Page 1

Burn.Now
User Guide
Ulead Systems, Inc.
June 2006
Page 2

Ulead® Burn.Now® 4.0
Copyright © 2003-2006 Ulead Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
recording or storing in a retrieval system, or translated into any language in any form without the express
written permission of Ulead Systems, Inc.
Software license
The software described in this document is furnished under a License Agreement which is included with the
product. This Agreement specifies the permitted and prohibited uses of the product.
Licenses and trademarks
ICI Library © 1991- 1992 C-Cube Microsystems.
Ulead, the Ulead logo, and Ulead Burn.Now are trademarks of Ulead Systems, Inc.
Manufactured under license from Dolby Laboratories. “Dolby” and the Double-D symbol are trademarks of
Dolby Laboratories.
Macromedia, Flash and Macromedia Flash are trademarks or registered trademarks of Macromedia, Inc. in
the United States and internationally.
All other product names and any registered and unregistered trademarks mentioned are used for
identification purpose only and remain the exclusive property of their respective owners.
© 2003-2005 Ulead Systems. This software is based in part on the work of the independent JPEG Group.
Portions of this program are licensed under U.S. Patent No. 4,558,302 and foreign counterparts.
Template files
Files provided as samples on the program CD can be used for personal demonstrations, productions and
presentations. No rights are granted for commercial reproduction or redistribution of any sample files.
North & South America
Ulead Systems Inc.
http://www.ulead.com
Support: http://www.ulead.com/tech
Germany
Ulead Systems GmbH
http://www.ulead.de
Support: http://www.ulead.de/tech
International
Ulead Systems, Inc.
http://www.ulead.com
http://www.asiapac.ulead.com
http://www.ulead.com.tw
Support:
http://www.ulead.com/tech
http://www.asiapac.ulead.com/tech
http://www.ulead.com.tw/tech
United Kingdom
http://www.ulead.co.uk
Support: http://www.ulead.co.uk/tech
Japan
Ulead Systems Inc.
http://www.ulead.co.jp
Support: http://www.ulead.co.jp/support
France
http://www.ulead.fr
Support: http://www.ulead.fr/tech
China
Ulead Systems, Inc.
http://www.ulead.com.cn
Support: http://www.ulead.com.cn/tech
Page 3

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 3
Table of Contents
Welcome to Ulead Burn.Now ................................................................... 5
Things you can do in Burn.Now ............................................................................. 5
Basics ...................................................................................................... 7
Running the program ....................................................................................................... 7
Using Burn.Now project files ............................................................................................. 7
The user interface: an overview ............................................................................ 8
Select a Task dialog box ................................................................................................... 8
Main Window .................................................................................................................. 9
Setting preferences ........................................................................................... 12
Choosing a disc burner ....................................................................................... 13
About file systems ............................................................................................. 14
Making a data disc ................................................................................. 15
Compiling a data disc ......................................................................................... 16
Burning the data disc ......................................................................................... 17
Making an audio disc ............................................................................. 18
Compiling an audio disc ..................................................................................... 19
Editing audio files .............................................................................................. 20
Trim audio .....................................................................................................................20
Audio gap ......................................................................................................................21
Export audio tracks .........................................................................................................21
Audio effects ..................................................................................................................21
Adding CD-Text (Audio CD only) .......................................................................... 22
Burning the audio disc ....................................................................................... 23
Music DVD-Video project settings ........................................................................ 25
Making an MP3 disc ............................................................................... 26
Compiling an MP3 disc ....................................................................................... 27
Burning the MP3 disc ......................................................................................... 28
Making a bootable disc .......................................................................... 29
Converting audio files ............................................................................ 29
Convert Audio Files dialog box ............................................................................ 30
Ripping CD audio ................................................................................... 32
Rip CD Audio dialog box ..................................................................................... 32
CD and file info ................................................................................................. 34
Disc burning options .............................................................................. 35
Close disc ......................................................................................................... 35
Direct burn ....................................................................................................... 36
Test before burning ........................................................................................... 36
Buffer underrun protection ................................................................................. 36
Check source files ............................................................................................. 36
Verify after burning ........................................................................................... 37
Burn with synchronization info ............................................................................ 37
Span disc ............................................................................................... 38
Editing a disc ......................................................................................... 40
Page 4

4 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Modifying disc contents .......................................................................................40
Burning the edited disc .......................................................................................42
Copying a disc ....................................................................................... 43
Making a disc to disc copy ...................................................................................43
Creating a disc image file ....................................................................................44
Burning a disc from a disc image file .....................................................................45
Handling rewritable discs ...................................................................... 46
Erase ..............................................................................................................46
UDF Format ......................................................................................................46
UDF Certify ......................................................................................................47
Checking burner and disc information ................................................... 48
Checking burner capabilities ................................................................................48
Checking disc properties .....................................................................................49
Appendix A: Menus and commands ....................................................... 50
Disc menu .................................................................................................................... 50
Edit menu ..................................................................................................................... 50
View menu ................................................................................................................... 51
Tools menu ................................................................................................................... 51
Burner menu ................................................................................................................. 51
Appendix B: Glossary ............................................................................ 52
Index .................................................................................................... 56
Page 5

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 5
Welcome to Ulead Burn.Now
Ulead Burn.Now is an easy-to-use burning tool versatile enough to handle a wide
range of recording tasks and storage media. All you really need to decide is what
kind of discs you want to use, and what you want to burn on them. You can burn
files and projects to CDs, DVDs, and dual-layer DVDs. Burn.Now allows multisession burning of dual-layer DVD-R using Layer-Jump Recording technology. It
also supports the next-generation Blu-ray Discs (BDs).
Things you can do in Burn.Now
Make and edit a data disc
Stores a collection of all types of files onto a disc. Burn.Now supports both ISO and
UDF file systems, including UDF 2.5 for writing data to discs. If you are working
with rewritable and appendable discs, whether CD or DVD, Burn.Now enables you
to edit the contents of discs that have already been burned. There is no need to
wipe the whole disc and start over, if you only wish to remove or add files, or simply
to reorganize your folders and files.
Make and edit an MP3 disc
Collects MP3 files and compiles them into an MP3 disc. MP3 is a very popular format
because of its relatively small file size. It is primarily played back on personal
computers and some set-top players that support it. Burn.Now also lets you edit
appendable MP3 discs.
Make an audio disc
Collects all types of sound files, and creates an Audio CD, DVD-Audio disc, or Music
DVD-Video disc.
Make a bootable disc
If you are using the ISO 9660 or ISO 9660 + Joliet file system, you can create
bootable discs that contain all the necessary operating system files for your
computer to start up without having to access the hard disk.
Note: If an MP3 disc is not DVD+/-RW, a new data session is created
after editing. This new session may not be readable on some MP3
players that reads the first session only.
Page 6

6 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Copy discs directly
Burns an exact replica of a disc straight to another disc without requiring any step
in between. This is a speedy method that has the further advantage of not
requiring a large amount of space on your computer if you copy on-the-fly.
Copy DVD-Video directly
Burns an existing VIDEO_TS folder directly to a disc. The VIDEO_TS folder (Video
Title Set) contains all the unencrypted files of the original DVD video. These are
VOB (Video Object) files which contain the video and audio of the movie and the
IFO (Information) files which contain the menu navigation information.
Burn from disc image
Alternatively, you can burn an image of the contents of a disc and store the image
on your computer. A disc can be burnt directly from the image file. This takes a
little longer, but is more stable and allows you the flexibility of creating the image
file on one occasion, and burning at a later date, as well as being more convenient
for burning multiple copies and for backup purposes.
Write to Blu-ray Disc (BD)
Burns data to the next-generation Blu-ray Disc format. A single-layer BD can hold
up to 25 GB of video and other data types while its dual-layer counterpart can store
up to 50 GB.
Use various disc tools
Burn.Now offers various disc tools. When using rewritable discs, you can erase the
entire contents to start from scratch. You can also format and certify the discs with
the UDF file system.
Page 7

