Page 1

5 low energy modules. It also describes the different options for
EVK-ANNA-B112
Evaluation Kit for ANNA-B112 Bluetooth 5 low energy
modules
User guide
Abstract
This document describes how to set up the EVK-ANNA-B112 evaluation kit to evaluate ANNA-B112
series standalone Bluetooth®
debugging and the development capabilities included in the evaluation board.
UBX-18018539 - R02
C1-Public www.u-blox.com
Page 2

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
u-blox or third parties may hold intellectual property rights in the products, names, logos and designs included in this
document. Copying, reproduction, modification or disclosure to third parties of this document or any part thereof is only
permitted with the
The information contained herein is provided “as is” and u
implied, is given, including but not limited
purpose of the information. This document may be revised by u
documents, visit www.u
Copyright © u
Document Information
Title EVK-ANNA-B112
Subtitle Evaluation Kit for ANNA-B112 Bluetooth 5 low energy modules
Document type User guide
Document number UBX-18018539
Revision and date R02 18-Dec-2020
Disclosure Restriction C1-Public
This document applies to the following products
Product name Type number Firmware version PCN reference
EVK-ANNA-B112U EVK-ANNA-B112U-00 All EVK-ANNA-B112C EVK-ANNA-B112C-00 All -
1
:
1
There is no separate EVK variant for the ANNA-B112-70B module variant. To simulate this module please erase the flash of the EVK.
express written permission of u-blox.
-blox assumes no liability for its use. No warranty, either express or
to, with respect to the accuracy, correctness, reliability and fitness for a particular
-blox at any time without notice. For the most recent
UBX-18018539 - R02 Document Information Page 2 of 31
C1-Public
-blox AG.
-blox.com.
Page 3

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Contents
Document Information ............................................................................................................................. 2
Contents ....................................................................................................................................................... 3
1 Product description ............................................................................................................................ 4
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................................ 4
1.2 Kit includes ................................................................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Key features ................................................................................................................................................. 5
1.4 EVK-ANNA-B112 block diagram .............................................................................................................. 6
1.5 Connectors ................................................................................................................................................... 7
1.6 Antennas ...................................................................................................................................................... 7
1.7 Powering options ......................................................................................................................................... 8
1.7.1 Selecting the power configuration jumpers .................................................................................. 8
1.7.2 Default power, 3.3 V ......................................................................................................................... 10
1.7.3 Battery powered, 3 V ........................................................................................................................ 10
1.7.4 Battery powered with protection diode, 2.7 V ............................................................................ 11
1.7.5 External supply .................................................................................................................................. 11
1.7.6 Raspberry Pi HAT .............................................................................................................................. 12
1.8 Arduino interface ...................................................................................................................................... 12
1.8.1 Arduino shield compatibility ........................................................................................................... 14
1.9 Raspberry Pi compatible interface ........................................................................................................ 14
1.9.1 Powering considerations ................................................................................................................. 17
1.9.2 UART ................................................................................................................................................... 17
1.9.3 EEPROM support .............................................................................................................................. 17
1.10 Buttons and LEDs ..................................................................................................................................... 18
1.11 Disconnecting ANNA signals from board peripherals ....................................................................... 18
1.12 Software debug options .......................................................................................................................... 20
2 Setting up the evaluation board .................................................................................................. 21
2.1 Evaluation board setup ............................................................................................................................ 21
2.2 Starting up ................................................................................................................................................. 21
2.2.1 EVK-ANNA-B112 .............................................................................................................................. 21
2.2.2 Getting the latest u-connectXpress software ............................................................................ 21
2.2.3 Open CPU............................................................................................................................................ 22
Appendix .................................................................................................................................................... 23
A Placement and Schematics .......................................................................................................... 23
B Glossary .............................................................................................................................................. 29
Related documents ................................................................................................................................ 30
Revision history ....................................................................................................................................... 30
Contact ....................................................................................................................................................... 31
UBX-18018539 - R02 Contents Page 3 of 31
C1-Public
Page 4

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
1 Product description
1.1 Overview
The u-blox EVK-ANNA-B112 evaluation kit is a versatile development platform that allows quick
prototyping of a variety of extremely low-power Internet of Things (IoT) applications, using
Bluetooth 5, Bluetooth mesh, and NFC.
The EVK-ANNA-B112 evaluation kit is available with two board variants that offer different antenna
solutions:
• EVK-ANNA-B112U – supplied with an ANNA-B112U module, u-connectXpress software, and
antenna connector for connecting to external antennas.
• EVK-ANNA-B112C – supplied with an ANNA-B112C module, u-connectXpress software, and
internal, 2.4 GHz antenna (integrated in the SiP).
Through a variety of connectors, including Arduino™ Uno R3 and Raspberry Pi header connectors,
the EVK-ANNA-B112 provides access to all 25 IO pins on the ANNA-B112 module.
The stand-alone ANNA-B112 module, included in the kit, is based on the Nordic Semiconductor
nRF52832 chip. The nRF52832 uses an Arm
and 64 kB RAM, running at a system clock of 64 MHz.
The evaluation board offers simple USB drag-n-drop programming with a SEGGER J-Link debug
interface that can be used with the open CPU variants of the EVK. Nordic provide a free Software
Development Kit (SDK) with a broad selection of drivers, libraries, and example applications that can
be used for rapid prototyping.
®
Cortex®-M4F microcontroller with 512 kB internal flash
Figure 1: EVK-ANNA-B112 evaluation boards
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 4 of 31
C1-Public
Page 5

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Figure 2: Left: EVB ANNA-B112U including U.FL connector; Right: EVB ANNA-B112C including an internal antenna.
Figure 3: Left: EVB ANNA-B112U including NFC antenna; Right: EVB ANNA-B112U including NFC antenna, turned 180
degrees. Both options are valid.
1.2 Kit includes
The EVK-ANNA-B112 evaluation kit includes the following:
• EVK-ANNA-B112 evaluation board
• 2 pcs 2.4 GHz external antennas with U.FL connector (only in EVK-ANNA-B112U)
• NFC antenna
• USB cable
• Quick Start card
1.3 Key features
• u-blox ANNA-B112 Bluetooth low energy module based on the Nordic nRF52832 chipset:
o Bluetooth 5 support
o Bluetooth mesh
o NFC tag functionality
o Integrated Arm® Cortex®-M4F microcontroller with 512 kB flash, 64 kB RAM, and 64
MHz system clock
o Wide 1.7-3.6 V supply range
• The ANNA-B112 module supports different interfaces that can be configured to any of the
25 available IO pin(s):
o 8 analog capable inputs
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 5 of 31
C1-Public
Page 6

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
o 12 PWM capable outputs
o 3x SPI
o 1x UART with HW flow control
o 2x I
o 1x I
2
C
2
S
• Full UART to USB converter with a Virtual COM port that allows control of the extended UART
features of the u-blox u-connectXpress software
• On-board J-Link debugger/programmer:
o Mass Storage Device interface to PC, for drag-n-drop programming
o Debug port
o An additional Virtual COM port that, for example, may be connected to add-on boards
or to a debug UART on the ANNA-B112
• RGB LED and push buttons
• Arduino UNO R3 and Raspberry Pi compatible pin header interfaces
• Jumper headers and level shifters allow for flexible powering options of the ANNA-B112
module, even with full board support. They isolate the module entirely and control each power
net separately in order to precisely measure low power applications or disconnect only
unused parts of the board to save battery life.
• Multiple board power supply options:
o 5-12 V power plug
o 5 V USB supply
o 5-12 V Arduino VIN input
• Battery holder supporting CR2032 coin cell batteries
1.4 EVK-ANNA-B112 block diagram
The block diagram of EVK-ANNA-B112 is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: EVK-ANNA-B112 block diagram
The block diagram shows the major interfaces and internal connections of the EVK-ANNA-B112. The
following sections describe in detail how the different interfaces are connected and used, and how
the evaluation board may be configured to suit the needs of the user.
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 6 of 31
C1-Public
Page 7

