Page 1

u-center
GNSS evaluation software for Windows
User guide
Abstract
This document leads you through the efficient use of the u-center
evaluation software, the powerful and easy to use tool from u-blox for
evaluating, performance analysis and configuration of u-blox GNSS
positioning chips and modules.
www.u-blox.com
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public
Page 2

u-center-User guide
Document information
Title u-center
Subtitle GNSS evaluation software for Windows
Document type User guide
Document number UBX-13005250
Revision and date R26 15-Mar-2021
Document status Production information
Disclosure restriction C1-Public
This document applies to the following products:
Product name Type number Firmware version PCN reference
u-center
u-blox or third parties may hold intellectual property rights in the products, names, logos and designs included in this
document. Copying, reproduction, modification or disclosure to third parties of this document or any part thereof is only
permitted with the express written permission of u-blox.
The information contained herein is provided "as is" and u-blox assumes no liability for its use. No warranty, either express
or implied, is given, including but not limited to, with respect to the accuracy, correctness, reliability and fitness for a
particular purpose of the information. This document may be revised by u-blox at any time without notice. For the most recent
documents, visit www.u-blox.com.
Copyright © 2021, u-blox AG.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
Page 2 of 71
Page 3

u-center-User guide
Contents
1 Preface.......................................................................................................................................5
1.1 Overview.................................................................................................................................................... 5
1.2 Using this guide.......................................................................................................................................5
1.3 Technical support....................................................................................................................................5
1.3.1 Worldwide Web............................................................................................................................... 5
1.3.2 By email............................................................................................................................................ 5
1.3.3 Helpful information when contacting technical support....................................................... 5
2 Features....................................................................................................................................6
3 Getting started...................................................................................................................... 7
3.1 General information about displayed values..................................................................................... 7
3.2 Connecting an u-blox evaluation kit to the PC................................................................................. 7
3.3 Installing u-center................................................................................................................................... 7
3.4 Connect to the receiver......................................................................................................................... 8
3.4.1 Select the port................................................................................................................................ 8
3.4.2 Select the baud rate (only for COM ports)................................................................................9
4 Concept and philosophy................................................................................................... 10
4.1 Color and satellite coding scheme....................................................................................................11
4.2 Operating modes.................................................................................................................................. 12
4.2.1 Online mode.................................................................................................................................. 13
4.2.2 Stop mode..................................................................................................................................... 13
4.2.3 Record mode................................................................................................................................. 13
4.2.4 Play mode.......................................................................................................................................13
4.2.5 Relations between modes..........................................................................................................13
4.2.6 Database limitations...................................................................................................................14
4.2.7 Receiver information................................................................................................................... 15
5 u-center menus and windows......................................................................................... 16
5.1 Main frame and toolbars.....................................................................................................................16
5.1.1 Standard menu bar..................................................................................................................... 16
5.1.2 Standard toolbar.......................................................................................................................... 25
5.1.3 Views toolbar................................................................................................................................ 25
5.1.4 Communication toolbar..............................................................................................................25
5.1.5 Logfile toolbar............................................................................................................................... 25
5.1.6 Action toolbar............................................................................................................................... 26
5.1.7 Standard statusbar..................................................................................................................... 26
5.2 Views and windows.............................................................................................................................. 27
5.2.1 Packet console.............................................................................................................................. 27
5.2.2 Binary console...............................................................................................................................28
5.2.3 Text console.................................................................................................................................. 29
5.2.4 Icons and text field of console views.......................................................................................30
5.2.5 Regular expression evaluation.................................................................................................. 30
5.2.6 Messages view..............................................................................................................................32
5.2.7 Generation 9 configuration view...............................................................................................34
5.2.8 Statistic view................................................................................................................................ 37
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
Contents Page 3 of 71
Page 4

5.2.9 Table view...................................................................................................................................... 38
5.2.10 Map view......................................................................................................................................39
5.2.11 Chart view................................................................................................................................... 45
5.2.12 Histogram view...........................................................................................................................48
5.2.13 Camera view................................................................................................................................50
5.2.14 Deviation map.............................................................................................................................50
5.2.15 Sky view....................................................................................................................................... 52
6 NTRIP...................................................................................................................................... 53
6.1 NTRIP client........................................................................................................................................... 53
6.2 NTRIP server/caster............................................................................................................................. 54
7 Google Earth server............................................................................................................56
8 Tools........................................................................................................................................ 58
8.1 Firmware update................................................................................................................................... 58
8.2 Legacy Firmware update u-blox 5 - 8............................................................................................... 60
8.3 Dump receiver diagnostics................................................................................................................. 61
8.4 GNSS configuration..............................................................................................................................61
8.4.1 Read/Write configuration files.................................................................................................. 62
8.4.2 Editing configuration file............................................................................................................ 62
8.5 Preferences.............................................................................................................................................63
9 How To.................................................................................................................................... 64
9.1 Change baud rate of receiver.............................................................................................................64
9.2 Save parameters to receiver non-volatile memory (BBR/Flash)................................................. 64
9.2.1 Saving parameters with UBX-CFG-CFG.................................................................................. 64
9.2.2 Saving parameters with GNSS configuration........................................................................65
9.3 Recording/Playing a log file.................................................................................................................65
9.4 Conduct sensitivity tests....................................................................................................................65
9.5 Read/Write configuration files...........................................................................................................66
9.6 Set GNSS configuration......................................................................................................................66
9.7 Change epoch detection method......................................................................................................66
10 Troubleshooting................................................................................................................ 68
Related documents................................................................................................................ 69
Revision history.......................................................................................................................70
Page 5

u-center-User guide
1 Preface
1.1 Overview
u-center is u-blox's powerful GNSS evaluation and visualization tool which can be downloaded freeof-charge from our website (www.u-blox.com). This user guide provides a description of the features
of this software. It allows end users to assess and test u-blox GNSS positioning chips and modules
for navigation and positioning performance.
The purpose of u-center is to enable users to:
• Conduct performance tests on u-blox and other GNSS devices.
• Configure u-blox GNSS positioning chips and modules.
• Update the firmware on GNSS modules.
• Test the added performance provided by u-blox's AssistNow service.
1.2 Using this guide
This guide assumes that the user has basic computer skills and is familiar with the Windows
Graphical User Interface (GUI) and GNSS receiver environments.
The following symbols are used to highlight important information:
An index finger points out key information pertaining to integration and performance.
A warning symbol indicates actions that could negatively impact u-center behavior.
1.3 Technical support
If you have questions about installing or using u-center:
• Read this user guide carefully.
• Check our homepage (https://www.u-blox.com) to ensure that your GNSS device, firmware and
the u-center software are the latest versions.
• Refer to our web based information service.
1.3.1 Worldwide Web
Our website (www.u-blox.com) is a rich pool of information. Product information and technical
documents can be accessed 24/7.
1.3.2 By email
If you have technical problems or cannot find the required information in the provided documents,
contact the closest technical support office. To ensure that we process your request as soon as
possible, use our service pool email addresses rather than personal staff email addresses. Contact
details are at the end of the document.
1.3.3 Helpful information when contacting technical support
When contacting technical support, have the following information ready:
• Receiver type (e.g. NEO-7N), firmware version (e.g. 1.00), u-center release (e.g. u-center 8.00).
• Receiver configuration and short description of the application.
• Your complete contact details.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
1 Preface Page 5 of 71
Page 6

u-center-User guide
2 Features
u-center evaluation software provides system integrators and end users with a quick and simple
way to interface with u-blox GNSS chipsets, modules and boards. It enables easy evaluation,
performance testing, development and debugging of GNSS positioning chips and modules. u-center
allows easy connection to u-blox products and provides a suite of features to view, log, and analyze
performance. The features include:
• Support for u-blox's receivers using u-blox positioning technology. u-center can communicate
with these receivers using either the UBX protocol or the NMEA-0183 standard protocol.
• Support for receivers that utilize standard NMEA strings.
• u-center presents all the information collected during the operation of the GNSS device. All
aspects of GNSS data (position, velocity, time, satellite tracking, etc.) can be monitored and
logged under various test scenarios for the evaluation of a receiver. u-center software allows
analysis of the collected data in order to investigate performance issues such as accuracy, road
test position and trajectory, satellite tracking, time to first fix, etc. All processed data can be
captured in ASCII format and ported into popular spreadsheets for creating additional plots
and statistics.
• Camera View: photographic data can be stored in the log file together with the navigation data
and later be replayed in the application.
• Export data files to Google Earth and Google Maps.
• Supports (Multiple GNSS) AssistNow Online and AssistNow Offline.
• Data recording and playback function.
• Structural and graphical data visualization in real-time.
• Export functionality to standard PC applications.
• Docking views (real-time cockpit instruments): Satellite constellation, compass, clock,
altimeter, speedometer, GNSS and satellite information views.
• Download firmware updates to GNSS positioning modules.
• Support for NTRIP server and NTRIP client functionality.
• Google Earth server support.
• SQLITE database support
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
2 Features Page 6 of 71
Page 7

u-center-User guide
3 Getting started
3.1 General information about displayed values
• Longitude and latitude are displayed according to the datum selected in the GNSS device
(either the default WGS-84 or based on user-defined parameters). This option can be polled
and set using the UBX-CFG-DAT message.
• Time is displayed with reference to UTC.
• Elevation is displayed with reference to either MSL (Height above Mean Sea Level or
Orthometric Height) or to HAE (Height Above WGS-84-Ellipsoid). The reference is controlled by
the GNSS configuration.
3.2 Connecting an u-blox evaluation kit to the PC
This section assumes that you have purchased an u-blox evaluation kit. Should you try to connect a
module or IC receiver directly to the PC, make sure you use appropriate RS-232 level shifters.
The evaluation kit can be connected to the PC by using either an USB or a serial cable. In case of using
the USB port, a driver is required (installed by the u-center for Windows installer or downloadable
from our homepage). Be sure to install the driver before connecting the evaluation kit to the
computer.
3.3 Installing u-center
The installation program guides you through the necessary steps for a successful program
installation. During the installation, you can choose the destination folder for the program.
u-center uses dynamic link libraries (DLL). The installation program will automatically install
the required DLL's into the u-center program directory. Should you try to copy a u-center
installation from one location to another after the installation, make sure you copy the DLL
files as well.
After a successful installation, u-center can be started from the Start Menu (All Programs > u-blox
> u-center > u-center) and will start up as shown in Figure 1.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
3 Getting started Page 7 of 71
Page 8

u-center-User guide
Figure 1: Start display
3.4 Connect to the receiver
3.4.1 Select the port
Locate the communication toolbar (Figure 2) and click on the arrow beside the icon. This will show
a list with all available COM ports (Figure 3). Select the corresponding COM port where the receiver
is connected. If a link could be established, the icon will turn green and the text in the status bar
changes from to (in this example u-center is connected to COM6). This does
not mean that the communication already works but only that the port could be opened.
Figure 2: Communication Toolbar
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
3 Getting started Page 8 of 71
Page 9

u-center-User guide
Figure 3: List of available COM ports
3.4.2 Select the baud rate (only for COM ports)
Again in the communication toolbar, click on the arrow beside the icon. This will show a
list with all available baud rates (Figure 4). Select the correct baud rate on which the receiver is
communicating (typically 9'600 baud). If u-center is able to decode data from the receiver, the status
bar begins to blink in green as shown in the following icon: . This means that the connection is
established successfully and the communication between the receiver and u-center is working.
Figure 4: List of available baud rates
Now you are ready to use the receiver.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
3 Getting started Page 9 of 71
Page 10

