Page 1

describes how to connect and configure Message Queuing Telemetry
u-connectXpress
MQTT
Application note
Abstract
This application note
Transport (MQTT) using u-connectXpress software.
UBX-19005066 - R03
C1-Public www.u-blox.com
Page 2

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
u-blox or third parties may hold intellectual property rights in the products, names, logos and designs included in this
document. Copying, reproduction, modification or disclosure to third parties of this document or any part thereof is only
permitted with the
The information contained herein is provided “as is” and u
implied, is given, including but not limited
purpose of the information. This document may be revised by u
documents, visit www.u
Copyright © u
Document information
Title u-connectXpress
Subtitle MQTT
Document type Application note
Document number UBX-19005066
Revision and date R03 22-Feb-2021
Disclosure restriction C1-Public
This document applies to the following products:
Product name Software version
NINA-W131 2.1.x onwards
NINA-W132 2.1.x onwards
NINA-W151 1.0.x onwards
NINA-W152 1.0.x onwards
NINA-W156 3.1.x onwards
ODIN-W260 7.0.x onwards
ODIN-W262 7.0.x onwards
ODIN-W263 7.0.x onwards
express written permission of u-blox.
-blox assumes no liability for its use. No warranty, either express or
to, with respect to the accuracy, correctness, reliability and fitness for a particular
-blox at any time without notice. For the most recent
-blox.com.
-blox AG.
UBX-19005066 - R03 Document information Page 2 of 18
C1-Public
Page 3

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
Contents
1 Overview ................................................................................................................................................ 4
2 MQTT-SN gateway ............................................................................................................................. 5
2.1 Connect MQTT-SN gateway to broker ................................................................................................... 6
2.1.1 URL format (for AT+UDCP and AT+UDDRP) ................................................................................ 6
2.1.2 Example Mosquitto test broker ....................................................................................................... 7
2.2 MQTT-SN client connect/disconnect ..................................................................................................... 8
2.3 MQTT-SN client publish ............................................................................................................................ 9
