Page 1

performance
blox M8
www.u-blox.com
NEO-M8L
u-blox M8 automotive dead reckoning modules
including 3D sensors
Hardware integration manual
Abstract
This document describes the features and specifications of NEO-M8L, a highautomotive dead reckoning (ADR) module with 3D sensors. The module includes the uconcurrent GNSS engine with reception of GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, Galileo and QZSS signals.
UBX-16010549 - R09
C1-Public
Page 2

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
u-blox or third parties may hold intellectual property rights in the products, names, logos and designs included in this
document. Copying, reproduction, modification or disclosure to third parties of this document or any part thereof is only
permitted wit
The information contained herein is provided “as is” and u
implied, is given, including but not limited
purpose of the information. This document may be revised by u
documents, visit www.u
Copyright © u
Document information
Title
Subtitle
Document type
Document number
Revision and date
Document status
Disclosure restriction
NEO-M8L
u-blox M8 automotive dead reckoning modules including 3D sensors
Hardware integration manual
UBX-16010549
R09 12-Feb-2021
Early Production Information
C1-Public
Product status
In Development /
Prototype
Engineering Sample Advance Information Data based on early testing. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
Initial Production Early Production Information Data from product verification. Revised and supplementary data may be published later.
Mass Production /
End of Life
Corresponding content status
Objective Specification Target values. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
Production Information Document contains the final product specification.
This document applies to the following products:
Product name Type number ROM/FLASH version PCN/IN reference
NEO-M8L NEO-M8L-0-12 Flash FW3.01 ADR 4.11 UBX-17049965
NEO-M8L-04B NEO-M8L-04B-00 Flash FW3.01 ADR 4.21 N/A
NEO-M8L-05B NEO-M8L-05B-00 Flash FW3.01 ADR 4.31 UBX-20014805
NEO-M8L-06B NEO-M8L-06B-00 Flash FW3.01 ADR 4.50 UBX-20053641
h the express written permission of u-blox.
-blox assumes no liability for its use. No warranty, either express or
to, with respect to the accuracy, correctness, reliability and fitness for a particular
-blox at any time without notice. For the most recent
-blox.com.
-blox AG.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Document information Page 2 of 28
Early Production Information
Page 3

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
Contents
Document information ................................................................................................................................ 2
Contents .......................................................................................................................................................... 3
1 Hardware description ........................................................................................................................... 5
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................................ 5
1.2 Configuration ............................................................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Connecting power ....................................................................................................................................... 5
1.3.1 VCC: Main supply voltage ................................................................................................................. 5
1.3.2 V_BCKP: Backup supply voltage ...................................................................................................... 5
1.3.3 VDD_USB: USB interface power supply ......................................................................................... 6
1.3.4 VCC_RF: Output voltage RF ............................................................................................................. 6
1.4 Interfaces ...................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.4.1 UART ..................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.4.2 USB ........................................................................................................................................................ 6
1.4.3 Display Data Channel (DDC) ............................................................................................................. 7
1.4.4 SPI .......................................................................................................................................................... 7
1.4.5 TX Ready signal ................................................................................................................................... 8
1.5 I/O pins ........................................................................................................................................................... 8
1.5.1 RESET_N: Reset input ....................................................................................................................... 8
1.5.2 WHEELTICK: Wheel tick input ......................................................................................................... 8
1.5.3 FWD: Forward/reverse input ............................................................................................................ 8
1.5.4 D_SEL: Interface select ..................................................................................................................... 9
1.5.5 LNA_EN: LNA enable .......................................................................................................................... 9
1.5.6 TIMEPULSE.......................................................................................................................................... 9
1.6 Electromagnetic interference on I/O lines ............................................................................................. 9
2 Design ..................................................................................................................................................... 10
2.1 Pin description ...........................................................................................................................................10
2.1.1 Pin name changes.............................................................................................................................10
2.2 Minimal design...........................................................................................................................................11
2.3 Layout: Footprint and paste mask ........................................................................................................11
2.4 Antenna .......................................................................................................................................................12
2.4.1 Antenna design with passive antenna .........................................................................................12
2.4.2 Active antenna design .....................................................................................................................13
3 Automotive dead reckoning ............................................................................................................ 14
3.1 Implementation .........................................................................................................................................14
3.2 Sensor calibration .....................................................................................................................................14
3.3 Software migration ...................................................................................................................................14
4 Product handling ................................................................................................................................. 15
4.1 Packaging, shipping, storage and moisture preconditioning ..........................................................15
4.2 Soldering .....................................................................................................................................................15
4.3 EOS/ESD/EMI precautions ......................................................................................................................19
4.4 Safety precautions ...................................................................................................................................21
UBX-16010549 - R09 Contents Page 3 of 28
C1-Public
Page 4

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
4.5 Applications with cellular modules ........................................................................................................22
Appendix ....................................................................................................................................................... 24
A Recommended parts ......................................................................................................................... 24
B Recommended antennas ................................................................................................................. 25
Related documents ................................................................................................................................... 26
Revision history .......................................................................................................................................... 27
Contact .......................................................................................................................................................... 28
UBX-16010549 - R09 Contents Page 4 of 28
C1-Public
Page 5