u-center-User guide
4 Concept and philosophy
Understanding the basic concept behind u-center is important in order to get the highest benefit out
of this powerful evaluation software. Figure 5 depicts the architecture of the software. The program
gets a data stream from either a communication port or a log file and splits this stream into protocol
messages. From the messages, relevant parameters are extracted and inserted into the current
dataset of the database that is used by the display and analysis features of the application.
In the current dataset, statistical values of the parameters are calculated. Average, minimum,
maximum and standard deviation are calculated for most parameters. If the available messages do
not provide a parameter, u-center tries to calculate the parameter from the ones that are available.
For example if velocity-north and velocity-east are available, u-center calculates the speed over
ground and course over ground, unless this data is already available in other messages.
Figure 5: Engine architecture
The u-center database size may be adjusted. If the size is exceeded u-center keeps only the latest
datasets and the oldest ones are removed. Refer to Database limitations for the details.
Very long recordings may decrease performance of u-center.
u-center provides various view classes (described below) for display and presentation. Most views
take their data from the database, but some get their data directly from the message without using
the database at all. The other views are updated when the database changes.
• Message Views display and decode a copy of every known message. These views allow observing
a single message in detail and they may also be used to configure the GNSS device. Refer to
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
4 Concept and philosophy Page 10 of 71
Page 11

u-center-User guide
Messages view for details. The configuration view is a subset of the message view and only
displays message to configure the receiver.
• Console Views display the messages in text form. There is also a wide range of information
available which is useful for evaluation and testing. Refer to sections Packet console, Binary
console and Text console for details.
• Graphical Views display parameters from the database in graphical form. Charts (see Chart
view), histograms (see Histogram view) and a map view (see Map view) can be created. There are
two more views (deviation map and sky view, see Deviation map and Sky view) that may be used
for statistical performance and antenna pattern analysis.
• Tabular Views show the parameters of the database in tabular form. They can be freely
configured to allow customized tables. Refer to Table view and Statistic view for details.
• Docking Windows can be docked to the frame of u-center. An analog watch, compass, world
map, altitude and speed meter are available. There are also docking windows showing the current
signal power and the constellation of the satellites received by the device as well as a summary
of the GNSS status.
Displaying various views and docking windows requires computing power. Minimizing or
closing them may significantly reduce CPU usage.
4.1 Color and satellite coding scheme
In the graphical views and some docking windows, colors are used to indicate data quality. Table 1
shows the color codes for graphical views depending on the quality of the navigation solution.
Color Meaning
Yellow
Orange
Green
Cyan
Magenta
Blue
Red
Table 1: Color-coding scheme for graphical views
Current value
Valid 3D navigation fix + Dead Reckoning
Valid 3D navigation fix
Valid 2D navigation fix
Dead Reckoning fix
Degraded navigation fix
No or invalid navigation fix
Table 2 gives the color-coding scheme for the docking windows and sky view. It indicates the state
of each satellite.
Color Meaning
Green
Olive
Dark Green
Satellite used in navigation (with Ephemeris)
Satellite used in navigation (with Ephemeris and PPP)
Satellite used in navigation (with aiding data: AssistNow Autonomous, AssistNow Online/Offline)
Cyan
Blue
Red
Table 2: Color-coding scheme for the docking windows and sky view
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
Satellite signal available, available for use in navigation
Satellite signal available, not available for use in navigation
Satellite signal not available
4 Concept and philosophy Page 11 of 71
Page 12

u-center-User guide
Table 3 gives the satellite-coding scheme for the docking windows and sky view. It indicates to which
GNSS a satellite belongs.
Code System
Gxx GPS
Rxx GLONASS
Bxx BeiDou
Exx Galileo
Sxx SBAS
Qxx QZSS
Table 3: Satellite-coding scheme for the docking windows and sky view
Figure 6 shows the Status Color configuration. This is available under: Tools > Preferences > Status
Colors.
Figure 6: Color-coding configuration
4.2 Operating modes
u-center has different operating modes (see Figure 7). The mode changes when you open or close
a log file or when you invoke the player. To be able to use the record mode you have to create a new
file, save to a new file or open an existing file. The record and play mode are only available if you have
created a new file or when you have opened a writable file.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
4 Concept and philosophy Page 12 of 71
Page 13

Figure 7: Relation between operating modes
u-center-User guide
4.2.1 Online mode
In this mode a GNSS device is directly connected to u-center via a COM port. u-center can control
and configure the receiver and it will display the data that the receiver is sending periodically.
4.2.2 Stop mode
In this mode no data from a receiver or a log file is forwarded to the database and views. u-center is
in this mode when a log file is open but player and recorder are not active.
4.2.3 Record mode
Record Mode is the same mode as the Online Mode, except u-center additionally creates a log file,
concatenating all the messages sent by the receiver. You enter this mode by creating a new log file
or opening an existing log file without write protection and pressing the record button. An example
of using this mode would be to make overnight measurements and evaluate the data at a later time.
u-blox customer support may request a log file from you when you are experiencing a problem with
one of our receivers and will usually need this to be recorded with debug data enabled (see Receiver).
4.2.4 Play mode
The Play Mode allows replaying a previously recorded log file step by step, in real-time or at an
accelerated rate. You enter this mode by opening a file and pressing the play, step or scan button.
4.2.5 Relations between modes
The operating mode depends on the status of the log file player. Modes are changed by user actions.
Each mode has different states that are changed by a user action or by an event (see Figure 7). In
Online mode and Record mode, u-center displays data from the receiver. In Play mode data from a
log file is displayed. Play mode has different states:
• Play reads and displays messages periodically from the log file. The user interface is derived from
that of a CD player. u-center updates the views after each message.
• Step gets one message from the log file and immediately returns to paused Play state.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
4 Concept and philosophy Page 13 of 71
Page 14

u-center-User guide
• Scan reads messages periodically but the display is only updated when paused or by changing
the state.
Position can be set in a log file. This behaves differently in Play mode and Stop mode. In Stop mode
the position is just set and no data is read and displayed. u-center will start recording or playing from
that position when changing the mode. If position is set in Play mode, u-center will load the data up
to this position from the log file and display the contents.
4.2.6 Database limitations
The number of epochs displayed by views that show history (Table, Chart, Histogram, Sky, Satellite
level history etc.) can be limited in order to allow an efficient analysis of large log files and not to
consume too much disk space. There is a setting which controls this history database limit, which
is available under: Tools > Preferences > General. By default the value for the number of epochs is
set to 0, which means the database size is not limited. Any other number higher than 0 will limit the
size of this history database. When this limit is set, then the oldest values will be discarded after the
database reaches this limit size. Data stored to a log file is not affected by the database limitation.
Also controlled in Tools > Preferences > General is the max number of messages stored. This limit
applies to how many messages from a log file can be loaded and are playable. The default value for
this is set very high, but can be reduced to save disk space, or increased if a very large log file cannot
be fully loaded.
Figure 8: Example of setting maximum number of epochs to keep in database
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
4 Concept and philosophy Page 14 of 71
Page 15

u-center-User guide
For long-term observations, it is recommended to record the messages to a log file.
If a high value of epochs is selected, the display of data in real-time cannot be guaranteed,
especially when graphical views are open.
4.2.7 Receiver information
u-center will try to retrieve some information about what kind of receiver is connected by sending
UBX-MON-VER message on every successful connection. In this way certain functionality can
automatically be disabled if it is not supported by the connected receiver. In some cases this might
not be the desired behavior as it might hinder some other operation where these extra messages
are not desired. There is a setting that controls if receiver information is auto-retrieved or not, and
that is available under: Tools > Preferences > General. By default the auto retrieval is enabled.
Figure 9: Enabling/disabling automatic receiver information retrieval
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
4 Concept and philosophy Page 15 of 71
Page 16

u-center-User guide
5 u-center menus and windows
5.1 Main frame and toolbars
The main frame is the primary display screen of u-center. It displays all tool bars and some of the
information provided by the device. In the standard status bar, information about communication,
UTC time, connection time, used protocol (NMEA or UBX), used file, etc. is shown.
Button tool tip: A description about each button in the toolbars can be obtained by holding the
mouse cursor over the button for a few seconds. A tool tip message will appear near the icon with
additional information while a detailed description is displayed in the status display.
Figure 10: u-center main frame and toolbars
5.1.1 Standard menu bar
All u-center functions can be accessed through the standard menu bar. Commands can also be
accessed by shortcuts that are listed in the menus. Some often used operations are also available
in the different toolbars.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 16 of 71
Page 17

5.1.1.1 File
Figure 11: File menu entries
u-center-User guide
Function Description Shortcut /
New... Creates a new log file. No data is yet written but only the file is opened. The
duration of the logging time is displayed in the status bar field Operating time.
Save... Creates a new log file, saves the data from the internal database to the log file and
starts immediately recording all new data from the receiver. This is useful when an
error or an unexpected event occurred and no log file was recorded. The size of the
ring buffer (4 MB) is large enough to retain the data for the last hour (approx.).
Open... Opens a stored log file to be replayed. Ctrl+O
Close Closes the active file.
Database Empty Deletes the internal database and all saved values.
Database Export Exports the internal database into HTML or KML data formats for displaying with
Google Map or Google Earth.
Google Map Html... Exports the internal database into HTML data format for displaying with Google
Map.
Google Earth Kml... Exports the internal database into KML data format for displaying with Google
Earth.
Google Earth Server... Starts u-center's Google Earth server which allows continuous and real time
tracking to be visualized in Google Earth.
Print... Prints the active document.
Print Preview Shows a preview of the print output.
Print Setup... Shows the setup dialog of the printer.
Recent Files Lists all recently used files.
Toolbar icon
Ctrl+N /
Ctrl+S /
Ctrl+E /
Exit Exits u-center. Ctrl+F4
Table 4: File menu entries
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 17 of 71
Page 18

5.1.1.2 Edit
Figure 12: Edit menu entries
u-center-User guide
Function Description Shortcut /
Cut Cut the current selection and put in to the clipboard. Ctrl+X / Shift
Copy Copy the current selection to the clipboard. Ctrl+C / Ctrl-
Paste Paste the clipboard content to the current position. Ctrl+V / Shift
Delete Delete the current selection. Del
Select All Select all in the current view. Ctrl+A
Clear All Clear all in the current view. Ctrl+Del
Table 5: Edit menu entries
Toolbar icon
+Del /
Insert /
+Insert /
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 18 of 71
Page 19