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 7
Basics
Burn.Now has a simple, straightforward user interface that frees you from the task
of configuring complex settings. All you need to do is choose the type of disc to
create, compile, and then burn the disc. This section introduces you to the
Burn.Now interface.
Running the program
Use any of the methods below to start Burn.Now:
•Use the DVD MovieFactory launcher and select a task (when it is associated
with Burn.Now).
• Open an existing Burn.Now project file with .ubn extension.
•Click Start: Programs and select Ulead DVD MovieFactory 5 Plus - Ulead
Burn.Now 4.0.
Using Burn.Now project files
To open a previously saved Burn.Now project file, either double-click the .ubn file,
select it from Existing project in the Select a Task - Create Disc dialog box, or
select Disc: Open on the Menu Bar. Make sure that the files associated with the
project is not moved or deleted to avoid lost file links.
Page 8
8 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
The user interface: an overview
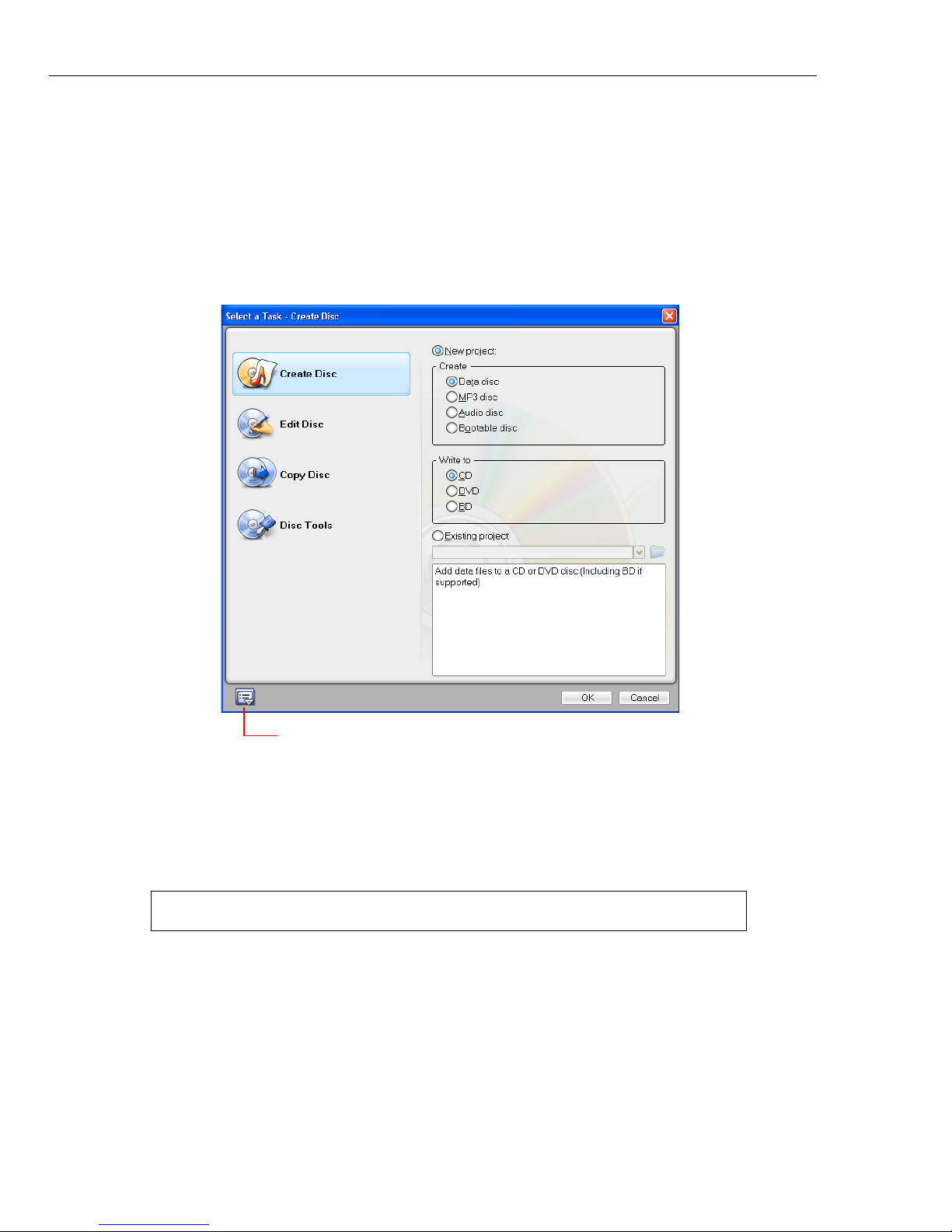
Select a Task dialog box
The easiest way to make sure you are heading in the right direction when compiling
a new disc is by beginning with the Select a Task dialog box. This is displayed
each time you launch Burn.Now.
The Select a Task dialog box displays the four available tasks on the left side.
When a task is selected, all the options available for that task are displayed on the
right. A brief description of the selected option is displayed in the lower half of the
Options Panel.
Note: If you click Cancel, Burn.Now will be closed.
Click to open the Preferences dialog box
Page 9
Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 9
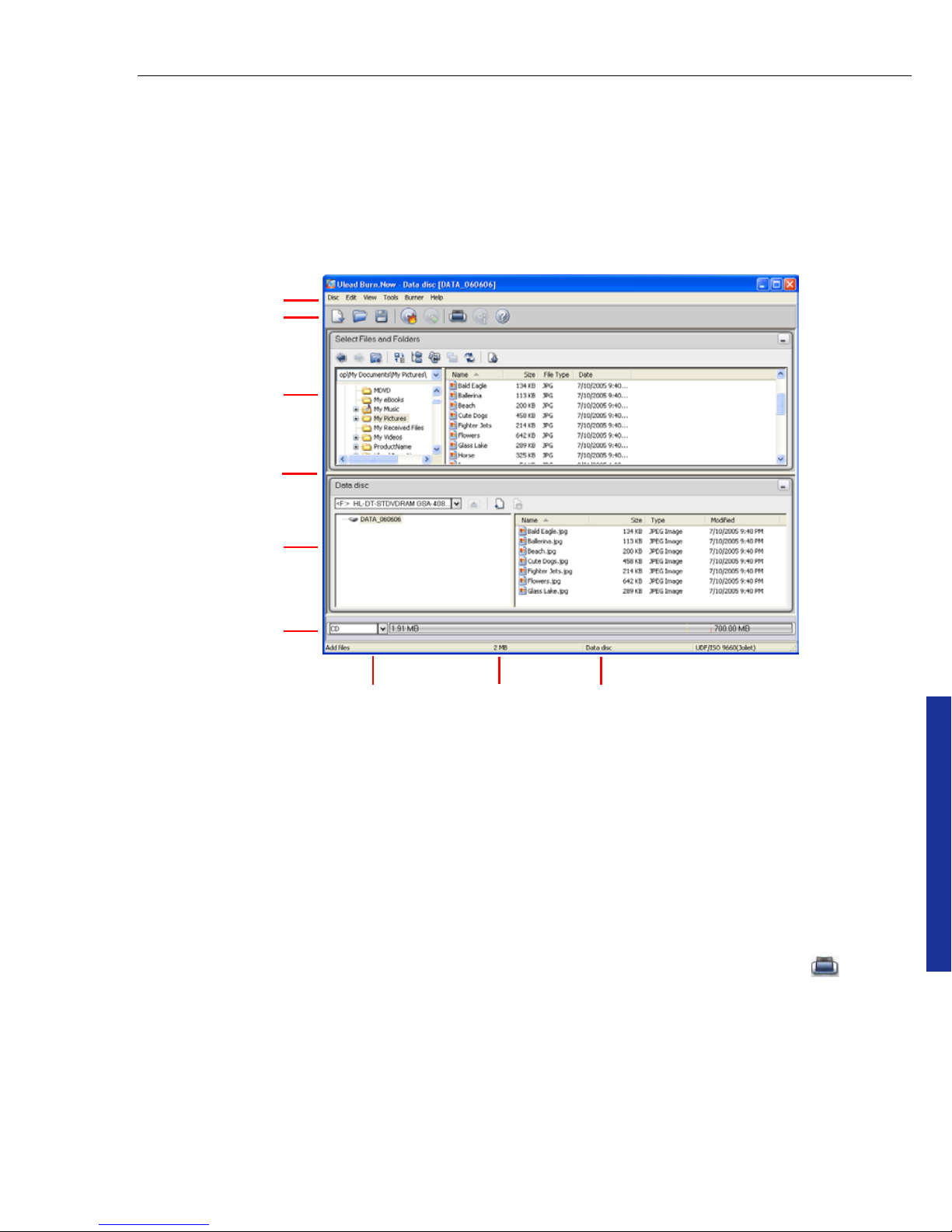
Main Window
The Main Window is where you add and organize the data to burn to disc. It is
composed of six parts: the Menu Bar, Toolbar, Source Explorer Window, Disc
Layout Window, Disc-space Meter, and Status Bar.
Menus and Toolbar
The Menu Bar comprises the general functionalities for Burn.Now, from creating a
new project to finding product updates. See “Appendix A: Menus and commands”
for more details.
The Toolbar enables you to access the most commonly used functions easily. The
buttons on the Toolbar are available through the menus, and some are also
available through the context menu in the Main Window. The options vary
depending on the selected task. You can also open Label@Once by clicking to
print disc labels based on the current project.
Menu
Toolbar
Source
Explorer
Splitter
Disc
Layout
Window
Disc-space
Meter
Status
Tot al f i l e
Tas k t y p e
Page 10
10 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
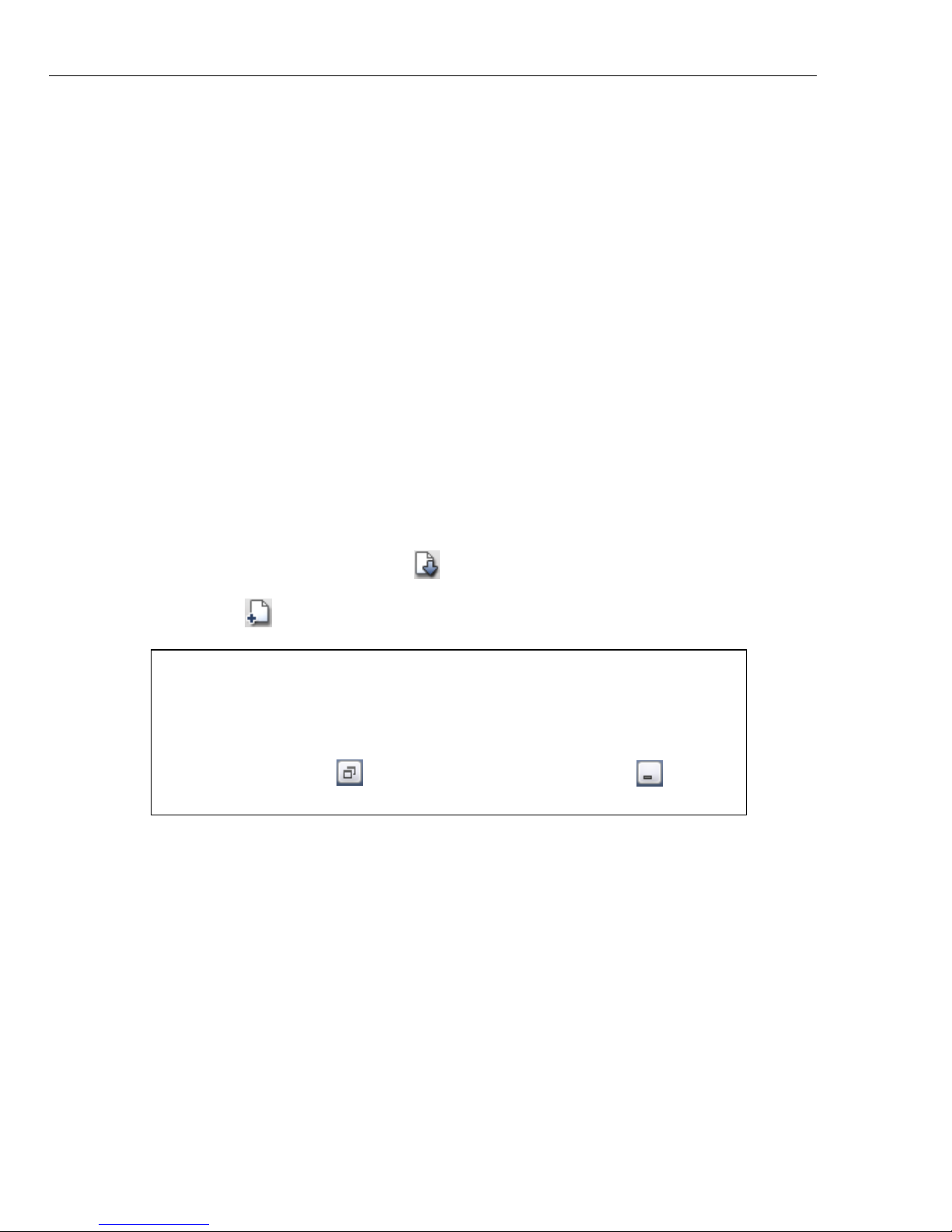
Source Explorer Window and Disc Layout Window
The Source Explorer Window is similar to Microsoft Windows Explorer. The left
pane displays the folders and disk drives available while the right pane displays the
files and folders inside the currently selected folder or disk drive. The toolbar at the
top contains commonly used commands. You can also right-click at the left and
right panes to display other useful commands.
The Disc Layout Window displays the files and folders to be burned to disc. The
panel will appear different depending on the task chosen. When creating data and
MP3 discs, the panel displays files and folders similar to the Source Explorer
Window. For audio tasks, the panel displays track information such as title and
duration.
Except for creating a bootable disc, most disc burning tasks require you to first
include the files from the Source Explorer Window to the Disc Layout Window.
Use any of the methods below:
• Drag the files or folders from the Source Explorer Window to the Disc Layout
Window.
• Select the files or folders and click .
• Click Add files .
Disc-space Meter
The Disc-space Meter indicates how much space will be occupied on the target
disc. A progress bar starting from the left side indicates the amount of space to be
occupied on the disc; or the total duration of tracks when compiling an audio CD.
The progress bar extends to the right as more data are added.
Safety markers (colored dotted lines) on the right running vertically down the
meter indicate capacity limits. The yellow marker indicates the recommended
maximum capacity, while the red one indicates the absolute maximum limit.
Notes:
• You can select multiple files by holding [Shift] or [Ctrl] as you
would in Windows Explorer.
• The size of both panels can be adjusted by dragging the Splitter.
Also, you can click at the upper right to expand or to
shrink them.
Page 11
Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 11
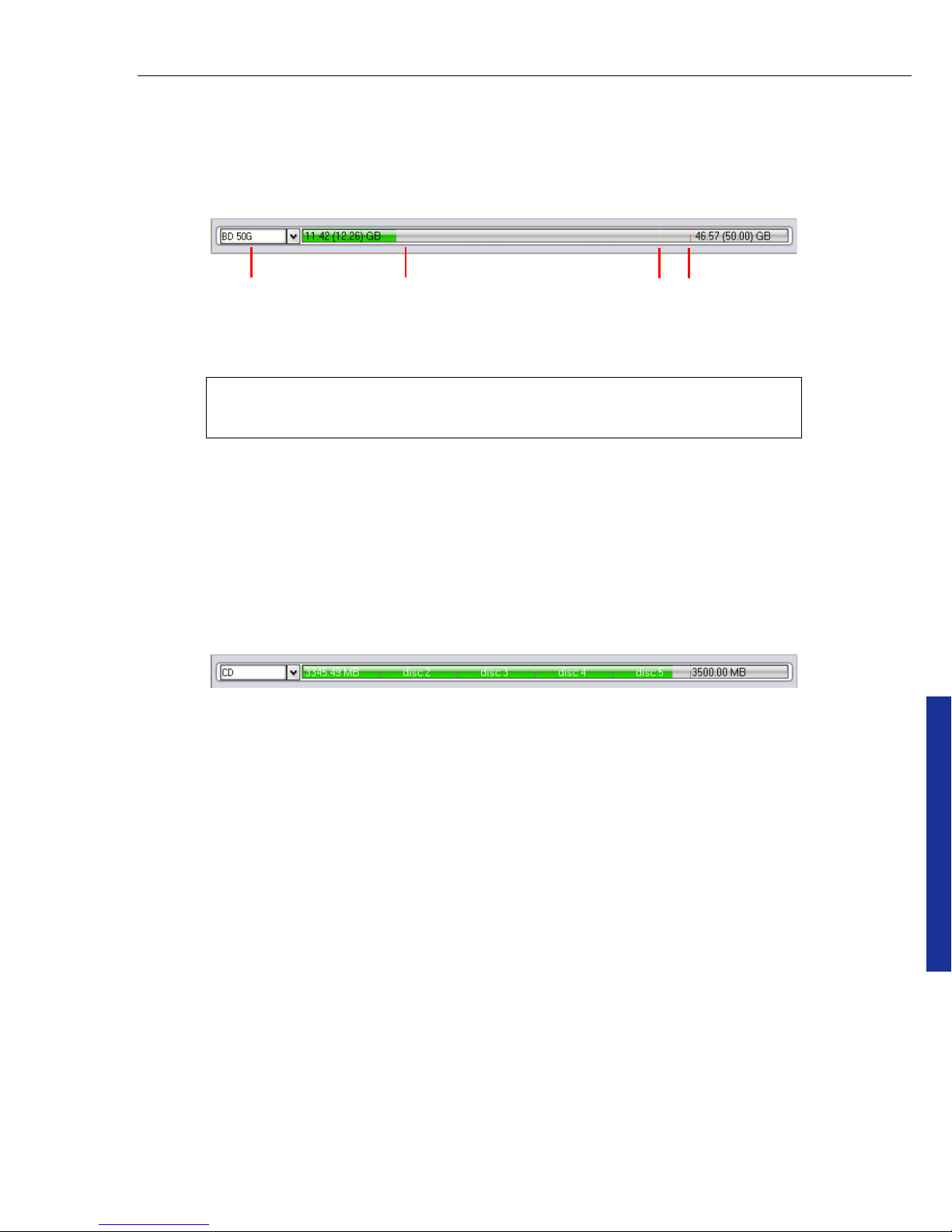
Increasing the quantity of data beyond the yellow marker is risky, if there is only
one disc available for burning all the files selected.
If the total file size exceeds the current disc’s capacity and you have enough discs
for burning, Span Disc (available depending on the Burn.Now version you
purchased) will automatically help you burn all files onto several discs. For details,
see “Span disc”. In such a case, the Disc-space Meter automatically shifts to
spanning mode and displays the estimated number of discs required as you add
your files.
Note: You can change the selected disc type anytime using Output
disc type (not available for audio CD.)
Safety markers
Project Size Bar
Output disc
type
Disc-space Meter in spanning mode
Page 12

