Ublox SARA-N210, SARA-N2 Series, SARA-N200 SARA-N201, SARA-N211, SARA-N280 System Integration Manual
Page 1

Abstract
This document describes the features and the system integration of the SARA-N2 series NB-IoT
modules. These modules are a complete and cost efficient solution offering single-band and
dual-band data transmission for the Internet of Things technology in the compact SARA form factor.
www.u-blox.com
UBX-17005143 - R06
SARA-N2 series
Power-optimized NB-IoT (LTE Cat NB1) modules
System Integration Manual
Page 2

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Title
SARA-N2 series
Subtitle
Power-optimized NB-IoT (LTE Cat NB1) modules
Document type
System Integration Manual
Document number
UBX-17005143
Revision and date
R06
30-Nov-2018
Disclosure Restriction
Product status
Corresponding content status
Functional Sample
Draft
For functional testing. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
In Development /
Prototype
Objective Specification
Target values. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
Engineering Sample
Advance Information
Data based on early testing. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
Initial Production
Early Production Information
Data from product verification. Revised and supplementary data may be published later.
Mass Production /
End of Life
Production Information
Document contains the final product specification.
Product name
Type number
Modem version
Application version
PCN reference
Product status
SARA-N200
SARA-N200-02B-00
06.57
A07.03
UBX-18005015
End of Life
SARA-N200-02B-01
06.57
A09.06
UBX-18048558
Mass Production
SARA-N201
SARA-N201-02B-00
06.57
A07.03
UBX-18005015
End of Life
SARA-N201-02B-01
06.57
A08.05
UBX-18023224
Mass Production
SARA-N210
SARA-N210-02B-00
06.57
A07.03
UBX-18005015
End of Life
SARA-N210-02B-01
06.57
A09.06
UBX-18048558
Mass Production
SARA-N211
SARA-N211-02X-00
06.57
A07.03
UBX-18005015
End of Life
SARA-N211-02X-01
06.57
A09.06
UBX-18048558
Mass Production
SARA-N280
SARA-N280-02B-00
06.57
A07.03
UBX-18005015
End of Life
SARA-N280-02B-01
06.57
A09.06
UBX-18048558
Mass Production
u-blox or third parties may hold intellectual property rights in the products, names, logos and designs included in this document.
Copying, reproduction, modification or disclosure to third parties of this document or any part thereof is only permitted with the
express written permission of u-blox.
The information contained herein is provided “as is” and u-blox assumes no liability for its use. No warranty, either express or
implied, is given, including but not limited to, with respect to the accuracy, correctness, reliability and fitness for a particular
purpose of the information. This document may be revised by u-blox at any time without notice. For the most recent documents,
visit www.u-blox.com.
Copyright © u-blox AG.
Document Information
This document applies to the following products:
UBX-17005143 - R06 Page 2 of 82
Page 3

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Contents
Document Information ................................................................................................................................ 2
Contents .......................................................................................................................................................... 3
1 System description ............................................................................................................................... 6
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................................ 6
1.2 Architecture ................................................................................................................................................. 7
1.3 Pin-out ........................................................................................................................................................... 8
1.4 Operating modes ....................................................................................................................................... 10
1.5 Supply interfaces ....................................................................................................................................... 11
1.5.1 Module supply input (VCC) .............................................................................................................. 11
1.5.2 Generic digital interfaces supply output (V_INT) ....................................................................... 13
1.6 System function interfaces .................................................................................................................... 14
1.6.1 Module power-on .............................................................................................................................. 14
1.6.2 Module power-off .............................................................................................................................. 15
1.6.3 Module reset ...................................................................................................................................... 15
1.7 Antenna interface ..................................................................................................................................... 16
1.7.1 Antenna RF interface (ANT) ........................................................................................................... 16
1.7.2 Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET)...................................................................................... 17
1.8 SIM interface ............................................................................................................................................... 17
1.9 Serial interfaces ......................................................................................................................................... 17
1.9.1 Asynchronous serial interface (UART) .......................................................................................... 17
1.9.2 Secondary asynchronous serial interface (Secondary UART)................................................. 19
1.9.3 DDC (I2C) interface ............................................................................................................................ 19
1.10 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) .................................................................................................. 20
1.11 Reserved pins (RSVD) .............................................................................................................................. 20
2 Design-in ................................................................................................................................................. 21
2.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................................21
2.2 Supply interfaces ...................................................................................................................................... 22
2.2.1 Module supply (VCC) ........................................................................................................................ 22
2.2.2 Interface supply (V_INT) .................................................................................................................. 31
2.3 System functions interfaces .................................................................................................................. 32
2.3.1 Module reset (RESET_N) ................................................................................................................. 32
2.4 Antenna interface ..................................................................................................................................... 33
2.4.1 Antenna RF interface (ANT) ........................................................................................................... 33
2.4.2 Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET)..................................................................................... 40
UBX-17005143 - R06 Page 3 of 82
Page 4

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
2.5 SIM interface .............................................................................................................................................. 43
2.6 Serial interfaces ........................................................................................................................................ 46
2.6.1 Asynchronous serial interface (UART) ......................................................................................... 46
2.6.2 Secondary asynchronous serial interface (Secondary UART)................................................. 48
2.6.3 DDC (I2C) interface ............................................................................................................................ 49
2.7 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) .................................................................................................. 49
2.8 Reserved pins (RSVD) .............................................................................................................................. 49
2.9 Module placement ....................................................................................................................................50
2.10 Module footprint and paste mask ......................................................................................................... 51
2.11 SARA-N211 integration in devices intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres ....... 52
2.11.1 General guidelines ............................................................................................................................ 52
2.11.2 Guidelines for VCC supply circuit design ..................................................................................... 54
2.11.3 Guidelines for antenna RF interface design ................................................................................ 55
2.12 Schematic for SARA-N2 series module integration .......................................................................... 56
2.13 Design-in checklist .................................................................................................................................... 57
2.13.1 Schematic checklist ......................................................................................................................... 57
2.13.2 Layout checklist ................................................................................................................................ 57
2.13.3 Antenna checklist ............................................................................................................................. 58
3 Handling and soldering ..................................................................................................................... 59
3.1 Packaging, shipping, storage and moisture preconditioning .......................................................... 59
3.2 Handling ...................................................................................................................................................... 59
3.3 Soldering ..................................................................................................................................................... 60
3.3.1 Soldering paste ................................................................................................................................. 60
3.3.2 Reflow soldering ................................................................................................................................ 60
3.3.3 Optical inspection ............................................................................................................................. 61
3.3.4 Cleaning .............................................................................................................................................. 61
3.3.5 Repeated reflow soldering .............................................................................................................. 62
3.3.6 Wave soldering .................................................................................................................................. 62
3.3.7 Hand soldering .................................................................................................................................. 62
3.3.8 Rework ................................................................................................................................................ 62
3.3.9 Conformal coating ............................................................................................................................ 62
3.3.10 Casting ................................................................................................................................................ 63
3.3.11 Grounding metal covers .................................................................................................................. 63
3.3.12 Use of ultrasonic processes ........................................................................................................... 63
4 Approvals ............................................................................................................................................... 64
4.1 Approvals overview ................................................................................................................................... 64
UBX-17005143 - R06 Page 4 of 82
Page 5

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
4.2 European Conformance CE mark .......................................................................................................... 65
4.3 ATEX conformance ................................................................................................................................... 66
4.4 Chinese conformance .............................................................................................................................. 67
4.5 Taiwanese conformance ......................................................................................................................... 67
5 Product testing ................................................................................................................................... 68
5.1 u-blox in-series production test ............................................................................................................. 68
5.2 Test parameters for OEM manufacturer ............................................................................................. 68
5.2.1 “Go/No go” tests for integrated devices ...................................................................................... 69
5.2.2 RF functional tests ........................................................................................................................... 69
Appendix ........................................................................................................................................................ 71
A Migration between SARA modules ................................................................................................ 71
A.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................................... 71
A.2 Pin-out comparison between SARA-G3, SARA-U2, SARA-R4 and SARA-N2 modules .............. 73
A.3 Schematic for SARA-G3 /-U2 /-R4 /-N2 modules integration .......................................................... 78
B Glossary .................................................................................................................................................. 79
Related documents .................................................................................................................................... 81
Revision history ........................................................................................................................................... 81
Contact .......................................................................................................................................................... 82
UBX-17005143 - R06 Page 5 of 82
Page 6

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Model
Region
Bands
Positioning
Interfaces
Features
Grade
3GPP Release Baseline 3GPP Category NB-IoT bands GNSS via modem AssistNow Software CellLocate® UART
USB 2.0 SPI DDC (I
2
C)
GPIO Antenna supervisor Power Save Mode eDRX
Deep sleep mode
Embedded UDP stack CoAP FW update over AT
(FOAT)
FW update over the air (FOTA)
Standard Professional Automotive
SARA-N200
Europe
APAC
13
NB1 8 2 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
SARA-N201
APAC
13
NB1 5 2 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● SARA-N210
Europe
13
NB1
20 2 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
SARA-N211
Europe
13
NB1
8,20 2 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
SARA-N280
South America
APAC
13
NB1
28 2 ●
● ● ● ● ● ●
●
●
1 System description
1.1 Overview
SARA-N2 series modules provide a Narrow Band Internet of Things (NB-IoT) solution in the miniature
SARA LGA form factor (26.0 x 16.0 mm, 96-pin). The modules offer IoT data communication over an
extended operating temperature range of –40 to +85 °C, with extremely low power consumption.
The SARA-N2 series includes four variants that support single-band communication over the LTE
bands 5, 8, 20 and 28, plus a dual-band variant designed to operate in the frequency range of the LTE
bands 8 and 20.
SARA-N2 series modules are ideally suited to battery-powered IoT applications characterized by
occasional communications of small amounts of data.
SARA-N2 series modules are the optimal choice for IoT devices designed to operate in locations with
very limited coverage and requiring low energy consumption to permit a very long operating life with
the primary batteries. Examples of applications include and are not limited to: smart grids, smart
metering, telematics, street lighting, environmental monitoring and control, security and asset
tracking.
Table 1 describes a summary of interfaces and features provided by SARA-N2 series modules.
Table 1: SARA-N2 series characteristics summary
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 6 of 82
Page 7

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Item
SARA-N200
SARA-N201
SARA-N210
SARA-N211
SARA-N280
NB-IoT protocol stack
3GPP Release 13
3GPP Release 13
3GPP Release 13
3GPP Release 13
3GPP Release 13
Operating band
Band 8 (900 MHz)
Band 5 (850 MHz)
Band 20 (800 MHz)
Band 8 (900 MHz),
Band 20 (800 MHz)
Band 28 (700 MHz)
Deployment mode
In-Band
Guard-Band
Standalone
In-Band
Guard-Band
Standalone
In-Band
Guard-Band
Standalone
In-Band
Guard-Band
Standalone
In-Band
Guard-Band
Standalone
Power Class
Class 3 (23 dBm)
Class 3 (23 dBm)
Class 3 (23 dBm)
Class 3 (23 dBm)
Class 3 (23 dBm)
Data rate
LTE category NB1:
Up to 31.25 kb/s UL
Up to 27.2 kb/s DL
LTE category NB1:
Up to 31.25 kb/s UL
Up to 27.2 kb/s DL
LTE category NB1:
Up to 31.25 kb/s UL
Up to 27.2 kb/s DL
LTE category NB1:
Up to 31.25 kb/s UL
Up to 27.2 kb/s DL
LTE category NB1:
Up to 31.25 kb/s UL
Up to 27.2 kb/s DL
Memory
V_INT
38.4 MHz
32.768 kHz
RF
Transceiver
Power
Management
Baseband
ANT
SAW
Filter
Switch
PA
VCC (Supply)
DDC (I2C)
UART
SIM
Secondary UART
RESET_N
GPIO
Antenna detection
Table 2 summarizes cellular radio access technology characteristics of SARA-N2 series modules.
Table 2: SARA-N2 series NB-IoT characteristics summary
1.2 Architecture
Figure 1 summarizes the architecture of SARA-N2 series modules, describing the internal blocks of
the modules, consisting of the RF, Baseband and Power Management main sections, and the available
interfaces.
Figure 1: SARA-N2 series modules block diagram
The RF section is composed of the following main elements:
LTE Power Amplifier, which amplifies the signals modulated by the RF transceiver
RF switches, which connect the antenna input/output pin (ANT) of the module to the suitable
RX/TX path
RX low-loss SAW filters
38.4 MHz crystal oscillator for the clock reference in active-mode and connected-mode
The Baseband and Power Management section is composed of the following main elements:
Baseband processor
Flash memory
Voltage regulators to derive all the system supply voltages from the module supply VCC
Circuit for the RTC clock reference in low power deep-sleep
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 7 of 82
Page 8

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Function
Pin Name
Pin No
I/O
Description
Remarks
Power
VCC
51, 52, 53
I
Module supply
input
All VCC pins must be connected to external supply.
VCC supply circuit affects the RF performance and
compliance of the device integrating the module with
applicable required certification schemes.
See section 1.5.1 for description and requirements.
See section 2.2.1 for external circuit design-in.
GND
1, 3, 5, 14, 20-22,
30, 32, 43, 50, 54,
55, 57-61, 63-96
N/A
Ground
GND pins are internally connected to each other.
External ground connection affects the RF and thermal
performance of the device.
V_INT
4
O
Generic Digital
Interfaces supply
output
V_INT = 1.8 V (typical) supply output, generated by
internal linear LDO regulator when the radio is on.
Provide a test point on this pin for diagnostic purpose.
See section 1.5.2 for functional description.
See section 2.2.2 for external circuit design-in.
System
RESET_N
18
I
External reset
input
Internal 78 k pull-up to VCC.
Provide a test point on this pin for diagnostic purpose.
See section 1.6.3 for functional description.
See section 2.3.1 for external circuit design-in.
Antenna
ANT
56
I/O
RF input/output
for antenna
50 nominal characteristic impedance.
Antenna circuit affects the RF performance and
compliance of the device integrating the module with
applicable required certification schemes.
See section 1.7 for description and requirements.
See section 2.4 for external circuit design-in.
ANT_DET
62
I
Input for antenna
detection
ANT_DET not supported by "02" product versions.
ADC input for antenna detection function.
See section 1.7.2 for functional description.
See section 2.4.2 for external circuit design-in.
SIM
VSIM
41 O SIM supply output
VSIM = 1.80 V (typical).
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
SIM_IO
39
I/O
SIM data
Internal 4.7 k pull-up to VSIM.
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
SIM_CLK
38 O SIM clock
Clock for external SIM, operating at VSIM voltage level.
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
SIM_RST
40 O SIM reset
Reset for external SIM, operating at VSIM voltage level.
See section 1.8 for functional description.
See section 2.5 for external circuit design-in.
1.3 Pin-out
Table 3 lists the pin-out of the SARA-N2 series modules, with pins grouped by function.
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 8 of 82
Page 9

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Function
Pin Name
Pin No
I/O
Description
Remarks
UART
RXD
13 O UART data output
Circuit 104 (RXD) in ITU-T V.24, for AT command and
data, FOAT and FW upgrade via dedicated tool.
It operates at VCC voltage level.
Provide a test point on this pin for diagnostic purpose.
See section 1.9.1 for functional description.
See section 2.6.1 for external circuit design-in.
TXD
12 I UART data input
Circuit 103 (TXD) in ITU-T V.24, for AT command and data,
FOAT and FW upgrade via dedicated tool.
No internal pull-up / pull-down.
Provide a test point on this pin for diagnostic purpose.
See section 1.9.1 for functional description.
See section 2.6.1 for external circuit design-in.
CTS
11
O
UART clear to send
output
HW flow control output signal (Circuit 106 in ITU-T V.24)
is not supported by "02" product versions.
The pin can be configured as described in section 1.10.
The pin operates at VCC voltage level.
See section 1.9.1 for functional description.
See section 2.6.1 for external circuit design-in.
RTS
10
I
UART ready to
send input
HW flow control input signal (Circuit 105 in ITU-T V.24) is
not supported by "02" product versions.
Internal active pull-up to VCC.
See section 1.9.1 for functional description.
See section 2.6.1 for external circuit design-in.
DDC
SCL
27 O I2C bus clock line
I2C interface is not supported by "02" product versions.
1.8 V open drain, without internal pull-up.
The pin operates at V_INT voltage level.
See section 1.9.3 for functional description.
See section 2.6.3 for external circuit design-in.
SDA
26
I/O
I2C bus data line
I2C interface is not supported by "02" product versions.
1.8 V open drain, without internal pull-up.
The pin operates at V_INT voltage level.
See section 1.9.3 for functional description.
See section 2.6.3 for external circuit design-in.
GPIO
GPIO1
16
I/O
GPIO
1.8 V secondary UART data output, for diagnostic
purpose.
The pin operates at V_INT voltage level.
Provide a test point on this pin for diagnostic purpose.
See sections 1.9.2 and 1.10 for functional description.
See sections 2.6.2 and 2.7 for external circuit design-in.
GPIO2
24
I/O
GPIO
GPIO2 function is not supported by "02" product versions.
The pin operates at V_INT voltage level.
See section 1.10 for functional description.
See section 2.7 for external circuit design-in.
Reserved
RSVD
33
N/A
RESERVED pin
This pin can be connected to GND.
See sections 1.11 and 2.8.
RSVD
2, 6-9, 15, 17,19, 23,
25, 28, 29, 31, 3437, 42, 44-49
N/A
RESERVED pin
Leave unconnected.
See sections 1.11 and 2.8.
Table 3: SARA-N2 series modules pin definition, grouped by function
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 9 of 82
Page 10

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
General Status
Operating Mode
Definition
Power-down
Not-Powered Mode
VCC supply not present or below operating range: module is switched off.
Normal operation
Deep-sleep mode
Module processor runs with internal 32 kHz reference; lowest current consumption
Active-Mode
Module processor runs with internal 38.4 MHz reference.
Connected-Mode
Module processor runs with internal 38.4 MHz reference; data
transmission/reception or signaling activity with the network enabled.
Mode
Description
Transition between operating modes
Not-Powered
Module is switched off.
Application interfaces are not accessible.
When VCC supply is removed, the module enters not-powered
mode.
When in not-powered mode, the modules can be switched on
applying VCC supply (see section 2.2.1) so that the module
switches from not-powered to active-mode.
Active
Module is switched on with application
interfaces enabled or not suspended: the
module is ready to communicate with an
external device by means of the application
interfaces.
The module enters active mode from not-powered mode by
applying VCC supply (see section 2.2.1).
Then, the module automatically switches from active to
deep-sleep mode whenever possible or switches to connected
mode in case there is any data to transmit or receive.
Deep-sleep
Only the internal 32 kHz reference is active;
the RF section is completely disabled. This is
the lowest current consumption mode.
The UART interface is still completely
functional and the module can accept and
respond to any AT command.
All the other interfaces are disabled. If a
trace is active on the secondary UART, it is
automatically suspended when the module
enters this mode.
In this mode the module is not able to
receive any down-link message or data
from the network. To do so, the module
must be in the active or connected mode.
The module automatically enters deepsleep mode whenever possible after a
network dependent time of inactivity.
The module automatically switches from active mode to deepsleep mode whenever possible.
The module wakes up from deep-sleep to active mode in the
following events:
Automatic periodic monitoring of the paging channel for
the paging block reception and periodic tracking area
update (TAU) according to network conditions
A send-data request is issued to the module using the
related commands (for more details, see the SARA-N2
series AT Commands Manual [3] and the u-blox NB-IoT
Application Development Guide [4]).
Connected
The module is transmitting/receiving data
to/from the network.
Both internal references at 32 kHz and
38.4 MHz are active.
When a data connection is initiated, the module enters
connected mode from active mode.
Connected-mode is suspended if Tx/Rx data is not in progress.
In such cases the module automatically switches from
connected to active mode and then the module automatically
switches to deep sleep mode whenever possible. Vice-versa, the
module wakes up re-entering connected mode upon resume of
RF Tx/Rx activity.
When a data connection is terminated, the module returns to
the active-mode and then the module automatically switches to
deep sleep mode whenever possible.
1.4 Operating modes
SARA-N2 series modules have several operating modes. The operating modes defined in Table 4 and
described in detail in Table 5 provide general guidelines for operation.
Figure 2 describes the transition between the different operating modes.
Table 4: Module operating modes definition
Table 5: Module operating modes description
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 10 of 82
Page 11

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Switch ON:
• Apply VCC
If there is no activity for
a defined time interval
• Network paging
• New up-link message request
from the Application Processor
Up-linlk transmission, reception
of network signalling indications
or downlink data reception
No RF Tx/Rx in progress
Not
powered
ActiveConnected Deep-sleep
Switch OFF:
• Remove VCC
Figure 2: Operating modes transitions
1.5 Supply interfaces
1.5.1 Module supply input (VCC)
The modules must be supplied via all the three VCC pins that represent the module power supply
input.
The VCC pins are internally connected to the RF power amplifier and to the integrated Power
Management Unit: all supply voltages needed by the module are generated from the VCC supply by
integrated voltage regulators, including V_INT (digital interfaces supply) and VSIM (SIM card supply).
During operation, the current drawn by the SARA-N2 series modules through the VCC pins can vary
by several orders of magnitude. This ranges from the high peak of current consumption during data
transmission at maximum power level in connected mode, to the low current consumption during
deep-sleep mode (as described in section 1.5.1.2).
1.5.1.1 VCC supply requirements
Table 6 summarizes the requirements for the VCC module supply. See section 2.2.1 for all the
suggestions to properly design a VCC supply circuit compliant to the requirements listed in Table 6.
⚠ VCC supply circuit design may affect the RF compliance of the device integrating SARA-N2 series
modules with applicable required certification schemes. Compliance is not guaranteed if the VCC
requirements summarized in the Table 6 are not fulfilled.
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 11 of 82
Page 12

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Item
Requirement
Remark
VCC nominal voltage
Within VCC normal operating range:
3.1 V min. / 4.0 V max
The module cannot be switched on if VCC voltage
value is below the normal operating range minimum
limit.
Ensure that the input voltage at VCC pins is above
the minimum limit of the normal operating range
for at least more than 3 s after the module
switch-on.
VCC voltage during
normal operation
Within VCC extended operating range:
2.75 V min. / 4.2 V max
The module may switch off when VCC voltage drops
below the extended operating range minimum limit.
Operation above extended operating range limit is
not recommended and may affect device reliability.
When operating below the normal operating range
minimum limit, the internal PA may not be able to
transmit at the network-required power level.
VCC average current
Support with margin the highest averaged VCC
current consumption value in connected mode
specified in SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1].
The maximum average current consumption can be
greater than the specified value according to the
actual antenna mismatching, temperature and
supply voltage.
VCC voltage ripple
Noise in the supply has to be minimized
High supply voltage ripple values during RF
transmissions in connected-mode directly affect
the RF compliance with applicable certification
schemes.
Table 6: Summary of VCC supply requirements
☞ For the additional specific requirements applicable to the integration of SARA-N211 modules in
devices intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres, see section 2.11.
1.5.1.2 VCC current consumption profile
Figure 3 shows an example of the module VCC current consumption profile starting from the switch-
on event, followed by different phases and operating modes:
Network registration and context activation procedure
Transmission of an up-link datagram
RRC connection release and related signaling operations
Cyclic paging reception
Deep sleep mode
Timings in the figure are purely indicative since these may significantly change depending on the
network signaling activity. The current consumption peaks occur when the module is in the connected
(transmitting) mode and the value of these peaks is strictly dependent on the transmitted power,
which is regulated by the network. See the electrical specification section in the SARA-N2 series Data
Sheet [1] for more details about the current consumption values in the different modes and the
influence of the transmitting power level.
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 12 of 82
Page 13