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
1.5 Connectors
Figure 5 shows the available connectors on the EVK-ANNA-B112 and their layout. Table 1 describes
the connectors and their uses in detail.
Figure 5: Available connectors and their pinout
Connector
annotation
J5 Power supply 2.1 mm power jack, the center pin is the positive terminal. 5 – 12 V input.
J17 Power supply Pin header that can be used to connect external power supplies. 5 – 12 V input.
BT1 Battery holder CR2032 coin cell battery holder. CR2032 usually has a 3 V potential when fully
J11 NFC antenna
J10 2.4 GHz RF antenna
J12 Cortex Debug
J21 Cortex Debug+ETM
J8 Power supply, COM
Table 1: EVK-ANNA-B112 connector description
Function Description
charged.
Pin header that connects to the u-blox NFC antenna included in the kit.
connector
U.FL coaxial connector that can be used to connect antennas or RF equipment. This
connector
connector
connector
port and debug USB
connector is included only in the EVK-ANNA-B112U.
10-pin, 50 mil pitch connector that can be used to connect external debuggers to
the ANNA-B112 module. The ANNA-B112 modules support Serial Wire debug
(SWD) and Serial Wire Viewer, but not JTAG debug.
20-pin, 50 mil pitch connector. This extended connector has the same features as
J12, but also allows for instruction trace operations via the Embedded Trace
Macrocell (ETM) of the Cortex
This requires a special external debugger. Note that the 50 mil pitch pin header is
not soldered onto the evaluation board by default.
The main USB connector that is used to program, debug, and communicate with the
ANNA-B112 module. It can also be used to power the entire board.
®
-M4F microcontroller inside the ANNA-B112 module.
1.6 Antennas
The ANNA-B112 can be used both with external and internal antenna. The EVK-ANNA-B112C uses
the internal antenna of the ANNA-B112 and the EVK-ANNA-B112U has the antenna signal
connected to an U.FL connector.
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 7 of 31
C1-Public
Page 8

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
The EVK-ANNA-B112U is delivered with two different types of external antennas.
• FXP75.07.0045B
• PC17.07.0070A
Both are design to be mounted on a plastic casing for best performance.
For more details on the parameters of the internal and the external antennas, see the ANNA-B112
Data Sheet [1].
1.7 Powering options
Power can be supplied to the board in one of the following ways:
• Via the USB connector, J8
• Using the power jack, J5
• Using the Arduino interface VIN pin
• Using the pin header J17
• Plugging in a battery to the battery holder BT1
These power supply sources are distributed to the rest of the board as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Block diagram of the power net distribution
1.7.1 Selecting the power configuration jumpers
The EVK-ANNA-B112 offers flexible powering options for the ANNA-B112 module and the board
itself. To configure this, jumpers are added to or removed from pin headers, shorting two of the pins
together and connecting or disconnecting different power nets on the evaluation board. Figure 7
shows the location of the power configuration jumper headers. The 3V3 net is supplied by the board
and is always powered so long as any of the power sources shown in Figure 6 are connected. The 3V3
net does not provide power unless a jumper is added to jumper header J7.
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 8 of 31
C1-Public
Page 9

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Figure 7: Jumper headers J7 and J22 are used to select power configurations
Connector
annotation
J7 1 3V3 Regulated 3.3 V net. This net is supplied by the board and will always be powered
J22 1 VCC ANNA-B112 module voltage supply that connects to the module VCC pin. Shorted
Table 2: Pinout of jumper headers J7 and J22 used to configure the board power nets
Pin
number
2 3V3_PI Connects to the Raspberry Pi header’s (J14) 3V3 pins. If a Raspberry Pi is
3 VBAT_DIODE To protect the battery from current back surges, connect the battery to the
4 VDD_ANNA Connects to J22 pin 3, from where it can be connected to the module supply pin or
5 VBAT Battery + terminal
6 VDD_ANNA Connects to J22 pin 3, from where it can be connected to the module supply pin or
7 3V3 Regulated 3.3 V net. This net is supplied by the board and will always be powered
8 VDD_ANNA Connects to J22 pin 3, from where it can be connected to the module supply pin or
9 3V3 Regulated 3.3 V net. This net is supplied by the board and will always be powered
10 VDD_MCU Supply net for the board functions not directly connected to the ANNA-B112
11 GND Ground net.
12 GND Ground net.
2 VCC_IO VCC_IO pin not connected.
3 VDD_ANNA Connects to J7 pins 4, 6 and 8. Short J22 pins 1 and 3 allow the EVK to power the
4 VDD_IO Supply net for LEDs and peripherals connected directly to the ANNA-B112 module.
5 GND Ground net.
6 GND Ground net.
Schematic
net name
Description
as long as a power source is connected.
connected, this net must be floating to prevent back currents. If a HAT is
connected, this net can be shorted to the EVK 3.3 V supply to power the HAT.
ANNA-B112 module via a protection diode using this pin.
somewhere else.
somewhere else.
as long as a power source is connected.
somewhere else.
as long as a power source is connected.
module; Interface MCU, USB hub, UART to USB converter etc.
to the VCC_IO net via 0 Ω resistor R4 by default.
ANNA-B112 module.
Short J22 pins 2 and 4.
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 9 of 31
C1-Public
Page 10

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
The following sections describe different jumper configurations and power scenarios that is available
on the board, including the default configuration.
⚠ Check the jumper positions carefully; if a jumper is connected in a wrong way, it can permanently
damage the components that are on the board or connected to it.
1.7.2 Default power, 3.3 V
This is the default power configuration for the evaluation board, and the jumpers are installed out of
the box with this power configuration. All board peripherals are powered up, the ANNA module is
directly supplied by the board and everything is running at 3.3 V.
Figure 8: Jumper positions for default power configuration
Connector
annotation
J7 7, 8 Selects the board regulated 3.3 V net as source for the VDD_ANNA net.
J22 1, 3 Powers up the ANNA module. The ANNA VCC and VCC_IO pins are connected to the selected
Table 3: Jumper positions for default power configuration
Add jumper
to pins
9, 10 Powers up the Interface MCU, USB hub, and UART to USB converter with 3.3 V.
2, 4 Powers up the peripherals directly connected to ANNA such as LEDs and external memory
Description
source for the VDD_ANNA net.
with the ANNA supply voltage.
1.7.3 Battery powered, 3 V
When using a battery, Figure 9 shows the default configuration. The battery voltage is connected to
VDD_ANNA, which in turn, is connected to the ANNA-B112 VCC supply. If needed, a jumper can be
added to J22 pins 2 and 4 to supply LEDs and other peripherals with power, as long as this does not
exceed the maximum current rating of the battery. If the ANNA module has to be configured, the
VDD_MCU net can be connected to enable PC communications by adding a jumper to J7 pins 9 and
10.
Figure 9: Jumper positions for battery powered operation, two jumpers are optional
Connector
annotation
J7 5, 6 Selects the battery connected to the battery holder as source for the VDD_ANNA net.
J22 1, 3 Powers up the ANNA module. The ANNA VCC and VCC_IO pins are connected to the selected
Table 4: Jumper positions for battery powered operation, two jumpers are optional
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 10 of 31
C1-Public
Add jumper
to pins
9, 10 (Optional) Powers up the Interface MCU, USB hub, and UART to USB converter with 3.3 V.
2, 4 (Optional) Powers up the peripherals directly connected to ANNA such as LEDs and external
Description
source for the VDD_ANNA net.
memory with the ANNA supply voltage.
Page 11

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
1.7.4 Battery powered with protection diode, 2.7 V
This use case is meant to protect the battery from current back surges. When using the NFC
interface, there is a risk that the applied electromagnetic field can cause back surges that will
typically damage a non-chargeable battery. To prevent this damage, a schottky diode can be added
in series to the battery, which will block any back current surges. A jumper should then be added to
J7 pins - 3 and 4 instead of 5 and 6.
The diode will lower the voltage level of the battery by about 0.3 V.
Figure 10: Jumper positions for battery powered operation with a protection diode, two jumpers are optional
Connector
annotation
J7 3, 4 Selects the diode protected battery as a source for the VDD_ANNA net.
J22 1, 3 Powers up the ANNA module. The ANNA VCC and VCC_IO pins are connected to the selected
Table 5: Jumper positions for battery powered operation with a protection diode, two jumpers are optional
Add jumper
to pins
9, 10 (Optional) Powers up the Interface MCU, USB hub, and UART to USB converter with 3.3 V.
2, 4 (Optional) Powers up the peripherals directly connected to ANNA such as LEDs and external
Description
source for the VDD_ANNA net.
memory with the ANNA supply voltage.
1.7.5 External supply
When measuring current consumption or performing other ANNA-B112 module characterization
measurements, it can be useful to power the module with an external source such as a DC power
analyzer. In such a case, all jumpers can be removed and the required supply nets can be fed
externally by connecting to the pin headers. For example, the ANNA-B112 module can be powered
by connecting an external supply directly to the J22 pin 1 and GND.
☞ Take care that unpowered parts of the board are properly isolated. If a voltage is applied to the
signal of an unpowered device, current might leak through various protection circuits of the
device. This might give false readings when measuring current consumption etc.
Figure 11 below shows a few optional jumper connections that can be helpful when supplying the
module with an external supply.
Figure 11: Optional jumper positions while using an external power supply
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 11 of 31
C1-Public
Page 12

