Page 1

Abstract
This document describes the features and the system integration of
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series multi-mode cellular modules.
These modules are a complete and cost efficient LTE/3G/2G solution
offering up to 150 Mb/s download and 50 Mb/s upload data rates,
covering up to six LTE bands, up to five WCDMA/DC-HSPA+ bands
and four GSM/EGPRS bands in the compact TOBY LGA form factor of
TOBY-L2 modules or in the industry standard PCI Express Mini Card
form factor of MPCI-L2 modules.
TOBY-L2 series
www.u-blox.com
UBX-13004618 - R04
MPCI-L2 series
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series
LTE/DC-HSPA+/EGPRS modules
System Integration Manual
Page 2

Document Information
Title
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series
Subtitle
LTE/DC-HSPA+/EGPRS modules
Document type
System Integration Manual
Document number
UBX-13004618
Revision and date
R04
30-Sep-2014
Document status
Advance Information
Document status explanation
Objective Specification
Document contains target values. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
Advance Information
Document contains data based on early testing. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
Early Production Information
Document contains data from product verification. Revised and supplementary data may be published later.
Production Information
Document contains the final product specification.
Name
Type number
Firmware version
PCN / IN
TOBY-L200
TOBY-L200-00S-00
09.40
UBX-14040967
TOBY-L210
TOBY-L210-00S-00
09.40
UBX-14040967
MPCI-L200
MPCI-L200-00S-00
09.34
UBX-14040967
MPCI-L210
MPCI-L210-00S-00
09.34
UBX-14040967
This document applies to the following products:
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
u-blox reserves all rights to this document and the information contained herein. Products, names, logos and designs described herein may in
whole or in part be subject to intellectual property rights. Reproduction, use, modification or disclosure to third parties of this document or
any part thereof without the express permission of u-blox is strictly prohibited.
The information contained herein is provided “as is” and u-blox assumes no liability for the use of the information. No warranty, either
express or implied, is given, including but not limited, with respect to the accuracy, correctness, reliability and fitness for a particular purpose
of the information. This document may be revised by u-blox at any time. For most recent documents, please visit www.u-blox.com.
Copyright © 2014, u-blox AG
u-blox® is a registered trademark of u-blox Holding AG in the EU and other countries. PCI, PCI Express, PCIe, and PCI-SIG are trademarks or
registered trademarks of PCI-SIG. Microsoft and Windows are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries. ARM® is a registered trademark of ARM Limited in the EU and other countries. All other registered
trademarks or trademarks mentioned in this document are property of their respective owners.
UBX-13004618 - R04
Page 2 of 141
Page 3

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Preface
u-blox Technical Documentation
As part of our commitment to customer support, u-blox maintains an extensive volume of technical
documentation for our products. In addition to our product-specific technical data sheets, the following manuals
are available to assist u-blox customers in product design and development.
AT Commands Manual: This document provides the description of the AT commands supported by the
u-blox cellular modules.
System Integration Manual: This document provides the description of u-blox cellular modules’ system
from the hardware and the software point of view, it provides hardware design guidelines for the optimal
integration of the cellular modules in the application device and it provides information on how to set up
production and final product tests on application devices integrating the cellular modules.
Application Note: These documents provide guidelines and information on specific hardware and/or
software topics on u-blox cellular modules. See Related documents for a list of Application Notes related to
your Cellular Module.
How to use this Manual
The TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series System Integration Manual provides the necessary information to successfully
design and configure the u-blox cellular modules.
This manual has a modular structure. It is not necessary to read it from the beginning to the end.
The following symbols are used to highlight important information within the manual:
An index finger points out key information pertaining to module integration and performance.
A warning symbol indicates actions that could negatively impact or damage the module.
Questions
If you have any questions about u-blox Cellular Integration:
Read this manual carefully.
Contact our information service on the homepage http://www.u-blox.com/
Technical Support
Worldwide Web
Our website (http://www.u-blox.com/) is a rich pool of information. Product information, technical documents
can be accessed 24h a day.
By E-mail
Contact the closest Technical Support office by email. Use our service pool email addresses rather than any
personal email address of our staff. This makes sure that your request is processed as soon as possible. You will
find the contact details at the end of the document.
Helpful Information when Contacting Technical Support
When contacting Technical Support, have the following information ready:
Module type (TOBY-L200) and firmware version
Module configuration
Clear description of your question or the problem
A short description of the application
Your complete contact details
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Preface
Page 3 of 141
Page 4

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Contents
Preface ................................................................................................................................ 3
Contents .............................................................................................................................. 4
1 System description ....................................................................................................... 8
1.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................................. 8
1.2 Architecture ........................................................................................................................................ 10
1.2.1 Internal blocks ............................................................................................................................. 11
1.3 Pin-out ............................................................................................................................................... 12
1.3.1 TOBY-L2 series pin assignment .................................................................................................... 12
1.3.2 MPCI-L2 series pin assignment .................................................................................................... 16
1.4 Operating modes ................................................................................................................................ 18
1.5 Supply interfaces ................................................................................................................................ 20
1.5.1 Module supply input (VCC or 3.3Vaux) ....................................................................................... 20
1.5.2 RTC supply input/output (V_BCKP) .............................................................................................. 27
1.5.3 Generic digital interfaces supply output (V_INT) ........................................................................... 28
1.6 System function interfaces .................................................................................................................. 29
1.6.1 Module power-on ....................................................................................................................... 29
1.6.2 Module power-off ....................................................................................................................... 31
1.6.3 Module reset ............................................................................................................................... 33
1.6.4 Module configuration selection by host processor ....................................................................... 33
1.7 Antenna interface ............................................................................................................................... 34
1.7.1 Antenna RF interfaces (ANT1 / ANT2) .......................................................................................... 34
1.7.2 Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET) ...................................................................................... 37
1.8 SIM interface ...................................................................................................................................... 37
1.8.1 SIM interface ............................................................................................................................... 37
1.8.2 SIM detection interface ............................................................................................................... 37
1.9 Data communication interfaces .......................................................................................................... 38
1.9.1 Universal Serial Bus (USB) ............................................................................................................ 38
1.9.2 Asynchronous serial interface (UART)........................................................................................... 42
1.9.3 DDC (I2C) interface ...................................................................................................................... 44
1.9.4 Secure Digital Input Output interface (SDIO) ................................................................................ 45
1.10 Audio .............................................................................................................................................. 45
1.10.1 Digital audio over I2S interface ..................................................................................................... 45
1.11 General Purpose Input/Output ........................................................................................................ 46
1.12 Mini PCIe specific signals (W_DISABLE#, LED_WWAN#) .................................................................. 47
1.13 Reserved pins (RSVD) ...................................................................................................................... 47
1.14 Not connected pins (NC) ................................................................................................................. 47
1.15 System features............................................................................................................................... 48
1.15.1 Network indication ...................................................................................................................... 48
1.15.2 Antenna supervisor ..................................................................................................................... 48
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Contents
Page 4 of 141
Page 5

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.15.3 Jamming detection ...................................................................................................................... 48
1.15.4 IP modes of operation ................................................................................................................. 49
1.15.5 Dual stack IPv4/IPv6 ..................................................................................................................... 49
1.15.6 TCP/IP and UDP/IP ....................................................................................................................... 49
1.15.7 FTP and FTPS ............................................................................................................................... 49
1.15.8 HTTP and HTTPS .......................................................................................................................... 50
1.15.9 SSL .............................................................................................................................................. 50
1.15.10 AssistNow clients and GNSS integration ................................................................................... 50
1.15.11 Hybrid positioning and CellLocate® .......................................................................................... 50
1.15.12 Firmware update Over AT (FOAT)............................................................................................. 53
1.15.13 Firmware update Over The Air (FOTA) ...................................................................................... 53
1.15.14 In-band Modem (eCall / ERA-GLONASS) .................................................................................. 54
1.15.15 SIM Access Profile (SAP) ........................................................................................................... 54
1.15.16 Smart temperature management ............................................................................................. 56
1.15.17 Power saving ........................................................................................................................... 58
2 Design-in ..................................................................................................................... 59
2.1 Overview ............................................................................................................................................ 59
2.2 Supply interfaces ................................................................................................................................ 60
2.2.1 Module supply (VCC or 3.3Vaux)................................................................................................. 60
2.2.2 RTC supply output (V_BCKP) ....................................................................................................... 72
2.2.3 Generic digital interfaces supply output (V_INT) ........................................................................... 74
2.3 System functions interfaces ................................................................................................................ 75
2.3.1 Module power-on (PWR_ON) ...................................................................................................... 75
2.3.2 Module reset (RESET_N or PERST#) .............................................................................................. 76
2.3.3 Module configuration selection by host processor ....................................................................... 77
2.4 Antenna interface ............................................................................................................................... 78
2.4.1 Antenna RF interfaces (ANT1 / ANT2) .......................................................................................... 78
2.4.2 Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET) ...................................................................................... 86
2.5 SIM interface ...................................................................................................................................... 88
2.5.1 Guidelines for SIM circuit design.................................................................................................. 88
2.5.2 Guidelines for SIM layout design ................................................................................................. 94
2.6 Data communication interfaces .......................................................................................................... 95
2.6.1 Universal Serial Bus (USB) ............................................................................................................ 95
2.6.2 Asynchronous serial interface (UART)........................................................................................... 97
2.6.3 DDC (I2C) interface .................................................................................................................... 101
2.6.4 Secure Digital Input Output interface (SDIO) .............................................................................. 105
2.7 Audio interface ................................................................................................................................. 106
2.7.1 Digital audio interface ............................................................................................................... 106
2.8 General Purpose Input/Output .......................................................................................................... 108
2.9 Mini PCIe specific signals (W_DISABLE#, LED_WWAN#) .................................................................... 109
2.10 Reserved pins (RSVD) .................................................................................................................... 110
2.11 Module placement ........................................................................................................................ 111
2.12 TOBY-L2 series module footprint and paste mask ......................................................................... 112
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Contents
Page 5 of 141
Page 6

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
2.13 MPCI-L2 series module installation ................................................................................................ 113
2.14 Thermal guidelines ........................................................................................................................ 115
2.15 ESD guidelines .............................................................................................................................. 116
2.15.1 ESD immunity test overview ...................................................................................................... 116
2.15.2 ESD immunity test of TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series reference designs ........................................ 117
2.15.3 ESD application circuits .............................................................................................................. 117
2.16 Schematic for TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series module integration .................................................... 118
2.17 Design-in checklist ........................................................................................................................ 120
2.17.1 Schematic checklist ................................................................................................................... 120
2.17.2 Layout checklist ......................................................................................................................... 121
2.17.3 Antenna checklist ...................................................................................................................... 121
3 Handling and soldering ........................................................................................... 122
3.1 Packaging, shipping, storage and moisture preconditioning ............................................................. 122
3.2 Handling ........................................................................................................................................... 122
3.3 Soldering .......................................................................................................................................... 123
3.3.1 Soldering paste.......................................................................................................................... 123
3.3.2 Reflow soldering ....................................................................................................................... 123
3.3.3 Optical inspection ...................................................................................................................... 124
3.3.4 Cleaning .................................................................................................................................... 124
3.3.5 Repeated reflow soldering ......................................................................................................... 125
3.3.6 Wave soldering.......................................................................................................................... 125
3.3.7 Hand soldering .......................................................................................................................... 125
3.3.8 Rework ...................................................................................................................................... 125
3.3.9 Conformal coating .................................................................................................................... 125
3.3.10 Casting ...................................................................................................................................... 125
3.3.11 Grounding metal covers ............................................................................................................ 125
3.3.12 Use of ultrasonic processes ........................................................................................................ 125
4 Approvals .................................................................................................................. 126
4.1 Product certification approval overview ............................................................................................. 126
4.2 Federal Communications Commission and Industry Canada notice ................................................... 127
4.2.1 Safety warnings review the structure ......................................................................................... 127
4.2.2 Declaration of Conformity – United States only ......................................................................... 127
4.2.3 Modifications ............................................................................................................................ 127
4.3 R&TTED and European Conformance CE mark ................................................................................. 129
5 Product testing ......................................................................................................... 130
5.1 u-blox in-series production test ......................................................................................................... 130
5.2 Test parameters for OEM manufacturer ............................................................................................ 131
5.2.1 “Go/No go” tests for integrated devices .................................................................................... 131
5.2.2 RF functional tests ..................................................................................................................... 131
Appendix ........................................................................................................................ 133
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Contents
Page 6 of 141
Page 7

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
A Glossary .................................................................................................................... 133
B Migration between TOBY-L1 and TOBY-L2 ............................................................ 135
B.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................... 135
B.2 Pin-out comparison between TOBY-L1 and TOBY-L2 ........................................................................ 136
B.3 Schematic for TOBY-L1 and TOBY-L2 integration .............................................................................. 138
Related documents......................................................................................................... 139
Revision history .............................................................................................................. 140
Contact ............................................................................................................................ 141
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Contents
Page 7 of 141
Page 8

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Module
LTE
UMTS
GSM
Positioning
Interfaces
Audio
Features
LTE category
Bands
HSDPA category
HSUPA category
Bands
GPRS/EDGE multi-slot class
Bands
GNSS receiver
GNSS Via Modem
Assist Now Software
CellLocate
®
UART
USB 2.0
SDIO
DCC (I
2
C)
GPIOs
MIMO 2x2 / Rx Diversity
Analog audio
Digital Audio
Network indication
Antenna supervisor
Jamming detection
Embedded TCP/UDP stack
Embedded HTTP,FTP,SSL
FOTA
eCall / ERA GLONASS
Dual stack IPv4/IPv6
TOBY-L200
4
2,4,5,
7,17
24
6
850/900/AWS
1900/2100
12
Quad
F F F F • F F F • F • F F F F F F
•
TOBY-L210
4
1,3,5,
7,8,20
24
6
850/900
1900/2100
12
Quad
F F F F • F F F • F • F F F F F F
•
MPCI-L200
4
2,4,5,
7,17
24
6
850/900/AWS
1900/2100
12
Quad • • • F F F F •
MPCI-L210
4
1,3,5,
7,8,20
24
6
850/900
1900/2100
12
Quad • • • F F F F •
F = will be supported in future product version “01”
1 System description
1.1 Overview
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series comprises LTE/3G/2G multi-mode modules supporting up to six LTE bands, up to
five UMTS/DC-HSPA+ bands and four GSM/(E)GPRS bands for voice and/or data transmission as following:
TOBY-L200 and MPCI-L200 are designed primarily for operation in America
TOBY-L210 and MPCI-L210 are designed primarily for operation in Europe, Asia and other countries
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series are designed in two different form-factors suitable for applications as following:
TOBY-L2 modules are designed in the small TOBY 152-pin Land Grid Array form-factor (35.6 x 24.8 mm),
easy to integrate in compact designs and form-factor compatible with the u-blox cellular module families:
this allows customers to take the maximum advantage of their hardware and software investments, and
provides very short time-to-market.
MPCI-L2 modules are designed in the industry standard PCI Express Full-Mini Card form-factor (51 x 30 mm)
easy to integrate into industrial and consumer applications and also ideal for manufacturing of small series.
With LTE Category 4 data rates at up to 150 Mb/s (down-link) and 50 Mb/s (up-link), the modules are ideal for
applications requiring the highest data-rates and high-speed internet access. TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series
modules are the perfect choice for consumer fixed-wireless terminals, mobile routers and gateways, and
applications requiring video streaming. They are also optimally suited for industrial (M2M) applications, such as
remote access to video cameras, digital signage, telehealth, and security and surveillance systems.
Table 1 summarizes the TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series main features and interfaces.
Table 1: TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series main features summary
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 8 of 141
Page 9

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
4G LTE
3G UMTS/HSDPA/HSUPA
2G GSM/GPRS/EDGE
3GPP Release 9
Long Term Evolution (LTE)
Evolved Uni.Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA)
Frequency Division Duplex (FDD)
DL Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) 2 x 2
3GPP Release 8
Dual-Cell HS Packet Access (DC-HSPA+)
UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (UTRA)
Frequency Division Duplex (FDD)
DL Rx diversity
3GPP Release 8
Enhanced Data rate GSM Evolution (EDGE)
GSM EGPRS Radio Access (GERA)
Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
DL Advanced Rx Performance (DARP) Phase 1
Band support:
TOBY-L200 / MPCI-L200:
Band 17 (700 MHz)
Band 5 (850 MHz)
Band 4 (1700 MHz)
Band 2 (1900 MHz)
Band 7 (2600 MHz)
TOBY-L210 / MPCI-L210:
Band 20 (800 MHz)
Band 5 (850 MHz)
Band 8 (900 MHz)
Band 3 (1800 MHz)
Band 1 (2100 MHz)
Band 7 (2600 MHz)
Band support:
TOBY-L200 / MPCI-L200:
Band 5 (850 MHz)
Band 8 (900 MHz)
Band 4 (AWS, 1700 MHz)
Band 2 (1900 MHz)
Band 1 (2100 MHz)
TOBY-L210 / MPCI-L210:
Band 5 (850 MHz)
Band 8 (900 MHz)
Band 2 (1900 MHz)
Band 1 (2100 MHz)
Band support
TOBY-L200 / MPCI-L200:
GSM 850 MHz
E-GSM 900 MHz
DCS 1800 MHz
PCS 1900 MHz
TOBY-L210 / MPCI-L210:
GSM 850 MHz
E-GSM 900 MHz
DCS 1800 MHz
PCS 1900 MHz
LTE Power Class
Power Class 3 (23 dBm)
for LTE mode
WCDMA/HSDPA/HSUPA Power Class
Power Class 3 (24 dBm)
for UMTS/HSDPA/HSUPA mode
GSM/GPRS Power Class
Power Class 4 (33 dBm)
for GSM/E-GSM bands
Power Class 1 (30 dBm)
for DCS/PCS bands
EDGE Power Class
Power Class E2 (27 dBm)
for GSM/E-GSM bands
Power Class E2 (26 dBm)
for DCS/PCS bands
Data rate
LTE category 4:
up to 150 Mb/s DL, 50 Mb/s UL
Data rate
TOBY-L200 / MPCI-L200:
HSDPA cat.14, up to 21 Mb/s DL
1
HSUPA cat.6, up to 5.6 Mb/s UL
TOBY-L210 / MPCI-L210:
HSDPA cat.24, up to 42 Mb/s DL
HSUPA cat.6, up to 5.6 Mb/s UL
Data rate2
GPRS multi-slot class 12
3
, CS1-CS4,
up to 85.6 kb/s DL/UL
EDGE multi-slot class 12
3
, MCS1-MCS9
up to 236.8 kb/s DL/UL
1
2
3
Table 2 reports a summary of LTE, 3G and 2G cellular radio access technologies characteristics and features of
the TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules.
Table 2: TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series LTE, 3G and 2G characteristics summary
HSDPA category 24 capable
GPRS/EDGE multi-slot class determines the number of timeslots available for upload and download and thus the speed at which data can
be transmitted and received, with higher classes typically allowing faster data transfer rates.
GPRS/EDGE multi-slot class 12 implies a maximum of 4 slots in DL (reception) and 4 slots in UL (transmission) with 5 slots in total.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 9 of 141
Page 10

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Cellular
Base-band
Processor
Memory
Power Management Unit
26 MHz
32.768 kHz
ANT1
RF
Transceiver
ANT2
V_INT (I/O)
V_BCKP (RTC)
VCC (Supply)
SIM
USB
GPIO
Power On
External Reset
PAs
LNAs Filters
Filters
Duplexer
Filters
PAs
LNAs Filters
Filters
Duplexer
Filters
LNAs FiltersFilters
LNAs FiltersFilters
Switch
Switch
DDC(I2C)
SDIO
UART
Digital audio (I2S)
ANT_DET
Host Select
ANT1
SIM
USB
W_DISABLE#
TOBY-L2
series
Signal
Conditioning
ANT2
PERST#
LED_WWAN#
U.FL
U.FL
3.3Vaux (Supply)
Boost
Converter
VCC
1.2 Architecture
Figure 1 summarizes the internal architecture of TOBY-L2 series modules.
Figure 1: TOBY-L2 series block diagram
As described in the Figure 2, each MPCI-L2 series module integrates one TOBY-L2 series module:
The MPCI-L200 integrates a TOBY-L200 module
The MPCI-L210 integrates a TOBY-L210 module
The TOBY-L2 module represents the core of the device, providing the related LTE/3G/2G modem and processing
functionalities. Additional signal conditioning circuitry is implemented for PCI Express Mini Card compliance, and
two UF.L connectors are available for easy antenna integration.
Figure 2: MPCI-L2 series block diagram
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 10 of 141
Page 11

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.2.1 Internal blocks
As described in Figure 2, each MPCI-L2 series module integrates one TOBY-L2 series module, which consists of
the following internal sections: RF, baseband and power management.
RF section
The RF section is composed of RF transceiver, PAs, LNAs, crystal oscillator, filters, duplexers and RF switches.
Tx signal is pre-amplified by RF transceiver, then output to the primary antenna input/output port (ANT1) of the
module via power amplifier (PA), SAW band pass filters band, specific duplexer and antenna switch.
Dual receiving paths are implemented according to LTE Down-Link MIMO 2 x 2 and 3G Receiver Diversity radio
technologies supported by the modules as LTE category 4 and HSDPA category 24 User Equipments: incoming
signals are received through the primary (ANT1) and the secondary (ANT2) antenna input ports which are
connected to the RF transceiver via specific antenna switch, diplexer, duplexer, LNA, SAW band pass filters.
RF transceiver performs modulation, up-conversion of the baseband I/Q signals for Tx, down-conversion and
demodulation of the dual RF signals for Rx. The RF transceiver contains:
Automatically gain controlled direct conversion Zero-IF receiver,
Highly linear RF demodulator / modulator capable GMSK, 8-PSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM,
Fractional-N Sigma-Delta RF synthesizer,
VCO.
Power Amplifiers (PA) amplify the Tx signal modulated by the RF transceiver
RF switches connect primary (ANT1) and secondary (ANT2) antenna ports to the suitable Tx / Rx path
Low Noise Amplifiers (LNA) enhance the received sensitivity
SAW duplexers separate the Tx and Rx signal paths and provide RF filtering
SAW band pass filters enhance the rejection of out-of-band signals
26 MHz crystal oscillator generates the clock reference in active-mode or connected-mode.
Baseband and power management section
The Baseband and Power Management section is composed of the following main elements:
A mixed signal ASIC, which integrates
Microprocessor for control functions
DSP core for LTE/3G/2G Layer 1 and digital processing of Rx and Tx signal paths
Memory interface controller
Dedicated peripheral blocks for control of the USB, SIM and GPIO digital interfaces
Analog front end interfaces to RF transceiver ASIC
Memory system, which includes NAND flash and LPDDR
Voltage regulators to derive all the subsystem supply voltages from the module supply input VCC
Voltage sources for external use: V_BCKP and V_INT (not available on MPCI-L2 series modules)
Hardware power on
Hardware reset
Low power idle-mode support
32.768 kHz crystal oscillator to provide the clock reference in the low power idle-mode, which can be set by
enable power saving configuration using the AT+UPSV command.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 11 of 141
Page 12

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Function
Pin Name
Pin No
I/O
Description
Remarks
Power
VCC
70,71,72
I
Module supply input
VCC pins are internally connected each other.
VCC supply circuit affects the RF performance and
compliance of the device integrating the module with
applicable required certification schemes.
See section 1.5.1 for functional description and
requirements for the VCC module supply.
See section 2.2.1 for external circuit design-in.
GND
2, 30, 32, 44,
46, 69, 73, 74,
76, 78, 79, 80,
82, 83, 85, 86,
88-90, 92-152
N/A
Ground
GND pins are internally connected each other.
External ground connection affects the RF and thermal
performance of the device.
See section 1.5.1 for functional description.
See section 2.2.1 for external circuit design-in.
V_BCKP
3
I/O
RTC supply
input/output
V_BCKP = 3.0 V (typical) generated by internal regulator
when valid VCC supply is present.
See section 1.5.2 for functional description.
See section 2.2.2 for external circuit design-in.
V_INT
5 O Generic digital
interfaces supply
output
V_INT = 1.8 V (typical) generated by internal regulator
when the module is switched on.
See section 1.5.3 for functional description.
See section 2.2.3 for external circuit design-in.
System
PWR_ON
20 I Power-on input
Internal active pull-up to the VCC enabled.
See section 1.6.1 for functional description.
See section 2.3.1 for external circuit design-in.
RESET_N
23 I External reset input
Internal active pull-up to the VCC enabled.
See section 1.6.3 for functional description.
See section 2.3.2 for external circuit design-in.
HOST_SELECT0
26 I Selection of module
configuration by the
host processor
Note: Not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S product version
See section 1.6.4 for functional description.
See section 2.3.3 for external circuit design-in.
HOST_SELECT1
62 I Selection of module
configuration by the
host processor
Note: Not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S product version
See section 1.6.4 for functional description.
See section 2.3.3 for external circuit design-in.
Antennas
ANT1
81
I/O
Primary antenna
Main Tx / Rx antenna interface.
50 nominal characteristic impedance.
Antenna circuit affects the RF performance and application
device compliance with required certification schemes.
See section 1.7 for functional description / requirements.
See section 2.4 for external circuit design-in.
ANT2
87 I Secondary antenna
Rx only for MIMO 2x2 and Rx diversity.
50 nominal characteristic impedance.
Antenna circuit affects the RF performance and application
device compliance with required certification schemes.
See section 1.7 for functional description / requirements
See section 2.4 for external circuit design-in.
ANT_DET
75 I Antenna detection
Note: antenna detection not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
See section 1.7.2 for functional description.
See section 2.4.2 for external circuit design-in.
1.3 Pin-out
1.3.1 TOBY-L2 series pin assignment
Table 3 lists the pin-out of the TOBY-L2 series modules, with pins grouped by function.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 12 of 141
Page 13

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Function
Pin Name
Pin No
I/O
Description
Remarks
SIM
VSIM
59 O SIM supply output
VSIM = 1.8 V / 3 V automatically generated according to
the connected SIM type.
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
SIM_IO
57
I/O
SIM data
Data input/output for 1.8 V / 3 V SIM
Internal 4.7 k pull-up to VSIM.
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
SIM_CLK
56 O SIM clock
3.25 MHz clock output for 1.8 V / 3 V SIM
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
SIM_RST
58 O SIM reset
Reset output for 1.8 V / 3 V SIM
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
USB
VUSB_DET
4 I USB detect input
Input for VBUS (5 V typical) USB supply sense.
See section 1.9.1 for functional description.
See section 2.6.1 for external circuit design-in.
USB_D-
27
I/O
USB Data Line D-
USB interface for AT commands, data communication,
FOAT, FW update by u-blox EasyFlash tool and diagnostic.
90 nominal differential impedance (Z0)
30 nominal common mode impedance (Z
CM
)
Pull-up or pull-down resistors and external series resistors
as required by the USB 2.0 specifications [4] are part of the
USB pad driver and need not be provided externally.
See section 1.9.1 for functional description.
See section 2.6.1 for external circuit design-in.
USB_D+
28
I/O
USB Data Line D+
USB interface for AT commands, data communication,
FOAT, FW update by u-blox EasyFlash tool and diagnostic.
90 nominal differential impedance (Z0)
30 nominal common mode impedance (Z
CM
)
Pull-up or pull-down resistors and external series resistors
as required by the USB 2.0 specifications [4] are part of the
USB pad driver and need not be provided externally.
See section 1.9.1 for functional description.
See section 2.6.1 for external circuit design-in.
UART
RXD
17 O UART data output
Note: UART not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V output, Circuit 104 (RXD) in ITU-T V.24,
for AT command, data communication, FOAT.
Add Test-Point and series 0 to access for diagnostic.
See section 1.9.2 for functional description.
See section 2.6.2 for external circuit design-in.
TXD
16 I UART data input
Note: UART not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V input, Circuit 103 (TXD) in ITU-T V.24,
for AT command, data communication, FOAT.
Add Test-Point and series 0 to access for diagnostic.
See section 1.9.2 for functional description.
See section 2.6.2 for external circuit design-in.
CTS
15 O UART clear to send
output
Note: UART not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V output, Circuit 106 (CTS) in ITU-T V.24.
Add Test-Point and series 0 to access for diagnostic.
See section 1.9.2 for functional description.
See section 2.6.2 for external circuit design-in.
RTS
14 I UART ready to send
input
Note: UART not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V input, Circuit 105 (RTS) in ITU-T V.24.
Add Test-Point and series 0 to access for diagnostic.
See section 1.9.2 for functional description.
See section 2.6.2 for external circuit design-in.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 13 of 141
Page 14