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Current [mA]
20
0
150
100
50
0
5 10 15 20 25 30 4035
Time [s]
Registration and
context activation
RRC connection release
(signaling operations)
Up-link
data
45 50 6055
Cyclic paging reception Deep Sleep
25
0
65 70 8075 85 90 100950
Baseband
Processor
51
VCC
52
VCC
53
VCC
4
V_INT
LDO
Digital I/O
Interfaces
Power
Management
SARA-N2 series
A proper power supply circuit for SARA-N2 series modules must be able to withstand the current
values present during the data transmission at maximum power, even though NB-IoT systems should
be designed to keep the module in deep-sleep mode for most of the time, with an extremely low
current consumption in the range of few microamps.
Figure 3: Example of module current consumption from the switch-on event up to deep-sleep mode
1.5.2 Generic digital interfaces supply output (V_INT)
The same 1.8 V voltage domain used internally to supply the generic digital interfaces (GDI) of
SARA-N2 series modules is also available on the V_INT supply output pin, as described in Figure 4.
The internal regulator that generates the V_INT supply is a low drop out (LDO) converter that is
directly supplied from the VCC main supply input of the module.
The V_INT supply output provides internal short circuit protection to limit start-up current and
protect the load to short circuits.
The V_INT voltage regulator output is disabled (i.e. 0 V) when the module is switched off, while it can
be used to monitor the operating mode when the module is switched on:
When the radio is off, the voltage level is kept low (i.e. 0 V)
When the radio is on, the voltage level is maintained high (i.e. 1.8 V)
☞ Provide a test point connected to the V_INT pin for diagnostic purpose.
Figure 4: SARA-N2 series interfaces supply output (V_INT) simplified block diagram
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 13 of 82
Page 14

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
VCC
RESET_N
V_INT
HIGH when radio is ON
LOW when radio is OFF
RXD
System State
OFF
ON
0 s
~3.5 s
Module is
operational
Start-up
event
Greeting te xt
1.6 System function interfaces
1.6.1 Module power-on
1.6.1.1 Switch-on events
When the SARA-N2 series modules are in the not-powered mode (i.e. switched off with the VCC
module supply not applied), they can be switched on by:
Rising edge on the VCC supply input to a valid voltage value for module supply, starting from a
voltage value lower than 1.8 V, so that the module switches on applying a proper VCC supply within
the normal operating range. (See SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1].)
Alternately, the RESET_N pin can be held low during the VCC rising edge, so that the module
switches on by releasing the RESET_N pin when the VCC voltage stabilizes at its nominal value
within the normal range.
1.6.1.2 Switch-on sequence from not-powered mode
Figure 5 shows the modules power-on sequence from the not-powered mode, describing the following
phases:
The external supply is applied to the VCC module supply inputs, representing the start-up event.
The RESET_N line rises suddenly to high logic level due to internal pull-up to VCC.
The V_INT generic digital interfaces supply output is enabled by the integrated power
management unit.
The RXD UART data output pin also rises to the high logic level, at VCC voltage value
A greeting message is sent on the RXD pin (for more details see SARA-N2 series AT Commands
Manual [3]). From now on the module is fully operational and the UART interface is functional
Figure 5: SARA-N2 series power-on sequence from not-powered mode
☞ No voltage driven by an external application should be applied to the UART interface of the module
before applying the VCC supply, to avoid latch-up of circuits and allow a proper boot of the module.
☞ No voltage driven by an external application should be applied to any generic digital interface of
the module (GPIOs, I2C interface) before the switch-on of the generic digital interface supply
source of the module (V_INT), to avoid latch-up of circuits and allow a proper boot of the module.
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 14 of 82
Page 15
SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Baseband Processor
18
RESET_N
SARA-N2 series
VCC
Reset
~78 k
1.6.2 Module power-off
The SARA-N2 series modules can be switched off by:
Removal of the VCC supply supply; the voltage drops below the operating range minimum limit
☞ It is highly recommended to avoid an abrupt removal of the VCC supply during module normal
operation: the VCC supply should be removed only when the V_INT supply output is switched off
by the module.
1.6.3 Module reset
SARA-N2 series modules can be properly reset (rebooted) by:
AT command (see the SARA-N2 series AT Commands Manual [3] for more details).
This command causes an “internal” or “software” reset of the module, which is an asynchronous reset
of the module baseband processor. The current parameter settings are saved in the module’s non-
volatile memory and a proper network detach is performed: this is the proper way to reset the
modules.
An abrupt hardware reset occurs on SARA-N2 series modules when a low level is applied on the
RESET_N input pin for a specific time period. In this case, the current parameter settings are not
saved in the module’s non-volatile memory and a proper network detach is not performed.
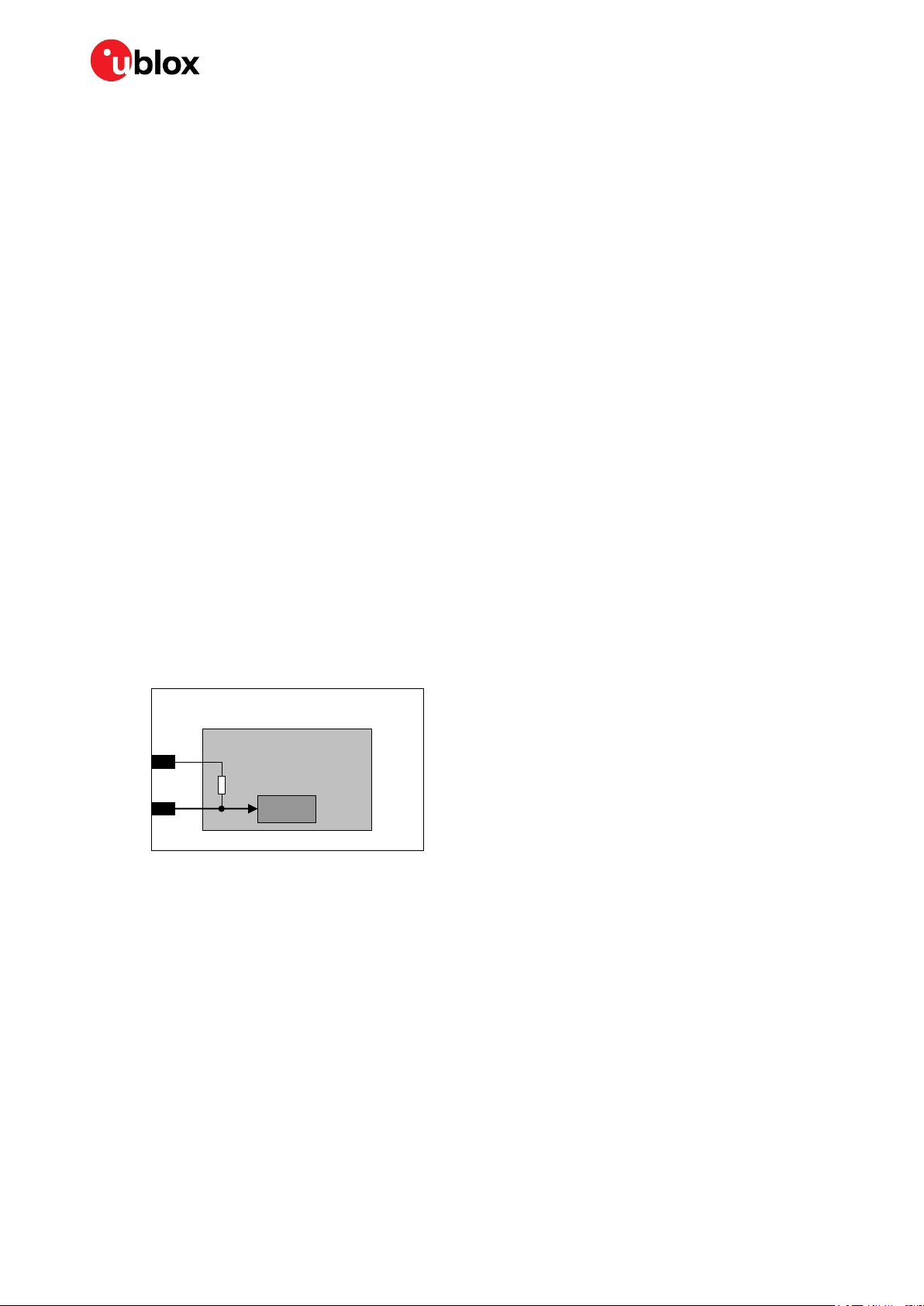
As described in Figure 6, the RESET_N input pin is equipped with an internal active pull-up to the VCC
supply.
Figure 6: SARA-N2 series RESET_N input equivalent circuit description
☞ For more electrical characteristics details see the SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1].
☞ It is highly recommended to avoid an abrupt hardware reset of the module by forcing a low level on
the RESET_N input pin during module normal operation: the RESET_N line should be set low only
if reset via AT command fails if the module does not provide a reply to a specific AT command after
a time period longer than the one defined in the SARA-N2 series AT Commands Manual [3].
☞ Provide a test point connected to the RESET_N pin for diagnostic purpose.
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 15 of 82
Page 16
SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Item
Requirements
Remarks
Impedance
50 nominal characteristic impedance
The nominal characteristic impedance of the
antenna RF connection must match the ANT pin
50 impedance.
Frequency range
See the SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1]
The required frequency range of the antenna
depends on the operating bands supported by the
cellular module.
Return Loss
S11 < -10 dB (VSWR < 2:1) recommended
S11 < -6 dB (VSWR < 3:1) acceptable
The Return loss or the S11, as the VSWR, refers to the
amount of reflected power, measuring how well the
RF antenna connection matches the 50
impedance.
The impedance of the antenna RF termination must
match as much as possible the 50 impedance of
the ANT pin over the operating frequency range,
reducing as much as possible the amount of
reflected power.
Efficiency
> -1.5 dB ( > 70%) recommended
> -3.0 dB ( > 50%) acceptable
The radiation efficiency is the ratio of the radiated
power to the power delivered to antenna input: the
efficiency is a measure of how well an antenna
receives or transmits.
The efficiency needs to be enough high over the
operating frequency range to comply with the OverThe-Air radiated performance requirements, as
Total Radiated Power and Total Isotropic Sensitivity,
specified by certification schemes
Maximum Gain
See section 4.2 for maximum gain limits
The power gain of an antenna is the radiation
efficiency multiplied by the directivity: the maximum
gain describes how much power is transmitted in the
direction of peak radiation to that of an isotropic
source.
The maximum gain of the antenna connected to
ANT pin must not exceed the values stated in
section 4.2 to comply with regulatory agencies
radiation exposure limits.
Input power
> 0.5 W peak
The antenna connected to ANT pin must support the
maximum power transmitted by the modules.
1.7 Antenna interface
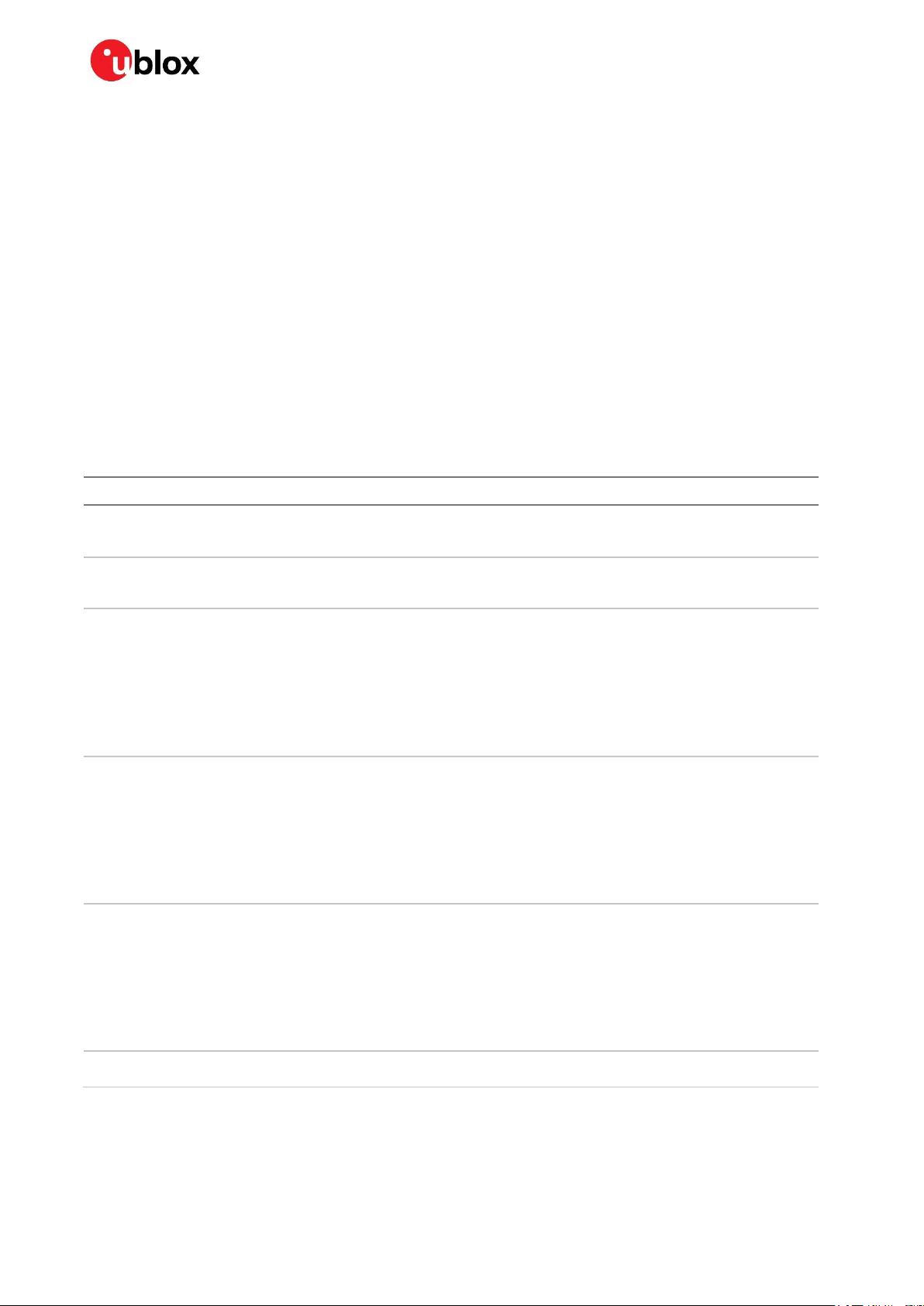
1.7.1 Antenna RF interface (ANT)
The ANT pin of SARA-N2 series modules represents the RF input/output for the cellular RF signals
reception and transmission. The ANT pin has a nominal characteristic impedance of 50 and must
be connected to the antenna through a 50 transmission line for proper RF signals reception and
transmission.
1.7.1.1 Antenna RF interface requirements
Table 7 summarizes the requirements for the antenna RF interface (ANT). See section 2.4.1 for
suggestions to properly design an antenna circuit compliant to these requirements.
⚠ The antenna circuit affects the RF compliance of the device integrating SARA-N2 series module
with applicable required certification schemes.
Table 7: Summary of antenna RF interface (ANT) requirements
☞ For the additional specific requirements applicable to the integration of SARA-N211 modules in
devices intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres, see section 2.11.
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 16 of 82
Page 17

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
1
1
1.7.2 Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET)
☞ Antenna detection interface is not supported in the "02" version of the product.
The ANT_DET pin is an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) input used to sense the antenna presence
evaluating the resistance from the ANT pin to GND by means of an external antenna detection circuit
implemented on the application board. This optional functionality can be managed by dedicated AT
command (for more details see the SARA-N2 series AT Commands Manual [3]).
1.8 SIM interface
SARA-N2 series modules provide a high-speed SIM/ME interface working at 1.8 V, which is available
to connect an external SIM / UICC.
The VSIM supply output provides internal short circuit protection to limit start-up current and protect
the external SIM / UICC to short circuits.
1.9 Serial interfaces
SARA-N2 series modules provide the following serial communication interfaces:
UART interface: 5-wire unbalanced asynchronous serial interface, operating at VCC voltage level
(~3.6 V), supporting (see 1.9.1):
o AT command
o FW upgrades by means of the FOAT feature
o FW upgrades by means of the dedicated tool
Auxiliary UART interface: 2-wire unbalanced asynchronous serial interface, operating at V_INT
level (1.8 V), supporting (see 1.9.2):
o Trace log capture (diagnostic purpose)
DDC interface
1.9.3):
o Communication with external chips and sensors
o Communication with external u-blox GNSS chips / modules
: I2C-bus compatible interface, operating at V_INT level (1.8 V), supporting (see
1.9.1 Asynchronous serial interface (UART)
1.9.1.1 UART features
The UART interface is a 5-wire unbalanced asynchronous serial interface, supporting:
AT command
FW upgrades by means of the FOAT feature
FW upgrades by means of the dedicated tool
The main characteristics of the interface are the following:
Serial port with RS-232 functionality working at the VCC voltage domain (0 V for low data bit or
ON state and ~3.6 V, i.e. VCC, for high data bit or OFF state)
Data lines (RXD as module data output, TXD as module data input)
Hardware flow control lines (CTS as module output, RTS as module input)
Default baud rate: 9600 b/s (4800, 57600 and 115200 b/s baud rates are also supported)
Fixed frame format: 8N1 (8 data bits, No parity, 1 stop bit)
Not supported on “02” product version
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 17 of 82
Page 18

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
Start of 1-Byte
transfer
Start Bit
(Always 0)
Possible Start of
next transfer
Stop Bit
(Always 1)
t
bit
= 1/(Baudrate)
Normal Transfer, 8N1
The CTS output line can be configured as RING indicator, to signal an incoming message received by
the module or an URC event, or as Network status indicator (for more details see section 1.10 and the
SARA-N2 series AT Commands Manual [3], +URING, +UGPIOC AT commands).
☞ Hardware flow control lines CTS and RTS are not supported by "02" product versions.
The UART interface provides RS-232 functionality conforming to the ITU-T V.24 Recommendation
(more details available in ITU Recommendation [5]): SARA-N2 series modules are designed to operate
as a cellular modem, which represents the Data Circuit-terminating Equipment (DCE) according to
ITU-T V.24 Recommendation [5]. The application processor connected to the module through the
UART interface represents the Data Terminal Equipment (DTE).
☞ The signal names of the SARA-N2 series modules’ UART interface conform to the ITU-T V.24
Recommendation [5]: e.g. the TXD line represents the data transmitted by the DTE (application
processor data line output) and received by the DCE (module data line input).
Figure 7 describes the 8N1 frame format, which is the default configuration with fixed baud rate.
Figure 7: Description of UART default frame format (8N1) with fixed baud rate
1.9.1.2 UART signal behavior
At the module switch-on, before the UART interface initialization (as described in the power-on
sequence reported in Figure 5), each pin is first tri-stated and then is set to its related internal reset
state. At the end of the boot sequence, the UART interface is initialized and the UART interface is
enabled as AT commands interface.
The configuration and the behavior of the UART signals after the boot sequence are described below.
See section 1.4 for definition and description of module operating modes referred to in this section.
RXD signal behavior
The module data output line (RXD) is set by default to the OFF state (high level) at UART initialization.
The greeting message is sent on the RXD line after the completion of the boot sequence to indicate
the completion of the UART interface initialization.
The module holds RXD in the OFF state until the module does not transmit some data.
TXD signal behavior
The module data input line (TXD) is assumed to be controlled by the external host once UART is
initialized.
There is no internal pull-up / pull-down inside the module on the TXD input.
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 18 of 82
Page 19

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
1.9.1.3 UART and deep sleep mode
To limit the current consumption, SARA-N2 modules automatically enter deep-sleep mode whenever
possible, that is if there is no data to transmit or receive. When in deep-sleep mode the UART interface
is still completely functional and the module can accept and respond to any AT command. All the other
interfaces are disabled.
The application processor should go in standby (or lowest power consumption mode) as soon as the
SARA-N2 module enters the deep-sleep mode and there is no more data to be transmitted.
At any time the DTE can request the module to send data using the related commands (for more
details, see the SARA-N2 series AT Commands Manual [3] and the u-blox NB-IoT Application
Development Guide [4]); these commands automatically force the module to exit the deep-sleep
mode.
1.9.2 Secondary asynchronous serial interface (Secondary UART)
The secondary auxiliary UART interface is a 2-wire unbalanced asynchronous serial interface,
providing:
Trace diagnostic log delivered by the module
The main characteristics of the secondary auxiliary UART interface are:
Serial port with RS-232 functionality working at the V_INT voltage domain (0 V for low data bit or
ON state and 1.8 V, i.e. V_INT, for high data bit or OFF state)
Data line (GPIO1 as module data output)
No flow control
Fixed baud rate: 921600 b/s
Fixed frame format: 8N1 (8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit)
☞ Provide a test point connected to the GPIO1 pin for diagnostic purpose.
☞ The trace diagnostic log is temporarily stopped when the module is in deep-sleep mode.
1.9.3 DDC (I
☞ DDC (I
The SDA and SCL pins represent an I2C bus compatible Display Data Channel (DDC) interface,
operating at the V_INT voltage level (1.8 V).
2
C) interface is not supported in the "02" version of the product.
2
C) interface
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 19 of 82
Page 20

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Function
Description
Default GPIO
Configurable GPIOs
Network status indication
Network status: registered home network,
registered roaming, data transmission, no
service
--
CTS
RING indicator
Indicates an incoming message received by the
module or an URC event
--
CTS
Secondary UART
Secondary UART data output for diagnostic
purpose, to capture diagnostic logs delivered
by the module
GPIO1
GPIO1
Pin disabled
Tri-state with an internal active pull-down
enabled
CTS
CTS
1.10 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
SARA-N2 series modules provide the following pins:
GPIO1 pin, working at the V_INT (1.8 V) voltage domain, supporting the Secondary UART data
output functionality (see section 1.9.2 and Table 8)
GPIO2 pin, working at the V_INT (1.8 V) voltage domain, not supported by "02" product versions
CTS pin, working at the VCC (3.6 V typical) voltage domain, supporting the Network status
indication and the RING indicator functionality (see section 1.9.1 and Table 8)
For more details about how the pins can be configured, see SARA-N2 series AT Commands
Manual [3], +UGPIOC, +URING AT commands.
☞ Provide a test point connected to the GPIO1 pin for diagnostic purpose.
Table 8: GPIO custom functions configuration
1.11 Reserved pins (RSVD)
SARA-N2 series modules have pins reserved for future use, marked as RSVD.
All the RSVD pins are to be left unconnected on the application board, except for the RSVD pin number
33 that can be externally connected to ground.
UBX-17005143 - R06 System description Page 20 of 82
Page 21