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Connector
annotation
J7 7, 8 (Optional) Selects the board regulated 3.3 V net as a source for the VDD_ANNA net.
J22 3, 4 (Optional) Powers up the peripherals directly connected to ANNA such as LEDs and external
Table 6: Optional jumper positions while using an external supply
Add jumper
to pins
9, 10 (Optional) Powers up the interface MCU, USB hub, and UART to USB converter with 3.3 V.
Description
memory with the selected source for the VDD_ANNA net.
1.7.6 Raspberry Pi HAT
When connecting a HAT to the Raspberry Pi interface, the following jumper configuration can be
used. Depending on how the ANNA module should communicate with a test PC over USB or with the
HAT, the VDD_MCU net can be left unpowered.
⚠ The 3V3_PI supply net must only be powered when connecting to a Raspberry Pi expansion board
(HAT). If connecting to a Raspberry Pi board, the jumper must be disconnected.
Figure 12: Jumper configuration when connected to a Raspberry Pi HAT
Connector
annotation
J7 1,2 Connects the 3V3_PI net to the regulated 3.3 V supply.
J22 1, 3 Powers up the ANNA module. The ANNA VCC and VCC_IO pins are connected to the selected
Table 7: Jumper configuration when connected to a Raspberry Pi HAT
Add jumper
to pins
7, 8 Selects the board regulated 3.3 V net as a source for the VDD_ANNA net.
9, 10 (Optional) Powers up the Interface MCU, USB hub, and UART to USB converter with 3.3 V.
2, 4 (Optional) Powers up the peripherals directly connected to ANNA such as LEDs and external
Description
source for the VDD_ANNA net.
memory with the ANNA supply voltage.
1.8 Arduino interface
The EVK-ANNA-B112 includes a set of pin headers and mounting holes that are compatible with
certain Arduino or Arduino inspired shields. Figure 13 shows the layout of the Arduino interface and
Table 8 explains the pinout in more detail. Section 1.8.1 describes what specifications must be met
for a shield to be compatible for use with the EVK-ANNA-B112.
☞ The silk screen text on EVB marked UBXH60-0000474 J3 pin 6 shall be IO_31.
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 12 of 31
C1-Public
Page 13

Figure 13: Pin headers that are compatible with some Arduino shields
UART_DTR/
EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Conn. Pin
J1 1 N/C Not Connected - - Not connected
J2 1 A0 Analog input IO_24 P0.04 Analog function capable IO
J3 1 D0/RX Digital I/O, UART RX UART_RXD P0.02 UART_RXD signal on ANNA-B1
Arduino
No.
pin
2 IOREF I/O reference voltage level.
3 RESET Reset signal input. Active low logic RESET_N P0.21
4 3.3V 3.3 V DC regulated supply output 3V3 -
5 5V 5 V regulated supply output 5V - Cannot be used as supply input, use
6 GND Ground GND GND
7 GND Ground GND GND
8 VIN External DC supply input, 5 – 12 VDC VIN -
2 A1 Analog input IO_23 P0.05 Analog function capable IO
3 A2 Analog input IO_28 P0.28 Analog function capable IO
4 A3 Analog input IO_27 P0.29 Analog function capable IO
5 A4 Analog input UART_DSR/
6 A5 Analog input
2 D1/TX Digital I/O, UART TX UART_TXD P0.03 UART_TXD signal on ANNA-B1
3 D2 Digital I/O UART_CTS P0.19 UART_CTS signal on ANNA-B1
4 D3 Digital I/O UART_RTS P0.11 UART_RTS signal on ANNA-B1
5 D4 Digital I/O IO_29 P0.27 RED
6 D5 Digital I/O IO_31 P0.26 BLUE
7 D6 Digital I/O IO_22 P0.10 Signal not connected by defualt,
8 D7 Digital I/O IO_21 P0.09 Signal not connected by defualt,
Description Schematic
net name
VDD_IO - See section 1.6
Selectable by user to 1.7 – 3.6 V
IO_26
IO_25
nRF52
pin
P0.30 Analog function capable IO,
P0.31 Analog function capable IO,
u-blox connectivity and alternate
functions with notes
VIN instead. Only supplied by USB
VBUS.
UART_DSR signal on ANNA-B1
UART_DTR signal on ANNA-B1
configured for NFC use
configured for NFC use
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 13 of 31
C1-Public
Page 14

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Conn. Pin
J4 1 D8 Digital I/O IO_13 P0.14
Table 8: Pinout of the Arduino UNO R3 compatible interface
Arduino
No.
pin
2 D9 Digital I/O IO_38 P0.24 SWITCH_2 on ANNA-B1.
3 D10 Digital I/O IO_36 P0.22
4 D11 Digital I/O IO_37 P0.23
5 D12 Digital I/O IO_16 P0.18
6 D13 Digital I/O IO_45 P0.20
7 GND Ground GND
8 AREF Analog reference voltage level - - Not connected
9 SDA I2C data signal IO_14 P0.15
10 SCL I2C clock signal IO_15 P0.16
Description Schematic
net name
nRF52
pin
u-blox connectivity and alternate
functions with notes
This signal is pulled low when the
button SW2 is pressed
1.8.1 Arduino shield compatibility
The EVK-ANNA-B112 has an I/O voltage range of 1.7-3.6 V. It can therefore be used only with shields
that also support an I/O voltage within this range.
The EVK-ANNA-B112 has a pinout that is compatible with some Arduino or Arduino inspired shields.
This section describes the features of the EVK pins that a shield must comply with:
• IOREF: The I/O voltage level of the ANNA-B112 module is 3.3 V by default, but the EVK can
be modified to allow other voltages (1.7-3.6 V).
• RESET: Is connected to the RESET button (SW0).
• 3.3 V: A regulated 3.3 V output. Should not be used as a voltage supply input, use the VIN pin
instead.
• 5 V: Is only a 5 V supply output if the EVK is being powered by USB. If any other power
configuration is used, this pin will be unconnected (floating). It is safe to connect an external
5 V supply to this pin even when a USB cable is connected. This pin cannot be used to power
the board, use the VIN pin instead.
• VIN: May be used as a 5 -12 V supply input to power the EVK-ANNA-B112.
• Pin 0 (RX): Is connected to the ANNA-B112 UART RX pin (ANNA pin 23).
• Pin 1 (TX): Is connected to the ANNA-B112 UART TX pin (ANNA pin 22).
Note on SCL/SDA: On some Arduino boards, the I
2
C signals, SCL, and SDA are connected to the pins
A4 and A5 and to the SCL and SDA pins in the top right-hand corner. Since these pins will be shorted
together it might cause problems when connected to the EVK-ANNA-B112, which has not shorted
these pins together.
Note on digital I/O pins: Some of the digital I/O pins can be connected to the on-board debug MCU,
thus allowing serial communication and flashing/debugging over USB. This can cause interference
on the signals that are also used by an Arduino shield. See section 1.11 on how to disconnect these
signals from the debug MCU.
1.9 Raspberry Pi compatible interface
The EVK-ANNA-B112 includes a 40-pin IO header that can be used to interface with either a
Raspberry Pi computer board or with a Raspberry Pi expansion board (HAT). The EVK-ANNA-B112
uses different hardware and software configurations depending on if it is connected to a Pi or a HAT;
the differences are covered in this section. The default configuration is to connect to a Pi.
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 14 of 31
C1-Public
Page 15

