U-MEDIA WUB-710A User Manual

2.4GHz/5GHz Wireless USB Adapter
Model: WUB-710A
User's Guide

Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
For operation within 5.15 ~ 5.25GHz frequency range, it is restricted to indoor environment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. End users must follow the specific operating instructions for satisfying RF
exposure compliance. To maintain compliance with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements,
please follow operation instruction as documented in this manual.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
SAR compliance has been established in typical laptop computer(s) with USB slot, and product
could be used in typical laptop computer with USB slot. Other application like handheld PC or
similar device has not been verified and may not compliance with related RF exposure rule and
such use shall be prohibited.
The availability of some specific channels and/or operational frequency bands are country
dependent and are firmware programmed at the factory to match the intended destination. The
firmware setting is not accessible by the end user.
WUB-710A with Printed antenna and max. antenna gain is 1dBi in 2.4G and 2dBi in 5G.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference,
in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operation in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter.
2

Table of Contents
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Interference statement
CE Mark Warning
Chapter 1 – Wireless LAN Networking
Transmission Rate
Type of Wireless Networks
Ad-Hoc (IBSS) Network
Infrastructure (BSS) Network
Wireless LAN Security
Data Encryption with WEP
Chapter 2 - Getting Started
About Your 2.4GHz/5GHz Wireless USB Adapter
Package Content
System Requirement
LED Definition
Wireless Utility and Adapter Hardware Installation
Using the Utility to Configure Your Network
Link Information
Site Survey
Profile
Chapter 3 – Maintenance
Uninstalling the Driver and Utility
Glossary
3

Chapter 1- Wireless LAN Networking
This section provides background information on wireless LAN networking technology.
T
HE INFORMATION IN THIS SECTION IS FOR YOUR REFERENCE. CHANGING
NETWORK SETTINGS AND PARTICULARLY SECURITY SETTTINGS SHOULD
ONLY BE DONE BY AN AUTHORIZED ADMINISTRATOR.
Transmission Rate (Transfer Rate)
The adapter provides various transmission (data) rate options for you to select. Options include Fully
Auto, 1 Mbps, 2 Mbps, 5.5 Mbps, 11 Mbps, 6 Mbps, 9 Mbps, 12 Mbps, 18 Mbps, 22 Mbps, 24 Mbps, 36
Mbps, 48 Mbps, 54 Mbps and 108Mbps. In most networking scenarios, the factory default Fully Auto
setting proves the most efficient. This setting allows your adapter to operate at the maximum transmission
(data) rate. When the communication quality drops below a certain level, the adapter automatically
switches to a lower transmission (data) rate. Transmission at lower data speeds is usually more reliable.
However, when the communication quality improves again, the adapter gradually increases the
transmission (data) rate again until it reaches the highest available transmission rate.
Types of Wireless Networks
Wireless LAN networking works in either of the two modes: ad-hoc and infrastructure. In infrastructure
mode, wireless devices communicate to a wired LAN via access points. Each access point and its wireless
devices are known as a Basic Service Set (BSS). An Extended Service Set (ESS) is two or more BSSs in the
same subnet. In ad hoc mode (also known as peer-to-peer mode), wireless devices communicate with each
other directly and do not use an access point. This is an Independent BSS (IBSS).
To connect to a wired network within a coverage area using access points, set the adapter operation mode to
Infrastructure (BSS). To set up an independent wireless workgroup without an access point, use Ad-hoc
(IBSS) mode.
D-HOC (IBSS) NETWORK
A
Ad-hoc mode does not require an access point or a wired network. Two or more wireless stations
communicate directly to each other. An ad-hoc network may sometimes be referred to as an Independent
Basic Service Set (IBSS).
To set up an ad-hoc network, configure all the stations in ad-hoc mode. Use the same SSID and channel
for each.
