN EMERGENCY
■
EQUIPMENT
Do not let people take chances. An operator who is
overworked or fatigued, an operator who is feeling
unwell, or an operator who is intoxicated must not
be allowed in the driver’s seat.
Fire extinguishers and first aid kits should be
provided and maintained for use in case of a fire
or accident. All personnel should understand the
location and use of emergency equipment.
1-4
FOR SUPERVISORS
PLANNING AND WORKING AREA
KNOW WHO TO CALL IN AN
■
EMERGENCY
Contacts in emergency
....................................
....................................
.............................
...........................
Keep i nformation on hand to allow immediate
calls for help in case of a fire, accident or other
emergency.
MAKE AN OPERATING PLAN AND
■
DISCUSS IT
SET SPEED LIMITS
■
(Example)
Yard Speed
Limit
Set appropriate speed limits on your company
grounds, and post signs that are clearly visible.
KEEP PEOPLE OUT OF THE
■
OPERATING AREA
Before using the lift truck, plan out the travel routes
and operating procedures, and thoroughly discuss
the details with all involved personnel.
MARK THE TRAVEL LANES
■
Closed to Pedestrians
No Pedestrians
No other personnel should be allowed in areas
where the lift truck is used.
Where other people must be present, post a guide
whose job is to make sure people stay clear of
moving vehicles.
Designate the travel lanes for the lift truck and mark
them clearly, so they will be kept free of obstruction.
1-5
FOR SUPERVISORS
PLANNING AND WORKING AREA
KEEP UNAUTHORIZED VEHICLES OUT
■
vehicles
No entry of
unauthorized
Unauthorized vehicles must be kept out of the
load handling areas. Post signs or give signals as
required.
ASSIGN TRAFFIC GUIDES TO
■
CONGESTED AREAS
PROVIDE ADEQUATE LIGHTING
■
Safe operation requires well-lit traveling routes, so
pedestrians and obstacles can be easily seen. Use
headlights, taillights, helmet lamps or other lights as
appropriate.
KEEP THE GROUND LEVEL AND DRY
■
Post a trafc guide in conned or congested areas
wh ere other people or vehicles may pass . All
personnel must obey the guide’s signals.
Be sure that all areas where the lift truck travels are
level and regular. Clear away pools of oil or water.
SAFETY MEASURES FOR DANGER SPOTS
■
Post warn ing sig ns or tak e other approp riate
measures to ensure that lift truck operators keep
away from danger spots as they travel.
1-6
FOR SUPERVISORS
INSTALL CURBS OR RAILINGS
■
If the truck is to be used on a loading dock, shore
wall or other raised surface, install curbs or railings.
DO NOT RELY ON THE OVERHEAD
■
PLANNING AND WORKING AREA
GUARD
The overhead guard is a protective device that
will moderate the impact of an object falling from
overhead, but it cannot withstand every impact. If a
heavy object seems likely to fall on the truck, make
every effort to prevent it from doing so.
1-7
FOR SUPERVISORS
PROPER AND IMPROPER USES
PROPER USE OF THE LIFT TRUCK
■
The proper use of a lift truck is to transport a load
which is placed on the pallet and stacked within the
prescribed height limit.
With a proper attachment, a lift truck may be used
to transport a load which is stacked elsewhere than
on the pallet.
■
IMPROPER USE
Transporting a person, elevating a person, and
towing a n o t her veh i c l e ar e examp l e s of t h e
improper use of a lift truck. Uses which this manual
species as improper must never be requested or
permitted, under any circumstances.
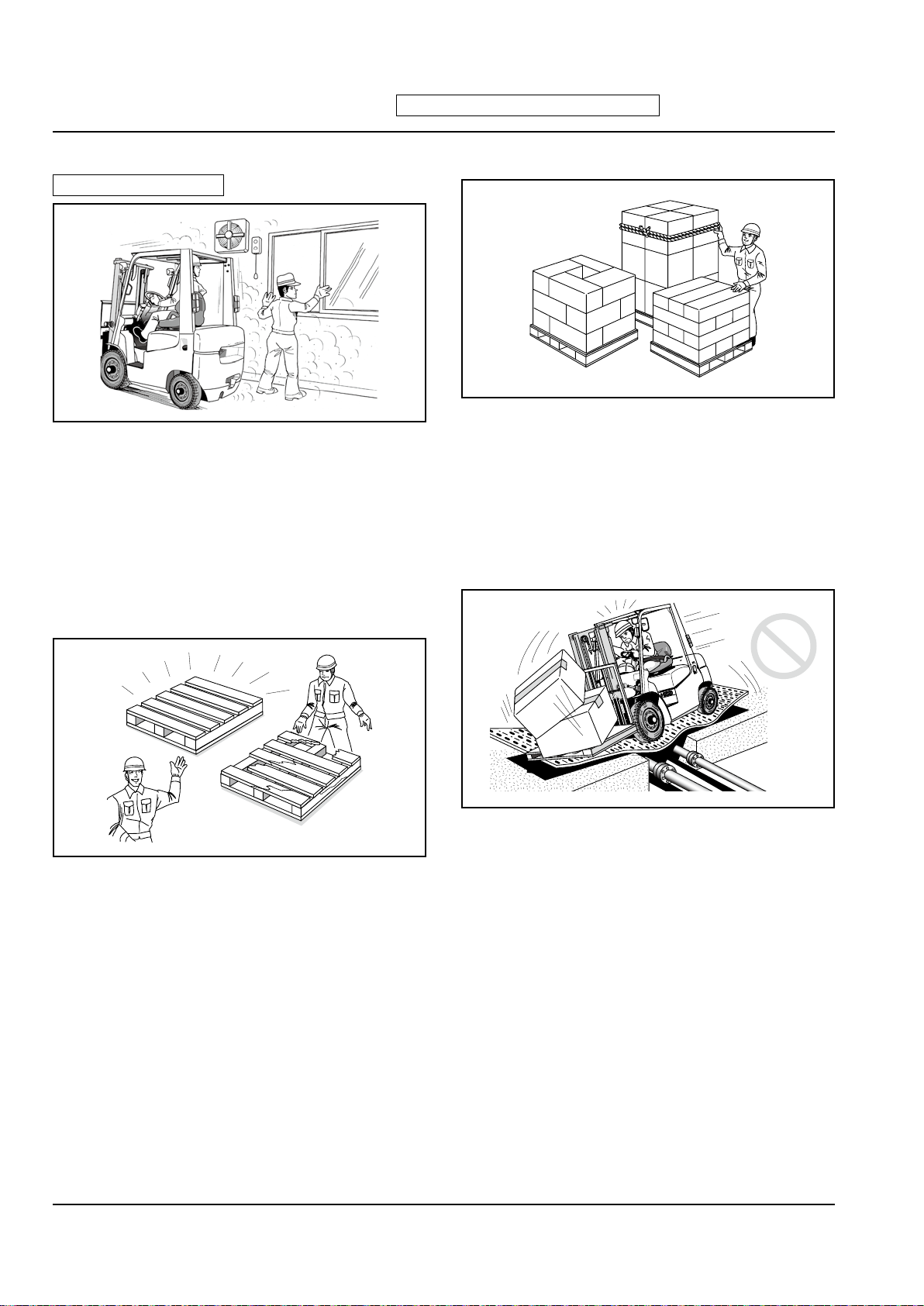
(Examples of Improper Use)
Transporting or elevating a person on the forks or
•
pallet.
Carrying a person on the pallet to control the
•
load.
Hanging wire ropes from forks to lift a load.
•
Towing another vehicle.
•
Pushing a load or another vehicle with the forks.
•
Using the forks or truck body to close or open the
•
door of a freight vehicle.
1-8
FOR SUPERVISORS
TYPES OF VEHICLES AND LOADS
READ MANUAL AND DECALS
■
Read t h e Op e r a tion & Ma i n t enance man u a l
an d caution plates on the tr uck, a nd bec ome
familiar with your truck and operating procedures.
Re membe r that individual lift truck s migh t be
di fferent i n design an d construc tion from o ne
another. Observe the caution decals on the truck.
Keep this Operation and Maintenance manual on
the truck as a ready reference for anyone who may
drive or service it.
KEEP DECALS LEGIBLE
■
YOU MUST FOLLOW THESE RULES TO AVOID SEVERE INJURY OR
DEATH TO YOURSELF AND OTHERS.
1. Operate truck only if trained and authorized by your employer. Know
2. Safety check truck every day. Do not start if damaged or faulty; stop if
Repair allowed only by trained, authorized mechanics.