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
1 Hardware description
1.1 Overview
The NEO-M8L modules are 3D dead reckoning GNSS receivers for automotive applications using a
built-in 6-axis sensor (3-axis gyroscope and 3-axis accelerometer) and featuring the highperformance u-blox M8 concurrent positioning engine. Available in the NEO industry standard
leadless chip carrier (LCC) package, they are easy to integrate and they combine exceptional
positioning performance with highly flexible power, design, and connectivity options. SMT pads allow
fully automated assembly with standard pick & place and reflow-soldering equipment for costefficient, high-volume production enabling short time-to-market.
☞ For more information about the product features, see the corresponding product data sheet [1],
or [2] in the Related documents section.
☞ To determine which u-blox product best meets your needs, see the product selector tables on the
u-blox website www.u-blox.com.
1.2 Configuration
The configuration settings can be modified using UBX protocol configuration messages (see the ublox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification
remain effective until power-down or reset. If these settings have been stored in battery-backed RAM
(BBR), then the modified configuration will be retained, as long as the backup battery supply is not
interrupted.
[3]). The modified settings
For NEO-M8L modules, the configuration can be saved permanently in SQI flash.
1.3 Connecting power
The NEO-M8L positioning modules have up to three power supply pins: VCC, V_BCKP and VDD_USB.
1.3.1 VCC: Main supply voltage
The VCC pin provides the main supply voltage. During operation, the current drawn by the module can
vary by some orders of magnitude, especially if enabling low-power operation modes. For this reason,
it is important that the supply circuitry be able to support the peak power for a short time (see the
corresponding product data sheet in the Related documents section for the specifications).
☞ When switching from backup mode to normal operation or at start-up, the NEO-M8L modules
must charge the internal capacitors in the core domain. In certain situations, this can result in a
significant current draw. For low power applications using power save and backup modes, it is
important that the power supply or low ESR capacitors at the module input can deliver this
current/charge.
☞ Use a proper GND concept. Do not use any resistors or coils in the power line.
1.3.2 V_BCKP: Backup supply voltage
If the module supply has a power failure, the V_BCKP pin supplies the real-time clock (RTC) and
battery-backed RAM (BBR). Use of valid time and the GNSS orbit data at startup will improve the
GNSS performance, as with hot starts, warm starts, AssistNow Autonomous and AssistNow Offline.
If no backup battery is connected, the module performs a cold start at power up.
☞ A backup supply voltage should be provided to the NEO-M8L to enable navigation by dead
reckoning before the first GNSS fix.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Hardware description Page 5 of 28
C1-Public
Page 6
000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
☞ Avoid high resistance on the V_BCKP line: During the switch from main supply to backup supply,
a short current adjustment peak can cause high voltage drop on the pin with possible
malfunctions.
☞ If no backup supply voltage is available, connect the V_BCKP pin to VCC.
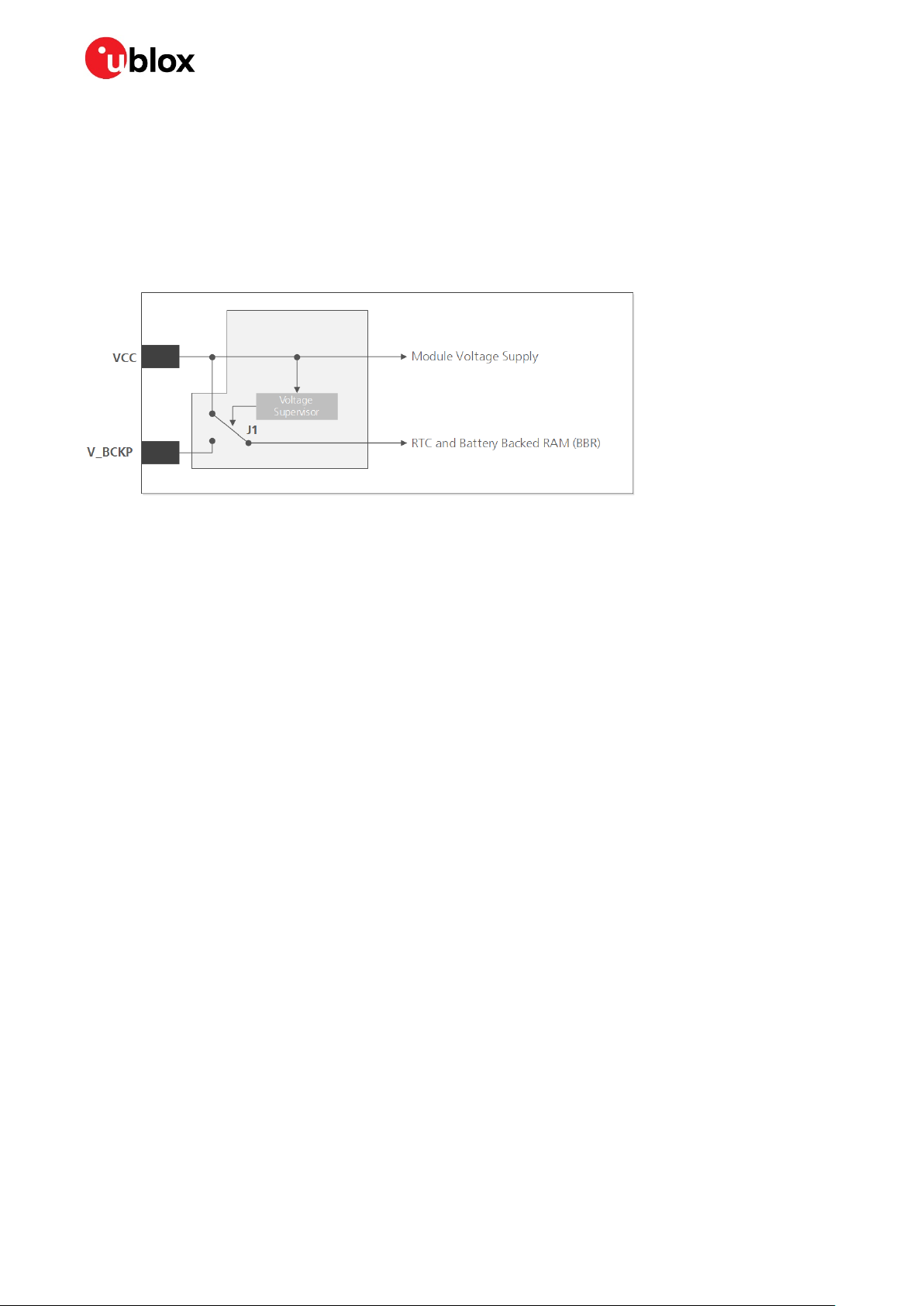
☞ As long as power is supplied to the NEO-M8L modules through the VCC pin, the backup battery is
disconnected from the RTC and the BBR to avoid unnecessary battery drain (see Figure 1). In this
case, VCC supplies power to the RTC and BBR.
Figure 1: Backup battery and voltage (for exact pin orientation, see the corresponding product data sheet)
1.3.3 VDD_USB: USB interface power supply
VDD_USB supplies the USB interface. If the USB interface is not used, the VDD_USB pin must be
connected to GND. For more information about correctly handling the VDD_USB pin, see section 1.4.
1.3.4 VCC_RF: Output voltage RF
The VCC_RF pin can supply an active antenna or external LNA. For more information, see section 2.4.
1.4 Interfaces
For more information about the interfaces (baud rates, bandwidth, speed and clock frequency, and so
on), see the corresponding product data sheet [1], or [2] in the Related documents section.
1.4.1 UART
NEO-M8L 3D dead reckoning modules include a Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter
(UART) serial interface RXD/TXD supporting configurable baud rates.
The signal output and input levels are 0 V to VCC. An interface based on RS232 standard levels (+/12 V) can be implemented using level shifters such as Maxim MAX3232. Hardware handshake signals
and synchronous operation are not supported.
1.4.2 USB
A USB version 2.0 FS (full speed, 12 Mb/s) compatible interface is available for communication as an
alternative to the UART. The USB_DP integrates a pull-up resistor to signal a full-speed device to the
host. The VDD_USB pin supplies the USB interface.
u-blox provides Microsoft® certified USB drivers for Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 and
Windows 10. These drivers are available at our website, www.u-blox.com.
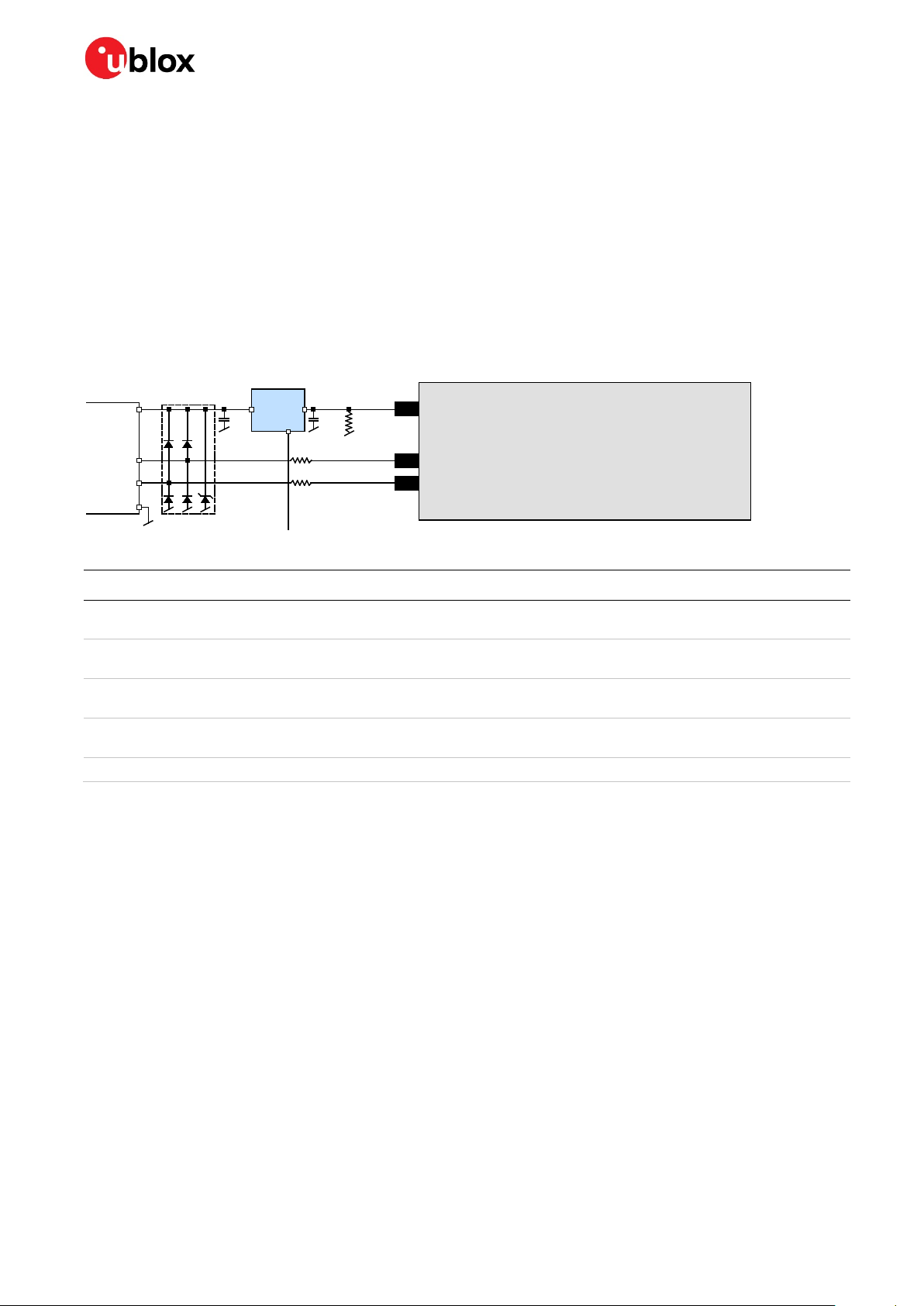
USB external components
The USB interface requires some external components to implement the physical characteristics
required by the USB 2.0 specification. These external components are shown in Figure 2 and listed in
UBX-16010549 - R09 Hardware description Page 6 of 28
C1-Public
Page 7
000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
Module
VDD_USB
LDO
VDD_USB
R4
USB_DP
USB_DM
R5
C24 C23
D2
VBUS
DP
DM
GND
USB Device Connector
U1
EN
R11
EN
Almost no current requirement (~1 mA) if the GNSS receiver is
Table 1. To comply with USB specifications, VBUS must be connected through an LDO (U1) to pin
VDD_USB on the module.
In USB self-powered mode, the power supply (VCC) can be turned off and the digital block is not
powered. In this case, since VBUS is still available, the USB host would still receive the signal indicating
that the device is present and ready to communicate. This should be avoided by disabling the LDO
(U1) using the enable signal (EN) of the VCC-LDO or the output of a voltage supervisor. Depending on
the characteristics of the LDO (U1), it is recommended to add a pull-down resistor (R11) at its output
to ensure VDD_USB is not floating if the LDO (U1) is disabled or the USB cable is not connected, that
is, VBUS is not supplied.
☞ USB bus-powered mode is not supported.
Figure 2: USB interface
Name Component Function Comments
U1 LDO
C23,
C24
D2 Protection diodes
R4, R5
R11 Resistor
Table 1: Summary of USB external components
Capacitors Required according to the specification of LDO U1.
Serial termination
resistors
Regulates VBUS (4.4 …5.25 V)
down to a voltage of 3.3 V.
Protect circuit from overvoltage /
ESD when connecting.
Establish a full-speed driver
impedance of 28…44 Ω
operated as a USB self-powered device.
Use low-capacitance ESD protection such as ST
Microelectronics USBLC6-2.
A value of 27 Ω is recommended.
100 kΩ is recommended for USB self-powered setup.
1.4.3 Display Data Channel (DDC)
An I2C-compatible Display Data Channel (DDC) interface is available with a NEO-M8L module for serial
communication with an external host CPU. The interface only supports operation in slave mode
(master mode is not supported). The DDC protocol and electrical interface are fully compatible with
the fast mode of the I2C industry standard. DDC pins SDA and SCL have internal pull-up resistors.
For more information about the DDC implementation, see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver
Description Including Protocol Specification [3]. For timing, parameters consult the I2C-bus
specification [8].
☞ The NEO-M8L DDC interface supports serial communication with u-blox cellular modules. See the
specification of the applicable cellular module to confirm compatibility.
1.4.4 SPI
An SPI interface is available for communication to a host CPU.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Hardware description Page 7 of 28
C1-Public
Page 8