2.4 MQTT-SN client subscribe ...................................................................................................................... 10
2.5 MQTT-SN client PING ............................................................................................................................... 11
2.6 MQTT-SN sleeping clients ...................................................................................................................... 12
3 MQTT client gateway ...................................................................................................................... 14
3.1 Connect MQTT client gateway to broker ............................................................................................. 14
A Publish packet size limitations .................................................................................................... 15
B Glossary .............................................................................................................................................. 16
UBX-19005066 - R03 Contents Page 3 of 18
C1-Public
Page 4
u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
broker
MQTT-SN
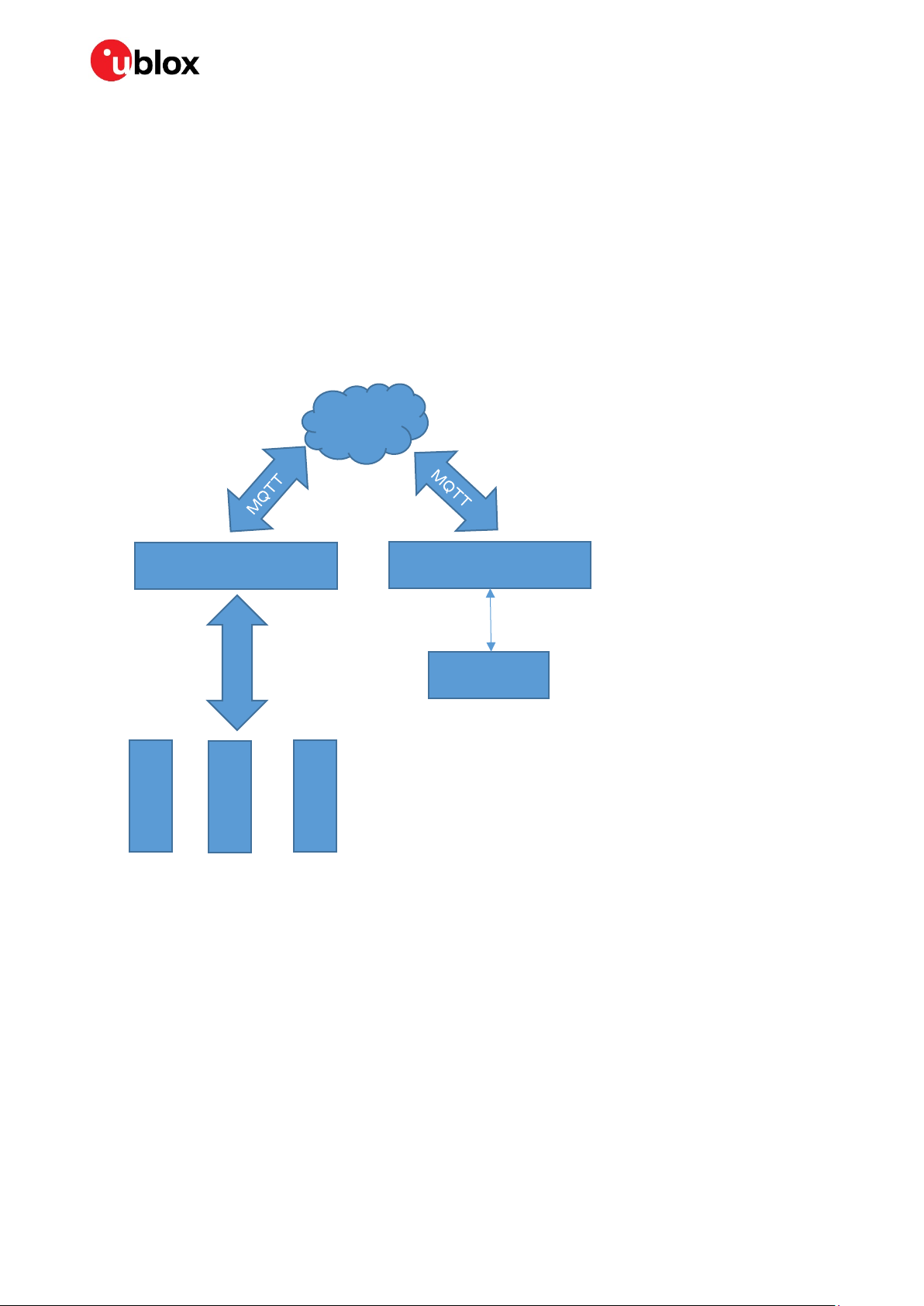
1 Overview
Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is a publish/subscribe, simple messaging protocol,
designed for communication between multiple devices. This application note describes how to
connect and configure MQTT using u-connectXpress software.
It is possible to configure the gateway as an MQTT-SN gateway. This is intended for end devices that
do not support TCP/TLS directly; instead, an end device connects to the gateway using a serial
connection such as Bluetooth SPS or SPP and communicates with the gateway using the MQTT-SN
protocol, as described in Figure 1.
It is also possible to configure the gateway as an MQTT client gateway. The host of the gateway can
then transmit or receive transparent MQTT data directly over the UART.
Figure 1: Gateway using a serial connection such as Bluetooth SPS or SPP with gateway communication using MQTT-SN
MQTT-SN gateway
SPP or SPS
End device
End device
MQTT
TCP / TLS
MQTT client gateway
UART
Host
End device
Different combinations of the configurations described in Figure 1 can also be achieved. Hence, it is
possible for the host, and the end devices to communicate with the MQTT broker via the same
gateway simultaneously.
For information about how to get started with a module, see the corresponding EVK user guides (EVKODIN-W2 user guide [1] and EVK-NINA-W1 and EVK-NINA-B2 user guide [4].
See the u-connect AT commands manual [3] for details of the AT commands that can be used with ublox short range stand-alone modules and the u-connectXpress user guide [2] for more information