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
2 Design-in
2.1 Overview
For an optimal integration of SARA-N2 series modules in the final application board, follow the design
guidelines stated in this section.
Every application circuit must be properly designed to guarantee the correct functionality of the
related interface, however a number of points require higher attention during the design of the
application device.
The following list provides a ranking of importance in the application design, starting from the highest
relevance:
1. Module antenna connection: ANT pin. Antenna circuit directly affects the RF compliance of the
device integrating a SARA-N2 series module with the applicable certification schemes. Very
carefully follow the suggestions provided in section 2.4 for schematic and layout design.
2. Module supply: VCC and GND pins. The supply circuit affects the RF compliance of the device
integrating a SARA-N2 series module with applicable certification schemes as well as antenna
circuit design. Very carefully follow the suggestions provided in section 2.2 for schematic and
layout design.
3. SIM interface: VSIM, SIM_CLK, SIM_IO, SIM_RST pins. Accurate design is required to guarantee
SIM card functionality and compliance with applicable conformance standards, reducing also the
risk of RF coupling. Carefully follow the suggestions provided in section 2.5 for schematic and
layout design.
4. System function: RESET_N pin. Accurate design is required to guarantee that the voltage level is
well defined during operation. Carefully follow the suggestions provided in section 2.3 for
schematic and layout design.
5. Other digital interfaces: UART and secondary UART interfaces, DDC I
GPIOs. Accurate design is required to guarantee proper functionality and reduce the risk of digital
data frequency harmonics coupling. Follow the suggestions provided in sections 2.6 and 2.7 for
schematic and layout design.
2
C-compatible interface and
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 21 of 82
Page 22

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Main Supply
Available?
Battery
LiSOCl23.6 V
Linear LDO
Regulator
Main Supply
Voltage > 5V?
Switching Step-Down
Regulator
No, portable device
No, less than 5 V
Yes, greater than 5 V
Yes, always available
2.2 Supply interfaces
2.2.1 Module supply (VCC)
2.2.1.1 General guidelines for VCC supply circuit selection and design
All the available VCC pins must be connected to the external supply minimizing the power loss due to
series resistance.
GND pins are internally connected but connect all the available pins to a solid ground on the
application board, since a good (low impedance) connection to external ground can minimize power
loss and improve RF and thermal performance.
SARA-N2 series modules must be supplied through the VCC pins by a proper DC power supply that
should comply with the module VCC requirements summarized in Table 6.
The proper DC power supply can be selected according to the application requirements (see Figure 8)
between the different possible supply sources types, which most common ones are the following:
Primary (disposable) battery
Rechargeable Lithium-ion (Li-Ion) or Lithium-ion polymer (Li-Pol) battery
Switching regulator
Low Drop-Out (LDO) linear regulator
Figure 8: VCC supply concept selection
The NB-IoT technology is primarly intended for battery powered applications. A Lithium Thionyl
Chloride (LiSOCl2) battery directly connected to VCC pins is the usual choice for battery-powered
devices. See sections 2.2.1.2, 2.2.1.3 and 2.2.1.6, 2.2.1.7, 2.2.1.8 for specific design-in.
The DC/DC switching step-down regulator is the typical choice when the available primary supply
source has a nominal voltage much higher (e.g. greater than 5 V) than the modules VCC operating
supply voltage. The use of switching step-down provides the best power efficiency for the overall
application and minimizes current drawn from the main supply source. See sections 2.2.1.2, 2.2.1.4 and
2.2.1.6, 2.2.1.7, 2.2.1.8 for specific design-in.
The use of an LDO linear regulator becomes convenient for a primary supply with a relatively low
voltage (e.g. less than 5 V). In this case the typical 90% efficiency of the switching regulator
diminishes the benefit of voltage step-down and no true advantage is gained in input current savings.
On the opposite side, linear regulators are not recommended for high voltage step-down as they
dissipate a considerable amount of energy in thermal power. See sections 2.2.1.2, 2.2.1.5 and 2.2.1.6,
2.2.1.7, 2.2.1.8 for specific design-in.
The use of rechargeable batteries is not the typical solution for NB-IoT applications, but it is feasible
to implement a suitable external charger circuit. The charger circuit has to be designed to prevent
over-voltage on VCC pins of the module, and it should be selected according to the application
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 22 of 82
Page 23

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
requirements: a DC/DC switching charger is the typical choice when the charging source has an high
nominal voltage (e.g. ~12 V), whereas a linear charger is the typical choice when the charging source
has a relatively low nominal voltage (~5 V). If both a permanent primary supply / charging source (e.g.
~12 V) and a rechargeable back-up battery (e.g. 3.7 V Li-Pol) are simultaneously available in the
application as possible supply sources, then a proper charger / regulator with integrated power path
management function can be selected to supply the module while simultaneously and independently
charging the battery.
The usage of more than one DC supply at the same time should be carefully evaluated: depending on
the supply source characteristics, different DC supply systems can be mutually exclusive.
The usage of supercapacitors on the VCC supply line is generally not recommended since these
components are highly temperature sensitive and may increase current leakages draining the battery
faster.
The following sections highlight some design aspects for power-supply scenarios, providing
application circuit design-in compliant with the module VCC requirements summarized in Table 6.
☞ For the additional specific requirements applicable to the integration of SARA-N211 modules in
devices intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres, see section 2.11.
2.2.1.2 Guidelines to optimize power consumption
The NB-IoT technology is primarly intended for applications that require small amount of data
exchange per day (i.e. few bytes in uplink and downlink per day) and these are typically battery
powered. Depending on the application type, an operating life of 5 to 15 years is usually required. For
these reasons, the whole application board should be optimized in terms of current consumption and
should carefully take into account the following aspects:
Minimize current leakages on the power supply line
Optimize the antenna matching since an un-matched antenna leads to higher current
consumptions
Use an application processor with UART interface working at the same level of the VCC supply
input of the SARA-N2 module (for example, 3.3 V or 3.6 V). In this way it is possible to avoid voltage
translators on the UART interface, which operates at the VCC voltage level
The application processor should go in standby (or lowest power consumption mode) as soon as
the SARA-N2 module enters the deep-sleep mode and there’s no more data to be transmitted: the
module will automatically enter the deep-sleep mode whenever possible to limit current
consumption and avoid further network registration procedures each time there is an up-link
message to be transmitted.
The application processor can monitor the V_INT level to sense when radio is on or off.
The application processor can detect the presence of down-link messages monitoring the CTS
pin, which provides the Ring Indicator functionality, notifying incoming data received by the
module or an URC event.
Possibility to request new network timers and select the optimum set of values depending on the
intended application use case
2.2.1.3 Guidelines for VCC supply circuit design using a primary battery
The characteristics of a battery connected to VCC pins should meet the following prerequisites to
comply with the module VCC requirements summarized in Table 6:
Maximum pulse and DC discharge current: the non-rechargeable battery with its output circuit
must be capable of delivering to VCC pins the specified average current during a transmission at
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 23 of 82
Page 24

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
SARA-N2
52
VCC
53
VCC
51
VCC
3V6
C3
Battery pack
C2C1 C4
maximum power (see the SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1] for more details). The antenna matching
influences the current consumption; for this reason, the current consumption at maximum Tx
power with the intended antenna (i.e. on the final application board) should be used to characterize
the battery maximum pulse requirements.
The maximum DC discharge current is not always reported in battery data sheets, but it is typically
almost equal to the battery capacity in Amp-hours divided by 1 hour.
DC series resistance: the non-rechargeable battery with its output circuit must be capable to limit
as much as possible the DC resistance provided on the VCC supply line.
The LiSOCl2 (Lithium Thionyl Chloride Batteries) is currently the best technology available for NB-IoT
applications since it provides:
Very low self-discharge behavior and resulting ability to last longer
Highest specific energy per unit weight and energy density per unit volume
Wide operating temperature range
For the selection of the proper battery type, the following parameters should be taken into account:
Capacity: > 3 Ah
Continuous current capability: ~400 mA (the consumption of whole application with the actual
antenna should be considered)
Temperature range: -20 °C to +85 °C
Capacity vs temperature behavior: battery capacity is highly influenced by the temperature. This
must be considered to properly estimate the battery life time
Capacity vs discharge current performance
Voltage vs temperature behavior: the battery voltage typically decreases at low temperatures
values (for example, in the -10 °C / -20 °C range). In all the temperature conditions the battery
voltage must always be above the SARA-N2 minimum extended operating voltage level
Voltage vs pulse duration behavior: this information is typically not provided by battery
manufacturers, and many batteries reach too low voltage values during a long pulse. It is
recommended to execute stress tests on battery samples to verify the voltage behavior as a
function of the pulse duration and to guarantee that the battery voltage is always above the
minimum extended operating voltage level of SARA-N2 series.
Construction technology: spiral wound batteries are generically preferred over the bobbin
construction
o This technology typically supports high current pulses without the need for supercaps
o A bobbin type battery usually does not support the current pulse
Figure 9 shows an example of connection of SARA-N2 module with a primary battery. Table 9 lists
different batty pack part numbers that can be used.
Figure 9: Suggested schematic design for the VCC voltage supply application circuit using a LiSOCl2 primary battery
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 24 of 82
Page 25

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
100 µ F Capacitor Tantalum B_SIZE 20% 6.3V 15m
T520B107M006ATE015 - Kemet
C2
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
C3
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C4
56 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1E560JA01 - Murata
Battery pack
Size FAT A LiSOCl battery, spiral wound, 3.2Ah
ER18505M - Titus Battery
Size C LiSOCl battery, spiral wound, 6.5Ah
ER26500M - Titus Battery
Size D LiSOCl battery, spiral wound, 13Ah
ER34615M - Titus Battery
Size C LiSOCl battery, spiral wound, 5.8Ah
LSH14 – Saft
Size D LiSOCl battery, spiral wound, 13Ah
LSH20 - Saft
SARA-N2
52
VCC
53
VCC
51
VCC
3V3
C3 C5C4
C1
LX2
VIN
FB
PGND
VOUT
C2
L1
U1
Battery
pack
4
V_INT
BYPS
LX1
EN
GND
T1
3V3
R1
R
2
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
10 µ F Capacitor Ceramic X5R 0603 20% 6.3 V
GRM188R60J106ME47 - Murata
C2
100 µ F Capacitor Tantalum B_SIZE 20% 6.3V 15m
T520B107M006ATE015 - Kemet
L1
1 µ H Inductor 20% 3.1 A 60 m
TFM201610GHM-1R0MTAA - TDK
C3
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
C4
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C5
56 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1E560JA01 - Murata
R1
100 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-07100KL - Yageo Phycomp
R2
1 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-071KL - Yageo Phycomp
T1
N-channel MOSFET
DMG1012T - Diodes Incorporated
U1
High Efficiency Low Power Buck-Boost Regulator with
Bypass mode
ISL9120IRTNZ - Intersil
Table 9: Suggested components for the VCC voltage supply application circuit using a LiSOCl2 primary battery
An alternative battery design solution can be realized combining:
Generic primary battery pack: not necessarily an optimized LiSOCl
spiral wound
2
DC/DC buck-boost converter
Load switch
There are switching regulators that integrate the load switch and the DC/DC converter logic with a so
called bypass mode. See Figure 10 and Table 10 for an example of such an application circuit. In this
case V_INT can be used to select between bypass and buck-boost modes:
V_INT = 0 V, Radio = Off, Bypass mode
V_INT = 1.8 V, Radio = On, Buck-Boost mode
Figure 10: Alternative schematic design for the VCC voltage supply application circuit using a generic primary battery
Table 10: Suggested components for an alternative VCC voltage supply application circuit using a generic primary battery
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 25 of 82
Page 26

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
12V
R5
C6
C1
VCC
INH
FSW
SYNC
OUT
GND
2
6
3
1
7
8
C3
C2
D1
R1
R2
L1
U1
FB
COMP
5
4
R3
C4
R4
C5
SARA-N2
52
VCC
53
VCC
51
VCC
GND
3V6
C7
C8
C9
2.2.1.4 Guidelines for VCC supply circuit design using a switching regulator
The use of a switching regulator is suggested when the difference from the available supply rail to the
VCC value is high: switching regulators provide good efficiency transforming a 12 V or greater voltage
supply to the typical 3.6 V value of the VCC supply.
The characteristics of the switching regulator connected to VCC pins should meet the following
prerequisites to comply with the module VCC requirements summarized in Table 6:
Power capability: the switching regulator with its output circuit must be capable of providing a
voltage value to the VCC pins within the specified operating range and must be capable of
delivering to VCC pins the specified average current during a transmission at maximum power
(see SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1]).
Low output ripple: the switching regulator together with its output circuit must be capable of
providing a clean (low noise) VCC voltage profile.
PWM mode operation: it is preferable to select regulators with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
mode. While in connected-mode Pulse Frequency Modulation (PFM) mode and PFM/PWM mode,
transitions must be avoided to reduce the noise on the VCC voltage profile. Switching regulators
that are able to switch between low ripple PWM mode and high efficiency burst or PFM mode can
be used, provided the mode transition occurs when the module changes status from active-mode
to connected-mode: it is suggest to use a regulator that switches from the PWM mode to the
burst or PFM mode at an appropriate current threshold (e.g. 10 mA).
Figure 11 and the components listed in Table 11 show an example of a power supply circuit, where the
module VCC is supplied by a step-down switching regulator capable of delivering the specified
maximum current to the VCC pins, with low output ripple and with fixed switching frequency in PWM.
Figure 11: Suggested schematic design for the VCC voltage supply application circuit using a step-down regulator
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 26 of 82
Page 27

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
22 µ F Capacitor Ceramic X5R 1210 10% 25 V
GRM32ER61E226KE15 - Murata
C2
100 µ F Capacitor Tantalum B_SIZE 20% 6.3V 15m
T520B107M006ATE015 - Kemet
C3
5.6 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 50 V
GRM155R71H562KA88 - Murata
C4
6.8 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 50 V
GRM155R71H682KA88 - Murata
C5
56 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H560JA01 - Murata
C6
220 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0603 10% 25 V
GRM188R71E224KA88 - Murata
C7
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
C8
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C9
56 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1E560JA01 - Murata
D1
Schottky Diode 25V 2 A
STPS2L25 - STMicroelectronics
L1
5.2 µ H Inductor 30% 5.28A 22 m
MSS1038-522NL - Coilcraft
R1
4.7 k Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-074K7L - Yageo
R2
1 k Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RC0402FR-071KL - Yageo
R3
82 Resistor 0402 5% 0.063 W
RC0402JR-0782RL - Yageo
R4
8.2 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.063 W
RC0402JR-078K2L - Yageo
R5
39 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.063 W
RC0402JR-0739KL - Yageo
U1
Step-Down Regulator 8-VFQFPN 0.7 A 1 MHz
L5980TR - ST Microelectronics
Table 11: Suggested components for the VCC voltage supply application circuit using a step-down regulator
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 27 of 82
Page 28

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
5V
C1
IN OUT
ADJ
GND
1
2
4
5
3
C2
R1
R2
U1
EN
SARA-N2
52
VCC
53
VCC
51
VCC
GND
3V6
C3
C4
C5
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
10 µ F Capacitor Ceramic X5R 0603 20% 6.3 V
GRM188R60J106ME47 - Murata
C2
100 µ F Capacitor Tantalum B_SIZE 20% 6.3V 15m
T520B107M006ATE015 - Kemet
R1
29.4 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402FR-0729K4L - Yageo Phycomp
R2
4.7 k Resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
RC0402JR-074K7L - Yageo Phycomp
U1
LDO Linear Regulator ADJ 800 mA
LP38511TJ-ADJ/NOPB - Texas Instrument
C3
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
C4
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C5
56 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1E560JA01 - Murata
2.2.1.5 Guidelines for VCC supply circuit design using an LDO linear regulator
The use of a linear regulator is suggested when the difference from the available supply rail and the
VCC value is low: linear regulators provide high efficiency when transforming a 5 V supply to a voltage
value within the module VCC normal operating range.
The characteristics of the LDO linear regulator connected to the VCC pins should meet the following
prerequisites to comply with the module VCC requirements summarized in Table 6:
Power capabilities: the LDO linear regulator with its output circuit must be capable of providing a
proper voltage value to the VCC pins and of delivering to VCC pins the specified maximum average
current during a transmission at maximum power (see the SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1])
Power dissipation: the power handling capability of the LDO linear regulator must be checked to
limit its junction temperature to the maximum rated operating range (i.e. check the voltage drop
from the max input voltage to the min output voltage to evaluate the power dissipation of the
regulator)
Figure 12 and the components listed in Table 12 show a power supply circuit example, where the VCC
module supply is provided by an LDO linear regulator capable of delivering the specified current.
It is recommended to configure the LDO linear regulator to generate a voltage supply value slightly
below the maximum limit of the module VCC normal operating range. This reduces the power on the
linear regulator and improves the whole thermal design of the supply circuit.
Figure 12: Suggested schematic design for the VCC voltage supply application circuit using an LDO linear regulator
Table 12: Suggested components for VCC voltage supply application circuit using an LDO linear regulator
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 28 of 82
Page 29

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
C1
GND
C2
SARA-N2
52
VCC
53
VCC
51
VCC
3V6
C4
VCC line
Capacitor with
SRF ~900 MHz
C1 C3C2
C3
C4
SARA-N2
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
56 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1E560JA01 - Murata
C2
10 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C103KA01 - Murata
C3
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
C4
100 µ F Capacitor Tantalum B_SIZE 20% 6.3V 15m
T520B107M006ATE015 - Kemet
2.2.1.6 Additional guidelines for VCC supply circuit design
To reduce voltage drops, use a low impedance power source. The resistance of the power supply lines
(connected to the VCC and GND pins of the module) on the application board and battery pack should
also be considered and minimized: cabling and routing must be as short as possible to minimize power
losses.
Three pins are allocated for VCC supply. Another twenty pins are designated for GND connection. It is
highly recommended to properly connect all the VCC pins and all the GND pins to supply the module,
to minimize series resistance losses.
To reduce voltage noise, especially if the application device integrates an internal antenna, place the
following bypass capacitors near the VCC pins:
56 pF capacitor with Self-Resonant Frequency in 700/800/900 MHz range (e.g. Murata
GRM1555C1E560J) to filter transmission EMI in the NB-IoT bands 28 / 20 / 5 / 8
10 nF capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R71C103K) to filter digital logic noise from clocks and data
sources
100 nF capacitor (e.g Murata GRM155R61C104K) to filter digital logic noise from clocks and data
sources
100 µF low ESR capacitor (e.g Kemet T520B107M006ATE015) to avoid voltage undershoot and
overshoot at the start and end of a RF transmit burst, stabilizing the voltage profle at max Tx
power, recommended in particular for noise sensitive applications
For devices integrating an internal antenna, it is recommended to provide space to allocate all the
components shown in Figure 13 and listed in Table 13.
Figure 13: Suggested schematic and layout design for the VCC line, highly recommended when using an integrated antenna
Table 13: Suggested components to reduce noise on VCC
☞ ESD sensitivity rating of the VCC supply pins is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-
A114). Higher protection level can be required if the line is externally accessible on the application
board, e.g. if accessible battery connector is directly connected to VCC pins. Higher protection
level can be achieved by mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array)
close to accessible point.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 29 of 82
Page 30

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
2.2.1.7 Guidelines for VCC supply layout design
Good connection of the module VCC pins with DC supply source is required for correct RF
performance. Guidelines are summarized in the following list:
All the available VCC pins must be connected to the DC source.
VCC connection must be as wide as possible and as short as possible.
Any series component with Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) greater than few milliohms must
be avoided.
VCC connection must be routed through a PCB area separated from sensitive analog signals and
sensitive functional units: it is good practice to interpose at least one layer of PCB ground between
VCC track and other signal routing.
The bypass capacitors in the pF range described in Figure 13 and Table 13 should be placed as close
as possible to the VCC pins. This is highly recommended if the application device integrates an
internal antenna.
High frequency voltage ripples on the VCC line may result in unwanted spurious modulation of
transmitter RF signal. This is more likely to happen with switching DC-DC converters, in which
case it is better to select the highest operating frequency for the switcher and add a large L-C filter
before connecting to the SARA-N2 series modules in the worst case.
If VCC is protected by transient voltage suppressor to ensure that the voltage maximum ratings
are not exceeded, place the protecting device along the path from the DC source toward the
cellular module, preferably closer to the DC source (otherwise protection functionality may be
compromised).
2.2.1.8 Guidelines for grounding layout design
Good connection of the module GND pins with application board solid ground layer is required for
correct RF performance. It significantly reduces EMC issues and provides a thermal heat sink for the
module.
Connect each GND pin with application board solid GND layer. It is strongly recommended that
each GND pin surrounding VCC pins have one or more dedicated via down to the application board
solid ground layer.
The VCC supply current flows back to main DC source through GND as ground current: provide
adequate return path with suitable uninterrupted ground plane to main DC source.
It is recommended to implement one layer of the application board as ground plane as wide as
possible.
If the application board is a multilayer PCB, then all the board layers should be filled with GND plane
as much as possible and each GND area should be connected together with complete via stack
down to the main ground layer of the board.
If the whole application device is composed by more than one PCB, then it is required to provide a
good and solid ground connection between the GND areas of all the different PCBs.
Good grounding of GND pins also ensures thermal heat sink. This is critical during call connection,
when the real network commands the module to transmit at maximum power: proper grounding
helps prevent module overheating.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 30 of 82
Page 31

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
2.2.2 Interface supply (V_INT)
2.2.2.1 Guidelines for V_INT circuit design
The V_INT digital interfaces 1.8 V supply output can be mainly used to:
Indicate when the module is switched on, and radio is on (see section 1.6.1 for more details)
☞ Do not apply loads that might exceed the limit for maximum available current from V_INT supply,
as this can cause malfunctions in internal circuitry supplies to the same domain. The SARA-N2
series Data Sheet [1] describes the detailed electrical characteristics.
☞ V_INT can only be used as an output; do not connect any external regulator on V_INT.
☞ V_INT supply output pin provides internal short circuit protection to limit start-up current and
protect the device in short circuit situations. No additional external short circuit protection is
required.
☞ ESD sensitivity rating of the V_INT supply pin is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-
A114). Higher protection level could be required if the line is externally accessible on the application
board. Higher protection level can be achieved by mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS
CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) close to accessible point.
☞ It is recommended providing direct access to the V_INT supply output pin on the application board
by means of testpoint directly accessible for diagnostic purpose
2.2.2.2 Guidelines for V_INT layout design
There are no specific layout design recommendations for V_INT output.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 31 of 82
Page 32