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Function
Pin Name
Pin No
I/O
Description
Remarks
DSR
10
O /
I/O
UART data set ready
output / GPIO
Note: UART / GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V, Circuit 107 in ITU-T V.24, configurable as GPIO.
Add Test-Point and series 0 to access for diagnostic.
See section 1.9.2 and 1.11 for functional description.
See section 2.6.2 and 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
RI
11
O /
I/O
UART ring indicator
output / GPIO
Note: UART / GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V, Circuit 125 in ITU-T V.24, configurable as GPIO.
Add Test-Point and series 0 to access for diagnostic.
See section 1.9.2 and 1.11 for functional description.
See section 2.6.2 and 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
DTR
13
I /
I/O
UART data terminal
ready input / GPIO
Note: UART / GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V, Circuit 108/2 in ITU-T V.24, configurable as GPIO.
Add Test-Point and series 0 to access for diagnostic.
See section 1.9.2 and 1.11 for functional description.
See section 2.6.2 and 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
DCD
12
O /
I/O
UART data carrier
detect output / GPIO
Note: UART / GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V, Circuit 109 in ITU-T V.24, configurable as GPIO.
Add Test-Point and series 0 to access for diagnostic.
See section 1.9.2 and 1.11 for functional description.
See section 2.6.2 and 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
DDC
SCL
54 O I2C bus clock line
Note: I2C not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V open drain, for communication with u-blox GNSS
receivers and other I2C-slave devices as an audio codec.
External pull-up required.
See section 1.9.3 for functional description.
See section 2.6.3 for external circuit design-in.
SDA
55
I/O
I2C bus data line
Note: I2C not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V open drain, for communication with u-blox GNSS
receivers and other I2C-slave devices as an audio codec.
External pull-up required.
See section 1.9.3 for functional description.
See section 2.6.3 for external circuit design-in.
SDIO
SDIO_D0
66
I/O
SDIO serial data [0]
Note: SDIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
SDIO interface for communication with external Wi-Fi chip
See section 1.9.4 for functional description.
See section 2.6.4 for external circuit design-in.
SDIO_D1
68
I/O
SDIO serial data [1]
Note: Not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
SDIO interface for communication with external Wi-Fi chip
See section 1.9.4 for functional description.
See section 2.6.4 for external circuit design-in.
SDIO_D2
63
I/O
SDIO serial data [2]
Note: SDIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
SDIO interface for communication with external Wi-Fi chip
See section 1.9.4 for functional description.
See section 2.6.4 for external circuit design-in.
SDIO_D3
67
I/O
SDIO serial data [3]
Note: SDIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
SDIO interface for communication with external Wi-Fi chip
See section 1.9.4 for functional description.
See section 2.6.4 for external circuit design-in.
SDIO_CLK
64 O SDIO serial clock
Note: SDIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
SDIO interface for communication with external Wi-Fi chip
See section 1.9.4 for functional description.
See section 2.6.4 for external circuit design-in.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 14 of 141
Page 15

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Function
Pin Name
Pin No
I/O
Description
Remarks
SDIO_CMD
65
I/O
SDIO command
Note: SDIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
SDIO interface for communication with external Wi-Fi chip
See section 1.9.4 for functional description.
See section 2.6.4 for external circuit design-in.
Audio
I2S_TXD
51
O /
I/O
I2S transmit data /
GPIO
Note: I2S and GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
I2S transmit data output, alternatively configurable as GPIO.
See sections 1.10 and 1.11 for functional description.
See sections 2.7 and 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
I2S_RXD
53
I /
I/O
I2S receive data /
GPIO
Note: I2S and GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
I2S receive data input, alternatively configurable as GPIO.
See sections 1.10 and 1.11 for functional description.
See sections 2.7 and 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
I2S_CLK
52
I/O /
I/O
I2S clock /
GPIO
Note: I2S and GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
I2S serial clock, alternatively configurable as GPIO.
See sections 1.10 and 1.11 for functional description.
See sections 2.7 and 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
I2S_WA
50
I/O /
I/O
I2S word alignment /
GPIO
Note: I2S and GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
I2S word alignment, alternatively configurable as GPIO.
Note: I2S not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
See sections 1.10 and 1.11 for functional description.
See sections 2.7 and 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
GPIO
GPIO1
21
I/O
GPIO
Note: GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S except for
Wireless Network status indication configured on GPIO1.
1.8 V GPIO with alternatively configurable functions
See section 1.11 for functional description.
See section 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
GPIO2
22
I/O
GPIO
Note: GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V GPIO with alternatively configurable functions
See section 1.11 for functional description.
See section 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
GPIO3
24
I/O
GPIO
Note: GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V GPIO with alternatively configurable functions
See section 1.11 for functional description.
See section 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
GPIO4
25
I/O
GPIO
Note: GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V GPIO with alternatively configurable functions
See section 1.11 for functional description.
See section 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
GPIO5
60
I/O
GPIO
Note: GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V GPIO with alternatively configurable functions
See section 1.11 for functional description.
See section 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
GPIO6
61
I/O
GPIO
Note: GPIO not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
1.8 V GPIO
See section 1.11 for functional description.
See section 2.8 for external circuit design-in.
Reserved
RSVD
6
N/A
Reserved pin
This pin must be connected to ground.
See section 2.10
RSVD
1, 7-9, 18,
19, 29, 31,
33-43, 45,
47-49, 77,
84, 91
N/A
Reserved pin
Leave unconnected.
See section 2.10
Table 3: TOBY-L2 series module pin definition, grouped by function
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 15 of 141
Page 16

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Function
Pin Name
Pin No
I/O
Description
Remarks
Power
3.3Vaux
2, 24, 39,
41, 52
I
Module supply input
3.3Vaux pins are internally connected each other.
3.3Vaux supply circuit affects the RF performance and
compliance of the device integrating the module with
applicable required certification schemes.
See section 1.5.1 for functional description and
requirements for the 3.3Vaux module supply.
See section 2.2.1 for external circuit design-in.
GND
4, 9, 15, 18,
21, 26, 27,
29, 34, 35,
37, 40, 43, 50
N/A
Ground
GND pins are internally connected each other.
External ground connection affects the RF and thermal
performance of the device.
See section 1.5.1 for functional description.
See section 2.2.1 for external circuit design-in.
Auxiliary
Signals
PERST#
22 I External reset input
Internal 45 k pull-up to 3.3 V supply.
See section 1.6.3 for functional description.
See section 2.3.2 for external circuit design-in.
Antennas
ANT1
U.FL
I/O
Primary antenna
Main Tx / Rx antenna interface.
50 nominal characteristic impedance.
Antenna circuit affects the RF performance and
compliance of the device integrating the module with
applicable required certification schemes.
See section 1.7 for functional description / requirements.
See section 2.4 for external circuit design-in.
ANT2
U.FL I Secondary antenna
Rx only for MIMO 2x2 and Rx diversity.
50 nominal characteristic impedance.
Antenna circuit affects the RF performance and
compliance of the device integrating the module with
applicable required certification schemes.
See section 1.7 for functional description / requirements
See section 2.4 for external circuit design-in.
SIM
UIM_PWR
8 O SIM supply output
UIM_PWR = 1.8 V / 3 V automatically generated
according to the connected SIM type.
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
UIM_DATA
10
I/O
SIM data
Data input/output for 1.8 V / 3 V SIM
Internal 4.7 k pull-up to UIM_PWR.
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
UIM_CLK
12 O SIM clock
3.25 MHz clock output for 1.8 V / 3 V SIM
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
UIM_RESET
14 O SIM reset
Reset output for 1.8 V / 3 V SIM
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
1.3.2 MPCI-L2 series pin assignment
Table 4 lists the pin-out of the MPCI-L2 series modules, with pins grouped by function.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 16 of 141
Page 17

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Function
Pin Name
Pin No
I/O
Description
Remarks
USB
USB_D-
36
I/O
USB Data Line D-
USB interface for AT commands, data communication,
FOAT, FW update by u-blox EasyFlash tool and diagnostic.
90 nominal differential impedance (Z0)
30 nominal common mode impedance (Z
CM
)
Pull-up or pull-down resistors and external series resistors
as required by the USB 2.0 specifications [4] are part of the
USB pad driver and need not be provided externally.
See section 1.9.1 for functional description.
See section 2.6.1 for external circuit design-in.
USB_D+
38
I/O
USB Data Line D+
USB interface for AT commands, data communication,
FOAT, FW update by u-blox EasyFlash tool and diagnostic.
90 nominal differential impedance (Z0)
30 nominal common mode impedance (Z
CM
)
Pull-up or pull-down resistors and external series resistors
as required by the USB 2.0 specifications [4] are part of the
USB pad driver and need not be provided externally.
See section 1.9.1 for functional description.
See section 2.6.1 for external circuit design-in.
Specific
Signals
LED_WWAN#
42 O LED indicator output
Open drain active low output.
See section 1.12 for functional description.
See section 2.9 for external circuit design-in.
W_DISABLE#
20 I Wireless radio
disable input
Internal 22 k pull-up to 3.3Vaux.
See section 1.12 for functional description.
See section 2.9 for external circuit design-in.
Not
Connected
NC
1, 3, 5-7, 11,
13, 16, 17, 19,
23, 25, 28,
30-33, 44-46,
47-49, 51
N/A
Not connected
Internally not connected.
See section 1.14 for the description.
Table 4: MPCI-L2 series module pin definition, grouped by function
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 17 of 141
Page 18

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
General Status
Operating Mode
Definition
Power-down
Not-Powered Mode
VCC or 3.3Vaux supply not present or below operating range: module is switched off.
Power-Off Mode
VCC or 3.3Vaux supply within operating range and module is switched off.
Normal Operation
Idle-Mode
Module processor core runs with 32 kHz reference generated by the internal oscillator.
Active-Mode
Module processor core runs with 26 MHz reference generated by the internal oscillator.
Connected-Mode
RF Tx/Rx data connection enabled and processor core runs with 26 MHz reference.
Operating Mode
Description
Transition between operating modes
Not-Powered Mode
Module is switched off.
Application interfaces are not accessible.
When VCC or 3.3Vaux supply is removed, the modules
enter not-powered mode.
When in not-powered mode, TOBY-L2 modules cannot be
switched on by PWR_ON, RESET_N or RTC alarm and
enter active-mode after applying VCC supply (see 1.6.1).
When in not-powered mode, MPCI-L2 modules cannot be
switched on by RTC alarm and enter active-mode after
applying 3.3Vaux supply (see 1.6.1).
Power-Off Mode
Module is switched off: normal shutdown by an
appropriate power-off event (see 1.6.2).
Application interfaces are not accessible.
MPCI-L2 modules do not support Power-Off Mode
but halt mode (see 1.6.2 and u-blox AT Commands
Manual [3], AT+CFUN=127 command).
When the modules are switched off by an appropriate
power-off event (see 1.6.2), the modules enter power-off
mode from active-mode.
When in power-off mode, TOBY-L2 modules can be
switched on by PWR_ON, RESET_N or an RTC alarm.
When in power-off mode, TOBY-L2 modules enter the
not-powered mode after removing VCC supply.
Idle-Mode
Module is switched on with application interfaces
disabled or suspended: the module is temporarily not
ready to communicate with an external device by
means of the application interfaces as configured to
reduce the current consumption.
The module enters the low power idle-mode
whenever possible if power saving is enabled by
AT+UPSV (see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3])
reducing current consumption (see 1.5.1.5).
Power saving configuration is not enabled by default:
it can be enabled by the AT+UPSV command (see
the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
The modules automatically switch from active-mode to low
power idle-mode whenever possible if power saving is
enabled (see sections 1.5.1.5, 1.9.1.4, 1.9.2.4 and u-blox
AT Commands Manual [3], AT+UPSV).
The modules wake up from idle-mode to active-mode in
the following events:
Automatic periodic monitoring of the paging channel
for the paging block reception according to network
conditions (see 1.5.1.5)
The connected USB host forces a remote wakeup of
the module as USB device (see 1.9.1.4)
A preset RTC alarm occurs (see u-blox AT Commands
Manual [3], AT+CALA)
Active-Mode
Module is switched on with application interfaces
enabled or not suspended: the module is ready to
communicate with an external device by means of
the application interfaces unless power saving
configuration is enabled by AT+UPSV (see 1.9.1.4,
1.9.2.4 and u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
When the modules are switched on by an appropriate
power-on event (see 1.6.1), the module enter active-mode
from power-off mode.
If power saving configuration is enabled by the AT+UPSV
command, the module automatically switches from active
to idle-mode whenever possible and the module wakes up
from idle to active-mode in the events listed above (see
idle-mode to active-mode transition description above).
When a RF Tx/Rx data connection is initiated or when RF
Tx/Rx is required due to a connection previously initiated,
the module switches from active to connected-mode.
1.4 Operating modes
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules have several operating modes. The operating modes are defined in Table 5
and described in detail in Table 6, providing general guidelines for operation.
Table 5: TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules operating modes definition
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 18 of 141
Page 19

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Operating Mode
Description
Transition between operating modes
Connected-Mode
RF Tx/Rx data connection is in progress.
The module is prepared to accept data signals from
an external device unless power saving configuration
is enabled by AT+UPSV (see sections 1.9.1.4, 1.9.2.4
and u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
When a data connection is initiated, the module enters
connected-mode from idle-mode.
If power saving configuration is enabled by the AT+UPSV
command, the module automatically switches from
connected to active and then idle-mode whenever possible
and the module wakes up from idle to active and then
connected mode if RF Transmission/Reception is necessary.
When a data connection is terminated, the module returns
to the active-mode.
TOBY-L2 Switch ON:
• Apply VCC
MPCI-L2 Switch ON:
• Apply 3.3Vaux
If power saving is enabled
and there is no activity for
a defined time interval
Any wake up event described
in the module operating
modes summary table above
Incoming/outgoing call or
other dedicated device
network communication
No RF Tx/Rx in progress,
Call terminated,
Communication dropped
TOBY-L2x0
Switch ON:
• PWR_ON
• RESET_N
• RTC alarm
Not
powered
Power off
ActiveConnected Idle
TOBY-L2x0
Switch OFF:
• AT+CPWROFF
• RESET_N
MPCI-L2:
• Remove 3.3Vaux
TOBY-L2:
• Remove VCC
Table 6: TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules operating modes description
Figure 3 describes the transition between the different operating modes.
Figure 3: TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules operating modes transition
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 19 of 141
Page 20

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Item
Requirement
Remark
VCC or 3.3Vaux
nominal voltage
Within VCC or 3.3Vaux normal operating range:
See “Supply/Power pins” section in the TOBY-L2 Data
Sheet [1] or in the MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2].
The modules cannot be switched on if the supply voltage
is below the normal operating range minimum limit.
VCC or 3.3Vaux
voltage during
normal operation
Within VCC or 3.3Vaux extended operating range:
See “Supply/Power pins” section in the TOBY-L2 Data
Sheet [1] or in the MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2].
The modules may switch off if the supply voltage drops
below the extended operating range minimum limit.
VCC or 3.3Vaux
average current
Support with adequate margin the highest averaged
current consumption value in connected-mode
conditions specified for VCC in TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1]
or specified for 3.3Vaux in MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2].
The maximum average current consumption can be
greater than the specified value according to the actual
antenna mismatching, temperature and supply voltage.
Sections 1.5.1.2, 1.5.1.3 and 1.5.1.4 describe current
consumption profiles in 2G, 3G and LTE connected-mode.
VCC or 3.3Vaux
peak current
Support with margin the highest peak current
consumption value in 2G connected-mode conditions
specified for VCC in TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1] or
specified for 3.3Vaux in MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2].
The specified maximum peak of current consumption
occurs during GSM single transmit slot in 850/900 MHz
connected-mode, in case of mismatched antenna.
Section 1.5.1.2 describes 2G Tx peak/pulse current.
VCC or 3.3Vaux
voltage drop during
2G Tx slots
Lower than 400 mV
Supply voltage drop values greater than recommended
during 2G TDMA transmission slots directly affect the RF
compliance with applicable certification schemes.
Figure 5 describes supply voltage drop during 2G Tx slots.
VCC or 3.3Vaux
voltage ripple during
RF transmission
Noise in the supply has to be minimized
High supply voltage ripple values during LTE/3G/2G RF
transmissions in connected-mode directly affect the RF
compliance with applicable certification schemes.
Figure 5 describes supply voltage ripple during RF Tx.
VCC or 3.3Vaux
under/over-shoot at
start/end of Tx slots
Absent or at least minimized
Supply voltage under-shoot or over-shoot at the start or
the end of 2G TDMA transmission slots directly affect the
RF compliance with applicable certification schemes.
Figure 5 describes supply voltage under/over-shoot
1.5 Supply interfaces
1.5.1 Module supply input (VCC or 3.3Vaux)
TOBY-L2 modules are supplied via the three VCC pins, and MPCI-L2 modules are supplied via the five 3.3Vaux
pins. All supply voltages used inside the modules are generated from the VCC or the 3.3Vaux supply input by
integrated voltage regulators, including the V_BCKP RTC supply, the V_INT generic digital interface supply, and
the VSIM or UIM_PWR SIM interface supply.
The current drawn by the TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules through the VCC or 3.3Vaux pins can vary by
several orders of magnitude depending on radio access technology, operation mode and state. It is important
that the supply source is able to support both the high peak of current consumption during 2G transmission at
maximum RF power level (as described in the section 1.5.1.2) and the high average current consumption during
3G and LTE transmission at maximum RF power level (as described in the sections 1.5.1.3 and 1.5.1.4).
1.5.1.1 VCC or 3.3Vaux supply requirements
Table 7 summarizes the requirements for the VCC or 3.3Vaux modules supply. See section 2.2.1 for suggestions
to properly design a VCC or 3.3Vaux supply circuit compliant with the requirements listed in Table 7.
The supply circuit affects the RF compliance of the device integrating TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2
series modules with applicable required certification schemes as well as antenna circuit design.
Compliance is guaranteed if the requirements summarized in the Table 7 are fulfilled.
Table 7: Summary of VCC or 3.3Vaux modules supply requirements
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 20 of 141
Page 21

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Time [ms]
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
Current [A]
200 mA
60-120 mA
1900 mA
Peak current depends
on TX power and
actual antenna load
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
60-120 mA
10-40 mA
0.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
2.0
2.5
Time [ms]
undershoot
overshoot
ripple
drop
Voltage [mV]
3.8 V
(typ)
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
RX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
unused
slot
unused
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
1.5.1.2 VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption in 2G connected-mode
When a GSM call is established, the VCC or 3.3Vaux module current consumption is determined by the current
consumption profile typical of the GSM transmitting and receiving bursts.
The peak of current consumption during a transmission slot is strictly dependent on the RF transmitted power,
which is regulated by the network. The transmitted power in the transmit slot is also the more relevant factor for
determining the average current consumption.
If the module is transmitting in 2G single-slot mode in the 850 or 900 MHz bands, at the maximum RF power
level (approximately 2 W or 33 dBm in the allocated transmit slot/burst) the current consumption can reach an
high peak (see the “Current consumption” section in the TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1] or the MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2])
for 576.9 µs (width of the transmit slot/burst) with a periodicity of 4.615 ms (width of 1 frame = 8 slots/burst),
so with a 1/8 duty cycle according to GSM TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access).
If the module is transmitting in 2G single-slot mode in the 1800 or 1900 MHz bands, the current consumption
figures are quite less high than the one in the low bands, due to 3GPP transmitter output power specifications.
During a GSM call, current consumption is not so significantly high in receiving or in monitor bursts and is low in
the inactive unused bursts.
Figure 4 shows an example of the module current consumption profile versus time in 2G single-slot mode.
Figure 4: VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption profile versus time during a 2G single-slot call (1 TX slot, 1 RX slot)
Figure 5 illustrates VCC or 3.3Vaux voltage profile versus time during a 2G single-slot call, according to the
relative VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption profile described in Figure 4.
Figure 5: VCC or 3.3Vaux voltage profile versus time during a 2G single-slot call (1 TX slot, 1 RX slot)
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 21 of 141
Page 22

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Time [ms]
RX
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
TX
slot
TX
slot
TX
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
RX
slot
unused
slot
TX
slot
TX
slot
TX
slot
TX
slot
MON
slot
unused
slot
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
Current [A]
200mA
60-130mA
Peak current depends
on TX power and
actual antenna load
GSM frame
4.615 ms
(1 frame = 8 slots)
1600 mA
0.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
2.0
2.5
When a GPRS connection is established, more than one slot can be used to transmit and/or more than one slot
can be used to receive. The transmitted power depends on network conditions, which set the peak current
consumption, but following the 3GPP specifications the maximum Tx RF power is reduced if more than one slot
is used to transmit, so the maximum peak of current is not as high as can be in case of a 2G single-slot call.
If the module transmits in GPRS class 12 in the 850 or 900 MHz bands, at the maximum RF power control level,
the current consumption can reach a quite high peak but lower than the one achievable in 2G single-slot mode.
This happens for 2.307 ms (width of the 4 transmit slots/bursts) with a periodicity of 4.615 ms (width of 1 frame
= 8 slots/bursts), so with a 1/2 duty cycle, according to 2G TDMA.
If the module is in GPRS connected mode in the 1800 or 1900 MHz bands, the current consumption figures are
quite less high than the one in the low bands, due to 3GPP transmitter output power specifications.
Figure 6 reports the current consumption profiles in GPRS class 12 connected mode, in the 850 or 900 MHz
bands, with 4 slots used to transmit and 1 slot used to receive.
Figure 6: VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption profile during a 2G GPRS/EDGE multi-slot connection (4 TX slots, 1 RX slot)
In case of EDGE connections the VCC current consumption profile is very similar to the GPRS current profile, so
the image shown in Figure 6, representing the current consumption profile in GPRS class 12 connected mode, is
valid for the EDGE class 12 connected mode as well.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 22 of 141
Page 23

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Time
[ms]
3G frame
10 ms
(1 frame = 15 slots)
Current [mA]
Current consumption value
depends on TX power and
actual antenna load
170 mA
1 slot
666 µs
850 mA
0
300
200
100
500
400
600
700
800
1.5.1.3 VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption in 3G connected mode
During a 3G connection, the module can transmit and receive continuously due to the Frequency Division Duplex
(FDD) mode of operation with the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA).
The current consumption depends again on output RF power, which is always regulated by network commands.
These power control commands are logically divided into a slot of 666 µs, thus the rate of power change can
reach a maximum rate of 1.5 kHz.
There are no high current peaks as in the 2G connection, since transmission and reception are continuously
enabled due to FDD WCDMA implemented in the 3G that differs from the TDMA implemented in the 2G case.
In the worst scenario, corresponding to a continuous transmission and reception at maximum output power
(approximately 250 mW or 24 dBm), the average current drawn by the module at the VCC pins is high (see the
“Current consumption” section in TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1] or in MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2]). Even at lowest output
RF power (approximately 0.01 µW or -50 dBm), the current is still not so low due to module baseband
processing and transceiver activity.
Figure 7 shows an example of current consumption profile of the module in 3G WCDMA/DC-HSPA+ continuous
transmission mode.
Figure 7: VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption profile versus time during a 3G connection (TX and RX continuously enabled)
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 23 of 141
Page 24

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Time
[ms]
Current [mA]
Current consumption value
depends on TX power and
actual antenna load
1 Slot
1 Resource Block
(0.5 ms)
1 LTE Radio Frame
(10 ms)
0
300
200
100
500
400
600
700
800
1.5.1.4 VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption in LTE connected-mode
During a LTE connection, the module can transmit and receive continuously due to LTE radio access technology.
The current consumption is strictly dependent on the transmitted RF output power, which is always regulated by
network commands. These power control commands are logically divided into a slot of 0.5 ms (time length of
one Resource Block), thus the rate of power change can reach a maximum rate of 2 kHz.
Figure 8 shows an example of the module current consumption profile versus time in LTE connected-mode.
Detailed current consumption values can be found in TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1] and in MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2].
Figure 8: VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption profile versus time during LTE connection (TX and RX continuously enabled)
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 24 of 141
Page 25

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
~50 ms
IDLE MODE ACTIVE MODE IDLE MODE
Active Mode
Enabled
Idle Mode
Enabled
2G case: 0.44-2.09 s
3G case: 0.61-5.09 s
LTE case: 0.27-2.51 s
IDLE MODE
~50 ms
ACTIVE MODE
Time [s]
Current [mA]
Time [ms]
Current [mA]
RX
Enabled
0
100
0
100
1.5.1.5 VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption in cyclic idle/active mode (power saving enabled)
The power saving configuration is by default disabled, but it can be enabled using the AT+UPSV command (see
the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]). When power saving is enabled, the module automatically enters the low
power idle-mode whenever possible, reducing current consumption.
During low power idle-mode, the module processor runs with 32 kHz reference clock frequency.
When the power saving configuration is enabled and the module is registered or attached to a network , the
module automatically enters the low power idle-mode whenever possible, but it must periodically monitor the
paging channel of the current base station (paging block reception), in accordance to the 2G/3G/LTE system
requirements, even if connected-mode is not enabled by the application. When the module monitors the paging
channel, it wakes up to the active-mode, to enable the reception of paging block. In between, the module
switches to low power idle-mode. This is known as discontinuous reception (DRX).
The module processor core is activated during the paging block reception, and automatically switches its
reference clock frequency from 32 kHz to the 26 MHz used in active-mode.
The time period between two paging block receptions is defined by the network. This is the paging period
parameter, fixed by the base station through broadcast channel sent to all users on the same serving cell.
In case of 2G radio access technology, the paging period can vary from 470.76 ms (DRX = 2, length of 2 x 51 2G
frames = 2 x 51 x 4.615 ms) up to 2118.42 ms (DRX = 9, length of 9 x 51 2G frames = 9 x 51 x 4.615 ms).
In case of 3G radio access technology, the paging period can vary from 640 ms (DRX = 6, i.e. length of 26 3G
frames = 64 x 10 ms) up to 5120 ms (DRX = 9, length of 29 3G frames = 512 x 10 ms).
In case of LTE radio access technology, the paging period can vary from 320 ms (DRX = 5, length of 25 LTE
frames = 32 x 10 ms) up to 2560 ms (DRX = 8, length of 28 LTE frames = 256 x 10 ms).
Figure 9 illustrates a typical example of the module current consumption profile when power saving is enabled.
The module is registered with network, automatically enters the low power idle-mode and periodically wakes up
to active-mode to monitor the paging channel for the paging block reception. Detailed current consumption
values can be found in TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1] and in MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2].
Figure 9: VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption profile with power saving enabled and module registered with the network:
the module is in idle-mode and periodically wakes up to active-mode to monitor the paging channel for paging block reception
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 25 of 141
Page 26

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
ACTIVE MODE
2G case: 0.44-2.09 s
3G case: 0.61-5.09 s
LTE case: 0.32-2.56 s
Paging period
Time [s]
Current [mA]
Time [ms]
Current [mA]
RX
Enabled
0
100
0
100
1.5.1.6 VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption in fixed active-mode (power saving disabled)
When power saving is disabled, the module does not automatically enter the low power idle-mode whenever
possible: the module remains in active-mode. Power saving configuration is by default disabled. It can also be
disabled using the AT+UPSV command (see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3] for detail usage).
The module processor core is activated during idle-mode, and the 26 MHz reference clock frequency is used. It
would draw more current during the paging period than that in the power saving mode.
Figure 10 illustrates a typical example of the module current consumption profile when power saving is disabled.
In such case, the module is registered with the network and while active-mode is maintained, the receiver is
periodically activated to monitor the paging channel for paging block reception.
Figure 10: VCC or 3.3Vaux current consumption profile with power saving disabled and module registered with the network:
active-mode is always held and the receiver is periodically activated to monitor the paging channel for paging block reception
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 26 of 141
Page 27

