
Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
unibrain
e-mail: ubinfo@unibrain.com web-site: http://www.unibrain.com
September 2001
The FireWire Innovators
1

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Dear Firenet™ Customer,
Thank you for purchasing Unibrain’s FireNet™ software, THE FIRST AND ONLY FireWire™
Networking Solution for Windows and Macintosh. Firenet is a system-independent software
product that gives you full Ethernet compatibility at speeds of up to 400Mbps.
There are two different versions of FireNet; which one you choose depends upon your operating system.
• FireNet™ 2.2 Station for Windows 98, Windows 98SE, Windows Millennium, Win-
dows 2000 Professional & Windows XP using any OHCI 1394 Link Controller (i.e., Uni-
brain's Fireboard 400-OHCI, PCI to 1394 controller).
• FireNet™ 2.2 Server for Windows 2000 Server using any OHCI 1394 Link Controller
(i.e., Unibrain's Fireboard 400-OHCI, PCI to 1394 controller).
Features:
• Complete Ethernet emulation.
• Supports various network protocols: TCP/IP, NetBEUI, IPX/SPX, etc.
• 1394 Bus can be used simultaneously for other purposes (e.g. DV, 1394 Hard Disk).
• High speed – more than 2.5 faster than 100Mbps fast Ethernet.
• No hubs, no routers, complicated cabling, or complex installations.
• Works with any host 1394 interface on PC or Mac.
• Fast and Easy installation.
2

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Table of Contents
TABLE OF CONTENTS ..................................................................................3
T
ECHNICAL SUPPORT INFORMATION.............................................................4
I
NTRODUCTION............................................................................................5
Free Evaluation of Firenet ............................................................................ 5
PRODUCT KEYS ......................................................................................... 5
IRENET™ INSTALLATION ...........................................................................6
F
FIRENET™ INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS 98/98SE/ME................................ 7
FIRENET™ INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS 2000 ......................................... 11
FIRENET™ INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS XP............................................. 14
USING FIRENET WITH PROTOCOLS OTHER THAN TCP/IP ............................. 24
UTHORIZATION PROCEDURE.....................................................................26
A
U
N-INSTALLING FIRENET™ .......................................................................27
A
PPENDIX B: BENCHMARKS FOR FIRENET™ ..............................................30
NETWORK PERFORMANCE – SOME CONSIDERATIONS ................................ 36
A
PPENDIX C: CONNECTING FIRENET WITH ETHERNET..................................38
A
PPENDIX D: FIRENET AND VAIO NOTEBOOKS ...........................................40
A
PPENDIX E: FIRENET AND MAC OS ..........................................................41
FIRENET FOR MAC OS X 10.1 (OR LATER).................................................. 43
PPENDIX F: FIRENET FAQ.......................................................................45
A
A
PPENDIX G: FIRENET REVISION HISTORY..................................................49
A
PPENDIX H: HARDWARE COMPATIBILITY LIST ...........................................50
3

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Technical Support Information
Technical Support is available by phone or email. Our standard office hours are Monday
through Friday from 8:00AM to 4:00PM (Pacific Standard & Central European Time zones).
Email: Direct all technical support questions to support@unibrain.com
Phone:
North & South America
(USA) +1-925-866-3000
Europe & Asia
(GREECE) +30-1-6640580
.
4
Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Introduction
This document explains in detail the required setup and operation procedures for FireNet™
2.2 product on Windows 98/SE, Windows Millennium, Windows 2000 and Windows XP using
any 1394 OHCI controller.
Free Evaluation of Firenet
The FireNet software you are about to install is the complete and fully functioning version of Unibrain’s high-speed networking solution for Windows and Macintosh. Upon
initial installation, usage is restricted to an evaluation period of 30 minutes, at the end
of which the application will automatically turn off (without affecting the rest of your
computer operations in any way). You can repeat the demo as many times as you wish
by simply rebooting your PC.
PRODUCT KEYS
To enable unrestricted use or “authorized” use of FireNet software, a Product Key is
required for each and every computer on your FireNet network.
Product keys may be purchased online at the 1394store.com or from any distributor.
5
FireNet™ Installation
Before installing FireNet™, please verify that:
Description
Your PC operating system is Windows 98SE / Windows Me / Win-
1.
dows 2000 Professional/Server or Windows XP.
Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
CHECK? (√)
Your PC has a Firewire (i-Link) IEEE-1394 interface based on any
2.
OHCI controller or built-in 1394 support (i.e. Sony’s Vaio, Mac G4
etc.)
If you are going to upgrade from FireNet 1.x to Version 2, please
3.
uninstall the previous version before you proceed.
(Upgrade from Version 2.0 to 2.2 or later needs no special action)
IMPORTANT! Always UNPLUG the connecting IEEE-1394 cables between all network
computers before you begin installing or uninstalling FireNet software.
6
Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
FireNet™ Installation for Windows 98/98SE/Me
Installing FireNet in Windows 98, Windows 98SE or Windows ME is simple and straightforward. Note that steps 1 through 6 apply whether you are installing FireNet for evaluation or
entering product key numbers to enable continuous use of the software.
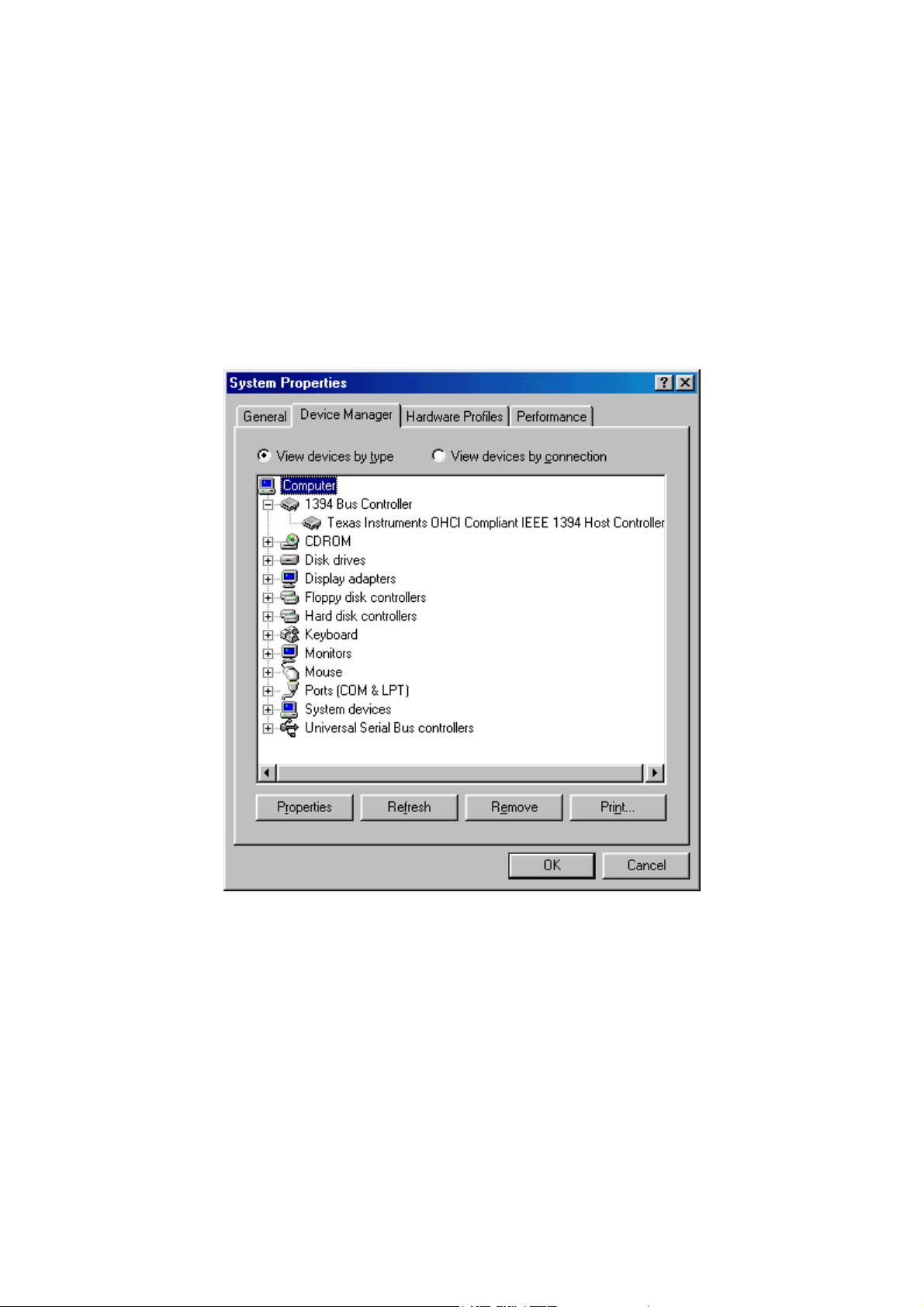
Step 1: Make sure that your 1394 OHCI controller is correctly installed and properly recognized by your operating system by going to the System Properties window and clicking on
Device Manager. The following example shows the host PC has a Texas Instruments OHCI
Compliant IEEE-1394 Host Controller (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Step 2: Important! Always UNPLUG the connecting IEEE-1394 cables between all network
computers before you begin installing or uninstalling FireNet software.
Step 3: Run the installation executable and follow the instructions on the dialog boxes.
7
Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
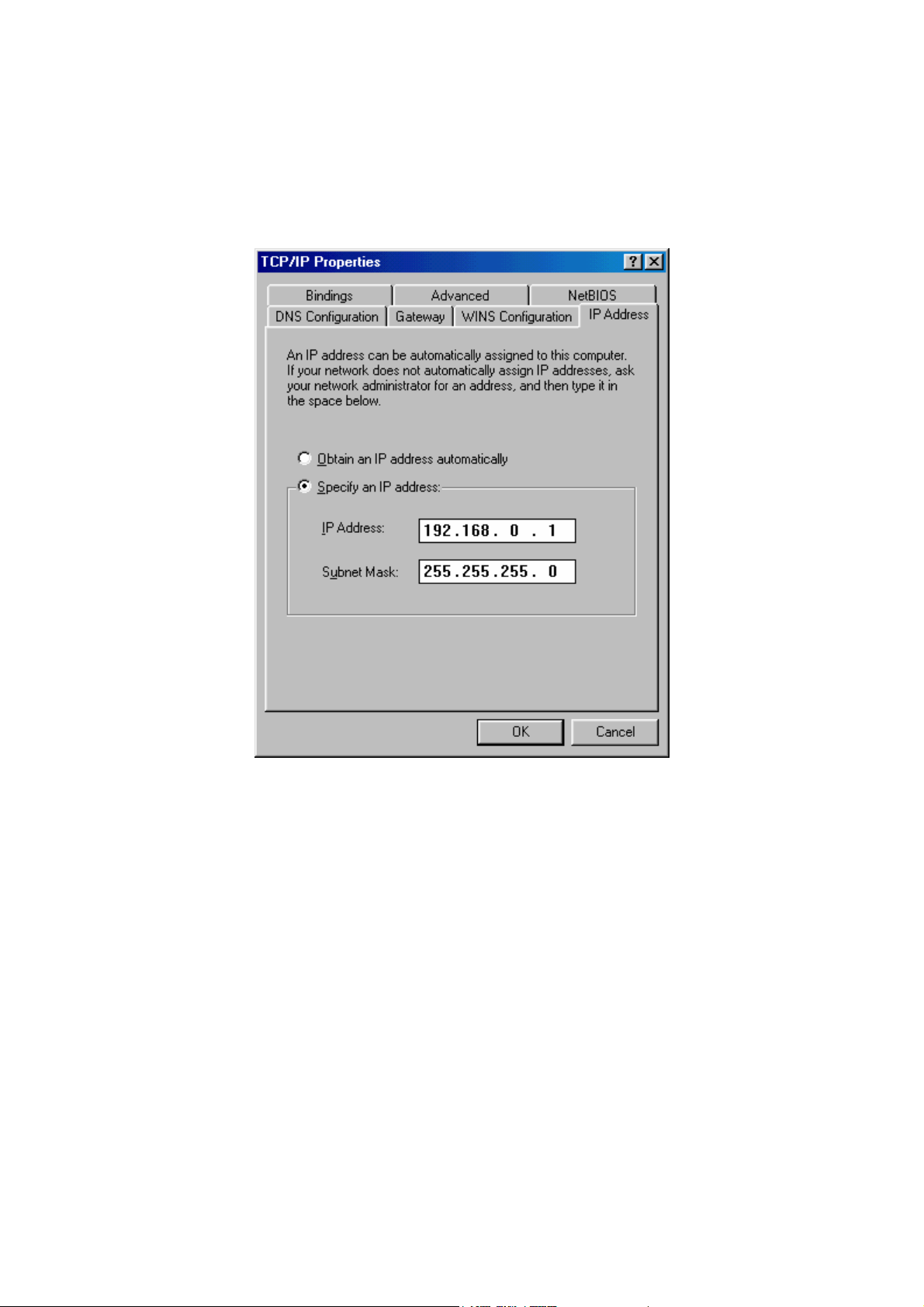
Step 4: Immediately after software installation, go to the TCP/IP Properties window (Figure
2) to configure this network protocol (TCP/IP) over the FireNet application. Specify the cor-
rect IP address for the current host PC and fill in the Subnet Mask field.
Note: You can skip Step 4 if you do not wish to install the TCP/IP protocol over FireNet.
However, you must install the network protocol provided, such as NetBEUI.
Figure 2
Step 5: When prompted, restart your PC.
Step 6: Connect the 1394 cables.
You now have installed on your PC a complete and fully functioning version of FireNet software. Upon initial installation, its usage is restricted to an evaluation period of 30 minutes, at
the end of which the application will automatically turn off (without affecting the rest of your
computer operations in any way). You can repeat the demo as many times as you wish by
simply rebooting your PC.
8