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Not all the Raspberry Pi versions and HATs are supported, since it requires the 40-pin IO header,
which older versions did not have. Table 9 lists the compatible Raspberry Pi versions.
Compatible Raspberry Pi boards
Raspberry Pi 1 Model A+
Raspberry Pi 1 Model B+
Raspberry Pi 2 Model B
Raspberry Pi 3 Model B
Raspberry Pi Zero
Raspberry Pi Zero W
Table 9: Compatible Raspberry Pi boards
Figure 14: Pin header J14 that is compatible with the Raspberry Pi IO connectors
Figure 14 shows the layout of the Raspberry Pi interface and Table 10 explains the pinout in detail.
There are three mounting holes that can be used for increased mechanical stability. The two on
either side of connector J14 are common to all Raspberry Pi boards, but the third one is only
compatible with the Pi Zero boards.
Conn. Pin
J14 1 3.3 V 3.3 V supply pin 3V3_PI - Not connected by default, see section 1.6
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 15 of 31
C1-Public
Raspberry
No.
Pi pin
2 5 V 5 V supply pin 5V - Cannot be used as supply input. Supplied
3 IO02 Digital I/O IO_14 P0.15
4 5 V 5 V supply pin 5V - Cannot be used as supply input. Supplied
5 IO03 Digital I/O IO_15 P0.16
Description Schematic
net name
nRF52
pin
Alternate functions and notes
by USB VBUS and protected from back
powering.
by USB VBUS and protected from back
powering.
Page 16

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Conn. Pin
Table 10: Pinout of the Raspberry Pi compatible interface
Raspberry
No.
Pi pin
6 GND Ground GND GND
7 IO04 Digital I/O N/C
8 IO14 Digital I/O, UART TX/RX RASP_TXD P0.02 Connected to ANNA UART_RXD pin by
9 GND Ground GND GND
10 IO15 Digital I/O, UART RX/TX RASP_RXD P0.03 Connected to ANNA UART_TXD pin by
11 IO17 Digital I/O N/C
12 IO18 Digital I/O RESET_N P0.21
13 IO27 Digital I/O IO_13 P0.14
14 GND Ground GND GND
15 IO22 Digital I/O IO_17 Can be connected to IO_17 via zero
16 IO23 Digital I/O IO_16 P0.18
17 3.3 V 3.3 V supply pin 3V3_PI - Not connected by default, see section 1.6
18 IO24 Digital I/O IO_18
19 IO10 Digital I/O IO_25 P0.31
20 GND Ground GND GND
21 IO09 Digital I/O IO_21 P0.09 Can be connected to IO_21 via zero Ω
22 IO25 Digital I/O IO_22 P0.10 Can be connected to IO_22 via zero Ω
23 IO11 Digital I/O IO_23 P0.05
24 IO08 Digital I/O IO_24 P0.04
25 GND Ground GND GND
26 IO07 Digital I/O IO_26 P0.30
27 ID_SD EEPROM config I2C data
28 ID_SC EEPROM config I2C clock
29 IO05 Digital I/O IO_29 P0.27
30 GND Ground GND GND
31 IO06 Digital I/O IO_31 P0.26
32 IO12 Digital I/O IO_30 P0.25
33 IO13 Digital I/O UART_RTS P0.11
34 GND Ground GND GND
35 IO19 Digital I/O UART_CTS P0.19
36 IO16 Digital I/O IO_36 P0.22
37 IO26 Digital I/O IO_37 P0.23
38 IO20 Digital I/O IO_38 P0.24
39 GND Ground GND GND
40 IO21 Digital I/O IO_45 P0.20
Description Schematic
signal
signal
nRF52
net name
IO_27 P0.29 Should only be used to read or simulate
IO_28 P0.28 Should only be used to read or simulate
pin
Alternate functions and notes
default, see section 1.9.2
default, see section 1.9.2
Ωresistor. Resistor not mounted by
default. IO_17 is connected to 32.768 LPO
crystal by default
resistor. Resistor not mounted by default.
IO_21 is connected to NFC antenna by
default
resistor. Resistor not mounted by default.
IO_22 is connected to NFC antenna by
default
HAT EEPROMs, see section 1.9.3
HAT EEPROMs, see section 1.9.3
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 16 of 31
C1-Public
Page 17

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
1.9.1 Powering considerations
There are two voltage nets used in the Raspberry Pi interface 3V3_PI and 5V. Both the 3V3_PI and
5V nets can be used to power HATs, but these should not be used when connecting to a Raspberry
Pi. See section 1.7.6 for more information.
⚠ The 3V3_PI power net must not be connected to the 3.3 V supply when connected to a Raspberry
Pi board. Connecting the power net in this way could damage both boards.
1.9.2 UART
The Raspberry Pi interface provides two pins - IO14 and IO15, which can be used for UART
communications. In UART communications, signals are always connected RX <-> TX and vice versa.
This means that on a Raspberry Pi board IO14 will be TX and on a HAT it will be RX. To support talking
to both HATs and Pi boards, the zero Ω resistors - R57, R58, R59 and R60 can be used to toggle the
ANNA TX and RX pins between IO14 and IO15. If an ANNA-B112 is used, this switch can also be made
in the software. By default, the EVK-ANNA-B112 will be configured to simulate a HAT, and IO14 is
connected to the ANNA UART_RXD pin and IO15 is connected to the ANNA UART_TXD pin
respectively.
1.9.3 EEPROM support
The Raspberry Pi interface supports a unique EEPROM solution to store the HAT specific IO
configurations on the HAT board, to be read by the Raspberry Pi before configuring its IOs. The two
pins used for this are ID_SD and ID_SC and are connected to the ANNA-B112 module. The
ANNA-B112 module can thus either read the IO configuration from a HAT, or simulate an EEPROM
and send configurations to a connected Pi. This requires an ANNA-B112 module and a custom built
application.
It is not mandatory to use this EEPROM solution; if not used, the two ANNA pins - IO_42 and IO_41
can be without configurations.
Two pull-up resistors - R44 and R50, can be added to the I
on the evaluation board by default.
Visit https://github.com/raspberrypi/hats/blob/master/designguide.md for more information on the
ID EEPROM specification.
2
C lines if needed. They are not mounted
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 17 of 31
C1-Public
Page 18
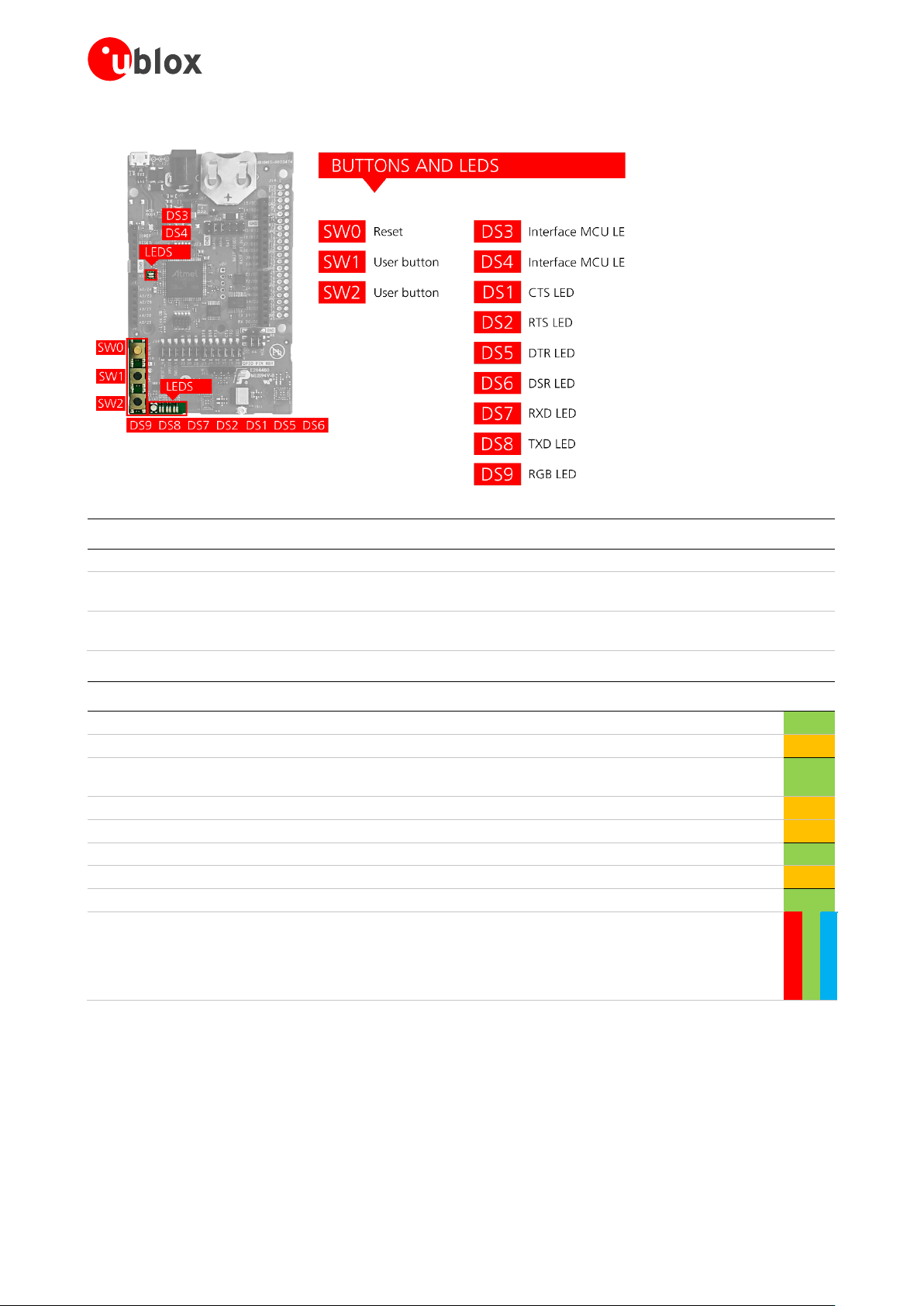
1.10 Buttons and LEDs
Figure 15: Position of the push-buttons and LEDs on the evaluation board
EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Annotation Function Description
SW0 Reset button Connected directly to the ANNA RESET_N pin.
SW1 User button Push button for application use. Connected directly to the ANNA SWITCH_1
(IO_30) pin
SW2 User button Push button for application use. Connected directly to the ANNA SWITCH_2
(IO_38) pin
Table 11: EVK-ANNA-B112 buttons
Annotation Function Description Color
DS1 UART CTS LED Connected to the ANNA UART_CTS (IO_35) pin via jumper header J9
DS2 UART RTS LED Connected to the ANNA UART_RTS (IO_34) pin via jumper header J9
DS3 Interface MCU LED Blinks on USB enumeration and activity, lit when the Interface MCU is
connected via USB
DS4 Interface MCU LED Error LED
DS5 UART DTR LED Connected to the ANNA UART_DTR (IO_25) pin via jumper header J9
DS6 UART DSR LED Connected to the ANNA UART_DSR (IO_26) pin via jumper header J9
DS7 UART RXD LED Connected to the ANNA UART_RXD (IO_20 pin via jumper header J9
DS8 UART TXD LED Connected to the ANNA UART_TXD (IO_19) pin via jumper header J9
DS9 RGB LED Connected to the ANNA RED (IO_29), GREEN (IO_30) and BLUE (IO_31)
pins via jumper header J19.
Used as status indication for u-connectXpress software. For further
information, see also the RGB system status signals section in the ANNAB112 data sheet [1].
Table 12: EVK-ANNA-B112 LED indicators
1.11 Disconnecting ANNA signals from board peripherals
All evaluation board peripherals, such as level shifters, LEDs, and the interface MCU will be
connected to the ANNA-B112 module by default. This might not suit all evaluation scenarios. All
peripherals can be switched off by disconnecting their power supplies (see section 1.6), but if only
specific signals have to be isolated, it will require finer control.
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 18 of 31
C1-Public
Page 19