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
1:1 scaling
SARA-N2 series
18
RESET_N
Reset
push button
ESD
Open
Drain
Output
Application
Processor
SARA-N2 series
18
RESET_N
TP
TP
~78k
VCC
~78k
VCC
Reference
Description
Remarks
ESD
Varistor for ESD protection
CT0402S14AHSG - EPCOS
2.3 System functions interfaces
2.3.1 Module reset (RESET_N)
2.3.1.1 Guidelines for RESET_N circuit design
As described in SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1], the module has an internal pull-up resistor on the reset
input line, so an external pull-up is not required on the application board.
When the RESET_N input is connected to a push button that shorts the RESET_N pin to ground, the
pin will be externally accessible on the application device. According to EMC/ESD requirements of the
application, provide an additional ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) on the
line connected to this pin, close to accessible point, as described in Figure 14 and Table 14.
☞ ESD sensitivity rating of the RESET_N pin is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-A114).
Higher protection level can be required if the line is externally accessible on the application board,
e.g. if an accessible push button is directly connected to RESET_N pin. Higher protection level can
be achieved by mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) close to
accessible point.
When the RESET_N input is connected to an external device (e.g. application processor), an open drain
output can be directly connected without any external pull-up, as described in Figure 14 and Table 14.
The internal pull-up resistor provided by the module pulls the line to the high logic level when the
application processor does not force the RESET_N pin low. A compatible push-pull output of an
application processor can be used too.
Figure 14: RESET_N application circuits using a push button and an open drain output of an application processor
Table 14: Example of ESD protection component for the RESET_N application circuit
☞ If the external reset function is not required by the customer application, the RESET_N input pin
can be left unconnected to external components, but it is recommended providing direct access
on the application board by means of accessible testpoint for diagnostic purpose.
2.3.1.2 Guidelines for RESET_N layout design
The reset circuit (RESET_N) requires careful layout due to the pin function: ensure that the voltage
level is well defined during operation and no transient noise is coupled on this line, otherwise the
module might detect a spurious reset request. It is recommended to keep the connection line to
RESET_N as short as possible.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 32 of 82
Page 33

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
2.4 Antenna interface
The ANT pin, provided by all the SARA-N2 series modules, represents the RF input/output used to
transmit and receive the RF cellular signals: the antenna must be connected to this pin. The ANT pin
has a nominal characteristic impedance of 50 and must be connected to the antenna through a 50
transmission line to allow transmission and reception of radio frequency (RF) signals in the
operating bands.
2.4.1 Antenna RF interface (ANT)
2.4.1.1 General guidelines for antenna selection and design
The cellular antenna is the most critical component to be evaluated: care must be taken about it at
the start of the design development, when the physical dimensions of the application board are under
analysis/decision, since the RF compliance of the device integrating a SARA-N2 series module with all
the applicable required certification schemes depends from antenna radiating performance.
Cellular antennas are typically available as:
External antenna (e.g. linear monopole):
o External antenna usage basically does not imply physical restrictions on the design of the PCB
where the SARA-N2 series module is mounted.
o The radiation performance mainly depends on the antenna: select the antenna with optimal
radiating performance in the operating bands.
o If antenna detection functionality is required, select an antenna assembly provided with a
proper built-in diagnostic circuit with a resistor connected to ground: see section 2.4.2.
o Select an RF cable with minimum insertion loss: additional insertion loss due to low quality or
long cable reduces radiation performance.
o Select a suitable 50 connector providing proper PCB-to-RF-cable transition: it is
recommended to strictly follow the layout and cable termination guidelines provided by the
connector manufacturer.
Integrated antenna (PCB antennas such as patches or ceramic SMT elements):
o Internal integrated antenna implies physical restriction to the design of the PCB: the ground
plane can be reduced down to a minimum size that must be similar to the quarter of the
wavelength of the minimum frequency that has to be radiated. As numerical example:
Frequency = 750 MHz Wavelength = 40 cm Minimum GND plane size = 10 cm
o The radiation performance depends on the whole PCB and antenna system design, including
product mechanical design and usage: select the antenna with optimal radiating performance
in the operating bands according to the mechanical specifications of the PCB and the whole
product.
o Select a complete custom antenna designed by an antenna manufacturer if the required
ground plane dimensions are very small (e.g. less than 6.5 cm long and 4 cm wide): the antenna
design process should begin at the start of the whole product design process.
o Select an integrated antenna solution provided by an antenna manufacturer if the required
ground plane dimensions are large enough according to the related integrated antenna
solution specifications: the antenna selection and the definition of its placement in the product
layout should begin at the start of the product design process.
o It is highly recommended to strictly follow the detailed and specific guidelines provided by the
antenna manufacturer regarding correct installation and deployment of the antenna system,
including PCB layout and matching circuitry.
o Further to the custom PCB and product restrictions, the antenna may require tuning to obtain
the required performance to comply with applicable certification schemes. It is recommended
to ask the antenna manufacturer for design-in guidelines related to the custom application.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 33 of 82
Page 34

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Min.
250 µm
Min. 400 µm
GND
ANT
GND clearance
on very close buried layer
below ANT pad
GND clearance
on top layer
around ANT pad
In both cases, selecting an external or an internal antenna, observe these recommendations:
Select an antenna providing optimal return loss (or V.S.W.R.) figure over all the operating
frequencies.
Select an antenna providing optimal efficiency figure over all the operating frequencies.
Select an antenna providing appropriate gain figure (i.e. combined antenna directivity and
efficiency figure) so that the electromagnetic field radiation intensity do not exceed the regulatory
limits specified in some countries (e.g. by FCC in the United States).
☞ For the additional specific guidelines for SARA-N211 modules integration in applications intended
for use in potentially explosive atmospheres, see section 2.11.
2.4.1.2 Guidelines for antenna RF interface design
Guidelines for ANT pin RF connection design
Proper transition between the ANT pin and the application board PCB must be provided,
implementing the following design-in guidelines for the layout of the application PCB close to the pad
designed for the ANT pin:
On a multi layer board, the whole layer stack below the RF connection should be free of digital lines
Increase GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a void area) around the ANT pad, on the top layer of the
application PCB, to at least 250 µm up to adjacent pads metal definition and up to 400 µm on the
area below the module, to reduce parasitic capacitance to ground, as described in the left picture
in Figure 15
Add GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a void area) on the buried metal layer below the ANT pad if the
top-layer to buried layer dielectric thickness is below 200 µm, to reduce parasitic capacitance to
ground, as described in the right picture in Figure 15
Figure 15: GND keep-out area on the top layer around ANT pad and on the very close buried layer below ANT pad
Guidelines for RF transmission line design
The transmission line from the ANT pad up to antenna connector or up to the internal antenna pad
must be designed so that the characteristic impedance is as close as possible to 50 .
The transmission line can be designed as a micro strip (consists of a conducting strip separated from
a ground plane by a dielectric material) or a strip line (consists of a flat strip of metal which is
sandwiched between two parallel ground planes within a dielectric material). The micro strip,
implemented as a coplanar waveguide, is the most common configuration for printed circuit board.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 34 of 82
Page 35

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
35 µm
35 µm
35 µm
35 µm
270 µm
270 µm
760 µm
L1 Copper
L3 Copper
L2 Copper
L4 Copper
FR-4 dielectric
FR-4 dielectric
FR-4 dielectric
380 µm 500 µm500 µm
35 µm
35 µm
1510 µm
L2 Copper
L1 Copper
FR-4 dielectric
1200 µm 400 µm400 µm
Figure 16 and Figure 17 provide two examples of proper 50 coplanar waveguide designs. The first
transmission line can be implemented in case of 4-layer PCB stack-up herein described, the second
transmission line can be implemented in case of 2-layer PCB stack-up herein described.
Figure 16: Example of 50 coplanar waveguide transmission line design for the described 4-layer board layup
Figure 17: Example of 50 coplanar waveguide transmission line design for the described 2-layer board layup
If the two examples do not match the application PCB layup, the 50 characteristic impedance
calculation can be made using the HFSS commercial finite element method solver for
electromagnetic structures from Ansys Corporation, or using freeware tools like AppCAD from
Agilent (www.agilent.com) or TXLine from Applied Wave Research (www.mwoffice.com), taking care
of the approximation formulas used by the tools for the impedance computation.
To achieve a 50 characteristic impedance, the width of the transmission line must be chosen
depending on:
the thickness of the transmission line itself (e.g. 35 µm in the example of Figure 16 and Figure 17)
the thickness of the dielectric material between the top layer (where the transmission line is
routed) and the inner closer layer implementing the ground plane (e.g. 270 µm in Figure 16, 1510 µm
in Figure 17)
the dielectric constant of the dielectric material (e.g. dielectric constant of the FR-4 dielectric
material in Figure 16 and Figure 17)
the gap from the transmission line to the adjacent ground plane on the same layer of the
transmission line (e.g. 500 µm in Figure 16, 400 µm in Figure 17)
If the distance between the transmission line and the adjacent GND area (on the same layer) does not
exceed 5 times the track width of the micro strip, use the “Coplanar Waveguide” model for the 50
calculation.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 35 of 82
Page 36

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
SARA module
SMA
connector
SARA module
SMA
connector
High-pass filter for
SARA-N2 ANT port
ESD immunity increase
Additionally to the 50 impedance, the following guidelines are recommended for the transmission
line design:
Minimize the transmission line length: the insertion loss should be minimized as much as possible,
in the order of a few tenths of a dB.
Add GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a void area) on buried metal layers below any pad of component
present on the RF transmission line, if top-layer to buried layer dielectric thickness is below
200 µm, to reduce parasitic capacitance to ground.
The transmission line width and spacing to GND must be uniform and routed as smoothly as
possible: avoid abrupt changes of width and spacing to GND.
Add GND vias around transmission line, as described in Figure 18.
Ensure solid metal connection of the adjacent metal layer on the PCB stack-up to main ground
layer, providing enough on the adjacent metal layer, as described in Figure 18.
Route RF transmission line far from any noise source (as switching supplies and digital lines) and
from any sensitive circuit (as analog audio lines).
Avoid stubs on the transmission line.
Avoid signal routing in parallel to transmission line or crossing the transmission line on buried
metal layer.
Do not route microstrip line below discrete component or other mechanics placed on top layer.
Two examples of proper RF circuit design are reported in the Figure 18, where the antenna detection
circuit is not implemented (if the antenna detection function is required by the application, follow the
guidelines for circuit and layout implementation reported in section 2.4.2):
In the first example described on the left, the ANT pin is directly connected to an SMA connector
by means of a proper 50 transmission line, designed with proper layout.
In the second example described on the right, the ANT pin is connected to an SMA connector by
means of a proper 50 transmission line, designed with proper layout, with an additional high
pass filter (consisting of a proper series capacitor and a proper shunt inductor, as for example the
Murata GRM1555C1H150JA01 15 pF capacitor and the Murata LQG15HN39NJ02 39 nH inductor
with Self-Resonant Frequency ~1 GHz) to improve the ESD immunity at the antenna port of
SARA-N2 modules
Figure 18: Suggested circuit and layout for antenna RF circuit on application board, if antenna detection is not required
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 36 of 82
Page 37

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Guidelines for RF termination design
The RF termination must provide a characteristic impedance of 50 as well as the RF transmission
line up to the RF termination itself, to match the characteristic impedance of the ANT pin of the
module.
However, real antennas do not have perfect 50 load on all the supported frequency bands.
Therefore, to reduce as much as possible performance degradation due to antenna mismatch, the RF
termination must provide optimal return loss (or V.S.W.R.) figure over all the operating frequencies,
as summarized in Table 7.
If an external antenna is used, the antenna connector represents the RF termination on the PCB:
Use a suitable 50 connector providing proper PCB-to-RF-cable transition.
Strictly follow the connector manufacturer’s recommended layout, for example:
o SMA Pin-Through-Hole connectors require GND keep-out (i.e. clearance, a void area) on all the
layers around the central pin up to annular pads of the four GND posts, as shown in Figure 18.
o U.FL surface mounted connectors require no conductive traces (i.e. clearance, a void area) in
the area below the connector between the GND land pads.
Cut out the GND layer under RF connectors and close to buried vias, to remove stray capacitance
and thus keep the RF line 50 : e.g. the active pad of U.FL connectors needs to have a GND keepout (i.e. clearance, a void area) at least on first inner layer to reduce parasitic capacitance to ground
If an integrated antenna is used, the RF termination is represented by the integrated antenna itself:
Use an antenna designed by an antenna manufacturer, providing the best possible return loss (or
V.S.W.R.).
Provide a ground plane large enough according to the related integrated antenna requirements:
the ground plane of the application PCB can be reduced to a minimum size that must be similar to
one quarter of wavelength of the minimum frequency that has to be radiated. As numerical
example:
Frequency = 750 MHz Wavelength = 40 cm Minimum GND plane size = 10 cm
It is highly recommended to strictly follow the detailed and specific guidelines provided by the
antenna manufacturer regarding correct installation and deployment of the antenna system,
including PCB layout and matching circuitry.
Further to the custom PCB and product restrictions, the antenna may require a tuning to comply
with all the applicable required certification schemes. It is recommended to consult the antenna
manufacturer for the design-in guidelines for the antenna related to the custom application.
Additionally, these recommendations regarding the antenna system must be followed:
Do not include antenna within closed metal case.
Do not place the antenna in close vicinity to end users, since the emitted radiation in human tissue
is limited by regulatory requirements.
Place the antenna far from sensitive analog systems or employ countermeasures to reduce
electromagnetic compatibility issues.
Take care of interaction between co-located RF systems since the cellular transmitted RF power
may interact or disturb the performance of companion systems.
The antenna shall provide optimal efficiency figure over all the operating frequencies.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 37 of 82
Page 38

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Manufacturer
Part Number
Product Name
Description
Taoglas
PA.710.A
Warrior
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2300..2400 MHz, 2490..2690 MHz
40.0 x 6.0 x 5.0 mm
Taoglas
PCS.06.A
Havok
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2500..2690 MHz
42.0 x 10.0 x 3.0 mm
Taoglas
MCS6.A
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2690 MHz
42.0 x 10.0 x 3.0 mm
Antenova
SR4L002
Lucida
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2300..2400 MHz, 2490..2690 MHz
35.0 x 8.5 x 3.2 mm
Ethertronics
P822601
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2490..2700 MHz
50.0 x 8.0 x 3.2 mm
Ethertronics
P822602
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2490..2700 MHz
50.0 x 8.0 x 3.2 mm
Ethertronics
1002436
GSM / WCDMA / LTE Vertical Mount Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2700 MHz
50.6 x 19.6 x 1.6 mm
Pulse
W3796
Domino
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1427..1661 MHz, 1695..2200 MHz, 2300..2700 MHz
42.0 x 10.0 x 3.0 mm
TE Connectivity
2118310-1
GSM / WCDMA / LTE Vertical Mount Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2300..2700 MHz
74.0 x 10.6 x 1.6 mm
Molex
1462000001
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1700..2700 MHz
40.0 x 5.0 x 5.0 mm
Cirocomm
DPAN0S07
GSM / WCDMA / LTE SMD Antenna
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2500..2700 MHz
37.0 x 5.0 x 5.0 mm
The antenna shall provide appropriate gain figure (i.e. combined antenna directivity and efficiency
figure) so that the electromagnetic field radiation intensity does not exceed the regulatory limits
specified in some countries (e.g. by FCC in the United States).
Consider including extra footprints for a “pi” network in between the cellular module and the
antenna, for further improvement in the antenna matching circuit to reach optimal antenna
performance.
Examples of antennas
Table 15 lists some examples of possible internal on-board surface-mount antennas
Table 15: Examples of internal surface-mount antennas
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 38 of 82
Page 39

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Manufacturer
Part Number
Product Name
Description
Taoglas
FXUB63.07.0150C
GSM / WCDMA / LTE PCB Antenna with cable and U.FL connector
698..960 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2400..2690 MHz
96.0 x 21.0 mm
Taoglas
FXUB66.07.0150C
Maximus
GSM / WCDMA / LTE Antenna on flexible PCB with cable and U.FL
698..960 MHz, 1390..1435 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz,
2400..2700 MHz, 3400..3600 MHz, 4800..6000 MHz
120.2 x 50.4 mm
Antenova
SRFL029
Moseni
GSM / WCDMA / LTE Antenna on flexible PCB with cable and U.FL
689..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2300..2400 MHz, 2500..2690 MHz
110.0 x 20.0 mm
Antenova
SRFL026
Mitis
GSM / WCDMA / LTE Antenna on flexible PCB with cable and U.FL
689..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2300..2400 MHz, 2500..2690 MHz
110.0 x 20.0 mm
Ethertronics
1002289
GSM / WCDMA / LTE Antenna on flexible PCB with cable and U.FL
698..960 MHz, 1710..2700 MHz
140.0 x 75.0 mm
EAD
FSQS35241-UF-10
SQ7
GSM / WCDMA / LTE PCB Antenna with cable and U.FL connector
690..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2500..2700 MHz
110.0 x 21.0 mm
Manufacturer
Part Number
Product Name
Description
Taoglas
GSA.8827.A.101111
Phoenix
GSM / WCDMA / LTE low-profile adhesive-mount Antenna with cable
and SMA(M) connector
698..960 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2490..2690 MHz
105 x 30 x 7.7 mm
Taoglas
TG.30.8112
GSM / WCDMA / LTE swivel dipole Antenna with SMA(M) connector
698..960 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2400..2700 MHz
148.6 x 49 x 10 mm
Taoglas
MA241.BI.001
Genesis
GSM / WCDMA / LTE MIMO 2in1 adhesive-mount combination
antenna waterproof IP67 rated with cable and SMA(M)
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2400..2700 MHz
205.8 x 58 x 12.4 mm
Laird Tech.
TRA6927M3PW-001
GSM / WCDMA / LTE screw-mount antenna with N-type(F)
698..960 MHz, 1710..2170 MHz, 2300..2700 MHz
83.8 x Ø 36.5 mm
Laird Tech.
CMS69273
GSM / WCDMA / LTE ceiling-mount Antenna with N-type(F) connector
698..960 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, 1710..2700 MHz
86 x Ø 199 mm
Laird Tech.
OC69271-FNM
GSM / WCDMA / LTE pole-mount Antenna with N-type(M) connector
698..960 MHz, 1710..2690 MHz
248 x Ø 24.5 mm
Pulse
Electronics
WA700/2700SMA
GSM / WCDMA / LTE clip-mount MIMO antenna with cables and
SMA(M)
698..960 MHz,1710..2700 MHz
149 x 127 x 5.1 mm
Table 16 lists some examples of possible internal off-board PCB-type antennas with cable and
connector.
Table 16: Examples of internal antennas with cable and connector
Table 17 lists some examples of possible external antennas.
Table 17: Examples of external antennas
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 39 of 82
Page 40

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Application Board
Antenna Cable
SARA-N2 series
56
ANT
62
ANT_DET
R1
C1 D1
L1
C2
J1
Z0= 50
Ω
Z0= 50
Ω
Z0= 50 ohm
Antenna Assembly
R
2
C4
L3
Radiating
Element
Diagnostic
Circuit
GND
L2
C3
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1
27 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H270J - Murata
C2
33 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H330J - Murata
D1
Very Low Capacitance ESD Protection
PESD0402-140 - Tyco Electronics
L1
68 nH Multilayer Inductor 0402 (SRF ~1 GHz)
LQG15HS68NJ02 - Murata
R1
10 k Resistor 0402 1% 0.063 W
RK73H1ETTP1002F - KOA Speer
J1
SMA Connector 50 Through Hole Jack
SMA6251A1-3GT50G-50 - Amphenol
C3
15 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H150J - Murata
L2
39 nH Multilayer Inductor 0402 (SRF ~1 GHz)
LQG15HN39NJ02 - Murata
C4
22 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 25 V
GRM1555C1H220J - Murata
L3
68 nH Multilayer Inductor 0402 (SRF ~1 GHz)
LQG15HS68NJ02 - Murata
R2
15 k Resistor for Diagnostic
Various Manufacturers
2.4.2 Antenna detection interface (ANT_DET)
☞ Antenna detection interface is not supported in the "02" version of the product.
2.4.2.1 Guidelines for ANT_DET circuit design
Figure 19 and Table 18 describe the recommended schematic and components for the antenna
detection circuit to be provided on the application board for the diagnostic circuit that must be
provided on the antenna assembly to achieve antenna detection functionality.
Figure 19: Suggested schematic for antenna detection circuit on application board and diagnostic circuit on antenna
assembly
Table 18: Suggested components for antenna detection circuit on application board and diagnostic circuit on antenna
assembly
The antenna detection circuit and diagnostic circuit suggested in Figure 19 and Table 18 are here
explained:
When antenna detection is forced by the dedicated AT command (see SARA-N2 series AT
Commands Manual [3]), the ANT_DET pin generates a DC current measuring the resistance (R2)
from the antenna connector (J1) provided on the application board to GND.
DC blocking capacitors are needed at the ANT pin (C2) and at the antenna radiating element (C4)
to decouple the DC current generated by the ANT_DET pin.
Choke inductors with a Self Resonance Frequency (SRF) in the range of 1 GHz are needed in series
at the ANT_DET pin (L1) and in series at the diagnostic resistor (L3), to avoid a reduction of the RF
performance of the system, improving the RF isolation of the load resistor.
Additional components (R1, C1 and D1 in Figure 19) are needed at the ANT_DET pin as ESD
protection.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 40 of 82
Page 41

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Additional high pass filter (C3 and L2 in Figure 19) is provided at the ANT pin as ESD immunity
improvement
The ANT pin must be connected to the antenna connector by means of a transmission line with
nominal characteristics impedance as close as possible to 50 .
The DC impedance at RF port for some antennas may be a DC open (e.g. linear monopole) or a DC short
to reference GND (e.g. PIFA antenna). For those antennas, without the diagnostic circuit of Figure 19,
the measured DC resistance is always at the limits of the measurement range (respectively open or
short), and there is no mean to distinguish between a defect on antenna path with similar
characteristics (respectively: removal of linear antenna or RF cable shorted to GND for PIFA antenna).
Furthermore, any other DC signal injected to the RF connection from ANT connector to radiating
element will alter the measurement and produce invalid results for antenna detection.
☞ It is recommended to use an antenna with a built-in diagnostic resistor in the range from 5 k to
30 k to assure good antenna detection functionality and avoid a reduction of module RF
performance. The choke inductor should exhibit a parallel Self Resonance Frequency (SRF) in the
range of 1 GHz to improve the RF isolation of load resistor.
For example:
Consider an antenna with built-in DC load resistor of 15 k. Using the dedicated AT command (see
SARA-N2 series AT Commands Manual [3]), the module reports the resistance value evaluated from
the antenna connector provided on the application board to GND:
Reported values close to the used diagnostic resistor nominal value (i.e. values from 13 k to 17 k
if a 15 k diagnostic resistor is used) indicate that the antenna is properly connected.
Values close to the measurement range maximum limit, or an open-circuit “over range” report,
means that that the antenna is not connected or the RF cable is broken.
Reported values below the measurement range minimum limit (1 k) highlights a short to GND at
antenna or along the RF cable.
Measurement inside the valid measurement range and outside the expected range may indicate
an improper connection, damaged antenna or wrong value of antenna load resistor for diagnostic.
Reported value could differ from the real resistance value of the diagnostic resistor mounted
inside the antenna assembly due to antenna cable length, antenna cable capacity and the used
measurement method.
☞ If the antenna detection function is not required by the customer application, the ANT_DET pin
can be left not connected and the ANT pin can be directly connected to the antenna connector by
means of a 50 transmission line as described in Figure 18.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 41 of 82
Page 42