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Note: You may receive, during the installation process, a message requiring the “FireNet In-
stall Disk” (indicating that the “ubfwdev.sys” file cannot be found).
In this case press OK. The Copying Files Window will prompt you to enter the Windows system folder in the Copying files from dialog box (i.e. C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM\) as the Figure 3
below shows:
Figure 3
9
Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Important Note for Windows Millennium users
For the Windows ME operating system ONLY, Microsoft has included FireWire networking
support through its “NDIS 1394 Net Adapter”, which is based on the IP over 1394 specification. This is a feature which is similar to FireNet but with less performance.
Because both FireNet and NDIS 1394 Net Adapter are based on the IP/1394 specification,
when FireNet is installed in Windows ME, it will disable NDIS 1394 Net Adapter and enable
the Unibrain 1394 FireNet Adapter. You can verify this configuration by going to the System
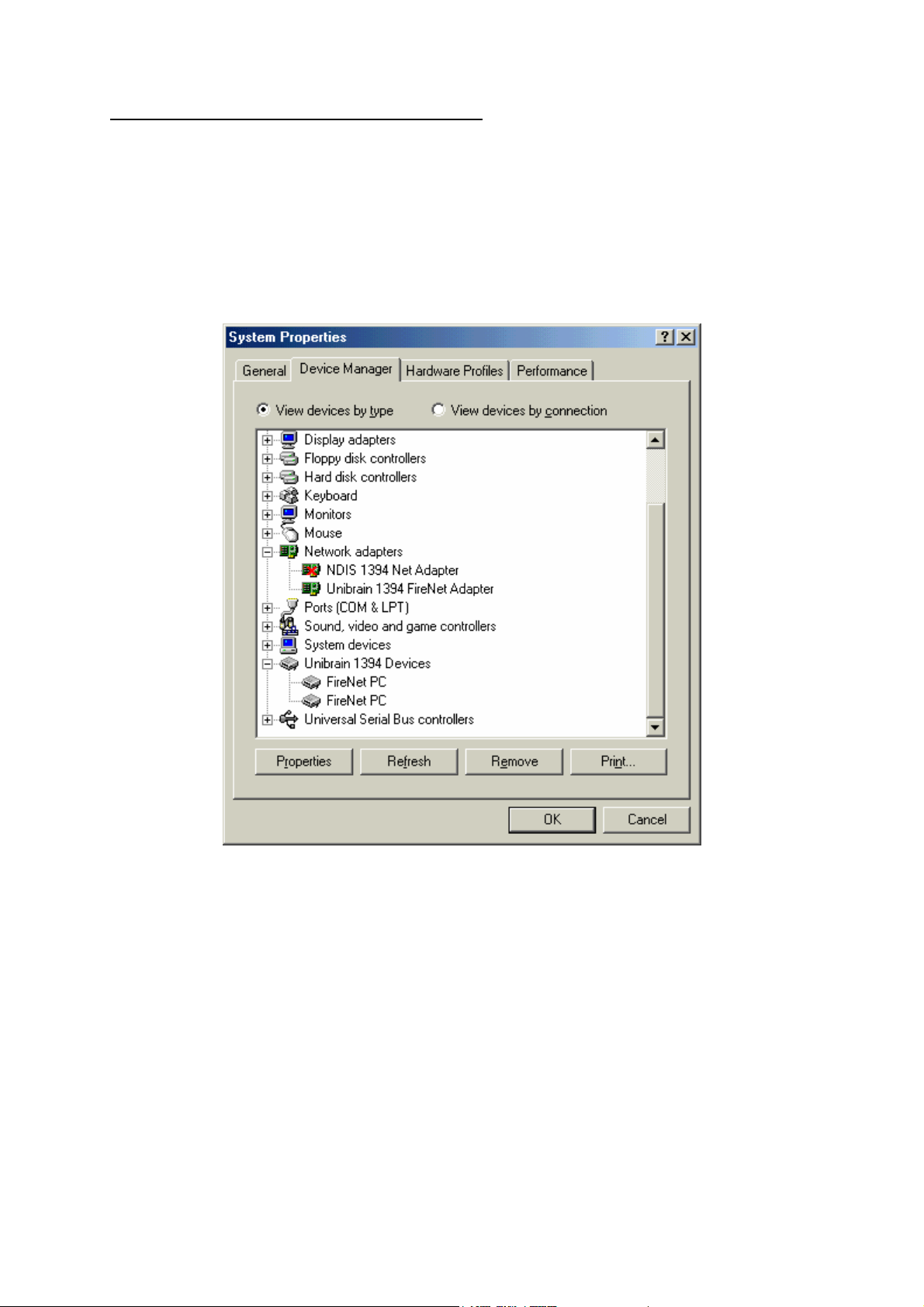
Properties window and clicking on Device Manager, as Figure 4 below shows:
Figure 4
IMPORTANT: If you wish to enable the Microsoft "NDIS 1394 Net Adapter", you must first
uninstall the FireNet software and then reboot your machine.
10