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
All the ANNA module signals that are connected to board peripherals have thus been routed via
jumper headers, so that jumpers can be pulled or added as needed by the evaluation board user,
isolating, or connecting specific signals. Figure 16 shows the layout of these jumper headers.
Figure 16: Jumper headers J19 and J9 that are used to isolate specific ANNA signals
Connector
annotation
J19 1 RESET_N Reset signal, active low
J9 1 IO_25/
Pin number Schematic net
name
2 RESET_N_I Connects to the Interface MCU’s reset line
3 SWDIO SWD data signal
4 SWDIO_I Interface MCU SWD data signal, used to program/debug the ANNA
5 SWDCLK SWD clock signal
6 SWDCLK_I Interface MCU SWD data signal, used to program/debug the ANNA
7 IO_31 ANNA-B112: BLUE signal
8 BLUE RGB diode blue signal, active low
9 IO30/
SWITCH_1
10 GREEN RGB diode green signal, active low
11 IO_29 ANNA-B112: RED signal
12 RED RGB diode red signal, active low
UART_DTR
2 UART_DTR_I UART to USB DTR signal
3 IO_26/
UART_DSR
4 UART_DSR_I UART to USB DSR signal
5 IO_34/
UART_RTS
6 UART_RTS_I UART to USB RTS signal
7 IO_35/
UART_CTS
8 UART_CTS_I UART to USB CTS signal
Description
module
module
ANNA-B112: SWITCH_1 and GREEN signal
ANNA-B112: UART DTR output
ANNA-B112: UART DSR input
ANNA-B112: UART RTS output
ANNA-B112: UART CTS input
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 19 of 31
C1-Public
Page 20
EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Connector
annotation
Table 13: Pinout of jumper headers - J19 and J9
Pin number Schematic net
name
9 IO_19/
UART_TXD
10 UART_TXD_I UART to USB TXD signal
11 IO_20/
UART_RXD
12 UART_RXD_I UART to USB RXD signal
Description
ANNA-B112: UART TXD output
ANNA-B112: UART RXD input
1.12 Software debug options
You can debug the software using the following two options in EVK-ANNA-B112:
• Onboard debug solution available on the USB connector
• An external debugger connected to J12 connector
An external debugger connected to the J12 connector is useful when powering the evaluation board
with the CR2032 coin cell battery, or through the external power supply connector J5. It could also
be useful in a scenario where the debug MCU interface has been disconnected from the ANNA-B112
module using the jumpers on J9 header. The SEGGER J-Link software [4] is required to debug using
the onboard J-Link hardware on the EVK-ANNA-B112.
UBX-18018539 - R02 Product description Page 20 of 31
C1-Public
Page 21

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
2 Setting up the evaluation board
2.1 Evaluation board setup
The EVK-ANNA-B112 is delivered with u-blox u-connectXpress software pre-flashed to the module.
Before connecting the module, download and install the latest s-center evaluation software from the
u-blox website.
To use Bluetooth Low Energy on the EVK-ANNA-B112, connect a 2.4 GHz antenna to the U.FL
antenna connector (J10). The EVK-ANNA-B112C has an onboard antenna.
Plug in either an external power supply in J5 connector or connect to a USB host with a USB cable
attached to J8 connector. You can also power the evaluation board with a CR2032 coin cell battery.
The status light (DS6) turns green when power is applied to the board. The NFC antenna can be
connected to the J11 connector. The connector pinning is symmetrical, so the antenna can be
positioned either up or down in relation to the evaluation board.
⚠ Be careful to check polarity before connecting an external power supply to the EVK-ANNA-B112
evaluation board. Center conductor is positive (+) and the ring is negative (-).
The very first time you connect the unit to a new computer, drivers need to be installed. The
operating system should handle this automatically.
⚠ If the drivers are not installed automatically, download the nRF Connect application from
www.nordicsemi.com that includes the Jlink CDC UART driver.
Windows automatically assigns a COM to the unit by. Perform the following actions to view the
assigned COM ports on Windows 7:
1. Open the Control Panel and click Hardware and Sound.
2. Click Device Manager in Devices and Printers. This opens Device Manager window where you can
view the assigned COM ports.
2.2 Starting up
2.2.1 EVK-ANNA-B112
Perform the following steps to enable communication with the module:
1. Start the s-center evaluation software.
2. Use the default baud rate 115200, 8N1 with flow control. You should now be able to
communicate with the module using AT commands.
For a list of available AT commands, see the u-blox u-connect AT commands manual [3]. To get
started with a basic use case setup of the EVK-ANNA-B112 with u-blox u-connectXpress software,
see the u-connectXpress user guide [5].
2.2.2 Getting the latest u-connectXpress software
Go to the u-blox support webpage to get the latest firmware. Instructions for flashing the EVKANNA-B112 can be found in the Software section of the ANNA-B112 system integration manual [2].
UBX-18018539 - R02 Setting up the evaluation board Page 21 of 31
C1-Public
Page 22