5.1.1.3 View
u-center-User guide
Figure 13: View menu entries
Function Description Shortcut /
Packet Console Opens the packet console.
Binary Console Opens the binary console.
Text Console Opens the text console.
Messages View Opens the dialog with all supported messages.
Configuration View Opens the dialog with all configuration messages. This is a subset of the
Generation 9
Configuration View
Statistic View Opens the statistic view with all data from the internal database.
Table View Opens the empty table view. All values from the internal database can be
Recent Table View Lists all the table views that have been opened. This information comes from the
Map View Opens a window allowing to display a map.
Recent Map View Lists all the maps views that have been opened. This information comes from the
Messages View.
Opens the dialog for Generation 9 Advance configuration view. All the Generation
9 receivers should be configured with this new dialog.
displayed individually.
Windows registry and is also valid after a restart of u-center.
Windows registry and is also valid after a restart of u-center.
Toolbar icon
F6 /
F7 /
F8 /
F9 /
Ctrl-F9 /
F10 /
F11 /
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 19 of 71
Page 20

u-center-User guide
Function Description Shortcut /
Chart View Opens a window with chart functionality. All values from the internal database can
be displayed individually.
Recent Chart View Lists all the chart views that have been opened. This information comes from the
Windows registry and is also valid after a restart of u-center.
Histogram View Opens a window with histogram functionality. All values from the internal
database can be displayed individually.
Recent Histogram View Lists all the histogram views that have been opened. This information comes from
the Windows registry and is also valid after a restart of u-center.
Camera View Opens a window allowing to connect to a web cam and visualize and save the
image.
Deviation Map Opens a window with a position deviation map.
Sky View Opens a window with the sky view. The current position of the satellites and their
values from the internal database are shown.
Docking Windows Opens a list with all available docking windows that can be shown.
Satellite Position Shows or hide the current satellite positions.
Satellite Level Shows or hide the current satellite levels.
Satellite Level History Shows or hide the history of the satellite levels.
World Position Shows or hide the current position on the world map.
Data Shows or hide data from the navigation solution (like position, TTFF, accuracy and
DOPs).
Altitude Meter Shows or hide the altitude meter.
Toolbar icon
F12 /
Compass Shows or hide the compass.
Speed Meter Shows or hide the speed meter.
Watch Shows or hide the clock.
Toolbars Opens a list with all available toolbars that can be shown.
Standard Toolbar Shows or hide the standard toolbar.
Views Toolbar Shows or hide the views toolbar.
Receiver Toolbar Shows or hide the receiver toolbar.
Player Toolbar Shows or hide the player toolbar.
Action Toolbar Shows or hide the action toolbar.
Table 6: View menu entries
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 20 of 71
Page 21

5.1.1.4 Player
Figure 14: Player menu entries
u-center-User guide
Function Description Shortcut /
Eject Closes the active log file.
Pause Pauses reading or recording from the active log file.
Record Starts recording to a new or already opened log file. Any data in the internal
database will not be written to the file. If you want to save this data into a log file,
open the File menu and click Save. To stop recording, press the same button.
Stepback Single step function. The previous message is read.
Step Single step function. The next message is read. Ctrl+Space /
Play Starts reading from the active log file. The speed of the action can be chosen on
the sub-menu.
Scan Reads the entire log file into the database and updates the display at the end of
the scan period.
Goto Begin Sets the read position to the beginning of the log file.
Goto End Sets the read position to the end of the log file.
Table 7: Player menu entries
Toolbar icon
Ctrl+E /
Ctrl+P /
Ctrl+R /
Ctrl+B /
Ctrl+G /
Ctrl+F /
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 21 of 71
Page 22

5.1.1.5 Receiver
u-center-User guide
Figure 15: Receiver menu entries
Function Description Shortcut /
Connection Defines the port u-center connects to. The list is generated automatically using
the enumeration method under Tools > Preferences > Generic > Serial ports. The
currently used port will be indicated.
Disconnect Disconnects from a connected receiver.
COMx Connects to COMx with the current baud rate.
Network connection Connects to a receiver through network.
Location API Connects to the receiver using the Location API available in windows 7 onwards.
Sensor API Connects to the receiver using the Sensor API in Windows 7 and Windows 8 (the
USB Sensor driver is required in this case) but not in Windows 10.
Baud rate Defines the baud rate of the communication. The list is predefined and cannot be
changed. The currently set baud rate will be indicated.
NTRIP Server/Caster Enables u-center to act as a NTRIP server.
NTRIP Client Enables u-center to act as a NTRIP client.
Autobauding Enables or disables autobauding for the current communication with the receiver.
Debug Messages Enables all debug messages in the receiver. Can be requested from u-blox
support.
Generation Defines the generation of the attached u-blox GNSS receiver. u-center also tries to
detect automatically the correct generation.
Protocol Filter Sets the message filter against versions of protocol specification.
Action Lists all possible actions that can be performed with the u-blox GNSS receiver.
Toolbar icon
Ctrl+[1...9]
(if available)
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 22 of 71
Page 23

u-center-User guide
Function Description Shortcut /
Hot start Sends a hot start command to the receiver. No data is deleted in the receiver.
Warm start Sends a warm start command to the receiver. Only the ephemeris are deleted
Cold start Sends a cold start command to the receiver. All information is deleted from the
Save Config Saves the current receiver configuration to the memory so that it will be loaded
Load Config Loads the last saved configuration from the memory.
Revert Config Deletes all configurations in the memory and reverts the receiver to the default
Auto Detect Enable/Disables the automatic polling of the UBX-MON-VER message to allow u-
Get Information Manually polls the receiver for a UBX-MON-VER message. On receiving the
Differential DGNSS
Interface…
Epoch detection… Defines which time information determines the boundary of an epoch detection in
Table 8: Receiver menu entries
from the memory.
memory.
after a restart.
configuration.
center to obtain information about the receiver. On receiving the message, the
receiver information contained within the message is extracted, stored and used
by u-center for any receiver specific features. Having this feature enabled allows
u-center to automatically be aware of the type of receiver attached. Disabling
this feature might be useful when the random appearance of UBX-MON-VER
messages could interfere with the current users task.
message, the receiver information contained within the message is extracted,
stored and used by u-center for any receiver specific features. Typical use would
be when the users need auto detection disabled, but would like u-center to be
aware of the connected receiver's details.
Allows the streaming of RTCM messages to the receiver for high precision
applications.
u-center (see Change epoch detection method).
Toolbar icon
5.1.1.6 Tools
Figure 16: Tools menu entries
Some of the menu items will only be displayed when the correct receiver generation is connected
and identified by u-center. If you cannot select one option, change the receiver generation under
Receiver > Generation.
Function Description Shortcut /
Firmware Update u-blox
5 - 8...
Dump Receiver
Diagnostics...
Opens the firmware update dialog for u-blox 5 - 8 generation receivers. Ctrl+U
Tool to create the receiver diagnostic. Can be requested by the u-blox support
team.
Toolbar icon
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 23 of 71
Page 24

u-center-User guide
Function Description Shortcut /
u-blox 7/8/M8 Retrieve
Log...
AssistNow Offline Opens the AssistNow Offline dialog. Please switch over to AssistNow Offline as
AssistNow Online Opens the AssistNow Online dialog. Please switch over to AssistNow Online as the
GNSS Configuration... Opens the dialog to save the receiver configuration to a file on the PC or to restore
File transfer... Opens the dialog to transfer a file to the receiver.
Preferences... Opens the dialog for the u-center preferences.
Table 9: Tools menu entries
Opens the dialog to download log information from the receiver. This is supported
only since u-blox 7 receivers.
the Legacy AssistNow Offline service is marked deprecated.
Legacy AssistNow Online service is marked deprecated.
a configuration from a file on the PC.
Toolbar icon
5.1.1.7 Window
Figure 17: Window menu entries
Function Description Shortcut /
Cascade Arranges all open dialogs cascaded.
Tile Horizontally Arranges all open dialogs horizontally.
Tile Vertically Arranges all open dialogs vertically.
Close All Closes all open dialogs and windows.
Save Workspace As... Saves the position of the open dialogs and windows to a file on the computer.
Restore Workspace
From...
Recent Workspace Lists all recently used workspace files.
Arrange Icons Arranges the icons at the bottom of the window.
List of dialogs and
windows
Table 10: Window menu entries
Restores the position of the dialogs and windows from a file on the computer.
Lists all visible and hidden dialogs and windows in u-center.
Toolbar icon
5.1.1.8 Help
Figure 18: Help menu entries
Function Description Shortcut /
Contents... Gives a reference to this user guide. F1
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 24 of 71
Toolbar icon
Page 25

u-center-User guide
Function Description Shortcut /
About u-center... Shows the about dialog with the software version and the used libraries and their
versions.
Table 11: Help menu entries
Toolbar icon
5.1.2 Standard toolbar
The standard toolbar gives access to standard operations like opening and saving files, print the
current view or empty the database.
5.1.3 Views toolbar
5.1.4 Communication toolbar
5.1.5 Logfile toolbar
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 25 of 71
Page 26

5.1.6 Action toolbar
u-center-User guide
5.1.7 Standard statusbar
The standard status bar is updated automatically and shows the information about the opened file,
the connection and the time. The following fields are available:
Status display: Displays the current action or the function of a button if the mouse cursor is over
the button.
NTRIP client information: Shows the connection to an NTRIP caster (only when activated through
Receiver > NTRIP Client...). Clicking on it will show up to 100 of the last errors between u-center and
connected NTRIP caster.
NTRIP server information: Shows the status and number of clients currently connected to ucenter's NTRIP caster (only when activated through Receiver > NTRIP Server/Caster...). Clicking on
it will show up to 100 of the last errors between u-center's NTRIP caster and connected clients.
DGNSS information: Shows the connection to a DGNSS source (only when activated through
Receiver > Differential GNSS Interface...).
Receiver generation: u-center tries to automatically detect the type of device connected and
activates the appropriate mode of operation in order to take optimal advantage of the features. The
mode can also be manually selected through the menu bar (Receiver > Generation).
Port information: Shows the active COM port and baud rate. Color coding of the icon:
Disconnected
Waiting for first data
Data is being received but errors are detected (mostly because of wrong baud rate settings)
Last data received was valid but there is no data to collect at this time
No data is being received but errors have been detected in the past
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 26 of 71
Page 27

u-center-User guide
Data is being received and collected at the correct baud rate
File: The file opened in the u-center player.
Protocol information: This box indicates the current message set that is being used to
communicate with the device.
Operating time: The time elapsed since you started u-center.
UTC time: The current time sent by the device. This field is only updated if a receiver is connected.
Receiver status: Shows the last known status of the receiver. Color coding of the icon:
Power status of receiver is unknown
Receiver is powered on
Receiver is powered off
5.2 Views and windows
5.2.1 Packet console
The packet console lists all incoming and outgoing messages, and provides information about
message length and type. The direction of the message is shown in the following way:
R <- Indicates the message was sent to the receiver
R -> Indicates the message came from the receiver
L -> Indicates the message came from the log file
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 27 of 71
Page 28

u-center-User guide
Figure 19: Packet console
Refer to Table 12 for an explanation of the icons and text field.
5.2.2 Binary console
The binary console lists all incoming messages in binary and ASCII format.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 28 of 71
Page 29

u-center-User guide
Figure 20: Binary console
Refer to Table 12 for an explanation of the icons and text field.
5.2.3 Text console
The text console displays the content messages in textual form such as UBX-INF or NMEA
messages.
NMEA messages are shown with heading $Gxyyy, where x stands for the satellite system (P = GPS,
SBAS, QZSS, L = GLONASS, A = Galileo, B = BeiDou, N = Any combination of GNSS) and yyy for the
type of message (e.g. ZDA=Time & Date).
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 29 of 71
Page 30