3. Turn, start, stop, and handle loads smoothly and slowly.
Carry loads low and tilted back; stack only on level using minimum tilt.
4. Look where you are going. Watch out for people, hazards on oors
5. Truck overturn can kill you. Slow for turns even when empty. Never
6. Do not lift overweight or loose loads.
Move slowly with wide, high, or long loads.
Keep forks wide and fully under loads.
Travel in reverse if loads block view.
Attachments require special training, ask your employer.
7. Keep loads upgrade on all inclines. Stay clear of ramp and dock
8. Overhead guard and load backrest must be on truck.
Always keep yourself completely inside guard.
9. Stop engine when refueling. Follow Operation & Maintenance Manual
10. Forks can fall rapidly even with light loads.
Do not raise people or allow them under forks.
No passengers allowed on truck.
11. Park only in authorized areas, never on inclines.
Lower forks to bottom, put direction control in neutral, turn off key and
12. Fasten the seat belt, when operating the lift truck.
WARNING
Operation & Maintenance Manual and all work rules.
problems start.
and overhead, drop-offs and tail swing clearance.
turn on inclines.
edges. Make sure dockboards and trailers are secure before going on
them.
and employer’s work rules about fuel, battery and tire maintenance
hazards.
make sure parking brake is set.
The decals on the truck describe safety precautions
and operating instructions. Replace any damaged
or missing decals. Check that the decals are legible
during regular inspections.
USE THE RIGHT TRUCK FOR THE JOB
■
Be sure the type and capacity of the lift truck is
suitable for the work environment.
Check Point Choice
Capacity Load capacities range from 0.5 to 42
Power Source G a soline , natur a l gas, di esel, and
Balance On co u nt e r b ala n c e d mo d els , the
Tires For indoor use, there are models with
Flammable
Materials
tons. Pay particular attention to the load
center.
(UniCarriers Lift Truck Capacities: 0.5,
0.7, 0.9, 1, 1.35, 1.5, 2, 2.25, 2.5, 2.75, 3,
3.5, 4, 4.5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 10.5, 11.5, 12,
13.5, 15, 18, 20, 22, 23, 24, 25, 30, 37,
or 42 tons.)
battery- powered models are available.
Fuel costs and exhaust composition will
vary.
counterweight at the rear makes the
vehicle longer than reach trucks. A reach
truck performs loading and unloading
by extending the front part of the mast
outward, which gives it the advantage of
compactness.
solid tires (best for reach trucks) and
cushion tires (engine type or battery
type). Both are compact.
For outdoor use, pneumatic tires work
well. Solid cushion tires, with the same
dimensions as pneumatic tires, may be
the best choice in cases where the load
materials or surface conditions could
puncture pneumatic tires.
For handling fl a m m a b l e ma t e r i als
such as petrochemicals, a combustion
engine is too dangerous. An electric
vehicle with explosion-proof or safetyreinforced construction is required. (A
ba tte ry pow er sou rce always offe rs
bett er protectio n again st fi re th an a
combustion engine.)
1-9
FOR SUPERVISORS
TYPES OF VEHICLES AND LOADS
USE THE PROPER ATTACHMENT
■
WARNING
Avoid hoisting a load with wire rope hung
from the forks or an attachment, or avoid
lifting a freight container with forks, because
ther e is da n ger o f t h e tr u ck t i pping . If
necessary, have a qualified operator use a
hook or crane arm attachment.
Popular Attachment Examples
① : Roll Clamp
(For paper roll or
drum handling)
③ : Hinged Fork
(for lumber handling)
② : Rotating Fork
(For damping work
or charging work)
④ : Side Shift
(For precise stacking
in containers or other
narrow spaces)
⑤ : Crane Arm
(For slinging work)
1-10
FOR SUPERVISORS
TYPES OF VEHICLES AND LOADS
HAVE A GOOD VENTILATION
■
Engine-powered trucks
When the engine is run indoors such as in an
enclosed warehouse, have a fresh-air ventilation.
Exhaust fumes can cause chemical poisoning, and
in the worst case exhaust fumes can kill. When
warming up or operating the truck indoors, open the
windows and doors or use a fan to make sure there
is a good ventilation.
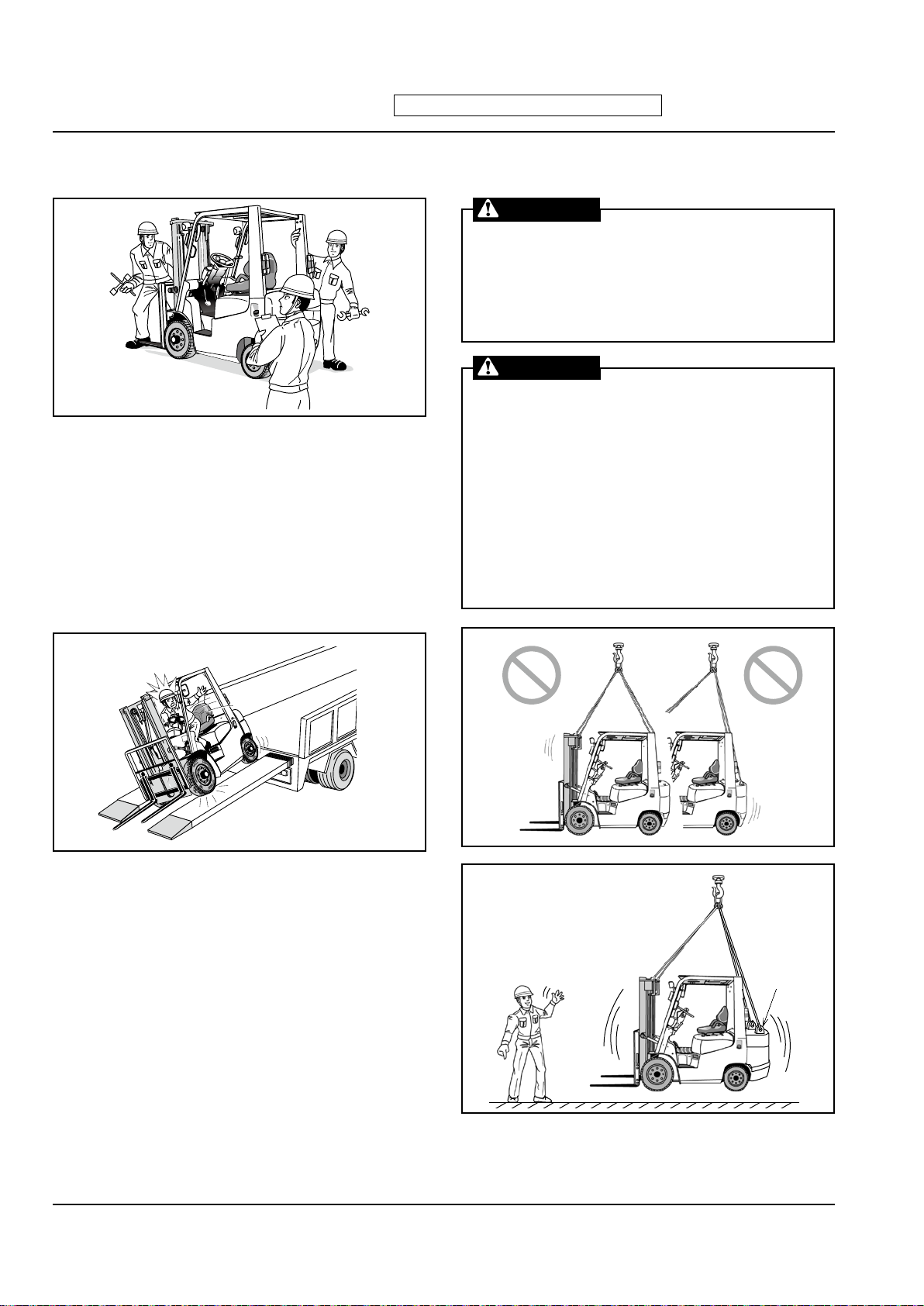
STACK LOADS SECURELY
■
Whe n stacki ng loads , place them i n a stable
manner that they will not easily come apart, and be
sure the weight is evenly distributed. Secure the top
layer with a cord wrapped like a headband or in a
similar fashion.
KNOW THE WITHSTAND LOAD OF
■
YOUR FLOOR
USE STURDY PALLET MATERIALS
■
Pallets and skids m u s t b e strong enough t o
withstand t h e heavy w e i ghts of l o a d i n g and
unloading. Remove or repair any damaged pallet.