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Baseband
Processor
70
VCC
71
VCC
72
VCC
3
V_BCKP
Linear
LDO
Power
Management
TOBY-L2 series
32 kHz
RTC
1.5.2 RTC supply input/output (V_BCKP)
The RTC supply V_BCKP pin is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
The V_BCKP pin of TOBY-L2 series modules connects the supply for the Real Time Clock (RTC). A linear LDO
regulator integrated in the Power Management Unit internally generates this supply, as shown in Figure 11, with
low current capability (see the TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1]). The output of this regulator is always enabled
when the main module voltage supply applied to the VCC pins is within the valid operating range.
Figure 11: TOBY-L2 series RTC supply (V_BCKP) simplified block diagram
The RTC provides the module time reference (date and time) that is used to set the wake-up interval during the
low power idle-mode periods, and is able to make available the programmable alarm functions.
The RTC functions are available also in power-down mode when the V_BCKP voltage is within its valid range
(specified in the “Input characteristics of Supply/Power pins” table in TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1]). The RTC
can be supplied from an external back-up battery through the V_BCKP, when the main module voltage supply is
not applied to the VCC pins. This lets the time reference (date and time) run until the V_BCKP voltage is within
its valid range, even when the main supply is not provided to the module.
Consider that the module cannot switch on if a valid voltage is not present on VCC even when the RTC is
supplied through V_BCKP (meaning that VCC is mandatory to switch on the module).
The RTC has very low current consumption, but is highly temperature dependent. For example, V_BCKP current
consumption at the maximum operating temperature can be higher than the typical value at 25 °C specified in
the “Input characteristics of Supply/Power pins” table in the TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1].
If V_BCKP is left unconnected and the module main supply is not applied to the VCC pins, the RTC is supplied
from the bypass capacitor mounted inside the module. However, this capacitor is not able to provide a long
buffering time: within few milliseconds the voltage on V_BCKP will go below the valid range (1.4 V min). This
has no impact on cellular connectivity, as all the module functionalities do not rely on date and time setting.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 27 of 141
Page 28

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Baseband
Processor
70
VCC
71
VCC
72
VCC
5
V_INT
Switching
Step-Down
Power
Management
TOBY-L2 series
Digital I/O
1.5.3 Generic digital interfaces supply output (V_INT)
The generic digital interfaces supply V_INT pin is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
The V_INT output pin of the TOBY-L2 series modules is connected to an internal 1.8 V supply with current
capability specified in the TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1]. This supply is internally generated by a switching stepdown regulator integrated in the Power Management Unit and it is internally used to source the generic digital
I/O interfaces of the TOBY-L2 module, as described in Figure 12. The output of this regulator is enabled when
the module is switched on and it is disabled when the module is switched off.
Figure 12: TOBY-L2 series generic digital interfaces supply output (V_INT) simplified block diagram
The switching regulator operates in Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) mode for greater efficiency at high output
loads and it automatically switches to Pulse Frequency Modulation (PFM) power save mode for greater efficiency
at low output loads. The V_INT output voltage ripple is specified in the TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1].
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 28 of 141
Page 29

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Baseband
Processor
20
PWR_ON
TOBY-L2 series
VCC
Power-on
Power
Management
Power-on
50k
1.6 System function interfaces
1.6.1 Module power-on
The PWR_ON input pin is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
When the TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules are in the not-powered mode (switched off, i.e. the VCC or
3.3Vaux module supply is not applied), they can be switched on as following:
Rising edge on the VCC or 3.3Vaux supply input to a valid voltage for module supply, so that the module
switches on applying a proper VCC or 3.3Vaux supply within the normal operating range.
Alternately, the RESET_N or PERST# pin can be held to the low level during the VCC or 3.3Vaux rising
edge, so that the module switches on releasing the RESET_N or PERST# pin when the VCC or 3.3Vaux
module supply voltage stabilizes at its proper nominal value within the normal operating range.
The status of the PWR_ON input pin of TOBY-L2 modules while applying the VCC module supply is not relevant:
during this phase the PWR_ON pin can be set high or low by the external circuit.
When the TOBY-L2 modules are in the power-off mode (i.e. switched off with valid VCC module supply applied),
they can be switched on as following:
Low level on the PWR_ON pin, which is normally set high by an internal pull-up, for a valid time period.
Low level on the RESET_N pin, which is normally set high by an internal pull-up, for a valid time period.
RTC alarm, i.e. pre-programmed alarm by AT+CALA command (see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
As described in Figure 13, the TOBY-L2 series PWR_ON input is equipped with an internal active pull-up resistor
to the VCC module supply: the PWR_ON input voltage thresholds are different from the other generic digital
interfaces. Detailed electrical characteristics are described in TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1].
Figure 13: TOBY-L2 series PWR_ON input description
For more pin information and electrical characteristics, see the TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1] and MPCI-L2 Data
Sheet [2].
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 29 of 141
Page 30

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
VCC or 3.3Vaux
V_BCKP
PWR_ON
RESET_N or PERST#
V_INT
Internal Reset
System State
BB Pads State
Internal Reset → Operational Operational
Tristate / Floating
Internal Reset
OFF
ON
0 ms
~10 ms
~20 s
Start of interface
configuration
Module interfaces
are configured
Start-up
event
~5 ms
Figure 14 shows the module power-on sequence from the not-powered mode, describing the following phases:
The external supply is applied to the VCC or 3.3Vaux module supply inputs, representing the start-up event.
The PWR_ON and the RESET_N or PERST# pins suddenly rise to high logic level due to internal pull-ups.
The V_BCKP RTC supply output is suddenly enabled by the module as VCC reaches a valid voltage value.
All the generic digital pins of the module are tri-stated until the switch-on of their supply source (V_INT).
The internal reset signal is held low: the baseband core and all the digital pins are held in the reset state.
The reset state of all the digital pins is reported in the pin description table of TOBY-L2 Series Data Sheet [1].
When the internal reset signal is released, any digital pin is set in a proper sequence from the reset state to
the default operational configured state. The duration of this pins’ configuration phase differs within generic
digital interfaces and the USB interface due to host / device enumeration timings (see section 1.9.1).
The module is fully ready to operate after all interfaces are configured.
Figure 14: TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series power-on sequence description
The Internal Reset signal is not available on a module pin, but the host application can monitor:
Before the switch-on of the generic digital interface supply source (V_INT) of the module, no voltage
Before the TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series module is fully ready to operate, the host application processor
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 30 of 141
The V_INT pin to sense the start of the TOBY-L2 module power-on sequence.
The USB interface to sense the start of the MPCI-L2 module power-on sequence: the module, as USB
device, informs the host of the attach event via a reply on its status change pipe for proper bus
enumeration process according to Universal Serial Bus Revision 2.0 specification [6].
driven by an external application should be applied to any generic digital interface of TOBY-L2 module.
should not send any AT command over the AT communication interfaces (USB, UART) of the module.
Page 31

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.6.2 Module power-off
TOBY-L2 series can be properly switched off by:
AT+CPWROFF command (see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]). The current parameter settings are saved in
the module’s non-volatile memory and a proper network detach is performed.
The MPCI-L2 series modules do not switch off by the AT+CPWROFF command as the TOBY-L2 modules,
but the AT+CPWROFF command causes a reset (reboot) of the module due to the MPCI-L2 module’s
internal configuration: the command stores the actual parameter settings in the non-volatile memory of
MPCI-L2 modules and performs a network detach, with a subsequent reset (reboot) of the module.
An abrupt under-voltage shutdown occurs on TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules when the VCC or 3.3Vaux
module supply is removed. If this occurs, it is not possible to perform the storing of the current parameter
settings in the module’s non-volatile memory or to perform the proper network detach.
It is highly recommended to avoid an abrupt removal of the VCC supply during TOBY-L2 modules normal
operations: the power off procedure must be started by the AT+CPWROFF command, waiting the
command response for a proper time period (see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]), and then a proper
VCC supply has to be held at least until the end of the modules’ internal power off sequence, which
occurs when the generic digital interfaces supply output (V_INT) is switched off by the module.
It is highly recommended to avoid an abrupt removal of the 3.3Vaux supply during MPCI-L2 modules
normal operations: the power off procedure must be started by setting the MPCI-L2 module in the halt
mode by the AT+CFUN=127 command (which stores the actual parameter settings in the non-volatile
memory of the module and performs a network detach), waiting the command response for a proper
time period (see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]), and then the 3.3Vaux supply can be removed.
An abrupt hardware shutdown occurs on TOBY-L2 series modules when a low level is applied on the RESET_N
pin for a specific time period. In this case, the current parameter settings are not saved in the module’s
non-volatile memory and a proper network detach is not performed.
It is highly recommended to avoid an abrupt hardware shutdown of the module by forcing a low level on
the RESET_N input pin during module normal operation: the RESET_N line should be set low only if reset
or shutdown via AT commands fails or if the module does not reply to a specific AT command after a time
period longer than the one defined in the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3].
An over-temperature or an under-temperature shutdown occurs on TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules when
the temperature measured within the cellular module reaches the dangerous area, if the optional Smart
Temperature Supervisor feature is enabled and configured by the dedicated AT command. For more details see
u-blox AT Commands Manual [3], +USTS AT command.
The Smart Temperature Supervisor feature is not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S and MPCI-L2x0-00S
product versions.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 31 of 141
Page 32

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
VCC
V_BCKP
PWR_ON
RESET_N
V_INT
Internal Reset
System State
BB Pads State Operationa l
OFF
Tristate / Floa ting
ON
Operational → Tristate
AT+CPWROFF
sent to the module
OK
replied by the module
VCC
can be removed
3.3Vaux
PERST#
Internal Reset
System State
BB Pads State
OFF
ON
Tristate / Floating
Operational
AT+CFUN=127
sent to the module
OK
replied by the module
3.3Vaux
can be removed
Figure 15 describes the TOBY-L2 power-off sequence by means of AT+CPWROFF with the following phases:
When the +CPWROFF AT command is sent, the module starts the switch-off routine.
The module replies OK on the AT interface: the switch-off routine is in progress.
At the end of the switch-off routine, all the digital pins are tri-stated and all the internal voltage regulators
are turned off, including the generic digital interfaces supply (V_INT), except the RTC supply (V_BCKP).
Then, the module remains in power-off mode as long as a switch on event does not occur (e.g. applying a
proper low level to the PWR_ON input, or applying a proper low level to the RESET_N input), and enters
not-powered mode if the supply is removed from the VCC pins.
Figure 15: TOBY-L2 series power-off sequence description
The Internal Reset signal is not available on a module pin, but the application can monitor the V_INT pin
to sense the end of the power-off sequence.
Figure 16 describes the MPCI-L2 power-off procedure with the following phases:
When the AT+CFUN=127 command is issued, the module starts the halt mode setting routine.
The module replies OK on the AT interface: after this, the module is set in the halt mode.
Then, the module remains in the Halt mode and enters not-powered mode if the supply is removed from the
3.3Vaux pins.
Figure 16: MPCI-L2 series power-off procedure description
The duration of each phase in the TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules’ switch-off routines can largely
vary depending on the application / network settings and the concurrent module activities.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 32 of 141
Page 33

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Baseband
Processor
23
RESET_N
TOBY-L2 series
VCC
Reset
Power
Management
Reset
50k
Baseband
Processor
22
PERST#
MPCI-L2 series
Reset
Power
Management
Reset
45k
3.3 V
1.6.3 Module reset
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules can be properly reset (rebooted) by:
AT+CFUN command (see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
MPCI-L2 series modules can be additionally properly reset (rebooted) by:
AT+CPWROFF command (see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]): the behavior differs than TOBY-L2 series, as
MPCI-L2 modules will reboot rather than remain switched off due to modules’ internal configuration.
In the cases listed above an “internal” or “software” reset of the module is executed: the current parameter
settings are saved in the module’s non-volatile memory and a proper network detach is performed.
An abrupt hardware reset occurs on TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules when a low level is applied on the
RESET_N or PERST# input pin for a specific time period. In this case, the current parameter settings are not
saved in the module’s non-volatile memory and a proper network detach is not performed.
It is highly recommended to avoid an abrupt hardware reset of the module by forcing a low level on the
RESET_N or PERST# input during modules normal operation: the RESET_N or PERST# line should be set
low only if reset or shutdown via AT commands fails or if the module does not provide a reply to a specific
AT command after a time period longer than the one defined in the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3].
As described in Figure 17, the RESET_N and PERST# input pins are equipped with an internal pull-up to the
VCC supply in the TOBY-L2 series and to the 3.3 V in the MPCI-L2 series.
Figure 17: TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series RESET_N and PERST# input equivalent circuit description
For more electrical characteristics details see TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1] and MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2].
1.6.4 Module configuration selection by host processor
The HOST_SELECT0 and HOST_SELECT1 pins are not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
The functionality of the HOST_SELECT0 and HOST_SELECT1 pins is not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
TOBY-L2 series modules include two input pins (HOST_SELECT0 and HOST_SELECT1) for the selection of the
module configuration by the host application processor.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 33 of 141
Page 34

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Base Station
Tx-1
Antenna
Tx-2
Antenna
TOBY-L2 series
MPCI-L2 series
ANT1
Rx-1
Antenna
ANT2
Rx-2
Antenna
Data Stream 1
Data Stream 2
1.7 Antenna interface
1.7.1 Antenna RF interfaces (ANT1 / ANT2)
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules provide two RF interfaces for connecting the external antennas:
The ANT1 represents the primary RF input/output for transmission and reception of LTE/3G/2G RF signals.
The ANT1 pin of TOBY-L2 series modules has a nominal characteristic impedance of 50 and must be
connected to the primary Tx / Rx antenna through a 50 transmission line to allow proper RF transmission
and reception.
The ANT1 Hirose U.FL-R-SMT coaxial connector receptacle of MPCI-L2 series modules has a nominal
characteristic impedance of 50 and must be connected to the primary Tx / Rx antenna through a mated RF
plug with a 50 coaxial cable assembly to allow proper RF transmission and reception.
The ANT2 represents the secondary RF input for the reception of the LTE RF signals for the Down-Link
MIMO 2 x 2 radio technology supported by TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules as required feature for LTE
category 4 UEs, and for the reception of the 3G RF signals for the Down-Link Rx diversity radio technology
supported by TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules as additional feature for 3G DC-HSDPA category 24 UEs.
The ANT2 pin of TOBY-L2 series modules has a nominal characteristic impedance of 50 and must be
connected to the secondary Rx antenna through a 50 transmission line to allow proper RF reception.
The ANT2 Hirose U.FL-R-SMT coaxial connector receptacle of MPCI-L2 series modules has a nominal
characteristic impedance of 50 and must be connected to the secondary Rx antenna through a mated RF
plug with a 50 coaxial cable assembly to allow proper RF reception.
The Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) radio technology is an essential component of LTE radio systems
based on the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver sides to improve communication
performance and achieve highest possible bit rate. A MIMO m x n system consists of m transmit and n receive
antennas, where the data to be transmitted is divided into m independent data streams. Note that the terms
Input and Output refer to the radio channel carrying the signal, not to the devices having antennas, so that in
the Down-Link MIMO 2 x 2 system supported by TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules:
The LTE data stream is divided into 2 independent streams by the Tx-antennas of the base station
The cellular modules, at the receiver side, receives both LTE data streams by 2 Rx-antennas (ANT1 / ANT2)
Figure 18: Description of the LTE Down-Link MIMO 2 x 2 radio technology supported by TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules support the LTE MIMO 2 x 2 radio technology in the Down-Link path only
(from the base station to the module): the ANT1 port is the only one RF interface that is used by the module to
transmit the RF signal in the Up-Link path (from the module to the base station).
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 34 of 141
Page 35

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Item
Requirements
Remarks
Impedance
50 nominal characteristic impedance
The impedance of the antenna RF connection must
match the 50 impedance of the ANT1 port.
Frequency Range
See the TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1] and the
MPCI-L2 series Data Sheet [2]
The required frequency range of the antenna connected
to ANT1 port depends on the operating bands of the
used cellular module and the used mobile network.
Return Loss
S11 < -10 dB (VSWR < 2:1) recommended
S11 < -6 dB (VSWR < 3:1) acceptable
The Return loss or the S11, as the VSWR, refers to the
amount of reflected power, measuring how well the
primary antenna RF connection matches the 50
characteristic impedance of the ANT1 port.
The impedance of the antenna termination must match
as much as possible the 50 nominal impedance of the
ANT1 port over the operating frequency range, reducing
as much as possible the amount of reflected power.
Efficiency
> -1.5 dB ( > 70% ) recommended
> -3.0 dB ( > 50% ) acceptable
The radiation efficiency is the ratio of the radiated power
to the power delivered to antenna input: the efficiency is
a measure of how well an antenna receives or transmits.
The radiation efficiency of the antenna connected to the
ANT1 port needs to be enough high over the operating
frequency range to comply with the Over-The-Air (OTA)
radiated performance requirements, as Total Radiated
Power (TRP) and the Total Isotropic Sensitivity (TIS),
specified by applicable related certification schemes.
Maximum Gain
According to radiation exposure limits
The power gain of an antenna is the radiation efficiency
multiplied by the directivity: the gain describes how
much power is transmitted in the direction of peak
radiation to that of an isotropic source.
The maximum gain of the antenna connected to ANT1
port must not exceed the herein stated value to comply
with regulatory agencies radiation exposure limits.
For additional info see the section 4.2.2.
Input Power
> 33 dBm ( > 2 W )
The antenna connected to the ANT1 port must support
with adequate margin the maximum power transmitted
by the modules.
1.7.1.1 Antenna RF interfaces requirements
Table 8, Table 9 and Table 10 summarize the requirements for the antennas RF interfaces (ANT1 / ANT2). See
section 2.4.1 for suggestions to properly design antennas circuits compliant with these requirements.
The antenna circuits affect the RF compliance of the device integrating TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2
series modules with applicable required certification schemes (for more details see section 4).
Compliance is guaranteed if the antenna RF interfaces (ANT1 / ANT2) requirements summarized
in Table 8, Table 9 and Table 10 are fulfilled.
Table 8: Summary of primary Tx/Rx antenna RF interface (ANT1) requirements
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 35 of 141
Page 36

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Item
Requirements
Remarks
Impedance
50 nominal characteristic impedance
The impedance of the antenna RF connection must
match the 50 impedance of the ANT2 port.
Frequency Range
See the TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1] and the
MPCI-L2 series Data Sheet [2]
The required frequency range of the antennas connected
to ANT2 port depends on the operating bands of the
used cellular module and the used Mobile Network.
Return Loss
S11 < -10 dB (VSWR < 2:1) recommended
S11 < -6 dB (VSWR < 3:1) acceptable
The Return loss or the S11, as the VSWR, refers to the
amount of reflected power, measuring how well the
secondary antenna RF connection matches the 50
characteristic impedance of the ANT2 port.
The impedance of the antenna termination must match
as much as possible the 50 nominal impedance of the
ANT2 port over the operating frequency range, reducing
as much as possible the amount of reflected power.
Efficiency
> -1.5 dB ( > 70% ) recommended
> -3.0 dB ( > 50% ) acceptable
The radiation efficiency is the ratio of the radiated power
to the power delivered to antenna input: the efficiency is
a measure of how well an antenna receives or transmits.
The radiation efficiency of the antenna connected to the
ANT2 port needs to be enough high over the operating
frequency range to comply with the Over-The-Air (OTA)
radiated performance requirements, as the TIS, specified
by applicable related certification schemes.
Item
Requirements
Remarks
Efficiency imbalance
< 0.5 dB recommended
< 1.0 dB acceptable
The radiation efficiency imbalance is the ratio of the
primary (ANT1) antenna efficiency to the secondary
(ANT2) antenna efficiency: the efficiency imbalance is a
measure of how much better an antenna receives or
transmits compared to the other antenna.
The radiation efficiency of the secondary antenna needs
to be roughly the same of the radiation efficiency of the
primary antenna for good RF performance.
Envelope Correlation
Coefficient
< 0.4 recommended
< 0.5 acceptable
The Envelope Correlation Coefficient (ECC) between the
primary (ANT1) and the secondary (ANT2) antenna is an
indicator of 3D radiation pattern similarity between the
two antennas: low ECC results from antenna patterns
with radiation lobes in different directions.
The ECC between primary and secondary antenna needs
to be enough low to comply with radiated performance
requirements specified by related certification schemes.
Isolation
> 15 dB recommended
> 10 dB acceptable
The antenna to antenna isolation is the loss between the
primary (ANT1) and the secondary (ANT2) antenna: high
isolation results from low coupled antennas.
The isolation between primary and secondary antenna
needs to be high for good RF performance.
Table 9: Summary of secondary Rx antenna RF interface (ANT2) requirements
Table 10: Summary of primary (ANT1) and secondary (ANT2) antennas relationship requirements
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 36 of 141
Page 37

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.7.2 Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET)
Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET) is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET) is not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version.
The antenna detection is based on ADC measurement. The ANT_DET pin is an Analog to Digital Converter
(ADC) provided to sense the antenna presence.
The antenna detection function provided by ANT_DET pin is an optional feature that can be implemented if the
application requires it. The antenna detection is forced by the +UANTR AT command. See the u-blox AT
Commands Manual [3] for more details on this feature.
The ANT_DET pin generates a DC current (for detailed characteristics see the TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1]) and
measures the resulting DC voltage, thus determining the resistance from the antenna connector provided on the
application board to GND. So, the requirements to achieve antenna detection functionality are the following:
an RF antenna assembly with a built-in resistor (diagnostic circuit) must be used
an antenna detection circuit must be implemented on the application board
See section 2.4.2 for antenna detection circuit on application board and diagnostic circuit on antenna assembly
design-in guidelines.
1.8 SIM interface
1.8.1 SIM interface
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules provide high-speed SIM/ME interface including automatic detection and
configuration of the voltage required by the connected SIM card or chip.
Both 1.8 V and 3 V SIM types are supported. Activation and deactivation with automatic voltage switch from
1.8 V to 3 V are implemented, according to ISO-IEC 7816-3 specifications. The VSIM or UIM_PWR supply
output provides internal short circuit protection to limit start-up current and protect the SIM to short circuits.
The SIM driver supports the PPS (Protocol and Parameter Selection) procedure for baud-rate selection, according
to the values determined by the SIM card or chip.
1.8.2 SIM detection interface
SIM detection interface (GPIO5) is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
SIM detection interface (GPIO5) is not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version.
The GPIO5 pin is by default configured to detect the SIM card mechanical / physical presence. The pin is
configured as input with an internal active pull-down enabled, and it can sense SIM card presence only if
properly connected to the mechanical switch of a SIM card holder as described in section 2.5:
Low logic level at GPIO5 input pin is recognized as SIM card not present
High logic level at GPIO5 input pin is recognized as SIM card present
The SIM card detection function provided by GPIO5 pin is an optional feature that can be implemented / used or
not according to the application requirements: an Unsolicited Result Code (URC) is generated each time that
there is a change of status (for more details see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
The optional function “SIM card hot insertion/removal” can be additionally enabled on the GPIO5 pin by specific
AT command (see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 37 of 141
Page 38

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.9 Data communication interfaces
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules provide the following serial communication interface:
USB interface: High-Speed USB 2.0 compliant interface available for the communication with an external
host application processor, for AT commands, data communication, FW upgrade by means of the FOAT
feature, FW upgrade by means of the u-blox EasyFlash tool and for diagnostic purpose (see section 1.9.1 for
functional description)
TOBY-L2 series modules additionally provide the following serial communication interfaces:
UART interface: asynchronous serial interface available for the communication with an external host
application processor, for AT commands, data communication, FW upgrade by means of the FOAT feature
(see section 1.9.2 for functional description)
DDC interface: I
chips/modules and with external I2C devices as an audio codec (see section 1.9.3 for functional description)
SDIO interface: Secure Digital Input Output interface available for the communication with an external Wi-Fi
chip or module (see section 1.9.4 for functional description)
1.9.1 Universal Serial Bus (USB)
2
C bus compatible interface available for the communication with u-blox GNSS positioning
1.9.1.1 USB features
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules include a High-Speed USB 2.0 compliant interface with maximum data
rate of 480 Mb/s, representing the main interface for transferring high speed data with a host application
processor: the USB interface is available for AT commands, data communication, FW upgrade by means of the
FOAT feature, FW upgrade by means of the u-blox EasyFlash tool and for diagnostic purpose.The module itself
acts as a USB device and can be connected to a USB host such as a Personal Computer or an embedded
application microprocessor equipped with compatible drivers.
The USB_D+ / USB_D- lines carry the USB serial bus data and signaling, providing all the functionalities for the
bus attachment, configuration, enumeration, suspension or remote wakeup according to the Universal Serial Bus
Revision 2.0 specification [6]
The additional VUSB_DET input pin is available on TOBY-L2 series modules as optional feature to sense the USB
VBUS supply (5.0 V typical) from the host, providing the complete bus detach functionality for further reduction
of the module current consumption in particular during low-power idle mode with power saving enabled:
TOBY-L2 series modules disable the USB interface when a low logic level is sensed after a high-to-low logic level
transition on the VUSB_DET input pin, reducing the current consumption.
The VUSB_DET pin is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
The USB interface is controlled and operated with:
AT commands according to 3GPP TS 27.007 [8], 3GPP TS 27.005 [9], 3GPP TS 27.010 [10]
u-blox AT commands
For the complete list of supported AT commands and their syntax see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3].
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 38 of 141
Page 39

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Default profile configuration
Interface 0 Wireless Controller – Remote NDIS
Interface 1 Communication Data
EndPoint Transfer: Interrupt
EndPoint Transfer: Bulk
EndPoint Transfer: Bulk
Interface 2 Communication Control – AT commands
EndPoint Transfer: Interrupt
Interface 3 Communication Data
EndPoint Transfer: Bulk
EndPoint Transfer: Bulk
Function RNDIS
Function CDC Serial
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 modules provide by default the following USB profile with the listed set of USB functions:
1 RNDIS for Ethernet-over-USB connection
1 CDC-ACM for AT commands and data communication
The USB profile of TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 modules identifies itself by its VID (Vendor ID) and PID (Product ID)
combination, included in the USB device descriptor according to the USB 2.0 specifications [6].
The VID and PID of the default USB profile configuration with the set of functions described above (1 RNDIS for
Ethernet-over-USB and 1 CDC-ACM for AT commands and data) are the following:
VID = 0x1546
PID = 0x1146
Figure 19 summarizes the USB end-points available with the default USB profile configuration.
Figure 19: TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series USB End-Points summary for the default USB profile configuration
The USB of the modules can be configured by the AT+UUSBCONF command (for more details see the u-blox AT
Commands Manual [3]) to select different sets of USB functions available in mutually exclusive way, selecting the
active USB profile consisting of a specific set of functions with various capabilities and purposes, such as:
CDC-ACM for AT commands and data
CDC-ACM for GNSS tunneling
CDC-ACM for SIM Access Profile (SAP)
CDC-ACM for diagnostic
RNDIS for Ethernet-over-USB
CDC-ECM for Ethernet-over-USB
CDC-NCM for Ethernet-over-USB
MBIM for Ethernet-over-USB
CDC-ACM for GNSS tunneling, CDC-ACM for SIM Access Profile (SAP), and CDC-NCM and MBIM
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 39 of 141
functions are not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S and MPCI-L2x0-00S product versions.
Page 40

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
For example, the default USB profile configuration which provides 2 functions (1 RNDIS for Ethernet-over-USB
and 1 CDC-ACM for AT commands and data) can be changed by means of the AT+UUSBCONF command
switching to a USB profile configuration which provides the following 6 functions:
3 CDC-ACM for AT commands and data
1 CDC-ACM for GNSS tunneling
1 CDC-ACM for SIM Access Profile (SAP)
1 CDC-ACM for diagnostic
As each USB profile of TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 modules identifies itself by its specific VID and PID combination
included in the USB device descriptor according to the USB 2.0 specifications [6], the VID and PID combination
changes as following by switching the active USB profile configuration to the set of 6 functions described above:
VID = 0x1546
PID = 0x1141
Alternatively, as another example, the USB profile configuration can be changed by means of the
AT+UUSBCONF command switching to a USB profile configuration which provides the following 4 functions:
1 CDC-ECM for Ethernet-over-USB
3 CDC-ACM for AT commands and data
In case of this USB profile with the set of 4 functions described above, the VID and PID are the following:
VID = 0x1546
PID = 0x1143
The switch of the active USB profile selected by the AT+UUSBCONF command is not performed immediately.
The settings are saved in the non-volatile memory of the module at the power off, and the new configuration is
effective at the subsequent reboot of the module.
If the USB is connected to the host before the module is switched on, or if the module is reset (rebooted) with
the USB connected to the host, the VID and PID are automatically updated during the boot of the module. First,
VID and PID are the following:
VID = 0x1546
PID = 0x1140
This VID and PID combination identifies a USB profile where no USB function described above is available: AT
commands must not be sent to the module over the USB profile identified by this VID and PID combination.
Then, after a time period (roughly 20 s, depending on the host / device enumeration timings), the VID and PID
are updated to the ones related to the USB profile selected by the AT+UUSBCONF command.
For more details regarding the TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules USB configurations and capabilities,
see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3], +UUSBCONF AT command.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 40 of 141
Page 41