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
☞ SPI is not available in the default configuration, because its pins are shared with the UART and
DDC interfaces. The SPI interface can be enabled by connecting D_SEL to ground. For speed and
clock frequency, see the corresponding product data sheet in the Related documents section.
1.4.5 TX Ready signal
The TX Ready signal indicates that the receiver has data to transmit. A listener can wait on the TX
Ready signal instead of polling the DDC or SPI interfaces. The UBX-CFG-PRT message lets you
configure the polarity and the number of bytes in the buffer before the TX Ready signal goes active.
The TX Ready signal can be mapped to UART TXD (PIO 06). The TX Ready function is disabled by
default.
☞ The TX Ready functionality can be enabled and configured by AT commands sent to the u-blox
cellular module supporting the feature. For more information, see the GPS Implementation and
Aiding Features in u-blox wireless modules
[9].
1.5 I/O pins
1.5.1 RESET_N: Reset input
Driving RESET_N low activates a hardware reset of the system. Use this pin to reset the module only.
Do not use RESET_N to turn the module on and off, since the reset state increases power
consumption. With the NEO-M8L modules the RESET_N pin is an input only.
☞ Use RESET_N in critical situations only to recover the system. RESET_N also resets the real-time
clock which means that the receiver cannot perform hot start immediately after RESET_N.
1.5.2 WHEELTICK: Wheel tick input
The wheel tick input, also known as the HW interface, is used to provide speed pulse (wheel tick)
information to the NEO-M8L modules. By default the wheel tick count is based on the rising edge of
the wheel tick pulse signal. To improve performance with lower rate mechanically derived wheel-tick
signals, the receiver may be configured to use both the rising and falling edges of the wheel tick signal
on the condition that the wheel tick pulses have approximately 1:1 mark:space ratio regardless of
speed. The minimum recommended pulse width is 10 us.
The pulse interval (WT resolution) should be less than 40 cm per tick over distance travelled. For best
performance, less than 2 cm/tick is recommended. The wheel tick pulse output shall change linearly
with the change in speed (navigation filter estimates only the linear scale factor). If the vehicle is
standing still, there should be no wheel tick pulses. This is particularly important at system shut down
and power up. If there is a dead-band (wheel tick pulse does not change or is not output below a certain
speed), performance will be affected at low speed.
If the speed pulse is available from the host processor, then the information can also be provided by
SW interface using the UBX-ESF-MEAS message. In this particular case, the wheel-tick pin can be
configured as EXTINT1 and used to provide a time mark for the message. For more information, see
the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification [3].
☞ Do not exceed the maximum voltage of 3.6 V at the input when using the HW interface.
1.5.3 FWD: Forward/reverse input
The forward/reverse input is used to indicate the moving direction by an external signal (HW
interface). By default the wheel-tick direction pin polarity is automatically initialized once the vehicle
has reached required minimum speed of 30 km/h. The forward/reverse input polarity can also be set
manually. If the forward/reverse information is available from the host processor, the UBX-ESF-MEAS
UBX-16010549 - R09 Hardware description Page 8 of 28
C1-Public
Page 9
000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
TX
RX
GNSS
Receiver
FB
FB
BLM 15HD102SN1
>10mm
message can also be used to provide the direction of motion (SW interface). For more information,
see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification [3].
☞ Do not exceed the maximum voltage of 3.6 V at the input when using the HW interface. When
using a SW interface this pin is not used and can be left open.
☞ No forward or reverse input will cause incorrect operation.
1.5.4 D_SEL: Interface select
The D_SEL pin selects the available interfaces. SPI cannot be used simultaneously with the
UART/DDC. If open, UART and DDC are available. If pulled low, the SPI interface is available.
1.5.5 LNA_EN: LNA enable
In power save mode, the system can turn on/off an optional external LNA using the LNA_EN signal to
optimize power consumption.
1.5.6 TIMEPULSE
A configurable time pulse signal is available with the NEO-M8L modules. It generates pulse trains
synchronized with GPS or UTC time grid with intervals configurable over a wide frequency range. For
more information, see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification
[3].
☞ The NEO-M8L time-pulse output is configured using messages for “TIMEPULSE2”.
☞ The time pulse output must not be held LOW during start-up.
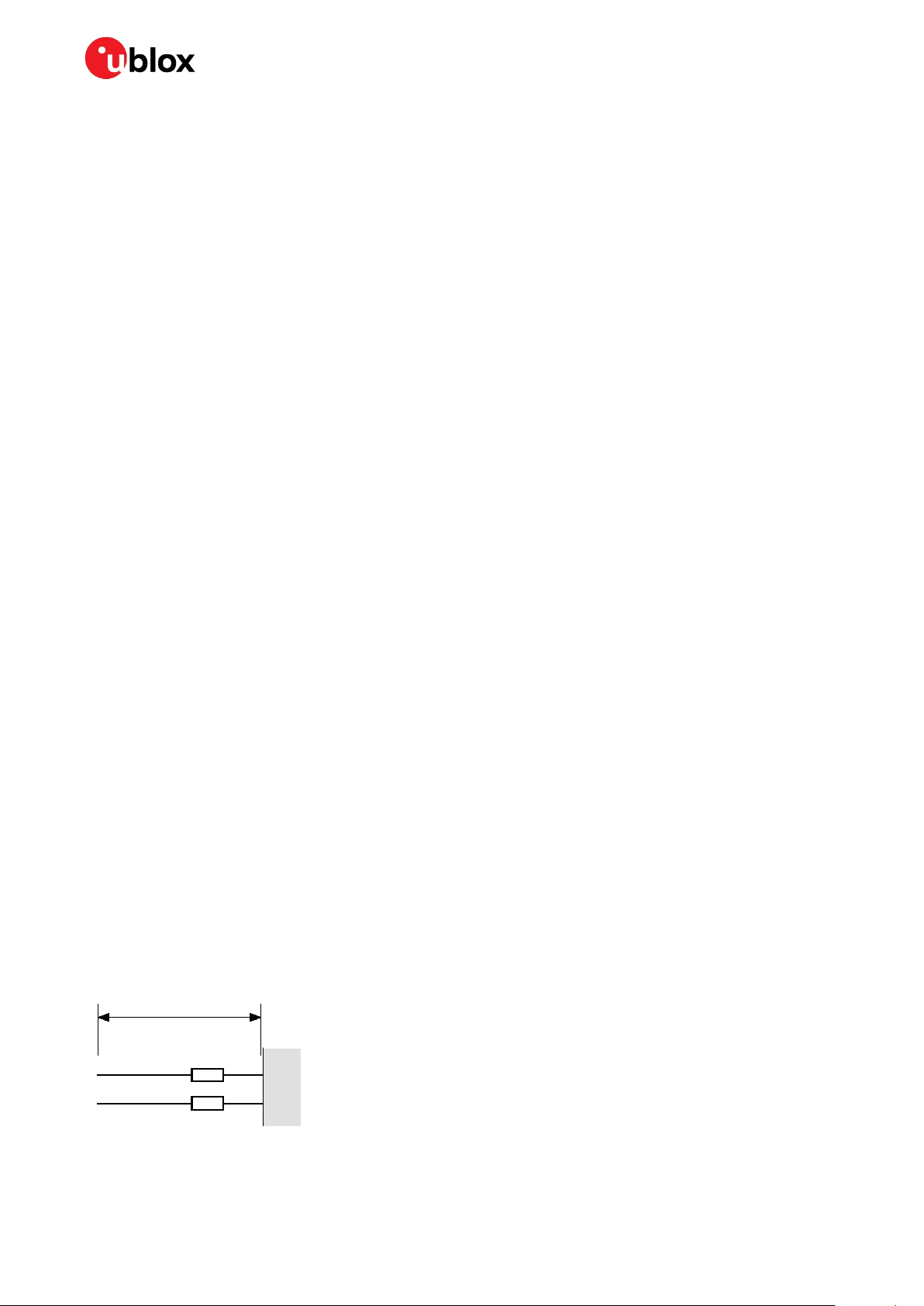
1.6 Electromagnetic interference on I/O lines
Any I/O signal line with a length greater than approximately 3 mm can act as an antenna and may pick
up arbitrary RF signals transferring them as noise into the GNSS receiver. This specifically applies to
unshielded lines, in which the corresponding GND layer is remote or missing entirely, and lines close
to the edges of the printed circuit board.
If, for example, a cellular signal radiates into an unshielded high-impedance line, it is possible to
generate noise in the order of volts and not only distort receiver operation but also damage it
permanently.
On the other hand, noise generated at the I/O pins will emit from unshielded I/O lines. Receiver
performance may be degraded when this noise is coupled into the GNSS antenna (see Figure 16).
To avoid interference by improperly shielded lines, it is recommended to use resistors (for example,
R>20 Ω), ferrite beads (for example, BLM15HD102SN1) or inductors (for example, LQG15HS47NJ02)
on the I/O lines in series. Choose these components carefully because they also affect the signal rise
times.
Figure 3 shows an example of EMI protection measures on the RX/TX line using a ferrite bead.
Figure 3: EMI precautions
More information is available in section 4.3.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Hardware description Page 9 of 28
C1-Public
Page 10