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
FireNet™ Installation for Windows 2000
Before you begin, it’s helpful to note that installation instructions are common for both Windows 2000 Professional and Windows 2000 Server/Advanced Server.
You need though a different Product Key for each version. (See Authorization Procedure for
product key requirements.)
FireNet 2.0 SERVER (and later) offers two new important features:
Mac OS compatibility, through the File Services for Macintosh, which are included in the
server versions of Windows 2000. Firenet 2 (or later) for Mac clients is also required.
Multiple 1394 adapter support. This gives the ability to extend the 400 Mbps bandwidth by
adding up to four OHCI adapters.
Installing FireNet on Windows 2000 is simple and straightforward. Note that steps 1 through
6 apply whether you are installing FireNet for evaluation or entering product key numbers to
enable continuous use of the software.
Step1: Check that your 1394 OHCI controller is correctly installed and properly recognized
by your operating system by going to the System Properties window and clicking on Device
Manager.
Step 2: IMPORTANT! Always UNPLUG the connecting IEEE-1394 cables between all net-
work computers before you begin installing or uninstalling FireNet software.
Step 3: Locate and run the "firenet.exe” executable file, and follow the instructions on the
dialog boxes. The installation procedure will install all the required FireNet software into your
system along with the Authorization application and the driver’s version checking utility.
When the “Digital Signature Not Found” dialog box will appears, press “Yes” to continue
(Figure 5).
Figure 5
11
Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Note: Since installing drivers in Windows 2000 requires Administrator privileges, if a user
with non-administrative rights attempts to install FireNet, the following error message will appear:
Figure 6
If this is the case, abort the installation, log off and logon as an Administrator.
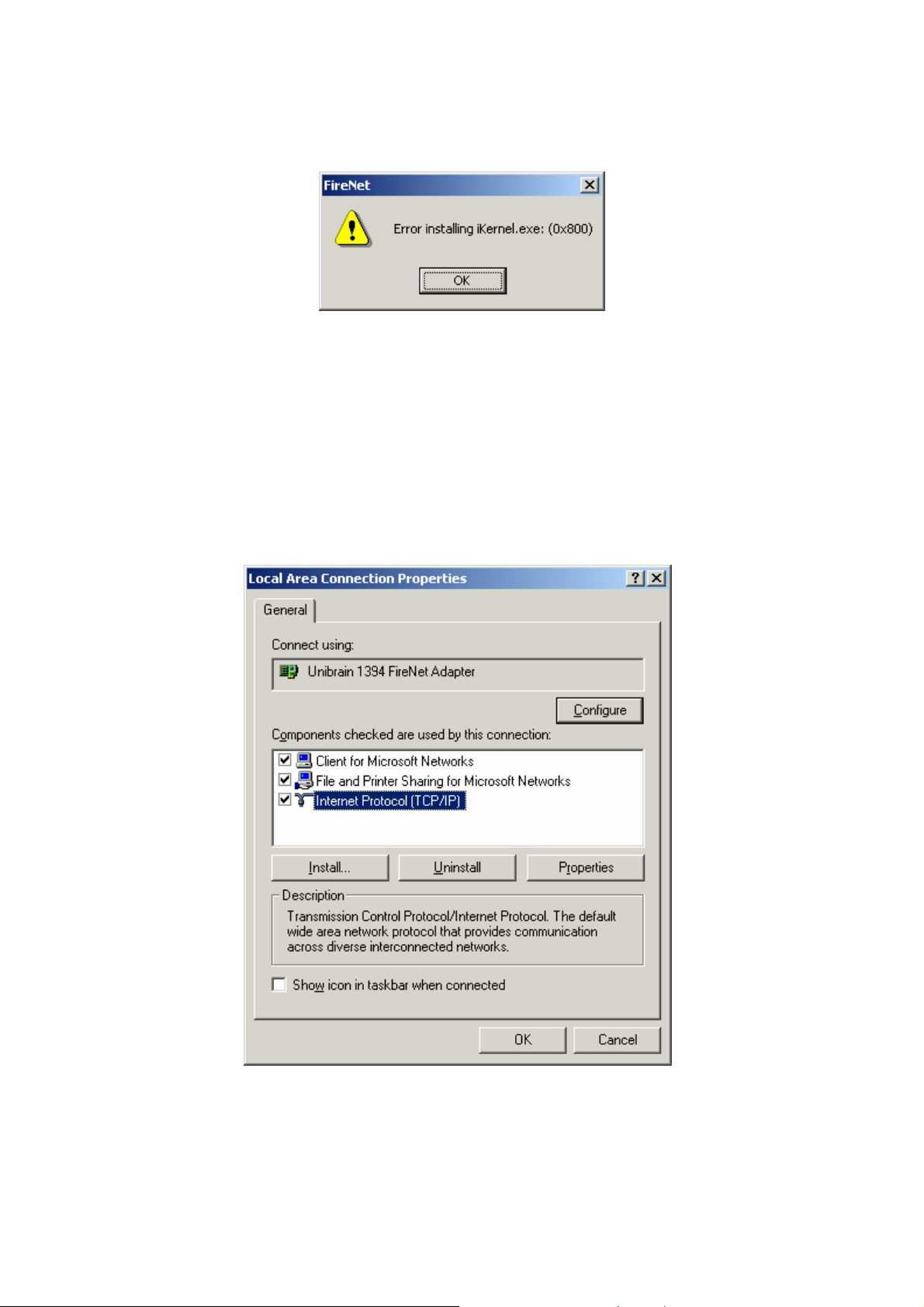
Step 4: Immediately after FireNet™ installation for Windows 2000, you have to complete the
TCP/IP properties in order to configure this network protocol over the FireNet™ application.
Click on "Start
Æ
Settings Æ Control Panel Æ Network and Dial-up Connections Æ Local
Area Connection" to see the Local Area Connection status. Click on Properties and you will
get the next dialog box:
Figure 7
12
Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
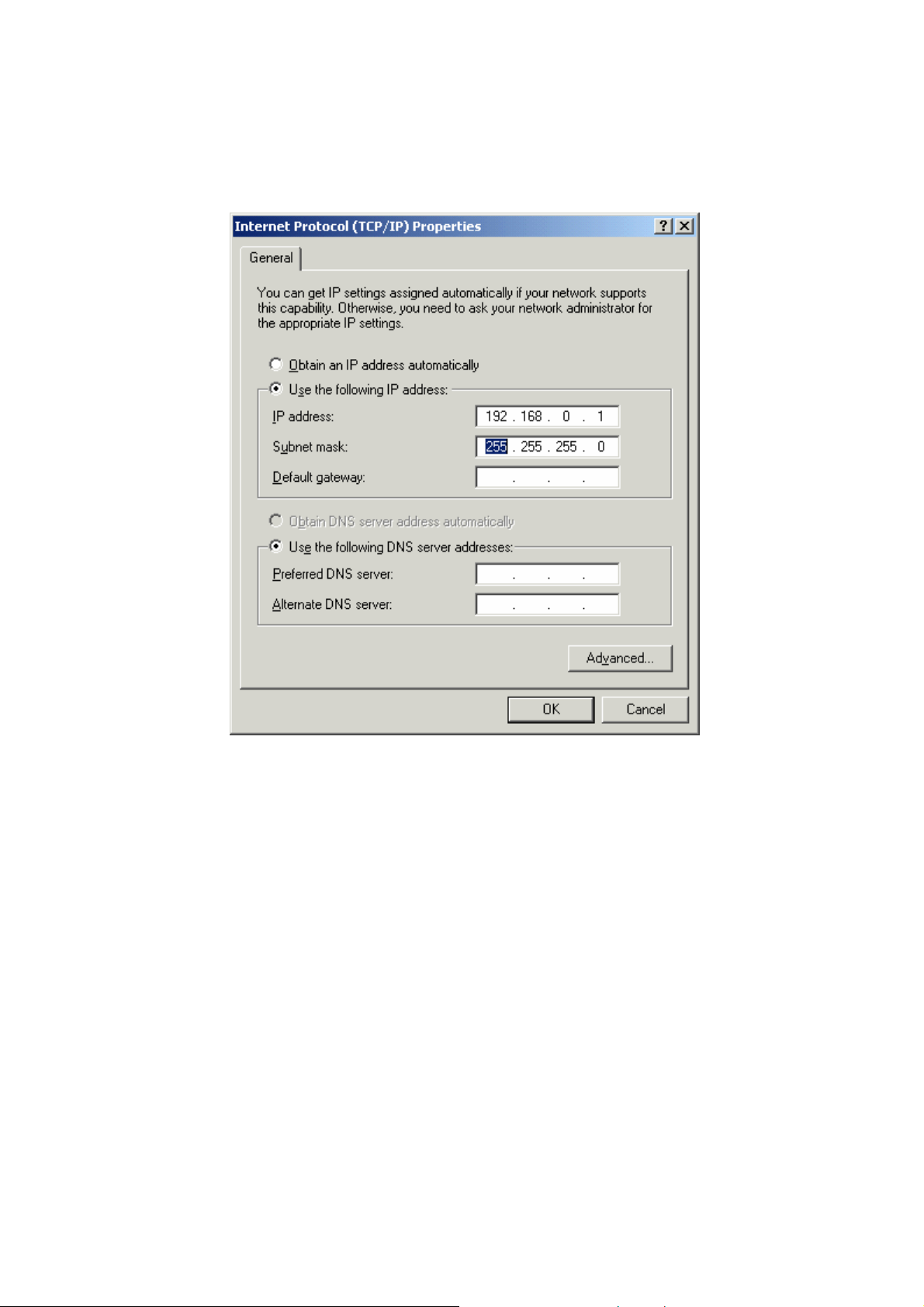
Highlight the "Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)" component and press the Properties button to configure the TCP/IP properties. Please specify the correct IP address for the current host PC
and fill in the Subnet Mask field, as Figure 8 shows:
Figure 8
IMPORTANT: You can skip this step if you do not want to install the TCP/IP protocol