4
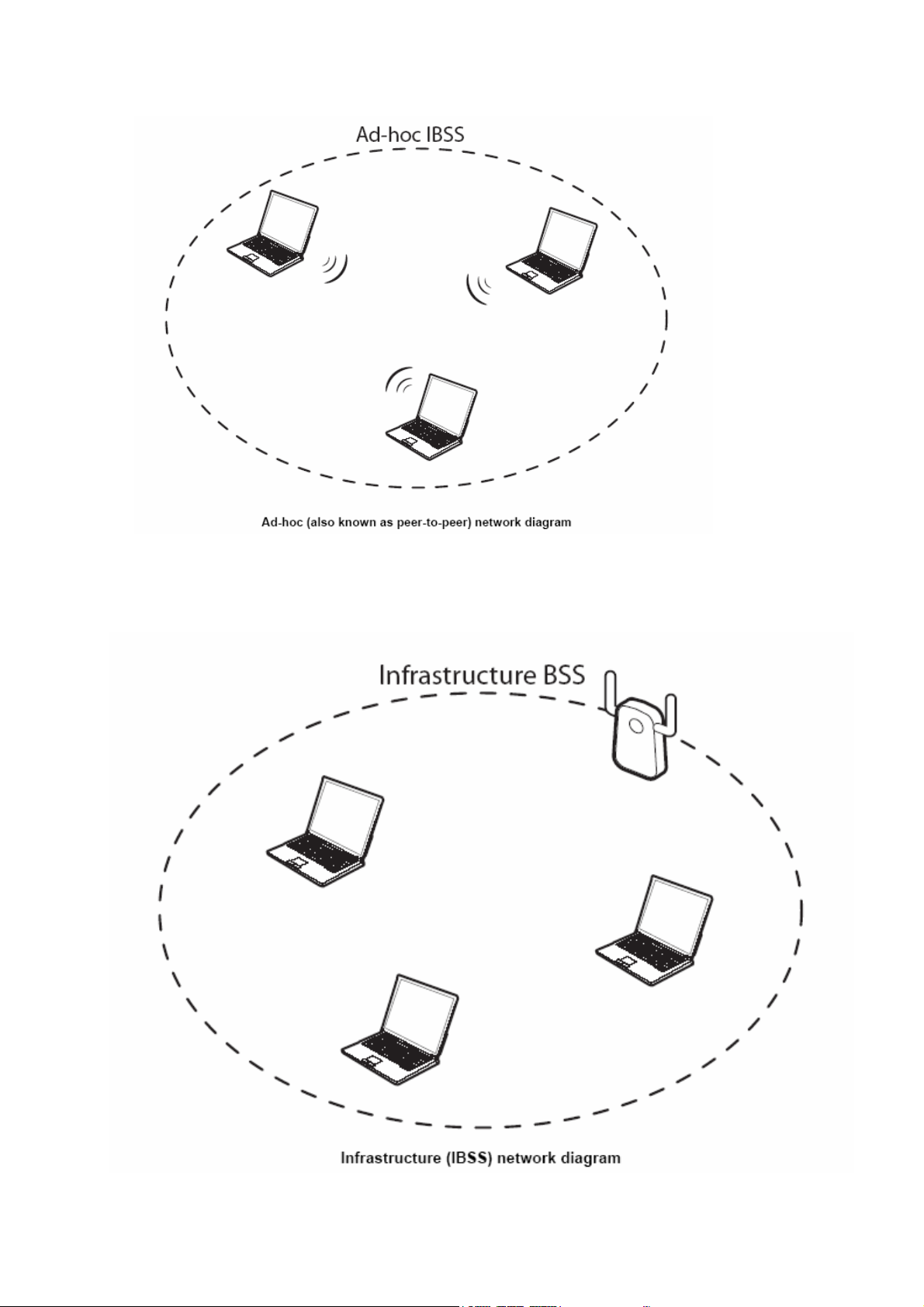
When a number of wireless stations are connected using a single access point, you have a Basic Service Set
(BSS).