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
2 Design
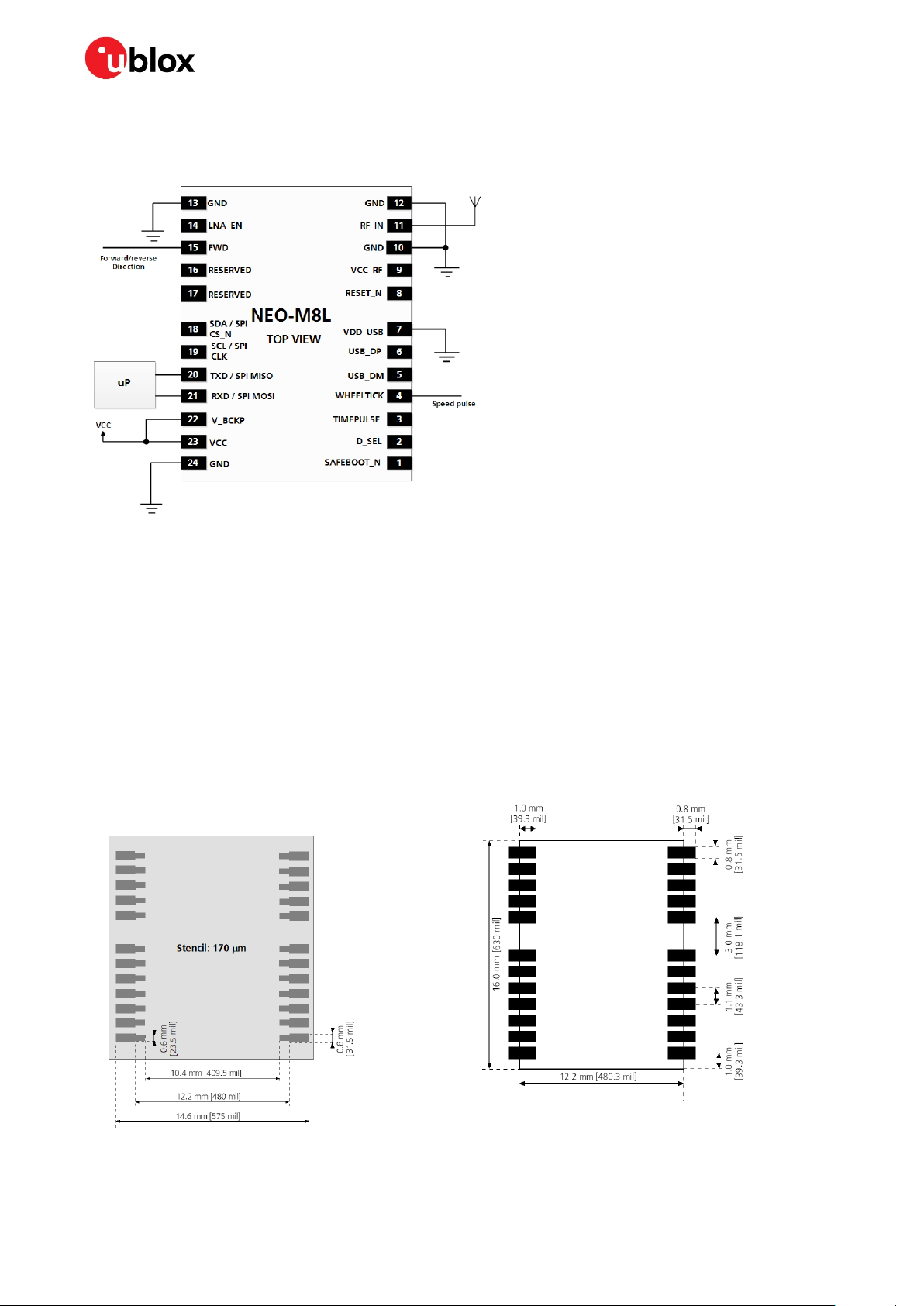
2.1 Pin description
No. Name I/O Description
1 SAFEBOOT_N I SAFEBOOT_N, test-point for service use (leave OPEN)
2 D_SEL I Interface select
3 TIMEPULSE I/O
4 WHEELTICK I Wheel tick input
5 USB_DM I/O USB data
6 USB_DP I/O USB data
7 VDD_USB I USB supply
8 RESET_N I RESET_N
9 VCC_RF O Output voltage RF section
10 GND I Ground
11 RF_IN I GNSS signal input
12 GND I Ground
13 GND I Ground
14 LNA_EN O LNA enable
15 FWD I Forward/reverse input for speed pulse
16 RESERVED - Reserved
17 RESERVED - Reserved
18 SDA / SPI CS_N I/O DDC data if D_SEL =1 (or open) / SPI chip select if D_SEL = 0
19 SCL / SPI CLK I/O DDC clock if D_SEL =1(or open) / SPI clock if D_SEL = 0
20 TXD / SPI MISO O Serial port if D_SEL =1(or open) / SPI MISO if D_SEL = 0
21 RXD / SPI MOSI I Serial port if D_SEL =1(or open) / SPI MOSI if D_SEL = 0
22 V_BCKP I Backup voltage supply
23 VCC I Supply voltage
24 GND I Ground
Table 2: Pinout of NEO-M8L modules
Time pulse (disabled by default). Do not pull low during reset.
Note: configured using TIMEPULSE2 messages (see u-blox 8 / u-blox M8
Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification
[3])
2.1.1 Pin name changes
Selected pin names have been updated to agree with a common naming convention across u-blox
modules. The pins have not changed their operation and are the same physical hardware, but with
updated names. The table below lists the pins that have a changed name along with their old and new
names.
No Previous name New name
14 ANT_ON LNA_EN
16 NC RESERVED
17 NC RESERVED
20 TxD / SPI MISO TXD / SPI MISO
21 RxD / SPI MOSI RXD / SPI MOSI
Table 3: Pin name changes in NEO-M8L-0 (Professional grade)
UBX-16010549 - R09 Design Page 10 of 28
C1-Public
Page 11
000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
2.2 Minimal design
This is a minimal design for a NEO-M8L GNSS receiver.
Figure 4: NEO-M8L passive antenna design
2.3 Layout: Footprint and paste mask
Figure 5 describes the footprint and provides recommendations for the paste mask for NEO-M8L
modules. These are recommendations only and not specifications. Note that the copper and solder
masks have the same size and position.
To improve the wetting of the half vias, reduce the amount of solder paste under the module and
increase the volume outside of the module by defining the dimensions of the paste mask to form a Tshape (or equivalent) extending beyond the copper mask. For the stencil thickness, see section 4.2.
☞ Consider the paste mask outline when defining the minimal distance to the next component. The
exact geometry, distances, stencil thicknesses and solder paste volumes must be adapted to the
specific production processes (e.g. soldering) of the customer.
Figure 5: NEO-M8L paste mask / footprint
UBX-16010549 - R09 Design Page 11 of 28
C1-Public
Page 12

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
2.4 Antenna
2.4.1 Antenna design with passive antenna
A design using a passive antenna requires more attention to the layout of the RF section. Typically, a
passive antenna is located near electronic components; therefore, care should be taken to reduce
electrical noise that may interfere with the antenna performance. Passive antennas do not require a
DC bias voltage and can be directly connected to the RF input pin RF_IN. Sometimes, they may also
need a passive matching network to match the impedance to 50 Ω.
Figure 6 shows a minimal setup for a design with a good GNSS patch antenna. For exact pin
orientation, see the Appendix and the corresponding product Data sheet [1], or [2] in the Related
documents section.
Figure 6: Module design with passive antenna
☞ Use an antenna that has sufficient bandwidth to receive all GNSS constellations. For more
information, see and the GPS Antenna Application Note [5].
Figure 7 shows a design using an external LNA and SAW to increase the sensitivity for best
performance with passive antenna.
Figure 7: Module design with passive antenna and an external LNA and SAW
The LNA_EN pin (LNA enable) can be used to turn an optional external LNA on and off.
The VCC_RF output can be used to supply the LNA with a filtered supply voltage.
☞ A standard GNSS LNA has enough bandwidth to amplify GPS/GLONASS/BeiDou/Galileo signals.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Design Page 12 of 28
C1-Public
Page 13

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
☞ An external LNA is only required if the passive antenna is placed far away from the module. In that
case the LNA must be placed directly to the passive antenna.
2.4.2 Active antenna design
An active antenna makes use of an integrated low-noise amplifier, which requires a power supply that
will contribute to the total GNSS system power consumption budget with additional 5 to 20 mA
typically.
If the supply voltage of the NEO-M8L module matches the supply voltage of the active antenna (for
example, 3.0 V), use the filtered supply voltage available at pin VCC_RF as shown in Figure 8.
Active antenna design using VCC_RF pin to supply the active antenna
Figure 8: Active antenna design, external supply from VCC_RF
If the VCC_RF voltage does not match with the supply voltage of the active antenna, use a filtered
external supply as shown in Figure 9.
For exact pin orientation, see the corresponding product Data sheet [1], or [2] in the Related
documents section.
Active antenna design powered from an external supply
Figure 9: Active antenna design, direct external supply
☞ The circuit shown in Figure 9 works with all u-blox M8 modules, also with modules without VCC_RF
output.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Design Page 13 of 28
C1-Public
Page 14

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
3 Automotive dead reckoning
3.1 Implementation
The NEO-M8L 3D dead reckoning modules make use of an internal 6-axis sensor (3-axis gyroscope
and 3-axis accelerometer), meaning that only speed pulse and forward/reverse information must be
provided externally. This can be done by applying speed pulse and forward/reverse signals directly at
the dedicated HW interface pins of the NEO-M8L (see section 1.5) or by transmitting the same
information to the module in UBX-ESF-MEAS messages (SW interface) sent from a host processor to
the module. Where the software interface is used, the customer can re-configure the hardware wheel
tick pin (as EXTINT) to indicate the reference time of the speed and forward/reverse information in
the following UBX message from the processor. Figure 10 shows the orientation of the IMU frame.
Figure 10: NEO-M8L with IMU sensor frame
☞ More information about the ADR functionality can be found in the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver
Description Including Protocol Specification [3].
3.2 Sensor calibration
The availability of “Sensor Fusion Mode” dead reckoning depends on the configuration of some
mandatory sensor characteristic data and optional parameter refinements. If only the mandatory
data are provided at installation, the navigation quality may be degraded on first use. The receiver
continuously refines sensor calibration to account for tire wear, temperature, and aging. Data from
continuous calibration are stored for future use in non-volatile memory.
☞ For more information about mandatory, calibration and optional configuration parameters, refer
to the ADR configuration section of u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol
Specification
[3].
☞ Note that the performance of the ADR solution relies on stable sensor location and orientation
with respect to the vehicle frame. The module must be mounted securely within the vehicle.
3.3 Software migration
☞ For an overall description of the module software operation, see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver
Description Including Protocol
[3].
UBX-16010549 - R09 Automotive dead reckoning Page 14 of 28
C1-Public
Page 15

