Page 1
Abstract
This document describes the hardware features and specifications of u-blox EVA-8M and EVA-M8
series GNSS modules. The EVA series modules boast the industry’s smallest form factor and are a
fully tested standalone solution that requires no host integration. The EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series
modules combine excellent GNSS performance with highly flexible power, design, and serial
communication options.
www.u-blox.com
UBX-16010593 - R08
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series
u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 GNSS SiP modules
Hardware integration manual
Page 2

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Title
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series
Subtitle
u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 GNSS SiP modules
Document type
Hardware integration manual
Document number
UBX-16010593
Revision and date
R08
28-May-2020
Document status
Production information
Product status
Corresponding content status
In Development /
Prototype
Objective Specification
Target values. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
Engineering Sample
Advance Information
Data based on early testing. Revised and supplementary data will be published later.
Initial Production
Early Production Information
Data from product verification. Revised and supplementary data may be published later.
Mass Production /
End of Life
Production Information
Document contains the final product specification.
European Union regulatory compliance
EVA-8M, EVA-M8M, and EVA-M8Q comply with all relevant requirements for RED 2014/53/EU. The EVA-8M and EVA-M8M/Q
Declaration of Conformity (DoC) is available at www.u-blox.com within Support > Product resources > Conformity Declaration.
Product name
Type number
ROM/FLASH version
PCN reference
EVA-M8M
EVA-M8M-0-10
ROM SPG 3.01 / Flash FW SPG 3.01
UBX-16012546
EVA-M8M
EVA-M8M-1-10
ROM SPG 3.01 / Flash FW SPG 3.01
UBX-16012546
EVA-M8Q
EVA-M8Q-0-10
ROM SPG 3.01 / Flash FW SPG 3.01
N/A
EVA-8M
EVA-8M-0-10
ROM SPG 3.01
N/A
u-blox or third parties may hold intellectual property rights in the products, names, logos and designs included in this
document. Copying, reproduction, modification or disclosure to third parties of this document or any part thereof is only
permitted with the express written permission of u-blox.
The information contained herein is provided “as is” and u-blox assumes no liability for its use. No warranty, either express or
implied, is given, including but not limited to, with respect to the accuracy, correctness, reliability and fitness for a particular
purpose of the information. This document may be revised by u-blox at any time without notice. For the most recent
documents, visit www.u-blox.com.
Copyright © u-blox AG.
Document information
This document applies to the following products:
UBX-16010593 - R08 Page 2 of 47
Production information Document information
Page 3

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Contents
Document information ................................................................................................................................ 2
Contents .......................................................................................................................................................... 3
1 Hardware description ........................................................................................................................... 6
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................................ 6
2 Design-in ................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.1 Power management ................................................................................................................................... 7
2.1.1 Overview ............................................................................................................................................... 7
2.1.2 Power management configuration ................................................................................................. 8
2.2 Interfaces ...................................................................................................................................................... 9
2.2.1 UART interface .................................................................................................................................... 9
2.2.2 Display data channel (DDC) interface ...........................................................................................10
2.2.3 SPI interface ......................................................................................................................................10
2.2.4 USB interface .....................................................................................................................................10
2.2.5 SQI flash memory .............................................................................................................................11
2.3 I/O pins .........................................................................................................................................................12
2.3.1 Time pulse ..........................................................................................................................................12
2.3.2 External interrupt .............................................................................................................................13
2.3.3 Active antenna supervisor ..............................................................................................................13
2.3.4 Electromagnetic interference and I/O lines .................................................................................14
2.4 Real-time clock (RTC) ...............................................................................................................................15
2.4.1 RTC using a crystal ...........................................................................................................................15
2.4.2 RTC derived from the system clock: single crystal feature .....................................................15
2.4.3 RTC using an external clock ...........................................................................................................15
2.4.4 Time aiding .........................................................................................................................................16
2.5 RF input .......................................................................................................................................................16
2.5.1 Active antenna ..................................................................................................................................16
2.5.2 Passive antenna ................................................................................................................................16
2.5.3 Improved jamming immunity .........................................................................................................17
2.6 Safe boot mode (SAFEBOOT_N) ............................................................................................................17
2.7 System reset (RESET_N) ........................................................................................................................18
2.8 Design-in checklists .................................................................................................................................18
2.8.1 General considerations ....................................................................................................................18
2.8.2 Schematic design-in for EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules .......................................18
2.9 Pin description ...........................................................................................................................................19
2.9.1 Pin name changes.............................................................................................................................20
2.10 Layout design-in checklist ......................................................................................................................20
2.11 Layout ..........................................................................................................................................................21
2.11.1 Footprint .............................................................................................................................................21
2.11.2 Paste mask ........................................................................................................................................21
2.11.3 Placement ..........................................................................................................................................22
UBX-16010593 - R08 Page 3 of 47
Production information Contents
Page 4

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
2.12 Layout design-in: Thermal management .............................................................................................22
2.13 Migration considerations ........................................................................................................................22
2.13.1 Hardware migration from EVA-7M to EVA-8M / EVA-M8M / EVA-M8Q ..............................23
2.13.2 C88-M8M - Evaluating EVA-M8M on existing NEO-xM sockets ............................................24
2.14 EOS/ESD/EMI precautions ......................................................................................................................25
2.14.1 Electrostatic discharge (ESD) ........................................................................................................26
2.14.2 ESD protection measures ...............................................................................................................26
2.14.3 Electrical overstress (EOS) .............................................................................................................26
2.14.4 EOS protection measures ...............................................................................................................26
2.14.5 Electromagnetic interference (EMI) .............................................................................................27
2.14.6 Applications with cellular modules ...............................................................................................27
3 Product handling and soldering ..................................................................................................... 30
3.1 Packaging, shipping, storage and moisture preconditioning ..........................................................30
3.2 ESD handling precautions .......................................................................................................................30
3.3 Soldering .....................................................................................................................................................30
3.3.1 Soldering paste .................................................................................................................................30
3.3.2 Reflow soldering ................................................................................................................................31
3.3.3 Optical inspection .............................................................................................................................31
3.3.4 Repeated reflow soldering ..............................................................................................................31
3.3.5 Wave soldering ..................................................................................................................................31
3.3.6 Rework ................................................................................................................................................31
3.3.7 Use of ultrasonic processes ...........................................................................................................31
4 Product testing ................................................................................................................................... 32
4.1 Test parameters for OEM manufacturer .............................................................................................32
4.2 System sensitivity test ............................................................................................................................32
4.2.1 Guidelines for sensitivity tests ......................................................................................................32
4.2.2 “Go/No go” tests for integrated devices ......................................................................................32
Appendix ....................................................................................................................................................... 33
A Reference schematics ....................................................................................................................... 33
A.1 Cost-optimized circuit .............................................................................................................................33
A.2 Best-performance circuit with passive antenna ................................................................................34
A.3 Improved jamming immunity with passive antenna .........................................................................35
A.4 Circuit using active antenna ...................................................................................................................36
A.5 USB self-powered circuit with passive antenna .................................................................................37
A.6 USB bus-powered circuit with passive antenna .................................................................................38
A.7 Circuit using 2-pin antenna supervisor ................................................................................................39
A.8 Circuit using 3-pin antenna supervisor ................................................................................................40
B Component selection ........................................................................................................................ 41
B.1 External RTC (Y1) ......................................................................................................................................41
B.2 RF band-pass filter (F1) ...........................................................................................................................41
B.3 External LNA protection filter (F2) ........................................................................................................41
B.4 USB line protection (D2) ..........................................................................................................................42
UBX-16010593 - R08 Page 4 of 47
Production information Contents
Page 5

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
B.5 USB LDO (U1) .............................................................................................................................................42
B.6 External LNA (U1) .....................................................................................................................................42
B.7 Optional SQI Flash (U3) ............................................................................................................................42
B.8 RF ESD protection diode (D2) .................................................................................................................43
B.9 Operational amplifier (U6) .......................................................................................................................43
B.10 Open-drain buffer (U4, U7 and U8) ........................................................................................................43
B.11 Ferrite beads (FB1) ...................................................................................................................................43
B.12 Antenna supervisor switch transistor (T1) .........................................................................................44
B.13 Feed-through capacitors .........................................................................................................................44
B.14 Inductor (L1) ...............................................................................................................................................44
B.15 Standard capacitors .................................................................................................................................44
B.16 Standard resistors ....................................................................................................................................44
C Glossary ................................................................................................................................................. 45
Related documents ................................................................................................................................... 46
Revision history .......................................................................................................................................... 46
Contact .......................................................................................................................................................... 47
UBX-16010593 - R08 Page 5 of 47
Production information Contents
Page 6

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
1 Hardware description
1.1 Overview
The EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules feature the excellent performance of the u-blox 8 / ublox M8 positioning engine. The EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series delivers high sensitivity and minimal
acquisition times in the ultra-compact EVA form factor.
The EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series is an ideal solution for cost and space-sensitive applications. It is easy
to design-in, only requiring an external GNSS antenna in most applications. The layout of the EVA-8M
/ EVA-M8 modules is especially designed to ease the customer’s design and limit near field
interferences since RF and digital domains are kept separated.
The EVA-8M and EVA-M8M series module uses a crystal oscillator for lower system costs, while EVAM8Q with TCXO provides the best performance. Like other u-blox GNSS modules, the EVA series uses
components selected for functioning reliably in the field over the full operating temperature range.
The EVA-M8M and EVA-M8Q modules include a dual-frequency RF front-end, with which the u-blox
M8 concurrent GNSS engine is able to intelligently use the highest amount of visible satellites from
up to three GNSS (GPS/Galileo, together with GLONASS or BeiDou) systems for reliable positioning.
The EVA-M8M series comes in two variants. The EVA-M8M-0 defaults to GPS/QZSS/GLONASS and
fits global applications, whereas EVA-M8M-1 defaults to GPS/QZSS/BeiDou, making it the ideal
module for China. The right satellite constellations can be selected without touching software,
reducing the design and testing effort.
The EVA-8M includes a single-frequency RF front-end, and can receive and track either GPS or
GLONASS signals.
The EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series modules can be easily integrated in manufacturing, thanks to the
QFN-like package and low moisture sensitivity level. The modules are available in 500 pcs/reel, ideal
for small production batches. The EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series modules combine a high level of
integration capability with flexible connectivity options in a miniature package. This makes them
perfectly suited for industrial and mass-market end products with strict size and cost requirements.
The DDC (I2C-compliant) interface provides connectivity and enables synergies with u-blox cellular
modules.
The EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series modules are qualified as stipulated in the JESD47 standard.
☞ For applications needing data logging capability, storing configurations and keeping AssistNow
data, the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules must be connected to an external SQI flash
memory. Firmware update from SQI flash memory is only supported with EVA-M8M and EVA-M8Q
series GNSS modules. For more information about product features, see the EVA-M8 data sheet
[1] and the EVA-8M data sheet [2]
☞ To determine which u-blox product best meets your needs, see the product selector tables on the
u-blox website www.u-blox.com.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Hardware description Page 6 of 47
Production information
Page 7
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
2 Design-in
To obtain good performance with EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS receiver modules, there are a
number of issues requiring careful attention during the design-in. These include:
Power supply: Good performance requires a clean and stable power supply.
Interfaces: Ensure correct wiring, rate and message setup on the module and your host
system.
Antenna interface: For optimal performance, seek short routing, matched impedance and no
stubs.
External LNA: With EVA-M8 and EVA-M8M modules, an additional external LNA is
mandatory if a passive antenna is used. With EVA-M8Q module, an
additional external LNA is recommended with passive antenna.
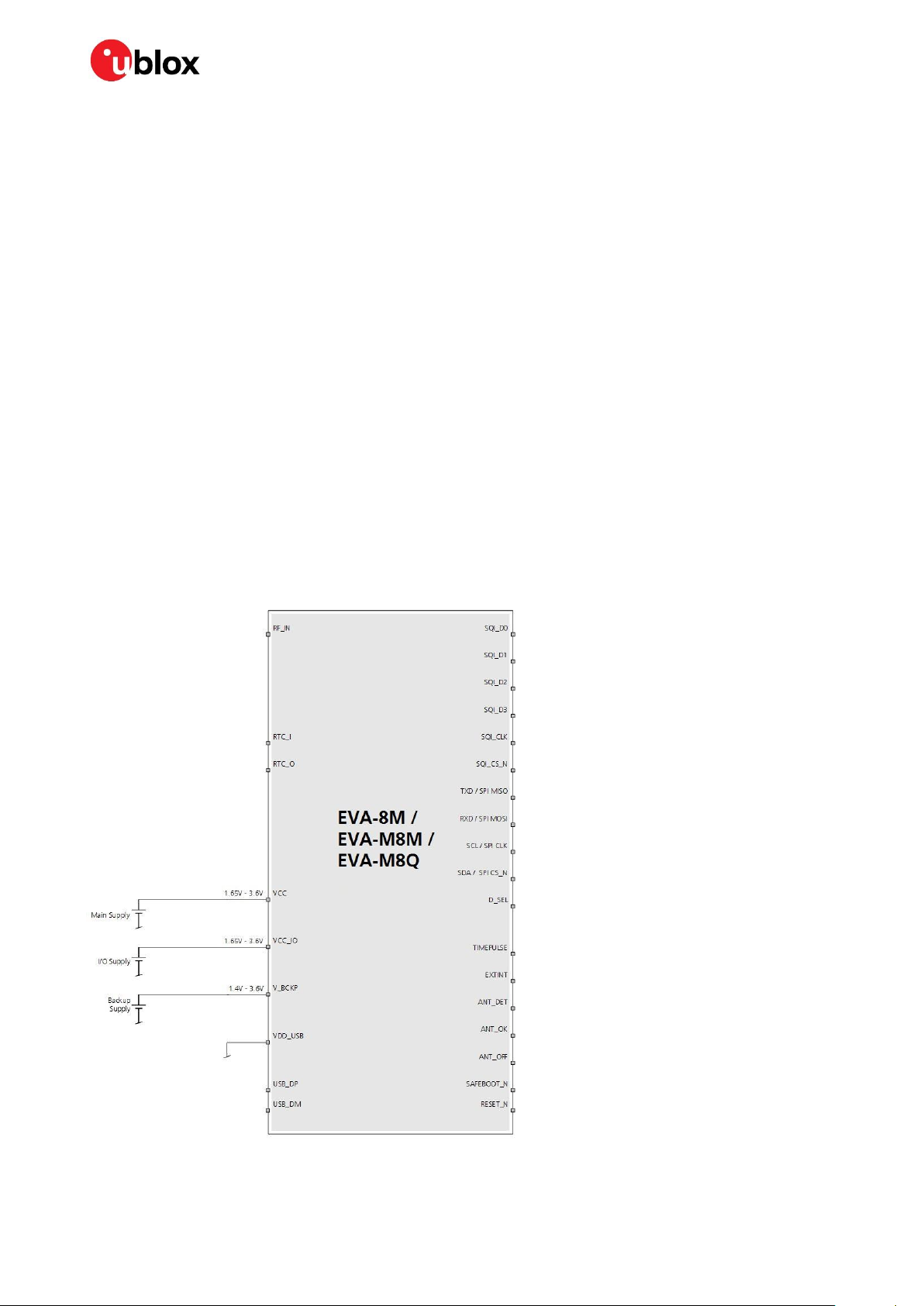
2.1 Power management
2.1.1 Overview
The EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules provide four supply pins: VCC, VCC_IO, V_BCKP and
VDD_USB. They can be supplied independently or tied together to adapt various concepts, depending
on the intended application. The following subsections explain the different supply voltages.
Figure 1 shows an example to supply the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series modules when not using the USB
interface. In this case, the VDD_USB pin is connected to ground.
Figure 1: EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series power supply example
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 7 of 47
Production information
Page 8