12 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Setting preferences
Click in the Select a Task dialog box, select Disc: Preferences in the
program window, or press [F6] to open the Preferences dialog box and specify
settings for various tasks.
General
By default, Burn.Now automatically ejects the disc after burning is complete. To
disable auto-eject, select Don’t eject disc after burning.
Also, you can use Check Ulead Web site every XX days to specify how
frequently the program checks the Ulead Web site for news and updates.
Audio gap on audio CD determines the length of the silent gap in between tracks
when making an audio CD. The value can be changed from 0 to 10 seconds. The
default value uses the industry standard of 2 seconds. (See “Audio gap” for more
details).
Working folder is the temporary folder used by Burn.Now for placing temporary
files. You can change the default folder by entering the path name on the text box
or by clicking . Available space shows the available and maximum disk space
in the working folder.
CD Info
Select Get CD-Text info from audio CD to extract disc and track information
embedded on an audio CD that you copy. These are album titles, artist names,
track titles, and other information.
Burn.Now is also freedb-aware, letting you access freedb.org for free online music
information, like artists, track lists, and others. When Get CD info from the
freedb database on the Internet is selected, using Rip CD audio lets you add
additional information taken from freedb.org.
Note: Some burners do not refresh the disc contents after writing,
and thus, the new disc contents may not be read properly by other
applications. Such burners have to be forced to do a refresh by
ejecting and closing the disc tray.
Note: Some Internet connections may require a proxy server. Check
with your Internet Service Provider for proper settings if needed.
Page 13

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 13
If you have already configured your Web browser to use a proxy, select Use
internet connection proxy settings. Select No proxy if you do not want to use
a proxy, even if one is already configured for your Web browser. To enter new proxy
settings, select User-defined.
Edit Disc
Under Synchronization settings, select Refresh compilation automatically to
synchronize recorded files and folders with their original location on your hard disk.
This applies everytime you insert a data disc created by Burn.Now. Select options
for replacing files, removing them from, or adding them to your compilation.
Choosing a disc burner
When creating discs, you would usually specify a physical burner drive with which
to burn the disc. However, instead of directly recording to a burner, Burn.Now
provides an alternative method. When compiling a new disc, it is not necessary to
burn it immediately to a disc. Instead, you can save it as a disc image file on your
computer, and store it there to be burnt to disc later.
Choose Burner: Select Burner. You can then choose a physical burner if you want
to burn directly to disc. Click Advanced to view your burner’s read and write
capabilities.
To burn a disc image file, select Disc image file from the drop-down list. When
you start the burning process, you will be prompted to specify where to save the
image file and what file format to use. The file can be saved as an .ixb file which is
the Ulead native format and is readable only in Burn.Now. You can also save it as
an .iso file which is the industry standard format and is compatible with all burning
software. You will need sufficient space on your hard disk to store the disc image
file.
Note: Synchronization of data is possible only with discs that were
created with synchronization info in Burn.Now. For more details, see
“Burn with synchronization info”.
Notes:
• You can also select the burner at the Disc Layout Window
toolbar.
• Burn.Now can create ISO 9660 and UDF/ISO 9660 disc image files
only. For UDF 1.5 file system or above, the program can only
directly burn to disc. (See “About file systems” for more
information on file systems.)
Page 14