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.9.1.2 USB in Windows
The USB drivers (INF files) are provided for Windows systems and should be installed properly by following the
step-by-step instruction in EVK-L20 / EVK-L21 User Guide [4].
USB drivers are available for the following operating system platforms:
Windows Vista
Windows 7
Windows 8
Windows 8.1
Windows Embedded Compact 7
The module firmware can be upgraded over the USB interface by means of the FOAT feature, or using the u-blox
EasyFlash tool (for more details see Firmware Update Application Note [4]).
1.9.1.3 USB in Linux/Android
It is not required to install a specific driver for each Linux-based or Android-based operating system (OS) to use
the module USB interface, which is compatible with standard Linux/Android USB kernel drivers.
The full capability and configuration of the module USB interface can be reported by running ‘lsusb –v’ or an
equivalent command available in the host operating system when the module is connected.
1.9.1.4 USB and power saving
If power saving is enabled by the AT+UPSV command, the modules automatically enter the USB suspended state
when the device has observed no bus traffic for a specific time period according to the USB 2.0 specification [6].
In suspended state, the module maintains any USB internal status as device. In addition, the module enters the
suspended state when the hub port it is attached to is disabled. This is referred to as USB selective suspend.
The module exits suspend mode when there is bus activity. If the USB is connected and not suspended, the
module is forced to stay in active-mode, therefore the AT+UPSV settings are overruled but they have effect on
the power saving configuration of the other interfaces.
The modules are capable of USB remote wake-up signaling: i.e. it may request the host to exit suspend mode or
selective suspend by using electrical signaling to indicate remote wake-up. This notifies the host that it should
resume from its suspended mode, if necessary, and service the external event. Remote wake-up is accomplished
using electrical signaling described in the USB 2.0 specifications [6].
For the module current consumption description with power saving enabled and USB suspended, or with power
saving disabled and USB not suspended, see the sections 1.5.1.5, 1.5.1.6 and the TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1] or the
MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2].
The additional VUSB_DET input pin available on TOBY-L2 series modules provides the complete bus detach
functionality: the modules disable the USB interface when a low logic level is sensed after a high-to-low logic
level transition on the VUSB_DET input pin. This allows a further reduction of the module current consumption,
in particular as compared to the USB suspended status during low-power idle mode with power saving enabled.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 41 of 141
Page 42

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Interface
AT Settings
Comments
UART interface
AT interface: enabled
AT command interface is enabled by default on the UART physical interface
MUX protocol: disabled
Multiplexing mode is disabled by default and it can be enabled by AT+CMUX command.
For more details, see the Mux Implementation Application Note [11].
The following virtual channels are defined:
Channel 0: Control channel
Channel 1 – 5: AT commands / data connection
Channel 6: GNSS tunneling
Channel 7: SIM Access Profile
1.9.2 Asynchronous serial interface (UART)
The UART interface is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
The UART interface is not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version.
1.9.2.1 UART features
The UART interface is a 9-wire 1.8 V unbalanced asynchronous serial interface (UART) that can be connected to
an application host processor for AT commands and data communication.
The module firmware can be upgraded over the UART interface by means of the Firmware upgrade over AT
(FOAT) feature only: for more details see section 1.15 and Firmware update application note [4].
UART interface provides RS-232 functionality conforming to the ITU-T V.24 Recommendation (more details
available in ITU Recommendation [7]), with CMOS compatible signal levels: 0 V for low data bit or ON state, and
1.8 V for high data bit or OFF state. For detailed electrical characteristics see TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1].
TOBY-L2 modules are designed to operate as LTE/3G/2G cellular modems, i.e. the data circuit-terminating
equipment (DCE) is according to the ITU-T V.24 Recommendation [7]. A customer application processor
connected to the module through the UART interface represents the data terminal equipment (DTE).
The signal names of the UART interface of the TOBY-L2 series modules conform to the ITU-T V.24
Recommendation [7]: e.g. TXD line represents the data transmitted by the DTE (application processor data
output) and received by the DCE (module data input).
The UART interface is controlled and operated with:
AT commands according to 3GPP TS 27.007 [8], 3GPP TS 27.005 [9], 3GPP TS 27.010 [10]
u-blox AT commands
For the complete list of supported AT commands and their syntax see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3].
1.9.2.2 UART interface configuration
The UART interface of TOBY-L2 series modules is configured as described in Table 11 (for information about
further settings, see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
Table 11: Default UART interface configuration
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 42 of 141
Page 43

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.9.2.3 UART signals behavior
At the module switch-on, before the UART interface initialization (as described in the power-on sequence
reported in Figure 14), each pin is first tri-stated and then is set to its relative internal reset state. At the end of
the boot sequence, the UART interface is initialized, the module is by default in active-mode, and the UART
interface is enabled.
1.9.2.4 UART and power-saving
The power saving configuration is controlled by the AT+UPSV command (for the complete description, see the
u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]). When power saving is enabled, the module automatically enters low power
idle-mode whenever possible, and otherwise the active-mode is maintained by the module (see section 1.4 for
definition and description of module operating modes referred to in this section).
The AT+UPSV command configures both the module power saving and also the UART behavior in relation to the
power saving. The conditions for the module entering low power idle-mode also depend on the UART power
saving configuration, as the module does not enter the low power idle-mode according to any required activity
related to the network (within or outside an active call) or any other required concurrent activity related to the
functions and interfaces of the module, including the UART interface.
1.9.2.5 UART multiplexer protocol
TOBY-L2 series modules have a software layer with multiplexer functionality as per 3GPP TS 27.010 Multiplexer
Protocol [10], available on the UART physical link.
This is a data link protocol (layer 2 of OSI model) which uses HDLC-like framing and operates between the
module (DCE) and the application processor (DTE) and allows a number of simultaneous sessions over the used
physical link (the UART interface): the user can concurrently use AT command interface on one MUX channel
and data communication on another multiplexer channel.
The following virtual channels are defined:
Channel 0: control channel
Channel 1 – 5: AT commands / data connection
Channel 6: GNSS tunneling
Channel 7: SIM Access Profile
For more details, see Mux implementation Application Note [11].
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 43 of 141
Page 44

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.9.3 DDC (I
The I
2
C) interface
2
C bus compatible Display Data Channel interface is not available on the MPCI-L2 series modules, as
AssistNow embedded GNSS positioning aiding, CellLocate® positioning through cellular information and
custom functions over GPIOs for the integration with u-blox positioning chips / modules.
The I
2
C bus compatible Display Data Channel interface is not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product
version, as AssistNow embedded GNSS positioning aiding, CellLocate® positioning through cellular
information and custom functions over GPIOs for the integration with u-blox positioning chips / modules.
The SDA and SCL pins of TOBY-L2 series modules represent an I2C bus compatible Display Data Channel (DDC)
interface for the communication with u-blox GNSS receivers and with other external I2C devices as audio codecs:
an I2C master can communicate with more I2C slaves in accordance to the I2C bus specifications [12].
The DDC (I2C) interface is the only one interface dedicated for communication between u-blox cellular module
and u-blox positioning receivers. The AT commands interface is not available on the DDC (I2C) interface.
The DDC (I2C) interface pads of the module, serial data (SDA) and serial clock (SCL), are open drain output and
external pull up resistors must be used conforming to the I2C bus specifications [12].
u-blox has implemented special features in the cellular modules to ease the design effort for the integration of a
u-blox cellular module with a u-blox GNSS receiver (details in GNSS Implementation Application Note [13]).
Combining a u-blox cellular module with a u-blox GNSS receiver allows designers to full access the GNSS receiver
directly via the cellular module: it relays control messages to the GNSS receiver via a dedicated DDC (I2C)
interface. A 2nd interface connected to the GNSS receiver is not necessary: AT commands via the AT interfaces of
the cellular module (UART, USB) allows a full control of the GNSS receiver from any host processor.
u-blox cellular modules feature embedded GNSS aiding that is a set of specific features developed by u-blox to
enhance GNSS performance, decreasing Time To First Fix (TTFF), thus allowing to calculate the position in a
shorter time with higher accuracy.
Additional custom functions over GPIO pins are designed to improve the integration with u-blox GNSS receivers:
GNSS receiver power-on/off: “GNSS supply enable” function over the GPIO2 pin improves the positioning
receiver power consumption. When the GNSS functionality is not required, the positioning receiver can be
completely switched off by the cellular module controlled by the application processor over AT commands
The wake up from idle-mode when the GNSS receiver is ready to send data: “GNSS data ready” function
over the GPIO3 pin improves the cellular module power consumption. When power saving is enabled in the
cellular module by the AT+UPSV command and the GNSS receiver does not send data by the DDC (I2C)
interface, the module automatically enters idle-mode whenever possible. With the “GNSS data ready”
function the GNSS receiver can indicate to the cellular module that it is ready to send data: the positioning
receiver can wake up the cellular module to avoid data loss even if power saving is enabled.
The RTC synchronization signal to the GNSS receiver: “GNSS RTC sharing” function over the GPIO4 pin
improves GNSS receiver performance, decreasing the Time To First Fix (TTFF), and thus allowing to calculate
the position in a shorter time with higher accuracy. When GNSS local aiding is enabled, the cellular module
automatically uploads data such as position, time, ephemeris, almanac, health and ionospheric parameter
from the positioning receiver into its local memory, and restores this to the GNSS receiver at the next power
up of the positioning receiver
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 44 of 141
Page 45

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.9.4 Secure Digital Input Output interface (SDIO)
Secure Digital Input Output interface is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
Secure Digital Input Output interface is not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version.
TOBY-L2 series modules include a 4-bit Secure Digital Input Output interface (SDIO_D0, SDIO_D1, SDIO_D2,
SDIO_D3, SDIO_CLK, SDIO_CMD) designed to communicate with an external Wi-Fi chip.
1.10 Audio
1.10.1 Digital audio over I
Digital audio over I
Digital audio over I
TOBY-L2 series modules include a 4-wire I2S digital audio interface (I2S_TXD, I2S_RXD, I2S_CLK, I2S_WA) that
can be configured by AT command to transfer digital audio data with an external device as an audio codec (for
more details see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
2
S interface is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
2
S interface is not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version.
2
S interface
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 45 of 141
Page 46

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Function
Description
Default GPIO
Configurable GPIOs
Network status
indication
Network status: registered home network, registered
roaming, data transmission, no service
GPIO1
GPIO1
GNSS supply enable
Enable/disable the supply of u-blox GNSS receiver
connected to cellular module
GPIO2
GPIO2
GNSS data ready
Sense when u-blox GNSS receiver connected to the module
is ready for sending data by the DDC (I2C)
GPIO3
GPIO3
GNSS RTC sharing
Real Time Clock synchronization signal to u-blox GNSS
receiver connected to cellular module
GPIO4
GPIO4
SIM card detection
SIM card physical presence detection
GPIO5
GPIO5
SIM card hot
insertion/removal
SIM card hot insertion/removal
--
GPIO5
I2S digital audio interface
I2S digital audio interface
I2S_RXD, I2S_TXD,
I2S_CLK, I2S_WA
I2S_RXD, I2S_TXD,
I2S_CLK, I2S_WA
26 MHz clock output
26 MHz clock output for an external audio codec or an
external Wi-Fi chip/module
GPIO6
GPIO6
Wi-Fi enable
Enable/disable the supply of the external Wi-Fi chip or
module connected to the cellular module
--
GPIO1, GPIO4, DSR
Wi-Fi data ready
Sense when the external Wi-Fi chip/module connected to
the cellular module is ready for sending data by the SDIO,
waking up the cellular module from low power idle mode
--
GPIO3, DTR
Wi-Fi reset
Reset the external Wi-Fi chip or module connected to the
cellular module
--
GPIO3, DCD
Wi-Fi power saving
Enable/disable the low power mode of the external Wi-Fi
chip/module connected to the cellular module
--
GPIO2, RI
32 kHz clock output
32 kHz clock output for an external Wi-Fi chip or module
--
GPIO4
Antenna tuning
4-bit tunable antenna control signals mapping the actual
operating RF band over a 4-pin interface provided for the
implementation of external antenna tuning solutions
--
I2S_RXD, I2S_TXD,
I2S_CLK, I2S_WA
DSR, DTR, DCD, RI
DSR
UART data set ready output
DSR
DSR
DTR
UART data terminal ready input
DTR
DTR
DCD
UART data carrier detect output
DCD
DCD
RI
UART ring indicator output
RI
RI
General purpose input
Input to sense high or low digital level
--
All
General purpose output
Output to set the high or the low digital level
--
All
Pin disabled
Tri-state with an internal active pull-down enabled
--
All
1.11 General Purpose Input/Output
General Purpose Input / Output pins are not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version except for
the Wireless Wide Area Network status indication configured on the GPIO1 pin.
General Purpose Input / Output pins are not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
TOBY-L2 series modules include 14 pins (GPIO1-GPIO6, I2S_TXD, I2S_RXD, I2S_CLK, I2S_WA, DTR, DSR,
DCD, RI) that can be configured as General Purpose Input/Output or to provide custom functions via u-blox AT
commands (see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]), as summarized in Table 12.
Table 12: TOBY-L2 series GPIO custom functions configuration
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 46 of 141
Page 47

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Baseband
Processor
20
W_DISABLE#
MPCI-L2 series
3.3Vaux
W_DISABLE#
22k
1.12 Mini PCIe specific signals (W_DISABLE#, LED_WWAN#)
Mini PCI Express specific signals (W_DISABLE#, LED_WWAN#) are not available on TOBY-L2 series.
MPCI-L2 series modules include the W_DISABLE# active-low input signal to disable the radio operations as
specified by the PCI Express Mini Card Electromechanical Specification [14].
As described in Figure 20, the W_DISABLE# input is equipped with an internal pull-up to the 3.3Vaux supply.
The W_DISABLE# input detailed electrical characteristics are described in the MPCI-L2 series Data Sheet [2].
Figure 20: MPCI-L2 series modules W_DISABLE# input circuit description
MPCI-L2 series modules include the LED_WWAN# active-low open drain output to provide the Wireless Wide
Area Network status indication as specified by the PCI Express Mini Card Electromechanical Specification [14].
For more electrical characteristics details see the MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2].
1.13 Reserved pins (RSVD)
Pins reserved for future use, marked as RSVD, are not available on MPCI-L2 series.
TOBY-L2 series modules have pins reserved for future use, marked as RSVD: they can all be left unconnected on
the application board, except the RSVD pin number 6 that must be externally connected to ground.
1.14 Not connected pins (NC)
Pins internally not connected, marked as NC, are not available on TOBY-L2 series.
MPCI-L2 series modules have pins internally not connected, marked as NC: they can be left unconnected or they
can be connected on the application board according to any application requirement, given that none function is
provided by the modules over these pins.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 47 of 141
Page 48

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.15 System features
1.15.1 Network indication
Network status indication over GPIO1 is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules which include the
LED_WWAN# active-low open drain output to provide the Wireless Wide Area Network status indication
as specified by the PCI Express Mini Card Electromechanical Specification [14].
General Purpose Input / Output pins are not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version except for
the Wireless Wide Area Network status indication configured on the GPIO1 pin.
The GPIO1 can be configured by the AT+UGPIOC command to indicate network status as described below:
No service (no network coverage or not registered)
Registered 2G / 3G / LTE home network
Registered 2G / 3G / LTE visitor network (roaming)
Call enabled (RF data transmission / reception)
For the detailed description of the network status indication configuration, see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3],
GPIO commands.
1.15.2 Antenna supervisor
Antenna supervisor (i.e. antenna detection) is not available on MPCI-L2 series.
Antenna supervisor (i.e. antenna detection) is not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version.
The antenna detection function provided by the ANT_DET pin is based on an ADC measurement as optional
feature that can be implemented if the application requires it. The antenna supervisor is forced by the +UANTR
AT command (see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3] for more details).
The requirements to achieve antenna detection functionality are the following:
an RF antenna assembly with a built-in resistor (diagnostic circuit) must be used
an antenna detection circuit must be implemented on the application board
See section 1.7.2 for detailed antenna detection interface functional description and see section 2.4.2 for
detection circuit on application board and diagnostic circuit on antenna assembly design-in guidelines.
1.15.3 Jamming detection
Congestion detection (i.e. jamming detection) is not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S and MPCI-L2x0-00S.
In real network situations modules can experience various kind of out-of-coverage conditions: limited service
conditions when roaming to networks not supporting the specific SIM, limited service in cells which are not
suitable or barred due to operators’ choices, no cell condition when moving to poorly served or highly interfered
areas. In the latter case, interference can be artificially injected in the environment by a noise generator covering
a given spectrum, thus obscuring the operator’s carriers entitled to give access to the LTE/3G/2G service.
The congestion (i.e. jamming) detection feature can be enabled and configured by the +UCD AT command: the
feature consists of detecting an anomalous source of interference and signaling the start and stop of such
conditions to the host application processor with an unsolicited indication, which can react appropriately by e.g.
switching off the radio transceiver of the module (i.e. configuring the module in “airplane mode” by means of
the +CFUN AT command) in order to reduce power consumption and monitoring the environment at constant
periods (for more details see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 48 of 141
Page 49

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.15.4 IP modes of operation
IP modes of operation refer to the TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules configuration related to the network IP
termination and network interfaces settings in general. IP modes of operation are the following:
Bridge mode: In bridge mode the module acts as a cellular modem dongle connected to the host over
serial interface (USB). The IP termination of the network is placed on the host IP stack. The module is
configured as a bridge which means the network IP address is assigned to the host (host IP termination).
Router mode: In router mode the module acts as a cellular modem router which means the IP termination
of the network is placed on the internal IP stack of the module (on-target IP termination). In particular, in
this configuration the application processor belongs to a private network and is not aware of the mobile
connectivity setup of the module.
For more details about IP modes of operation see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3].
1.15.5 Dual stack IPv4/IPv6
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series support both Internet Protocol version 4 and Internet Protocol version 6 in parallel.
For more details about dual stack IPv4/IPv6 see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3].
1.15.6 TCP/IP and UDP/IP
Embedded TCP/IP and UDP/IP stack as well as Direct Link mode are not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S
and MPCI-L2x0-00S product versions.
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules provide embedded TCP/IP and UDP/IP protocol stack: a PDP context can be
configured, established and handled via the data connection management packet switched data commands.
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules provide Direct Link mode to establish a transparent end-to-end
communication with an already connected TCP or UDP socket via serial interfaces (USB, UART). In Direct Link
mode, data sent to the serial interface from an external application processor is forwarded to the network and
vice-versa.
For more details about embedded TCP/IP and UDP/IP functionalities see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3].
1.15.7 FTP and FTPS
Embedded FTP and FTPS services as well as Direct Link mode are not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S
and MPCI-L2x0-00S product versions.
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series provide embedded File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and Secure File Transfer Protocol
(FTPS, i.e. FTP with SSL encryption) services. Files are read and stored in the local file system of the module.
FTP files can also be transferred using FTP Direct Link:
FTP download: data coming from the FTP server is forwarded to the host processor via USB / UART serial
interfaces (for FTP without Direct Link mode the data is always stored in the module’s Flash File System)
FTP upload: data coming from the host processor via USB / UART serial interface is forwarded to the FTP
server (for FTP without Direct Link mode the data is read from the module’s Flash File System)
When Direct Link is used for a FTP file transfer, only the file content pass through USB / UART serial interface,
whereas all the FTP commands handling is managed internally by the FTP application.
For more details about embedded FTP and FTPS functionalities see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3].
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 49 of 141
Page 50

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.15.8 HTTP and HTTPS
Embedded HTTP and HTTPS services are not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S and MPCI-L2x0-00S.
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules provide the embedded Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and the Secure
Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol (HTTPS, i.e. HTTP with TLS / SSL encryption) services via AT commands for sending
requests to a remote HTTP server, receiving the server response and transparently storing it in the module’s Flash
File System (FFS).
For more details about embedded HTTP and HTTPS functionalities see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3].
1.15.9 SSL
Embedded Transport Layer Security (TLS) / Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols are not supported by the
TOBY-L2x0-00S and MPCI-L2x0-00S product versions.
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules provide the Transport Layer Security (TLS) / Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
encryption protocols to enable security over the FTP and HTTP protocols via AT commands.
For more details about embedded TLS / SSL functionalities see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3].
1.15.10 AssistNow clients and GNSS integration
AssistNow clients and u-blox GNSS receiver integration are not available on MPCI-L2 series.
AssistNow clients and u-blox GNSS receiver integration are not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S.
For customers using u-blox GNSS receivers, TOBY-L2 series cellular modules feature embedded AssistNow clients.
AssistNow A-GPS provides better GNSS performance and faster Time-To-First-Fix. The clients can be enabled and
disabled with an AT command (see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
TOBY-L2 series cellular modules act as a stand-alone AssistNow client, making AssistNow available with no
additional requirements for resources or software integration on an external host micro controller. Full access to
u-blox GNSS receivers is available via the TOBY-L2 series cellular module, through the DDC (I2C) interface, while
the available GPIOs can handle the positioning chipset / module power-on/off. This means that cellular module
and GNSS receiver can be controlled through a single serial port from any host processor.
1.15.11 Hybrid positioning and CellLocate
Hybrid positioning and CellLocate
Hybrid positioning and CellLocate
Although GNSS is a widespread technology, its reliance on the visibility of extremely weak GNSS satellite signals
means that positioning is not always possible. Especially difficult environments for GNSS are indoors, in enclosed
or underground parking garages, as well as in urban canyons where GNSS signals are blocked or jammed by
multipath interference. The situation can be improved by augmenting GNSS receiver data with cellular network
information to provide positioning information even when GNSS reception is degraded or absent. This additional
information can benefit numerous applications.
®
are not available on MPCI-L2 series.
®
are not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version.
®
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 50 of 141
Page 51

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Positioning through cellular information: CellLocate®
u-blox CellLocate® enables the estimation of device position based on the parameters of the mobile network cells
visible to the specific device. To estimate its position the u-blox cellular module sends the CellLocate® server the
parameters of network cells visible to it using a UDP connection. In return the server provides the estimated
position based on the CellLocate® database. The u-blox cellular module can either send the parameters of the
visible home network cells only (normal scan) or the parameters of all surrounding cells of all mobile operators
(deep scan).
The CellLocate® database is compiled from the position of devices which observed, in the past, a specific cell or
set of cells (historical observations) as follows:
1. Several devices reported their position to the CellLocate
®
server when observing a specific cell (the As in the
picture represent the position of the devices which observed the same cell A)
2. CellLocate
®
server defines the area of Cell A visibility
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 51 of 141
Page 52

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
3. If a new device reports the observation of Cell A CellLocate
®
is able to provide the estimated position from
the area of visibility
4. The visibility of multiple cells provides increased accuracy based on the intersection of areas of visibility.
CellLocate® is implemented using a set of two AT commands that allow configuration of the CellLocate® service
(AT+ULOCCELL) and requesting position according to the user configuration (AT+ULOC). The answer is provided
in the form of an unsolicited AT command including latitude, longitude and estimated accuracy.
The accuracy of the position estimated by CellLocate
®
depends on the availability of historical observations
in the specific area.
Hybrid positioning
With u-blox Hybrid positioning technology, u-blox cellular devices can be triggered to provide their current
position using either a u-blox GNSS receiver or the position estimated from CellLocate®. The choice depends on
which positioning method provides the best and fastest solution according to the user configuration, exploiting
the benefit of having multiple and complementary positioning methods.
Hybrid positioning is implemented through a set of three AT commands that allow configuration of t he GNSS
receiver (AT+ULOCGNSS), configuration of the CellLocate® service (AT+ULOCCELL), and requesting the position
according to the user configuration (AT+ULOC). The answer is provided in the form of an unsolicited AT
command including latitude, longitude and estimated accuracy (if the position has been estimated by
CellLocate®), and additional parameters if the position has been computed by the GNSS receiver.
The configuration of mobile network cells does not remain static (e.g. new cells are continuously added or
existing cells are reconfigured by the network operators). For this reason, when a Hybrid positioning method has
been triggered and the GNSS receiver calculates the position, a database self-learning mechanism has been
implemented so that these positions are sent to the server to update the database and maintain its accuracy.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 52 of 141
Page 53

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
The use of hybrid positioning requires a connection via the DDC (I2C) bus between the TOBY-L2 series cellular
module and the u-blox GNSS receiver (see sections 1.9.3 and 2.6.3).
See GNSS Implementation Application Note [13] for the complete description of the feature.
u-blox is extremely mindful of user privacy. When a position is sent to the CellLocate
unable to track the SIM used or the specific device.
®
server u-blox is
1.15.12 Firmware update Over AT (FOAT)
This feature allows upgrading the module firmware over USB / UART serial interfaces, using AT commands.
The +UFWUPD AT command triggers a reboot followed by the upgrade procedure at specified a baud rate
A special boot loader on the module performs firmware installation, security verifications and module reboot
Firmware authenticity verification is performed via a security signature during the download. The firmware is
then installed, overwriting the current version. In case of power loss during this phase, the boot loader
detects a fault at the next wake-up, and restarts the firmware download. After completing the upgrade, the
module is reset again and wakes-up in normal boot
For more details about Firmware update Over AT procedure see the Firmware Update Application Note [4] and
the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3], +UFWUPD AT command.
1.15.13 Firmware update Over The Air (FOTA)
Firmware update Over The Air (FOTA) is not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S and MPCI-L2x0-00S.
This feature allows upgrading the module firmware over the LTE/3G/2G air interface. The main idea with
updating Firmware over the air is to reduce the amount of data required for transmission to the module. This is
achieved by downloading only a “delta file” instead of the full firmware. The delta contains only the differences
between the two firmware versions (old and new), and is compressed.
For more details about Firmware update Over The Air procedure see the Firmware Update Application Note [4]
and the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3], +UFOTA AT command.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 53 of 141
Page 54

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
1.15.14 In-band Modem (eCall / ERA-GLONASS)
In-band modem for eCall / ERA-GLONASS emergency applications is not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S
and MPCI-L2 series.
In-band Modem solution for eCall and ERA-GLONASS emergency call applications over cellular networks is
implemented according to 3GPP TS 26.267 [15], BS EN 16062:2011 [16] and ETSI TS 122 101 [17] specifications.
eCall (European) and ERA-GLONASS (Russian) are initiatives to combine mobile communications and satellite
positioning to provide rapid assistance to motorists in the event of a collision, implementing automated
emergency response system based the first on GPS the latter on GLONASS positioning system.
When activated, the in-vehicle systems (IVS) automatically initiate an emergency call carrying both voice and data
(including location data) directly to the nearest Public Safety Answering Point (PSAP) to determine whether
rescue services should be dispatched to the known position.
Figure 21: eCall and ERA-GLONASS automated emergency response systems diagram flow
For more details regarding the In-band Modem solution for the European eCall and the Russian ERA-GLONASS
emergency call applications, see the u-blox eCall / ERA-GLONASS Application Note [18].
1.15.15 SIM Access Profile (SAP)
SIM Access Profile (SAP) is not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S and MPCI-L2 series.
SIM access profile (SAP) feature allows accessing and using a remote SIM card / chipping instead of the local SIM
directly connected to the module SIM interface.
A dedicated SAP channel over USB and a dedicated multiplexed SAP channel over UART are implemented for
communication with the remote SIM card/chip.
Communication between TOBY-L2 series module and the remote SIM is conformed to client-server paradigm:
The module is the SAP client establishing a connection and performing data exchange to a SAP server directly
connected to the remote SIM that is used by the module for LTE/3G/2G network-related operations. The SAP
communication protocol is based on the SIM Access Profile Interoperability Specification [19].
A typical application using the SAP feature is the scenario where a device such as an embedded car -phone with
an integrated TOBY-L2 series module uses a remote SIM included in an external user device (e.g. a simple SIM
card reader or a portable phone), which is brought into the car. The car-phone accesses the LTE/3G/2G network
using the remote SIM in the external device.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 54 of 141
Page 55