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Main supply voltage (VCC)
During operation, the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules are supplied through the VCC pin. It
makes use of an internal DC/DC converter for improved power efficiency. In the following step, builtin LDOs generate stabilized voltages for the Core and RF domains of the chip, respectively. The
current at VCC depends heavily on the current state of the system and is in general very dynamic.
☞ Do not add any series resistance (< 0.2 Ω) to the VCC supply, as it will generate input voltage noise
due to the dynamic current conditions.
☞ The equipment must be supplied by an external limited power source in compliance with the clause
2.5 of the standard IEC 60950-1.
I/O supply voltage (VCC_IO)
The digital I/Os of the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules can be supplied with a separate voltage
from the host system connected to the VCC_IO pin of the module. The wide range of VCC_IO allows
seamless interfacing to standard logic voltage levels. However, in most applications VCC_IO and VCC
share the same voltage level and are tied together. VCC_IO supplies also the RTC and the backup RAM
(BBR) during normal operation.
The EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules come in two different IO voltage range flavors:
1. EVA-M8Q with IO voltage from 2.7 V to 3.6 V.
2. EVA-M8M and EVA-8M with the wider range from 1.65 V to 3.6 V. The level should be set
according to section 2.2.5.
☞ VCC_IO must be supplied for the system to boot.
☞ When running the firmware from the external SQI flash, most of the VCC_IO current is consumed
by the SQI bus.
Backup power supply (V_BCKP)
In the event of a power failure at VCC_IO, the backup domain is supplied by V_BCKP.
☞ If no backup supply is available, connect V_BCKP to VCC_IO.
☞ Avoid high resistance on the V_BCKP line: During the switch from main supply to backup supply,
a short current adjustment peak can cause high voltage drop on the pin with possible
malfunctions.
☞ If the single crystal feature is enabled (which derives the RTC frequency from the main clock), the
V_BCKP pin also supplies the clock domain if there is a power failure at VCC_IO, meaning that the
V_BCKP current will also be higher. Ensure that the capacity of the backup battery chosen meets
your requirements. EVA-M8Q module uses TCXO oscillator and does not support the single crystal
feature. For more information about the single crystal feature, see section 2.4.2.
USB interface power supply
VDD_USB supplies I/Os of the USB interface. If the USB interface is being used, the system can be
either self-powered, that is, powered independently from the USB bus, or it can be bus-powered, that
is, powered through the USB connection. In the bus-powered mode, the system supply voltages need
to be generated from the USB supply voltage VBUS.
☞ If the USB interface is not used, the VDD_USB pin must be connected to GND.
2.1.2 Power management configuration
Depending on the application, the power supply schematic differs. Some examples are shown in the
following sections:
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 8 of 47
Production information
Page 9

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Pin 32 (D_SEL) = “high” (left open)
Pin 32 (D_SEL) = “Low” (connected to GND)
UART TXD
SPI MISO
UART RXD
SPI MOSI
DDC SCL
SPI CLK
DDC SDA
SPI CS_N
Single supply voltage for VCC and VCC_IO, no backup supply: see Appendix, Figure 13
Separate supply voltages for VCC, VCC_IO and V_BCKP: see Appendix, Figure 14
Single supply voltage for VCC and VCC_IO, use of a backup supply: see Appendix, Figure 16
☞ For description of the different power operating modes see the EVA-M8 data sheet [1] and the
EVA-8M data sheet [2].
2.2 Interfaces
The EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules provide UART, SPI and DDC (I2C-compatible) interfaces
for communication with a host CPU. A USB interface is also available on dedicated pins (see section
2.2.4). Additionally, an SQI interface is available for connecting the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS
modules with an optional external flash memory.
The UART, SPI and DDC pins are supplied by VCC_IO and operate at this voltage level.
Four dedicated pins can be configured as either 1 x UART and 1 x DDC or a single SPI interface
selectable by D_SEL pin. Table 1 below provides the port mapping details.
Table 1: Communication Interfaces overview
☞ It is not possible to use the SPI interface simultaneously with the DDC or UART interface.
☞ For debugging purposes, it is recommended to have a second interface available, for example,
USB, that is independent from the application and accessible via test-points.
For each interface, a dedicated pin can be defined to indicate that data is ready to be transmitted.
The TXD ready signal indicates that the receiver has data to transmit. Each TXD ready signal is
associated with a particular interface and cannot be shared. A listener can wait on the TXD ready
signal instead of polling the DDC or SPI interfaces. The UBX-CFG-PRT message lets you configure the
polarity and the number of bytes in the buffer before the TXD ready signal goes active. The TXD ready
function is disabled by default.
☞ The TXD ready functionality can be enabled and configured by proper AT commands sent to the
involved u-blox cellular module supporting the feature. For more information see the GPS
Implementation and Aiding Features in u-blox wireless modules [6].
☞ The TXD ready feature is supported on several u-blox cellular module products.
2.2.1 UART interface
A UART interface is available for serial communication to a host CPU. The UART interface supports
configurable data rates with the default at 9600 baud. Signal levels are related to the VCC_IO supply
voltage. An interface based on RS232 standard levels (+/- 7 V) can be realized using level shifter ICs
such as the Maxim MAX3232.
Hardware handshake signals and synchronous operation are not supported.
A signal change on the UART RXD pin can also be used to wake up the receiver in power save mode
(see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification [3]).
☞ Designs must allow access to the UART and the SAFEBOOT_N pin for future service, updates, and
reconfiguration.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 9 of 47
Production information
Page 10
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Module
VDD_USB
LDO
VDD_USB
R4
USB_DP
USB_DM
R5
C24 C23
D2
VBUS
DP
DM
GND
USB
Device Connector
U1
EN R11
EN
2.2.2 Display data channel (DDC) interface
An I2C-compatible display data channel (DDC) interface is available for serial communication with a
host CPU.
☞ The SCL and SDA pins have internal pull-up resistors sufficient for most applications. However,
depending on the speed of the host and the load on the DDC lines additional external pull-up
resistors might be necessary. For speed and clock frequency see the EVA-M8 data sheet [1] and
the EVA-8M data sheet [2].
☞ To make use of DDC interface the D_SEL pin has to be left open.
☞ The EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules DDC interface provides serial communication with
u-blox cellular modules. See the specification of the applicable cellular module to confirm
compatibility.
2.2.3 SPI interface
The SPI interface can be used to provide a serial communication with a host CPU. If the SPI interface
is used, UART and DDC are deactivated because they share the same pins.
☞ To make use of the SPI interface, the D_SEL pin has to be connected to GND.
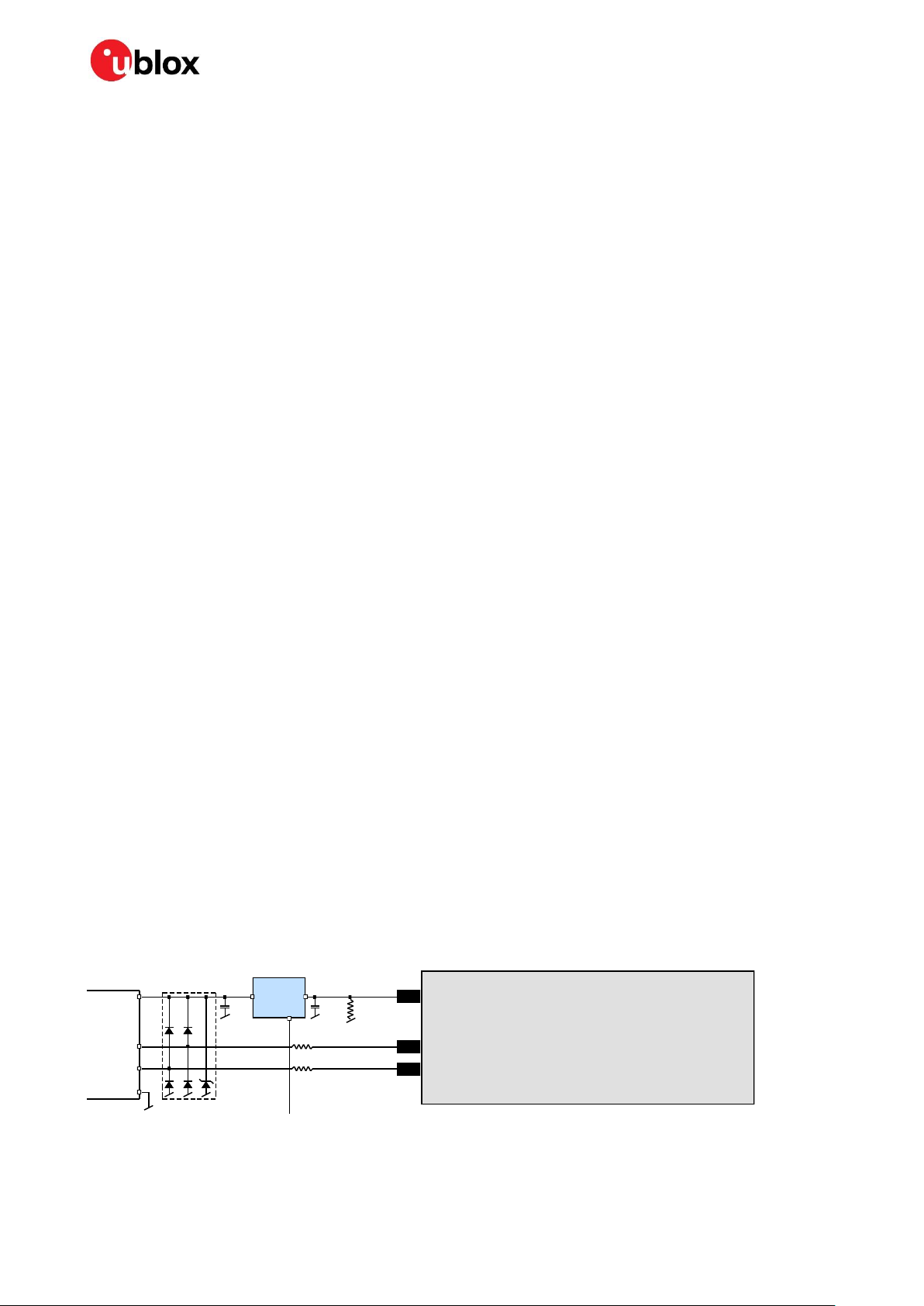
2.2.4 USB interface
The USB interface of the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules supports the full-speed data rate
of 12 Mbit/s. It is compatible with the USB 2.0 FS standard. To implement the physical characteristics
required by the USB 2.0 specification, the interface requires some external components. Figure 2
shows the interface pins and additional external components. To comply with USB specifications,
VBUS must be connected through an LDO (U1) to pin VDD_USB of the module. This ensures that the
internal 1.5 kΩ pull-up resistor on USB_DP gets disconnected when the USB host shuts down VBUS.
Depending on the characteristics of the LDO (U1), for a self-powered design it is recommended to add
a pull-down resistor (R8) at its output to ensure VDD_USB does not float if a USB cable is not
connected, that is, when VBUS is not present. In USB self-powered mode, the power supply (VCC) can
be turned off and the digital block is not powered. In this case, since VBUS is still available, the USB
host still receives the signal indicating that the device is present and ready to communicate. This can
be avoided by disabling the LDO (U1) using the enable signal (EN) of the VCC-LDO or the output of a
voltage supervisor.
The interface can be used either in self-powered or bus-powered mode. The required mode can be
configured using the UBX-CFG-USB message. Also, the vendor ID, vendor string, product ID and
product string can be changed.
To get the 90 Ω differential impedance in between the USB_DM and USB_DP data line, a 27 Ω series
resistor (R4, R5) must be placed into each data line (USB_DM and USB_DP).
Figure 2: USB interface
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 10 of 47
Production information
Page 11
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Name
Component
Function
Comments
U1
LDO
Regulates VBUS (4.4 …5.25
V) down to a voltage of 3.3 V).
Almost no current requirement (~1 mA) if the GNSS receiver is
operated as a USB self-powered device, but if bus-powered LDO (U1), it
must be able to deliver the maximum current of ~100 mA.
C24,
C23
Capacitors
Required according to the specification of LDO U1.
D2
Protection
diodes
Protects circuit from
overvoltage / ESD when
connecting.
Use low-capacitance ESD protection such as ST Microelectronics
USBLC6-2.
R4, R5
Serial
termination
resistors
Establishes a full-speed
driver impedance of 28…44
Ω.
A value of 27 Ω is recommended.
R11
Resistor
Ensures defined signal at
VDD_USB when VBUS is not
connected / powered.
100 kΩ is recommended for USB self-powered setup. For bus-powered
setup R8 is not required.
Table 2: Summary of USB external components
See Appendix A.5 and Appendix A.6 for reference schematics for self- and bus-powered operation.
☞ If the USB interface is not used, connect VDD_USB to GND.
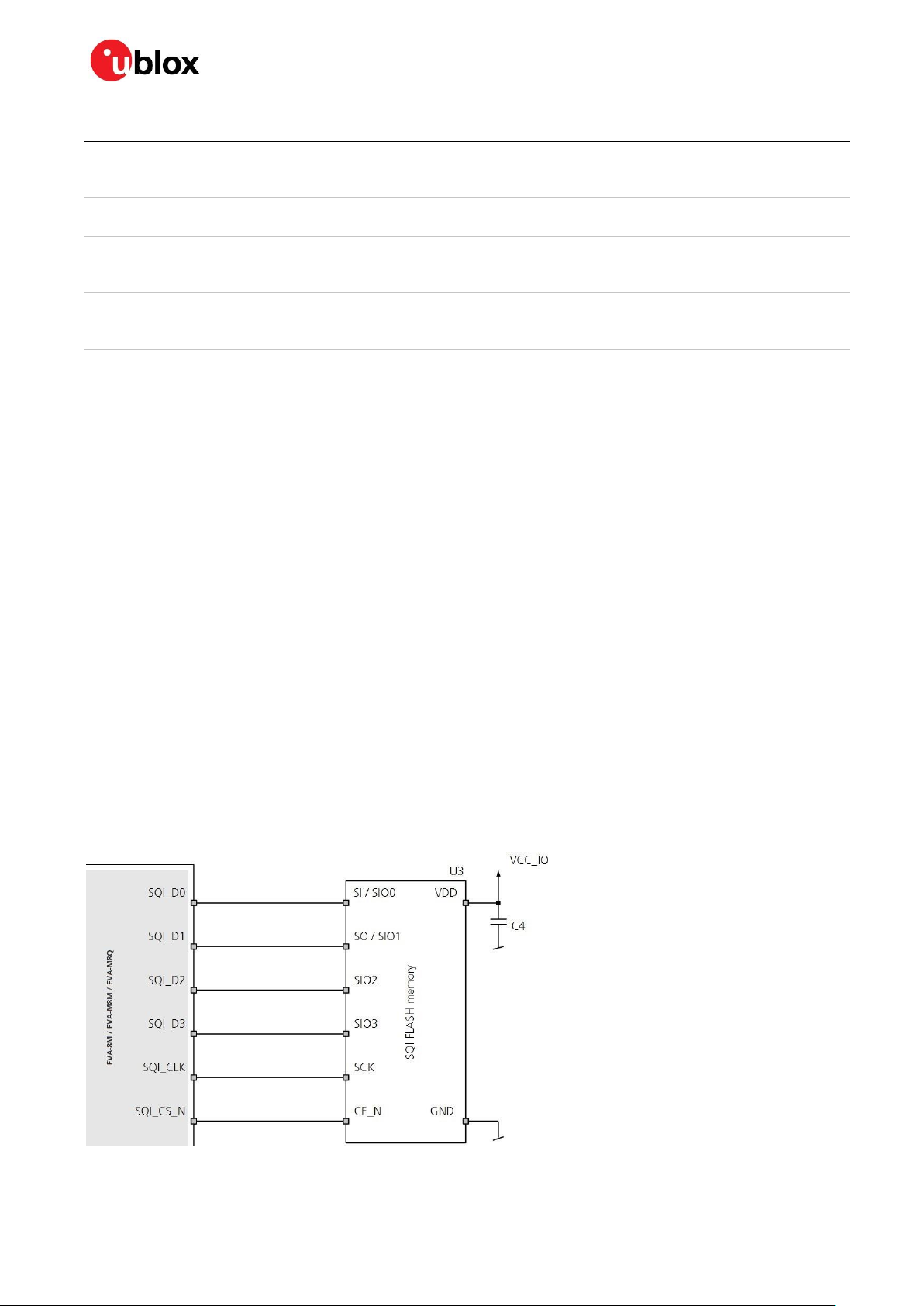
2.2.5 SQI flash memory
An external SQI (Serial Quad Interface) flash memory can be connected to the EVA-8M / EVA-M8
series GNSS modules. The SQI interface provides the following options:
Stores the current configuration permanently
Saves data logging results
Holds AssistNow Offline and AssistNow Autonomous data
☞ In addition, the EVA-M8M and EVA-M8Q GNSS modules can make use of a dedicated flash
firmware with an external SQI flash memory. The flash memory with these modules can be used
to run firmware out of flash and to update the firmware as well. Running the firmware from the
SQI flash requires a minimum SQI flash size of 8 Mbit.
☞ The voltage level of the SQI interface follows the VCC_IO level. Therefore, the SQI flash must be
supplied with the same voltage as VCC_IO of the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 module. It is recommended to
place a decoupling capacitor (C4) close to the supply pin of the SQI flash.
☞ Make sure that the SQI flash supply range matches the voltage supplied at VCC_IO.
Figure 3 : Connecting an external SQI flash memory
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 11 of 47
Production information
Page 12

