Page 1
alone multiradio modules.
NINA-W15 series
Stand-alone multiradio modules with Wi-Fi and
Bluetooth
Data sheet
Abstract
This technical data sheet describes the NINA-W15 series standNINA‑W15 modules come with pre-flashed application software, Wi-Fi (802.11b/g/n) and Bluetooth
dual-mode (Bluetooth BR/EDR and Bluetooth Low Energy). NINA-W15 has several important
embedded security features, including secure boot which ensures that only authenticated software
can run on the module. This makes NINA-W15 ideal for critical IoT applications where security is
important.
UBX-18006647 - R08
C1-Public www.u-blox.com
Page 2

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
u-blox or third parties may hold intellectual property rights in the products, names, logos and designs included in this
document. Copying, reproduction, modification or disclosure to third parties of this document or any part thereof is only
permitted wit
The information contained herein is provided “as is” and u
implied, is given, including but not limited to, with respect to the accuracy, corr
purpose of the information. This document may be revised by u
documents, visit www.u
Copyright © u
Document information
Title
NINA-W15 series
Subtitle Stand-alone multiradio modules with Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Document type
Document number
Data sheet
UBX-18006647
Revision and date R08 18-Mar-2021
Disclosure restriction C1-Public
Product status
Functional sample Draft For functional testing. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
In development /
Prototype
Engineering sample Advance information Data based on early testing. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
Initial production Early production information Data from product verification. Revised and supplementary data may be published later.
Mass production /
End of life
Corresponding content status
Objective specification Target values. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
Production information Document contains the final product specification.
This document applies to the following products:
u-connectXpress
Product name Type number
NINA-W151 NINA-W151-00B-01 1.0.0 06 UBX-19051875 Initial production
NINA-W151-02B-00 3.0.0 07 N/A Initial production
NINA-W151-03B-00 4.0.0 07 N/A In Development
NINA-W152 NINA-W152-00B-01 1.0.0 06 UBX-19051875 Initial production
NINA-W152-02B-00 3.0.0 07 N/A Initial production
NINA-W152-03B-00 4.0.0 07 N/A In Development
NINA-W156 NINA-W156-03B-00 4.0.0 06 N/A Engineering sample
software version
Hardware
version
PCN reference Product status
UBX-18006647 - R08 Document information Page 2 of 55
C1-Public
h the express written permission of u-blox.
-blox assumes no liability for its use. No warranty, either express or
ectness, reliability and fitness for a particular
-blox at any time without notice. For the most recent
-blox.com.
-blox AG.
Page 3

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Contents
Document information ............................................................................................................................. 2
Contents ....................................................................................................................................................... 3
1 Functional description ....................................................................................................................... 6
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................................ 6
1.2 Applications ................................................................................................................................................. 6
1.3 Block diagram .............................................................................................................................................. 7
1.4 Product variants .......................................................................................................................................... 7
1.4.1 NINA-W151 .......................................................................................................................................... 7
1.4.2 NINA-W152 .......................................................................................................................................... 7
1.4.3 NINA-W156 .......................................................................................................................................... 7
1.5 Radio performance ..................................................................................................................................... 8
1.6 Software options ......................................................................................................................................... 8
1.6.1 AT command support ........................................................................................................................ 8
1.6.2 Software upgrade ............................................................................................................................... 8
1.7 IEEE 802.11d and additional regulatory domains ................................................................................ 9
1.7.1 NINA-W15 IEEE 802.11d implementation description .............................................................. 9
1.8 MAC addresses ......................................................................................................................................... 10
2 Interfaces ........................................................................................................................................... 11
2.1 Power supply .............................................................................................................................................. 11
2.1.1 Module supply input (VCC) ............................................................................................................. 11
2.1.2 Digital I/O interfaces reference voltage (VCC_IO) ...................................................................... 11
2.2 Low Power Clock ........................................................................................................................................ 11
2.3 System functions ...................................................................................................................................... 11
2.3.1 Module power on ............................................................................................................................... 11
2.3.2 Module power off .............................................................................................................................. 12
2.3.3 Module reset ...................................................................................................................................... 12
2.3.4 ACTIVE mode ..................................................................................................................................... 12
2.3.5 STANDBY mode ................................................................................................................................ 12
2.3.6 SLEEP mode ...................................................................................................................................... 12
2.3.7 STOP mode ........................................................................................................................................ 13
2.4 Boot strapping pins .................................................................................................................................. 13
2.5 RF antenna interface ................................................................................................................................ 14
2.5.1 Internal antenna ................................................................................................................................ 14
2.5.2 External RF antenna interface ....................................................................................................... 14
2.6 IO signals ..................................................................................................................................................... 15
2.6.1 Drive capability .................................................................................................................................. 15
2.6.2 System status IO signals ................................................................................................................ 15
2.6.3 System control IO signals ............................................................................................................... 15
2.6.4 UART IO signals ................................................................................................................................ 15
UBX-18006647 - R08 Contents Page 3 of 55
C1-Public
Page 4

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
2.7 Data and command interfaces ............................................................................................................... 16
2.7.1 UART ................................................................................................................................................... 17
2.7.2 RMII ...................................................................................................................................................... 17
2.7.3 SPI ........................................................................................................................................................ 17
3 Pin definition...................................................................................................................................... 19
3.1 Pin assignment .......................................................................................................................................... 19
4 Electrical specifications ................................................................................................................. 22
4.1 Absolute maximum ratings .................................................................................................................... 22
4.1.1 Maximum ESD ratings ..................................................................................................................... 22
4.2 Operating conditions ................................................................................................................................ 22
4.2.1 Operating temperature range ........................................................................................................ 23
4.2.2 Supply/Power pins ............................................................................................................................ 23
4.2.3 RESET_N pin ...................................................................................................................................... 23
4.2.4 Digital pins.......................................................................................................................................... 23
4.2.5 Current consumption ....................................................................................................................... 24
4.2.6 Wi-Fi radio characteristics.............................................................................................................. 25
4.2.7 Bluetooth radio characteristics ..................................................................................................... 25
4.2.8 Bluetooth low energy characteristics ........................................................................................... 26
4.2.9 Antenna radiation patterns ............................................................................................................ 26
5 Mechanical specifications ............................................................................................................. 29
5.1 NINA-W151 Mechanical specification .................................................................................................. 29
5.2 NINA-W152 Mechanical specification .................................................................................................. 30
5.3 NINA-W156 Mechanical specification .................................................................................................. 31
6 Qualification and approvals .......................................................................................................... 32
6.1 Country approvals ..................................................................................................................................... 32
6.2 European Union regulatory compliance ............................................................................................... 32
6.2.1 Radio Equipment Directive (RED) 2014/53/EU .......................................................................... 32
6.2.2 Compliance with the RoHS directive ............................................................................................ 32
6.3 FCC/IC Compliance ................................................................................................................................... 32
6.3.1 FCC Compliance ................................................................................................................................ 32
6.3.2 FCC statement .................................................................................................................................. 33
6.3.3 RF exposure statement ................................................................................................................... 33
6.3.4 End-product user manual instructions ........................................................................................ 33
6.3.5 End-product labeling requirements .............................................................................................. 34
6.3.6 End product compliance .................................................................................................................. 35
6.4 Japan radio equipment compliance ...................................................................................................... 36
6.5 NCC Taiwan compliance .......................................................................................................................... 36
6.5.1 Taiwan NCC Warning Statement .................................................................................................. 36
6.5.2 NINA-W151 labeling requirements for end product ................................................................. 36
6.5.3 NINA-W152 labeling requirements for end product ................................................................. 37
6.6 KCC South Korea compliance ................................................................................................................. 37
6.7 Brazil compliance ...................................................................................................................................... 37
UBX-18006647 - R08 Contents Page 4 of 55
C1-Public
Page 5

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
6.8 Australia and New Zealand regulatory compliance ........................................................................... 38
6.9 South Africa regulatory compliance ..................................................................................................... 38
6.10 Safety Compliance .................................................................................................................................... 38
6.11 Bluetooth qualification information ...................................................................................................... 39
7 Antennas ............................................................................................................................................ 40
7.1 Antenna accessories ................................................................................................................................ 41
7.2 Approved antennas .................................................................................................................................. 41
7.2.1 Single band antennas ...................................................................................................................... 41
7.2.2 Dual-band antennas ......................................................................................................................... 44
8 Product handling .............................................................................................................................. 46
8.1 Packaging ................................................................................................................................................... 46
8.1.1 Reels .................................................................................................................................................... 46
8.1.2 Tapes ................................................................................................................................................... 46
8.2 Moisture sensitivity levels ....................................................................................................................... 48
8.3 Reflow soldering ........................................................................................................................................ 48
8.4 ESD precautions ........................................................................................................................................ 48
9 Labeling and ordering information ............................................................................................. 49
9.1 Product labeling ......................................................................................................................................... 49
9.2 Explanation of codes ................................................................................................................................ 50
9.3 Ordering information ................................................................................................................................ 50
Appendix .................................................................................................................................................... 51
A Glossary .............................................................................................................................................. 51
Related documents ................................................................................................................................ 53
Revision history ....................................................................................................................................... 54
Contact ....................................................................................................................................................... 55
UBX-18006647 - R08 Contents Page 5 of 55
C1-Public
Page 6