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
SARA module
C2
R1
D1
C1
L1
J1
C3 L2
2.4.2.2 Guidelines for ANT_DET layout design
Figure 20 describes the recommended layout for the antenna detection circuit to be provided on the
application board to achieve antenna detection functionality, implementing the recommended
schematic described in the previous Figure 19 and Table 18.
Figure 20: Suggested layout for antenna detection circuit on application board
The antenna detection circuit layout suggested in Figure 20 is here explained:
The ANT pin is connected to the antenna connector by means of a 50 transmission line,
implementing the design guidelines described in section 2.4.1 and the recommendations of the
SMA connector manufacturer.
DC blocking capacitor at the ANT pin (C2) is placed in series to the 50 transmission line.
The ANT_DET pin is connected to the 50 transmission line by means of a sense line.
Choke inductor in series at the ANT_DET pin (L1) is placed so that one pad is on the 50
transmission line and the other pad represents the start of the sense line to the ANT_DET pin.
The additional components (R1, C1 and D1) on the ANT_DET line are placed as ESD protection.
The additional high pass filter (C3 and L2) on the ANT line are placed as ESD immunity
improvement.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 42 of 82
Page 43

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
2.5 SIM interface
2.5.1.1 Guidelines for SIM circuit design
Guidelines for SIM cards, SIM connectors and SIM chips selection
The ISO/IEC 7816, the ETSI TS 102 221 and the ETSI TS 102 671 specifications define the physical,
electrical and functional characteristics of Universal Integrated Circuit Cards (UICC) which contains
the Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) integrated circuit that securely stores all the information
needed to identify and authenticate subscribers over the cellular network.
Removable UICC / SIM card contacts mapping is defined by ISO/IEC 7816 and ETSI TS 102 221 as
follows:
Contact C1 = VCC (Supply) It must be connected to VSIM
Contact C2 = RST (Reset) It must be connected to SIM_RST
Contact C3 = CLK (Clock) It must be connected to SIM_CLK
Contact C4 = AUX1 (Auxiliary contact) It must be left not connected
Contact C5 = GND (Ground) It must be connected to GND
Contact C6 = VPP (Programming supply) It can be left not connected
Contact C7 = I/O (Data input/output) It must be connected to SIM_IO
Contact C8 = AUX2 (Auxiliary contact) It must be left not connected
A removable SIM card can have 6 contacts (C1 = VCC, C2 = RST, C3 = CLK, C5 = GND, C6 = VPP, C7 =
I/O) or 8 contacts, providing also the auxiliary contacts C4 = AUX1 and C8 = AUX2 for USB interfaces
and other uses. Only 5 contacts are required and must be connected to the module SIM card interface
as described above, since the modules do not support the additional auxiliary features (contacts C4 =
AUX1 and C8 = AUX2).
Removable SIM card are suitable for applications where the SIM changing is required during the
product lifetime.
A SIM card holder can have 6 or 8 positions if a mechanical card presence detector is not provided, or
it can have 6+2 or 8+2 positions if two additional pins related to the normally-open mechanical switch
integrated in the SIM connector for the mechanical card presence detection are provided.
Solderable UICC / SIM chip contacts mapping (M2M UICC Form Factor) is defined by ETSI TS 102 671
as follows:
Package Pin 8 = UICC Contact C1 = VCC (Supply) It must be connected to VSIM
Package Pin 7 = UICC Contact C2 = RST (Reset) It must be connected to SIM_RST
Package Pin 6 = UICC Contact C3 = CLK (Clock) It must be connected to SIM_CLK
Package Pin 5 = UICC Contact C4 = AUX1 (Auxiliary contact) It must be left not connected
Package Pin 1 = UICC Contact C5 = GND (Ground) It must be connected to GND
Package Pin 2 = UICC Contact C6 = VPP (Programming supply) It can be left not connected
Package Pin 3 = UICC Contact C7 = I/O (Data input/output) It must be connected to SIM_IO
Package Pin 4 = UICC Contact C8 = AUX2 (Auxiliary contact) It must be left not connected
A solderable SIM chip has 8 contacts and can provide also the auxiliary contacts C4 = AUX1 and C8 =
AUX2 for USB interfaces and other uses, but only 5 contacts are required and must be connected to
the module SIM card interface as described above, since the SARA-N2 series modules do not support
the additional auxiliary features (contacts C4 = AUX1 and C8 = AUX2).
Solderable SIM chips are suitable for M2M applications where it is not required to change the SIM
once installed.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 43 of 82
Page 44

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
SARA-N2
41
VSIM
39
SIM_IO
38
SIM_CLK
40
SIM_RST
SIM CARD
HOLDER
C5C6C
7
C1C2C
3
SIM Card
bottom view
(contacts side)
C1
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
C2 C3 C5
J1
C4
D1 D2 D3 D4
C
8
C
4
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3, C4
47 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H470JA01 - Murata
C5
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
D1, D2, D3, D4
Very Low Capacitance ESD Protection
PESD0402-140 - Tyco Electronics
J1
SIM Card Holder
6 positions, without card presence switch
Various Manufacturers,
C707 10M006 136 2 - Amphenol
Guidelines for SIM card connection
An application circuit for the connection to a removable SIM card placed in a SIM card holder is
described in Figure 21.
Follow these guidelines connecting the module to a SIM connector:
Connect the UICC / SIM contacts C1 (VCC) to the VSIM pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C7 (I/O) to the SIM_IO pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C3 (CLK) to the SIM_CLK pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C2 (RST) to the SIM_RST pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C5 (GND) to ground.
Provide a 100 nF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R71C104K) at the SIM supply line (VSIM),
close to the related pad of the SIM connector, to prevent digital noise.
Provide a bypass capacitor of about 22 pF to 47 pF (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H470J) on each SIM
line (VSIM, SIM_CLK, SIM_IO, SIM_RST), very close to each related pad of the SIM connector, to
prevent RF coupling especially in case the RF antenna is placed closer than 10 - 30 cm from the
SIM card holder.
Provide a low capacitance (i.e. less than 10 pF) ESD protection (e.g. Tyco Electronics PESD0402-
140) on each externally accessible SIM line, close to each related pad of the SIM connector ESD
sensitivity rating of the SIM interface pins is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-A114),
so that, according to the EMC/ESD requirements of the custom application, higher protection level
can be required if the lines are externally accessible on the application device.
Limit capacitance and series resistance on each SIM signal (SIM_CLK, SIM_IO, SIM_RST) to
match the requirements for the SIM interface regarding maximum allowed rise time on the lines.
Figure 21: Application circuit for the connection to a single removable SIM card
Table 19: Example of components for the connection to a removable SIM card
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 44 of 82
Page 45

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
41
VSIM
39
SIM_IO
38
SIM_CLK
40
SIM_RST
SIM CHIP
SIM Chip
bottom view
(contacts side)
C1
VPP (C6)
VCC (C1)
IO (C7)
CLK (C3)
RST (C2)
GND (C5)
C2 C3 C5
U1
C4
2
8
3
6
7
1
C1 C5
C2 C6
C3 C7
C4 C8
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
SARA-N2
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3, C4
47 pF Capacitor Ceramic C0G 0402 5% 50 V
GRM1555C1H470JA01 - Murata
C5
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R71C104KA01 - Murata
U1
SIM chip (M2M UICC Form Factor)
Various Manufacturers
Guidelines for single SIM chip connection
Figure 22 describes an application circuit for the connection to a solderable SIM chip (M2M UICC Form
Factor).
Follow these guidelines connecting the module to a solderable SIM chip:
Connect the UICC / SIM contacts C1 (VCC) to the VSIM pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C7 (I/O) to the SIM_IO pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C3 (CLK) to the SIM_CLK pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C2 (RST) to the SIM_RST pin of the module.
Connect the UICC / SIM contact C5 (GND) to ground.
Provide a 100 nF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM155R71C104K) at the SIM supply line (VSIM)
close to the related pad of the SIM chip, to prevent digital noise.
Provide a bypass capacitor of about 22 pF to 47 pF (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H470J) on each SIM
line (VSIM, SIM_CLK, SIM_IO, SIM_RST), to prevent RF coupling especially in case the RF antenna
is placed closer than 10 - 30 cm from the SIM card holder.
Limit capacitance and series resistance on each SIM signal (SIM_CLK, SIM_IO, SIM_RST) to
match the requirements for the SIM interface regarding maximum allowed rise time on the lines.
Figure 22: Application circuit for the connection to a single solderable SIM chip
Table 20: Example of components for the connection to a solderable SIM chip
2.5.1.2 Guidelines for SIM layout design
The layout of the SIM card interface lines (VSIM, SIM_CLK, SIM_IO, SIM_RST) may be critical if the
SIM card is placed far away from the SARA-N2 series modules or in close proximity to the RF antenna:
these two cases should be avoided or at least mitigated as described below.
In the first case, the long connection can cause the radiation of some harmonics of the digital data
frequency as any other digital interface: keep the traces short and avoid coupling with RF line or
sensitive analog inputs.
In the second case, the same harmonics can be picked up and create self-interference that can reduce
the sensitivity of the receiver channels whose carrier frequency is coincidental with harmonic
frequencies: placing the RF bypass capacitors suggested in 2.5.1.1 near the SIM connector will
mitigate the problem.
In addition, since the SIM card is typically accessed by the end user, it can be subjected to ESD
discharges: add adequate ESD protection as suggested in 2.5.1.1 to protect module SIM pins near the
SIM connector.
Limit capacitance and series resistance on each SIM signal to match the SIM specifications: the
connections should always be kept as short as possible.
Avoid coupling with any sensitive analog circuit, since the SIM signals can cause the radiation of some
harmonics of the digital data frequency.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 45 of 82
Page 46

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
TxD
Application Processor
(3.3V DTE)
RxD
GND
SARA-N2
(DCE)
12
TXD
13
RXD
GND
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
52
VCC
3V3
3V3
VCC
51
VCC
53
VCC
52
VCC
TxD
Application Processor
(1.8V DTE)
SARA-N2
(DCE)
12
TXD
3V6
B A
GND
U1
VCCB
VCCA
Unidirectional
Voltage Translator
C1
C2
1V8
DIR
VCC
0Ω
TP
51
VCC
53
VCC
RxD
GND
13
RXD
GND
GND
DIR
0Ω
TP
3V6
B A
U2
VCCB
VCCA
Unidirectional
Voltage Translator
C3
C4
1V8
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2, C3, C4
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R61A104KA01 - Murata
U1, U2
Unidirectional Voltage Translator
SN74LVC1T45 - Texas Instruments
2.6 Serial interfaces
2.6.1 Asynchronous serial interface (UART)
Guidelines for UART circuit design without RING indication
If a 3.3 V Application Processor (DTE) is used, the UART interface of SARA-N2 module can be directly
connected with the UART interface of the DTE as shown in Figure 23:
Connect DTE TxD output line with the TXD input pin of SARA-N2
Connect DTE RxD input line with the RXD output pin of SARA-N2
RTS and CTS lines of the module can be left unconnected and floating, because HW flow control
is not supported by "02" product versions
Use the same external supply rail (for example, at 3.3 V or 3.6 V) for both the SARA-N2 module and
the Application Processor (DTE), so that the interface of both devices operates at the same level,
considering that the UART interface of SARA-N2 module operates at the VCC voltage level
Figure 23: UART interface application circuit with partial V.24 link (3-wire) in the DTE/DCE serial communication (3.3 V DTE)
If a 1.8 V Application Processor (DTE) is used, then it is recommended to connect the UART interface
of the module (DCE) by means of appropriate unidirectional voltage translators using the module VCC
line as the supply for the voltage translators on the module side, as described in Figure 24.
Figure 24: UART interface application circuit with partial V.24 link (3-wire) in DTE/DCE serial communication (1.8 V DTE)
Table 21: Component for UART application circuit with partial V.24 link (3-wire) in DTE/DCE serial communication (1.8 V DTE)
☞ It is not recommended to use V_INT pin as control and/or supply line for the external voltage
translator.
☞ It is recommended to provide a direct access to the TXD and RXD lines by means of accessible
testpoints for diagnostic purpose.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 46 of 82
Page 47

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
TxD
Application Processor
(3.3V DTE)
RxD
RI
GND
SARA-N2
(DCE)
12
TXD
13
RXD
10
RTS
11
CTS
GND
0Ω
TP
0Ω
TP
52
VCC
3V3
3V3
VCC
51
VCC
53
VCC
2.6.1.1 Guidelines for UART circuit design with RING indication
If the application board requires a RING indication to get notifications when an URC or when new data
is available, the CTS line can be used for such a functionality. In this case the circuit should be
implemented as shown in Figure 25:
Connect DTE TxD output line with the TXD input pin of SARA-N2
Connect DTE RxD input line with the RXD output pin of SARA-N2
Connect DTE RI input line with the CTS output pin of SARA-N2
Leave RTS line of the module unconnected and floating.
Use the same external supply rail (for example, at 3.3 V or 3.6 V) for both the SARA-N2 module and
the Application Processor (DTE), so that the interface of both devices operates at the same level,
considering that the UART interface of SARA-N2 module operates at the VCC voltage level
☞ Hardware flow control lines CTS and RTS are not supported by "02" product versions.
Figure 25: UART application circuit with partial V.24 link (3-wire) serial communication and RING indication (3.3 V DTE)
2.6.1.2 Additional considerations
If a 1.8 V Application Processor (DTE) is used, the voltage scaling from any UART output of the module
(DCE), working at VCC voltage level (3.6 V nominal), to the apposite 1.8 V input of the DTE can be
implemented, as an alternative low-cost solution, by means of an appropriate voltage divider.
Consider the value of the pull-up integrated at the input of the Application Processor (DTE), if any, for
the correct selection of the voltage divider resistance values.
Mind that any DTE signal connected to the UART interface of the module has to be tri-stated or set
low before applying VCC supply, to avoid latch-up of circuits and allow a proper boot of the module.
☞ There is no internal pull-up / pull-down inside the TXD input of the module, which is assumed to be
controlled by the external host once UART is initialized: to avoid an increase in current
consumption, consider to add an external pull-up resistor of about 47 k to 100 k, biased by VCC
module supply rail, if the TXD input is left floating by the external host in some application
scenario.
☞ ESD sensitivity rating of UART pins is 1 kV (HBM according to JESD22-A114). Higher protection
level could be required if the lines are externally accessible on the application board. Higher
protection level can be achieved by mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG
varistor) close to accessible points.
2.6.1.3 Guidelines for UART layout design
The UART serial interface requires the same consideration regarding electro-magnetic interference
as any other digital interface. Keep the traces short and avoid coupling with RF line or sensitive analog
inputs, since the signals can cause the radiation of some harmonics of the digital data frequency.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 47 of 82
Page 48

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
scaling
SARA-N2 series
(DCE)
16
GPIO1
GND
TestPoint
4
V_INT
TestPoint
scaling
TxD
Application Processor
(1.8V DTE)
SARA-N2 series
(DCE)
16
GPIO1
GND GND
0 ohm
TestPoint
4
V_INT
TestPoint
4
V_INT
TxD
Application Processor
(3.3V DTE)
GND
SARA-N2 series
(DCE)
16
GPIO1
GND
1V8
B A
GND
U1
VCCB
VCCA
Unidirectional
Voltage Translator
C1
C2
3V3
DIR
VCC
0 ohm
TP
TP
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
C1, C2
100 nF Capacitor Ceramic X7R 0402 10% 16 V
GRM155R61A104KA01 - Murata
U1
Unidirectional Voltage Translator
SN74LVC1T45 - Texas Instruments
2.6.2 Secondary asynchronous serial interface (Secondary UART)
2.6.2.1 Guidelines for Secondary UART circuit design
The Secondary UART interface is provided on the GPIO1 pin and can be used for diagnostic, to collect
trace logs.
A suitable application circuit can be the one illustrated in Figure 26, where direct external access is
provided for diagnostic purpose by means of Test-Points made available on the application board for
GPIO1 and V_INT lines.
Figure 26: UART AUX interface application circuit providing direct external access for diagnostic purpose
The circuit with a 1.8 V application processor should be implemented as described in Figure 27.
Figure 27: UART AUX interface application circuit connecting a 1.8 V application processor
If a 3.3 V application processor is used, then it is recommended to connect the 1.8 V auxiliary UART
interface of the module by means of appropriate unidirectional voltage translators using the module
V_INT output as 1.8 V supply for the voltage translators on the module side, as described in Figure 28.
Figure 28: UART AUX interface application circuit connecting a 3.3 V application processor
Table 22: Component for UART AUX interface application circuit connecting a 3.3 V application processor
☞ It is recommended to provide a direct access to the GPIO1 pin by means of accessible testpoints
for diagnostic purpose
☞ ESD sensitivity rating of auxiliary UART pins is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-
A114). Higher protection level could be required if the lines are externally accessible on the
application board. Higher protection level can be achieved by mounting an ESD protection (e.g.
EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) close to accessible points.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 48 of 82
Page 49

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
SARA-N2 series
CTS
R1
R3
3V6
Network Indicator
R2
11
DL1
T1
TestPoint
GPIO1
16
Secondary UART for Diagnostic
Reference
Description
Part Number - Manufacturer
R1
10 k resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
Various manufacturers
R2
47 k resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
Various manufacturers
R3
820 resistor 0402 5% 0.1 W
Various manufacturers
DL1
LED red SMT 0603
LTST-C190KRKT - Lite-on Technology Corporation
T1
NPN BJT Transistor
BC847 - Infineon
2.6.3 DDC (I
☞ DDC (I
2
C) interface is not supported by the "02" version of the product.
2
C) interface
2.7 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
A typical usage of SARA-N2 series modules’ GPIOs follows:
GPIO1 pin providing secondary UART data output, available to collect trace diagnostic logs
delivered by the module: it is recommended to provide a direct access to the GPIO1 pin by means
of an accessible testpoint for diagnostic purposes (see sections 1.9.2 and 2.6.2)
CTS pin set as Network Indicator (see Figure 29 / Table 23 below) or Ring Indicator (see section
2.6.1.1)
Figure 29: Application circuit for network indication provided over CTS
Table 23: Components for network indication application circuit
☞ Use transistors with at least an integrated resistor in the base pin or otherwise put a 10 kΩ resistor
on the board in series to the GPIO of SARA-N2 series modules.
☞ Do not apply voltage to any GPIO of the module before the switch-on of the GPIO’s supply (V_INT),
to avoid latch-up of circuits and allow a proper boot of the module.
☞ ESD sensitivity rating of the GPIO pins is 1 kV (Human Body Model according to JESD22-A114).
A higher protection level could be required if the lines are externally accessible and it can be
achieved by mounting an ESD protection (e.g. EPCOS CA05P4S14THSG varistor array) close to
accessible points.
☞ If GPIO pins are not used, they can be left unconnected on the application board, but it is
recommended to provide direct access to the GPIO1 pin by means of accessible testpoints for
diagnostic purposes.
2.8 Reserved pins (RSVD)
SARA-N2 series modules have pins reserved for future use, marked as RSVD.
All the RSVD pins are to be left unconnected on the application board, except for the RSVD pin number
33 that can be externally connected to ground.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 49 of 82
Page 50

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
2.9 Module placement
Optimize placement for minimum length of RF line and closer path from DC source for VCC.
Make sure that the module, RF and analog parts / circuits are clearly separated from any possible
source of radiated energy, including digital circuits that can radiate some digital frequency harmonics,
which can produce Electro-Magnetic Interference affecting module, RF and analog parts / circuits’
performance or implement proper countermeasures to avoid any possible Electro-Magnetic
Compatibility issue.
Make sure that the module, RF and analog parts / circuits, high speed digital circuits are clearly
separated from any sensitive part / circuit which may be affected by Electro-Magnetic Interference or
employ countermeasures to avoid any possible Electro-Magnetic Compatibility issue.
Provide enough clearance between the module and any external part: clearance of at least 0.4 mm per
side is recommended to permit suitable mounting of the parts.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 50 of 82
Page 51

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
K
M1
M1
M2
E G H’ J’ E
ANT pin
B
Pin 1
K
G
H’
J’
A
D
D
O’
O’
L N L
I’
F’
F’
K
M1
M1
M2
E G H’’ J’’ E
ANT pin
B
Pin 1
K
G
H’’
J’’
A
D
D
O’’
O’’
L N L
I’’
F’’
F’’
Stencil: 150
µm
Parameter
Value
Parameter
Value
Parameter
Value
A
26.0 mm G
1.10 mm K
2.75 mm
B
16.0 mm H’
0.80 mm L
2.75 mm
C
3.00 mm H’’
0.75 mm
M1
1.80 mm
D
2.00 mm I’
1.50 mm
M2
3.60 mm
E
2.50 mm I’’
1.55 mm N
2.10 mm
F’
1.05 mm J’
0.30 mm O’
1.10 mm
F’’
1.00 mm J’’
0.35 mm O’’
1.05 mm
2.10 Module footprint and paste mask
Figure 30 and Table 24 describe the suggested footprint (i.e. copper mask) and paste mask layout for
SARA modules: the proposed land pattern layout reflects the modules’ pins layout, while the proposed
stencil apertures layout is slightly different (see the F’’, H’’, I’’, J’’, O’’ parameters compared to the F’,
H’, I’, J’, O’ ones).
The Non Solder Mask Defined (NSMD) pad type is recommended over the Solder Mask Defined (SMD)
pad type, implementing the solder mask opening 50 µ m larger per side than the corresponding copper
pad.
The recommended solder paste thickness is 150 µ m, according to application production process
requirements.
Figure 30: SARA-N2 series modules suggested footprint and paste mask (application board top view)
Table 24: SARA-N2 series modules suggested footprint and paste mask dimensions
☞ These are recommendations only and not specifications. The exact copper, solder and paste mask
geometries, distances, stencil thicknesses and solder paste volumes must be adapted to the
specific production processes (e.g. soldering etc.) of the customer.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 51 of 82
Page 52

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
2.11 SARA-N211 integration in devices intended for use in
potentially explosive atmospheres
2.11.1 General guidelines
SARA-N211 modules are certified as components intended for use in potentially explosive
atmospheres (see section 4.3 and see the “Approvals” section of the SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1]
for further details), with the following marking:
Ex II 1G, Ex ia IIC
According to the marking stated above, SARA-N211 modules are certified as electrical equipment of:
group “II”: intended for use in areas with explosive gas atmosphere other than mines susceptible
to firedamp.
category “1G”: intended for use in zone 0 hazardous areas, in which an explosive atmospheres is
caused by mixtures of air and gases, or when vapours or mists are continuously or frequently
present for long periods. The modules are also suitable for applications intended for use in zone 1
and zone 2 hazardous areas.
level of protection “ia”: intrinsically safe apparatus with very high level of protection, not capable
of causing ignition in normal operation and with the application of one countable fault or a
combination of any two countable fault plus those non-countable faults which give the most
onerous condition.
subdivision “IIC”: intended for use in areas where the nature of the explosive gas atmosphere is
considered very dangerous based on the Maximum Experimental Safe Gap or the Minimum
Ignition Current ratio of the explosive gas atmosphere in which the equipment may be installed
(typical gases are hydrogen, acetylene, carbon disulphide), so that the modules are also suitable
for applications intended for use in subdivision IIB (typical gases are ethylene, coke oven gas and
other industrial gases) and subdivision IIA (typical gases are industrial methane, propane, petrol
and the majority of industrial gases).
The temperature range of use of SARA-N211 modules is defined in the “Operating temperature range”
section of the SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1]. The modules are suitable for temperature class T4
applications, as long as the maximum input power does not exceed 2.0 W.
Even if SARA-N211 modules are certified as components intended for use in potentially explosive
atmospheres as described above, the application device that integrates the module must be approved
under all the certification schemes required by the specific application device that will be deployed in
the market as apparatus intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres.
The certification scheme approvals required for the application device integrating SARA-N211 module,
intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres, may differ depending on the following topics:
the country or the region where the application device must be deployed
the classification of the application device in relation to the use in potentially explosive
atmospheres
the classification of the hazardous areas in which the application device is intended for use
☞ Any specific applicable requirement for the implementation of the apparatus integrating SARA-
N211 module, intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres, must be fulfilled according to
the exact applicable standards: check the detailed requisites on the pertinent norms for the
application, as for example the IEC 60079-0 [15], IEC 60079-11[16], IEC 60079-26 [17] standards.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 52 of 82
Page 53