over FireNet™. However you must install another networking protocol, such as
NetBEUI (check the section “Using Firenet with protocols other than TCP/IP”, on page
16).
Step 5: Reboot is NOT required after FireNet installation for Windows 2000!
Step 6: Connect the 1394 cables.
You now have installed on your PC a complete and fully functioning version of FireNet software. Upon initial installation, its usage is restricted to an evaluation period of 30 minutes, at
the end of which the application will automatically turn off (without affecting the rest of your
computer operations in any way). You can repeat the demo as many times as you wish by
simply rebooting your PC.
13
Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
FireNet™ Installation for Windows XP
Installing FireNet for Windows XP is similar to installing it for Windows 2000. Although, there
are some important differences due to XP’s built-in 1394 networking (which is based on IP
over 1394). In order for FireNet to operate properly, it must disable this inherent XP networking. Thus, please follow these steps when installing FireNet for Windows XP (Home and Pro
Editions):
Step1: Check that your 1394 OHCI controller is correctly installed and properly recognized
by your operating system by going to the System Properties window and clicking on Device
Manager.
Step 2: IMPORTANT! Always remember to UNPLUG the connecting IEEE-1394 cables be-
tween all network computers before you begin installing or uninstalling FireNet software.
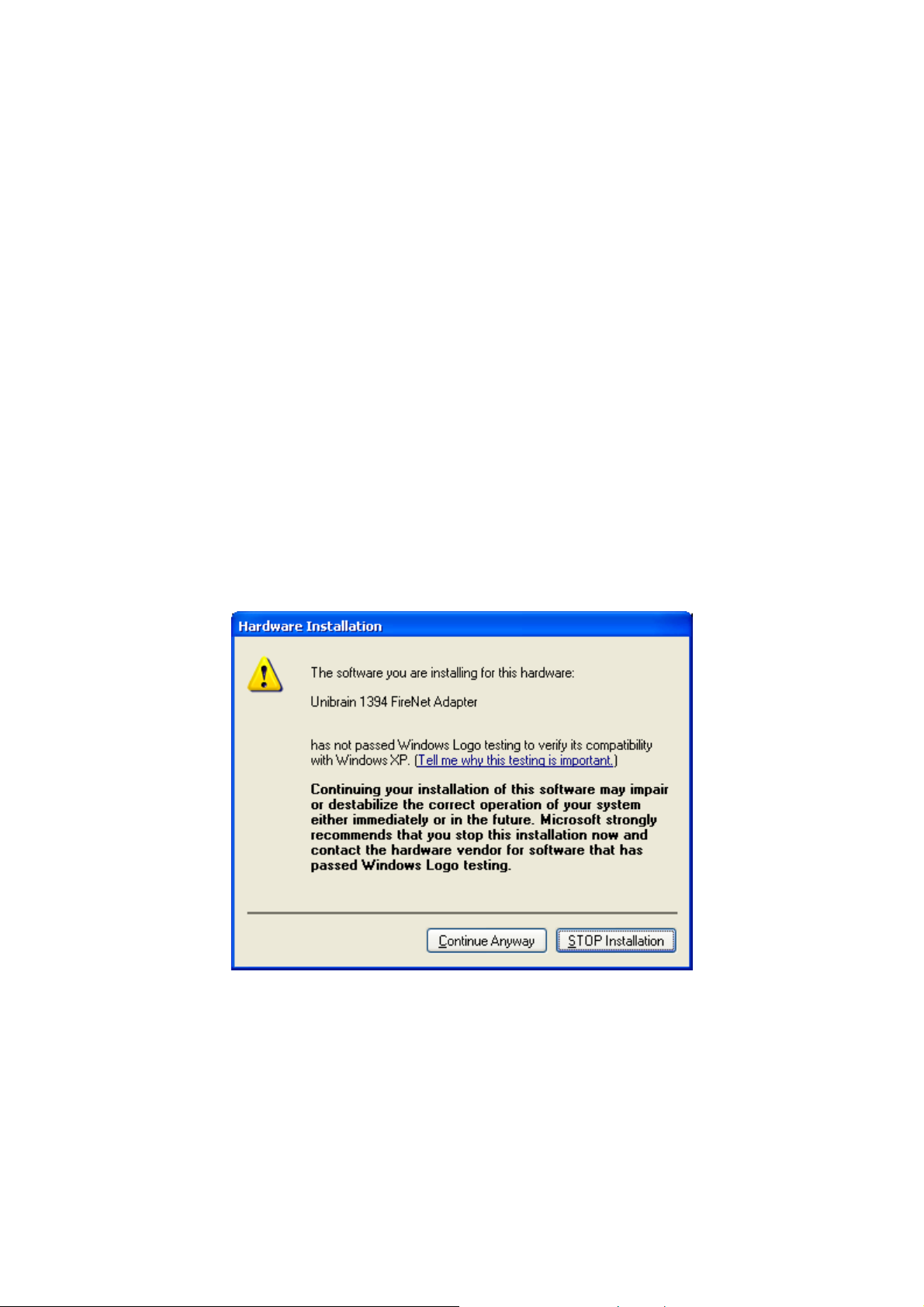
Step 3: Execute the FireNet installation file and follow the instructions on the dialog boxes.
The installation procedure will install all the required FireNet software into your system along
with the Authorization application and the driver’s version checking utility.
When the following dialog box appears, press “Continue Anyway” in order to continue the installation:
Figure 9
Note: This dialog appears because the current version of FireNet is not WHQL certified. Fu-
ture versions (2.3 and later) will get the Windows XP Logo and, and this dialog box will not
appear.
Step 4: When the installation procedures is complete, select Finish and reboot your system.
You can safely now plug-in the 1394 cable.
14
Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Step 5: When the system restarts (and after you have connected your FireWire cables), the
Found New Hardware Wizard dialog box should appear (Figure 10). If it does not appear,
jump straight to Step 6.
Figure 10
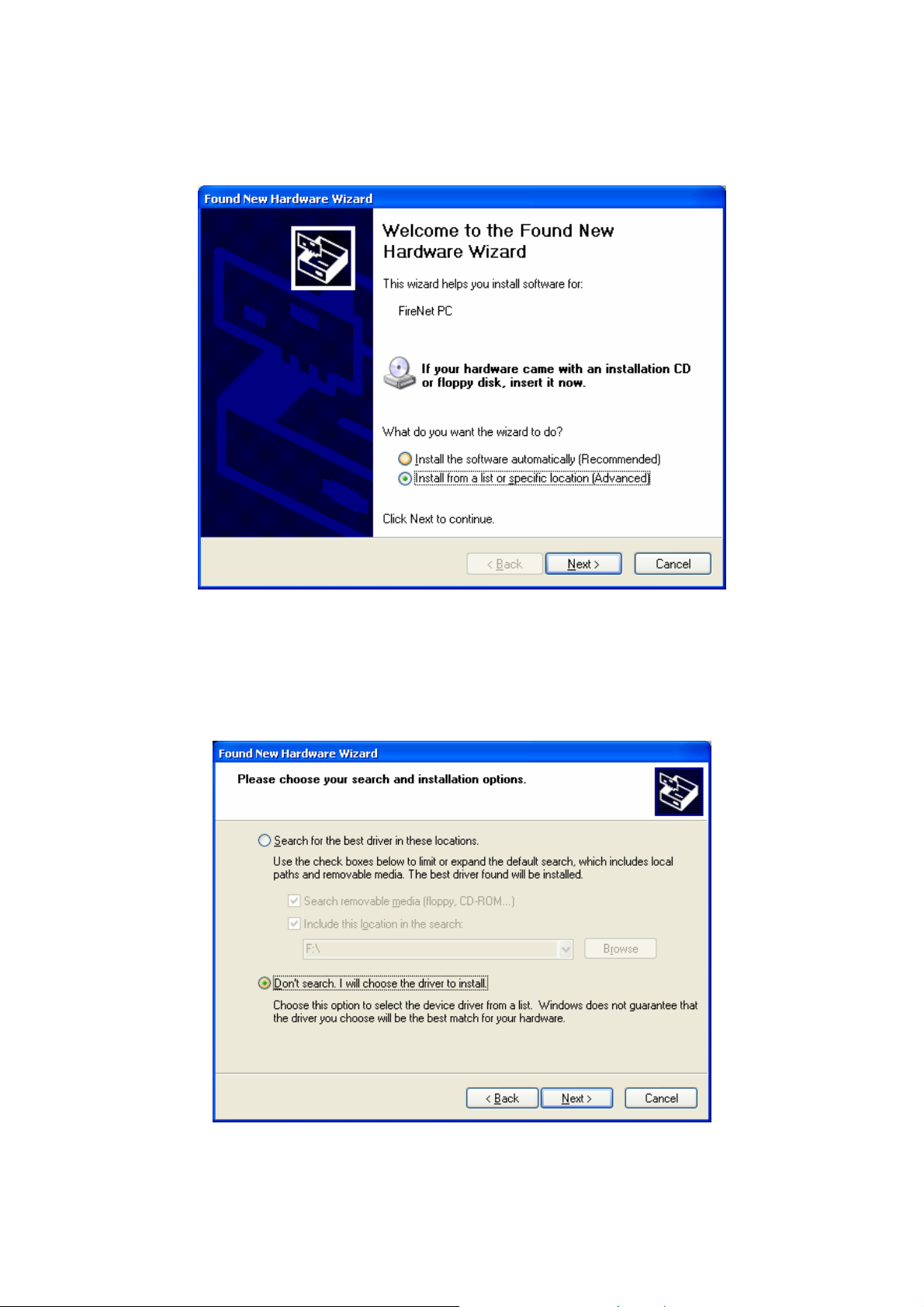
In the Found New Hardware Wizard dialog box, choose “Install from a list or specific location”
as Figure 10 depicts and press “Next”.
From the dialog box that appears, choose “Don’t Search. I will choose the driver to install”, as
Figure 11 shows:
Figure 11
The Hardware Update Wizard dialog box will appear. Choose “FireNet PC” and press Next.
You are now ready to continue to Step 6 of the installation.
15