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
4 Product handling
4.1 Packaging, shipping, storage and moisture preconditioning
For information pertaining to reels and tapes, Moisture Sensitivity levels (MSL), shipment and
storage information, as well as drying for preconditioning, see the corresponding product data sheet
[1], or [2] or the u-blox Package Information guide [4] in the Related documents section.
Population of modules
☞ When populating the modules, make sure that the pick and place machine is aligned to the copper
pins of the module and not on the module edge. Note that a MEMS device is present internally.
4.2 Soldering
Soldering paste
Use of "no clean" soldering paste is highly recommended, as it does not require cleaning after the
soldering process has taken place. The paste in the example below meets these criteria.
Soldering paste: OM338 SAC405 / Nr.143714 (Cookson Electronics)
Alloy specification: Sn 95.5/ Ag 4/ Cu 0.5 (95.5% tin/ 4% silver/ 0.5% copper)
Melting temperature: 217 °C
Stencil thickness: see section 2.3
The final choice of the soldering paste depends on the approved manufacturing procedures.
The paste-mask geometry for applying soldering paste should meet the recommendations.
☞ The quality of the solder joints on the connectors (’half vias’) should meet the appropriate IPC
specification.
Reflow soldering
A convection type-soldering oven is highly recommended over the infrared type radiation oven.
Convection-heated ovens allow precise control of the temperature, and all parts will heat up evenly,
regardless of material properties, thickness of components and surface color.
As a reference for the professional grade NEO-M8L, see the IPC-7530 Guidelines for temperature
profiling for mass soldering (reflow and wave) processes, published in 2001. For the Automotive Grade
NEO-M8L-01A module, see the IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020E, December 2014.
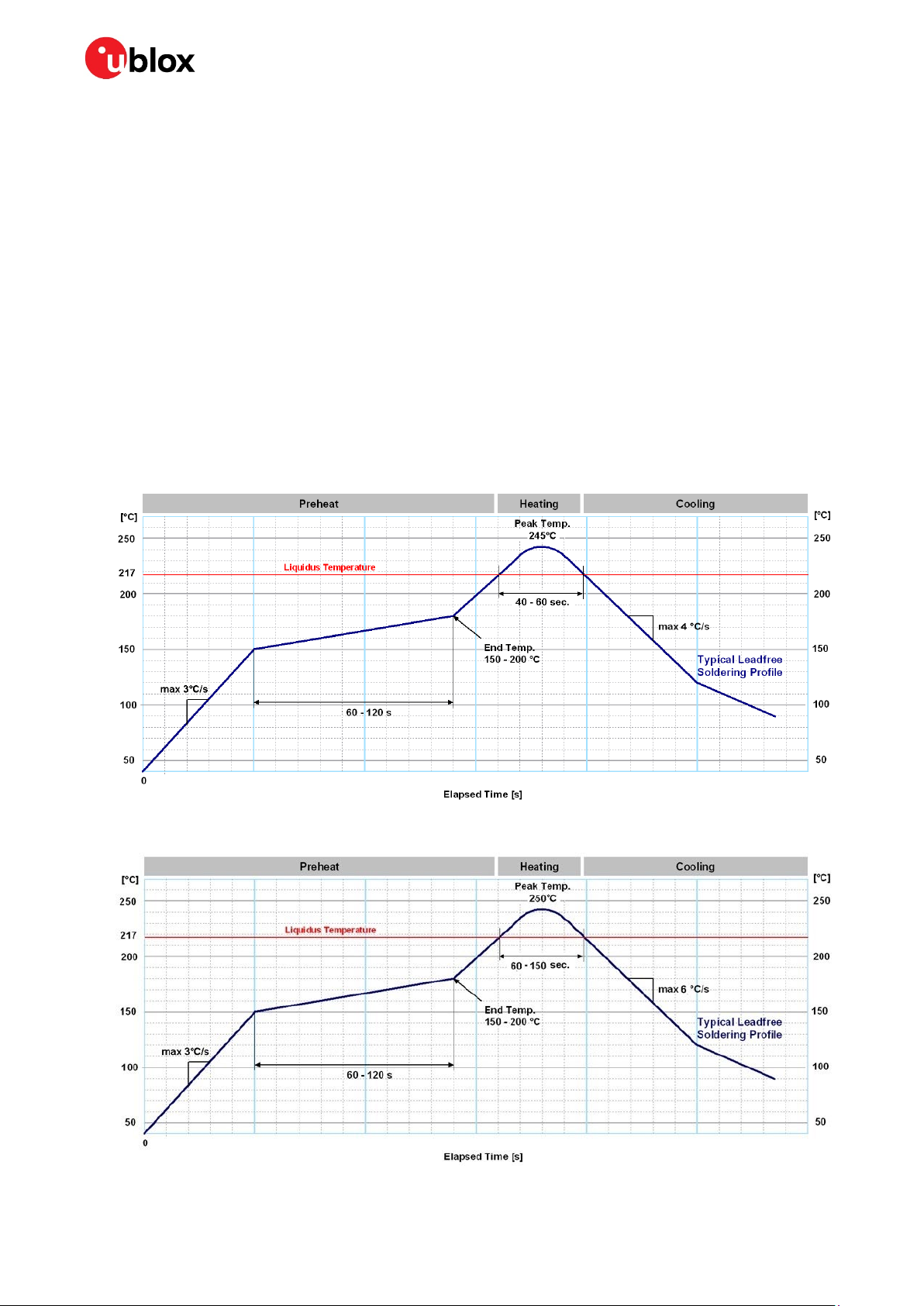
Preheat phase
During the initial heating of component leads and balls, residual humidity will be dried out. Note that
this preheat phase will not replace prior baking procedures.
• Temperature rise rate: max 3 °C/s. If the temperature rise is too rapid in the preheat phase it may
cause excessive slumping.
• Time: 60 - 120 s. If the preheat is insufficient, rather large solder balls tend to be generated.
Conversely, if performed excessively, fine balls and large balls will be generated in clusters.
• End temperature: 150 - 200 °C. If the temperature is too low, non-melting tends to be caused in
areas containing large heat capacity.
Heating/ Reflow phase
The temperature rises above the liquidus temperature of 217 °C. Avoid a sudden rise in temperature
as the slump of the paste could become worse.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Product handling Page 15 of 28
C1-Public
Page 16
000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
• For the professional grade NEO-M8L, limit time above 217 °C liquidus temperature to 40 - 60 s.
For the NEO-M8L-01A (automotive grade), the time above 217 °C should be limited to 60-150
seconds.
• Peak reflow temperature for professional grade NEO-M8L is 245 °C, and for NEO-M8L-01A it is
250 °C.
Cooling phase
A controlled cooling avoids negative metallurgical effects of the solder (solder becomes more brittle)
and possible mechanical tensions in the products. Controlled cooling helps to achieve bright solder
fillets with a good shape and low contact angle.
• Temperature fall rate: max 4 °C/s for the NEO-M8L, max 6 °C/s for the NEO-M8L-01A.
☞ To avoid falling off, the NEO-M8L module should be placed on the topside of the motherboard
during soldering.
The final soldering temperature chosen at the factory depends on additional external factors like
choice of soldering paste, size, thickness and properties of the base board, and so on. Exceeding the
maximum soldering temperature in the recommended soldering profile may permanently damage the
module.
Figure 11: Recommended soldering profile for the professional grade NEO-M8L
Figure 12: Recommended soldering profile for the automotive grade NEO-M8L-01A
UBX-16010549 - R09 Product handling Page 16 of 28
C1-Public
Page 17

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
☞ NEO-M8L modules must not be soldered with a damp heat process.
Optical inspection
After soldering the NEO-M8L modules, consider an optical inspection step to check whether:
• The module is properly aligned and centered over the pads
• All pads are properly soldered
• No excess solder has created contacts to neighboring pads, or possibly to pad stacks and vias
nearby
Cleaning
In general, cleaning the populated modules is strongly discouraged. Residues underneath the
modules cannot be easily removed with a washing process.
• Cleaning with water will lead to capillary effects where water is absorbed in the gap between the
baseboard and the module. The combination of residues of soldering flux and encapsulated water
leads to short circuits or resistor-like interconnections between neighboring pads.
• Cleaning with alcohol or other organic solvents can result in soldering flux residues flooding into
the two housings, areas that are not accessible for post-wash inspections. The solvent will also
damage the sticker and the ink-jet printed text.
• Ultrasonic cleaning will permanently damage the module, in particular the quartz oscillators.
The best approach is to use a "no clean" soldering paste and eliminate the cleaning step after the
soldering.
Repeated reflow soldering
Only single reflow soldering processes are recommended for boards populated with NEO-M8L
modules. To avoid upside down orientation during the second reflow cycle, the NEO-M8L module
should not be submitted to two reflow cycles on a board populated with components on both sides. In
this case, the module should always be placed on that side of the board, which is submitted into the
last reflow cycle. The reason for this (besides others) is the risk of the module falling off due to the
significantly higher weight in relation to other components.
Two reflow cycles can be considered by excluding the upside down scenario described above and
taking into account the rework conditions described in section 4
.
☞ Repeated reflow soldering processes and soldering the module upside down are not
recommended.
Wave soldering
Base boards with combined through-hole technology (THT) components and surface-mount
technology (SMT) devices require wave soldering to solder the THT components. Only a single wave
soldering process is encouraged for boards populated with NEO-M8L modules.
Hand soldering
Hand soldering is allowed. Use a soldering iron temperature setting equivalent to 350 °C. Place the
module precisely on the pads. Start with a cross-diagonal fixture soldering (for example, pins 1 and
15), and then continue from left to right.
Rework
The NEO-M8L modules can be unsoldered from the baseboard using a hot air gun. When using a hot
air gun for unsoldering the module, a maximum of one reflow cycle is allowed. In general, using a hot
air gun is not recommended because this is an uncontrolled process and might damage the module.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Product handling Page 17 of 28
C1-Public
Page 18

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
⚠ Attention: use of a hot air gun can lead to overheating and severely damage the module. Always
avoid overheating the module.
After the module is removed, clean the pads before placing and hand soldering a new module.
⚠ Never attempt a rework on the module itself, for example, replacing individual components. Such
actions immediately terminate the warranty.
In addition to the two reflow cycles, manual rework on particular pins by using a soldering iron is
allowed. Manual rework steps on the module can be done several times.
Conformal coating
®
Certain applications employ a conformal coating of the PCB using HumiSeal
products. These materials affect the HF properties of the NEO-M8L modules and it is important to
prevent them from flowing into the module. The RF shields do not provide 100% protection for the
module from coating liquids with low viscosity; therefore, care is required in applying the coating.
or other related coating
☞ Conformal coating of the module will void the warranty.
Casting
If casting is required, use viscose or another type of silicon potant. The OEM is strongly advised to
qualify such processes in combination with the NEO-M8L modules before implementing this in the
production.
☞ Casting will void the warranty.
Grounding metal covers
Attempts to improve grounding by soldering ground cables, wick or other forms of metal strips
directly onto the EMI covers is done at the customer's own risk. The numerous ground pins should be
sufficient to provide optimum immunity to interferences and noise.
☞ u-blox offers no warranty for damages to the NEO-M8L modules caused by soldering metal cables
or any other forms of metal strips directly onto the EMI covers.
Use of ultrasonic processes
Some components on the u-blox M8 module are sensitive to ultrasonic waves. Use of any ultrasonic
processes (cleaning, welding etc.) may cause damage to the GNSS receiver.
☞ u-blox offers no warranty against damages to the NEO-M8L modules caused by any ultrasonic
processes.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Product handling Page 18 of 28
C1-Public
Page 19