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
SQI flash size of 8 Mbit is sufficient to save AssistNow Offline and AssistNow Autonomous
information as well as the current configuration data. However, for EVA-M8M and EVA-M8Q to run
firmware from the SQI flash and provide space for logging results, a minimum size of 8 Mbit may not
be sufficient, depending on the amount of data to be logged.
☞ For more information about supported SQI flash devices see Table 18.
EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series modules have a configurable VCC_IO monitor threshold (iomonCfg) to
ensure that the module only start if the VCC_IO supply is within the supply range of the SQI flash
device (VCC_IO is used to supply the SQI flash). This will ensure that any connected SQI flash memory
will be detected correctly at startup.
See the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification [3] for setting the
iomonCfg value.
With EVA-8M and EVA-M8M modules the VCC_IO monitor threshold is set to default 1.54 V value for
using a 1.8 V Flash memory device.
With EVA-M8Q module, the VCC_IO monitor threshold is set to default 2.69 V value in production, but
may be increased to 3.0 V.
If the default value for the VCC_IO monitor threshold is not suitable it can be set according to the IO
supply voltage level (VCC_IO) in the eFuse by the low level configuration.
If VCC_IO voltage 2.7 V to 3.0 V is used, send the following sequence to the module:
B5 62 06 41 0C 00 00 00 03 1F 04 BA CF 67 FF 7F FF FF E5 95
If VCC_IO voltage 3.0 V to 3.6 V is used, send the following sequence to the module:
B5 62 06 41 0C 00 00 00 03 1F 4F 22 4C 5C FF 7F 7F FF 8A 7C
☞ Applying these sequences results in a permanent change and cannot be reversed. An unstable
supply voltage at the VCC_IO pin while applying these sequences can also damage the receiver.
☞ Make sure that the SAFEBOOT_N pin is available for entering safe boot mode. Programming the
SQI flash memory with flash firmware is done typically at production. For this purpose the EVAM8M and EVA-M8Q GNSS modules have to enter the safe boot mode. For more information about
SAFEBOOT_N pin, see section 2.6.
☞ When the EVA-M8M-1 variant is attached with an external SQI flash without running flash
firmware, the default concurrent reception of GPS/QZSS/SBAS and BeiDou remains unchanged.
In case the flash is also used for execution of firmware update, the default reception will be reset
to GPS/QZSS/SBAS and GLONASS. EVA-M8M-1 can be changed back to concurrent
GPS/QZSS/SBAS and BeiDou by sending a dedicated UBX message (UBX-CFG-GNSS) to the
module. For more information, see the u-blox 8 / ublox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol
Specification [3].
2.3 I/O pins
All I/O pins make use of internal pull-ups. Thus, there is no need to connect unused pins to VCC_IO.
2.3.1 Time pulse
A configurable time pulse signal is available with the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules.
The TIMEPULSE output generates pulse trains synchronized with GPS or UTC time grid with intervals
configurable over a wide frequency range. Thus it may be used as a low-frequency time
synchronization pulse or as a high-frequency reference signal.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 12 of 47
Production information
Page 13

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Function
I/O
Description
Remarks
ANT_OK
I
Antenna OK
“high” = Antenna OK
“low” = Antenna not OK
Default configuration
ANT_OFF
O
Control signal to turn on and off the antenna supply
“high” = Antenna OFF
“low” = Antenna ON
Default configuration
By default, the time pulse signal is disabled. For more information, see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8
Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification [3].
2.3.2 External interrupt
EXTINT is an external interrupt pin with fixed input voltage thresholds with respect to VCC_IO (see
the EVA-M8 data sheet [1] and the EVA-8M data sheet [2] for more information). It can be used for
wake-up functions in power save mode on all u-blox M8 modules and for aiding. Leave open if unused;
its function is disabled by default. By default, the external interrupt is disabled.
If the EXTINT is not used for an external interrupt function, it can be used for some other purpose, for
example, as an output pin for the TXD ready feature to indicate that the receiver has data to transmit.
For further information, see the pin assignment in section 2.9 and the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver
Description Including Protocol Specification [3].
☞ If EXTINT is configured for on/off switching of the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules, the
internal pull-up becomes disabled. Make sure the EXTINT input is always driven within the defined
voltage level by the host.
2.3.3 Active antenna supervisor
The EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules support active antenna supervisors. The antenna
supervisor gives information about the status of the active antenna and turns off the supply to the
active antenna in case a short is detected, or to optimize the power consumption when in power save
mode.
There is either a 2-pin or a 3-pin antenna supervisor. By default the 2-pin antenna supervisor is
enabled.
2-pin antenna supervisor
The 2-pin antenna supervisor function, which is enabled by default, consists of the ANT_OK input and
the ANT_OFF output pins.
Table 3: 2-pin antenna supervisor pins
The circuitry, as shown in Appendix A.7 (see Figure 19) provides antenna supply short circuit
detection. It will prevent antenna operation via transistor T1 if a short circuit has been detected or if
it is not required (for example, in power save mode).
The status of the active antenna can be checked by the UBX-MON-HW message. For more
information, see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification [3].
Open drain buffers U4 and U7 (for example, Fairchild NC7WZ07) are needed to shift the voltage levels.
R3 is required as a passive pull-up to control T1 because U4 has an open drain output. R4 serves as a
current limiter in the event of a short circuit.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 13 of 47
Production information
Page 14
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Function
I/O
Description
Remarks
ANT_DET
I
(pull-up)
Antenna detected
“high” = Antenna detected
“low” = Antenna not detected
Byte sequence given in section 2.3.3.2
should be applied.
ANT_OK
I
(pull-up)
Antenna not shorted
“high” = antenna has no short
“low” = antenna has a short
Byte sequence given in section 2.3.3.2
should be applied.
ANT_OFF
O
Control signal to turn on and off the antenna
supply
“high” = turn off antenna supply
“low” = short to GND
Byte sequence given in section 2.3.3.2
should be applied.
3-pin antenna supervisor
The 3-pin antenna supervisor is comprised of the ANT_DET (active antenna detection), ANT_OK
(short detection) and ANT_OFF (antenna on/off control) pins. This function must be activated by
sending the following sequence to the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series receivers in production:
B5 62 06 41 0C 00 00 00 03 1F CD 1A 38 57 FF FF F6 FF DE 11
☞ Applying this sequence results in a permanent change and cannot be reversed. An unstable supply
voltage at the VCC_IO pin while applying this sequence can also damage the receiver.
Table 4: 3-pin Antenna supervisor pins
The external circuitry, as shown in Appendix A.8 (see Figure 20), provides detection of an active
antenna connection status. If the active antenna is present, the DC supply current exceeds a preset
threshold defined by R4, R5, and R6. It will shut down the antenna via transistor T1 if a short circuit
has been detected via U7 or if it is not required (for example, in power save mode).
The status of the active antenna can be checked by the UBX-MON-HW message. More information
see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description Including Protocol Specification [3].
The open drain buffers U4, U7 and U8 (for example, Fairchild NC7WZ07) are needed to shift the
voltage levels. R3 is required as a passive pull-up to control T1 because U4 has an open drain output.
R4 serves as a current limiter in the event of a short circuit.
2.3.4 Electromagnetic interference and I/O lines
Any I/O signal line (length > ~3 mm) can act as an antenna and may pick up arbitrary RF signals
transferring them as noise into the GNSS receiver. This specifically applies to unshielded lines, lines
where the corresponding GND layer is remote or missing entirely, and lines close to the edges of the
printed circuit board. If for example, a cellular signal radiates into an unshielded high-impedance line,
it is possible to generate noise in the order of volts and not only distort receiver operation but also
damage it permanently.
On the other hand, noise generated at the I/O pins will emit from unshielded I/O lines. Receiver
performance may be degraded when this noise is coupled into the GNSS antenna (see Figure 9).
In case of improper shielding, it is recommended to use resistors or ferrite beads (see Appendix B.11)
on the I/O lines in series. Choose these components with care because they also affect the signal rise
times. Alternatively, feed-through capacitors with good GND connection close to the GNSS receiver
can be used (see Appendix B.12).
EMI protection measures are particularly useful when RF emitting devices are placed next to the
GNSS receiver and/or to minimize the risk of EMI degradation due to self-jamming. An adequate
layout with a robust grounding concept is essential to protect against EMI. For more information, see
subsection 2.14.6.3.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 14 of 47
Production information
Page 15
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
2.4 Real-time clock (RTC)
The use of the RTC is optional to maintain time in the event of power failure at VCC_IO. The RTC is
required for hot start, warm start, AssistNow Autonomous, AssistNow Offline and in some power save
mode operations. The time information can either be generated by connecting an external RTC crystal
to the module, by deriving the RTC from the internal crystal oscillator, by connecting an external
32.768 kHz signal to the RTC input, or by time aiding of the GNSS receiver at every startup.
If a power save mode is used, an external RTC crystal must be connected. Optionally the RTC
frequency can be derived from the system clock, or an external 32.768 kHz signal can be provided.
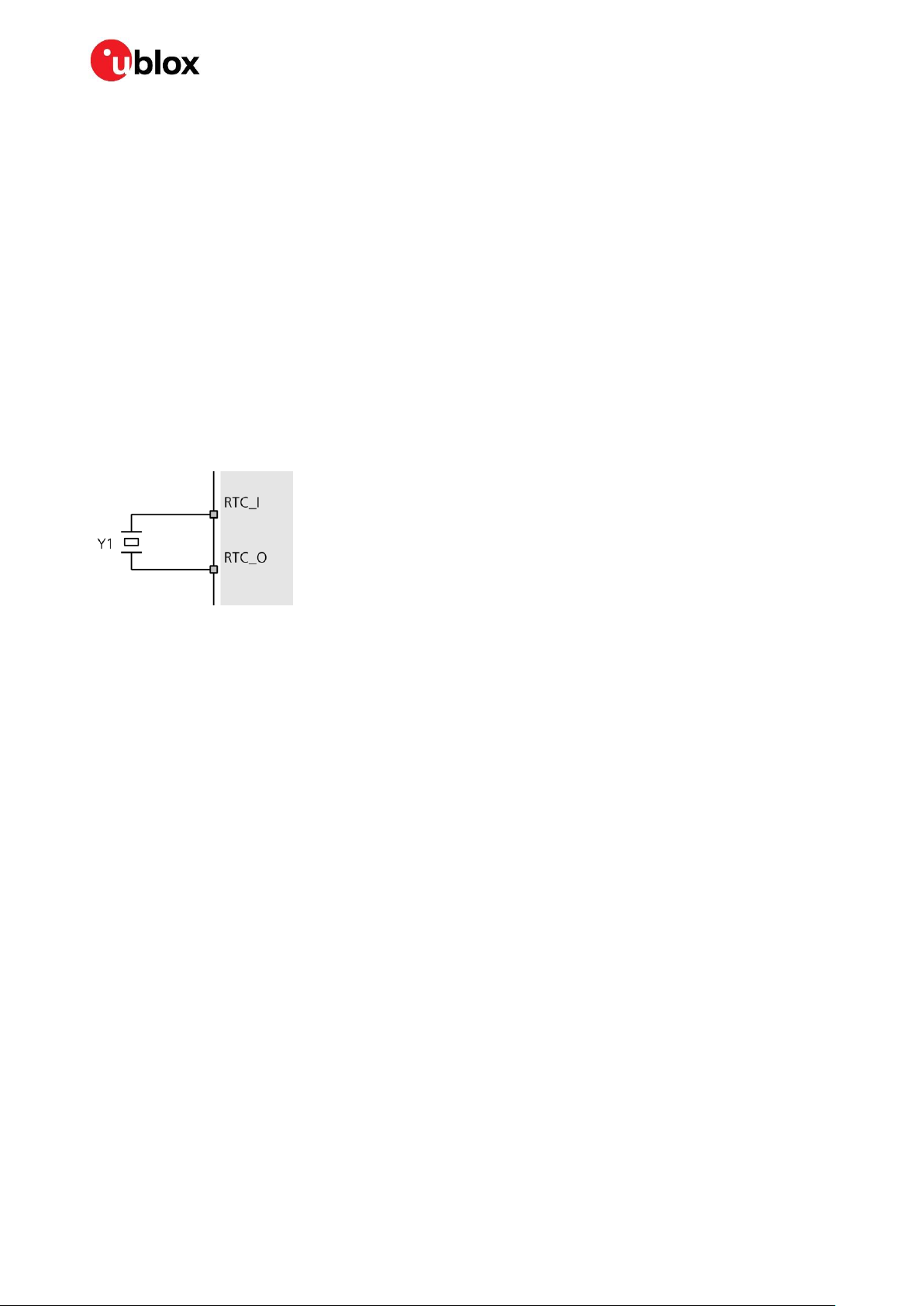
2.4.1 RTC using a crystal
The easiest way to provide time information to the receiver is to connect an RTC crystal to the
corresponding pins of the RTC oscillator, RTC_I and RTC_O. There is no need to add load capacitors
to the crystal for frequency tuning, because they are already integrated in the chip. Using an RTC
crystal will provide the lowest current consumption to V_BCKP in case of a power failure. On the other
hand, it will increase the BOM costs and requires space for the RTC crystal.
Figure 4: RTC crystal
2.4.2 RTC derived from the system clock: single crystal feature
The crystal-based EVA-8M / EVA-M8M GNSS modules can be configured in such way that the
reference frequency for the RTC is internally derived from the 26 MHz crystal oscillator. For this
feature RTC_I must be connected to ground and RTC_O left open. The capacity of the backup battery
at V_BCKP must be dimensioned accordingly, taking into account the higher than normal current
consumption at V_BCKP in the event of power failure at VCC_IO.
☞ Deriving RTC clock from internal oscillator is not available on TCXO-based EVA-M8Q module.
☞ With EVA-8M / EVA-M8M modules the single crystal feature can be configured by sending the
following sequence to the receiver:
B5 62 06 41 0C 00 00 00 03 1F 06 C3 CC B4 FF FF FD FF B8 CF
☞ Applying this sequence results in a permanent change and cannot be reversed. An unstable supply
voltage at the VCC_IO pin while applying this sequence can also damage the receiver.
2.4.3 RTC using an external clock
Some applications can provide a suitable 32.768 kHz external reference to drive the module RTC. The
external reference can simply be connected to the RTC_I pin. Make sure that the 32.768 kHz reference
signal is always turned on and the voltage at the RTC_I pin does not exceed 350 mVpp. Adjusting of
the voltage level (typically 200 mVpp) can be achieved with a resistive voltage divider followed by a DC
blocking capacitor in the range of 1 nF to 10 nF. Also make sure the frequency versus temperature
behavior of the external clock is within the recommended crystal specification shown in section B.1.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 15 of 47
Production information
Page 16