The lift truck is heavier than it appears . F o r
example, a 2-ton truck weighs almost 3.5 tons
even when empty. Furthermore, when loaded, 80
to 90% of the total weight is concentrated on the
front wheels. Check the strength of your oors and
roadways, and if necessary reinforce them.

1-11
FOR SUPERVISORS
INSPECTION
ALWAYS INSPECT BEFORE
■
OPERATING
The operator should always inspect the truck before
each use to verify that all essential safety features
are working. Any abnormality is to be reported to
the supervisor, who is responsible for correcting it.
PERIODIC INSPECTIONS ARE
■
MANDATORY
Monthly and annual inspections must be performed
thoroughly, and any abnormality promptly repaired.
Only a certied expert who has the advanced skills
and equipment is allowed to conduct inspections.
NEVER USE AN UN-MAINTAINED
■
TRUCK
Out of
Service
A truck that has not passed an inspection must
never be operated. Hang a sign on the truck and
remove the ignition switch, to make sure no one
uses it. Then report the problem to the supervisor
and wait for the repair to be completed.
REPLACE SAFETY PARTS REGULARLY
■
Name of safety parts
Master cylinder and wheel cylinder cups
1
and dust seals
2 Power steering hose 2
3 Reserve tank tubing 2 – 4
4 Fuel hose (Engine-powered trucks) 2 – 4
Torque converter rubber hose
5
(Engine-powered trucks)
6 Rubber parts inside power steering unit 2
7 Lift chain 2 – 4
8 Load handling means hoses 1 – 2
Recommended
replacement interval
(year)
1
2
Certain critical parts must be replaced at regular
intervals. Since it is difficult to detect wear on the
above parts by visual inspection, they must be
replaced at the intervals specied, because a failure
would result in a falling load or runaway truck.
1-12
FOR SUPERVISORS
TRANSPORTING THE LIFT TRUCK
DESIGNATE A REPAIR AND ASSEMBLY
■
SUPERVISOR
Repairs and the mounting and dismounting of
attachments must be performed under the direction
of a designated supervisor. The body and major
parts of the lift truck are quite heavy and under very
high pressure. Repair or assembly work undertaken
without careful and thorough preparation can lead
to serious injury.
TRANSPORTING THE LIFT TRUCK
■
USE OPTIONAL “LIFTING EYES” FOR
■
LIFTING YOUR LIFT TRUCK
WARNING
Never hoist your lift truck at its overhead
guard or counterweight; otherwise there is a
danger of the truck falling.
If hoisting the lift truck is necessary for any
reason, use optional “Lifting Eyes.”
WARNING
Observe the following conditions when lifting
the lift truck:
Use optional “Lifting Eyes”.
•
Use ropes strong enough to withstand the
•
weight of the truck.
Do not use any wire rope which is kinked,
•
deformed or frayed.
Lifting the truck should be performed only
•
by qualied personnel.
Do not enter under a lifted truck.
•
Use a level, hard road surface when loading the
truck onto or unloading from a trailer and when
unl o ading it. Be certai n t hat the ramps h a ve
sufficient length and width as well as strength.
Do not load or unload the truck when it is raining,
unless the ramps are fitted with an anti-slipping
surfaces.
It is safe s t to use a self- loading trail e r truck
equipped with a jack and winch. For loading, tilt
the truck bed with the jack, attach the winch to
the towing pin of the lift truck, and pull it up. The
operator must not ride on the l ift truck during
loading or unloading.
LIFTING
EYES
1-13
FOR SUPERVISORS
TRAVELING ON PUBLIC ROADS
GOT A LICENSE?
■
Before traveling on a public road, be sure that the
truck has been licensed and inspected as required
by local laws.
NO LOAD, NO TOWING
■
OBEY TRAFFIC LAWS, AND TURN OFF
■
YOUR LIGHTS
On a public road, the lift truck must obey the same
laws as any other vehicle. Do not use rear working
light.
It is usually illegal to carry a load on a public road. It
is also not allowed to make a sideways travel or tow
another vehicle on a public road (with the possible
exception of a disabled vehicle). Never tow another
vehicle, even on company property.
1-14
FOR SUPERVISORS
MODIFICATIONS
NO OPERATION WITHOUT LIGHTS,
■
OVERHEAD GUARD, OR BACKREST
Load
backrest
Lamps
The lift truck cannot be used if the headlights,
taillights, overhead guard, backrest, horn or turn
signals have been removed. Any parts that have
been temporarily removed for some reason must be
reattached immediately.
OBTAIN APPROVAL FOR ANY
■
Overhead
guard
MODIFICATION
IMPLEMENTATION OF MODIFICATIONS
■
Only in the event that the truck manufacturer is no
longer in business and there is no successor in the
interest to the business, the user may arrange for
a modication or alteration to a powered industrial
truck, provided, however, that the user shall:
a) arrange for the modification or alteration to
be designed, tested and implemented by an
engineer(s) expert in industrial trucks and their
safety;
b) maintain a permanent record of the design,
test(s) and implementation of the modication or
alteration;
c) approve and make appropriate changes to the
capacity plate(s), decals, tags and instruction
handbook;
d) affix a permanent and readily visible label to
the truck stating the manner in which the truck
has been modified or altered together with the
date of the modification or alteration, and the
name and addres s of the o rganization that
accomplished the tasks.
Modifications or additions that affect the capacity,
construction or strength of the truck must not be
performed by the user without the manufacturer’s
or his authorized representative’s prior permission.
For example, don’t add a counterweight.

1-15
HOW THE LIFT TRUCK WORKS?
KEEPING THE TRUCK BALANCED
■
Lift trucks are equipped with load handling means
including a mast and forks at its front part. The front
wheels of the truck work as a fulcrum to balance
the center of gravity of the truck and the center of
gravity of the load. The relationship between the
locations of those two centers of gravity is vitally
important for safety.
KNOW THE CENTER OF GRAVITY OF
■
YOUR LOAD
HOW THE CENTER OF GRAVITY
■
SHIFTS
Truck’s center of gravity
with high mast raised
Truck’s center of gravity
with standard mast raised
The higher the load,
the higher the truck’s
center of gravity
Truck’s center of
gravity with truck tilted
Load’s
center
gravity
Distance
Allowable load (kg)
Weight x distance = moment (constant)
Basic load center
Load center (from fork root) mm
Materials of various shapes such as boxes or flat
or cylindrical items may be loaded on the lift truck.
In order to accurately judge the stability of the
truck, it is vitally important for the operator to know
the location of the center of gravity for each type of
load.
Lift truck viewed from front
The stability of the lift truck is determined by the
overall center of gravity, which is the product of the
centers of gravity of the truck and the load. When
the truck is empty, this point is the same as the
center of gravity for the truck, and when it is loaded
it shifts according to the center of gravity of the
load. Since the center of gravity of the load changes
whenever the mast is tilted forward or backward or
the fork is raised or lowered, the overall center of
gravity also changes. The center of gravity is also
governed by the following factors:
Size, weight and shape of the load
•
Unloading height
•
Tilt angle of the fork
•
Tire material
•
Acceleration, deceleration and turning
•
Surface condition and gradient of the road
•
Type of attachment
•
1-16
HOW THE LIFT TRUCK WORKS?