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Device including TOBY-L2
LTE/3G/2G
Interface
Local SIM
(opt ional)
TOBY-L2
SAP Client
Application
Processor
Device including SIM
SAP
Serial Interface
Remote SIM
Mobile
Equipment
SAP Server
SAP
Serial Interface
(SAP channel over
USB or UART)
Device including TOBY-L2
SAP
Serial Interface
(SAP channel over
USB or UART)
LTE/3G/2G
Interface
Local SIM
(opt ional)
TOBY-L2
SAP Client
Application
Processor
SAP
Bluetooth
Interface
Bluetooth
Transceiver
Device including SIM
Remote SIM
Mobile
Equipment
SAP Server
Bluetooth
Transceiver
TOBY-L2 series modules, acting as an SAP client, can be connected to an SAP server by a completely wired
connection, as shown in Figure 22.
Figure 22: Remote SIM access via completely wired connection
As stated in the SIM Access Profile Interoperability Specification [19], the SAP client can be connected to the SAP
server by means of a Bluetooth wireless link, using additional Bluetooth transceivers. In this case, the application
processor wired to TOBY-L2 series module establishes and controls the Bluetooth connection using the SAP
profile, and routes data received over a serial interface channel to data transferred over a Bluetooth interface
and vice versa, as shown in Figure 23.
Figure 23: Remote SIM access via Bluetooth and wired connection
The application processor can start an SAP connection negotiation between TOBY-L2 series module SAP client
and an SAP server using custom AT command (for more details see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
While the connection with the SAP server is not fully established, the TOBY-L2 series module continues to
operate with the attached (local) SIM, if present. Once the connection is established and negotiated, the module
performs a detach operation from the local SIM followed by an attach operation to the remote one. Then the
remotely attached SIM is used for any LTE/3G/2G network operation.
URC indications are provided to inform the user about the state of both the local and remote SIM. The insertion
and the removal of the local SIM card are notified if a proper card presence detection circuit using the GPIO5 of
TOBY-L2 series modules is implemented as shown in section 2.5, and if the related “SIM card detection” and
“SIM hot insertion/removal” functions described in section 1.8.2 are enabled by AT commands (for more details
see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
Upon SAP deactivation, the TOBY-L2 series modules perform a detach operation from the remote SIM followed
by an attach operation to the local one, if present.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 55 of 141
Page 56

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Warning
area
t
-1
t
+1
t
+2
t
-2
Valid temperature range
Safe
area
Dangerous
area
Dangerous
area
Warning
area
1.15.16 Smart temperature management
Smart temperature management is not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S and MPCI-L2x0-00S.
Cellular modules – independent of the specific model – always have a well defined operating temperature range.
This range should be respected to guarantee full device functionality and long life span.
Nevertheless there are environmental conditions that can affect operating temperature, e.g. if the device is
located near a heating/cooling source, if there is/isn’t air circulating, etc.
The module itself can also influence the environmental conditions; such as when it is transmitting at full power.
In this case its temperature increases very quickly and can raise the temperature nearby.
The best solution is always to properly design the system where the module is integrated. Nevertheless an extra
check/security mechanism embedded into the module is a good solution to prevent operation of the device
outside of the specified range.
Smart Temperature Supervisor (STS)
The Smart Temperature Supervisor is activated and configured by a dedicated AT+USTS command. See the
u-blox AT Commands Manual [3] for more details.
The cellular module measures the internal temperature (Ti) and its value is compared with predefined thresholds
to identify the actual working temperature range.
Temperature measurement is done inside the cellular module: the measured value could be different from
the environmental temperature (Ta).
Figure 24: Temperature range and limits
The entire temperature range is divided into sub-regions by limits (see Figure 24) named t-2, t-1, t+1 and t+2.
Within the first limit, (t
In the Warning Area, (t
< Ti < t+1), the cellular module is in the normal working range, the Safe Area
-1
< Ti < t.1) or (t+1 < Ti < t+2), the cellular module is still inside the valid temperature
-2
range, but the measured temperature approaches the limit (upper or lower). The module sends a warning to
the user (through the active AT communication interface), which can take, if possible, the necessary actions
to return to a safer temperature range or simply ignore the indication. The module is still in a valid and good
working condition
Outside the valid temperature range, (Ti < t
) or (Ti > t+2), the device is working outside the specified range
-2
and represents a dangerous working condition. This condition is indicated and the device shuts down to
avoid damage
For security reasons the shutdown is suspended in case an emergency call in progress. In this case the
device will switch off at call termination.
The user can decide at anytime to enable/disable the Smart Temperature Supervisor feature. If the feature
is disabled there is no embedded protection against disallowed temperature conditions.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 56 of 141
Page 57
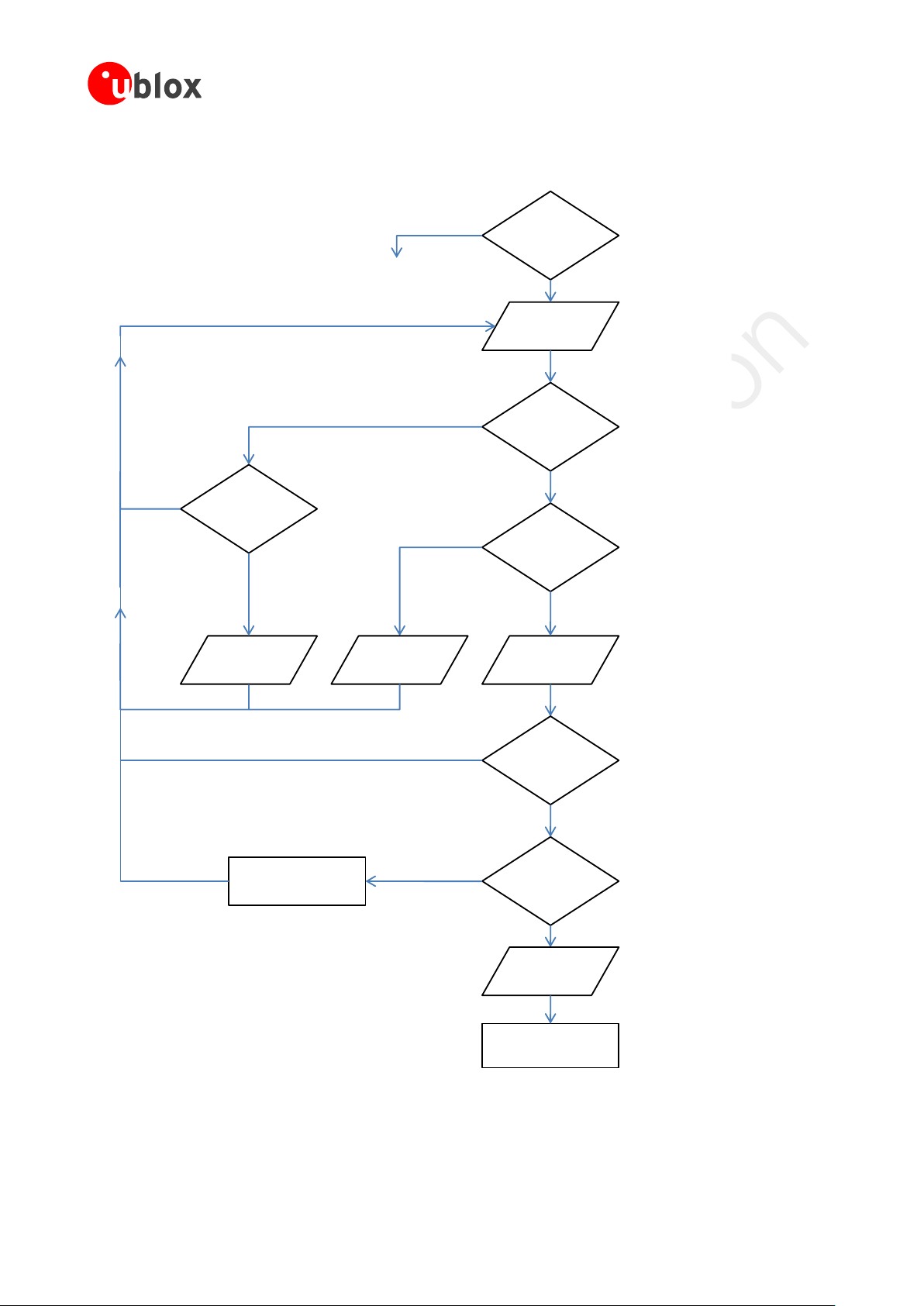
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
IF STS
enabled
Read
temperature
IF
(t-1<Ti<t+1)
IF
(t-2<Ti<t+2)
Send
notification
(warning)
Send
notification
(dangerous)
Wait emergency
call termination
IF
emerg.
call in
progress
Shut the device
down
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
Yes
Send
shutdown
notification
Feature enabled
(full logic or
indication only)
IF
Full Logic
Enabled
Feature disabled:
no action
Temperature is
within normal
operating range
Yes
Tempetature
is within
warning area
Tempetature is
outside valid
temperature range
No
Featuere enabled
in full logic mode
Feature enabled in
indication only mode:
no further actions
Send
notification
(safe)
Previously
outside of
Safe Area
Tempetature
is back to
safe area
No
No
further
actions
Yes
Figure 25 shows the flow diagram implemented for the Smart Temperature Supervisor.
Figure 25: Smart Temperature Supervisor (STS) flow diagram
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 57 of 141
Page 58

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Threshold Definitions
When the application of cellular module operates at extreme temperatures with Smart Temperature Supervisor
enabled, the user should note that outside the valid temperature range the device will automatically shut down
as described above.
The input for the algorithm is always the temperature measured within the cellular module (Ti, internal). This
value can be higher than the working ambient temperature (Ta, ambient), as (for example) during transmission
at maximum power a significant fraction of DC input power is dissipated as heat This behavior is partially
compensated by the definition of the upper shutdown threshold (t+2) that is slightly higher than the declared
environmental temperature limit.
The sensor measures board temperature inside the shields, which can differ from ambient temperature.
1.15.17 Power saving
The power saving configuration is by default disabled, but it can be enabled using the AT+UPSV command (for
the complete description of the AT+UPSV command, see the u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]).
When power saving is enabled, the module automatically enters the low power idle-mode whenever possible,
reducing current consumption (see section 1.5.1.5, TOBY-L2 Data Sheet [1] and MPCI-L2 Data Sheet [2]).
During the low power idle-mode, the module is not ready to communicate with an external device, as it is
configured to reduce power consumption. The module wakes up from low power idle-mode to active-mode in
the following events:
Automatic periodic monitoring of the paging channel for the reception of the paging block sent by the base
station according to network conditions (see section 1.5.1.5)
The connected USB host forces a remote wakeup of the module as USB device (see section 1.9.1.4)
A preset RTC alarm occurs (see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3], AT+CALA)
For the definition and the description of TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules operating modes, including the
events forcing transitions between the different operating modes, see the section 1.4.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information System description
Page 58 of 141
Page 59

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
2 Design-in
2.1 Overview
For an optimal integration of TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules in the final application board follow the
design guidelines stated in this section.
Every application circuit must be properly designed to guarantee the correct functionality of the relative
interface, however a number of points require high attention during the design of the application device.
The following list provides a rank of importance in the application design, starting from the highest relevance:
1. Module antenna connection: ANT1, ANT2 and ANT_DET.
Antenna circuit directly affects the RF compliance of the device integrating a TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series
module with applicable certification schemes. Very carefully follow the suggestions provided in the relative
section 2.4 for schematic and layout design.
2. Module supply: VCC or 3.3Vaux and GND pins.
The supply circuit affects the RF compliance of the device integrating a TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series module
with applicable required certification schemes as well as antenna circuit design. Very carefully follow the
suggestions provided in the relative section 2.2.1 for schematic and layout design.
3. USB interface: USB_D+, USB_D- pins.
Accurate design is required to guarantee USB 2.0 high-speed interface functionality. Carefully follow the
suggestions provided in the relative section 2.6.1 for schematic and layout design.
4. SIM interface: VSIM, SIM_CLK, SIM_IO, SIM_RST or UIM_PWR, UIM_DATA, UIM_CLK, UIM_RESET pins.
Accurate design is required to guarantee SIM card functionality reducing the risk of RF coupling. Carefully
follow the suggestions provided in the relative section 2.5 for schematic and layout design.
5. SDIO interface: SDIO_D0, SDIO_D1, SDIO_D2, SDIO_D3, SDIO_CLK, SDIO_CMD pins.
Accurate design is required to guarantee SDIO interface functionality. Carefully follow the suggestions
provided in the relative section 2.6.4 for schematic and layout design.
6. System functions: RESET_N or PERST#, PWR_ON pins.
Accurate design is required to guarantee that the voltage level is well defined during operation. Carefully
follow the suggestions provided in the relative section 2.3 for schematic and layout design.
7. Other supplies: V_BCKP RTC supply and V_INT generic digital interfaces supply.
Accurate design is required to guarantee proper functionality. Follow the suggestions provided in the
corresponding sections 2.2.2 and 2.2.3 for schematic and layout design.
8. Other digital interfaces: UART, I
Accurate design is required to guarantee proper functionality. Follow the suggestions provided in sections
2.6.2, 2.6.3, 2.7.1, 2.3.3, 2.8, 2.9 and 2.10 for schematic and layout design.
2
C, I2S, Host Select, GPIOs, Mini PCIe specific signals and Reserved pins.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 59 of 141
Page 60

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Main Supply
Available?
Battery
Li-Ion 3.7 V
Linear LDO
Regulator
Main Supply
Voltage > 5V?
Switching Step-Down
Regulator
No, portable device
No, less than 5 V
Yes, greater than 5 V
Yes, always available
2.2 Supply interfaces
2.2.1 Module supply (VCC or 3.3Vaux)
2.2.1.1 General guidelines for VCC or 3.3Vaux supply circuit selection and design
VCC or 3.3Vaux pins are internally connected. Application design shall connect all the available pads to the
external supply to minimize the power loss due to series resistance.
GND pins are internally connected. Application design shall connect all the available pads to solid ground on the
application board, since a good (low impedance) connection to external ground can minimize power loss and
improve RF and thermal performance.
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules must be sourced through the VCC or the 3.3Vaux pins with a proper DC
power supply that should meet the following prerequisites to comply with the modules’ VCC or 3.3Vaux
requirements summarized in Table 7.
The proper DC power supply can be selected according to the application requirements (see Figure 26) between
the different possible supply sources types, which most common ones are the following:
Switching regulator
Low Drop-Out (LDO) linear regulator
Rechargeable Lithium-ion (Li-Ion) or Lithium-ion polymer (Li-Pol) battery, for TOBY-L2 series only
Primary (disposable) battery, for TOBY-L2 series only
Figure 26: VCC supply concept selection
The switching step-down regulator is the typical choice when the available primary supply source has a nominal
voltage much higher (e.g. greater than 5 V) than the operating supply voltage of TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series.
The use of switching step-down provides the best power efficiency for the overall application and minimizes
current drawn from the main supply source. See 2.2.1.2, 2.2.1.6, 2.2.1.9, 2.2.1.10 for specific design-in.
The use of an LDO linear regulator becomes convenient for a primary supply with a relatively low voltage (e.g.
less or equal than 5 V). In this case the typical 90% efficiency of the switching regulator diminishes the benefit
of voltage step-down and no true advantage is gained in input current savings. On the opposite side, linear
regulators are not recommended for high voltage step-down as they dissipate a considerable amount of energy
in thermal power. See 2.2.1.3, 2.2.1.6, 2.2.1.9, 2.2.1.10 for specific design-in.
If TOBY-L2 modules are deployed in a mobile unit where no permanent primary supply source is available, then a
battery will be required to provide VCC. A standard 3-cell Li-Ion or Li-Pol battery pack directly connected to VCC
is the usual choice for battery-powered devices. During charging, batteries with Ni-MH chemistry typically reach
a maximum voltage that is above the maximum rating for VCC, and should therefore be avoided. See 2.2.1.4,
2.2.1.6, 2.2.1.9, 2.2.1.10 for specific design-in.
Keep in mind that the use of rechargeable batteries requires the implementation of a suitable charger circuit
which is not included in the modules. The charger circuit has to be designed to prevent over-voltage on VCC
pins of the module, and it should be selected according to the application requirements: a DC/DC switching
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 60 of 141
Page 61

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
charger is the typical choice when the charging source has an high nominal voltage (e.g. ~12 V), whereas a
linear charger is the typical choice when the charging source has a relatively low nominal voltage (~5 V). If both
a permanent primary supply / charging source (e.g. ~12 V) and a rechargeable back-up battery (e.g. 3.7 V Li-Pol)
are available at the same time in the application as possible supply source, then a proper charger / regulator with
integrated power path management function can be selected to supply the module while simultaneously and
independently charging the battery. See 2.2.1.7, 2.2.1.8 and 2.2.1.6, 2.2.1.9, 2.2.1.10 for specific design-in.
The use of a primary (not rechargeable) battery is in general uncommon, but appropriate parts can be selected
given that the most cells available are seldom capable of delivering the maximum current specified in TOBY-L2
series Data Sheet [1] during connected-mode. Carefully evaluate the usage of super-capacitors as supply source
since aging and temperature conditions significantly affect the actual capacitor characteristics. See 2.2.1.5 and
2.2.1.6, 2.2.1.9, 2.2.1.10 for specific design-in.
Rechargeable 3-cell Li-Ion or Li-Pol and Ni-MH chemistry batteries reach a maximum voltage that is above the
maximum rating for the 3.3Vaux supply of MPCI-L2 modules, and should therefore be avoided. The use of
rechargeable, not-rechargeable battery or super-capacitors is very uncommon for Mini PCI Express applications,
so that these supply sources types are not considered for MPCI-L2 modules.
The usage of more than one DC supply at the same time should be carefully evaluated: depending on the supply
source characteristics, different DC supply systems can result as mutually exclusive.
The following sections highlight some design aspects for each of the supplies listed a bove providing application
circuit design-in compliant with the module VCC requirements summarized in Table 7.
2.2.1.2 Guidelines for VCC or 3.3Vaux supply circuit design using a switching regulator
The use of a switching regulator is suggested when the difference from the available supply rail to the VCC or
the 3.3Vaux value is high, since switching regulators provide good efficiency transforming a 12 V or greater
voltage supply to the typical 3.8 V value of the VCC supply or the typical 3.3 V value of the 3.3Vaux supply.
The characteristics of the switching regulator connected to VCC or 3.3Vaux pins should meet the following
prerequisites to comply with the module VCC or 3.3Vaux requirements summarized in Table 7:
Power capability: the switching regulator with its output circuit must be capable of providing a voltage
value to the VCC or 3.3Vaux pins within the specified operating range and must be capable of delivering to
VCC or 3.3Vaux pins the maximum peak / pulse current consumption during Tx burst at maximum Tx
power specified in the TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1] or in the MPCI-L2 series Data Sheet [2].
Low output ripple: the switching regulator together with its output circuit must be capable of providing a
clean (low noise) VCC or 3.3Vaux voltage profile.
High switching frequency: for best performance and for smaller applications it is recommended to select a
switching frequency ≥ 600 kHz (since L-C output filter is typically smaller for high switching frequency). The
use of a switching regulator with a variable switching frequency or with a switching frequency lower than
600 kHz must be carefully evaluated since this can produce noise in the VCC or 3.3Vaux voltage profile and
therefore negatively impact LTE/3G/2G modulation spectrum performance. An additional L-C low-pass filter
between the switching regulator output to VCC or 3.3Vaux supply pins can mitigate the ripple at the input
of the module, but adds extra voltage drop due to resistive losses on series inductors.
PWM mode operation: it is preferable to select regulators with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) mode.
While in connected-mode, the Pulse Frequency Modulation (PFM) mode and PFM/PWM modes transitions
must be avoided to reduce the noise on the VCC or 3.3Vaux voltage profile. Switching regulators can be
used that are able to switch between low ripple PWM mode and high ripple PFM mode, provided that the
mode transition occurs when the module changes status from the idle/active-modes to connected-mode. It
is permissible to use a regulator that switches from the PWM mode to the burst or PFM mode at an
appropriate current threshold.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 61 of 141
Page 62

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
12V
C5
R3
C4
R2
C2C1
R1
VIN
RUN
VC
RT
PG
SYNC
BD
BOOST
SW
FB
GND
6
7
10
9
5
C6
1
2
3
8
11
4
C7 C8
D1
R4
R5
L1
C3
U1
TOBY-L2 series
71
VCC
72
VCC
70
VCC
GND
12V
C5
R3
C4
R2
C2C1
R1
VIN
RUN
VC
RT
PG
SYNC
BD
BOOST
SW
FB
GND
6
7
10
9
5
C6
1
2
3
8
11
4
C7 C8
D1
R6
R5
L1
C3
U1
MPCI-L2 series
24
3.3Vaux
39
3.3Vaux
2
3.3Vaux
GND
41
3.3Vaux
52
3.3Vaux
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
10 µF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 5750 15% 50 V
C5750X7R1H106MB - TDK
C2
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C3
680 pF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71H681KA01 - Murata
C4
22 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1H220JZ01 - Murata
C5
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C6
470 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0603 10% 25 V
GRM188R71E474KA12 - Murata
C7
22 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 1210 10% 25 V
GRM32ER61E226KE15 - Murata
C8
330 µF Capacitor Tantalum D_SIZE 6.3 V 45 m
T520D337M006ATE045 - KEMET
D1
Schottky Diode 40 V 3 A
MBRA340T3G - ON Semiconductor
L1
10 µH Inductor 744066100 30% 3.6 A
744066100 - Wurth Electronics
R1
470 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
2322-705-87474-L - Yageo
R2
15 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
2322-705-87153-L - Yageo
R3
22 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
2322-705-87223-L - Yageo
R4
390 k Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-07390KL - Yageo
R5
100 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
2322-705-70104-L - Yageo
R6
330 k Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-07330KL - Yageo
U1
Step-Down Regulator MSOP10 3.5 A 2.4 MHz
LT3972IMSE#PBF - Linear Technology
Figure 27 and Table 13 show an example of a high reliability power supply circuit, where the module VCC or
3.3Vaux input is supplied by a step-down switching regulator capable of delivering maximum current with low
output ripple and with fixed switching frequency in PWM mode operation greater than 1 MHz.
Figure 27: Example of high reliability VCC and 3.3Vaux supply application circuit using a step-down regulator
Table 13: Components for high reliability VCC and 3.3Vaux supply application circuit using a step-down regulator
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 62 of 141
Page 63

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TOBY-L2 series
12V
R5
C6C1
VCC
INH
FSW
SYNC
OUT
GND
2
6
3
1
7
8
C3
C2
D1
R1
R2
L1
U1
GND
FB
COMP
5
4
R3
C4
R4
C5
71
VCC
72
VCC
70
VCC
12V
R5
C6C1
VCC
INH
FSW
SYNC
OUT
GND
2
6
3
1
7
8
C3
C2
D1
R6
R7
L1
U1
GND
FB
COMP
5
4
R3
C4
R4
C5
MPCI-L2 series
24
3.3Vaux
39
3.3Vaux
2
3.3Vaux
41
3.3Vaux
52
3.3Vaux
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
22 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 1210 10% 25 V
GRM32ER61E226KE15 – Murata
C2
100 µF Capacitor Tantalum B_SIZE 20% 6.3V 15m
T520B107M006ATE015 – Kemet
C3
5.6 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 50 V
GRM155R71H562KA88 – Murata
C4
6.8 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 50 V
GRM155R71H682KA88 – Murata
C5
56 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H560JA01 – Murata
C6
220 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0603 10% 25 V
GRM188R71E224KA88 – Murata
D1
Schottky Diode 25V 2 A
STPS2L25 – STMicroelectronics
L1
5.2 µH Inductor 30% 5.28A 22 m
MSS1038-522NL – Coilcraft
R1
4.7 k Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-074K7L – Yageo
R2
910 Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-07910RL – Yageo
R3
82 Resistor 0402 5% 0.063 W
RC0402JR-0782RL – Yageo
R4
8.2 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.063 W
RC0402JR-078K2L – Yageo
R5
39 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.063 W
RC0402JR-0739KL – Yageo
R6
1.5 k Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-071K5L – Yageo
R7
330 Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-07330RL – Yageo
U1
Step-Down Regulator 8-VFQFPN 3 A 1 MHz
L5987TR – ST Microelectronics
Figure 28 and the components listed in Table 14 show an example of a low cost power supply circuit, where the
VCC module supply is provided by a step-down switching regulator capable of delivering to VCC pins the
specified maximum peak / pulse current, transforming a 12 V supply input.
Figure 28: Example of low cost VCC and 3.3Vaux supply application circuit using step-down regulator
Table 14: Components for low cost VCC and 3.3Vaux supply application circuit using a step-down regulator
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 63 of 141
Page 64
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
5V
C1 R1
IN OUT
ADJ
GND
1
2
4
5
3
C2R2
R3
U1
SHDN
TOBY-L2 series
71
VCC
72
VCC
70
VCC
GND
C3
5V
C1 R1
IN OUT
ADJ
GND
1
2
4
5
3
C2R4
R5
U1
SHDN
MPCI-L2 series
GND
C3
24
3.3Vaux
39
3.3Vaux
2
3.3Vaux
41
3.3Vaux
52
3.3Vaux
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2
10 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 0603 20% 6.3 V
GRM188R60J106ME47 - Murata
C3
330 µF Capacitor Tantalum D_SIZE 6.3 V 45 m
T520D337M006ATE045 - KEMET
R1
47 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-0747KL - Yageo Phycomp
R2
9.1 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-079K1L - Yageo Phycomp
R3
3.9 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-073K9L - Yageo Phycomp
R4
3.3 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-073K3L - Yageo Phycomp
R5
1.8 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-071K8L - Yageo Phycomp
U1
LDO Linear Regulator ADJ 3.0 A
LT1764AEQ#PBF - Linear Technology
2.2.1.3 Guidelines for VCC or 3.3Vaux supply circuit design using a Low Drop-Out linear regulator
The use of a linear regulator is suggested when the difference from the available supply rail and the VCC or the
3.3Vaux value is low. The linear regulators provide high efficiency when transforming a 5 VDC supply to a
voltage value within the module VCC or 3.3Vaux normal operating range.
The characteristics of the Low Drop-Out (LDO) linear regulator connected to VCC or 3.3Vaux pins should meet
the following prerequisites to comply with the module VCC or 3.3Vaux requirements summarized in Table 7:
Power capabilities: the LDO linear regulator with its output circuit must be capable of providing a voltage
value to the VCC or 3.3Vaux pins within the specified operating range and must be capable of delivering to
VCC or 3.3Vaux pins the maximum peak / pulse current consumption during Tx burst at maximum Tx
power specified in TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1] or in MPCI-L2 series Data Sheet [2].
Power dissipation: the power handling capability of the LDO linear regulator must be checked to limit its
junction temperature to the maximum rated operating range (i.e. check the voltage drop from the max input
voltage to the minimum output voltage to evaluate the power dissipation of the regulator).
Figure 29 and the components listed in Table 15 show an example of a power supply circuit, where the VCC or
3.3Vaux module supply is provided by an LDO linear regulator capable of delivering the required current, with
proper power handling capability.
It is recommended to configure the LDO linear regulator to generate a voltage supply value slightly below the
maximum limit of the module VCC or 3.3Vaux normal operating range (e.g. ~4.1 V for the VCC and ~3.44 V
for the 3.3Vaux as in the circuits described in Figure 29 and Table 15). This reduces the power on the linear
regulator and improves the thermal design of the circuit.
Figure 29: Suggested schematic design for the VCC and 3.3Vaux supply application circuit using an LDO linear regulator
Table 15: Suggested components for VCC and 3.3Vaux supply application circuit using an LDO linear regulator
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 64 of 141
Page 65