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
2.4.4 Time aiding
Time can also be sent by UBX message at every startup of the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS
modules. This can be done to enable warm starts, AssistNow Autonomous and AssistNow Offline.
This can be done when no RTC is maintained.
To enable hot starts correctly, the time information must be known accurately and the TimeMark
feature has to be used.
For more information about time aiding or timemark, see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description
Including Protocol Specification [3].
☞ For information of this use case, it is mandatory to contact u-blox support team.
☞ For power save mode operations where the RTC is needed, the time aiding cannot be used. This is
because the host does not have any information about when the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS
modules turn from OFF status to ON status during ON/OFF operation of power save mode.
2.5 RF input
The EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS module RF input is already matched to 50 Ω and has an internal
DC block. To achieve the performance values as written in the EVA-M8 data sheet [1] and the EVA8M data sheet [2], an active antenna with a good LNA inside or the mandatory LNA with passive
antenna in front of EVA-8M / EVA-M8M GNSS module must have a noise figure below 1 dB. EVA-M8Q
with the passive antenna an external LNA is only recommended.
The EVA-M8 series GNSS modules can receive and track multiple GNSS systems (for example, GPS,
Galileo, GLONASS, BeiDou and QZSS signals). Because of the dual-frequency RF front-end
architecture, two GNSS signals (GPS L1C/A, GLONASS L1OF, Galileo E1B/C and BeiDou B1) can be
received and processed concurrently. This concurrent operation is extended to 3 GNSS when GPS and
Galileo are used in addition to GLONASS or BeiDou
The EVA-8M can receive GPS L1C/A and GLONASS L1OF signals. However, because of differing
center frequencies, the receiver has to be switched to GPS or GLONASS mode by using a UBX
message.
☞ Concurrent reception of both GPS and GLONASS is not possible with the EVA-8M.
2.5.1 Active antenna
In case an active antenna is used, just the active antenna supply circuit has to be added in front of the
modules RF input, see Figure 16. In case the active antenna has to be supervised, either the 2-pin
active antenna supervisor circuit (see Figure 19) or the 3-pin active antenna supervisor circuit (see
Figure 20), has to be added to the active antenna circuit. These active antenna supervisor circuits also
make sure that the active antenna is turned off in power save mode stages.
2.5.2 Passive antenna
If a passive antenna is connected to a EVA-8M / EVA-M8M series GNSS module, it is mandatory to
use an additional LNA in front of module to achieve the performance values as written in the data
sheets for EVA-M8 [1] and the EVA-8M [2], see Appendix A. For EVA-M8Q with a passive antenna, an
external LNA is only recommended. An LNA (U1) alone would make the modules more sensitive to outband jammers, so an additional GNSS SAW filter (F1) has to be connected between the external LNA
(U1) and the EVA-8M / EVA-M8M series GNSS module RF input. If strong out-band jammers are close
to the GNSS antenna (for example, a GSM antenna), see section 2.5.3.
The LNA (U1) can be selected to deliver the performance needed by the application in terms of:
Noise figure (sensitivity)
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 16 of 47
Production information
Page 17

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Selectivity and linearity (robustness against jamming)
Robustness against RF power and ESD
☞ The external LNA (U1) must be placed close to the passive antenna to get best performance.
If power save mode is used and the minimum current consumption has to be achieved, the external
LNA should also be turned off. The ANT_OFF pin can be used to turn off an external LNA. The
ANT_OFF signal must be inverted for common LNAs which come with an enable pin which has be “low”
to turn off.
☞ The function of the ANT_OFF pin can be inverted by sending the following sequence to the
receiver:
B5 62 06 41 0C 00 00 00 03 1F 90 47 4F B1 FF FF EA FF 33 98
☞ Applying this sequence results in a permanent change and cannot be reversed. An unstable supply
voltage at the VCC_IO pin while applying this sequence can also damage the receiver.
☞ A pull-down resistor (R7) is required to ensure correct operation of the ANT_OFF pin.
ESD discharge into the RF input cannot always be avoided during assembly and / or field use with this
approach! To provide additional robustness an ESD protection diode, as listed in Appendix B.7, can be
placed in front of the LNA to GND.
2.5.3 Improved jamming immunity
If strong out-band jammers are close to the GNSS antenna (for example, a GSM antenna) GNSS
performance can be degraded or the maximum input power of the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS
modules RF input can be exceeded. An additional SAW filter (F2) has to be placed in front of the
external LNA (U1), see Appendix A. If the external LNA can accept the maximum input power, the SAW
filter between the passive antenna and external LNA (LNA1) might not be necessary. This results in
a better noise figure than an additional SAW filter (F2) in front of the external LNA (U1).
If the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS module is exposed to an interference environment, it is
recommended to use additional filtering. Improved interference immunity with good GNSS
performance can be achieved when using a SAW/LNA/SAW configuration between the antenna and
the RF input. The single-ended SAW filter (F2) can be placed in front of the LNA matching network to
prevent receiver blocking due to strong interference, see Figure 15.
Note that the insertion loss of SAW filter (F2) directly affects the system noise figure and hence the
system performance. Choice of a component with low insertion loss is mandatory when a passive
antenna is used with this setup. An example schematic for an improved jamming immunity is shown
in Appendix A.3 (see Figure 15).
2.6 Safe boot mode (SAFEBOOT_N)
If the SAFEBOOT_N pin is “low” at startup, the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS module starts in safe
boot mode and does not begin GNSS operation. In safe boot mode the module runs from an internal
LC oscillator and starts regardless of any configuration provided by the configuration pins. Thus, it
can be used to recover from situations where the SQI flash has become corrupted.
Owing to the inaccurate frequency of the internal LC oscillator, the module is unable to communicate
via USB in safe boot mode. For communication by UART in safe boot mode, a training sequence (0x
55 55 at 9600 baud) can be sent by the host to the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules to enable
communication. After sending the training sequence, the host has to wait for at least 2 ms before
sending messages to the receiver. For further information see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver
Description Including Protocol Specification [3].
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 17 of 47
Production information
Page 18

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Safe boot mode is used in production to program the SQI flash. It is recommended to have the
possibility to pull the SAFEBOOT_N pin “low” when the module starts up. This can be provided using
an externally connected test point or via a host CPUs digital I/O port.
2.7 System reset (RESET_N)
The EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules provide a RESET_N pin to reset the system. The
RESET_N is input-only with an internal pull-up resistor. It must be at low level for at least 10 ms to
make sure that RESET_N is detected. Leave RESET_N open for normal operation. The RESET_N
complies with the VCC_IO level and can be actively driven high.
☞ Use RESET_N only used in critical situations to recover the system. The real-time clock (RTC) will
also be reset and thus immediately afterwards the receiver cannot perform a hot start.
☞ In reset state, the module consumes a significant amount of current. It is therefore recommended
to use RESET_N only as a reset signal and not as an enable/disable.
2.8 Design-in checklists
2.8.1 General considerations
Check power supply requirements and schematic:
Is the power supply voltage within the specified range? See how to connect power in section 2.1.
For USB devices: Is the voltage VDD_USB voltage within the specified range? Do you have a bus
or self-powered setup?
Compare the peak current consumption of EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules with the
specification of your power supply.
GNSS receivers require a stable power supply. Avoid series resistance in your power supply line
(the line to VCC) to minimize the voltage ripple on VCC.
Backup battery
For achieving a minimal time-to-first-fix (TTFF) after a power down (warm starts, hot starts),
make sure to connect a backup battery to V_BCKP, and use an RTC. If not used, make sure
V_BCKP is connected to VCC_IO.
Antenna/ RF input
The total noise figure including external LNA (or the LNA in the active antenna) should be around
1 dB.
With the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS module, an external LNA is mandatory if no active
antenna is used to achieve the performance values as written in the data sheets for EVA-M8 [1]
and EVA-8M [2] .
Make sure the antenna is not placed close to noisy parts of the circuitry and does not face any
noisy parts, such as micro-controller, display, etc.).
To optimize performance in environments with out-band jamming/interference sources, use an
additional SAW filter.
☞ For more information about dealing with interference issues see the GPS Antenna Application
Note [4].
Schematic
Inner pins of the package must all be connected to GND.
2.8.2 Schematic design-in for EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules
For a minimal design with the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules, the following functions and
pins need to be considered:
Connect the power supply to VCC, VCC_IO and V_BCKP.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 18 of 47
Production information
Page 19

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Pin #
Name
I/O
Description
Remark
1
RF_IN
I
RF Input
Add external LNA and SAW if no active antenna
used.
2
GND I Ground
Outer ground pin
3
Reserved
I/O
Reserved
Do not connect. Must be left open!
4
Reserved
I/O
Reserved
Do not connect. Must be left open!
5
USB_DM
I/O
USB data
Leave open if not used.
6
USB_DP
I/O
USB data
Leave open if not used.
7
VDD_USB
I
USB Interface power
Connect to GND if not used.
8
RTC_O
O
RTC Output
Leave open if no RTC Crystal attached.
9
RTC_I
I
RTC Input
Connect to GND if no RTC Crystal attached.
10
Reserved
I/O
Reserved
Do not connect. Must be left open!
11
Reserved
I/O
Reserved
Do not connect. Must be left open!
12
PIO14 / ANT_DET
I
Antenna detection
Leave open if not used.
13
PIO13 / EXTINT
I
External interrupt
Leave open if not used.
14
RESET_N
I
System reset
See section 2.7.
15
RXD / SPI MOSI
I
Serial interface
See section 2.2.
16
TXD / SPI MISO
O
Serial interface
See section 2.2.
17
Reserved
I/O
Reserved
Do not connect. Must be left open!
18
GND I Ground
Outer ground pin
19
VCC
I
Main supply
See section 2.1.
20
VCC_IO
I
I/O Supply
See section 2.1.
21
V_BCKP
I
Backup supply
See section 2.1.
22
SQI_D0
I/O
Data line 0 to external SQI flash
memory or reserved configuration pin.
Leave open if not used.
23
SQI_CLK
I/O
Clock for external SQI flash memory or
configuration pin.
Leave open if not used.
24
SQI_D2
I/O
Data line 2 to external SQI flash
memory or reserved configuration pin.
Leave open if not used.
25
SQI_D1
I/O
Data line 1 to external SQI flash
memory or reserved configuration pin.
Leave open if not used.
26
SQI_CS_N
I/O
Chip select for external SQI flash
memory or configuration enable pin.
Leave open if not used.
27
SQI_D3
I/O
Data line 3 to external SQI flash
memory or reserved configuration pin.
Leave open if not used.
28
Reserved
I/O
Reserved
Do not connect. Must be left open!
29
SCL / SPI CLK
I
Serial interface
See section 2.2.
30
SDA / SPI CS_N
I/O
Serial interface
See section 2.2.
VDD_USB: Connect the USB power supply to an LDO before feeding it to VDD_USB and VCC or
connect it to GND if USB is not used.
Ensure an optimal ground connection to all ground pins of the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS
modules.
Choose the required serial communication interfaces (UART, USB, SPI or DDC) and connect the
appropriate pins to your application.
If you need hot or warm start in your application, connect a backup battery to V_BCKP and add
RTC circuit.
If antenna bias is required, see Appendix A.4.
2.9 Pin description
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 19 of 47
Production information
Page 20