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Figure 12
Step 6: When the system restarts after the Firenet installation and the dialog box, mentioned on Step 5, does not appear, you must do the following:
Go to Device Manager (Control Panel Æ System Æ Hardware) and from the View Menu
choose “Show Hidden devices”, as shown in Figure 13:
Figure 13
Select “IEEE 1394 IP Network Enumerator” from the list of hidden devices. When expanded,
it allows you to see the number of FireWire networked systems that exist on the 1394 bus (all
named “1394 Host”). For example, in Figure 14, you can see 2 such entries which means
that the total number of networked systems, through Firewire, is 3.
Right click on the first “1394 Host” entry and choose “Update Driver…”
16

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
The following dialog box appears:
Figure 14
Figure 15
Choose “Install from a list or specific location” and follow the guidelines exactly as described
in Step 5 (Figure 11 and forth).
FireNet is now completely installed. You can verify this by going to Device Manager and
choosing Network Adapters (Figure 16). Both the disabled Microsoft XP “1394 Net Adapter”
and the enabled “Unibrain 1394 FireNet Adapter” are listed.
17

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
The “Unibrain 1394 Devices” (also shown in Figure 16) lists each computer as either “FireNet
PC” or “FireNet Mac”, depending on the types of systems networked in your infrastructure.
Figure 16
Step 7: Now, you’re ready to configure the rest of the TCP/IP & Network settings. Go to
Control Panel Æ Network Connections Æ Local Area Connection to see the Local Area Connection status.
Note: The “1394 Connection” (associated with Microsoft’s 1394 Net Adapter) will also be
disabled during FireNet installation, so there is no need to configure it. Additionally, if a Fast
Ethernet adapter is already present in your system, the FireNet connection may be given the
next available name (“Local Area Connection 2” or …3, 4 and so on).
Next, click on “Local Area Connection Properties” and choose a connection status. As an example, to enable continuous connection status, the “Show icon in notification area when connected” is selected below:
18

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Figure 17
Choose “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” and press the “Properties” button. From there you can
enter the appropriate TCP/IP address and Subnet Mask for your system. If there is a DHCP
server in your network, choose “Obtain an IP address automatically”.
Figure 18
IMPORTANT: If you wish to enable again the Microsoft “1394 Net Adapter", you must first
uninstall the FireNet software and then reboot your system.
19

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Installing FireNet™ Server Edition with multiple 1394 adapters
As we told above, you can install up to 4 OHCI-1394 adapters in a Windows 2000 Server &
Advanced Server system. Below we will describe the procedure for enabling more than one
Firenet Network Adapters, because the installation enables by default only 1 adapter, the 1
one that is enumerated from the PCI bus.
Follow Steps 1 through 4 to install each adapter, whether it has been preinstalled in the system or added after installation of FireNet software:
Step 1: Go to Control Panel and choose “Add/Remove Hardware”. In the dialog box that
appears, press “Next” and then “Add/Troubleshoot a device”.
Step 2: After some search for PnP hardware, a dialog box appears with numerous devices
listed. Choose “Add a new device” and press “Next".
Step 3: In the next dialog box, choose “No, I want to select the hardware from a list” and
press Next.
Step 4: From the Hardware Types list, choose “Network Adapters”, as Figure 9 below
shows:
st
Figure 19
Step 5: From the manufacturers list that appears, scroll down until you find “Unibrain 1394
FireNet adapter” and press “Next.” The driver will then be installed (the files were already installed during the initial FireNet installation) and the “Digital Signature” window will appear:
20

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Figure 20
Press “Yes” and then “Finish”. The adapter is now installed and you can immediately connect
extra clients into it.
You can see the extra adapter appear in the Windows Device Manager, as Figure 21 shows:
Figure 21
21

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Verifying Installation for Windows 98/98SE/Me/2000/XP
You can connect your networked PCs via 1394 cable in any topology as long as you do not
close the bus (i.e. connect them in a loop).
To verify that FireNet installation is complete go to the System Properties window and click
on Device Manager. Under "Unibrain 1394 Devices", the number of “FireNet PC" will equal
the total number of PC’s connected to your computer.
The example in Figure 22 below lists two FireNet PCs, verifying that there are two PC’s connected to the computer, for a total of three PCs in the bus.
Figure 22
Important Note: If you have successfully installed FireNet™ that DOES NOT IMPLY that
you have a network connection. YOU NEED TO SETUP A NETWORK PROTOCOL (i.e.
TCP/IP) BEFORE CONNECTING TO YOUR NETWORK NEIGHBORHOOD!
If you want to learn more about Windows networking, please refer to Appendix A.
22

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
The FireNet™ installation procedure installs the "File and printer sharing for Microsoft Networks" service, as seen in the Network Properties window (for Windows 98/SE/Me – Left
Figure) and the Local Area Connection Properties (for Windows 2000 - Right Figure).
Figure 23
Using the Start Menu Æ Program Files Æ FireNet shortcut, you will see the 2 installed tools:
"FireNet Authorize" and "FireNet Version". The last shortcut displays the versions of the
FireNet™ software components and the version of the Microsoft 1394 stack files. The following picture is from Windows XP Pro Edition and the latest version of Firenet (2.2).
Figure 24
23

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Using Firenet with protocols other than TCP/IP
If you intend to use FireNet with NetBeui or IPX/SPX, you will need to configure the Ethernet
packet size on the driver settings.
FireNet versions 1.21 and later have the added ability to automatically change the maximum
payload via the Advanced Settings Tab in the driver properties. The user can choose between two main options (Automatic or Ethernet Packet Size) or set the maximum payload
from 256 – 2048 bytes.
The FireNet automatic default setting is valid for TCP/IP and modern 400 Mbit 1394 OHCIbased PCI adapters.
When using FireNet with NetBeui or IPX/SPX, you must choose the “Ethernet Packet Size”,
as shown in Figure 25 below. This will require a reboot in Win98 & WinMe but not in Windows 2000.
There are also various sizes for the maximum payload value, ranging from 256 – 2048 bytes
in 256 byte increments. You can experiment with these sizes if you continue to have communications problems with older (or non Texas Instruments chipset) 1394 adapters when the
automatic setting does not resolve them. Please note that a smaller packet size can seriously
degrade network performance.
Figure 25
Technical Information about the Maximum Payload Setting:
24

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Ethernet adapters use packet size, with a maximum payload of 1514 bytes. All protocols
comply with this maximum 1514-byte payload, with the exception of the high-performance
TCP/IP protocol, which has the ability to take advantage of higher packet sizes.
Modern IEEE-1394 PCI adapters (400 Mbps) support maximum payload size for asynchronous packets of 2048 bytes while older ones (200 Mbps) support 1024 bytes. There are also
some 400 Mbps - 1394 PCI adapters (Orange Micro for example, which is based on the Nec
-OHCI chip) with a maximum payload of 1024 bytes. In such a case a Maximum payload size
of 1024 bytes or “Ethernet packet size” must be set.
FireNet versions 1.21 and later have provided the ability to automatically change the maximum payload via the Advanced Settings Tab in the driver properties. The user can choose
between two main options (Automatic or Ethernet Packet Size) or set the maximum payload
from 256 – 2048 bytes.
25