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
1 Functional description
1.1 Overview
NINA-W15 series stand-alone multiradio modules integrate Wi-Fi, Bluetooth BR/EDR and Bluetooth
low energy in a compact form factor. The modules support simultaneous operation on Wi-Fi and
Bluetooth dual-mode and can therefore serve as a gateway between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
NINA‑W15 modules come with pre-flashed application software, supporting Wi-Fi 802.11b/g/n and
dual-mode Bluetooth (Bluetooth BR/EDR v4.2+EDR and Bluetooth Low Energy v4.2) in the 2.4 GHz
ISM band. The host system can set up and control the module through the AT command interface.
Intended applications include telematics, industrial automation, connected buildings, wireless
sensors, point-of-sales, and medical devices.
NINA-W15 is assessed to comply with RED and is certified as a modular transmitter in the following
countries US (FCC), Canada (IC / ISED RSS), Japan (MIC), Taiwan (NCC), South Korea (KCC), Australia
/ New Zealand (ACMA), Brazil (Anatel), South Africa (ICASA). The modules are qualified for
professional grade operation, supporting an extended temperature range of –40 °C to +85 °C.
1.2 Applications
• Internet of Things (IoT)
• Wi-Fi and Bluetooth networks
• Telematics
• Point-of-sales
• Medical and industrial networking
• Access to laptops, mobile phones, and similar consumer devices
• Home/building automation
• Ethernet/Wireless Gateway
UBX-18006647 - R08 Functional description Page 6 of 55
C1-Public
Page 7
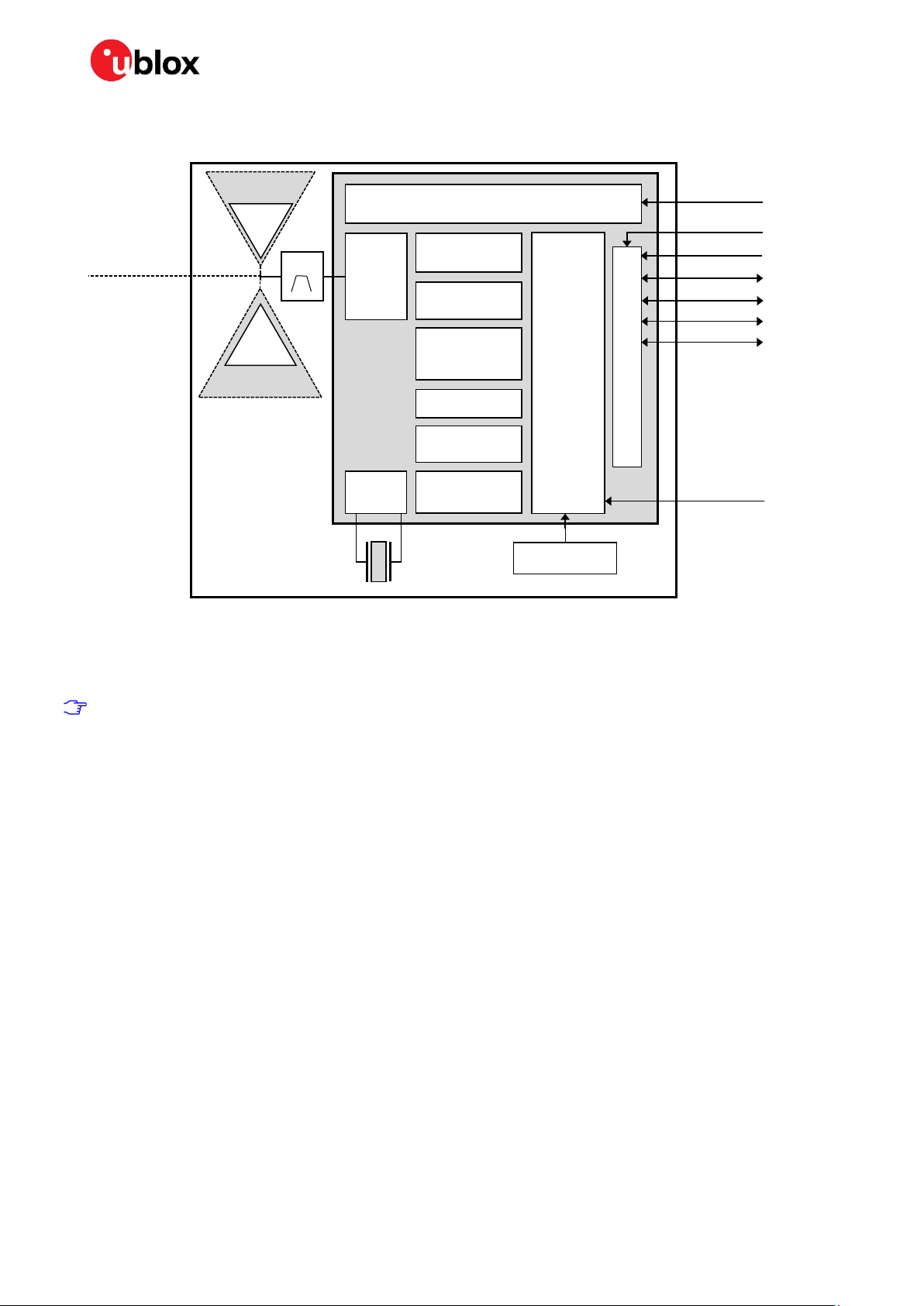
NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Baseband
accelerations
Quad SPI
VCC_IO
VCC (3.0- 3.6 V)
40 MHz
Reset
UART
SPI
LPO**
RMII
1.3 Block diagram
PIFA Antenna
(NINA-W152)
ANT (NINA-W151)
BPF*
RF
(NINA-W156)
PCB trace antenna
PLL
* Only on NINA-W151 and NINA-W152
** Only on NINA-W156
Figure 1: Block diagram of NINA-W15 series
Linear voltage regulators
Wi-Fi baseband
Bluetooth
Cryptographics
hardware
EFUSE
ROM
SRAM (4Mbit)
Flash (16Mbit)
GPIO
IO Buffers
2x Xtensa 32-bit LX6 MCU
External LPO is a planned feature for NINA-W156, not supported in the current software.
1.4 Product variants
NINA‑W15 series modules come with pre-flashed application software, supporting Wi-Fi
802.11b/g/n, Bluetooth BR/EDR and Bluetooth Low Energy v4.2 in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. The host
system can set up and control the module through the AT command interface. See u-connectXpress
AT commands manual [3] for more information about AT commands.
1.4.1 NINA-W151
NINA-W151 has no internal antenna. Instead, the RF signal is available at a module pin for routing to
an external antenna or antenna connector. The module outline is smaller compared to the module
variants with antenna, only 10.0 x 10.6 mm. The module height is 2.2 mm.
1.4.2 NINA-W152
NINA-W152 has an internal PIFA antenna mounted on the module. The RF signal is not connected to
any module pin. The module outline is 10.0 x 14.0 mm and the height 3.8 mm.
1.4.3 NINA-W156
NINA-W156 has an internal PCB trace antenna, using antenna technology licensed from ProAnt AB.
The RF signal is not connected to any module pin. The module outline is 10.0 x 14.0 mm and the height
2.2 mm.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Functional description Page 7 of 55
C1-Public
Page 8
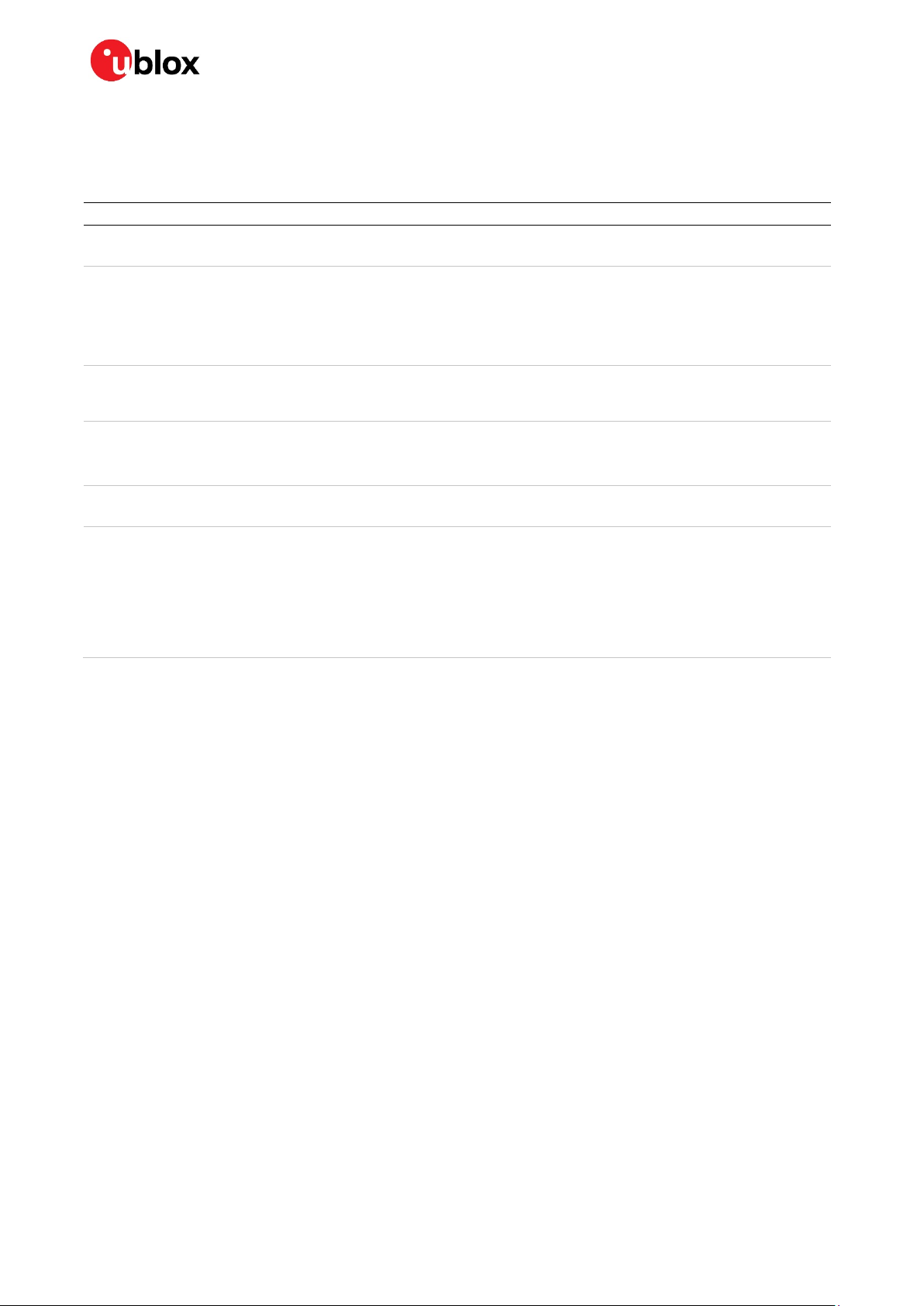
NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
1.5 Radio performance
NINA-W15 modules support Wi-Fi and conform to IEEE 802.11b/g/n single-band 2.4 GHz operation,
Bluetooth BR/EDR and Bluetooth Low Energy, as explained in Table 1.
Wi-Fi Bluetooth BR/EDR Bluetooth Low Energy
IEEE 802.11b/g/n
IEEE 802.11d
Band support
Station mode:
2.4 GHz, channel 1-13
Access Point mode:
2.4 GHz, channel 1-11
Typical conducted output power
15 dBm
Typical radiated output power
18 dBm EIRP
Conducted sensitivity
-96 dBm
Data rates:
IEEE 802.11b:
1 / 2 / 5.5 / 11 Mbit/s
IEEE 802.11g:
6 / 9 / 12 / 18 / 24 / 36 / 48 / 54 Mbit/s
IEEE 802.11n:
MCS 0-7, HT20 (6.5-72 Mbit/s)
* Maximum support for 802.11d depends on the region.
** RF power including maximum antenna gain (3 dBi).
Table 1: NINA-W15 series Wi-Fi and Bluetooth characteristics
**
*
Bluetooth v4.2+EDR
Maximum number of Peripherals: 5
Band support
2.4 GHz, 79 channels
Typical conducted output power
- 1 Mbit/s: 5 dBm
- 2/3 Mbit/s: 5 dBm
Typical radiated output power
- 1 Mbit: 8 dBm EIRP
- 2/3 Mbit/s: 8 dBm EIRP
Conducted sensitivity
-88 dBm
Data rates:
1 / 2 / 3 Mbit/s
**
**
Bluetooth 4.2 Bluetooth LE dual-mode
Band support
2.4 GHz, 40 channels
Typical conducted output power
5 dBm
Typical radiated output power
8 dBm EIRP
Conducted sensitivity
-88 dBm
Data rates:
1 Mbit/s
**
1.6 Software options
NINA‑W15 series modules come with the pre-flashed application software, supporting IEEE
802.11b/g/n single-band 2.4 GHz operation, Bluetooth BR/EDR and dual-mode Bluetooth. The host
system can set up and control the module through the AT command interface. NINA-W15 modules
provide top grade security, thanks to secure boot, which ensures the module boots up only with
original u-blox software. The modules addionally provide end-to-end security on the wireless link with
the latest 802.11i (WPA2) standard and enterprise security that provides a secure connection to the
infrastructure. This makes NINA-W15 ideal for critical IoT applications where security is important.
1.6.1 AT command support
You configure the NINA-W151, NINA-W152 and NINA-W156 modules with the u-blox s-center toolbox
software using AT commands. See u-connectXpress AT commands manual [3] for information about
supported AT commands.
The s-center evaluation software supporting the AT commands is also available free of charge and
can be downloaded from the u-blox website.
1.6.2 Software upgrade
Information on how to upgrade the software for the NINA-W15 series is provided in the NINA-W1
series system integration manual [1].
UBX-18006647 - R08 Functional description Page 8 of 55
C1-Public
Page 9

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
1.7 IEEE 802.11d and additional regulatory domains
NINA-W15 series modules support the IEEE 802.11d wireless network standard, which extends the
original IEEE 802.11 specification to include support for “additional regulatory domains”.
NINA-W15-based devices configure automatically to operate in accordance regulatory domains.
By passively scanning (listening) for beacons available wireless networks, NINA-W15 modules identify
the channels supported by each network and determine the best access point with which to connect.
The modules configure automatically to operate in accordance with the policies and regulations of the
regional domain in which they operate.
Passive scans are performed once on startup and then once every hour. After the first passive scan
the channel list will be filtered to according to 802.11d.
1.7.1 NINA-W15 IEEE 802.11d implementation description
When used as Wi-Fi stations, NINA-W1 modules passively scan access point (AP) beacons at startup. A new scan is performed every hour to update the regulatory domain. The algorithm is restarted
when the module is turned on or reset. It is not possible to override the algorithm described by
reconfiguring the device.
The beacons include information elements that describe the country name, data rates, channel
quantity, signal strength, and maximum transmission level of the wireless network that they
represent. Based on the information received from the beacons, the modules compare APs and
choose which one to use. NINA-W1 modules configure automatically to operate on all bands
supported in the regulatory domain of the chosen AP, as shown in Table 2.
NINA-W15 supports the following three domains:
• FCC: This is the regulatory body for products used in the US. If the scan results include country
information pertaining solely to the FCC the regulatory domain is set to FCC.
• ETSI: This is the regulatory domain for the products sold primarily in Europe. If at least three scan
results contain country information pertaining to non-FCC countries, and no other contrary
information is received, the regulatory domain is set to ETSI.
• WORLD: In this domain, NINA-W1 modules operate on all channels supported both by FCC, ETSI,
and most other countries in the world. This is the initial regulatory domain. If subsequent scans
contain country information for both FCC and non-FCC countries, the regulatory domain is always
set to WORLD. In this state is shown as WORLD-FINAL. This state is not exited until the device
is reset.
The state transition diagram shown in describes the algorithm for selecting the current regulatory
domain.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Functional description Page 9 of 55
C1-Public
Page 10
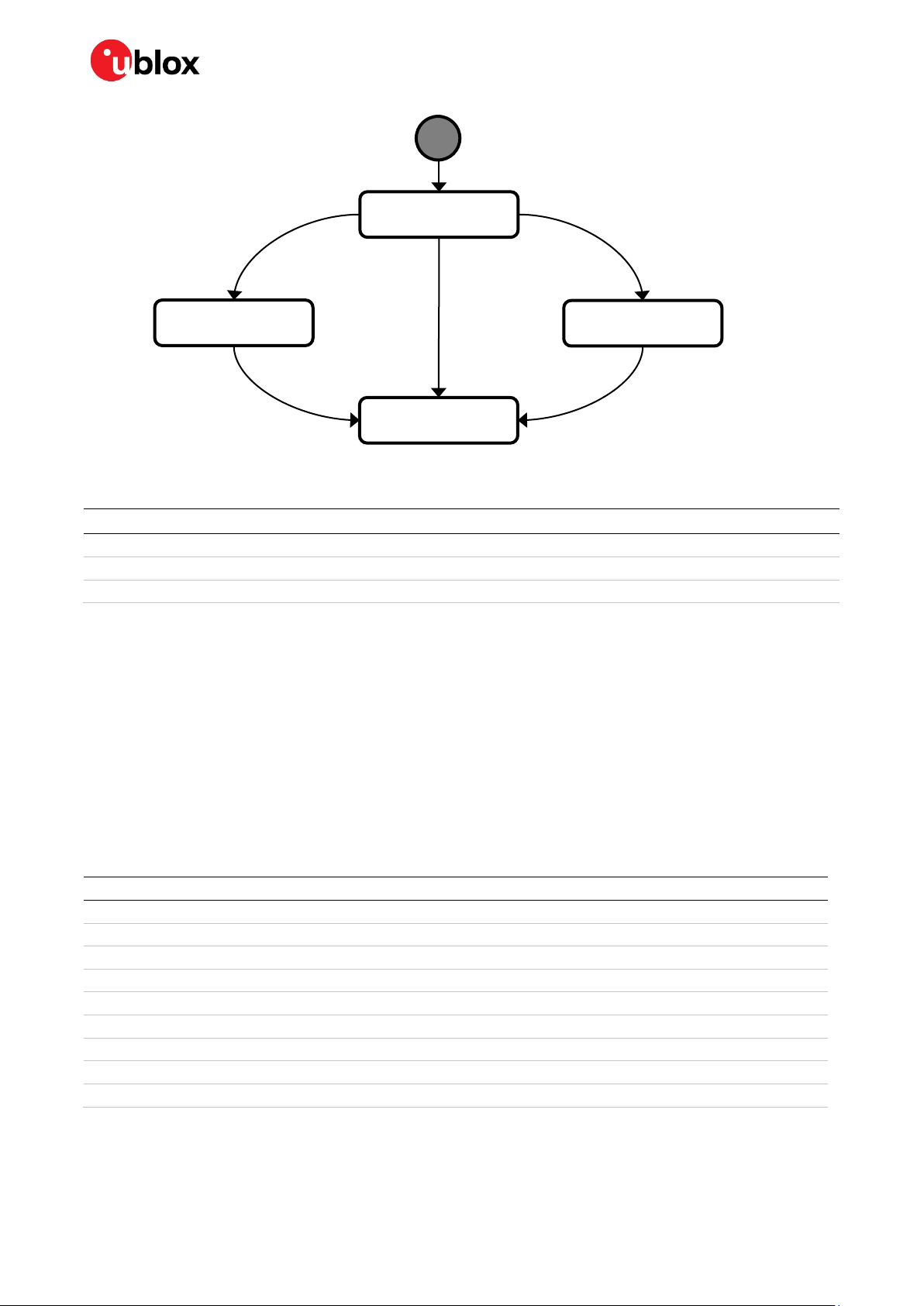
NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Scan complete
No non-FCC AP
Scan complete
Both FCC and
non
less than three
non
Entry start scan
S
tart scan every hour
Scan complete
No FCC AP
At least three non-FCC AP
ETSI
Scan complete
FCC AP found
WORLD
-FCC AP or
-FCC AP
WORLD-FINAL
At least one FCC AP
FCC
Scan complete
Non-FCC AP found
Figure 2: NINA-W15 series IEEE 802.11d state transition diagram
Table 2 shows the channels that are supported in the different regulatory domains.
Regulatory domain Band Tx channels
WORLD 2.4 GHz 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
ETSI 2.4 GHz 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13
FCC 2.4 GHz 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
Table 2 Channel list for supported regulatory domains
⚠ Channels 12 and 13 are not allowed in Taiwan. A device that is put on the Taiwanese market must
make these channels unavailable to an end-user.
The maximum output power is reduced on some channels depending on regulatory requirements.
For example, frequency band edge requirements can limit the output power on channels close to
band edges.
1.8 MAC addresses
The NINA-W15 module series has four unique consecutive MAC addresses reserved for each module
and the addresses are stored in the configuration memory during production. The first Wi-Fi MAC
address is available in the Data Matrix on the label (see section 9.1).
MAC address Assignment
Module 1, address 1 Wi-Fi 00
Module 1, address 2 RMII/Ethernet 01
Module 1, address 3 Bluetooth 10
Module 1, address 4 Reserved 11
Module 2, address 1 Wi-Fi 00
Module 2, address 2 RMII/Ethernet 01
Module 2, address 3 Bluetooth 10
Module 2, address 4 Reserved 11
Table 3: Example MAC addresses assignment for two modules
Last bits of MAC address Example
D4:CA:6E:90:04:90
D4:CA:6E:90:04:91
D4:CA:6E:90:04:92
D4:CA:6E:90:04:93
D4:CA:6E:90:04:94
D4:CA:6E:90:04:95
D4:CA:6E:90:04:96
D4:CA:6E:90:04:97
UBX-18006647 - R08 Functional description Page 10 of 55
C1-Public
Page 11