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
31
TIMEPULSE
O
Time pulse output
Leave open if not used.
32
D_SEL
I
Interface selector
See section 2.2.
33
SAFEBOOT_N
I
Used for programming the SQI flash
memory and testing purposes.
Leave open if not used.
34
ANT_OK
I
Antenna status
Leave open if not used.
35
ANT_OFF
O
Antenna control
Leave open if not used.
36
Reserved
I/O
Reserved
Do not connect. Must be left open!
37
GND I Ground
Inner ground pin
38
GND I Ground
Inner ground pin
39
GND I Ground
Inner ground pin
40
GND I Ground
Inner ground pin
41
GND I Ground
Inner ground pin
42
GND I Ground
Inner ground pin
43
GND I Ground
Inner ground pin
No
Previous name
New name
7
V_USB
VDD_USB
15
RX / MOSI
RXD / SPI MOSI
16
TX / MISO
TXD / SPI MISO
26
SQI_CS
SQI_CS_N
29
SCL / SCK
SCL / SPI CLK
30
SDA / CS_N
SDA / SPI CS_N
Table 5: EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules pin description
2.9.1 Pin name changes
Selected EVA-M8M pin names have been updated to agree with a common naming convention across
u-blox modules. The pins have not changed their operation and are the same physical hardware but
with updated names. The table below lists those pins along with their old and new names.
Table 6: EVA-M8M pin name changes
☞ For more information about pin assignment see the EVA-M8 Data sheet [1] and the EVA-8M Data
sheet [2].
2.10 Layout design-in checklist
Follow this checklist for the layout design to get an optimal GNSS performance.
Layout optimizations (section 2.11)
Is the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 module placed according to the recommendation in section 2.11.3?
Is the grounding concept optimal?
Has the 50 Ω line from antenna to module (micro strip / coplanar waveguide) been kept as short
as possible?
Assure low serial resistance in VCC power supply line (choose a line width > 400 um).
Keep power supply line as short as possible.
Design a GND guard ring around the optional RTC crystal lines and GND below the RTC circuit.
Add a ground plane underneath the GNSS module to reduce interference. This is especially
important for the RF input line.
For improved shielding, add as many vias as possible around the micro strip/coplanar waveguide,
around the serial communication lines, underneath the GNSS module, etc.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 20 of 47
Production information
Page 21

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Pin
1
Pin36
Calculation of the micro strip for RF input
The micro strip / coplanar waveguide must be 50 Ω and be routed in a section of the PCB where
minimal interference from noise sources can be expected. Make sure that there is only GND
around and under the RF line.
In case of a multi-layer PCB, use the thickness of the dielectric between the signal and the 1st
GND layer (typically the 2nd layer) for the micro strip / coplanar waveguide calculation.
If the distance between the micro strip and the adjacent GND area (on the same layer) does not
exceed 5 times the track width of the micro strip, use the “Coplanar Waveguide” model in
AppCad to calculate the micro strip and not the “micro strip” model.
2.11 Layout
This section provides important information for designing a reliable and sensitive GNSS system.
GNSS signals at the surface of the earth are about 15 dB below the thermal noise floor. Signal loss at
the antenna and the RF connection must be minimized as much as possible. When defining a GNSS
receiver layout, the placement of the antenna with respect to the receiver, as well as grounding,
shielding and jamming from other digital devices are crucial issues and need to be considered very
carefully.
2.11.1 Footprint
Figure 5: Recommended footprint (bottom view)
Units are in mm.
2.11.2 Paste mask
The paste mask shall be 50 µm smaller than the copper pads with a paste thickness of 100 µm.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 21 of 47
Production information
Page 22

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
☞ Consider the paste mask outline when defining the minimal distance to the next component.
☞ These are recommendations only and not specifications. The exact geometry, distances, stencil
thicknesses and solder paste volumes must be adapted to the customer’s specific production
processes (for example, soldering.
2.11.3 Placement
A very important factor in achieving maximum GNSS performance is the placement of the receiver on
the PCB. The connection to the antenna must be as short as possible to avoid jamming into the very
sensitive RF section.
Make sure that RF-critical circuits are clearly separated from any other digital circuits on the system
board. To achieve this, position the receiver digital part towards your digital section of the system
PCB.
2.12 Layout design-in: Thermal management
During design-in do not place the module near sources of heating or cooling. The receiver oscillator is
sensitive to sudden changes in ambient temperature which can adversely impact satellite signal
tracking. Sources can include co-located power devices, cooling fans or thermal conduction via the
PCB. Take into account the following questions when designing in the module.
Is the receiver placed away from heat sources?
Is the receiver placed away from air-cooling sources?
Is the receiver shielded by a cover/case to prevent the effects of air currents and rapid
environmental temperature changes?
⚠ High temperature drift and air vents can affect the GNSS performance. For best performance,
avoid high temperature drift and air vents near the module.
2.13 Migration considerations
u-blox is committed to ensuring that products in the same form factor are backwards-compatible
over several technology generations. Utmost care has been taken to ensure there is no negative
impact on function or performance and to make u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 modules as fully compatible as
possible with u-blox 7 versions. If using BeiDou, check the bandwidth of the external RF components
and the antenna. For power consumption information, see the data sheet for EVA-M8 [1] and EVA8M [2].
The EVA-M8M and EVA-M8Q GNSS modules provide flash firmware update capabilities when
connecting an external SQI flash memory device. For more information and recommendations for
using an external SQI flash, see section 2.2.5. It is highly advisable that customers consider a design
review with the u-blox support team to ensure the compatibility of key functionalities.
☞ EVA-7M design which makes use of the single crystal feature cannot be migrated to EVA-M8Q.
Single crystal feature is not supported on EVA-M8Q.
☞ For an overall description of the module software operation, see the u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver
Description Including Protocol Specification [3].
☞ For migration, see the u-blox 7 to u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 software migration guide [7].
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 22 of 47
Production information
Page 23

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Pin
EVA-7M
EVA-8M / EVA-M8M / EVA-M8Q
Pin name
Typical assignment
Pin name
Typical assignment
Remarks for
migration
1
RF input
Add external LNA and
SAW if no active
antenna used
RF input
Add external LNA and SAW if no active
antenna used
EVA-8M / EVA-M8M
require external LNA if
passive antenna is
used. External LNA is
recommended for
EVA-M8Q.
2
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
No difference
3
Reserved
Leave open.
Reserved
Leave open.
No difference
4
Reserved
Leave open.
Reserved
Leave open.
No difference
5
USB_DM
USB data
USB_DM
USB data
No difference
6
USB_DP
USB data
USB_DP
USB data
No difference
7
V_USB
USB supply
VDD_USB
USB supply
No difference
8
RTC_O
Leave open if no RTC
crystal is attached.
RTC_O
Leave open if no RTC crystal is
attached.
No difference
9
RTC_I
Connect to GND if no
RTC crystal is attached.
RTC_I
Connect to GND if no RTC crystal is
attached.
No difference
10
Reserved
Leave open.
Reserved
Leave open.
No difference
11
Reserved
Leave open.
Reserved
Leave open.
No difference
12
PIO14 /
ANT_DET
Antenna detection
PIO14 /
ANT_DET
Antenna detection
No difference
13
PIO13 /
EXTINT
External interrupt
PIO13 / EXTINT
External interrupt
No difference
14
RESET_N
Leave open.
RESET_N
Leave open.
No difference
15
RX / MOSI
Serial interface
RXD / SPI MOSI
Serial interface
No difference
16
TX / MISO
Serial interface
TXD / SPI MISO
Serial interface
No difference
17
Reserved
Serial interface
Reserved
Leave open.
No difference
18
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
No difference
19
VCC
Main voltage supply
EVA-7M 1.65 - 3.6 V
VCC
Main voltage supply
EVA-8M / EVA-M8M / 1.65 - 3.6 V
No difference
EVA-M8Q 2.7 - 3.6 V
Note: EVA-M8Q has a
higher voltage range.
20
VCC_IO
Supply voltage for PIOs
EVA-7M 1.65 – 3.6 V
VCC_IO
Supply voltage for PIOs
EVA-8M / EVA-M8M 1.65 - 3.6 V
No difference
EVA-M8Q 2.7 – 3.6 V
Note: EVA-M8Q has a
higher voltage range.
21
V_BCKP
Input voltage for backup
mode.
EVA-7M 1.4 – 3.6 V
V_BCKP
Input voltage for backup mode
EVA-8M / EVA-M8M / EVA-M8Q
1.4 – 3.6 V
No difference
22
Reserved
Leave open.
SQI_D0
Data line 0 to external SQI flash
memory or reserved configuration pin.
23
Reserved
Leave open.
SQI_CLK
Clock for external SQI flash memory or
configuration pin.
24
Reserved
Leave open.
SQI_D2
Data line 2 to external SQI flash
memory or reserved configuration pin.
25
Reserved
Leave open.
SQI_D1
Data line 1 to external SQI flash
memory or reserved configuration pin.
26
Reserved
Leave open.
SQI_CS_N
Chip select for external SQI flash
memory or configuration enable pin.
2.13.1 Hardware migration from EVA-7M to EVA-8M / EVA-M8M / EVA-M8Q
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 23 of 47
Production information
Page 24

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Pin
EVA-7M
EVA-8M / EVA-M8M / EVA-M8Q
Pin name
Typical assignment
Pin name
Typical assignment
Remarks for
migration
27
Reserved
Leave open.
SQI_D3
Data line 3 to external SQI flash
memory or reserved configuration pin.
28
Reserved
Leave open.
Reserved
Leave open.
No difference
29
SCL / SCK
Serial interface
SCL / SPI CLK
Serial interface
30
SDA / CS_N
Serial interface
SDA / SPI CS_N
Serial interface
31
TIMEPULSE
Time pulse output
TIMEPULSE
Time pulse output
No difference
32
D_SEL
Interface selector
D_SEL
Interface selector
33
Reserved
Leave open
SAFEBOOT_N
Used for programming the SQI flash
memory and testing purposes.
Leave open if not
used.
34
ANT_OK
Antenna status
ANT_OK
Antenna status
No difference
35
ANT_OFF
Antenna control
ANT_OFF
Antenna control
No difference
36
Reserved
Leave open.
Reserved
Leave open.
No difference
37
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
No difference
38
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
No difference
39
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
No difference
40
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
No difference
41
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
No difference
42
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
No difference
43
GND
Ground
GND
Ground
No difference
Pin
NEO-6M
C88-M8M
Pin name
Typical assignment
Pin name
Typical assignment
Remarks for migration
1
RESERVED
SAFEBOOT_N
(Leave open)
RESERVED
SAFEBOOT_N
(Leave open)
No difference
2
SS_N
SPI slave select
D_SEL
Leave open. If
connected to GND SPI
interface available on
pins 18-21.
Different functions. Only compatible if
this pin is left open!
3
TIMEPULSE
Time pulse (1PPS)
TIMEPULSE
Time pulse (1PPS)
No difference
4
EXTINT0
External interrupt pin
EXTINT0
External interrupt pin
No difference
5
USB_DM
USB data
USB_DM
USB data
No difference
6
USB_DP
USB data
USB_DP
USB data
No difference
7
VDD_USB
USB supply
VDD_USB
USB supply
No difference
8
RESERVED
Pin 8 and 9 must be
connected together.
RESET_N
Reset input
If pin 8 is connected to pin 9 on C88M8M, the device always runs. With
NEO-6Q, if r eset input is used, it
Table 7: Pin-out comparison EVA-7M vs. EVA-8M / EVA-M8M / EVA-M8Q
2.13.2 C88-M8M - Evaluating EVA-M8M on existing NEO-xM sockets
The C88-M8M GNSS application board is designed for easier evaluation and design-in of u-blox EVAM8M modules in the existing NEO-xM modules-based products. The C88-M8M series integrates the
EVA-M8M GNSS modules into a NEO form factor adaptor board (that is, with the same dimensions
and pinout as the NEO-6M, NEO-7M and NEO-M8M). The C88-M8M application board allows
straightforward integration of the u-blox EVA-M8M modules in customers’ existing end products
based on the u-blox NEO GNSS modules. It enables fast verification of the EVA-M8M functionalities
and performances before the design-in.
☞ Schematic of C88-M8M is available upon request.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 24 of 47
Production information
Page 25