14 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
About file systems
When creating a new disc, you need to select an appropriate file system that will
make the disc readable on the device or operating system where the disc will be
viewed or played. Choose the file system in the Burning Options dialog box
before burning the disc. (Click Burn disc on the Toolbar.) The file systems
that are available include:
• ISO 9660
ISO 9660 is a cross-platform file system that is readable on Windows,
Macintosh, and Unix. When you create an ISO 9660 disc with Joliet extensions,
names of files/folders burned onto discs can have up to 64 characters in length.
Burn.Now allows ISO 9660 to be used as the file system for data and MP3 discs.
• UDF 1.5, 2.0 and 2.01
UDF (Universal Disc Format) is a file system developed by OSTA (Optical Storage
Technology Association). There are various UDF versions. UDF 1.5 (readable on
Windows 2000 and above) and higher versions (readable on Windows XP and
above) support random packet writing and allows over 4 GB of data to be burnt
onto a DVD disc. (See “Appendix B: Glossary” for information on random packet
writing.)
• UDF 2.5
UDF 2.5 file system provides the Mirror UDF metadata option storing 2 copies
of your data structure in physically separated areas on a disc. This enhances the
integrity of the file system data on a disc.
• UDF 2.6 Low
UDF 2.6 file system supports the Pseudo OverWrite (POW) mechanism for
recording on write-once discs and drives such as BD-R (Blu-Ray Disc-Write
Once). The POW mechanism allows write-once media to function like a
rewritable disc. This file system also increases compatibility between consumer
electronics video recorders and computer systems.
• UDF/ISO 9660
UDF/ISO 9660 (also known as UDF Bridge) is a combination of two file systems:
UDF 1.02 and ISO 9660. Discs burned with this file system can be read by
Macintosh and Windows.
Page 15
Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 15
Making a data disc
A data disc is a disc that contains computer files. Computer files can include a wide
variety of data including word-processed documents, spreadsheets, multimedia
files including music, video clips, images, and more. Discs are extremely
convenient for storing data as they can hold large quantities. CDs can hold up to
700MB of data, while DVDs and BDs can hold gigabytes of data. Since recordable/
rewritable discs are relatively inexpensive, they are quick and convenient way of
backing up computer systems. As an added bonus, their compactness allows for
easy storage and transportation.
Burn.Now streamlines the process of putting together a data disc, taking care of all
the complicated decisions for you. All you need to do is decide the kind of disc to
use and what data to write onto your disc.
To create a data disc:
1. In the Select a Task dialog box, select Create Disc and then select Data disc.
2. Select the disc type (CD, DVD, or BD), and then click OK.
3. Choose Burner: Select Burner to select whether to burn to a physical disc
burner or create a disc image file.
4. Select the folders and files from the Source Explorer Window and add them to
the Disc Layout Window.
5. When you are ready to burn the data disc, click Burn disc on the Toolbar.
Note: You can also click to save your project for future use.
Page 16

16 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Compiling a data disc
The Main Window is where you compile and organize folders and files to burn to a
data disc.
To compile a data disc:
1. Add the files and folders to burn from the Source Explorer Window to the
Disc Layout Window using any of the methods mentioned at “Source Explorer
Window and Disc Layout Window”.
2. To reorganize data, click any file or folder in either pane of the Disc Layout
Window, and drag it to its new location, up or down the folder structure in the
left pane, or directly across to a different folder from the left pane to the right.
3. To create a new folder, right-click in the right pane then select New Folder from
the context menu.
4. To rename a selected folder or file, right-click the file or folder and select
Rename. The selected folder/file name will be highlighted and show a flashing
cursor, and a new name can be entered.
5. To delete any file or folder, select it then click Delete on the Toolbar. Select
Disc: Revert to reset all settings of an open project to its previous saved state.
Page 17
Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 17
Burning the data disc
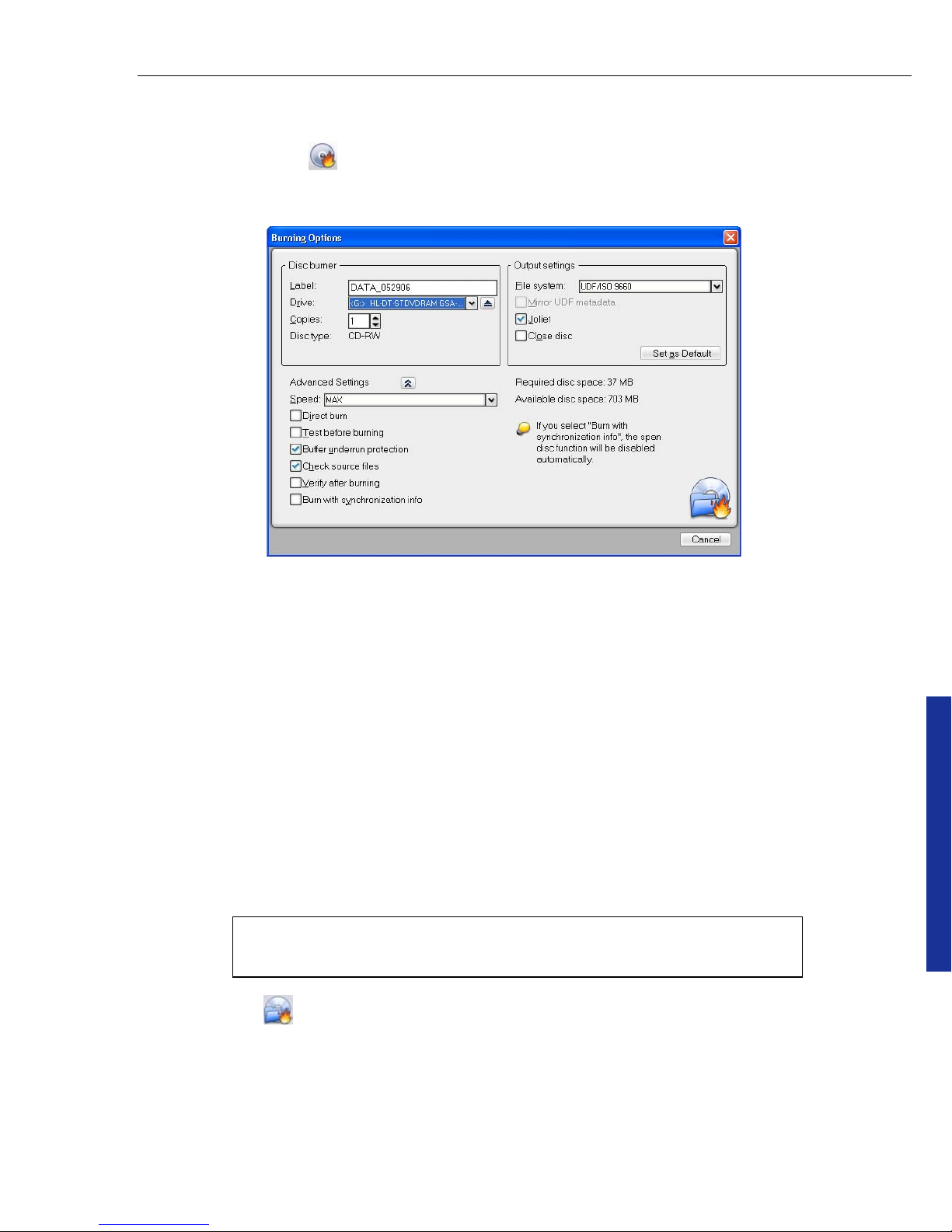
1. Click Burn disc on the Toolbar. The Burning Options dialog box will be
displayed.
2. In the top half of the dialog box, the disc label can be renamed and a File
system can be selected. The label name can have up to 16 characters in length.
If ISO 9660 is selected as the file system, the Joliet option will be available.
Joliet is an industry standard extension of ISO 9660 which supports Unicode in
file names and permits extended file names of up to 64 characters in length,
including spaces.
3. In the Disc burner area, you can specify whether to create a disc image file or
burn directly to disc.
If you are burning directly to a physical burner, the write Speed can also be
selected. If there is a disc inserted in the burner, the program will check the
write speed of the burner and the disc, and by default, will choose the highest
speed that both can handle.
4. Click Burn to start the burning process.
Note: For details on the other options available in this dialog box,
see “Disc burning options”.
Page 18

18 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Making an audio disc
An audio disc is a disc that holds songs or music. Burn.Now makes the audio disc
production process easy for you. Simply compile your audio files, then create your
audio disc.
To create an audio disc:
1. In the Select a Task dialog box, select Create Disc and then select Audio
disc.
2. Choose a data format that will allow your disc player to recognize and play the
disc:
• Audio CD - Records audio in Compact Disc-Digital Audio (CD-DA) format on
CD-R or CD-RW media. A disc may contain up to 99 tracks or songs. Audio CD
can be played on any CD or DVD player, such as portable units or the CDROM/DVD-ROM drive in your PC.
• DVD-Audio - Records audio in LPCM stereo (44.1 kHz, 16-bit stereo) on
DVD. A DVD disc can contain up to 99 tracks or songs. Audio are saved as
.aob files in the AUDIO_TS folder on the DVD.
DVDs burned in this format can be played in DVD-Audio capable players. When you
play the DVD, use the player’s controls or its remote control to select and playback
tracks.
• Music DVD-Video (Audio-only DVD-Video) - Records audio in DVD-Video
format. A DVD burned in this format is the same as a regular DVD movie disc
which can be played on your computer, home or car DVD player, except that
the DVD does not contain video content.
Audio can be recorded in MPEG audio, LPCM audio, or Dolby Digital audio (at
48 kHz 16-bit stereo). MPEG audio is a compact high-quality format which is
highly recommended for EU DVD players in areas using the PAL TV system.
LPCM provides uncompressed audio quality but with a larger file size, while
Dolby Digital offers a lossy audio compression format with a smaller file size.
A DVD disc, or each side of a dual-sided DVD, is divided into a maximum of
99 titles, and each title may contain up to 99 tracks or songs. Audio are saved
as .vob files in the VIDEO_TS folder on the DVD. When you play the DVD, a
playlist selection menu with a still background image will be displayed onscreen where you can select tracks to play.
3. Click OK. The Main Window will then appear where you can collect audio files
to be burned onto the disc. (See “Compiling an audio disc” for details.)
4. Choose Burner: Select Burner to decide whether to burn directly to a disc
burner or create a disc image file. (See “Disc burning options” for details.)
Page 19