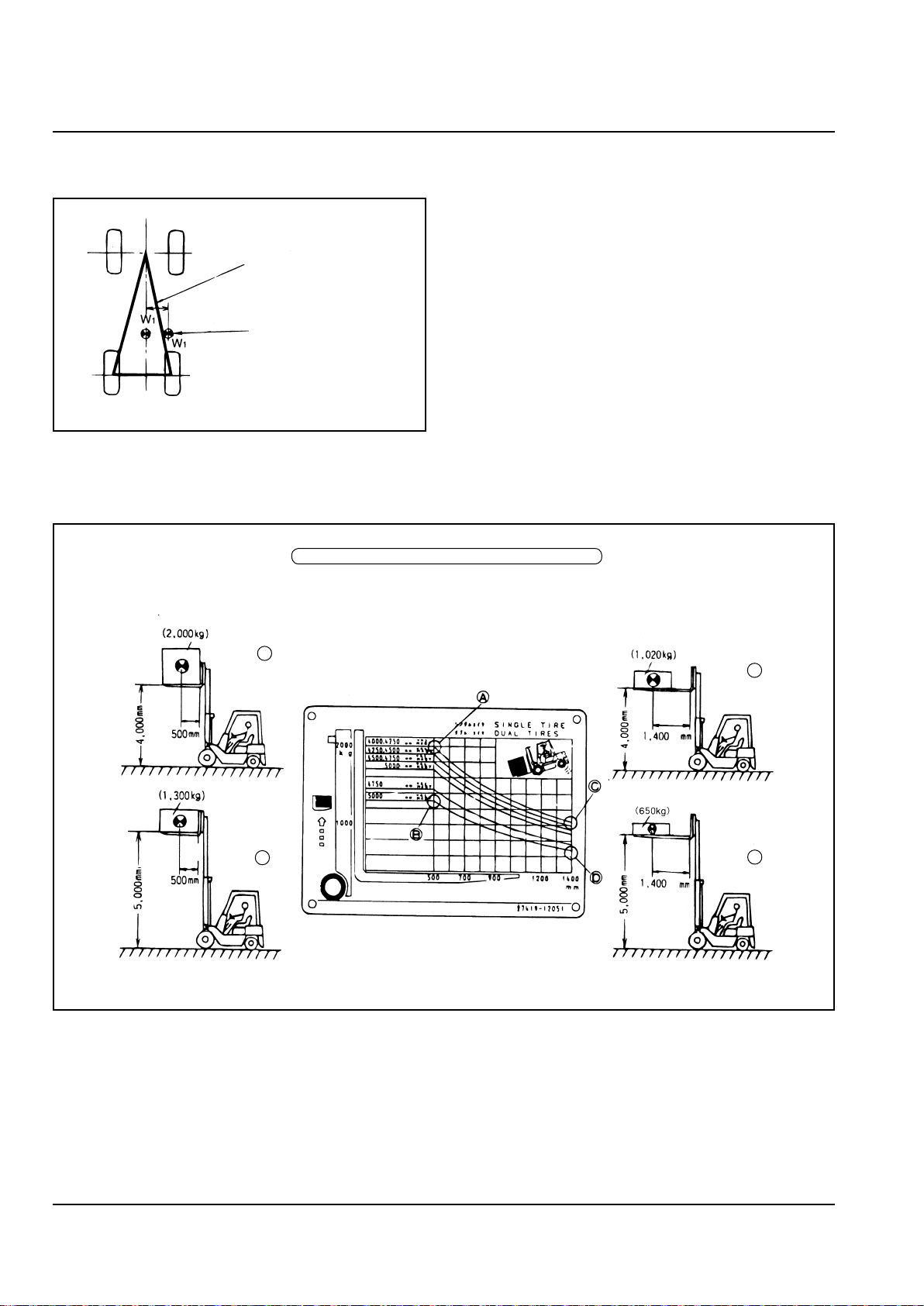
OUTSIDE THE TRIANGLE OF
■
BALANCE, THE TRUCK TIPS
Rear
Lift truck Viewed from Above
RATED LOAD (LOAD WEIGHT AND LOAD CENTER)
■
wheels
Front
wheels
Axis of lateral stability
If the center of gra vity W 1 moves
ou tw ar d pas t the axis of lat er al
stability, the truck will roll.
(A s the cen te r of gravit y com es
closer to the rear axle, the space
between the centerline of the truck
an d th e ax is of late ra l st abi li ty
narrows, and the truck will roll more
easily.)
For a lift truck to remain stable, the overall center
of gravity must be inside the triangle formed by the
contact points of the left and right front tires and
the center point between the steering wheels. The
triangle denes the area of stability for the center of
gravity.
If the overall center of gravity moves further forward
than the front wheels, the truck will tip forward with
the front wheels as the fulcrum. If the overall center
of gravity moves outside the triangle to the right or
the left, the truck will fall over in that direction.
HOW TO READ THE LOAD CHART
The higher the load is raised, and the further forward
from the front wheels the load is moved, the more the
weight of the load increases.
(Slightly heavier loads can be carried with dual tires)
A
Point
Point
B
Point
Point
C
D
The load center is the distance from the front face of the forks to the center of gravity of the load. The rated
load is the maximum weight allowable with the nominal load center.
The Load Chart, showing the relationship between the load center and the rated load, is attached to the truck
as a decal. The rated load decreases as the load center moves toward the tip of the forks, and as the overall
center of gravity moves forward.

1-17
HOW THE LIFT TRUCK WORKS?
ACCELERATING, DECELERATING AND
■
TURNING
The principle of inertia provides that a stationary
object will remain stationary as long as there is no
external force acting on it, and that a moving object
will continue moving at a constant speed as long as
there is no external force acting on it.
Due to inertia, when the lift truck starts to move
there is a momentary backward force, and when
it stops there is a momentary forward force. As a
result, if the brakes are applied suddenly, there
is a very strong hazard that the forward force will
become strong enough for the truck to tip forward.
Likewise, when the truck is turning there is a
centrifugal force that pulls it outward from the
turning center. This force can cause the truck to
fall sideways. Since the zone of lateral stability is
especially narrow, it is necessary to slow down
substantially when turning in order to prevent the
truck from tipping.
When the load is elevated the overall center of
gravity is raised, increasing the danger of the truck
tipping over to the front or side.
1-18
TRAVELING
Do not operate the lift truck until
preoperational checks are nished
If any defect is found during checking, report it to
the supervisor and have it repaired.
Do not operate the truck until the malfunction or
damage is properly repaired.
Mount properly
Never mount or dismount a moving truck. When
getting on and off the truck, make sure the truck is
at a complete stop and use the recommended hand
holds and steps with at least three points of support
(for example, put your left foot on a step, and hold
a hand hold with your left hand and the backrest
of the seat with your right hand). Keep the steps,
hand holds and the seat always clean. Repair if
damaged.
Caution to be taken when starting the
electric truck
Electric trucks
Before trying to start the truck (before turning the
key switch to ON), follow the procedure given
below:
1) Apply the parking brake.
2) Place the direction shift lever in neutral.
3) Adjust the steering wheel and operator’s seat
before turning the key switch ON. Do not try
to adjust them during operation; otherwise a
serious accident might occur.
After adjustment, make sure they are securely
locked.
4) Seat yourself in the operator’s seat and fasten
the seat belt.
5) Press the brake pedal.
6) Make sure there is no one under or around the
truck, and turn the key switch to ON.
Do not move controls unless properly
seated
When starting the engine
Engine-powered trucks
When starting the engine, make sure to:
1) Apply the parking brake securely.
2) Place the direction shift lever and speed range
shift lever into neutral.
3) Adjust the steering column angle and driver’s
seat position before starting the engine.
Do not try to adjust them during operation;
otherwise a serious accident might occur.
After adjustment, make sure they are securely
locked.
4) Seat yourself in the operator’s seat and fasten
the seat belt.
5) Press the clutch pedal (trucks with clutch) or
brake pedal (trucks with torque converter).
6) Make sure there is no one under or around the
truck, and start the engine.
Do not operate the controls (levers and pedals)
unless you are properly seated.
1-19
TRAVELING
Sound horn when starting
Before starting, make sure no one is near the truck.
Let other workmen and bystanders know you are
starting up by sounding horn.
Keep your hands clean
It is dangerous to operate the steering wheel and
levers with greasy hands. If grease, oil or soil is
sticking to your hands, clean if off.
Never use man as an additional
counterweight
Do not use man as an additional counterweight. Do
not offer rides to others.
Avoid sharp starts, stops and turns
Keep the truck’s center of gravity
low during traveling (when loaded in
particular)
About 20 cm above ground
When traveling (when loaded in particular), keep
the forks 20 cm above the oor or ground and tilted
back, so as to lower the truck’s center of gravity as
far as possible.
Start, stop and turn slowly. Before turning, slow
down the t r u ck sufficiently. I n pa r t i c u l a r, an
unloaded truck might tip over when it is turned
sharply, because the rear of the truck is heavy.
Before reversing the direction of travel,
bring the truck to a complete stop
It is dangerous to reverse the direction of travel
abruptly.
Carry the load low
It is dangerous to travel with forks lifted higher than
is appropriate, regardless of whether loaded or not.
Keep the load as low as possible while traveling. Do
not turn the truck with the load raised high.
1-20
TRAVELING
Stay away from the edge of road
Ther e i s a f e ar of the edge of a soft grou n d
breaking. Stay away from such a place. Keep
appropriate distance from the edge of a narrow
road or a platform.
Do not travel over a oor or ground
surface covered with water
Do not travel over a oor or ground surface covered
with water. Go round any pothole in the road.
Do not ride on obstacles (curb, railroad
tracks, ditches)
If unavoidable, be careful.
Safe traveling:
Do not get into a soft ground area
Avoid running on a slippery surface
Always look in the direction of travel
•
Always look in the direction of travel; failure to
do so will lead to an accident. When passing
an oncoming truck each other, slow down and
use caution to have a safe distance. Moreover,
maintain a safe distance from the truck ahead of
you at all times.