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Authorization procedure
To enable an unrestricted use of the FireNet™ software, a unique "Name" and “Product Key” combination per station is required. You can purchase Product Keys online
or at any local distributor, in order to enable FireNet™ to run continuously.
After obtaining a Product Key for each station (computer) on your FireWire network, run the
"FireNet Authorize Utility" application (Figure 26) by keying in the following:
Start
Æ
Program Files Æ FireNet Æ FireNet Authorize
Enter your Name and the Product Key in the appropriate fields and press OK. The application will display a message indicating if the operation was successful or not.
Figure 26: Unibrain FireNet 2.x Authorization Utility
Note: FireNet 2.x STATION product keys are different from those required for FireNet 2.x
SERVER. Thus, if you accidentally enter a computer key to a Windows 2000 Server, you’ll
see this error message:
26

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Un-installing FireNet™
Important: Always remember to UNPLUG all IEEE-1394 connecting cables between
PCs before Uninstalling or Installing FireNet software!
To uninstall FireNet software, go to the Control Panel and double click the Add/Remove Programs icon. Select the FireNet application and press OK.
When the uninstall procedure ends, please reboot your system.
Note: In case you have any problems with the uninstall procedure, please refer to our FAQ
section.
27

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Appendix A: General networking guidelines
1. From your desktop, right
click on the Network
Neighborhood icon, select
the Identification tab and en-
ter a unique name for this
computer that will identify it on the FireNet
network (i.e., Station 1). Next, enter a
Workgroup Name to be used for all computers on the network.
2. If this is the first time Windows networking is being installed on your computer,
you will be prompted for a network User
Name and Password when Windows restarts. Do NOT bypass this screen or you
will not be able to access your FireNet network or any other network: Do NOT press
the ESC key, cancel button, or “X” button in
the upper right corner to close this window.
Instead, continue by entering a User Name
Figure A1
(i.e., Station 1) and a (optional) Password
when prompted.
Figure A3
Figure A2
3. Other computers on the FireNet network cannot
access resources (drivers, folders, files, or local
printers) on your computer until you designate t
as “shared”. Likewise, you cannot access resources on another computer until those resources
have been shared. To do this, navigate to the drive
or folder you want to share. Right click on it and
select “Shared As:” Enter a share name; select the
type access that you want this resource to have
(i.e. “Full” for complete access to the resource).
Select apply and then OK.
Note: You can access shared resources on the
network by double clicking the Network Neighborhood icon on your desktop or through Windows Explorer. There may be a small delay (2-3 min) before
you will be able to “see” computers in the Network
hem
28

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Neighborhood. If you want to minimize the delay, or if you fail to see the computers in the
Network Neighborhood, right click on Network Neighborhood icon, and select “Find Computer”. In the pop-up window type the name of the computer you want to connect to and click
on “Find Now”. This will find the requested computer and automatically update and restore
the computer(s) in the list.
Note: The pictures above are captured from a Windows 98 system. The whole procedure is
the same for WinMe, but in Windows 2000, you will find the workgroup/domain and Computer Name information by first right-clicking the “My Computer” icon. Choose the “Network
Identification” tab and press the properties button:
Figure A4
29

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Appendix B: Benchmarks for FireNet™
The following is an overview of the performance of FireNet™ when used with Microsoft and
Mac operating systems. Extensive tests have been performed using workstation PCs
equipped with Pentium III at 866/128MB Ram, Ultra ATA/100 HDD and one Windows 2000
Server with PIII at 1 GHz/256 MB Ram, Ultra ATA 100 HDD. TCP/IP protocol was used for
the network interconnection of the PCs.
All the benchmarks were conducted in the Windows 2000 environment because this is the
only OS that can take advantage of the 400 Mbps bandwidth the 1394 bus offers.
Two kinds of tests were performed:
• The first group of tests consisted of various real-time file copies between two computers.
These tests demonstrated the real-life performance that a user can expect from FireNet.
But please notice that Firenet’s potential cannot be achieved in these tests, mainly because of the HDD bottleneck.
• To overcome those limitations we made another group of tests using network benchmark
utilities (like Ziff Davis Netbench
measure true network throughput without using the HDD. We also made our own custom
test for the PCs, which can be easily replicated by anyone, since they are based on simple file copies.
In the end of the section, there is a discussion about network speeds and some of the variables that can cause confusion surrounding real-world performance.
1
& netio for the PC and Helios LanTest2 for Mac), which
1
Ziff Davis NetBench 7.01 can be downloaded for free from the following location:
http://etestinglabs.com/benchmarks/netbench/netbench.asp
2
Helios LanTest can be downloaded for free from: http://www.helios.de/products/LanTest.html
30

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Tests using Network Benchmarks
i) Ziff Davis Netbench 7.01
Because this test is most oriented in corporate environments, you must use at least 3-4 clients in order to get reliable results.
Our configuration involved a Windows 2000 Server (which was running the Server/Controller
portion of the test) and 4 Windows 2000 Professional clients (which were running the client
portion of the test).
All systems were running the latest version of Firenet (2.2). As a 1394 adapter we used Unibrain’s Fireboard-400 OHCI adapter and the systems were connected with standard 4.5 m
6p to 6p 1394 cables.
Below you can see the graph results we got after running the Netbench network suite.
The results are for 1K, 2K, 4K, 8K, 16K, 32K & 64K packet size.
As you can see, for 32 K & 64 K packet sizes, Firenet reaches almost 240 Mbit/sec.
Figure B1
31

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
ii) netio benchmark: Point to Point (2 nodes) connection
This test involved two PCs (a Windows 2000 Server and a Windows 2000 Professional) in a
point-to-point connection while netio
3
benchmark run in both machines. The picture below
shows Windows 2000 Performance monitor, while netio benchmark runs.
The green line indicates the Network throughput while the red line indicates the CPU usage,
which starts from 100% occupancy and drops to around 65% for larger packet sizes.
Figure B2
The following picture shows the results of the netio benchmark for various file packet sizes:
Figure B3
Please notice that for a point to point connection, Firenet has a performance of around 23
MB/sec.
3
Netio can be obtained for free from: ftp://ftp.leo.org/pub/comp/os/os2/leo/systools/netio111.zip
32

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
2. Custom Unibrain Test on PCs
For the following test, we used three client computers running Windows 2000 Professional
connected to a Windows 2000 Server in a common 1394 bus. For each client a drive letter
map was created with a shared directory in the server and the following batch file was running:
: loop
copy p:\test /y
goto loop
Where p:\ is the server map and test is a 40 MB file.
The advantage of this test is that, because the Server is equipped with 256 MB of RAM, the
repetitive file copy does not affect its HDD. Everything is done on RAM. Thus, the benchmark
can measure true network throughput and performance.
The graph below (Figure B4) was captured from the server’s Performance Monitor. It shows
how Firenet gradually increases in performance while, one by one, the 3 clients start running
the batch command. The green line depicts the network throughput in MB/sec and the red
line indicates CPU usage. When the first client is connected there is a network throughput of
13 MB/sec. The second client increases throughput to 19 MB/sec and the third client increases it to 21-22 MB/sec.
Figure B4
33

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
For comparison, we repeated the same benchmark, but this time we connected both the
server and on a Fast Ethernet switch. As expected, the server network adapter topped at
around 11.5 MB/sec (90 Mbit/sec).
Figure B5
34

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
3. Firenet in Windows 2000 Server and Mac clients
The test was performed using a Windows 2000 Server and 3 Apple G4 clients, connected
one at a time and each running the Helios LanTest. Below (Figure B6) you can see the
Server Device Manager, which shows the 3 Mac G4 clients under the “Unibrain 1394 devices” group.
Figure B6
Figure B7
This picture (Figure B7) was captured from the server’s Performance Monitor. Notice how the
network performance increases as each G4 is connected.
35