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Pin
NEO-6M
C88-M8M
Pin name
Typical assignment
Pin name
Typical assignment
Remarks for migration
implements the 3k3 resistor from pin
8 to pin 9. This also works with
NEO-7N. If used with NEO-7N, do not
populate the pull-up resistor.
9
VCC_RF
Can be used for active
antenna or external LNA
supply.
VCC_RF
Can be used for active
antenna or external
LNA supply.
No difference
10
GND
GND
GND
GND
No difference
11
RF_IN
GPS signal input
RF_IN
GPS signal input
For designs with a passive antenna
directly connected to the RF_IN pin, an
additional LNA in front of C88-M8M is
recommended to achieve the
performance values shown in the EVAM8 data sheet [1]. The noise figure of
the C88-M8M is about 2 dB higher
than that of NEO-6M.
12
GND
GND
GND
GND
No difference
13
GND
GND
GND
GND
No difference
14
MOSI/
CFG_COM0
SPI MOSI / configuration
pin. Leave open if not used.
RESERVED
Leave open.
Different functions. Only compatible if
this pin is left open!
15
MISO/
CFG_COM1
SPI MISO / configuration
pin. Leave open if not used.
RESERVED
Leave open.
Different functions. Only compatible if
this pin is left open!
16
CFG_GPS0/
SCK
Power mode configuration
pin / SPI clock. Leave open
if not used.
RESERVED
Leave open.
Different functions. Only compatible if
this pin is left open!
17
RESERVED
Leave open.
RESERVED
Leave open.
No difference
18
SDA
DDC data
SDA
DDC data / SPI CS_N
No difference if pin 2 is left open. If pin
2 low = SPI chip select.
19
SCL
DDC clock
SCL
DDC clock / SPI SCK
No difference for DDC. If pin 2 low =
SPI clock.
20
TxD
Serial port
TxD
Serial port / SPI MISO
No difference for UART. If pin 2 low =
SPI MISO.
21
RxD
Serial port
RxD
Serial port / SPI MOSI
No difference for UART. If pin 2 low =
SPI MOSI.
22
V_BCKP
Backup supply voltage
V_BCKP
Backup supply voltage
No difference
23
VCC
Supply voltage
VCC
Supply voltage
24
GND
GND
GND
GND
No difference
Table 8: Replacing NEO-6M by C88-M8M
☞ NEO-6M cannot be replaced by C88-M8M if SPI interface or configuration pins (pin 2, pin 14, pin
15 and pin 16) are used.
☞ For the existing NEO-7M and NEO-M8M designs, C88-M8M is one-to-one compatible with the
exception of some performance differences.
2.14 EOS/ESD/EMI precautions
When integrating GNSS receivers into wireless systems, consider electromagnetic and voltage
susceptibility issues carefully. Wireless systems include components which can produce electrostatic
discharge (ESD), electrical overstress (EOS) and electro-magnetic interference (EMI). CMOS devices
are more sensitive to such influences because their failure mechanism is defined by the applied
voltage, whereas bipolar semiconductors are more susceptible to thermal overstress. The following
design guidelines are provided to help in designing robust yet cost-effective solutions.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 25 of 47
Production information
Page 26
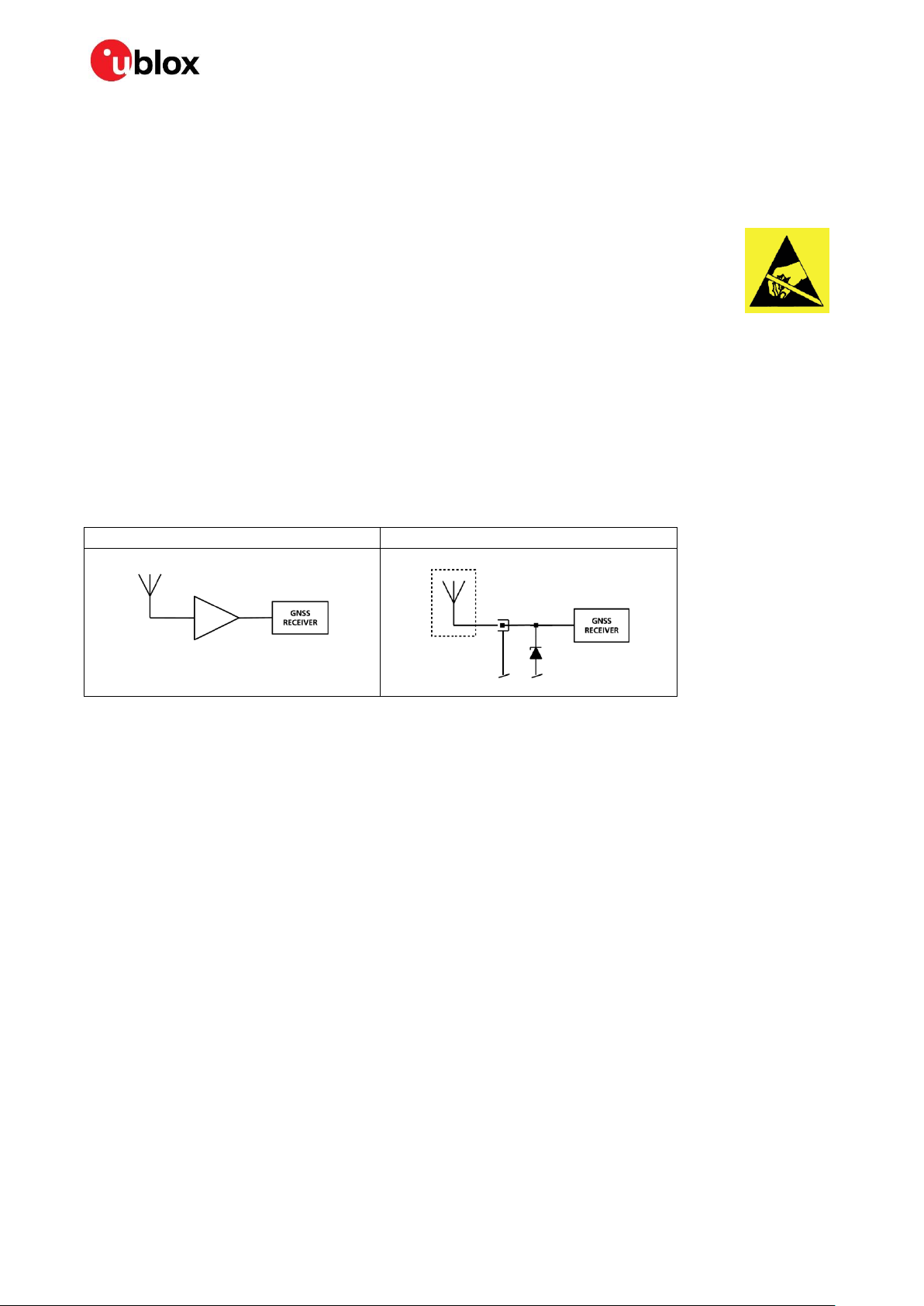
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Passive antennas
Active antennas
A B
LNA with appropriate ESD rating
RF ESD protection diode
⚠ To avoid overstress damage during production or in the field, observe strict EOS/ESD/EMI
handling and protection measures.
⚠ To prevent overstress damage at the RF_IN of your receiver, never exceed the maximum input
power as specified in the EVA-M8 data sheet [1] and the EVA-8M data sheet [2].
2.14.1 Electrostatic discharge (ESD)
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden and momentary electric current that flows
between two objects at different electrical potentials caused by direct contact or
induced by an electrostatic field. The term is usually used in the electronics and other
industries to describe momentary unwanted currents that may cause damage to electronic
equipment.
2.14.2 ESD protection measures
⚠ GNSS receivers are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD). Special precautions are required
when handling.
Most defects caused by ESD can be prevented by following strict ESD protection rules for production
and handling. When implementing passive antenna patches or external antenna connection points,
additional ESD measures as shown in Figure 6 can also avoid failures in the field.
Figure 6: ESD precautions
2.14.3 Electrical overstress (EOS)
Electrical overstress (EOS) usually describes situations where the maximum input power exceeds the
maximum specified ratings. EOS failure can happen if RF emitters are close to a GNSS receiver or its
antenna. EOS causes damage to the chip structures.
If the RF_IN is damaged by EOS, it is hard to determine whether the chip structures have been
damaged by ESD or EOS.
2.14.4 EOS protection measures
EOS protection measures as shown in Figure 7 are recommended for any designs combining wireless
communication transceivers (for example, GSM, GPRS) and GNSS in the same design or in close
proximity.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 26 of 47
Production information
Page 27

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Passive antennas
Active antennas (without internal filter
which need the module antenna
supervisor circuits)
C
D
LNA with appropriate ESD
rating and maximum input
power.
Figure 7: EOS and ESD precautions
2.14.5 Electromagnetic interference (EMI)
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is the addition or coupling of energy, which causes a spontaneous
reset of the GNSS receiver or results in unstable performance. In addition to EMI degradation due to
self-jamming (see section 2.3.4), any electronic device near the GNSS receiver can emit noise that can
lead to EMI disturbances or damage.
The following elements are critical regarding EMI:
Unshielded connectors (for example, pin rows)
Weakly shielded lines on PCB (for example, on top or bottom layer and especially at the border of
a PCB)
Weak GND concept (for example, small and/or long ground line connections)
EMI protection measures are recommended when RF emitting devices are near the GNSS receiver. To
minimize the effect of EMI a robust grounding concept is essential. To achieve electromagnetic
robustness follow the standard EMI suppression techniques.
http://www.murata.com/products/emc/knowhow/index.html
http://www.murata.com/products/emc/knowhow/pdf/4to5e.pdf
Improved EMI protection can be achieved by inserting a resistor or better yet a ferrite bead or an
inductor (see Table 16) into any unshielded PCB lines connected to the GNSS receiver. Place the
resistor as close as possible to the GNSS receiver pin.
Alternatively, feed-thru capacitors with good GND connection can be used to protect e.g. the VCC
supply pin against EMI. A selection of feed-thru capacitors are listed in Table 24.
Intended use
☞ To mitigate any performance degradation of a radio equipment under EMC disturbance, system
integration shall adopt appropriate EMC design practice and not contain cables over three meters
on signal and supply ports.
2.14.6 Applications with cellular modules
GSM terminals transmit power levels up to 2 W (+33 dBm) peak, 3G and LTE up to 250 mW
continuous. Consult the corresponding product data sheet in the Related documents section for the
absolute maximum power input at the GNSS receiver. Make sure that absolute maximum input power
level of the GNSS receiver is not exceeded.
☞ See the GPS Implementation and Aiding Features in u-blox wireless modules [6].
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 27 of 47
Production information
Page 28
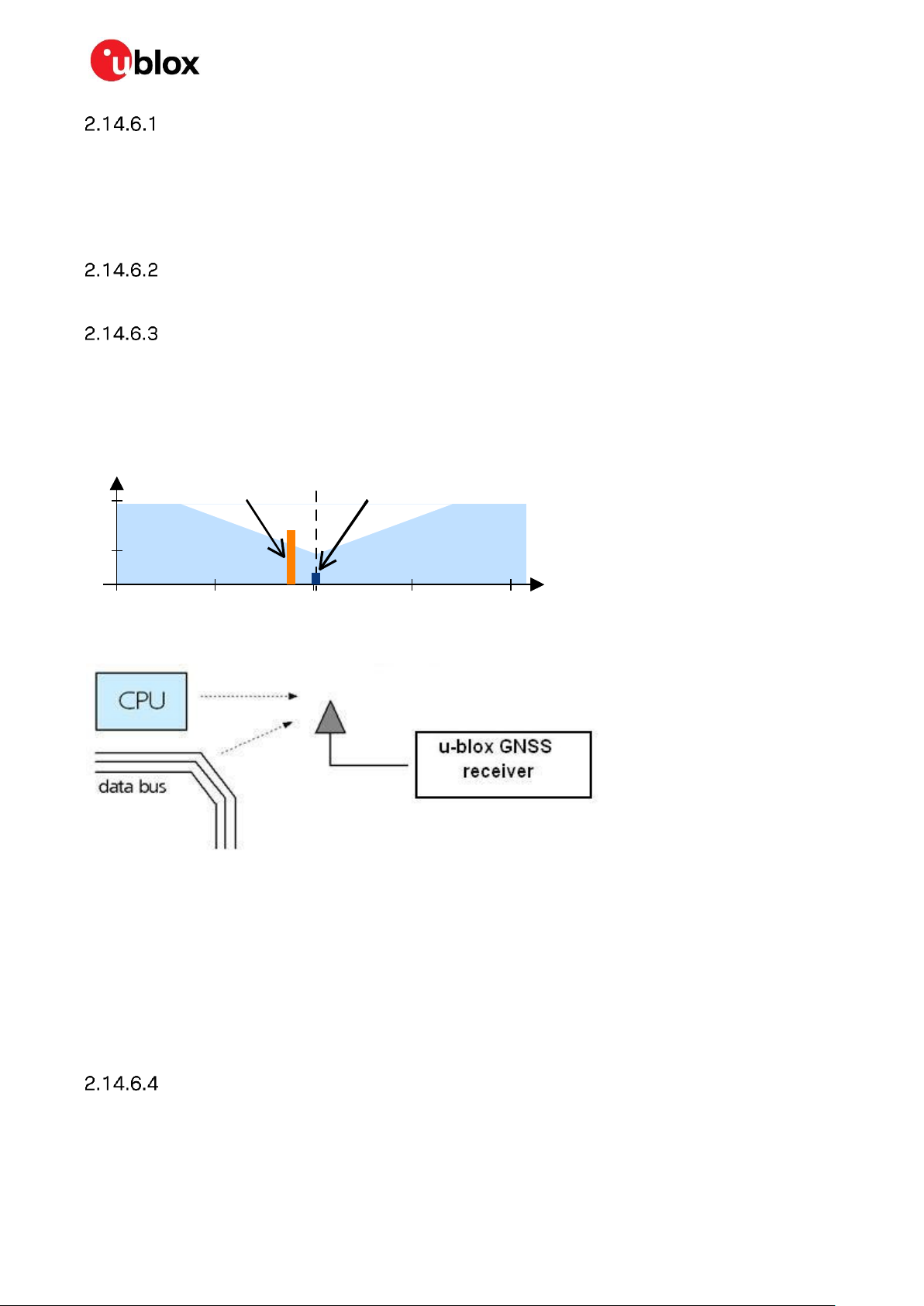
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
1525 1550 1625
GPS input filter
characteristics
1575 1600
0
-110
Jammin
g signal
1525 1550 1625
Frequency [MHz]
Power [dBm]
GPS input filter
characteristics
1575 1600
0
Interference
signal
GPS
signals
GPS Carrier
1575.4 MHz
Isolation between GNSS and GSM antenna
In a handheld type design, an isolation of approximately 20 dB can be reached with careful placement
of the antennas. If such isolation cannot be achieved, for example, in the case of an integrated
GSM/GNSS antenna, an additional input filter is needed on the GNSS side to block the high energy
emitted by the GSM transmitter. Examples of these kinds of filters would be the SAW Filters from
Epcos (B9444 or B7839) or Murata.
Increasing interference immunity
Interference signals come from in-band and out-band frequency sources.
In-band interference
With in-band interference, the signal frequency is very close to the GPS frequency of 1575 MHz (see
Figure 8). Such interference signals are typically caused by harmonics from displays, micro-controller,
bus systems, and so on.
Figure 8: In-band interference signals
Figure 9: In-band interference sources
Measures against in-band interference include:
Maintaining a good grounding concept in the design
Shielding
Layout optimization
Filtering, for example, resistors and ferrite beads
Placement of the GNSS antenna
Adding a CDMA, GSM, WCDMA bandbass filter before handset antenna
Out-band interference
Out-band interference is caused by signal frequencies that are different from the GNSS carrier (see
Figure 10). The main sources are wireless communication systems such as GSM, CDMA, WCDMA,
WiFi, BT, and so on.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 28 of 47
Production information
Page 29

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Figure 10: Out-band interference signals
Measures against out-band interference include maintaining a good grounding concept in the design
and adding a SAW or bandpass ceramic filter (as recommend in section 2.14.6) into the antenna input
line to the GNSS receiver (see Figure 11).
Figure 11: Measures against out-band interference
UBX-16010593 - R08 Design-in Page 29 of 47
Production information
Page 30