on the u-connectXpress software.
Refer to the MQTT-SN v1.2 protocol specification available at http://mqtt.org/documentation for
information about the MQTT-SN protocol.
UBX-19005066 - R03 Overview Page 4 of 18
C1-Public
Page 5
u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
MQTT-SN
MQTT
SPP or SPS
TCP/TLS
Streams bound
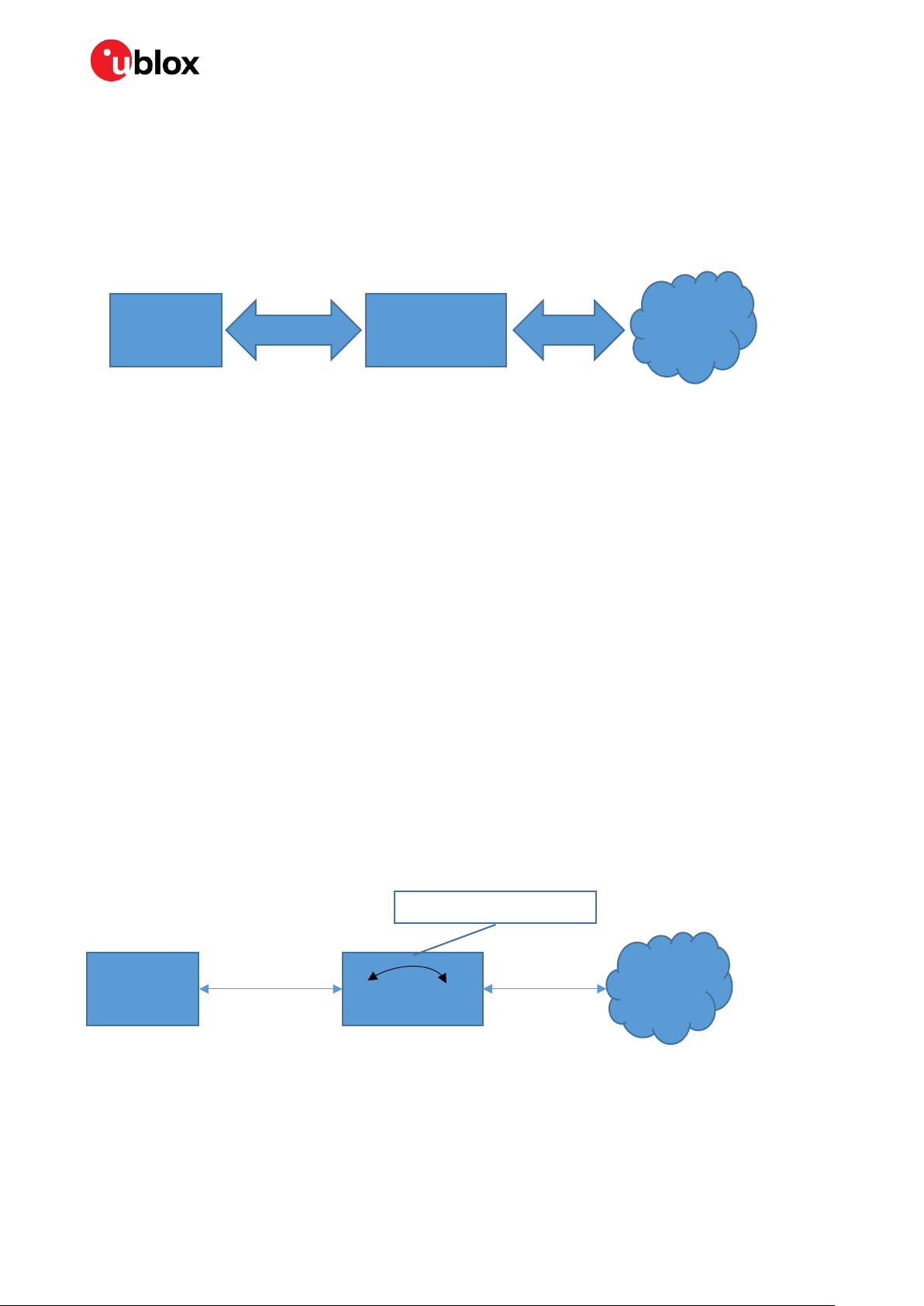
2 MQTT-SN gateway
An MQTT-SN (SN=Sensor Network) gateway enables end devices with no TCP/TLS support to
communicate with an MQTT broker (which requires TCP/TLS). The end device connects to the
gateway using a serial connection, such as Bluetooth SPS or SPP, and communicates using the
MQTT-SN protocol. The gateway then converts the MQTT-SN packets, from the end device, to MQTT
packets and sends to the broker and vice versa.
End Device
ANNA-B112 or
NINA-B1/B2/B3
Figure 2: End device connects to the gateway using serial connection
MQTT-SN
gateway
ODIN-W2 or
NINA-W15
MQTT
broker
The MQTT-SN gateway is an aggregating gateway, which means that there is only one TCP or TLS
connection to the MQTT broker. Hence, multiple end devices do not require one connection each as in
the case of a transparent gateway. This is good since many brokers limit the number of connections
and it is then better for many end nodes to share one TCP/TLS connection.
The end device will act as an MQTT-SN client (or client from here on) and it can publish or subscribe
to data identified by a unique topic string. The MQTT broker is data agnostic meaning it considers all
data to be a byte array. Hence, a publish data packet consists of:
• A topic string that uniquely identifies the data
• Data as a byte array.
The steps to get the MQTT-SN gateway configured and running typically are:
1. Create one or more MQTT streams by using the AT commands,
AT+UDCP or AT+UDDRP. The first
created stream will setup the actual TCP/TLS connection to the MQTT broker.
2. Create one or more end device streams, Bluetooth SPS or SPP, by using the AT commands,
AT+UDCP, AT+UDDRP or by enabling one of the associated services, AT+UDSC, for the end device to
connect to the gateway.
3. Bind the MQTT stream with the end device stream using one of the following:
o Dynamic bind, AT command
o Static bind configured using “
AT+UDBIND (requires host to execute the command)
sys.sid” key in stream URL (automatic bind once both the
connections are active)
End device
MQTT-SN
SPS
SPS
MQTT
MQTT on
TCP/TLS
MQTT
broker
Figure 3: End device acts as MQTT-SN client with agnostic MQTT broker
Gateway
☞ The end device must transmit and receive MQTT-SN packets on the Bluetooth SPS or SPP link.