u-center-User guide
Figure 21: Text console displaying UBX-INF and NMEA messages with "Show PC Time" and "Show/hide epoch markers"
enabled
Refer to Table 12 for an explanation of the icons and text field.
5.2.4 Icons and text field of console views
Element Name Description
Lock / Locked Prevents the console from being updated with new data when locked. Pause key can
/
Clear All Erases all data in the console.
Show/Hide PC time Shows/Hides the PC time in the console.
Show/Hide epoch
markers
Filter on/off Filters unwanted data from the data stream. This allows searching for certain
Pause player Pauses the player when the search expression is found. Only works in playback mode.
Table 12: Description of the buttons and text field of the console views
be used to Lock/Unlock the current console window.
Shows/Hides text for every new epoch with enumeration.
expression, e.g. all RMC messages.
5.2.5 Regular expression evaluation
Normally, when you search for a sub-string in a string, the match should be exact. So if we search
for a sub-string "abc" then the string being searched should contain these exact letters in the same
sequence for a match to be found. We can extend this kind of search to a case insensitive search
where the sub-string "abc" will find strings like "Abc", "ABC" etc. That is, the case is ignored but the
sequence of the letters should be exactly the same. Sometimes, a case insensitive search is also not
enough. For example, if we want to search for numeric digit, then we basically end up searching for
each digit independently. This is where regular expressions come in to our help. Regular expressions
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 30 of 71
Page 31

u-center-User guide
are text patterns that are used for string matching. Regular expressions are strings that contain a
mix of plain text and special characters to indicate what kind of matching to do. Here's a very brief
tutorial on using regular expressions.
Suppose, we are looking for a numeric digit then the regular expression we would search for is "[0-9]".
The brackets indicate that the character being compared should match any one of the characters
enclosed within the bracket. The dash (-) between 0 and 9 indicates that it is a range from 0 to 9.
Therefore, this regular expression will match any character between 0 and 9, that is, any digit. If we
want to search for a special character literally we must use a backslash before the special character.
For example, the single character regular expression "\*" matches a single asterisk. In the table below
the special characters are briefly described. A regular expression search is case-sensitive.
Character Description
^ Beginning of the string. The expression "^A" will match an "A" only at the beginning of the string.
[^ The caret (^) immediately following the left-bracket ([) has a different meaning. It is used to exclude the
$ The dollar sign ($) will match the end of the string. The expression "abc$" will match the sub-string "abc"
| The alternation or logic OR character (|) allows either expression on its side to match the target string. The
. The dot (.) will match any character.
* The asterisk (*) indicates that the character to the left of the asterisk in the expression should match 0 or
+ The plus (+) is similar to asterisk but there should be at least one match of the character to the left of the +
? The question mark (?) matches the character to its left 0 or 1 times.
() The parenthesis affects the order of pattern evaluation.
[] Brackets ([ and ]) enclosing a set of characters indicates that any of the enclosed characters may match the
Table 13: Regular expression syntax
remaining characters within brackets from matching the target string. The expression "[^0-9]" indicates
that the target character should not be a digit.
only if it is at the end of the string.
expression "a|b" will match "a" as well as "b".
more times.
sign in the expression.
target character.
5.2.5.1 Examples
Let's assume that the lines in Figure 22 would appear in the NMEA console without filtering.
Figure 22: Regular Expression Template
5.2.5.1.1 Example 1
Searching for the RMC with a valid position and all GGA Messages:
GP(GGA|RMC,.*,A,)"
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 31 of 71
Page 32

u-center-User guide
Figure 23: Regular Expression Example 1
5.2.5.1.2 Example 2
Searching for all GSV with the message index of "2" or "3":
GSV,.*,[2-3],
Figure 24: Regular Expression Example 2
5.2.5.1.3 Example 3
Searching for all messages starting with $GP, which have a "G" in the message identifier but not at
the first position:
^\$GP.+G.*,
Figure 25: Regular Expression Example 3
5.2.5.1.4 Example 4
Searching for all messages having a checksum of which the higher nibble is 3
\*3.$
Figure 26: Regular Expression Example 4
5.2.6 Messages view
The messages view is utilized to communicate with the device. Receiver output messages (e.g.
navigation output, status and debug information) are displayed; input messages (e.g. configuration
messages) can be sent. There are different sections for NMEA and UBX protocol. See Figure 27 for
an overview of the different elements in the messages view.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 32 of 71
Page 33

u-center-User guide
Figure 27: Messages view
/
Table 14: Description of the buttons in the messages view toolbar
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
Lock /
Locked
Clear All Erases the entire message view.
Send Sends the current message to the device.
Poll Polls the selected message once.
Auto poll Automatically polls a newly selected message once.
Message
Hotkey
Prevents the message view from being updated with new data when locked. Pause key can be used
to Lock/Unlock the current view window.
Assigns a hotkey to the selected message.
5 u-center menus and windows Page 33 of 71
Page 34

5.2.6.1 Receiver output messages
u-center-User guide
Figure 28: Message display of an output message
Double-clicking on an output message enables or disables the periodic message update if
the communication protocol is active. This feature is currently only supported for the UBX
protocol.
5.2.7 Generation 9 configuration view
The new u-blox Generation 9 configuration view allows the users to check the current configuration
of the receiver and change it if needed. This view can only be used to configure u-blox 9 generation
receivers.
By default, the configuration values being edited come from (and can be written back to) an
attached receiver. This view consists of two different sub-views, GNSS Configuration and Advanced
Configuration.
5.2.7.1 GNSS configuration
This GNSS configuration sub-view enables the users to poll and configure the basic and advanced
GNSS system configurations of the attached receiver. This sub-view describes sections below:
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 34 of 71
Page 35

u-center-User guide
Figure 29: u-blox Generation 9 Advanced Configuration View
Basic This section shows the GNSS constellation configuration of the receiver by pressing
Advanced This section shows the GNSS constellation signal information configured in the
Show Hex/ Hide Hex Shows or hides the hex values that make up the messages describing the receiver
Status Shows the status of the action taken. See position d.
Write to layer Once selected the desired layer, Send configuration button sends the GNSS
Poll Active Configuration (RAM
Layer)
Table 15: Description of the buttons and sections in the GNSS Configuration sub-view
Poll Active Configuration. The receiver’s GNSS constellations can also be configured
by enabling/disabling the required satellite constellations, and then pressing Send
Configuration. See position a.
receiver by pressing Poll Active Configuration. The receiver’s GNSS signals can also
be configured by enabling/disabling the required signals, and then pressing Send
Configuration. See position b.
configuration just sent or received. See position c.
constellation and signal information to the receiver. See position e.
Polls the GNSS constellation and signal configuration from RAM layer of the attached
receiver. See position f.
5.2.7.2 Advanced Configuration
In the Advanced Configuration sub-view, all groups of configuration items are displayed in a tree
structure. Expanding a group will show the RAM layer values for all readable configuration items in
that group. Each item is read individually from the receiver as the group is expanded. Some item
values may not be known to the receiver in which case the value will be shown as "-".
If no receiver is attached or if the receiver does not support the new configuration concept then no
values will be visible. If the receiver is not responding for some reason then close the group and open
it again to retry.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 35 of 71
Page 36

u-center-User guide
Figure 30: Advanced Configuration view
Users can expand items of interest and u-center will attempt to read values for all the other layers
such as BBR, flash, ROM, pin, etc. and display any that it finds. This sub-view contains sections
below:
Configuration item search To search for an item by name, type into the search text box just above the tree. The
Configuration item tree view All entries that contain the search text will be highlighted in red. The search will check
Selected Configuration Item This section describes the selected item in more detail. The field having the searched
Load differences from default Click on Load receiver differences from default to read the configuration values
Send config changes "Send config changes" will send the current set of settings to the attached receiver.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
search is case-insensitive. See position a.
for a match in group and item names, titles and descriptions. If a group contains an
item which matches then the group will be highlighted as well. See position b.
item is shown in red. See position c.
set in the receiver. This can be used to duplicate the current settings in another
receiver. The operation depends on the working mode of the tool. If used in the
normal, attached to receiver mode then the "writes" list will be populated with any
settings in the FS or BBR layers. See position d.
A tick will appear next to the items which were successfully altered in the receiver.If
the receiver does not acknowledge the request, a cross appears. If there is no tick or a
cross, the receiver does not respond to the request. Items are sent in groups of values
to be sent to the same layer. If one value for a layer cannot be written, then all values
for that layer will fail to be written and will show a cross. See position e.
5 u-center menus and windows Page 36 of 71
Page 37

u-center-User guide
Items to delete If an item that can be deleted from the receiver (if it is in the BBR or Flash layers) is
Items to set If a writable layer item is selected, then press one of the layer buttons to add write
Remove from list Removes the selected item from one of the lists. See position h.
Clear lists Removes all the items from all the lists. See position i.
Load from file... Loads a group of settings from a readable text file. See position j.
Save to file... To save the current list of settings to a readable text file, click Save to file... and
Message hex codes Lists the hex values for the UBX-CFG-VALSET message that will be constructed for
Table 16: Description of the buttons and sections in the Advanced Configuration sub-view
selected from the tree, then a button Delete will appear. If that button is selected
then it will be added to the list of deletions shown in the "Items to delete" section on
the right of the tree. See position f.
operations to a list of item writes. A value can be changed by clicking on it in the top
left sub-view area before writing. If two values for the same item are selected in the
same layer, then the earlier one will be highlighted in red to show that it will be ignored
as a duplicate setting. See position g.
choose a file path. This will produce a file in the ASCII format. See position k.
setting the selected configuration properties. See position l.
5.2.8 Statistic view
Figure 31: Statistic view
All available database values (transmitted from the device or calculated by u-center) are displayed.
The following statistics are displayed:
• Current value
• Minimum value
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 37 of 71
Page 38

u-center-User guide
• Maximum value
• Average value
• Standard Deviation
The following color scheme for the values is applied:
• Grey color: The value was not set for the current epoch
• Blue color: The value was calculated by the application from other data
• Empty field: No data is available
Choosing "Database Empty" in the file menu or pressing the button clears the statistic
view.
The content of the statistic view can easily be exported to other programs using Copy/
Paste.
5.2.9 Table view
Figure 32: Table view
All values from the database can be displayed in a tabular form (Figure 32). This is very useful when
analyzing the log file in detail.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 38 of 71
Page 39

u-center-User guide
To add a new column, first select the desired value (Figure 33) and click the button. To remove a
displayed value, click the button. To see the table header click the button. Statistical information
will be shown for 4 seconds.
Figure 33: Selecting a new value
The number of displayed epochs is set to 1800 by default.
Choosing "Database Empty" in the file menu or pressing the button clears the table view.
The content of the table view can easily be exported to other programs using Copy/Paste.
5.2.10 Map view
u-center can display positions on pre-calibrated or Google online (dynamic) maps (see Figure 34).
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 39 of 71
Page 40

u-center-User guide
Figure 34: Map view with Google online map
5.2.10.1 Using map view
If you want to use the Google online maps you have to enter an API key in Tools > Preferences >
Access Tokens. A missing API key can lead to the output shown in Figure 35.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 40 of 71
Page 41