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 19
5. Collect audio files from the Source Explorer Window and add them to the
Disc Layout Window.
6. When you are ready to burn the audio disc, click Burn disc on the Toolbar.
7. Set burning options as needed, and then click to start burning.
Compiling an audio disc
The Main Window is where you assemble and organize the audio tracks you want
to burn to disc.
To compile tracks for your audio disc:
1. If you chose to create a Music DVD-Video formatted disc in the Select a Task
dialog box, select the audio format for encoding audio on DVD by clicking on
the Disc Layout Window toolbar.
2. Add the audio files to burn from the Source Explorer Window to the Disc
Layout Window using any of the methods mentioned at “Source Explorer
Window and Disc Layout Window”.
Note: You can also click to save your project for future use.
Note: When adding audio tracks, check the Disc-space Meter to
ensure that you are not exceeding the capacity of the disc.
You can select MPEG audio, LPCM
audio, or Dolby Digital audio.
Note: You can add video files such as AVI and Windows Media
Video. Audio will be extracted from the video files and added as
audio tracks to the Disc Layout Window. To add Quicktime files,
you must first install QuickTime in your computer.
Page 20

20 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
3. Audio files will be added as tracks in the Disc Layout Window. To rearrange
tracks, select the track(s), then select Edit: Move Track - Up/Down or drag
the selected tracks to the desired position.
4. To delete a track, select it then click Delete on the Disc Layout Window
toolbar. Select Disc: Revert to reset all settings of an open project to its
previous saved state.
5. By default, each track has the same name as the audio file. To rename a track,
select the track then either click the track title, right-click and select Rename,
or press [F2].
Editing audio files
Burn.Now offers various tools that let you edit audio files before burning them to
discs. To use them, simply add the audio files to the Disc Layout Window and
click the tool to use from the toolbar.
Trim audio
Trim audio is used to extract part of an audio track. To do this, select the audio file
and click . You can set the part to be extracted by first dragging on the jog
bar to the start position and click , then, drag it to the end position and click
.
Note: Click Project settings to set the background, font,
and styles of your tracks and song info. For details, see “Music
DVD-Video project settings”.
Note: You can also apply fade-in/out effects on the audio track.
Mark-in/out
Fade-in/out
Jog Bar
Page 21

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 21
Audio gap
Audio gap is the silent area between audio tracks in audio CDs that tells the
listeners a new track is about to start. To change the audio gap length, select the
audio file/s and click to enter a value.
Export audio tracks
You can export audio tracks to mu-law (.au), MP3 Audio Files (.mp3), MP4 Audio
Files (.mp4), Ogg Vorbis Audio Format (.ogg), Microsoft WAV Files (.wav), and
Windows Media Audio (.wma).
To do this, select the audio files and click . The Export Audio Tracks dialog
box opens to allow you to specify the target location of your exported files, select
output format and quality.
Audio effects
Audio effects applies volume level control and removes unwanted elements in
your audio file. To add audio effects, select one or multiple audio files in Disc
Layout Window and click the icon of the audio effect to apply. You can apply
multiple effects to your audio files.
Volume Leveling normalizes volume at a fixed level, ranging from 83 (+0) to
95 (+12) db.
Vocal Reduction lowers human voice in your audio file.
Notes:
• The first audio track uses the industry standard of 2 seconds as
audio gap length before the track and cannot be changed.
• You can adjust the default audio gap length at General: Audio
gap on audio CD in Preferences.
Page 22

22 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Click Reduction diminishes clicking noise in your audio file.
Hiss Reduction diminishes hissing noise in your audio file.
To edit the audio effect, select your audio file, select Edit: Effects or right-click
your audio file in the Disc Layout Window and select Effects.
To delete audio effects, select the audio file(s) and click the icon of the audio effects
to remove. You can also right-click files and select Effects: Remove All to remove
all effects on the selected files.
Adding CD-Text (Audio CD only)
The CD-Text feature lets you store track and CD information onto an audio CD. To
display this information, the disc must be played on a CD player that supports CDTex t f e at ur es .
When you drag or add .cda files that contain CD-Text from the Source Explorer
Window to the Disc Layout Window, the CD-Text information is automatically
included in the disc that you will create.
When you drag or add other audio files to the Disc Layout Window, the metadata
information from these audio files can be used as CD-Text track info and included
on the disc that you will create.
If CD-Text is in another language, select the track and press [F2] to edit it directly
or you can configure Windows to display the appropriate language. For more
information, see “CD and file info”.
To add track and album information:
1. To add track information, select a track then click Add CD-Text Track
Information on the Disc Layout Window toolbar.
To add CD information, click Add CD-Text Album Information .
2. Enter information as prompted, then click OK.
Note: CD-Text can be written to an audio CD only when the disc is to
be closed.
Page 23

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 23
Burning the audio disc
1. To burn an Audio CD, insert a blank CD-R or CD-RW into the burning device.
To burn a DVD-Audio or Music DVD-Video disc, insert a blank DVD-R, DVD+R,
DVD-RW, or DVD+RW.
2. Click Burn disc on the Toolbar. The Burning Options dialog box will be
displayed.
Burning Options dialog box (Audio CD)
Burning Options dialog box (DVD-Audio and Music DVD-Video)
Page 24

24 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
3. For Audio CD, select Write CD-Text information and Close disc if you want to
add CD-Text (that is, track and album information) on the disc. (CD-Text cannot
be added if the disc is not closed.)
4. In the Disc burner area, you can confirm whether to save a disc image file or
burn directly onto a disc. (See “Choosing a disc burner”.)
If you are burning directly to a physical burner, the write Speed can also be
selected. If there is a disc inserted in the burner, the program will check the
write speed of the burner and the disc, and by default, choose the highest speed
that both can handle.
5. Click Burn to start the burning process.
Notes:
• If the Audio CD is closed, you will not be able to add additional
content to the CD at a later stage.
• DVDs are always closed.
Notes:
• For details on the other options available in this dialog box, see
“Disc burning options”.
• Since the audio size to be burned onto DVD is enormous, DVD
folders and files will first be created on your hard drive which
will then be burned onto the DVD. Before burning a DVD-Audio
or Music DVD-Video disc, make sure that your hard drive has
available space that is equivalent to, or higher than, the DVD
disc capacity. The temporary DVD folders and files will be
deleted from your hard drive after burning is complete.
Page 25

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 25
Music DVD-Video project settings
When creating a Music DVD-Video disc, click on the Disc Layout Window
toolbar to open the Project Settings dialog box. Here is where you can define the
environment by which your audience can monitor and switch tracks. Set screen
background, font, size, colors, and shadows. You can also set general preferences
such as output format and TV safe area.
TV system sets the standard in viewing your video. NTSC is generally used in
North America and Asia while PAL/SECAM is used in most of Europe.
The TV safe area defines the boundaries within which your track titles will
automatically fit. Parts of the background image that fall outside the margins may
be truncated when viewed on a TV screen.
Archive source audio and video files burns the source audio files to an archive
folder in the Music DVD-Video disc.
Auto repeat when disc playback ends sets the disc to replay automatically after
playback.
Use the Preview Window to view the results. To display tooltips, moved the
pointer over the font, size, colors and shadows controls.
Page 26

26 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Making an MP3 disc
MP3 is a popular audio file format that compresses sound files so that they take up
only about 1/10th of their original size. Even though it is highly compressed, its
sound quality is not noticeably compromised, except on extremely hi-fidelity sound
systems. MP3 is ideal for playback on your computer, and for traveling, since
compression enables a large number of MP3 files to be stored on disc for playback
on a small portable MP3 player or CD player. (A CD player that supports MP3
playback is required for playing MP3.)
Burn.Now lets you easily collect your favorite MP3 files and burn them to disc.
To create an MP3 disc:
1. In the Select a Task dialog box, select Create Disc then select MP3 disc.
2. Select the disc type (CD, DVD, or BD) that you will be burning to, then click OK.
3. Choose Burner: Select Burner to select whether to burn directly onto a disc or
create a disc image file. (See “Choosing a disc burner”.)
4. Collect MP3 files from the Source Explorer Window and add them to the Disc
Layout Window.
5. When you are ready to burn the MP3 disc, click Burn disc on the Toolbar.
Note: You can also click to save your project for future use.
Page 27

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 27
Compiling an MP3 disc
The Main Window is where you compile and organize MP3 folders and files to burn
onto a disc.
To compile MP3s for your MP3 disc:
1. Add the MP3 files and folders to burn from the Source Explorer Window to the
Disc Layout Window using any of the methods mentioned at “Source Explorer
Window and Disc Layout Window”.
2. To reorganize data, select any MP3 file or folder in either pane, and drag it to its
new location, up or down the folder structure in the left pane, or directly across
to a different folder from the left pane to the right.
3. To create a new folder, right-click in the right pane then select New Folder from
the menu.
4. To rename a selected folder or file, right-click and select Rename.
5. To delete any MP3 file or folder, select it then click Delete on the Disc
Layout Window toolbar. Select Disc: Revert to reset all settings of an open
project to its previous saved state.
Page 28

28 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Burning the MP3 disc
1. Click Burn disc on the Toolbar. The Burning Options dialog box will be
displayed.
2. In the top half of the dialog box, you can rename the disc label, which can have
up to 16 characters in length.
Only the ISO 9660 file system can be used for MP3 discs. To ensure that
complete MP3 folder and file names will be retained, you can select the Joliet
option. Joliet is an industry standard extension of ISO 9660 file system which
supports Unicode in file names and permits extended file names of up to 64
characters in length, including spaces.
3. In the Disc burner area, you can specify whether to create a disc image or burn
directly onto a disc. (See “Choosing a disc burner”.)
If you are burning directly to a physical burner, the write Speed can also be
selected. If there is a disc inserted in the burner, the program will check the
write speed of the burner and the disc, and by default, choose the highest speed
that both can handle.
4. Click Burn to start burning the disc.
Note: For details on the other options available in this dialog box,
see “Disc burning options”.
Page 29