Hence, some basic MQTT-SN packet parsing is required by the end device.
UBX-19005066 - R03 MQTT-SN gateway Page 5 of 18
C1-Public
Page 6
u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
MQTT on
TCP/TLS
The gateway does not support the full MQTT-SN specification. Only the following packet types are
supported:
• CONNECT / CONNACK (client connects to the gateway)
• DISCONNECT (client disconnects from the gateway or enter sleep mode)
• REGISTER / REGACK (client register topic to the gateway)
• PUBLISH / PUBACK (client or gateway forwards data)
• SUBSCRIBE / SUBACK (client subscribes to data identified with topic)
• PINGREQ / PINGRESP (client checks connection to the gateway or polls for data when in sleep
mode)
☞ To ease implementation of a propriety MQTT-SN end device, it is recommended to use the MQTT-
SN packet parser code available at https://github.com/eclipse/paho.mqtt-sn.embedded-c.
2.1 Connect MQTT-SN gateway to broker
The MQTT-SN gateway is configured using either the connect peer AT command, AT+UDCP, or the
default remote peer AT command,
AT+UDDRP.
Figure 4: MQTT-SN gateway connect to broker
Gateway
MQTT
broker
☞ One MQTT stream must be setup for every connected MQTT-SN end device. For example, if the
gateway must handle 5 parallel Bluetooth LE connected end devices, then five MQTT streams
must be activated. However, for sleeping clients, it is possible to have more clients than the MQTT
streams if they do not need to be connected simultaneously.
2.1.1 URL format (for AT+UDCP and AT+UDDRP)
mqtt://<host address>:<port>/?<keys>
• <host address>: Host name or IP address, e.g., test.mosquitto.org or 37.187.106.16
•
<port>: IP address port number, e.g., 1883
•
<keys>: key=value (with separating and character) for gateway to broker connection
MQTT related keys:
o client: Client name, e.g.,
o user: User name, e.g.,
client=my_client
user=my_user
☞ The end devices must ensure that data is transmitted to the broker within the keep-alive timeout.
o passwd: User password, e.g.,
o keepAlive: Keep alive timeout in seconds, e.g., keepAlive=60
o qos: Quality of Service level (0,1,2). Refer to the MQTT specification [5] for details.
If not, the broker may disconnect.
o
maxSnClients: Number of MQTT-SN clients supported, e.g., maxSnClients=24
Default is 16.
UBX-19005066 - R03 MQTT-SN gateway Page 6 of 18
C1-Public
passwd=my_passwd
Page 7

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
TLS related keys:
o
encr: TLS encryption without validating certificates if set to 1, e.g., encr=1
o
ca: Server CA for gateway to validate the server, e.g., ca=ca.pem
o
cert: Gateway client certificate, e.g., cert=client.pem
o
privKey: Gateway client private key, e.g., privKey=client.key
Static bind key:
o
sys.sid: Static bind of the MQTT stream to another stream, e.g., sys.sid=100
sys.sid 100-106: Incoming SPS service connections
sys.sid 200-206: Incoming SPP service connections
☞ A new incoming service connection will use the lowest free id currently.
•
sys.sid < 100: Used to bind two streams configured using +UDCP or +UDDRP. For
this case, use the same id for both streams.
The static bind will be activated when both streams have been connected or
reconnected.
☞ Since all MQTT streams share the same connection to the MQTT broker, most of the above
parameters must be identical for all the MQTT streams. The exception is the
will be different between the streams.
sys.sid key, which
☞ The certificates must be uploaded to the gateway using the security manager AT command
AT+USECMNG, or by using the s-center tool “Advanced connection and settings->Wi-Fi certificates”
tab.
2.1.2 Example Mosquitto test broker
List certificates
AT+USECMNG=3
"CA","mosquitto.org.crt"
"CC","client.pem"
"PK","client.key"
OK
TCP
at+udcp=mqtt://test.mosquitto.org:1883/?sys.sid=100
+UDCP:1
OK
+UUDPC:1,2,2,0.0.0.0,0,37.187.106.16,1883
TLS Encryption
at+udcp=mqtt://test.mosquitto.org:8883/?encr=1&sys.sid=100
+UDCP:1
OK
+UUDPC:1,2,2,0.0.0.0,0,37.187.106.16,8883
to make sure they are already uploaded:
TLS 1-way authentication
at+udcp=mqtt://test.mosquitto.org:8883/?ca=mosquitto.org.crt&sys.sid=100
+UDCP:1
OK
+UUDPC:1,2,2,0.0.0.0,0,37.187.106.16,8883
UBX-19005066 - R03 MQTT-SN gateway Page 7 of 18
C1-Public
Page 8

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
TLS 2-way-authentication
at+udcp=mqtt://test.mosquitto.org:8884/?ca=mosquitto.org.crt&cert=client.pem&privKey=clien
t.key&sys.sid=100
+UDCP:1
OK
+UUDPC:1,2,2,0.0.0.0,0,37.187.106.16,8884
☞ For the tests, the Mosquitto test broker (http://test.mosquitto.org/) is used. Note that this is an
open server and published data is visible to anyone. Hence, use only for initial testing.