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
2 Interfaces
2.1 Power supply
The power for NINA-W15 series modules is supplied through VCC and VCC_IO pins by DC voltage.
The system power supply circuit must be able to support peak power as during operation, the
current drawn from VCC and VCC_IO can vary significantly based on the power consumption
profile of the Wi-Fi technology.
2.1.1 Module supply input (VCC)
NINA-W15 series modules use an integrated Linear Voltage converter to transform the supply voltage
presented at the VCC pin into a stable system voltage.
2.1.2 Digital I/O interfaces reference voltage (VCC_IO)
All modules in the NINA-W15 series provide an additional voltage supply input for setting the I/O
voltage level. The separate VCC_IO pin enables integration of the module in many applications with
different voltage levels (for example, 1.8 V or 3.3 V) without any level converters. NINA-W15 modules
support only 3.3 V as IO voltage level currently.
2.2 Low Power Clock
External LPO is a planned feature not supported in the current software.
NINA-W15 does not have an internal low power oscillator (LPO), which is required for lowest power
modes. An external 32.768 KHz LPO signal can be supplied externally via the LPO_CLK pin of the
NINA-W156 module if low power modes are required. NINA-W152 and NINA-W151 do not support an
external LPO clock.
2.3 System functions
NINA-W15 series modules are power efficient devices capable of operating in different power saving
modes and configurations. Different sections of the modules can be powered off when they are not
needed, and complex wake up events can be generated from different external and internal inputs.
Sections 2.3.1to 2.3.7 describe the system power modes, power-on/off, reset behavior, and boot
strapping options.
The following system power modes are available:
• Automatic:
o ACTIVE mode
o STANDBY mode
• Manual:
o SLEEP mode
o STOP mode
2.3.1 Module power on
You can switch on or reboot the NINA-W15 series modules in one of the following ways:
• Rising edge on the VCC pin to a valid supply voltage
• Issuing a reset of the module (see section 2.3.3)
UBX-18006647 - R08 Interfaces Page 11 of 55
C1-Public
Page 12

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
If the u-connectXpress software has been configured to start in AT mode, +STARTUP is sent over the
UART interface when the software has booted and is ready to accept commands.
2.3.2 Module power off
There is no dedicated pin to power down the NINA-W15 series modules. Instead, the “STOP” power
mode can be used to keep the module in the deepest power save mode. STOP mode is more power
efficient than holding the module in reset.
2.3.3 Module reset
NINA-W15 series modules can be reset (rebooted) in any of the following ways:
• RESET_N low. Normally set high by an internal pull-up, a logical low state on this signal low causes
a “hardware” reset of the module. RESET_N should be driven by an open drain, open collector, or
contact switch.
• NINA-W15 modules can be reset using the
Holding the module in reset does not result in the lowest power consumption. For optimal power
reduction, set the module in “Stop mode”, as described in section 2.3.7.
AT+CPWROFF command.
2.3.4 ACTIVE mode
In this mode the module is actively transmitting or receiving data over one or more of its interfaces;
2.4 GHz radio, UART, and so on. The module CPU is operating at its highest clock speed. The module
seamlessly switches between ACTIVE mode and STANDBY automatically without user involvement.
2.3.5 STANDBY mode
In this mode the module “idles” and performs only background activities. As radio and physical
connections are maintained, no packets are lost in this mode. When necessary, the module
automatically enters ACTIVE mode without delay.
The user can further decrease current consumption in STANDBY mode by:
• Enabling Automatic Frequency Adaption (AFA)
• Increasing the Bluetooth low energy connection interval
• Increase the DTIM listen interval (Wi-Fi Station mode only)
• Storing and sending data in concentrated bursts
Automatic Frequency Adaption (AFA) allows the internal clocks to be automatically reduced whenever
possible. AFA is configured using the
AT+UPWRMNG command.
Enabling AFA limits the maximum baud rate of the UART interface to 1 Mbaud.
For more information about how to use AT commands for configuring u-connectXpress software,
see the u-connectXpress AT commands manual
[3] and u-connectXpress software user guide [6].
2.3.6 SLEEP mode
For radio modes that support SLEEP mode, the module operates with even lower power consumption
than that required in STANDBY mode.
As the module functionality is limited in this mode, it must be activated manually by the host.
In SLEEP mode, radio and peer connections are maintained, but incoming data or URCs are not sent
over the UART until SLEEP mode is deactivated, hence incoming data or URCs may be lost.
Enable SLEEP mode control using command
mode.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Interfaces Page 12 of 55
C1-Public
AT&D3 and toggle the UART DSR pin to enter/leave SLEEP
Page 13

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
SLEEP mode is supported in the following radio modes:
• Wi-Fi Station
• Radio turned off
To further decrease power consumption in SLEEP mode, the following software settings can be used:
• Enabling Automatic Frequency Adaption (AFA)
• Increasing the Bluetooth Low Energy connection interval
• Increase the DTIM listen interval (Wi-Fi Station mode only)
Enabling AFA can put limits on certain module functions, maximum UART baud rate, and so on.
Check the u-connectXpress AT commands manual
acceptable for your application.
[3] to determine which clock speeds are
See the u-connectXpress AT commands manual [3] and u-connectXpress software user guide [6]
for more information on how to use AT commands for configuring the u-connectXpress software.
2.3.7 STOP mode
STOP mode is the deepest power saving mode of NINA-W15 modules. To ensure minimum power
consumption during STOP mode, all functionality is stopped and all existing connections are dropped.
The system RAM is not retained. The module always reboots during the wake up from STOP mode.
The user must manually enter the STOP mode with one of the following methods:
• Enable STOP mode control using command
STOP mode.
• Use command
capable of controlling STOP mode are shown in Table 6.
• Use command
If the u-connectXpress software is configured to start in AT mode, the
the UART interface when the module is ready to accept commands.
AT+USTOP to configure which GPIO pin is used to enter/leave STOP mode. The GPIOs
AT+USTOP to configure a timer to automatically wake up after a delay set by the user.
AT&D4 and toggle the UART DSR pin to enter/leave
+STARTUP command is sent over
For more information on how to use AT commands to configure the u-connectXpress software,
see the u-connectXpress AT commands manual
[3] and u-connectXpress software user guide [6].
2.4 Boot strapping pins
Table 4 shows boot configuration pins on the module that must be set correctly during boot.
Boot strap pins are configured to their default state internally on the module and generally must NOT
be set externally. Exceptionally, pin 32 can be connected to GND to turn off printouts during start-up.
After the system has booted, pin 32 is reconfigured to the SPI chip-select signal SPI_CS.
Pin 27 is a boot strap pin but is also the RMII clock line. For more information about how to use the
RMII interface, see the NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1].
Pin 36 controls the voltage level of the internal flash during startup. After the system has booted this
pin is reconfigured as the SPI slave data output signal SPI_MISO. This signal must NOT be pulled
down by an external MCU or circuitry. After the module has booted, the RMII_CLK, UART_RXD,
SPI_DRDY and SPI_SCLK are used to determine which command interfaces to activate. See section
2.7 for more information.
Pin State during boot Default Behavior Description
27 0 ESP boot mode (factory boot) ESP Factory boot Mode/RMII clock line.
1 Pull-up* Normal boot from internal flash
32 0 Silent Printout on U0TXD during boot
UBX-18006647 - R08 Interfaces Page 13 of 55
C1-Public
Page 14
NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Pin State during boot Default Behavior Description
1 Pull-up* U0TXD toggling
36 0 VDD_SDIO=3.3 V (not allowed) Internal flash voltage
1 10 kΩ pull-up VDD_SDIO=1.8 V
(VDD_SDIO should always be at 1.8 V)
*About 45 kΩ
Table 4: NINA-W15 series boot strapping pins
2.5 RF antenna interface
The RF antenna interface of the NINA-W15 series supports Wi-Fi, Bluetooth BR/EDR and Bluetooth
Low Energy on the same antenna. The different communication protocols are time divided on the
antenna to switch between the Bluetooth and Wi-Fi data. Although communication using these
different protocols generally transparent in the application, these protocols are never active in the
module antenna at exactly the same time.
NINA-W15 series modules support either an internal antenna (NINA-W152 and NINA-W156) or an
external antenna connected through a dedicated antenna pin (NINA-W151).
2.5.1 Internal antenna
Both NINA-W152 and NINA-W156 have internal antennas specifically designed and optimized for the
NINA module. The NINA-W152 module has a 2.4 GHz PIFA antenna and the NINA-W156 module has
a 2.4 GHz PCB trace antenna.
It is recommended to place the NINA-W152 modules in such a way that the internal antenna is in the
corner of the host PCB (the corner closest to Pin 16 should be in the corner). The antenna side (with
the short side closest to the antenna) positioned along one side of the host PCB ground plane is the
second-best option.
For the NINA-W156 module, place it in such a way that the PCB trace antenna is placed on the side
edge of the host PCB and in the middle of the side.
For both NINA-W152 and NINA-W156, keep a minimum clearance of 5 mm between the antenna and
the casing. Keep a minimum of 10 mm free space from the metal around the antenna including the
area below. If a metal enclosure is required, use NINA-W151 and an external antenna. It is beneficial
to have a large solid ground plane on the host PCB and have a good grounding on the module. Minimum
ground plane size is 24x30 mm but recommended is more than 50x50 mm.
See the NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1] for more information about antenna related
design.
⚠ The ANT signal solder pin is unavailable on NINA-W152 and NINA-W156 modules.
2.5.2 External RF antenna interface
NINA-W151 modules have an antenna signal (ANT) pin for use with an external antenna.
An external SMD antenna (or PCB integrated antenna) can be used on the host board, and an antenna
connector for using an external antenna through a coaxial cable could also be implemented. A cable
antenna might be necessary if the module is mounted in a shielded enclosure such as a metal box or
cabinet.
The signal has a characteristic impedance of 50 Ω and supports both Tx and Rx.
An external antenna connector (U.FL. connector) reference design (see NINA-W1 series system
integration manual [1]) is available and must be followed to comply with the NINA-W1 FCC/IC modular
approvals. A list of approved antennas is shown in section 7.2.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Interfaces Page 14 of 55
C1-Public
Page 15