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Network Performance – Some Considerations
From recent correspondence, it has become increasingly clear that there is a considerable
amount of confusion whenever network speeds are discussed. Many users, who still have a problem understanding why 100 Mbps Ethernet does not perform in many cases in the expected 100
Mbit speed, are asking the entirely reasonable question of how the 400Mbps speed achieved with
IEEE-1394 will affect their network throughput.
It would be nice if it was possible to give a single specific answer to this question, but the true
picture is somewhat more complicated.
Network throughput will depend upon 2 main factors:
1. Network software and hardware implementation.
2. Network Bus Topology, Architecture and congestion scaling.
More analytically:
The 1st factor has to do with the Operating System’s Network stack efficiency and the
quality/design of the network adapter (the device that connects the actual computer with the
Network medium).
For example, Windows 9x line (Windows 95, 98 & 98SE, WinME), which was designed with
the home user in mind, cannot take advantage of faster network throughput than Fast
Ethernet. In fact, it can not fully initialize a Fast Ethernet network, no matter how fast the
hardware is.
In such a case, Firenet can not reach it’s true potential under this Operating Systems and, in
the best case, its speed is slightly better than Fast Ethernet.
Things are even worse in the Apple “camp”. Macintosh’s “Personal File Sharing” and
Appletalk provide very low performance even in the newest, state of the art G4 models and
have made Apple users desperate for a faster network solution. The reason behind this inefficiency is the design of these protocols, which has not evolved for many years. They were
designed at the age of 10 Mbit Ethernet and today with speeds reaching the Gbps range,
their inadequacy is larger than ever.
Appletalk has a packet size of just 600 bytes compared with Ethernet’s 1514 byte (and that’s
why it cannot even take advantage of a 100 Mbit Fast Ethernet network) and Firewire’s 2
Kbytes.
The new MacOS X, with its UNIX and TCP/IP roots, is promising to bring to the Mac
world, network performance equivalent with the Windows platform. However, even in MacOS
9.x there are some solutions that can improve network performance. For example, Mac clients can communicate through TCP/IP (bypassing Appletalk) with a Windows 2000 Server
with “File Services for Macintosh” installed. Or, with the use of 3rd party software (like Appleshare IP), they can communicate between them, much faster and reliably compared with
the traditional Appletalk protocol. Under these situations, Firenet performance improves also.
On the other side, Windows NT4, Windows 2000 & Windows XP, which are modern,
32 bit operating systems, can take advantage of the modern ultra fast network implementations. Under Windows 2000/XP, Firenet can reach a speed of around 250 Mbit, near the actual practical bandwidth the 1394 bus can provide.
36

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
An important role has the system architecture in the actual network performance. A
system with a slow CPU or (most importantly) a slow HDD will not be able to take advantage
of the speed a modern network bus can provide.
That’s because network data transfers will eventually end to reading/writing into a Hard Disk.
If the HDD cannot cope with the amount of data arriving, it will slow the whole transfer and
will be the major bottleneck. In the case of Firenet (due to the 1394 to Ethernet emulation
that has to be done), the CPU factor is more important compared with Fast Ethernet. Of
course, in the modern 800+ MHz systems, the overhead is negligible.
The 2nd factor has to do with the Network Architecture (i.e. star topology, ring topology, daisy chain topology etc) and how well it can handle the increasing number of connected nodes. Due to the 1394 bus architecture, Firenet does not have the collision problems
that traditional Ethernet has, as more and more nodes are connected to the same physical
network. Thus, it can scale, much better.
In fact, in point-to-point connections, the 1394 bus initialization barely exceeds the 50% even
under the best conditions (considering computer hardware, Operating System etc). As the
number of nodes, actively generating traffic, increases, Firenet performance improves. At
around 4-6 heavily active systems, Firenet exceeds by almost 300% Fast Ethernet performance.
If the IEEE-1394 bus is being used for other purposes (e.g. video transfer) simultaneously, no significant interference occurs until about 4-5 active stations are there. On the
MAC, the overhead at this time is somewhat greater, as the network conversion is done on
top of Appletalk. Accordingly, the two-station value is only about 70% of Ethernet performance, and 100% is not reached until 4 to 5 stations are in use. On the other hand, the lower
bus occupancy means that the IEEE-1394 bus remains generally free for other applications
such as cameras or printing.
37

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Appendix C: Connecting Firenet with Ethernet
If you have a number of computers networked with Firenet and you want to connect them either to the Ethernet network or to the Internet (through a router), you will have to use a computer as the bridge between the two different physical networks.
The computer that will play the role of the “bridge” will have both a 1394 adapter and an
Ethernet adapter and the operating system must be either an NT Workstation (or Windows
2000 Professional) or (preferably) a server OS (Windows 2000 Server or NT 4 Server)
addition, the TCP/IP protocol must be used throughout the whole network, since it’s a routable protocol.
Below, the Device Manager of a Windows 2000 computer lists both a D-Link Fast Ethernet
adapter and an OHCI 1394 adapter.
4
. In
4
Note, that if you use NT4, you can’t use Firenet because it does not have built in 1394 support. In this case you
can use Unibrain’s ubcore technology with Firenet 4.
38

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
So, the network topology will look like this:
Ethernet
Segment
Firenet
Segment
Win2K
Server
Each segment must belong in a different subnet and the two adapters should be configured
with an IP address of the subnet in which they belong.
For example, let’s assume your network is a class C network containing 64 addresses (so
the subnet mask is 255.255.255.192 or Network Bits are 26): 192.168.0.1 – 192.168.0.63. By
using two segments, we will have to divide the network into two segments. The first one will
use IP addresses from the group of 192.168.0.1 – 192.168.0.30 (Ethernet network) and the
second one from the group of 192.168.0.33 – 192.168.0.62 (Firenet network). The subnet
mask for both segments will be 255.255.255.224. The network address for the first group is
the 192.168.0.0, and for the second group it is 192.168.0.32.
The Ethernet adapter in the server will get an IP address from the first group and the Firenet
1394 adapter will get an IP address from the second group.
Note the IP Forwarding must be enabled in the “bridge” computer so that packets can travel
from one segment to the other. This can be done easily in NT4 by opening the Properties
dialog box for TCP/IP and clicking "Enable IP Forwarding." In Windows 2000/XP, though, this
is more complicated. You must edit the registry.
11. Open regedit to view the Registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
12. Modify this value as follows:
Value Name: IPEnableRouter
Value type: REG_DWORD, Value Data: 1
Note: If there is a DHCP server in the network (which provides IP addresses to the clients),
and you want to use it for the Firenet network, then a special service must be installed in the
“bridge” computer, the DHCP Relay service that will forward DHCP traffic between the two
subnets. This service is available only in Server Operating Systems (NT4 Server or Win2K
server). So Windows 2000 Professional (or NT4 workstation) cannot be used in this case.
39

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Appendix D: Firenet and VAIO notebooks
Sony VAIO notebooks have built-in 1394 support and run networking software called “Smart Connect” which is very similar to FireNet. ”Smart Connect” has two modes: Standard and VAIO mode.
The first is based on the “IP over 1394” standard whereas the second is based on a Sony proprietary method.
Firenet is incompatible with both modes and, when installed, VAIO computers by default (version
1.4 and later) disables “Smart Connect” in a similar way with Microsoft’s built-in “1394 NDIS” in
Windows Millennium.
Figure D1
installed. As you can see, the Fast Ethernet adapter (Intel 8255x) has not been affected at all (and
can continue to operate normally) but the “Sony i.link adapter” has been disabled.
shows the Device Manager of a Windows 2000 VAIO System after FireNet has been
Figure D1
To connect your VAIO computer with your desktop system via 1394, you must install FireNet on
BOTH computers.
40

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Appendix E: Firenet and Mac OS
Windows computers can communicate via FireNet with Mac OS 9.x only when you are using:
• Windows 2000 Server with Services for Macintosh installed
• FireNet version 1.2 for Mac or later.
To install Services for Macintosh in Windows 2000 Server:
1. Log on to the Windows 2000 Server system as a user with Administrative rights.
2. Go to Control Panel, Add/Remove Programs, Add/Remove Windows Components.
3. In the Windows Components dialog box, scroll down the list and choose “Other Network
File and Print Services”.
4. Press the “Details” button and check the file and/or print services for Macintosh, as
shown in Figure E1:
Figure E1
5. After the file is installed, open the “Computer Management” tool found in the Administra-
tive Tools. Select the “Shared Folders” option and then right-click and choose “Configure
File Server for Macintosh”. From there you can set a welcome message, passwords for
users, concurrent connections and so forth.
6. After you set up this, expand the “Shared Folders” option and right-click on the Shares
icon. Choose “New File Share”. In the window you can choose a local folder to share and
make it accessible from Windows & Mac clients, as the picture below shows.
41

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Figure E2
Mac computers will appear as Unibrain 1394 devices in the Windows Device Manager. The
picture below indicates a FireNet network of TWO PCs, One MAC, and an HP Printer
equipped with Unibrain’s Fireprint product.
Figure E3
42

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Firenet for Mac OS X 10.1 (or later)
If you have a system running Mac OS X 10.1 (or later) you can install the special version of
Firenet for it. In this case, the Mac will be able to communicate directly with the Windows client, without the need of a Windows 2000 Server system (with Mac Services installed) or a 3
party utility, like PCMacLan or DAVE.
This can be done with 2 ways:
i) by using the SMB protocol provided in Mac OS X
ii) by using pure TCP/IP connection through FTP, HTTP etc.
For more information on how to setup SMB in your Mac OS X system, please refer to the following URL:
Note: With SMB, the Mac will be able to connect to a Windows share but the opposite is not
feasible.
As soon as you install Firenet in the Mac OS X system and plug the cables, the following dialog box will pop-up in your Windows 2000/XP system:
http://www.opensource.apple.com/projects/documentation/howto/html/osxsmb.html
rd
Figure E4
Choose “Install from a list or specific location” and press Next. The following dialog box will
appear (Figure E5). Choose “Don’t search. I will choose the driver to install” and press Next.
Figure E5
43

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
The following dialog box will appear (Figure E6):
Figure E6
Choose “Firenet Mac” and press Next. The system will then add the “Firenet Mac” entry under the “Unibrain 1394 devices” list in Device Manager (Figure E7):
Figure E7
Note: While SMB network speed is very fast when copying rather small files, it gets very slow
for large file (i.e. above 100 MB) transfers.
44