u-center-User guide
Figure 35: Missing online map API key
Please go to https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/static-maps/?hl=en to
get a valid Google Static Maps API key.
You can access the view specific commands in two different ways:
• Using the command in the tool bar below the map view.
• Holding the cursor inside the map view and pressing the right mouse button. This will open the
following context menu (see Figure 36).
Figure 36: Map view context menu
Function Description Shortcut /
Cursor The position of the cursor is shown on the lower left edge of the u-center screen
Move The map inside the map view window can be moved.
Zoom In The map is enlarged by selecting a rectangle.
Zoom Out The size of the map is decreased.
Zoom Zoom the map to a specified level.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
(Longitude, Latitude and Pixel-Position). By holding the left mouse button and
moving the cursor over the map you can measure distance from one position to
another.
5 u-center menus and windows Page 41 of 71
Toolbar icon
Page 42

u-center-User guide
Function Description Shortcut /
Fit Map The map size is adjusted to fit the Map Window.
Markers Add or remove the defined markers (see also section Map calibration)
Meter Show or hide the ruler.
Speedvector Show or hide the speed vectors, and select where they are drawn from.
Follow Centers the map on the current GNSS position.
Drawing Mode The size and form of the displayed position can be changed in the menu Points;
Open Map... / Recent
Static Maps
Online Maps Use online maps. Select the type in the menu and also if they should be
Save map (only in
toolbar)
Image settings (only in
toolbar)
Table 17: Description of the buttons and context menu entries in map view
the connection line between the points can be selected in the menu Connect. To
see statistical values (average, minimum, maximum, standard deviation) directly
in the map, select the menu entry Statistic.
Open a new or one of 8 recently used static maps.
automatically downloaded when the current position moves out of the current
map tile (Auto Reload). The menu option Show Map Scales allows you to select a
different scale of the tiles. The menu option Show vector from reference to rover
will show the vector pointing from reference to rover if such configuration exists.
In this case, auto zoom capability exists to track the two by selecting the option
Auto zoom on reference and rover.
Save the current map view to a file (combined with all visible elements or only the
map).
Brightness, contrast and color saturation of map can be adjusted by moving the
glides.
Toolbar icon
/ /
/
Map Views can be copied to the clipboard using the "Print Screen" function.
Choosing "Database Empty" in the file menu or pressing the button clears the statistic
view.
5.2.10.2 Map calibration
To create your own map you will need a digitized map or a picture with orthogonal projection in one
of the following pixel graphics formats.
png Portable Network Graphics
bmp Windows Bitmap
dib Device Independent Bitmap
gif Graphics Interchange Format
jpg/jpeg Jpeg File Interchange Format
pcx PC Paintbrush
tif Tag Image File Format
If your map is not in one of the above formats, you can simply convert it in one of the supported
formats by a third party program.
To use a map in u-center, three calibration points are needed. For these points you have to know the
pixel coordinates and the according WGS84 coordinates in the latitude/longitude format in degrees
(longitude: -180.0° to 180.0°, latitude: -90.0° to 90.0°). These points are stored in the map calibration
file. The calibration file must be stored at the same location as the bitmap itself. It has the same
name but a different extension (*.mcf). The format of the calibration file is very simple and can be
edited in a simple editor like notepad.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 42 of 71
Page 43

u-center-User guide
5.2.10.2.1 Example
As an example we will have a look at the virtual map file world.png and its calibration file
world.mcf.
Figure 37: Digital map file: world.png
The Map has 1765 pixels (0 to 1764) in the horizontal and 1046 pixels (0 to 1045) in the vertical
direction. The origin is the upper left corner. To calibrate this map we will use the following three
calibration points (#1 to #3).
Pixel WGS84
Reference Point # X Y Longitude Latitude
Upper Left Corner 1 0 0 -180.0 90.0
Lower Right Corner 2 1764 1045 180.0 -90.0
Upper Right Corner 3 1764 0 180.0 90.0
Table 18: Calibration reference points
Coordinate
To determine the exact pixel position you can use Microsoft Paint (mspaint.exe) or any other pixelediting program.
The calibration file is a plain ASCII text file. The file may contain comments. The file consists of two
sections, which start with keywords encapsulated in braces.
The REFERENCE section, which is mandatory, contains the three points used to calibrate a map.
Each reference point is on a single line and has the following syntax: # = <x>, <y>, <lon>,
<lat> where
•
# is the index of the reference point
•
<x> is the horizontal image coordinate
•
<y> is the vertical image coordinate
•
<lat> is the latitude in degrees and WGS84
•
<lon> is the longitude in degrees and WGS84.
The optional MARKER section defines additional points on the map. Each point is on a single line with
the syntax: # = i, <x>, <y>[, <text>] or # = c, <lat>, <lon>[, <text>] where
•
# is the index of the marker point
•
i indicates that the coordinates relate to the image
•
c indicates that the coordinates relate to the world
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 43 of 71
Page 44

u-center-User guide
•
<x> is the horizontal image coordinate
•
<y> is the vertical image coordinate
•
<lat> is the latitude in degrees and WGS84
•
<lon> is the longitude in degrees and WGS84.
•
<text> is a optional string in quotes labeling the marker point.
The points must have a unique index from 1 to <num>. The maximum marker point index <num> is
written to the same section on a separate line with the syntax Count = <num>.
Figure 38: Map calibration file: world.mcf
5.2.10.2.2 Map calibration tool
u-center includes a built-in calibration tool for providing coordinates to maps and photographs in
supported data formats to create u-center maps. To use the tool open the map view window as seen
in Figure 39 and then open the file of the map to be calibrated.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 44 of 71
Page 45

u-center-User guide
Figure 39: Opening map view window
If the file to be opened has not been calibrated, the message in Figure 40 will appear.
Figure 40: No calibration information found
Select three points on the map and enter the calibration coordinates in the specified format as seen
in Figure 41.
Figure 41: Calibrating a map using calibration tool
Following these steps the map is now calibrated and can be used with u-center.
5.2.11 Chart view
Chart view allows you to conveniently view GNSS data records in graphical form. The data can be
scaled in many different ways and formats. It's even possible to print the entire chart. The examples
below illustrate two different typical applications.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 45 of 71
Page 46

u-center-User guide
Figure 42: Altitude as a function of Index (X = Index, Y = Alt)
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 46 of 71
Page 47

u-center-User guide
Figure 43: Latitude as a function of longitude (X =Longitude, Y = Latitude)
Function Description Shortcut /
Cursor The position of the cursor is shown on the lower left edge of the u-center screen
(Longitude, Latitude and Pixel-Position). By holding the left mouse button and
moving the cursor over the chart you can measure distance from one position to
another.
Move The chart inside the chart view window can be moved.
Zoom In Drawing a rectangle enlarges the chart to the new view. To zoom in the chart
double-click on the chart.
Zoom Out Drawing a rectangle decreases the chart to the new view. To zoom out the chart
double-click on the chart.
Drawing Mode The size and form of the displayed values can be changed in the menu points;
the connection line between the values can be selected in the menu connect. For
viewing the statically values (average, minimum, maximum, standard deviation)
directly in the chart select the statistics menu.
Fit Y range Fits the Y range.
Follow Y Follow the most current Y value (the most current Y-value is always in the middle
of the chart).
Index or Y value Switch between the index and the Y value.
Y value Select the Y value to be displayed.
Fit X range Fit the X range.
Follow X Follow the most current X value (the most current X value is always in the middle
of the chart).
Index or X value Switch between the index and the X value.
X value Select the X value to be displayed.
Toolbar icon
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 47 of 71
Page 48

u-center-User guide
Function Description Shortcut /
Moving average Adds a moving average. The average is calculated over the number of most recent
values, specified with the parameter.
Table 19: Description of the buttons in the chart view toolbar
Toolbar icon
The number of displayed epochs is set to 1800 by default.
5.2.12 Histogram view
Histogram views allow you to view GNSS data and probability distributions (see Figure 44) and print
the entire histogram if desired. The number of bins (storage containers) can be set by you.
Figure 44: Altitude Histogram View
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 48 of 71
Page 49

u-center-User guide
Figure 45: Probability chart
Function Description Shortcut /
Cursor The position of the cursor is shown on the lower left edge of the u-center screen
(Longitude, Latitude and Pixel-Position). By holding the left mouse button and
moving the cursor over the histogram you can measure distance from one
position to another.
Move The histogram inside the histogram view window can be moved.
Zoom In Drawing a rectangle enlarges the histogram to the new view. To zoom in the
histogram double-click on the histogram.
Zoom Out Drawing a rectangle decreases the histogram to the new view. To zoom out the
histogram double-click on the histogram.
Drawing Mode The size and form of the displayed values can be changed in the menu points;
the connection line between the values can be selected in the menu connect. For
viewing the statically values (average, minimum, maximum, standard deviation)
directly in the histogram select the statistics menu.
Probability Fit the Probability range.
Fit Probability Fit the Probability range
Y value Select the Y value to be displayed.
Bins The number of bins.
Table 20: Description of the buttons in the histogram view toolbar
Toolbar icon
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 49 of 71
Page 50

u-center-User guide
The number of displayed epochs is set to 1800 by default.
5.2.13 Camera view
The camera view function enables photographs, taken during recording of log files, to be linked to
the GNSS data stored in the corresponding log files. This allows a video depiction of the test, with
a picture assigned to a specific point of GNSS data.
Figure 46: Camera view
Using Camera View can result in very large log files and can slow down u-center when
playing such files.
5.2.14 Deviation map
The deviation map displays positions in longitude and latitude relative to a defined reference
position.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 50 of 71
Page 51