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 29
Making a bootable disc
Placing a bootable disc in your disc drive automatically loads a boot image and
powers-on or reboots your system. Burn.Now creates bootable data discs using the
ISO 9660 or ISO 9660 + Joliet file system.
To create a bootable disc:
1. Select Bootable disc and the output disc type in the Select a Task dialog box.
Then click OK.
2. In Select bootable source, specify the bootable image source. A boot image
can come from a floppy disk, a USB flash drive which is not mapped as a hard
drive, or a file in your local drive. Make sure that you have your bootable floppy
disk, USB flash drive, or other source files ready.
3. Follow the steps as you would for burning a data disc.
Converting audio files
When creating an audio disc, you can convert audio files to several audio file
formats: mu-law (.au), MP3 (.mp3), MPEG Audio (.mpa), OGG Vorbis (.ogg),
Microsoft WAV (.wav), and Windows Media Audio (.wma).
You can view the metadata information of your source files before you convert
them. These information include album title, track artist, genre, and year. These
metadata can be copied to your output file when you convert if you select an output
format that also supports metadata. Burn.Now has metadata support for .mp3,
.ogg, .wav, and .wma file formats.
Note: Install Apple QuickTime to use the mu-law format.
Page 30

30 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Convert Audio Files dialog box
Add Adds audio files to the list for conversion.
Delete Removes the selected audio file(s) from the list.
Delete All Deletes all audio file(s) from the list.
File Info Displays CD and file info of selected audio files.
Play Plays back the selected audio file.
Audio file list Displays the audio files to be converted.
Output folder Displays the location of the converted audio files. Click Browse to
locate a folder where the converted audio files will be saved.
File type Specifies the output format for the converted audio files.
Quality Specifies the output quality of the converted audio files.
Options Opens a dialog box where you can specify additional settings for the
selected audio encoding format. This option is enabled when User-defined is
selected in Quality.
Page 31

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 31
Information Displays additional information about the selected encoding format.
Add to project after converting Adds the converted files to your project in
Burn.Now.
Convert Converts all selected audio files in the list to the specified audio encoding
format.
To convert audio files:
1. Select Tools: Convert Audio Files (or click on the Toolbar).
2. Click Add to browse for the audio files to be converted. Select them and click
Open.
3. Click Browse to specify the output folder for the converted audio files.
4. Select an audio file format from File type.
5. Select the output quality from Quality.
6. Keep the checkboxes of the audio files to convert selected and click Convert to
start the conversion process. Press [Ctrl] or [Shift] to select or deselect
multiple files or checkboxes.
Note: You can select a file and click the title to rename it. You can
also click metadata information to modify them. When you click
Convert, Burn.Now will write the modified metadata information to
the converted files.
Note: Select User-defined and click Options to specify additional
settings for the selected audio encoding format.
Note: A progress bar under Status indicates the conversion status
for each file.
Page 32

32 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Ripping CD audio
The process of copying an audio track from an audio CD is commonly referred to as
ripping. When creating an audio disc, you can rip Audio CD files and convert them
to file formats compatible with most multimedia software. Supported file types are:
mu-law (.au), MP3 (.mp3), MPEG Audio (.mpa), OGG Vorbis (.ogg), Microsoft WAV
(.wav), and Windows Media Audio (.wma).
Rip CD Audio dialog box
Audio drive Specifies the CD drive which contains the audio CD.
CD and File Info Displays a menu for showing file information or updating CD
information either from the audio CD or the Internet.
Play Plays back the selected audio file.
Note: Install Apple QuickTime to use the mu-law format.
Page 33

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 33
Audio file list Displays the audio tracks to be ripped.
Output folder Displays the location of the ripped audio files. Click Browse to
locate a folder where the ripped audio files will be saved.
File type Specifies the output format for the ripped audio files.
Quality Specifies the output quality of the ripped audio files.
Options Opens a dialog box where you can specify additional settings for the
selected audio encoding format. This option is enabled when User-defined is
selected in Quality.
File naming rule Specifies how the ripped audio files will be named.
Information Displays additional information about the selected encoding format.
Add to project after ripping Adds the ripped files to your project in Burn.Now.
Rip Copies and saves all selected audio files from the list to your output folder.
To rip files from an Audio CD:
1. Insert an Audio CD into your CD-ROM drive.
2. Select Tools: Rip CD Audio, or click on the Toolbar.
3. In the Rip CD Audio dialog box, the track information of all your CD files are
displayed. Keep the checkbox(es) of the track(s) that you want to rip selected.
Clear the checkbox(es) of the track(s) that you do not want to rip. Press [Ctrl]
or [Shift] to select or deselect multiple files or checkboxes.
4. Browse for the folder where the audio file(s) will be stored.
5. Specify the audio encoding format for the audio files in File type.
6. Select the output quality from Quality.
Tip: You can click to play a selected track or click and select
Show File Info to view the properties of selected tracks. For details
on how to get CD info, see “CD and file info”.
Note: You can select a track and click the title to rename it. You can
also click metadata information on the list to modify them.
Page 34

34 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
7. Select how the ripped audio files will be named in File naming rule.
8. Click Rip to start ripping the audio tracks.
CD and file info
When you insert an audio CD into your disc drive and invoke the Rip CD Audio
dialog box, you automatically get information about your CD files such as title,
duration, artist, genre, and year.
You can also view other properties of your CD files or acquire additional information
by querying an Internet music database.
To do this, click
and select any of the following options:
• Show File Info Opens the File Properties dialog box to display file information
such as name, format, size, frame rate, and compression, and other attributes.
• Update CD Info from CD-Text on Audio CD Refreshes the CD info from the
CD-Text information encoded on the audio CD. An album and its tracks can have
separate CD-Text.
• Update CD Info from Internet Opens the Get CD Info from Internet
Database dialog box to allow you to query track info from the freedb server.
Click Access to start the connection then select the information to be included
on disc. Click Select when done.
Tip: To add the ripped tracks to the Disc Layout Window of your
project in Burn.Now, select Add to project after ripping.
Note: If the metadata language of your audio CD is different from
your computer’s operating system’s language, CD and file
information may not be displayed properly. To view these metadata
strings properly:
• Switch the code page of your operating system to the audio CD’s
language by setting options in Control Panel: Regional Settings.
• Install unicode tools that will re-map the unicode character sets if
you are using Windows 2000/XP.
Page 35

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 35
freedb.org is an online music database that includes CD artists, track lists, and
others. Burn.Now lets you connect to the freedb server to get the information from
the online database.
For more information on getting CD and file info, see “Setting preferences”.
Disc burning options
Burn.Now features a number of options to determine how your discs are burnt.
Close disc
Closing a disc prevents additional data to be written onto the disc after the burning
process is finished.
The following guidelines should be followed when deciding whether to close a disc
or leave it open:
• A data disc can be left open. CD-ROM and DVD-ROM drives will be able to read
open data discs.
• Leave an MP3 disc open to keep adding more MP3 files. CD-ROM drives, MP3
players and CD players that support MP3 playback will be able to play open MP3
discs.
• If an Audio CD is left open, it can be appended with data files and used as a data
disc as well. An Audio CD that contains both audio tracks and data tracks is
known as a CD-Extra disc.
Close an Audio CD when writing CD-Text onto the disc. Closing an Audio CD also
makes the disc more compatible with CD players that may not be able to play
open discs.
Note: Internet connection is needed to connect to the online
database.
Note: Burn.Now burns a disc in ‘Disc-at-Once’ mode when you close
the disc, and ‘Track-at-Once’ mode when the disc is left open.
Page 36

36 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Direct burn
Direct burn is a quick way of burning discs since it allows data to be written
directly onto the disc. When this feature is disabled, a temporary disc image file will
first be created on the hard drive before the disc is burnt.
Direct burn must be selected when burning a disc with UDF 1.5 file system or above
since Burn.Now does not allow the creation of disc image files with these file
systems. You can also select this option if you have a fast computer and burner.
You can clear the Direct burn option when burning a disc with ISO 9660 or UDF/ISO
9660 file system, or if you have a slow computer and faster burner device (with a
write speed of higher than 8X) to prevent burning errors.
Test before burning
Selecting this option simulates the recording process before burning data to disc.
This helps in checking if the system speed or CD-ROM/DVD-ROM speed is fast
enough to send data to the burner at the specified write speed. However, this
doubles the burning time.
Buffer underrun protection
If the burning device has buffer underrun protection capability, this feature is
enabled in the Burning Options dialog box. Selecting this option ensures an
uninterrupted flow of data to minimize the risk of errors in the burning process.
Check source files
This option verifies if each source file exists and is readable before starting the
burning process.
Note: It is recommended that multiple programs are not running
while directly burning to disc, to prevent burning errors and to
increase your computer’s performance.
Note: If your burning device has buffer underrun protection and this
function is enabled, you can clear the Test before burning option to
save time when burning discs.
Page 37

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 37
Verify after burning
When burning data, MP3, bootable, DVD-Audio, or Music DVD-Video, discs, you can
select this option to have Burn.Now compare the final result with the original data.
This will make sure the process is successful.
Burn with synchronization info
When creating a data disc, you can select this option to include synchronization info
when burning. The next time you edit the disc in Burn.Now, the recorded files will
be automatically compared with the files in the original location on the hard drive,
and the disc compilation will be updated based on settings in the Edit Disc tab of
the Preferences dialog box.
Page 38

38 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Span disc
When creating a data, MP3, or bootable disc and the total size of your compilation
in Disc Layout Window exceeds the capacity of your current disc, Burn.Now can
arrange or span your data in two or more discs. As you insert your files, the Disc-
space meter instantly shows the estimated number of required discs and the
amount of space used on each one.
Note: When creating a bootable disc and you need to apply the Span
disc function, you can choose to make only the first disc that you will
burn bootable or all the succeeding discs.
Page 39