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
•
•
•
• When soldering RF connectors and patch antennas to the
4.3 EOS/ESD/EMI precautions
When integrating GNSS positioning modules into wireless systems, careful consideration must be
given to electromagnetic and voltage susceptibility issues. Wireless systems include components
that can produce Electrical Overstress (EOS) and Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI). CMOS devices
are more sensitive to such influences because their failure mechanism is defined by the applied
voltage, whereas bipolar semiconductors are more susceptible to thermal overstress. The following
design guidelines are provided to help in designing robust yet cost-effective solutions.
⚠ Only Separated or Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) circuits are to be connected to the module
including interfaces and antennas.
⚠ To avoid overstress damage during production or in the field it is essential to observe strict
EOS/ESD/EMI handling and protection measures.
⚠ To prevent overstress damage at the receiver RF_IN, never exceed the maximum input power.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD)
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden and momentary electric current that flows
between two objects at different electrical potentials caused by direct contact or
induced by an electrostatic field. The term is usually used in the electronics and other
industries to describe momentary unwanted currents that may cause damage to
electronic equipment.
ESD handling precautions
ESD prevention is based on establishing an Electrostatic Protective Area (EPA). The EPA can be a
small working station or a large manufacturing area. The main principle of an EPA is that there are no
highly charging materials near ESD sensitive electronics, all conductive materials are grounded,
workers are grounded, and charge build-up on ESD sensitive electronics is prevented. International
standards are used to define typical EPA and can be obtained for example from International
Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
GNSS positioning modules are sensitive to ESD and require special precautions when handling.
Exercize particular care when handling patch antennas, due to the risk of electrostatic charges. In
addition to standard ESD safety practices, take the following measures into account whenever
handling the receiver.
Unless there is a galvanic coupling between the local GND (that is,
the work desk) and the PCB GND, then the first point of contact
when handling the PCB must always be between the local GND and
PCB GND.
• Before mounting an antenna patch, connect ground of the device.
When handling the RF pin, do not come into contact with any
charged capacitors and be careful when contacting materials that
can develop charges (e.g. patch antenna ~10 pF, coax cable ~50 80 pF/m, soldering iron).
To prevent electrostatic discharge through the RF input, do not
touch any exposed antenna area. If there is any risk that such
exposed antenna area is touched in non-ESD protected work area,
implement proper ESD protection measures in the design.
receiver’s RF pin, be sure to use an ESD-safe soldering iron (tip).
⚠ Failure to observe these precautions can result in severe damage to the GNSS module!
UBX-16010549 - R09 Product handling Page 19 of 28
C1-Public
Page 20
000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
RF_IN
GNSS
Receiver
LN A
L
RF_IN
GNSS
Receiver
D
RF_IN
GNSS
Receiver
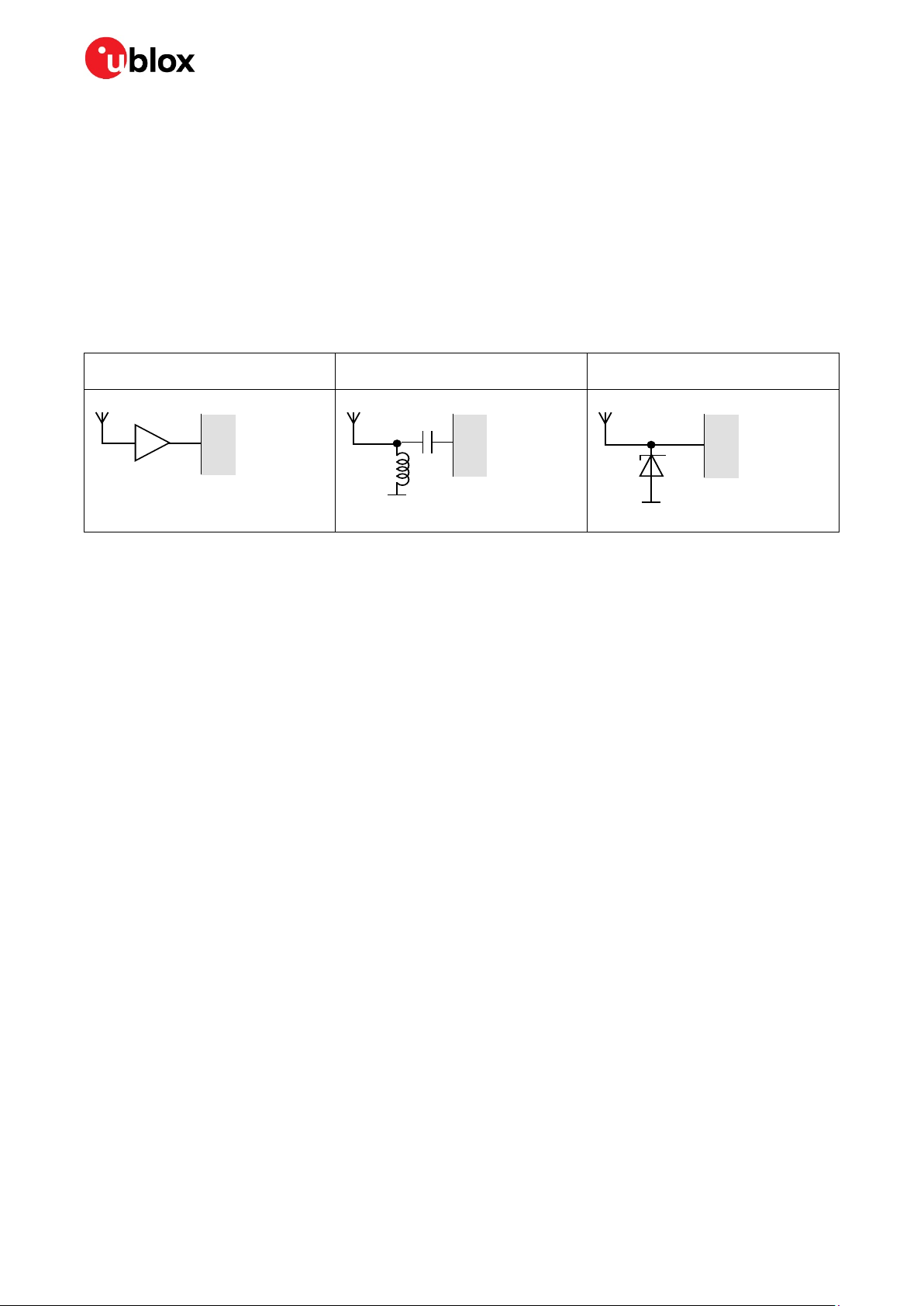
ESD protection measures
⚠ GNSS positioning modules are sensitive to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD). Special precautions are
required when handling.
☞ For more robust designs, employ additional ESD protection measures. Using an LNA with
appropriate ESD rating can provide enhanced GNSS performance with passive antennas and
increases ESD protection.
Most defects caused by ESD can be prevented by following strict ESD protection rules for production
and handling. When implementing passive antenna patches or external antenna connection points,
then additional ESD measures can also avoid failures in the field as shown in Figure 13.
Small passive antennas (<2 dBic and
performance critical)
A
Passive antennas (>2 dBic or
performance sufficient)
B
Active antennas
C
LNA with appropriate ESD rating
Figure 13: ESD precautions
☞ Protection measure A is preferred because it offers the best GNSS performance and best level of
ESD protection.
Electrical Overstress (EOS)
Electrical Overstress (EOS) usually describes situations when the maximum input power exceeds the
maximum specified ratings. EOS failure can happen if RF emitters are close to a GNSS receiver or its
antenna. EOS causes damage to the chip structures. If the RF_IN is damaged by EOS, it is hard to
determine whether the chip structures have been damaged by ESD or EOS.
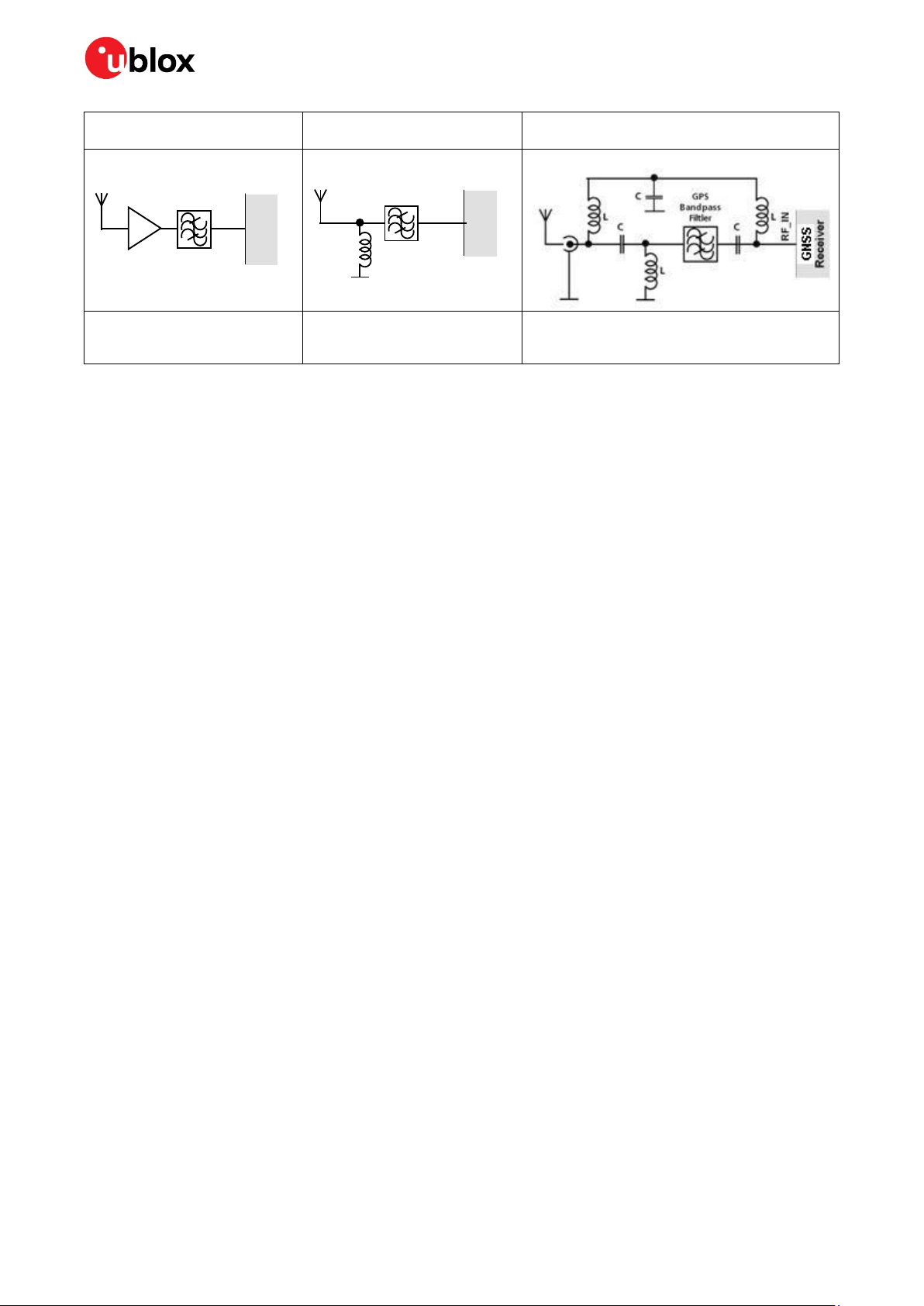
EOS protection measures
☞ For designs with GNSS positioning modules and wireless (e.g. GSM/GPRS) transceivers in close
proximity, ensure sufficient isolation between the wireless and GNSS antennas. If wireless power
output causes the specified maximum power input at the GNSS RF_IN to be exceeded, employ
EOS protection measures to prevent overstress damage.
For robustness, EOS protection measures as shown in Figure 14 are recommended for designs
combining wireless communication transceivers (e.g. GSM, GPRS) and GNSS in the same design or in
close proximity.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Product handling Page 20 of 28
C1-Public
Page 21
000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
RF_IN
GNSS
Receiver
LN A
GPS
Bandpass
Filtler
RF_IN
GNSS
Receiver
L
GPS
Bandpass
Filtler
Small passive antennas (<2 dBic
and performance critical)
D
LNA with appropriate ESD rating
and maximum input power
Figure 14: EOS and ESD precautions
Passive antennas (>2 dBic or
performance sufficient)
E
GNSS Band pass Filter: SAW or
Ceramic with low insertion loss
and appropriate ESD rating
Active antennas (without internal filter which
need the module antenna supervisor circuits)
F
Electromagnetic interference (EMI)
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is the addition or coupling of energy causing a spontaneous reset
of the GNSS receiver or resulting in unstable performance. In addition to EMI degradation due to selfjamming (see section 1.5) any electronic device near the GNSS receiver can emit noise that can lead
to EMI disturbances or damage.
The following elements are critical regarding EMI:
• Unshielded connectors (e.g. pin rows)
• Weakly shielded lines on PCB (e.g. on top or bottom layer and especially at the border of a PCB)
• Weak GND concept (e.g. small and/or long ground line connections)
EMI protection measures are recommended when RF-emitting devices are near the GNSS receiver.
To minimize the effect of EMI a robust grounding concept is essential. To achieve electromagnetic
robustness follow the standard EMI suppression techniques.
http://www.murata.com/products/emc/knowhow/index.html
http://www.murata.com/products/emc/knowhow/pdf/4to5e.pdf
Improved EMI protection can be achieved by inserting a resistor or better yet a ferrite bead or an
inductor (see Table 4) into any unshielded PCB lines connected to the GNSS receiver. Place the
resistor as close as possible to the GNSS receiver pin.
Alternatively, feed-through capacitors with good GND connection can be used to protect, for example,
the VCC supply pin against EMI. A selection of feed-through capacitors is listed in Table 4.
4.4 Safety precautions
The automotive grade NEO-M8L-01A modules must be supplied by an external limited power source
in compliance with the clause 2.5 of the standard IEC 60950-1. In addition to external limited power
source, only Separated or Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) circuits are to be connected to the module
including interfaces and antennas.
☞ For more information about SELV circuits see section 2.2 in Safety standard IEC 60950-1 0.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Product handling Page 21 of 28
C1-Public
Page 22
000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
1525
1550 1625
GPS input filte r
cha ract eristics
1575 1600
0
-110
Jammin
g signal
1525 1550 1625
Frequ ency [MHz]
Po w er [ d Bm]
GPS input filte r
cha ract eristics
1575 1600
0
Jamming
signal
GPS
signals
GPS C arr ier
1575.4 MHz
4.5 Applications with cellular modules
GSM terminals transmit power levels up to 2 W (+33 dBm) peak, 3G and LTE up to 250 mW
continuous. Consult the data sheet for the absolute maximum power input at the GNSS receiver.
☞ See the GPS Implementation and Aiding Features in u-blox wireless modules [9].
Isolation between GNSS and cellular antennas
In multi-antenna designs, an isolation of approximately 20 dB can be reached with careful placement
of the antennas. If such isolation cannot be achieved, for example, in the case of an integrated cellular
antenna, an additional input filter is needed on the GNSS side to block the high energy emitted by the
cellular transmitter. Examples of these kinds of filters would be the SAW Filters from Epcos (B9444
or B7839) or Murata.
Increasing interference immunity
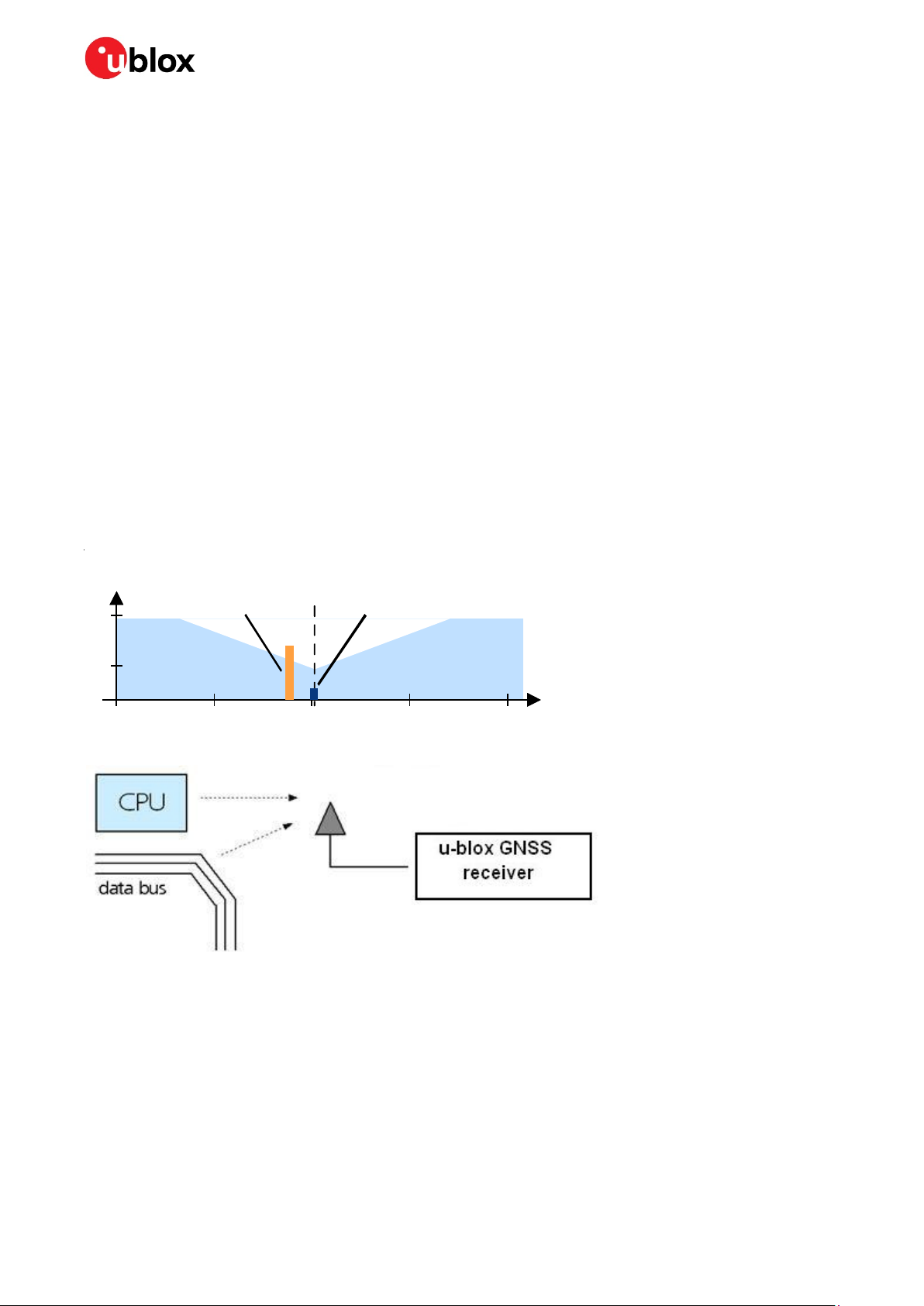
Interference signals come from in-band and out-band frequency sources.
In-band interference
With in-band interference, the signal frequency is very close to the GNSS constellation frequency
used, e.g. GPS frequency of 1575 MHz (see
by harmonics from displays, micro-controller, bus systems, and so on.
Figure 15). Such interference signals are typically caused
Figure 15: In-band interference signals
Figure 16: In-band interference sources
Measures against in-band interference include:
• Maintaining a good grounding concept in the design
• Shielding
• Layout optimization
• Filtering
• Placement of the GNSS antenna
• Adding a CDMA, GSM, WCDMA band pass filter before handset antenna
UBX-16010549 - R09 Product handling Page 22 of 28
C1-Public
Page 23
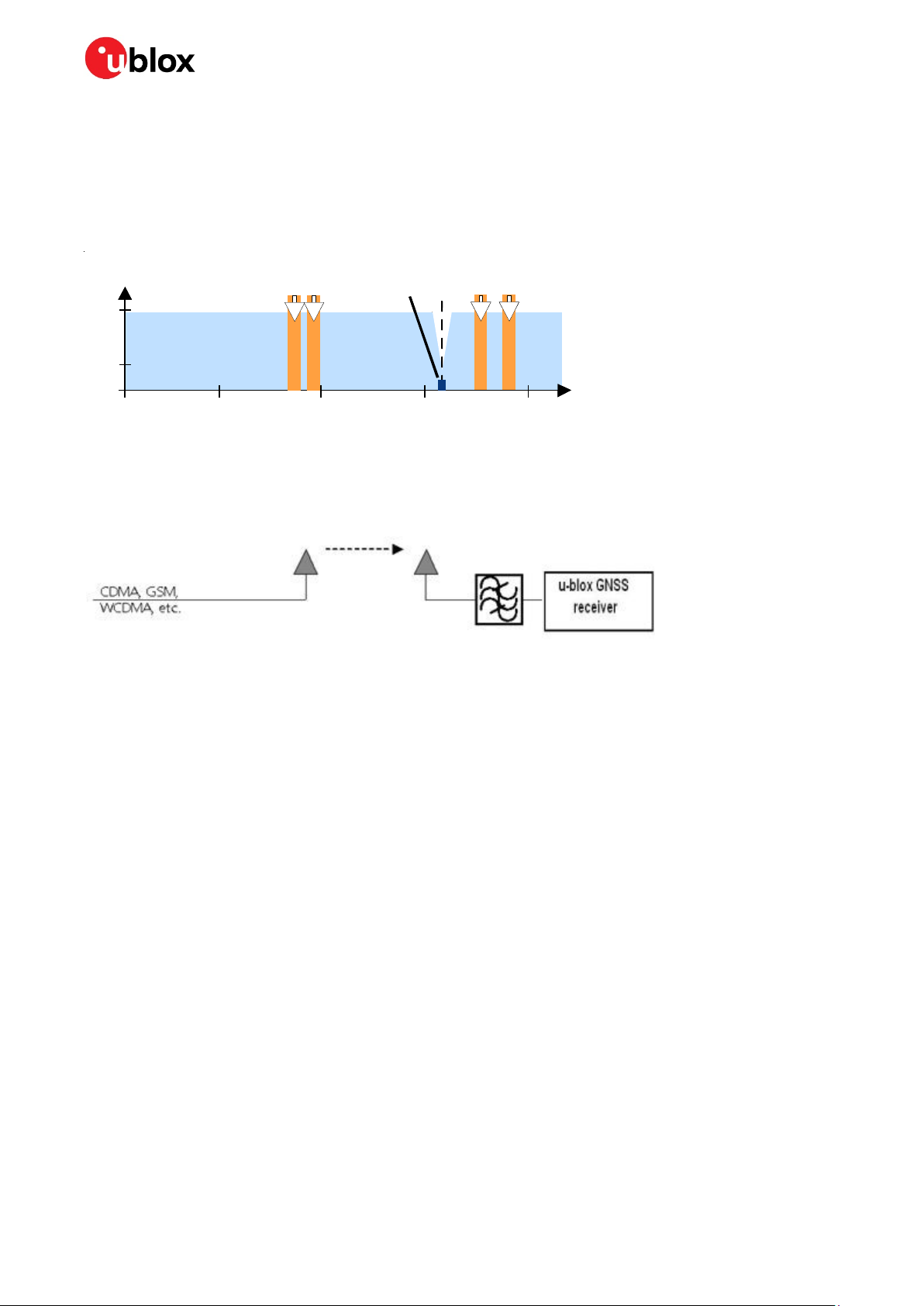
000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
0
500 1000 1500 2000
GPS input filte r
cha ract eristics
0
-110
0 500 1500 2000
Frequ ency [MHz]
GSM
900
GSM
1800
GSM
1900
Po w er [ d Bm]
GPS input filte r
cha ract eristics
GPS
1575
0
-110
GPS
signals
GSM
950
Out-of-band interference
Out-of-band interference is caused by signal frequencies that are different from the GNSS carrier (see
Figure 17). The main sources are wireless communication systems such as GSM, CDMA, WCDMA,
Wi-Fi, BT.
Figure 17: Out-of-band interference signals
Measures against out-of-band interference include maintaining a good grounding concept in the
design and adding a SAW or band pass ceramic filter (as recommend in
input line to the GNSS receiver (see
Figure 18).
section 4) into the antenna
Figure 18: Measures against out-band interference
☞ For design-in recommendations in combination to Cellular operation see the Appendix.
☞ See the GPS Implementation and Aiding Features in u-blox wireless modules [9].
UBX-16010549 - R09 Product handling Page 23 of 28
C1-Public
Page 24