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
2.2.3 Open CPU
To use the EVK-ANNA-B112 together with the Nordic Semiconductor SDK, refer to the software
section of the ANNA-B112 system integration manual [2] that describes how to:
• Create your own board file
• Adapt the examples in the Nordic Semiconductor SDK to use this board file
See also the u-blox short range open CPU github repository [6].
UBX-18018539 - R02 Setting up the evaluation board Page 22 of 31
C1-Public
Page 23
Appendix
Bottom view
A Placement and schematics
EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Top view
UBX-18018539 - R02 Appendix Page 23 of 31
C1-Public
Page 24
12345678
(TRACE _CLK)
(TRACE _D0)
(TRACE _D1)
(TRACE _D2)
(TRACE _D3)
E
IO_18
BI
IO_17
BI
5%
22P22P
R61R64
DNI
D
32.768KHZ
5%
22P
C
BI
BI
DNI
0R
(TRACE _CLK)
(TRACE _D0)
(TRACE _D1)
(TRACE _D2)
(TRACE _D3)
IO_18
IO_17
0R
5%
C54
R63
R62
DNI
DNI
0R
X3 X5X4
B
0R
32.768KHZ
(TRACE _CLK)
(TRAC E_D0)
5%
(TRAC E_D1)
(TRAC E_D2)
22P
(TRAC E_D3)
IO_18
BI
IO_17
BI
5%
22P
C56
A A
32.768KHZ
5%
22P
C57 C18C52C55
R66 R65
DNI0RDNI
0R
IO_45
BI
IO_16
BI
IO_15
BI
IO_14
BI
IO_13
BI
SWDCLK
BI
SWDIO
BI
RESET_ MODULE_N
BI
IO_37
BI
IO_36
BI
IO_29
BI
IO_30
BI
IO_31
BI
IO_38
BI
IO_28
BI
IO_27
BI
IO_24
BI
IO_23
BI
IO_26
BI
IO_25
BI
UART_R XD
BI
UART_T XD
BI
UART_C TS
BI
UART_R TS
BI
32.768 KHZ_XL1_CO NNECTOR
32.768 KHZ_XL2_CO NNECTOR
IO_45
BI
IO_16
BI
IO_15
BI
IO_14
BI
IO_13
BI
SWDCLK
BI
SWDIO
BI
RESET_ MODULE_N
BI
IO_37
BI
IO_36
BI
IO_29
BI
IO_30
BI
IO_31
BI
IO_38
BI
IO_28
BI
IO_27
BI
IO_24
BI
IO_23
BI
IO_26
BI
IO_25
BI
UART_R XD
BI
UART_T XD
BI
UART_C TS
BI
UART_R TS
BI
32.768 KHZ_XL1_CO RNER
32.768 KHZ_XL2_CO RNER
IO_45
BI
IO_16
BI
IO_15
BI
IO_14
BI
IO_13
BI
SWDCLK
BI
SWDIO
BI
RESET_ MODULE_N
BI
IO_37
BI
IO_36
BI
IO_29
BI
IO_30
BI
IO_31
BI
IO_38
BI
IO_28
BI
IO_27
BI
IO_24
BI
IO_23
BI
IO_26
BI
IO_25
BI
UART_R XD
BI
UART_T XD
BI
UART_C TS
BI
UART_R TS
BI
32.768 KHZ_XL1_ED GE
32.768 KHZ_XL2_ED GE
131614
12
M3
37 1
IO_37 ANT_PCB
36
IO_36
IO_29
IO_30
IO_38
IO_28
IO_27
IO_24
IO_23
IO_26
IO_25
UART_RXD
UART_TXD
UART_CTS
UART_RTS
RESET_N
29
30
38
28
27
24
23
26
25
20
19
35
34
17
12
M1
37
IO_37 ANT_PCB
36
IO_36
IO_29
IO_30
IO_38
IO_28
IO_27
IO_24
IO_23
IO_26
IO_25
UART_RXD
UART_TXD
UART_CTS
UART_RTS
RESET_N
29
30
38
28
27
24
23
26
25
20
19
35
34
17
12
M2
37 1
IO_37 ANT_PCB
36
IO_36
IO_29
IO_30
IO_38
IO_28
IO_27
IO_24
IO_23
IO_26
IO_25
UART_RXD
UART_TXD
UART_CTS
UART_RTS
RESET_N
29
30
38
28
27
24
23
26
25
20
19
35
34
17
15
40
39
SWD_IO
ANNA W ITH COAX C ONNECTOR
XL_1
XL_2
18
40
39
SWD_IO
ANNA I N A CORNER
XL_1
XL_2
18
40
39
SWD_IO
XL_1
XL_2
18
45
IO_15
IO_45
IO_13
IO_16
IO_14
SWD_CLK
ublox_anna_b1
GND_47
GND_44
GND_50
GND_48
GND_46
47
44
504846
13
16
14
15
45
IO_13
IO_16
IO_14
IO_15
IO_45
SWD_CLK
ublox_anna_b1
GND_47
GND_44
GND_50
GND_48
GND_46
504846
47
44
131614
15
45
IO_13
IO_16
IO_14
IO_15
IO_45
SWD_CLK
ANNA I N A EDGE
ublox_anna_b1
GND_47
GND_44
GND_50
GND_48
GND_46
47
44
504846
22
21
NFC_2
NFC_1
GND_42
GND_41
GND_33
GND_43
424133
43
22
21
NFC_2
NFC_1
GND_42
GND_41
GND_33
GND_43
424133
43
22
21
NFC_2
NFC_1
GND_42
GND_41
GND_33
GND_43
424133
43
ANT_GND_1
ANT_GND_2
GND_10IO_31
ANT_INT
GND_11
GND_49
GND_51
GND_52
GND_32
32
ANT_GND_1
ANT_GND_2
GND_10IO_31
ANT_INT
GND_11
GND_49
GND_51
GND_52
GND_32
32
ANT_GND_1
ANT_GND_2
GND_10IO_31
ANT_INT
GND_11
GND_49
GND_51
GND_52
GND_32
32
GND_4
GND_7
GND_8
GND_4
GND_7
GND_8
GND_4
GND_7
GND_8
ANT
VCC
ANT
VCC
ANT
VCC
NFC_2_ CONNECTOR
NFC_1_ CONNECTOR
2
3
4
1031
5
11
6
ANT_EX T
VCC
9
7
8
49
51
52
100N
NFC_2_ CORNER
NFC_1_ CORNER
1
ANT_HO ST_CORNER
2
3
4
1031
5
ANT_IN T_CORNER
11
6
VCC
9
7
8
49
51
52
100N
NFC_2_ EDGE
NFC_1_ EDGE
2
3
4
1031
5
ANT_IN T_EDGE
11
6
VCC
9
7
8
49
51
52
C8 C17 C13
100N
JUMPER HEADERS USE D TO CONNECT
GPIOS TO VAR IOUS BOARD FUNCTION S
ALL POSISTION S MOUNTED BY DEF AULT
VDD_IO
0R
DNI
10%
C47
100N
J10
1
NFC_2_ CONNECTOR
NFC_2_ CORNER
NFC_2_ EDGE
NFC_1_ CONNECTOR
NFC_1_ CORNER
NFC_1_ EDGE
CURRENT MEASURE MENT
VDD_AN NA
R26
R23
R27
C24
0R
330 P
10%
0R
NFC_2
0R
DNI
R24
0R
330 P
R35
R36
10%
0R
0R
NFC_1
C25
330 P
10%
VCC
DNI
R6
NFC ANTENNA
CONNECTOR
R22
0R
DNI
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
R18
0R
DNI
POSSIBILI TY TO SEPARATE RESET
R4
0R
J22
1
21
43
5 6
65
IO_22
BI
J11C51
IO_21
BI
VCC_IO
2
43
VDD_IO
SWDIO_ I
SWDCLK _I
IO_16
RESET_ N_I
UART_D TR_I
UART_D SR_I
UART_R TS_I
UART_C TS_I
UART_T XD_I
UART_R XD_I
R43
VCC
R67
RESET_ MODULE_N
10K
DNI
R68
0R
RESET_ N
10%
C19
100N
PRODUCT VARIANTS
BOM_ANT_C ORNER:ANNA-B1WITH INTERNAL ANTENNA MOUNTED IN A COR NER
TWO ANNA-B1 PLACEME NT OPTIONS FOR INT ERNAL ANTENNA
(ONLY ONE OPTION SETUP IS MOUNTED)
BOM_ANT_E DGE:ANNA-B1WITH INTERNAL ANTENNA MOUNTED ON A EDG E SIDE
BOM_ANT_C ONNECTOR:ANNA-B1WITH A COAX CONNECTOR
DRAWING TITLE :
ANNA MODULE
A3
EVB-ANNA-B1
PAGE 1 OF 6
DESIGN BY :
DATE :
GROUP :
U-BLOX AG
THALWIL
SWITZERLAND
mwe j
Fri Feb 16 12: 12:24 2018
u-blox AG $Change: 6053 27
345678 2
RESET_ N
SWDIO
SWDCLK
IO_31
IO_30
IO_29
IO_25
IO_26
UART_R TS
UART_C TS
UART_T XD
UART_R XD
VDD_MC U
ti_txs0104epwr
8
2 13
3
4
5
1
14
10%
C48
100N
TXS0108
10
OE
1
A1
3
A2 B2
4
A3
5
A4
6
A5
7
A6
8 13
A7
9
A8
2
VCCA
19
VCCB GND
10%
C20
100N
OE
A1 B1
A2
A3
A4
VCCA
VCCB
U4
J19
1
1
2
3
3
4
5
5
6
7
7
8
9 10
9
10
11
12
11
J9
1
1
2
3
3
4
5
5
6
7
7
8
9
10
11
12
11
U9
SWDIO_ LVL
12
SWDCLK _LVL
B2
11
SWO_LV L
B3
10
RESET_ N_LVL
B4
TO INTERFACE MCU
20
UART_D TR_LVL
B1
18
UART_D SR_LVL
17
UART_R TS_LVL
B3
16
UART_C TS_LVL
B4
15
UART_T XD_LVL
B5
14
UART_R XD_LVL
B6
B7
12
B8
TO FTDI CHI P
11
LEVEL SHIFTERS
VERSION :PROJECT :
PCB_VER.:
ICM:
2
RESET_ N_I
4
SWDIO_ I
6
SWDCLK _I
8
BLUE
GREEN
12
RED
2
UART_D TR_I
4
UART_D SR_I
6
UART_R TS_I
8
UART_C TS_I
109
UART_T XD_I
12
UART_R XD_I
02
B
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
1
E
D
C
B
Page 25