u-center-User guide
Figure 47: Deviation map
Function Description Shortcut /
Properties
Fit Automatically adjusts the reference position and the maximum deviation to fit all
Track Show track of values from the internal database.
Statistics Show statistics of the values from the internal database.
Maximum deviation
shortcut
Reference position
shortcut
Table 21: Description of the buttons in the deviation map toolbar
The reference position can be defined as:
• The average of all previously measured positions
• The current position
• A fixed, predefined value
• The radius of the outer circle can be adjusted with the Max. Deviation parameter.
positions into the deviation map.
Shortcut for changing the scale of the deviation map to prefixed values. The icons
represent Roman numerals, with "I" corresponding to a 1 m radius of the deviation
map, and "V"= 5 m, "X"= 10 m, "L"= 50 m, "C" = 100 m, "D" = 500 m, and "M" = 1000
m.
Shortcut for setting the reference position:
• A = average position
• C = current position
Toolbar icon
The number of displayed epochs is set to 1800 by default.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
5 u-center menus and windows Page 51 of 71
Page 52
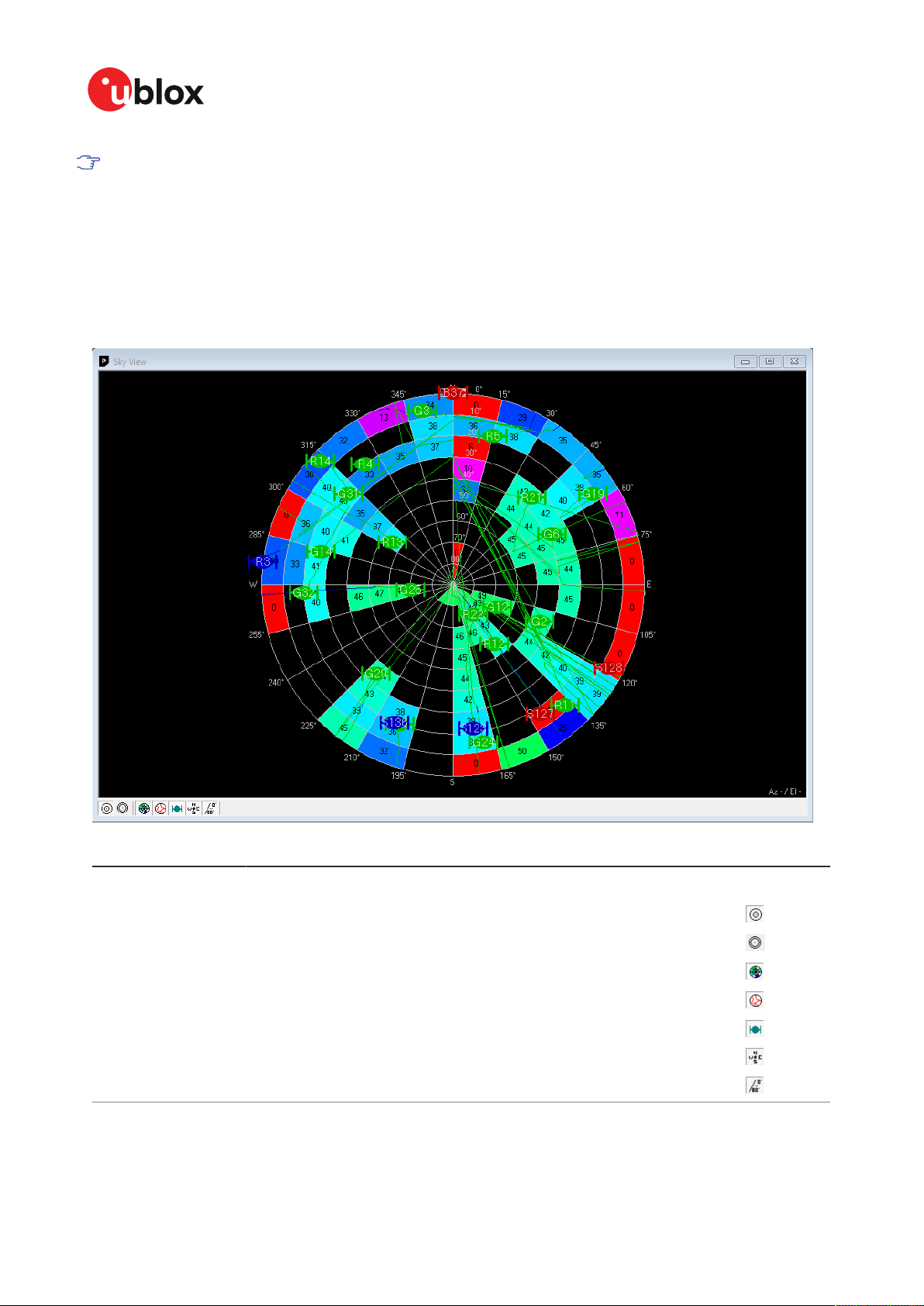
u-center-User guide
You can use the mouse scroll wheel to zoom in/out on the deviation map. Holding down the
Shift key allows you to zoom in beyond the default 1 m maximum zoom.
5.2.15 Sky view
Sky view is an excellent tool for analyzing the performance of antennas as well as the conditions
of the satellite observation environment. The polar plot graphically displays the averaged relative
satellite signal strength (see Figure 48), the position of satellites in the sky, identifies satellites by
number and indicates which satellites are being used in the receiver calculation. Right-clicking the
mouse on sky view allows the copying of C/N0 values in tabular form to another program.
Figure 48: Sky view
Function Description Shortcut /
Linear projection
Sine projection Displays the sky view with a sine projection.
C/N0 Displays or hides the averaged C/N0 values.
Orbits Displays or hides the satellite orbits.
Satellites Displays or hides the current satellite positions.
Coordinates Displays or hides the caption for the azimuth.
Elevation Displays or hides the caption for the elevation.
Table 22: Description of the buttons in the sky view toolbar
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
Displays the sky view with a linear projection.
5 u-center menus and windows Page 52 of 71
Toolbar icon
Page 53

u-center-User guide
6 NTRIP
This section will give an overview of the NTRIP support in u-center. Currently u-center supports both
NTRIP client and NTRIP caster/server functionality. Settings for both of them can be found under
"Receiver" menu.
Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol (NTRIP) is an application-level protocol that
supports the streaming of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) data over the Internet. NTRIP
is a generic, stateless protocol based on the Hypertext Transfer Protocol HTTP/1.1. The HTTP
objects are extended to GNSS data streams.
6.1 NTRIP client
NTRIP client allows connecting to any NTRIP compliant caster and receiving RTCM correction data
for receiver. Currently version 1 of NTRIP standard is implemented.
Perform the following steps to connect to the caster (steps 10 to 14 are only needed when the mount
point requires additional NMEA message to be sent by the client):
1. Establish the communication between u-center and the device (see also Connect to the
receiver).
2. Open NTRIP client settings dialog by clicking on Receiver > NTRIP Client...
Figure 49: NTRIP client settings dialog
3. Enter the address of the NTRIP caster. See position a.
4. Enter the port number of the NTRIP caster. See position b.
5. Enter the username which will be sent to the NTRIP caster. If no authentication is required by
the caster, then leave this field empty. See position c.
6. Enter the password which will be sent to the NTRIP caster. If no authentication is required by
the caster, then leave this field empty. See position d.
7. Click on Update source table to get an up to date list of all available mount points from the
caster. See position e.
8. To see the detailed attributes of mount points, click on Mount point details. This will bring up
a new dialog box listing all the mount points available and their attributes. See position f.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
6 NTRIP Page 53 of 71
Page 54

u-center-User guide
9. Select one of the mount points listed in the drop down box. See position g.
10. Click on Use manual position to enter values for position data. If this is not checked, the position
data will be retrieved directly from the receiver. See position h.
11. Enter the longitude in degrees, in either floating point or integer format. See position i.
12. Enter the latitude in degrees, in either floating point or integer format. See position j.
13. Enter the altitude in meters in floating point or integer format. See position k.
14. Enter the geoid separation in meters in floating point or integer format. See position l.
15. Click on OK to start receiving correction data.
6.2 NTRIP server/caster
The u-center NTRIP caster is able to accept requests from NTRIP compliant clients and send them
RTCM correction data. This is implemented according to NTRIP standard version 1. The server part
is not implemented according to the standard but we are currently supporting one mount point,
which gets data from direct connection to the receiver.
Perform the following steps to set up the caster:
1. Establish communication between u-center and the device (see also Connect to the receiver).
2. Open NTRIP server/caster settings dialog by clicking on Receiver > NTRIP Server/Caster...
There are two tabs. First tab contains the basic configuration (port only), while the second tab
contains the rest of the configuration options.
Figure 50: NTRIP server settings dialog, both the Basic and More tabs
3. Enter the port that will be used by the NTRIP caster. See position a.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
6 NTRIP Page 54 of 71
Page 55

u-center-User guide
4. Check "Enable authentication" if you want to enable basic authentication on your caster. See
position b.
5. Enter the username which will have to be provided by the clients (only if you enabled
authentication under 4). See position c.
6. Enter the password which will have to be provided by the clients (only if you enabled
authentication under 4). See position d.
7. Enter the name for the mount point. See position e.
8. Enter the identifier for the mount point e.g. name of the city next to mount point location. See
position f.
9. Enter the country code in ISO 3166 for the mount point. See position g.
10. Check Get configuration automatically to use longitude, latitude and RTCM message
configuration of the currently connected receiver that will be sent out on the mount point. In
this case, you can go directly to 16. See position h.
11. Enter the longitude for the mount point in integer or floating point format. See position i.
12. Enter the latitude for the mount point in integer or floating point format. See position j.
13. Select the RTCM messages that will be sent by the mount point. See position k.
14. For every selected RTCM message enter the period at which messages will be sent to the
clients. See position l.
15. Check Store configuration to receiver on exit to store the configuration of RTCM messages to
the receiver (using the UBX-CFG-MSG message). See position m.
16. Click OK to start NTRIP server/caster.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
6 NTRIP Page 55 of 71
Page 56

u-center-User guide
7 Google Earth server
This section gives an overview of the Google Earth server support in u-center.
The Google Earth server can continuously send positioning data in a specific format to the Google
Earth application. By hosting such a server in u-center we are able to visualize positioning data in
real time.
There are only a few settings that can be set via the Google Earth server dialog. This means a lot
of functionality and behavior of the Google Earth is still configurable from the application itself and
therefore out of control of u-center's direct control.
Perform the following steps to start the Google Earth server:
1. Establish the communication between u-center and the device (see also Connect to the
receiver).
2. Open Google Earth settings dialog by clicking on File > Database Export > Google Earth Server...
Figure 51: Google Earth settings dialog
3. Enter the port of the server. See position a.
4. Select the refresh mode. Supported modes are "On camera stop" where Google Earth will send
requests only when previous view has stabilized or "On interval" where requests from Google
Earth will be sent in regular intervals. See position b.
5. Enter the refresh time. This is the time between two consecutive requests in "On interval" mode
or delay after camera stops in "On camera stop" mode. See position c.
6. Enter the altitude in meters of the view. See position d.
7. Enter the tilt in degrees of the view. A value of 0 indicates that the view is aimed straight down
toward the earth and a value of 90 indicates that the view is aimed toward the horizon. See
position e.
8. Check this field if you want the heading of the camera to follow heading information coming
from UBX-NAV-PVT message. See position f.
9. Enter the number to set the line width in the view. Higher values mean a thicker tracking line.
See position g.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
7 Google Earth server Page 56 of 71
Page 57

u-center-User guide
10. Select the altitude mode for the view. The "absolute" mode sets the altitude relative to sea level,
"relativeToGround" mode sets it relative to the actual ground elevation in a particular location
and "clampToGround" ignores the altitude specification. See position h.
11. Click on Update preferences if you want to permanently store information about Line width and
Altitude mode. The same can be achieved through menu "Tools > Preferences > KML settings".
See position i.
12. Click on OK to start the server.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
7 Google Earth server Page 57 of 71
Page 58

u-center-User guide
8 Tools
This section will give an overview of the embedded tools of u-center. They can be used for different
purpose and should facilitate the usage of u-blox GNSS receivers. The tools can be found under the
"Tools" menu but some of the options are only displayed when a receiver is connected to u-center.
The firmware update tools also depend on the connected receiver generation.
8.1 Firmware update
This tool allows you to update the firmware of a receiver. For the firmware update to work, the
receiver must have a flash memory attached as the new firmware will be stored in this location.
In the earlier versions of u-center, firmware update was implemented as part of the u-center
application. Now, the firmware update is implemented as a separate application which u-center
launches and passes parameters to, depending on the options selected in the UI.
To update the firmware, perform the following steps:
1. Display the firmware update tool view by clicking on Tools > Firmware Update...
Figure 52: Firmware update view
2. Select the firmware image suitable for the connected receiver. See position a on Figure 52.
3. Select the flash information structure file (only needed if using u-blox receiver generation 7 or
later), or the flash definition file (only needed before u-blox receiver generation 7). These files
should be bundled with u-center. See position b on Figure 52.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
8 Tools Page 58 of 71
Page 59