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
A reference design for use with an external antenna connector (U.FL. connector) is described in
NINA W1 system integration manual
NINA-W1 FCC/IC modular approvals.
[1]). The design must be followed to comply with the
2.6 IO signals
NINA-W15 series modules have a versatile pin-out. Overall, there are up to 16 GPIO pins for
NINA-W151/W152 and 18 for NINA-W156.
2.6.1 Drive capability
All GPIO pins are normally configured for medium current consumption. Using this standard drive
capability, a pin configured as output can source and an input sink a certain amount of current. See
section 4.2.4.
2.6.2 System status IO signals
The RED, GREEN and BLUE pins are used to signal the status. They are active low and are intended
to be routed to an RGB LED. See u-connectXpress AT commands manual [3] for more information
about connectivity software signals IOs.
Mode Status RGB LED color GREEN BLUE RED
Data mode IDLE Green LOW HIGH HIGH
Command mode IDLE Orange LOW HIGH LOW
Data mode, Command mode
Data mode, Command mode
* = LED flashes on data activity
Table 5: System status indication
CONNECTING
CONNECTED
*
*
Purple HIGH LOW LOW
Blue HIGH LOW HIGH
The RED, GREEN and BLUE signals are disabled when the RMII interface is enabled.
2.6.3 System control IO signals
The following input signals are used to control the system (see u-connectXpress AT commands
manual [3] for more information about connectivity software signals IOs):
• RESET_N is used to reset the system. See section 2.6 for detailed information.
• If SWITCH_1 is driven low during start up, the UART serial settings are restored to their default
values.
• SWITCH_2 can be used to open a connection to a peripheral device.
• If both SWITCH_1 and SWITCH_2 are driven low during start up, the system will enter the
bootloader mode.
• If both SWITCH_1 and SWITCH_2 are driven low during start up and held low for 10 seconds, the
system will exit the bootloader mode and restore all settings to their factory defaults.
2.6.4 UART IO signals
In addition to the normal RXD, TXD, CTS, and RTS signals, the NINA-W15 software adds the DSR and
DTR pins to the UART interface. Although not used as they were originally intended, these pins control
the state of the NINA-W15 module. Depending on the current configuration, the DSR pin can be used
to:
• Enter command mode
• Disconnect and/or toggle connectable status
• Enable/disable the rest of the UART interface
UBX-18006647 - R08 Interfaces Page 15 of 55
C1-Public
Page 16
NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Enabled
Interfaces
no
no
• Enter/leave SLEEP mode
• Enter/leave STOP mode
If CTS/RTS flow control is disabled, those pins can be used as GPIOs.
2.7 Data and command interfaces
Although there are three data interfaces available on a NINA-W15 module (UART, RMII, and SPI),
these cannot be used at the same time. AT commands are used to enable or disable the interfaces
manually.
After the module has booted, the module checks for activity on each interface to determine which one
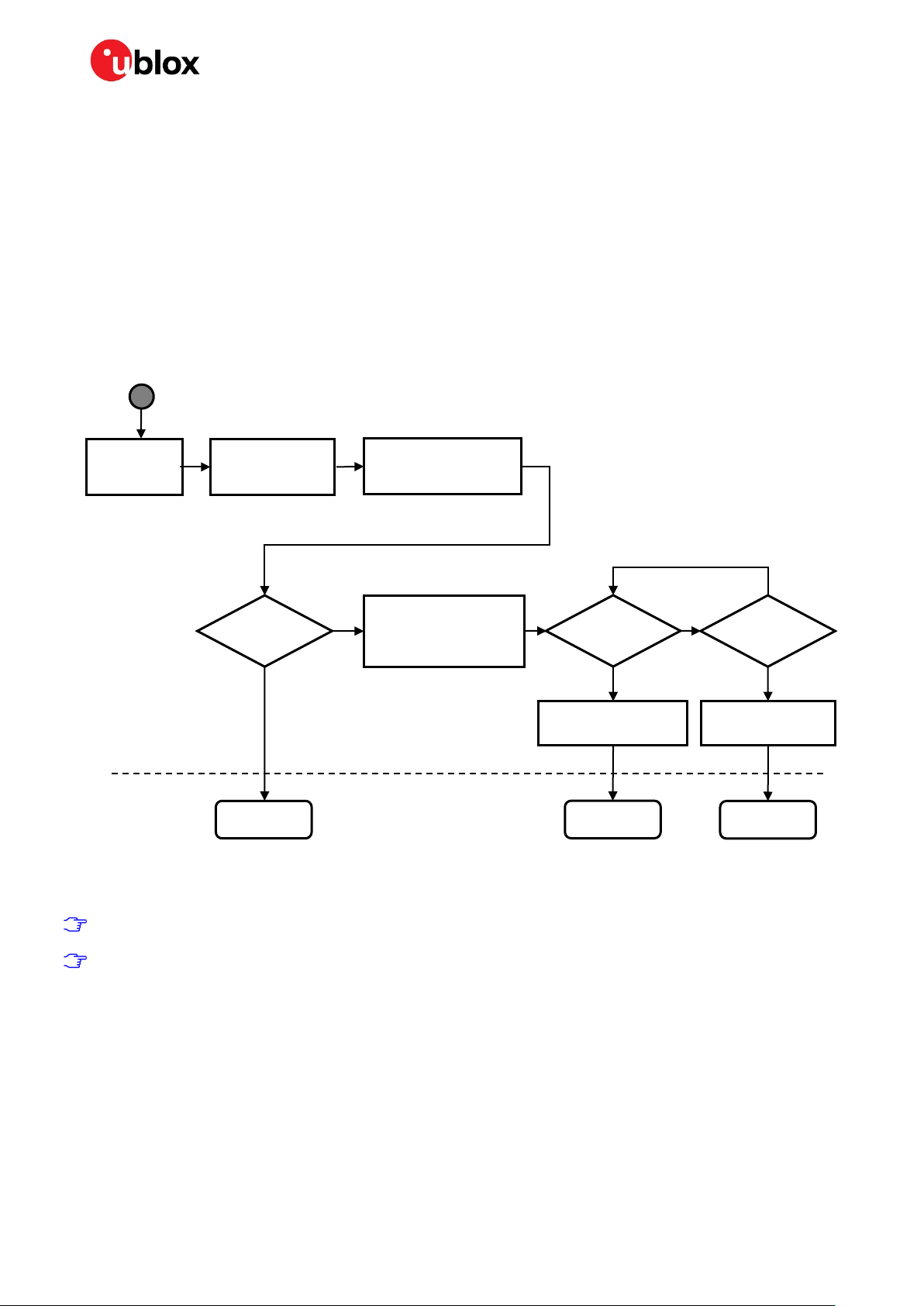
should be used. Figure 3 shows the startup and interface selection procedure.
Enable UART
interface
Figure 3: Interface detection flow chart
Send +STARTUP on
UART interface
Ethernet
detected?
RMII + UART
yes
Start Ethernet detection
Stop Ethernet detection
Disable RMII interface
Start SPI detection
Start UART detection
SPI
detected?
yes
Stop UART detection
Disable UART interface
SPI
no
UART
detected?
yes
Stop SPI detection
Disable SPI interface
UART
This process is active until an interface is successfully detected.
+STARTUP is always printed on the UART TXD line.
During Ethernet detection, the NINA-W15 module looks for a clock signal on RMII_CLK. If Ethernet is
detected, only the UART_RXD and UART_TXD signals are available on the UART interface.
If SPI detection is started, the NINA-W15 module toggles the SPI_DRDY signal periodically. Once the
SPI master has sent eight clock signals on the SPI_SCLK line, the SPI interface is considered active
and the UART interface is subsequently disabled.
If an AT command is sent to the NINA-W15 module over the UART interface, the SPI_DRDY signal
stops toggling and the SPI interface is disabled.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Interfaces Page 16 of 55
C1-Public
Page 17

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
For more information on how to use these data and command interfaces, see the u-connectXpress
software user guide [6] .
2.7.1 UART
NINA-W15 modules include a 6-wire UART for communication with an application host processor (AT
commands, data communication, and software upgrades).
The following UART signals are available:
• Data lines (RXD as input, TXD as output)
• Hardware flow control lines (CTS as input, RTS as output)
• Link status (DTR as output, DSR as input). DTR/DSR signal behavior is adapted to the
u-connectXpress software functionality and differs from the UART standard. For more
information about this, see section 2.6.4.
• Programmable baud-rate generator allows most industry standard rates, as well as non-standard
rates up to 3 Mbit/s.
• Frame format configuration:
o 8 data bits
o Even or no-parity bit
o 1 stop bit
• Default frame configuration is 8N1 means eight (8) data bits, no (N) parity bit, and one (1) stop bit.
2.7.2 RMII
The RMII (Reduced Media Independent Interface) Ethernet interface is intended for connecting to an
external PHY. The following signals are used:
• RMII_TXD0, RMII_TXD1 – Transmit data output bits 0 and 1.
• RMII_TXEN – Output signal used to indicate when data is being transmitted.
• RMII_RXD0, RMII_RXD1 – Receive data input bits 0 and 1.
• RMII_CRSDV – Carrier sense and RX data valid in signals, multiplexed on alternate clock cycles.
• RMII_CLK – 50 MHz clock input signal that must be supplied by an external oscillator or the
Ethernet PHY chip.
An MDIO (Management Data Input/Output) interface used for controlling the external PHY is also
available:
• RMII_MDCLK – Management interface clock output signal
• RMII_MDIO – Management interface data input and output signal
The flow control (RTS and CTS) of the UART interface is multiplexed with the RMII interface and
cannot be used simultaneously. The RED, GREEN and BLUE signals are also disabled when the RMII
interface is enabled because the BLUE signal is multiplexed with the RMII interface.
See NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1] for more information about how to use the RMII
interface.
2.7.3 SPI
The serial peripheral interface of NINA-W15 only runs in “SPI slave mode”, meaning a host controller
running in “SPI master mode” is intended to send commands to the NINA module.
The following signals are used:
• SPI_SCLK – Serial clock input signal
• SPI_MOSI – Serial data input signal
• SPI_MISO – Serial data output signal
UBX-18006647 - R08 Interfaces Page 17 of 55
C1-Public
Page 18

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
• SPI_CS – Chip Select input, enable control signal
• SPI_DRDY – (optional) Additional “Data Ready” output signal, used to indicate to the controller
when data is available. This signal can be disabled but is enabled by default.
• SPI_NORX – (optional) Additional flow control output signal used to indicate when the NINA module
cannot receive any more data. This signal is not enabled by default.
An SPI master must comply with the following:
• 10 MHz maximum clock speed
• SPI mode 1 or 3
• The SPI master must clock at least 8 bytes minimum and 4096 bytes maximum per transaction,
and transaction lengths must be on 4 byte boundary
See the following application note for more information on how to use the SPI interface [7].
UBX-18006647 - R08 Interfaces Page 18 of 55
C1-Public
Page 19

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
36
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
RED
GPI
GPI
GPI
GND
GREEN / SW I TCH _1
RM II_MDIO
RM II_MDCLK/SPI_DRDY
UART_RTS/RMII_TXD1
UART_CTS/RM II_TXD0
UA RT_TXD
UART_RXD
SYS_BOOT/ RM II_CLK
GPI O
GPI O
GND
GND
LPO_IN* / GPIO
SWITCH_2/RMII_CRS_DV
UART_DTR/RMII_RXD0
VCC_I O
VCC
UART_DSR/ RMII_RXD1
RESET_ N
NINA-W15
1514
13
12
11
GND
ANT
GND
GPI *
GPI *
RM II_TX_EN/BLUE
36
35
34
333231
GPI
RSVD
LOG_BO O T/ SPI_CS
SPI_SCLK
SPI_M OSI
SPI_M ISO
Top view
3 Pin definition
3.1 Pin assignment
Figure 4 describes the pin configuration used in the NINA-W15 series u-connectXpress modules.
*Only for NINA-W156
Figure 4: NINA-W15 pin assignment (top view)
The grey pins in the center of the modules are GND pins. The outline of NINA-W151 is limited by the
dotted line. The lower part is the antenna area of NINA-W152/W156. The four grey pins in the antenna
area are only present on NINA-W156.
See section 2.6 for more info about IO functionality.
Some of the signals are boot strap signals (see Table 6). It is important that these signals are in
the correct state during startup (see section 2.4 for more information).
External LPO (LPO_IN) is a planned feature not supported in the current software.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Pin definition Page 19 of 55
C1-Public
Page 20

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Pin Name I/O Description Alt. function Remarks
1 RED O Logic Red LED Signal See section 2.6.2
2 GPI_2 I General Purpose Input WKUP_2 Can control STOP mode.
3 GPI_3 I General Purpose Input WKUP_3 Can control STOP mode.
4 GPI_4 I General Purpose Input WKUP_4 Can control STOP mode.
5 LPO_IN/
GPIO_5
6 GND Ground
7 GREEN/
SWITCH_1
8 BLUE/
RMII_TXEN
9 VCC_IO I Module I/O level voltage input IO voltage supply
10 VCC I Module supply voltage input Module voltage supply
11 GPI_11 I General Purpose Input GPI only for NINA-W156. For NINA-
12 GND Ground
13 ANT I/O NINA-W151: Antenna Tx/Rx
14 GND Ground
15 GPI_15 I General Purpose Input GPI only for NINA-W156. For NINA-
16 UART_DTR/
RMII_RXD0
17 UART_DSR/
RMII_RXD1
18 SWITCH_2/
RMII_CRSDV
19 RESET_N I External system reset input Active low
20 UART_RTS/
RMII_TXD1
21 UART_CTS/
RMII_TXD0
22 UART_TXD O UART data output See section 2.7.1
23 UART_RXD I UART data input See section 2.7.1
24 RMII_MDIO I/O RMII Management data GPIO_24 See section RMII 2.7.2
25 RMII_MDCLK/
SPI_DRDY
26 GND Ground
27 RMII_CLK/
SYS_BOOT
28 GPIO_28 I/O General Purpose Input /Output
29 GPIO_29 I/O General Purpose Input /Output
30 GND Ground
31 SPI_SCLK I SPI clock input signal GPIO_31
I
Low Power Oscillator Input
I/O
General Purpose Input /Output
I/O GREEN: System status signal /
SWITCH_1: Multiple functions
O Logic Blue LED Signal/
RMII Transmit Enable output
interface
I/O UART Data Terminal Ready/
RMII Receive Data input 0
I UART Data Set Ready/
RMII Receive Data input 1
I SWITCH_2: Multiple functions
RMII_CRSDV: Carrier
Sense/Receive Data Valid input
O UART request to send/
RMII Transmit Data output 1
I/O UART clear to send/
RMII Transmit Data output 0
O RMII Management data
Clock/ SPI data ready output
I/O RMII clock input/
Boot Mode
LPO_IN is only supported on NINA-W156.
Active low. See sections 2.6.2, 2.6.3 and
2.7.2
See sections 2.6.2 and 2.7.2
W151/W152 do not connect.
50 Ω nominal characteristic impedance
W151/W152 do not connect.
The DTR signaling is not according to UART
standard (see section 2.6.4). See section
RMII 2.7.2
The DSR signaling is not according to UART
standard (see section 2.6.4). See section
RMII 2.7.2
WKUP_18 Active low. See sections 2.6.3 and RMII
2.7.2
Can control STOP mode
GPIO_20 Active low
See sections UART 2.6.4 and RMII 2.7.2
GPIO_21 Active low
See sections UART 2.6.4 and RMII 2.7.2
GPO_25 See section RMII 2.7.2
GPO_27 Default pulled-up. Bootstrap pin, see
section 2.4. See section RMII 2.7.2.
Can control STOP mode
WKUP_31
See section SPI 2.7.3
UBX-18006647 - R08 Pin definition Page 20 of 55
C1-Public
Page 21