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
5V
C1
IN OUT
ADJ
GND
1
2
4
5
3
C2R1
R2
U1
EN
TOBY-L2 series
71
VCC
72
VCC
70
VCC
GND
C3
5V
C1
IN OUT
ADJ
GND
1
2
4
5
3
C2R3
R4
U1
EN
MPCI-L2 series
GND
C3
24
3.3Vaux
39
3.3Vaux
2
3.3Vaux
41
3.3Vaux
52
3.3Vaux
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2
10 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 0603 20% 6.3 V
GRM188R60J106ME47 - Murata
C3
330 µF Capacitor Tantalum D_SIZE 6.3 V 45 m
T520D337M006ATE045 - KEMET
R1
27 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-0727KL - Yageo Phycomp
R2
4.7 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-074K7L - Yageo Phycomp
R3
12 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-0712KL - Yageo Phycomp
R4
2.7 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-072K7L - Yageo Phycomp
U1
LDO Linear Regulator ADJ 3.0 A
LP38501ATJ-ADJ/NOPB - Texas Instrument
Figure 30 and the components listed in Table 16 show an example of a low cost power supply circuit, where the
VCC module supply is provided by an LDO linear regulator capable of delivering the specified highest peak /
pulse current, with proper power handling capability. The regulator described in this example supports a limited
input voltage range and it includes internal circuitry for current and thermal protection.
It is recommended to configure the LDO linear regulator to generate a voltage supply value slightly below the
maximum limit of the module VCC normal operating range (e.g. ~4.1 V as in the circuit described in Figure 30
and Table 16). This reduces the power on the linear regulator and improves the whole thermal design of the
supply circuit.
Figure 30: Suggested schematic design for the VCC and 3.3Vaux supply application circuit using an LDO linear regulator
Table 16: Suggested components for VCC voltage supply application circuit using an LDO linear regulator
2.2.1.4 Guidelines for VCC supply circuit design using a rechargeable Li-Ion or Li-Pol battery
Rechargeable Li-Ion or Li-Pol batteries connected to the VCC pins should meet the following prerequisites to
comply with the module VCC requirements summarized in Table 7:
Maximum pulse and DC discharge current: the rechargeable Li-Ion battery with its related output circuit
connected to the VCC pins must be capable of delivering a pulse current as the maximum peak current
consumption during Tx burst at maximum Tx power specified in TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1] and must be
capable of extensively delivering a DC current as the maximum average current consumption specified in
DC series resistance: the rechargeable Li-Ion battery with its output circuit must be capable of avoiding a
TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1]. The maximum discharge current is not always reported in battery data sheets,
but the maximum DC discharge current is typically almost equal to the battery capacity in Amp-hours
divided by 1 hour.
VCC voltage drop below the operating range summarized in Table 7 during transmit bursts.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 65 of 141
Page 66

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
2.2.1.5 Guidelines for VCC supply circuit design using a primary (disposable) battery
The characteristics of a primary (non-rechargeable) battery connected to VCC pins should meet the following
prerequisites to comply with the module VCC requirements summarized in Table 7:
Maximum pulse and DC discharge current: the non-rechargeable battery with its related output circuit
connected to the VCC pins must be capable of delivering a pulse current as the maximum peak current
consumption during Tx burst at maximum Tx power specified in TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1] and must be
capable of extensively delivering a DC current as the maximum average current consumption specified in
TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1]. The maximum discharge current is not always reported in battery data sheets,
but the maximum DC discharge current is typically almost equal to the battery capacity in Amp-hours
divided by 1 hour.
DC series resistance: the non-rechargeable battery with its output circuit must be capable of avoiding a
VCC voltage drop below the operating range summarized in Table 7 during transmit bursts.
2.2.1.6 Additional guidelines for VCC or 3.3Vaux supply circuit design
To reduce voltage drops, use a low impedance power source. The series resistance of the power supply lines
(connected to the modules’ VCC / 3.3Vaux and GND pins) on the application board and battery pack should
also be considered and minimized: cabling and routing must be as short as possible to minimize power losses.
Three pins are allocated to VCC supply and five pins to 3.3Vaux supply. Several pins are designated for GND
connection. Even if all the VCC / 3.3Vaux pins and all the GND pins are internally connected within the module,
it is recommended to properly connect all of them to supply the module to minimize series resistance losses.
To avoid voltage drop undershoot and overshoot at the start and end of a transmit burst during a GSM call
(when current consumption on the VCC or 3.3Vaux supply can rise up as specified in TOBY-L2 series Data
Sheet [1] or in MPCI-L2 series Data Sheet [2]), place a bypass capacitor with large capacitance (at least 100 µF)
and low ESR near the VCC pins, for example:
330 µF capacitance, 45 m ESR (e.g. KEMET T520D337M006ATE045, Tantalum Capacitor)
To reduce voltage ripple and noise, improving RF performance especially if the application device integrates an
internal antenna, place the following bypass capacitors near the VCC / 3.3Vaux pins:
68 pF capacitor with Self-Resonant Frequency in the 800/900 MHz range (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H680J)
to filter EMI in the RF low frequencies bands
15 pF capacitor with Self-Resonant Frequency in 1800/1900 MHz range (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1E150J)
to filter EMI in the RF high frequencies bands
8.2 pF capacitor with Self-Resonant Frequency in 2500/2600 MHz range (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H8R2D)
to filter EMI in the RF very high frequencies band
10 nF capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R71C103K) to filter digital logic noise from clocks and data sources
100 nF capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R61C104K) to filter digital logic noise from clocks and data sources
A suitable series ferrite bead can be properly placed on the VCC / 3.3Vaux line for additional noise filtering if
required by the specific application according to the whole application board design.
The necessity of each part depends on the specific design, but it is recommended to provide all the bypass
capacitors described in Figure 31 / Table 17 if the application device integrates an internal antenna.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 66 of 141
Page 67

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
C2
GND
C3 C4
TOBY-L2 series
71
VCC
72
VCC
70
VCC
C1 C5 C6
3V8
C2
GND
C3 C4
MPCI-L2 series
C1 C5 C6
3V3
24
3.3Vaux
39
3.3Vaux
2
3.3Vaux
41
3.3Vaux
52
3.3Vaux
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
68 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H680JA01 - Murata
C2
15 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H150JA01 - Murata
C3
8.2 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H8R2DZ01 - Murata
C4
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C5
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
C6
330 µF Capacitor Tantalum D_SIZE 6.3 V 45 m
T520D337M006ATE045 - KEMET
Figure 31: Suggested schematic for the VCC / 3.3Vaux bypass capacitors to reduce ripple / noise on supply voltage profile
Table 17: Suggested components to reduce ripple / noise on VCC / 3.3Vaux
ESD sensitivity rating of the VCC / 3.3Vaux supply pins is 1 kV (HBM according to JESD22-A114). Higher
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 67 of 141
protection level can be required if the line is externally accessible on the application board, e.g. if
accessible battery connector is directly connected to the supply pins. Higher protection level can be
achieved by mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor) close to accessible point.
Page 68

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
C5 C8C7C6 C9
GND
TOBY-L2 series
71
VCC
72
VCC
70
VCC
+
USB
Supply
C3
R4
θ
U1
IUSB
IAC
IEND
TPRG
SD
VIN
VINSNS
MODE
ISEL
C2C1
5V0
TH
GND
VOUT
VOSNS
VREF
R1
R2
R3
Li-Ion/Li-Pol
Battery Pack
D1
B1
C4
Li-Ion/Li-Polymer
Battery Charger IC
C10
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
B1
Li-Ion (or Li-Polymer) battery pack with 470 NTC
Various manufacturer
C1, C4
1 µF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0603 10% 16 V
GRM188R71C105KA12 - Murata
C2, C6
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C3
1 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 50 V
GRM155R71H102KA01 - Murata
C5
330 µF Capacitor Tantalum D_SIZE 6.3 V 45 m
T520D337M006ATE045 - KEMET
C7
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R61A104KA01 - Murata
C8
68 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H680JA01 - Murata
C9
15 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H150JA01 - Murata
C10
8.2 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H8R2DZ01 - Murata
D1
Low Capacitance ESD Protection
USB0002RP or USB0002DP - AVX
R1, R2
24 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-0724KL - Yageo Phycomp
R3
3.3 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-073K3L - Yageo Phycomp
R4
1.0 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-071K0L - Yageo Phycomp
U1
Single Cell Li-Ion (or Li-Polymer) Battery Charger IC
L6924U - STMicroelectronics
2.2.1.7 Guidelines for external battery charging circuit
TOBY-L2 modules do not have an on-board charging circuit. Figure 32 provides an example of a battery charger
design, suitable for applications that are battery powered with a Li-Ion (or Li-Polymer) cell.
In the application circuit, a rechargeable Li-Ion (or Li-Polymer) battery cell, that features proper pulse and DC
discharge current capabilities and proper DC series resistance, is directly connected to the VCC supply input of
TOBY-L2 module. Battery charging is completely managed by the STMicroelectronics L6924U Battery Charger IC
that, from a USB power source (5.0 V typ.), charges as a linear charger the battery, in three phases:
Pre-charge constant current (active when the battery is deeply discharged): the battery is charged with a
low current, set to 10% of the fast-charge current
Fast-charge constant current: the battery is charged with the maximum current, configured by the value
of an external resistor to a value suitable for USB power source (~500 mA)
Constant voltage: when the battery voltage reaches the regulated output voltage (4.2 V), the L6924U
starts to reduce the current until the charge termination is done. The charging process ends when the
charging current reaches the value configured by an external resistor to ~15 mA or when the charging timer
reaches the value configured by an external capacitor to ~9800 s
Using a battery pack with an internal NTC resistor, the L6924U can monitor the battery temperature to protect
the battery from operating under unsafe thermal conditions.
Alternatively the L6924U, providing input voltage range up to 12 V, can charge from an AC wall adapter. When
a current-limited adapter is used, it can operate in quasi-pulse mode, reducing power dissipation.
Figure 32: Li-Ion (or Li-Polymer) battery charging application circuit
Table 18: Suggested components for Li-Ion (or Li-Polymer) battery charging application circuit
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 68 of 141
Page 69

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
GND
Power path management IC
VoutVin
θ
Li-Ion/Li-Pol
Battery Pack
GND
System
12 V
Primary
Source
Charge
controller
DC/DC converter
and battery FET
control logic
Vbat
2.2.1.8 Guidelines for external battery charging and power path management circuit
Application devices where both a permanent primary supply / charging source (e.g. ~12 V) and a rechargeable
back-up battery (e.g. 3.7 V Li-Pol) are available at the same time as possible supply source should implement a
suitable charger / regulator with integrated power path management function to supply the module and the
whole device while simultaneously and independently charging the battery.
Figure 33 reports a simplified block diagram circuit showing the working principle of a charger / regulator with
integrated power path management function. This component allows the system to be powered by a permanent
primary supply source (e.g. ~12 V) using the integrated regulator which simultaneously and independently
recharges the battery (e.g. 3.7 V Li-Pol) that represents the back-up supply source of the system: the power path
management feature permits the battery to supplement the system current requirements when the primary
supply source is not available or cannot deliver the peak system currents.
A power management IC should meet the following prerequisites to comply with the module VCC requirements
summarized in Table 7:
High efficiency internal step down converter, compliant with the performances specified in section 2.2.1.2
Low internal resistance in the active path Vout – Vbat, typically lower than 50 m
High efficiency switch mode charger with separate power path control
Figure 33: Charger / regulator with integrated power path management circuit block diagram
Figure 34 and the components listed in Table 19 provide an application circuit example where the MPS MP2617
switching charger / regulator with integrated power path management function provides the supply to the
cellular module while concurrently and autonomously charging a suitable Li-Ion (or Li-Polymer) battery with
proper pulse and DC discharge current capabilities and proper DC series resistance according to the rechargeable
battery recommendations described in section 2.2.1.4.
The MP2617 IC constantly monitors the battery voltage and selects whether to use the external main primary
supply / charging source or the battery as supply source for the module, and starts a charging phase accordingly.
The MP2617 IC normally provides a supply voltage to the module regulated from the external main primary
source allowing immediate system operation even under missing or deeply discharged battery: the integrated
switching step-down regulator is capable to provide up to 3 A output current with low output ripple and fixed
1.6 MHz switching frequency in PWM mode operation. The module load is satisfied in priority, then the
integrated switching charger will take the remaining current to charge the battery.
Additionally, the power path control allows an internal connection from battery to the module with a low series
internal ON resistance (40 m typical), in order to supplement additional power to the module when the current
demand increases over the external main primary source or when this external source is removed.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 69 of 141
Page 70

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
C10 C13
GND
C12C11 C14
TOBY-L2 series
71
VCC
72
VCC
70
VCC
+
Primary
Source
R3
U1
EN
ILIM
ISET
TMR
AGND
VIN
C2C1
12V
NTC
PGND
SW
SYS
BAT
C4
R1
R2
D1
θ
Li-Ion/Li-Pol
Battery Pack
B1
C5
Li-Ion/Li-Polymer Battery
Charger / Regulator with
Power Path Managment
VCC
C3 C6
L1
BST
D2
VLIM
R4
R5
C7 C8 C9
C15
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
B1
Li-Ion (or Li-Polymer) battery pack with 10 k NTC
Various manufacturer
C1, C5, C6
22 µF Capacitor Ceramic X5R 1210 10% 25 V
GRM32ER61E226KE15 - Murata
C2, C4, C11
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R61A104KA01 - Murata
C3
1 µF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0603 10% 25 V
GRM188R71E105KA12 - Murata
C7, C13
68 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H680JA01 - Murata
C8, C14
15 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1E150JA01 - Murata
C9, C15
8.2 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H8R2DZ01 - Murata
C10
330 µF Capacitor Tantalum D_SIZE 6.3 V 45 m
T520D337M006ATE045 - KEMET
C12
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
D1, D2
Low Capacitance ESD Protection
CG0402MLE-18G - Bourns
R1, R3, R5
10 k Resistor 0402 5% 1/16 W
RC0402JR-0710KL - Yageo Phycomp
R2
1.0 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-071K0L - Yageo Phycomp
R4
22 k Resistor 0402 5% 1/16 W
RC0402JR-0722KL - Yageo Phycomp
L1
1.2 µH Inductor 6 A 21 m 20%
7447745012 - Wurth
U1
Li-Ion/Li-Polymer Battery DC/DC Charger / Regulator
with integrated Power Path Management function
MP2617 - Monolithic Power Systems (MPS)
Battery charging is managed in three phases:
Pre-charge constant current (active when the battery is deeply discharged): the battery is charged with a
low current, set to 10% of the fast-charge current
Fast-charge constant current: the battery is charged with the maximum current, configured by the value
of an external resistor to a value suitable for the application
Constant voltage: when the battery voltage reaches the regulated output voltage (4.2 V), the current is
progressively reduced until the charge termination is done. The charging process ends when the charging
current reaches the 10% of the fast-charge current or when the charging timer reaches the value configured
by an external capacitor
Using a battery pack with an internal NTC resistor, the MP2617 can monitor the battery temperature to protect
the battery from operating under unsafe thermal conditions.
Several parameters as the charging current, the charging timings, the input current limit, the input voltage limit,
the system output voltage can be easily set according to the specific application requirements, as the actual
electrical characteristics of the battery and the external supply / charging source: proper resistors or capacitors
have to be accordingly connected to the related pins of the IC.
Figure 34: Li-Ion (or Li-Polymer) battery charging and power path management application circuit
Table 19: Suggested components for Li-Ion (or Li-Polymer) battery charging and power path management application circuit
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 70 of 141
Page 71

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
2.2.1.9 Guidelines for VCC or 3.3Vaux supply layout design
Good connection of the module VCC or 3.3Vaux pins with DC supply source is required for correct RF
performance. Guidelines are summarized in the following list:
All the available VCC / 3.3Vaux pins must be connected to the DC source
VCC / 3.3Vaux connection must be as wide as possible and as short as possible
Any series component with Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) greater than few milliohms must be avoided
VCC / 3.3Vaux connection must be routed through a PCB area separated from RF lines / parts, sensitive
analog signals and sensitive functional units: it is good practice to interpose at least one layer of PCB ground
between the VCC / 3.3Vaux track and other signal routing
Coupling between VCC / 3.3Vaux and digital lines, especially USB, must be avoided.
The tank bypass capacitor with low ESR for current spikes smoothing described in section 2.2.1.6 should be
placed close to the VCC / 3.3Vaux pins. If the main DC source is a switching DC-DC converter, place the
large capacitor close to the DC-DC output and minimize VCC / 3.3Vaux track length. Otherwise consider
using separate capacitors for DC-DC converter and module tank capacitor
The bypass capacitors in the pF range described in Figure 31 and Table 17 should be placed as close as
possible to the VCC / 3.3Vaux pins. This is highly recommended if the application device integrates an
internal antenna
Since VCC / 3.3Vaux input provide the supply to RF Power Amplifiers, voltage ripple at high frequency may
result in unwanted spurious modulation of transmitter RF signal. This is more likely to happen with switching
DC-DC converters, in which case it is better to select the highest operating frequency for the switcher and
add a large L-C filter before connecting to the TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules in the worst case
If VCC / 3.3Vaux is protected by transient voltage suppressor to ensure that the voltage maximum ratings
are not exceeded, place the protecting device along the path from the DC source toward the module,
preferably closer to the DC source (otherwise protection functionality may be compromised)
2.2.1.10 Guidelines for grounding layout design
Good connection of the module GND pins with application board solid ground layer is required for correct RF
performance. It significantly reduces EMC issues and provides a thermal heat sink for the module.
Connect each GND pin with application board solid GND layer. It is strongly recommended that each GND
pad surrounding VCC pins have one or more dedicated via down to the application board solid ground layer
The VCC supply current flows back to main DC source through GND as ground current: provide adequate
return path with suitable uninterrupted ground plane to main DC source
It is recommended to implement one layer of the application board as ground plane as wide as possible
If the application board is a multilayer PCB, then all the board layers should be filled with GND plane as
much as possible and each GND area should be connected together with complete via stack down to the
main ground layer of the board
If the whole application device is composed by more than one PCB, then it is required to provide a good and
solid ground connection between the GND areas of all the different PCBs
Good grounding of GND pads also ensures thermal heat sink. This is critical during connection, when the
real network commands the module to transmit at maximum power: proper grounding helps prevent
module overheating.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 71 of 141
Page 72

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TOBY-L2 series
C1
(a)
3
V_BCKP
R2
TOBY-L2 series
C2
(superCap)
(b)
3
V_BCKP
D3
TOBY-L2 series
B3
(c)
3
V_BCKP
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
100 µF Tantalum Capacitor
GRM43SR60J107M - Murata
R2
4.7 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-074K7L - Yageo Phycomp
C2
70 mF Capacitor
XH414H-IV01E - Seiko Instruments
2.2.2 RTC supply output (V_BCKP)
The RTC supply V_BCKP pin is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
2.2.2.1 Guidelines for V_BCKP circuit design
TOBY-L2 series modules provide the V_BCKP RTC supply input/output, which can be mainly used to:
Provide RTC back-up when VCC supply is removed
If RTC timing is required to run for a time interval of T [s] when VCC supply is removed, place a capacitor with a
nominal capacitance of C [µF] at the V_BCKP pin. Choose the capacitor using the following formula:
C [µF] = (Current_Consumption [µA] x T [s]) / Voltage_Drop [V]
= 1.25 x T [s]
For example, a 100 µF capacitor can be placed at V_BCKP to provide RTC backup holding the V_BCKP voltage
within its valid range for around 80 s at 25 °C, after the VCC supply is removed. If a longer buffering time is
required, a 70 mF super-capacitor can be placed at V_BCKP, with a 4.7 k series resistor to hold the V_BCKP
voltage within its valid range for approximately 15 hours at 25 °C, after the VCC supply is removed. The purpose
of the series resistor is to limit the capacitor charging current due to the large capacitor specifications, and also
to let a fast rise time of the voltage value at the V_BCKP pin after VCC supply has been provided. These
capacitors allow the time reference to run during battery disconnection.
Figure 35: Real time clock supply (V_BCKP) application circuits: (a) using a 100 µF capacitor to let the RTC run for ~80 s after VCC
removal; (b) using a 70 mF capacitor to let RTC run for ~15 hours after VCC removal; (c) using a non-rechargeable battery
Table 20: Example of components for V_BCKP buffering
If very long buffering time is required to allow the RTC time reference to run during a disconnection of the VCC
supply, then an external battery can be connected to V_BCKP pin. The battery should be able to provide a
proper nominal voltage and must never exceed the maximum operating voltage for V_BCKP (specified in the
Input characteristics of Supply/Power pins table in TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1]). The connection of the battery
to V_BCKP should be done with a suitable series resistor for a rechargeable battery, or with an appropriate
series diode for a non-rechargeable battery. The purpose of the series resistor is to limit the battery charging
current due to the battery specifications, and also to allow a fast rise time of the voltage value at the V_BCKP
pin after the VCC supply has been provided. The purpose of the series diode is to avoid a current flow from the
module V_BCKP pin to the non-rechargeable battery.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 72 of 141
Page 73

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
If the RTC timing is not required when the VCC supply is removed, it is not needed to connect the
V_BCKP pin to an external capacitor or battery. In this case the date and time are not updated when VCC
is disconnected. If VCC is always supplied, then the internal regulator is supplied from the main supply
and there is no need for an external component on V_BCKP.
Combining a cellular module with a u-blox GNSS positioning receiver, the positioning receiver VCC supply is
controlled by the cellular module by means of the “GNSS supply enable” function provided by the GPIO2 of the
cellular module. In this case the V_BCKP supply output of the cellular module can be connected to the V_BCKP
backup supply input pin of the GNSS receiver to provide the supply for the positioning real time clock and
backup RAM when the VCC supply of the cellular module is within its operating range and the VCC supply of
the GNSS receiver is disabled. This enables the u-blox GNSS receiver to recover from a power breakdown with
either a hot start or a warm start (depending on the duration of the positioning VCC outage) and to maintain
the configuration settings saved in the backup RAM. See section 2.6.3 for more details regarding the application
circuit with a u-blox GNSS receiver.
V_BCKP supply output pin provides internal short circuit protection to limit start-up current and protect the
device in short circuit situations. No additional external short circuit protection is required.
Do not apply loads which might exceed the limit for maximum available current from V_BCKP supply (see
TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1]) as this can cause malfunctions in internal circuitry.
ESD sensitivity rating of the V_BCKP supply pin is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-A114).
Higher protection level could be required if the line is externally accessible and it can be achieved by
mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) close to the accessible point.
2.2.2.2 Guidelines for V_BCKP layout design
V_BCKP supply requires careful layout: avoid injecting noise on this voltage domain as it may affect the stability
of the internal circuitry.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 73 of 141
Page 74

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
2.2.3 Generic digital interfaces supply output (V_INT)
The generic digital interfaces supply V_INT pin is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
2.2.3.1 Guidelines for V_INT circuit design
TOBY-L2 series provide the V_INT generic digital interfaces 1.8 V supply output, which can be mainly used to:
Indicate when the module is switched on (as described in sections 1.6.1, 1.6.2)
Pull-up SIM detection signal (see section 2.5 for more details)
Supply voltage translators to connect 1.8 V module generic digital interfaces to 3.0 V devices (e.g. see 2.6.2)
Pull-up DDC (I
Supply a 1.8 V u-blox 6 or subsequent u-blox GNSS receiver generation (see section 2.6.3 for more details)
V_INT supply output pin provides internal short circuit protection to limit start-up current and protect the device
in short circuit situations. No additional external short circuit protection is required.
2
C) interface signals (see section 2.6.3 for more details)
Do not apply loads which might exceed the limit for maximum available current from V_INT supply (see
the TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1]) as this can cause malfunctions in internal circuitry.
Since the V_INT supply is generated by an internal switching step-down regulator, the V_INT voltage
ripple can range as specified in the TOBY-L2 series Data Sheet [1]: it is not recommended to supply
sensitive analog circuitry without adequate filtering for digital noise.
V_INT can only be used as an output: do not connect any external supply source on V_INT.
ESD sensitivity rating of the V_INT supply pin is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-A114).
Higher protection level could be required if the line is externally accessible and it can be achieved by
mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) close to the accessible point.
It is recommended to provide direct access to the V_INT pin on the application board by means of an
accessible test point directly connected to the V_INT pin.
2.2.3.2 Guidelines for V_INT layout design
V_INT supply output is generated by an integrated switching step-down converter. Because of this, it can be a
source of noise: avoid coupling with sensitive signals.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 74 of 141
Page 75

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TOBY-L2 series
50 k
VCC
20
PWR_ON
Power-on
push button
ESD
Open
Drain
Output
Application
Processor
TOBY-L2 series
50 k
VCC
20
PWR_ON
TP
TP
Reference
Description
Remarks
ESD
CT0402S14AHSG - EPCOS
Varistor array for ESD protection
2.3 System functions interfaces
2.3.1 Module power-on (PWR_ON)
The PWR_ON input pin is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
2.3.1.1 Guidelines for PWR_ON circuit design
TOBY-L2 series PWR_ON input is equipped with an internal active pull-up resistor to the VCC module supply as
described in Figure 36: an external pull-up resistor is not required and should not be provided.
If connecting the PWR_ON input to a push button, the pin will be externally accessible on the application
device. According to EMC/ESD requirements of the application, an additional ESD protection should be provided
close to the accessible point, as described in Figure 36 and Table 21.
ESD sensitivity rating of the PWR_ON pin is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-A114). Higher
protection level can be required if the line is externally accessible on the application board, e.g. if an
accessible push button is directly connected to PWR_ON pin, and it can be achieved by mounting an ESD
protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor) close to the accessible point.
An open drain or open collector output is suitable to drive the PWR_ON input from an application processor as
PWR_ON input is equipped with an internal active pull-up resistor to the VCC supply, as described in Figure 36.
A compatible push-pull output of an application processor can also be used. In any case, take care to set the
proper level in all the possible scenarios to avoid an inappropriate module switch-on.
Figure 36: PWR_ON application circuits using a push button and an open drain output of an application processor
Table 21: Example ESD protection component for the PWR_ON application circuit
It is recommended to provide direct access to the PWR_ON pin on the application board by means of an
accessible test point directly connected to the PWR_ON pin.
2.3.1.2 Guidelines for PWR_ON layout design
The power-on circuit (PWR_ON) requires careful layout since it is the sensitive input available to switch on the
TOBY-L2 modules. It is required to ensure that the voltage level is well defined during operation and no transient
noise is coupled on this line, otherwise the module might detect a spurious power-on request.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 75 of 141
Page 76

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TOBY-L2 series
VCC
23
RESET_N
Power-on
push button
ESD
Open
Drain
Output
Application
Processor
TOBY-L2 series
VCC
23
RESET_N
TP
TP
50 k
50 k
MPCI-L2 series
22
PERST#
Power-on
push button
ESD
Open
Drain
Output
Application
Processor
MPCI-L2 series
22
PERST#
45 k 45 k
3V3
3V3
Reference
Description
Remarks
ESD
Varistor for ESD protection
CT0402S14AHSG - EPCOS
2.3.2 Module reset (RESET_N or PERST#)
2.3.2.1 Guidelines for RESET_N and PERST# circuit design
The TOBY-L2 series RESET_N is equipped with an internal pull-up to the VCC supply and the MPCI-L2 series
PERST# is equipped with an internal pull-up to the 3.3 V rail, as described in Figure 37. An external pull-up
resistor is not required and should not be provided.
If connecting the RESET_N or PERST# input to a push button, the pin will be externally accessible on the
application device. According to EMC/ESD requirements of the application, an additional ESD protection device
(e.g. the EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor) should be provided close to accessible point on the line connected to
this pin, as described in Figure 37 and Table 22.
ESD sensitivity rating of the RESET_N and PERST# pins is 1 kV (HBM according to JESD22-A114). Higher
protection level can be required if the line is externally accessible on the application board, e.g. if an
accessible push button is directly connected to the RESET_N or PERST# pin, and it can be achieved by
mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor) close to accessible point.
An open drain output is suitable to drive the RESET_N and PERST# inputs from an application processor as they
are equipped with an internal pull-up to VCC supply and to the 3.3 V rail respectively, as described in Figure 37.
A compatible push-pull output of an application processor can also be used. In any case, take care to set the
proper level in all the possible scenarios to avoid an inappropriate module reset, switch-on or switch-off.
Figure 37: RESET_N and PERST# application circuits using a push button and an open drain output of an application processor
Table 22: Example of ESD protection component for the RESET_N and PERST# application circuits
If the external reset function is not required by the customer application, the RESET_N input pin can be
left unconnected to external components, but it is recommended providing direct access on the
application board by means of an accessible test point directly connected to the RESET_N pin.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 76 of 141
Page 77