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Unless there is a galvanic coupling between the local GND (i.e.
the work table) and the PCB GND, the first point of contact
when handling the PCB shall always be between the local GND
and PCB GND.
Before mounting an antenna patch, connect ground of the
device.
GND
Local GND
When handling the RF pin, do not come into contact with any
charged capacitors and be careful when contacting materials
that can develop charges (e.g. patch antenna ~10 pF, coax cable
~50-80 pF/m, soldering iron).
ESD
Sensitive!
RF_IN
To prevent electrostatic discharge through the RF input, do not
touch the mounted patch antenna.
When soldering RF connectors and patch antennas to the
receiver’s RF pin, make sure to use an ESD-safe soldering iron
(tip).
RF_IN
ESD Safe
3 Product handling and soldering
3.1 Packaging, shipping, storage and moisture preconditioning
For information pertaining to reels and tapes, moisture sensitivity levels (MSD), shipment and
storage information, as well as drying for preconditioning see the data sheets for EVA-M8 [1] and
EVA-8M [2].
3.2 ESD handling precautions
ESD prevention is based on establishing an electrostatic protective area (EPA). The EPA can be a
small working station or a large manufacturing area. The main principle of an EPA is that there are no
highly charging materials in the vicinity of ESD-sensitive electronics, all conductive materials are
grounded, workers are grounded, and charge build-up on ESD-sensitive electronics is prevented.
International standards are used to define typical EPA and can be obtained for example from
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
GNSS receivers are sensitive to ESD and require special precautions when handling. Exercise
particular care when handling patch antennas, due to the risk of electrostatic charges. In addition to
standard ESD safety practices, take the following measures into account whenever handling the
receiver.
⚠ Failure to observe these precautions can result in severe damage to the GNSS receiver!
3.3 Soldering
3.3.1 Soldering paste
Use of "no clean" soldering paste is strongly recommended, as it does not require cleaning after the
soldering process has taken place. The paste in the example below meets these criteria.
Soldering paste: OM338 SAC405 / Nr.143714 (Cookson Electronics)
Alloy specification: Sn 95.5/ Ag 4/ Cu 0.5 (95.5% Tin/ 4% Silver/ 0.5% Copper)
Melting temperature: 217 °C
Stencil thickness: 100 to 150 µm for base boards
The final choice of the soldering paste depends on the approved manufacturing procedures.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Product handling and soldering Page 30 of 47
Production information
Page 31

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Condition
Abbreviation
Recommendation
Preheat/ soak temperature min.
Preheat/ soak temperature max.
Preheat/ soak time from T
smin
to T
smax
T
smin
T
smax
Ts (T
smin
to T
smax
)
150 °C
180 °C
< 90 seconds
Liquidus temperature
Time maintained above TL
TL
tL
217°C
40 to 60 seconds
Peak package body temperature
TP
250 °C
Ramp-up rate (TL to TP)
3 °C / second max.
Time within +0°C…-5°C of TP
30 seconds
Ramp-down rate (TP to TL)
4 °C / second max.
The paste-mask geometry for applying soldering paste should meet the recommendations given in
section 2.11.2.
3.3.2 Reflow soldering
Table 9: Recommended conditions for reflow process
The peak temperature must not exceed 250 °C. The time above 245 °C must not exceed 30 seconds.
☞ EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules must not be soldered with a damp heat process.
3.3.3 Optical inspection
After soldering the modules, consider an optical inspection step to check whether:
The module is properly aligned and centered over the pads
3.3.4 Repeated reflow soldering
Only single reflow soldering process is recommended for boards populated with EVA-8M / EVA-M8
series GNSS modules.
3.3.5 Wave soldering
Base boards with combined through-hole technology (THT) components and surface-mount
technology (SMT) devices require wave soldering to solder the THT components. Only a single wave
soldering process is encouraged for boards populated with EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules.
3.3.6 Rework
Not recommended.
3.3.7 Use of ultrasonic processes
Some components on the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules are sensitive to ultrasonic waves.
Use of any ultrasonic processes (cleaning, welding) may cause damage to the GNSS receiver.
☞ u-blox offers no warranty against damages to the EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules caused
by any ultrasonic processes.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Product handling and soldering Page 31 of 47
Production information
Page 32

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
The best way to test the sensitivity of a GNSS device is
with the use of a multi-GNSS generator. It assures
reliable and constant signals at every measurement.
u-blox recommends the following multi-GNSS generator:
Spirent GSS6300
Spirent Communications Positioning Technology
www.positioningtechnology.co.uk
Figure 12: Multi-GNSS generator
4 Product testing
4.1 Test parameters for OEM manufacturer
Because of the testing done by u-blox, an OEM manufacturer does not need to repeat firmware tests
or measurements of the GNSS parameters/characteristics (for example, TTFF) in their production
test.
An OEM manufacturer should focus on:
Overall sensitivity of the device (including antenna, if applicable)
Communication to a host controller
4.2 System sensitivity test
4.2.1 Guidelines for sensitivity tests
1. Connect a multi-GNSS generator to the OEM product.
2. Choose the power level in a way that the “Golden Device” would report a C/No ratio of 38-40 dBHz.
3. Power up the device under test (DUT) and allow enough time for the acquisition.
4. Read the C/N0 value from the NMEA GSV or the UBX-NAV-SVINFO message (use, for example, u-
center).
5. Compare the results to a “Golden Device” or the u-blox EVA-8M / EVA-M8 series evaluation kits.
4.2.2 “Go/No go” tests for integrated devices
The best test is to bring the device to an outdoor position with excellent sky view (HDOP < 3.0). Let
the receiver acquire satellites and compare the signal strength with a “Golden Device”.
☞ As the electro-magnetic field of a redistribution antenna is not homogenous, indoor tests are in
most cases not reliable. These kind of tests may be useful as a ‘go/no go’ test, but not for
sensitivity measurements.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Product testing Page 32 of 47
Production information
Page 33

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Appendix
A Reference schematics
A.1 Cost-optimized circuit
Passive antenna
No RTC crystal
No backup battery
UART and DDC for communication to host
Figure 13: Cost-optimized circuit
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 33 of 47
Production information
Page 34
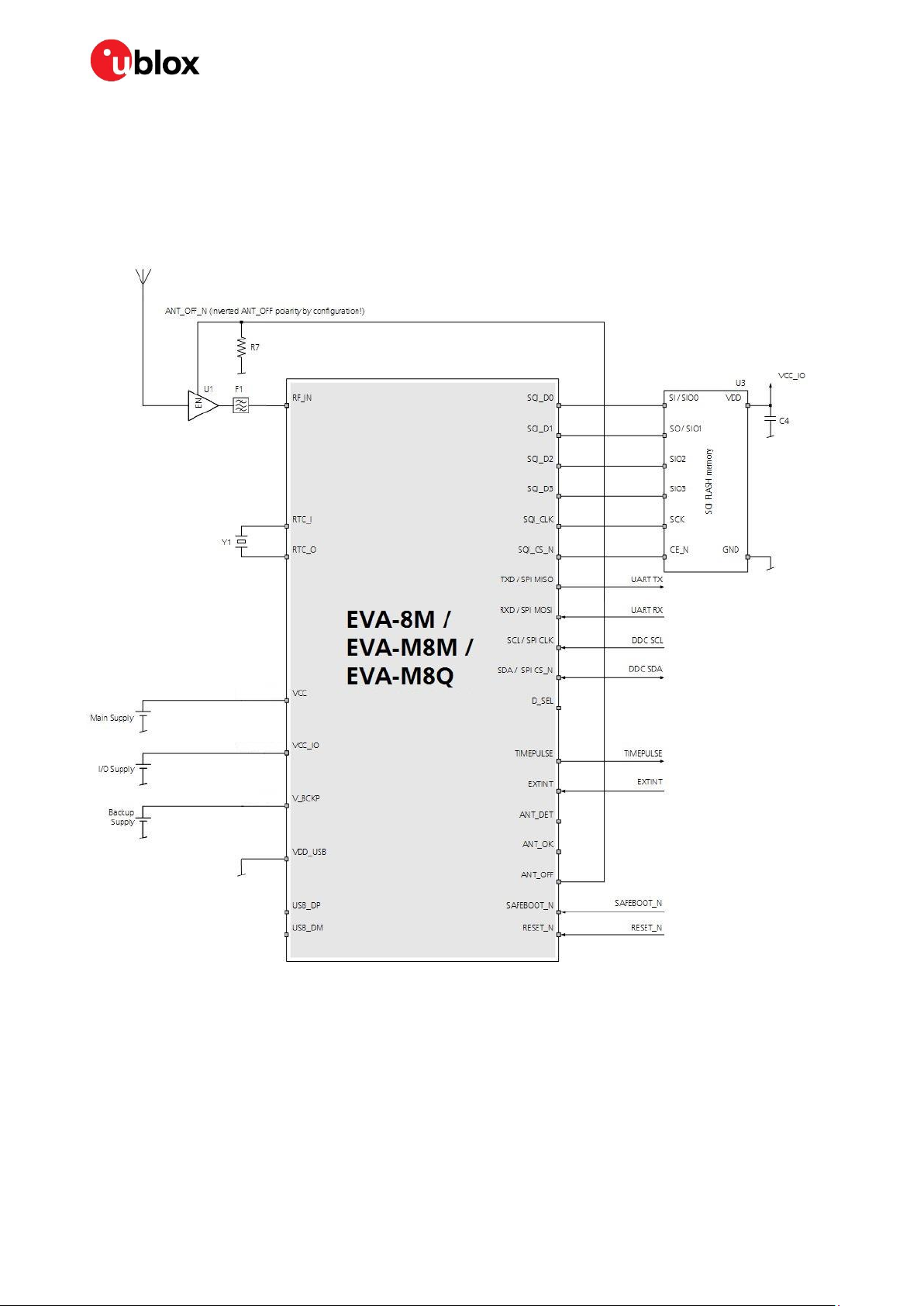
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
A.2 Best-performance circuit with passive antenna
External LNA
RTC crystal
Backup battery
UART and DDC for communication to host
Figure 14: Best performance circuit
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 34 of 47
Production information
Page 35

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
A.3 Improved jamming immunity with passive antenna
External SAW filter – LNA – SAW filter
RTC crystal
Backup battery
UART and DDC for communication to host
Figure 15: Standard circuit for an improved jamming immunity
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 35 of 47
Production information
Page 36

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
A.4 Circuit using active antenna
Active antenna
RTC crystal
Backup battery
UART and DDC for communication to host
Figure 16: Standard circuit using active antenna
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 36 of 47
Production information
Page 37
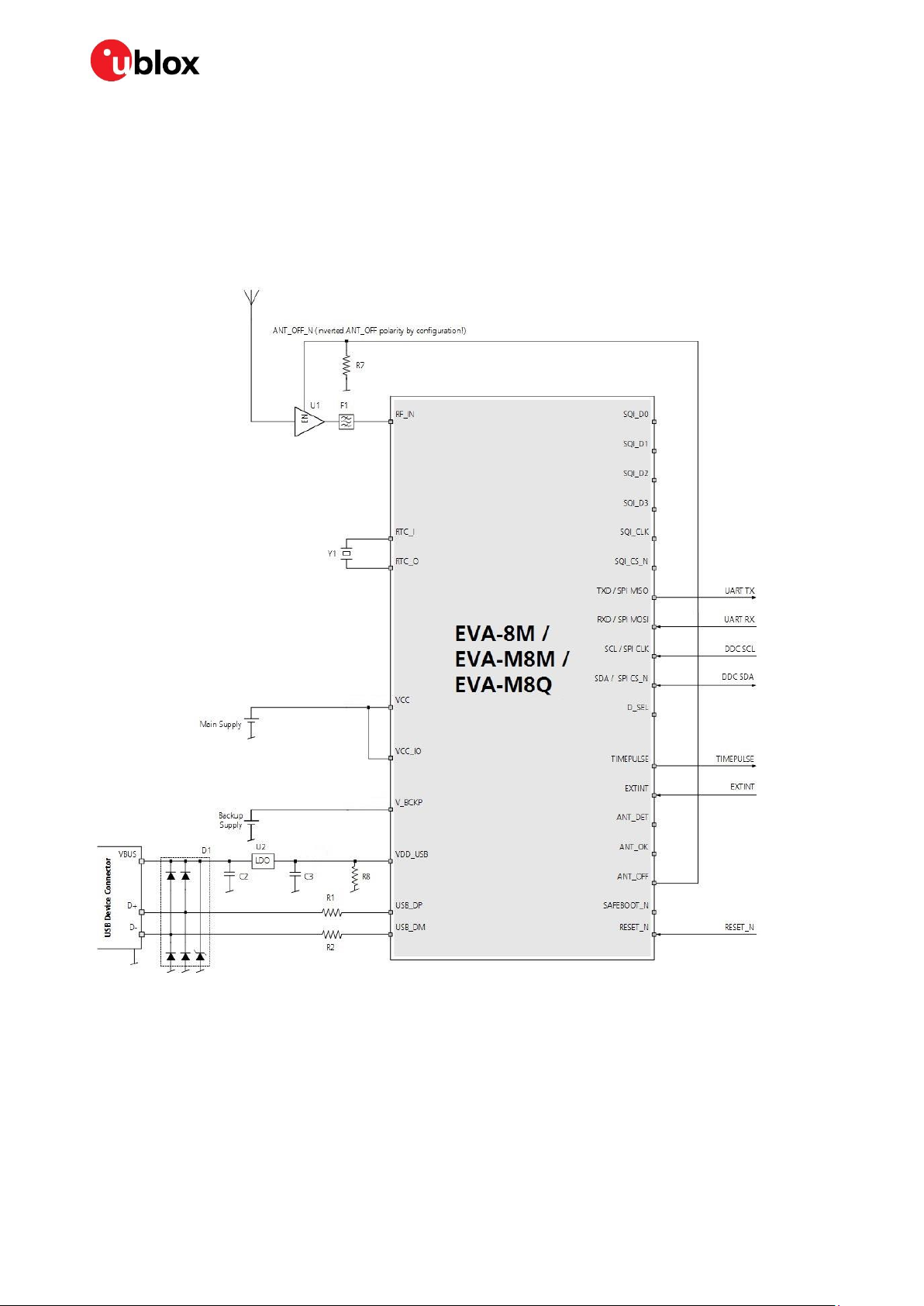
EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
A.5 USB self-powered circuit with passive antenna
External LNA
RTC crystal
Backup battery
UART and DDC for communication to host
USB interface
Figure 17: USB self-powered circuit
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 37 of 47
Production information
Page 38

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
A.6 USB bus-powered circuit with passive antenna
External LNA
RTC crystal
Backup battery
SPI for communication to host
USB interface
Figure 18: USB bus-powered circuit
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 38 of 47
Production information
Page 39

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
A.7 Circuit using 2-pin antenna supervisor
2-pin antenna supervisor
RTC crystal
Backup battery
UART and DDC for communication to host
Figure 19: Circuit using 2-pin antenna supervisor
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 39 of 47
Production information
Page 40

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
A.8 Circuit using 3-pin antenna supervisor
3-pin antenna supervisor
RTC crystal
Backup battery
UART and DDC for communication to host
Figure 20: Circuit using 3-pin antenna supervisor
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 40 of 47
Production information
Page 41