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Pin Name I/O Description Alt. function Remarks
32 LOG_BOOT/
SPI_CS
33 RSVD Reserved for future use Do not connect
34 GPI_34 I General Purpose Input WKUP_34 Can control Stop mode.
35 SPI_MOSI I SPI serial data in signal GPIO_35
36 SPI_MISO O SPI serial data out signal GPO_36 Default pulled-up. Bootstrap pin, see
Table 6: NINA-W151/NINA-W152/NINA-W156 pinout
I/O Debug printout on UART enable/
SPI chip select signal
GPIO_32 Default pulled-up. Bootstrap pin, see
section 2.4. See section SPI 2.7.3
Can control Stop mode. See section SPI
WKUP_35
2.7.3
section 2.4. See section SPI 2.7.3
UBX-18006647 - R08 Pin definition Page 21 of 55
C1-Public
Page 22

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
4 Electrical specifications
⚠ Stressing the device above one or more of the ratings listed in the Absolute maximum rating
section may cause permanent damage. These are stress ratings only. Operating the module at
these or at any conditions other than those specified in the Operating conditions section of this
document should be avoided. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
Operating condition ranges define those limits within which the functionality of the device is
guaranteed. Where application information is given, it is advisory only and does not form part of
the specification.
4.1 Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Description Condition Min Max Unit
VCC/ VCC_IO Module supply voltage Input DC voltage at VCC and VCC_IO pins -0.3 3.6 V
I
+
VCC MAX
I
VCC_IO MAX
DPV Digital pin voltage Input DC voltage at any digital I/O pin -0.3 3.6 V
P_ANT Maximum power at receiver Input RF power at antenna pin 0 dBm
Tstr Storage temperature -40 +85 ºC
Table 7: Absolute maximum ratings
Absolute maximum power
consumption
500 mA
⚠ The product is not protected against overvoltage or reversed voltages. If necessary, voltage spikes
exceeding the power supply voltage specification, given in table above, must be limited to values
within the specified boundaries by using appropriate protection devices.
4.1.1 Maximum ESD ratings
Parameter Min. Typical Max. Unit Remarks
ESD immunity ±8* kV Indirect discharge according to IEC 61000-4-2
ESD sensitivity, tested for all pins
except ANT and RSVD pins #11, #15,
#33
* Tested on EVK-NINA-W1 evaluation board.
Table 8: Maximum ESD ratings
2.5 kV Human body model according to JEDEC JS001
⚠ NINA-W15 series modules are Electrostatic Sensitive Devices and require special precautions
while handling. See section 8.4 for ESD handling instructions.
4.2 Operating conditions
⚠ Operation beyond the specified operating conditions is not recommended and extended exposure
beyond them may affect device reliability.
Unless otherwise specified, all operating condition specifications are at an ambient temperature
of 25 °C and at a supply voltage of 3.3 V.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Electrical specifications Page 22 of 55
C1-Public
Page 23

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
4.2.1 Operating temperature range
Parameter Min Max Unit
Operating temperature
* See voltage supply condition for lowest temperature range in section 4.2.2.
Table 9: Temperature range
-40
*
+85 °C
4.2.2 Supply/Power pins
Symbol Parameter Condition Min Typ Max Unit
VCC Input supply voltage Ambient temperature -20 °C to +85 °C 3.00 3.30 3.60 V
Ambient temperature -40 °C to +85 °C 3.00 3.30 3.45 V
VCC_IO I/O reference voltage Ambient temperature -20 °C to +85 °C 3.00 3.30 3.60 V
Ambient temperature -40 °C to +85 °C 3.00 3.30 3.45 V
Table 10: Input characteristics of voltage supply pins
4.2.3 RESET_N pin
Pin name Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
RESET_N Low-level input 0 0.3*VCC V
Internal pull-up resistance 100 kΩ
Internal capacitance 10 nF
t_Startup Startup time after release of reset 2.6 s
Table 11: RESET_N pin characteristics
4.2.4 Digital pins
Pin name Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Remarks
Any digital pin Input characteristic:
Low-level input
Input characteristic:
high-level input
Output characteristic:
Low-level output
Output characteristic:
High-level output
Drive capability 12 mA Source/Sink
Pull-up/pull-down
resistance
Table 12: Digital pin characteristics
0 0.3*VCC_IO V
0.7*VCC_IO VCC_IO V
0 0.4 V
VCC_IO-0.4 VCC_IO V
45 kΩ.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Electrical specifications Page 23 of 55
C1-Public
Page 24

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
4.2.5 Current consumption
Table 13 shows the typical current consumption for NINA-W15 modules using u-connectXpress
v3.0.0 software. Unless stated otherwise, the module is powered at 3.3 V and uses factory default
configurations.
Radio mode Activity Power mode Role Typ Unit Remarks
Wi-Fi to UART Transmitting ACTIVE AP 120 mA Data throughput 1 Mbit/s
Station 120 mA Data throughput 1 Mbit/s
Receiving ACTIVE AP 110 mA Data throughput 1 Mbit/s
Station 110 mA Data throughput 1 Mbit/s
Connected STANDBY* AP 100 mA
Station 30 mA
SLEEP* AP 100 mA
Station 3.5 mA
Wi-Fi to RMII Transmitting
(15 dBm)
Receiving ACTIVE AP 125 mA
Connected STANDBY AP 115 mA
Bluetooth
BR/EDR
(Bluetooth LE
disabled)
Bluetooth LE
Transmitting ACTIVE Peripheral/Central 150 mA Data throughput 1.25 Mbit/s
Receiving ACTIVE Peripheral/Central 110 mA Data throughput 1.25 Mbit/s
Connected STANDBY** Peripheral/Central 100 mA
Inquiry ACTIVE - 100 mA
Transmitting ACTIVE Peripheral/Central 60 mA Data throughput 30 kbit/s
Receiving ACTIVE Peripheral/Central 50 mA Data throughput 30 kbit/s
Connected STANDBY** Peripheral 35 mA
Advertising STANDBY** Peripheral 30 mA
ACTIVE AP 170 mA
Station 130 mA
Station 115 mA
Station 40 mA
80 mA Data throughput 180 kbit/s
60 mA Data throughput 180 kbit/s
Central 35 mA
Discovery ACTIVE Central 100 mA
Idle STANDBY** Central 60 mA Not connected
Disabled None STANDBY* - 30 mA
SLEEP* - 1.5 mA
STOP* - 5 uA
Reset Reset - 35 uA Module held in reset
Table 13: Current consumption during typical use cases
*AFA enabled, minimum allowed clock speed set to 80 MHz, Wi-Fi Station beacon listen interval set to 10.
**AFA enabled, minimum allowed clock speed set to 80 MHz.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Electrical specifications Page 24 of 55
C1-Public
Page 25

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
4.2.6 Wi-Fi radio characteristics
Parameter Operation Mode Specification Unit
RF Frequency Range 802.11b/g/n 2.400 – 2.4835 GHz
Channels 1-13*
Modulation 802.11b CCK and DSSS
802.11g/n OFDM
Supported Data Rates 802.11b 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbit/s
802.11g 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 Mbit/s
802.11n MCS0 – MCS7
Supported Bandwidth 802.11n 20 MHz
Supported Guard Interval 802.11n 400, 800 ns
Conducted Transmit Power (typical) 802.11b Channel 6 1 Mbit/s 13** ± 1 dBm
11 Mbit/s 13** ± 1 dBm
802.11g Channel 6 6 Mbit/s 15** ± 1 dBm
54 Mbit/s 12** ± 1 dBm
802.11n
Receiver Sensitivity (typical) 802.11b 1 Mbit/s -96 ± 2 dBm
802.11g 6 Mbit/s -92 ± 2 dBm
802.11n 20 MHz MCS0 -91 ± 2 dBm
Characteristics assume VCC = 3.3 V, Tamb = 25 °C
* Maximum support for 802.11d depends on the region.
** There is lower output power on band edge channels and also on the highest data rates.
Table 14: Wi-Fi radio characteristics
Channel 6 MCS0 15** ± 1 dBm
MCS7 11** ± 1 dBm
11 Mbit/s -88 ± 2 dBm
54 Mbit/s -74 ± 2 dBm
MCS7 -72 ± 2 dBm
4.2.7 Bluetooth radio characteristics
Parameter Operation Mode Specification Unit
RF Frequency Range 2.400 – 2.4835 GHz
Supported Modes Bluetooth v4.2+EDR
Number of channels 79
Modulation 1 Mbit/s GFSK (BDR)
2 Mbit/s π/4-DQPSK (EDR)
3 Mbit/s 8-DPSK (EDR)
Conducted Transmit Power (typical) 1 Mbit/s 5 ± 1 dBm
2 / 3 Mbit/s 5 ± 1 dBm
Receiver Sensitivity (typical) 1 Mbit/s -88 ± 2 dBm
2 Mbit/s -86 ± 2 dBm
3 Mbit/s -80 ± 2 dBm
Characteristics assume VCC = 3.3 V, Tamb = 25 °C
Table 15: Bluetooth radio characteristics
UBX-18006647 - R08 Electrical specifications Page 25 of 55
C1-Public
Page 26

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
4.2.8 Bluetooth low energy characteristics
VCC = 3.3 V, T
Parameter Specification Unit
RF Frequency Range 2.400 – 2.4835 GHz
Supported Modes Bluetooth v4.2
Number of channels 40
Modulation GFSK
Transmit Power
(typical)
Receiver Sensitivity
(typical)
Table 16: Bluetooth Low Energy characteristics
= 25 °C
amb
5 ± 1 dBm
-88 ± 2 dBm
4.2.9 Antenna radiation patterns
The radiation patterns displayed in Table 17 and Table 18 show the radiation patterns of the NINAW152 with internal PIFA antenna and the NINA-W156 with internal PCB trace antenna. Figure 5 gives
an overview of the measurement procedure, and how the NINA-W152/NINA-W156 module is aligned
to the XYZ-coordinate system.
Figure 5: Measurement procedure for determining radiation patterns. A measurement is taken at every dot in the figure to
the left and is represented as a grid point in the radiation pattern to the right.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Electrical specifications Page 26 of 55
C1-Public
Page 27

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Table 17: NINA-W152 antenna radiation patterns
UBX-18006647 - R08 Electrical specifications Page 27 of 55
C1-Public
Page 28

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Table 18: NINA-W156 antenna radiation patterns
UBX-18006647 - R08 Electrical specifications Page 28 of 55
C1-Public
Page 29

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Parameter
Description
Typical
Tolerance
A
Module PCB length [mm]
10.6
(417.3 mil)
+0.20/-0.10
(+7.9/-3.9 mil)
B
Module PCB width [mm]
10.0
(393.7 mil)
+0.20/-0.10
(+7.9/-3.9 mil)
C
Module thickness [mm]
2.2
(86.6 mil)
+0.40/-0.20
(+15.8/-7.9
ccc
Seating plane coplanarity [mm]
0.10
(3.9 mil)
+0.02/-0.10
(+0.8/-3.9 mil)
D
Horizontal edge to lateral pin no 1 edge [mm]
0.45
(17.7 mil)
+0.10/-0.10
(+3.9/-3.9 mil)
E
Vertical and horizontal edge to lateral pin no 1 edge
0.30
(11.8 mil)
+0.10/-0.10
(+3.9/-3.9 mil)
F
Vertical pin no1 edge to lateral pin edge [mm]
2.35
(92.5 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
G
Depanalizing residual [mm]
0.10
(3.9 mil)
+0.25/-0.10
(+9.8/-3.9 mil)
H
Lateral and antenna row pin to pin pitch [mm]
1.0
(39.4 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
I
Lateral and antenna row pin width [mm]
0.70
(27.6 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
J
Lateral and antenna row pin height [mm]
1.15
(45.3 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
K
Horizontal pin no1 edge to central pin edge [mm]
2.78
(109.4 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
L
Vertical pin no1 edge to central pin edge [mm]
2.63
(103.5 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
M
Horizontal pin no1 edge to inner row pin edge [mm]
1.45
(57.1 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
N
Vertical pin no1 edge to inner row pin edge [mm]
1.6
(63.0 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
O
Central pin and inner row width and height [mm]
0.70
(27.6 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
P
Central pin to pin pitch [mm]
1.15
(45.3 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
Q
Inner row pin to pin pitch [mm]
1.1
(43.3 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
R
Horizontal pin no1 edge to antenna row pin edge [mm]
8.7
(342.5 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
Module weight [g]
<1.0
5 Mechanical specifications
5.1 NINA-W151 Mechanical specification
Figure 6: NINA-W151 mechanical outline
Table 19: NINA-W151 mechanical outline data
UBX-18006647 - R08 Mechanical specifications Page 29 of 55
C1-Public
Page 30