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
2.3.2.2 Guidelines for RESET_N and PERST# layout design
The RESET_N and PERST# circuits require careful layout due to the pin function: ensure that the voltage level is
well defined during operation and no transient noise is coupled on this line, otherwise the module might detect
a spurious reset request. It is recommended to keep the connection line to RESET_N and PERST# pins as short
as possible.
2.3.3 Module configuration selection by host processor
The HOST_SELECT0 and HOST_SELECT1 pins are not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
2.3.3.1 Guidelines for HOST_SELECTx circuit design
The functionality of the HOST_SELECT0 and HOST_SELECT1 pins is not supported by the
TOBY-L2x0-00S product version: the two input pins should be not driven by the host application
processor.
TOBY-L2 series modules include two input pins (HOST_SELECT0 and HOST_SELECT1) for the selection of the
module configuration by the host application processor.
Guidelines for HOST_SELECT0 and HOST_SELECT1 pins circuit design will be described in detail in a
successive release of the document.
Do not apply voltage to HOST_SELECT0 and HOST_SELECT1 pins before the switch-on of their supply
source (V_INT), to avoid latch-up of circuits and allow a proper boot of the module. If the external signals
connected to the cellular module cannot be tri-stated or set low, insert a multi channel digital switch (e.g.
TI SN74CB3Q16244, TS5A3159, or TS5A63157) between the two-circuit connections and set to high
impedance before V_INT switch-on.
ESD sensitivity rating of the HOST_SELECT0 and HOST_SELECT1 pins is 1 kV (HBM as per JESD22-A114).
Higher protection level could be required if the lines are externally accessible and it can be achieved by
mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) close to accessible points
If the HOST_SELECT0 and HOST_SELECT1 pins are not used, they can be left unconnected on the
application board.
2.3.3.2 Guidelines for HOST_SELECTx layout design
The input pins for the selection of the module configuration by the host application processor (HOST_SELECT0
and HOST_SELECT1) are generally not critical for layout.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 77 of 141
Page 78

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
2.4 Antenna interface
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules provide two RF interfaces for connecting the external antennas:
The ANT1 pin represents the primary RF input/output for LTE/3G/2G RF signals transmission and reception.
The ANT2 pin represents the secondary RF input for LTE MIMO 2 x 2 or 3G Rx diversity RF signals reception.
Both the ANT1 and the ANT2 pins have a nominal characteristic impedance of 50 and must be connected to
the related antenna through a 50 transmission line to allow proper transmission / reception of RF signals.
Two antennas (one connected to ANT1 pin and one connected to ANT2 pin) must be used to support the
Down-Link MIMO 2 x 2 radio technology. This is a required feature for LTE category 4 User Equipments
(up to 150 Mb/s Down-Link data rate) according to 3GPP specifications.
2.4.1 Antenna RF interfaces (ANT1 / ANT2)
2.4.1.1 General guidelines for antenna selection and design
The antenna is the most critical component to be evaluated. Designers must take care of the antennas from all
perspective at the very start of the design phase when the physical dimensions of the application board are
under analysis/decision, since the RF compliance of the device integrating TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules
with all the applicable required certification schemes depends on antennas radiating performance.
LTE/3G/2G antennas are typically available in the types of linear monopole or PCB antennas such as patches or
ceramic SMT elements.
External antennas (e.g. linear monopole)
o External antennas basically do not imply physical restriction to the design of the PCB where the
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series module is mounted.
o The radiation performance mainly depends on the antennas. It is required to select antennas with
optimal radiating performance in the operating bands.
o RF cables should be carefully selected to have minimum insertion losses. Additional insertion loss
will be introduced by low quality or long cable. Large insertion loss reduces both transmit and
receive radiation performance.
o A high quality 50 RF connector provides proper PCB-to-RF-cable transition. It is recommended to
strictly follow the layout and cable termination guidelines provided by the connector manufacturer.
Integrated antennas (e.g. patch-like antennas):
o Internal integrated antennas imply physical restriction to the design of the PCB:
Integrated antenna excites RF currents on its counterpoise, typically the PCB ground plane of the
device that becomes part of the antenna: its dimension defines the minimum frequency that can be
radiated. Therefore, the ground plane can be reduced down to a minimum size that should be
similar to the quarter of the wavelength of the minimum frequency that has to be radiated, given
that the orientation of the ground plane relative to the antenna element must be considered.
The isolation between the primary and the secondary antennas has to be as high as possible and
the correlation between the 3D radiation patterns of the two antennas has to be as low as possible.
In general, a separation of at least a quarter wavelength between the two antennas is required to
achieve a good isolation and low pattern correlation.
As numerical example, the physical restriction to the PCB design can be considered as following:
Frequency = 750 MHz Wavelength = 40 cm Minimum GND plane size = 10 cm
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 78 of 141
Page 79

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Min.
250 µm
Min. 400 µm
GND
ANT1
GND clearance
on very close buried layer
below ANT1 pad
GND clearance
on top layer
around ANT1 pad
Min.
250 µm
Min. 400 µm
GND
ANT2
GND clearance
on very close buried layer
below ANT2 pad
GND clearance
on top layer
around ANT2 pad
o Radiation performance depends on the whole PCB and antenna system design, including product
mechanical design and usage. Antennas should be selected with optimal radiating performance in
the operating bands according to the mechanical specifications of the PCB and the whole product.
o It is recommended to select a pair of custom antennas designed by an antennas’ manufacturer if
the required ground plane dimensions are very small (e.g. less than 6.5 cm long and 4 cm wide).
The antenna design process should begin at the start of the whole product design process
o It is highly recommended to strictly follow the detailed and specific guidelines provided by the
antenna manufacturer regarding correct installation and deployment of the antenna system,
including PCB layout and matching circuitry
o Further to the custom PCB and product restrictions, antennas may require tuning to obtain the
required performance for compliance with all the applicable required certification schemes. It is
recommended to consult the antenna manufacturer for the design-in guidelines for antenna
matching relative to the custom application
In both of cases, selecting external or internal antennas, these recommendations should be observed:
Select antennas providing optimal return loss (or V.S.W.R.) figure over all the operating frequencies.
Select antennas providing optimal efficiency figure over all the operating frequencies.
Select antennas providing similar efficiency for both the primary (ANT1) and the secondary (ANT2) antenna.
Select antennas providing appropriate gain figure (i.e. combined antenna directivity and efficiency figure) so
that the electromagnetic field radiation intensity do not exceed the regulatory limits specified in some
countries (e.g. by FCC in the United States, as reported in the section 4.2.2).
Select antennas capable to provide low Envelope Correlation Coefficient between the primary (ANT1) and
the secondary (ANT2) antenna: the 3D antenna radiation patterns should have lobes in different directions.
2.4.1.2 Guidelines for antenna RF interface design
Guidelines for TOBY-L2 series ANT1 / ANT2 pins RF connection design
Proper transition between ANT1 / ANT2 pads and the application board PCB must be provided, implementing
the following design-in guidelines for the layout of the application PCB close to the ANT1 / ANT2 pads:
On a multilayer board, the whole layer stack below the RF connection should be free of digital lines
Increase GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a void area) around the ANT1 / ANT2 pads, on the top layer of the
Add GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a void area) on the buried metal layer below the ANT1 / ANT2 pads if
Figure 38: GND keep-out area on top layer around ANT1 / ANT2 pads and on very close buried layer below ANT1 / ANT2 pads
application PCB, to at least 250 µm up to adjacent pads metal definition and up to 400 µm on the area
below the module, to reduce parasitic capacitance to ground, as described in the left picture in Figure 38
the top-layer to buried layer dielectric thickness is below 200 µm, to reduce parasitic capacitance to ground,
as described in the right picture in Figure 38
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 79 of 141
Page 80
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Manufacturer
Series
Remarks
Hirose
U.FL® Ultra Small Surface Mount Coaxial Connector
Recommended
I-PEX
MHF® Micro Coaxial Connector
Tyco
UMCC® Ultra-Miniature Coax Connector
Amphenol RF
AMC® Amphenol Micro Coaxial
Lighthorse Technologies, Inc
IPX ultra micro-miniature RF connector
MPCI-L2 series
Baseboard
Stripline/Microstrip
Internal
Antenna
Baseboard
Application
Chassis
Connector to
External Antenna
MPCI-L2 series
Latch for
Mini PCIe
Latch for Mini PCIe
Guidelines for MPCI-L2 series ANT1 / ANT2 receptacles RF connection design
The Hirose U.FL-R-SMT RF receptacles implemented on the MPCI-L2 series modules for ANT1 / ANT2 ports
require a suitable mated RF plug from the same connector series. Due to its wide usage in the industry, several
manufacturers offer compatible equivalents.
Table 23 lists some RF connector plugs that fit MPCI-L2 series modules RF connector receptacles, based on the
declaration of the respective manufacturers. Only the Hirose has been qualified for the MPCI-L2 series modules;
contact other producers to verify compatibility.
Table 23: MPCI-L2 series U.FL compatible plug connector
Typically the RF plug is available as a cable assembly: several kinds are available and the user should select the
cable assembly best suited to the application. The key characteristics are:
RF plug type: select U.FL or equivalent
Nominal impedance: 50
Cable thickness: typically from 0.8 mm to 1.37 mm. Select thicker cables to minimize insertion loss
Cable length: standard length is typically 100 mm or 200 mm, custom lengths may be available on request.
Select shorter cables to minimize insertion loss
RF connector on the other side of the cable: for example another U.FL (for board-to-board connection) or
SMA (for panel mounting)
For applications requiring an internal integrated SMT antenna, it is suggested to use a U-FL-to-U.FL cable to
provide RF path from the MPCI-L2 series module to PCB strip line or micro strip connected to antenna pads as
shown in Figure 39. Take care that the PCB-to-RF-cable transition, strip line and antenna pads must be designed
so that the characteristic impedance is as close as possible to 50 : see the following subsections for specific
guidelines regarding RF transmission line design and RF termination design.
If an external antenna is required, consider that the connector is typically rated for a limited number of insertion
cycles. In addition, the RF coaxial cable may be relatively fragile compared to other types of cables. To increase
application ruggedness, connect U.FL to a more robust connector (e.g. SMA or MMCX) fixed on panel or on
flange as shown in Figure 39.
Figure 39: Example of RF connections, U.FL-to-U.FL cable for internal antenna and U.FL-to-SMA for external antenna
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 80 of 141
Page 81

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
35 µm
35 µm
35 µm
35 µm
270 µm
270 µm
760 µm
L1 Copper
L3 Copper
L2 Copper
L4 Copper
FR-4 dielectric
FR-4 dielectric
FR-4 dielectric
380 µm 500 µm500 µm
35 µm
35 µm
1510 µm
L2 Copper
L1 Copper
FR-4 dielectric
1200 µm 400 µm400 µm
Guidelines for RF transmission line design
Any RF transmission line, such as the ones from the ANT1 and ANT2 pads up to the related antenna connector
or up to the related internal antenna pad, must be designed so that the characteristic impedance is as close as
possible to 50 .
RF transmission lines can be designed as a micro strip (consists of a conducting strip separated from a ground
plane by a dielectric material) or a strip line (consists of a flat strip of metal which is sandwiched between two
parallel ground planes within a dielectric material). The micro strip, implemented as a coplanar waveguide, is the
most common configuration for printed circuit board.
Figure 40 and Figure 41 provide two examples of proper 50 coplanar waveguide designs. The first example of
RF transmission line can be implemented in case of 4-layer PCB stack-up herein described, and the second
example of RF transmission line can be implemented in case of 2-layer PCB stack-up herein described.
Figure 40: Example of 50 coplanar waveguide transmission line design for the described 4-layer board layup
Figure 41: Example of 50 coplanar waveguide transmission line design for the described 2-layer board layup
If the two examples do not match the application PCB stack-up the 50 characteristic impedance calculation
can be made using the HFSS commercial finite element method solver for electromagnetic structures from Ansys
Corporation, or using freeware tools like AppCAD from Agilent (www.agilent.com) or TXLine from Applied
Wave Research (www.mwoffice.com), taking care of the approximation formulas used by the tools for the
impedance computation.
To achieve a 50 characteristic impedance, the width of the transmission line must be chosen depending on:
the thickness of the transmission line itself (e.g. 35 µm in the example of Figure 40 and Figure 41)
the thickness of the dielectric material between the top layer (where the transmission line is routed) and the
inner closer layer implementing the ground plane (e.g. 270 µm in Figure 40, 1510 µm in Figure 41)
the dielectric constant of the dielectric material (e.g. dielectric constant of the FR-4 dielectric material in
Figure 40 and Figure 41)
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 81 of 141
Page 82

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
SMA Connector
Primary Antenna
SMA Connector
Secondary Antenna
TOBY-L2 series
the gap from the transmission line to the adjacent ground plane on the same layer of the transmission line
(e.g. 500 µm in Figure 40, 400 µm in Figure 41)
If the distance between the transmission line and the adjacent GND area (on the same layer) does not exceed 5
times the track width of the micro strip, use the “Coplanar Waveguide” model for the 50 calculation.
Additionally to the 50 impedance, the following guidelines are recommended for transmission lines design:
Minimize the transmission line length: the insertion loss should be minimized as much as possible, in the
order of a few tenths of a dB,
Add GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a void area) on buried metal layers below any pad of component present
on the RF transmission lines, if top-layer to buried layer dielectric thickness is below 200 µm, to reduce
parasitic capacitance to ground,
The transmission lines width and spacing to GND must be uniform and routed as smoothly as possible: avoid
abrupt changes of width and spacing to GND,
Add GND stitching vias around transmission lines, as described in Figure 42,
Ensure solid metal connection of the adjacent metal layer on the PCB stack-up to main ground layer,
providing enough vias on the adjacent metal layer, as described in Figure 42,
Route RF transmission lines far from any noise source (as switching supplies and digital lines) and from any
sensitive circuit (as USB),
Avoid stubs on the transmission lines,
Avoid signal routing in parallel to transmission lines or crossing the transmission lines on buried metal layer,
Do not route microstrip lines below discrete component or other mechanics placed on top layer
An example of proper RF circuit design is reported in Figure 42. In this case, the ANT1 and ANT2 pins are
directly connected to SMA connectors by means of proper 50 transmission lines, designed with proper layout.
Figure 42: Suggested circuit and layout for antenna RF circuits on application board
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 82 of 141
Page 83

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Guidelines for RF termination design
RF terminations must provide a characteristic impedance of 50 as well as the RF transmission lines up to the RF
terminations themselves, to match the characteristic impedance of the ANT1 / ANT2 ports of the modules.
However, real antennas do not have perfect 50 load on all the supported frequency bands. Therefore, to
reduce as much as possible performance degradation due to antennas mismatch, RF terminations must provide
optimal return loss (or V.S.W.R.) figure over all the operating frequencies, as summarized in Table 8 and Table 9.
If external antennas are used, the antenna connectors represent the RF termination on the PCB:
Use suitable 50 connectors providing proper PCB-to-RF-cable transition.
Strictly follow the connector manufacturer’s recommended layout, for example:
o SMA Pin-Through-Hole connectors require GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a void area) on all the
layers around the central pin up to annular pads of the four GND posts, as shown in Figure 42
o U.FL surface mounted connectors require no conductive traces (i.e. clearance, a void area) in the
area below the connector between the GND land pads.
Cut out the GND layer under RF connectors and close to buried vias, to remove stray capacitance and thus
keep the RF line 50 , e.g. the active pad of UFL connectors needs to have a GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a
void area) at least on first inner layer to reduce parasitic capacitance to ground.
If integrated antennas are used, the RF terminations are represented by the integrated antennas themselves. The
following guidelines should be followed:
Use antennas designed by an antenna manufacturer, providing the best possible return loss (or V.S.W.R.).
Provide a ground plane large enough according to the relative integrated antenna requirements. The ground
plane of the application PCB can be reduced down to a minimum size that must be similar to one quarter of
wavelength of the minimum frequency that has to be radiated. As numerical example,
Frequency = 750 MHz Wavelength = 40 cm Minimum GND plane size = 10 cm
It is highly recommended to strictly follow the detailed and specific guidelines provided by the antenna
manufacturer regarding correct installation and deployment of the antenna system, including PCB layout
and matching circuitry.
Further to the custom PCB and product restrictions, antennas may require a tuning to comply with all the
applicable required certification schemes. It is recommended to consult the antenna manufacturer for the
design-in guidelines for the antenna matching relative to the custom application.
Additionally, these recommendations regarding the antenna system placement must be followed:
Do not place antennas within closed metal case.
Do not place the antennas in close vicinity to end user since the emitted radiation in human tissue is limited
by regulatory requirements.
Place the antennas far from sensitive analog systems or employ countermeasures to reduce EMC issues.
Take care of interaction between co-located RF systems since the LTE/3G/2G transmitted power may interact
or disturb the performance of companion systems.
Place the two LTE/3G antennas providing low Envelope Correlation Coefficient (ECC) between primary
(ANT1) and secondary (ANT2) antenna: the antenna 3D radiation patterns should have lobes in different
directions. The ECC between primary and secondary antenna needs to be enough low to comply with the
radiated performance requirements specified by related certification schemes, as indicated in Table 10.
Place the two LTE/3G antennas providing enough high isolation (see Table 10) between primary (ANT1) and
secondary (ANT2) antenna. The isolation depends on the distance between antennas (separation of at least
a quarter wavelength required for good isolation), antenna type (using antennas with different polarization
improves isolation), antenna 3D radiation patterns (uncorrelated patterns improve isolation).
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 83 of 141
Page 84

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Manufacturer
Part Number
Product Name
Description
Taoglas
PCS.06.A
Havok
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2500..2690 MHz
42.0 x 10.0 x 3.0 mm
700..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz
Taoglas
PA.710.A
Warrior
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2300..2400 MHz, 2490..2690 MHz
40.0 x 6.0 x 5.0 mm
Manufacturer
Part Number
Product Name
Description
Taoglas
FXUB63.07.0150C
GSM / WCDMA / LTE PCB Antenna with cable and U.FL
698..960 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2400..2690 MHz
96.0 x 21.0 mm
Taoglas
FXUB66.07.0150C
Maximus
GSM / WCDMA / LTE PCB Antenna with cable and U.FL
698..960 MHz, 1390..1435 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz,
2400..2700 MHz, 3400..3600 MHz, 4800..6000 MHz
120.2 x 50.4 mm
Taoglas
FXUB70.A.07.C.001
GSM / WCDMA / LTE PCB MIMO Antenna with cables and U.FL
698..960 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2400..2690 MHz
182.2 x 21.2 mm
Ethertronics
5001537
Prestta
GSM / WCDMA / LTE PCB Antenna with cable
704..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2300..2400 MHz, 2500..2690 MHz
80.0 x 18.0 mm
EAD
FSQS35241-UF-10
SQ7
GSM / WCDMA / LTE PCB Antenna with cable and U.FL
690..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2500..2700 MHz
110.0 x 21.0 mm
Examples of antennas
Table 24 lists some examples of possible internal on-board surface-mount antennas.
Table 24: Examples of internal surface-mount antennas
Table 25 lists some examples of possible internal off-board PCB-type antennas with cable and connector.
Table 25: Examples of internal antennas with cable and connector
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 84 of 141
Page 85

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Manufacturer
Part Number
Product Name
Description
Taoglas
GSA.8827.A.101111
Phoenix
GSM / WCDMA / LTE adhesive-mount Antenna with cable and SMA(M)
698..960 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2490..2690 MHz
105 x 30 x 7.7 mm
Taoglas
TG.30.8112
GSM / WCDMA / LTE swivel dipole Antenna with SMA(M)
698..960 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2400..2700 MHz
148.6 x 49 x 10 mm
Laird Tech.
TRA6927M3PW-001
GSM / WCDMA / LTE screw-mount Antenna with N-type(F)
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2300..2700 MHz
83.8 x Ø 36.5 mm
Laird Tech.
CMS69273
GSM / WCDMA / LTE ceiling-mount Antenna with cable and N-type(F)
698..960 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2700 MHz
86 x Ø 199 mm
Laird Tech.
OC69271-FNM
GSM / WCDMA / LTE pole-mount Antenna with N-type(M)
698..960 MHz, 1710..2690 MHz
248 x Ø 24.5 mm
Laird Tech.
CMD69273-30NM
GSM / WCDMA / LTE ceiling-mount MIMO Antenna with cables & N-type(M)
698..960 MHz, 1710..2700 MHz
43.5 x Ø 218.7 mm
Pulse Electronics
WA700/2700SMA
GSM / WCDMA / LTE clip-mount MIMO antenna with cables and SMA(M)
698..960 MHz,1710..2700 MHz
149 x 127 x 5.1 mm
Table 26 lists some examples of possible external antennas.
Table 26: Examples of external antennas
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 85 of 141
Page 86

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Application Board
Antenna Cable
TOBY-L2 series
81
ANT1
75
ANT_DET
R1
C1 D1
C2
J1
Z0= 50 ohm Z0= 50 ohm
Z0= 50 ohm
Primary Antenna Assembly
R2
C4
L3
Radiating
Element
Diagnostic
Circuit
L2
L1
Antenna Cable
87
ANT2
C3
J2
Z0= 50 ohm Z0= 50 ohm
Z0= 50 ohm
Secondary Antenna Assembly
R3
C5
L4
Radiating
Element
Diagnostic
Circuit
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
27 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H270J - Murata
C2, C3
33 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H330J - Murata
D1
Very Low Capacitance ESD Protection
PESD0402-140 - Tyco Electronics
L1, L2
68 nH Multilayer Inductor 0402 (SRF ~1 GHz)
LQG15HS68NJ02 - Murata
R1
10 k Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RK73H1ETTP1002F - KOA Speer
J1, J2
SMA Connector 50 Through Hole Jack
SMA6251A1-3GT50G-50 - Amphenol
C4, C5
22 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1H220J - Murata
L3, L4
68 nH Multilayer Inductor 0402 (SRF ~1 GHz)
LQG15HS68NJ02 - Murata
R2, R3
15 k Resistor for Diagnostic
Various Manufacturers
2.4.2 Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET)
Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET) is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET) is not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version.
2.4.2.1 Guidelines for ANT_DET circuit design
Figure 43 and Table 27 describe the recommended schematic / components for the antennas detection circuit
that must be provided on the application board and for the diagnostic circuit that must be provided on the
antennas’ assembly to achieve primary and secondary antenna detection functionality.
Figure 43: Suggested schematic for antenna detection circuit on application board and diagnostic circuit on antennas assembly
Table 27: Suggested components for antenna detection circuit on application board and diagnostic circuit on antennas assembly
The antenna detection circuit and diagnostic circuit suggested in Figure 43 and Table 27 are explained here:
When antenna detection is forced by AT+UANTR command, ANT_DET generates a DC current measuring
the resistance (R2 // R3) from antenna connectors (J1, J2) provided on the application board to GND.
DC blocking capacitors are needed at the ANT1 / ANT2 pins (C2, C3) and at the antenna radiating element
(C4, C5) to decouple the DC current generated by the ANT_DET pin.
Choke inductors with a Self Resonance Frequency (SRF) in the range of 1 GHz are needed in series at the
ANT_DET pin (L1, L2) and in series at the diagnostic resistor (L3, L4), to avoid a reduction of the RF
performance of the system, improving the RF isolation of the load resistor.
Additional components (R1, C1 and D1 in Figure 43) are needed at the ANT_DET pin as ESD protection
The ANT1 / ANT2 pins must be connected to the antenna connector by means of a transmission line with
nominal characteristics impedance as close as possible to 50 .
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 86 of 141
Page 87

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
The DC impedance at RF port for some antennas may be a DC open (e.g. linear monopole) or a DC short to
reference GND (e.g. PIFA antenna). For those antennas, without the diagnostic circuit of Figure 43, the measured
DC resistance is always at the limits of the measurement range (respectively open or short), and there is no
means to distinguish between a defect on antenna path with similar characteristics (respectively: removal of
linear antenna or RF cable shorted to GND for PIFA antenna).
Furthermore, any other DC signal injected to the RF connection from ANT connector to radiating element will
alter the measurement and produce invalid results for antenna detection.
It is recommended to use an antenna with a built-in diagnostic resistor in the range from 5 k to 30 k
to assure good antenna detection functionality and avoid a reduction of module RF performance. The
choke inductor should exhibit a parallel Self Resonance Frequency (SRF) in the range of 1 GHz to improve
the RF isolation of load resistor.
For example:
Consider an antenna with built-in DC load resistor of 15 k. Using the +UANTR AT command, the module
reports the resistance value evaluated from the antenna connector provided on the application board to GND:
Reported values close to the used diagnostic resistor nominal value (i.e. values from 13 k to 17 k if a
15 k diagnostic resistor is used) indicate that the antenna is properly connected.
Values close to the measurement range maximum limit (approximately 50 k) or an open-circuit
“over range” report (see u-blox AT Commands Manual [3]) means that that the antenna is not connected or
the RF cable is broken.
Reported values below the measurement range minimum limit (1 k) highlights a short to GND at antenna
or along the RF cable.
Measurement inside the valid measurement range and outside the expected range may indicate an improper
connection, damaged antenna or wrong value of antenna load resistor for diagnostic.
Reported value could differ from the real resistance value of the diagnostic resistor mounted inside the
antenna assembly due to antenna cable length, antenna cable capacity and the used measurement method.
If the primary / secondary antenna detection function is not required by the customer application, the
ANT_DET pin can be left not connected and the ANT1 / ANT2 pins can be directly connected to the
related antenna connector by means of a 50 transmission line as described in Figure 42.
2.4.2.1 Guidelines for ANT_DET layout design
The recommended layout for the primary antenna detection circuit to be provided on the application board to
achieve the primary antenna detection functionality, implementing the recommended schematic described in
Figure 43 and Table 27, is explained here:
The ANT1 / ANT2 pins have to be connected to the antenna connector by means of a 50 transmission
line, implementing the design guidelines described in section 2.4.1 and the recommendations of the SMA
connector manufacturer.
DC blocking capacitor at ANT1 / ANT2 pins (C2, C3) has to be placed in series to the 50 RF line.
The ANT_DET pin has to be connected to the 50 transmission line by means of a sense line.
Choke inductors in series at the ANT_DET pin (L1, L2) have to be placed so that one pad is on the 50
transmission line and the other pad represents the start of the sense line to the ANT_DET pin.
The additional components (R1, C1 and D1) on the ANT_DET line have to be placed as ESD protection.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 87 of 141
Page 88

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
2.5 SIM interface
SIM detection interface (GPIO5) is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
SIM detection interface (GPIO5) is not supported by the TOBY-L2x0-00S product version: the pin should
not be driven by any external device.
2.5.1 Guidelines for SIM circuit design
Guidelines for SIM cards, SIM connectors and SIM chips selection
The ISO/IEC 7816, the ETSI TS 102 221 and the ETSI TS 102 671 specifications define the physical, electrical and
functional characteristics of Universal Integrated Circuit Cards (UICC), which contains the Subscriber
Identification Module (SIM) integrated circuit that securely stores all the information needed to identify and
authenticate subscribers over the LTE/3G/2G network.
Removable UICC / SIM card contacts mapping is defined by ISO/IEC 7816 and ETSI TS 102 221 as follows:
Contact C1 = VCC (Supply) It must be connected to VSIM or UIM_PWR
Contact C2 = RST (Reset) It must be connected to SIM_RST or UIM_RESET
Contact C3 = CLK (Clock) It must be connected to SIM_CLK or UIM_CLK
Contact C4 = AUX1 (Auxiliary contact) It must be left not connected
Contact C5 = GND (Ground) It must be connected to GND
Contact C6 = VPP (Programming supply) It must be connected to VSIM or UIM_PWR
Contact C7 = I/O (Data input/output) It must be connected to SIM_IO or UIM_DATA
Contact C8 = AUX2 (Auxiliary contact) It must be left not connected
A removable SIM card can have 6 contacts (C1, C2, C3, C5, C6, C7) or 8 contacts, also including the auxiliary
contacts C4 and C8 . Only 6 contacts are required and must be connected to the module SIM interface.
Removable SIM cards are suitable for applications requiring a change of SIM card during the product lifetime.
A SIM card holder can have 6 or 8 positions if a mechanical card presence detector is not provided, or it can
have 6+2 or 8+2 positions if two additional pins relative to the normally-open mechanical switch integrated in
the SIM connector for the mechanical card presence detection are provided. Select a SIM connector providing
6+2 or 8+2 positions if the optional SIM detection feature (not available on MPCI-L2 series) is required by the
custom application, otherwise a connector without integrated mechanical presence switch can be selected.
Solderable UICC / SIM chip contact mapping (M2M UICC Form Factor) is defined by ETSI TS 102 671 as:
Case Pin 8 = UICC Contact C1 = VCC (Supply) It must be connected to VSIM or UIM_PWR
Case Pin 7 = UICC Contact C2 = RST (Reset) It must be connected to SIM_RST or UIM_RESET
Case Pin 6 = UICC Contact C3 = CLK (Clock) It must be connected to SIM_CLK or UIM_CLK
Case Pin 5 = UICC Contact C4 = AUX1 (Aux.contact) It must be left not connected
Case Pin 1 = UICC Contact C5 = GND (Ground) It must be connected to GND
Case Pin 2 = UICC Contact C6 = VPP (Progr. supply) It must be connected to VSIM or UIM_PWR
Case Pin 3 = UICC Contact C7 = I/O (Data I/O) It must be connected to SIM_IO or UIM_DATA
Case Pin 4 = UICC Contact C8 = AUX2 (Aux. contact) It must be left not connected
A solderable SIM chip has 8 contacts and can also include the auxiliary contacts C4 and C8 for other uses, but
only 6 contacts are required and must be connected to the module SIM card interface as described above.
Solderable SIM chips are suitable for M2M applications where it is not required to change the SIM once installed.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 88 of 141
Page 89