6
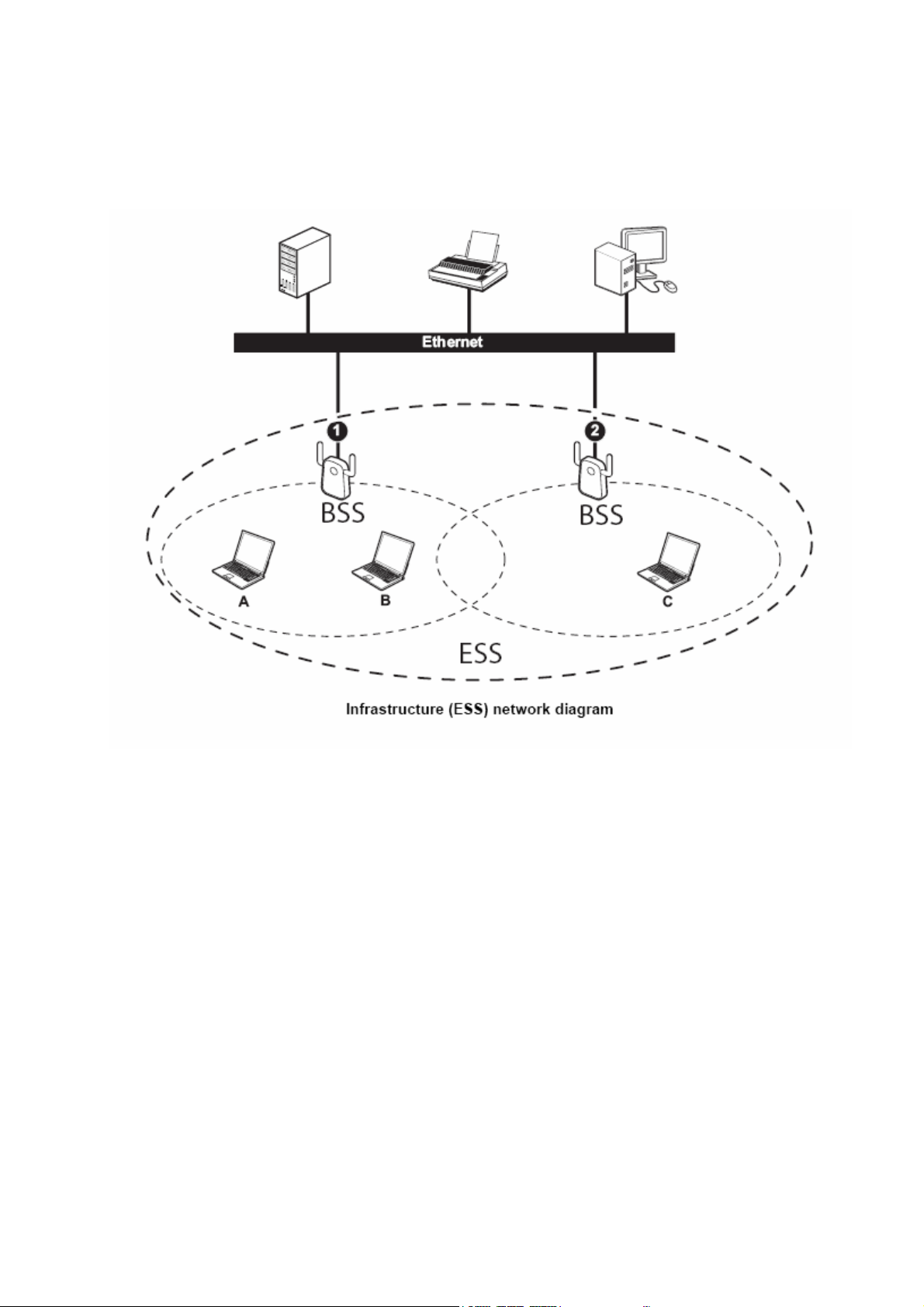
In the ESS diagram below, communication is done through the access points, which relay data packets to
other wireless stations or devices connected to the wired network. Wireless stations can then access
resources, such as a printer, on the wired network.
7
 Loading...
Loading...