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Parameter
Description
Typical
Tolerance
A
Module PCB length [mm]
14.0
(551.2 mil)
+0.20/-0.10
(+7.9/-3.9 mil)
B
Module PCB width [mm]
10.0
(393.7 mil)
+0.20/-0.10
(+7.9/-3.9 mil)
C
Module thickness [mm]
3.8
(149.6 mil)
+0.40/-0.20
(+15.8/-7.9
ccc
Seating plane coplanarity [mm]
0.10
(3.9 mil)
+0.02/-0.10
(+0.8/-3.9 mil)
D
Horizontal edge to lateral pin no 1 edge [mm]
0.45
(17.7 mil)
+0.10/-0.10
(+3.9/-3.9 mil)
E
Vertical and horizontal edge to lateral pin no 1 edge
0.30
(11.8 mil)
+0.10/-0.10
(+3.9/-3.9 mil)
F
Vertical pin no1 edge to lateral pin edge [mm]
2.35
(92.5 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
G
Depanalizing residual [mm]
0.10
(3.9 mil)
+0.25/-0.10
(+9.8/-3.9 mil)
H
Lateral and antenna row pin to pin pitch [mm]
1.0
(39.4 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
I
Lateral and antenna row pin width [mm]
0.70
(27.6 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
J
Lateral and antenna row pin height [mm]
1.15
(45.3 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
K
Horizontal pin no1 edge to central pin edge [mm]
2.78
(109.4 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
L
Vertical pin no1 edge to central pin edge [mm]
2.63
(103.5 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
M
Horizontal pin no1 edge to inner row pin edge [mm]
1.45
(57.1 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
N
Vertical pin no1 edge to inner row pin edge [mm]
1.6
(63.0 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
O
Central pin and inner row width and height [mm]
0.70
(27.6 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
P
Central pin to central pin pitch [mm]
1.15
(45.3 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
Q
Inner row pin to pin pitch [mm]
1.1
(43.3 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
R
Horizontal pin no1 edge to antenna row pin edge [mm]
8.7
(342.5 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
S
PCB and shield cover thickness [mm]
2.2
(86.6 mil)
+0.40/-0.20
(+15.8/-7.9
T
Module antenna width [mm]
3.8
(149.6 mil)
+0.20/-0.20
(+7.9/-7.9 mil)
U
Antenna overhang outside module outline on any side
0.0
(0.0 mil)
+0.60
(+23.6 mil)
module weight [g]
<1.0
5.2 NINA-W152 Mechanical specification
Figure 7: NINA-W152 mechanical outline
Table 20: NINA-W152 mechanical outline data
UBX-18006647 - R08 Mechanical specifications Page 30 of 55
C1-Public
Page 31

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Parameter
Description
Typical
Tolerance
A
Module PCB length [mm]
14.0
(551.2 mil)
+0.20/-0.10
(+7.9/-3.9 mil)
B
Module PCB width [mm]
10.0
(393.7 mil)
+0.20/-0.10
(+7.9/-3.9 mil)
ccc
Seating plane coplanarity [mm]
0.10
(3.9 mil)
+0.02/-0.10
(+0.8/-3.9 mil)
D
Horizontal edge to lateral pin no 1 edge [mm]
0.45
(17.7 mil)
+0.10/-0.10
(+3.9/-3.9 mil)
F
Vertical pin no1 edge to lateral pin edge [mm]
2.35
(92.5 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
G
Depanalizing residual [mm]
0.10
(3.9 mil)
+0.25/-0.10
(+9.8/-3.9 mil)
H
Lateral and antenna row pin to pin pitch [mm]
1.0
(39.4 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
I
Lateral and antenna row pin width [mm]
0.70
(27.6 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
J
Lateral and antenna row pin height [mm]
1.15
(45.3 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
K
Horizontal pin no1 edge to central pin edge [mm]
2.78
(109.4 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
L
Vertical pin no1 edge to central pin edge [mm]
2.63
(103.5 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
M
Horizontal pin no1 edge to inner row pin edge [mm]
1.45
(57.1 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
N
Vertical pin no1 edge to inner row pin edge [mm]
1.6
(63.0 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
O
Central pin and inner row width and height [mm]
0.70
(27.6 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
P
Central pin to central pin pitch [mm]
1.15
(45.3 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
Q
Inner row pin to pin pitch [mm]
1.1
(43.3 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
R
Horizontal pin no1 edge to antenna row pin edge [mm]
8.7
(342.5 mil)
+0.05/-0.05
(+2.0/-2.0 mil)
S
PCB and shield cover thickness [mm]
2.2
(86.6 mil)
+0.40/-0.20
(+15.8/-7.9
T
Module PCB antenna width [mm]
4.0
(157.5 mil)
+0.20/-0.20
(+7.9/-7.9 mil)
A
B
F
H
J
E
M
K
R
F
O
O
P
N
Q
P
L
P
P
H
D
E
I
J
I
H
ZA1
ZA2
F !CCC! A
S
A
#
T
P
i
n
1
Bottom view T
op
vi
ew
De
p
an
a
li
zi
n
g
Residual
G
G
Pin 1
5.3 NINA-W156 Mechanical specification
Figure 8: NINA-W156 mechanical outline
E Vertical and horizontal edge to lateral pin no 1 edge
[mm]
0.30 (11.8 mil) +0.10/-0.10 (+3.9/-3.9 mil)
ZA1 Horizontal pin no. 1 corner to first set of antenna GND
pins pin center [mm]
ZA2 Horizontal pin no. 1 corner to second set of antenna
Module weight [g] <1.0
Table 21: NINA-W156 mechanical outline data
GND pins pin center [mm]
UBX-18006647 - R08 Mechanical specifications Page 31 of 55
C1-Public
10.35 (407.8 mil) +0.20/-0.10 (+7.9/-3.9 mil)
12.90 (507.9 mil) +0.20/-0.10 (+7.9/-3.9 mil)
Page 32

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
6 Qualification and approvals
⚠ Country approval for NINA-W156 is pending.
6.1 Country approvals
The NINA-W15 module series is certified for use in the following countries/regions:
• Europe (RED)
• USA (FCC)
• Canada (IC)
• Japan (MIC)
• Taiwan (NCC)*
• South Korea (KCC)*
• Brazil (ANATEL)*
• Australia and New Zeeland (ACMA)
• South Africa (ICASA)*
*
Country approval for NINA-W156 is pending
See the following sections for additional information.
6.2 European Union regulatory compliance
Information about regulatory compliance of the European Union for NINA-W15 series modules is
available in the NINA-W15 Declaration of Conformity [5].
6.2.1 Radio Equipment Directive (RED) 2014/53/EU
The NINA-W15 series modules comply with the essential requirements and other relevant provisions
of Radio Equipment Directive (RED) 2014/53/EU.
6.2.2 Compliance with the RoHS directive
The NINA-W15 series modules comply with the Directive 2011/65/EU (EU RoHS 2) and its
amendment Directive (EU) 2015/863 (EU RoHS 3).
6.3 FCC/IC Compliance
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules and with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS
standard(s).
⚠ Any changes or modifications NOT explicitly APPROVED by u-blox AG may cause the module to
not comply with the FCC rules part 15 thus void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
6.3.1 FCC Compliance
The NINA-W15 modules are for OEM integrations only. The end-product will be professionally
installed in such manner that only the authorized antennas can be used.
For NINA-W151, an external antenna connector (U.FL. connector) reference design (see the
NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1]) is available and must be followed to comply with the
NINA-W15 FCC/IC modular approval.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Qualification and approvals Page 32 of 55
C1-Public
Page 33

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
6.3.2 FCC statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that the
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
6.3.3 RF exposure statement
6.3.3.1 IC Compliance
This equipment complies with the requirements of IC RSS-102 issue 5 radiation exposure limits set
forth for an uncontrolled environment.
To ensure that the output power remains below the SAR evaluation Exemption limits defined in RSS102 issue 5, customer applications integrating NINA-W156 must include a separation distance of at
least 40 mm between the user (or bystander) and the antenna (or radiating element). For applications
integrating NINA-W151 and NINA-W152 the separation distance of 30 mm is needed.
6.3.3.2 FCC Compliance
This device complies with the FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment.
To ensure that the output power remains below the SAR evaluation Exemption limits defined in SAR
test exclusion limits in KDB 447498 D01v06, customer applications integrating NINA-W156 must
include a separation distance of at least 25 mm between the user (or bystander) and the antenna (or
radiating element). For applications integrating NINA-W151 and NINA-W152 the separation distance
of 45 mm is needed.
6.3.4 End-product user manual instructions
6.3.4.1 IC Compliance
User manuals for license-exempt radio apparatus shall contain the following text, or an equivalent
notice that shall be displayed in a conspicuous location, either in the user manual or on the device, or
both:
This device complies with Industry Canada’s license-exempt RSSs. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
(1)
This device may not cause interference; and
UBX-18006647 - R08 Qualification and approvals Page 33 of 55
C1-Public
Page 34

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
(2) This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired
operation of the device.
Under Industry Canada regulations, this radio transmitter can only operate using an antenna of a type
and maximum (or lesser) gain approved for the transmitter by Industry Canada. To reduce potential
radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain should be chosen in such a way that
the equivalent isotropically radiated power (e.i.r.p.) is not more than that is necessary for successful
communication.
Le manuel d’utilisation des appareils radio exempts de licence doit contenir l’énoncé qui suit, ou
l’équivalent, à un endroit bien en vue dans le manuel d’utilisation ou sur l’appareil, ou encore aux
deux endroits.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d’Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
exempts de licence. L’exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes:
(1) l’appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage;
(2) l’utilisateur de l’appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le
brouillage est susceptible d’en compromettre le fonctionnement.
Conformément aux réglementations d’Industry Canada, cet émetteur radio ne peut fonctionner qu’à
l’aide d’une antenne dont le type et le gain maximal (ou minimal) ont été approuvés pour cet émetteur
par Industry Canada. Pour réduire le risque d’interférences avec d’autres utilisateurs, il faut choisir le
type d’antenne et son gain de telle sorte que la puissance isotrope rayonnée équivalente (p.i.r.e) ne
soit pas supérieure à celle requise pour obtenir une communication satisfaisante.
6.3.5 End-product labeling requirements
6.3.5.1 IC Compliance
The host product shall be properly labelled to identify the modules within the host product.
The Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada certification label of a module shall be
clearly visible at all times when installed in the host product; otherwise, the host product must be
labelled to display the Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada certification number
for the module, preceded by the word “Contains” or similar wording expressing the same meaning, as
shown in Figure 9.
Le produit hôte devra être correctement étiqueté, de façon à permettre l’identification des modules
qui s’y trouvent.
L’étiquette d’homologation d’un module d’Innovation, Sciences et Développement économique
Canada devra être posée sur le produit hôte à un endroit bien en vue, en tout temps. En l’absence
d’étiquette, le produit hôte doit porter une étiquette sur laquelle figure le numéro d’homologation du
module d’Innovation, Sciences et Développement économique Canada, précédé du mot « contient »,
ou d’une formulation similaire allant dans le même sens et qui va comme suit:
This device contains
FCC ID: XPYNINAW15
IC: 8595A-NINAW15
Figure 9 Example of an end product label
NINA-W156 has other IDs, as described in Table 21.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Qualification and approvals Page 34 of 55
C1-Public
Page 35

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
6.3.5.2 FCC Compliance
For an end product that uses the NINA-W151, NINA-W152 or NINA-W156 modules, there must be a
label containing, at least, the information shown in Figure 9:
The label must be affixed on an exterior surface of the end product such that it will be visible upon
inspection in compliance with the modular approval guidelines developed by the FCC.
In accordance with 47 CFR § 15.19, the end-product shall bear the following statement in a
conspicuous location on the device:
"This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions;
(1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation."
When the device is so small or for such use that it is not practicable to place the statement above on
it, the information shall be placed in a prominent location in the instruction manual or pamphlet
supplied to the user or, alternatively, shall be placed on the container in which the device is marketed.
In case, where the final product will be installed in locations where the end user is unable to see the
FCC ID and/or this statement, the FCC ID and the statement shall also be included in the end product
manual.
Model FCC ID IC Certification Number
NINA-W151 XPYNINAW15 8595A-NINAW15
NINA-W152 XPYNINAW15 8595A-NINAW15
NINA-W156 XPYNINAW106 8595A-NINAW106
Table 22: FCC and IC IDs for the NINA-W15 series modules
6.3.6 End product compliance
6.3.6.1 General requirements
• Any changes to hardware, hosts or co-location configuration may require new radiated emission
and SAR evaluation and/or testing.
• The regulatory compliance of NINA-W151 and NINA-W152 does not exempt the end product from
being evaluated against applicable regulatory demands; for example, FCC Part 15B criteria for
unintentional radiators.
• Only authorized antenna(s) may be used.
• Any notification to the end user about how to install or remove the integrated radio module is NOT
allowed.
6.3.6.2 Co-location (simultaneous transmission)
If the module is to be co-located with another transmitter, additional measurement for simultaneous
transmission is required.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Qualification and approvals Page 35 of 55
C1-Public
Page 36

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
含發射器模組
6.4 Japan radio equipment compliance
204-810001
Figure 10: Giteki mark, R and the NINA-W151/NINA-W152 MIC certification number
203-JN1166
Figure 11: Giteki mark, R and the NINA-W156 MIC certification number
For information about compliance of the NINA-W151/NINA-W152/NINA-W156 modules with the
Giteki certification, see the NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1].
6.5 NCC Taiwan compliance
⚠ Approval for NINA-W156 is pending.
6.5.1 Taiwan NCC Warning Statement
• 經型式認證合格之低功率射頻電機,非經許可,公司、商號或使用者均不得擅自變更頻率、 加大功率或變更
原設計之特性及功能。
• 低功率射頻電機之使用不得影響飛航安全及干擾合法通信;經發現有干擾現象時,應立即停用,並改善至無
干擾時方得繼續使用。前項合法通信,指依電信法規定作業之無線電通信。低功率射頻電機須忍受合法通信
或工業、科學及醫療用電波輻射性電機設備之干擾。
Statement translation:
• Without permission granted by the NCC, any company, enterprise, or user is not allowed to change
frequency, enhance transmitting power or alter original characteristic as well as performance to
an approved low power radio frequency devices.
• The low power radio frequency devices shall not influence aircraft security and interfere legal
communications; if found, the user shall cease operating immediately until no interference is
achieved. The said legal communications means radio communications is operated in compliance
with the Telecommunications Act. The low power radio frequency devices must be susceptible
with the interference from legal communications or ISM radio wave radiated devices.
6.5.2 NINA-W151 labeling requirements for end product
When a product integrated with an NINA-W151 module is placed on the Taiwan market, the product
must be affixed with a label marking as shown below. The label can use wording such as the following:
Contains Transmitter Module
Any similar wording that expresses the same meaning may be used. The marking must be visible for
inspection.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Qualification and approvals Page 36 of 55
C1-Public
內
::
CCAJ18LP0B43T4
Page 37