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
Appendix
A Recommended parts
Recommended parts are selected on data sheet basis only. Other components may also be used.
Part Manufacturer Part ID Remarks Parameters to consider
Diode ON
semiconductor
SAW TDK/ EPCOS B8401: B39162B8401P810 GPS+GLONASS High attenuation
TDK/ EPCOS B3913: B39162B3913U410 GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou For automotive application
TDK/ EPCOS B4310: B39162B4310P810 GPS+GLONASS Compliant to the AEC-Q200 standard
ReyConns NDF9169 GPS+ BeiDou
Murata SAFFB1G56KB0F0A GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou
Murata SAFEA1G58KB0F00 GPS+GLONASS
Murata SAFEA1G58KA0F00 GPS+GLONASS
Murata SAFFB1G58KA0F0A GPS+GLONASS
Murata SAFFB1G58KB0F0A GPS+GLONASS
TAI-SAW TA1573A GPS+GLONASS Low insertion loss
TAI-SAW TA1343A GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou Low insertion loss
TAI-SAW TA0638A GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou Low insertion loss
LNA JRC NJG1143UA2 LNA
Inductor Murata LQG15HS27NJ02 L, 27 nH
Capacitor Murata GRM1555C1E470JZ01 C, 47 pF DC-block
Ferrite
bead
Feed through Murata
capacitor
for signal
Feed
through
capacitor
Resistor
Table 4: Recommended parts
Murata BLM15HD102SN1 FB High IZI at fGSM
Murata NFM18PC ….
ESD9R3.3ST5G Standoff voltage>3.3 V Low capacitance < 0.5 pF
ESD9L3.3ST5G Standoff voltage>3.3 V
ESD9L5.0ST5G Standoff voltage>5 V Low inductance
NFL18SP157X1A3
NFA18SL307V1A45
NFM21P….
10 Ω ± 10%, min 0.250 W
560 Ω ± 5%
100 kΩ ± 5%
Monolithic type
Array type
0603 2A
0805 4A
R
bias
R2
R3, R4
Standoff voltage > Voltage for active
antenna
Low insertion loss, only for mobile
application
Low insertion loss, only for mobile
application
Low insertion loss, only for mobile
application
High attenuation, only for mobile
application
High attenuation, only for mobile
application
Low insertion loss, only for mobile
application
Low noise figure, up to 15 dBm RF input
power
Impedance at freq GPS > 500 Ω
Load capacitance appropriate to baud
rate
CL < xxx pF
Rs < 0.5 Ω
UBX-16010549 - R09 Appendix Page 24 of 28
C1-Public
Page 25