Observe speed limits
•
Observe the specied speed limits.
Make sure there is no one or obstacle around
•
the truck and in the direction of travel or turning
Do not go past other trucks where vision is
•
restricted
Do not go past other trucks at intersections,
corners, narrow aisles and other locations where
your vision is restricted.
Slow down at corners
•
Slow down and sound horn at intersections and
other locations where your vision is restricted.
Come to a complete stop before crossing
•
roads or at corners
1-21
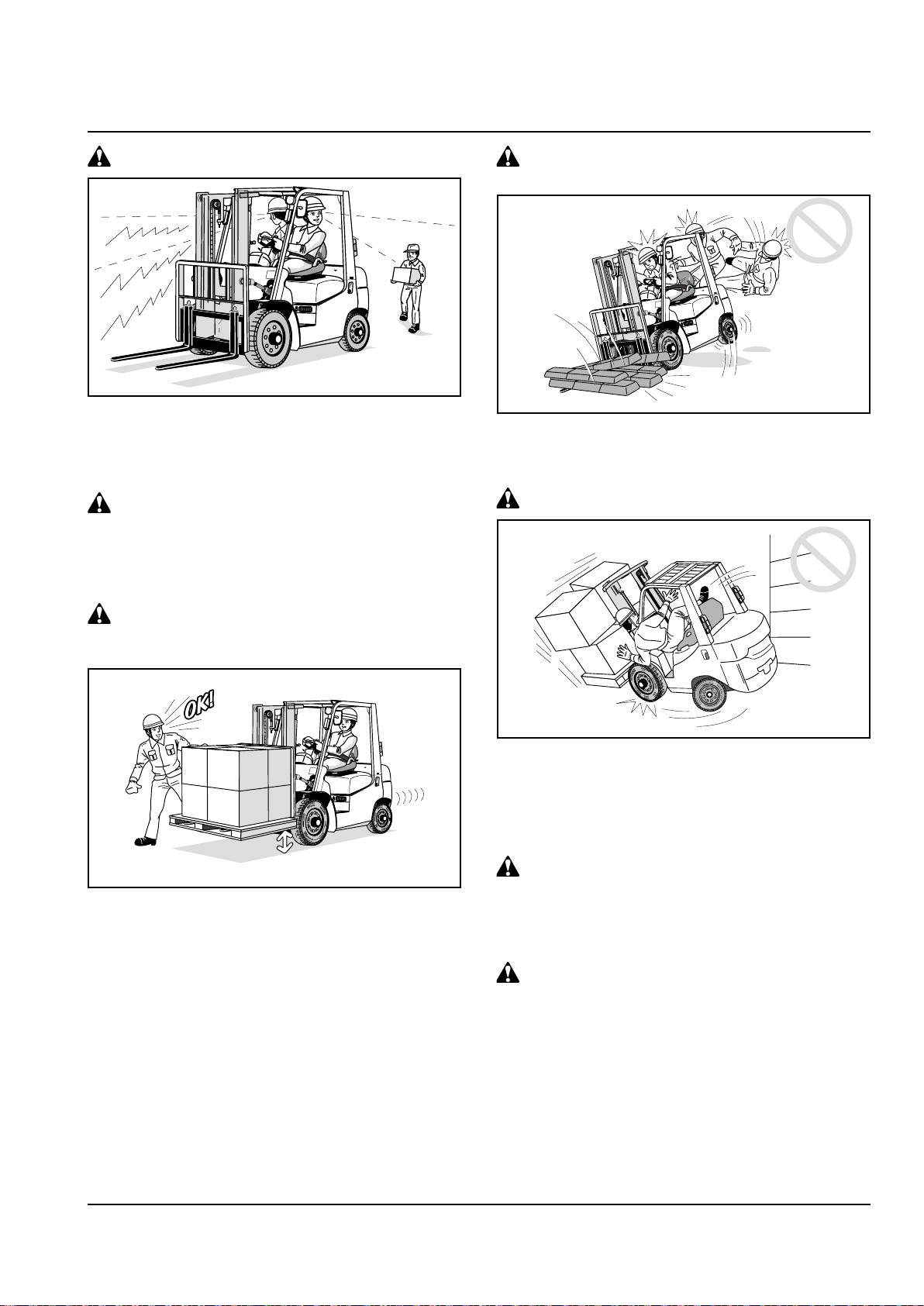
TRAVELING
When going into areas where there
are limits in height and width, use the
following cautions:
Make sure there is enough height and width for
•
the truck to pass.
Do not put your hands and feet outside the truck.
•
Make sure there is no one around the truck.
•
Watch out for outdoor electric cables and other
•
obstacles.
Rear steer, rear swing
Have a guide when handling bulky loads
When handling bulky loads which restrict your
vision, operate the truck in reverse and have a
guide.
Reverse travel
When the truck is turned in forward driving, the rear
of the truck swings outwards. Before turning, make
sure there is enough clearance from the wall and
other obstacles.
When t raveling in reverse, always look in the
direction of travel. Do not rely too much on the
si devi ew mi rrors (if so equipped) a nd backup
buzzer.
1-22
TRAVELING
Back down and drive up:
Do not make turns on a gradient. There is danger
•
of the truck upsetting.
Keep the forks and pallet at an appropriate
•
ground clearance height.
When operating an unloaded truck on grades,
•
have the rear end of your truck pointed up-hill.
When operating a loaded truck on grades, have
•
the rear end of your truck pointed down-hill.
When descending a grade, use engine braking.
•
Engine-powered trucks
If the truck goes faster than you want, press the
foot brake pedal from time to time. While using
engine braking, do not operate the shift lever(s)
nor press the inching pedal.
When descending a grade, use the brake pedal.
•
Electric trucks
If the truck goes faster than you want, use the
foot and regenerative brakes from time to time to
slow down the truck.
Brake the truck in good time
The truck takes a little longer to come to a stop on a
slippery surface than on a usual surface. Brake the
truck in good time.
In addition, the stopping distance of the truck is
longer on a downhill. Keep the traveling speed
under your control.
Do not shut off the engine during
traveling (trucks with power steering and
power brake)
Engine-powered trucks
If the engine stops during traveling, both the power
steering unit and the power brake goes inoperative.
Do not turning off key switch during
traveling
Electric trucks
If the key switch is turned off during traveling, power
steering becomes disabled to make steering hard.
Engine braking is not available when the
inching pedal is pressed
Engine-powered trucks
When the inching pedal is pressed to the bottom,
the brake i s a pplied to the t r uck, but engi n e
braking is not available because the clutch unit is
disengaged.