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
含發射器模組
6.5.3 NINA-W152 labeling requirements for end product
When a product integrated with a NINA-W152 module is placed on the Taiwan market, the product
must be affixed with a label marking as shown below. The label can use wording such as the following:
Contains Transmitter Module
內
Any similar wording that expresses the same meaning may be used. The marking must be visible for
inspection.
::
CCAJ18LP0B53T7
6.6 KCC South Korea compliance
⚠ Approval for NINA-W156 is pending.
The NINA-W15 series modules are certified by the Korea Communications Commission (KCC).
When a product containing a NINA-W151 or NINA-W152 module is placed on the South Korean
market, the product must be affixed with a label or marking containing the KCC logo and certification
number as shown in the figure below. NINA-W151 and NINA-W152 has the same certification
number. This information must also be included in the product user manuals.
R-C-ULX-NINA-W151
The height of the KCC logo must be at least 5 mm.
6.7 Brazil compliance
⚠ Approval for NINA-W156 is pending.
When a product containing NINA-W151 or NINA-W152 module is placed on the Brazilian market, the
product must be affixed with a label or marking containing the Anatel logo, NINA-W151/
NINA-W152 Homologation number: 06870-18-05903 and a statement claiming that the device may
not cause harmful interference but must accept it (Resolution No 506).
06870-18-05903
“Este equipamento opera em caráter secundário, isto é,
não tem direito a proteção contra interferência prejudicial,
mesmo de estações do mesmo tipo, e não pode causar
interferência a sistemas operando em caráter primário.”
Statement translation:
“This equipment operates on a secondary basis and, consequently, must accept harmful interference,
including from stations of the same kind, and may not cause harmful interference to systems
operating on a primary basis.”
When the device is so small or for such use that it is not practicable to place the statement above on
it, the information shall be placed in a prominent location in the instruction manual or pamphlet
supplied to the user or, alternatively, shall be placed on the container in which the device is marketed.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Qualification and approvals Page 37 of 55
C1-Public
Page 38

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
APPROVED
TA-2018/2693
In cases, where the final product will be installed in locations where the end user is unable to see the
Anatel logo, NINA-W151/NINA-W152 Homologation number and/or this statement, the Anatel logo,
NINA-W151/NINA-W152 Homologation number, and the statement shall also be included in the end
product manual.
6.8 Australia and New Zealand regulatory compliance
NINA-W151, NINA-W152 and NINA-W156 modules are compliant with the standards
made by the Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA).
The modules are compliant with AS/NZS 4268:2012 standard – Radio equipment and systems – Short
range devices – Limits and methods of standard measurement. The NINA-W151, NINA-W152 and
NINA-W156 modules test reports can be used as part of the product certification and compliance
folder. For more information on the test reports, send an email to the respective support team mail
address as mentioned in the Contact section based on your location.
To meet overall Australian and/or New Zealand end product compliance, the integrator must create a
compliance folder containing all the relevant compliance test reports such as RF, EMC, electrical
safety and DoC (Declaration of Conformity) and so on. It is the responsibility of the integrator to know
what is required in the compliance folder for ACMA compliance.
For more information on Australia compliance, refer to the Australian Communications and Media
Authority web site http://www.acma.gov.au/.
For more information on New Zealand compliance, refer to the New Zealand Radio Spectrum
Management Group web site www.rsm.govt.nz.
6.9 South Africa regulatory compliance
⚠ Approval for NINA-W156 is pending.
NINA-W151 and NINA-W152 modules are compliant and certified by the Independent
Communications Authority of South Africa (ICASA). End products that are made available for sale or
lease or is supplied in any other manner in South Africa shall have a legible label permanently affixed
to its exterior surface. The label shall have the ICASA logo and the ICASA issued license number as
shown in the figure below. The minimum width and height of the ICASA logo shall be 3 mm. The
approval labels must be purchased by the customer’s local representative directly from the approval
authority ICASA. A sample of an NINA-W151/NINA-W152 ICASA label is included below:
More information on registration as a Responsible Integrator and labeling requirements can be found
at the following website:
Independent Communications Authority of South Africa (ICASA) web site - https://www.icasa.org.za
6.10 Safety Compliance
In order to fulfill the safety standard EN 60950-1, the NINA-W15 series modules must be supplied
with a Class-2 Limited Power Source.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Qualification and approvals Page 38 of 55
C1-Public
Page 39

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
6.11 Bluetooth qualification information
End products are required to be qualified and listed for the Bluetooth Special Interest Group
(SIG).
Product declarations are submitted through the Bluetooth SIG Launch Studio website, see the link
below:
Bluetooth Launch Studio website
NINA-W151, NINA-W152 and NINA-W156 modules have been qualified as a Controller Subsystem
according to the Bluetooth 4.2 specification.
To list your product that integrates NINA-W151 or NINA-W152 as an End product with no required
testing, combine the pre-qualified Controller Subsystem (QD ID 107058) and the Host Subsystem
(QD ID 110883) listed in the table below.
To list your product that integrates NINA-W156 as an End product with no required testing,
combine the pre-qualified Controller Subsystem (QD ID 152314) and the Host Subsystem (QD ID
110883) listed in the table below.
Model Product type QD ID Listing Date
NINA-W151, NINA-W152 Controller Subsystem 107058 14-Mar-
2018
NINA-W156 Controller Subsystem 152314 17-Dec-
2020
NINA-W151, NINA-W152, NINA-W156 Host Subsystem 110883 30-Apr-2018
Table 23: NINA-W151/NINA-W152/NINA-W156 Bluetooth QD ID.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Qualification and approvals Page 39 of 55
C1-Public
Page 40

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
7 Antennas
This chapter gives an overview of the different external antennas that can be used together with the
module.
⚠ This radio transmitter IC: 8595A-NINAW15 has been approved by Industry Canada to operate with
the antenna types listed below with the maximum permissible gain and required antenna
impedance for each antenna type indicated. Antenna types not included in this list, having a gain
greater than the maximum gain indicated for that type, are strictly prohibited for use with this
device.
⚠ Cet émetteur radio IC: 8595A-NINAW15 été approuvé par Industry Canada pour fonctionner avec
les types d’antenne énumérés ci-dessous avec le gain maximum autorisé et l’impédance
nécessaire pour chaque type d’antenne indiqué. Les types d’antenne ne figurant pas dans cette
liste et ayant un gain supérieur au gain maximum indiqué pour ce type-là sont strictement
interdits d’utilisation avec cet appareil.
For each antenna, the "Approvals" field defines in which test reports the antenna is included.
Definitions of the «Approvals» field are:
• FCC - The antenna is included in the FCC test reports and thus approved for use in countries that
accept the FCC radio approvals, primarily US.
• IC - The antenna is included in the IC (Industrie Canada) test reports and thus approved for use in
countries that accept the IC radio approvals, primarily Canada.
• RED - The antenna is included in the ETSI test reports and thus approved for use in countries that
accept the Radio Equipment Directive, primarily the European countries.
• MIC - The antenna is included in the Japanese government affiliated MIC test reports and thus
approved for use in the Japanese market.
• NCC - The antenna is included in the Taiwan NCC test reports and thus approved for use in Taiwan.
• KCC - The antenna is included in the Korea KCC test reports and thus approved for use in Korea.
• ANATEL – The antenna is included in the Brazil Anatel test reports and thus approved for use in
Brazil.
• ACMA – The antenna is included in the Australia and New Zeeland test reports and thus approved
for use in Australia and New Zeeland.
• ICASA – The antenna is included in the South Africa ICASA test reports and thus approved for use
in South Africa.
In general, antennas with SMD connection, Reverse Polarity SMA connector or U.FL connector are
included in FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA radio tests. The antennas with
SMA connector are included in RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA radio tests but not in
the FCC or IC due to FCC/IC regulations.
The external antennas are connected to the board through U.FL connectors. Some antennas are
connected directly to the U.FL connector of the board while some are connected using an SMA or
reversed polarity SMA connector through a short U.FL to SMA or reversed polarity SMA adapter cable.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Antennas Page 40 of 55
C1-Public
Page 41

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Should not be mounted inside a metal enclosure,
7.1 Antenna accessories
Name U.FL to SMA adapter cable
Connector U.FL and SMA jack (outer thread and pin receptacle)
Impedance 50 Ω
Minimum cable loss 0.5 dB, The cable loss must be above the minimum cable
loss to meet the regulatory requirements. Minimum cable
length 100 mm.
Comment The SMA connector can be mounted in a panel.
See NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1] for
information how to integrate the U.FL connector.
Approval RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
Name U.FL to Reverse Polarity SMA adapter cable
Connector U.FL and Reverse Polarity SMA jack (outer thread and pin)
Impedance 50 Ω
Minimum cable loss 0.5 dB, The cable loss must be above the minimum cable
loss to meet the regulatory requirements. Minimum cable
length 100 mm.
Comment The Reverse Polarity SMA connector can be mounted in a
panel.
See NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1] for
information how to integrate the U.FL connector. It is
required to follow this reference design to comply with the
NINA-W15 FCC/IC modular approvals.
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
7.2 Approved antennas
7.2.1 Single band antennas
NINA-W152
Manufacturer ProAnt
Gain +3 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size (HxWxL) 3.0 x 3.8 x 9.9 mm
Type PIFA
Comment SMD PIFA antenna on NINA-W152. Should not be mounted inside a metal
enclosure, see section for more info 2.5.1.
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
NINA-W156
Manufacturer ProAnt
Gain +3 dBi
Impedance N/A
Size (HxWxL)
Type PCB trace
Comment PCB antenna on NINA-W156.
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC and ACMA
1.1 x 3.4 x 10 mm
see section for more info 2.5.1.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Antennas Page 41 of 55
C1-Public
Page 42

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
GW.26.0111
Manufacturer Taoglas
Polarization Vertical
Gain +2.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size Ø 7.9 x 30.0 mm
Type Monopole
Connector SMA (M) .
Comment To be mounted on the U.FL to SMA adapter cable.
Approval RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
ANT-2.4-CW-RH-RPS
Manufacturer Linx
Polarization Vertical
Gain -1.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size Ø 7.4 x 27.0 mm
Type Monopole
Connector Reverse Polarity SMA plug (inner thread and pin receptacle).
Comment To be mounted on the U.FL to Reverse Polarity SMA adapter cable.
An SMA version antenna is also available but not recommended for use (ANT-
2.4-CW-RH-SMA).
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
Ex-IT 2400 RP-SMA 28-001
Manufacturer ProAnt
Polarization Vertical
Gain +3.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size Ø 12.0 x 28.0 mm
Type Monopole
Connector Reverse Polarity SMA plug (inner thread and pin receptacle).
Comment This antenna requires to be mounted on a metal ground plane for best
performance.
To be mounted on the U.FL to Reverse Polarity SMA adapter cable.
An SMA version antenna is also available but not recommended for use (Ex-IT
2400 SMA 28-001).
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
Ex-IT 2400 MHF 28
Manufacturer ProAnt
Polarization Vertical
Gain +2.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size Ø 12.0 x 28.0 mm
Type Monopole
Cable length 100 mm
Connector U.FL. connector
UBX-18006647 - R08 Antennas Page 42 of 55
C1-Public
Page 43

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Ex-IT 2400 MHF 28
Comment This antenna requires to be mounted on a metal ground plane
for best performance.
To be mounted on a U.FL connector.
See NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1] for
information how to integrate the U.FL connector. It is required
to follow this reference design to comply with the NINA -W15
FCC/IC modular approvals.
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
Ex-IT 2400 RP-SMA 70-002
Manufacturer ProAnt
Polarization Vertical
Gain +3.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size Ø 10 x 83 mm
Type Monopole
Connector Reverse Polarity SMA plug (inner thread and pin receptacle)
Comment To be mounted on the U.FL to Reverse Polarity SMA adapter
cable.
An SMA version antenna is also available but not recommended
for use (Ex-IT 2400 SMA 70-002).
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
Ex-IT 2400 MHF 70-001
Manufacturer ProAnt
Polarization Vertical
Gain +3.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size Ø 9.4 x 70.5 mm
Type Monopole
Cable length 100 mm
Connector U.FL. connector
Comment To be mounted on a U.FL connector.
See NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1] for information
how to integrate the U.FL connector. It is required to follow this
reference design to comply with the NINA-W1 FCC/IC modular
approvals.
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
InSideTM 2400
Manufacturer ProAnt
Gain +3.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size 27 x 12 mm (triangular)
Type Patch
Cable length 100 mm
Connector U.FL. connector
Comment Should be attached to a plastic enclosure or part for best
performance.
To be mounted on a U.FL connector.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Antennas Page 43 of 55
C1-Public
Page 44

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
InSideTM 2400
See NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1] for information
how to integrate the U.FL connector. It is required to follow this
reference design to comply with the
NINA-W15 FCC/IC modular approvals.
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
FlatWhip-2400
Manufacturer ProAnt
Gain +3.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size Ø 50.0 x 30.0 mm
Type Monopole
Connector SMA plug (inner thread and pin)
Comment To be mounted on the U.FL to SMA adapter cable.
Approval RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
OutsideTM-2400
Manufacturer ProAnt
Gain +3.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size 36.0 x 18.0 x 16.0 mm
Type Patch
Cable length 70 mm
Connector U.FL. connector
Comment To be mounted on a U.FL connector.
See NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1] for information
how to integrate the U.FL connector. It is required to follow this
reference design to comply with the NINA-W15 FCC/IC modular
approvals.
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
7.2.2 Dual-band antennas
InSideTM WLAN
Manufacturer ProAnt
Gain +3.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size 27 x 12 mm (triangular)
Type Patch
Cable length 100 mm
Connector U.FL. connector
Comment Should be attached to a plastic enclosure or part for best
performance.
Dual-band (2.4 GHz / 5 GHz) antenna to be mounted on a U.FL
connector.
See NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1] for information
how to integrate the U.FL connector. It is required to follow this
reference design to comply with the
NINA-W15 FCC/IC modular approvals.
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
UBX-18006647 - R08 Antennas Page 44 of 55
C1-Public
Page 45