u-center-User guide
4. Select the options for your receiver. See position c on Figure 52.
Option Description Recommended
Use this Baud rate for
update
Selects the speed of the communication for updating the firmware
on the receiver. Only has an effect when the receiver is connected
over a serial port.
115200
Program FIS only Writes only the flash information structure (FIS) into the external
memory and does not update the firmware. This option is used for
receivers running from ROM but with an attached SQI memory (for
example for logging). Only supported after and including u-blox
receiver generation 7.
Enter Safeboot before
update
USB alternative update
method
Send Training sequence Sends the training sequence after safeboot was entered. This
Use chip erase Erases the flash using an single command instead of individual
Transfer image to RAM Transfers the firmware image directly to the receiver's RAM. Not
Sends the command to enter safeboot. In this state, the receiver
boots from the internal ring oscillator and does not rely on any
external components. GNSS functionality is not started and the
receiver does not output any data. Don't use this method when
having the receiver connected over USB.
Enables updating the receiver via USB. "Enter Safeboot before
update" will be disabled automatically if that option has been
chosen.
synchronizes the internal ring oscillator so that a communication
can be established.
sector erases.
stored to flash.
disabled
disabled
enabled (using
USB only)
enabled
check support
disabled
5. The additional options field allows more command options to be specified than are presented
in the UI. This feature should only be needed if the firmware update utility launched by u-center
has additional features which the development of th UI has not caught up with yet. See position
d on Figure 52.
6. The command line field displays the actual command line and parameters used to launch the
firmware update utility from u-center. This can be used to help diagnose any issues that may
occur when performing a firmware update. See position e on Figure 52.
7. The status fields display information about the connected receiver, the presence of the
firmware and FIS files, and if the firmware update utility can be found. See position f on Figure
52. If there is a problem with any of these items, the Go button, which starts the update process,
will be greyed out.
8. Press the Go button to start the firmware update process. This button will only be enabled if u-
center can see the receiver and can find the specified files. If this button is greyed out, check
the status display to see what is wrong. See position g on Figure 52.
9. Press the Stop button to terminate the firmware update process. This will only be enabled when
the update process is running. See position h on Figure 52.
10. During firmware update, a progress bar is displayed. See position i on Figure 52.
11. A log is also displayed during the update process. See position j on Figure 52.
12. A detailed image of the flash erase and writing progress will also be shown. See position k on
Figure 52.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
8 Tools Page 59 of 71
Page 60

u-center-User guide
8.2 Legacy Firmware update u-blox 5 - 8
This is the legacy receiver firmware update tool, which is built into the u-center binary. It can be
used to program u-blox 5 to u-blox 8 receivers. Further feature development has been stopped and
u-center now uses the stand alone command line firmware update utility as the primary firmware
update mechanism. This is documented in the previous section. In the future, this legacy firmware
update tool will be removed permanently from u-center.
As with the primary firmware update tool, the receiver has to have a flash memory attached as the
firmware has to be stored in this location.
Perform the following steps to update the firmware:
1. Establish the communication between u-center and the device (see also Connect to the
receiver).
2. Open firmware update tool by clicking Tools > Legacy Firmware Update...
Figure 53: Legacy firmware update window
3. Select the firmware image suitable for the connected receiver. See position a on Figure 53.
4. Select the flash definition file (only needed before u-blox receiver generation 7). This file is
bundled with u-center. Point to the latest file version. See position b on Figure 53.
5. Select the flash information structure file (when using u-blox receiver generation 7 or later).
This file is also bundled with u-center. Point to the latest file version. See position c on Figure 53.
6. Select the correct options for your receiver. See position d on Figure 53.
Option Description Recommended
Use this Baud rate for
update
Clear BBR before update Deletes the complete battery-backed memory (BBR) so that the
Program FIS only Writes only the flash information structure (FIS) into the external
Selects the speed of the communication for updating the firmware
on the receiver. Only has an effect when the receiver is connected
over a serial port.
receiver will start with the default configuration.
memory and does not update the firmware. This option is used for
receivers running from ROM but with an attached SQI memory (for
example for logging). Only supported after and including u-blox
receiver generation 7.
115200
enabled
disabled
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
8 Tools Page 60 of 71
Page 61
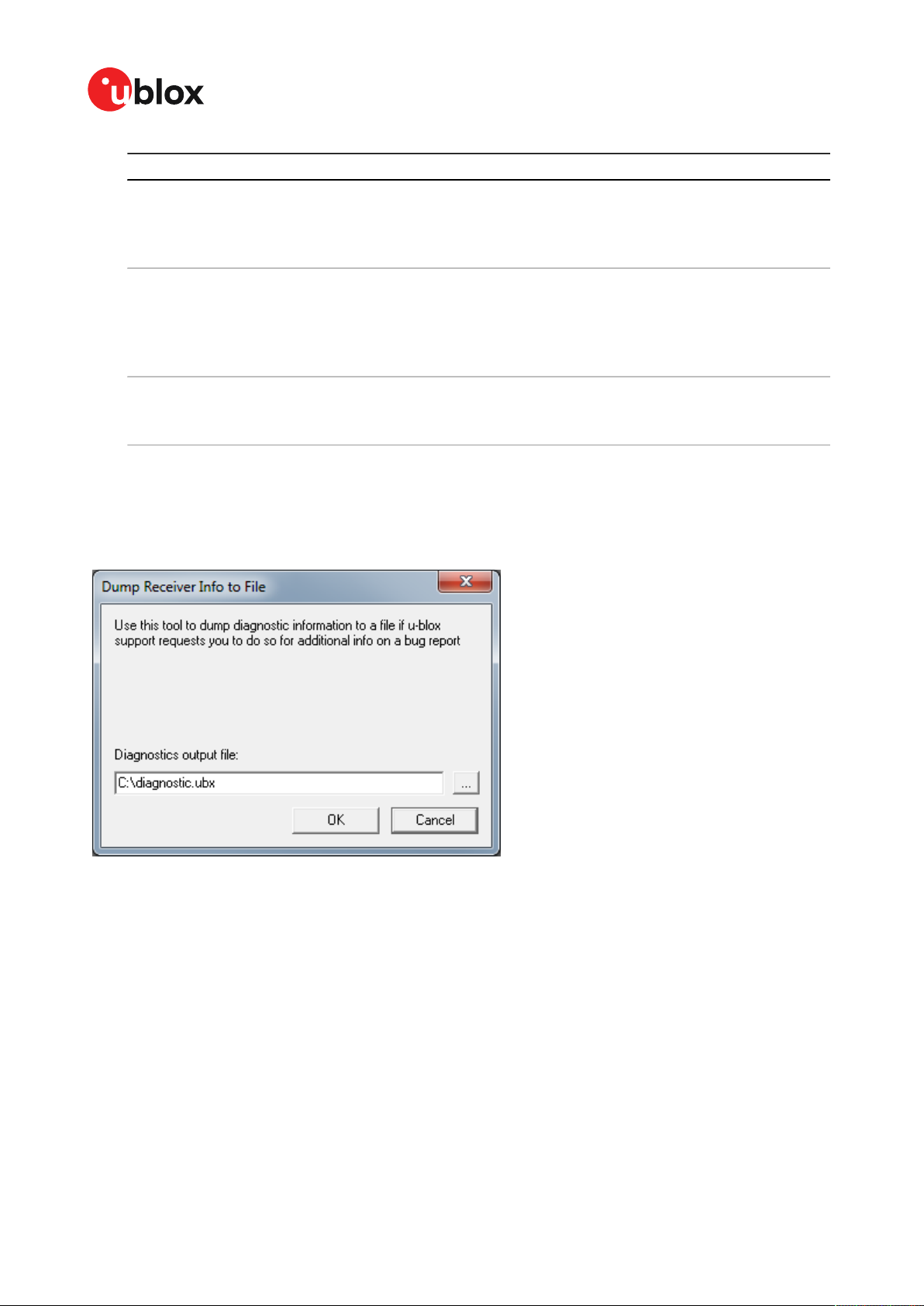
u-center-User guide
Option Description Recommended
USB alternative update
method
Erases the first sector of the flash memory and restarts the receiver.
The receiver will then start from ROM and the flash firmware can be
updated. Use this method if you want to update the firmware of a
receiver connected over USB.
disabled
Enter Safeboot before
update
Send Training sequence Sends the training sequence after safeboot was entered. This
Sends the command to enter safeboot. In this state, the receiver
boots from the internal ring oscillator and does not rely on any
external components. GNSS functionality is not started and the
receiver does not output any data. Don't use this method when
having the receiver connected over USB.
synchronizes the internal ring oscillator so that a communication
can be established.
enabled
enabled
7. Click OK.
8.3 Dump receiver diagnostics
This tool is used to dump the receiver diagnostic to a file. Use this tool if requested by the support
team.
Figure 54: Dump receiver diagnostics tool
8.4 GNSS configuration
u-center is capable of getting the actual configuration of a u-blox GNSS positioning chip or module
and storing it to an ASCII text file containing hexadecimal records. Such a file can be edited and
stored to a u-blox GNSS device again. In u-center Tools menu, select GNSS Configuration to open
the GNSS Configuration dialog box. The following functions are available:
• Specify the name of a new configuration file to store current configuration from the u-blox GNSS
device
• Specify the name of an existing configuration file and load this configuration into the u-blox GNSS
device
• A flag can be set to force storing the configuration into a battery-backed RAM (BBR) or flash,
applicable for u-blox 5 to u-blox 8/M8 only.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
8 Tools Page 61 of 71
Page 62

u-center-User guide
Figure 55: GNSS configuration tool
8.4.1 Read/Write configuration files
1. Connect to the device.
2. Open "Tools > GNSS Configuration".
3. Select the u-blox receiver generation connected from the Generation drop down menu.
4. To read an existing configuration file, select the name of the file, then click Transfer file >
GNSS button. The GNSS Configuration window then closes and the progress window pops
up, showing the configuration being sent to the receiver. This progress window closes after
successful transfer.
5. To write a new configuration file, click " Transfer GNSS > File". The GNSS Configuration window
closes and the progress window pops up, showing the configurations being polled and stored
into a local file in ASCII format.
Select Store configuration into BBR/Flash checkbox if the parameters need to be stored
into the device's non-volatile memory (BBR/Flash). This option is applicable for u-blox 5 to ublox 8/M8 generation receivers.
Sending a configuration to a u-blox GNSS device may fail due to a baud rate change on the
current serial port of the receiver to which the configuration is being sent. If this happens,
simply change the u-center baud rate and send the configuration again.
If reading or writing configuration data fails too frequently, try to increase the number of retries ucenter should do on a single message if one fails.
The user can abort the transfer by clicking the Abort button. It is not possible to close the window
unless the transfer is complete or aborted by the user.
It is not recommended to read/write configuration while the u-blox GNSS device is in sleep
mode.
8.4.2 Editing configuration file
When clicking the Edit button in the GNSS Configuration dialog, the Notepad editor opens (standard
Windows software). Configurations are stored the following way:
• The first line contains the version of the u-blox GNSS receiver where the configuration is from.
Never change this line!
•
For the second and following lines, each line contains the same: <class ID>-<message ID> -
<hexadecimal byte code of the message>. The byte code consists of class and message
IDs (2 bytes), payload length (2 bytes), payload (payload length bytes). The sync characters and
the checksum are not included. They will be calculated automatically.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
8 Tools Page 62 of 71
Page 63

u-center-User guide
Refer to u-blox Receiver Description including Protocol Specification for detailed information and
ranges.
Figure 56: Content of GNSS configuration file
8.5 Preferences
The preferences tool can be used to configure a number of u-center parameters.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
8 Tools Page 63 of 71
Page 64