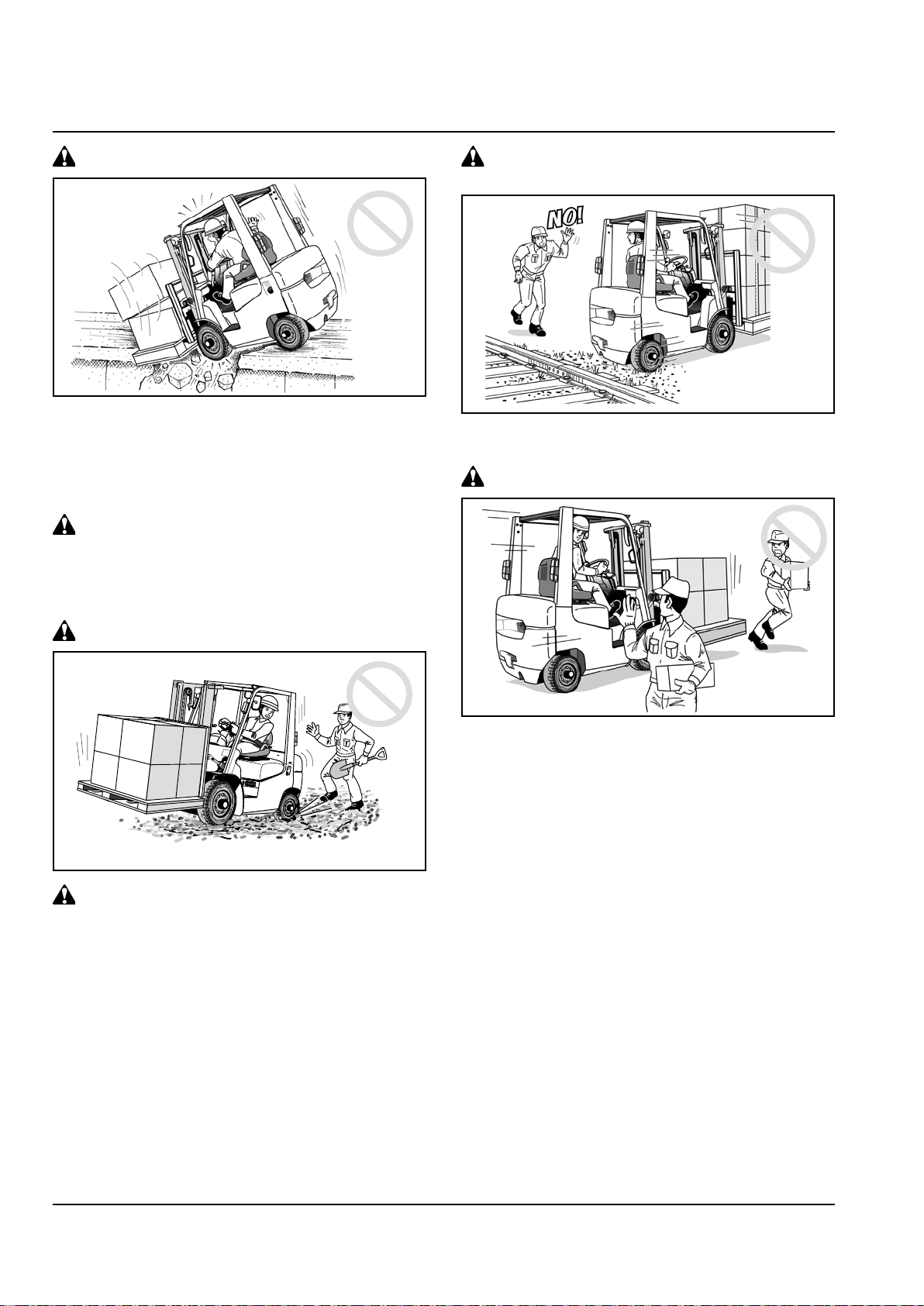
When driving over a dockboard:
Do not ride on the edge of the dockboard or
•
bridgeplates; otherwise the truck might fall down,
leading to personal injury or even death.
Before driving over a dockboard or bridgeplate,
•
make sure it is properly secured. Never exceed
its rated c a p a c i t y. Do not u s e a dama g e d
dockboard or bridgeplate.
Have the brakes set and wheels blocked in place
•
to prevent the trailer from moving.
Jacks must be installed to support the trailer
•
when the truck goes into the trailer.
Drive carefully and slowly across the dockboard
•
or bridgeplate.
Watch for bystanders.
•
Give instructions to the trailer driver not to move
•
the trailer until load handling is nished.
Mak e sure the dock board or bri dgepla te is
•
secured.
1-23
TRAVELING
Know the load bearing capacity of the
oor
Before entering a building or going into an elevator,
make sure the floor is strong enough to withstand
the weights of the truck and the loads.
Practice safe driving and load handling
techniques
Before using the l ift tru ck, you must pr actice
safe driving and load handling techniques. Even
after getting familiar with the operation of the
truck, operate the truck carefully; reckless driving
and operation will cause a personal injury or an
accident.
When using multiple trucks
When operating multiple trucks, remember that their
operating controls have their own characteristics
even if the trucks are of the same specification. If
you change the trucks, keep this point in mind. In
particular, pay attention to the brake system.
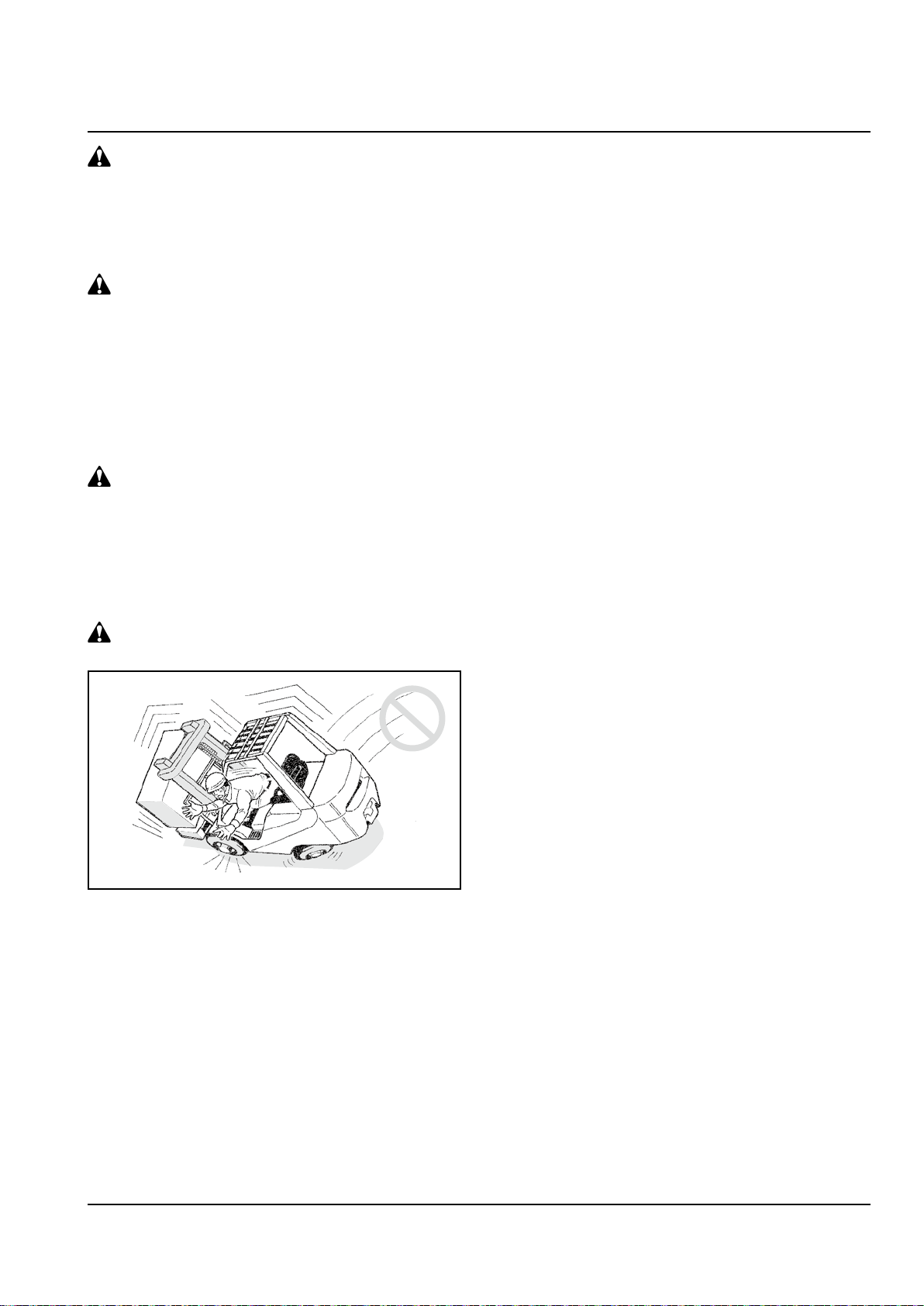
Stay inside if the truck seems like it is
about to turn over
The operator must always fasten his seat belt. If the
truck turns over, the operator might be thrown out
and, in the worst case, the operator can be crushed
under the truck causing severe injury or even death.
If it seems like the truck is about turn over, stay in
the operator’s seat. Hold on to the steering wheel
rmly, brace your feet rmly on the oor, lean your
body away the direction in which the truck seems
like it is going to turn over. Never jump out of the
truck!