☞ The “sys.sid=100” key would automatically bind the MQTT-SN stream to the first incoming SPS
connection.
☞ For the +UUDPC event, the local IP and port is not supported and is always set to 0.
2.2 MQTT-SN client connect/disconnect
For an end device to setup an MQTT-SN connection to the gateway, the CONNECT packet must be
sent. To terminate a previously setup MQTT-SN connection, the DISCONNECT packet is sent.
Figure 5: MQTT-SN client connect/disconnect
Sample packets:
CONNECT: 0x0A040001000041424344
Length: 0x0A
Type: 0x04 (CONNECT)
Flags: 0x00
Protocol id: 0x01
Duration: 0x0040 (Keep alive duration in seconds)
Client id: 0x41424344 (“ABCD”)
UBX-19005066 - R03 MQTT-SN gateway Page 8 of 18
C1-Public
Page 9

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
CONNACK 0x030500
Length: 0x03
Type: 0x05 (CONNACK)
Result: 0x00 (OK)
DISCONNECT: 0x0218
Length: 0x02
Type: 0x18 (DISCONNECT)
☞ It is recommended to set duration for the connect message. This prevents the gateway from
keeping track of clients that are no longer available. When the duration timer for a client has
elapsed, the gateway will delete the client.
☞ If the connection (for example, SPS or SPP) is lost and setup again, the end device should send
another
CONNECT (“unique client id”) or PINGREQ (“unique client id) to identify itself once again.
☞ For the CONNECT flags parameter, it is not supported.
2.3 MQTT-SN client publish
Before an MQTT-SN client can publish data to the MQTT broker, it must first register the data topic
to the gateway. It registers the topic name (string) and gets back a two-byte id, which is then used for
publishing data of that topic.
Figure 6: MQTT-SN client publish
Sample packets:
REGISTER: 0x090A00001234303132
Length: 0x09
Type: 0x0A (REGISTER)
Topic Id: 0x0000
Message id: 0x1234 (id or sequence number returned in the REGACK message)
Topic name: 0x303132 (“012”)
REGACK 0x070B0001123400
Length: 0x07
Type: 0x0B (REGACK)
Topic Id: 0x0001 (Returned topic id to used in PUBLISH)
Message id: 0x1234 (id or sequence number of the REGISTER message)
Result: 0x00 (OK)
UBX-19005066 - R03 MQTT-SN gateway Page 9 of 18
C1-Public
Page 10

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
PUBLISH: 0x0A0C0000012345010203
Length: 0x0A
Type: 0x0C (PUBLISH)
Flags: 0x00
Topic Id: 0x0001
Message id: 0x2345 (id or sequence number returned in the PUBACK message)
Data: 0x010203
PUBACK 0x070D0001234500
Length: 0x07
Type: 0x0D (PUBACK)
Topic Id: 0x0001
Message id: 0x2345 (id or sequence number of the PUBLISH message)
Result: 0x00 (OK)
☞ Set the PUBLISH flags parameter to 0 as it is not supported. The gateway will use DUP=0 (first
time),
which is 2-byte id)
QoS=0 (send once), Retain=0 (do not store), Will=0 (no will), TopicIdType=0 (normal topic id,
2.4 MQTT-SN client subscribe
An MQTT-SN client can subscribe on topics using the SUBSCRIBE message. When data for a subscribed
topic is updated, the
PUBLISH message is received from the gateway.
Figure 7: MQTT client subscribe
SUBSCRIBE: 0x0812001234303132
Length: 0x08
Type: 0x12 (SUBSCRIBE)
Flags: 0x00
Message id: 0x1234 (id or sequence number returned in the SUBACK message)
Topic name: 0x303132 (“012”)
SUBACK 0x0813000001123400
Length: 0x08
Type: 0x13 (SUBACK)
Flags: 0x00
Topic Id: 0x0001 (Returned topic id used in PUBLISH)
Message id: 0x1234 (id or sequence number of the SUBSCRIBE message)
Result: 0x00 (OK)
PUBLISH: 0x0A0C0000010000010203
Length: 0x0A
UBX-19005066 - R03 MQTT-SN gateway Page 10 of 18
C1-Public
Page 11

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
Type: 0x0C (PUBLISH)
Flags: 0x00
Topic Id: 0x0001
Message id: 0x0000 (not used by gateway for PUBLISH messages)
Data: 0x010203
☞ Flags in the SUBSCRIBE message is not supported. Hence, set to 0. Gateway will use DUP=0 (first
time),
QoS=0 (send once), TopicIdType=0 (topic name as string).