9 How To
9.1 Change baud rate of receiver
1. Connect to the device.
2. Open View / Messages View (Hotkey: F9).
3.
Select UBX-CFG-PRT.
4.
Poll the current configuration from the receiver ( ).
5. Change the setting to the desired baud rate.
6.
Send the message to the receiver ( ).
u-center-User guide
Figure 57: Changing baud rate (using UBX-CFG-PRT)
9.2 Save parameters to receiver non-volatile memory (BBR/
Flash)
There are 2 ways to save parameters to the receiver's non-volatile memory (BBR/Flash).
9.2.1 Saving parameters with UBX-CFG-CFG
1. Connect to the device.
2. Open View / Messages View (Hotkey: F9).
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
9 How To Page 64 of 71
Page 65

3.
Select UBX-CFG-CFG.
4. Select “save current configuration” (see Figure 58).
5.
Send the message to the receiver ( ).
u-center-User guide
Figure 58: Saving Parameters (using UBX-CFG-CFG)
9.2.2 Saving parameters with GNSS configuration
Refer to chapter Read/Write configuration files
9.3 Recording/Playing a log file
u-center allows recording and playing log files. Use the player controls, to record or playback a log
file. Select the log file to be opened through the file menu tool bar. The series of buttons in the player
toolbar can be used to navigate through the log file. The records will be displayed on the navigation
display window, in the same way that live GNSS data is displayed when using u-center. Refer to Player
for a description of the menu items.
9.4 Conduct sensitivity tests
u-center is a useful tool for conducting sensitivity tests of GNSS positioning chips and modules and
receiver designs. To do so, under open sky conditions record a log file of the receiver to be tested and
an Evaluation Kit as reference. Make sure that the log files are recorded under the same conditions.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
9 How To Page 65 of 71
Page 66

u-center-User guide
Using the Statistic View or Table View windows from u-center, compare the C/N0 values of the five
strongest satellites. With Table view, export the values to a spreadsheet for analysis.
9.5 Read/Write configuration files
Refer to chapter Read/Write configuration files
9.6 Set GNSS configuration
1. Connect to the device.
2. Open View / Messages View (Hotkey: F9).
3.
Select UBX-CFG-GNSS.
4. Place or remove the checkmark for the desired GNSS under Enable.
5.
Send the message to the receiver ( ).
The following figure shows an example that configures the device to receive GPS and GLONASS.
Figure 59: GNSS configuration (using UBX-CFG-GNSS)
9.7 Change epoch detection method
u-center looks for epochs in the incoming messages from the receiver, and uses them as a heartbeat
to trigger view updates and calculate the statistics. To detect new epochs, u-center examines
various groups of fields in the incoming message stream. It is possible to specify which field
groups u-center is interested in for epoch detection. Opening the dialog under "Receiver > Epoch
detection..." allows the user to do this.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
9 How To Page 66 of 71
Page 67

u-center-User guide
Figure 60: Select epoch detection method
From the "Select Epoch detection Scheme" window, the following options can be configured:
Option Description Default
iTOW Monitor the "iTOW" database element. Trigger an epoch if a difference is seen.
HNR TOW Monitor the "NAV-HNR iTOW" database element. Trigger an epoch if a difference
UTC-TIME Monitor the "UTC" database element. Trigger an epoch if a difference is seen.
GPS-TIME Monitor the "GPS time" database element. Trigger an epoch if a difference is seen.
NAV-EOE Monitor for incoming UBX-NAV-EOE messages. Trigger an epoch if one is seen. Yes
ITFM Status Monitor the "ITFM Status" database element. Trigger an epoch if a difference is
NMEA repeat Monitor for NMEA messages. Trigger an epoch if the same NMEA message is
No additional
filtering
Only trigger on
priority mode
messages
Only trigger on
non-priority mode
messages
Table 23: Epoch detection method options
Typically UBX-NAV messages cause this trigger.
is seen. HNR based messages cause this trigger.
Typically NMEA messages cause this trigger.
Typically PUBX messages cause this trigger.
seen. The UBX-RXM-INTF message causes this trigger.
seen twice since the last epoch. Excluding GxGRS and GxGSA.
No additional filtering performed when looking for epoch triggers. Yes
Trigger an epoch on a priority navigation output message. No
Trigger an epoch on a non priority navigation output message. No
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
The default configuration can be restored by clicking the Restore defaults button.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
9 How To Page 67 of 71
Page 68

u-center-User guide
10 Troubleshooting
NMEA or UBX protocol is not available in the Messages View
u-center uses dynamic link libraries (DLL). The installation program will automatically install the
required DLLs into the u-center program directory. Should you try to copy a u-center installation
from one location to another, make sure you also copy the DLL files. Verify, the version of u-center
matches the DLL version.
u-center does not display all messages
Make sure the baud rate is sufficient. If the bandwidth is insufficient, receivers will skip excessive
messages. Some serial port cards/adapters (i.e. USB to RS-232 converter) frequently generate
errors. If a communication error occurs while u-center receives a message, the message will be
discarded.
Some COM port are not shown in the port list
Only the COM ports that are available on your computer will show up in the COM port drop down list.
If a COM port is grayed out, another application in the computer is using it.
PC is very slow when u-center runs
If a high value of epochs is selected, the display in real-time cannot be guaranteed, especially when
many graphical views are open. u-center does not update minimized views and console in real-time.
Close or minimize as many of the graphical views and consoles as possible and u-center will run
faster.
Log file/data are only partly displayed
The number of epochs displayed in u-center can be limited in order to allow an efficient analysis of
larger log files. When this limit is set then the oldest values will be discarded after the database
reaches this limit size. Data stored to a log file are not affected by the database limitation. Refer to
Database limitations for instructions on how to increase or remove this limit. When planning long-
term observations, it's recommended to start recording a log file before analysis begins.
Output messages are not updated in the Messages View
Make sure that the protocol you would like to receive is enabled. If so, double-click on the desired
output message. Double-clicking on an output message enables or disables the periodic message
update if the respective protocol is active. Alternatively, select the desired input or output message
and press the Poll button. If you would like to get UBX-INF-* messages in the log file, configure the
receiver accordingly with the UBX-CFG-INF input message.
No log file is recorded
After a new log file is created, logging will not automatically start but only after selecting the Record
button in the Player Toolbar.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
10 Troubleshooting Page 68 of 71
Page 69

u-center-User guide
Related documents
[1] GPS Compendium, Doc No GPS-X-02007
[2] u-blox 5 Receiver Description including Protocol Specification, Document number: GPS.G5-
X-07036
[3] u-blox 6 Receiver Description including Protocol Specification, Document number: GPS.G6-
SW-10018
[4] u-blox 7 Receiver Description including Protocol Specification V14, Document number:
GPS.G7-SW-12001
[5] u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification (Public version),
Document number: UBX-13003221
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
Related documents Page 69 of 71
Page 70

u-center-User guide
Revision history
Revision Date Name Status / Comments
- 08-Oct-2008 tgri Initial release
A 22-Jul-2009 tgri New CI
A1 17-Feb-2011 tgri Third party libraries
B 01-Nov-2011 tgri Google Earth View added
C 03-Jun-2012 khir Updated for u-center 6.3. GNSS configuration added
R06 09-Dec-2013 mfre Update for u-center 8.01 and u-blox 7 and M8 generations
R07 01-Oct-2014 jbow Packet view update describing message direction indicators
R08 23-Feb-2015 yzha Updated menu pictures and shortcut key list corresponding to latest version
R09 04-Sep-2015 smos Updated Contact page
R10 12-Dec-2015 mfre Remove Google Earth support
R11 29-Mar-2016 mfre Epoch detection, DGNSS interface and receiver status icons description
R12 15-Jul-2016 mfre Map view updated, removed EVK-6PPP how to
R13 01-Oct-2016 rsmr NTRIP support added
R14 19-Dec-2016 rsmr Google Earth server added, new RTCM messages added
R15 31-Mar-2017 rsmr Support for Sqlite database added, improved UI processing, support for
R16 29-Jun-2017 jbow Limiting the database size, automatic receiver identification
R17 28-Sep-2017 msul Firmware update view modernized
R18 04-Dec-2017 msul Addition of the "Transfer image to RAM" checkbox in firmware update window
R19 29-May-2018 msul Addition of the "Stepback" button in log file toolbar and additional bar to
R20 28-Sep-2018 msul Addition of the "USB alternative update method" checkbox in firmware update
R21 11-Mar-2019 msul Added Generation 9 Advanced Configuration View
R22 25-Jun-2019 msul Updated figures 8, 9, 29, 53 and 56. Updated section 8.4.1 Read/Write
R23 30-Aug-2019 msul Updated figures 19, 20, 21 and table 12 for new epoch marker. Updated figure
R24 02-Oct-2019 msul Updated section 5.2.7.2 Advanced Configuration View.
R25 23-Oct-2019 msul Added a hex field to the Advanced Configuration View.
R26 15-Mar-2021 msul Updated figures 8 and 9.
added, legacy aiding marked deprecated, pictures updated
moving baseline added
NTRIP server/caster settings screen
window
configuration files accordingly.
60 and table 23 for advanced filtering introduction in epoch detection scheme.
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
Revision history Page 70 of 71
Page 71

u-center-User guide
Contact
For complete contact information visit us at www.u-blox.com.
u-blox Offices
North, Central and South America Headquarters Asia, Australia, Pacific
u-blox America, Inc. u-blox AG u-blox Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Phone: +1 703 483 3180 Phone: +41 44 722 74 44 Phone: +65 6734 3811
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com E-mail: info@u-blox.com E-mail: info_ap@u-blox.com
Support: support@u-blox.com Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office West Coast Regional Office Australia
Phone: +1 408 573 3640 Phone: +61 3 9566 7255
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com E-mail: info_anz@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Technical Support Regional Office China (Beijing)
Phone: +1 703 483 3185 Phone: +86 10 68 133 545
E-mail: support_us@u-blox.com E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Chongqing)
Phone: +86 23 6815 1588
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shanghai)
Phone: +86 21 6090 4832
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shenzhen)
Phone: +86 755 8627 1083
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office India
Phone: +91 80 4050 9200
E-mail: info_in@u-blox.com
Support: support_in@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Osaka)
Phone: +81 6 6941 3660
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Tokyo)
Phone: +81 3 5775 3850
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Korea
Phone: +82 2 542 0861
E-mail: info_kr@u-blox.com
Support: support_kr@u-blox.com
Regional Office Taiwan
Phone: +886 2 2657 1090
E-mail: info_tw@u-blox.com
Support: support_tw@u-blox.com
Europe, Middle East, Africa
UBX-13005250 - R26
C1-Public Production information
Page 71 of 71
 Loading...
Loading...