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
☞ The certification of the application device that integrates a SARA-N211 module and the
compliance of the application device with all the applicable certification schemes, directives and
standards required for use in potentially explosive atmospheres are the sole responsibility of the
application device manufacturer.
The application device integrating a SARA-N211 module for use in potentially explosive atmospheres
must be designed so that any circuit/part of the apparatus shall not invalidate the specific
characteristics of the type of protection of the module.
The intrinsic safety “i” type of protection of SARA-N211 modules is based on the restriction of the
electrical energy within equipment and of the interconnecting wiring exposed to the explosive
atmosphere to a level below that which can cause ignition by either sparking or heating effects.
The following input and equivalent parameters must be considered integrating a SARA-N211 module
in an application device intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres:
Total internal capacitance, Ci (see Table 25)
Total internal inductance, Li (see Table 25)
The module does not contain blocks which increase the voltage (e.g. like step-up, duplicators,
boosters, etc.)
The nameplate of SARA-N211 modules is described in the “Product labeling” section of the SARA-N2
series Data Sheet [1]. For additional info and modules’ certificate of compliancy for use in potentially
explosive atmospheres, see our website (www.u-blox.com) or contact the u-blox office or sales
representative nearest you.
☞ The final enclosure of the application device integrating SARA-N211 modules, intended for use in
potentially explosive atmospheres, must guarantee a minimum degree of ingress protection of
IP20.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 53 of 82
Page 54

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Parameter
SARA-N211
Ui
4.2 V
Ii
0.5 A
Ci
68.1 µF
Li
8.5 µH
2.11.2 Guidelines for VCC supply circuit design
The power supply ratings, average and pulse, must be considered in the design of the VCC supply
circuit on the application device integrating SARA-N211 module, implementing proper circuits
providing adequate maximum voltage and current to the VCC supply input of the modules, according
to the specific potentially explosive gas atmosphere category subdivision where the apparatus is
intended for use.
Table 25 lists the maximum input and equivalent parameters that must be considered in the sub-
division IIC, the sub-division IIB and the sub-division IIA for SARA-N211 modules.
Table 25: Maximum input and equivalent parameters for sub-division IIC
Primary and secondary cells and batteries
Cells and batteries incorporated into equipment with intrinsic safety “i” protection to potentially
explosive gas atmosphere shall conform to the requirements of the IEC 60079-0 [15],
IEC 60079-11 [16] ATEX standards.
Shunt voltage limiters
For Level of Protection “ia”, the application of controllable semiconductor components as shunt
voltage limiting devices, for example transistors, thyristors, voltage/current regulators, etc., may be
permitted if both the input and output circuits are intrinsically safe circuits or where it can be shown
that they cannot be subjected to transients from the power supply network. In circuits complying with
the above, two devices are considered to be an infallible assembly.
For Level of Protection “ia”, three independent active voltage limitation semiconductor circuits may
be used in associated apparatus provided the transient conditions of the clause 7.5.1 of IEC 60079-11
standard are met. These circuits shall also be tested in accordance with the clause 10.1.5.3 of the IEC
60079-11 standard [16].
Series current limiters
The use of three series blocking diodes in circuits of Level of Protection “ia” is permitted, however,
other semiconductors and controllable semiconductor devices shall be used as series current-limiting
devices only in Level of Protection “ib” or “ic” apparatus. However, for power limitation purposes, Level
of Protection “ia” apparatus may use series current limiters consisting of controllable and noncontrollable semiconductor devices.
The use of semiconductors and controllable semiconductor devices as current-limiting devices for
spark ignition limitation is not permitted for Level of Protection “ia” apparatus because of their
possible use in areas in which a continuous or frequent presence of an explosive atmosphere may
coincide with the possibility of a brief transient which could cause ignition. The maximum current that
may be delivered may have a brief transient but will not be taken as Io, because the compliance with
the spark ignition test of the clause 10.1 of IEC 60079-11 standard [16] would have established the
successful limitation of the energy in this transient.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 54 of 82
Page 55

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Gas group II subdivision
RF threshold power limits according to the IEC 60079-0 ATEX standard
IIA (a typical gas is propane)
6.0 W
IIB (a typical gas is ethylene)
3.5 W
IIC (a typical gas is hydrogen)
2.0 W
Protection against polarity reversal
Protection against polarity reversal shall be provided within intrinsically safe apparatus to prevent
invalidation of the type of protection as a result of reversal of the polarity of supplies to that
intrinsically safe apparatus or at connections between cells of a battery where this could occur. For
this purpose, single diode shall be acceptable.
Other considerations
All the recommendations reported in section 2.11.1 must be considered for the implementation of the
VCC supply circuit on application integrating SARA-N211 modules intended for use in potentially
explosive atmospheres. Any specific applicable requirement for the VCC supply circuit design must
be fulfilled according to all the exact applicable standards for the apparatus.
☞ Check the detailed requisites on the pertinent norms for the application apparatus, as for example
the IEC 60079-0 [15], IEC 60079-11 [16], IEC 60079-26 [17] standards.
2.11.3 Guidelines for antenna RF interface design
The RF radiating power of SARA-N211 modules is compliant to all the applicable 3GPP / ETSI
standards, with a maximum of 250 mW RF average power according to the LTE Cat NB1 Power Class
stated in Table 2.
The RF threshold power of the application device integrating a SARA-N211 module is defined,
according to the IEC 60079-0 ATEX standard [15], as the product of the effective output power of the
module multiplied by the antenna gain (implemented/used on the application device).
The RF threshold power of the application device integrating a SARA-N211 module must not exceed
the limits shown in Table 26, according to the IEC 60079-0 ATEX standard [15].
Table 26: RF threshold power limits for the different gas group II subdivisions according to the IEC 60079-0 ATEX standard [15]
☞ The system antenna(s) implemented/used on the application device integrating SARA-N211
module must be designed/selected so that the antenna gain (i.e. the combined transmission line,
connector, cable losses and radiating element gain) multiplied by the output power of the module
does not exceed the limits shown in Table 26.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 55 of 82
Page 56

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
3V6
GND
100uF 10nF
SARA-N2 series
52 VCC
53 VCC
51 VCC
68pF
SDA
SCL
26
27
RSVD
GND
18
RESET_N
Application
Processor
Open
drain
output
TP
12
TXD
13
RXD
10
RTS
11
CTS
TP
TP
TXD
RXD
RI
3.6V DTE
GND
0Ω
0Ω
47pF
SIM Card Holder
CCVCC (C1)
CCVPP (C6)
CCIO (C7)
CCCLK (C3)
CCRST (C2)
GND (C5)
47pF 47pF 100nF
41VSIM
39SIM_IO
38
SIM_CLK
40
SIM_RST
47pF
4V_INT
ESD ESD ESD ESD
Test-Point
62
ANT_DET
10k
27pF
ESD
68nH
56
Connector
External
antenna
33pF
ANT
39nH
15pF
24
16
GPIO2
GPIO1
15pF100nF
VCC
3V6
Test-Point
Network
Indicator
3V6
GND
2.12 Schematic for SARA-N2 series module integration
Figure 31 is an example of a schematic diagram where a SARA-N2 series module “02” product version
is integrated into an application board, using all the available interfaces and functions of the module.
Figure 31: Example of schematic diagram to integrate a SARA-N2 module “02” product version using all available interfaces
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 56 of 82
Page 57

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
2.13 Design-in checklist
2.13.1 Schematic checklist
The following are the most important points for a simple schematic check:
DC supply must provide a nominal voltage at VCC pin above the minimum operating range
limit.
DC supply must be capable of providing, at VCC pins, the specified average current during a
transmission at maximum power with a voltage level above the minimum operating range
limit.
VCC supply should be clean, with very low ripple/noise.
Do not apply loads which might exceed the limit for maximum available current from V_INT
supply.
Check that voltage level of any connected pin does not exceed the relative operating range.
Capacitance and series resistance must be limited on each SIM signal to match the SIM
specifications.
Insert the suggested capacitors on each SIM signal and low capacitance ESD protections if
accessible.
Check UART signals direction, since the signal names follow the ITU-T V.24
Recommendation [5].
Provide accessible testpoints directly connected to the following pins: TXD, RXD, GPIO1, V_INT
and RESET_N for diagnostic purpose.
Provide proper precautions for ESD immunity as required on the application board.
Any external signal connected to the UART interface pin must be tri-stated or set low before
applying VCC supply, to avoid latch-up of circuits and let a proper boot of the module.
Any external signal connected to any generic digital interface pin (GPIO, I2C) must be tri-stated
or set low when the module is in not-powered mode and during the module power-on sequence
(at least until the activation of the V_INT output), to avoid latch-up of circuits and let a proper
boot of the module.
All unused pins can be left unconnected.
2.13.2 Layout checklist
The following are the most important points for a simple layout check:
Check 50 nominal characteristic impedance of the RF transmission line connected to the
ANT pad (antenna RF input/output interface).
Follow the recommendations of the antenna producer for correct antenna installation and
deployment (PCB layout and matching circuitry).
Ensure no coupling occurs between the RF interface and noisy or sensitive signals (like SIM
signals and high-speed digital lines).
VCC line should be wide and short.
Route VCC supply line away from sensitive analog signals.
Ensure proper grounding.
Optimize placement for minimum length of RF line and closer path from DC source for VCC.
Keep routing short and minimize parasitic capacitance on the SIM lines to preserve signal
integrity.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 57 of 82
Page 58

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
2.13.3 Antenna checklist
Antenna termination should provide 50 characteristic impedance with V.S.W.R at least less
than 3:1 (recommended 2:1) on operating bands in deployment geographical area.
Follow the recommendations of the antenna producer for correct antenna installation and
deployment (PCB layout and matching circuitry).
Ensure compliance with any regulatory agency RF radiation requirement.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Design-in Page 58 of 82
Page 59

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
3 Handling and soldering
☞ No natural rubbers, no hygroscopic materials or materials containing asbestos are employed.
3.1 Packaging, shipping, storage and moisture preconditioning
For information pertaining to reels and tapes, Moisture Sensitivity levels (MSD), shipment and
storage information, as well as drying for preconditioning see the SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1] and
the u-blox Package Information Guide [2].
3.2 Handling
The SARA-N2 series modules are Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) sensitive devices.
⚠ Ensure ESD precautions are implemented during handling of the module.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden and momentary electric current that flows between two
objects at different electrical potentials caused by direct contact or induced by an electrostatic field.
The term is usually used in the electronics and other industries to describe momentary unwanted
currents that may cause damage to electronic equipment.
The ESD sensitivity for each pin of SARA-N2 series modules (as Human Body Model according to
JESD22-A114F) is specified in the SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1].
ESD prevention is based on establishing an Electrostatic Protective Area (EPA). The EPA can be a
small working station or a large manufacturing area. The main principle of an EPA is that there are no
highly charging materials near ESD sensitive electronics, all conductive materials are grounded,
workers are grounded, and charge build-up on ESD sensitive electronics is prevented. International
standards are used to define typical EPA and can be obtained for example from International
Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
In addition to standard ESD safety practices, the following measures should be taken into account
whenever handling the SARA-N2 series modules:
Unless there is a galvanic coupling between the local GND (i.e. the work table) and the PCB GND,
then the first point of contact when handling the PCB must always be between the local GND and
PCB GND.
Before mounting an antenna patch, connect ground of the device.
When handling the module, do not come into contact with any charged capacitors and be careful
when contacting materials that can develop charges (e.g. patch antenna, coax cable, soldering
iron,…).
To prevent electrostatic discharge through the RF pin, do not touch any exposed antenna area. If
there is any risk that such exposed antenna area is touched in non ESD protected work area,
implement proper ESD protection measures in the design.
When soldering the module and patch antennas to the RF pin, make sure to use an ESD safe
soldering iron.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Handling and soldering Page 59 of 82
Page 60

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
3.3 Soldering
3.3.1 Soldering paste
Use of "No Clean" soldering paste is strongly recommended, as it does not require cleaning after the
soldering process has taken place. The paste listed in the example below meets these criteria.
Soldering Paste: OM338 SAC405 / Nr.143714 (Cookson Electronics)
Alloy specification: 95.5% Sn / 3.9% Ag / 0.6% Cu (95.5% Tin / 3.9% Silver / 0.6% Copper)
95.5% Sn / 4.0% Ag / 0.5% Cu (95.5% Tin / 4.0% Silver / 0.5% Copper)
Melting Temperature: 217 °C
Stencil Thickness: 150 µ m for base boards
The final choice of the soldering paste depends on the approved manufacturing procedures.
The paste-mask geometry for applying soldering paste should meet the recommendations in section
2.10.
☞ The quality of the solder joints should meet the appropriate IPC specification.
3.3.2 Reflow soldering
A convection type-soldering oven is strongly recommended over the infrared type radiation oven.
Convection heated ovens allow precise control of the temperature and all parts will be heated up
evenly, regardless of material properties, thickness of components and surface color.
Consider the "IPC-7530 Guidelines for temperature profiling for mass soldering (reflow and wave)
processes, published 2001".
Reflow profiles are to be selected according to the following recommendations.
⚠ Failure to observe these recommendations can result in severe damage to the device!
Preheat phase
Initial heating of component leads and balls. Residual humidity will be dried out. Note that this preheat
phase will not replace prior baking procedures.
Temperature rise rate: max 3 °C/s If the temperature rise is too rapid in the preheat phase it
may cause excessive slumping.
Time: 60 to 120 s If the preheat is insufficient, rather large solder balls tend
to be generated. Conversely, if performed excessively, fine
balls and large balls will be generated in clusters.
End Temperature: 150 to 200 °C If the temperature is too low, non-melting tends to be
caused in areas containing large heat capacity.
Heating/ reflow phase
The temperature rises above the liquidus temperature of 217 °C. Avoid a sudden rise in temperature
as the slump of the paste could become worse.
Limit time above 217 °C liquidus temperature: 40 to 60 s
Peak reflow temperature: 245 °C
UBX-17005143 - R06 Handling and soldering Page 60 of 82
Page 61

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Preheat Heating Cooling
[°C]
Peak Temp. 245°C
[°C]
## ##
Liquidus Temperature
217 217
## ##
40 - 60 s
End Temp.
max 4°C/s
150 - 200°C
150 150
max 3°C/s
60 - 120 s
100 Typical Leadfree 100
Soldering Profile
50 50
Elapsed time [s]
Cooling phase
A controlled cooling avoids negative metallurgical effects (solder becomes more brittle) of the solder
and possible mechanical tensions in the products. Controlled cooling helps to achieve bright solder
fillets with a good shape and low contact angle.
Temperature fall rate: max 4 °C/s
☞ To avoid falling off, modules should be placed on the topside of the motherboard during soldering.
The soldering temperature profile chosen at the factory depends on additional external factors like
choice of soldering paste, size, thickness and properties of the base board, etc.
⚠ Exceeding the maximum soldering temperature and the maximum liquidus time limit in the
recommended soldering profile may permanently damage the module.
Figure 32: Recommended soldering profile
☞ SARA-N2 series modules must not be soldered with a damp heat process.
3.3.3 Optical inspection
After soldering the module, inspect it optically to verify that the module is properly aligned and
centered.
3.3.4 Cleaning
Cleaning the soldered modules is not recommended. Residues underneath the modules cannot be
easily removed with a washing process.
Cleaning with water will lead to capillary effects where water is absorbed in the gap between the
baseboard and the module. The combination of residues of soldering flux and encapsulated water
leads to short circuits or resistor-like interconnections between neighboring pads. Water will also
damage the sticker and the ink-jet printed text.
Cleaning with alcohol or other organic solvents can result in soldering flux residues flooding into
the two housings, areas that are not accessible for post-wash inspections. The solvent will also
damage the sticker and the ink-jet printed text.
Ultrasonic cleaning will permanently damage the module, in particular the quartz oscillators.
For best results use a "no clean" soldering paste and eliminate the cleaning step after the soldering.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Handling and soldering Page 61 of 82
Page 62

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
3.3.5 Repeated reflow soldering
Repeated reflow soldering processes and soldering the module upside down are not recommended.
Boards with components on both sides may require two reflow cycles. In this case, the module should
always be placed on the side of the board that is submitted into the last reflow cycle. The reason for
this (besides others) is the risk of the module falling off due to the significantly higher weight in
relation to other components.
☞ u-blox gives no warranty against damages to the SARA-N2 series modules caused by performing
more than a total of two reflow soldering processes (one reflow soldering process to mount the
SARA-N2 series module, plus one reflow soldering process to mount other parts).
3.3.6 Wave soldering
SARA-N2 series LGA modules must not be soldered with a wave soldering process.
Boards with combined through-hole technology (THT) components and surface-mount technology
(SMT) devices require wave soldering to solder the THT components. No more than one wave
soldering process is allowed for board with a SARA-N2 series module already populated on it.
⚠ Performing a wave soldering process on the module can result in severe damage to the device!
☞ u-blox gives no warranty against damages to the SARA-N2 series modules caused by performing
more than a total of two soldering processes (one reflow soldering process to mount the SARA-N2
series module, plus one wave soldering process to mount other THT parts on the application
board).
3.3.7 Hand soldering
Hand soldering is not recommended.
3.3.8 Rework
Rework is not recommended.
☞ Never attempt a rework on the module itself, e.g. replacing individual components. Such actions
immediately terminate the warranty.
3.3.9 Conformal coating
Certain applications employ a conformal coating of the PCB using HumiSeal® or other related coating
products.
These materials affect the RF properties of the SARA-N2 series modules and it is important to
prevent them from flowing into the module.
The RF shields do not provide 100% protection for the module from coating liquids with low viscosity,
therefore care is required in applying the coating.
☞ Conformal Coating of the module will void the warranty.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Handling and soldering Page 62 of 82
Page 63

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
3.3.10 Casting
If casting is required, use viscose or another type of silicon pottant. The OEM is strongly advised to
qualify such processes in combination with the SARA-N2 series modules before implementing this in
the production.
☞ Casting will void the warranty.
3.3.11 Grounding metal covers
Attempts to improve grounding by soldering ground cables, wick or other forms of metal strips
directly onto the EMI covers is done at the customer's own risk. The numerous ground pins should be
sufficient to provide optimum immunity to interferences and noise.
☞ u-blox gives no warranty for damages to the SARA-N2 series modules caused by soldering metal
cables or any other forms of metal strips directly onto the EMI covers.
3.3.12 Use of ultrasonic processes
SARA-N2 series modules contain components which are sensitive to Ultrasonic Waves. Use of any
Ultrasonic Processes (cleaning, welding etc.) may cause damage to the module.
☞ u-blox gives no warranty against damages to the SARA-N2 series modules caused by any
Ultrasonic Processes.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Handling and soldering Page 63 of 82
Page 64

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Certification Scheme
SARA-N200
SARA-N201
SARA-N210
SARA-N211
SARA-N280
CE (European Conformity)
• • •
GCF (Global Certification Forum)
•
CCC (China Compulsory Certification)
• •
SRRC (State Radio Regulation of China)
• •
NCC (National Communications Commission
Taiwan)
• • •
Anatel (Agência Nacional de Telecomunicações
Brazil)
•
RCM (Regulatory Compliance Mark Australia)
•
NBTC (Thailand Regulatory Certification)
•
IMDA (Singapore Regulatory Certification)
•
ATEX (Atmosphere Explosive)
•
China Telecom (Chinese Network Operator)
•
China Unicom (Chinese Network Operator)
•
Deutsche Telekom (German Network Operator)
• • •
4 Approvals
4.1 Approvals overview
Product certification approval is the process of certifying that a product has passed all tests and
criteria required by specifications, typically called “certification schemes”, which can be divided into
three distinct categories:
Regulatory certification
o Country-specific approval required by local government in most regions and countries, such
as:
CE (Conformité Européenne) marking for European Union
FCC (Federal Communications Commission) approval for United States
NCC (National Communications Commission) approval for Taiwan
Industry certification
o Telecom industry-specific approval verifying the interoperability between devices and
networks:
GCF (Global Certification Forum), partnership between mainly European device
manufacturers and network operators to ensure and verify global interoperability between
devices and networks
PTCRB (PCS Type Certification Review Board), created by United States network operators
to ensure and verify interoperability between devices and North America networks
Operator certification
Operator-specific approvals required by some mobile network operator, such as:
China Telecom network operator in China
AT&T network operator in United States
Table 27 lists the main approvals of SARA-N2 series modules.
Table 27: SARA-N2 series main certification approvals
☞ For all the certificates of compliancy and for the complete list of approvals (including countries’
and network operators’ approvals) of SARA-N2 series modules, see our website
(http://www.u-blox.com/) or contact the u-blox office or sales representative nearest you.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Approvals Page 64 of 82
Page 65

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Even if SARA-N2 series modules are approved under all major certification schemes, the application
device that integrates SARA-N2 series modules must also be approved under all the certification
schemes required by the specific application device to be deployed in the market.
The required certification scheme approvals and relative testing specifications differ depending on
the country or the region where the device that integrates SARA-N2 series modules is intended to be
deployed, on the relative vertical market of the device, on type, features and functionalities of the
whole application device, and on the network operators where the device is intended to operate.
The u-blox cellular module’s approval can be re-used for the approval of the integrating application
device, but the possible re-use depends on the physical characteristics of the integrating application
device, also considering the configuration used for the approvals of SARA-N2 series modules, and it
also depends on related certification scheme approvals required for the integrating application device
as explained above.
☞ Check the appropriate applicability of the SARA-N2 series module’s approvals while starting the
certification process of the device integrating the module: the re-use of the u-blox cellular
module’s approval can significantly reduce the cost and time to market of the application device
certification.
☞ The certification of the application device that integrates a SARA-N2 series module and the
compliance of the application device with all the applicable certification schemes, directives and
standards are the sole responsibility of the application device manufacturer.
4.2 European Conformance CE mark
SARA-N200, SARA-N210 and SARA-N211 modules have been evaluated against the essential
requirements of the Radio Equipment Directive 2014/53/EU.
In order to satisfy the essential requirements of the 2014/53/EU RED, the modules are compliant with
the following standards:
Radio Spectrum Efficiency (Article 3.2):
o EN 301 908-1
o EN 301 908-13
Electromagnetic Compatibility (Article 3.1b):
o EN 301 489-1
o EN 301 489-52
Health and Safety (Article 3.1a)
o EN 62368-1
o EN 62311
⚠ Radiofrequency radiation exposure Information: this equipment complies with radiation exposure
limits prescribed for an uncontrolled environment for fixed and mobile use conditions. This
equipment should be installed and operated with a minimum distance of 20 cm between the
radiator and the body of the user or nearby persons. This transmitter must not be co-located or
operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter except as authorized in the
certification of the product.
⚠ The gain of the system antenna(s) used for the SARA-N200, SARA-N210 and SARA-N211 modules
(i.e. the combined transmission line, connector, cable losses and radiating element gain) must not
exceed the values stated in the Declaration of Conformity of the modules, for mobile and fixed or
mobile operating configurations:
9.2 dBi in 800 MHz, i.e. LTE FDD-20 band
9.4 dBi in 900 MHz, i.e. LTE FDD-8 band
UBX-17005143 - R06 Approvals Page 65 of 82
Page 66