1-24
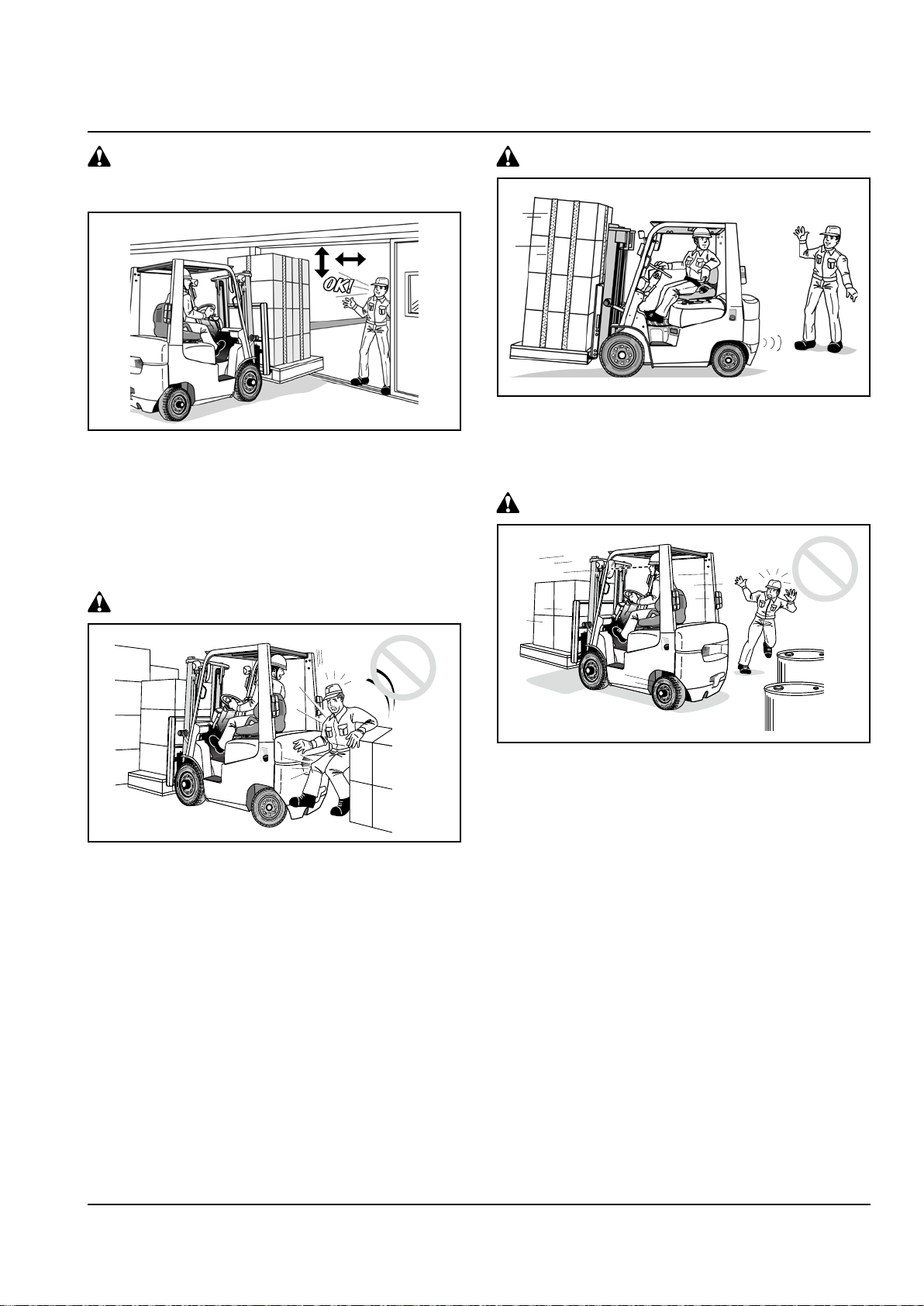
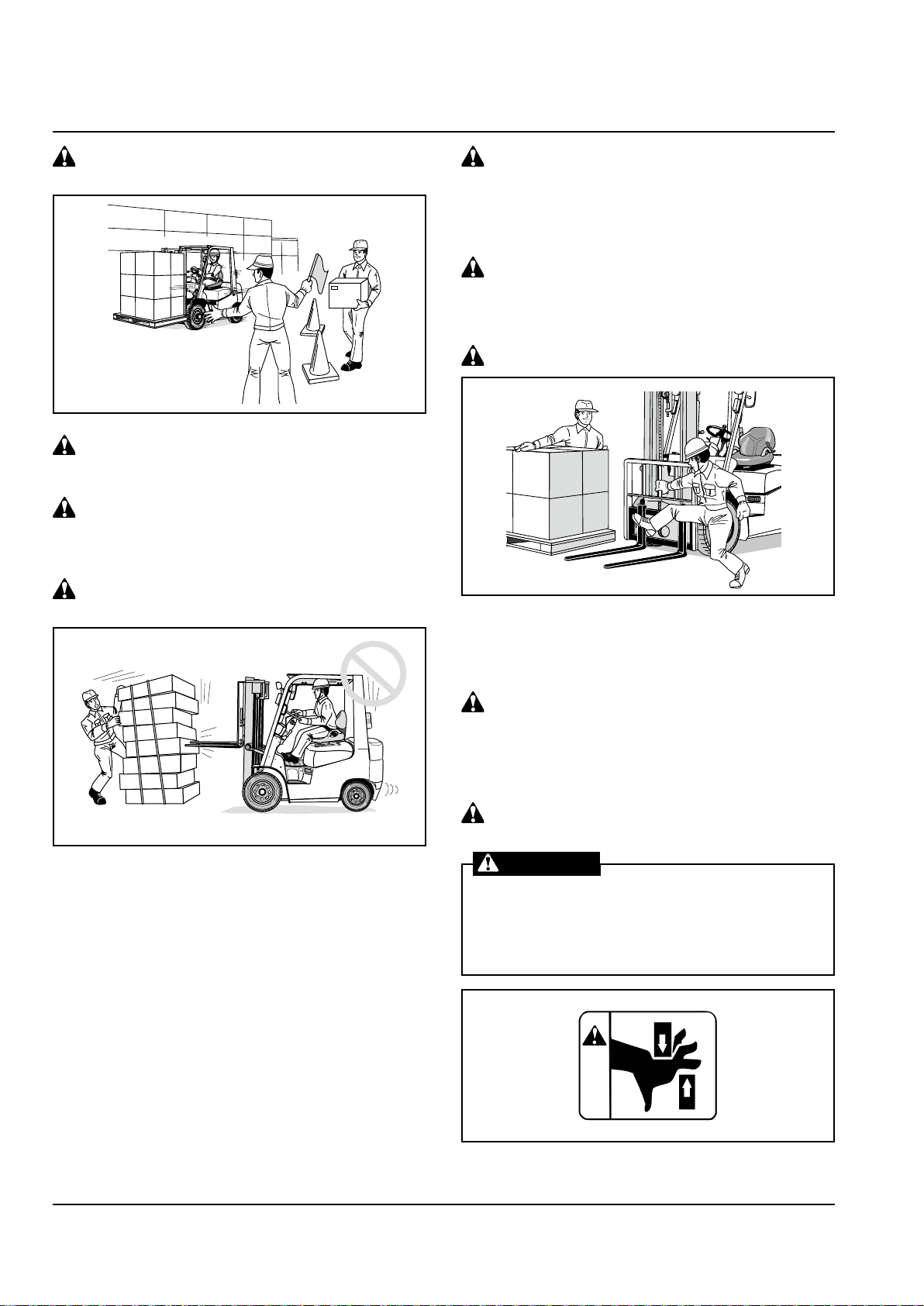
LOAD HANDLING
Keep anyone but a guide away from the
working area
Do not let other persons or truck
approach your lift truck during operation
When working in a group, have a person
present to give guidance and follow his
instructions
Do not use your truck for purposes other
than specied:
Pay attention to the fork tips
The fork tips are sharp and could cause personal
injury. In addition, if they catch on obstructions, the
truck might lose control, leading to an accident.
Adjust fork spacing properly
Adjust the fork spacing suitable according to the
size of the load.
Adjust fork spacing with your feet
Adjust the fork spacing with your feet. Do not use
your hands. You hands might get pinched between
the forks and carriage.
Do not use the truck to open or close the doors of
•
freight cars or warehouses.
Do not push other trucks.
•
Do not hoist loads, using ropes hung on the
•
forks.
Do not tow another vehicle using the draw bar.
•
Do not push or pull loads with forks; otherwise,
•
the load might fall off or get damaged. In
particular, the truck with the max. lift height of
more than 150 cm might tip over, if you try to do
that.
Make sure forks are securely locked
After adjusting the fork spacing, lock the forks
with fork stoppers. Unlocked forks will slide during
traveling, causing the load to fall off.