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Appendix F: Firenet FAQ
1. I have installed Firenet and the computers seem to be connected because can ping
each other and see shares. However, when I try to actually copy files, I get a time
out or a connection error.
A: Your 1394 adapter is using a chip that utilizes a buffer block size of 1 Kbyte instead of
2 Kbytes. 1 Kbyte is the standard according to the 400 Mbit specification. There are sev-
eral companies that make this type of adapter. For example, 1394 adapters based on the
NEC chipset use 1-Kbyte packet sizes.
Solution 1: Install the latest Firenet version, which automatically adjusts the block size
with the one supported by the adapter.
Solution 2: If the above does not solve the problem, change the Firenet maximum pay-
load either to 1 Kbyte or to “Ethernet Packet size”, as described in page 19 of this man-
ual.
2. During the Firenet installation in Windows 98/WinME, a dialog box appears asking
for the location of the ubfwnet.sys.
A: This is an installation glitch, which has to do with the implementation of the networking
components installation in Windows 98/WinME. Simply complete the path of the
\windows\system directory (i.e.: c:\windows\system) and the installation will continue and
finish normally.
3. Can I connect a computer with Firenet installed to a Windows Me (or Windows XP)
PC with Microsoft’s 1394 NDIS?
A: For the moment "no". Firenet is not compatible with MSNDIS1394 because the latter
is based on “IP over 1394”. Firenet is based on Unibrain’s proprietary technology,
“Ethernet Emulation” which is much more efficient for network connections.
Firenet 3, scheduled for release in 4
have full compatibility with MS 1394 NDIS of Windows Me/XP.
th
Quarter of 2001, will support IP over 1394 and will
4. When I copy large files in Windows ME, performance drops dramatically.
A: This is a problem with Microsoft’s NDIS driver. It has nothing to do with FireNet (the
same problem exists with Ethernet). After the file transfer is complete, reboot the com-
puter to regain the network speed.
45

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
5. I have noticed that Firenet does not assign a permanent Mac address to the 1394
adapter. How can this be solved?
A: Because you have not yet authorized Firenet for unrestricted use. Once you’ve obtained a
Product Key number and have entered it in the system, the 1394 adapter will be assigned a
permanent MAC address.
6. I have installed Firenet in Windows 2000 and the network does not work and/or the
computer crashes.
A: You are probably using another protocol other than TCP/IP. Either remove all other proto-
cols and use TCP/IP, or go to the driver advanced settings and adjust the maximum payload
to “Ethernet Packet Size”. (See the section “Using Firenet with protocols other than TCP/IP”).
7. My notebook cannot recover from standby/sleep mode when I have Firenet installed.
A: When establishing connections between more than three computers via IEEE-1394 be
sure to set all the computers so that they do not go into suspend, hibernation, or standby
mode.
If more than three computers are connected and one of the computers enters suspend, hiber-
nate, or standby mode, file transfer between the other connected computers may be dis-
rupted. If this occurs: i) first, remember to disconnect all 1394 connecting cables between the
networked computers. ii) Restore the computer that has entered suspend, hibernation or
standby mode, and reconnect the 1394 cable.
Important: Also note that standby mode should always be disabled in Win98/WinMe but it is
not necessary to disable it in Windows 2000. Firenet 1.4 or later can handle power manage-
ment issues in a more efficient way.
8. Can I install Firenet in my desktop PC and connect it to my VAIO notebook?
A: No. Firenet is incompatible with Sony’s “Smart Connect” software, which can be found in
VAIO notebooks. You must install Firenet in both computers. (For more information, refer to
Appendix D of this manual).
9. How can I connect my Mac computers to a network with Windows PCs via FireNet?
A: You’ll need to install a Windows 2000 Server with Services for Macintosh. In this case, Mac
computers will be able to use a file-share directory in the Windows 2000 Server computer. For
more information and directions on how to install Services for Mac, refer to Appendix E: Fire-
Net and Mac OS.
Alternatively, if you don’t have a Windows 2000 Server, there are third-party utilities which can
connect your Mac computers with any Windows 98/WinMe or Windows 2000 Professional
PC. The most widely known are Dave and PcMacLan (http://www.miramar.com
).
46

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
10. Although I have PC MacLan or Dave, my Mac cannot communicate with my Windows
system(s).
A: You probably have Firewire support Version 2.7 or later installed in your MacOS 9.x. With this
version Apple changed the address of the Configuration ROM and made it totally incompatible
with Microsoft Firewire support.
The only way to handle this is to revert to Version 2.5. You can download this version of Firewire,
from our web site: http://www.unibrain.com/download/files/firewire25.hqx
.
11. During the installation I receive the following message:
Or this message (in Windows 2000):
A: This is a known bug of the Install Shield installation program. Press OK and the installation
will finish successfully and Firenet operations will not be affected in the least.
12. I have connected 2 notebooks with Firewire-PCMCIA adapters and Firenet does not
work.
A: The reason for this is that PCMCIA adapters cannot provide the required power to the 1394
bus. A 1394 repeater (or hub) with external power must intercede between them.
47

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
13. I want to remove Firenet but when I choose to uninstall it from Control Panel’s
“Add/Remove programs” applet, nothing happens.
A: You have come across a bug of the InstallShield installation program. Unfortunately the instal-
lation log file has been corrupted and you must uninstall Firenet manually.
Please follow carefully the instructions below:
1) Go to Device Manager, expand the "Network Adapters" section, right-click on "Unibrain
1394 adapter" and choose "Uninstall".
2) Go to the Program Files directory and delete the folder "Unibrain".
3) Go to the Program Files\InstallShield Installation Information\ directory and delete the
(hidden) directory: {4C2F992E-32DC-11D4-AC0D-0080C8ECCD31}
(In order to enable viewing of hidden files, open Windows Explorer, go to Tools menu,
choose Folder Options, click on the “View” tab and in the “Hidden files and folders section”,
choose “Show Hidden files and folders”).
4) Reboot your system.
5) When your system restarts, edit the registry:
Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\
and delete the key {4C2F992E-32DC-11D4-AC0D-0080C8ECCD31}
Note: Please be very careful when dealing with the registry!
14. I have installed Firenet for Mac OS X and I want to communicate with my Windows sys-
tem via Firewire. Is this possible?
A: Yes, it is. You can connect your Mac OS X system either via TCP/IP or via SMP (Samba) Pro-
tocol. For more information on how to use SMB, please visit the following link:
http://www.opensource.apple.com/projects/documentation/howto/html/osxsmb.html
48

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Appendix G: Firenet Revision History
1.1
1.2
1.21
1.22
1.4
• First official release
• Unibrain 1394 devices appear in Device Manager.
• Automatic adjustment of packet size for various 1394 OHCI adapters.
• In Advanced settings, the Maximum Payload option has been added, with 3 main
choices: Automatic, Ethernet Packet Size and various packet sizes ranging from 2562048 bytes. This permits Firenet to work with NetBeui or IPX/SPX, as well as with
boards that do not support the 2 Kbytes block size.
• An interim update to correct minor bugs reported in prior release.
• Firenet now automates installation in VAIO notebook computers with Sony “Smart
Connect”. Automatically disables Smart Connect and installs Firenet
• Better handling of power management issues, especially in Windows 2000.
• Reduced amount of memory required for asynchronous transmits, greatly improves
integration with other drivers that require a lot of memory.
• Under Windows 2000, added indication if node is not connected to any FireNet node
in the taskbar tray area.
2.0
2.2
• 2 separate versions: Firenet Station (for Win98 SE/WinMe & Win2K Pro) and Firenet
Server edition (for Win2K Server & Advanced Server).
• New features in the Server edition: Multiple 1394 adapters support and Mac client
support (through Services for Mac).
• New authorization scheme. A User Name is now required along with the Product
Key.
• Fixed a bug that sometimes caused a crash on fast dual processor systems running
Windows 2000.
• Better co-existence with external Hard Drives (SBP2) in the same 1394 bus.
• Fixed the following errors that appeared in some Windows 98SE/WinME systems at
shutdown or restart:
Fatal Exception OE has occurred at …… in VXD ubfwnet(01)
Fatal Exception OE has occurred at 0028:c001F303 in VXD NDIS (01) +…
• Added Windows XP support (for Firenet Station version only).
• Added Multilanguage support. Languages currently supported: English, French,
German, Italian, Spanish and Greek.
Known Problems:
Under Win98 when a FireNet PC is connected via FireNet and goes into a power save mode,
it’s possible that the PC may stop responding when the user tries to resume. This problem is
documented in the technical support section of Microsoft‘s
web site.
49

Unibrain FireNet™ 2.2 Installation Guide
Appendix H: Hardware Compatibility List
Below you will find a list of various 1394 OHCI adapters with which Firenet has been extensively
tested. In general though, Firenet should operate fine with any adapter that uses TI-OHCI compatible chips.
ADS Technologies, Pyro 1394 adapter
Unibrain’s Fireboard 400-OHCI, Firewire PCI adapter
1394 Lucent based adapters
Orange Micro 1394 adapter
Creative Labs Audigy
Western Digital 1394 Adapter
Pinnacle FireWire PCI adapter
50
 Loading...
Loading...