12345678
E
D
E
D
THIS PAGE IS INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK DUE TO LICENSE AGREEMENTS
C
C
B
A A
DESIGN BY :
DATE :
GROUP :
mwe j
Fri May 25 11: 22:49 2018
U-BLOX AG
THALWIL
SWITZERLAND
345678 2
DRAWING TITLE :
INTERFACE MCU
A3
EVB-ANNA-B1
PAGE 2 OF 6u-blox AG $Change: 6053 27
VERSION :PROJECT :
PCB_VER.:
ICM:
02
B
1
B
Page 26

12345678
E
E
VDD_MC UVDD_MC U VDD_MC UVDD_MC U
VBUS_M CU
R25
D
USB_HU B_DM
BI
BI
USB_HU B_DP
C
C14
8P2
+/-0.5 P
R51
100K
X2
24.000MHZ
30PPM
+/-0.5 P
HUB_DE TECT
R52
100K 100N
XTAL1
XTAL2
C15
8P2
C53
U2
19
USBDM_UP OCS2_N
20
USBDP_UP
21
XTALOUT
XTALIN
PLLFILT
24
RBIAS
R53
12K
1%
VDD_MC U
C16
100N
B
10K
14
15
181716113
SMBCLK
RESET_N
SUSP_IND
VBUS_DET
microchip_usb2422
USBDP_DN2
USBDM_DN2
USBDP_DN1
USBDM_DN1
VDD33_1 VDD33_18
3
245
39R
39R
NON_RE M0
NON_RE M1
SMBDATANC
PRTPWR2
PRTPWR1
6
R2
5%
5%
R3
CFG_SE L
CRFILT
VDD33_9
OCS1_N
DHSD_P
DHSD_N
DFSD_P
DFSD_N
R55
100K
R54
100K
12
11
10
922
823
7
1U
1U
BI
BI
BI
BI
BOOT STRAPPING
CONFIG
R56
100K
USB_FT DI_DM
USB_FT DI_DP
VDD_MC U
4U7
C23C45C22C21
100N
10
9
8
11
C46
100N
U8
3V3OUT
USBDM
USBDP
RESET_N
12
VCC
ftdi_ft231x
GND_3
GND_13
3
13
20
17
TXD
RXD
VCCIO
RTS_N
CTS_N
DTR_N
DSR_N
DCD_N
RI_N
CBUS0
CBUS1
CBUS2
CBUS3
GND_21
UART_R XD_LVL
1
UART_T XD_LVL
19
UART_C TS_LVL
6
UART_R TS_LVL
18
UART_D SR_LVL
4
UART_D TR_LVL
5
2
15
CBUS0
14
CBUS1
7
CBUS2
16
CBUS3
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
TP4
TP6
TP7
TP5
21
D
C
B
A A
U-BLOX AG
THALWIL
SWITZERLAND
DESIGN BY :
DATE :
GROUP :
mwe j
Thu Feb 15 14: 33:41 2018
u-blox AG $Change: 6053 27
345678 2
DRAWING TITLE :
HUB, FTDI AND FLASH
A3
EVB-ANNA-B1
PAGE 3 OF 6
VERSION :PROJECT :
PCB_VER.:
ICM:
02
B
1
Page 27

12345678
3V3
5V
J1
1
1
2
2
3
RESET_ N
3
4
4
E
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
VDD_IO
BI
VIN
J4
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
IO_15
10
IO_14
9
8
7
IO_45
6
IO_16
5
IO_37
4
IO_36
3
IO_38
2
IO_13
1
BI
BI
BI
BI
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
TRACE_CLK
TRACE_D0
TRACE_D3
TRACE_D1
TRACE_D2
BOOT JUMPER
J18
2
1
IO_30
DNI
RESET_ N
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
TP24
1
3
C9
100N
SW0
RESET
2
4
IO_38
BI
VDD_MC U
TP26
C11
DNI
100N
SW2
1
3
2
4
E
SWITCH 2
J2
1
IO_24
1
2
IO_23
2
3
IO_28
3
4
IO_27
4
5
IO_26
5
6
IO_25
6
D
VDD_IO
J12
21
1
3
3
5 6
5
7 8
7
9
SWDIO
2
4
SWDCLK
4
IO_16
6
8
10
RESET_ N
109
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
UART_D SR
BI
UART_D TR
ARDUINO INTERFA CE
BI
(SWO)
BI
BI
BI
VDD_IO
CORTEX DEBUG
C
CORTEX DEBUG + ETM
DEBUG CONNECT ORS RASPBERRY PI INT ERFACE
VDD_IO
B
GREEN
BI
BI
BI
wurth_150141m173100
1
1 7
3 5
RED
6
BLUE
VCC=VD D_IO;GND=G ND
DS9
A
74LVC3G07
1
1
1
2
B
3
R
4
G
2K7
U3
5%
5%
2
J3
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
IO_21
8
IO_22
7
IO_31
6
IO_29
5
UART_R TS
4
UART_C TS
3
UART_T XD
2
UART_R XD
1
BI
BI
BI
BI
NFC_1
BI
NFC_2
BLUE
BI
RED
BI
IO_30
BI
BI
1
3
C10
DNI
100N
SWITCH 1
2
4
BI
IMCU_B OOT
SWITCHES
IO_14
IO_15
IO_27
IO_28
3V3_PI
IO_14
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
IO_15
11
IO_13
IO_17
BI
IO_25
BI
IO_21
IO_23
BI
IO_27
BI
IO_29
IO_31
BI
UART_R TS
UART_C TS
BI
IO_37
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
27
29
31
33
35
37
39
VDD_IO
J21
1
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
2
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
DNI
SWDIO
2
43
SWDCLK
4
6
IO_16
6
8
8
10
RESET_ N
10
12
IO_45
12
14
IO_16
14
16
IO_15
16
18
IO_14
181917
20
IO_13
20
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
(SWO)
(TRACE_CLK)
BI
(TRACE_D0)
(TRACE_D1)
BI
(TRACE_D2)
(TRACE_D3)
BI
3K9
R69
DNI
3K9
R70
R44
DNI
DNI
3K9
3K9
R50
DNI
I2C PULL UP S
R57
UART_T XD
BI
UART_R XD
BI
RASP_T XD
DNI
R58
RASP_R XD
0R
R59
RASP_T XD
0R
R60
RASP_R XD
DNI
RX/TX SELECTION
LEDS
R21R20R19
1K01K0
5%
UART_C TS_I
BI
UART_R TS_I
BI
UART_D TR_I
BI BI
74LVC3G07 74LVC3G07
1
3
1
6
1
VCC=VD D_IO;GND=G ND
7
5
2
DTR_LE D
VDD_IO
AC
DS1
GREEN
1K0
A
DS2
ORANGE
C
AC
DS5
ORANGE
1K0 1K0
BI
BI
UART_R XD_ICTS_LE D
UART_T XD_I
UART_D SR_I
U7U5
11
3
VCC=VD D_IO;GND=G ND
7
1
5
1
26
1
RXD_LE D
TXD_LE DRTS_LE D
DSR_LE D
VDD_IO
A
DS7
GREEN
C
A
AC
DS6
DS8
GREEN
ORANGE
C
R8R40 R39R7R11R10
1K01K0 1 K0
R41
10K
TP27
DNI
C49
100N
1
3
DNI
MCU BOOT
SW3SW1
2
4
D
5V
J14
1
3
5
7
9
2
2
1
4
3
4
6
5
6
8
7
8
9
10
12
11
14
13
16
15
17
18
19
20
21
22
24
23
26
25
27
28
30
29
32
31
34
33
35
36
38
37
40
39
RASP_T XD
10
RASP_R XD
12
RESET_ N
14
16
IO_16
18
IO_18
20
22
IO_22
24
IO_24
26
IO_26
28
IO_28
30
32
IO_30
34
36
IO_36
38
IO_38
40
IO_45
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
BI
C
DNI
B
A A
U-BLOX AG
THALWIL
SWITZERLAND
DESIGN BY :
DATE :
GROUP :
mwe j
Thu Feb 15 14: 40:35 2018
u-blox AG $Change: 6053 27
345678 2
DRAWING TITLE :
HEADERS & BUTTONS
A3
EVB-ANNA-B1
PAGE 4 OF 6
VERSION :PROJECT :
PCB_VER.:
ICM:
02
B
1
Page 28