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Parameter
SARA-N211
Ui
4.2 V
Ii
0.5 A
Ci
68.1 µF
Li
8.5 µH
The conformity assessment procedure for SARA-N200 and SARA-N210 modules, referred to in Article
17 and detailed in Annex II of Directive 2014/53/EU, has been followed.
Thus, the following marking is included in the product:
The conformity assessment procedure for SARA-N211 modules, referred to in Article 17 and detailed
in Annex II of Directive 2014/53/EU, has been followed. According to the ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU,
Article 13, Paragraph 1-3, the CE mark is not affixed to the product label.
The following marking is included in the product:
1304
4.3 ATEX conformance
SARA-N211 modules are certified as components intended for use in potentially explosive
atmospheres compliant to the following standards:
IEC 60079-0
IEC 60079-11
IEC 60079-26
The certification numbers of the modules, according to the ATEX directive 2014/34/EU, are:
SIQ 18 ATEX 104 U
The certification numbers of the modules, according to the IECEx conformity assessment system,
are:
IECEx SIQ 18.0004U
According to the standards listed above, SARA-N211 modules are certified with the following marking:
Ex II 1G, Ex ia IIC
The temperature range for using SARA-N211 modules is defined in the “Operating temperature range”
section of the SARA-N2 series Data Sheet [1]. The modules are suitable for temperature class T4
applications, as long as the maximum input power does not exceed 2.0 W on SARA-N211 modules.
The RF radiating profile of SARA-N211 modules is compliant to all the applicable 3GPP / ETSI
standards, with a maximum of 250 mW RF average power according to the LTE Cat NB1 Power Class
stated in Table 2.
The nameplate of SARA-N211 modules is described in the “Product labeling” section of the SARA-N2
series Data Sheet [1].
Table 28 lists the maximum input and equivalent parameters that must be considered in the sub-
division IIC, the sub-division IIB and the sub-division IIA for SARA-N211 modules.
Table 28: Maximum input and equivalent parameters for sub-division IIC, IIB and IIA
UBX-17005143 - R06 Approvals Page 66 of 82
Page 67

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
CCAI17Z10210T5
CCAI17Z10270T0
CCAI17Z10200T2
4.4 Chinese conformance
SARA-N200 and SARA-N201 modules have the applicable regulatory approval for China:
CMIIT ID: 2018CJ1113
4.5 Taiwanese conformance
SARA-N200, SARA-N211 and SARA-N280 modules have the applicable regulatory approval for Taiwan
(NCC)
SARA-N200 modules NCC ID: CCAI17Z10210T5
SARA-N211 modules NCC ID: CCAI17Z10270T0
SARA-N280 modules NCC ID: CCAI17Z10200T2
UBX-17005143 - R06 Approvals Page 67 of 82
Page 68

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
5 Product testing
5.1 u-blox in-series production test
u-blox focuses on high quality for its products. All units produced are fully tested. Defective units are
analyzed in detail to improve the production quality.
This is achieved with automatic test equipment, which delivers a detailed test report for each unit.
The following measurements are done:
Digital self-test (firmware download, Flash firmware verification, IMEI programming)
Measurement of voltages and currents
Functional tests (serial interface communication, real time clock)
Digital tests (GPIOs, digital interfaces)
Measurement and calibration of RF characteristics in all supported bands (Receiver S/N
verification, frequency tuning of reference clock, calibration of transmitter and receiver power
levels)
Verification of RF characteristics after calibration (modulation accuracy, power levels and
spectrum performance are checked to be within tolerances when calibration parameters are
applied)
Figure 33: Automatic test equipment for module tests
5.2 Test parameters for OEM manufacturer
Because of the testing done by u-blox (with 100% coverage), an OEM manufacturer does not need to
repeat firmware tests or measurements of the module RF performance or tests over analog and
digital interfaces in their production test.
An OEM manufacturer should focus on:
Module assembly on the device; it should be verified that:
Soldering and handling process did not damaged the module components
All module pins are well soldered on device board
There are no short circuits between pins
Component assembly on the device; it should be verified that:
Communication with host controller can be established
The interfaces between module and device are working
Overall RF performance test of the device including antenna
UBX-17005143 - R06 Product testing Page 68 of 82
Page 69

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Dedicated tests can be implemented to check the device. For example, AT commands can be used to
perform functional tests on the digital interfaces (communication with the host controller, check the
SIM interface, GPIOs, etc.) or to perform RF performance tests (see the following section 5.2.2 for
details).
5.2.1 “Go/No go” tests for integrated devices
A “Go/No go” test is typically used to compare the signal quality with a “Golden Device” in a location
with excellent network coverage and known signal quality. This test should be performed after the
data connection has been established. AT+CSQ is the typical AT command used to check signal
quality in term of Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI). See the SARA-N2 series AT Commands
Manual [3] for the AT+CSQ command syntax description and usage.
☞ These kinds of test may be useful as a “go/no go” test but not for RF performance measurements.
This test is suitable to check the functionality of communications with the host controller, the SIM
card and the power supply. It is also a means to verify if components at the antenna interface are wellsoldered.
5.2.2 RF functional tests
The overall RF functional test of the device including the antenna can be performed with basic
instruments such as a spectrum analyzer (or an RF power meter) and a signal generator with the
assistance of the AT+UTEST command over the AT command user interface.
The AT+UTEST command provides a simple interface to set the module to Rx or Tx test modes
ignoring the cellular signaling protocol. The command can set the module into:
transmitting mode in a specified channel and power level in all supported bands
receiving mode in a specified channel to return the measured power level in all supported bands
☞ See the SARA-N2 series AT Commands Manual [3] for the AT+UTEST command description and
usage.
This feature allows the measurement of the transmitter and receiver power levels to check the
component assembly related to the module antenna interface and to check other device interfaces
on which the RF performance depends.
⚠ To avoid module damage during a transmitter test, a suitable antenna according to module
specifications or a 50 termination must be connected to the ANT port.
⚠ To avoid module damage during a receiver test, the maximum power level received at the ANT port
must meet module specifications.
☞ The AT+UTEST command sets the module to emit RF power ignoring cellular signaling protocol.
This emission can generate interference that can be prohibited by law in some countries. The use
of this feature is intended for testing purposes in controlled environments by qualified users and
must not be used during the normal module operation. Follow the instructions suggested in the
u-blox documentation. u-blox assumes no responsibilities for the inappropriate use of this feature.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Product testing Page 69 of 82
Page 70

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Application Board
SARA-N2 series
ANT
Application
Processor
AT
commands
Cellular
antenna
Spectrum
Analyzer
or
Power
Meter
IN
Wideband
antenna
TX
Application Board
SARA-N2 series
Application
Processor
AT
commands
Signal
Generator
OUT
Wideband
antenna
RX
ANT
Cellular
antenna
Figure 34 illustrates a typical test setup for such an RF functional test.
Figure 34: Setup with spectrum analyzer or power meter and signal generator for radiated measurements
UBX-17005143 - R06 Product testing Page 70 of 82
Page 71

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
64 63 61 60 58 57 55 54
22 23 25 26 28 29 31 32
11
10
8
7
5
4
2
1
21
19
18
16
15
13
12
43
44
46
47
49
50
52
53
33
35
36
38
39
41
42
65 66 67 68 69 70
71 72 73 74 75 76
77 78
79 80
81 82
83 84
85 86 87 88 89 90
91 92 93 94 95 96
CTS
RTS
DCD
RI
V_INT
RSVD
GND
GPIO6
RESET_N
GPIO1
PWR_ON
RXD
TXD
3
20
17
14
9
6
24 27 30
51
48
45
40
37
34
5962 56
GND
GND
DSR
DTR
GND
VUSB_DET
GND
GND
USB_D-
USB_D+
RSVD
GND
GPIO2
GPIO3
SDA
SCL
GPIO4
GND
GND
GND
SDIO_D2
SDIO_CMD
SDIO_D0
SDIO_D1
GND
VCC
VCC
RSVD
I2S_TXD/SPI_CS
I2S_CLK/SPI_CLK
SIM_CLK
SIM_IO
VSIM
GPIO5
VCC
SDIO_D3
SDIO_CLK
SIM_RST
I2S_RXD/SPI_MISO
I2S_WA/SPI_MOSI
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
ANT_DET
ANT
SARA-R4
Top View
Pin 65-96: GND
64 63 61 60 58 57 55 54
22 23 25 26 28 29 31 32
11
10
8
7
5
4
2
1
21
19
18
16
15
13
12
43
44
46
47
49
50
52
53
33
35
36
38
39
41
42
65 66 67 68 69 70
71 72 73 74 75 76
77 78
79 80
81 82
83 84
85 86 87 88 89 90
91 92 93 94 95 96
CTS
RTS
DCD
RI
V_INT
V_BCKP
GND
RSVD
RESET_N
GPIO1
PWR_ON
RXD
TXD
3
20
17
14
9
6
24 27 30
51
48
45
40
37
34
5962 56
GND
GND
DSR
DTR
GND
RSVD
GND
GND
TXD_AUX
RSVD
GND
GPIO2
GPIO3
SDA
SCL
GPIO4
GND
GND
GND
SPK_P
MIC_BIAS
MIC_GND
MIC_P
GND
VCC
VCC
RSVD
I2S_TXD
I2S_CLK
SIM_CLK
SIM_IO
VSIM
SIM_DET
VCC
MIC_N
SPK_N
SIM_RST
I2S_RXD
I2S_WA
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
ANT_DET
ANT
SARA-G3
Top View
Pin 65-96: GND
64 63 61 60 58 57 55 54
22 23 25 26 28 29 31 32
11
10
8
7
5
4
2
1
21
19
18
16
15
13
12
43
44
46
47
49
50
52
53
33
35
36
38
39
41
42
65 66 67 68 69 70
71 72 73 74 75 76
77 78
79 80
81 82
83 84
85 86 87 88 89 90
91 92 93 94 95 96
CTS
RTS
DCD
RI
V_INT
V_BCKP
GND
CODEC_CLK
RESET_N
GPIO1
PWR_ON
RXD
TXD
3
20
17
14
9
6
24 27 30
51
48
45
40
37
34
5962 56
GND
GND
DSR
DTR
GND
VUSB_DET
GND
GND
USB_D-
USB_D+
RSVD
GND
GPIO2
GPIO3
SDA
SCL
GPIO4
GND
GND
GND
RSVD
RSVD
RSVD
RSVD
GND
VCC
VCC
RSVD
I2S_TXD
I2S_CLK
SIM_CLK
SIM_IO
VSIM
SIM_DET
VCC
RSVD
RSVD
SIM_RST
I2S_RXD
I2S_WA
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
ANT_DET
ANT
SARA-U2
Top View
Pin 65-96: GND
64 63 61 60 58 57 55 54
22 23 25 26 28 29 31 32
11
10
8
7
5
4
2
1
21
19
18
16
15
13
12
43
44
46
47
49
50
52
53
33
35
36
38
39
41
42
65 66 67 68 69 70
71 72 73 74 75 76
77 78
79 80
81 82
83 84
85 86 87 88 89 90
91 92 93 94 95 96
CTS
RTS
RSVD
RSVD
V_INT
RSVD
GND
RSVD
RESET_N
GPIO1
RSVD
RXD
TXD
3
20
17
14
9
6
24 27 30
51
48
45
40
37
34
5962 56
GND
GND
RSVD
RSVD
GND
RSVD
GND
GND
RSVD
RSVD
RSVD
GND
RSVD
GPIO2
SDA
SCL
RSVD
GND
GND
GND
RSVD
RSVD
RSVD
RSVD
GND
VCC
VCC
RSVD
RSVD
RSVD
SIM_CLK
SIM_IO
VSIM
RSVD
VCC
RSVD
RSVD
SIM_RST
RSVD
RSVD
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
ANT_DET
ANT
SARA-N2
Top View
Pin 65-96: GND
LISA cellular module
LARA cellular module
SARA cellular module
Nested application board
TOBY cellular module
Appendix
A Migration between SARA modules
A.1 Overview
The SARA-G3 2G modules, the SARA-U2 3G / 2G modules, the SARA-R4 LTE Cat M1/NB1 / 2G modules
and the SARA-N2 LTE Cat NB1 modules have exactly the same u-blox SARA form factor
(26.0 x 16.0 mm, 96-pin LGA), with compatible pin assignment as described in Figure 35, so that the
modules can be alternatively mounted on a single application board using exactly the same copper
mask, solder mask and paste mask.
Figure 35: SARA-G3, SARA-U2, SARA-R4 and SARA-N2 series modules’ layout and pin assignment
SARA modules are also form-factor compatible with the u-blox LISA, LARA and TOBY cellular module
families: although each has a different form factor, the footprints for the TOBY, LISA, SARA and LARA
modules have been developed to ensure layout compatibility.
With the u-blox “nested design” solution, any TOBY, LISA, SARA or LARA module can be alternatively
mounted on the same space of a single “nested” application board as described in Figure 36.
Guidelines in order to implement a nested application board, description of the u-blox reference
nested design and comparison between TOBY, LISA, SARA and LARA modules are provided in the
Nested Design Application Note [7].
Figure 36: TOBY, LISA, SARA, LARA modules’ layout compatibility: all modules are accommodated on the same nested
footprint
UBX-17005143 - R06 Appendix Page 71 of 82
Page 72

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Modules
RAT
Power
System
SIM
Serial
Audio
Other
Module supply
input RTC supply I/O 1.8 V supply Output Switch
-on input
Switch
-off input
Reset input SIM interfa
ce
SIM detection UART
UART AUX SPI
USB SDIO DDC (I
2
C)
Analog audio Digital audio 13/26 MHz output GPIOs Network indication Antenna detection GNSS via modem
SARA-G3
2G
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
SARA-U2
3G, 2G
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
SARA-R4
LTE M1 / NB1, 2G
• • • • • • • •
□ • □ •
□
□
• • •
•
SARA-N2
LTE NB1
• • • • • • • •
● = supported by available product version
□ = supported by future product versions
880
SARA-G300
SARA-G340
SARA-G310
SARA-G350
SARA-U260
SARA-U270
SARA-U280
SARA-U201
900
800 850 900 950
900 1800 1800
1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000 2050 2100 2150 2200
880 960 1710 1880
750
850
900
850
800 850 900 950
900 1800
1900 1900
1800
1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000
2050 2100 2150 2200
824 960 1710 1990
750700
700
800 850 900 950
VV II II
850850 1900 1900
1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000
2050 2100 2150 2200
824 894 1850 1990
750700
900
800 850 900 950
900 1800 1800
1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000
2050 2100 2150 2200
IIVIIIVIII
960 1710 2170
750700
800 850 900 950
VV II II
1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000 2050 2100 2150 2200
824 894 1850 1990
750700
II II
850
900
800 850 900 950
900 1800
1900 1900
1800
1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000 2050 2100 2150 2200
II
VIIIVIII
824 960 1710 2170
750700
V
XIXXIX
V
850
SARA-R404M
800 850 900 950 1700 1750 1 800 1850 1900 1950 2000
2050 2100 2150 2200
1313
746 787
750700
824 894
960880
= 3G bands
= 2G bands
= LTE Cat M1 bands
LEGENDA
= LTE Cat NB1 bands
20 20
SARA-N200
800 850 900 950 1700 1750 1 800 1850 1900 1950 2000
2050 2100 2150 2200
750700
SARA-N201
800 850 900 950 1700 1750 1 800 1850 1900 1950 2000
2050 2100 2150 2200
750700
SARA-N210
800 850 900 950 1700 1750 1 800 1850 1900 1950 2000 2050 2100 2150 2200
791 862
750700
SARA-N211
800 850 900 950 1700 1750 1 800 1850 1900 1950 2000 2050 2100 2150 2200
791 960
750700
SARA-N280
800 850 900 950 1700 1750 1 800 1850 1900 1950 2000
2050 2100 2150 2200
803
750700
8 8
55
20 20 8 8
28 28
703
SARA-R410M
800 850 900 950 1700 1750 1 800 1850 1900 1950 2000
2050 2100 2150 2200
699 1710
750700
960 2170
12
4 42 2
12
55
1313
28
3 3 11
88
28
19 191717
20 20
26 26 25 25
12
4 42 2
12
55
1313
28
3 3 11
88
28
19 191717
20 20 39
26 26 25 25
18 18
18 18
SARA-R412M
800 850 900 950 1700 1750 1 800 1850 1900 1950 2000
2050 2100 2150 2200
699 1710
750700
960 2170
12
4 42 2
12
55
1313
28
3 3 11
88
28
19 191717
20 20
26 26 25 25
12
4 42 2
12
55
1313
28
3 3 11
88
28
19 191717
20 20 39
26 26 25 25
18 18
18 18
850
900900 1800
1900 1900
1800
850
Table 29 summarizes the interfaces provided by SARA-G3, SARA-U2, SARA-R4 and SARA-N2 series
modules, while Figure 37 summarizes the frequency ranges of the modules’ operating bands.
Table 29: Summary of SARA-G3, SARA-U2, SARA-R4 and SARA-N2 series modules interfaces
Figure 37: Summary of operating frequency bands supported by SARA-G3, SARA-U2, SARA-R4 and SARA-N2 series modules
UBX-17005143 - R06 Appendix Page 72 of 82
Page 73

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
SARA-G3
SARA-U2
SARA-R4
SARA-N2
No
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Remarks for migration
1
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
2 V_BCKP
RTC Supply I/O
V_BCKP
RTC Supply I/O
RSVD
Reserved
RSVD
Reserved
RTC supply vs Reserved
3
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
4
V_INT
Interfaces Supply Output:
1.8 V typ, 70 mA max
V_INT
Interfaces Supply Output:
1.8 V typ, 70 mA max
V_INT
Interfaces Supply Output:
1.8 V typ, 70 mA max
Switched-off in deep-sleep
V_INT
Interfaces Supply Output:
1.8 V typ, 70 mA max
Switched-off when radio is
off
V_INT is switched off in deep
sleep (R4), or if radio is off (N2)
TestPoint always
recommended
5
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
6
DSR
UART DSR Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 6 mA
DSR
UART DSR Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 1 mA
DSR
UART DSR Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
RSVD
Reserved
Not supported by SARA-N2
Diverse driver strength
7
RI
UART RI Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 6 mA
RI
UART RI Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
RI
UART RI Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
RSVD
Reserved
Not supported by SARA-N2
Diverse driver strength
8
DCD
UART DCD Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 6 mA
DCD
UART DCD Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
DCD
UART DCD Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
RSVD
Reserved
Not supported by SARA-N2
Diverse driver strength
9
DTR
UART DTR Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Internal pull-up: ~33 k
It must be set low to have
greeting text sent over
UART
DTR
UART DTR Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Internal pull-up: ~14 k
It must be set low to have
greeting text sent over
UART
DTR
UART DTR Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Internal pull-up: ~100 k
It must be set low to have
URCs sent over UART
RSVD
Reserved
Not supported by SARA-N2
Diverse internal pull-up value
10
RTS
UART RTS Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Internal pull-up:~58 k
RTS
UART RTS Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Internal pull-up: ~8 k
RTS
UART RTS Input2
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Internal pull-up: ~100 k
It must be set low to use
UART on ‘00’, ‘01’ product
versions
RTS
UART RTS Input2
VCC level (3.6 V typ.)
Internal pull-up: ~78 k
Diverse level (V_INT vs VCC)
Diverse internal pull-up value
Diverse functions
supported.
2
A.2 Pin-out comparison between SARA-G3, SARA-U2, SARA-R4 and SARA-N2 modules
Not supported by “00”, “01” and “02” product versions
UBX-17005143 - R06 Appendix Page 73 of 82
Page 74

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
SARA-G3
SARA-U2
SARA-R4
SARA-N2
No
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Remarks for migration
11
CTS
UART CTS Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 6 mA
CTS
UART CTS Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 6 mA
CTS
UART CTS Output2
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
CTS
UART CTS Output2
VCC level (3.6 V typ.)
Driver strength: 1 mA
Configurable as Ring
Indicator or Network
Indicator
Diverse level (V_INT vs VCC)
Diverse driver strength.
Diverse functions
supported.
12
TXD
UART Data Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Internal pull-up:~18 k
TXD
UART Data Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Internal pull-up: ~8 k
TXD
UART Data Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Internal pull-up/-down:
~100k
TXD
UART Data Input
VCC level (3.6 V typ.)
No internal pull-up/-down
Diverse level (V_INT vs VCC)
Diverse internal pull-up value
TestPoint always
recommended
13
RXD
UART Data Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 6 mA
RXD
UART Data Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 6 mA
RXD
UART Data Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
RXD
UART Data Output
VCC level (3.6 V typ.)
Driver strength: 1 mA
Diverse level (V_INT vs VCC)
Diverse driver strength
TestPoint always
recommended
14
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
15
PWR_ON
Power-on Input
No internal pull-up
L-level: -0.10 V ÷ 0.65 V
H-level: 2.00 V ÷ 4.50 V
ON L-level time:
5 ms min
OFF L-level pulse time:
Not Available
PWR_ON
Power-on Input
No internal pull-up
L-level: -0.30 V ÷ 0.65 V
H-level: 1.50 V ÷ 4.40 V
ON L-level pulse time:
50 µs min / 80 µs max
OFF L-level pulse time:
1 s min
PWR_ON
Power-on Input
200 k internal pull-up
L-level: -0.30 V ÷ 0.35 V
H-level: 1.17 V ÷ 2.10 V
ON L-level pulse time:
0.15 s min – 3.2 s max
OFF L-level pulse time:
1.5 s min
RSVD
Reserved
Not supported by SARA-N2
Internal vs No internal pull-up
Diverse voltage levels.
Diverse timings.
Diverse functions
supported.
TestPoint recommended for
R4
16
GPIO1 /
RSVD
GPIO (G340/G350)
Reserved (G300/G310)
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: Pin disabled
Driver strength: 6 mA
GPIO1
GPIO
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: Pin disabled
Driver strength: 6 mA
GPIO1
GPIO
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: Pin disabled
Driver strength: 2 mA
GPIO1
GPIO
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Configurable as secondary
UART data output:
TestPoint recommended
for diagnostic
Diverse driver strength
TestPoint recommended for
N2
17
RSVD
Reserved
VUSB_DET
5 V, USB Supply Detect
Input
VUSB_DET
5 V, USB Supply Detect
Input
RSVD
Reserved
USB detection vs Reserved
TestPoint recommended for
U2/R4
18
RESET_N
Reset input
Internal diode & pull-up
L-level: -0.30 V ÷ 0.30 V
H-level: 2.00 V ÷ 4.70 V
Reset L-level pulse time:
50 ms min (G340/G350)
3 s min (G300/G310)
RESET_N
Abrupt shutdown / reset
input
10 k internal pull-up
L-level: -0.30 V ÷ 0.51 V
H-level: 1.32 V ÷ 2.01 V
Reset L-level pulse time:
50 ms min
RESET_N
Abrupt shutdown input
37 k internal pull-up
L-level: -0.30 V ÷ 0.35 V
H-level: 1.17 V ÷ 2.10 V
OFF L-level pulse time:
10 s min
RESET_N
Reset input
78 k internal pull-up
L-level: -0.30 V ÷ 0.36*VCC
H-level: 0.52*VCC ÷ VCC
Reset L-level pulse time:
500 ns min
Diverse internal pull-up
Diverse voltage levels.
Diverse timings.
Diverse functions
supported.
TestPoint always
recommended
UBX-17005143 - R06 Appendix Page 74 of 82
Page 75