☞ The message id (sequence number) of the PUBLISH message is always 0 when sent by the
gateway.
☞ For the subscribe topic, neither the multi-level character, “#”, or the single-level character, “+”, is
supported.
2.5 MQTT-SN client PING
An MQTT-SN client may use the PING message to check that the connection to the gateway is alive.
Also, if the keep-alive duration for the MQTT-SN connection is set, it is the client that must assure
that data is transmitted to avoid a disconnection. The PINGREQ can then be used.
Figure 8: MQTT-SN client PING
The PINGREQ with client identifier can also be used if the serial connection, e.g., SPS or SPP, is lost
and reconnected. It may then be necessary for the client to identify itself in order for the gateway to
associate the client with a new stream. Hence, it is recommended to always start with a PINGREQ
including the unique client id after a reconnection of the serial link, for example, SPS or SPP.
PINGREQ: 0x0216
Length: 0x02
Type: 0x16 (PINGREQ)
PINGREQ with client id: 0x0816434C49454E54
Length: 0x08
Type: 0x16 (PINGREQ)
Client id: 0x434C49454E54 (“CLIENT”)
PINGRESP 0x0217
Length: 0x02
Type: 0x17 (PINGRESP)
UBX-19005066 - R03 MQTT-SN gateway Page 11 of 18
C1-Public
Page 12

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
☞ If a response to a PINGREQ is a DISCONNECT (instead of a PINGRESP), it means that the gateway
has lost track of the client or even deleted it. It may then be needed to do a CONNECT, REGISTER,
SUBSCRIBE to restore the connection.
2.6 MQTT-SN sleeping clients
It is possible for an MQTT-SN client that is in sleep mode to terminate the serial connection (for
example, SPS or SPP), enter low power mode (to save power), wake-up and setup the serial connection
and poll if there has been any data transmitted to the client while asleep. The gateway will store the
messages subscribed by the client while asleep.
Figure 9: MQTT-SN sleeping clients
Once the client has set up the connection, it uses the PINGREQ message with the unique client
identifier to poll the gateway for data. The gateway then sends stored messages to the client and
ends with the PINGRESP message to indicate that no more data is available.
☞ The gateway only stores the latest update for each topic.
☞ By default, the gateway can serve a maximum of 16 clients. It is possible to change this by using
the URL
UBX-19005066 - R03 MQTT-SN gateway Page 12 of 18
C1-Public
maxSnClients keyword when configuring the MQTT stream(s).
Page 13

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
☞ If the gateway needs to store a lot of messages for many clients, it is possible that it may run out