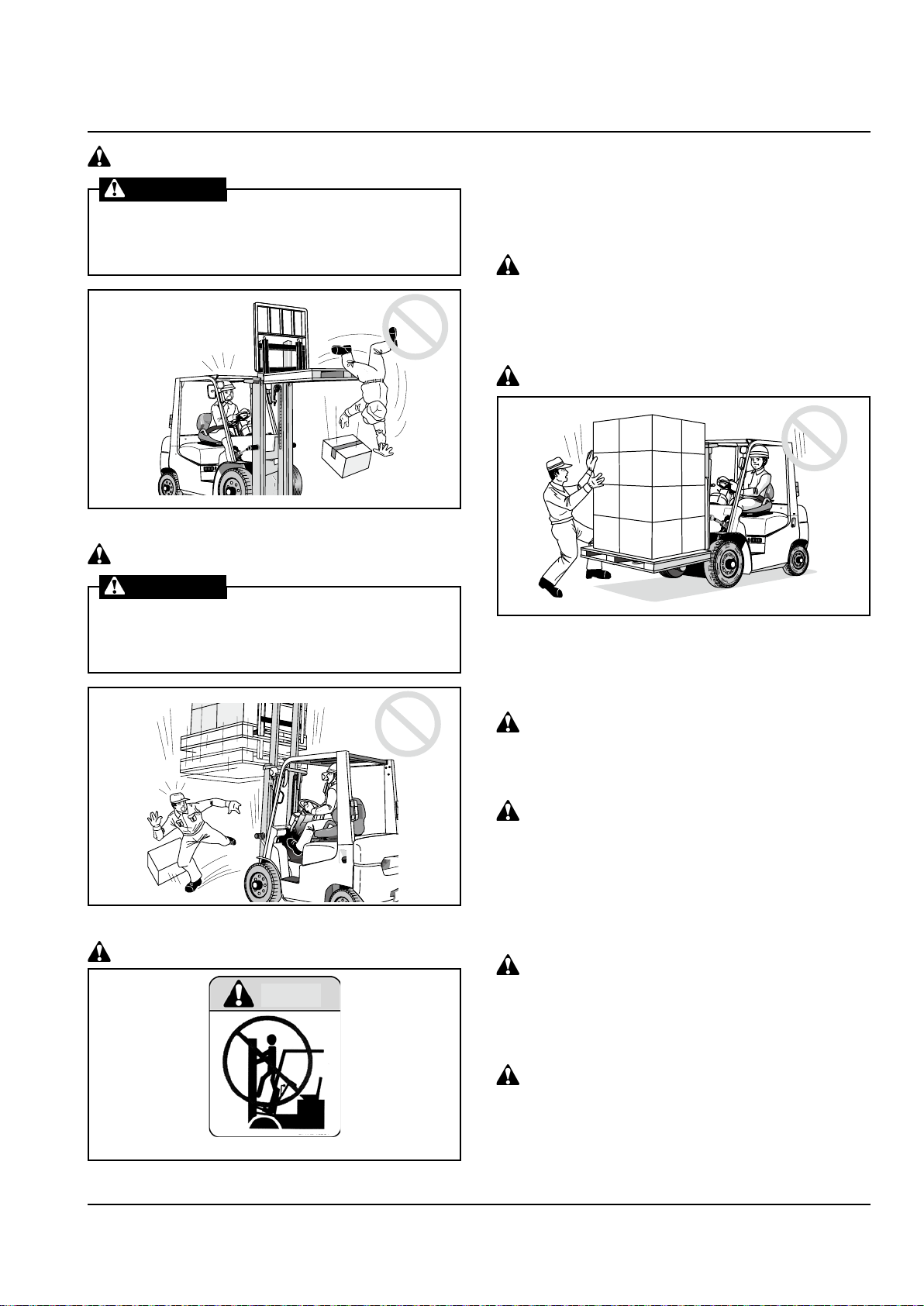
Do not put your hands or feet into the
load handling system
WARNING
Never put your hands or feet on the mast or
mast connecting members; otherwise your
hands or feet might be cut if the mast moves
unexpectedly.
WARNING
1-25
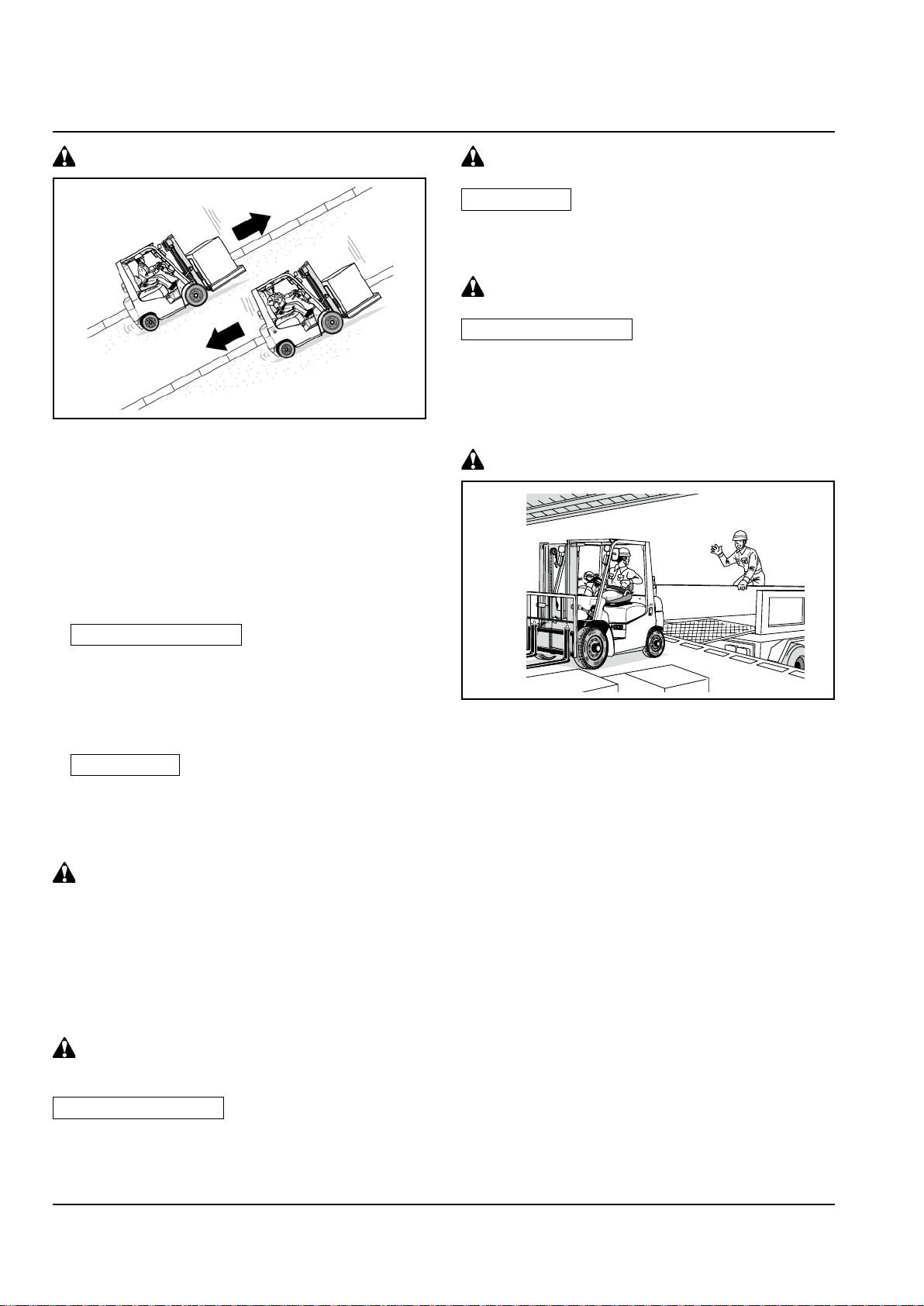
LOAD HANDLING
Never elevate a man
WARNING
Never allow other person(s) to ride on the
forks. He might fall off the forks, getting
injured.
Never lift a load over anyone
WARNING
It is dangerous to use the truck body or mast as a
ladder to ride on a high place.
You might be caught between the mast and truck
body, resulting in a serious accident.
Do not pick up loads from other truck
Do not pick up loads from raised forks of other
truck. This might cause an off-centered load or the
load to fall off.
Do not hold loads on the forks by hand
Never permit anyone to stand under raised
forks. The forks might fall down unexpectedly,
thus causing a personal injury.
Do not ride on front guard
WARNING
Do not hold loads on the forks by hand. If the truck
moves unexpectedly, the load might fall off, getting
the person caught under it.
Make loads in contact with load backrest
Insert the forks into the pallet as far as possible to
make the loads in contact with the load backrest.
Do not stack loads too high on forks
Do not stack loads on forks in such a way that the
top of loads exceeds the load backrest height;
otherwis e, loads migh t fall o n the pa rt of t he
operator, and in the worst case lead to a serious
injury or death.
Do not lift unstable loads
Do not handle unstable loads. When handling loose
loads, make sure they are stable enough before
lifting.
Use special caution when stacking or
unstacking loads
When stacking or unstacking loads, stabilize them
with ropes or others, to prevent from falling off.
 Loading...
Loading...