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
ID
Parameter
Value
1
Frequency specifications
1.1
Oscillation mode
Fundamental mode
1.2
Nominal frequency at 25 ºC
32.768 kHz
1.3
Frequency calibration tolerance at 25 ºC
< ±100 ppm
2
Electrical specifications
2.1
Load capacitance CL
7 pF
2.2
Equivalent series resistance RS
< 100 k
Manufacturer
Order no.
Micro Crystal
CC7V-T1A 32.768 kHz 7.0 pF +/- 100 ppm
Manufacturer
Order no.
System supported
Comments
TDK/ EPCOS
B8401: B39162B8401P810
GPS+GLONASS
High attenuation
TDK/ EPCOS
B3913: B39162B3913U410
GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou
For automotive application
TDK/ EPCOS
B9416: B39162B9416K610
GPS
High input power
TDK/ EPCOS
B4310: B39162B4310P810
GPS+GLONASS
Compliant to the AEC-Q200 standard
TDK/ EPCOS
B4327: B39162B4327P810
GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou
Low insertion loss
TDK/ EPCOS
B9482: B39162B9482P810
GPS+GLONASS
Low insertion loss
Murata
SAFFB1G56KB0F0A
GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou
Low insertion loss, only for mobile application
Murata
SAFEA1G58KA0F00
GPS+GLONASS
Only for mobile application
Murata
SAFFB1G58KA0F0A
GPS+GLONASS
Only for mobile application
Triquint
856561
GPS
Compliant to the AEC-Q200 standard
TAI-SAW
TA1573A
GPS+GLONASS
Low insertion loss
TAI-SAW
TA1343A
GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou
Low insertion loss
Manufacturer
Order no.
System supported
Comments
TDK/ EPCOS
B8401: B39162-B8401-P810
GPS+GLONASS
High attenuation
TDK/ EPCOS
B3913: B39162B3913U410
GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou
For automotive application
TDK/ EPCOS
B4310: B39162B4310P810
GPS+GLONASS
Compliant to the AEC-Q200 standard
B Component selection
This section provides information about components that are critical for the performance of the EVA8M / EVA-M8 series GNSS modules. Recommended parts are selected on a data sheet basis only.
Temperature range specifications need only be as wide as required by the application. For the purpose
of this document, specifications for industrial temperature range (-40 to +85 °C) are provided.
B.1 External RTC (Y1)
Table 10: RTC crystal specifications
Table 11: Recommend parts list for RTC crystal
B.2 RF band-pass filter (F1)
Depending on the application circuit, consult manufacturer data sheet for DC, ESD and RF power
ratings.
Table 12: Recommend parts list for RF band-pass filter
B.3 External LNA protection filter (F2)
Depending on the application circuit, see manufacturer data sheet for DC, ESD and RF power ratings.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 41 of 47
Production information
Page 42

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Manufacturer
Order no.
System supported
Comments
TDK/ EPCOS
B4327: B39162B4327P810
GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou
Low insertion loss
TDK/ EPCOS
B9850: B39162B9850P810
GPS
Low insertion loss
TDK/ EPCOS
B8400: B39162B8400P810
GPS
ESD protected and high input power
TDK/ EPCOS
B9416: B39162B9416K610
GPS
High input power
Murata
SAFFB1G56KB0F0A
GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou
Low insertion loss, only for mobile application
Murata
SAFEA1G58KB0F00
GPS+GLONASS
Low insertion loss, only for mobile application
Murata
SAFEA1G58KA0F00
GPS+GLONASS
High attenuation, only for mobile application
Murata
SAFFB1G58KA0F0A
GPS+GLONASS
High attenuation, only for mobile application
Murata
SAFFB1G58KB0F0A
GPS+GLONASS
Low insertion loss, only for mobile application
Triquint
B9850
GPS
Compliant to the AEC-Q200 standard
CTS
CER0032A
GPS
Ceramic filter also offers robust ESD protection
TAI-SAW
TA1573A
GPS+GLONASS
Low insertion loss
TAI-SAW
TA1343A
GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou
Low insertion loss
Manufacturer
Order no.
ST Microelectronics
USBLC6-2
Manufacturer
Order no.
Seiko Instruments Inc.
S-1206B33-I6T2G
ID
Parameter
Value
1
Gain and noise Figure at1.575 GHz
1.1
Gain
> 17 dB
1.2
Noise figure
< 2 dB
Manufacturer
Order no.
Comments
Maxim
MAX2659ELT+
Low noise figure, up to 10 dBm RF input power
JRC New Japan Radio
NJG1143UA2
Low noise figure, up to 15 dBm RF input power
NXP
BGU8006
Low noise figure, small size
Manufacturer
Order no.
Module
Comments
Adesto
AT25SL641
EVA-M8M
1.8 V, 64 Mbit (only 32 Mbit usable), several package/temperature
options
EVA-8M
1.8 V, 64 Mbit (only 32 Mbit usable), several package/temperature
options
Gigadevice
GD25Q32C
All
3 V, 32 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Table 13: Recommended parts for the LNA protection filter
B.4 USB line protection (D2)
Table 14: Recommend parts list for USB line protection
B.5 USB LDO (U1)
Table 15: Recommend parts list for USB LDO
B.6 External LNA (U1)
Table 16: External LNA specifications
Table 17: Recommend parts list for external LNA
B.7 Optional SQI Flash (U3)
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 42 of 47
Production information
Page 43

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Manufacturer
Order no.
Module
Comments
Macronix
MX25L3233F
All
3 V, 32 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Macronix
MX25V8035F
All
3 V, 8 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Macronix
MX25V1635F
All
3 V, 16 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Macronix
MX25R8035Fxxxx1
All
1.8 V and 3 V, 8 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Macronix
MX25R8035Fxxxx3
All
1.8 V and 3 V, 8 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Macronix
MX25R1635FxxxH1
All
1.8 V and 3 V, 16 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Winbond
W25Q80DV
All
3 V, 8 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Winbond
W25Q80EW
EVA-8M and
EVA-M8M
1.8 V, 8 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Winbond
W25Q16FW
EVA-8M and
EVA-M8M
1.8 V, 16 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Winbond
W25Q16JV
All
3 V, 16 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Winbond
W25Q16JVSNIM
All
3 V, 16 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Winbond
W25Q32JV
All
3 V, 32 Mbit, several package/temperature options
Winbond
W25Q64JV
All
3 V, 64 Mbit (only 32Mbit usable) , several package/temperature
options
Manufacturer
Order no.
ON Semiconductor
ESD9R3.3ST5G
Infineon
ESD5V3U1U-02LS
Manufacturer
Order no.
Linear Technology
LT6000
Linear Technology
LT6003
Manufacturer
Order no.
Fairchild
NC7WZ07P6X
Manufacturer
Order no.
Comments
MuRata
BLM15HD102SN1
High impedance at 1.575 GHz
MuRata
BLM15HD182SN1
High impedance at 1.575 GHz
TDK
MMZ1005F121E
High impedance at 1.575 GHz
TDK
MMZ1005A121E
High impedance at 1.575 GHz
Table 18: Recommend parts list for optional SQI flash
B.8 RF ESD protection diode (D2)
Table 19: Recommend parts list for RF ESD protection diode
B.9 Operational amplifier (U6)
Table 20: Recommend parts list for operational amplifier
B.10 Open-drain buffer (U4, U7 and U8)
Table 21: Recommend parts list for open-drain buffer
B.11 Ferrite beads (FB1)
Table 22: Recommend parts list for ferrite beads FB1
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 43 of 47
Production information
Page 44

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Manufacturer
Order no.
Vishay
Si1016X-T1-E3 (p-channel)
Manufacturer
Order no.
Comments
Murata
NFL18SP157X1A3
For data signals, 34 pF load capacitance
Murata
NFA18SL307V1A45
For data signals, 4 circuits in 1 package
Murata
NFM18PC474R0J3
For power supply < 2 A, size 0603
Murata
NFM21PC474R1C3
For power supply < 4 A, size 0805
Manufacturer
Order no.
Murata
LQG15H Series LQG15HS47NJ02 (47 nH, 5%, 300 mA). LQG15HN27NJ02,
LQG15HS27NJ02, LQG15HN33NJ02, LQG15HS33NJ02, LQG15HS39NJ02
Murata
LQW15A Series LQW15AN47NJ80, LQW15AN51NJ80, LQW15AN53NJ80,
LQW15AN56NJ80, LQW15AN68NJ80, LQW15AN75NJ80
Johanson Technology
L-07W Series 39 nH L-07W39NJV4T or any other inductor which is compatible
with the above-mentioned Murata inductors
Name
Use
Type / Value
C0
RF-input DC block
COG 47P 5% 25 V
C1
Decoupling capacitor
X7R 10N 10% 16 V
C24
Decoupling capacitor at VBUS
Depends on USB LDO (U1) specification
C23
Decoupling capacitor at VBUS
Depends on USB LDO (U1) specification
C4
Decoupling VCC_IO at SQI flash supply pin
X5R 1U0 10% 6.3 V
Name
Use
Type / Value
R4
USB data serial termination
27R 5% 0.1 W
R5
USB data serial termination
27R 5% 0.1 W
R3
Pull-up at antenna supervisor transistor
100K 5% 0.1 W
R4
Antenna supervisor current limiter
10R 5% 0.25 W
R5
Antenna supervisor voltage divider
560R 5% 0.1 W
R6
Antenna supervisor voltage divider
100K 5% 0.1 W
R7
Pull-up at LNA enable
10K 5% 0.1 W
R11
Pull-down at VDD_USB
100K 5% 0.1 W
B.12 Antenna supervisor switch transistor (T1)
Table 23: Recommend parts list for antenna supervisor switch transistor (p-channel MOSFET)
B.13 Feed-through capacitors
Table 24: Recommend parts list for feed thru capacitors
B.14 Inductor (L1)
Table 25: Recommend parts list for inductor
B.15 Standard capacitors
Table 26: Standard capacitors
B.16 Standard resistors
Table 27: Standard resistors
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 44 of 47
Production information
Page 45

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Abbreviation
Definition
ANSI
American National Standards Institute
BeiDou
Chinese satellite navigation system
CDMA
Code Division Multiple Access
EMI
Electromagnetic interference
EOS
Electrical Overstress
EPA
Electrostatic Protective Area
ESD
Electrostatic discharge
Galileo
European navigation system
GLONASS
Russian satellite system
GND
Ground
GNSS
Global Navigation Satellite System
GPS
Global Positioning System
GSM
Global System for Mobile Communications
IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission
PCB
Printed circuit board
SBAS
Satellite-Based Augmentation System
QZSS
Quasi-Zenith Satellite System
WCDMA
Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
C Glossary
Table 28: Explanation of the abbreviations and terms used
UBX-16010593 - R08 Appendix Page 45 of 47
Production information
Page 46

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
Revision
Date
Name
Comments
R01
31-May-2016
njaf
Advance Information
R02
25-Aug-2016
njaf
Added EVA-M8Q variant and updated relevant contents
R03
09-Feb-2017
jesk
Early Production Information, Updated information about EVA-M8Q VCC,
VCC_IO, and V_BCKP voltage ranges, updated eFuse configuration messages,
updated section 2.2.4 and Figure 2 (USB interface), added section 2.13.1
(migration from EVA-7M to EVA-8M/M8M/M8Q), updated Figures in Appendix A
(Reference schematics), updated list of compatible SQI flash models, added
note about IEC 60950-1 standard to section 2.1.1.1.
R04
11-Nov-2017
msul
Updated section 3.3.1 (Soldering paste). Added information on RED DoC in
European Union regulatory compliance (page 2), added Intended use statement
in section 2.13 EOS/ESD/EMI precautions, updated legal statement in cover
page and added Documentation feedback e-mail address in contacts page.
R05
30-May-2018
jesk
Updated EVA-M8Q voltage range in section 2.13.1. Updated supported SQI
Flash list in section B.7.
R06
07-Feb-2019
jesk
Clarified alternative uses for the EXTINT pin in section 2.3.2. Updated power
save limitations in section 2.4. Updated supported SQI Flash list in section B.7.
Updated the list of recommended inductors in section B.14.
R07
20-May-2019
jesk
Updated document status on page 2.
R08
28-May-2020
mala
Added section 2.12 Layout design-in: Thermal management.
Editorial changes to reflect the latest style guide changes.
Related documents
[1] EVA-M8 Data sheet, UBX-16014189
[2] EVA-8M Data sheet, UBX-16009928
[3] u-blox 8 / u-blox M8 Receiver Description including Protocol Specification (Public version),
UBX-13003221
[4] GPS Antenna Application Note,
GPS-X-08014
[5] GPS Compendium, GPS-X-02007
[6] GPS Implementation and Aiding Features in u-blox wireless modules, GSM.G1-CS-09007
[7] u-blox 7 to u-blox 8 / M8 Software Migration Guide, UBX-15031124
☞ For regular updates to u-blox documentation and to receive product change notifications, register
on our homepage (www.u-blox.com).
Revision history
UBX-16010593 - R08 Related documents Page 46 of 47
Production information
Page 47

EVA-8M and EVA-M8 series - Hardware integration manual
u-blox Offices
North, Central and South America
u-blox America, Inc.
Phone: +1 703 483 3180
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Regional Office West Coast:
Phone: +1 408 573 3640
E-mail: info_us@u-blox.com
Technical Support:
Phone: +1 703 483 3185
E-mail: support@u-blox.com
Headquarters
Europe, Middle East, Africa
u-blox AG
Phone: +41 44 722 74 44
E-mail: info@u-blox.com
Support: support@u-blox.com
Asia, Australia, Pacific
u-blox Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Phone: +65 6734 3811
E-mail: info_ap@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office Australia:
Phone: +61 2 8448 2016
E-mail: info_anz@u-blox.com
Support: support_ap@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Beijing):
Phone: +86 10 68 133 545
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Chongqing):
Phone: +86 23 6815 1588
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shanghai):
Phone: +86 21 6090 4832
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office China (Shenzhen):
Phone: +86 755 8627 1083
E-mail: info_cn@u-blox.com
Support: support_cn@u-blox.com
Regional Office India:
Phone: +91 80 405 092 00
E-mail: info_in@u-blox.com
Support: support_in@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Osaka):
Phone: +81 6 6941 3660
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Japan (Tokyo):
Phone: +81 3 5775 3850
E-mail: info_jp@u-blox.com
Support: support_jp@u-blox.com
Regional Office Korea:
Phone: +82 2 542 0861
E-mail: info_kr@u-blox.com
Support: support_kr@u-blox.com
Regional Office Taiwan:
Phone: +886 2 2657 1090
E-mail: info_tw@u-blox.com
Support: support_tw@u-blox.com
Contact
For complete contact information, visit us at www.u-blox.com.
UBX-16010593 - R08 Contact Page 47 of 47
Production information
 Loading...
Loading...