of RAM memory, which will cause the gateway to restart. Hence, it is very important to test every
specific configuration to make sure that the gateway is not overloaded.
☞ The number of active MQTT-SN streams limits the number of parallel active clients.
UBX-19005066 - R03 MQTT-SN gateway Page 13 of 18
C1-Public
Page 14
u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
MQTT
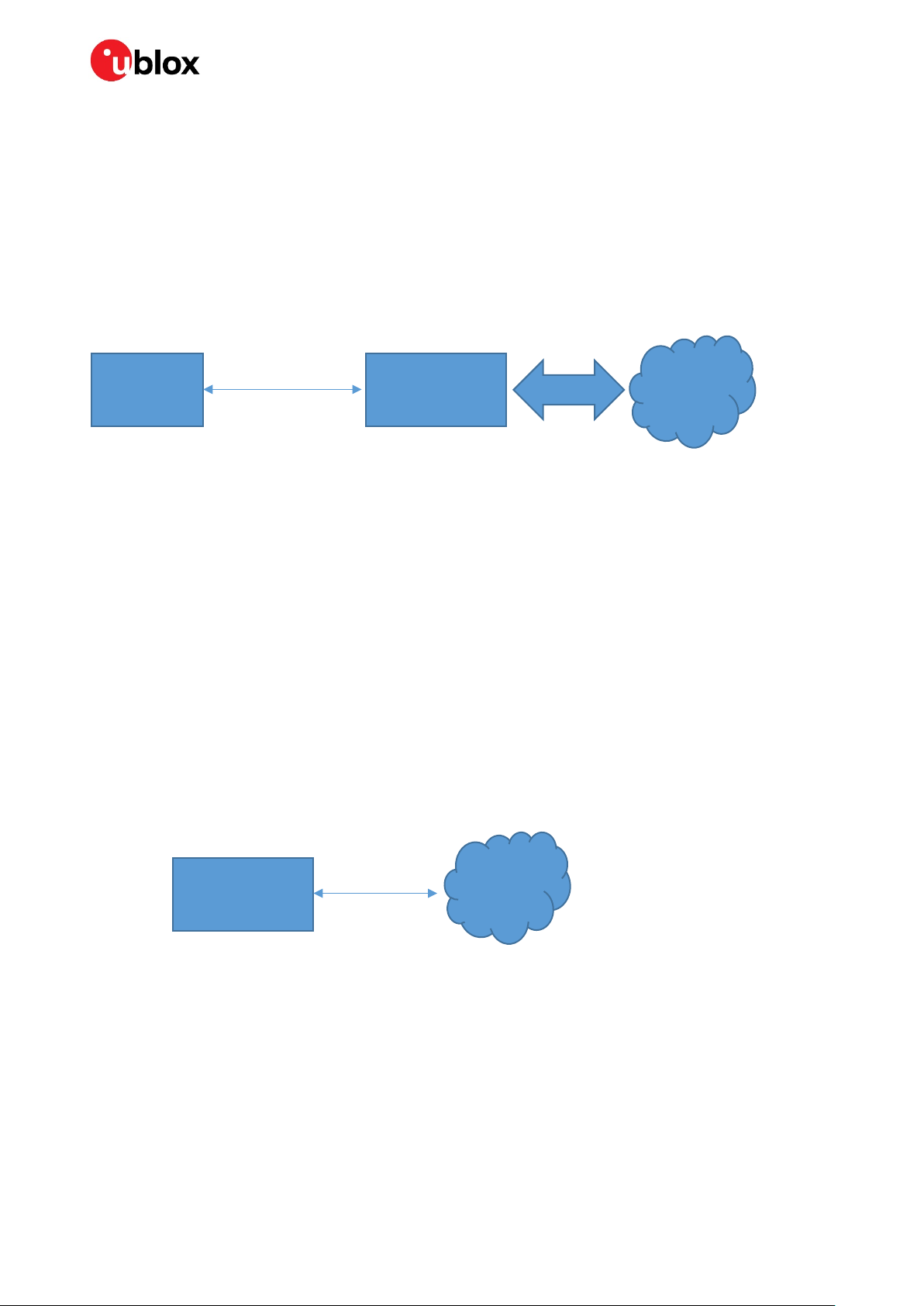
3 MQTT client gateway
The gateway can also be configured as an MQTT client gateway and not as a full MQTT-SN gateway.
It is then possible for a host to transmit and receive MQTT data on the UART transparently.
In data mode, transmitted data will be published to one configured publish topic and received data will
be received from one configured subscribe topic.
In EDM (extended data mode) mode, it is possible to configure one publish topic and one subscribe
topic for every EDM channel. The host can then transmit and receive data on separate channels and
thus publish and subscribe to as many topics as there are defined by the channels.
Host MQTT gateway
UART
(data mode or EDM)
ODIN-W2 or NINA-W13/
Figure 10: MQTT client gateway
NINA-W15
TCP/TLS
MQTT
broker
The data transmitted and received on the UART is the actual MQTT data only without any topic
information (configuration specifies what topic it is). For the data mode, it means that if the host
transmits two consecutive packets of size 5 and 10 bytes, it may be written to the MQTT Broker as
one packet of 15 bytes since there is no delimiting information. Similarly, long packets may be split
before being sent to the MQTT broker. For EDM, this is not an issue since every EDM write packet is
transmitted separately to the MQTT broker. For EDM related restriction refer to the u-blox Extended
Data Mode protocol specification [6].
An MQTT client stream is configured using the commands
+UDCP or +UDDRP. The first created stream
will setup the actual TCP/TLS connection to the MQTT broker.
3.1 Connect MQTT client gateway to broker
The MQTT client gateway support is implemented as an MQTT stream according to the u-connect
software concepts. This means that it is configured using URLs either with the connect command
(AT+UDCP) or the default remote peer command
AT+UDDRP.
Gateway
MQTT on
TCP/TLS
MQTT
broker
Figure 11: MQTT client connect to broker
The URL format is similar to the MQTT-SN URL format, except for the following keys:
•
pt: Publish topic, e.g., pt=ubx/test/1
•
st: Subscribe topic, e.g., st=ubx/test/1
•
maxSnClients: Not used
☞ If an MQTT stream is configured without the “pt” and “st” keys, the stream will be an MQTT-SN
stream. If any of the “
pt” or “st” keys are used, the stream will be an MQTT client stream.