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 39
After clicking the Burn button in the Burning Options dialog box, the program
checks your disc and prompts you to confirm if you want to span your data. Clicking
Yes opens the Span Disc Options dialog box for you to select the way your data
will be arranged.
• Fast (same file order) arranges your files in their originally sequence.
Although this method may require more disc space, it is the faster and easier
way to burn to multiple discs.
• Optimize (minimum number of discs) rearranges your files to save on disc
space. Processing time may take longer.
Clicking OK continues the disc spanning process.
Tips:
• When burning multiple discs, use discs of the same brand and
media type to avoid possible differences in size.
• The Span disc function cannot be applied if Burn with
synchronization info is selected under Advanced Settings in
the Burning Options dialog box.
• A single large file cannot be spanned into multiple discs.
Page 40

40 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Editing a disc
Burn.Now harnesses the versatility of rewritable discs by allowing you to edit the
contents of a data disc or MP3 disc without needing to erase or format it first. You
can also add files and folders on appendable discs.
Modifying disc contents
To add and edit data on a disc:
1. Insert the rewritable disc to be edited into the disc burner.
2. In the Select a Task dialog box, select Edit Disc and then specify the disc
burner.
3. Select the type of disc (Data disc or MP3 disc) to be edited and then click OK.
The contents of the disc will be displayed in the Disc Layout Window.
Existing files and folders will be shown in grayed-out text, but can be moved,
deleted, renamed and reorganized in the same way as when compiling a new
disc. Once existing files are edited, they are no longer shown as grayed text, but
black.
Tip: Detailed information about both the burner and the disc can be
viewed by clicking then selecting Drive Information and Disc
Information. respectively.
Note: If Refresh compilation automatically is selected in
Preferences, and the disc was created with synchronization info in
Burn.Now, the disc contents will be automatically compared with
their original files located on the hard drive.
Page 41

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 41
4. To add more files or folders, use any of the methods mentioned at “Source
Explorer Window and Disc Layout Window”.
New and modified files and folders are shown in black.
To add and edit data on a specific disc session:
1. Insert a rewritable multi-session disc into the disc burner.
2. In the Select a Task dialog box, select Edit Disc and then specify the disc
burner.
3. Select the type of disc (Data disc or MP3 disc) to be edited and then click OK.
4. The contents of the disc will be displayed in the Disc Layout Window.
5. Select Disc: Edit Existing Session.
6. Select the session to edit in the Selection Session dialog box and click OK to
continue editing.
7. To add more files or folders, use any of the methods mentioned at “Source
Explorer Window and Disc Layout Window”.
New and modified files and folders are shown in black.
Note: If a file name (or folder name) that you want to add already
exists on the disc, you will be prompted to confirm whether or not to
overwrite the existing files.
Page 42

42 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Burning the edited disc
1. Click Burn disc on the Toolbar. The Burning Options dialog box opens.
2. In the top half of the dialog box, you can rename the disc label, which can have
up to 16 characters in length. The file system cannot be changed. The disc will
be burned using the existing file system.
3. In the lower half of the dialog box, you can change the write Speed.
If a disc is
already inserted in the burner, the program will check the write speed of the
burner and the disc, and by default, will choose the highest speed that both can
handle.
4. Click Burn to start the burning process.
Notes:
• If the disc was created in Burn.Now, the Burn with
synchronization info option under Advanced Settings
cannot be changed.
• For details on the other options available in this dialog box, see
“Disc burning options”.
Page 43

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 43
Copying a disc
Burn.Now’s Copy Disc feature lets you duplicate any type of disc, including VCDs,
SVCDs and DVDs, as long as it is not copy protected. You can make direct disc to
disc copies, or copy a disc as a disc image file. You can also duplicate a disc from a
disc image file and copy from a DVD-Video folder.
To use the Copy Disc feature, select Copy Disc in the Select a Task dialog box or
select Disc: Copy Disc on the Menu Bar.
Making a disc to disc copy
Burn.Now allows you to copy ‘on-the-fly’, that is, to directly copy the contents from
a source disc to a new disc.
To make a disc to disc copy:
1. Insert the source disc into your CD-ROM or DVD-ROM drive and a blank disc into
your disc burner.
2. In the Select a Task dialog box, select Copy Disc.
3. Under Source, select Disc/Folder then choose your source drive. Under
Destination, choose your burner drive.
4. Click to see more burning options.
5. Set the Read speed. If there is a disc inserted in the source CD-ROM/DVD-ROM
drive, the program will check the read speed of the drive and the disc, and by
default, will choose the highest speed that both can handle.
Note: DVD-VR/+VR contents will be converted to DVD-Video.
Note: Your disc burner can both be your source drive and
destination drive. While copying, Burn.Now will prompt you to
insert the source disc and then the blank disc.
Tip: When copying audio CDs, choose a low read speed to
preserve the audio quality. When copying data discs or other
types of discs, choosing a high read speed minimizes buffer
underrun errors.
Page 44

44 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
6. Set the Write speed. If there is a disc inserted in the burner drive, the program
will check the write speed of the burner and the disc, and by default, will choose
the highest speed that both can handle.
7. Specify the number of disc Copies to burn.
8. Select On-the-fly to directly copy from the source disc.
9. Select Buffer underrun protection to prevent interruptions in the flow of data
from the source disc to the burner and ensure a safe burn.
10.Click Copy to start copying.
Creating a disc image file
A disc image file is a single file that has captured the entire contents and file
structure of a disc. Creating a disc image file on your hard disk allows you to
archive the source disc contents for backup or future burning.
To create a disc image file:
1. Insert the source disc into your CD-ROM or DVD-ROM drive.
2. In the Select a Task dialog box, select Copy Disc.
3. Under Source, select Disc/Folder then choose your source drive.
4. Under Destination, select Disc image file.
5. Click Copy. The Save As dialog box will be displayed.
6. Select a file format. The disc image file can be saved in .iso which is a standard
disc image format or .ixb which is Ulead’s native format.
7. Specify a file name for the disc image file, and click Save to create the disc
image file.
Note: If you encounter a buffer underrun error even with the Buffer
underrun protection option selected, choose a lower write speed or
clear On-the-fly and try copying the disc again. Disabling on-the-fly
copying allows a temporary disc image file of the source disc
contents to be saved first in the hard drive before burning the disc.
This reduces the risk of copying failure.
Page 45

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 45
Burning a disc from a disc image file
If you created a disc image file from a source disc, or if you previously saved a disc
image file for a data, MP3, or audio disc created in Burn.Now, you can easily burn
multiple disc copies using the image file.
To burn a disc from a disc image file:
1. Insert a blank disc in your disc burner.
2. In the Select a Task dialog box, select Copy Disc.
3. Under Source, select Disc image file then click Browse to open an image file.
4. Under Destination, choose your burner drive.
5. Click Advanced to see more burning options.
6. Set the Write speed. If there is a disc inserted in the burner drive, the program
will check the write speed of the burner and the disc, and by default, will choose
the highest speed that both can handle.
7. Specify the number of disc Copies to burn.
8. Select Buffer underrun protection to prevent interruptions in the flow of data
from the hard disk to the burner and ensure a safe burn.
9. Click Copy to start the burning process.
Page 46

46 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Handling rewritable discs
Rewritable discs such as CD-RW, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, and DVD-RAM are often used
for regular backups, and they can be easily erased or reformatted to be written
over again using Burn.Now’s Disc Tools.
To access the tools, select Disc Tools in the Select a Task dialog box or select
them from the Disc menu in the program window.
Erase
Erasing a rewritable disc removes the disc contents. There are two ways to erase a
disc:
• Quick erase - Deletes only the Table of Contents of the disc. The file system,
tracks and sectors on the disc are not physically removed. This method simply
allows the disc to be overwritten.
• Full erase - Deletes all the information, including the file system, tracks and
sectors from the disc.
UDF Format
UDF Format writes the UDF (Universal Disc Format) file system to a rewritable
disc to enable random packet writing. Random packet writing allows disc space to
be used more efficiently when burning data onto the disc. It allows data to be
written onto the disc in the same way as the hard disk, freeing disc space as data
are deleted, and reusing freed space. A disc can be formatted with UDF 1.5 or
above. To format a disc, click Disc: Format Disc. There are two options for
formatting a disc:
Page 47

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 47
• Quick format - Provides a fast way of reformatting CD-RW, DVD+RW and DVDRW discs that have previously been full formatted. It simply removes the file
system table from the disc without checking for defects (that is, bad sectors) and
writes the selected UDF file system to the disc.
• Full format - Completely formats a disc using the selected UDF file system, and
writes new tracks and sectors onto the disc. This formatting method takes a
longer time to complete, but it makes the disc error-free. Burn.Now supports full
formatting of all types of discs.
If Full format is selected or your disc had been fully formatted and you are
using the UDF 2.5 file system, you can select the Mirror UDF metadata option.
This records 2 copies of your data structure in physically separated areas on
your disc to enhance the readability of your disc.
UDF Certify
For a UDF formatted DVD-RW and CD-RW, you can apply disc certification to scan
the disc and check if there is any problem. The certification process marks bad
sectors to improve future writing reliability. On DVD-RW and CD-RW burners that
support DRT-DM (Distributed Real-Time Defect Management), the certification
process also moves the data in the recoverable defected sectors (DRT-DM Level-1
and Level-2 defects, if any) to healthy sectors for further improvement in data
reliability.
Page 48

48 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Checking burner and disc information
Before burning a disc, check the burner information to find out the capabilities of
your burner. It is also recommended that you check disc status and other
information before overwriting its contents.
Checking burner capabilities
To find out about the capabilities of your burner, select Burner: Select Burner and
choose the burner drive. The dialog box will show the read and write speeds of your
burner.
Click Advanced to see more information about the burner. A list of disc formats
and write methods will then be displayed. Items with check marks indicate the disc
formats that your burner can read from and write to as well as the different write
and error-handling methods that your burner uses when burning a disc.
Page 49

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 49
Checking disc properties
Select Burner: Disc Information to check how much information has already
been written to the disc. The dialog box will show the disc media type, its capacity,
and the number of tracks and sessions that have been written onto the disc.
Click Advanced to see more information about your disc. Items with check marks
indicate the current status of your disc (for instance, whether it is blank or a
formatted disc), and the types of operations that can be performed on your disc.
Note: You can also check burner information in Edit Disc, Copy
Disc, or Disc Tools. Click in the Select a Task dialog box then
select Drive Information.
Note: You can also check disc information in Edit Disc, Copy Disc,
or Disc Tools. Click in the Select a Task dialog box then select
Disc Information.
Page 50