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TOBY-L2 series
59
VSIM
57
SIM_IO
56
SIM_CLK
58
SIM_RST
SIM CARD
HOLDER
C5C6C
7
C1C2C
3
SIM Card
Bottom View
(contacts side)
C1
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
C2 C3 C5
J1
C4
D1 D2 D3 D4
C
8
C
4
MPCI-L2 series
8
UIM_PWR
10
UIM_DATA
12
UIM_CLK
14
UIM_RESET
SIM CARD
HOLDER
C5C6C
7
C1C2C
3
SIM Card
Bottom View
(contacts side)
C1
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
C2 C3 C5
J1
C4
D1 D2 D3 D4
C
8
C
4
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3, C4
47 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H470JA01 - Murata
C5
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
D1, D2, D3, D4
Very Low Capacitance ESD Protection
PESD0402-140 - Tyco Electronics
J1
SIM Card Holder, 6 p, without card presence switch
Various manufacturers, as C707 10M006 136 2 - Amphenol
Guidelines for single SIM card connection without detection
A removable SIM card placed in a SIM card holder must be connected to the SIM card interface of TOBY-L2 and
MPCI-L2 series modules as described in Figure 44, where the optional SIM detection feature is not implemented.
Follow these guidelines to connect the module to a SIM connector without SIM presence detection:
Connect the UICC / SIM contacts C1 (VCC) and C6 (VPP) to the VSIM / UIM_PWR pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C7 (I/O) to the SIM_IO / UIM_DATA pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C3 (CLK) to the SIM_CLK / UIM_CLK pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C2 (RST) to the SIM_RST / UIM_RESET pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C5 (GND) to ground.
Provide a 100 nF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R71C104K) on SIM supply line, close to the relative
pad of the SIM connector, to prevent digital noise.
Provide a bypass capacitor of about 22 pF to 47 pF (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H470J) on each SIM line, very
close to each related pad of the SIM connector, to prevent RF coupling especially in case the RF antenna is
placed closer than 10 - 30 cm from the SIM card holder.
Provide a very low capacitance (i.e. less than 10 pF) ESD protection (e.g. Tyco PESD0402-140) on each
externally accessible SIM line, close to each relative pad of the SIM connector. ESD sensitivity rating of the
SIM interface pins is 1 kV (HBM). So that, according to EMC/ESD requirements of the custom application,
higher protection level can be required if the lines are externally accessible on the application device.
Limit capacitance and series resistance on each SIM signal to match the SIM requirements (27.7 ns is the
maximum allowed rise time on clock line, 1.0 µs is the maximum allowed rise time on data and reset lines).
Figure 44: Application circuits for the connection to a single removable SIM card, with SIM detection not implemented
Table 28: Example of components for the connection to a single removable SIM card, with SIM detection not implemented
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 89 of 141
Page 90

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TOBY-L2 series
59
VSIM
57
SIM_IO
56
SIM_CLK
58
SIM_RST
SIM CHIP
SIM Chip
Bottom View
(contacts side)
C1
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
C2 C3 C5
U1
C4
2
8
3
6
7
1
C1 C5
C2 C6
C3 C7
C4 C8
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
MPCI-L2 series
8
UIM_PWR
10
UIM_DATA
12
UIM_CLK
14
UIM_RESET
SIM CHIP
SIM Chip
Bottom View
(contacts side)
C1
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
C2 C3 C5
U1
C4
2
8
3
6
7
1
C1 C5
C2 C6
C3 C7
C4 C8
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3, C4
47 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H470JA01 - Murata
C5
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
U1
SIM chip (M2M UICC Form Factor)
Various Manufacturers
Guidelines for single SIM chip connection
A solderable SIM chip (M2M UICC Form Factor) must be connected the SIM card interface of TOBY-L2 and
MPCI-L2 series modules as described in Figure 45.
Follow these guidelines to connect the module to a solderable SIM chip without SIM presence detection:
Connect the UICC / SIM contacts C1 (VCC) and C6 (VPP) to the VSIM / UIM_PWR pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C7 (I/O) to the SIM_IO / UIM_DATA pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C3 (CLK) to the SIM_CLK / UIM_CLK pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C2 (RST) to the SIM_RST / UIM_RESET pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C5 (GND) to ground.
Provide a 100 nF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R71C104K) at the SIM supply line close to the
relative pad of the SIM chip, to prevent digital noise.
Provide a bypass capacitor of about 22 pF to 47 pF (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H470J) on each SIM line, to
prevent RF coupling especially in case the RF antenna is placed closer than 10 - 30 cm from the SIM lines.
Limit capacitance and series resistance on each SIM signal to match the SIM requirements (27.7 ns is the
maximum allowed rise time on clock line, 1.0 µs is the maximum allowed rise time on data and reset lines).
Figure 45: Application circuits for the connection to a single solderable SIM chip, with SIM detection not implemented
Table 29: Example of components for the connection to a single solderable SIM chip, with SIM detection not implemented
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 90 of 141
Page 91

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TOBY-L2 series
5
V_INT
60
GPIO5
SIM CARD
HOLDER
C5C6C
7
C1C2C
3
SIM Card
Bottom View
(contacts side)
C1
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
C2 C3 C5
J1
C4
SW1
SW2
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6
R2
R1
C
8
C
4
TP
59
VSIM
57
SIM_IO
56
SIM_CLK
58
SIM_RST
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3, C4
47 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H470JA01 - Murata
C5
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
D1, … , D6
Very Low Capacitance ESD Protection
PESD0402-140 - Tyco Electronics
R1
1 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-071KL - Yageo Phycomp
R2
470 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-07470KL- Yageo Phycomp
J1
SIM Card Holder, 6 + 2 p, with card presence switch
Various manufacturers, as CCM03-3013LFT R102 - C&K
Guidelines for single SIM card connection with detection
A removable SIM card placed in a SIM card holder must be connected to the SIM card interface of TOBY-L2
modules as described in Figure 46, where the optional SIM card detection feature is implemented.
Follow these guidelines to connect the module to a SIM connector implementing SIM presence detection:
Connect the UICC / SIM contacts C1 (VCC) and C6 (VPP) to the VSIM pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C7 (I/O) to the SIM_IO pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C3 (CLK) to the SIM_CLK pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C2 (RST) to the SIM_RST pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C5 (GND) to ground.
Connect one pin of the mechanical switch integrated in the SIM connector (e.g. the SW2 pin as described in
Figure 46) to the GPIO5 input pin of the module.
Connect the other pin of the mechanical switch integrated in the SIM connector (e.g. the SW1 pin as
described in Figure 46) to the V_INT 1.8 V supply output of the module by means of a strong (e.g. 1 k)
pull-up resistor, as the R1 resistor in Figure 46.
Provide a weak (e.g. 470 k) pull-down resistor at the SIM detection line, as the R2 resistor in Figure 46
Provide a 100 nF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R71C104K) at the SIM supply line, close to the
related pad of the SIM connector, to prevent digital noise.
Provide a bypass capacitor of about 22 pF to 47 pF (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H470J) on each SIM line, very
close to each related pad of the SIM connector, to prevent RF coupling especially in case the RF antenna is
placed closer than 10 - 30 cm from the SIM card holder.
Provide a very low capacitance (i.e. less than 10 pF) ESD protection (e.g. Tyco PESD0402-140) on each
externally accessible SIM line, close to each related pad of the SIM connector: ESD sensitivity rating of the
SIM interface pins is 1 kV (HBM), so that, according to the EMC/ESD requirements of the custom application,
higher protection level can be required if the lines are externally accessible on the application device.
Limit capacitance and series resistance on each SIM signal to match the SIM requirements (27.7 ns is the
maximum allowed rise time on clock line, 1.0 µs is the maximum allowed rise time on data and reset lines).
Figure 46: Application circuit for the connection to a single removable SIM card, with SIM detection implemented
Table 30: Example of components for the connection to a single removable SIM card, with SIM detection implemented
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 91 of 141
Page 92

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Guidelines for dual SIM card / chip connection
Two SIM card / chip can be connected to the SIM interface of TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules as described
in the application circuits of Figure 47.
TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series modules do not support the usage of two SIM at the same time, but two SIM can
be populated on the application board, providing a proper switch to connect only the first or only the second
SIM at a time to the SIM interface of the modules, as described in Figure 47.
TOBY-L2x0-00S and MPCI-L2 modules do not support SIM hot insertion / removal: the physical connection
between the external SIM and the module has to be provided before the module boot and then held for normal
operation. Switching from one SIM to another can only be properly done within one of these two time periods:
after module switch-off by the AT+CPWROFF and before module switch-on by PWR_ON
after network deregistration by AT+COPS=2 and before module reset by AT+CFUN=16
TOBY-L2 modules (except TOBY-L2x0-00S) support SIM hot insertion / removal on the GPIO5 pin: if the feature
is enabled using the specific AT commands (see sections 1.8.2 and 1.11, and u-blox AT Commands Manual [3],
+UGPIOC, +UDCONF commands), the switch from first SIM to the second SIM can be properly done when a
Low logic level is present on the GPIO5 pin (‘SIM not inserted’ = SIM interface not enabled), without the
necessity of a module re-boot, so that the SIM interface will be re-enabled by the module to use the second SIM
when a high logic level is re-applied on the GPIO5 pin.
In the application circuit example represented in Figure 47, the application processor will drive the SIM switch
using its own GPIO to properly select the SIM that is used by the module. Another GPIO may be used to handle
the SIM hot insertion / removal function of TOBY-L2 modules, which can also be handled by other external
circuits or by the cellular module GPIO according to the application requirements.
The dual SIM connection circuit described in Figure 47 can be implemented for SIM chips as well, providing
proper connection between SIM switch and SIM chip as described in Figure 45.
If it is required to switch between more than 2 SIM, a circuit similar to the one described in Figure 47 can be
implemented: in case of 4 SIM circuit, using proper 4-throw switch instead of the suggested 2-throw switches.
Follow these guidelines to connect the module to two external SIM connectors:
Use a proper low on resistance (i.e. few ohms) and low on capacitance (i.e. few pF) 2-throw analog switch
(e.g. Fairchild FSA2567) as SIM switch to ensure high-speed data transfer according to SIM requirements.
Connect the contacts C1 (VCC) and C6 (VPP) of the two UICC / SIM to the VSIM / UIM_PWR pin of the
module by means of a proper 2-throw analog switch (e.g. Fairchild FSA2567).
Connect the contact C7 (I/O) of the two UICC / SIM to the SIM_IO / UIM_DATA pin of the module by
means of a proper 2-throw analog switch (e.g. Fairchild FSA2567).
Connect the contact C3 (CLK) of the two UICC / SIM to the SIM_CLK / UIM_CLK pin of the module by
means of a proper 2-throw analog switch (e.g. Fairchild FSA2567).
Connect the contact C2 (RST) of the two UICC / SIM to the SIM_RST / UIM_RESET pin of the module by
means of a proper 2-throw analog switch (e.g. Fairchild FSA2567).
Connect the contact C5 (GND) of the two UICC / SIM to ground.
Provide a 100 nF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R71C104K) at the SIM supply (VSIM / UIM_PWR),
close to the related pad of the two SIM connectors, to prevent digital noise.
Provide a bypass capacitor of about 22 pF to 47 pF (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H470J) on each SIM line, very
close to each related pad of the two SIM connectors, to prevent RF coupling especially in case the RF
antenna is placed closer than 10 - 30 cm from the SIM card holders.
Provide a very low capacitance (i.e. less than 10 pF) ESD protection (e.g. Tyco Electronics PESD0402-140) on
each externally accessible SIM line, close to each pad of the two SIM connectors, according to the EMC/ESD
requirements of the custom application.
Limit capacitance and series resistance on each SIM signal to match the SIM requirements (27.7 ns is the
maximum allowed rise time on clock line, 1.0 µs is the maximum allowed rise time on data and reset lines).
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 92 of 141
Page 93

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TOBY-L2 series
C1
FIRST
SIM CARD
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
C2 C3 C5
J1
C4
D1 D2 D3 D4
GND
U1
59
VSIM
VSIM
1VSIM
2VSIM
VCC
C11
4PDT
Analog
Switch
3V8
57
SIM_IO
DAT
1DAT
2DAT
56
SIM_CLK
CLK
1CLK
2CLK
58
SIM_RST
RST
1RST
2RST
SEL
SECOND
SIM CARD
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
J2
C6 C7 C8 C10
C9
D5 D6 D7 D8
Application
Processor
GPIO
R1
MPCI-L2 series
C1
FIRST
SIM CARD
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
C2 C3 C5
J1
C4
D1 D2 D3 D4
GND
U1
8
UIM_PWR
VSIM
1VSIM
2VSIM
VCC
C11
4PDT
Analog
Switch
3V8
10
UIM_DATA
DAT
1DAT
2DAT
12
UIM_CLK
CLK
1CLK
2CLK
14
UIM_RESET
RST
1RST
2RST
SEL
SECOND
SIM CARD
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
J2
C6 C7 C8 C10
C9
D5 D6 D7 D8
Application
Processor
GPIO
R1
Reference
Description
Part Number – Manufacturer
C1 – C4, C6 – C9
33 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1H330JZ01 – Murata
C5, C10, C11
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 – Murata
D1 – D8
Very Low Capacitance ESD Protection
PESD0402-140 - Tyco Electronics
R1
47 kΩ Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-0747KL- Yageo Phycomp
J1, J2
SIM Card Holder, 6 + 2 p., with card presence switch
CCM03-3013LFT R102 - C&K Components
U1
4PDT Analog Switch,
with Low On-Capacitance and Low On-Resistance
FSA2567 - Fairchild Semiconductor
Figure 47: Application circuit for the connection to two removable SIM cards, with SIM detection not implemented
Table 31: Example of components for the connection to two removable SIM cards, with SIM detection not implemented
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 93 of 141
Page 94

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
2.5.2 Guidelines for SIM layout design
The layout of the SIM card interface lines (VSIM, SIM_CLK, SIM_IO, SIM_RST or UIM_PWR, UIM_DATA,
UIM_CLK, UIM_RESET) may be critical if the SIM card is placed far away from the TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series
modules or in close proximity to the RF antenna: these two cases should be avoided or at least mitigated as
described below.
In the first case, the long connection can cause the radiation of some harmonics of the digital data frequency as
any other digital interface. It is recommended to keep the traces short and avoid coupling with RF line or
sensitive analog inputs.
In the second case, the same harmonics can be picked up and create self-interference that can reduce the
sensitivity of LTE/3G/2G receiver channels whose carrier frequency is coincidental with harmonic frequencies. It is
strongly recommended to place the RF bypass capacitors suggested in Figure 44 near the SIM connector.
In addition, since the SIM card is typically accessed by the end user, it can be subjected to ESD discharges. Add
adequate ESD protection as suggested to protect module SIM pins near the SIM connector.
Limit capacitance and series resistance on each SIM signal to match the SIM specifications. The connections
should always be kept as short as possible.
Avoid coupling with any sensitive analog circuit, since the SIM signals can cause the radiation of some harmonics
of the digital data frequency.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 94 of 141
Page 95

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
D+
D-
GND
28
USB_D+
27
USB_D-
GND
USB DEVICE
CONNECTOR
VBUS
D+
D-
GND
28
USB_D+
27
USB_D-
GND
USB HOST
PROCESSOR
D+
D-
GND
38
USB_D+
36
USB_D-
GND
USB DEVICE
CONNECTOR
VBUS
TOBY-L2 series TOBY-L2 series
MPCI-L2 series MPCI-L2 series
D+
D-
GND
38
USB_D+
36
USB_D-
GND
USB HOST
PROCESSOR
VBUS
4
VUSB_DET
4
VUSB_DET
D1 D2C1D3
D1 D2
C1
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R61A104KA01 - Murata
D1, D2, D3
Very Low Capacitance ESD Protection
PESD0402-140 - Tyco Electronics
2.6 Data communication interfaces
2.6.1 Universal Serial Bus (USB)
2.6.1.1 Guidelines for USB circuit design
The USB_D+ and USB_D- lines carry the USB serial data and signaling. The lines are used in single ended mode
for full speed signaling handshake, as well as in differential mode for high speed signaling and data transfer.
USB pull-up or pull-down resistors and external series resistors on USB_D+ and USB_D- lines as required by the
USB 2.0 specification [6] are part of the module USB pin driver and do not need to be externally provided.
The additional VUSB_DET input pin can be optionally connected the USB VBUS supply (5.0 V typical) provided
by the host, to allow the complete bus detach functionality for further reduction of the current consumption: the
module disables the USB interface after a high-to-low logic level transition on the VUSB_DET input pin.
Routing the USB pins to a connector, they will be externally accessible on the application device. According to
EMC/ESD requirements of the application, an additional ESD protection device with very low capacitance should
be provided close to accessible point on the line connected to this pin, as described in Figure 48 and Table 32.
The USB interface pins ESD sensitivity rating is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-A114F).
Higher protection level could be required if the lines are externally accessible and it can be achieved by
mounting a very low capacitance (i.e. less or equal to 1 pF) ESD protection (e.g. Tyco Electronics
PESD0402-140 ESD protection device) on the lines connected to these pins, close to accessible points.
The USB_D+ and USB_D- pins of the modules can be directly connected to the USB host application processor
without additional ESD protections if they are not externally accessible or according to EMC/ESD requirements.
Figure 48: USB Interface application circuits
Table 32: Component for USB application circuits
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 95 of 141
Page 96

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
35 µm
35 µm
35 µm
35 µm
270 µm
270 µm
760 µm
L1 Copper
L3 Copper
L2 Copper
L4 Copper
FR-4 dielectric
FR-4 dielectric
FR-4 dielectric
350 µm 400 µm400 µm350 µm400 µm
35 µm
35 µm
1510 µm
L2 Copper
L1 Copper
FR-4 dielectric
740 µm 410 µm410 µm740 µm410 µm
2.6.1.2 Guidelines for USB layout design
The USB_D+ / USB_D- lines require accurate layout design to achieve reliable signaling at the high speed data
rate (up to 480 Mb/s) supported by the USB serial interface.
The characteristic impedance of the USB_D+ / USB_D- lines is specified by the Universal Serial Bus Revision 2.0
specification [6]. The most important parameter is the differential characteristic impedance applicable for the
odd-mode electromagnetic field, which should be as close as possible to 90 differential. Signal integrity may
be degraded if PCB layout is not optimal, especially when the USB signaling lines are very long.
Use the following general routing guidelines to minimize signal quality problems:
Route USB_D+ / USB_D- lines as a differential pair
Route USB_D+ / USB_D- lines as short as possible
Ensure the differential characteristic impedance (Z
Ensure the common mode characteristic impedance (Z
) is as close as possible to 90
0
) is as close as possible to 30
CM
Consider design rules for USB_D+ / USB_D- similar to RF transmission lines, being them coupled differential
micro-strip or buried stripline: avoid any stubs, abrupt change of layout, and route on clear PCB area
Figure 49 and Figure 50 provide two examples of coplanar waveguide designs with differential characteristic
impedance close to 90 and common mode characteristic impedance close to 30 . The first transmission line
can be implemented in case of 4-layer PCB stack-up herein described, the second transmission line can be
implemented in case of 2-layer PCB stack-up herein described.
Figure 49: Example of USB line design, with Z0 close to 90 and ZCM close to 30 , for the described 4-layer board layup
Figure 50: Example of USB line design, with Z0 close to 90 and ZCM close to 30 , for the described 2-layer board layup
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 96 of 141
Page 97

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TxD
Application Processor
(1.8V DTE)
RxD
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
RI
DCD
GND
TOBY-L2 series
(1.8V DCE)
16
TXD
13
DTR
17
RXD
14
RTS
15
CTS
10
DSR
11
RI
12
DCD
GND
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
5
V_INT
TxD
Application Processor
(3.0V DTE)
RxD
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
RI
DCD
GND
TOBY-L2 series
(1.8V DCE)
16
TXD
13
DTR
17
RXD
14
RTS
15
CTS
10
DSR
11
RI
12
DCD
GND
1V8
B1 A1
GND
U1
B3A3
VCCBVCCA
Unidirectional
Voltage Translator
C1
C2
3V0
DIR3
DIR2 OE
DIR1
VCC
B2 A2
B4A4
DIR4
1V8
B1 A1
GND
U2
B3A3
VCCBVCCA
Unidirectional
Voltage Translator
C3
C4
3V0
DIR1
DIR3 OE
B2 A2
B4A4
DIR4
DIR2
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3, C4
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R61A104KA01 - Murata
U1, U2
Unidirectional Voltage Translator
SN74AVC4T774 - Texas Instruments
2.6.2 Asynchronous serial interface (UART)
The UART interface is not available on MPCI-L2 series modules.
2.6.2.1 Guidelines for UART circuit design
The UART is not supported by TOBY-L2x0-00S: the pins should be not driven by any external device.
Providing the full RS-232 functionality (using the complete V.24 link)
If RS-232 compatible signal levels are needed, two different external voltage translators can be used to provide
full RS-232 (9 lines) functionality: e.g. using the Texas Instruments SN74AVC8T245PW for the translation from
1.8 V to 3.3 V, and the Maxim MAX3237E for the translation from 3.3 V to RS-232 compatible signal level.
If a 1.8 V host processor is used, for complete RS-232 functionality, the complete UART interface of the module
(DCE) must be connected to a 1.8 V application processor (DTE) as described in Figure 51.
Figure 51: UART interface application circuit with complete V.24 link in DTE/DCE serial communication (1.8V DTE)
If a 3.0 V Application Processor is used, appropriate unidirectional voltage translators must be provided using the
module V_INT output as 1.8 V supply, as described in Figure 52.
Figure 52: UART interface application circuit with complete V.24 link in DTE/DCE serial communication (3.0 V DTE)
Table 33: Component for UART application circuit with complete V.24 link in DTE/DCE serial communication (3.0 V DTE)
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 97 of 141
Page 98

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TxD
Application Processor
(1.8V DTE)
RxD
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
RI
DCD
GND
TOBY-L2 series
(1.8V DCE)
16
TXD
13
DTR
17
RXD
14
RTS
15
CTS
10
DSR
11
RI
12
DCD
GND
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
TP
TP
TP
5
V_INT
TxD
Application Processor
(3.0V DTE)
RxD
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
RI
DCD
GND
TOBY-L2 series
(1.8V DCE)
16
TXD
13
DTR
17
RXD
14
RTS
15
CTS
10
DSR
11
RI
12
DCD
GND
1V8
B1 A1
GND
U1
B3A3
VCCBVCCA
Unidirectional
Voltage Translator
C1
C2
3V0
DIR3
DIR2 OE
DIR1
VCC
B2 A2
B4A4
DIR4
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
TP
TP
TP
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R61A104KA01 - Murata
U1
Unidirectional Voltage Translator
SN74AVC4T774 - Texas Instruments
Providing the TXD, RXD, RTS and CTS lines only (not using the complete V.24 link)
If the functionality of the DSR, DCD, RI and DTR lines is not required in, or the lines are not available:
Connect the module DTR input line to GND using a 0 series resistor, since the module requires DTR active
Leave DSR, DCD and RI lines of the module unconnected and floating
If RS-232 compatible signal levels are needed, the Maxim 13234E voltage level translator can be used. This chip
translates voltage levels from 1.8 V (module side) to the RS-232 standard.
If a 1.8 V Application Processor is used, the circuit should be implemented as described in Figure 53.
Figure 53: UART interface application circuit with partial V.24 link (5-wire) in the DTE/DCE serial communication (1.8V DTE)
If a 3.0 V Application Processor is used, appropriate unidirectional voltage translators must be provided using the
module V_INT output as 1.8 V supply, as described in Figure 54.
Figure 54: UART interface application circuit with partial V.24 link (5-wire) in DTE/DCE serial communication (3.0 V DTE)
Table 34: Component for UART application circuit with partial V.24 link (5-wire) in DTE/DCE serial communication (3.0 V DTE)
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 98 of 141
Page 99

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
TxD
Application Processor
(1.8V DTE)
RxD
RTS
CTS
DTR
DSR
RI
DCD
GND
TOBY-L2 series
(1.8V DCE)
16
TXD
13
DTR
17
RXD
14
RTS
15
CTS
10
DSR
11
RI
12
DCD
GND
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
TP
0Ω
TP
TP
TP
TP
5
V_INT
TxD
Application Processor
(3.0V DTE)
RxD
DTR
DSR
RI
DCD
GND
TOBY-L2 series
(1.8V DCE)
16
TXD
13
DTR
17
RXD
10
DSR
11
RI
12
DCD
GND
1V8
B1 A1
GND
U1
VCCBVCCA
Unidirectional
Voltage Translator
C1
C2
3V0
DIR1
DIR2 OE
VCC
B2 A2
RTS
CTS
14
RTS
15
CTS
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
TP
0Ω
TP
TP
TP
TP
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R61A104KA01 - Murata
U1
Unidirectional Voltage Translator
SN74AVC2T245 - Texas Instruments
Providing the TXD and RXD lines only (not using the complete V24 link)
If the functionality of the CTS, RTS, DSR, DCD, RI and DTR lines is not required in the application, or the lines
are not available, the circuit with a 1.8 V Application Processor should be implemented as described in Figure 55:
Connect the module RTS input line to GND or to the CTS output line of the module: since the module
requires RTS active (low electrical level) if HW flow-control is enabled (AT&K3, that is the default setting),
the pin can be connected using a 0 series resistor to GND or to the active-module CTS (low electrical level)
when the module is in active-mode, the UART interface is enabled and the HW flow-control is enabled
Connect the module DTR input line to GND using a 0 series resistor, as the module requires DTR active
Leave DSR, DCD and RI lines of the module unconnected and floating
Figure 55: UART interface application circuit with partial V.24 link (3-wire) in the DTE/DCE serial communication (1.8V DTE)
If a 3.0 V Application Processor is used, appropriate unidirectional voltage translators must be provided using the
module V_INT output as 1.8 V supply, as described in Figure 56.
Figure 56: UART interface application circuit with partial V.24 link (3-wire) in DTE/DCE serial communication (3.0 V DTE)
Table 35: Component for UART application circuit with partial V.24 link (3-wire) in DTE/DCE serial communication (3.0 V DTE)
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 99 of 141
Page 100

TOBY-L2 and MPCI-L2 series - System Integration Manual
Additional considerations
Do not apply voltage to any UART interface pin before the switch-on of the UART supply source (V_INT),
to avoid latch-up of circuits and allow a proper boot of the module. If the external signals connected to
the cellular module cannot be tri-stated or set low, insert a multi channel digital switch (e.g. TI
SN74CB3Q16244, TS5A3159, or TS5A63157) between the two-circuit connections and set to high
impedance before V_INT switch-on.
ESD sensitivity rating of UART interface pins is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-A114).
Higher protection level could be required if the lines are externally accessible and it can be achieved by
mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) close to accessible points.
If the UART interface pins are not used, they can be left unconnected on the application board, but it is
recommended providing accessible test points directly connected to all the UART pins (TXD, RXD, RTS,
CTS, DTR, DSR, DCD, RI) for diagnostic purpose, in particular providing a 0 series jumper on each line
to detach each UART pin of the module from the DTE application processor.
2.6.2.2 Guidelines for UART layout design
The UART serial interface requires the same consideration regarding electro-magnetic interference as any other
digital interface. Keep the traces short and avoid coupling with RF line or sensitive analog inputs, since the
signals can cause the radiation of some harmonics of the digital data frequency.
UBX-13004618 - R04 Advance Information Design-in
Page 100 of 141
 Loading...
Loading...