☞ For the subscribe topic, the multi-level character, ‘#’, is supported, as in st=ubx/test/#. The single-
level character ‘
UBX-19005066 - R03 MQTT client gateway Page 14 of 18
C1-Public
+’ is not supported.
Page 15

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
Appendix
A Publish packet size limitations
NINA-W13/NINA-W15 MQTT MQTT-SN
u-connectXpress 3.0 onwards topic length + payload length + 8 <=1024 topic length + payload length + 8 <=1024
u-connectXpress 2.1 and earlier topic length + payload length + 8 <= 320 MQTT-SN header length + payload length
<= 255 bytes
Table 1 NINA-W1x packet size limitations (bytes).
ODIN-W2 MQTT MQTT-SN
SW 7.2 and earlier topic length + payload length + 8 <= 320 MQTT-SN header length + payload
length <= 255 bytes
SW 8.0 and later topic length + payload length + 8 <= 320 topic length + payload length + 8 <= 320
Table 2 ODIN-W2 packet size limitations (bytes).
☞ MQTT header length is 8 bytes (6 bytes with QOS=0)
☞ MQTT-SN header is 2-4 bytes.
☞ MQTT-SN payload also contains 5 bytes of flags, TopicId and MsgId.
☞ The memory used for MQTT messages is a ring buffer and maximizing message size and sending messages frequently
may result in buffer overruns.
UBX-19005066 - R03 Appendix Page 15 of 18
C1-Public
Page 16

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
B Glossary
Abbreviation Definition
CA Certification Authority
EDM Extended Data Mode
IP Internet Protocol
LE Low Energy
MQTT Message Queuing Telemetry Transport
MQTT-SN MQTT for Sensor Networks
QOS Quality Of Service
SN Sensor Network
SPP Serial Port Profile
SPS Serial Port Service
TCP Transmission Control Protocol
TLS Transport Layer Security
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
Table 3: Explanation of the abbreviations and terms used.
UBX-19005066 - R03 Appendix Page 16 of 18
C1-Public
Page 17

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
W2 in some
W1x modules in some
Related documents
[1] EVK-ODIN-W2 user guide, UBX-16007132
[2] u-connectXpress user guide, UBX-16024251
[3] u-connectXpress AT commands manual, UBX-14044127
[4] EVK-NINA-W1 and EVK-NINA-B2 user guide, UBX-17011007
[5] MQTT home page, https://mqtt.org
[6] u-blox Extended Data Mode, Protocol specification, UBX-14044126
☞ For product change notifications and regular updates of u-blox documentation, register on our
website, www.u-blox.com.
Revision history
Revision Date Name Comments
R01 19-Mar-2019 tfri, cmag Initial release.
R02 30-Oct-2019 flun Included NINA-W13 v2.1.x and NINA-W15 v1.0.x in the applicable products
table on page 2.
Provided reference to NINA-W1x modules in addition to ODIN-
sections. Provided reference to ANNA-B112/NINAfigures. Added links to related documents.
R03 22-Feb-2021 mape Added appendix A. Included NINA-W156 and ODIN-W263. Other minor fixes.
UBX-19005066 - R03 Related documents Page 17 of 18
C1-Public
Page 18

u-connectXpress MQTT - Application note
Contact
For complete contact information, visit us at www.u-blox.com.
u-blox Offices
North, Central and South America
u-blox America, Inc.
Phone: +1 703 483 3180
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Regional Office West Coast:
Phone: +1 408 573 3640
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Technical Support:
Phone: +1 703 483 3185
E-mail: support@u-blox.com
Headquarters
Europe, Middle East, Africa
u-blox AG
Phone: +41 44 722 74 44
E-mail: info@u-blox.com
Support: support@u-blox.com
Asia, Australia, Pacific
u-blox Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Phone: +65 6734 3811
E-mail: info_ap@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office Australia:
Phone: +61 3 9566 7255
E-mail: info_anz@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Beijing):
Phone: +86 10 68 133 545
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Chongqing):
Phone: +86 23 6815 1588
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shanghai):
Phone: +86 21 6090 4832
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shenzhen):
Phone: +86 755 8627 1083
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office India:
Phone: +91 80 405 092 00
E-mail: info_in@u-blox.com
Support: support_in@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Osaka):
Phone: +81 6 6941 3660
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Tokyo):
Phone: +81 3 5775 3850
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Korea:
Phone: +82 2 542 0861
E-mail: info_kr@u-blox.com
Support: support_kr@u-blox.com
Regional Office Taiwan:
Phone: +886 2 2657 1090
E-mail: info_tw@u-blox.com
Support: support_tw@u-blox.com
UBX-19005066 - R03 Contact Page 18 of 18
C1-Public
 Loading...
Loading...