50 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Appendix A: Menus and commands
Disc menu
Create Disc Creates a new data, audio, or MP3 disc.
Edit Disc Modifies the contents of a disc.
Copy Disc Copies disc to disc, disc to image file, or
image file to disc.
Burn from Disc
Image
Creates a disc from a disc image file.
Edit Existing
Session
Adds or edits files in a specific session on a
disc created in Burn.Now.
Open Opens a Burn.Now project file.
Save Stores the current project.
Save As Stores the project using a specified name.
Revert Restores current project to its previous
saved state.
Burn Disc Writes information to a disc.
Label@Once Opens the Label@Once program.
Erase Disc Removes the contents of a disc.
Format Disc Formats a rewritable disc with the UDF file
system.
Certify Disc Scans and marks the disc for bad sectors.
Load/Eject Disc Inserts/removes the current disc into/from
the burner.
Preferences Opens the Preferences dialog box.
Recent File Lists recently opened files.
Exit Closes Ulead Burn.Now.
Edit menu
Cut Cuts a selection to the clipboard.
Copy Copies a selection to the clipboard.
Paste Pastes a selection from the clipboard.
Delete Removes selected folders/files.
Page 51

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 51
New Folder Creates a new folder in Disc Layout
Window.
Select All Selects all folders/files.
Select None Clears all selections.
Invert Selection Reverses the selection to the unselected
folders/files.
Sort by Arranges folders/files in a specified order.
Move Track Moves a selected track up or down.
Play Plays a selected audio file.
Pause Pauses playback.
Stop Stops playback.
Effects Applies volume level control and removes
unwanted elements in your audio file.
View menu
Toolbar Shows or hides the Toolbar.
Disc-space Meter Shows or hides the Disc-space Meter.
Status Bar Shows or hides the Status Bar.
Tools menu
Convert Audio
Files
Opens a dialog box where you can change
an audio file's format and then save it as
another file.
Rip CD Audio Opens a dialog box where you can copy
files from an audio CD and then store them
in your hard drive.
Find Finds a file in your computer.
Add Files Adds files to the Disc Layout Window.
Burner menu
Select Burner Selects the disc burner.
Disc Information Displays disc status and other information.
Edit menu
Page 52

52 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Appendix B: Glossary
Blu-ray Disc (BD)
A next-generation disc format to record, rewrite, and playback high-definition video
(HD). The format is also likely to become a standard for PC data storage and highdefinition movies in the future.
Bootable disc
A disc containing a bootable image that the user can use to start a computer.
CD-Text
Disc and track-related information on Audio CDs. CD-Text can only be read and
displayed by CD-ROM drives and CD players that support the feature.
Disc-At-Once
A writing mode that allows data to be written continuously on the disc, without any
interruptions. This mode closes the disc after the writing process.
Dolby Digital audio
An audio compression format developed by Dolby Lab for multiple audio channels.
Burn.Now supports 2 audio channels.
DVD-Audio (DVD-A)
A format that allocates most of the DVD disc space to audio and is primarily used
for recording high-quality songs and music on DVD. Audio can be recorded on DVD
in a wide range of sampling frequencies between 44.1 kHz to 192 kHz and
resolutions of 16, 20 or 24 bits, with up to six discrete channels.
A DVD-Audio disc contains two folders: AUDIO_TS and VIDEO_TS. AUDIO_TS
stores high-quality audio as .aob files along with still images (for use as menu
backgrounds), navigation, and text. A limited amount of conventional DVD-Video
data can be recorded in the VIDEO_TS folder.
DVD-Audio discs can only be played in DVD-Audio capable players.
Page 53

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 53
DVD-Video (DVD-V)
The standard format used for recording movies on DVD. MPEG-2 is the dominant
video encoding method used in recording movies for its superlative video quality,
although MPEG-1 may also be used. The audio part of the video can be encoded in
formats such as PCM, Dolby Digital, or DTS (Digital Theater Sound). DVD-Video
provides standard 4:3 and widescreen 16:9 aspect ratios, up to 9 camera angles,
up to 8 languages, up to 32 subtitle tracks, fully interactive menus, and instant
search of titles, chapters, music tracks, and timecode. DVD-Video discs can be
played on standalone DVD players or on computers equipped with a DVD-ROM
drive.
Incremental Write
A writing mode that sequentially appends data to the disc until the disc is full.
Joliet
A Microsoft extension to the ISO 9660 file system that handles long file names (up
to 64 characters in length, including spaces).
Linear Pulse Code Modulation, Linear PCM (LPCM)
An uncompressed audio format that is similar to CD audio but with higher sampling
frequencies and resolutions. It encodes audio on a DVD with a sampling frequency
of 48 or 96kHz, resolution of 16, 20 or 24 bits per sample, and with up to eight
channels. LPCM’s maximum bit rate is 6.144 Mb/s, which is higher than Dolby
Digital or MPEG-2.
Mount Rainier
A storage format for CD-RW media that is developed by the Mount Rainier Technical
Group. It intends to make the use of CD-RW discs a lot easier by allowing dragand-drop file copying. Unlike conventional CD-RW burners, Mount Rainier capable
burners provide background formatting and defect management features.
Music DVD-Video
A DVD burned in this format using Ulead Burn.Now is the same as the regular DVDVideo disc, except that the DVD is recorded with audio data only (without any video
content). Similarly, recordings are stored as .vob files in the VIDEO_TS folder on
the DVD.
Page 54

54 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
OGG Vorbis
An open, free, and not patented audio compression format developed by Xiph.Org.
This audio format can rival other proprietary, patented audio formats.
On-the-fly
A writing process that allows direct disc-to-disc copying without saving a temporary
disc image file on the hard disk.
Random Packet Write
A writing process where small amounts of data can be written and deleted in one
action. This writing method allows disc space to be used more efficiently when
burning data onto the disc. It allows data to be written onto the disc in the same
way as the hard disk, freeing disc space as data are deleted and reusing freed
space.
Raw Mode
A disc writing process which reads and writes data as is. In this mode, the disc
burner does not correct or repair errors before burning data onto the disc. If this
method is used, errors on the original source will also be present on the disc.
Restricted Overwrite
A writing method for DVD-RW that allows random overwriting of data. This method
can only be used on pre-formatted DVD-RW discs.
Session-At-Once
A method that writes data in one uninterrupted sequence, that is, by session. A
session is an area on the disc that contains one or more tracks depending on the
amount of data burnt at a time. This writing method always closes each session but
leaves the disc open.
Page 55

Burn.Now
ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 55
Session
A collection of one or more tracks. In CD disc, each recording process generates a
session containing all the tracks recorded at that time. A CD recorded in multiple
recording sessions is known as a multi-session CD. In DVD disc, there is only one
session in the disc.
Span disc
A feature that arranges files into multiple discs when the total size of a compilation
exceeds the capacity of the current disc.
Test Write
A simulation of the burning process before actually writing data to the disc.
Track-At-Once
A writing mode that writes data to a disc by track. When burning a disc in this
mode, the burner’s laser turns on and off in between tracks, creating a gap
between tracks. (This is equivalent to two-second gaps of silence between audio
tracks on an Audio CD.)
Page 56

56 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
Index
A
Audio CD 18
adding CD-Text 22
audio disc
burning 23
compiling 19
creating 18
data format 18
Audio CD 18
DVD-Audio 18
Audio effects 21
audio files 29
Audio gap 21
B
Blu-ray Disc 6
burner 13
Burner menu 51
burning 23
audio disc 23
data disc 17
edited disc 41
from a disc image file 45
MP3 disc 28
options 35
Burning Options dialog box 23
audio CD 23
data disc 17
edited disc 42
MP3 disc 28
C
CD audio 32
CD-Text 22, 24, 52
checking 48
burner capabilities 48
disc properties 49
commands 50
copy 43
copying a disc 43
burning a disc from a disc image
file 45
creating a disc image file 44
making a disc to disc copy 43
D
data disc 15
burning 17
compiling 16
creating 15
disc burner 13
choosing a disc burner 13
disc burning options 35
Buffer underrun protection 36
Check source files 36
Close disc 35
Direct burn 36
Test before burning 36
Verify after burning 37
Disc image file 13
disc image file
Page 57

ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE 57
Burn.Now
.iso 13
.ixb 13
creating 44
Disc Information dialog box 49
Disc Layout Window 10
Disc menu 50
Disc Tools 46
Disc-At-Once 52
Disc-space Meter 10
Dolby Digital 19, 52
DVD-Audio 18, 52
DVD-Video 53
E
Edit Existing Session 41
Edit menu 50
editing audio files 20
eject 12
Erase 46
Full erase 46
Quick erase 46
Export audio tracks 21
F
file systems 14
ISO 9660 14
UDF 1.5, 2.0 and 2.01 14
UDF 2.5 14
UDF/ISO 9660 14
format 46
I
Incremental Write 53
ISO 9660 14
J
Joliet 53
L
LPCM 19, 53
M
Main Window 9
making a bootable disc 28
menus 50
Menus and Toolbar 9
Mount Rainier 53
MP3 disc 26
burning 28
compiling 27
creating 26
editing 38
Music DVD-Video 18, 53
O
OGG Vorbis 54
On-the-fly 54
P
Preferences dialog box 12
CD Info 12
Edit Disc 13
General 12
Project Settings 25
Page 58

58 ULEAD BURN.NOW USER GUIDE
R
Random Packet Write 54
Raw Mode 54
Restricted Overwrite 54
rewritable discs 46
erasing 46
formatting 46
ripping 32
running the program 7
S
Select a Task dialog box 8
Session-At-Once 54
Source Explorer Window 10
Span disc 38
T
Test Write 55
Tools menu 51
Track-At-Once 55
Trim audio 20
U
UDF 14
UDF 1.5, 2.0 and 2.01 14
UDF 2.5 14
UDF 2.6 Low 14
UDF Certify 47
UDF Format 46
Full format 47
Quick format 47
UDF/ISO 9660 14
user interface 8
V
View menu 51
 Loading...
Loading...