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
B Recommended antennas
Manufacturer Order no. Comments
Hirschmann (www.hirschmann-car.com) GLONASS 9 M GPS+GLONASS active
Taoglas (www.taoglas.com ) AA.160.301111 36 x 36 x 4 mm, 3-5 V 30 mA active
Taoglas (www.taoglas.com ) AA.161.301111 36 x 36 x 3 mm, 1.8 to 5.5 V / 10 mA at 3 V active
INPAQ (www.inpaq.com.tw) B3G02G-S3-01-A 2.7 to 3.9 V / 10 mA active
Amotech (www.amotech.co.kr) B35-3556920-2J2 35 x 35 x 3 mm GPS+GLONASS passive
Amotech (www.amotech.co.kr) A25-4102920-2J3 25 x 25 x 4 mm GPS+GLONASS passive
Amotech (www.amotech.co.kr) A18-4135920-AMT04 18 x 18 x 4 mm GPS+GLONASS passive
INPAQ (www.inpaq.com.tw) ACM4-5036-A1-CC-S 5.2 x 3.7 x 0.7 mm GPS+GLONASS passive
Additional antenna Manufacturer: Allis Communications, 2J, Tallysman Wireless
Table 5: Recommend antennas
UBX-16010549 - R09 Appendix Page 25 of 28
C1-Public
Page 26

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
Related documents
[1] NEO-M8L-0 (ADR4) Data sheet, UBX-15028320
[2] NEO-M8L-06B (ADR4) Data sheet, UBX-20058645
[3] u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification, UBX-13002887
[4] u-blox Package information reference guide, UBX-14001652
[5] GPS Antenna Application Note, UBX-15030289
[6] NEO-M8L, NEO-M8U Information Note, UBX-20053641
[7] GPS Compendium, GPS-X-02007
[8] http://www.nxp.com/documents/user_manual/UM10204.pdf – I2C-bus specification and user
manual, Revision 6, 20140404
[9] GPS Implementation and Aiding Features in u-blox wireless modules, GSM.G1-CS-09007
https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/4024 – Information technology equipment, Safety
Standard IEC 60950-1
☞ For regular updates to u-blox documentation and to receive product change notifications, register
on our homepage (www.u-blox.com).
UBX-16010549 - R09 Related documents Page 26 of 28
C1-Public
Page 27

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
Revision history
Revision Date Name Comments
R01 13-May-2016 ghun/mpel Advance Information
R02 28-Jun-2016 mpel Early production Information
R03 09-Nov-2016 njaf Production Information, added NEO-M8L-01A Data Sheet reference.
R04 28-Feb-2017 njaf Firmware update for NEO-M8L-0-12.
R05 09-Sep-2017 njaf Firmware version update for NEO-M8L-0-12, new PCN added.
R06 12-Sep-2018 njaf Added information about the new product type, NEO-M8L-04B.
R07 20-Mar-2020 ssid Advance information for NEO-M8L-05B
R08 23-Jun-2020 mala Early production information.
Added information on NEO-M8L, NEO-M8U information note in Document
information and Related documents.
Added disclosure restriction C1-Public.
R09 12-Feb-2021 njaf Added information about new product type number, NEO-M8L-06B .
Firmware version update for NEO-M8L-06B.
UBX-16010549 - R09 Revision history Page 27 of 28
C1-Public
Page 28

000000 NEO-M8L - Hardware integration manual
Contact
For complete contact information, visit us at www.u-blox.com.
u-blox Offices
North, Central and South America
u-blox America, Inc.
Phone: +1 703 483 3180
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Regional Office West Coast:
Phone: +1 408 573 3640
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Technical Support:
Phone: +1 703 483 3185
E-mail: support@u-blox.com
Headquarters
Europe, Middle East, Africa
u-blox AG
Phone: +41 44 722 74 44
E-mail: info@u-blox.com
Support: support@u-blox.com
Asia, Australia, Pacific
u-blox Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Phone: +65 6734 3811
E-mail: info_ap@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office Australia:
Phone: +61 3 9566 7255
E-mail: info_anz@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Beijing):
Phone: +86 10 68 133 545
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Chongqing):
Phone: +86 23 6815 1588
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shanghai):
Phone: +86 21 6090 4832
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shenzhen):
Phone: +86 755 8627 1083
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office India:
Phone: +91 80 405 092 00
E-mail: info_in@u-blox.com
Support: support_in@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Osaka):
Phone: +81 6 6941 3660
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Tokyo):
Phone: +81 3 5775 3850
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Korea:
Phone: +82 2 542 0861
E-mail: info_kr@u-blox.com
Support: support_kr@u-blox.com
Regional Office Taiwan:
Phone: +886 2 2657 1090
E-mail: info_tw@u-blox.com
Support: support_tw@u-blox.com
UBX-16010549 - R09 Contact Page 28 of 28
C1-Public
 Loading...
Loading...