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
SARA-G3
SARA-U2
SARA-R4
SARA-N2
No
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Remarks for migration
19
RSVD
Reserved
CODEC_CLK
13 or 26 MHz Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: Pin disabled
Driver strength: 4 mA
GPIO6
GPIO
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: Pin disabled
Driver strength: 2 mA
RSVD
Reserved
Clock / GPIO vs Reserved
20-22
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
23
GPIO2 /
RSVD
GPIO (G340/G350)
Reserved (G300/G310)
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: GNSS supply enable
Driver strength: 6 mA
GPIO2
GPIO
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: GNSS supply enable
Driver strength: 1 mA
GPIO2
GPIO
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: Pin disabled
Driver strength: 2 mA
RSVD
Reserved
GPIO vs Reserved
24
GPIO3 /
32K_OUT
GPIO (G340/G350)
32 kHz Output (G300/G310)
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: GNSS data ready
Driver strength: 5 mA
GPIO3
GPIO
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: GNSS data ready
Driver strength: 6 mA
GPIO3
GPIO
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: Pin disabled
Driver strength: 2 mA
GPIO2
GPIO4
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: Pin disabled
Driver strength: 1 mA
Diverse driver strength
25
GPIO4 /
RSVD
GPIO (G340/G350)
Reserved (G300/G310)
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: GNSS RTC sharing
Driver strength: 6 mA
GPIO4
GPIO
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: GNSS RTC sharing
Driver strength: 6 mA
GPIO4
GPIO
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Default: Output/Low
Driver strength: 2 mA
RSVD
Reserved
GPIO vs Reserved
26
SDA /
RSVD
I2C Data I/O (G340/G350)
Reserved (G300/G310)
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Open drain
No internal pull-up
SDA
I2C Data I/O
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Open drain
No internal pull-up
SDA
I2C Data I/O3
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Open drain
Internal 2.2 k pull-up
SDA
I2C Data I/O4
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Open drain
No internal pull-up
Internal vs No internal pull-up
27
SCL /
RSVD
I2C Clock Output
(G340/G350) Reserved
(G300/G310)
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Open drain
No internal pull-up
SCL
I2C Clock Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Open drain
No internal pull-up
SCL
I2C Clock Output3
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Open drain
Internal 2.2 k pull-up
SCL
I2C Clock Output4
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Open drain
No internal pull-up
Internal vs No internal pull-up
28
RXD_AUX
Aux UART Data Out
V_INT level (1.8 V)
USB_D-
USB Data I/O (D-)
High-Speed USB 2.0
USB_D-
USB Data I/O (D-)
High-Speed USB 2.0
RSVD
Reserved
USB / AUX UART vs
Reserved
TestPoint recommended for
SARA-G3/U2/R4 modules
3
4
Not supported by “00” and “01” product versions
Not supported by “02” product versions
UBX-17005143 - R06 Appendix Page 75 of 82
Page 76

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
SARA-G3
SARA-U2
SARA-R4
SARA-N2
No
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Remarks for migration
29
TXD_AUX
Aux UART Data In
V_INT level (1.8 V)
USB_D+
USB Data I/O (D+)
High-Speed USB 2.0
USB_D+
USB Data I/O (D+)
High-Speed USB 2.0
RSVD
Reserved
USB / AUX UART vs Reserved
TestPoint recommended for
SARA-G3/U2/R4 modules
30
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
31
RSVD /
EXT32K
Reserved (G340/G350)
32 kHz Input (G300/G310)
RSVD
Reserved
RSVD
Reserved
RSVD
Reserved
32 kHz Input vs Reserved
32
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
33
RSVD
It must be connected to GND
RSVD
It must be connected to GND
RSVD
It can be connected to GND
RSVD
It can be connected to GND
34
I2S_WA /
RSVD
I2S Word Align.(G340/G350)
Reserved (G300/G310)
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 6 mA
I2S_WA
I2S Word Alignment
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
I2S_WA /
SPI_MOSI
I2S Word Alignm5 / SPI
MOSI5
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
RSVD
Reserved
I2S vs SPI vs Reserved
35
I2S_TXD /
RSVD
I2S Data Output
(G340/G350) Reserved
(G300/G310)
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 5 mA
I2S_TXD
I2S Data Output
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
I2S_TXD /
SPI_CS
I2S Data Out5 / SPI chip
select5
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
RSVD
Reserved
I2S vs SPI vs Reserved
36
I2S_CLK /
RSVD
I2S Clock (G340/G350)
Reserved (G300/G310)
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 5 mA
I2S_CLK
I2S Clock
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
I2S_CLK /
SPI_CLK
I2S Clock5 / SPI clock5
V_INT level (1.8 V)
Driver strength: 2 mA
RSVD
Reserved
I2S vs SPI vs Reserved
37
I2S_RXD /
RSVD
I2S Data Input
(G340/G350) Reserved
(G300/G310)
V_INT level (1.8 V)
I2S_RXD
I2S Data Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
I2S_RXD /
SPI_MISO
I2S Data Input5 / SPI MISO5
V_INT level (1.8 V)
RSVD
Reserved
I2S vs SPI vs Reserved
38
SIM_CLK
1.8V/3V SIM Clock Output
SIM_CLK
1.8V/3V SIM Clock Output
SIM_CLK
1.8V/3V SIM Clock Output
SIM_CLK
1.8V SIM Clock Output
39
SIM_IO
1.8V/3V SIM Data I/O
Internal 4.7 k pull-up
SIM_IO
1.8V/3V SIM Data I/O
Internal 4.7 k pull-up
SIM_IO
1.8V/3V SIM Data I/O
Internal 4.7 k pull-up
SIM_IO
1.8V SIM Data I/O
Internal 4.7 k pull-up
40
SIM_RST
1.8V/3V SIM Reset Output
SIM_RST
1.8V/3V SIM Reset Output
SIM_RST
1.8V/3V SIM Reset Output
SIM_RST
1.8V SIM Reset Output
41
VSIM
1.8V/3V SIM Supply Output
VSIM
1.8V/3V SIM Supply Output
VSIM
1.8V/3V SIM Supply Output
VSIM
1.8V SIM Supply Output
42
SIM_DET
SIM Detection Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
SIM_DET
SIM Detection Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
GPIO5
SIM Detection Input
V_INT level (1.8 V)
RSVD
Reserved
SIM Detection vs Reserved
43
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
44
SPK_P /
RSVD
Analog Audio Out (+) /
Reserved
RSVD
Reserved
SDIO_D2
SDIO serial data [2]5
RSVD
Reserved
Analog Audio vs SDIO vs
RSVD
45
SPK_N /
RSVD
Analog Audio Out (-) /
Reserved
RSVD
Reserved
SDIO_CLK
SDIO serial clock5
RSVD
Reserved
Analog Audio vs SDIO vs
RSVD
5
Not supported by “00”, “01” and “02” product version
UBX-17005143 - R06 Appendix Page 76 of 82
Page 77

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
SARA-G3
SARA-U2
SARA-R4
SARA-N2
No
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Pin Name
Description
Remarks for migration
46
MIC_BIAS /
RSVD
Microphone Supply Out /
Reserved
RSVD
Reserved
SDIO_CM
D
SDIO command5
RSVD
Reserved
Analog Audio vs SDIO vs
RSVD
47
MIC_GND /
RSVD
Microphone Ground /
Reserved
RSVD
Reserved
SDIO_D0
SDIO serial data [0]5
RSVD
Reserved
Analog Audio vs SDIO vs
RSVD
48
MIC_N /
RSVD
Analog Audio In (-) /
Reserved
RSVD
Reserved
SDIO_D3
SDIO serial data [3]5
RSVD
Reserved
Analog Audio vs SDIO vs
RSVD
49
MIC_P /
RSVD
Analog Audio In (+) /
Reserved
RSVD
Reserved
SDIO_D1
SDIO serial data [1]5
RSVD
Reserved
Analog Audio vs SDIO vs
RSVD
50
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
51-53
VCC
Module Supply Input
Normal op. range:
3.35 V – 4.5 V
Extended op. range:
3.00 V – 4.5 V
Current consumption:
~2.0A pulse current in 2G
(recommended ≥100uF
cap.)
Switch-on by applying VCC
VCC
Module Supply Input
Normal op. range:
3.3 V – 4.4 V
Extended op. range:
3.1 V – 4.5 V
Current consumption:
~2.0A pulse current in 2G
(recommended ≥100uF
cap.)
Ferrite bead for GHz noise
recommended for U201
Switch-on by applying VCC
VCC
Module Supply Input
Normal op. range:
3.2 V – 4.2 V
Extended op. range:
3.0 V – 4.3 V
Current consumption:
~2.0A pulse current in 2G
(recommended ≥100 µF
cap.) ~0.5A pulse current
in LTE
(recommended 10uF cap.)
No switch-on by applying
VCC
VCC
Module Supply Input
Normal op. range:
3.1 V – 4.0 V
Extended op. range:
2.75 V – 4.2 V
Current consumption:
~0.3A pulse current in
NB-IoT
(recommended 100uF
cap.)
Switch-on by applying VCC
Diverse voltage levels.
Diverse current consumption.
Diverse recommended
external capacitors and
other parts.
Regular pF / nF recommended
Diverse functions
supported.
54-55
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
56
ANT
RF Antenna I/O
ANT
RF Antenna I/O
ANT
RF Antenna I/O
ANT
RF Antenna I/O
Diverse bands supported
(summarized in Figure 37)
5761
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
62
ANT_DET /
RSVD
Antenna Detection Input /
Reserved
ANT_DET
Antenna Detection Input
ANT_DET
Antenna Detection Input
ANT_DET
Antenna Detection Input6
Antenna Detection vs
Reserved
63-96
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
6
Table 30: SARA-G3, SARA-U2, SARA-R4 and SARA-N2 series modules pin assignment with remarks for migration
☞ For further details regarding the characteristics, capabilities, usage or settings applicable for each interface of the SARA-G3, SARA-U2, SARA-
R4 and SARA-N2 series cellular modules, see the related Data Sheet [8], [9], [12], [1], the related System Integration Manual [10], [13], the
related AT Commands Manual [11], [14], [3] and the Nested Design Application Note [7].
Not supported by “02” product version
UBX-17005143 - R06 Appendix Page 77 of 82
Page 78

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
RI
DCD
DTR
DSR
GND
GND
3.6V UART DTE
3.6V UART DTE
Application
Processor
Open
Drain
Output
Open
Drain
Output
TXD
RXD
VBUS
D+
D-
GND
USB 2.0 Host
12 TXD
7
RI / RSVD
13 RX D
10 RTS
11 CTS
8
DCD / RSVD
9
DTR / RSVD
6
DSR / RSVD
GND
3V6
GND
330µF
10nF
100nF
56pF
SARA-G3 / SARA-U2 / SARA-R4 / SARA-N2
52 VCC
53 VCC
51 V CC
+
100µF
2 V_BCKP / RSVD
GND
GND
RTC
back-up
18
RESET_N
15
PWR_ON / RSVD
100k
29
TXD_AUX / USB_D+ / RSVD
28
RXD_AUX / USB_D- / RSVD
TP
TP
15pF
33 RSVD
V_BCKP
TP
TP
17
RSVD / VUSB_DET
GND
0Ω
0Ω
0Ω or
Ferrite Bead
0Ω
0Ω
TP
TP
TP
+
0Ω
TP
TP
47pF
SIM Card
Connector
CCVCC (C1)
CCVPP
(C6)
CCIO (C7)
CCCLK
(C3)
CCRST
(C2)
GND (C5)
47pF 47pF
100n
F
41
VSIM
39
SIM_IO
38
SIM_CLK
40
SIM_RST
47pF
SW1
SW2
4
V_INT
42
RSVD / SIM_DET / GPIO5
470k
ESD ESD ESD ESD ESDESD
56ANT
62ANT_DET
10k 68nH
33pF
Connector
27pF
ESD
External
Antenna
1k
TP
u-blox 1.8V
GNSS Receiver
4.7
k
OUTIN
GND
LDO Regulator
SHDN
RSVD / SDA
RSVD / SCL
4.7
k
3V6
1V8_GPS
SDA2
SCL2
32K_OUT / GPIO3 / GPIO2
RSVD /
GPIO4
TxD1
EXTINT0
26
27
24
25
47k
VCC
RSVD / GPIO2
23
V_INT
0Ω for SARA-G300 /-G310
15pF
39nH
0Ω
TP
V_INT
B1 A1
VCCBVCCA
Voltage Translator
SN74AVC2T245
3V6
B2 A2
V_INT
B1 A1
VCCBVCCA
Voltage Translator
SN74AVC2T245
3V6
B2 A2
V_INT
BCLK
LRCLK
10µF1µF
Audio Codec
MAX9860
SDIN
SDOUT
SDA
SCL
36
RSVD / I2S_CLK
34
RSVD / I2S_WA
35
RSVD / I2S_TXD
37
RSVD / I2S_RXD
19
RSVD / CODEC_CLK / GPIO6
MCLK
IRQn
10k
100nF
VDD
Speaker
OUTP
OUTN
Microphone
MICBIAS
1µF
2.2k
1µF
1µF
MICLN
MICLP
MICGND
2.2k
ESD ESD
V_INT
10nF
10nF
EMI
EMI
27pF
27pF
10nF
EMI
EMI
ESD ESD
27pF27pF10nF
31EXT32K / RSVD
0Ω
49
RSVD / MIC_P
2.2k
2.2k 2.2k
48
RSVD / MIC_N
2.2k
10uF
46
RSVD / MIC_BIAS
47
RSVD / MIC_GND
100nF
100nF
44
RSVD / SPK_P
45
RSVD / SPK_N
Mount for SARA-G300 /-G310
Mount for SARA-G340 /-G350
Mount for SARA-U2
Mount for SARA-G3
Mount for SARA-G340 /-G350 /-U2
Mount for SARA-G3 /-U2 /-R4 /-N2
LEGEND
TP
TP
TP
TP
Mount for SARA-G3 /-U2
Mount for SARA-G3 /-U2 /-R4
Mount for SARA-N2
Mount for SARA-G340 /-G350 /-U2 /-R4
0Ω
V_INT
B1 A1
VCCBVCCA
Voltage Translator
SN74AVC2T245
3V6
B2 A2
V_INT
B1 A1
VCCBVCCA
Voltage Translator
SN74AVC2T245
3V6
B2 A2
V_INT
B1 A1
VCCBVCCA
Voltage Translator
SN74AVC2T245
3V6
B2 A2
0Ω
16RSVD / GPIO1
3V6
Network
Indicator
TP
Mount for SARA-G340 /-G350 /-U2 /-R4 /-N2
Mount for SARA-U2 /-R4
CTS
A.3 Schematic for SARA-G3 /-U2 /-R4 /-N2 modules integration
Figure 38 shows an example of schematic diagram where a SARA-G3, SARA-U2, SARA-R4 or
SARA-N2 series module can be integrated into the same application board, using all the available
interfaces and functions of the modules. The different mounting options for the external parts are
highlighted in different colors as described in the legend, according to the interfaces supported by the
relative modules.
Figure 38: Example of complete schematic diagram to integrate SARA-G3 /-U2 /-R4 /-N2 modules on the same application
board
UBX-17005143 - R06 Appendix Page 78 of 82
Page 79

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Abbreviation
Definition
3GPP
3rd Generation Partnership Project
AP
Application Processor
AT
AT Command Interpreter Software Subsystem, or attention
CTS
Clear To Send
DC
Direct Current
DCD
Data Carrier Detect
DCE
Data Communication Equipment
DDC
Display Data Channel interface
DL
Down-link (Reception)
DRX
Discontinuous Reception
DSP
Digital Signal Processing
DSR
Data Set Ready
DTE
Data Terminal Equipment
DTR
Data Terminal Ready
eDRX
Extended Discontinuous Reception
EMC
Electro-magnetic Compatibility
EMI
Electro-magnetic Interference
ESD
Electro-static Discharge
ESR
Equivalent Series Resistance
FEM
Front End Module
FOAT
Firmware Over AT commands
FW
Firmware
GND
Ground
GNSS
Global Navigation Satellite System
GPIO
General Purpose Input Output
HF
Hands-free
HW
Hardware
I/Q
In phase and Quadrature
I2C
Inter-Integrated Circuit interface
IP
Internet Protocol
LDO
Low-Dropout
LGA
Land Grid Array
LNA
Low Noise Amplifier
M2M
Machine-to-Machine
N/A
Not Applicable
N.A.
Not Available
NB-IoT
Narrow Band – Internet of Things
PA
Power Amplifier
PCM
Pulse Code Modulation
PCN
Sample Delivery Note / Information Note / Product Change Notification
PFM
Pulse Frequency Modulation
PMU
Power Management Unit
PWM
Pulse Width Modulation
RF
Radio Frequency
B Glossary
UBX-17005143 - R06 Appendix Page 79 of 82
Page 80

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Abbreviation
Definition
RI
Ring Indicator
RRC
Radio Resource Control
RTC
Real Time Clock
RTS
Request To Send
SAW
Surface Acoustic Wave
SIM
Subscriber Identification Module
TBD
To Be Defined
TP
Test-Point
UART
Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
UICC
Universal Integrated Circuit Card
UL
Up-link (Transmission)
VSWR
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
Table 31: Explanation of the abbreviations and terms used
UBX-17005143 - R06 Appendix Page 80 of 82
Page 81

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
Revision
Date
Name
Status / Comments
R01
06-Jun-2017
sfal / sses
Initial release
R02
31-Oct-2017
sses
Updated VCC, V_INT, Power-on, Reset, Antenna Detection, CTS and GPIO
description.
Updated main certification approvals.
R03
22-Feb-2018
sses
Extended document applicability to SARA-N211-02X and updated product
status
Updated VCC and switch-on info.
Updated Antenna Detection, CTS and GPIO features info.
Updated approvals info.
Additional design-in examples, minor corrections and improvements.
R04
22-Jun-2018
sses
Extended the document applicability to SARA-N201-02B-01.
Updated SARA-N211-02X product status.
Added ATEX and approvals info.
Updated TXD info.
Minor corrections and clarifications.
R05
27-Aug-2018
lpah
Extended the document applicability to SARA-N200-02B-01,
SARA-N210-02B-01, SARA-N211-02X-01, SARA-N280-02B-01.
R06
30-Nov-2018
lpah
SARA-N200-02B-01, SARA-N210-02B-01, SARA-N211-02X-01,
SARA-N280-02B-01 product status update.
Related documents
[1] u-blox SARA-N2 series Data Sheet, Docu No UBX-15025564
[2] u-blox Package Information Guide, Docu No UBX-14001652
[3] u-blox SARA-N2 series AT Commands Manual, Docu No UBX-16014887
[4] u-blox NB-IoT Application Development Guide, Docu No UBX-16017368
[5] ITU-T Recommendation V.24 - 02-2000 - List of definitions for interchange circuits between
the Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and the Data Circuit-terminating Equipment (DCE).
http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-V.24-200002-I/en
[6] I2C-bus specification and user manual - Rev. 5 - 9 October 2012 - NXP Semiconductors,
http://www.nxp.com/documents/user_manual/UM10204.pdf
[7] u-blox Nested Design Application Note, Docu No UBX-16007243
[8] u-blox SARA-G3 series Data Sheet, Docu No UBX-13000993
[9] u-blox SARA-U2 series Data Sheet, Docu No UBX-13005287
[10] u-blox SARA-G3 / SARA-U2 series System Integration Manual Docu No UBX-13000995
[11] u-blox AT Commands Manual, Docu No UBX-13002752
[12] u-blox SARA-R4 series Data Sheet, u-blox Document UBX-16024152
[13] u-blox SARA-R4 series System Integration Manual, Docu No UBX-16029218
[14] u-blox SARA-R4 series AT Commands Manual, Docu No UBX-17003787
[15] IEC 60079-0 - Explosive atmospheres, Part 0: Equipment general requirements
[16] IEC 60079-11 - Explosive atmospheres, Part 11: Equipment protection by intrinsic safety “i”
[17] IEC 60079-26 - Explosive atmospheres, Part 26: Equipment with EPL Ga
☞ For regular updates to u-blox documentation and to receive product change notifications, register
on our homepage (www.u-blox.com).
Revision history
UBX-17005143 - R06 Related documents Page 81 of 82
Page 82

SARA-N2 series - System Integration Manual
u-blox Offices
North, Central and South America
u-blox America, Inc.
Phone: +1 703 483 3180
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Regional Office West Coast:
Phone: +1 408 573 3640
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Technical Support:
Phone: +1 703 483 3185
E-mail: support@u-blox.com
Headquarters
Europe, Middle East, Africa
u-blox AG
Phone: +41 44 722 74 44
E-mail: info@u-blox.com
Support: support@u-blox.com
Asia, Australia, Pacific
u-blox Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Phone: +65 6734 3811
E-mail: info_ap@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office Australia:
Phone: +61 2 8448 2016
E-mail: info_anz@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Beijing):
Phone: +86 10 68 133 545
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Chongqing):
Phone: +86 23 6815 1588
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shanghai):
Phone: +86 21 6090 4832
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shenzhen):
Phone: +86 755 8627 1083
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office India:
Phone: +91 80 405 092 00
E-mail: info_in@u-blox.com
Support: support_in@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Osaka):
Phone: +81 6 6941 3660
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Tokyo):
Phone: +81 3 5775 3850
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Korea:
Phone: +82 2 542 0861
E-mail: info_kr@u-blox.com
Support: support_kr@u-blox.com
Regional Office Taiwan:
Phone: +886 2 2657 1090
E-mail: info_tw@u-blox.com
Support: support_tw@u-blox.com
Contact
For complete contact information, visit us at www.u-blox.com.
UBX-17005143 - R06 Contact Page 82 of 82
 Loading...
Loading...