E
EXTERNAL SU PPLY
D
LOW CURRENT LEAKAGE CAP S FOR SUPPLY HIGH CURR ENT PE AKS
IF USED, THE 5V NET MUS T BE SUPPLIED
BY AN EX TERNA L SOURCE, USB ETC.
5V
5-12 V
J5
CON_PWR_03_SWITCH
D2
A
VIN
2
3
J17
DCDC_I N
C
F1
FUSE
1
2
1
COIN CELL BAT TERY 3V
VBATVBAT
100U
C58
DNI
C59
100U
VBAT
3V
BT1
3.3V REGULATED
C7
R5
100K
22U4U7
BATTERY PRO TECTI ON:
NFC CAN CAUSE REVERSE
SW_1
SW_2
SW_3
VOS
AGND
PGND_1
PGND_2
PG
U1
L2L1
2U22U2
1
2
3
14
4
5
FB
68
15
16
TPS6213X
11
PVIN_1
12
C50
D3
2
CATAN
D6 J7
CA1
C2C1C3
10U
100N
C5
3N3
PVIN_2
10
AVIN
13
EN
9
SS/TR
DEF
7
FSW
VBAT
3V3
D4
A
CURRENT FLO W
62132 3.3V VER SION
POWER SOURCE SEL ECTOR
12345678
E
3V3_PI
1
1
2
3
C
3
4
5
5
6
7
7
8
9
9
10
11
12
11
VDD_AN NA VDD _MCU
2
4
6
8
10
12
D
C
J8
VUSB
USB MICRO B
DM
DP
N.C.
GND
SGND=G NDA
SUSB_M ICRO_B_4TH GND
B
GNDA
1
2
3
4
5
10M
100N
R1
C6
VBUS_M CU
USB_DM _MCUCON
USB_DP _MCUCON
TP38
TP35
TP8
TP9
USBLC6 2SC6
1
I/O1 I/O1
3
I/O2 I/O2
2
D1
VBUS_M CU
VCCGND
6
4
5
USB_HU B_DM
USB_HU B_DP
BI
BI
100N
USB
'ZERO VOLT DIO DE' - PROTECTS FROM BACK C URREN T O N VBUS LINES
5V
P_CHANNEL _MOSFET
DMG2305UX
21
Q1
4
E2 C2
5
A A
BASE_1
R9
10K
B2
6
3
2
BASE_1
B1
1
E1C1
VBUS_M CU
3
D
Q2
G S
47K
R71
DESIGN BY :
DATE :
GROUP :
mwe j
Fri Feb 16 12: 12:25 2018
u-blox AG $Change: 6053 27
U-BLOX AG
THALWIL
SWITZERLAND
345678 2
DRAWING TITLE :
POWER SUPPLY
A3
EVB-ANNA-B1
PAGE 5 OF 6
VERSION :PROJECT :
PCB_VER.:
ICM:
02
B
1
C
B
Page 29

B Glossary
Name Definition
API Application Programming Interface
CTS Clear To Send
DSR Data Set Ready
DTR Data Terminal Ready
EVB Evaluation Board
EVK Evaluation Kit
GND Ground
IO General-Purpose Input/Output
LED Light-Emitting Diode
MCU Micro Controller Unit
MSD Mass Storage Device
NFC Near Field Communication
U.FL Coaxial RF connector
USB Universal Serial Bus
RTS Request To Send
RXD Receive Data
SDK Software Development Kit
SPA Serial Port Application
TXD Transmit Data
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
Table 14: Explanation of abbreviations used
EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
UBX-18018539 - R02 Appendix Page 29 of 31
C1-Public
Page 30

EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Related documents
[1] ANNA-B112 data sheet, UBX-18011707
[2] ANNA-B112 series system integration manual, UBX-18009821
[3] u-connect AT commands manual, UBX-14044127
[4] SEGGER J-Link software - https://www.segger.com/jlink-software.html
[5] u-connectXpress user guide, UBX-16024251
[6] https://github.com/u-blox/u-blox-sho-OpenCPU
☞ For regular updates to u-blox documentation and to receive product change notifications, register
on our homepage (www.u-blox.com).
Revision history
Revision Date Name Comments
R01 5-Jun-2018 hekf, mwej, kgom Initial release.
R02 18-Dec-2020 mape, fbro, mhan Updated description for RGB LED in Table 12.
Added more info on the antennas delivered with the EVK.
Clarified open CPU information.
Added information about module variant ANNA-B112-70B.
UBX-18018539 - R02 Related documents Page 30 of 31
C1-Public
Page 31

Contact
For complete contact information, visit us at www.u-blox.com.
u-blox Offices
North, Central and South America
u-blox America, Inc.
Phone: +1 703 483 3180
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Regional Office West Coast:
Phone: +1 408 573 3640
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Technical Support:
Phone: +1 703 483 3185
E-mail: support@u-blox.com
Headquarters
Europe, Middle East, Africa
u-blox AG
Phone: +41 44 722 74 44
E-mail: info@u-blox.com
Support: support@u-blox.com
EVK-ANNA-B112 - User guide
Asia, Australia, Pacific
u-blox Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Phone: +65 6734 3811
E-mail: info_ap@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office Australia:
Phone: +61 2 8448 2016
E-mail: info_anz@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Beijing):
Phone: +86 10 68 133 545
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Chongqing):
Phone: +86 23 6815 1588
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shanghai):
Phone: +86 21 6090 4832
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shenzhen):
Phone: +86 755 8627 1083
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office India:
Phone: +91 80 405 092 00
E-mail: info_in@u-blox.com
Support: support_in@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Osaka):
Phone: +81 6 6941 3660
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Tokyo):
Phone: +81 3 5775 3850
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Korea:
Phone: +82 2 542 0861
E-mail: info_kr@u-blox.com
Support: support_kr@u-blox.com
Regional Office Taiwan:
Phone: +886 2 2657 1090
E-mail: info_tw@u-blox.com
Support: support_tw@u-blox.com
UBX-18018539 - R02 Contact Page 31 of 31
C1-Public
 Loading...
Loading...