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
InSideTM WLAN Square
Manufacturer ProAnt
Gain +3.0 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size 24x22x1 mm with mounting hole
Type Patch
Cable length 100 mm
Connector U.FL. connector
Comment Should be attached to a plastic enclosure or part for best
performance.
Dual-band (2.4 GHz / 5 GHz) antenna to be mounted on a U.FL
connector.
See NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1] for
information how to integrate the U.FL connector. It is required
to follow this reference design to comply with the NINA-W15
FCC/IC modular approvals.
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
Ex-IT WLAN RPSMA
Manufacturer ProAnt
Type ½ wave dipole dual-band antenna
Polarization Vertical
Gain +3 dBi
Impedance 50 Ω
Size 107 mm (Straight)
Type Monopole
Connector Reverse Polarity SMA plug (inner thread and pin receptacle)
Comment To be mounted on the U.FL to Reverse Polarity SMA adapter
cable.
Approval FCC, IC, RED, MIC, NCC, KCC, ANATEL, ACMA and ICASA
UBX-18006647 - R08 Antennas Page 45 of 55
C1-Public
Page 46

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
8 Product handling
8.1 Packaging
⚠ NINA-W15 series modules are in development status as mentioned in the table on page 2. Hence,
the information in this section will be valid and available only when the module is fully tested and
approved in the Initial Production stage.
8.1.1 Reels
NINA-W15 series modules are delivered as hermetically sealed, reeled tapes to enable efficient
production, production lot setup and tear-down. For more information about packaging, see the
u-blox package information guide [2].
NINA-W15 modules are deliverable in quantities of 500 pieces on a reel. The reel types for the
NINA-W15 modules are provided in Table 24 and detailed information about the reel types are
described in u-blox package information guide [2]
Model Reel type
NINA-W151 B
NINA-W152 A
NINA-W156 A
Table 24: Reel types for different models of the NINA-W15 series
.
8.1.2 Tapes
Figure 12 and Figure 13 shows the position and orientation of the NINA-W15 modules as they are
delivered on tape. The dimensions of the tapes are specified in Figure 14 and Figure 15.
Figure 12: Orientation of NINA-W151 module on tape
Figure 13: Orientation of NINA-W152/NINA-W156 module on tape
Feed
Feed
UBX-18006647 - R08 Product handling Page 46 of 55
C1-Public
Page 47

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Figure 14: NINA-W151 tape dimension
Figure 15: NINA-W152 tape dimension
UBX-18006647 - R08 Product handling Page 47 of 55
C1-Public
Page 48

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
8.2 Moisture sensitivity levels
⚠ NINA-W15 series modules are Moisture Sensitive Devices (MSD) in accordance with the
IPC/JEDEC specification.
The Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) relates to the required packaging and handling precautions. The
NINA-W15 series modules are rated at MSL level 4. For more information regarding moisture
sensitivity levels, labeling and storage, see the u-blox package information guide [2]
.
For MSL standards, see IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020, which can be downloaded from www.jedec.org.
8.3 Reflow soldering
Reflow profiles are to be selected according to u-blox recommendations. See NINA-W1 series system
integration manual [1]
for more information.
⚠ Failure to observe these recommendations can result in severe damage to the device.
8.4 ESD precautions
⚠ NINA-W15 series modules contain highly sensitive electronic circuitry and are Electrostatic
Sensitive Devices (ESD). Handling the NINA-W15 series modules without proper ESD protection
may destroy or damage them permanently.
NINA-W15 series modules are electrostatic sensitive devices (ESD) and require special ESD
precautions typically applied to ESD sensitive components. Section 4.1.1 provides the maximum ESD
ratings of the NINA-W15 series modules.
Proper ESD handling and packaging procedures must be applied throughout the processing, handling,
and operation of any application that incorporates the NINA-W15 series module. The ESD precautions
should be implemented on the application board where the module is mounted as described in the
NINA-W1 series system integration manual [1].
⚠ Failure to observe these recommendations can result in severe damage to the device.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Product handling Page 48 of 55
C1-Public
Page 49

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
9 Labeling and ordering information
9.1 Product labeling
The labels (7.5 x 7.5mm) of the NINA-W15 series modules include important product information as
described in this section.
Figure 16 shows the label of NINA-W15 series modules, which includes product type number and
revision, production date, Data Matrix with unique serial number (MAC address) and the u-blox logo.
1
4
2
5
3
Figure 16: Location of product type number on the NINA-W15 series module label
Reference Description
1 Date of unit production encoded YY/WW (year, week)
2 Major and minor product version info
3 Product model name (NINA-W151, NINA-W152 or NINA-W156)
4 Data Matrix with unique serial number of 19 alphanumeric symbols. The first 3 symbols represent a
unique module type number. The next 12 symbols represent the unique hexadecimal Wi-Fi MAC
address of the module AABBCCDDEEFF, and the last 4 symbols represent the hardware and
software version encoded HHFF.
See section 1.8 for more information about MAC addresses.
5 u-blox logo. The red dot is also indicating pin no 1.
Table 25: NINA-W15 series label description
UBX-18006647 - R08 Labeling and ordering information Page 49 of 55
C1-Public
Page 50

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
connectXpress software including secure
connectXpress software including secure
connectXpress software including secure
connectXpress software
connectXpress software
connectXpress software
press software
9.2 Explanation of codes
Three different product code formats are used. The Product Name is used in documentation such as
this data sheet and identifies all u-blox products, independent of packaging and quality grade. The
Ordering Code includes options and quality, while the Type Number includes the hardware and
software versions. Table 26 below details these three different formats:
Format Structure
Product Name PPPP-TGVV
Ordering Code PPPP -TGVV-TTQ
Type Number PPPP -TGVV-TTQ-XX
Table 26: Product code formats
Table 27 explains the parts of the product code.
Code Meaning Example
PPPP Form factor NINA
TG Platform (Technology and Generation)
T – Dominant technology, For example, W: Wi-Fi, B:
Bluetooth
G - Generation
VV Variant based on the same platform; range [00…99] 51: u-connectXpress software product with antenna
TT Major Product Version 00: first revision
Q Quality grade
A: Automotive
B: Professional
C: Standard
XX Minor product version (not relevant for certification) Default value is 00
Table 27: Part identification code
W1: Wi-Fi Generation 1
pin
B: professional grade
9.3 Ordering information
Ordering Code Product
NINA-W151-00B Wi-Fi IEEE802.11b/g/n module with antenna pin. With u-
boot. Using ESP32-D0WDQ6.
NINA-W151-02B Wi-Fi IEEE802.11b/g/n module with antenna pin. With u-
boot. Using ESP32-D0WDQ6-V3.
NINA-W151-03B Wi-Fi IEEE802.11b/g/n module with antenna pin. With u-
boot. Using ESP32-D0WDQ6-V3.
NINA-W152-00B Wi-Fi IEEE802.11b/g/n module with internal PIFA antenna. With u-
including secure boot. Using ESP32-D0WDQ6.
NINA-W152-02B Wi-Fi IEEE802.11b/g/n module with internal PIFA antenna. With u-
including secure boot. Using ESP32-D0WDQ6-V3.
NINA-W152-03B Wi-Fi IEEE802.11b/g/n module with internal PIFA antenna. With u-
including secure boot. Using ESP32-D0WDQ6-V3
NINA-W156-03B Wi-Fi IEEE802.11b/g/n module with internal PCB trace antenna. With u-connectX
including secure boot. Using ESP32-D0WD-V3.
Table 28: Product ordering codes
UBX-18006647 - R08 Labeling and ordering information Page 50 of 55
C1-Public
Page 51

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Appendix
A Glossary
Abbreviation Definition
ADC Analog to Digital Converter
AFA Automatic Frequency Adaptation
BLE Bluetooth Low Energy
BPF Band Pass Filter
CTS Clear To Send
DAC Digital to Analog Converter
DC Direct Current
DSR Data Set Ready
DTR Data Terminal Ready
ESD Electro Static Discharge
FCC Federal Communications Commission
GND Ground
GPIO General Purpose Input/Output
I Input (means that this is an input port of the module)
I2C Inter-Integrated Circuit
IC Industry Canada
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IoT Internet of Things
L Low
LPO Low Power Oscillator
MCU Micro Controller Unit
MDIO Management Data Input / Output
MII Media-Independent Interface
MISO Master In Slave Out (data output from slave)
MOSI Master Out Slave In (data output from master)
MRD Market Requirement Document
MSD Moisture Sensitive Device
N/A Not Applicable
O Output (means that this is an output port of the module)
PCN Product Change Notification
PIFA Planar Inverted F Antenna
PD Pull-Down
PU Pull-Up
QSPI Quad Serial Peripheral Interface
RMII Reduced Media Independent Interface
RTS Request To Send
RXD Receive Data
SDIO Secure Digital Input Output
SDK Software Development Kit
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface
TBD To Be Defined
UBX-18006647 - R08 Appendix Page 51 of 55
C1-Public
Page 52

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Abbreviation Definition
TXD Transmit Data
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
WKUP Wake Up
Table 29: Explanation of the abbreviations and terms used
UBX-18006647 - R08 Appendix Page 52 of 55
C1-Public
Page 53

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Related documents
[1] NINA-W1 series system integration manual, UBX-17005730
[2] u-blox package information guide, UBX-14001652
[3] u-connectXpress AT commands manual, UBX-14044127
[4] NINA-W15 series product summary, UBX-18052290
[5] NINA-W15 Declaration of Conformity, UBX-19027744
[6] u-connectXpress software user guide, UBX-16024251
[7] u-connectXpress SPI peripheral protocol specification, UBX-20028725
For product change notifications and regular updates of u-blox documentation, register on our
website,
www.u-blox.com.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Related documents Page 53 of 55
C1-Public
Page 54

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Modified the product status to Initial Production. Corrected information about
). Updated description of DSR
Absolute maximum module supply voltage and maximum RF input ratings
). Updated current
). Updated Bluetooth output power and sensitivity
). Added certification information
).
). Added
information that the RED, GREEN and BLUE signals are disabled when using
Fi and Bluetooth are time divided on the antenna and not
.
W151 and W152.
. Boot strap information is
. Note that pins 25, 32 and 36 have ceased to be boot
eft unconnected. ESD ratings in
is
added. Access Point Mode added in chapter 1.6 Radio Performance. Changed
in
Revised IEEE 802.11d statements. Updated module pinouts to
. Added
Prepared for
,
Updated Current consumption
Approved
New RF Frequency Range in
W156 changed status to Engineering Sample. Removed
Including RMII in the
U.FL to SMA adapter cable now approved by
Revision history
Revision Date Name Comments
R01 11-Dec-2018 mwej, kgom Initial release.
R02 4-Jan-2019 mwej, kgom Removed LPO functionality. Updated the information for pin 5 (Table 6).
Modified the ordering code (Table 28).
R03 12-Jul-2019 mwej
restoring UART setting to default (section 2.6.3
signal usage in section 2.6.4. Updated voltage supply range (section 4.2.2) and
(section 4.1). Updated maximum ESD ratings (section 4.1.1
consumption (section 4.2.5
(section 4.2.7 and 4.2.8).
Included RoHS 3 compliance (section 6.2.2
for Brazil, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa (sections 6.7 to 6.9
Updated information about approved antennas (chapter 7).
R04 14-Aug-2019 mwej Corrected information about BLUE signal in connected mode (Table 5
the RMII interface (sections 2.6.2 and 2.7.2).
R05 09-Jan-2020 mlju, mwej, Updated type numbers in the second table on page 2 with NINA-W15x-00B-
01. Clarified that Wiactive at the same time (section 2.5).
R06 17 Apr-2020 hekf Added IEEE 802.11d and additional regulatory domains in chapter 1.7
Included product NINA-W156 and new variants of NINAAntenna radiation pattern is added in Chapter 4.2.9
changed in chapter 2.4
strap and GPIO pins. Pins 32 and 36 must be l
chapter 4.1.1 is changed, GPIO drive capability current in chapter 4.2.4
the number of available GPIOs.
R07 29-Sep-2020 hekf, ajoh Added footnote in ESD section 4.1.1. Added SPI support in sections 1.3, 2.4,
2.7, and 3.1. Changed the number of GPIOs for NINA-W156 product variant
section 3.1.
include SPI and RMII. Added information on power modes, section 2.3
information on interface selection at module startup, section 2.7.
external LPO on NINA-W156 (section 2.2).
R08 18-Mar-2021 mape, hekf Updated Bluetooth terminology. Removed Product features table in section 1
added two GPIOs for NINA-W156 in section 3.
in Table 13, changed pull-up/pull-down resistance in section 4.2.4.
in EU/USA/Ca/Japan/Au/NZ. Bluetooth qualified.
section 4.2.6. NINAproducts NINA-W151-00B-00, NINA-W152-00B-00.
block diagram in section 1.3. A
NATEL, ACMA and ICASA in section 7.1. New GPIO clarifications in Table 6.
Changed Table 12. Clarified pin 25, 27 and 36 may be configured to GPO.
Adding product variants NINA-W151-03B and NINA-W132-03B in section 9.3.
UBX-18006647 - R08 Revision history Page 54 of 55
C1-Public
Page 55

NINA-W15 series - Data sheet
Contact
For complete contact information, visit us at www.u-blox.com.
u-blox Offices
North, Central and South America
u-blox America, Inc.
Phone: +1 703 483 3180
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Regional Office West Coast:
Phone: +1 408 573 3640
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Technical Support:
Phone: +1 703 483 3185
E-mail: support@u-blox.com
Headquarters
Europe, Middle East, Africa
u-blox AG
Phone: +41 44 722 74 44
E-mail: info@u-blox.com
Support: support@u-blox.com
Asia, Australia, Pacific
u-blox Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Phone: +65 6734 3811
E-mail: info_ap@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office Australia:
Phone: +61 3 9566 7255
E-mail: info_anz@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Beijing):
Phone: +86 10 68 133 545
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Chongqing):
Phone: +86 23 6815 1588
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shanghai):
Phone: +86 21 6090 4832
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shenzhen):
Phone: +86 755 8627 1083
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office India:
Phone: +91 80 405 092 00
E-mail: info_in@u-blox.com
Support: support_in@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Osaka):
Phone: +81 6 6941 3660
E-mail:
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Tokyo):
Phone: +81 3 5775 3850
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Korea:
Phone: +82 2 542 0861
E-mail: info_kr@u-blox.com
Support: support_kr@u-blox.com
Regional Office Taiwan:
Phone: +886 2 2657 1090
E-mail: info_tw@u-blox.com
Support: support_tw@u-blox.com
info_jp@u-blox.com
UBX-18006647 - R08 Contact Page 55 of 55
C1-Public
 Loading...
Loading...